Age: Muscle & Nerve
|
Muscle Child Adult Aging Morphology Sarcopenia Nerve NMJs |
 From Bramwell: Atlas of Clinical Medicine |
Aging (> 65 years): Muscle Changes 1
|
Increased age (> 85 years): Common features in muscle
Nuclear shapes: Irregular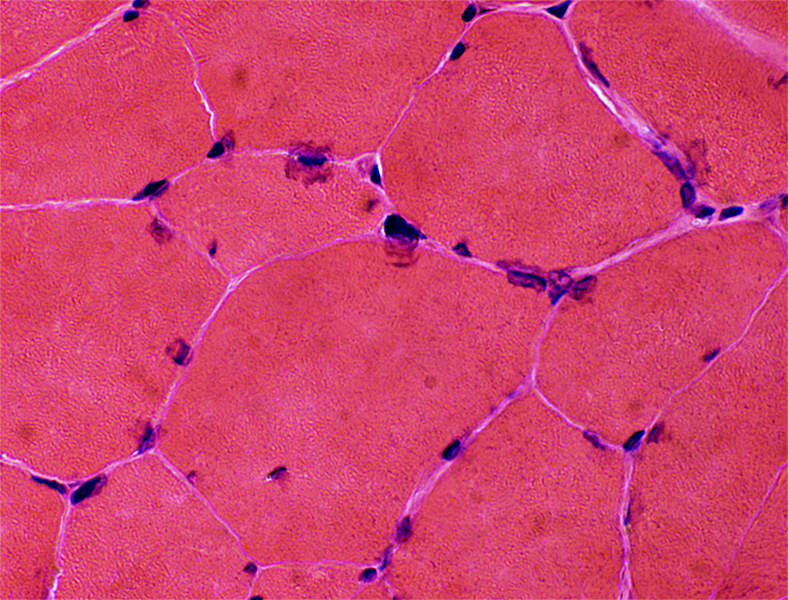 H&E stain |
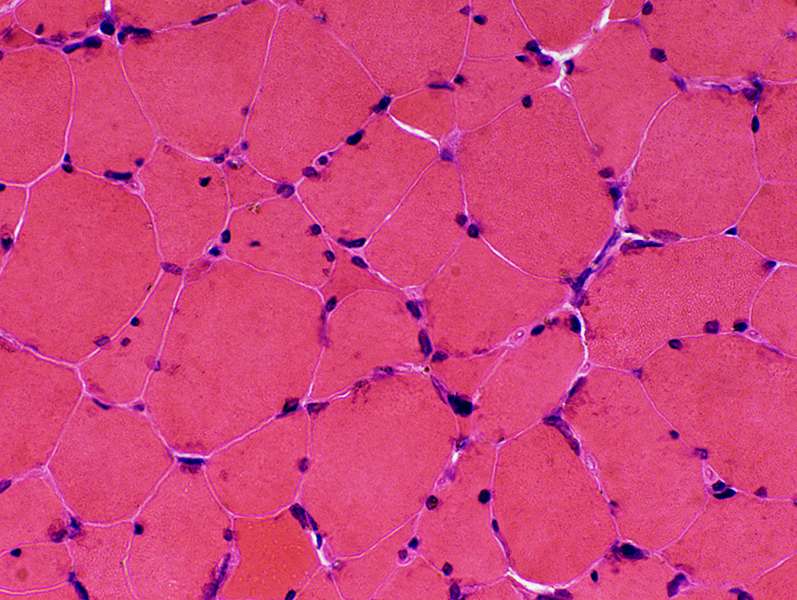 H&E stain Muscle fiber size: Varied |
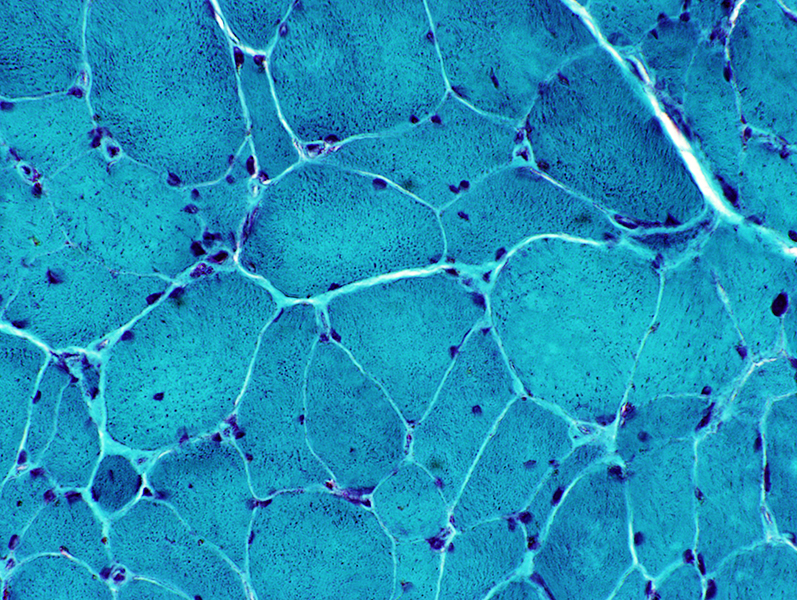 Gomori trichrome stain |
