- Transcriptome patterns: Cortex pathology
94
- ALS-Ox: Oxidative & Proteotoxic stress; snRNP70 splicing change; Most common pattern
- ALS-Glia: Glial activation increased
- ALS-TE: Retrotransposon expression high; TDP-43 dysfunction
- Han Chinese: ALS
47
- Onset age: Mean 49 years; 10 years younger than European population
- Onset region: Spinal (87%) more frequent than European population (70%)
- Susceptibiliy loci
- 1q32 (CAMK1G, rs6703183) OR 1.31
- 22p11 11 (CABIN1 & SUSD2, rs8141797) OR 1.52
- No association with many European loci
- ITPR2; FLJ10986; DPP6; UNC13A; MOBKL2B
- FALS: PFN1 & c9orf72 rare; SOD1 reported
- FALS genes: Mutations & variants occurring in "sporadic" ALS
51
- General
- Frequency: 28%
- Common: C9orf72 (9%); ATXN2 (3%);
SETX (9%); DCTN1 (3%)
- Multiple mutations in one patient
- Frequency: 3.8%
- ALS onset age: 10 years earlier
- "Sporadic" patients with FALS mutations
- More likely to have FH of Dementia
- C9orf72 mutations
- Frequency in "sporadic" ALS
- Usual: 4% to 8%
- Range: 0% to 21%
- More common: Finnish & Western populations
- Family history: May include dementia without ALS
- Chromosomal rearangements
14
- Frequency: 5.9% vs 0.05 to 0.1% in general population
- Types: Balanced translocations (3/85); Pericentric inversions (2/85)
- EAAT2 (glutamate transporter)
 : RNA processing errors : RNA processing errors
- APOE

