Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
Methods Selection of muscle to biopsy Biopsy freezing Biopsy procedures Biochemistry Glycogen pathways Mitochondria Stains Histochemical Immune Inherited myopathies Biopsy request form: PDF Clinical How to read a muscle biopsy Indications Results: Differential diagnosis Pathology: Index Unknowns Nerve biopsy |
 Vesalius |
 Gowers |
General questions to keep in mind
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Category | Method | Utility |
Perimysial Vessels: Normal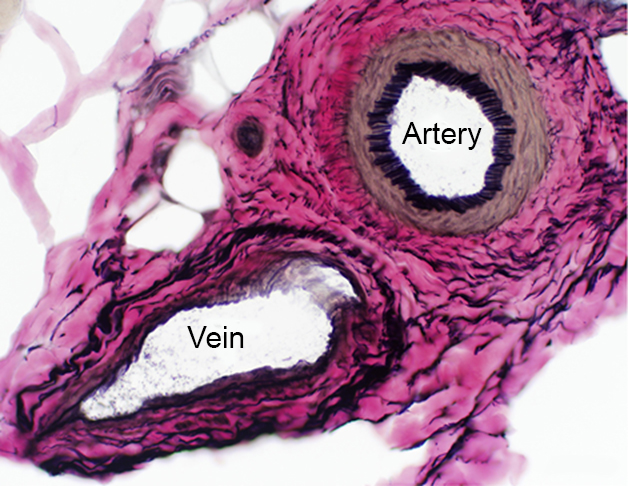 VvG stain |
| Morphology | Hematoxylin & Eosin
| Muscle fiber pathology; Nuclei | |
| Verhoeff van Gieson (VvG)
| Connective tissue; Vessel structure; Intramuscular nerve (Myelinated axons) |
||
| Gomori trichrome
|
Connective tissue;
Nemaline rods Cytoplasmic bodies |
||
| Fiber Type Enzymes (See MYH) |
Myofibrillar ATPase
|
Muscle fiber type grouping or Atrophy | |
| ATPase pH 9.4 | Myosin loss; Type 1 or 2 fiber atrophy | ||
| ATPase pH 4.6 | Type 2B muscle fibers | ||
| ATPase pH 4.3 | Type 2C (Immature) muscle fibers Blood vessels | ||
| Oxidative Enzymes |
NADH-TR
|
Muscle fiber internal architecture; Tubular aggregates; Cores |
|
|
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
|
Mitochondrial pathology Nuclear DNA encoded complex |
||
| Cytochrome oxidase (COX)
|
Mitochondrial pathology Mitochondrial & Nuclear DNA encoded |
||
| Glycolytic Enzymes |
Phosphorylase
|
Phosphorylase deficiency | |
| Phosphofructokinase (PFK) | PFK deficiency | ||
| Hydrolytic Enzymes |
Acid phosphatase
|
Histiocytes; Lysosomes; Lipofuscin | |
| Esterase, Non-specific
|
Histiocytes (Cytoplasm); Lysosomes; Neuromuscular & Myotendinous junctions Denervated (small angular) muscle fibers |
||
| Acetylcholinesterase
|
Neuromuscular & Myotendinous junctions | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase
|
Regenerating or Immature muscle fibers Immune disease: Connective tissue; Capillaries Muscle fiber necrosis |
||
| Storage material |
PAS
|
Glycogen & Carbohydrate disorders | |
| Alcian blue
|
Mucopolysaccharide | ||
| Sudan black B | Lipid storage | ||
| Oil red O
| Lipid storage | ||
| Menadione-αGP | Reducing bodies; Dense bodies | ||
| Other | Congo red | Amyloid; Inflammation; Vacuoles | |
| Myoadenylate deaminase (AMPDA) |
AMPDA deficiency Cytoplasmic aggregates | ||
| Methyl green pyronine
| RNA | ||
| Acridine orange | RNA | ||
| Von Kossa
| Calcium | ||
| Alizarin red | Calcium | ||
| Fixed muscle | Toluidine blue
| Muscle fibers; Capillaries |
|
Muscle fiber Damage Internal architecture Mitochondrial Necrosis Nuclei Size changes With age Atrophy Hypertrophy Storage Type disorders Vacuoles |
Amyloid Capillary pathology Complement Endomysial fibrosis Inflammation MHC-I Inherited myopathies Cytoplasmic proteins Extracellular proteins Nuclear proteins Sarcolemmal proteins Nuclear pathology |
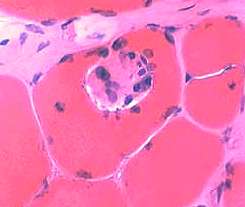 Focal invasion of muscle fiber |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cytoplasmic proteins Extracellular proteins Nuclear proteins Sarcolemmal proteins |