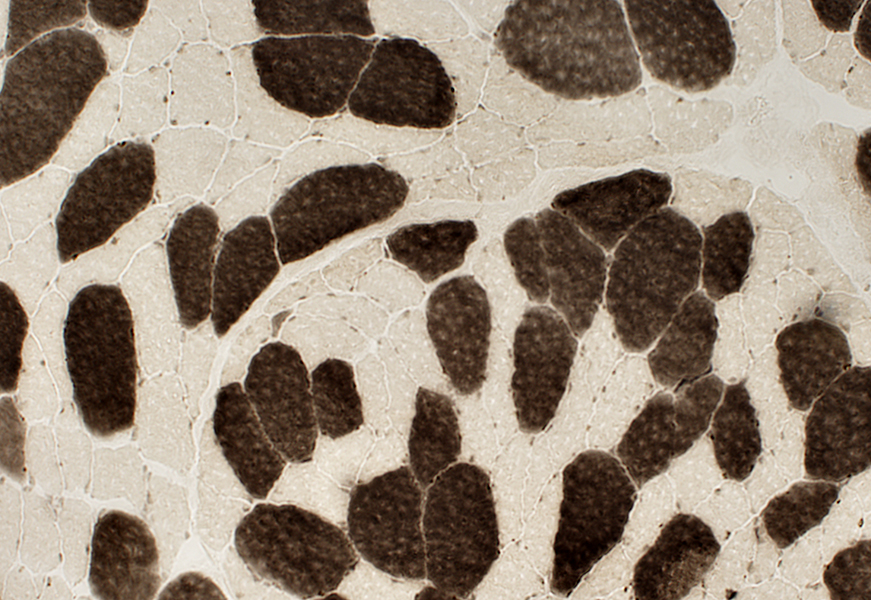 ATPase ph 4.3 stain Type 2 fibers small |
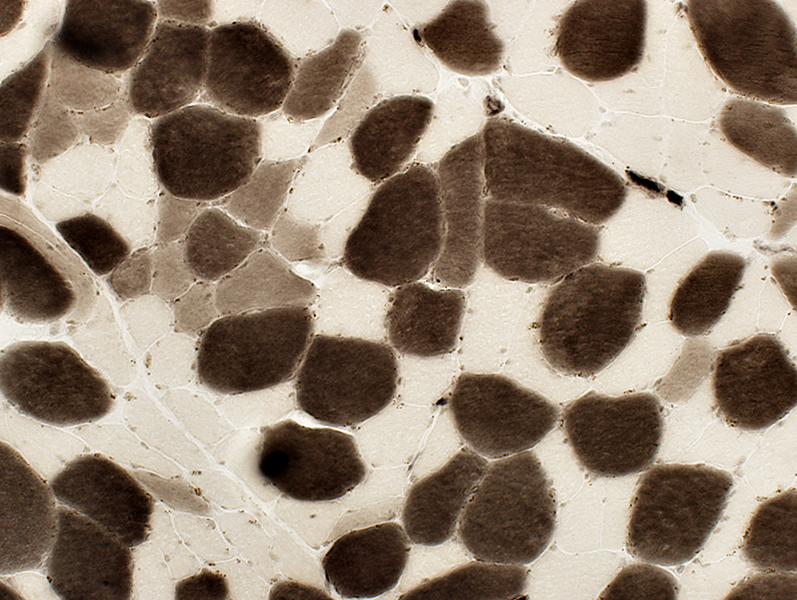 ATPase ph 4.6 stain |
Fiber types: Non-random distribution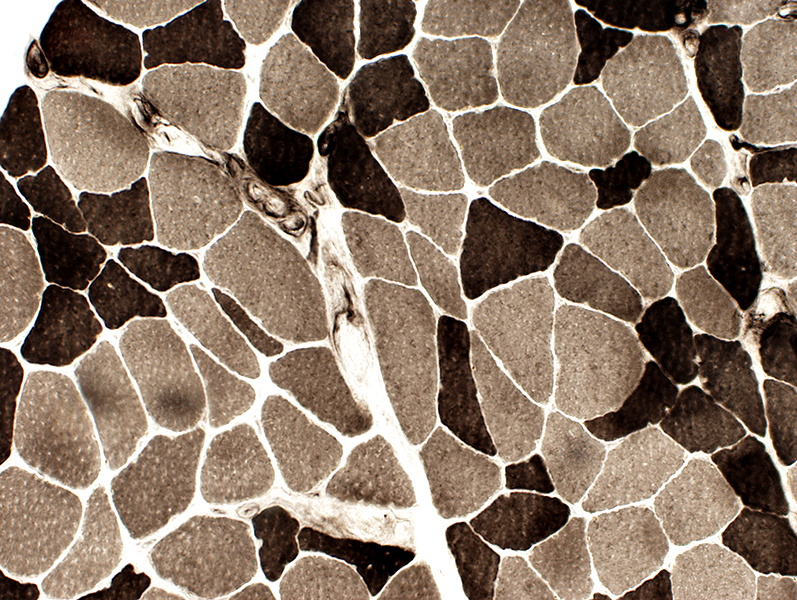 ATPase ph 9.4 stain |
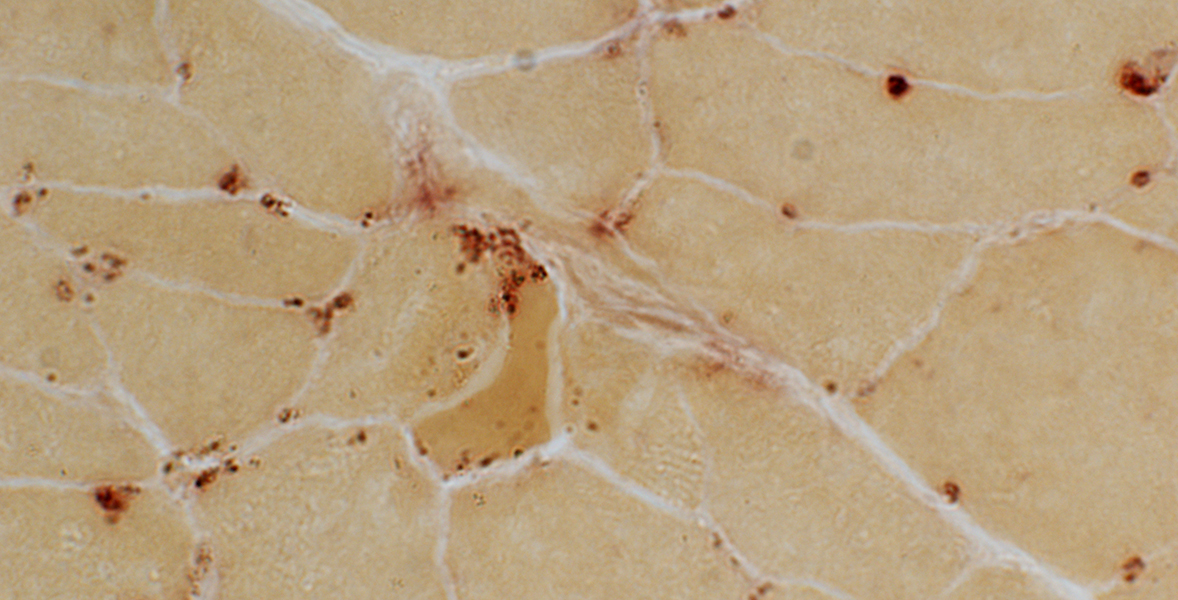 Acid phosphatase stain Lipofuscin: Punctate sub-sarcolemmal regions |
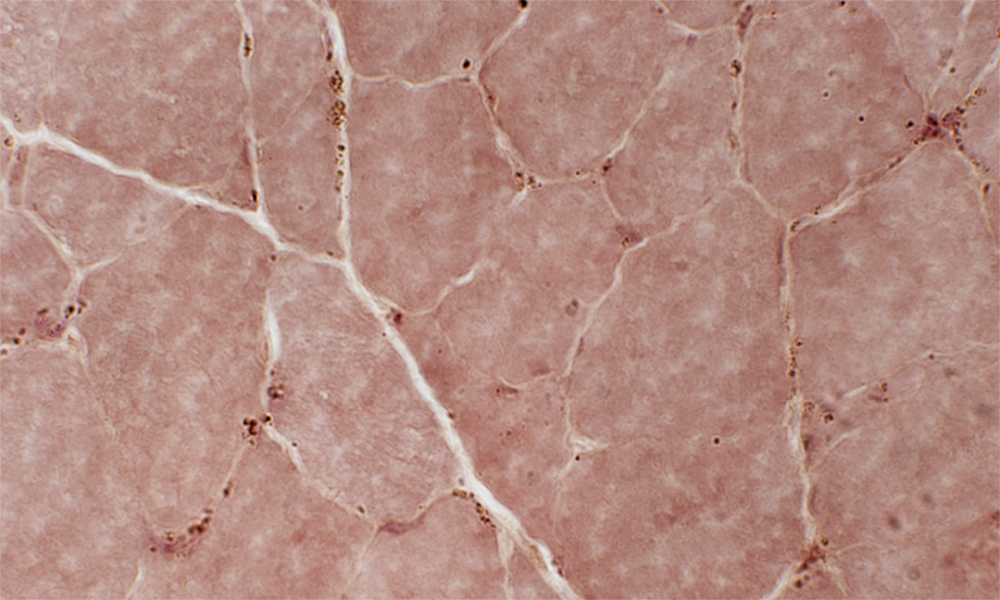 Esterase stain |
|
Internal architecture Mildly irregular Pale (Type 2) fibers small 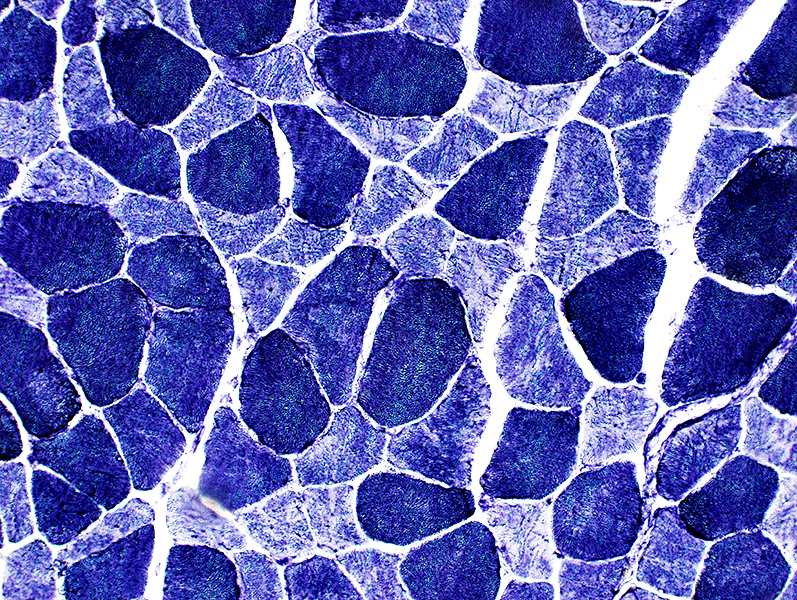 NADH stain |
