Trunk Muscles
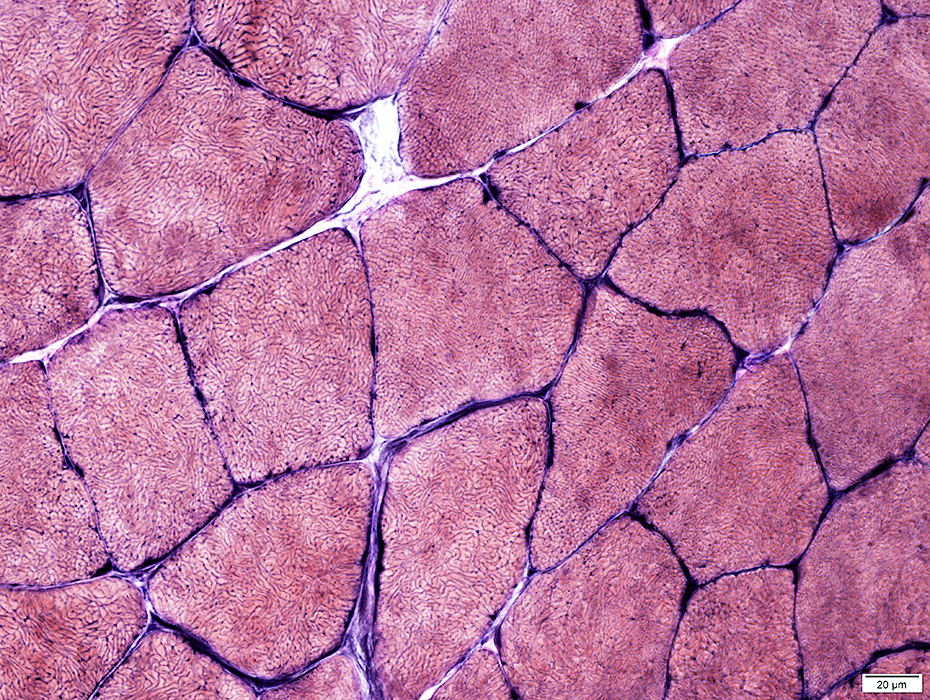
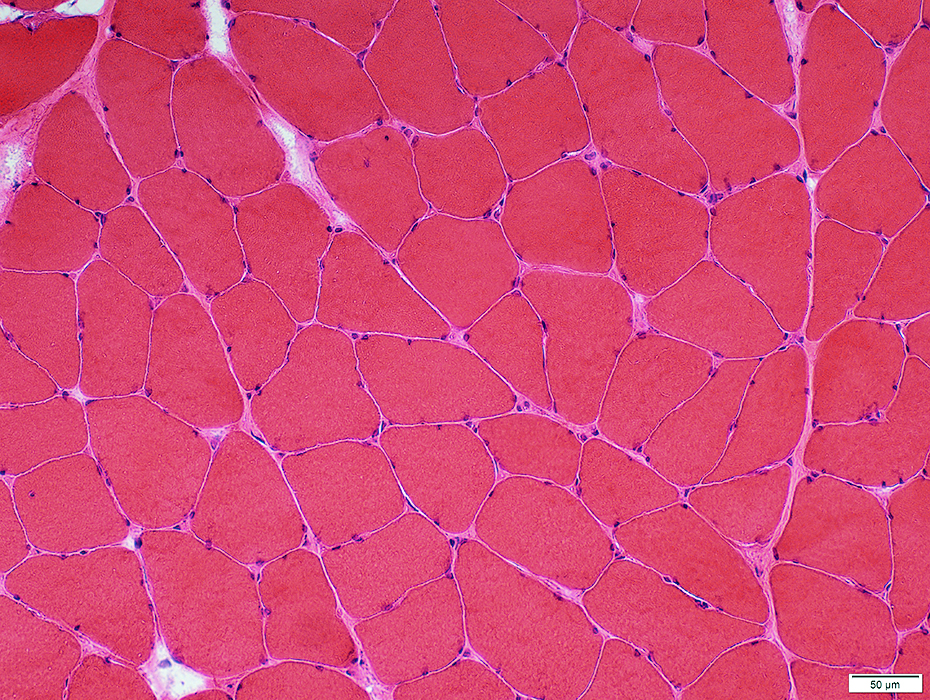 H&E stain |
Endomysial connective tissue: Normal
Perimysial Vessels: Normal
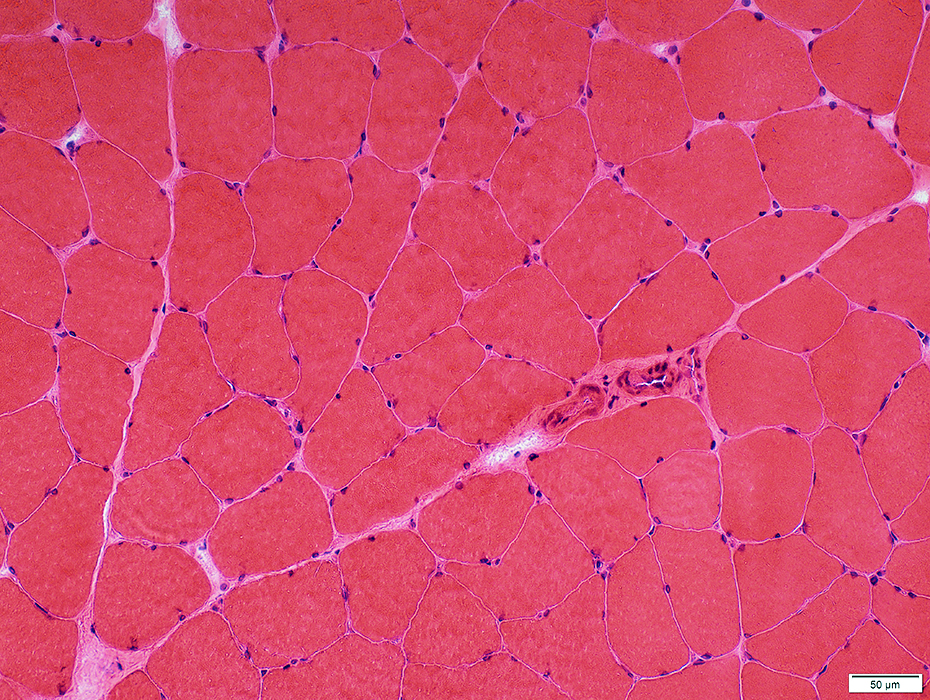 H&E stain |
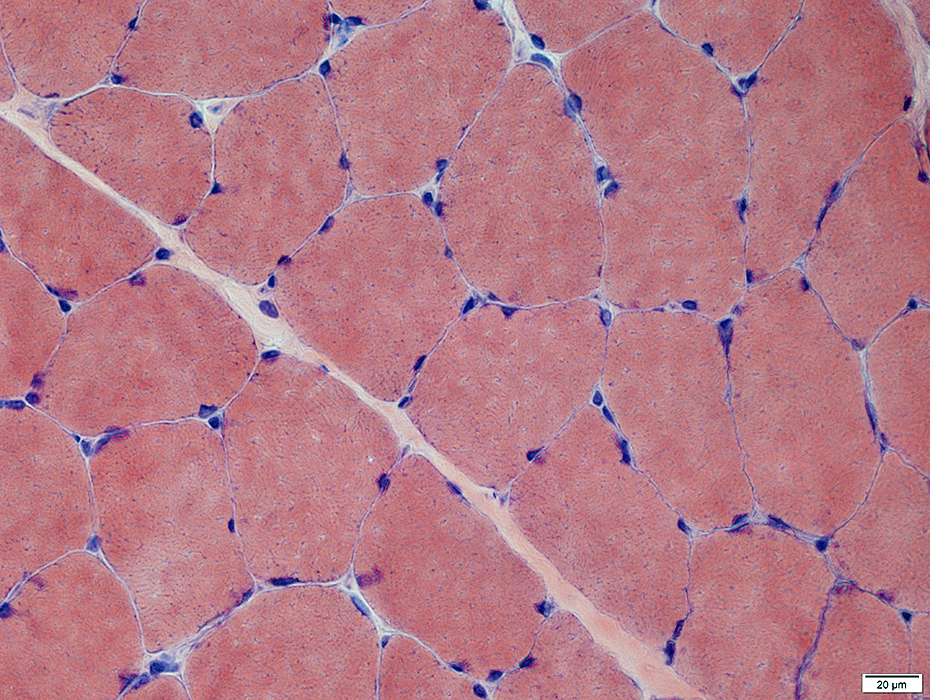 Congo red stain |
