|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
DYSTROPHINOPATHIES: Duchenne
|
Early age Mild Myopathic groups Regeneration Severe Later age Dystrophin Revertants General features |
|
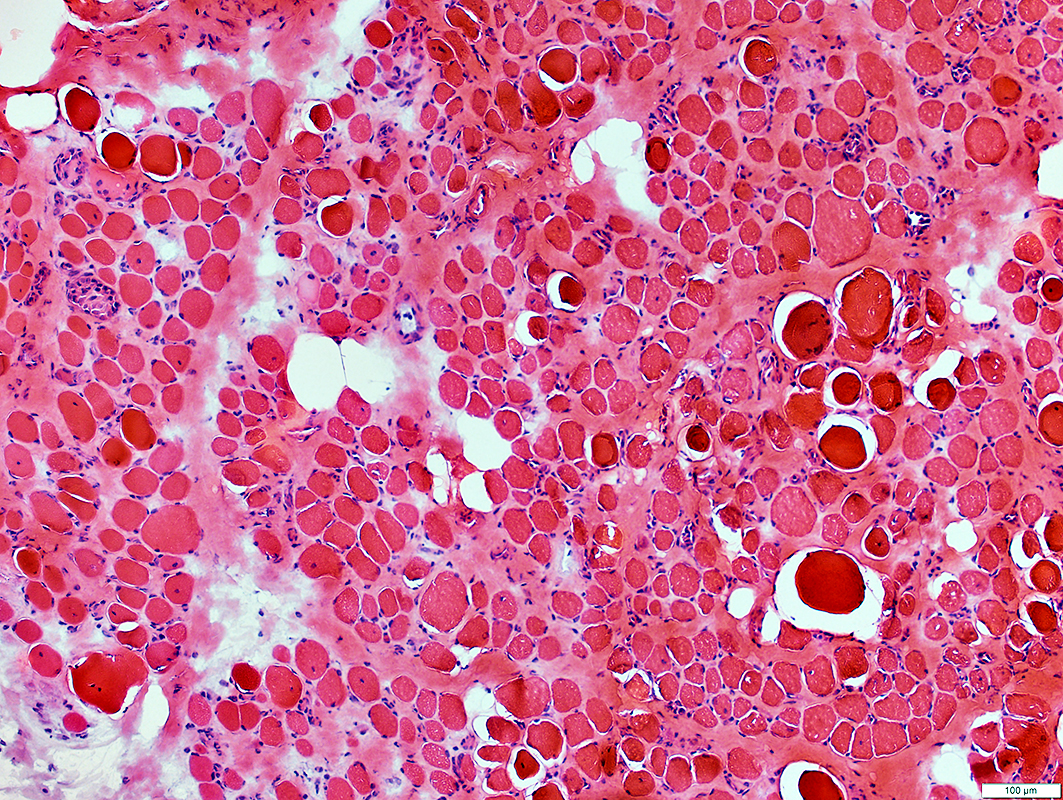
DMD Muscle pathology: General features
|
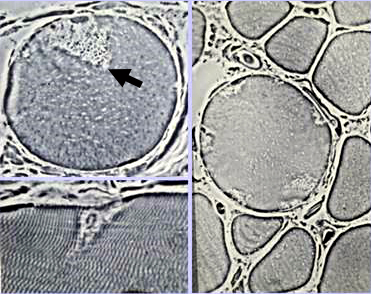 From: AG Engel Delta Lesions (Arrow)
Description: Focal wedge-shaped lesions Locations: Subsarcolemmal regions of muscle fibers |
|
Muscle fibers
Size: Varied
Shape: Small fibers round or polygonal
Internal nuclei
Hypercontracted
Necrosis
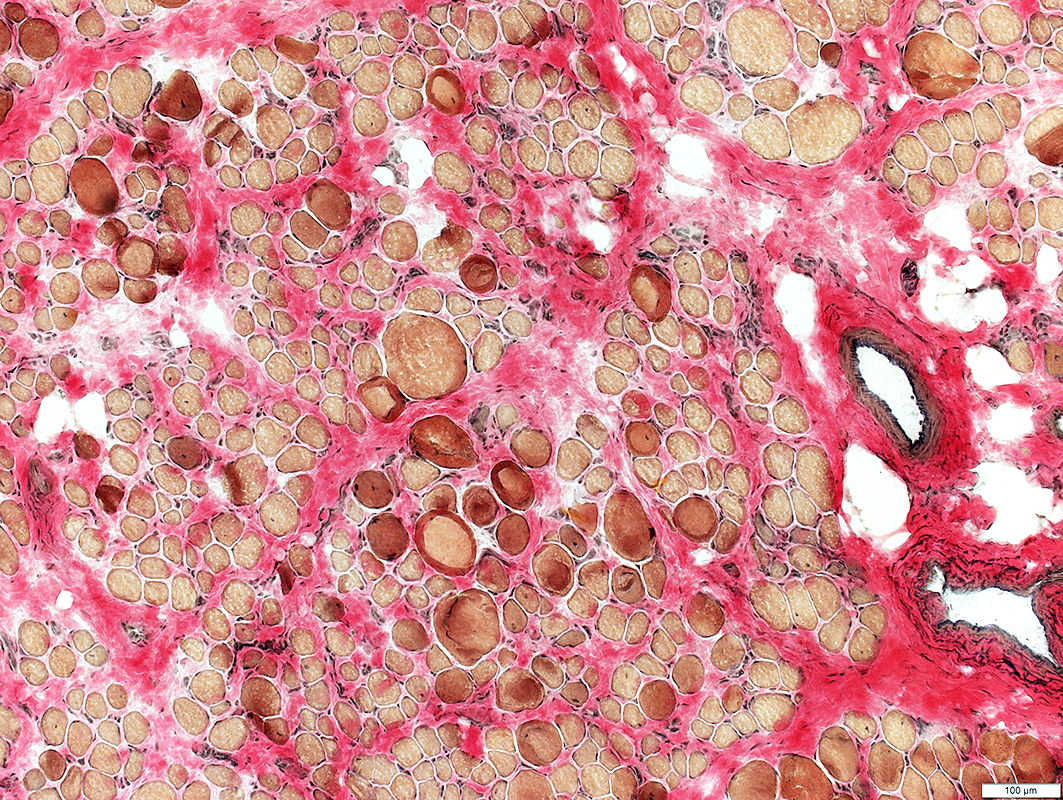
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased between muscle fibers
Fat: Increased in endomysium & preimysium
 H&E stain |
DMD
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased between muscle fibers
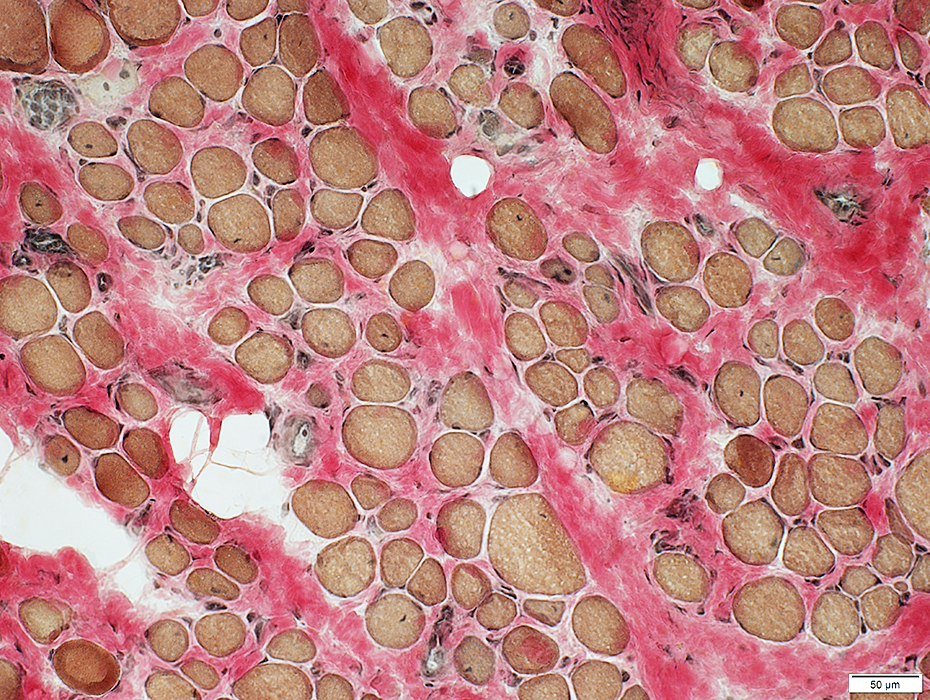 VvG stain |
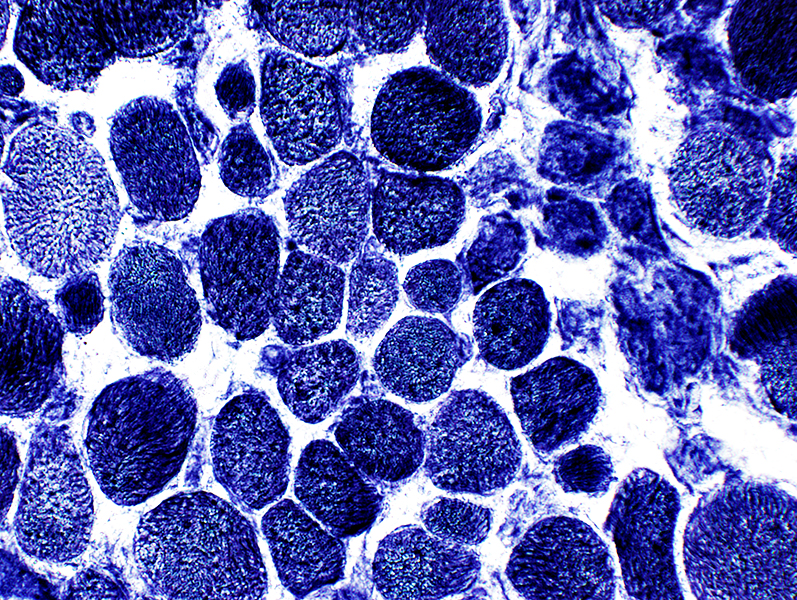 NADH stain |
Coarse internal architecture on NADH (Above)
2C fibers: Intermediate staining on ATPase pH 4.3 (Below)