- Plasma levels high
- Correlate with rapid deterioration & shorter survival time
- Relative risk = 0.647
- APOE phenotype: No clear correlations
- Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
 18
18
- Low VEGF producing homozygous haplotypes
- 1.8-fold higher risk of ALS
- Haplotypes: -2578A/-1,154A/-634G; -2578A/-1,154G/-634G
- Associated with low circulating VEGF levels
- Association found for both sporadic & familial ALS
- Earlier death in SOD mutant mice with impaired VEGF expression
- Granulin precursor (Progranulin; PGRN; GRN)
 31
31
●
Chromosome 17q21.31; Dominant with other CNS syndromes in family
- Allelic disorders
- ALS
- ALS-FTD
- Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP43 & Ubiquitin inclusions
 : Dominant : Dominant
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutations: Often produce haploinsufficiency
- 20% of FTD with TDP43 inclusions
- Aphasia, primary progressive
 : Dominant : Dominant
- Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, 11 (CLN11)
 : Recessive : Recessive
- ALS
- ALS mutations
- Types: Missense; 5' regulatory; DNA variants
- ALS clinical associations
- Mutations: IVS2 + 21G>A or IVS3-47-46insGTCA
- Younger ALS disease onset
- Shorter ALS survival
- FTD-ALS
- Epidemiology: > 40 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: A9D & missense
- Mutation effect: Haploinsufficiency due to loss of GRN secretion
- Clinical
- Onset age: 48 to 67 years; Later than c9orf72
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, atypical: Some patients
- Motor
- Dystonia: Focal
- Extrapyramidal disorder, atypical: Dysarthria; Hypomimia
- Apraxia
- Frontotemporal dementia: Behavioral variant
- Aphasia
- EOM: Limited or Apraxic
- Laboratory
- NCV: Mild slow; CMAP amplitudes small
- EMG: Fibrillations; Fasciculations
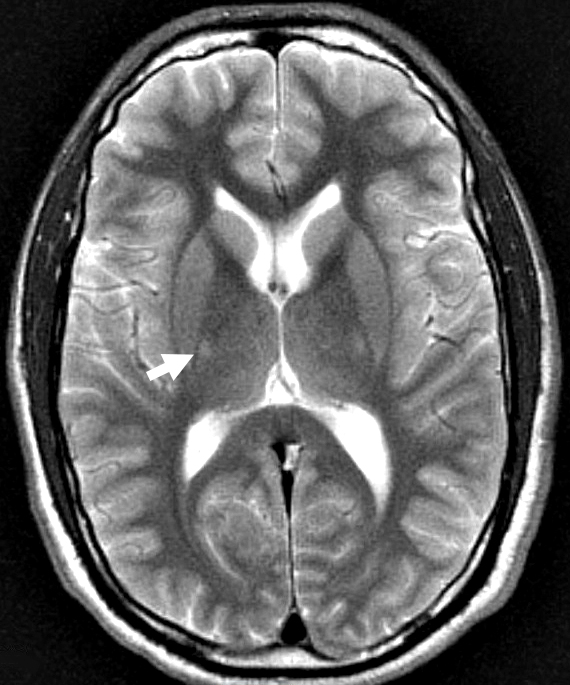
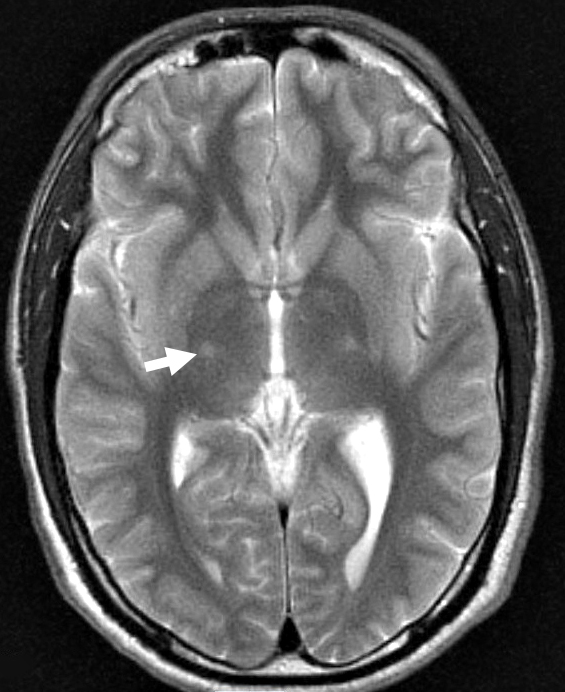
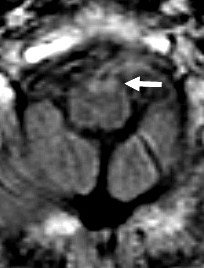
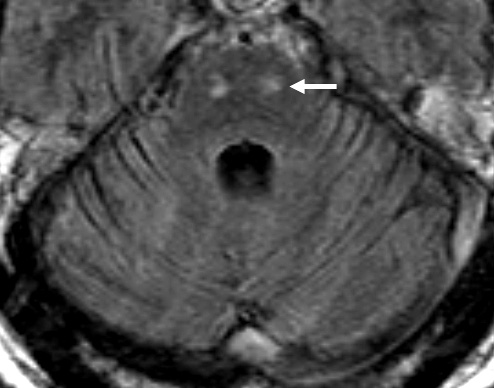
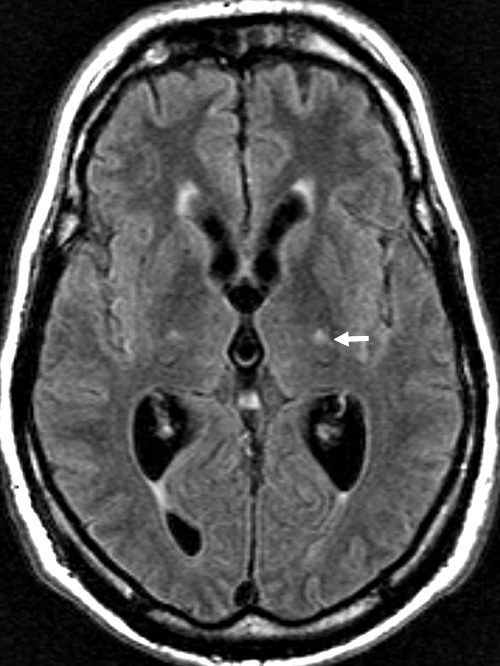
- MRI: Subcortical atrophy
- Pathology
- Motor neuron loss: Upper & Lower
- Neuronal or Glial cytoplasmic inclusions
- TDP43 pathology
- GRN variant: Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, 11 (CLN11)