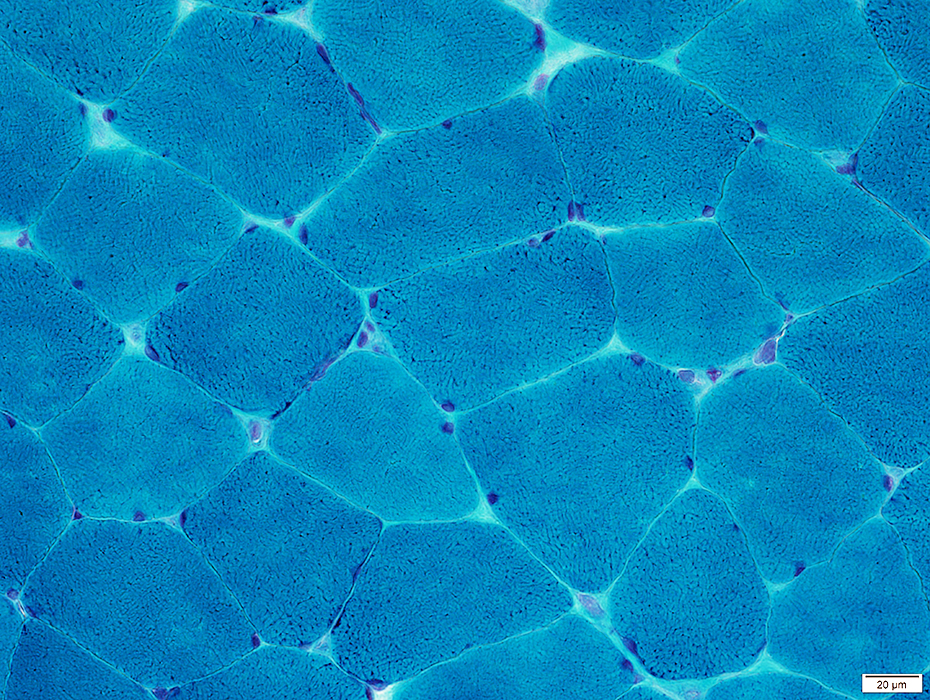 Gomori trichrome stain |
 VvG stain |
Internal architecture
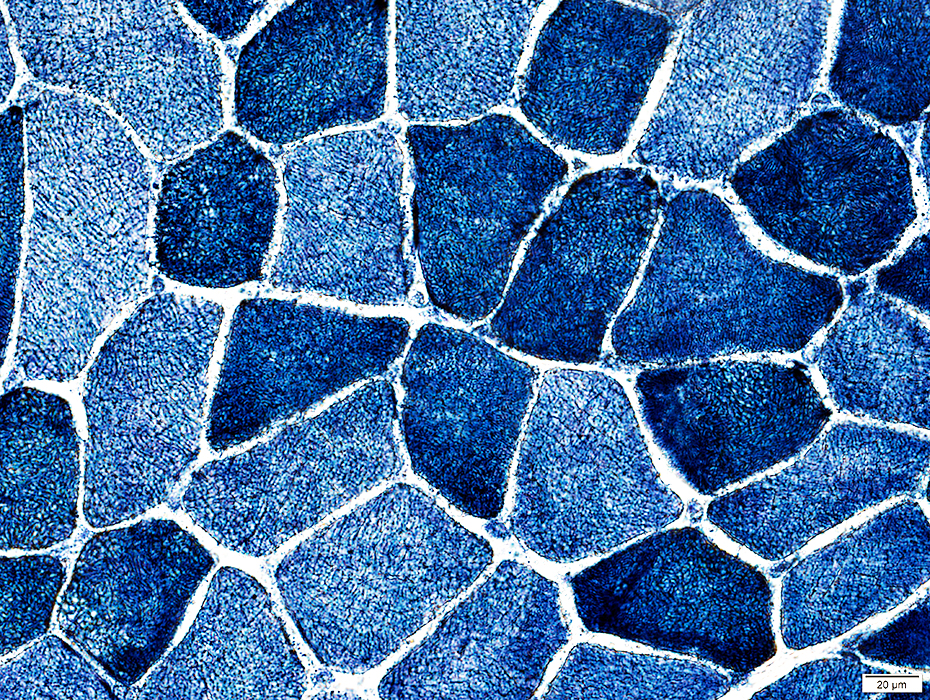 NADH stain |
|
Internal architecture Varied degrees of coarseness & irregularity "Alveolar" fibers: Similar to those