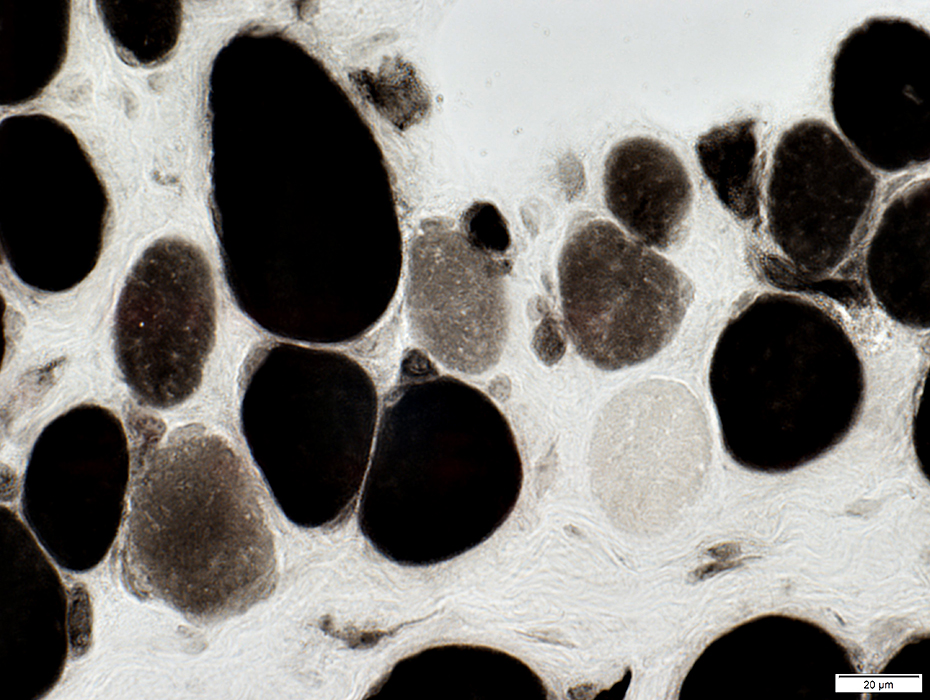 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
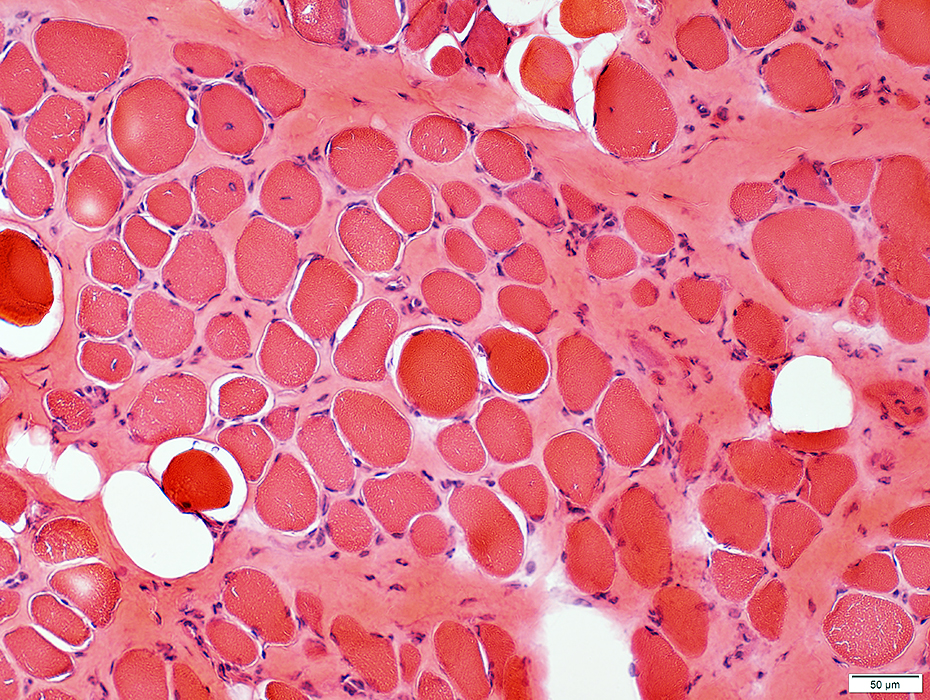
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Early Pathology
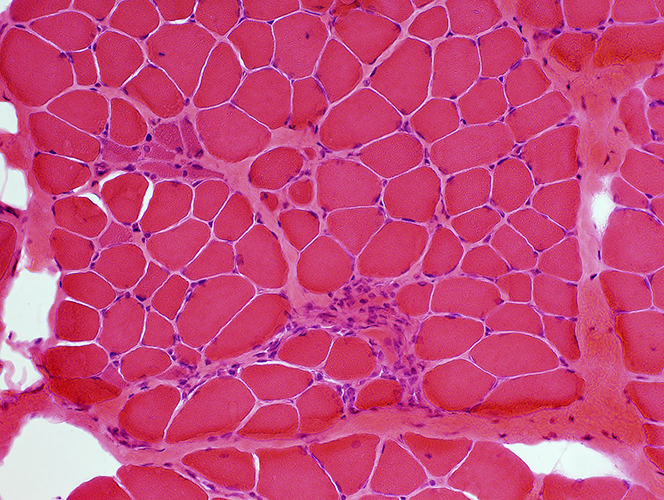 H & E stain |
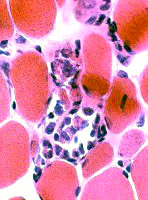
|
Muscle fibers Sizes: Varied; Small fibers are rounded or polygonal; Occasional hypertrophic fiber Necrosis (Left): Fibers scattered & in small groups Myopathic groups (Below): Clusters of small necrotic (Black arrow) & regenerating (White arrow) muscle fibers Internal nuclei: Occasional Endomysial connective tissue: Normal to mildly increased Perimysium: Early replacement by fat |
|
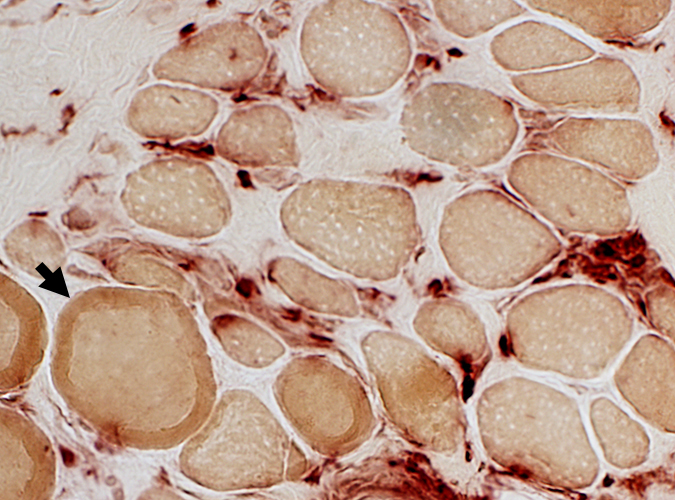 Acid phosphatase stain Acid phosphatase + cells Endomysium: Small Scattered cells Necrotic muscle fibers: Clusters of phagocytic cells Ring fibers (Arrow) |
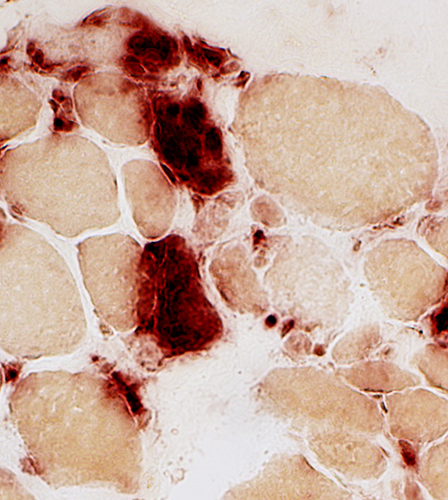 Acid phosphatase stain Acid phosphatase + cells Necrotic muscle fibers: Clusters of phagocytic cells |
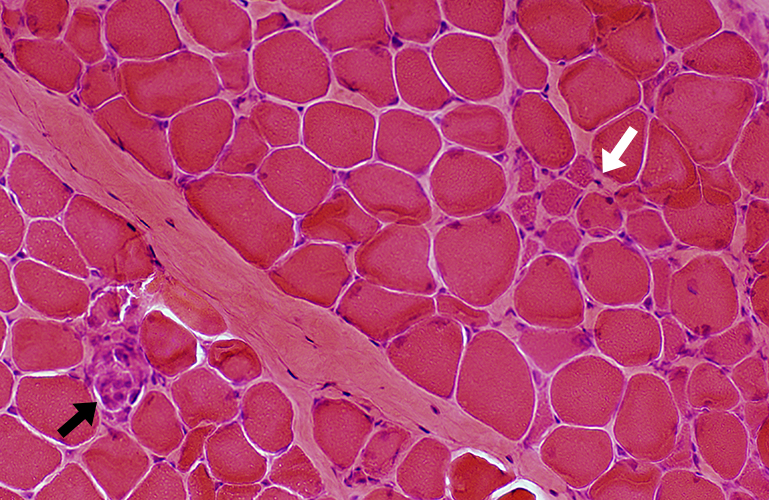
DMD: Muscle Fiber Necrosis
