Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
|
| CUTANEOUS SENSORY AFFERENT AXONS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanoreceptors: Low Threshold 13 | ||||||
| Light touch Mechanosensitive channel: PIEZO2 Indentation forces for activation: As low as 0.5 mN | ||||||
| Name | Stimulus Type | Skin End Organ | Axon Class | Sensation | Molecular Factor | |
| Survival | Functional | |||||
| Glabrous (Hairless) Skin | ||||||
| Rapid adapting |
Displacement velocity |
Meissner Corpuscle Dermal papillae apex |
Aαβ TrkB+: Rapid adapt Ret+: Slower adapt 26–91 m/s Receptive field Intermediate |
Vibration 40 to 60 Hz Tapping |
? | USH2A S100 Lamellar cells |
| Pacinian corpuscle Rapid adapt |
Displacement transient |
Pacinian Corpuscle Dermis, Deep Glabrous & Hairy Skin |
Aαβ Ret+ 26–91 m/s |
Vibration 100 to 400 Hz Buzz; Flutter |
? | S100 Lamellar cells |
| Slow adapting (SA) 1 |
Displacement | Merkel cell-Neurite Rete ridge Glabrous & Hairy Skin |
Aαβ TrkC 16–96 m/s Receptive field Small |
Sustained pressure (Indentation) Vibration Shape; Texture Light touch Itch |
NT3 | BDNF PIEZO2 Marker: Atoh1 |
| Slow adapting (SA) 2 |
Displacement | Ruffini Dermis |
Aαβ 20–100 m/s |
Stretch > Indentation |
? | ? |
| Hairy Skin | ||||||
| Field | Displacement velocity |
Hair follicles Awl/auchene zigzag Guard Nerve Ending Circumferential |
Aαβ TrkC+/Ret+ 15-25 m/s Receptive field Large |