seen in CACNA1S congenital myopathy 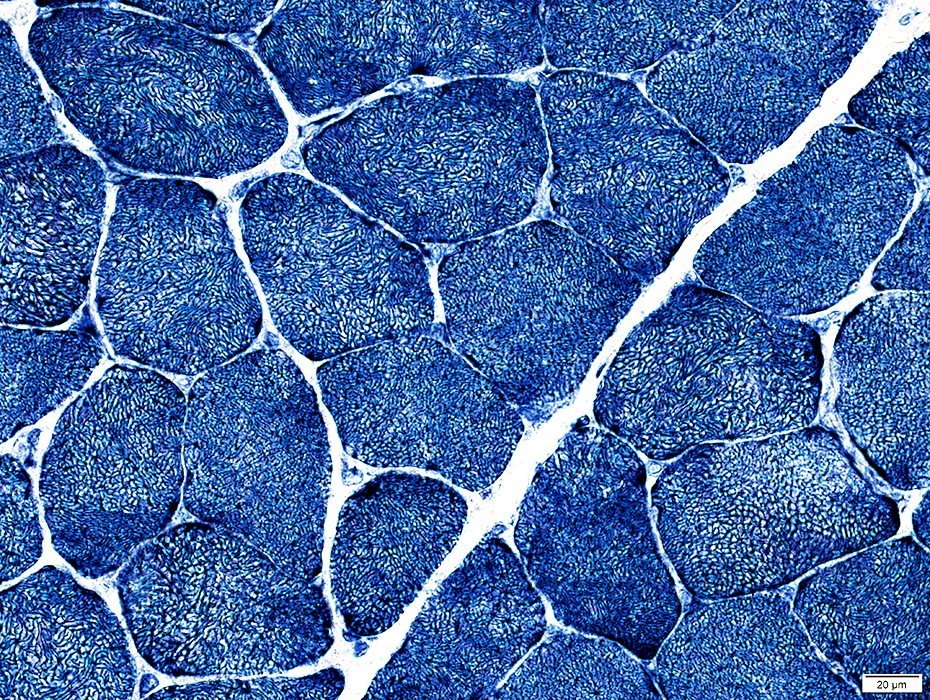 NADH stain |
Internal clear regions
Irregular internal architecture
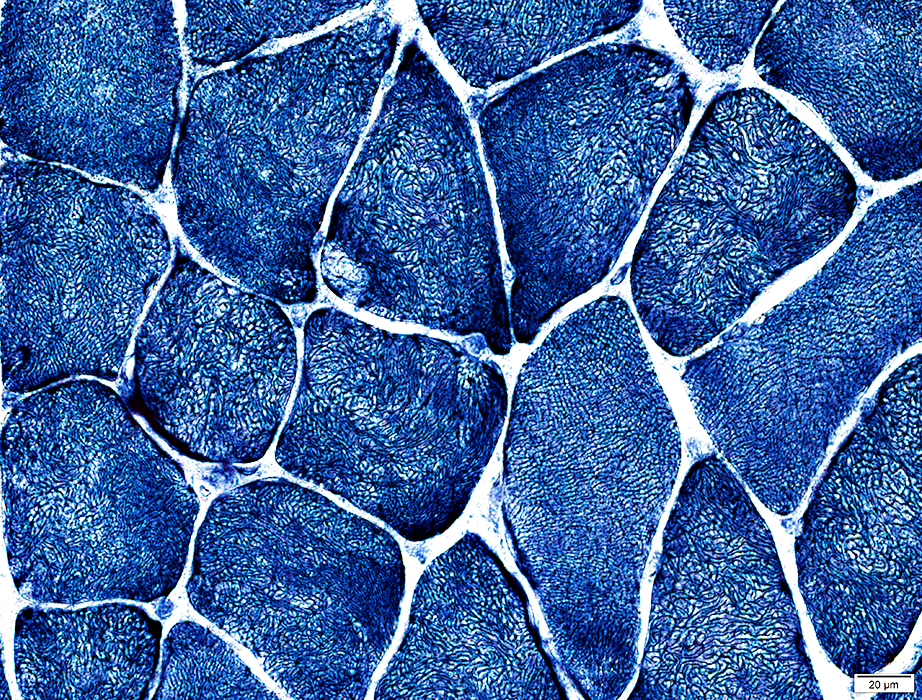 NADH stain |
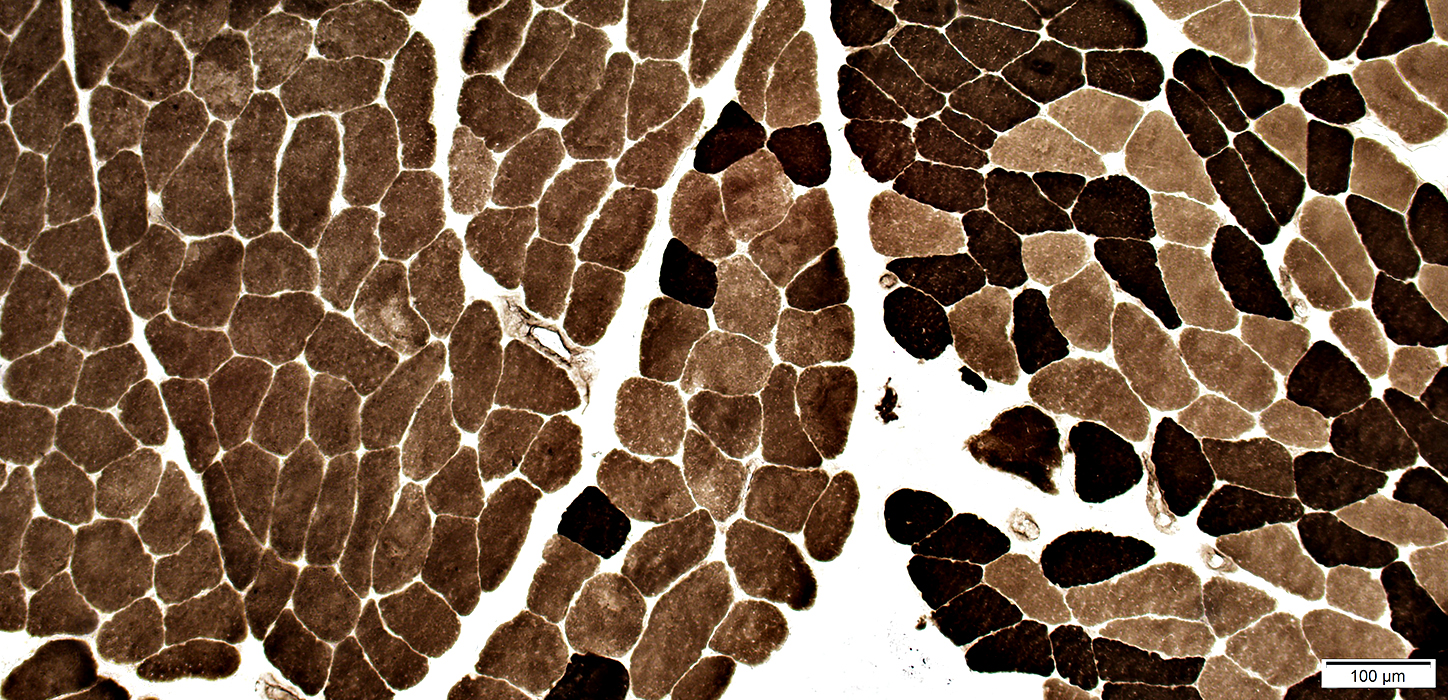 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Some