Necrotic Fibers: Scattered; Varied stages
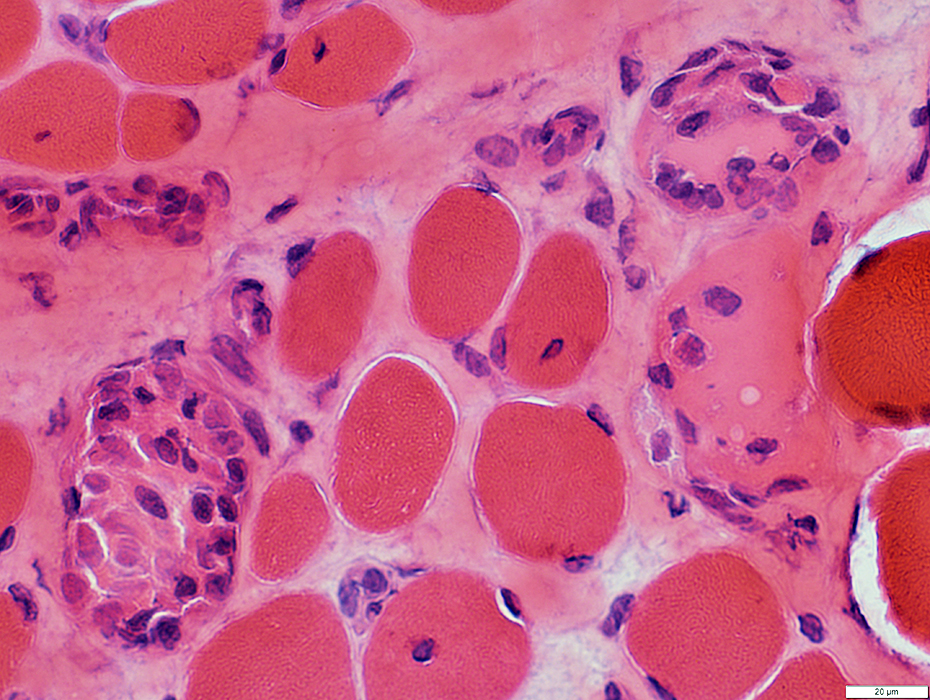 H&E stain |
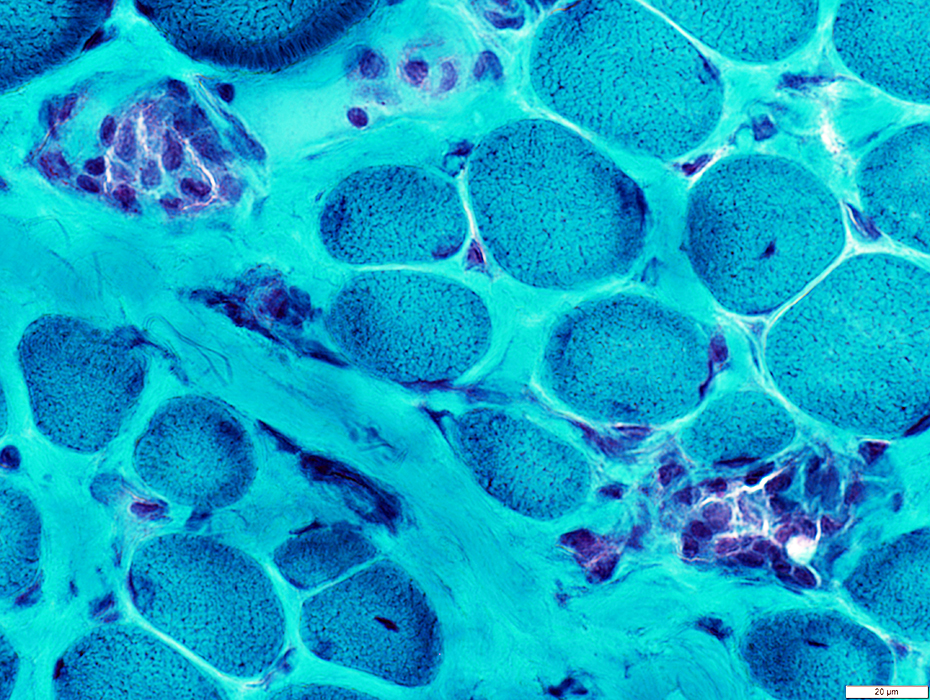 Gomori trichrome stain |
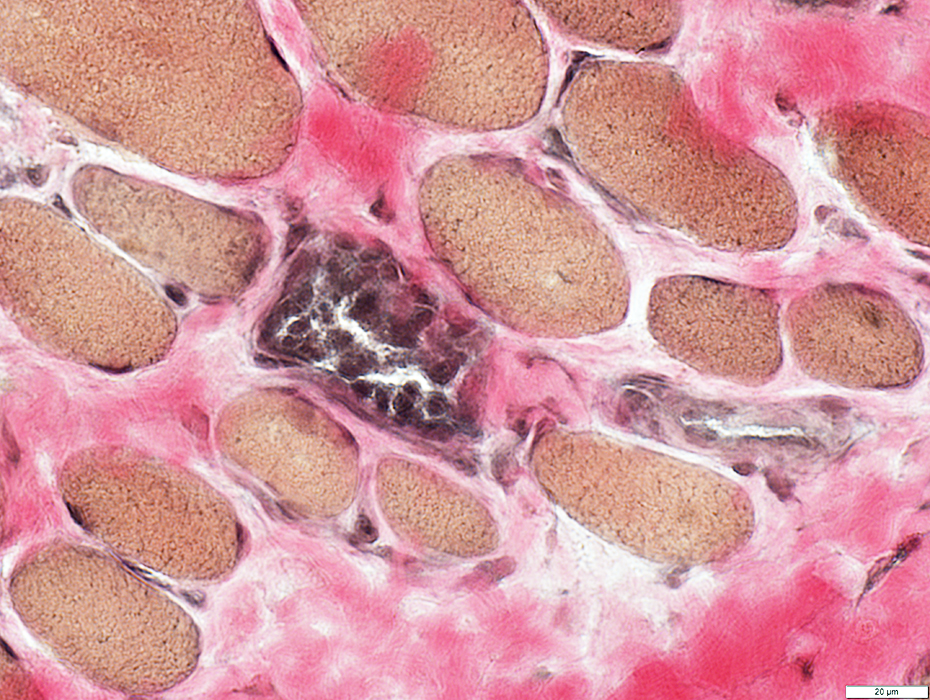 VvG stain |
Myopathic Grouping
|
Muscle fiber Stages Necrosis Regeneration Early Late |
Myopathic grouping: Necrotic muscle fibers, clustered
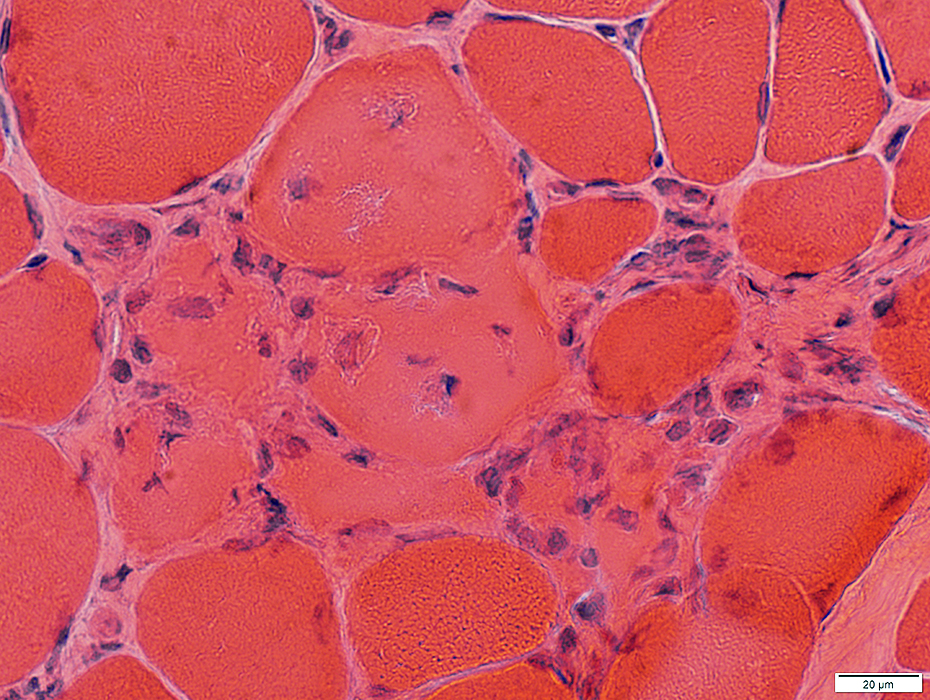 H&E stain |
Necrotic muscle fibers: Pale stained
Macrophages: Early invasion of muscle fibers
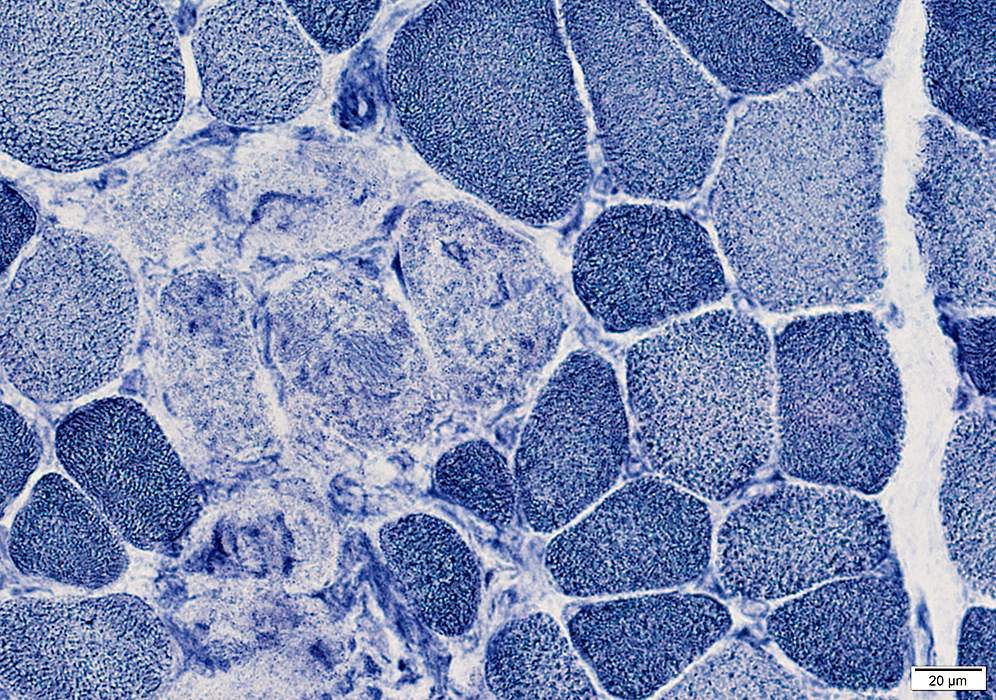 NADH stain Necrotic muscle fibers are pale on NADH stain |
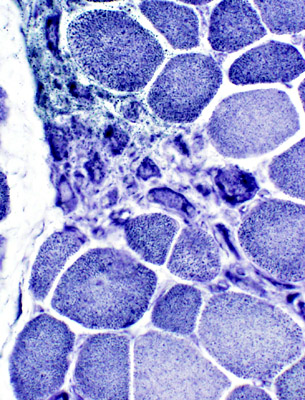
Myopathic grouping: Clusters of very small regenerating muscle fibers & histiocytic cells
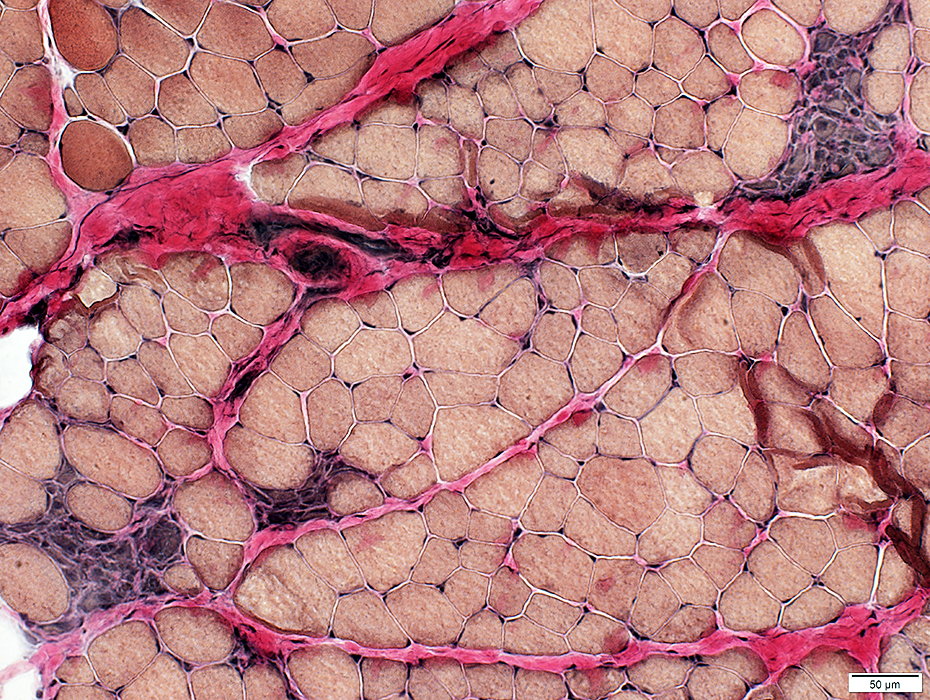 VvG stain |
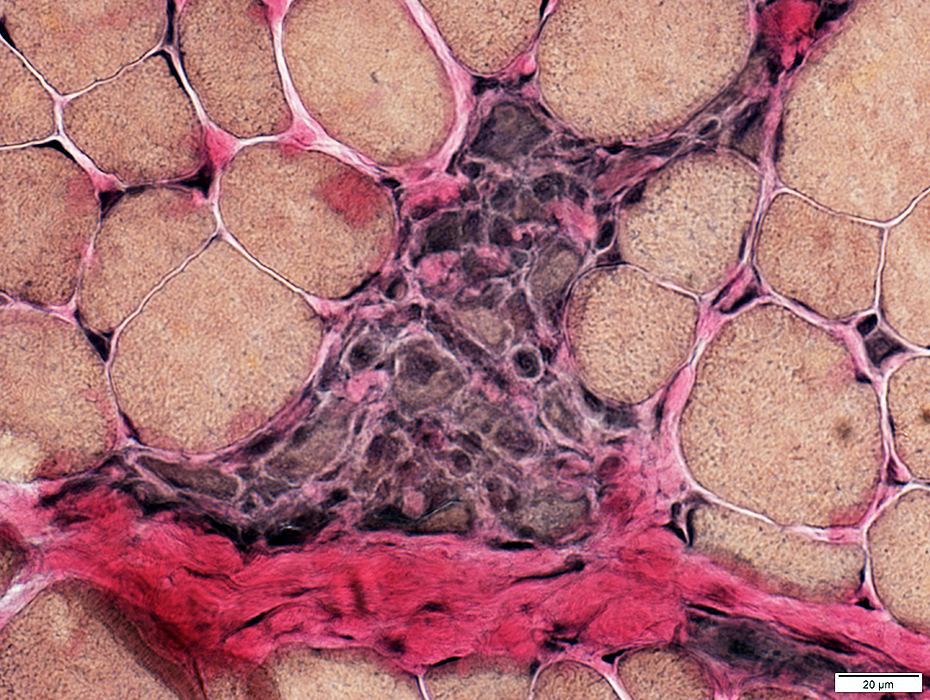 VvG stain |
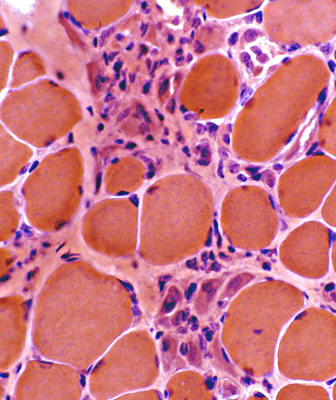 H & E stain |
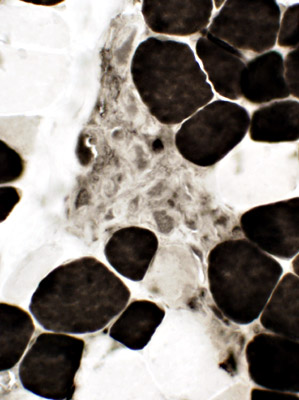 ATPase, pH 4.3 |
 NADH |
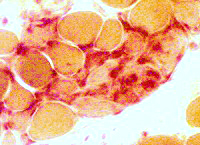 Clusters of small cells Many stain for Acid phosphatase 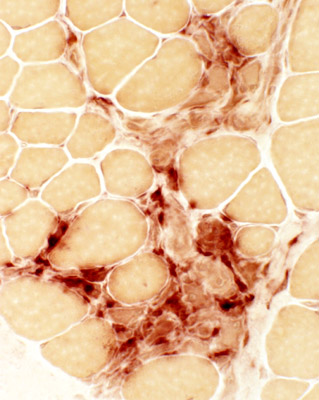 Acid phosphatase |
