AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS
|
Muscle Grouped atrophy Many small groups Mixed fiber types in groups 2C fibers Increased numbers vs other denervation Internal architecture SR Glycogen Esterase Neuromuscular junctions ALS course Early Rapidly progressive Slowly progressive Late ALS-SOD1 Nerves Intramuscular Sciatic Terminal Spinal cord Historical images ALS-HTT ALS-SOD1 Neuron Inclusions |
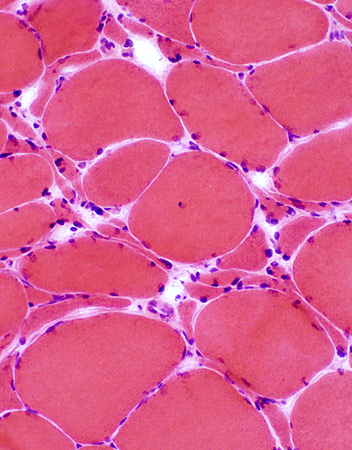
 ALS Muscle: Denervation, Reinnervation &
Atrophy of some Reinnervated Muscle fibers |
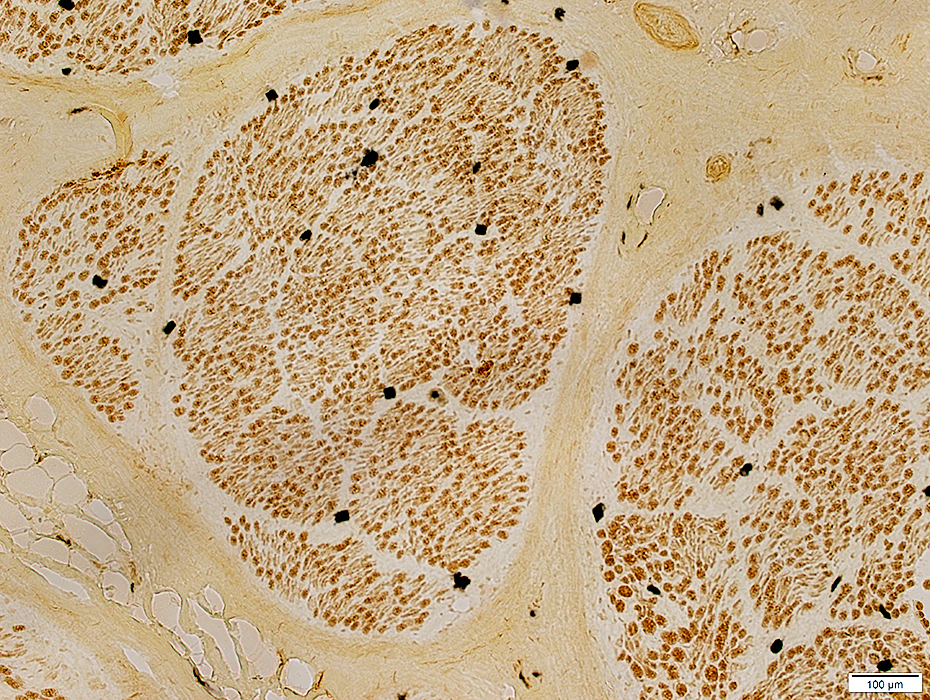
ALS: Common patterns of denervation in muscle
 H & E stain |
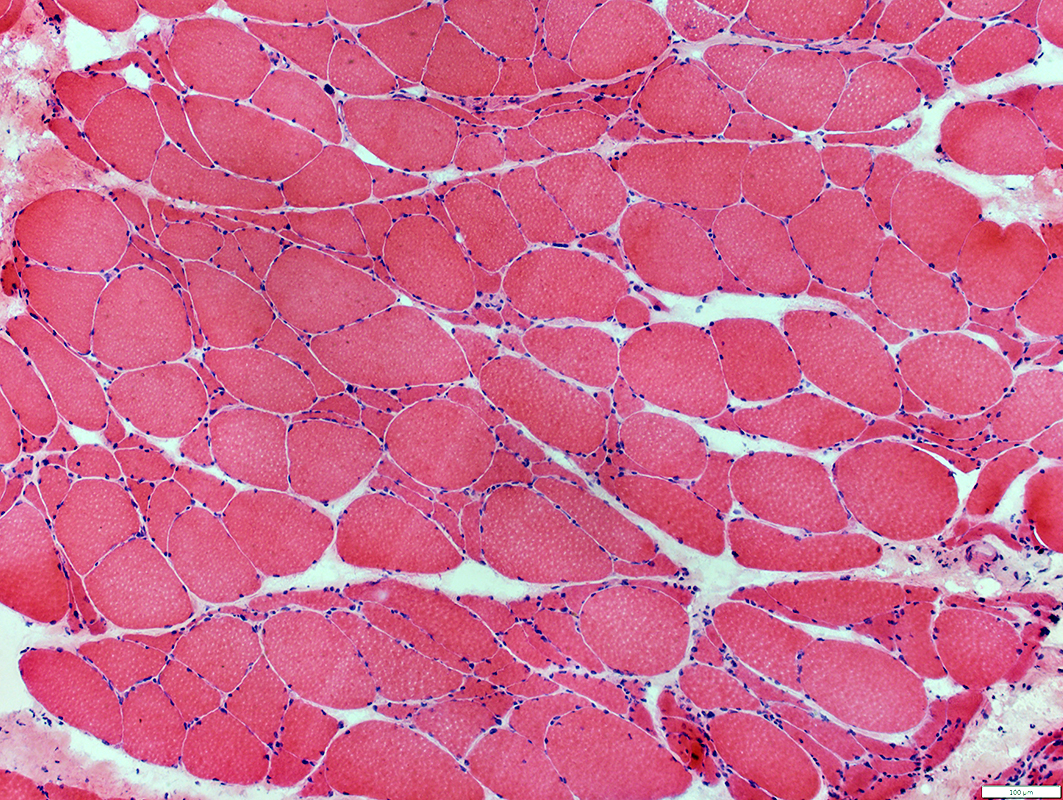
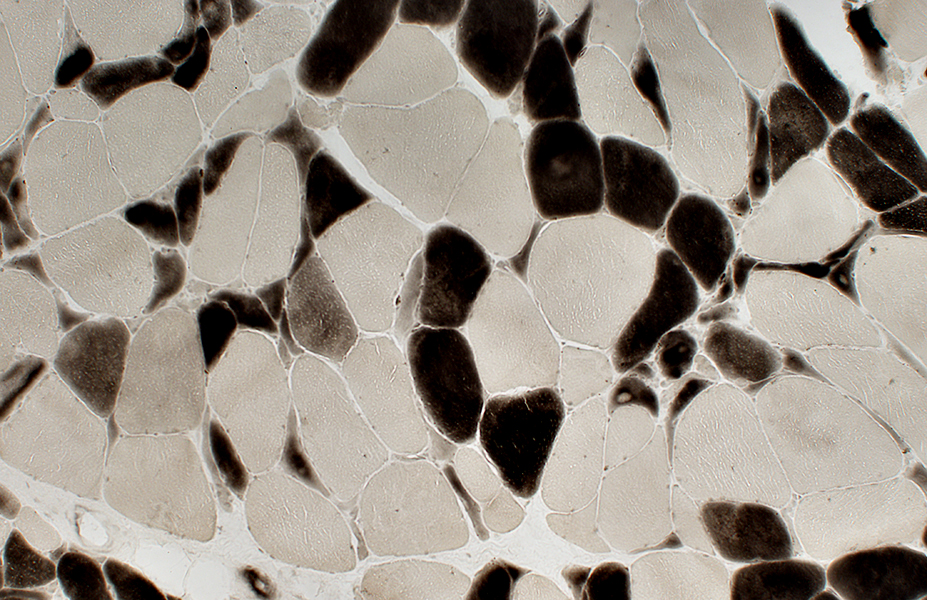
Grouped muscle fiber atrophy: Features in ALS
