ACID MALTASE DEFICIENCY
|
Onset Infant Child Adolescent Adult Storage patterns Ultrastructure Vascular |
 H&E stain |
Adolescent Onset
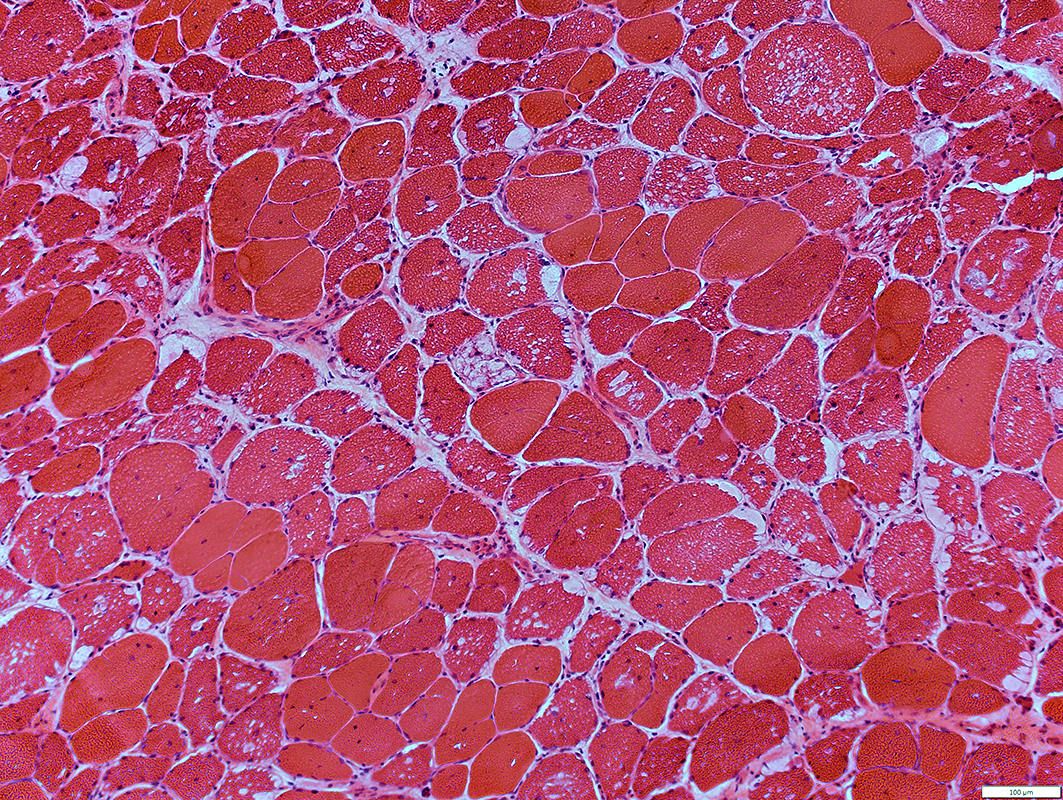 H & E stain |
Muscle fiber sizes: Varied
Vacuoles in muscle fibers
Locations: Subsarcolemmal & Internal
Contents: Clear or Pink-red staining material
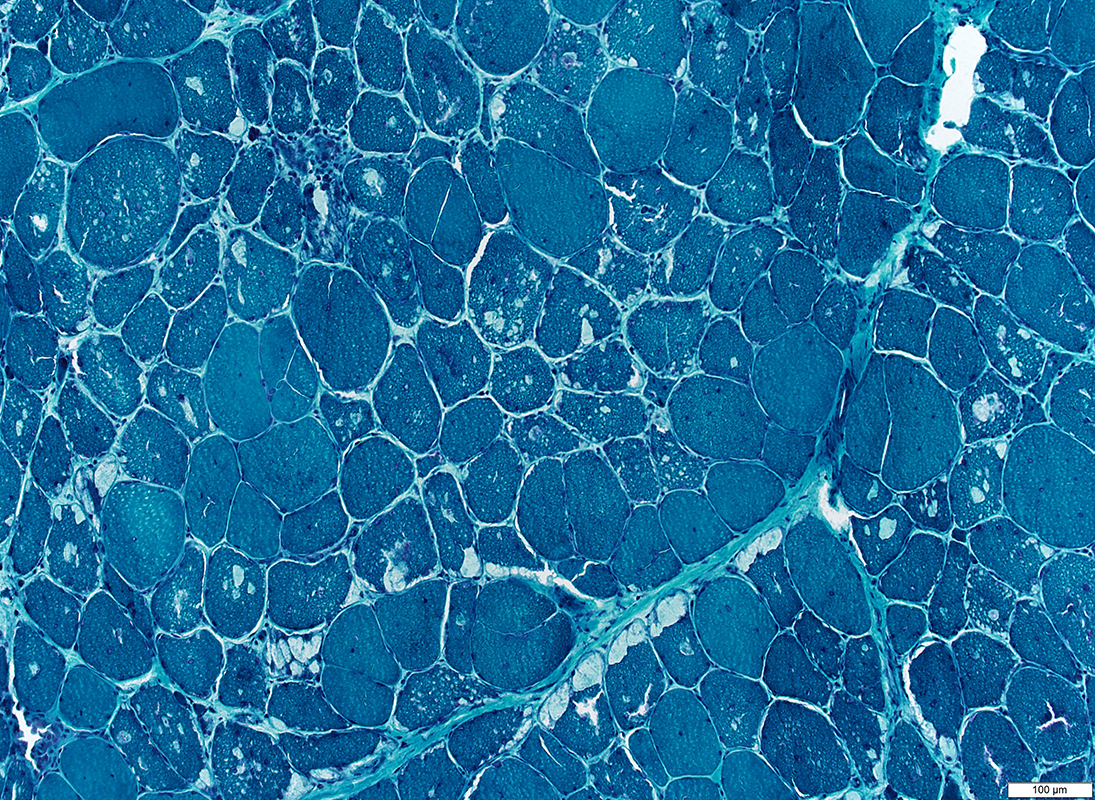 Gomori trichrome stain |
 H & E stain |
 H & E stain |
 H & E stain |
- Vacuoles
- Border: Sharp; No rim
- Location: Cytoplasmic & Subsarcolemmal
- Size: Variable: Small & Large, May occupy most of fiber area
- Multiple in individual fibers
- Most prominent in Type I muscle fibers
- More prominent in some muscles, especially weak ones
- Contents: Pale punctatew or wispy red material
- Muscle fibers: Other features
- Necrosis: Rare fibers (Above; Arrow)
- Size: Varied
- Myonuclei: Large
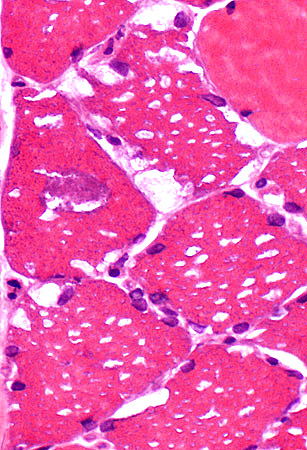
 H & E stain Clear vacuoles Size: Small or Large Location: Subsarcolemmal or Central Number: Multiple in individual muscle fibers May contain myonuclei May be marked variation in muscle fiber involvement (Below): Some severe, Others none |
