EMERY-DREIFUSS MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY 1 (EMD1)
|
Affected male Carrier female |
Affected Males
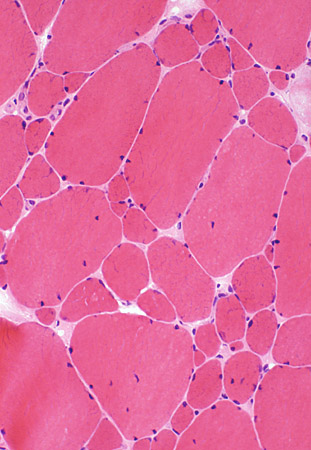 H & E stain |
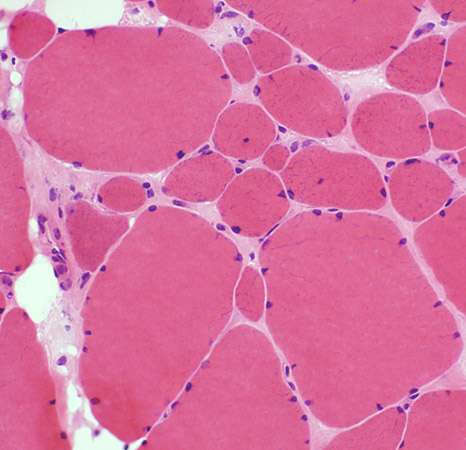 |
|
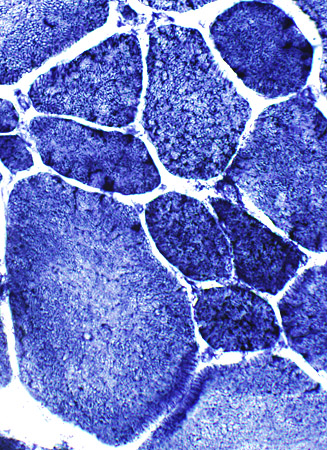
Myopathy Bimodal variation of fiber size Small fibers: Rounded Large fibers: Hypertrophied Increased endomysial connective tissue Internal nuclei: Some fibers |
|
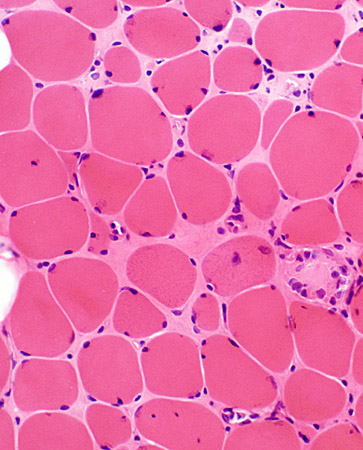 H & E stain |
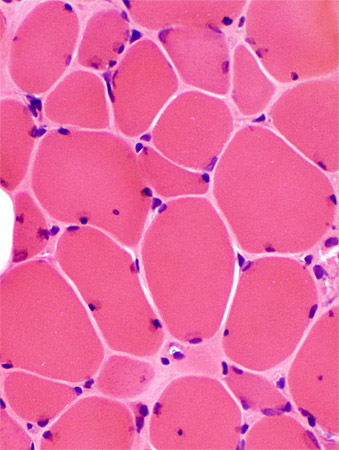 |
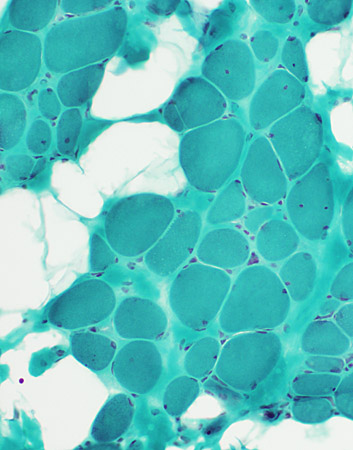 Gomori trichrome stain |
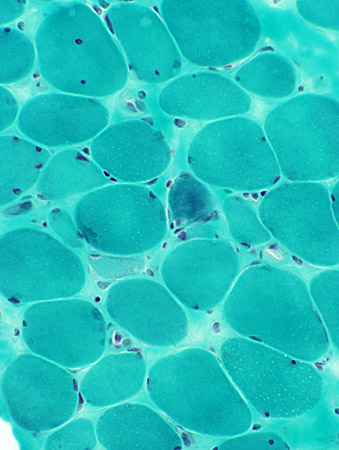 |
|
Chronic myopathy Varied fiber size Increased endomysial connective tissue Replacement of muscle by fat |
|
 ATPase ph 9.4 stain |
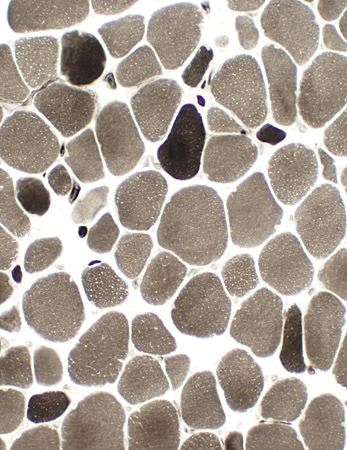 |
|
Fiber type abnormalities Small type 1 (Left) Type 1 predominance (Right) |
|
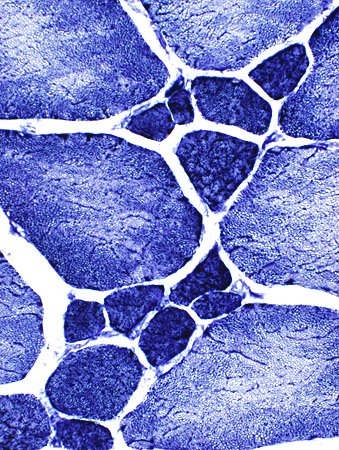 NADH stain |