Number: Many small regions of grouped atrophy
Muscle fibers in regions of grouped atrophy
Small
Angular
Similar size
Fiber types: Mixed
Often contain: Targets
Pyknotic nuclear clumps: Uncommon
Grouped atrophy size: Small; < 20 muscle fibers
Larger muscle fibers
Size: Often mildly hypertrophied
Shape: Rounded/Polygonal
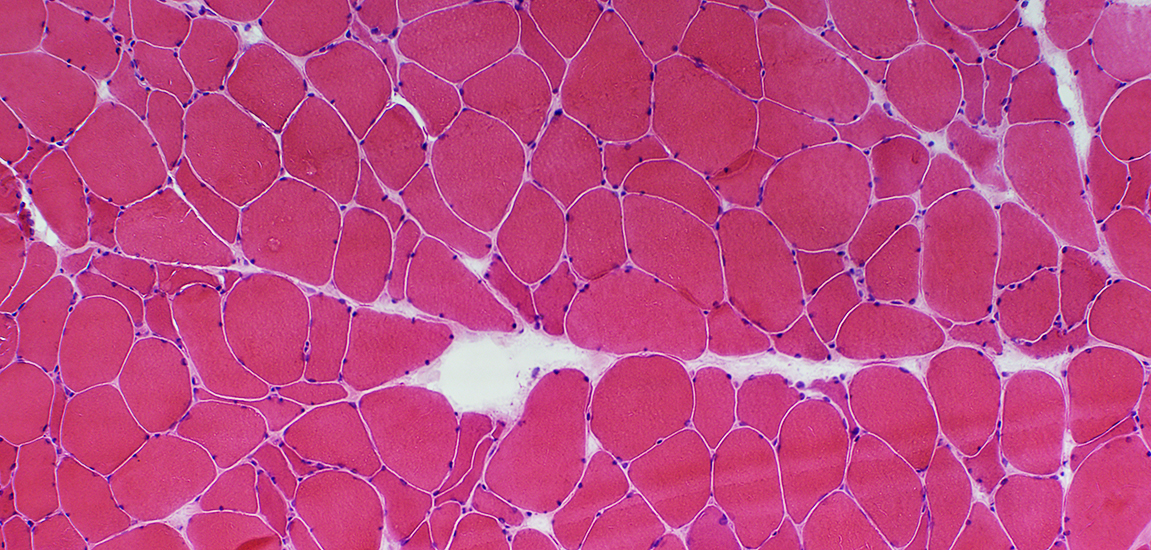 H & E stain |
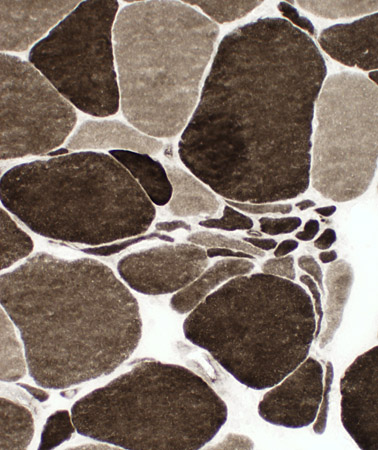
ALS Muscle: Fiber type changes
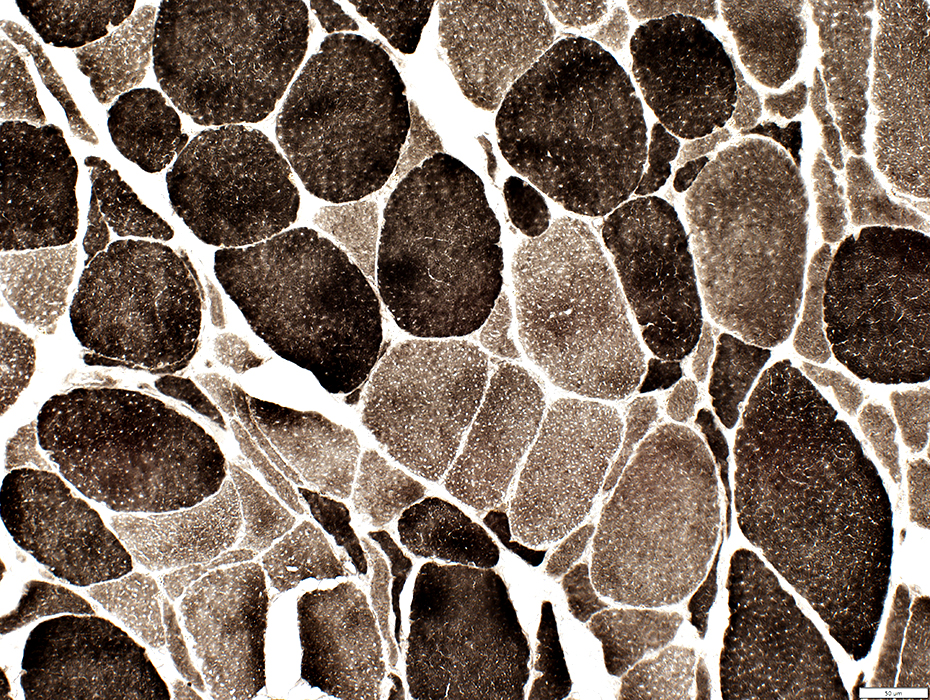 ATPase stain. pH 9.4 |
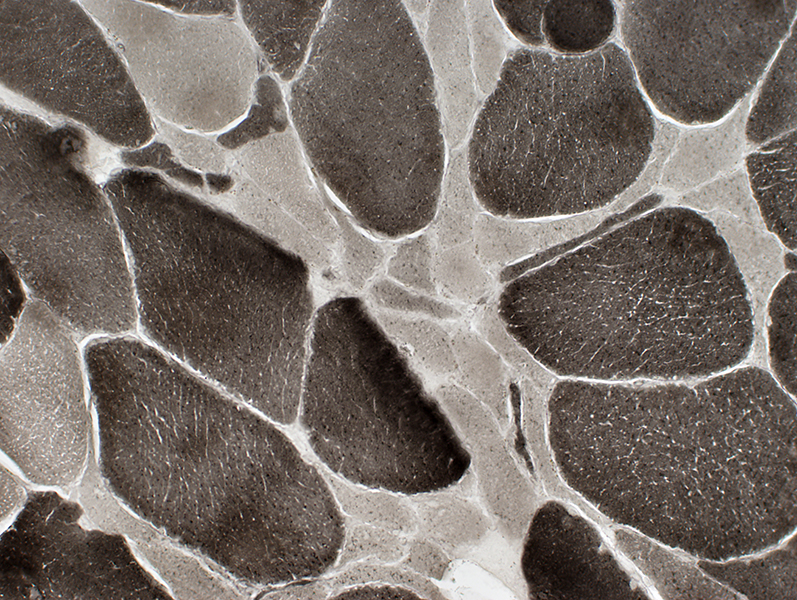 ATPase stain. pH 9.4 |
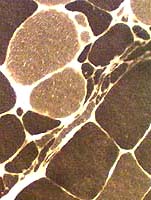 ATPase stain. pH 9.4 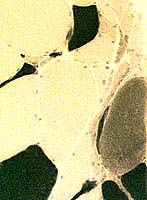 ATPase stain. pH 4.3 |
Little type grouping: Except in chronic, slowly progressive cases