fascicles, or entire muscles, can have marked type I fiber predominance
Fiber type proportions can vary among fascicles
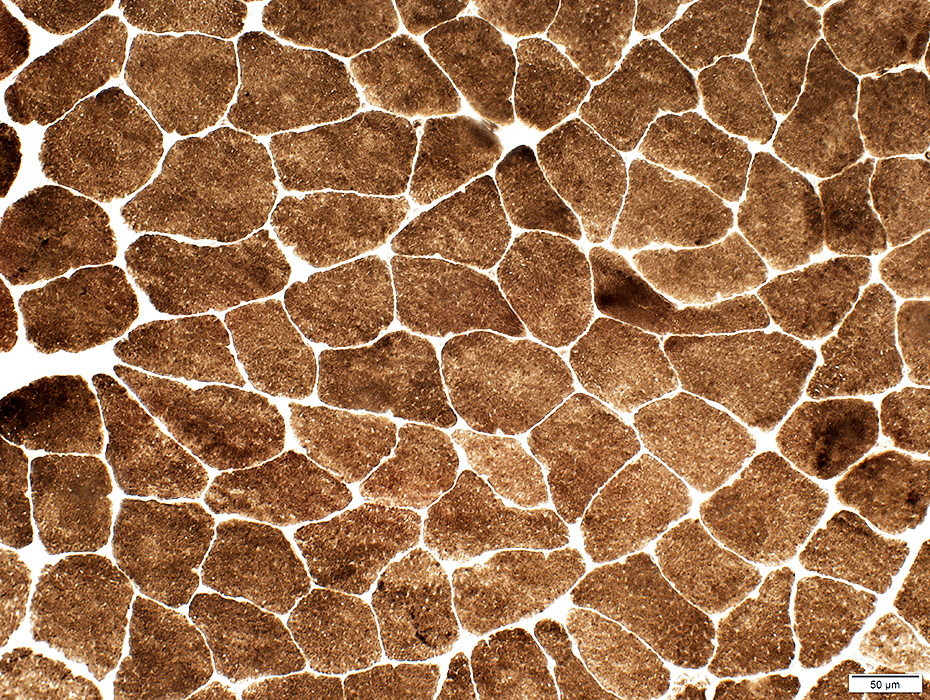 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
No fiber type grouping