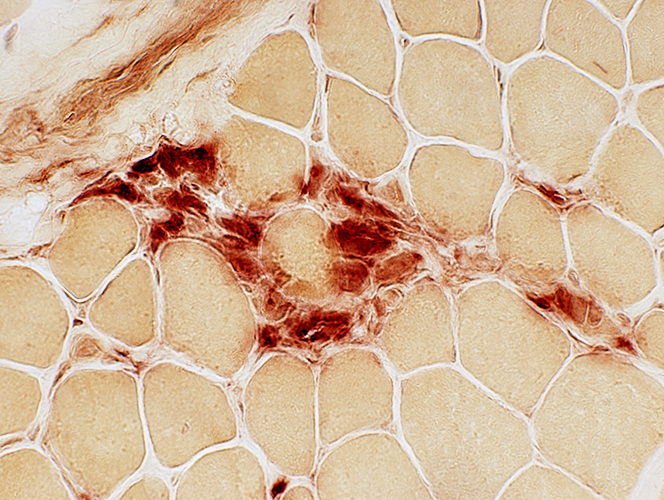 Acid phosphatase |
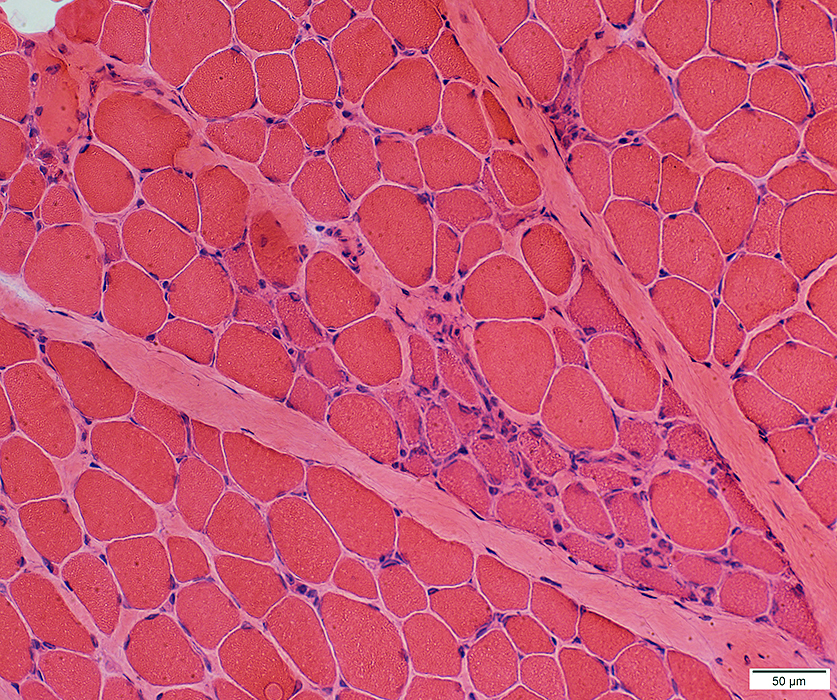 H & E stain |
Myopathic Grouping: Late
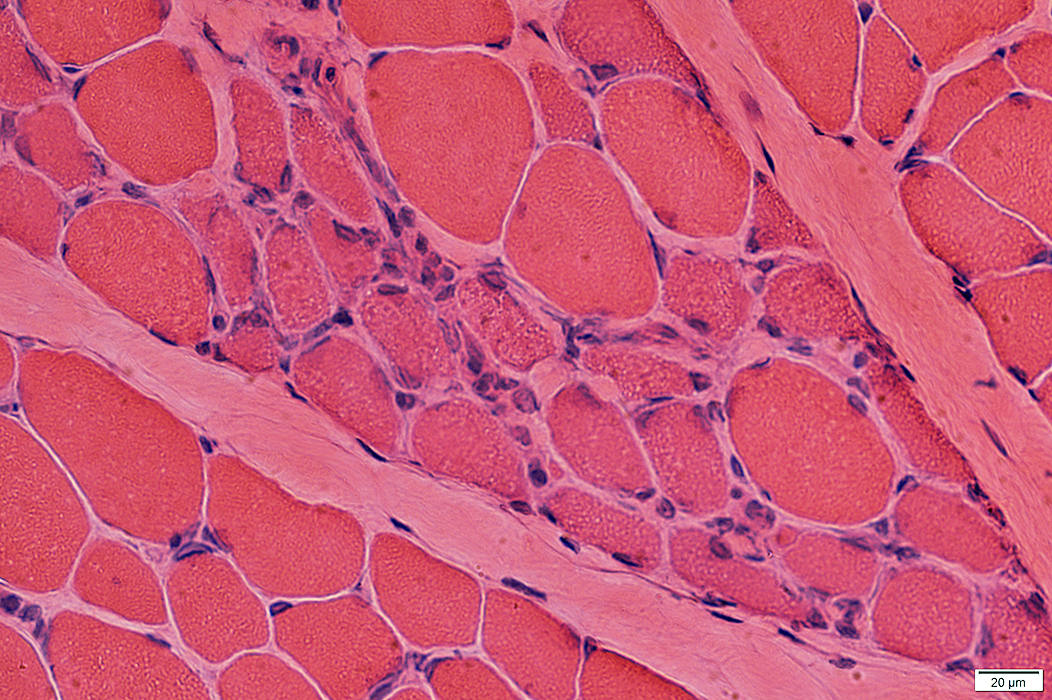 H & E stain |
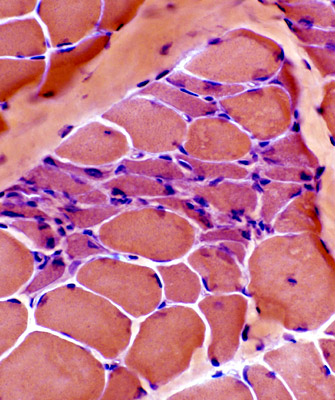 H & E stain Immature fibers are small & basophilic |
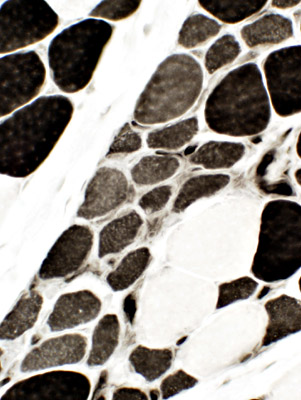 ATPase, pH 4.3 Immature fibers are: Small & 2C (Intermediate staining) |
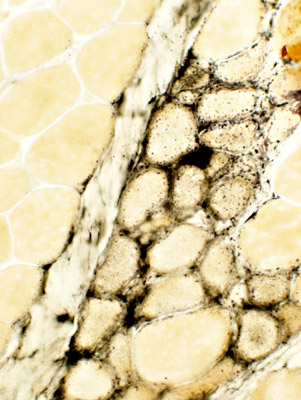 Alkaline phosphatase Immature small fibers have: Cytoplasmic staining |
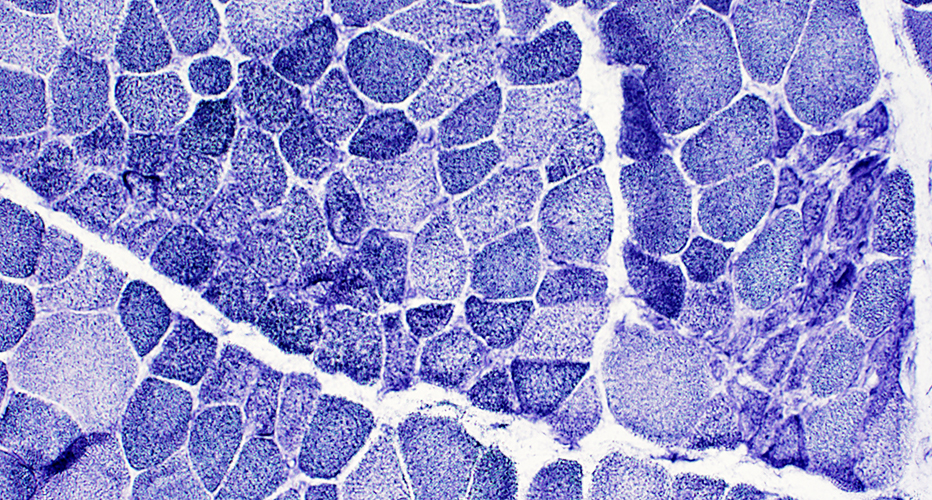 NADH Immature fibers have coarse cytoplasmic staining |
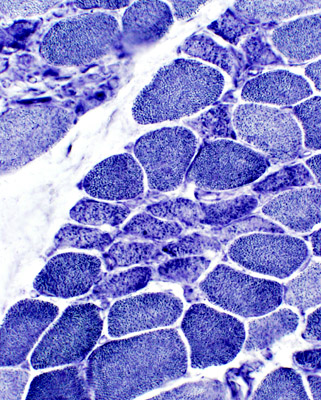 NADH |
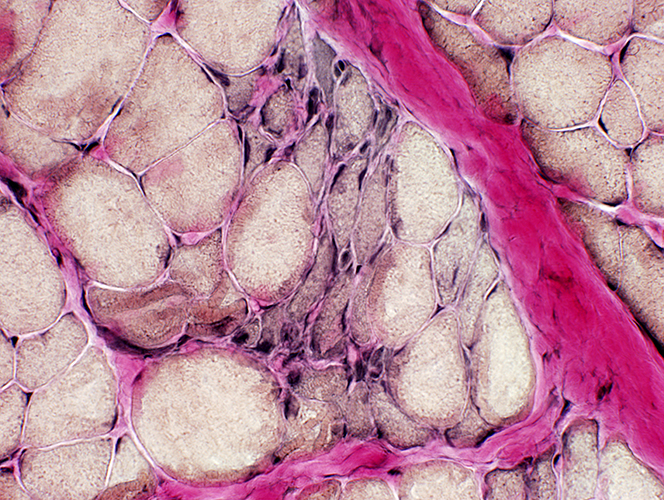 VvG Immature small fibers have coarse cytoplasmic staining |
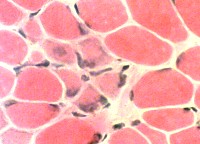
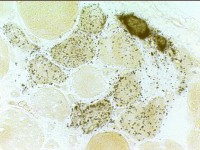
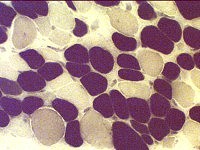
Immature muscle fibers: Many
|
|
|
