Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
M-line Muscle contraction Skeletal Smooth Myosin Associated proteins Disorders Fiber types Heavy chains Light chains Molecular regions Other: Non-muscle Structure Neuromuscular junction Presynaptic Postsynaptic Smooth muscle Thick filaments Myosin Non-myosin proteins Thin filaments Actin Regulatory proteins Tropomyosin Troponin Structural components Z-line Costameres Dystrophin & related proteins Muscle fiber structure & contraction |
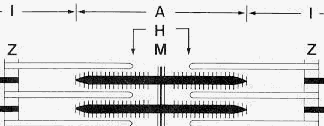
Click on structure for more information 
|
|
A-band: Entire length of thick filaments H-zone: Zone of thick filaments not associated with thin filaments I-band: Zone of thin filaments not associated with thick filaments M-line: Elements at center of thick filaments cross-linking them Z-Disc: Disc between I-bands | |
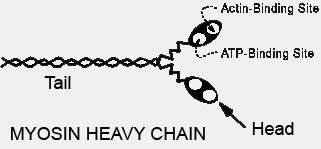
|
Images Myosin HC types |
Control Muscle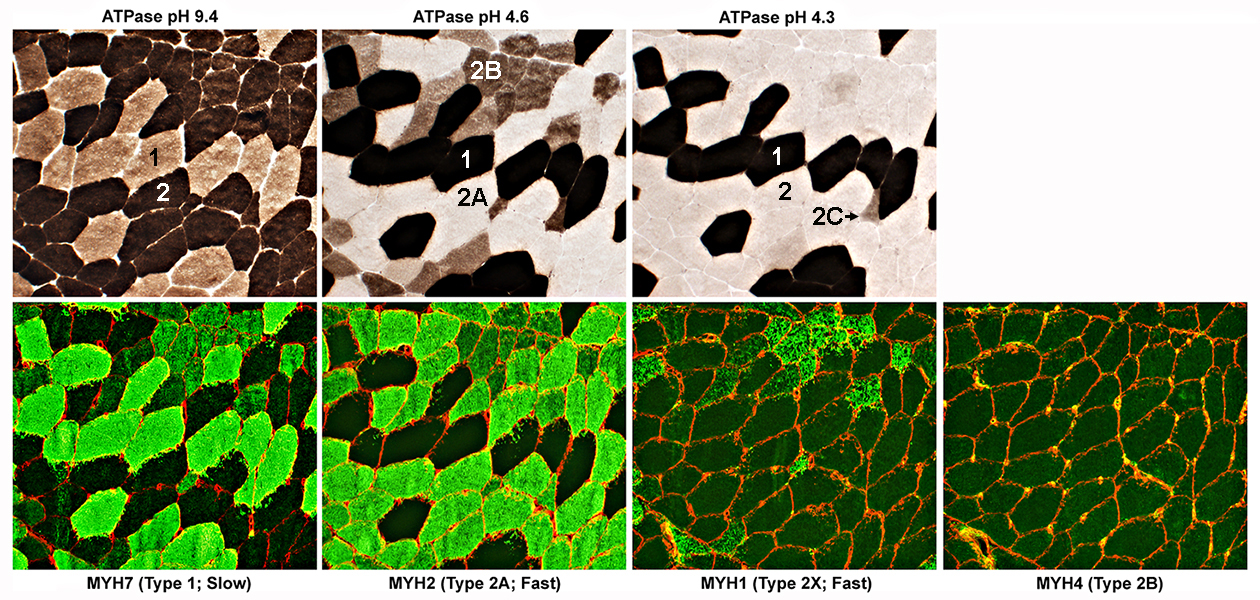 MYH stains = Green; Collagen IV = Red |
| Myosin Heavy Chain Types: Human Muscle | Muscle Features: Other | ||||||||||
| Fiber Type |
Myosin: Heavy Chain Types |
Tissue | Disorders | Myonuclear Domain Size |
Cytochrome Oxidase |
NADH | PAS & Phosphorylase |
Lipid | ATPase pH 4.3 |
ATPase pH 4.6 |
ATPase pH 9.4 |
| I; Slow | I (MYH7) (Cardiac β) |
Skeletal muscle MYH7: 6 wks to Adult Cardiac muscle Fetal Cardiomyopathy |
MYH7 Myopathies |
Moderate | High | High | Low | High | High | High | Moderate |
| IIa; Fast | IIA (MYH2)
± I (MYH7) |
Skeletal muscle MYH2: 24 wks to Adult |
MYH2 Myopathies |
Larger | Moderate | Moderate | High | Moderate | Absent or Low |
Absent or Low |
High |
| IIb; Fast |
IIA (MYH2)
+ IIX (MYH1) ± I (MYH7) |
Skeletal muscle | MYH1 MYHM (Horse) |
Largest | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Absent or Low |
Moderate | High |
| IIc |
I (MYH7)
> IIA (MYH2) |
Skeletal muscle Immature fibers |
Smaller | Low | High | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate- High |
|
| Fetal | IIB (MYH4)
|
Skeletal muscle Regeneration, Early Adult: Abnormal muscle Other adult mammals: 2B fibers |
Some LGMD | Small | |||||||
| Cardiac, adult |
Cardiac α (MYH6) |