Skin stroke | ? | ? |
| D hair | Displacement velocity Lowest mechanothreshold |
Hair follicles Awl/auchene zigzag Nerve Ending Longitudinal Lanceolate |
Aδ TrkB 5-30 m/s Receptive field Intermediate |
Hair deflection Direction- selective Skin stroke Indentation |
NT4;
NT3 via TrkB |
± p75;
?NT4 T-Ca++ channel (Cav3.2) 2 |
| C tactile (C-LTMR) |
Light touch Low threshold |
Lanceolate | C TH+ 0.2-2 m/s Receptive field Intermediate |
Hair deflection Skin stroke Indentation |
? | VGLUT3 Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| Rapidly Adapting |
Displacement transient |
Hair follicle Guard awl/auchene Nerve ending Longitudinal Lanceolate |
Aαβ 26-91 m/s |
Hair deflection Skin stroke Indentation |
? | ASIC-2 Na+ channel |
Mechanoreceptors: Other |
| High Threshold |
Displacement |
Hair follicles Epidermis Guard awl/auchene zigzag Nerve ending Free Circumferential |
Aαβ, Aδ, C 0.5-100 m/s |
High force Indentation Hair pull |
? | ? |
Thermoreceptors
|
| Name | Stimulus Type | End Organ | Class | Sensation | Trophic Factor | |
| Survival | Functional | |||||
| Cold | Cooling Menthol |
Unmyelinated neurite complex |
Aδ C |
Cool Innocuous |
? | ? |
| Cold Allodynia |
Cooling | ? | Large Neurons |
Pain | ? | ? |
| Warm | Warming Slow adapting Fast adapting |
? | C | Warm Innocuous |
? | ? |
|
Also see Temperature-sensitive channels Noxious temperature | ||||||
| Nociceptors | ||||||
