- Nosology: LGMD 2A
- Epidemiology
- 30% to 40% of LGMD
- Most common recessive LGMD worldwide
- Especially: Eastern Europe, Spain, Italy
- Denmark: Less common than 2I (FKRP) & 2L (ANO5)
- Genotype & Phenotype
- Mutations: > 500 identified
7
- Most common type: Missense
- Mutation patterns
- Private variant mutations in 70%
- Recurrent mutations
- Founder effect 1.5x more frequent than than recurrent
- Single base pair: 60% to 70%
- Missense: Most, ~80%
- Stop codons: Few
- Splicing defects: ~15%
- Small insertions or deletions
- Frequency: 30% to 40%
- Most cause frameshift & stop codon
- 1 Large genomic deletion
- 2° to unequal recombination between two intragenic Alu elements
- Overall ~45% of mutations are truncating
- Location: Present through most of gene
- Excess of mutations: Exon 21
- Excess of point mutations
- Exons 5, 11 (11 amino acid span with multiple CpG sites) & 21
- Excess of deletions/insertions: Exons 15, 17, & 22
- R490Q mutation
- Located in catalytic site
- Protein
- Autolytic activity: Lost
- CAPN3 protein present by Western blot
- CAPN3 remains after incubation of muscle without EDTA
130
- LGMD phenotype: Weakness severity = Variable
- G222R mutation
54
- Mutations: Compound heterozygote for R110X & G222R
- Loss of function: Size & Abundance normal
- Early onset weakness
- Disease foci: Geography
- Europe
- Réunion island
- 60% have IVS6-1G>A
- Amish & Basque populations
- Digenic inheritance: ??
- Guipuzcoa (Basque Country, Spain)
- Exon 22, 2362AG[→]TCATCT in 76%
- Italy
- Mocheni, Italian Alps: c.1193+6T>A
- Venetian lagoon (Chioggia): Arg490Gln
- Central & Eastern Europe
- c.1746-20C>G; Mutation frequency 1%
- Russia, Eastern Mediterrananean & North Italy
- 550delA: Mutation frequency 1/150
- North America
- US Northern Indiana Amish: Arg769Gln
- Tlaxcala, Mexico: Ala116Asp
- Asia
- China: c.2120A>G
- Japan: c.1795_1796insA
- Northern India: Asp780His, c.2099-1G>T, c.2051-1G>T, c.2338G>C
- Large (31,012-bp) deletion (Exons 2-8) (c.309+4469_c.1116-1204del)
- Occurs in different ethnic backgrounds
- Clinical correlations
- Severe phenotype
- Homozygous null mutations: Often but not always
- NS1 domain mutations; S86F
- Least severe phenotype: Homozygous missense mutations
- Allelic disorder: LGMD, Dominant
- Mutation Databases
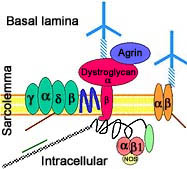
- Calpain-3 (p94) protein
145
- Localization
- Expressed prominantly in skeletal muscle: N2-line region
- Associates with
- C-terminus of titin (connectin) in muscle
- Filamin C
- Calmodulin kinase IIβ (CaMKIIβ).