 |
|
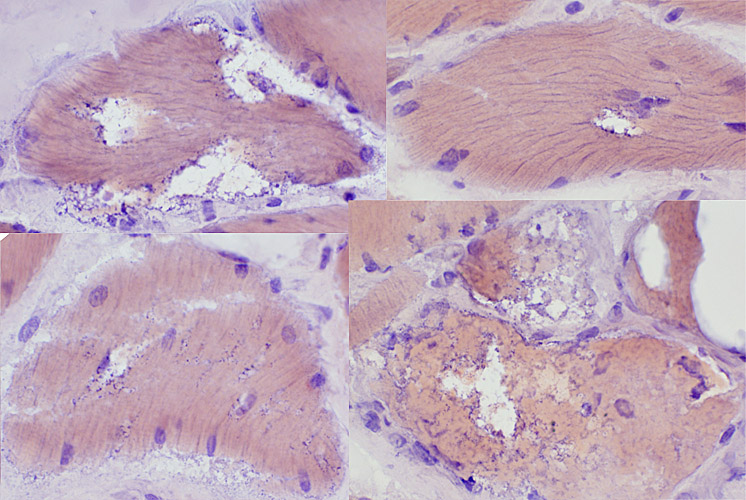
Abnormal internal architecture |
|
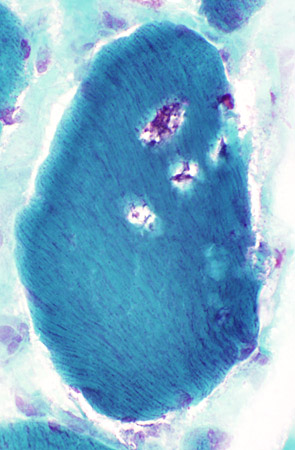 Gomori trichrome stain |
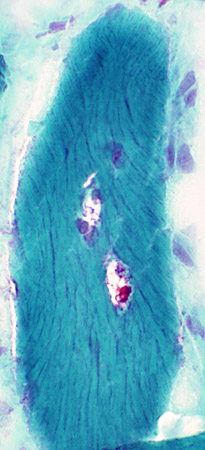 |
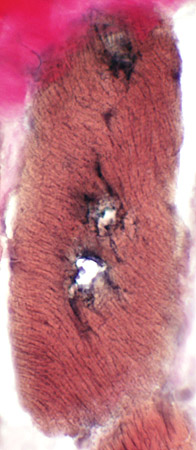 VvG stain |
 Congo red stain |
||
Normal muscle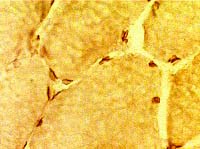 Emerin stain |
EDMD muscle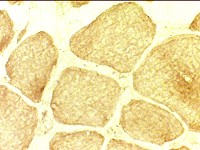 Emerin stain |
|
Muscle fiber nuclei, subsarcolemmal, are stained |
No emerin staining in myonuclei |
|
Normal muscle Emerin is present in varied amounts in different nuclei Subsarcolemmal myonuclei have abundant emerin (Green; Yellow arrow) Capillary nuclei have little emerin (Blue; White arrow) Dystrophin stains muscle fiber sarcolemma (Red) 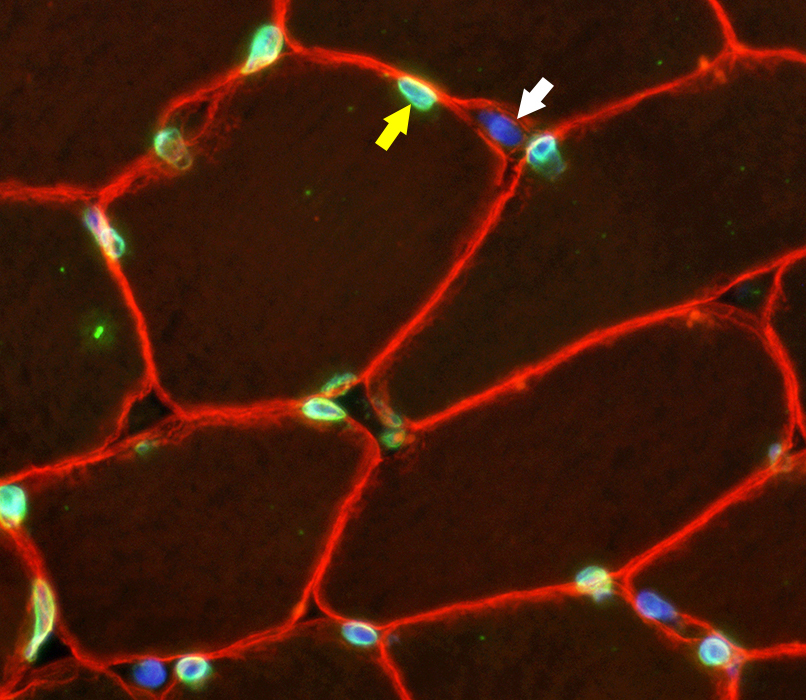 Emerin - Green; DAPI - Blue; Dystrophin - Red |
Manifesting Carrier (Female)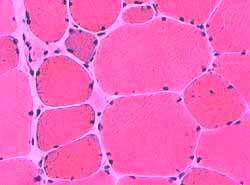 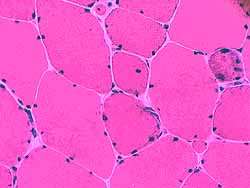 H & E stain |