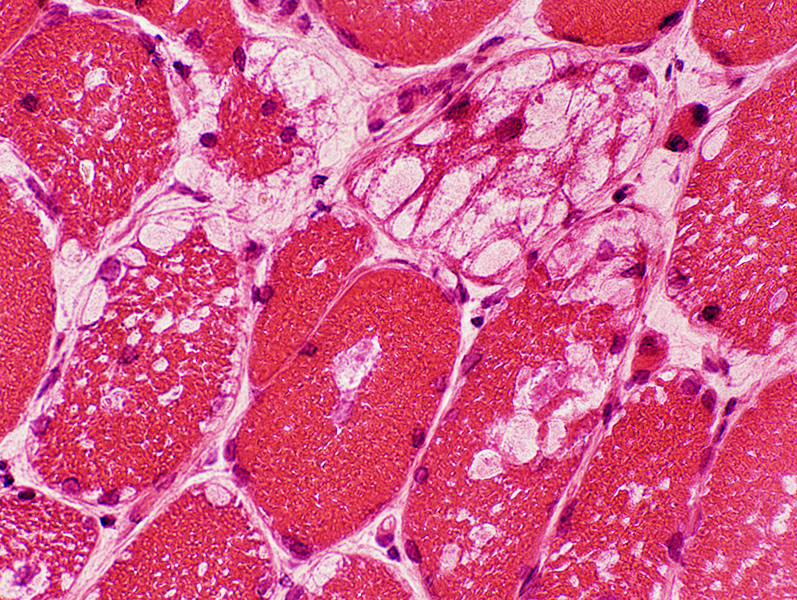
 H & E stain |
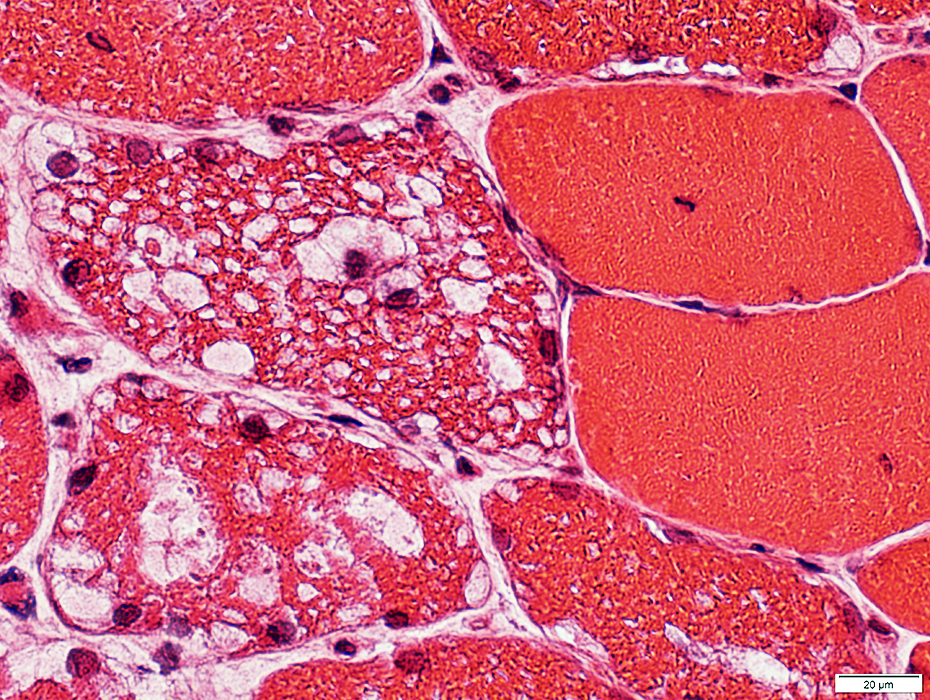 H & E stain |
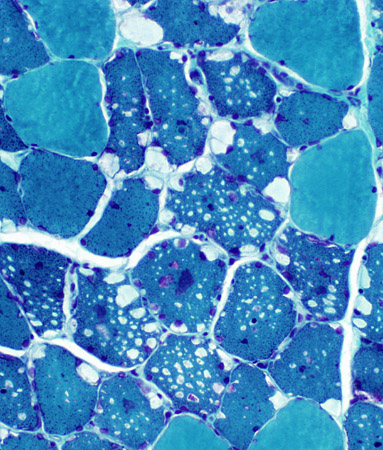 Gomori trichrome stain |
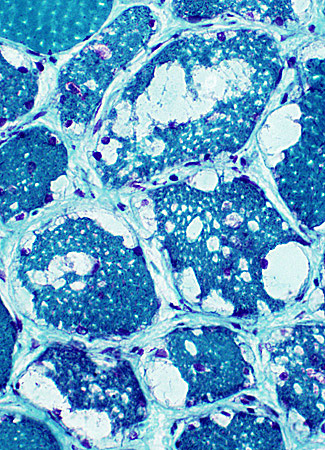 Gomori trichrome stain |
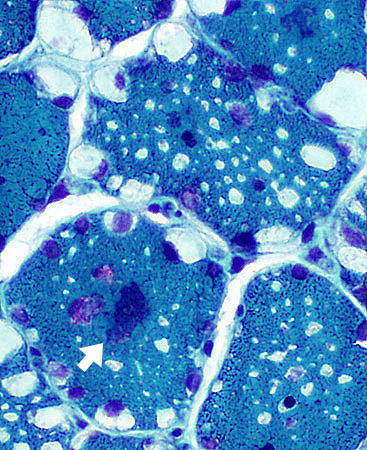 Gomori trichrome stain |
Clear vacuoles
Small aggregates: Red (Below); Purple (Above right; Arrow)
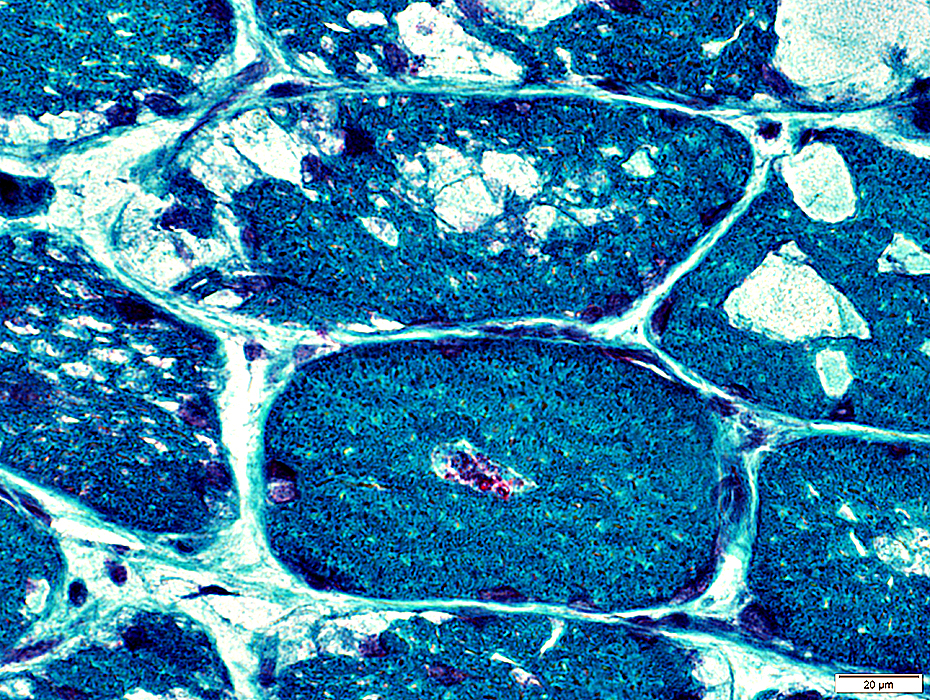 Gomori trichrome stain |
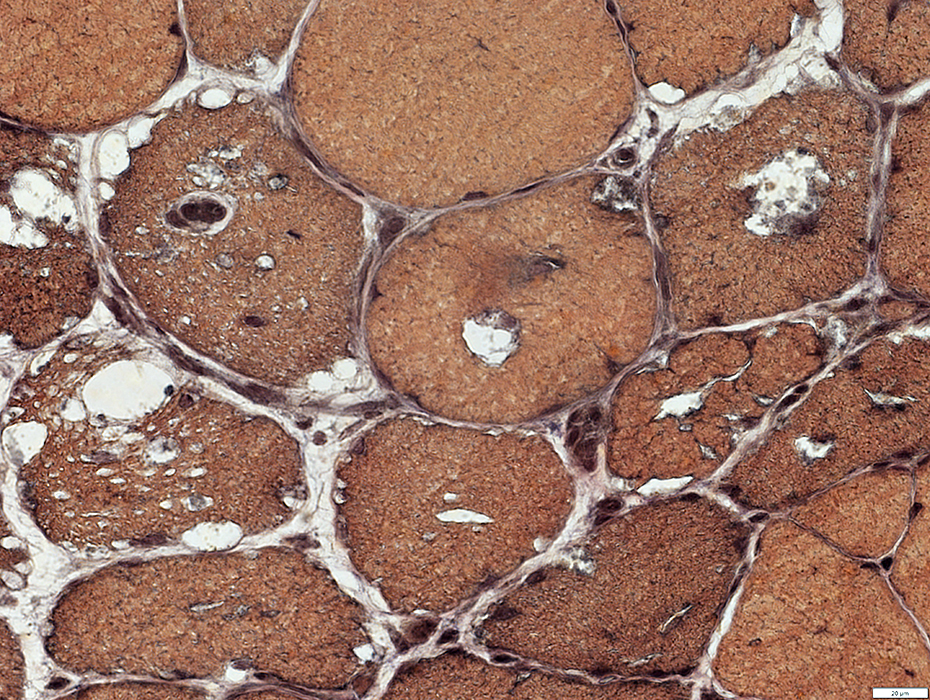 VvG stain |
Vacuoles & Aggregates in muscle fibers
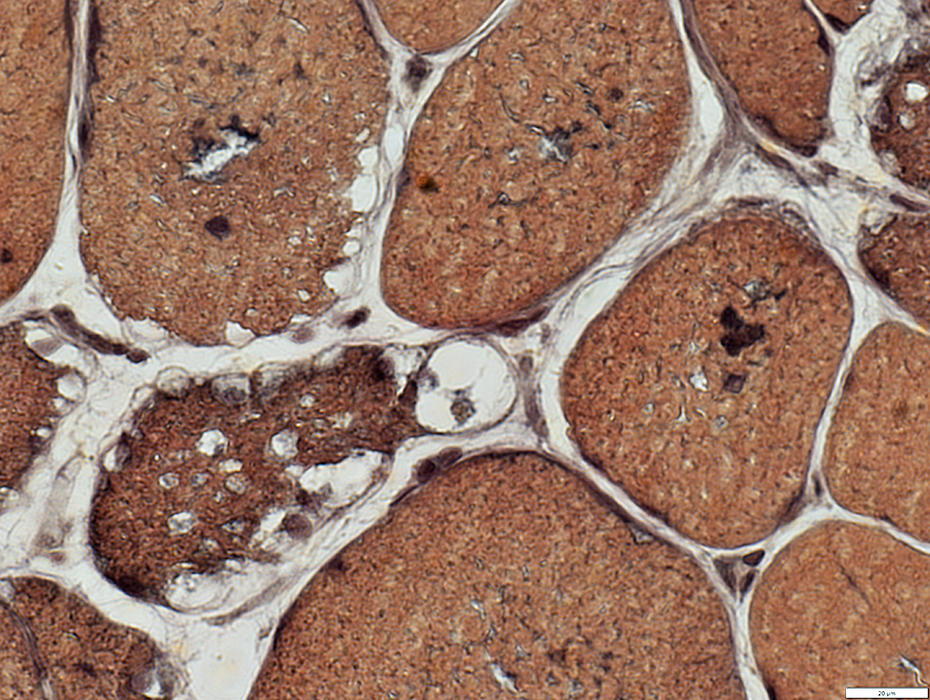 VvG stain |
Granules & Vacuoles: Acid phosphatase positive (Lysosomal)
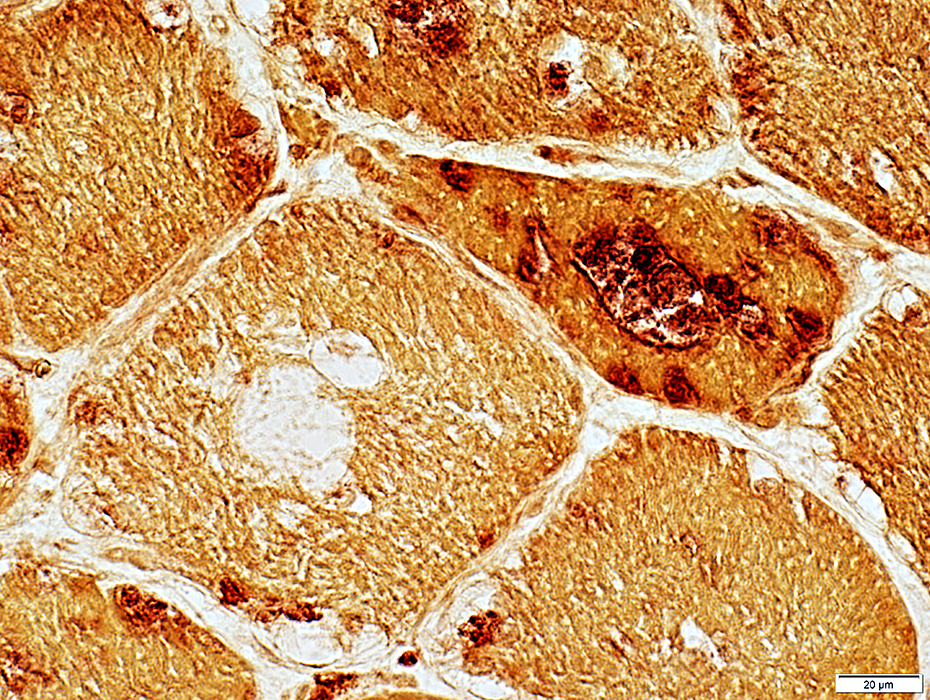 Acid phosphatase stain |
Acid phosphatase granules: May occur in muscle fibers without vacuoles (Below)
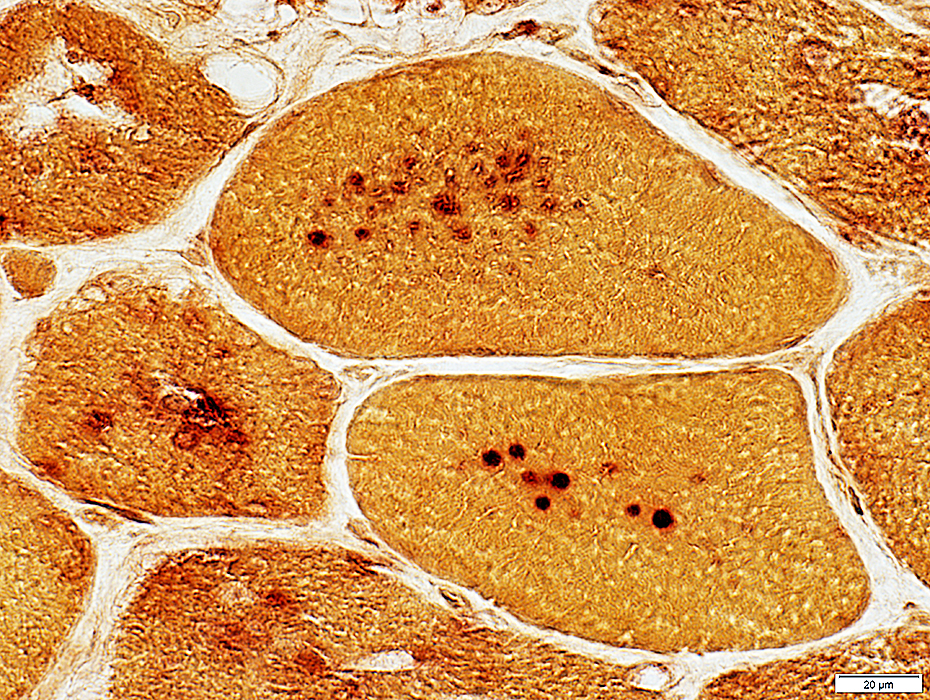 Acid phosphatase stain |
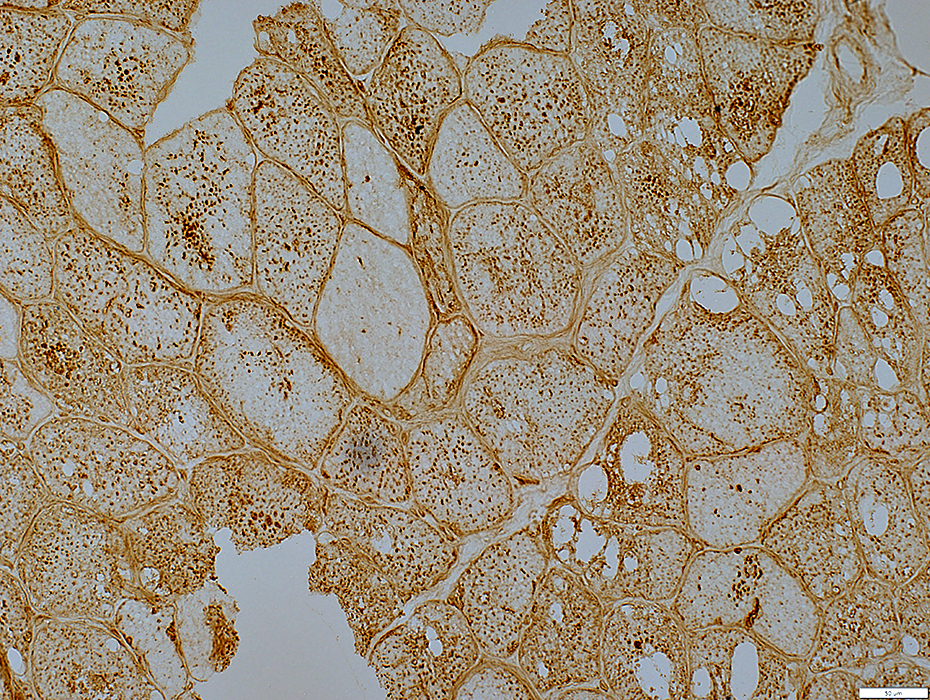 LAMP2 stain |
Lysosomal properties (LAMP2 stains) of punctate regions in muscle fibers
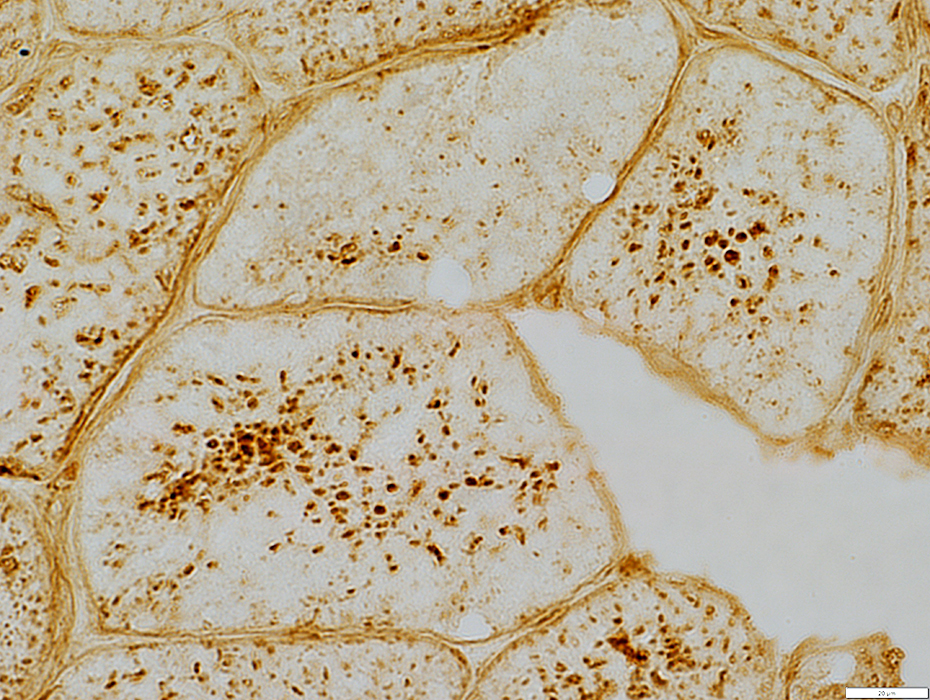 LAMP2 stain |
Esterase+ aggregates in a few muscle fibers