Type 2C fibers: Many Large & Small
 ATPase stain. pH 4.3 |
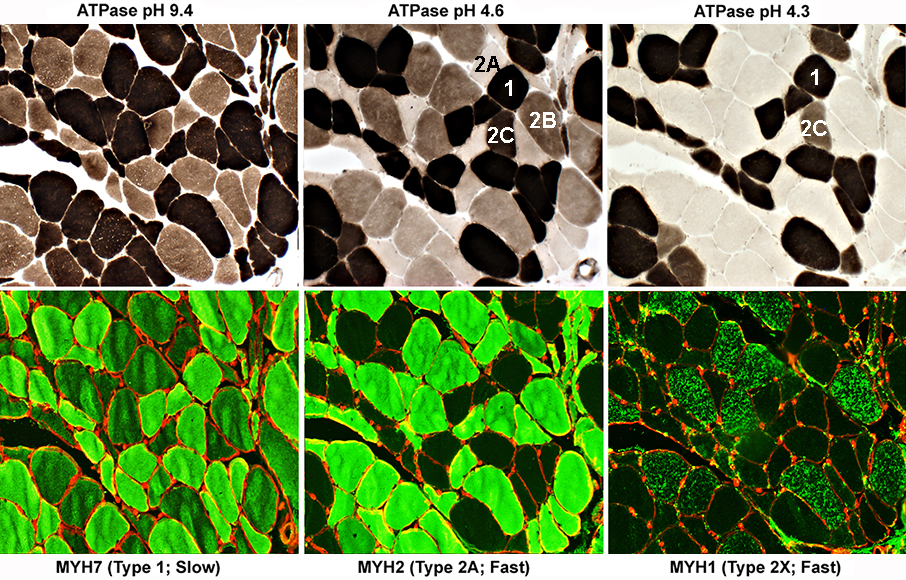
ALS Muscle: Fiber Types
Type 1 fibers: NormalATPase: Intermediate color at pH 9.4 & Dark at pH 4.6 & 4.3
All have MYH7, but not MYH2 or MYH1
Type 2 fibers: Variant
All have MYH2 & moderate MYH7
Type 2A fibers
All have MYH2 & Moderate MYH7, but no MYH1
ATPase: Dark at pH 9.4; Pale at pH 4.6 & 4.3
Type 2B fibers
All have MYH2 & Moderate MYH7 & MYH1
ATPase: Dark at pH 9.4; Intermediate at 4.6; Pale at pH 4.3
Type 2C fibers
All have MYH2 & MYH7, but no MYH1
ATPase: Moderately Dark at pH 9.4 & 4.6; Internediate at pH 4.3
 |
ALS Muscle fibers: Internal architecture
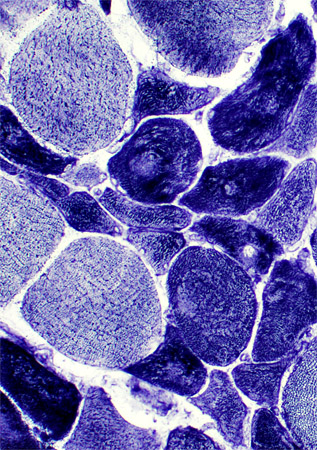 NADH stain Atrophic muscle fibers Many stain darkly May have targets or targetoid changes Larger muscle fibers Internal architecture may be Normal Moth-eaten Size: Some are mildly hypertrophied |