- Genetics: Recessive inheritance
- Clinical
- Retinal dystrophy: Visual loss
- Seizures
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Cognitive decline
- Course: Rapidly progressive
- Laboratory
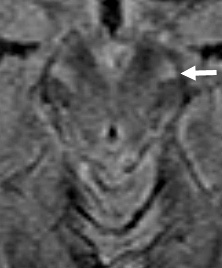
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
- SMN1
 & SMN2 & SMN2
- SMN1 & SMN2 Copy numbers
89
- No differences: ALS vs controls
- No effect: ALS onset age or survival
- FIG4
 32
32
- ALS Mutations
- Heterozygous
- Missense or Termination
- Frequency: 1% to 2% of ALS patients
- ALS type
- Family history: Familial or Sporadic
- Clinical pattern: ALS or PLS; Brisk tendon reflexes
- Also see: CMT 4J
- SLC11A2
 37
37
- Genetics
- Chromosome locus: 12q13.12
- Feature: rs407135 with C allele
- SLC11A2 protein
- Divalent metal transporter (DMT1)
- Carries iron, manganese, cobalt, nickel, cadmium, lead, copper & zinc
- Clinical correlation: Shorter sporadic ALS disease duration with leg onset
- Sequestome 1 (SQSTM1; p62)
 43
43
●
Chromosome 5q35.3
- Genetics: Allelic disorders
- SQSTM1 protein
- Clinical: Associated syndromes
- ALS
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Usually Sporadic
- SQSTM1 Mutations
- Some mutations only in ALS or FTLD
- ALS: Ala53Thr; V259L; P348L; P438L; Pro439Leu
- FTLD: K344E; -1221 G>A
- Types: Most often
- Heterozygous
- Missense or Promoter
- Variants more in ALS or FTLD
- Present in 2% to 3% of familial & sporadic ALS
- Also occur in controls
- K238E; E274D; E319K
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 33 to 69 years
- Site: Bulbar or Limb
- Weakness: Bulbar & Limbs
- Tendon reflexes: Increased or Decreased
- Course: Progressive; 1 to 16 years
- EMG: Denervation, diffuse
- Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration (FTDALS3; FTLD)
 : Behavioral variant
115 : Behavioral variant
115
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant or de novo
- Mutations: Missense; Pro392Leu
- Pro392Leu
- Varied phenotypes: Padget, FTD, Amnestic syndrome, Parkinsonism, Motor neuron disease
- 35 patients with FTD
- Penetrance: Reduced
- Frequency of SQSTM1 mutations in FTD: 2% to 3%
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Mean 61 years
- Intrafamilial variation
- Behavior
- Aggressiveness
- Mood changes
- Social detachment
- Motor: Some patients
- Weakness
- Tendon reflexes: Increased or Decreased
- Paget disease
- Laboratory
- MRI: Frontotemporal atrophy, asymmetric
- CSF: Phosphoτ increased in one patient
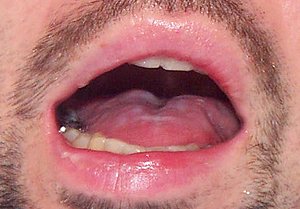
- Speech apraxia
- Atypical behavior
- Visuo-constructional deficits
- SQSTM1/p62 variant: Myopathy, Distal + Vacuoles (DMRV; MSP4)
 56
56
- Nosology: Multisystem proteinopathy 4
- Epidemiology: 24 patients; Male 75%
- SQSTM1 Genetics
- Inheritance: Sporadic, Dominant or Digenic
53
- Mutations
- Common
- TIA1 mutation: Asn357Ser
- SQSTM1 (p62) mutation: Pro392Leu most common
- Splice site (c.1165+1 G>A;): May have additional TIA1 mutation
103
- c.1175C>T
- Frameshift (c.542_549delACAGCCGC)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 4th to 7th decade; Median 52 years
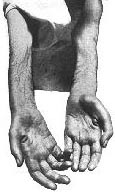
- Weakness: Distal legs
- Weakness: More in legs at onset than Welander