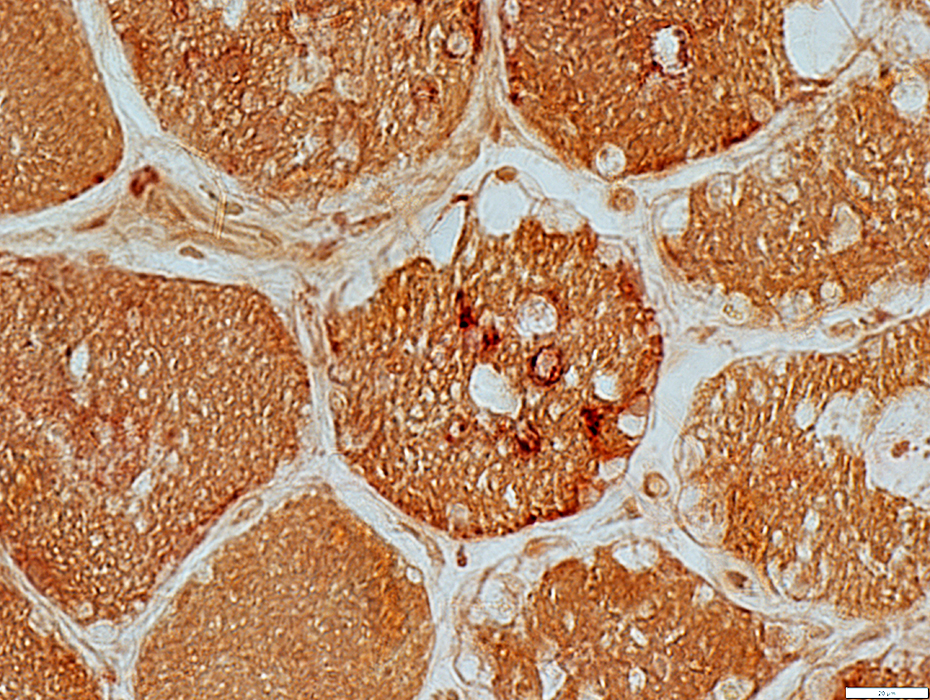 Esterase stain |
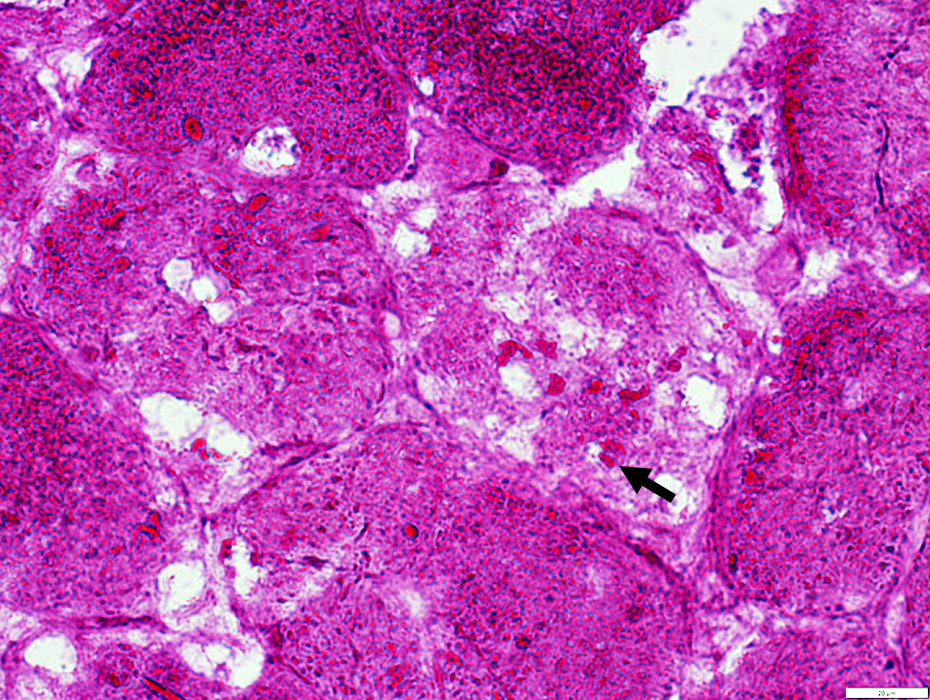 PAS stain |
- Diffuse, or patchy, increase in glycogen staining in muscle fiber cytoplasm
- Variably present in muscle fibers
- Vacuoles: Not clearly delineated; Many have no staining
- Aggregates: PAS+ (Arrow, Above)
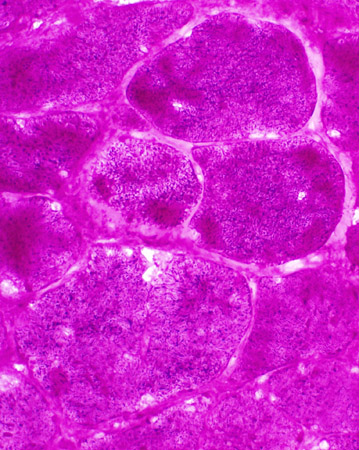 PAS stain |
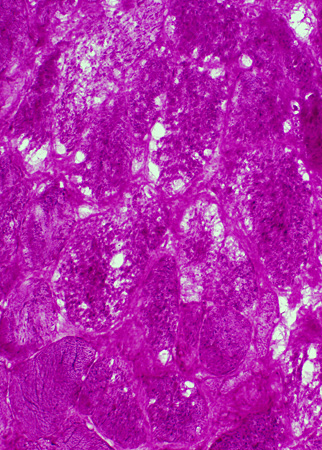 PAS stain |
Acid Maltase deficiency: Vacuoles & Fiber types
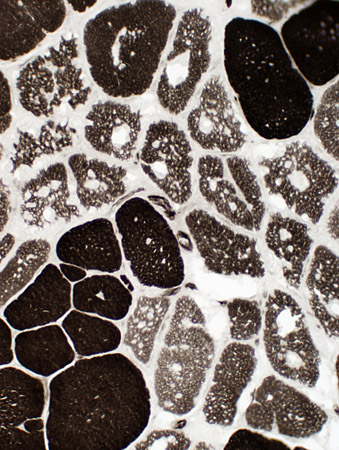 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
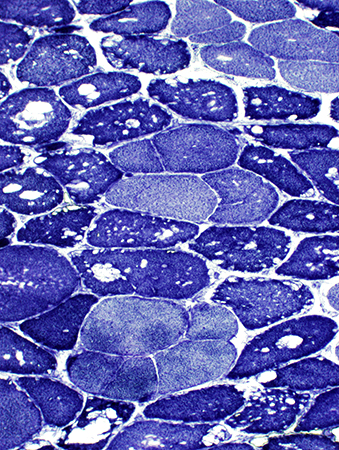 NADH stain |
Type I fibers: Pale on ATPase pH 9.4 (Left) & Darker on NADH (Right; Above)
Type 2 fiber sizes: Often larger than type I
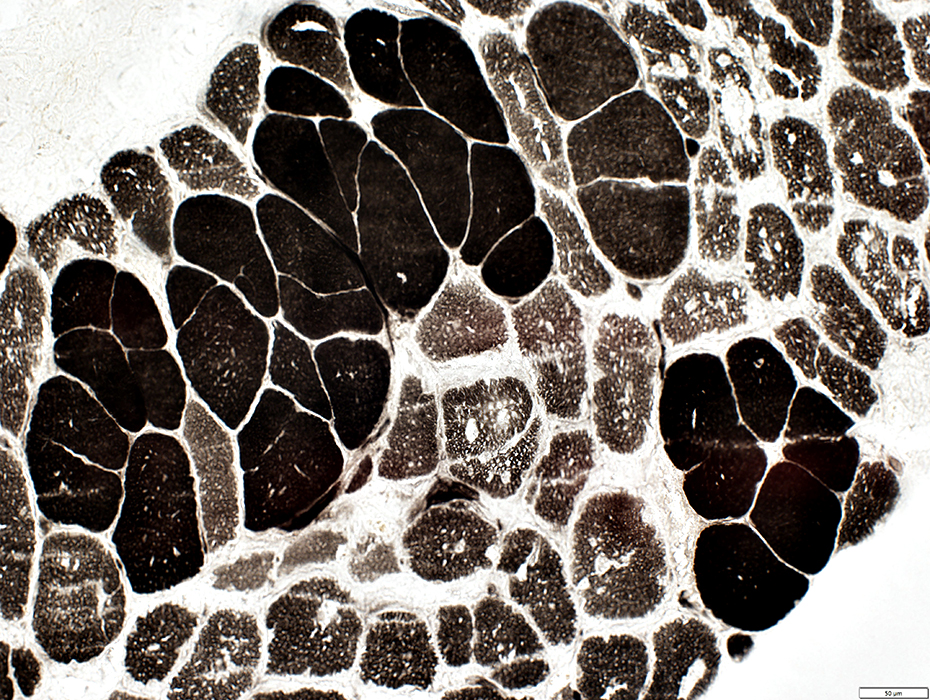 ATPase pH 9.4 stain stain |
Acid Maltase deficiency: Vacuoles & Fiber types
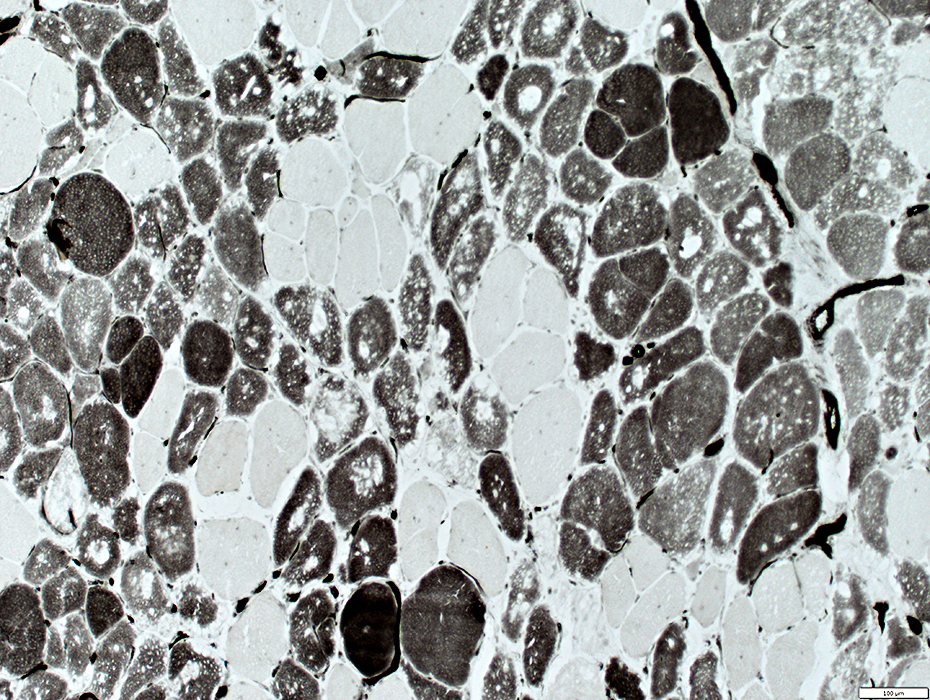 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Muscle fibers with vacuoles are often type 2C (Intermediate stained at pH 4.3)
On ATPase pH 9.4 fibers with vacuoles appear to be type 1.