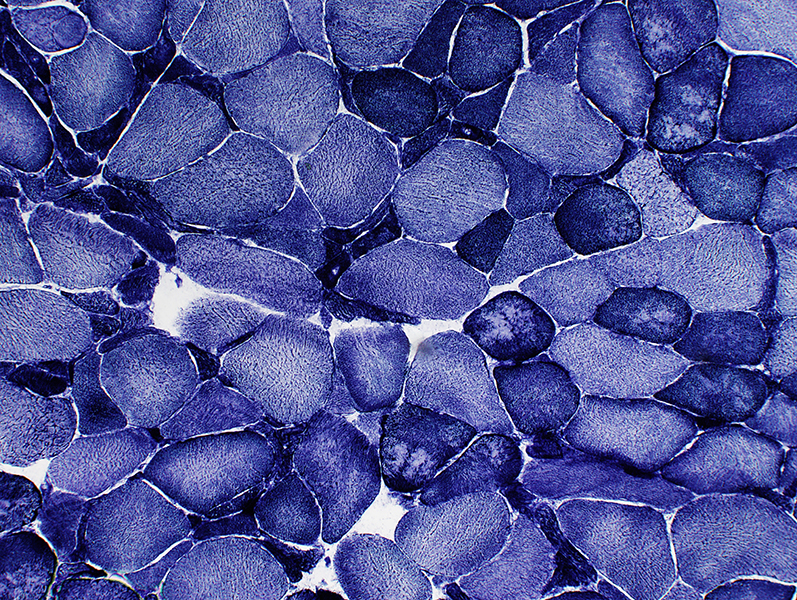 NADH stain |
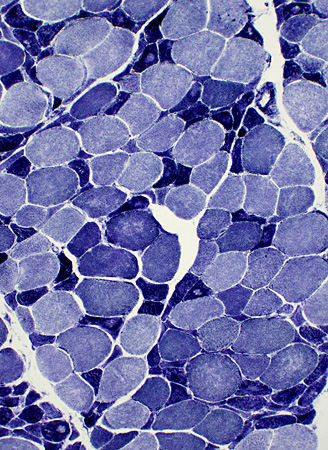 NADH stain |
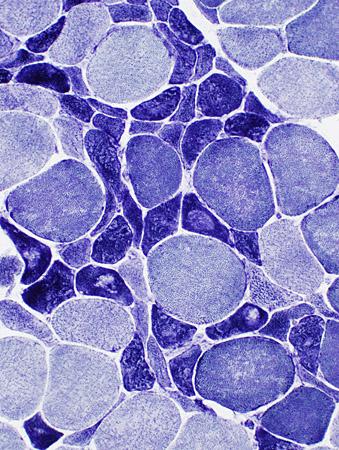 NADH stain |
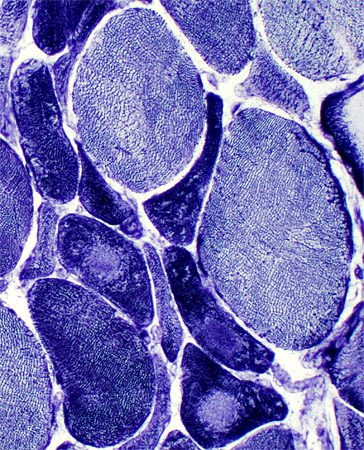 NADH stain |
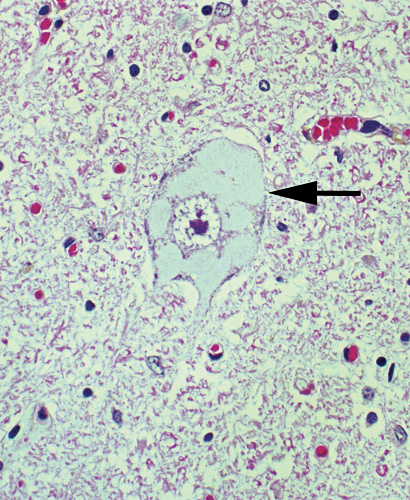
ALS Muscle: Targets & targetoid structures on many smaller (dark) muscle fibers
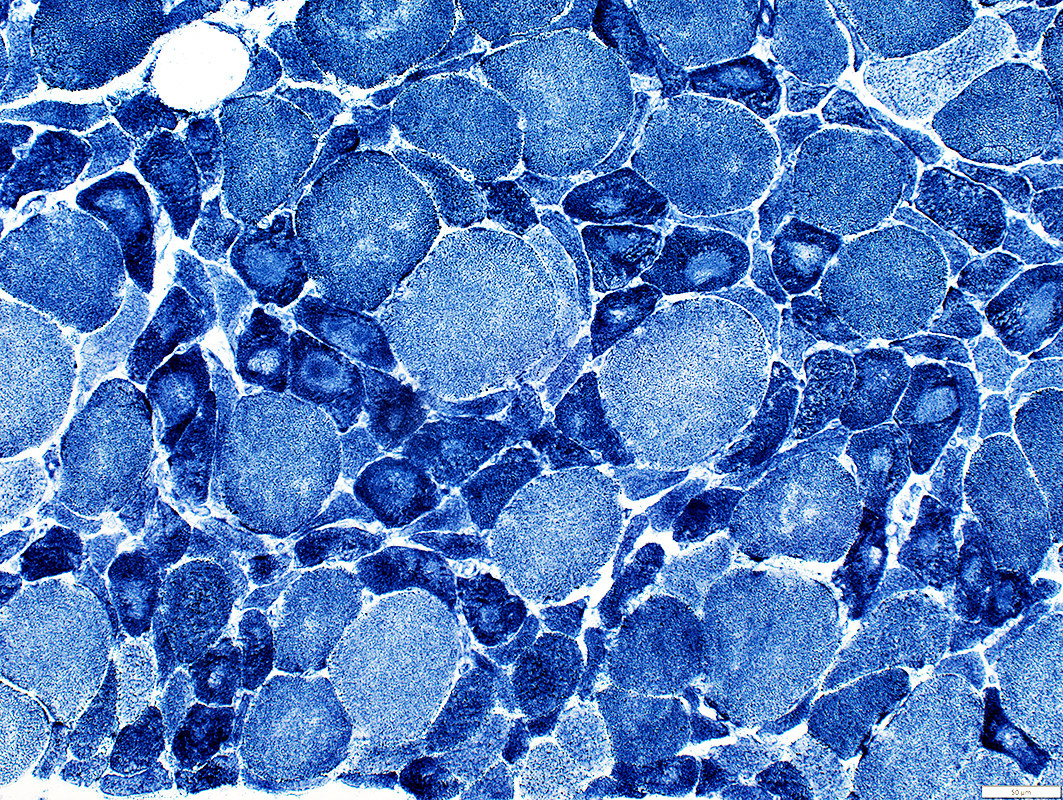 NADH stain |
Small muscle fibers: Reduced or absent glycogen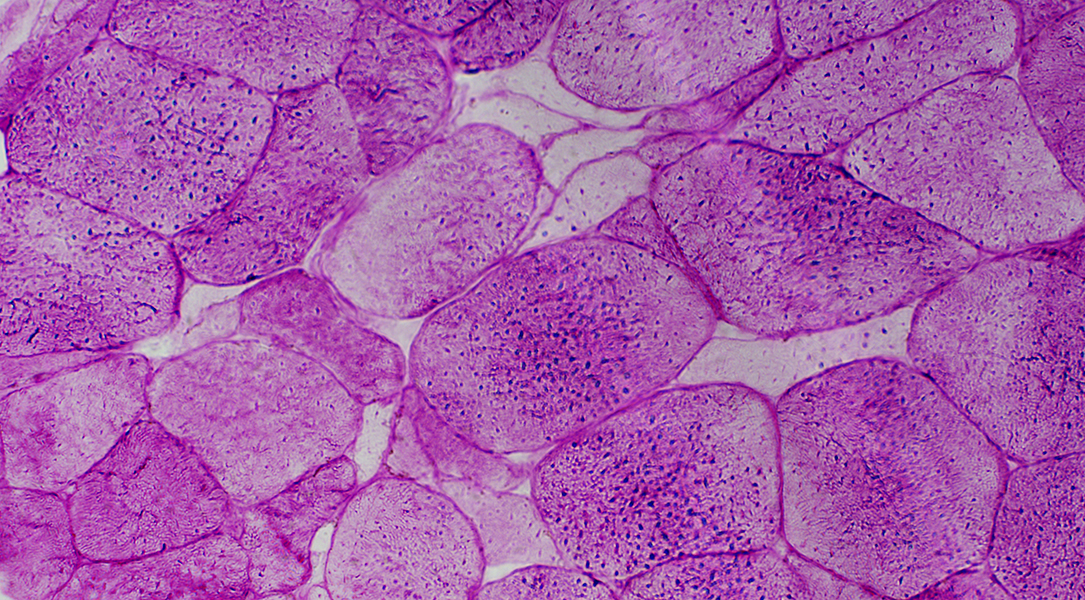 PAS stain |
|
Small muscle fibers: Darker on esterase stain 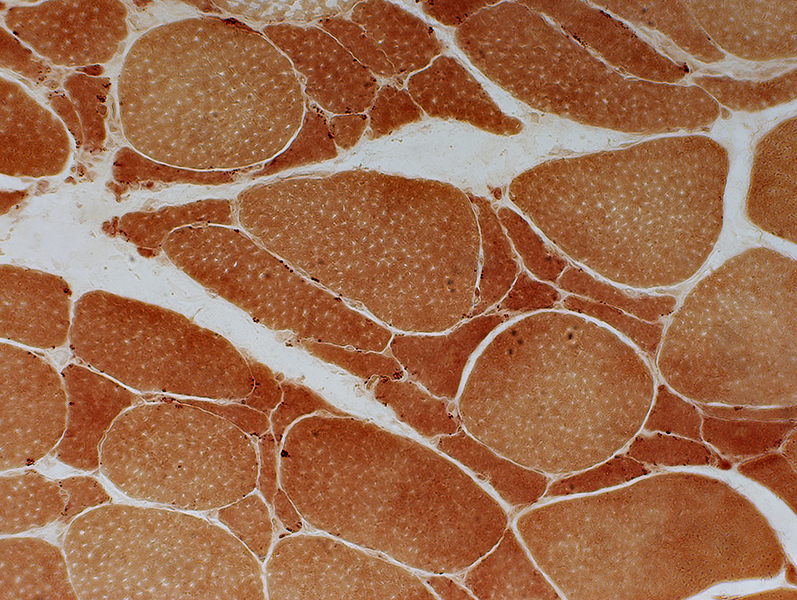 Esterase stain |
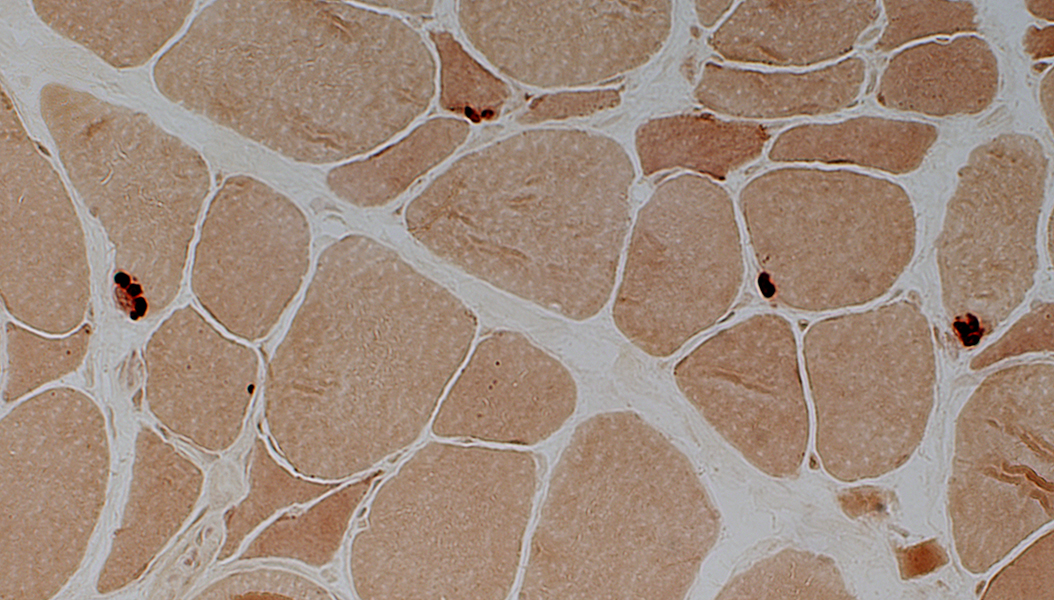 Esterase stain |
Dark
