Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
X-linked ataxias AIFM1 Arts Syndrome: PRPS1 Ataxia, Epilepsy & MR: OPHN1 Brain malformation: CASK Congenital Mental retardation-Epilepsy: SLC9A6 Pelizaeus-Merzbacher variant: PLP Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-α Rett syndrome: MECP2 SCAX 1 (CLA2): ATP2B3 2 (Extrapyramidal) 4 5 Sideroblastic anemia: ABCB7 FXTAS: FMR1; Xq27 Other ataxia syndromes Acquired Congenital DNA repair defects DNA repeat disorders Dominant Glycosylation disorders Hypogonadism Joubert Metabolic Mitochondrial Nephro-CNS (GAMOS) Pontocerebellar hypoplasia (PCH) Quadrupedal (CAMRQ) Refsum Spastic X-linked Recessive Ataxia Laboratory Neuromuscular associations Proteins |
| RECESSIVE ATAXIAS: General 129 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuromuscular-Associated | ||||
|
|
|||
| Protein Types | ||||
| ||||
| Laboratory Features | ||||
| ||||
|
Frataxin protein Genetic features Neurological features Pathology Systemic features Variant syndromes |
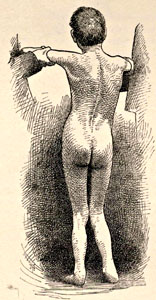
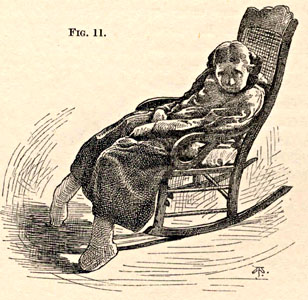 From Bramwell: Atlas of Clinical Medicine Friedreich Ataxia
|
 From Wikipedia |
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Charlevoix-Saguenay - Spastic Ataxia (ARSACS; SPAX 6)
● Sacsin (SACS; DNAJC29)
|
|
|
Leukoencephalopathies with Vanishing White Matter (VWM)
151 VWM1 ● Translocation initiation factor eIF2B1, α subunit VWM2 ● Translocation initiation factor eIF2B2, β subunit VWM3 ● Translocation initiation factor eIF2B3, γ subunit VWM4 ● Translocation initiation factor eIF2B4, δ subunit VWM5 ● Translocation initiation factor eIF2B5, ε subunit VWM (MC1DN10) ● MYC-induced mitochondrial protein (B17.2L; Mimitin) Other ● Dominant
|
|
|
Joubert: General features Types: Usually recessive
|
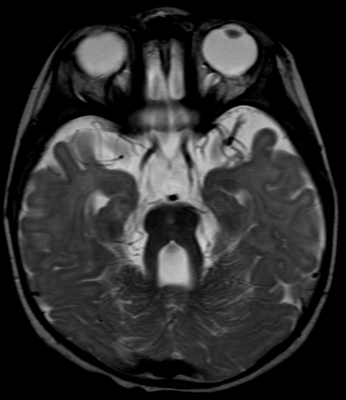 From: A Paciorkowski Molar Tooth Sign
|
|
1: TMEM67 2: CC2D2A 3: RPGRIP1L |
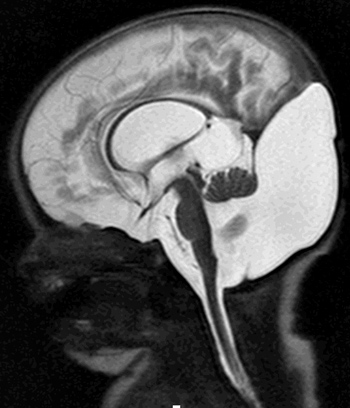 From: A Paciorkowski Dandy-Walker malformation: 2 day old child
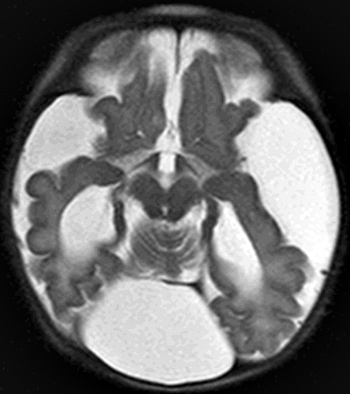
|
|
1: WDR73; 15q25 2: LAGE3; Xq28 3: OSGEP; 14q11 4: TP53RK; 20q13 5: TPRKB; 2p13 6: WDR4; 21q22 7: NUP107; 12q15 8: NUP133; 1q42 9: GON7; 14q32 10: YRDC; 1p34 |
|
PCH1 + Spinal muscular atrophy PCH1A: VRK1; 14q32 PCH1B: EXOSC3; 9p13 PCH1C: EXOSC8; 13q13 PCH1D: EXOSC9; 4q27 PCH1E: SLC25A46; 5q22 Lethal Congenital PCH1F: EXOSC1; 10q24 PCH: KIF26B; 1q44 PCH2: Progressive cerebral atrophy PCH2A: TSEN54; 17q25 PCH2B: TSEN2; 3p25 PCH2C: TSEN34; 19q13 PCH2D: SEPSECS; 4p15 PCH2E: VPS53; 17p13 PCH2F: TSEN15; 1q25 Also see: Congenital ataxia |
PCH3: Progressive microcephaly (CLAM); PCLO; 7q21 PCH4: Fatal infantile: TSEN54; 17q25 PCH5: Fetal onset PCH6: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia; RARS2; 6q15 PCH7: PCH + Hypogonadism; TOE1; 1p34 PCH8: PCH + Microcephaly; CHMP1A; 16q24 PCH9: PCH + Mega cisterna magna; AMPD2; 1p13 PCH10: PCH + Epilepsy; CLP1; 11p12 PCH11: TBC1D23; 3q12 PCH12: COASY; 17q21 PCH13: VPS51; 11q13 PCH14: PPIL1; 6p21 PCH15: CDC40; 6q21 PCH16: MINPP1; 10q23 PCH17: PRDM13; 6q16 PCH: HEATR5B; 2p22 PCH: MED17; 11q21 MIPCH: CASK; Xp11 PC Atrophy: SPTAN1; 9q34 PHRINL: ATAD3A; 1p36 GEMIN5: 5q33 |
Recessive
|
Dominant OPA1: 3q29 TBP: 6q27 X-linked CUL4B: Xq24 Mitochondrial Kearns-Sayre |