Type 2C fibers are the most abundant fiber type.
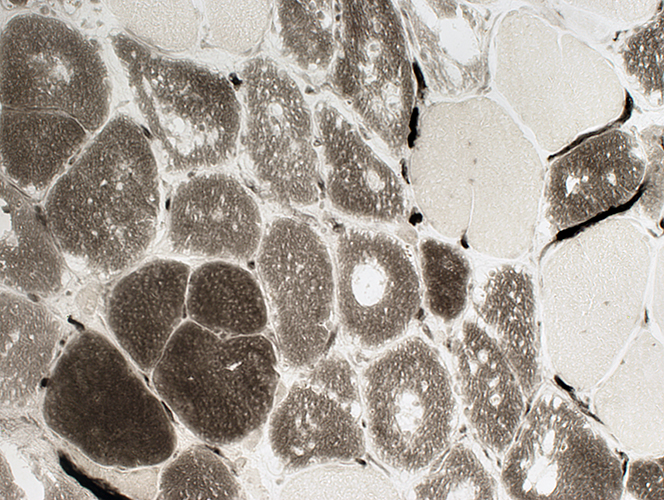 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Muscle fibers with vacuoles are moderately less dark than Type I fibers
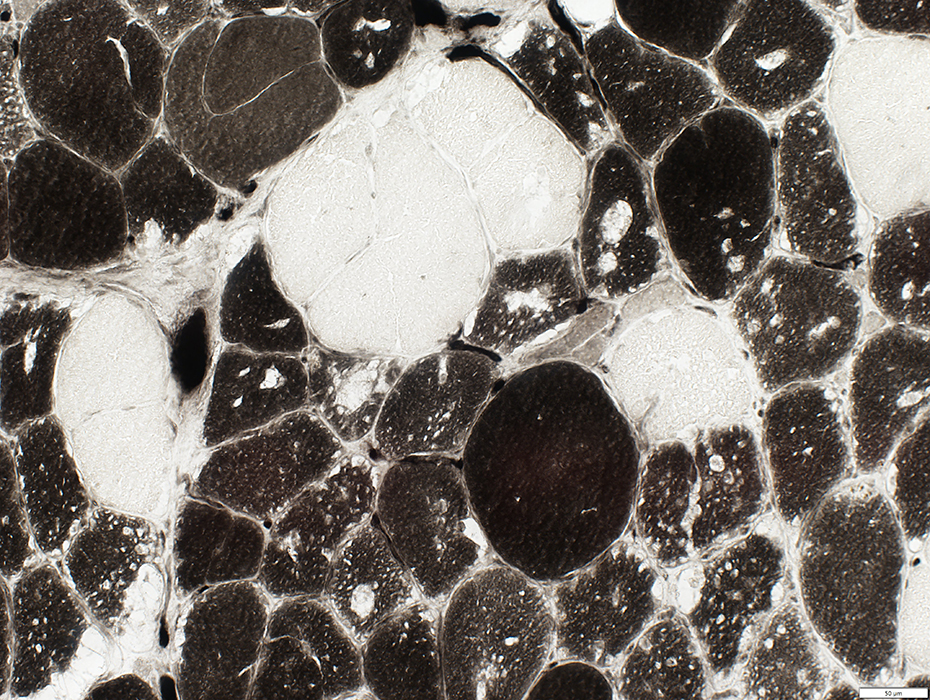 ATPase pH 4.6 stain |
Acid Maltase deficiency: Endomysial capillaries
Increased numbers of endomysial capillaries stain at ATPase pH 4.3
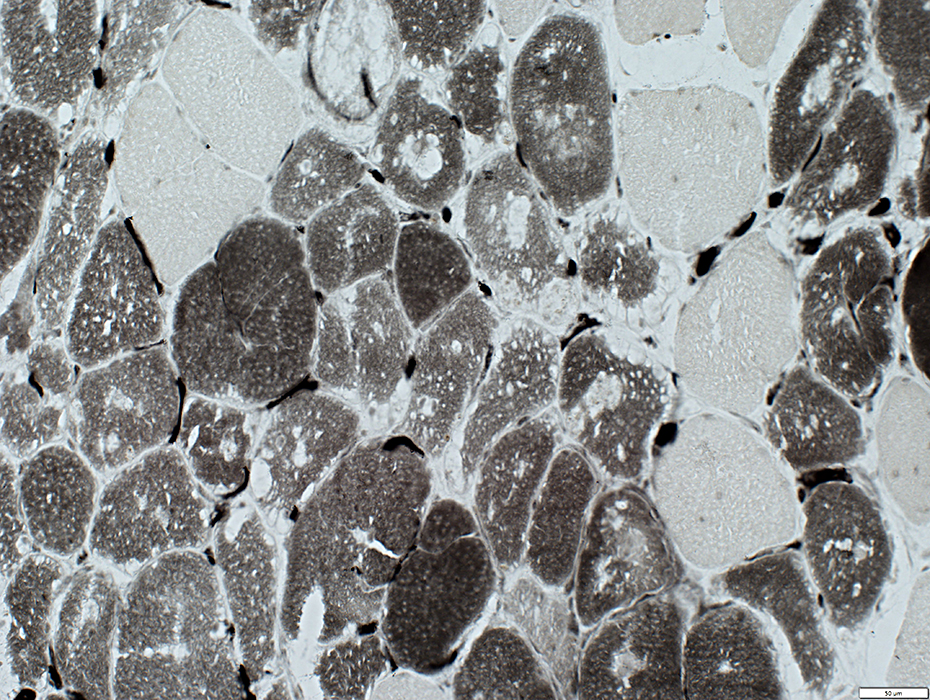 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Mid-Childhood Onset
Storage Contents in Muscle fibers: Patterns- Clear material: In small or large vacuoles, May replace most of a muscle fiber (Above), or
- Metachromatic purple granular material: Often replacing much of muscle fiber cytoplasm (Below)
- Aggregates: Stain best for acid phosphatase
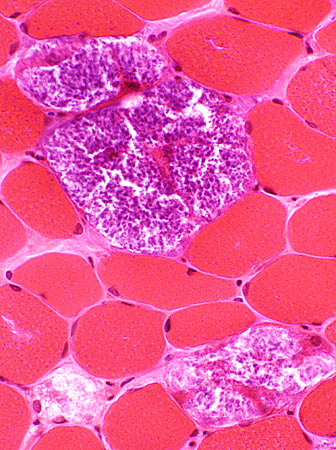 H & E stain |
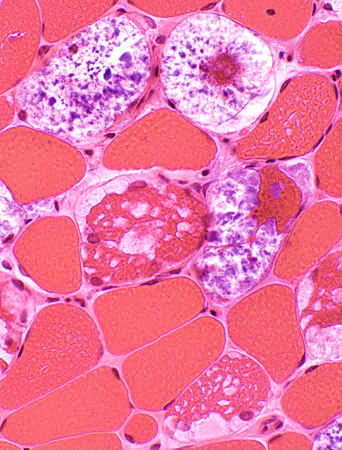 H & E stain |
- Clear vacuoles: Small or Large
- Purple granular material: Often replacing much of muscle fiber cytoplasm (Below)
- Darker staining cytoplasmic aggregates (Bottom row; Left; Arrow)