Compact or multisegmented
May remain on small muscle fibers
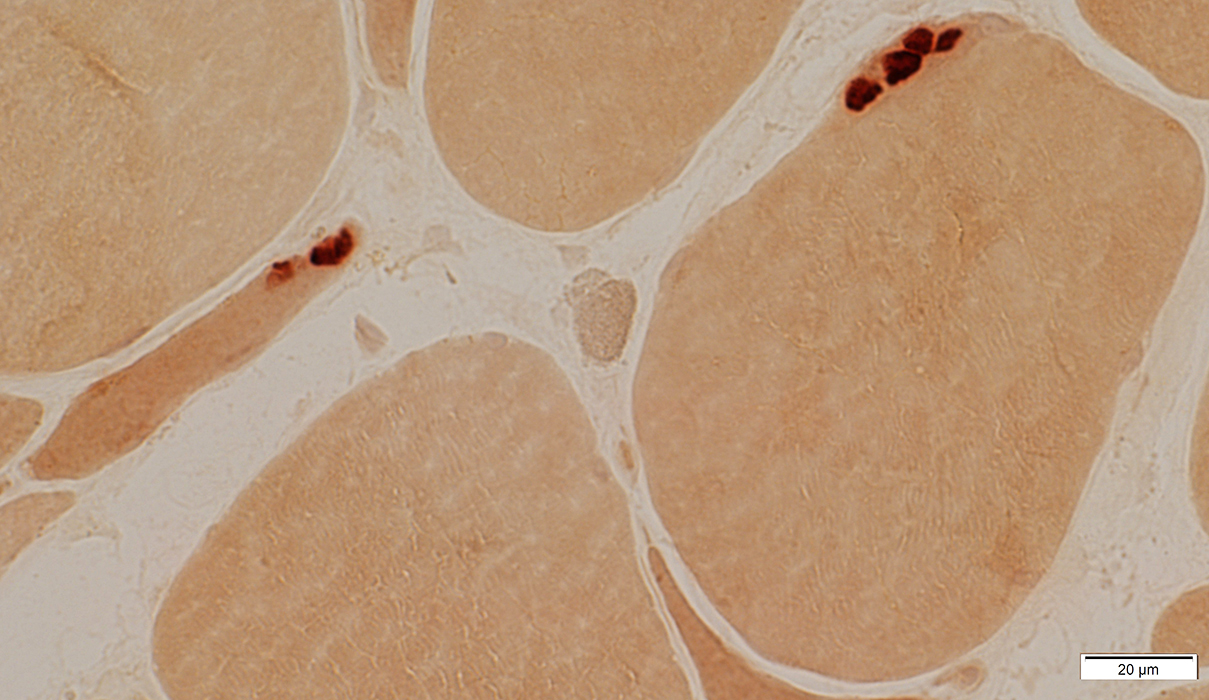 Esterase stain |
ALS: Early
Muscle Fiber Atrophy
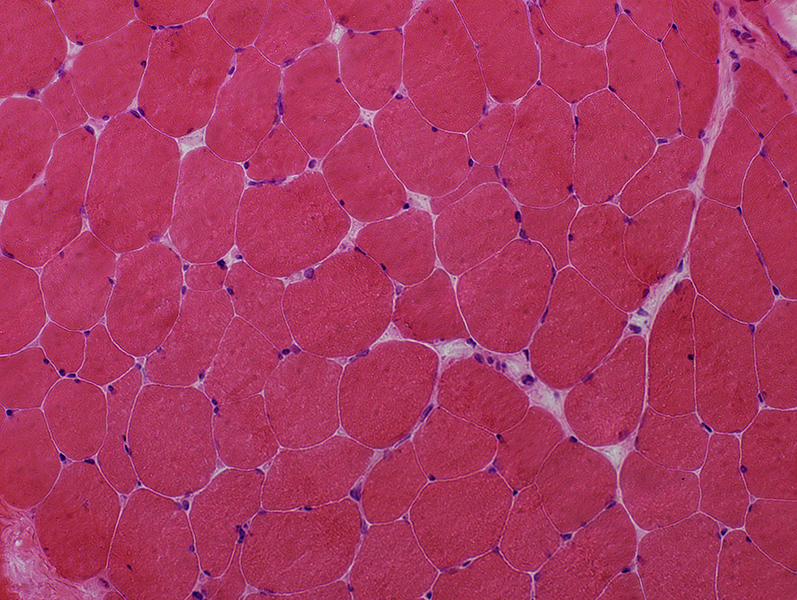 H&E stain |
Scattered
Intermediate-sized
Polygonal or Angular
Very small groups
2C muscle fibers
Common
Large & small fibers
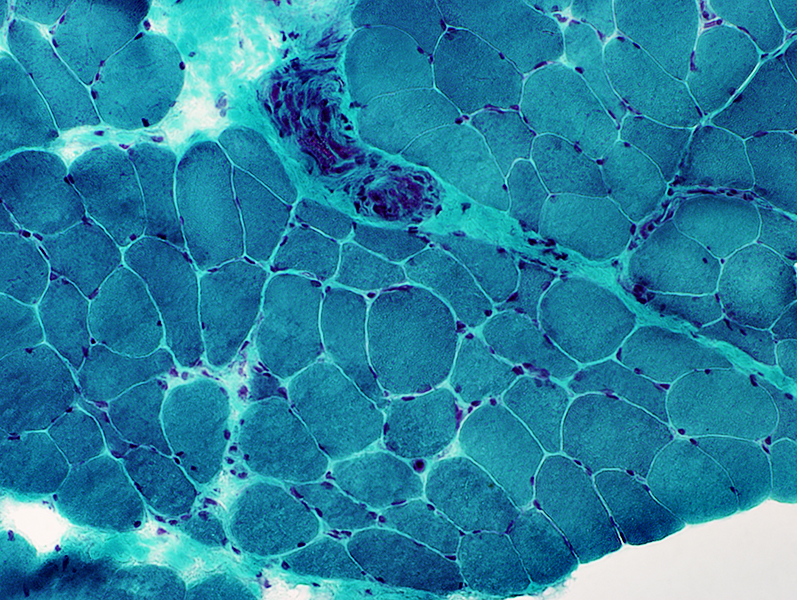 Gomori trichrome stain |
Small Muscle Fibers
Angular
Mildly dark stained
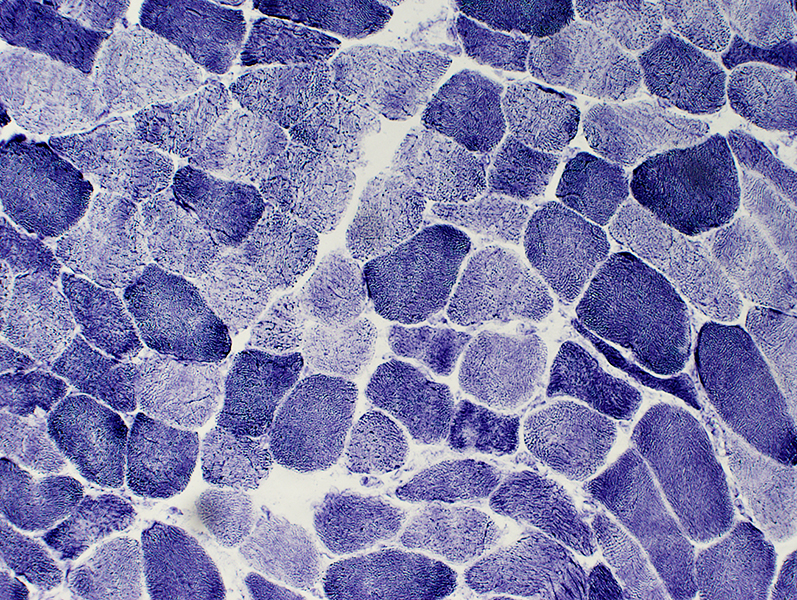 NADH stain |
Type 2C Muscle Fibers
Frequent
Large & Small size
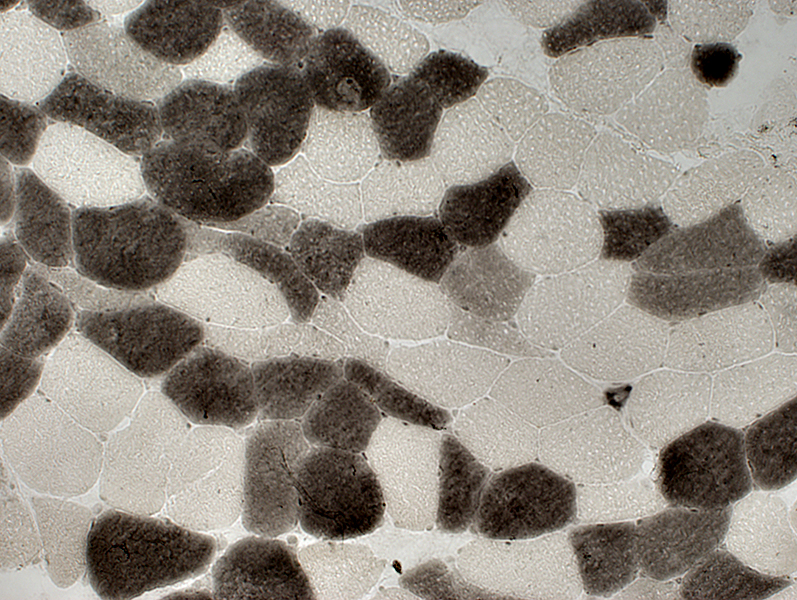 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
|
Small Angular Muscle Fibers Types I (Interrmediate-stained) and II (Dark-stained) 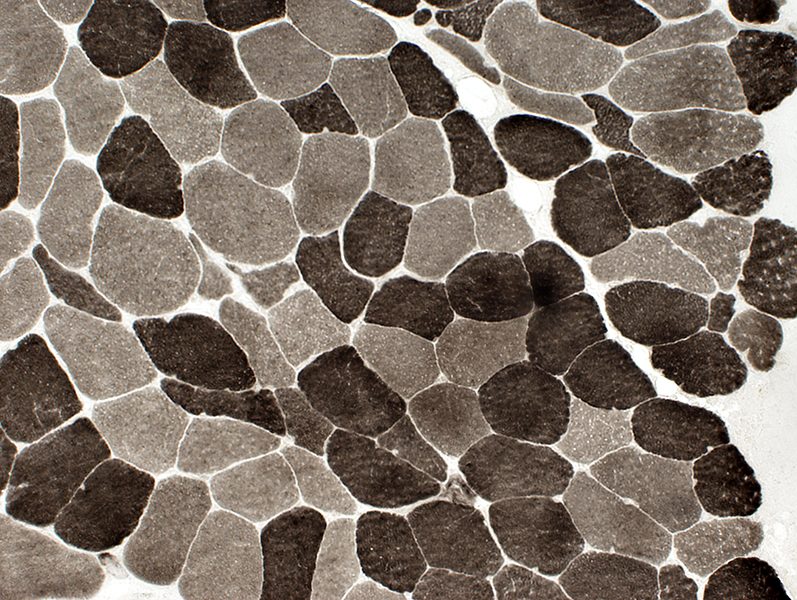 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