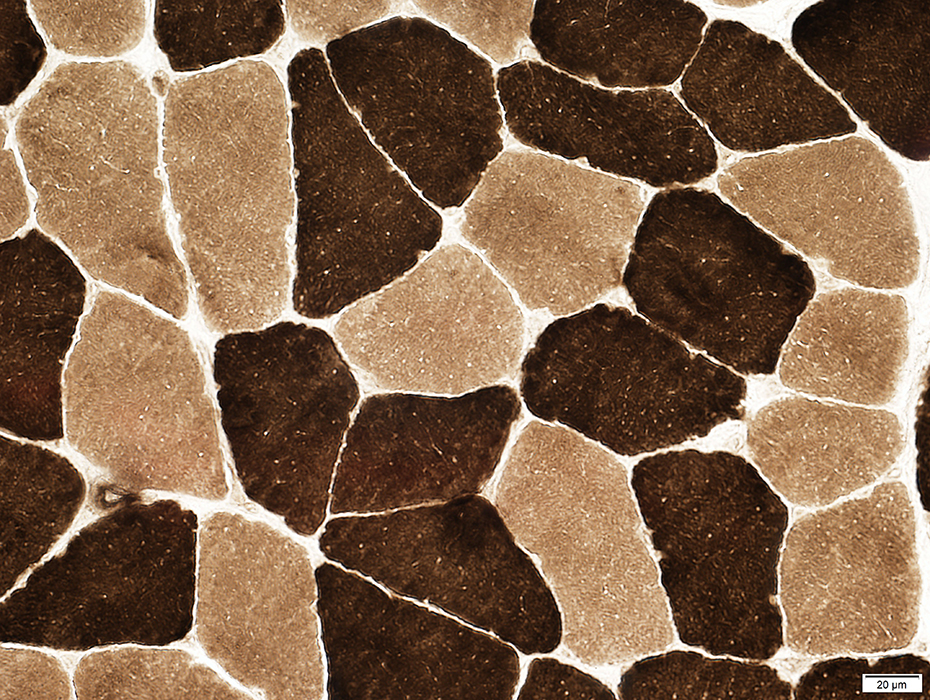 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
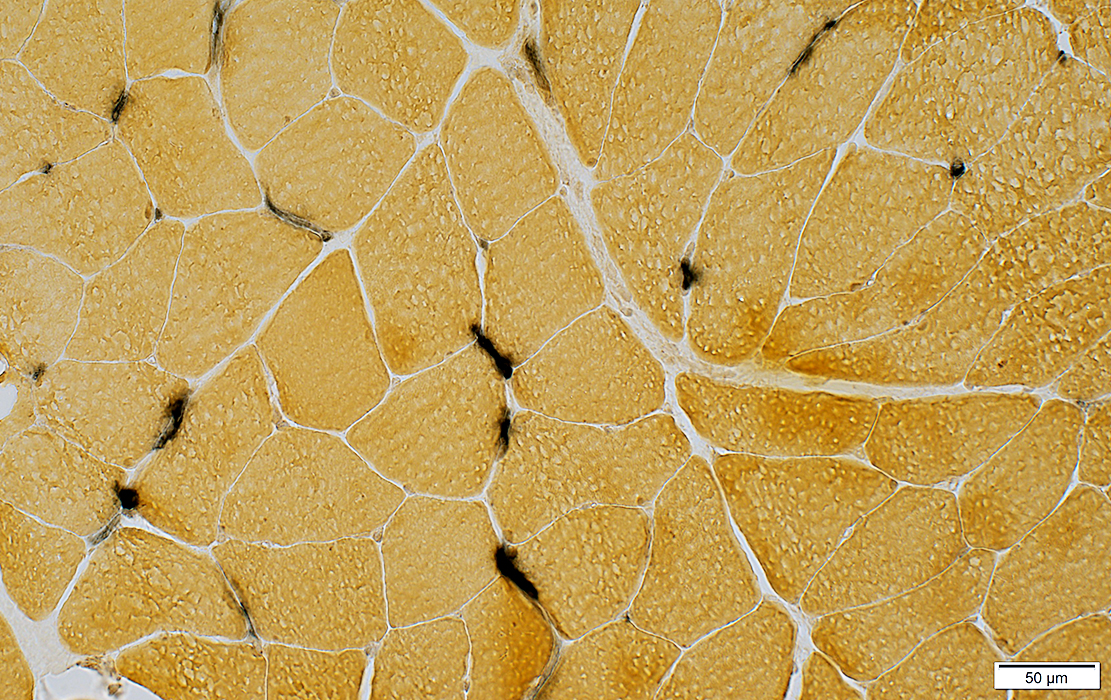 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Some, more than in limb muscles, stain for alkaline phosphatase