| Name | Stimulus Type | End Organ | Class | Sensation | Trophic Factor | |
| Survival | Functional | |||||
| Myelinated |
Pain | Unmyelinated Neurite-Schwann cell complex Basal epidermis Myelinated axons |
Aαβ Aδ |
Pain Sharp Stinging |
NGF | p75; NGF |
| C |
Inflammation
→ Hyperalgesia Not responsive to mechanical & heat pain |
Unmyelinated axons Project to spinal Lamina I & Lamina IIouter |
CMi | Pain Dull or Sharp Burn |
NGF trkA |
p75;
NGF; trkA; CGRP; Substance P & NK1 receptor |
|
Nerve injury
→ Hyperalgesia Responsive to mechanical & heat pain |
Unmyelinated axons Project to spinal Lamina IIinner Noxious heat: TRP-V1 |
CM | Pain Dull or Sharp Burn |
NGF trkA |
GDNF;
Ret GFRα; FRAP & TMP; P2X3 ATP Receptor | |
|
Heat Cold |
Unmyelinated axons |
C |
Temperature hypersensitive |
? | mTORC1 | |
|
Itch Histamine |
Unmyelinated axons Project to spinal Lamina I |
C | Itch | trkA | ? | |
| MUSCLE & TENDON AFFERENT AXONS: Proprioception | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Stimulus Type |
Afferent End Organ |
Efferent Termination |
Effect | Axon Class |
Trophic Factor |
Marker |
| 1° sensory | Muscle stretch Phasic Vibration |
Spindle Intrafusil fibers Nuclear region DB1; 1 branch SB2 & Chain; 2nd branch |
Motor Neuron Mono-synaptic |
Excite Homonymous muscle |
Ia | NT3 | Calb2 ? Lmcd1 |
| 2° sensory | Muscle stretch Tonic (Static) |
Spindle Nuclear chain fibers ± SB2 |