ALS, early: Neuromuscular Junctions
Compact
Normal staining density
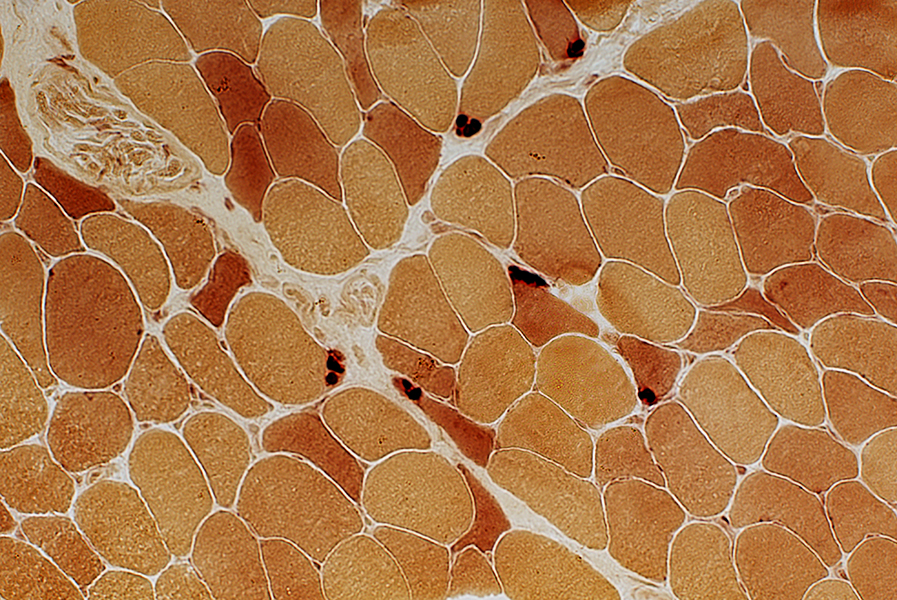 Esterase stain |
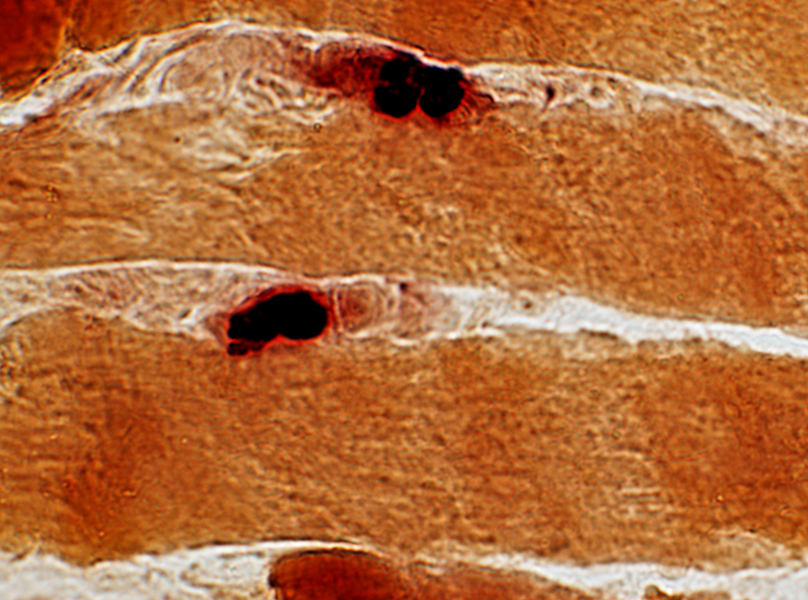 Esterase stain |
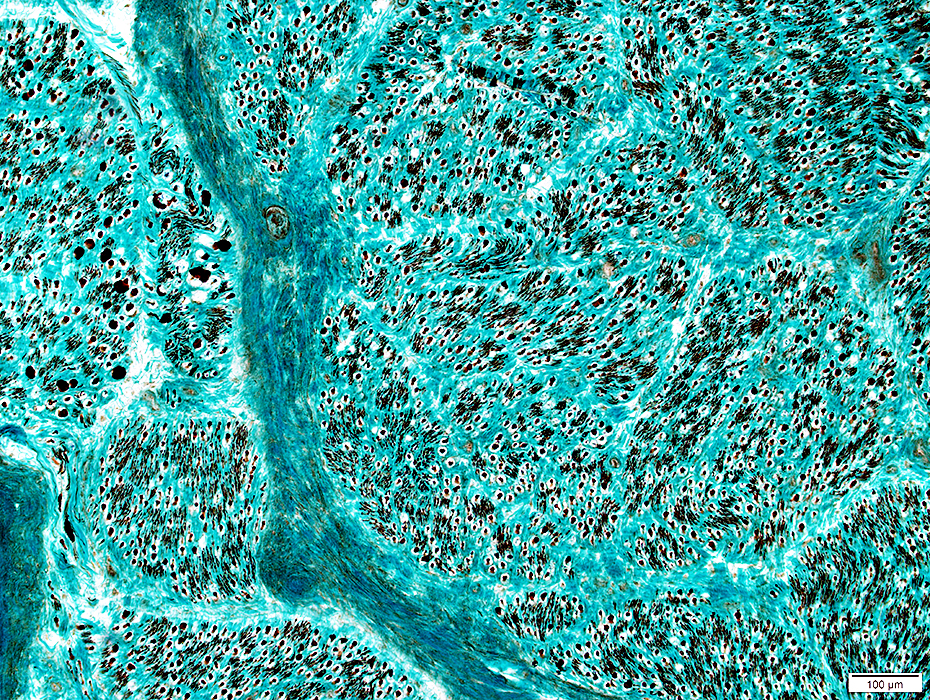
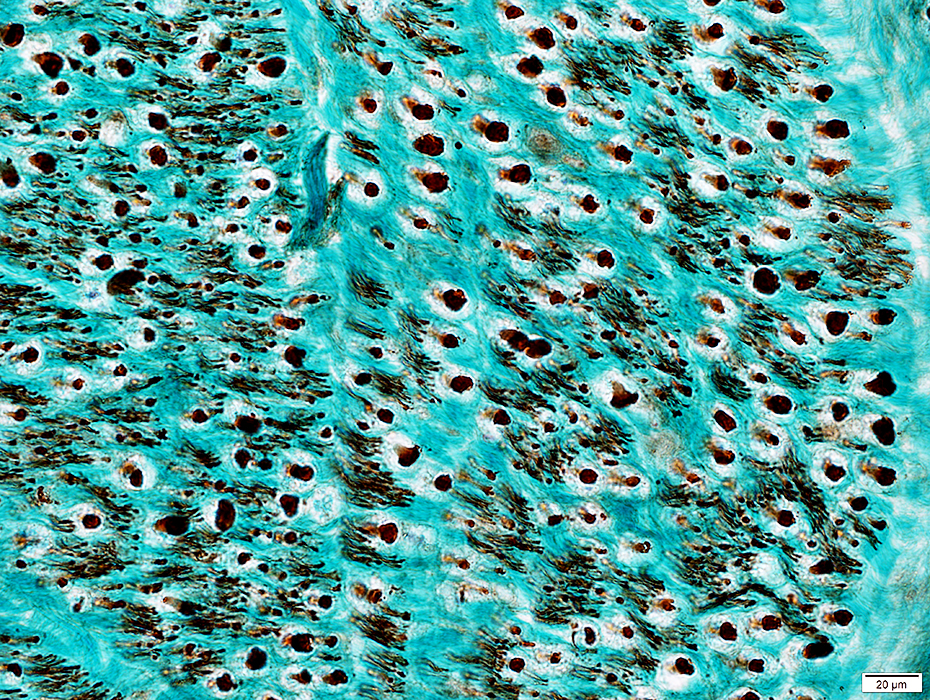
ALS: Slowly progressive
Grouped atrophy: Larger regionsFiber type grouping: More common
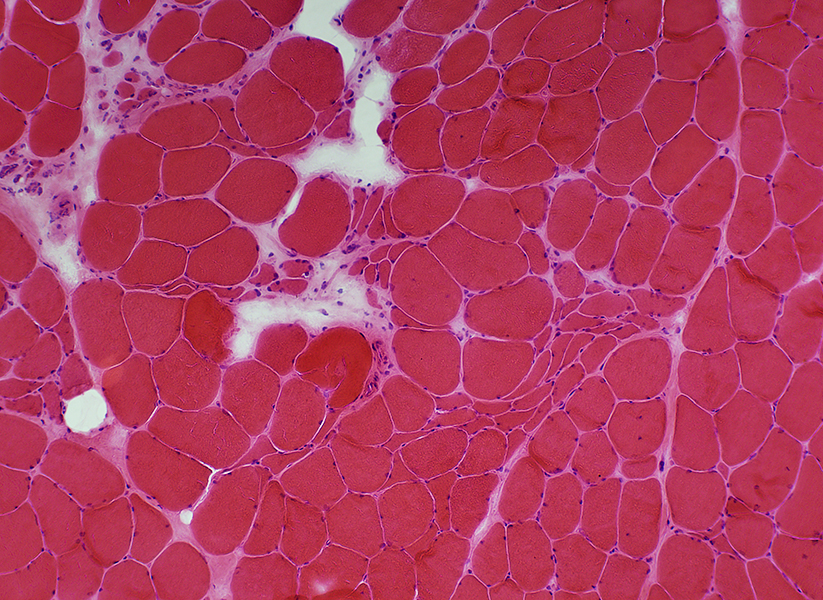 H& stain |
Grouped atrophy: Regions are often larger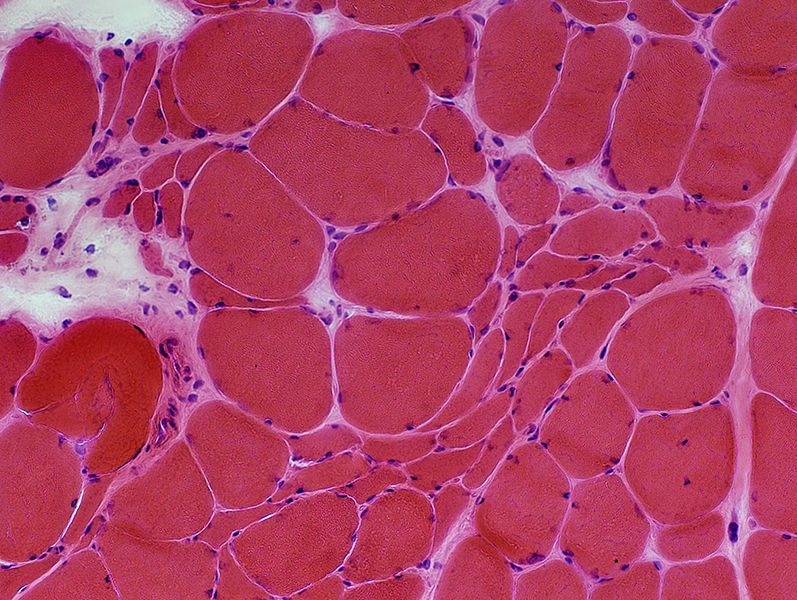 H&E stain |
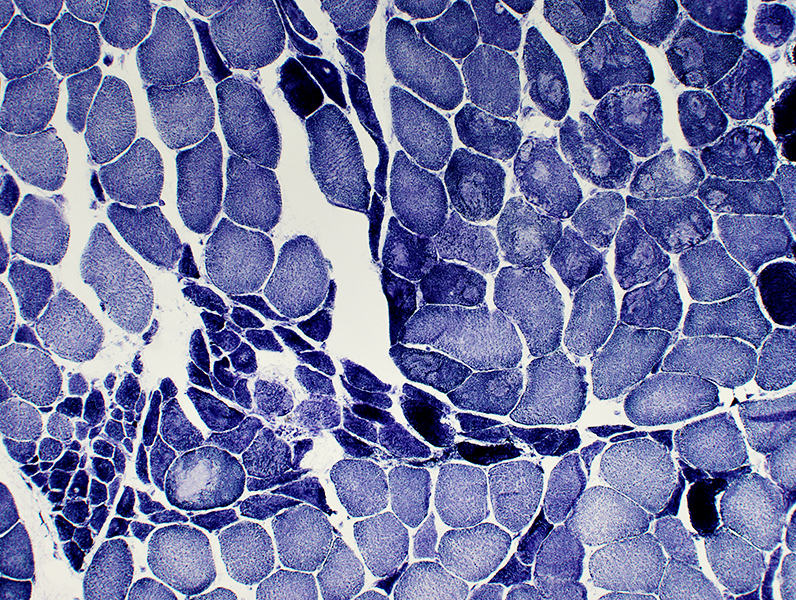 NADH stain |
|
Grouped atrophy: Small muscle fibers stain dark Targets & Targetoid changes 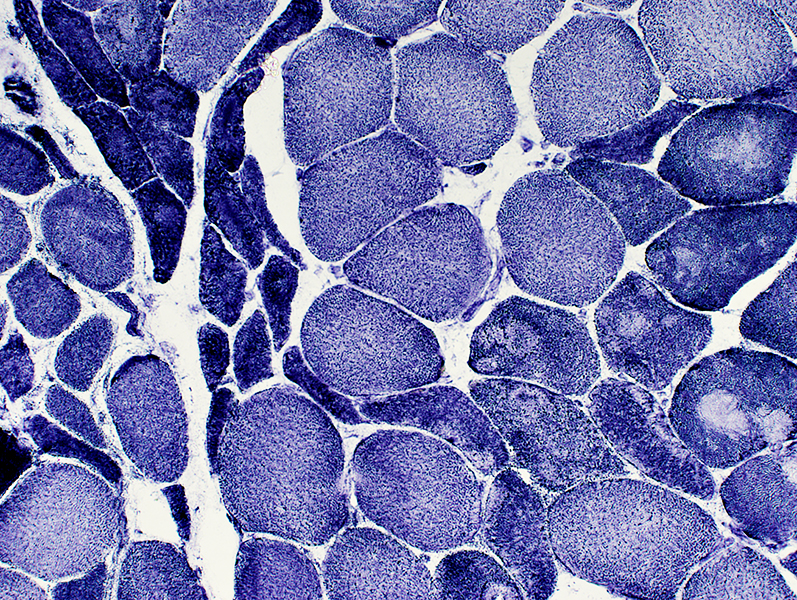 NADH stain |
|