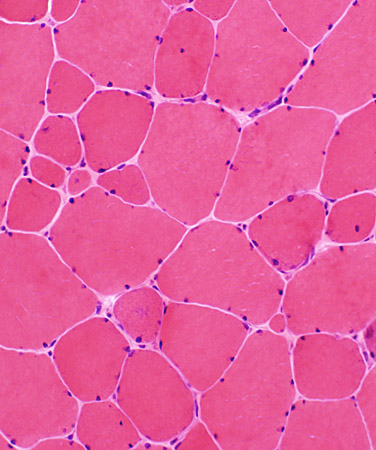 H & E stain |
|
Muscle fiber size: Variable Small fibers Rounded Some basophilic regenerating Large fibers: Hypertrophied. Internal nuclei: Some fibers Connective tissue: Mild increase 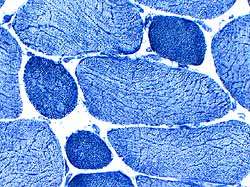 NADH |
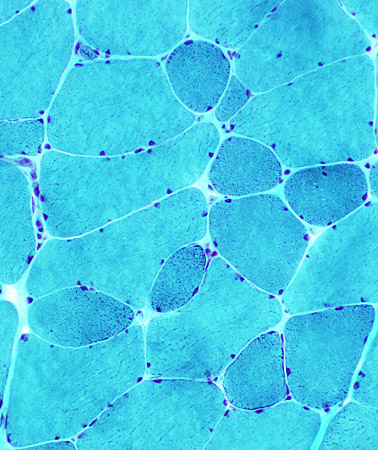 Gomori trichrome |
|
Abnormal internal architecture |
|
Fiber type disorder Most small fibers are type I Larger fibers are type I & II 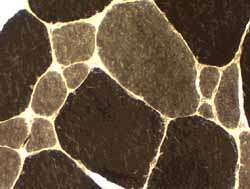 ATPase, pH 9.4 |
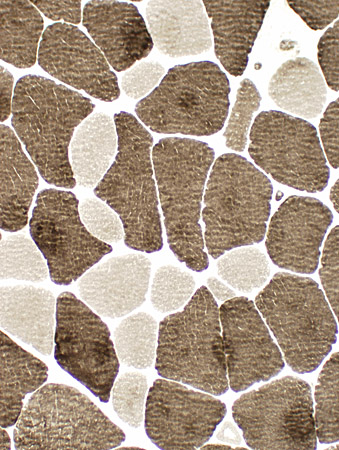 |
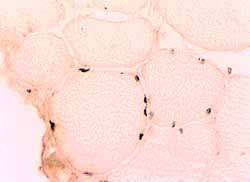
 Emerin immunohistochemistry |
|
|
Only some myonuclei stain for emerin. Emerin staining of nuclei is non-random and patchy. Some muscle fibers have many nuclei with emerin. Other muscle fibers have no nuclei with emerin. |
Return to Emery-Dreifuss.
Return to Neuromuscular syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular home page
10/31/2014