- Subcellular: Nucleus ± Cytosol; Not membrane related
- Substrates
- Metabolic
- Myofibrils (MLC1)
- Functions
- General
- Ca++ activated non-lysosomal cysteine thiol-protease
- Relies on Na+ activation
- Cleaves proteins into short polypeptides, not single amino acids
- Activity may not be Ca++ dependent
- Use cysteine as active site residue
- Limited proteolytic cleavage of substrate
- Related to location in cell
- Nuclear: Cell survival
- Cytoplasm: Cell motility; Skeletal plasticity
- Cytoskeletal remodeling
- Assembly & remodelling of contractile proteins in sarcomere
- Can bind & cleave titin
- Control of Ca++-efflux from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Membrane repair
- Muscle regeneration
- Mutations: Reduced affinity of calpain-3 for titin
- Half life
- Short (< 10 minutes)
- Rapid turnover related to insertion sequences (IS) not present in other calpains
- Autolysis: Not dependent on Ca++ activation
- Disease mutations: Effects on calpain function vary, may be selectve for
- Proteolytic activity vs fodrin substrate: Reduced
- Autolysis capacity: Reduced
- Titin binding: Reduced
- Altered maintenance & remodelling of contractile apparatus
- Abnormal calpain-3 proteolysis & cleavage of titin
- Expression in other disorders
- Increased: FSHD; Melanoma, Vitiligo, Cataract (Age-related)
- Reduced: Dystrophies (2B, 2J, Tibial, Duchenne, Ullrich); IBM; Rhabdomyolysis
- LGD 2A: Clinical features
21
- Onset
- Early motor milestones: Most normal; Toe walking common
- Range: 2 to 65 years; Median = 14 to 20 years; 71% between 6 to 18 years
- Weakness: Proximal legs; Rectus abdominus
- No clear sex differences; ? Females slightly younger than males
- Disease patterns: Various phenotypes
- General pattern
- Weakness: Scapula (Symmetric), Pelvic girdle
- Normal: Face
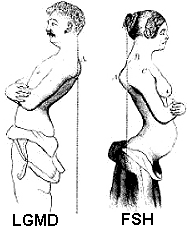
- Differential Diagnosis: FSH; LGMD 2I
- HyperCKemia, asymptomatic (14%): Male > Female 3:1
- Limb girdle types (76%)
- Early onset: < 12 year
- Group with most homogeneous progression
- Contractures more common
- Null mutations: Common
- Leyden-Mobius type
- Onset 13 to 29 years
- Weakness
- Early: Pelvic-Femoral girdle
- Later: Shoulders
- Late onset
- Age: > 30 years
- Weakness: Pelvic girdle
- Erb dystrophy type (10%): Scapular-Humeral phenotype
- Onset age: 16 to 37 years
- Weakness early: Shoulder girdle
- Male = Female
- Calpain-3 protein in muscle: Often normal
- Miyoshi muscular dystrophy phenotype
- Weakness
- General
- Symmetrical
- Proximal + Milder Distal
- Legs > Arms at onset: Most patients
- May be asymmetric
- Progressive
- Severity
- Heterogeneous: Mild to Early onset severe
- Mild phenotype in majority
- Male = Female
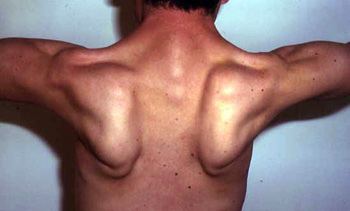
- Trunk
- Peri-Scapular
- Latissimus dorsi; Serratus magnus
- Scapular winging (83%): Symmetric
- Rectus abdominus
- Pelvic girdle
- Gluteus maximus
- Legs
- Most severe: Adductors; Knee flexion
- Ankle dorsiflexion: Some patients
- Arms