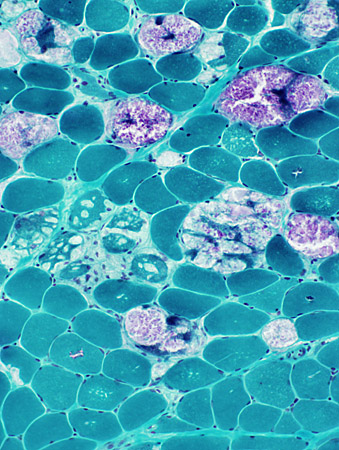 Gomori trichrome stain |
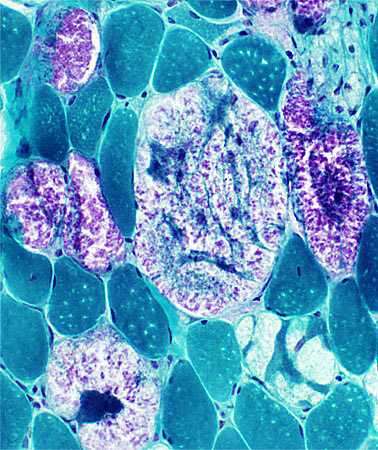 Gomori trichrome stain |
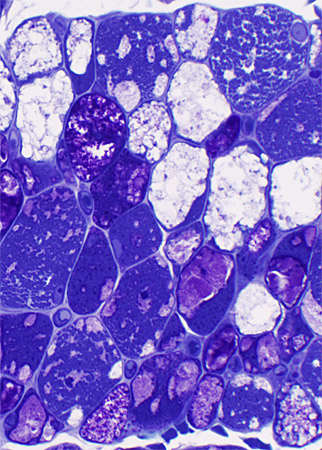 Plastic sections: Toluidine blue stain |
Acid phosphatase positive granules in muscle fibers
| |
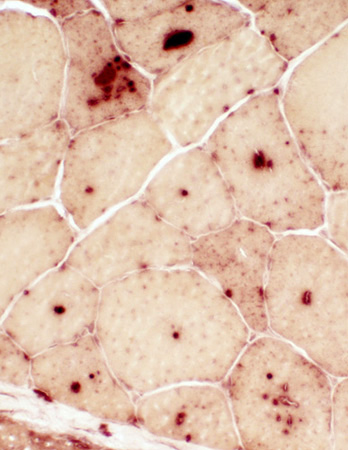 Acid phosphatase stain |
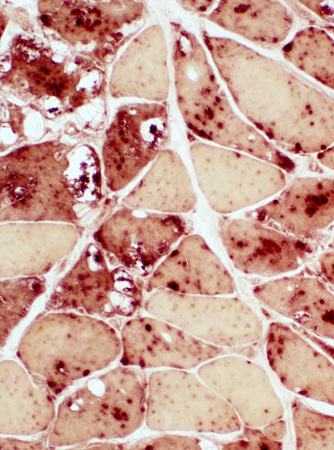 Acid phosphatase stain |
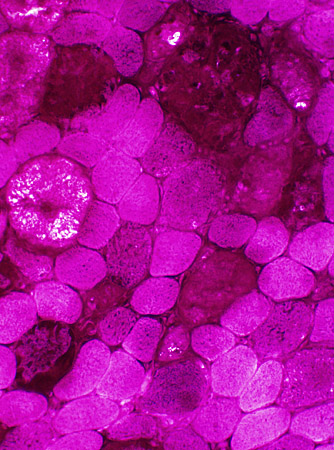 PAS stain |
 PAS stain |
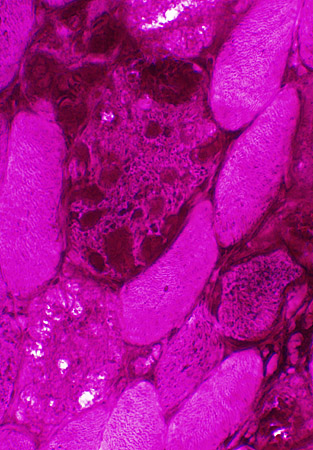
- Glycogen staining of vacuoles and cytoplasm in individual muscle fibers
- Some increased cytoplasm staining is present in many muscle fibers
- Cytoplasmic staining can be variable within fibers
 PAS stain |
|
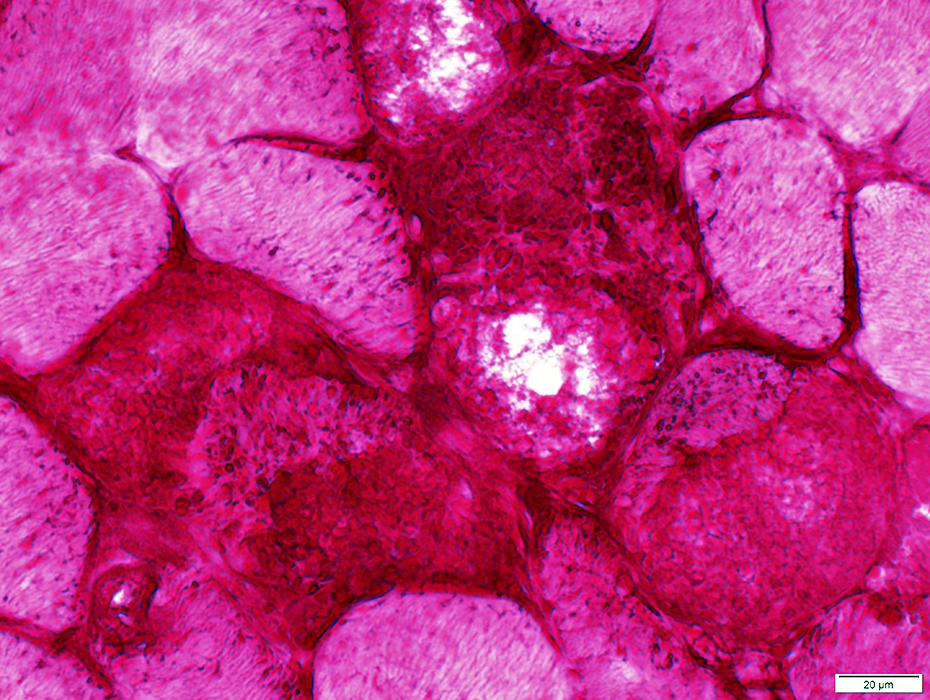
LAMP2 lysosomal granules: Scattered in muscle fiber cytoplasm; Not in vacuoles |
|
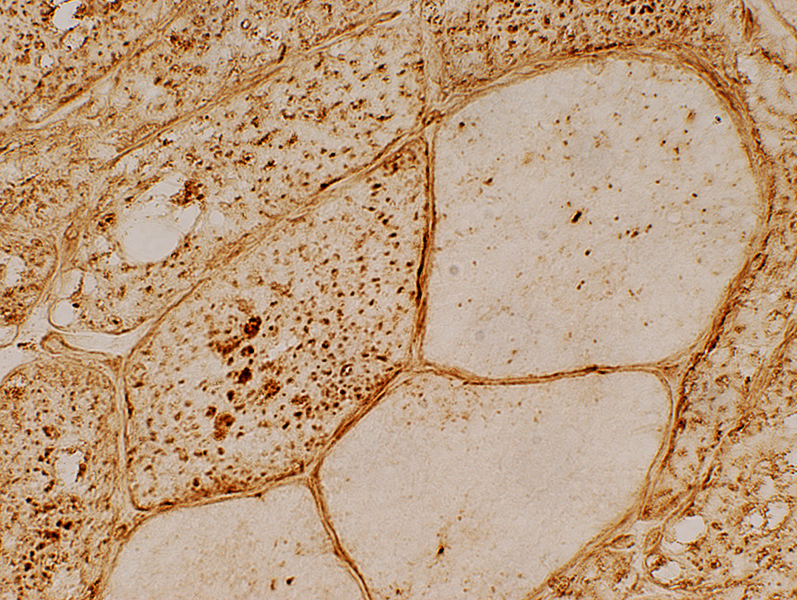 LAMP2 stain |
|
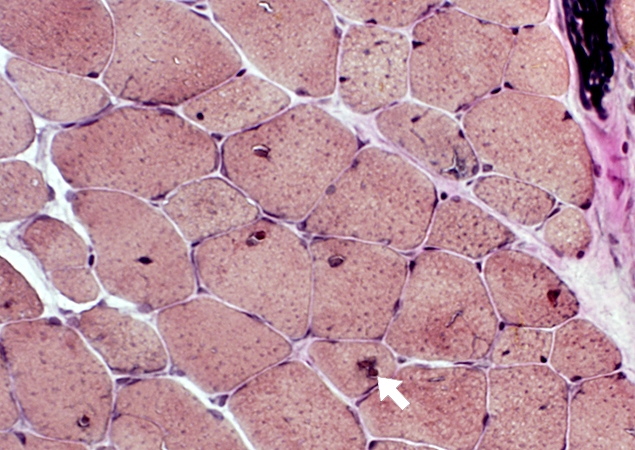
ACID MALTASE DEFICIENCY
Adult Onset
 H&E stain |
|
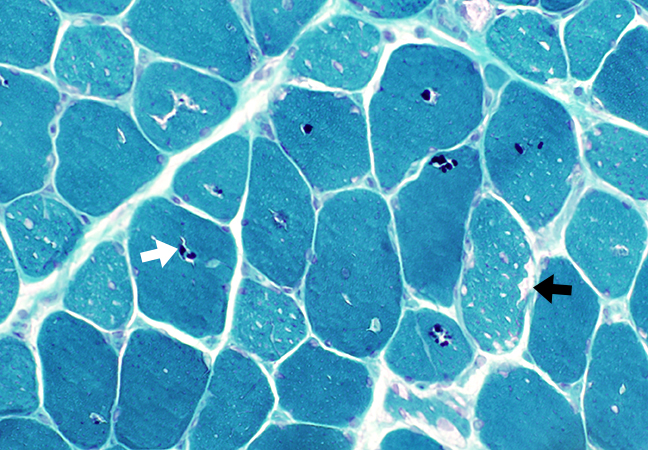 Gomori Trichrome stain |
Storage Contents & Aggregates
|
 VvG stain |
|