- Distal legs: Foot & toe dorsiflexion; Gait disorder
- Distal arms: Wrist & finger extensors
- Other: Pectorals; Scapular
- Asymmetric: Some patients
- Proximal predominant & neck weakness: Frameshift mutation
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Sensory loss: Distal; Some patients
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 100 to 500; High in 80%
- Muscle biopsy
- Fiber sizes
- Varied
- Groups of small fibers
- Internal nuclei
- Vacuoles: Rimmed
- Aggregates in fibers: SMI-31, TDP-43, LC3, SQSTM1
- COX- fibers: Few; Scattered
- Ultrastructure: Myofibril disorganization & Aggregates
- Muscle MRI
- Lower extremity: distal > Proximal
- Thigh: Quadriceps femoris & Posterior compartment in the thighs
- Legs: Medial gastrocnemius ± Anterior tibial
- EMG: Myopathic
- Possible association: Sensory-Motor neuropathy
- SQSTM1/p62 variant: Childhood Neurodegeneration (NADGP)
 62
62
- Epidemiology: > 30 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Truncation
- SQSTM1 defect: Autophagy impaired
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 6 to 15 years
- May be subacute
- CNS
- Ataxia (100%): Gait disorder; Dysarthria
- Extrapyramidal (40%): Dystonia; Athetosis
- EOM: Vertical gaze palsy; Saccade disorders
- Cognitive (100%): Decline
- Pyramidal signs (10%)
- Hypogonadism, Hypergonadotropic
- Laboratory
- Muscle biopsy
- Morphology: Unremarkable
- Complex IV activity: Mildly reduced
- Brain MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy: With disease progression
- Globus pallidus iron (10%)
- Epha4
 45
45
- Chromosome locus: 2q36.1
- Epha4 expression levels: Lower in ALS patients correlate with
- Onset age: Later
- Survival length: Greater
- EPHA4: Loss-of-function mutations
- Associated with long survival in 2 ALS patients
- Mutations: C1540T, R514X
- Inhibition of Epha4 expression
- Rescues motor neuron disorders in animal models: SOD1; TDP43; SMN1
- UNC13A
 34
34
- Genetics
- Chromosome locus: 19p13.3
- Common intron 21 variant rs12608932
- Polymorphisms: Variably associated with
- ALS susceptibility
- ALS & FTD-TDP susceptibility
- Shorter ALS survival
- Time: 1 year less
- rs4808092: G>A only in short survivors (4/25)
- Longer ALS survival
- Longer ALS survival with Lithium carbonate treatment
69
- rs12608932
86
- C allele
- Higher age symptom onset
- More bulbar onset
- C/C
- More ALS-FTD
- Lower forced vital capacity at diagnosis
- Shorter survival
- More upper motor neuron features: AA genotype
- Allelic disorder
- UNC13A protein: Presynaptic
- Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 10 (LRP10)
 87
87
- China ALS
- c.1721G>A (p.R574Q) associated with
- Bulbar ALS onset
- Worse prognosis
- Pathogenic variants found in 2% of ALS
- Associated with: Alzheimer; Parkinson
- ZNF512B
 46
46
- Genetics: SNP rs2275294 C allele
- ALS Survival: Shorter
- TREM2
 50
50
- Genetics
- Chromosome locus: 6p21.1
- ALS: Risk factor
- p.R47H (rs75932628) modification: Loss-of-function
- Lipid metabolism: Disrupted
- Phagocytic activity: Impaired
- sALS allele frequency: 0.45
- Control allele frequency: 0.19
- Allelic disorders
- R47H: Risk factor also for
- Alzheimer disease (AD17)