Age: Nerve changes
- Development
- Myelination
- Onset: 18 weeks of gestation
- Birth: All fibers initially myelinated
- Thickness: Increases through childhood
- Absolute thickness
- Relative to axon size
- Internodal length
- Birth: 200–300 μm
- Adult: 200 to 1,800 μm
- Increases in parallel with somatic growth
- Axons
- Number: Full at birth
- Density: Reduced with increasing age
- Diameter: Increases up to 5 years
- Size distribution: Myelinated axons
- Birth: Unimodal
- Adult: Bimodal
- Conduction velocity
- Endoneurial area: Increases with age
- Myelination
- Full maturity: 10 years
- Aging
- Axons
- Myelinated fiber densities: Decrease continuously through adult life
- By ~50% from 2nd to 8th decade
- Regeneration
- Regenerated axons: May become up to 25%
- Regenerating clusters: More frequent with increased age
- Conduction velocity
- Myelinated fiber densities: Decrease continuously through adult life
- Myelin & Schwann cells
- Denervated Schwann cells: Increase with age
- Myelin thickness & internode length: Increased scatter with age
- Pi granules: May be increased numbers in older patients
- Endoneurium
- Endoneurial area & Collagen: Increase with age
- Endoneurial nuclei: Stable number with age
- Endoneurial capillaries: Age changes
- Hyalinization: Increased
- Endothelial & Pericytic basement membrane: More duplication
- Perineurial basement membrane