- Most severe: Shoulder adduction; Elbow flexion
- Wrist extension: Some patients
- Respiratory
- Vital capacity: Declines over time; Rarely < 80%
- No nocturnal hypoventilation
- Quadriceps: May be selectively spared
- Gait
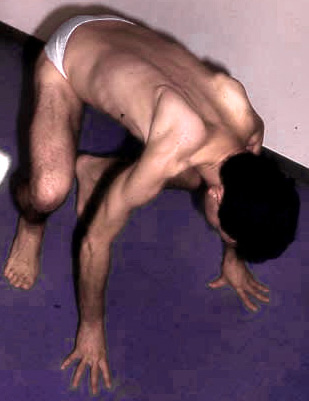
- Inability to walk on heels
- Lumbar lordosis
- Loss of walking: Mean late 2nd or 3rd decade
- Normal: Face; Ocular & Bulbar
- Some patients are asymptomatic with elevated serum CK levels
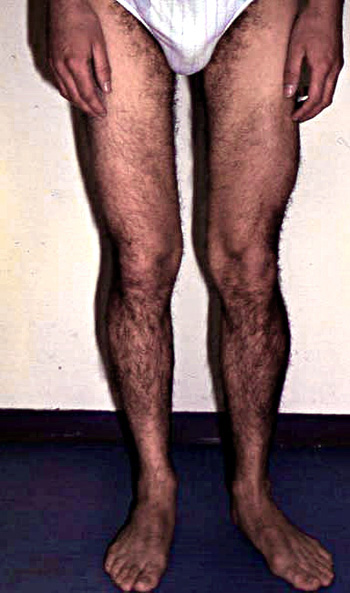
- Muscle size
- Atrophy
- Early in posterior compartments of limbs
- Different from Quadriceps wasting in Sarcoglycanopathies
- May be apparent on CT
- Most affected: Gluteus maximus & Thigh adductors
- Pelvic; Shoulder; Proximal limbs; Trunk; May be scapuloperoneal
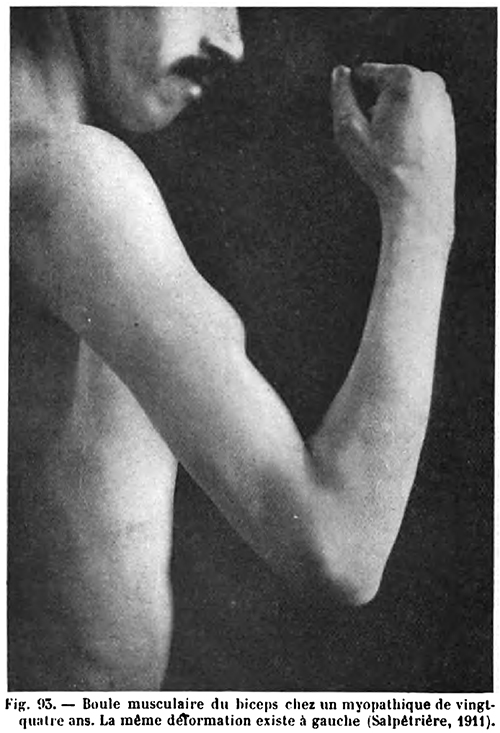
- Hypertrophy
- Some patients
- Earlier in disease course
- Especially in Brazil
- Most common: Calf (Not prominent); Proximal
- Contractures
- Onset: May occur early in disease course
- Calf: Toe walking may be presenting sign
- Other: Elbow, Wrist & Finger flexion
- Common late in disease progression: Rigid spine
- May be severe & require surgery
- Differential diagnosis: Emery-Dreifuss
- CNS
- Normal, or
- Mild mental retardation: Average IQ = 77
- Cardiac: No involvement
- Progression
- Slow: Earlier onset more rapid
- Loss of walking
- 10 to 30 years after onset
- 50% in 3rd decade
- Most by age 40 years
- Many patients can still stand, even when in wheelchair
- Syndrome variation
- Intrafamilial
- Similar onset age & severity in some families with null mutations
- Variation in others with
- 2 Missense mutations or
- Compound heterozygotes for missense & null mutation
- Onset 2.5 to 45 years
- Interfamilial: Prominent
- LGD 2A: Lab features
- Serum CK: Normal to 80 times normal; 190 to 11,000
- MRI
- Thigh: Varies with degree of function
- Prominent in most patients: Posterior
- Early involvement: Adductors; Semimembranosus
- Restricted ambulation
- Diffuse involvement: Posterolateral thigh & Vastus intermedius
- Sparing: Vastus lateralis, Sartorius & Gracilis
- Calf
- Involvement: Soleus; Gastrocnemius, Medial head
- Relative sparing: Gastrocnemius, Lateral head
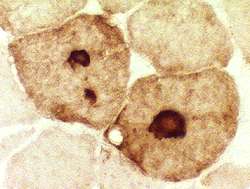
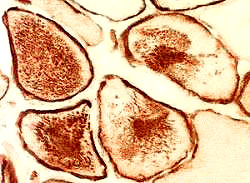
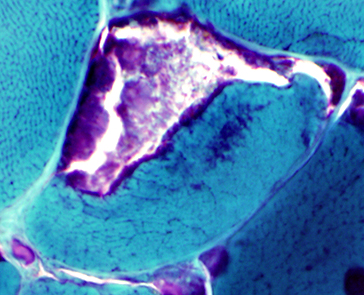
- Muscle Biopsy
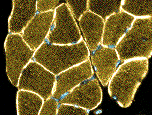
- Myopathic
- Muscle fibers
- Necrosis & Regeneration
- Active myopathic changes
- Eosinophils in some associated cell foci
- Myopathic groups
- May involve clusters or whole fascicles early in disease
34
- Size: Variable; Small rounded to Hypertrophic
- Internal architecture
- Usually unremarkable
- Regenerating fibers: Coarse internal architecture
- Lobulation of Type I fibers: Later in disease course
- Nuclei: Internal; Apoptosis with altered IκBα/NF-κB

 pathway
pathway
- Groups of atrophic (type 2) muscle fibers
- Endomysial fibrosis: Increased with longer disease course
- Fiber types
- Type 2 hypertrophy: Some patients