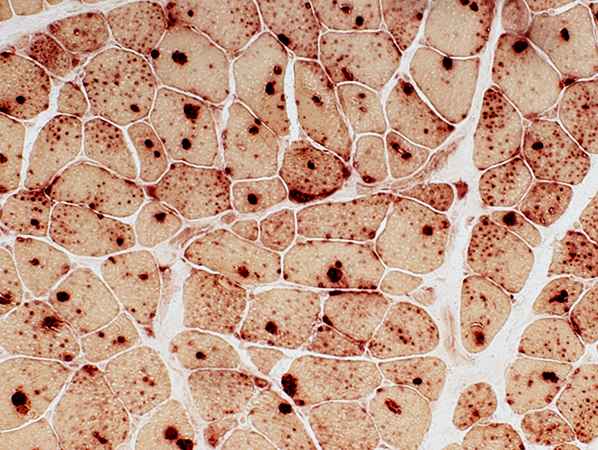 Acid Phosphatase stain |
Lysosomal Granules
|
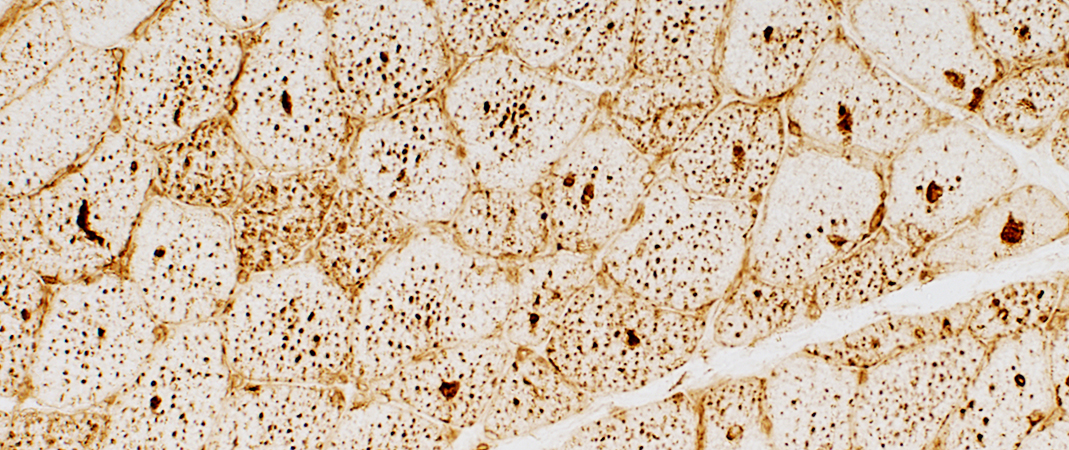 LAMP2 stain |
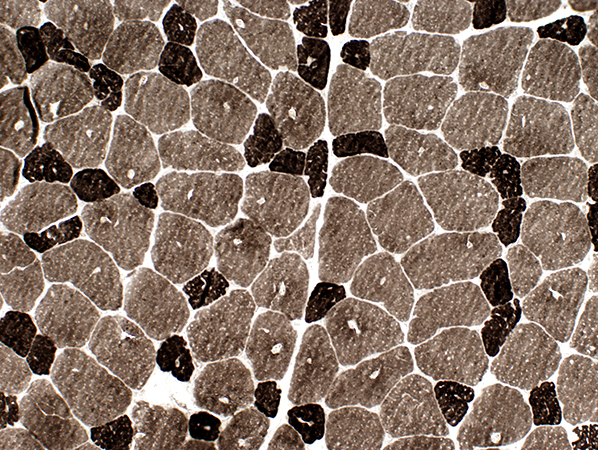 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Fiber types
|
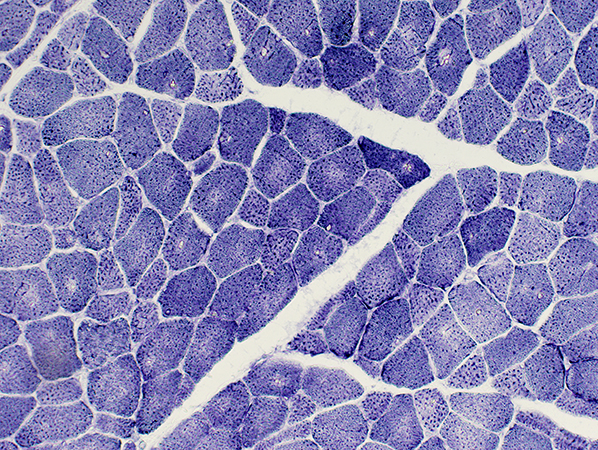 NADH stain |
Internal architecture
|
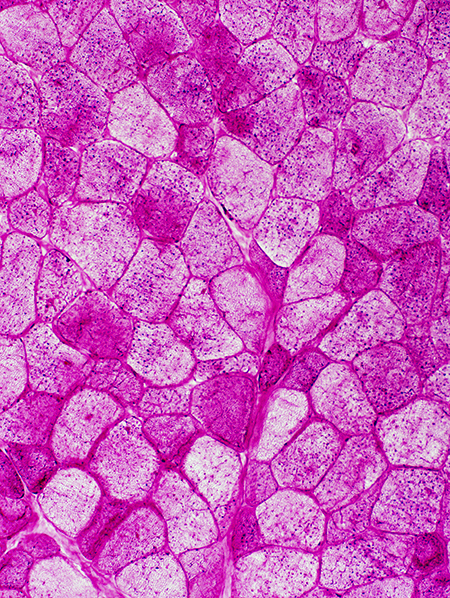 Patient |
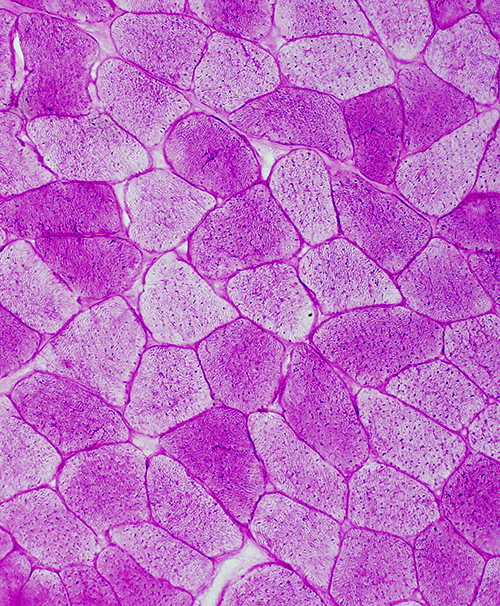 Normal Control |
|
Glycogen content (PAS stains): May appear near normal |
|
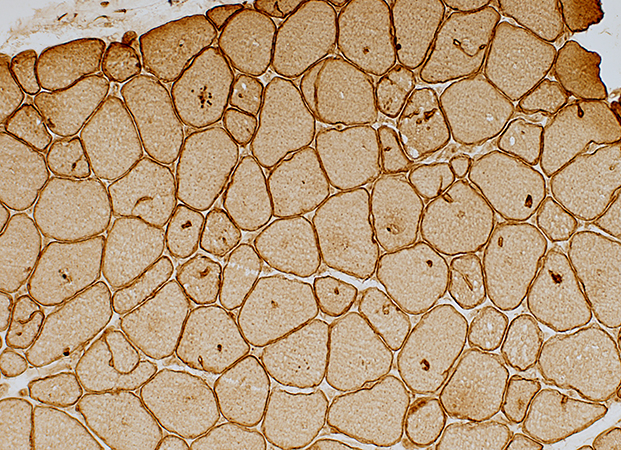 Caveolin-3 stain |
Aggregate Membranes
|
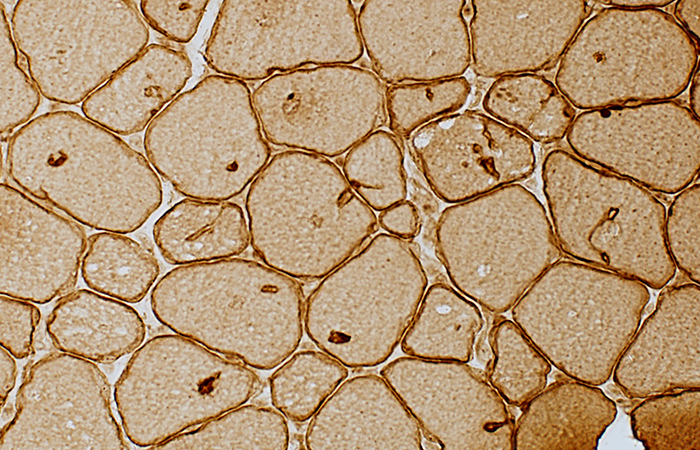 Caveolin-3 stain |
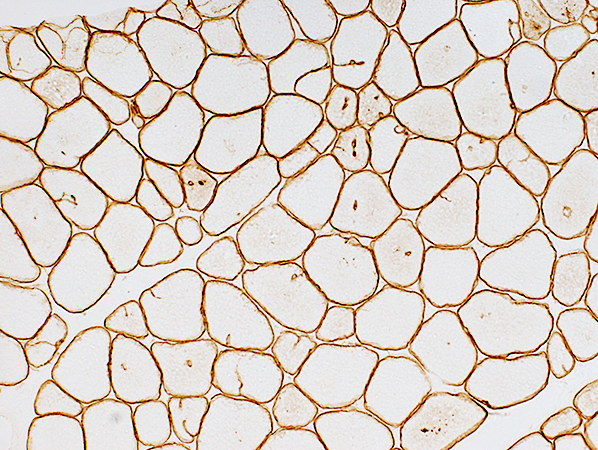 Dystrophin (Dys-2) stain |
Aggregate membranes
|
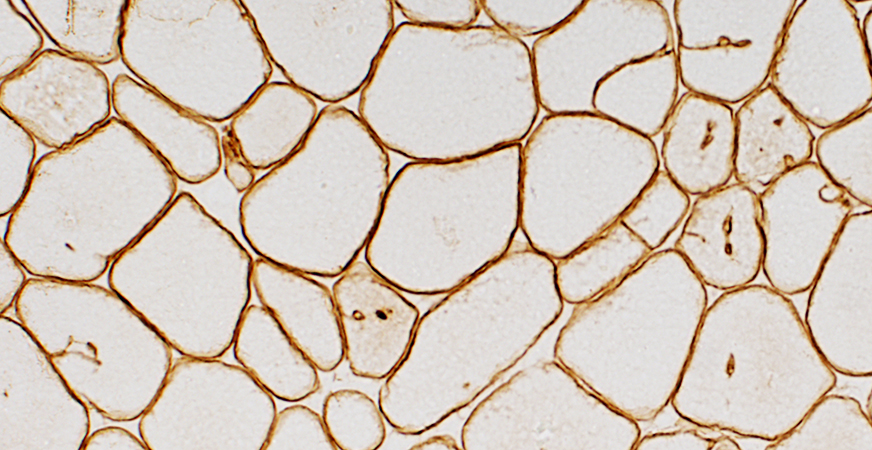 Dystrophin (Dys-2) stain |
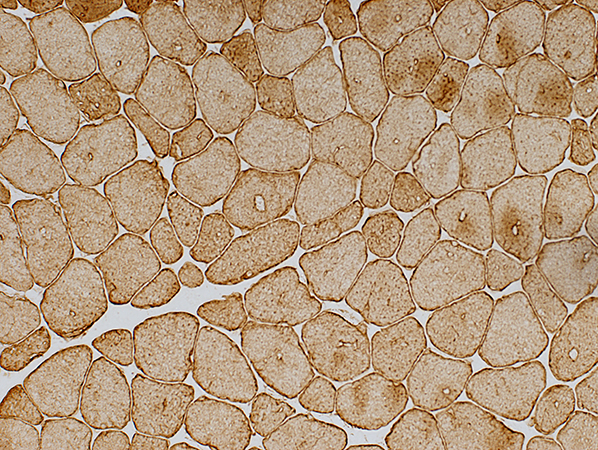 Desmin stain |
Desmin
|
Acid Maltase Deficiency: Myofiber Storage Patterns
Storage materialPale-staining
Metachromatic
Aggregates
Vacuoles with Pale-stained, wispy material
Vacuoles may be subsarcolemmal or internal
Some vacuoles contain nuclei
Multiple vacuoles in individual muscle fibers