- Increased thickness with age: Most at outer layers
- Axons
Age: Neuromuscular Junction Changes
NMJs: RatAge: 2 Months
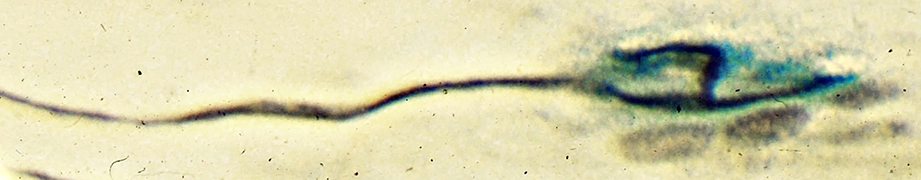 Silver-Esterase stain |
Age: 18 Months
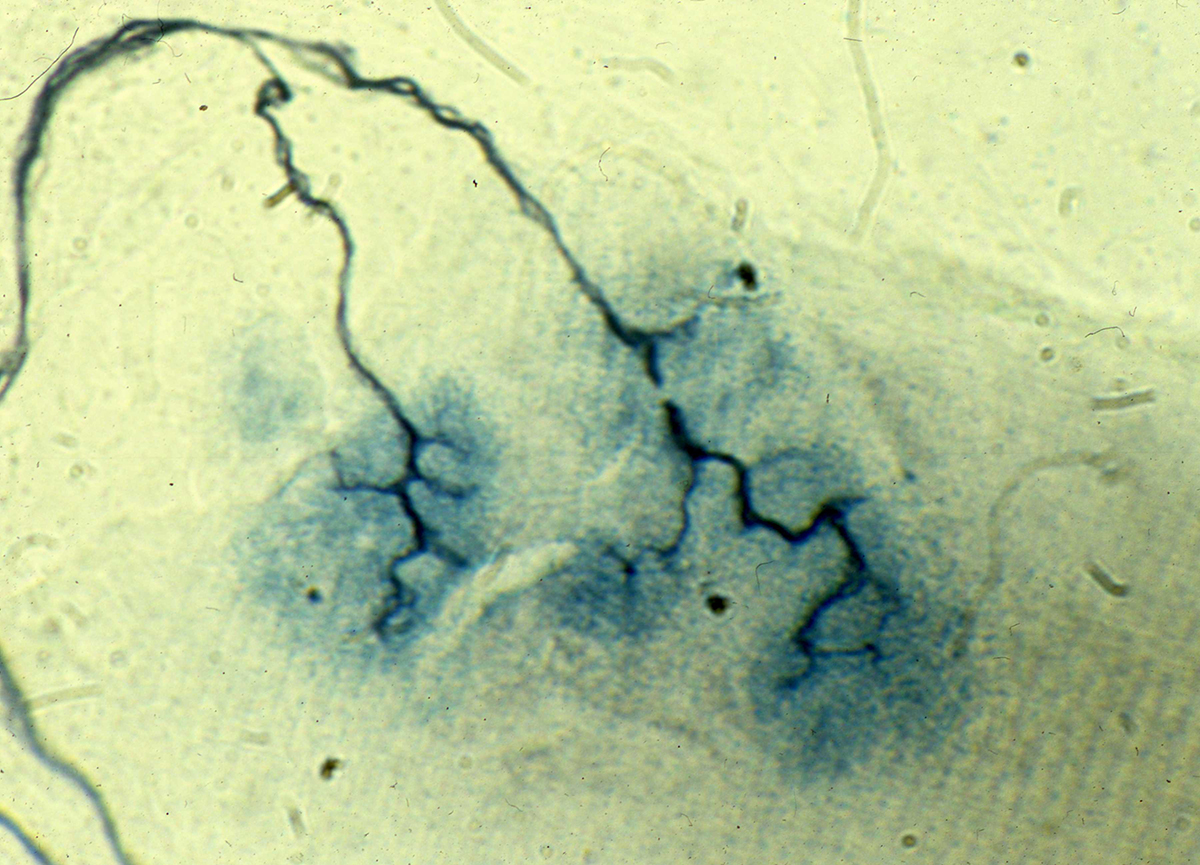 Silver-Esterase stain |
Age: 28 Months
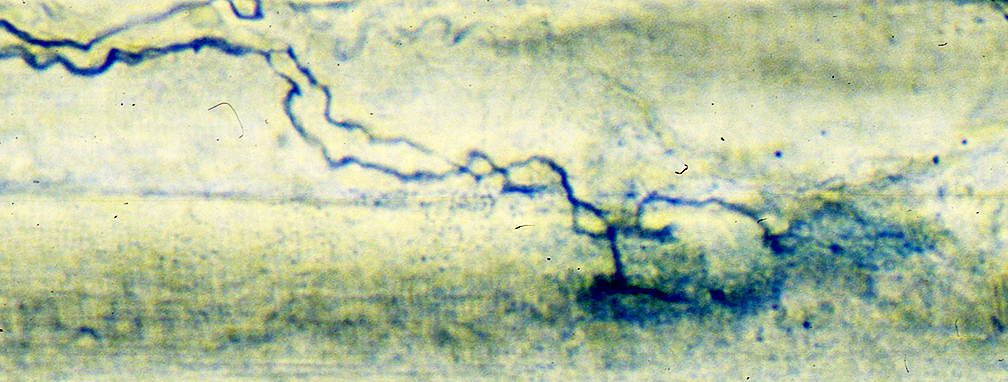 Silver-Esterase stain |
Return to Neuromuscular
References
1. J Am Geriatr Soc 2010;58:2069–2075
2. Muscle Nerve 2017;56:122-128
3. Cells 2019;8(12)
12/8/2022