Type grouping of larger fibers Groups often include 2C fibers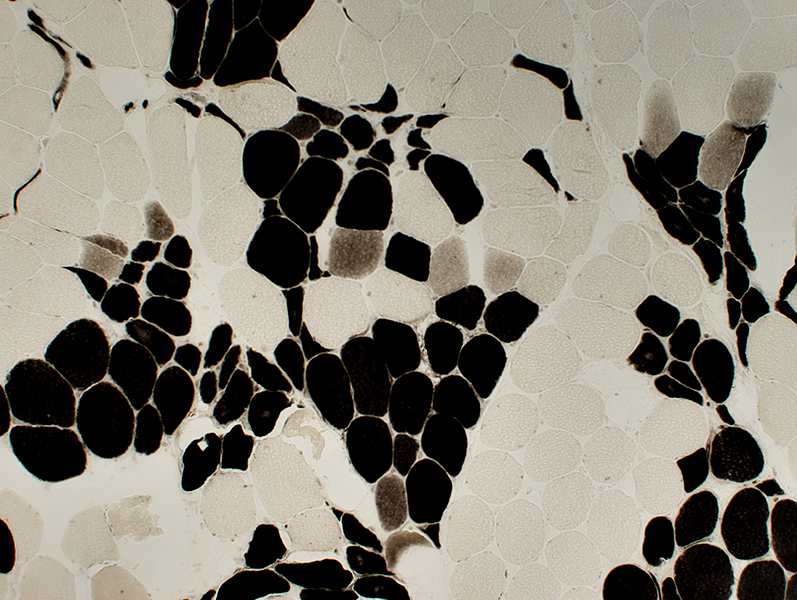  ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
|
Type grouping of larger fibers Grouped atrophy contains both fiber types 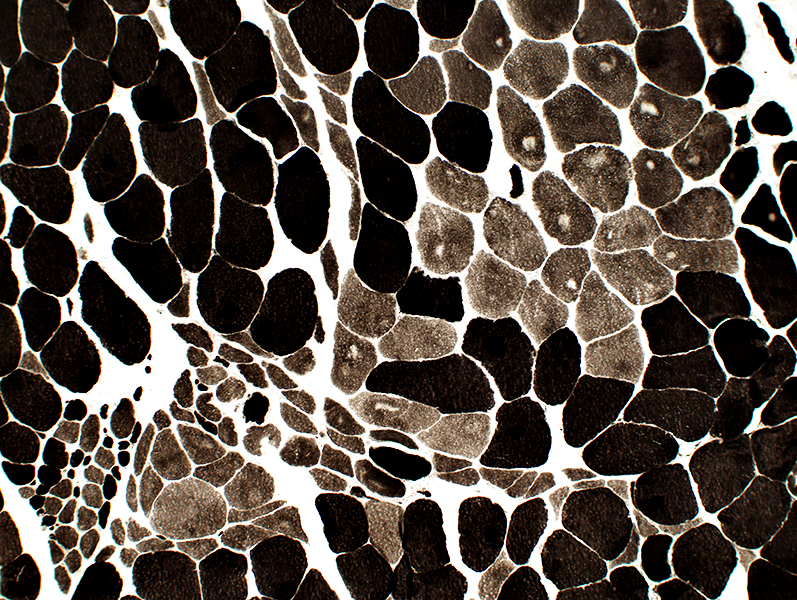 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
ALS: Rapidly progressive
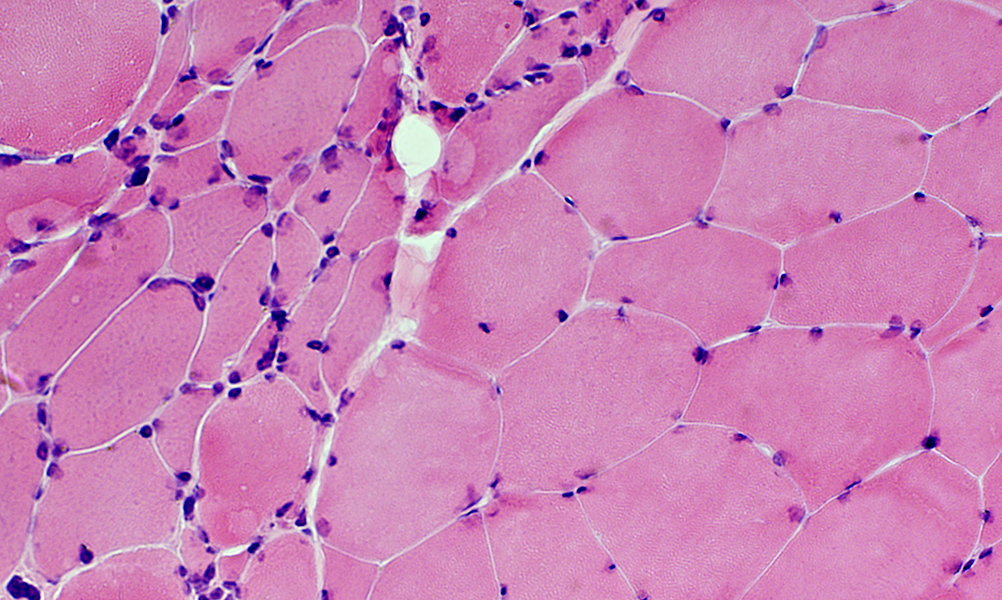 H&E stain Small angular fibers: Grouped Nuclei: Irregular shapes |
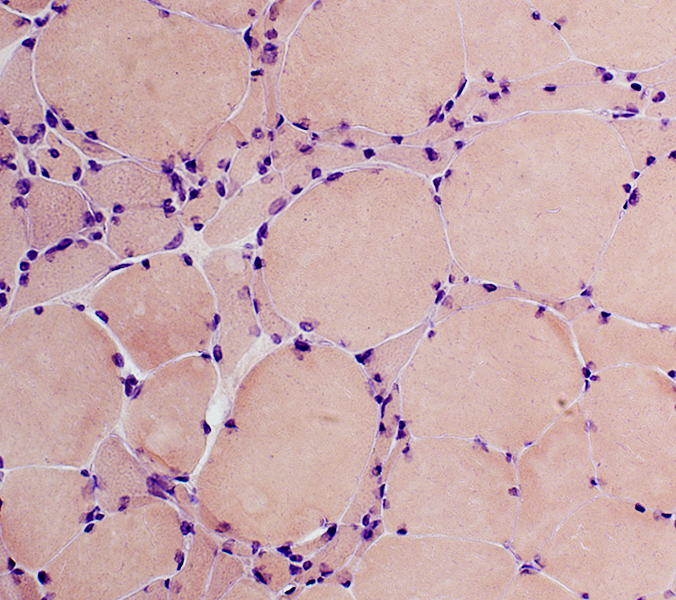 Congo red stain |
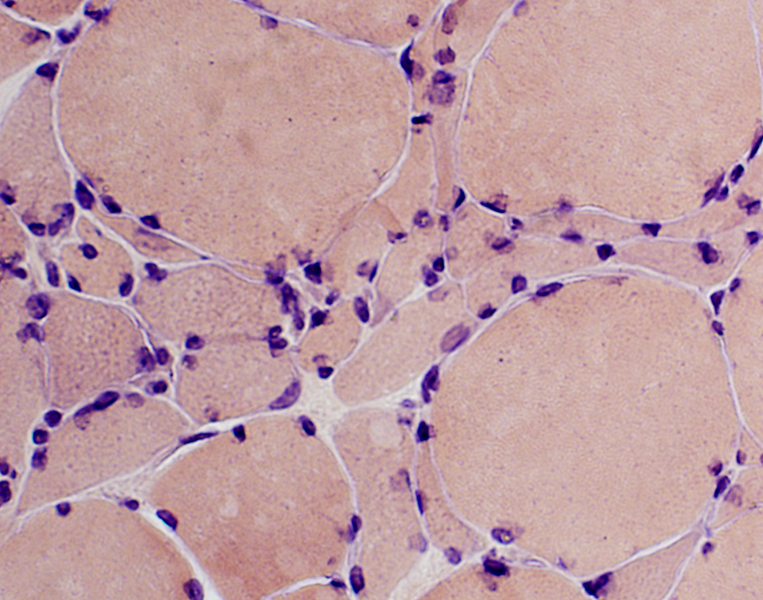 Congo red stain |
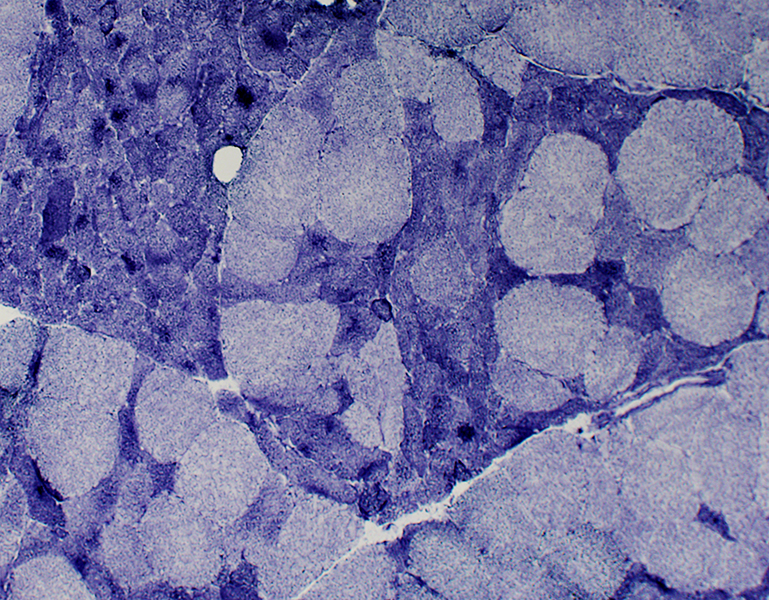 NADH stain Small angular fibers: Very small size; Dark stained |
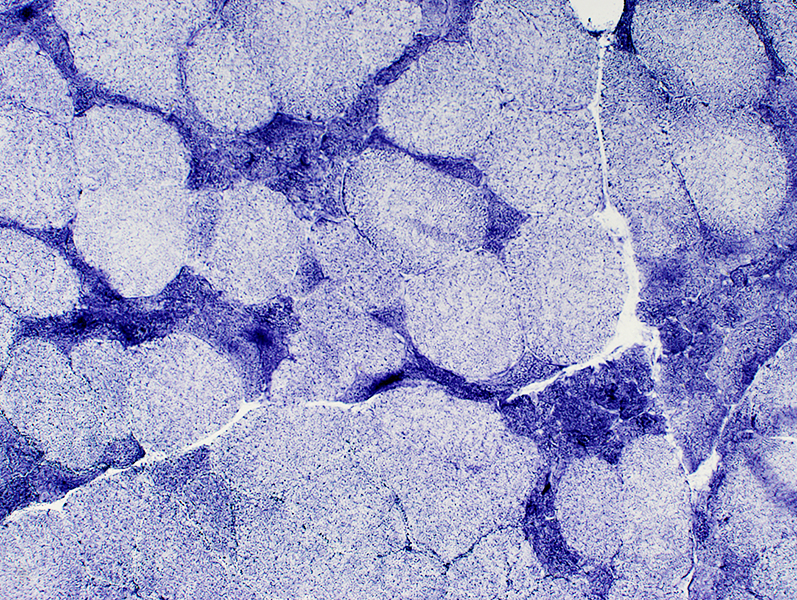 NADH stain |
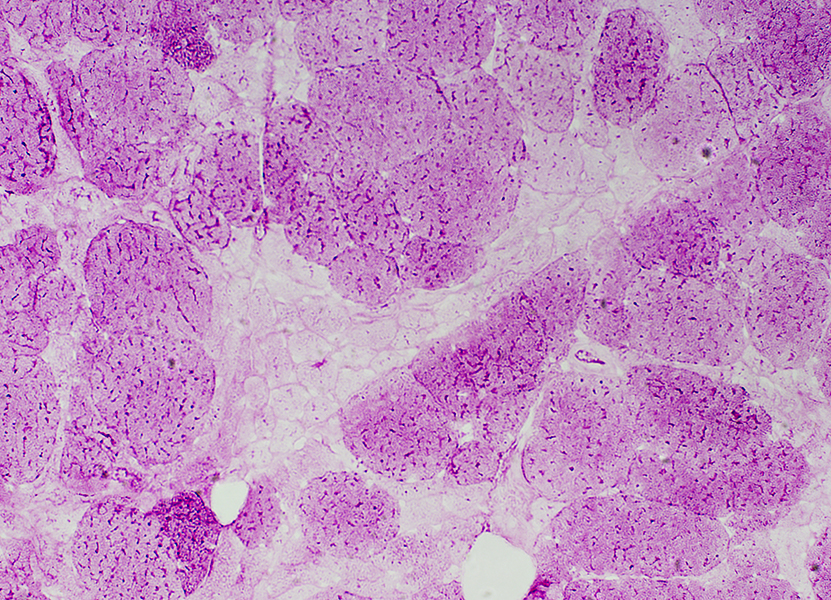 PAS stain Grouped, atrophic muscle fibers: Reduced PAS stain |