Staining properties of immature muscle fibers includes: 1. H & E (left): Basophilic fibers 2. Alkaline phosphatase positive (center) 3. 2C fibers: Intermediate staining on ATPase pH 4.3 (right) | |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Severe at age 2 years
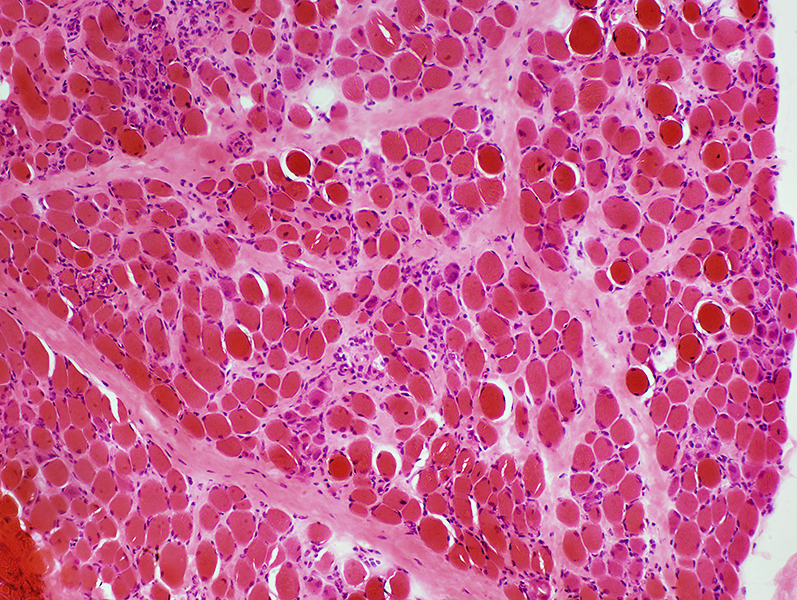 H&E stain |
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
Muscle fibers
Necrosis & Regeneration
Size: Varied
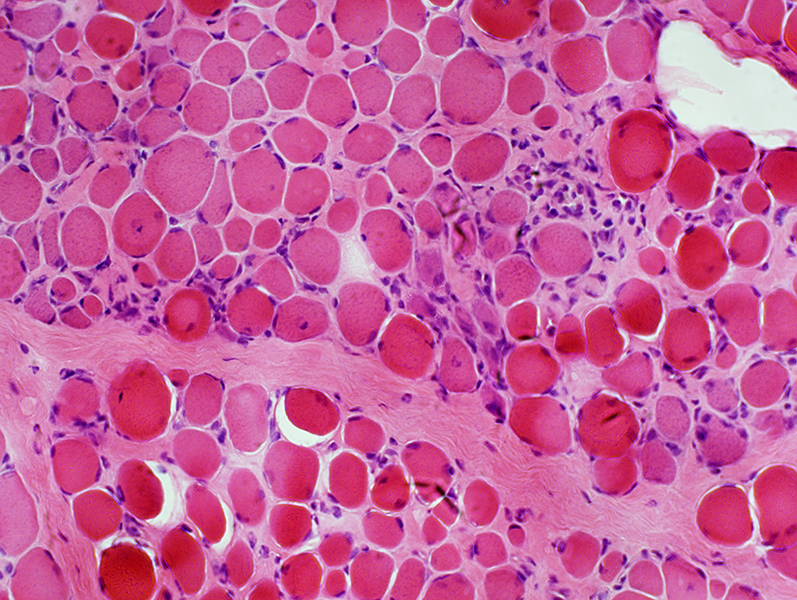 H&E stain |
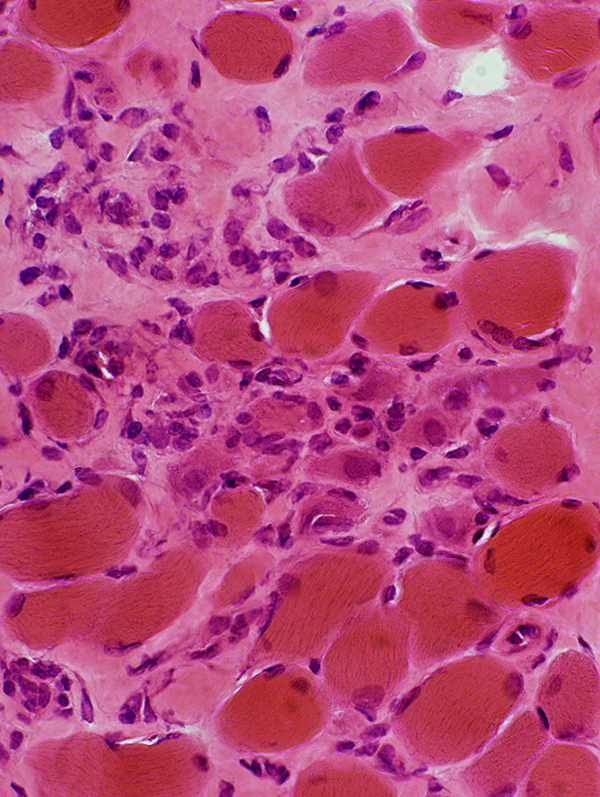
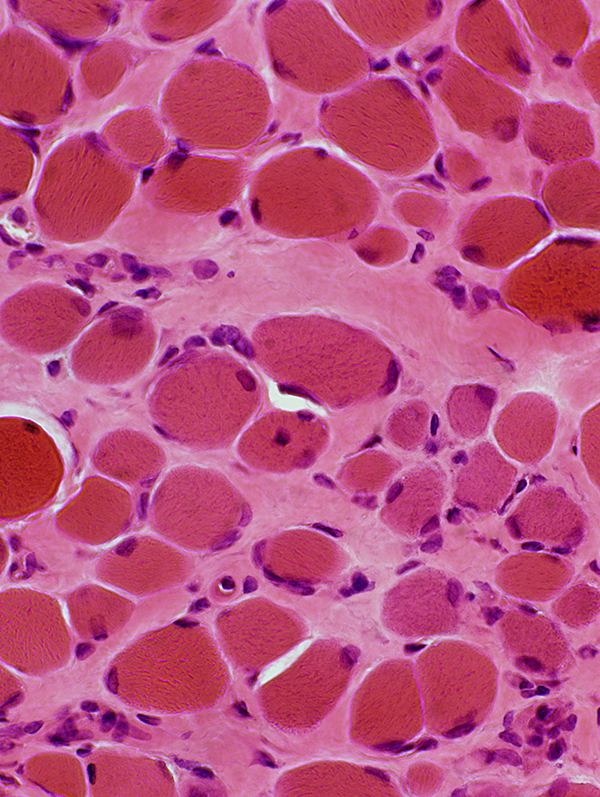 H&E stain |
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
Muscle fibers
Necrosis & Regeneration
Size: Varied
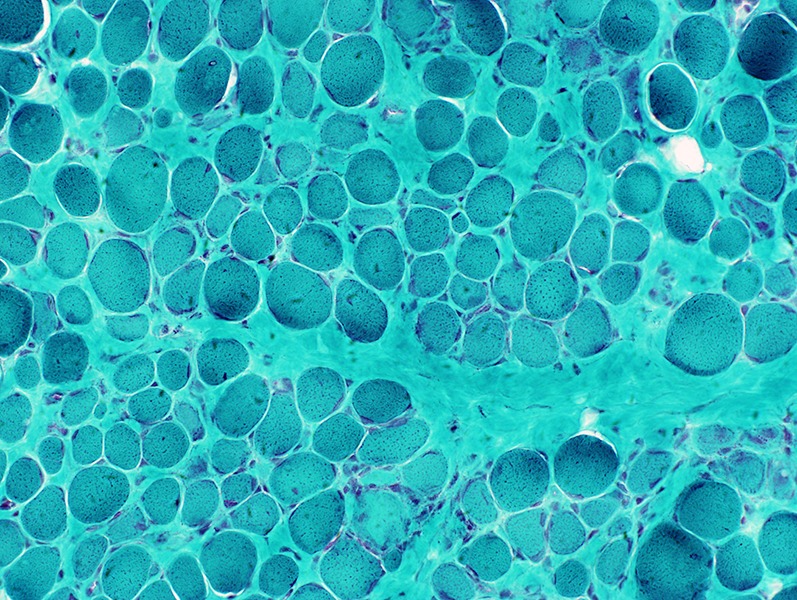 Gomori trichrome stain |
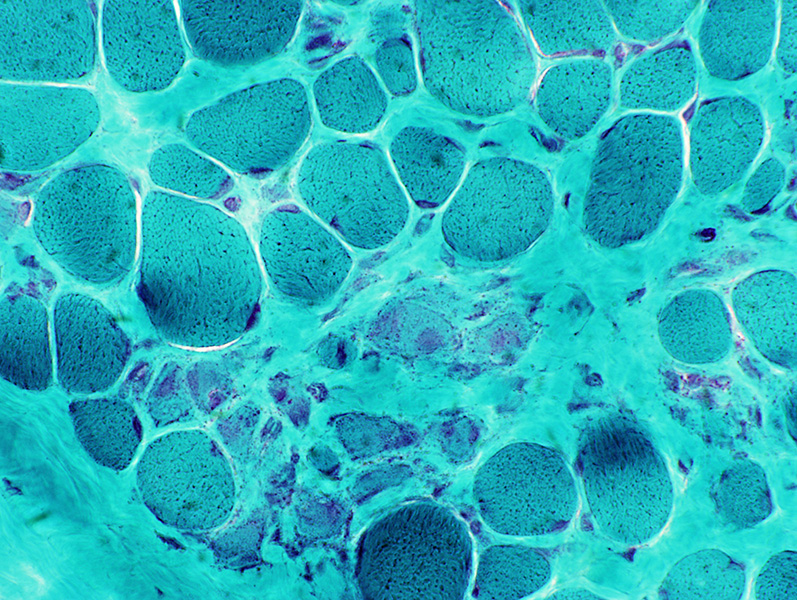 Gomori trichrome stain |
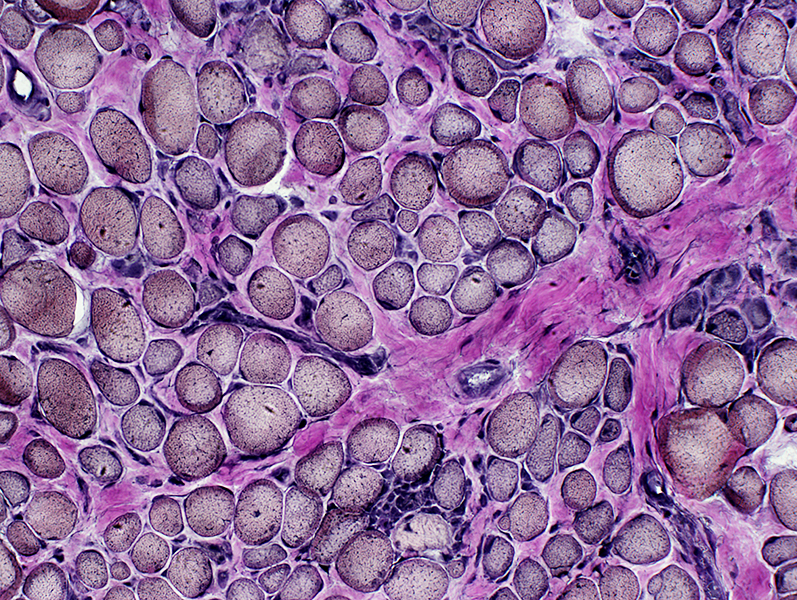 VvG stain |
DMD
Many intermediate-stained muscle fibers
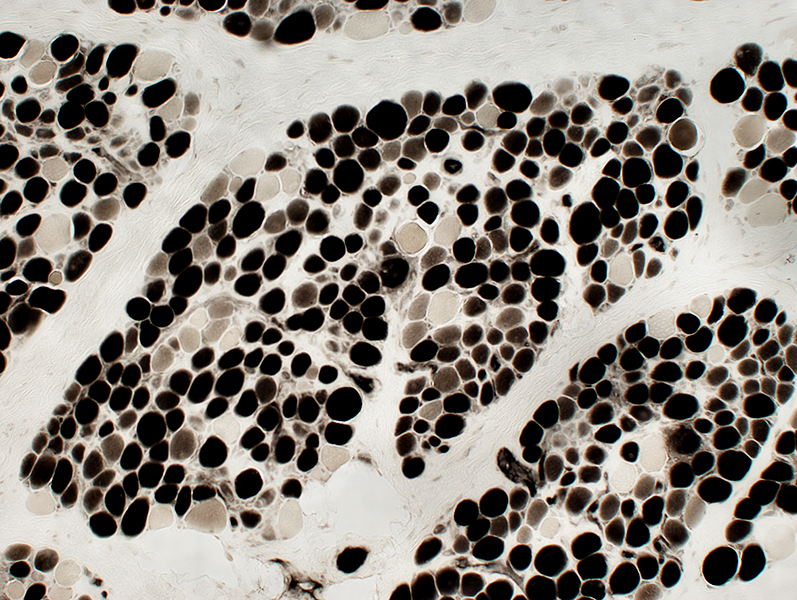 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Later Pathology (10 years)
|
Endomysial connective tissue Fat replacement Fiber types Internal architecture Necrotic fibers |
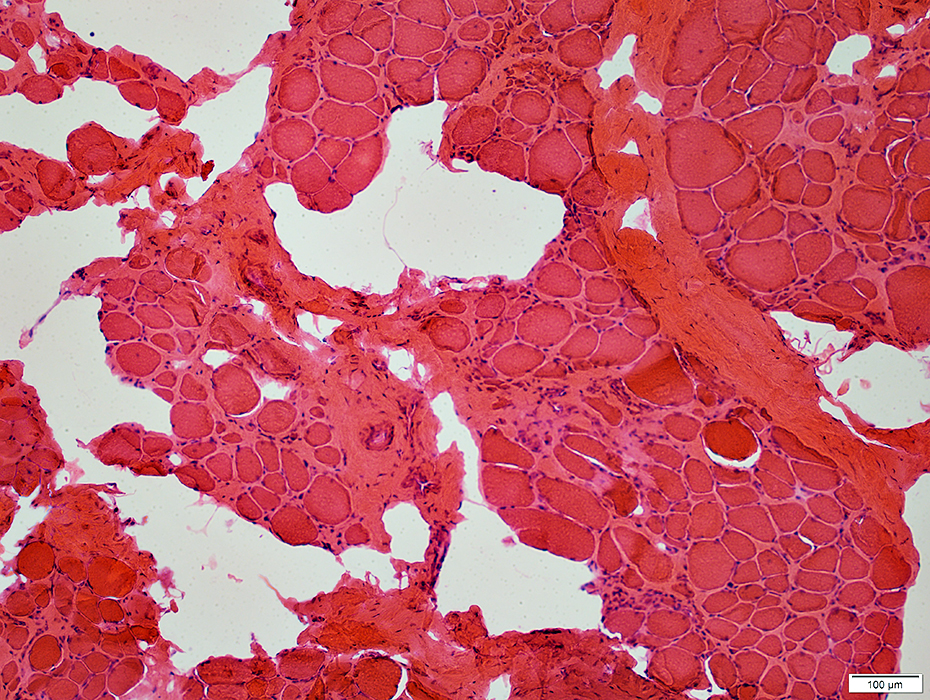 H&E stain |
Fiber size: Varied