Cardiac atria Jaw muscle, Some |
MYH6 Cardiomyopathies |
Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | |||||
| Congenital Myopathy |
I (MYH7)
+ IIX (MYH1) |
Skeletal muscle Most fibers |
Central core | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | |||||
| Other | Embryonic (MYH3) |
Skeletal muscle Fetal, 6 to 24 wks Adult: Regeneration EOM; Spindle (Chain) |
MYH3 Arthrogryposis |
||||||||
| Other |
(MYH8) |
Skeletal muscle Fetal, 7 wks to Birth Adult: Regeneration EOM; Spindle (Chain) |
MYH8 Arthrogryposis |
||||||||
| Super fast |
MYH13
(II eom) |
Extraocular, Laryngeal Intrafusal |
|||||||||
| Slow twitch | MYH15
|
Extraocular | |||||||||
| Slow tonic | MYH7B
|
Extraocular, Intrafusal Tensor tympani |
|||||||||
| Smooth |
Smooth muscle (MYH11) |
Aorta, Intestine |
MYH11 Aneurysm (AAT4) Visceral myopathy 2 MMIHS2 |
||||||||
| Other | MYH16
|
Jaw, Non-human | |||||||||
| Other | Myosin 6 (MYO6) |
Muscle Inner ear |
Hearing loss | ||||||||
| Myosin 14
|
Ear Muscle spindles Extraocular muscle |
Deafness PNMHH |
|||||||||
|
Myosin 15
|
Ear Muscle spindles Extraocular muscle |
Deafness
|
|||||||||
| Myosin 18B (MYO18B) |
Muscle Cardiac & Skeletal |
Skeletal + Myopathy |
|||||||||
|
Myosin 19 (MYO19) |
Mitochondrial | ||||||||||
| Non- muscle |
Type A (MYH9) |
Fibroblast Endothelial cell Macrophage |
MYH9 Hearing loss Thrombocytopenia |
||||||||
|
Type B (MYH10) |
Postsynaptic density Heart |
||||||||||
|
Myosin 7A
|
Ear | Hearing loss | |||||||||
|
Myosin 5A
|
Skin Immune cells |
||||||||||
|
MYO9B |
PNS & CNS | AR-CMT | |||||||||
|
Also see Fiber type disorders Myosin disorders | |||||||||||
Non-myosin components in thick filament
|
|
|
Actin Regulatory proteins Tropomyosin Troponin Profilins Other Structural components Z-line Costameres |
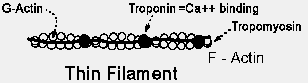 |
||
| Type 1 | Type 2 | |
| Color | Red | White |
| Twitch speed | Slow | Fast |
| Action | Tonic | Phasic |
| Oxidative enzymes | High Aerobic |
Low Anaerobic |
| Mitochondria | Many | Few |
| Lipid content | Moderate | Low |
| Glycogen content | Low | Moderate |
| ATPase staining pH 9.4 |
Light | Dark |
| ATPase staining pH 4.3 |
Dark | Light |