- Frontotemporaldementia
- Parkinson disease
- Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia +
Sclerosing leukoencephalopathy (PLOSL)

- TREM2 protein
120
- Cell surface receptor: Binds
- Phospholipids: Phosphatidylserine; Cardiolipin
- Apoptotic debris
- Bacterial components
- A&beta aggregates
- Immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily
- Reprograms microglia: Toward glycolysis & mitochondrial activation
- Associated systems
- Glycolysis
- TCA cycle
- HIF-1α
 : Lactylation : Lactylation
- Succinate
- SHP1
 -BTK -BTK

- TyroBP (DAP12)
- PI3K/Akt Pathway
- MAPK
- ALS: TREM2 expression
- Increased in spinal cord
- ALS survival: Negative correlation
- Immunomodulatory receptor
- Expressed on: Myeloid cells; Macrophages, Microglia
- Attenuates neuroinflammation
- Modulates microglial polarization
- Simultaneous activation of TREM2/TYROBP

- Potentially neuroprotective microglial state
- Improved phagocytosis of apoptotic cellular debris
- Downregulation of inflammatory cytokines
- Alzheimer interaction
- Promotes β-amyloid (Aβ) clearance
- Inhibits tau hyperphosphorylation
- Neoplasm: Progression & Therapeutic resistance
- Modulates metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages
- Activates: Pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme M (PKM)-dependent glycolysis

- Promotes immunosuppressive phenotype
- Diabetes & Obesity: Protective
- Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- Maintains lipid homeostasis
- NIMA-related Kinase 1 (NEK1)
 60
60
●
Chromosome 4q33; Dominant or Sporadic
- Epidemiology
- > 25 patients
- May be more common in China
- Genetics
- Mutations: Heterozygous
- Loss-of-function
- Missense (Arg261His common); Frameshift
- Allelic disorder
- Short-rib thoracic dysplasia 6 ± Polydactyly

- Inheritance: Probably Dominant
- Increased frequency of NEK1 mutations in sALS & fALS: ~3%
- Additional variants in other ALS-related genes (Up to 32%)
- NEK1 protein functions
- Cilia formation
- DNA-damage response
- Microtubule stability
- Neuronal morphology
- Axon polarity
- Clinical: ALS 24

- Onset age: 6th to 8th decade
- Weakness
- Bulbar: Common
- Respiratory
- Limbs: Upper > Lower
- Asymmetric
- Upper motor neuron
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Bulbar dysfunction
- Cognitive: Normal
- Course: Progressive; Death in 2 to 5 years
- CX3CR1
 65
65
- Genetics: V249I & T280M polymorphisms
- Protein
- Microglia-specific
- Involved in: Microglia-neuron crosstalk; Neuroinflammation
- Clinical
- Disease course
- Shorter: V249I VV & T280M MM genotypes
- No increased risk of ALS or change in onset age
- V249I Variant
- Neurofibrillary pathology progression in late-onset Alzheimer's disease
- c21orf2 (CFAP410)
 70
70
- Nosology: Cilia & flagella associated protein 410 (CFAP410)
- Genetics
- Non-synonymous & Loss-of-function mutations
- Allelic disorders
- Retinal dystrophy with macular staphyloma

- Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, axial (SMDAX)

- c21orf2 protein
- Basal body & Cilia
- Mutation effects
- Altered location
- Reduced protein amounts: Fewer primary cilia; Cilial length reduced
- Reduced: Cellular retinoic acid binding protein 1 (CRABP1)
- Ciliopathies, other
- Clinical: ALS relation
- Increased risk: 6x more frequent in ALS than controls
- Clinical ALS phenotype: Similar to other sporadic ALS
- DNAJC7
 82
82
- Genetics
- Mutation types: Protein-truncating variants
- Mutation frequency: 0.16% pf ALS patients
- DNAJC7 protein
- ALS relation
- Increased risk: Mutations more frequent in ALS than controls
- Sporadic ALS in Japan
- Mutation frequency: 0.87%
- Mutation type: Missense
- Mutation location: Near TRP domain
- DNAJC7 variant: Familial ALS, Recessive
114
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.518dupC frameshift; Homozygous
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4th to 8th decade
- Weakness
- Limbs
- Bulbar palsy
- Respiratory
- Course: Progressive
- Tendon reflexes: Often reduced; May be increased
- Sensation: Normal
- Laboratory
- Brain pathology
- Degeneration of upper & lower motor neurons
- Phosphorylated TDP-43-positive neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in frontal & temporal cortices
- Reduced DNAJC7 expression
- EMG: Acute & chronic denervation
|
ALS:
Possible Susceptibility
& Modifier Genes
26 |
| Gene |
Locus |
Variant |
ACSL5
 - -
ZDHHC6
 88
88 |
14q11.2 |
Mutations |
ALKBH3
 106
106
|
11p11.2 |
Polymorphism
Protective |
APEX1