- Type I predominance: With increasing weakness
- Type 2C: Common
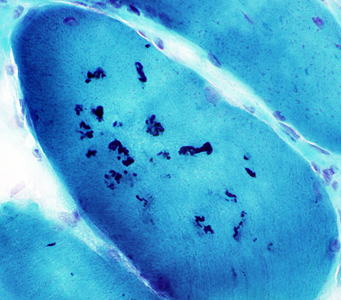
- Inflammation
- Some biopsies
- May be perivascular or endomysial
- Dystrophy-related proteins
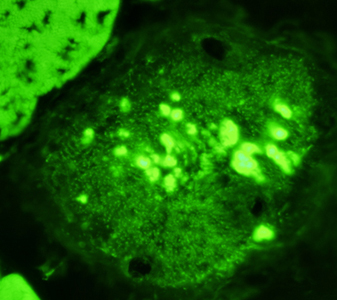
- Calpain-3: Western blot patterns
- Loss of all calpain-3 bands (94 kDa, 60 kDa & 30 kDa)
- High specificity for LGMD2A: Frequency 23%
- May have null or missense mutations
- Absence or reduction of 60 kDa bands
- High specificity (94%)
- Sensitive (64%)
- Absence or reduction of 30 kDa bands
- Specific (88%)
- Sensitive (58%)
- Increased lower MW 60 kDa region bands
- No mutations (92%)
- Suggests protein degradation artifact
- Normal full-sized calpain-3 protein
- Occurs in 23% of patients with 2 calpain-3 mutations
- Often have loss of autocatalytic function
- Abnormal Western blot with only 1 calpain-3 mutation
- Similar phenotype to patients with 2 mutations found
- Calpain-3 reduction may occur in other myopathies
- Dysferlin: Reduced or absent in some patients; Western blot normal
- Sarcoglycans & Dystrophin: Normal
- Ultrastructure: Patchy damage to
myofibrillar Z, I & A bands
- Diagnosis
41
- Genetics
- Difficult due to many different mutations
- More common in some regions of gene
- 87% of mutant alleles in exons 1, 4, 5, 8, 10, 11 & 21
- Some common mutations: 61% have one of eight mutations
- Directed mutation analysis: Geographic groups
- Some patients with only 1 detected mutation have
- Western blot
- Calpain-3 enzyme activity: Reduced
- Mouse model: Calpain-3 knockout
42
- Misaligned A-bands
- Abnormal sarcomere formation
- CAPN3 variant syndrome: LGMD, Dominant 4 (LGMD D4)
 104
104
- Nosology: LGMD 1I; LGMD D4
- Epidemiology: 37 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutations
- In-frame deletions: c.643_663del21; c.598_612del15; c.759–761delGAA [Lys254del]
- Missense: c.1333G>A [p.(Gly445Arg)]
- S86F heterozygotes: Mildly high serum CK; Normal strength
- Gly234Arg heterozygotes: Exertional myalgia
- Clinical: Milder than recessive CAPN3 mutations
- Onset age
- Mean 34 years: 16 years later than Recesive LGMD 2A
- Range: 13 to 84 years
- Pain (50%)
- Muscle
- Back
- Exertional
- May occur without weakness
- Weakness
- Severity: Milder than LGMD 2A
- Pattern: Similar to LGMD 2A
- Paraspinal: Lumbar; Camptocormia
- Leg: Proximal
- Distal leg: Gastrocnemius, medial
- Arms: Proximal
- Normal strength: Some patients
- Course: Variable
- Severe disability: Some patients
- Asymptomatic: Some patients
- Muscle wasting: Proximal arms
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High in 90%; Range 169 to 9,000
- Muscle MRI: Fat replacement
- Trunk: Paraspinal
- Pelvis: Glutei
- Thigh: Hamstring
- Leg: Gastrocnemius, medial
- Muscle pathology
- Myopathic
- Internal nuclei
- Fiber size: Varied
- Internal architecture: Lobulated
- Necrosis: Scattered
- Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
- Calpain-3 protein: Reduced (< 15% of control levels) or Normal
|
From: C Angelini
|
|