Intermediate Spinal cord Poly- > Mono- synaptic |
Excite Homonymous muscle | II | ? Fxyd7 | |
| Golgi tendon | Tendon stretch Sustained (Force) |
Myotendinous junction Golgi tendon organ |
Intermediate Spinal cord Poly-synaptic |
Inhibit Homonymous muscle |
Ib | ? Pou4f3 | |
|
Proprioception
8 Axon Current stimulus: Mechanical activation (MA); Muscle stretch Axon Current type: Rapidly adapting Neuron currents Ion: Na+ > > Ca++ Channel: Piezo2 Location: Muscle spindle & Golgi tendon organ sensory endings Function: Mechanotransduction Molecular markers Afferent neuron: Parvalbumin Limb-specific proprioceptors: Efna5 | |||||||
|
Disorders General Histology Innervation Afferent Efferent Structure Capsule Axons Muscle fibers |
|
||

| |||
| MOTOR EFFERENT AXONS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Low frequency stimulus effect |
Muscle Fibers Innervated | Ending type | Class | Trophic Factor |
|
| Dynamic γ | Minor contraction Increased stretch response |
Spindle (Intrafusil) Dynamic Bag1 (DB1) |
Indented plate at poles of fibers |
II | NT3 | |
| Static γ | Smooth contraction (SB2) | Spindle (Intrafusil) Static Bag2 (SB2) |
Indented plate | II | NT3 | |
| Oscillation |
Spindle (Intrafusil) Chain |
Trail | ||||
| Dynamic β | ? | Extrafusil Intrafusil: DB1 |
Compact (p1) endplate | . | . | |
| Static β | ? | Extrafusil Intrafusil: Chain |
Compact (p1) endplate | . | . | |