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
Fat replacement of muscle: Prominent
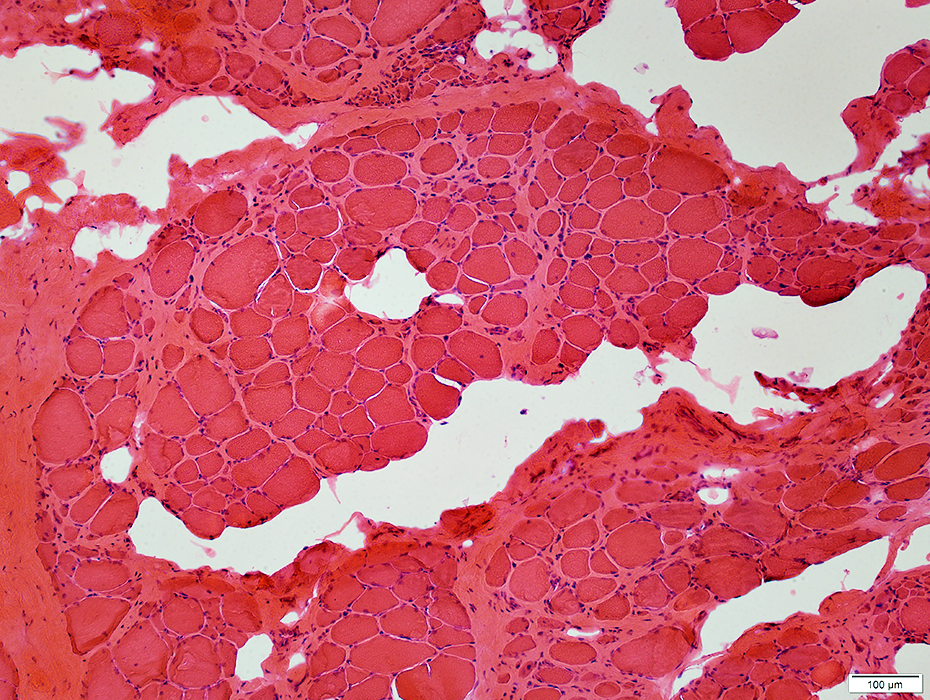 H&E stain |
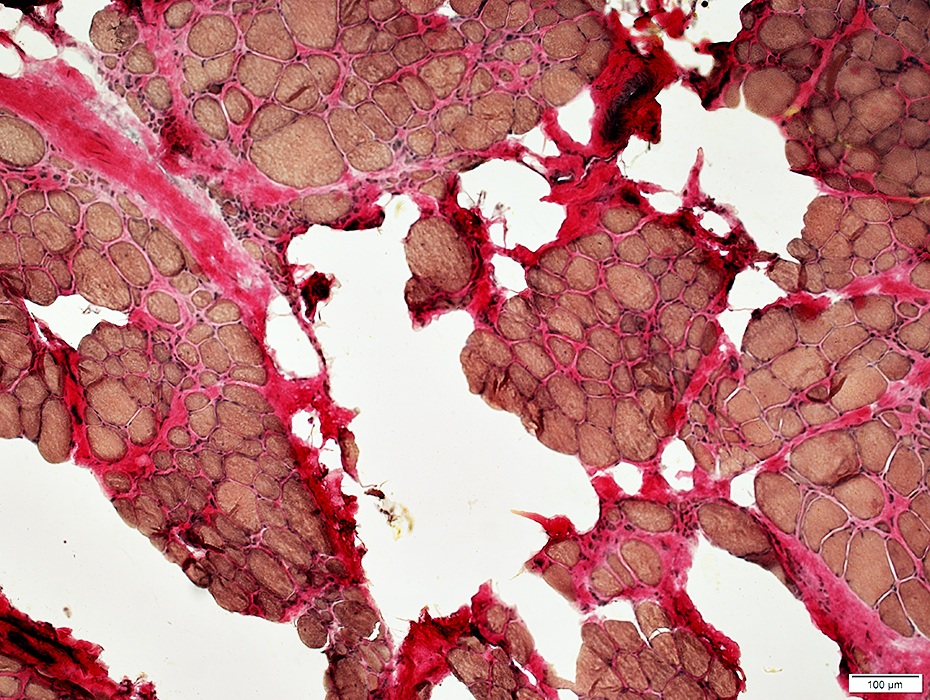 VvG stain |
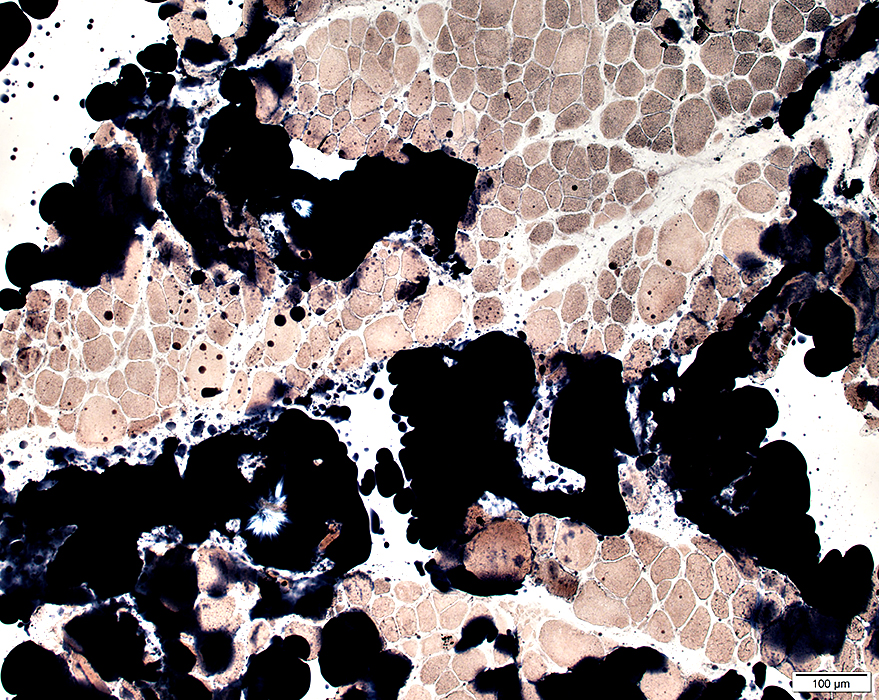 Sudan stain |
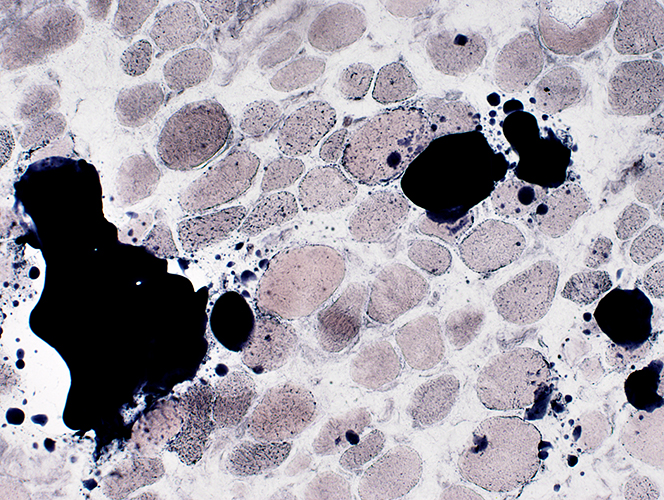 Sudan stain |
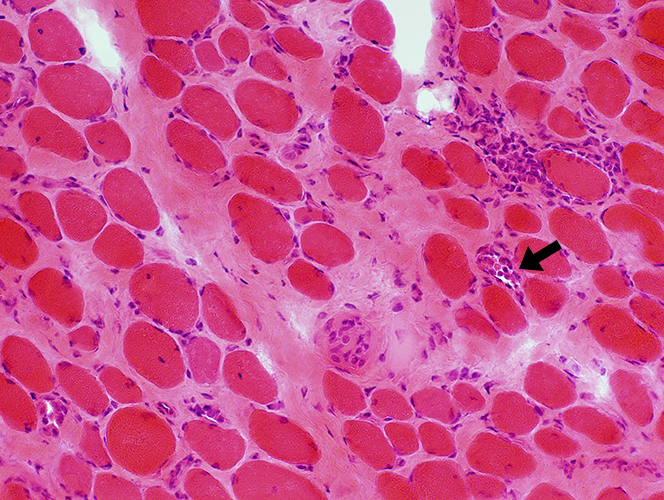 H&E stain Endomysial connective tissue: Increased Fiber size: Variable Small fibers: Rounded Large or hypercontracted muscle fibers: Scattered Necrotic fibers (Arrow): Scattered |
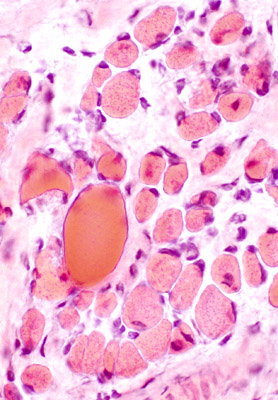
|
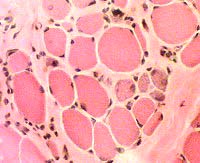 H&E stain 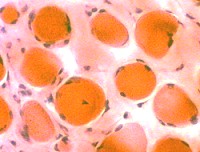 Endomysial connective tissue Increased between fibers |
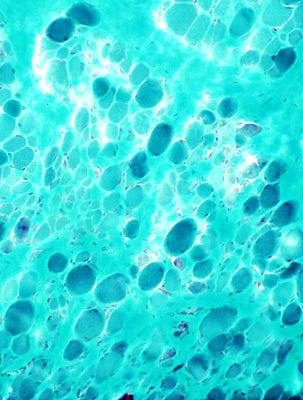
|
|
Muscle fiber size: Varied
Small & Large fibers: May be are either type (I = Dark; II = Light)
Many type IIC fibers: Smaller size; Intermediate stain
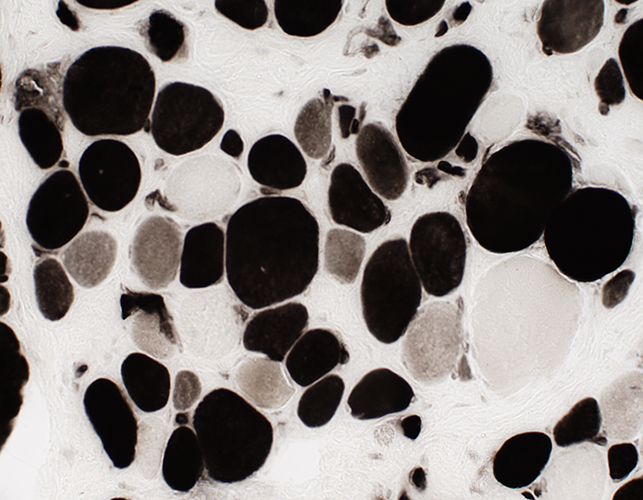 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
DMD late: Few necrotic muscle fibers