|
10q25.2 |
Mutations |
ApoE ε4
 |
19q13 |
ε4 genotype |
Ataxin-1

|
6p22.3 |
PolyQ expansions
Mild: ≥ 32 |
Ataxin-2

|
12q24.1 |
PolyQ expansions
Mild: 27–33
Reduced survival |
Ataxin-7

|
3p14.1 |
PolyQ expansion
ALS patient |
ATXN8OS

|
13q21 |
Non-coding expansion
Japanese ALS |
|
c9orf72
|
9p21 |
Mutations → ALS
Repeat length = 2
Longer or Shorter survival |
|
c21orf2
|
21q22 |
ALS risk |
|
CACNA1A
|
19p13.2 |
CAG repeat
Few patients |
CAMLG
 99
99
|
5q31 |
ALS risk |
CAMTA1

|
1p36 |
Reduced survival |
CHRNA3

CHRNA4

CHRNB4

|
15q25,
20q13,
15q24 |
Mutations
33 |
CNBP
 |
3q21 |
CCTG repeat |
CNTF
 |
11q12 |
Null allele |
CTIF
 |
18q21 |
Onset age
100 |
CX3CR1

|
3p22.2 |
Polymorphism |
| DHTKD1 |
10p14 |
Mutations |
DMPK
 |
19q13 |
CTG repeat in 3' UTR |
DNAJC7

|
17q21 |
Mutations |
DPP6

|
7 |
Linkage |
Dynactin

|
2p13 |
Mutations |
EAAT2
 |
11p13 |
Low expression |
ELP3
 |
8p21 |
Polymorphism |
| ERBB4 |
2q34 |
Insertion |
EPHA4

|
2q36.1 |
Disease modifier |
FGGY

|
1q32 |
Linkage |
FIG4

|
6q21 |
Mutations |
FMR1
 |
Xq27 |
CCG repeat in promoter |
FXN
 |
9q21 |
GAA repeats in intron |
GluR2
 |
4q32 |
RNA editing Δ |
HTT
 |
4p16 |
CAG repeat |
IL18RAP
 95
95 |
2q12 |
3'UTR Δ; Protective |
ITPR2
 |
12p11 |
Linkage |
KANK1
 |
9p24 |
Mutations |
| KIF1A |
2q37 |
Variants |
| KIF5A |
12q13 |
Progression rate |
|
LRP10
|
14q11 |
Mutation
Risk |
|
LRP12
|
8q22 |
CGG repeat |
MTHFR

|
1p36.22 |
Polymorphism
Female risk ↑ |
NEFH
 |
22q12 |
KSP deletions |
NEK1

|
4q33 |
Loss of function
Haploinsufficiency |
NIPA1

|
15q11 |
GCG repeat; Copy number |
NOP56

|
20p13 |
GGCCTG expansion |
|
NOTCH2NLC
|
1q21 |
CGG, GGC expansions |
NUP50
 97
97
|
22q13 |
Variants; ALS risk |
PON1

PON2

PON3

|
7q21.3 |
Linkage |
Progranulin

|
17q21.3 |
Mutations |
| RFC1 |
4p14 |
Expansions |
| SARM1
|
17q11 |
Gain function
Polymorphisms |
SCFD1

|
14q12 |
Risk factor |
SLC11A2

|
12q13 |
rs407135: C allele
Faster progression |
SMN1
 |
5q12 |
Copy number |
SMN2
 |
5q12 |
Copy number |
SQSTM1 (p62)

|
5q35 |
Mutations |
STMN2

|
8q21 |
CA repeat expansion |
TBP

|
6q27 |
CAG/CAA repeat expansion |
Titin

|
2q31.2 |
Reduced levels
Rapid progression |
TREM2

|
6p21.1 |
R47H |
UNC13A

|
19p13.3 |
Intron 21 link 34
Reduced survival |
VEGF
 |
6p12 |
Promoter SNPs |
| VCP |
9p13 |
Inversion |
ZNF512B

|
20q13.33 |
Mutation:
Reduced expression |
|