Vacuoles may partially or completely displace normal muscle fiber cytoplasm
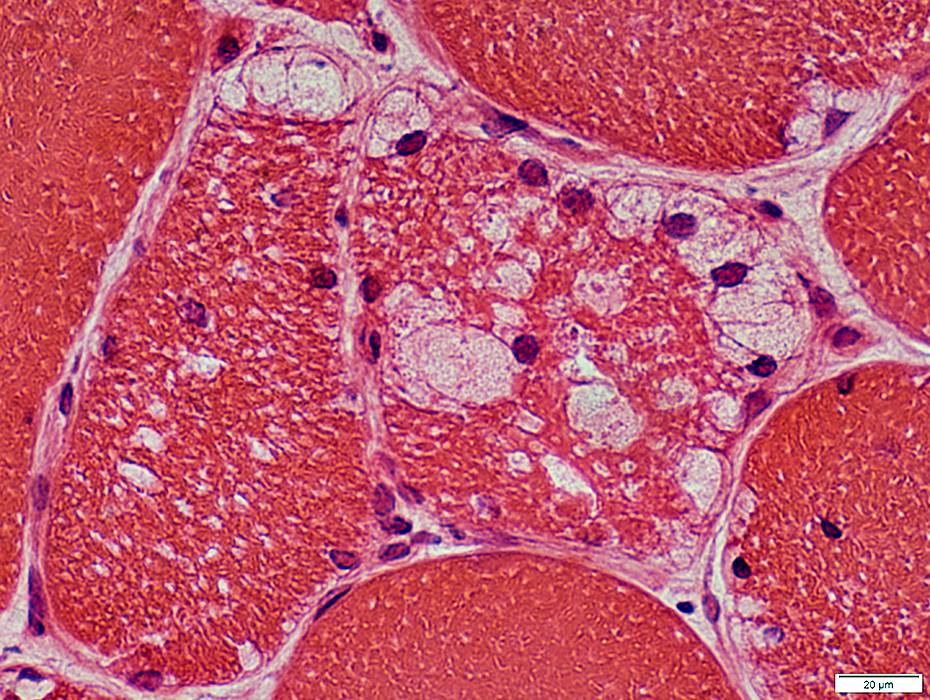 H&E stain |
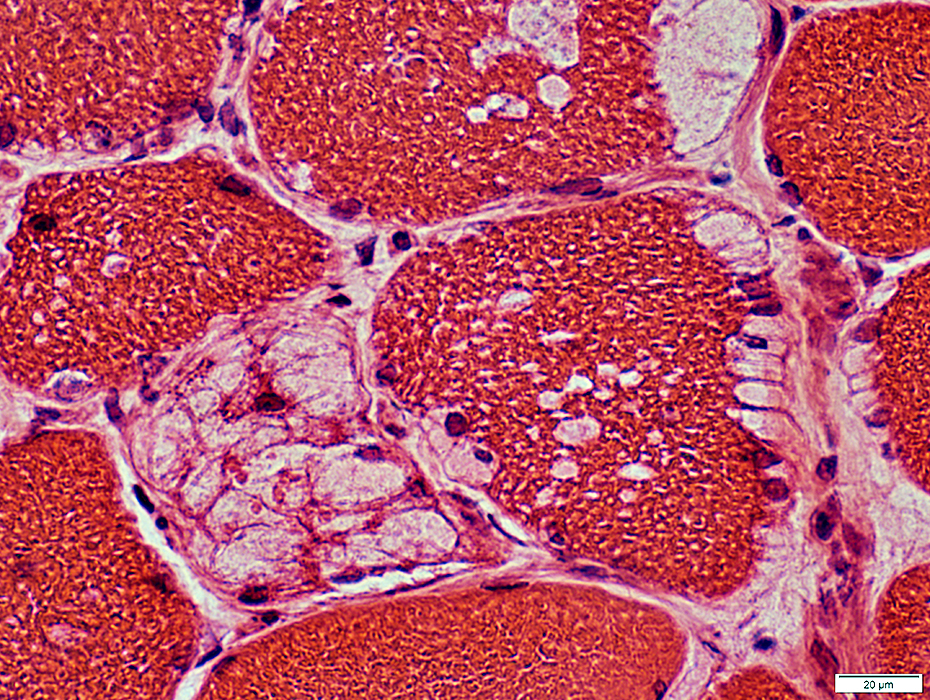 H&E stain |
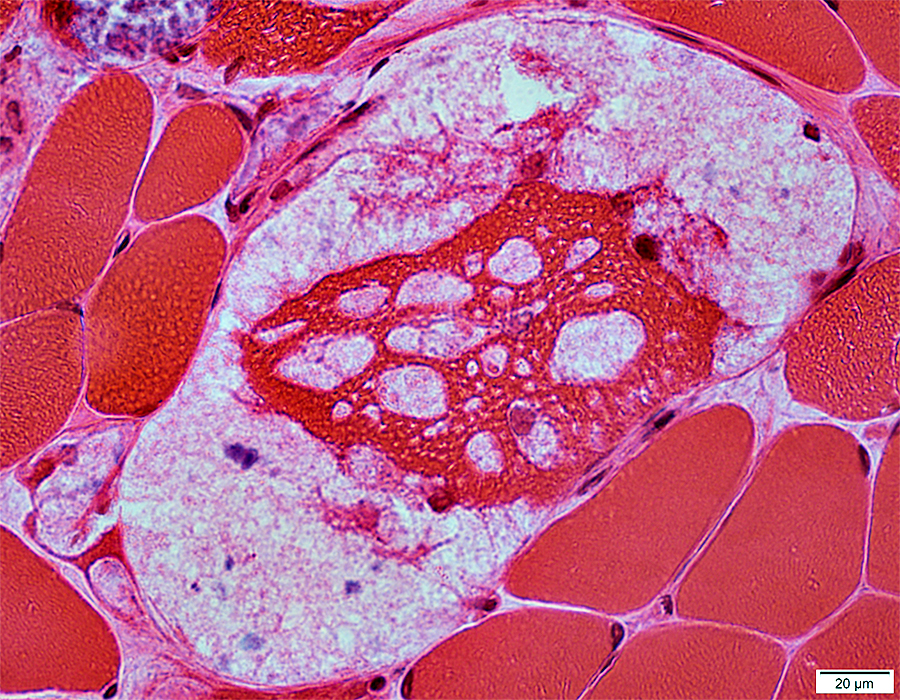 H&E stain |
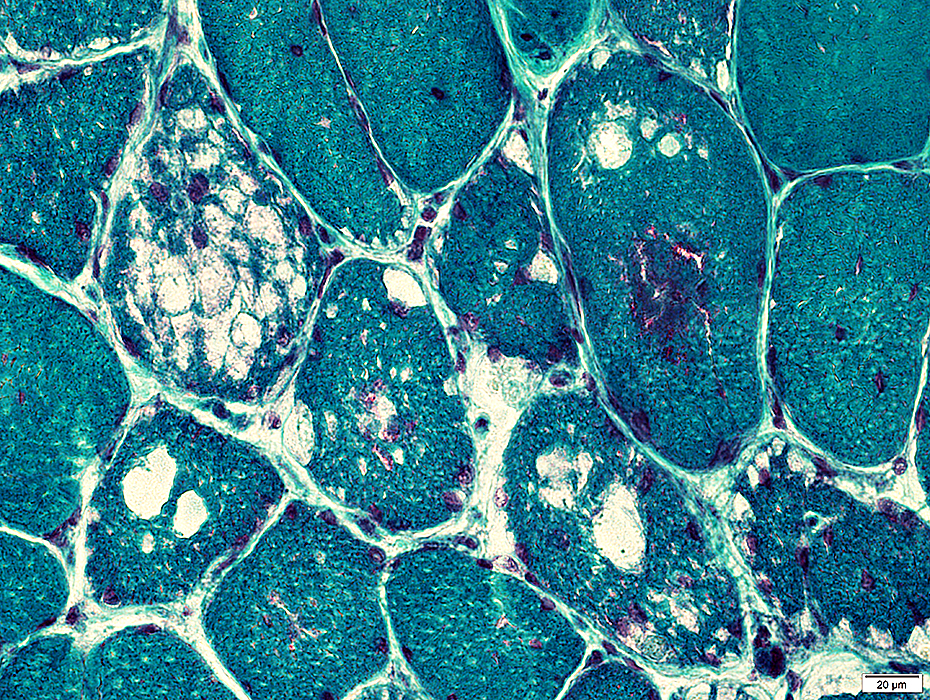 Gomori trichrome stain |
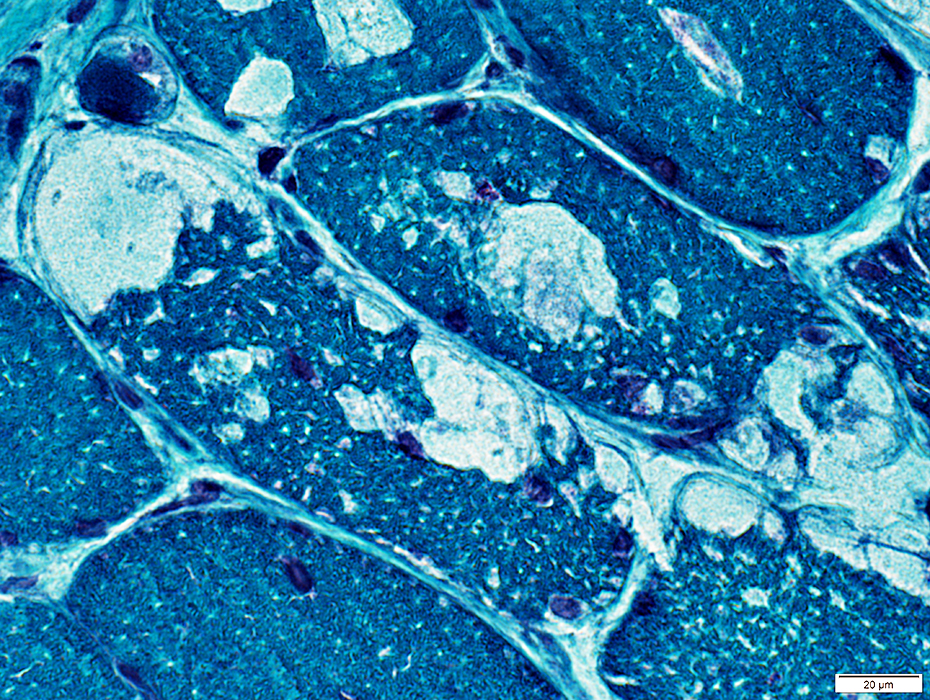 Gomori trichrome stain |
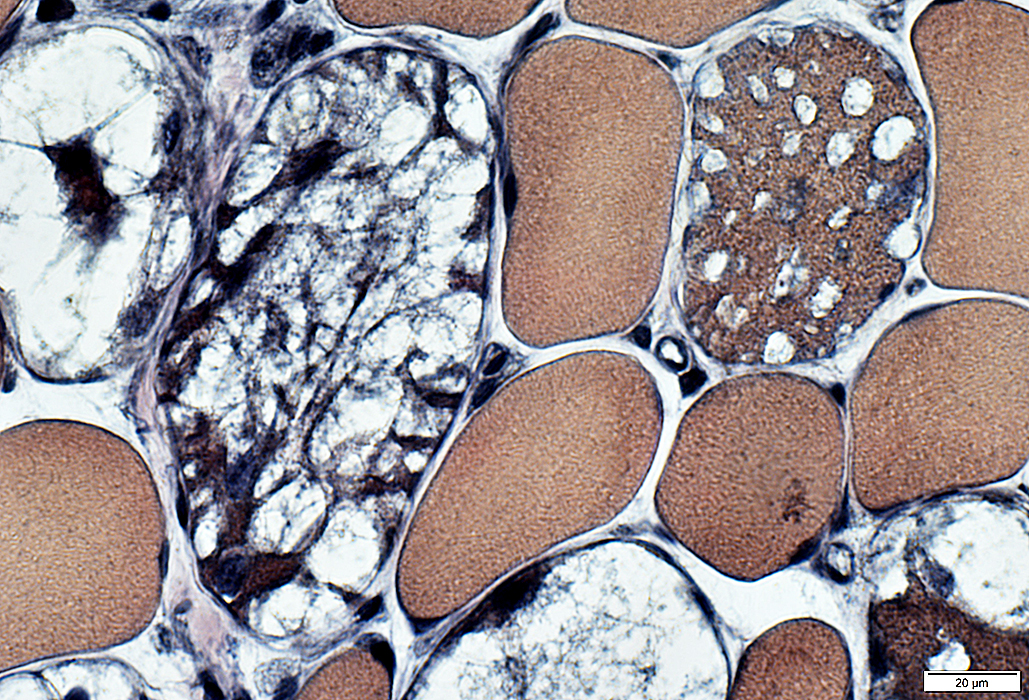 VvG stain |
Metachromatic, Granular Storage Material
Magenta-colored granular material
Probably later stage of pathology
Often replaces most, or all, of muscle fiber cytoplasm
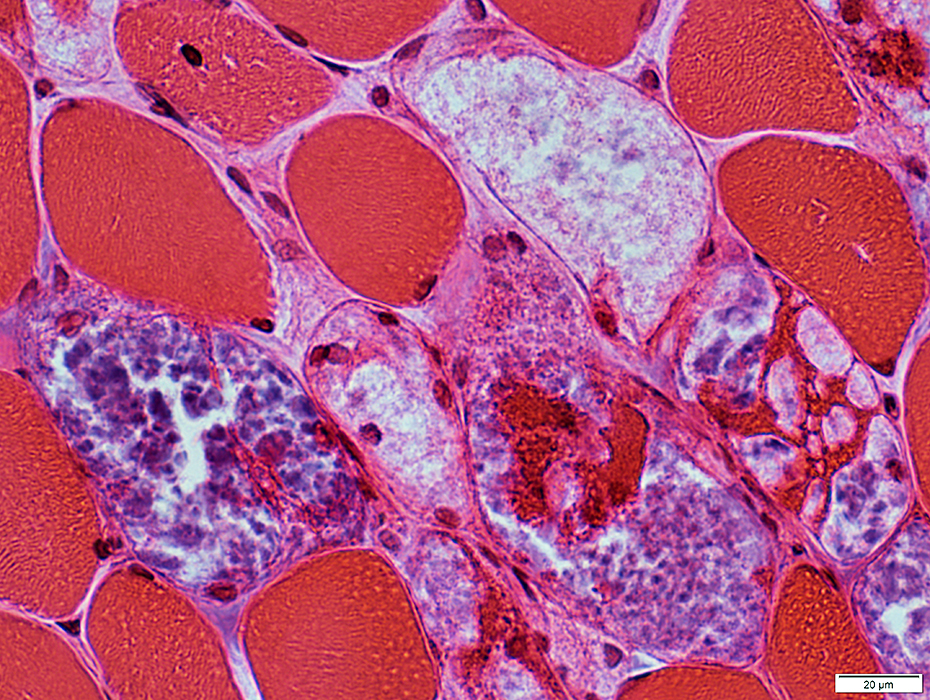 H&E stain |
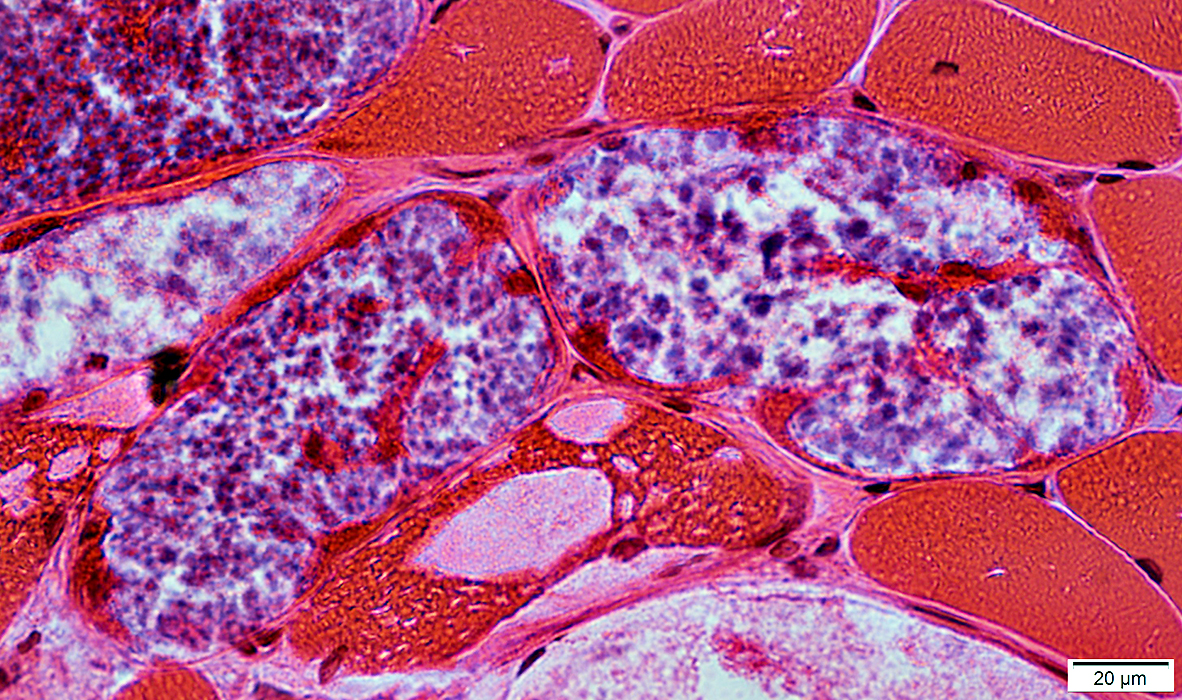 H&E stain |
Varied patterns of staining
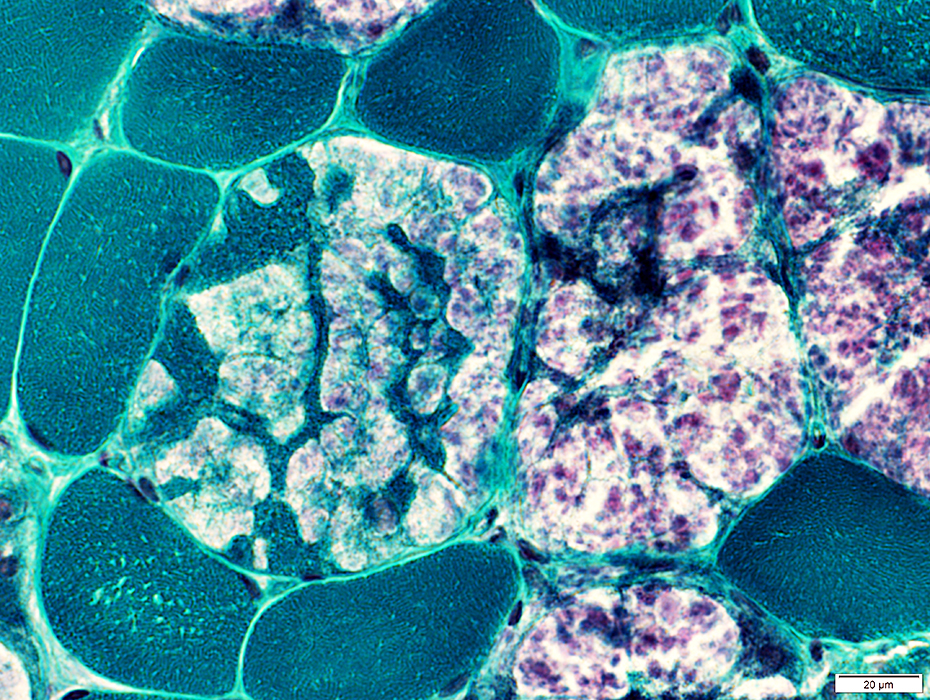 Gomori trichrome stain |
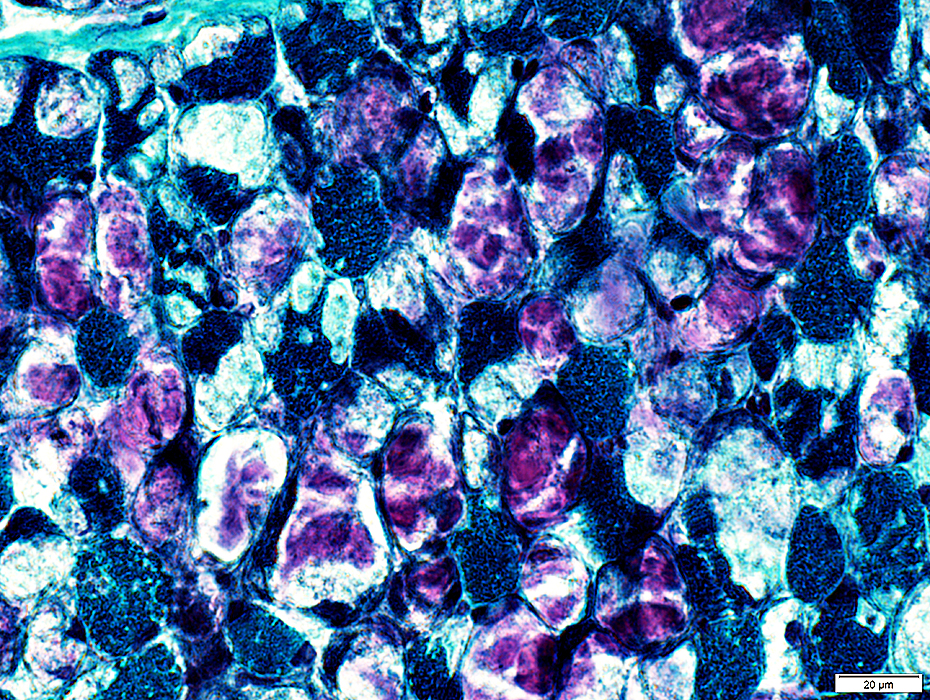 Gomori trichrome stain |
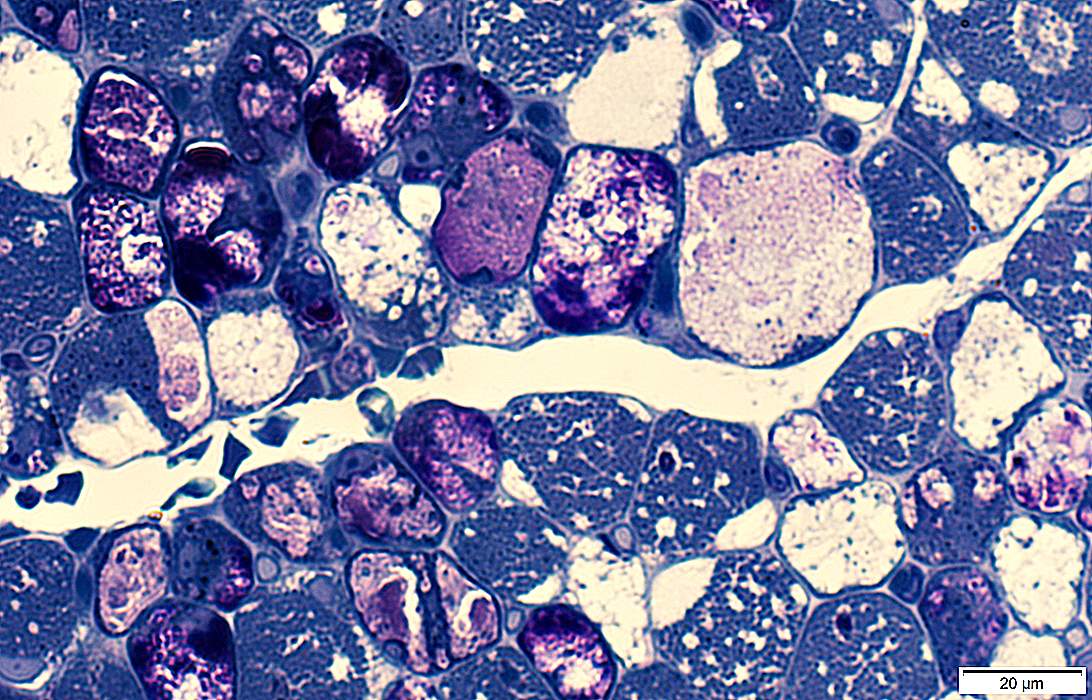 Toluidine blue stain |
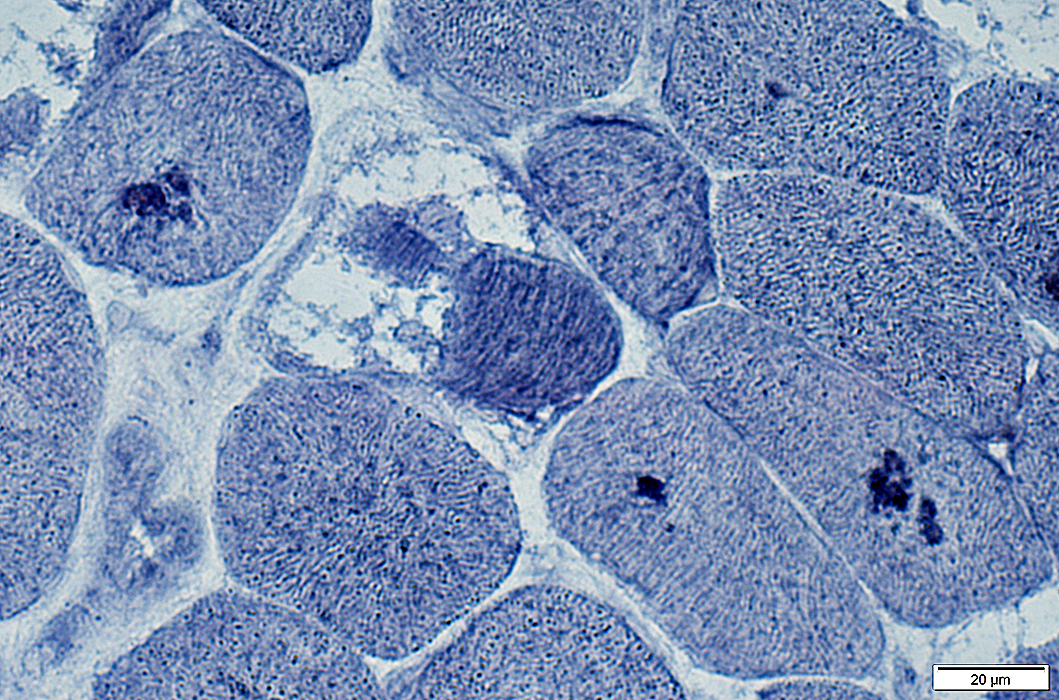 AMPDA stain |
Commonly stain for AMPDA
One or several per fiber
Often present if fibers without vacuoles
 AMPDA stain |