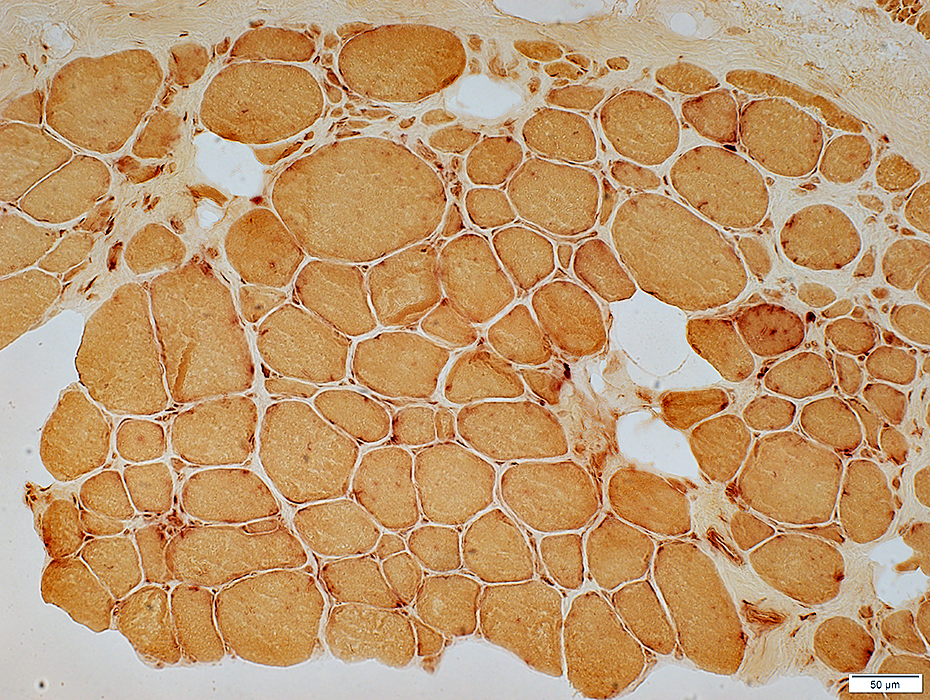 Acid phosphatase stain |
Muscle fiber internal architecture: Coarse
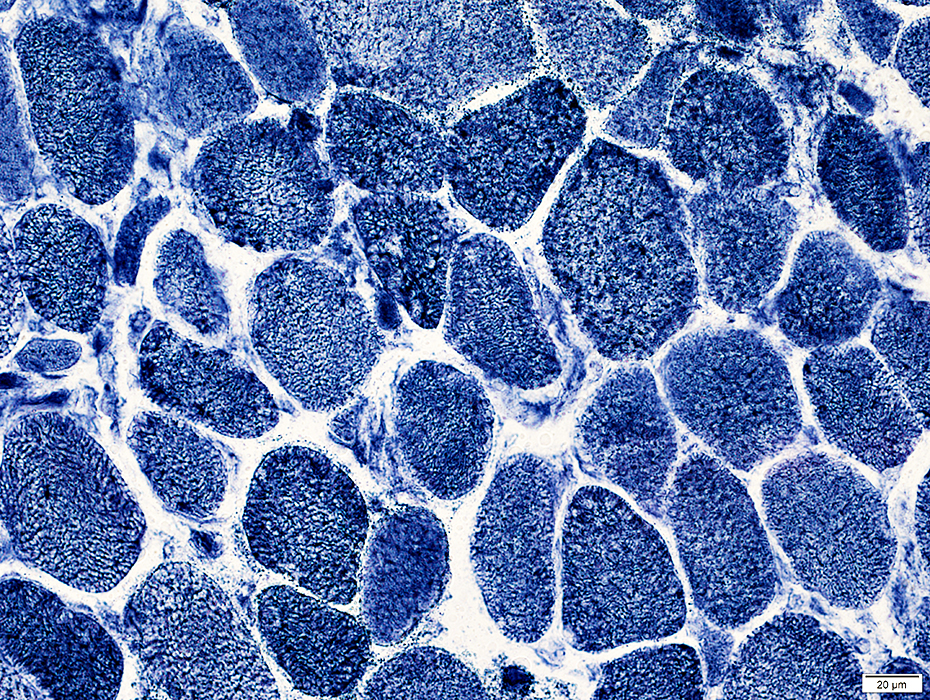 NADH stain |
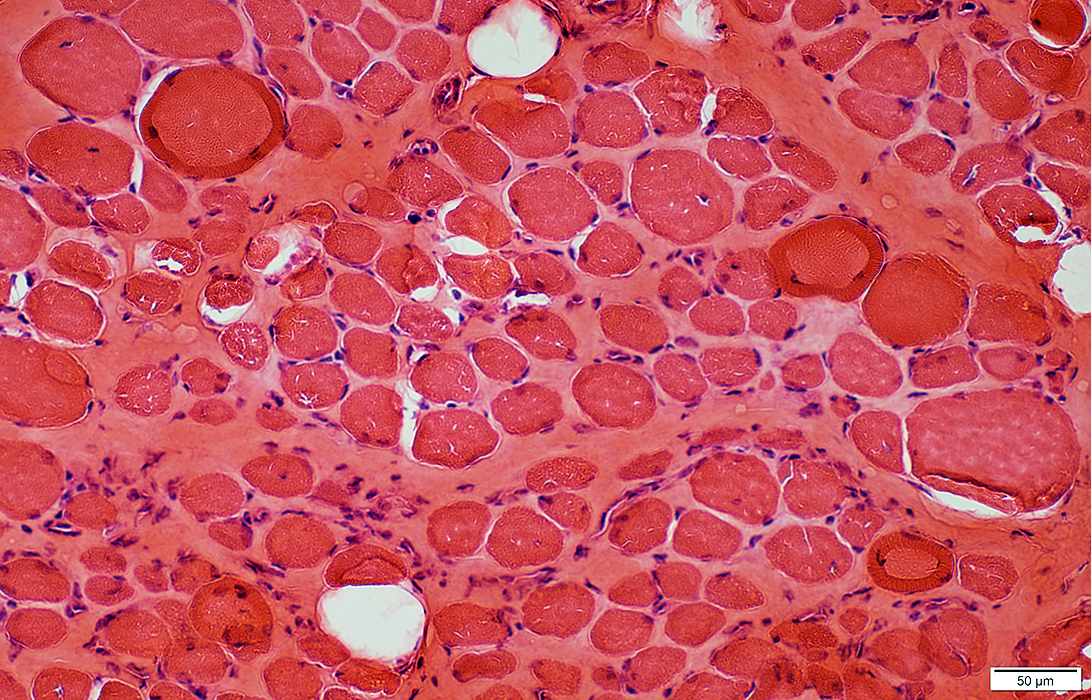 H&E stain |
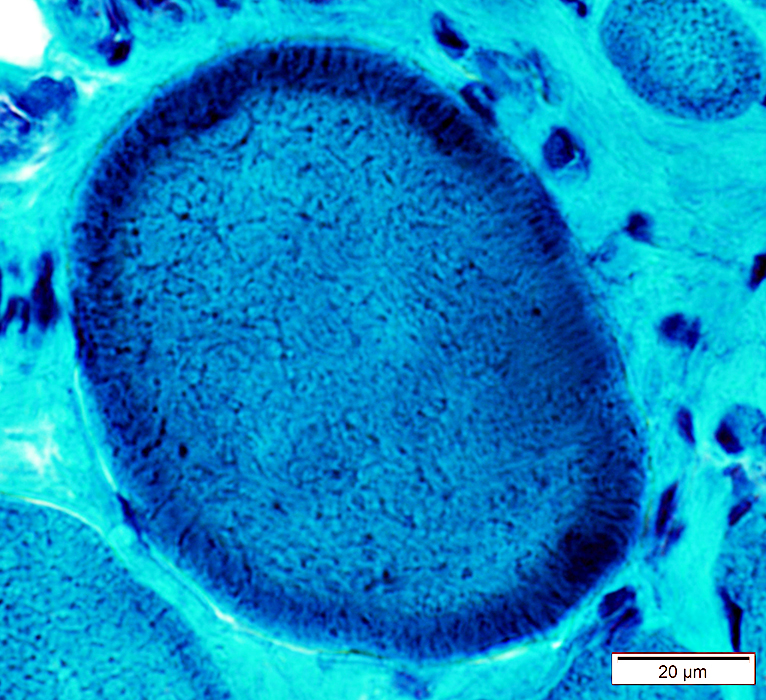 Gomori trichrome stain |
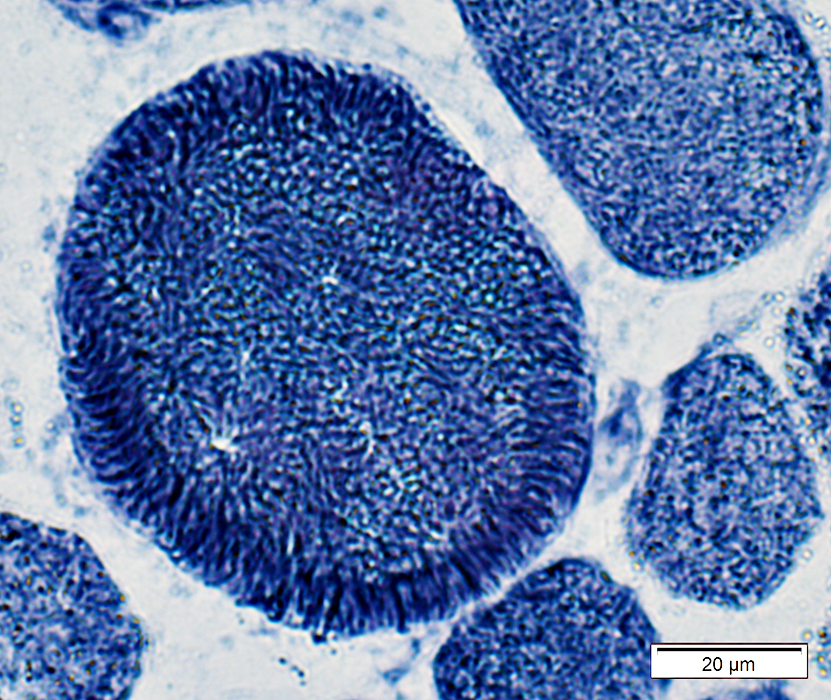 NADH stain |
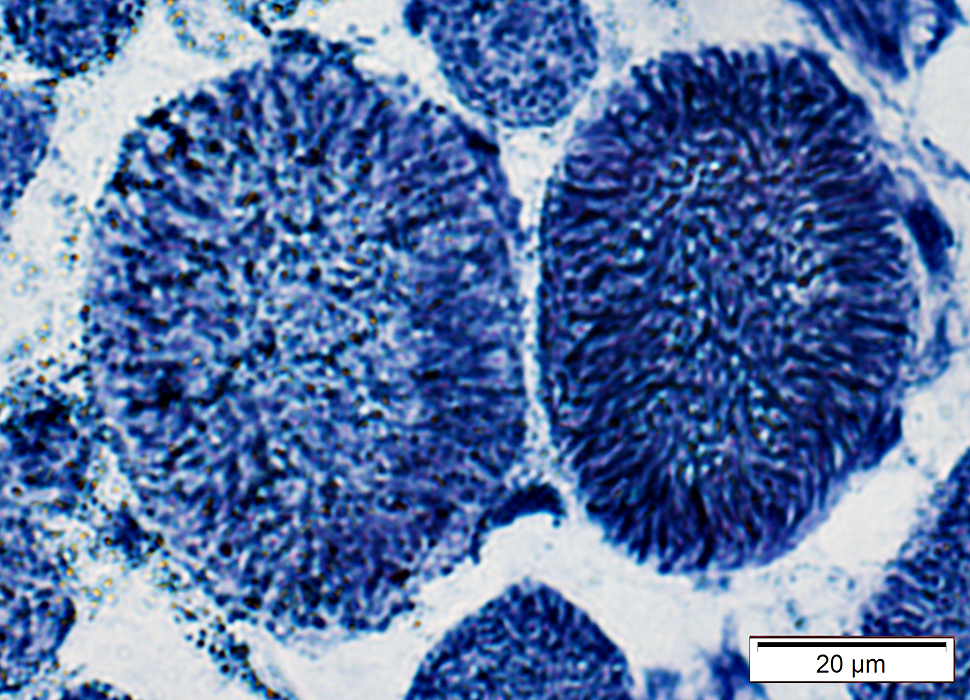 NADH stain |
Dystrophin staining
Normal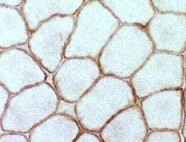
|
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: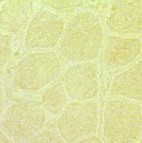
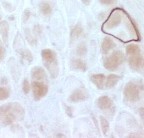
|
|
Normal dystrophin staining around the rim of muscle fibers. |
Absent dystrophin: Duchenne muscular dystrophy Left: No staining around the rim of any muscle fibers Right: No staining of most muscle fibers One "revertant" fiber with dystrophin staining. Revertant fibers reflect a somatic mutation allowing dystrophin expression |
|
Normal: Dystrophin present near surface of muscle fibers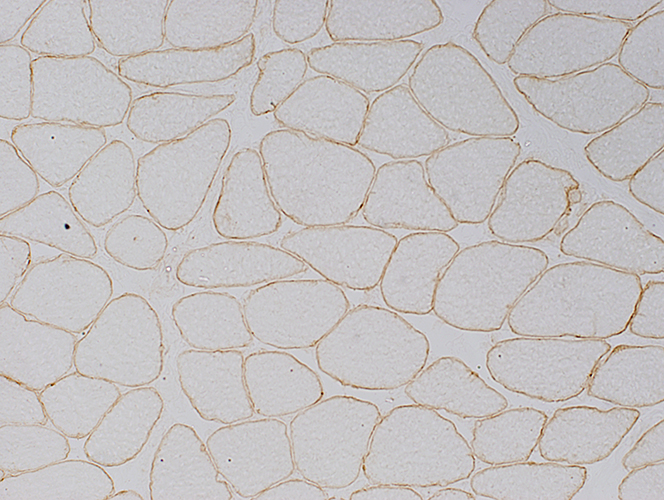  Dys1 stain Duchenne MD: Dystrophin absent from surface of muscle fibers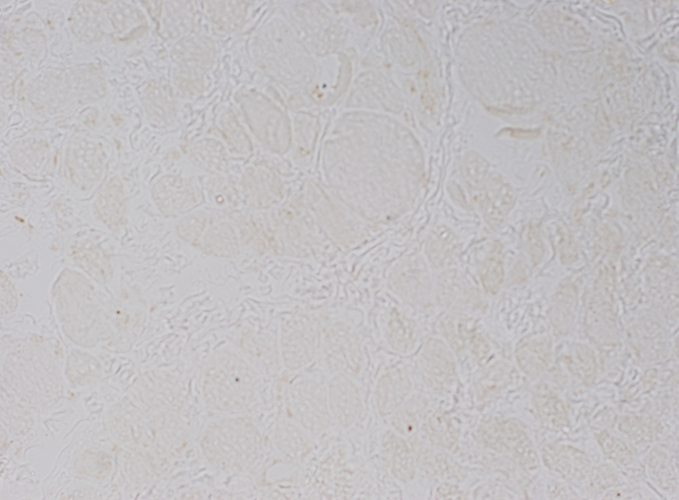  Dys1 stain |