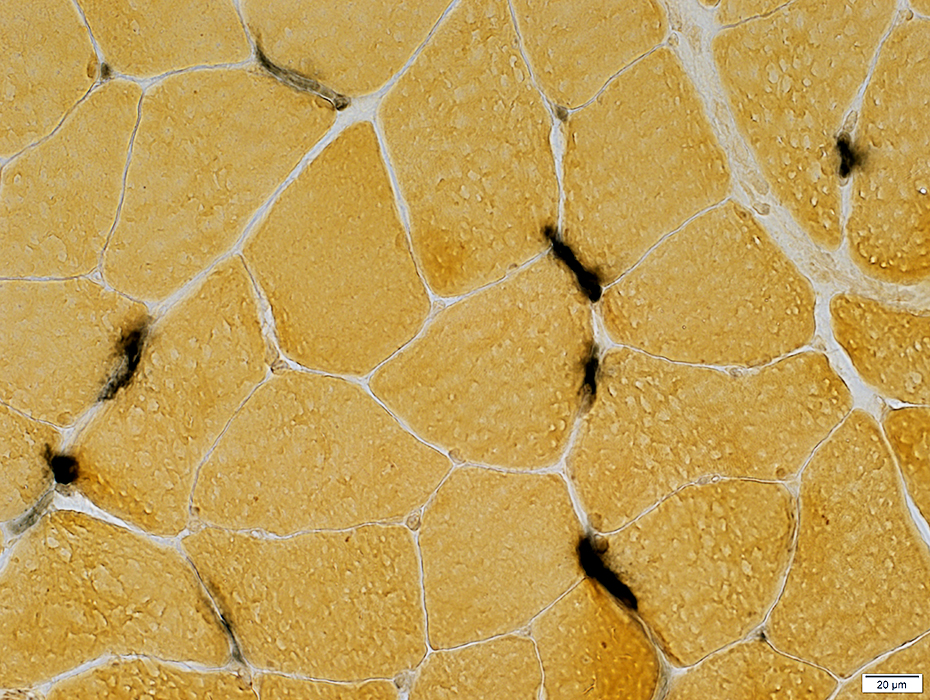 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Muscle: Other Structures
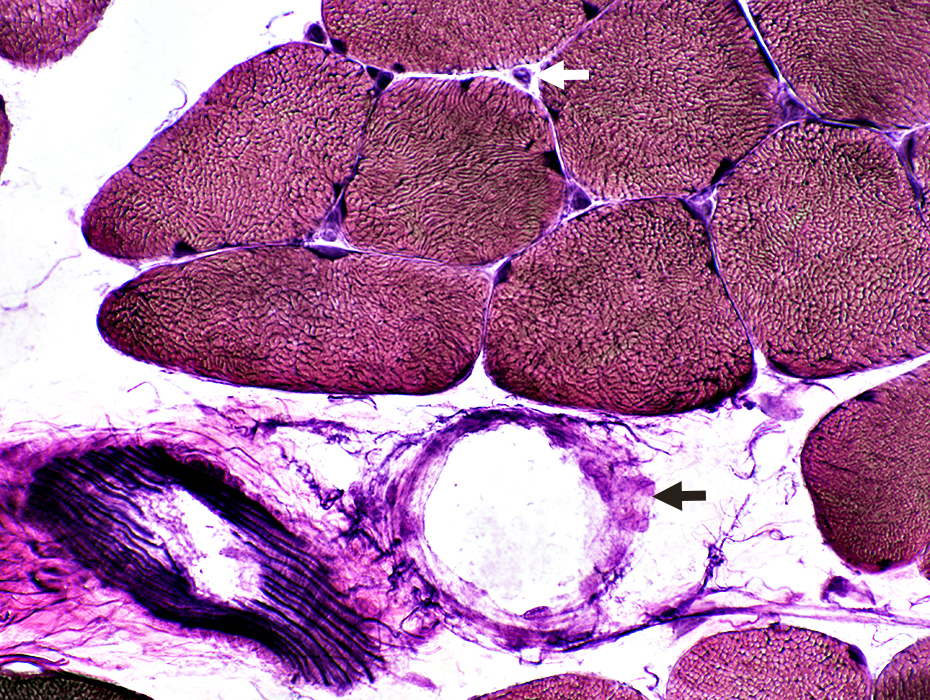 |
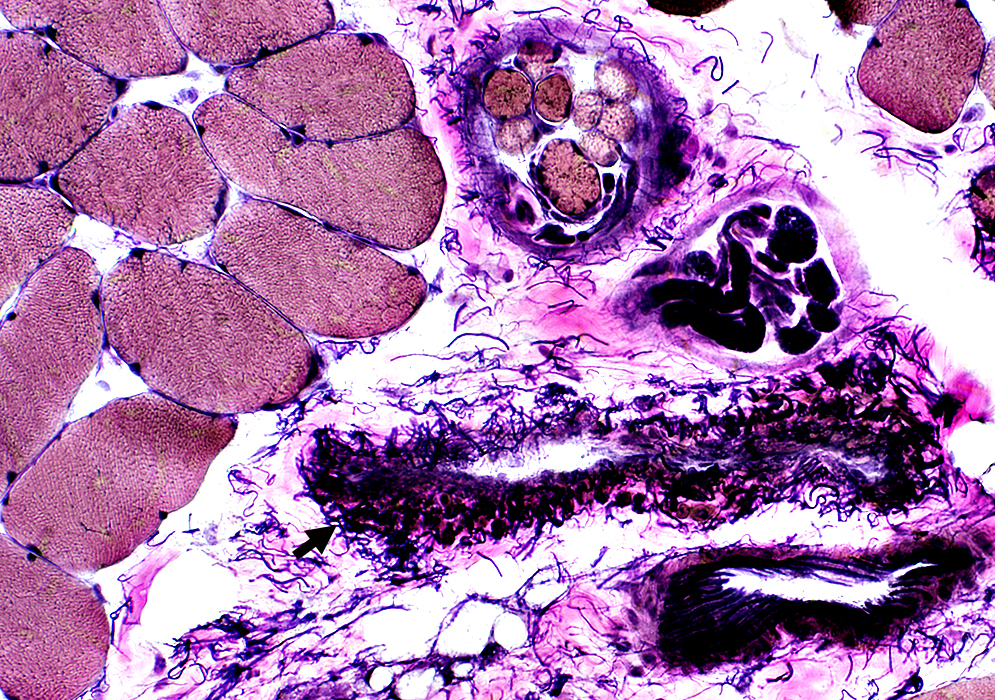
Vessels
Arteries: Fibrillar internal layer
Veins: (Black arrows): Wall may have no fibrils (Above) or many curved fibrils (Below)
Endomysial capillaries (White arrow)
Spindle (Contains small round muscle fibers)
Intramuscular nerve (Myelinated axons are dark-stained)
Perimysium: Connective tissue between fasciclas (Pink-stained): Contains irregular fibrils
Vascular perimysium: Contains intermediate-sized arteries & veins + lymphatics
Avascular perimysium: Contains no vessels
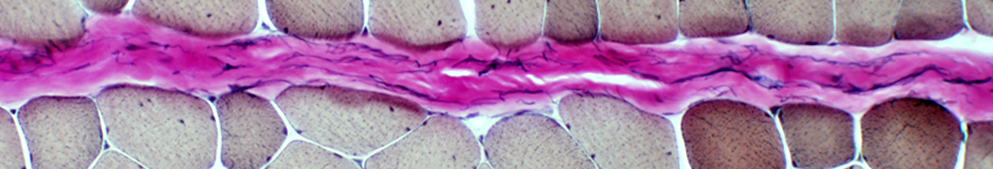
 |
Avascular Perimysium
 |
Return to Pathology index
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
5/10/2020