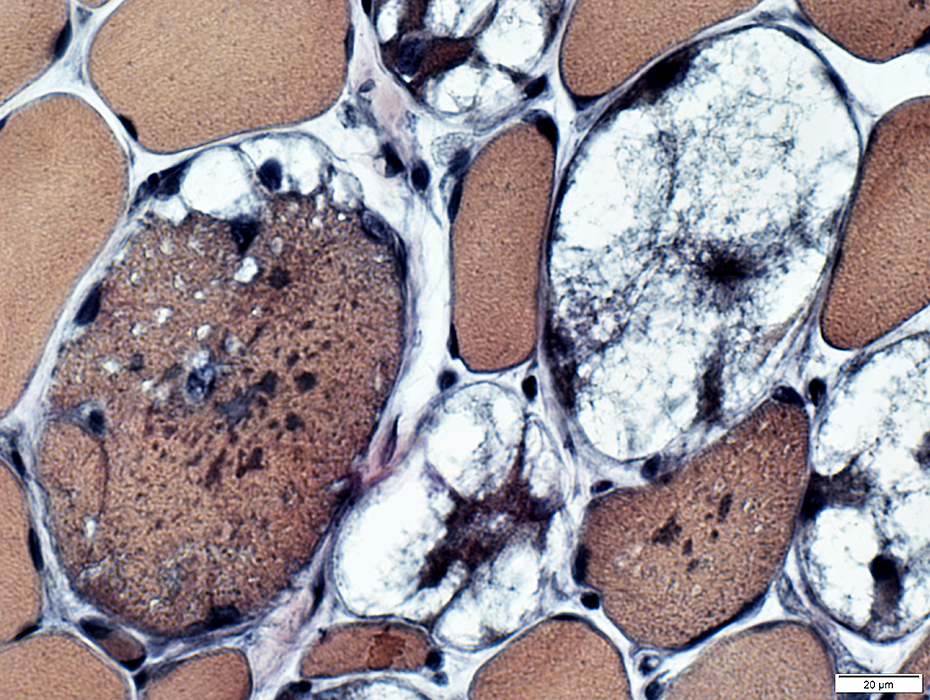 VvG stain |
Commonly stain dark on VvG
Acid phosphatase positive
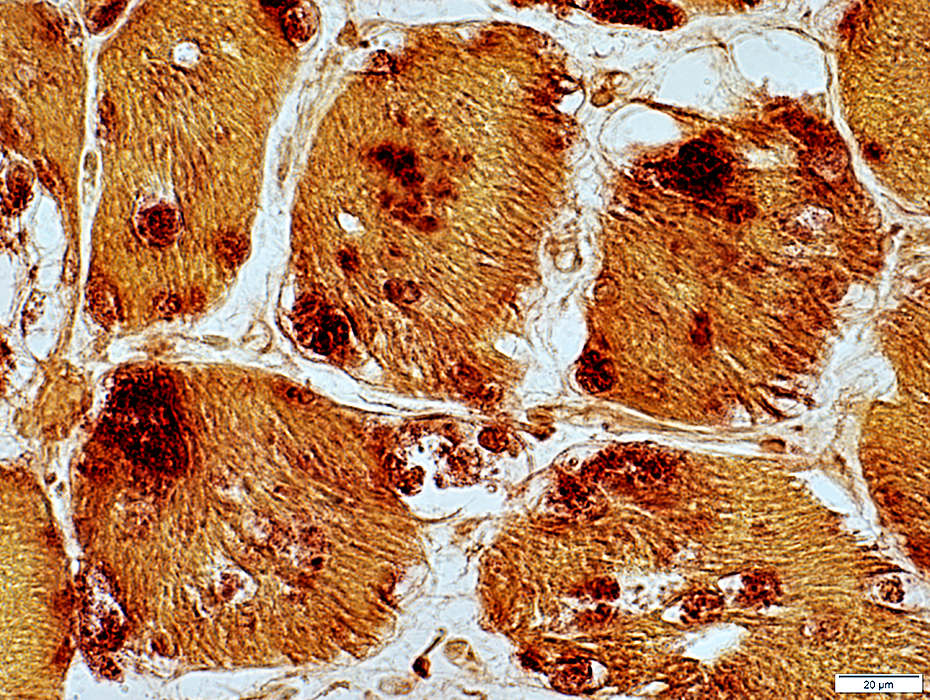 Acid phosphatase stain |
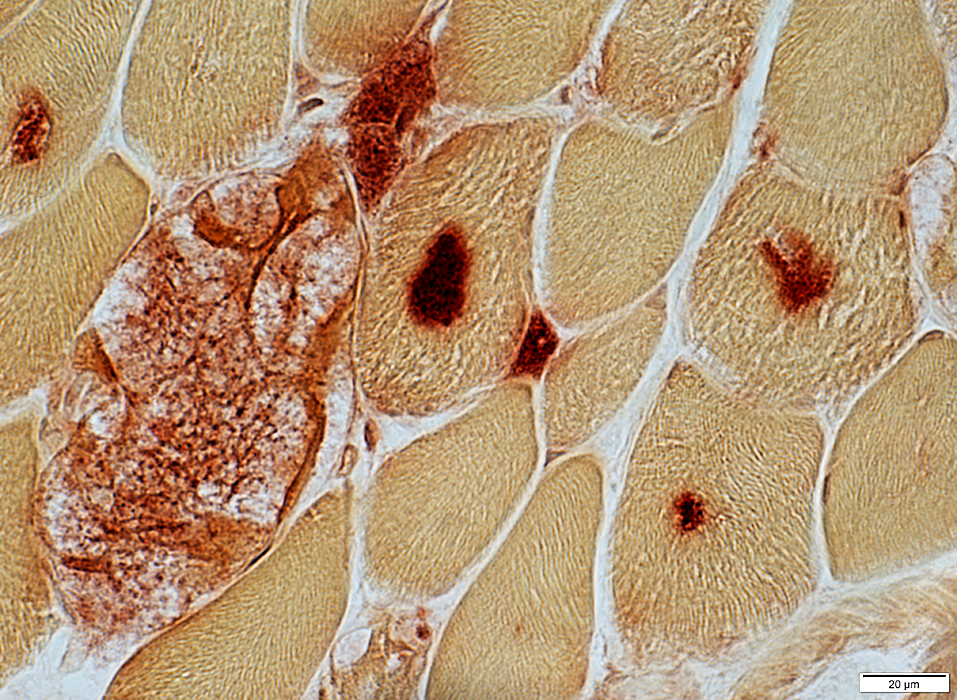 Acid phosphatase stain |
Acid Maltase Deficiency: Ultrastructure
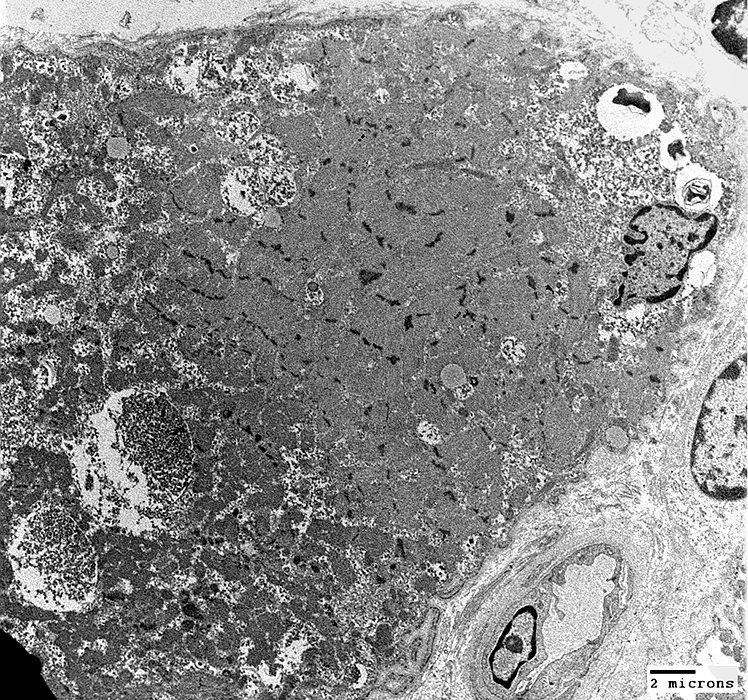 From: Robert Schmidt |
Rare membrane-like material (Upper right)
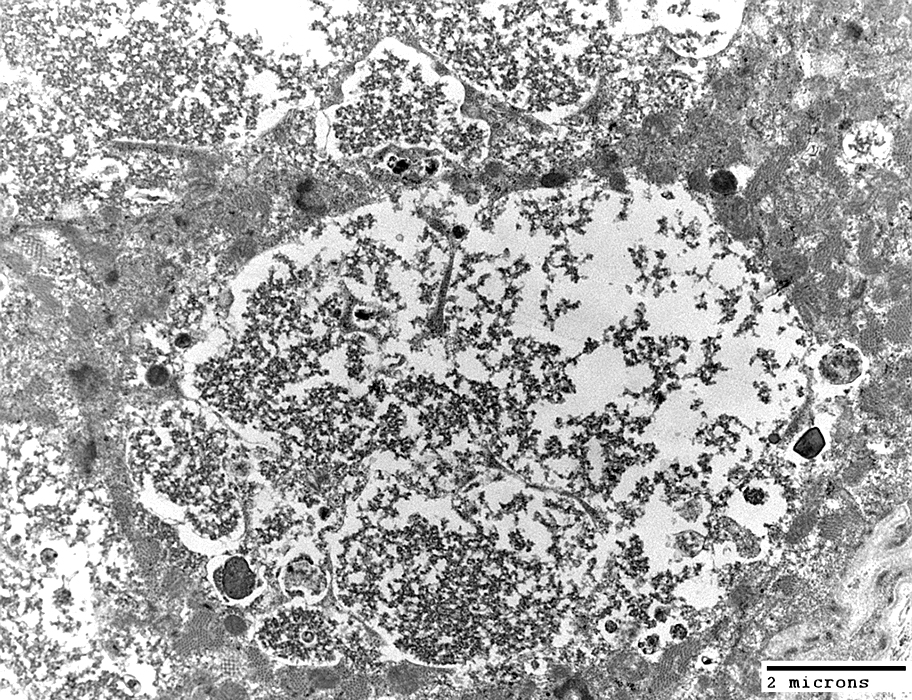 From: Robert Schmidt |
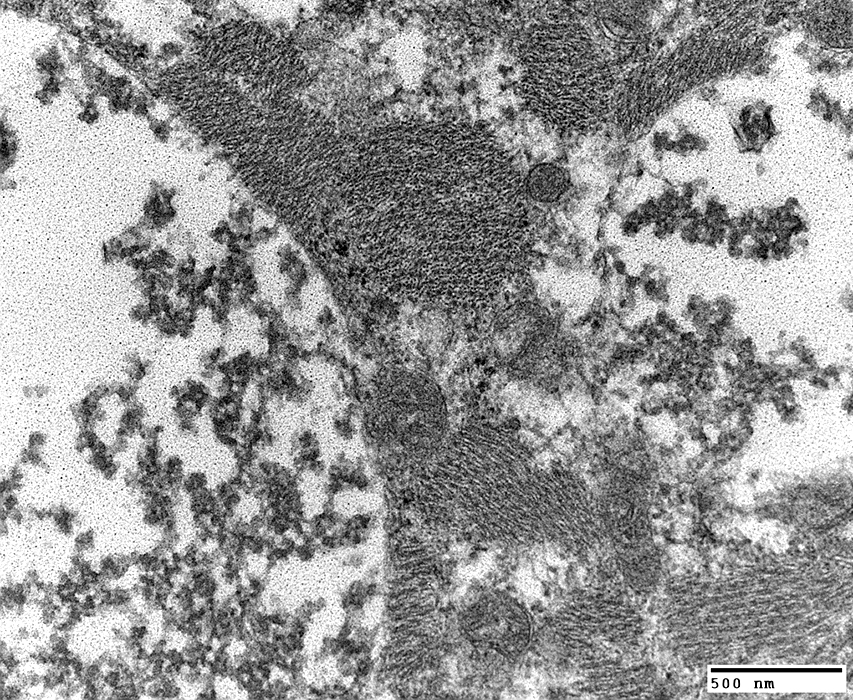 From: Robert Schmidt |
Cytoplasmic clusters of glycogen: Partially surrounded by membrane
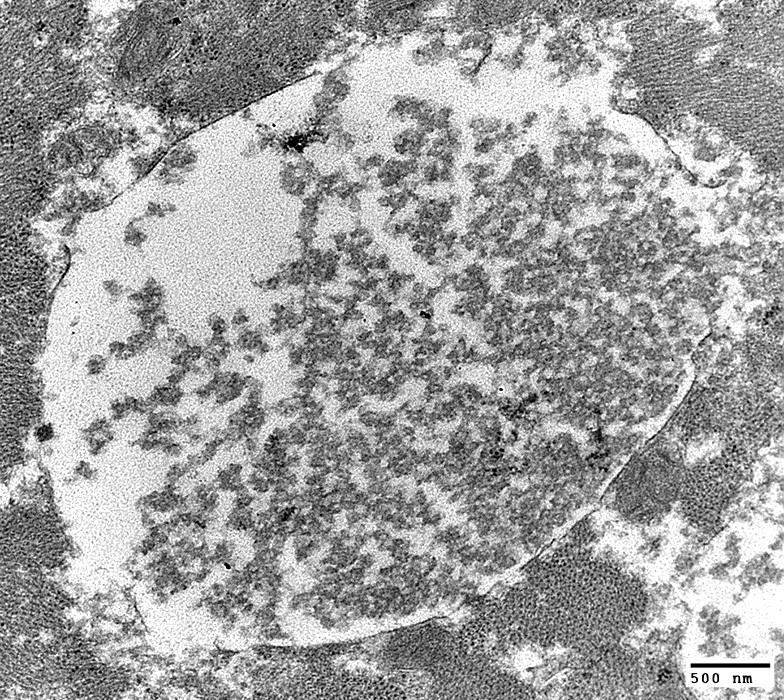 From: Robert Schmidt |
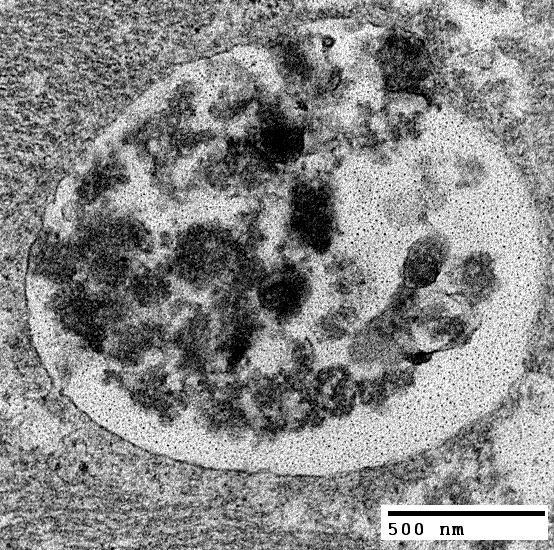 From: Robert Schmidt |
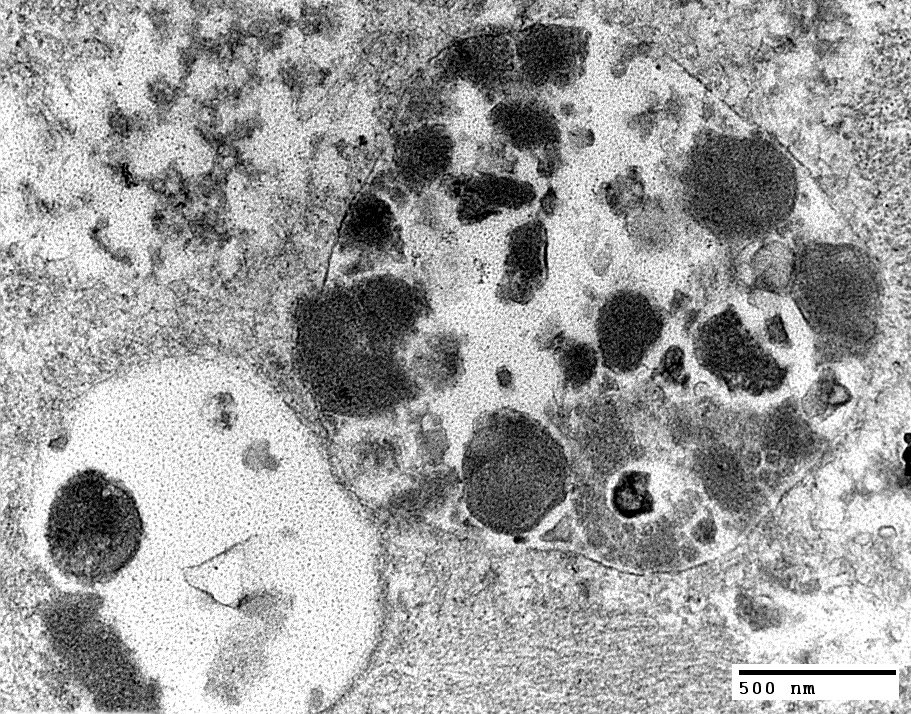 From: Robert Schmidt |
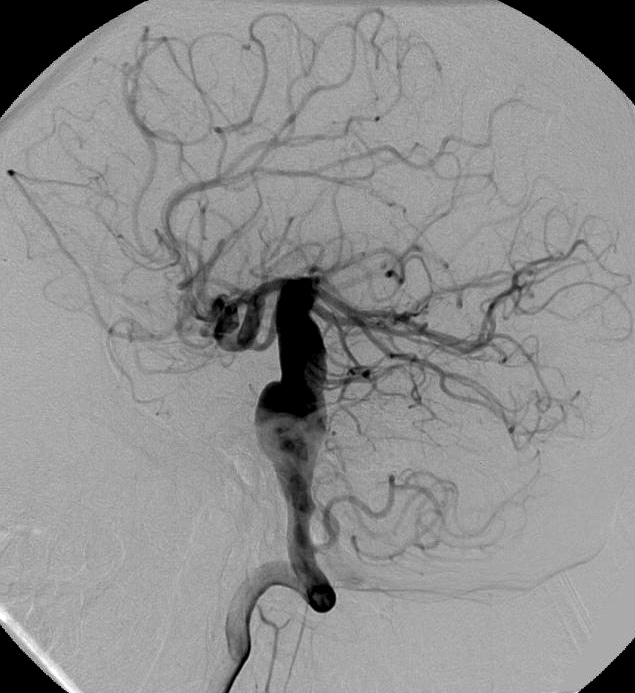
Acid Maltase Deficiency: CNS Aneurysms
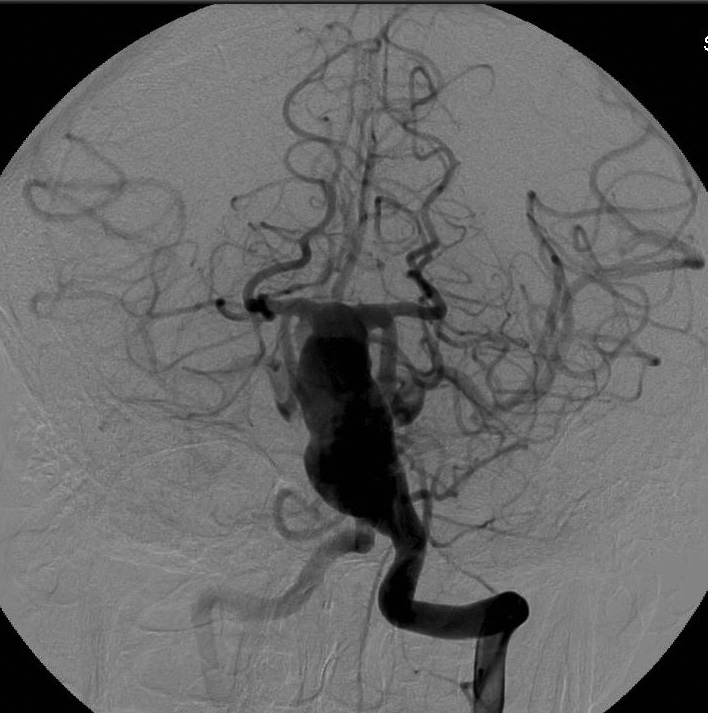
|
| Acid maltase deficiency, Adult onset: Fusiform basilar aneurysm |
|
Also see
Acid maltase deficiency in childhood
Phosphorylase deficiency
Return to Glycogen disorders
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
9/6/2024