Muscle from Duchenne MD male with large area of revertant muscle fibers
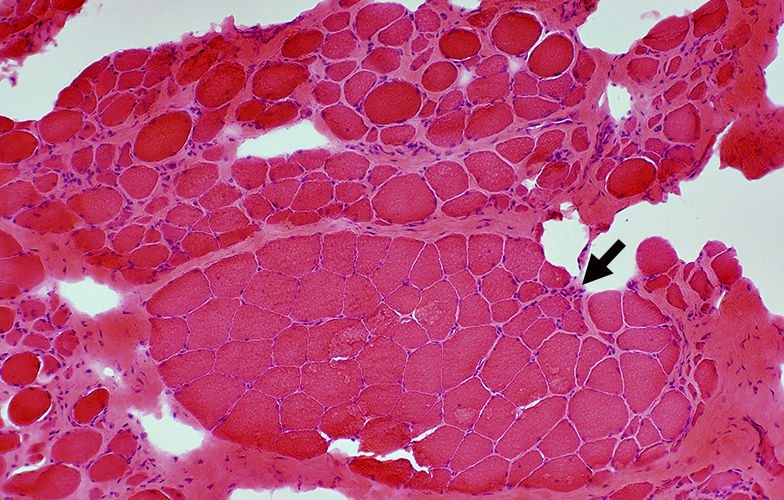
|
Dystrophin staining (Below): Muscle fibers in preserved fascicle are revertants with dystrophin present around their rim
Some revertant muscle fibers are present in myopathic regions as well.
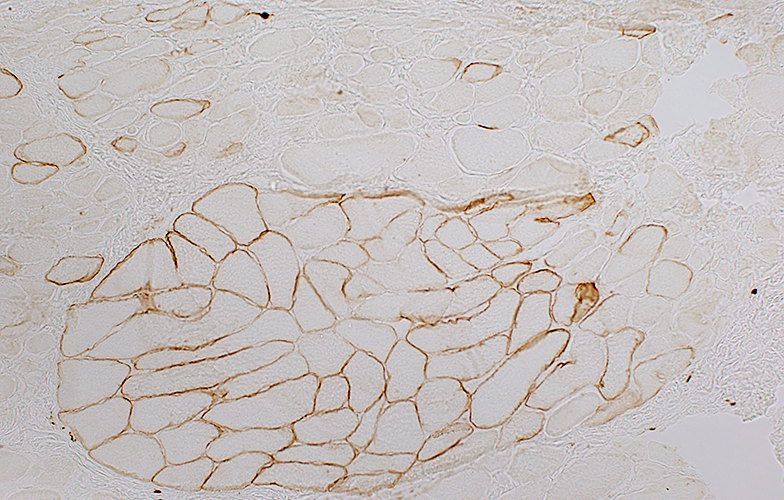
|
Western blot: Dystrophin from dystrophinopathies
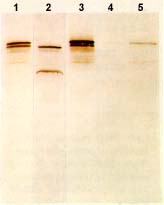 from Novocastra Lane 1: Becker dystrophy; Dystrophin has reduced abundance but normal size. Lane 2: Becker dystrophy; Dystrophin has reduced size and abundance. Lane 3: Normal; Dystrophin has normal size and amount. Lane 4: Duchenne dystrophy; Almost no protein is present. Lane 5: Duchenne outlier; Dystrophin has severely reduced abundance. |
Go to Becker muscular dystrophy pathology
Return to Dystrophinopathies.
Return to Neuromuscular syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular home page
References
1. J Gen Physiol 2022;15:e202213081
8/2/2023