| α | Muscle fiber contraction | Extrafusil | Compact (p1) endplate | I | . | |
|
Spindle images: Other AChE deficiency Fetal Focal myositis Mitochondrial disease Phosphorylase deficiency SMA-LED |
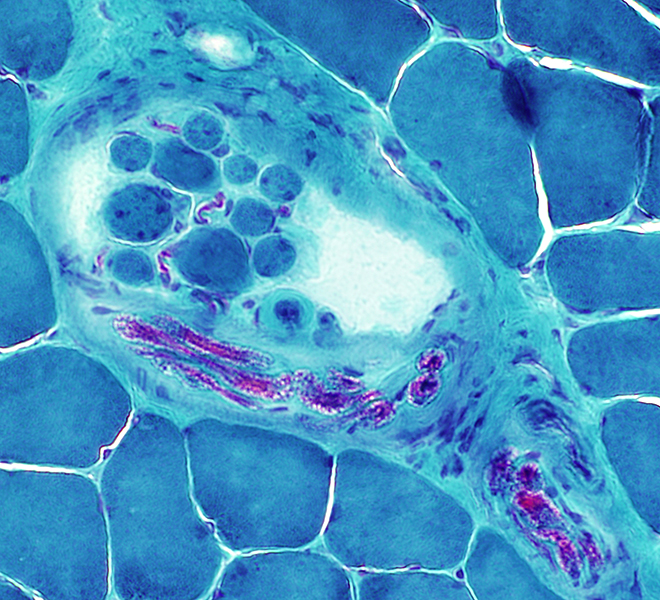 Gomori trichrome stain |
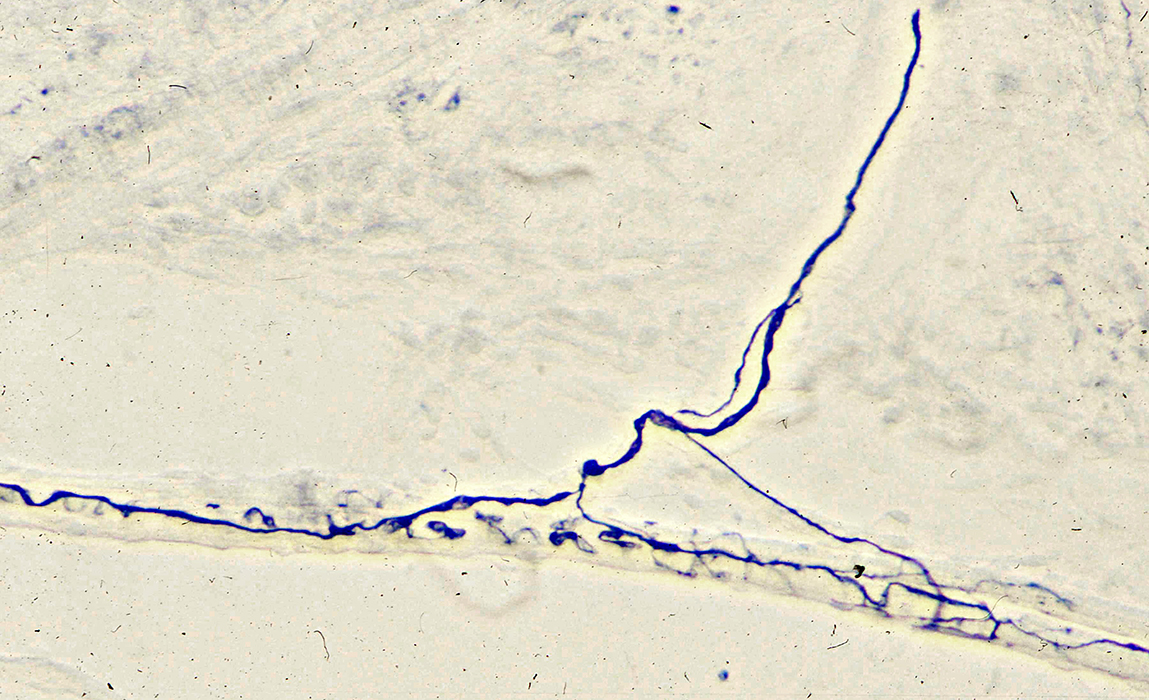 Silver stain |
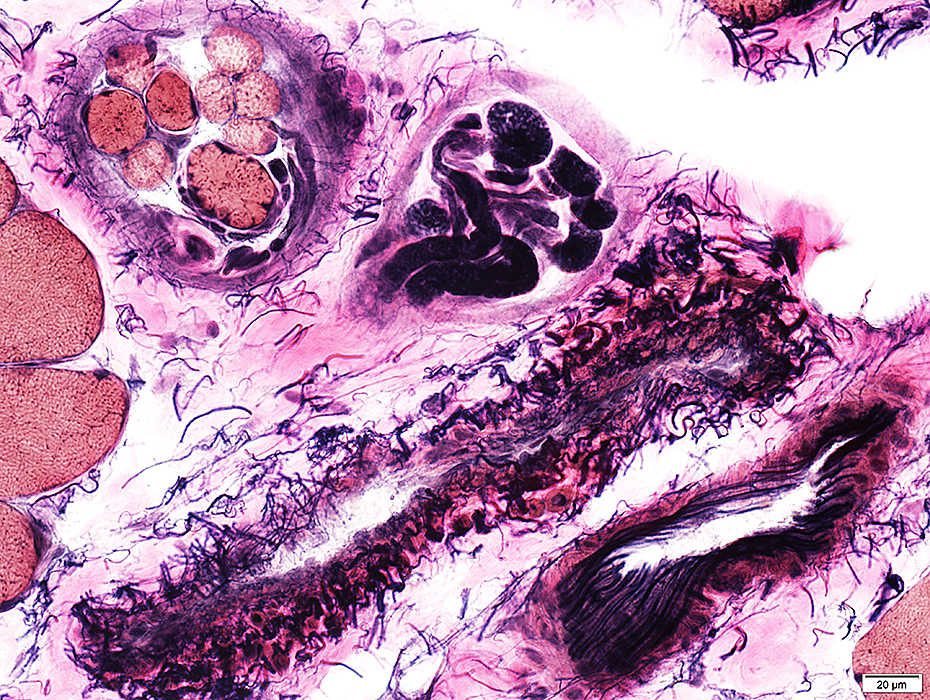 VvG stain |
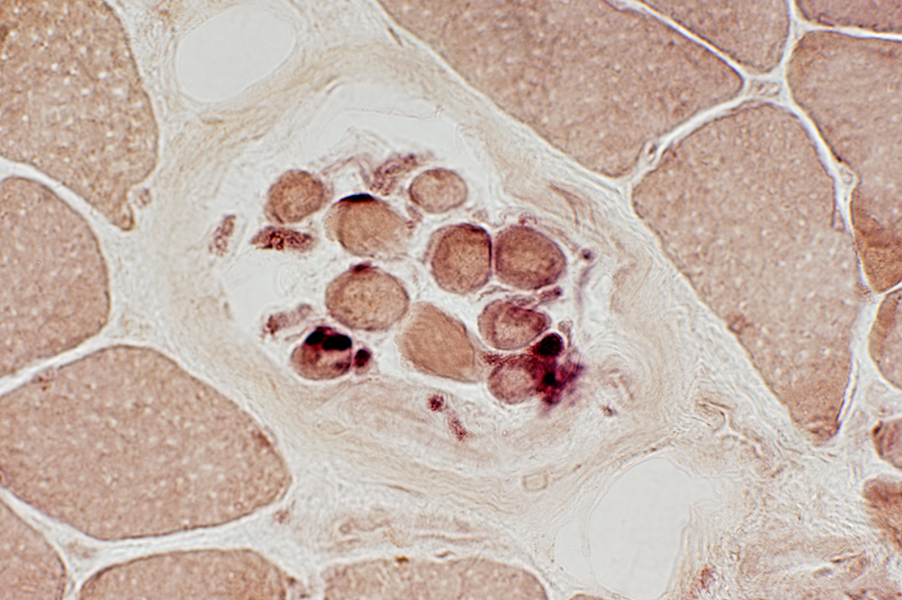 Esterase stain |
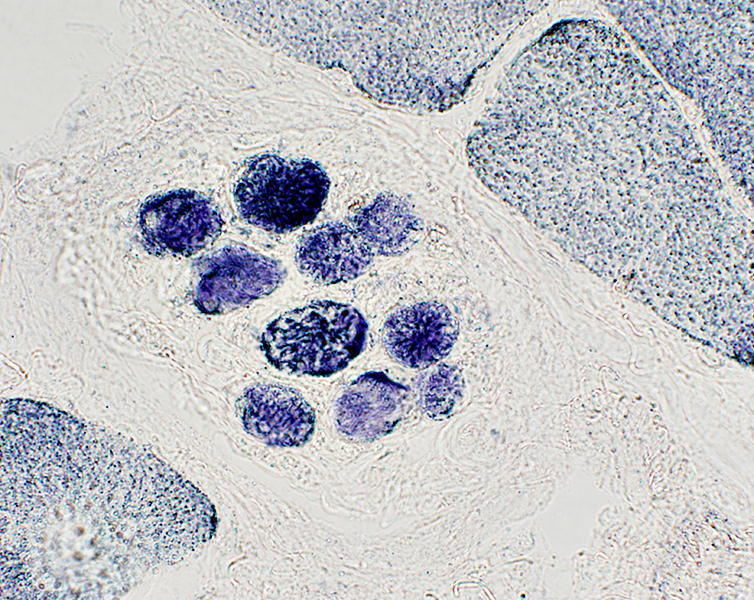 NADH stain |
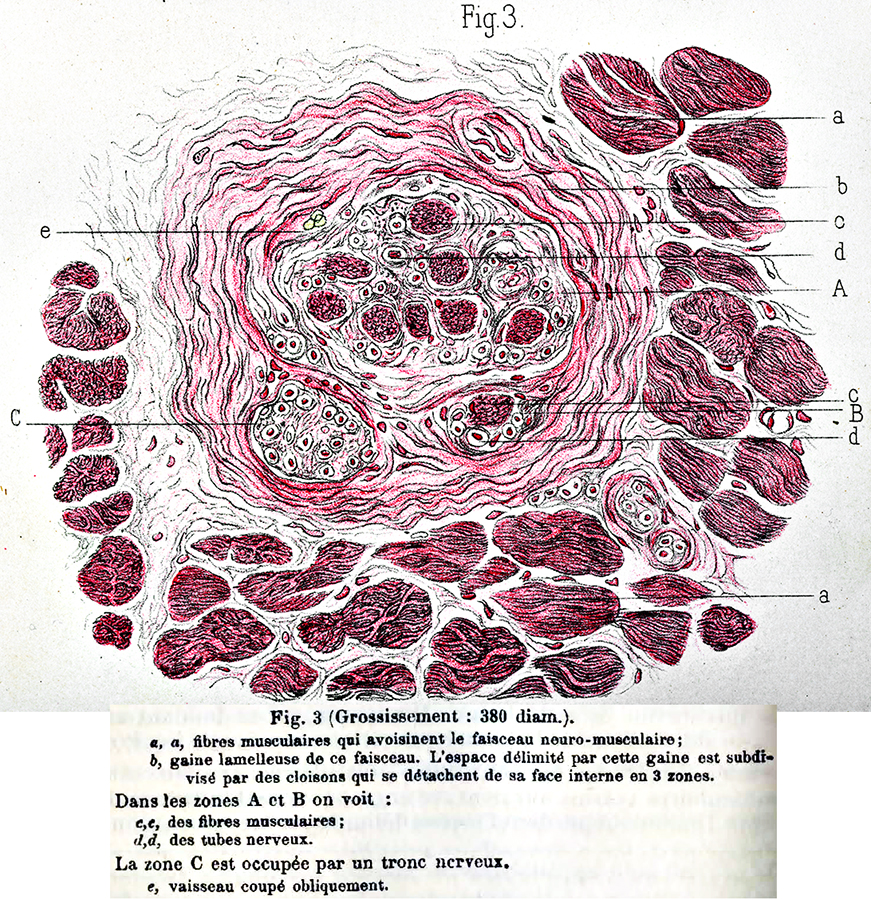 Babinski 1889 |
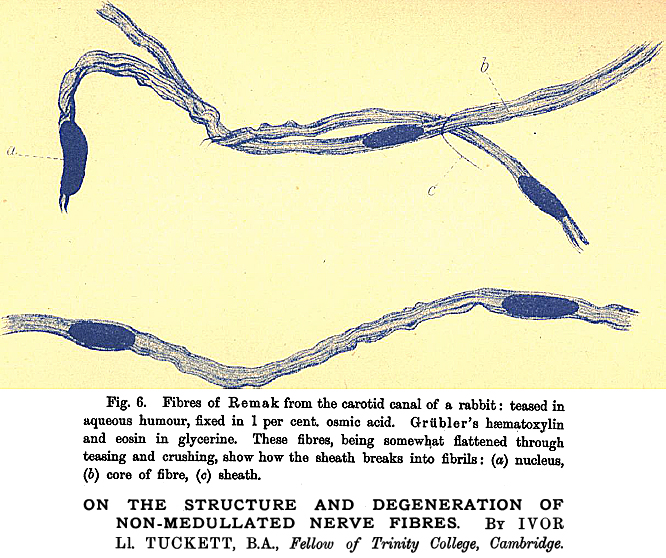 J Physiol 1896; 19:267–311 |
|
Disorders General substrates Types Anterograde Retrograde Synaptic regions |
| Skin Temperature |
< 15°C Noxious Cold |
15°C to 30°C Innocuous Cold |
30°C to 43°C Innocuous Warm |
> 43°C Noxious Heat |
||||
| Skin Sensation |
Cold Pain | Burning | Cold | Cool | Warm | Hot | Burning | Heat Pain |
| Thermal Comfort | ||||||||
| Afferent Neurons |
Cold Nociceptive Other stimuli Heat Mechano, Nociceptive | |||||||
| CNS Motor |
Protective | Protective | ||||||
| Ion channel | Activating temperature | Activators |
| VRL-1 (TRPV2) | 53 °C | Noxious heat |
| VR1 (TRPV1) | 45 °C | Noxious heat Capsaicin pH < 5.9 Vanilloids Endocannabinoids |
| TRPV3/TRPV4 (VRL-2) | 30 to 40 °C | Warm |
|
TRPM3 TRPV1 TRPA1 |
> 41 °C | Noxious heat |
| CMR1/TRPM8 | < 25 °C | Cold Menthol |
| TRPA1 (ANKTM1)
|
< 17 °C | Noxious cold Icilin |
| See | ||

|