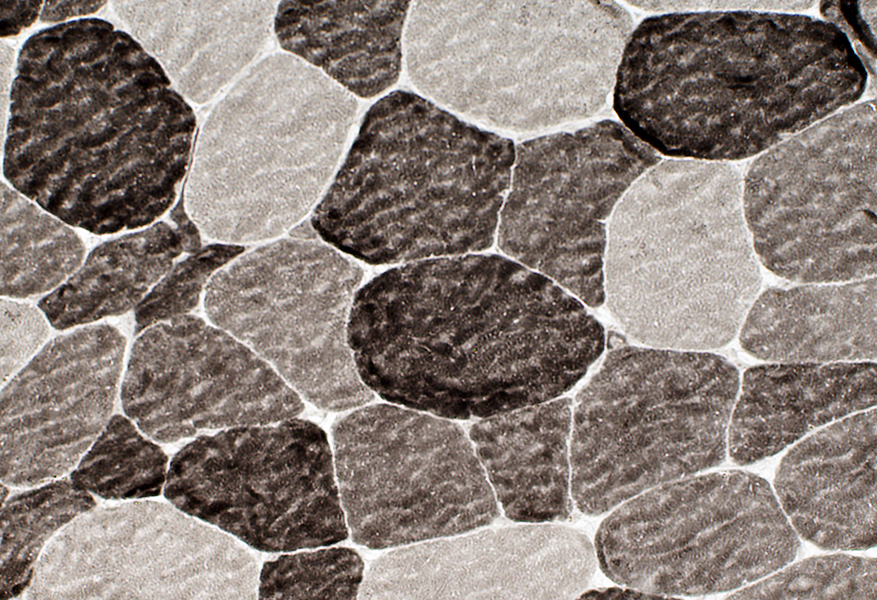 ATPase pH 9.4 stain Fiber types: I = Pale; II = Dark; Abnormal = Intermediate stained |
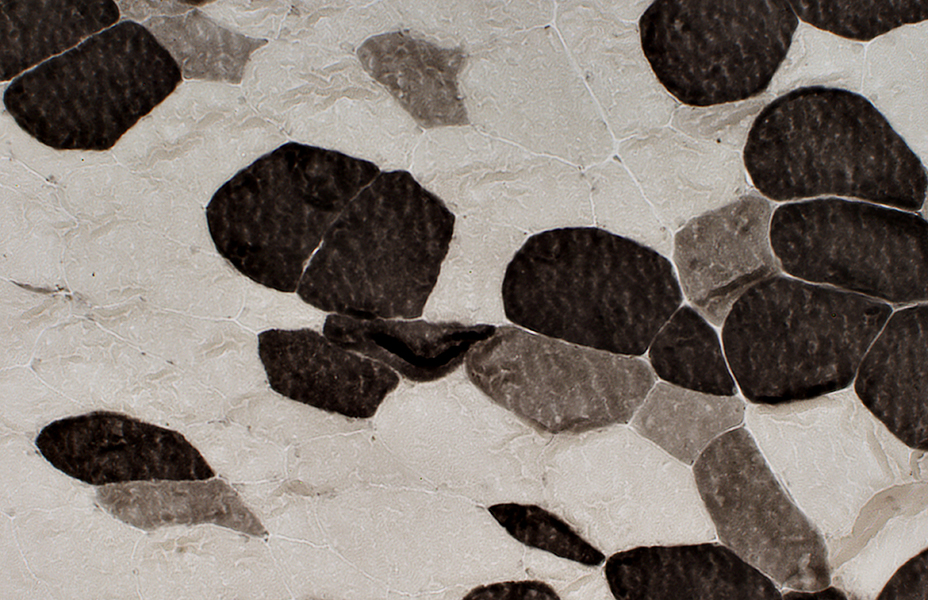 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Fiber types: Frequent 2C fibers, large and small |
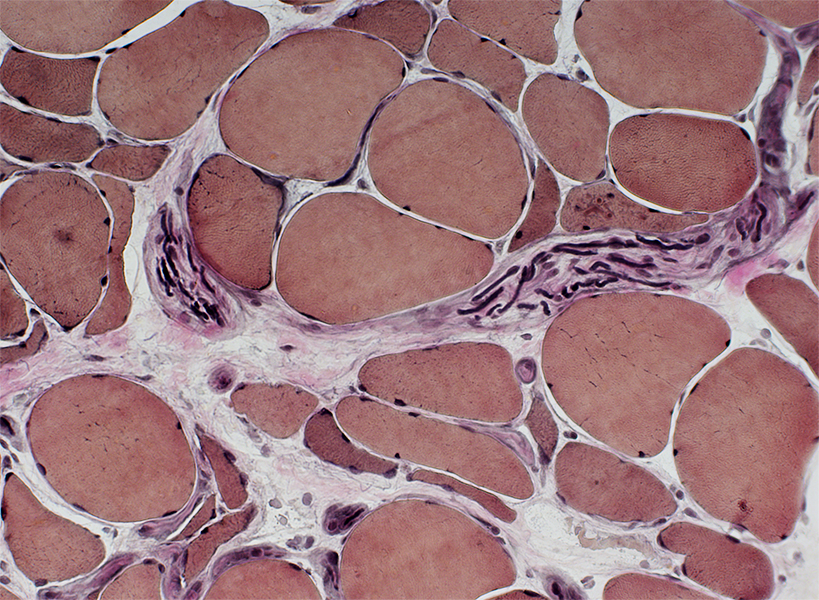
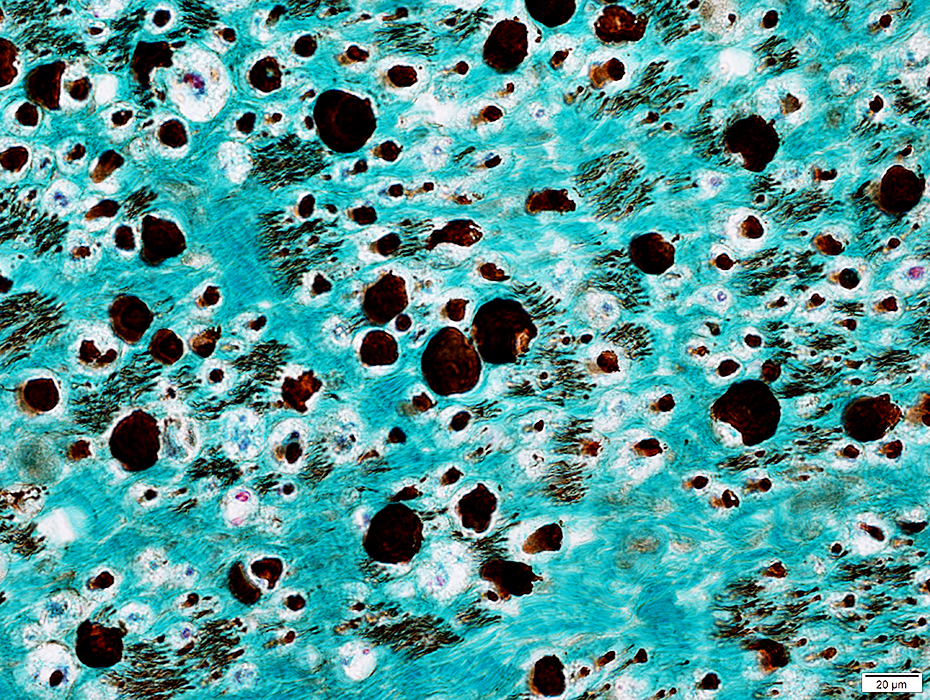
ALS: Late
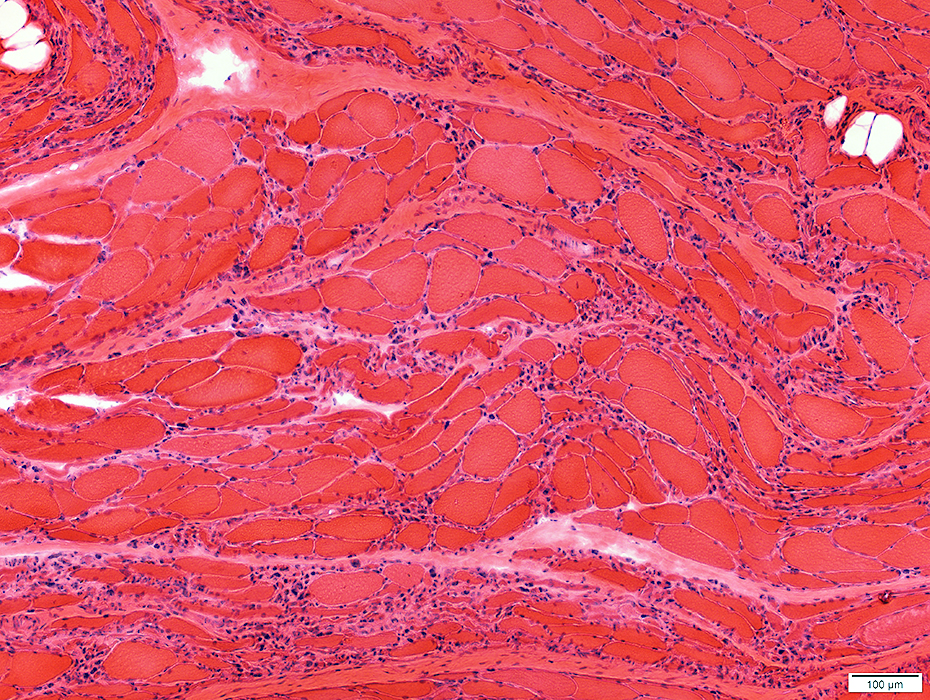 H&E stain |
Many small and moderate-sized regions with clusters of pyknotic nuclear clumps & very small muscle fibers
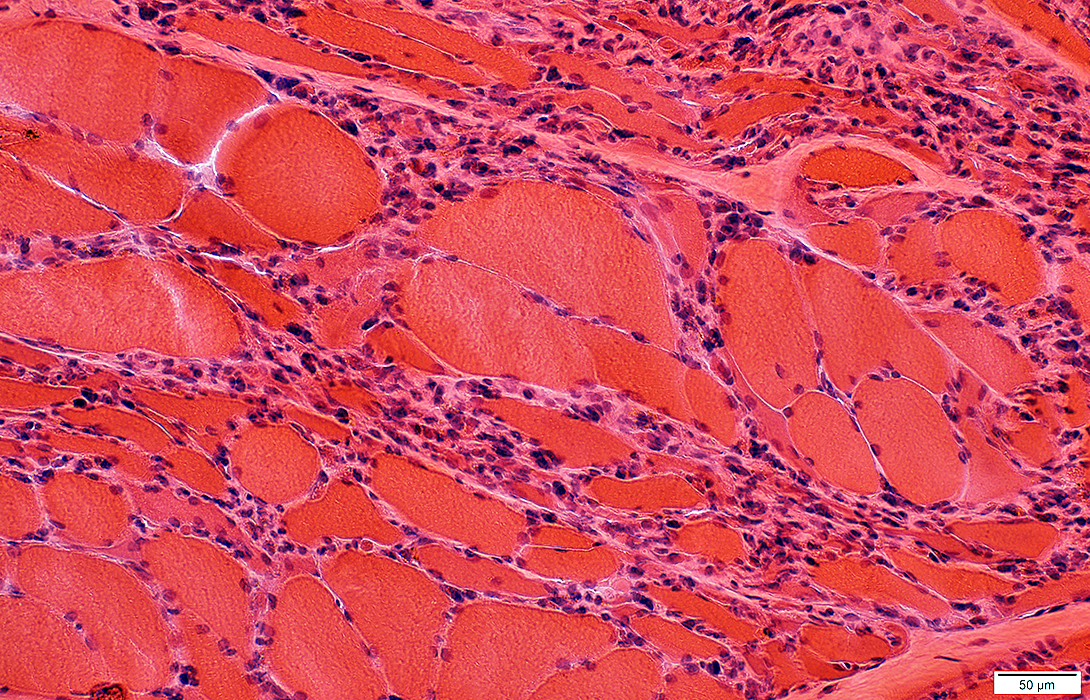
|
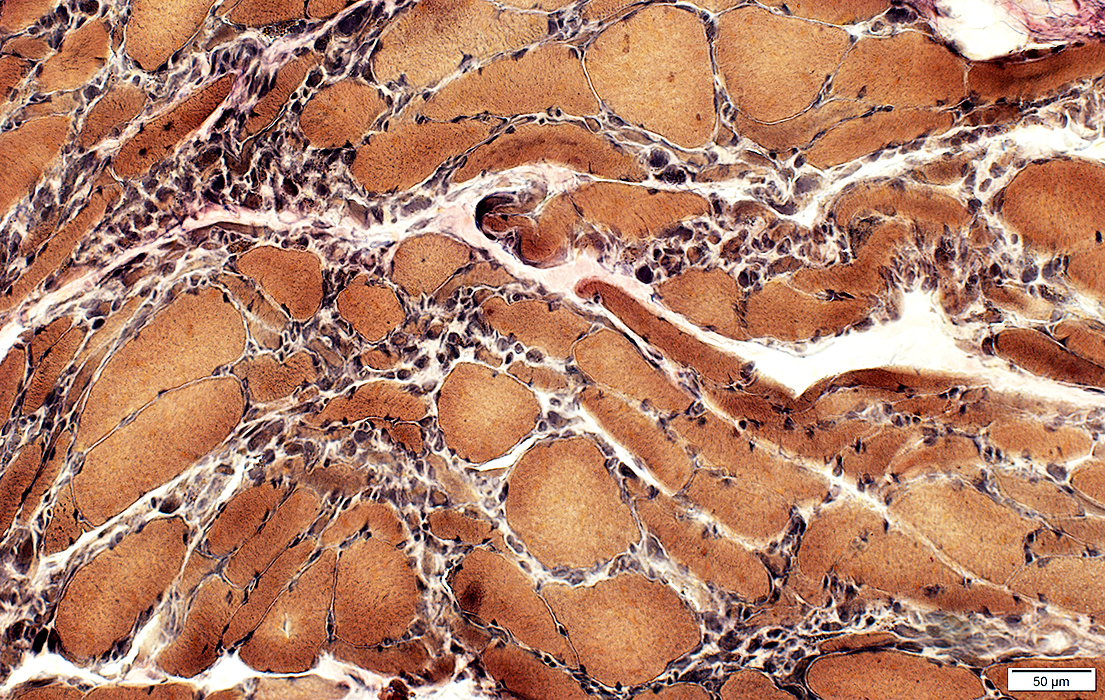
|
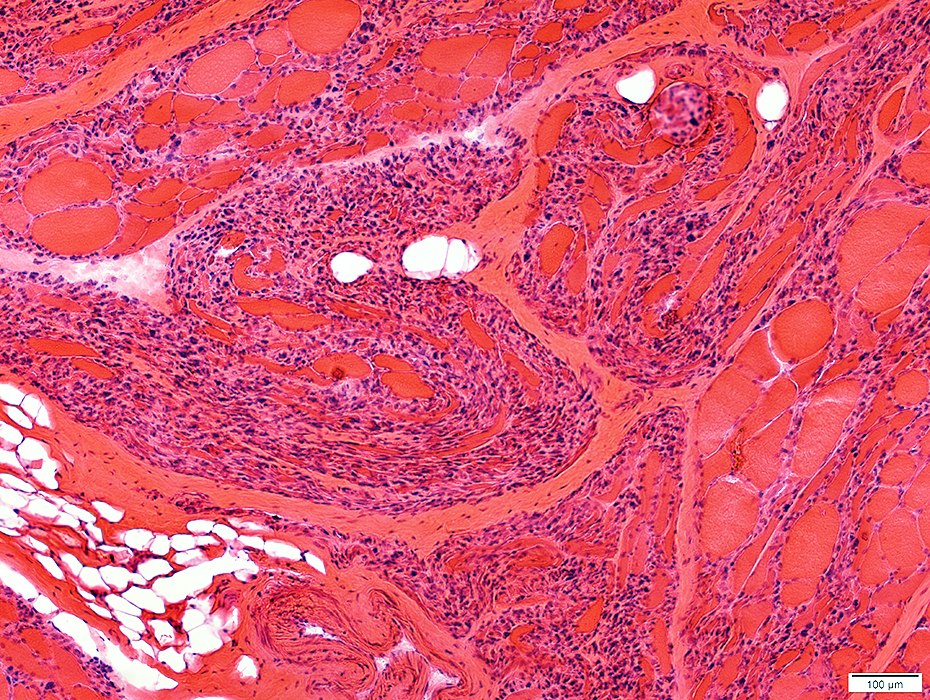 H&E stain |
Large clusters of pyknotic nuclear clumps & very small muscle fibers
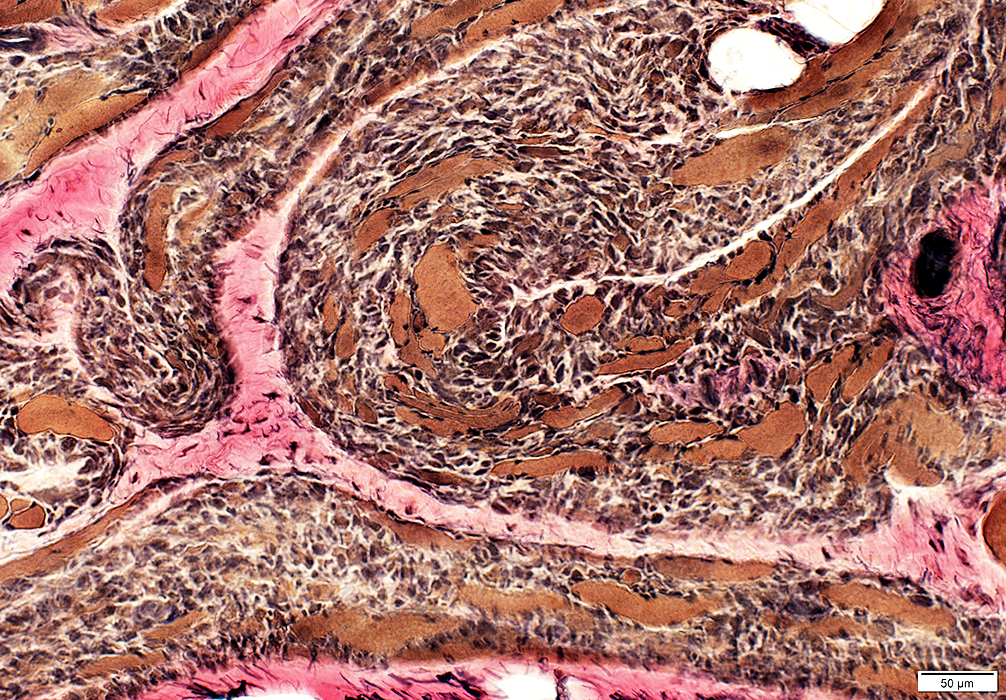 VvG stain |
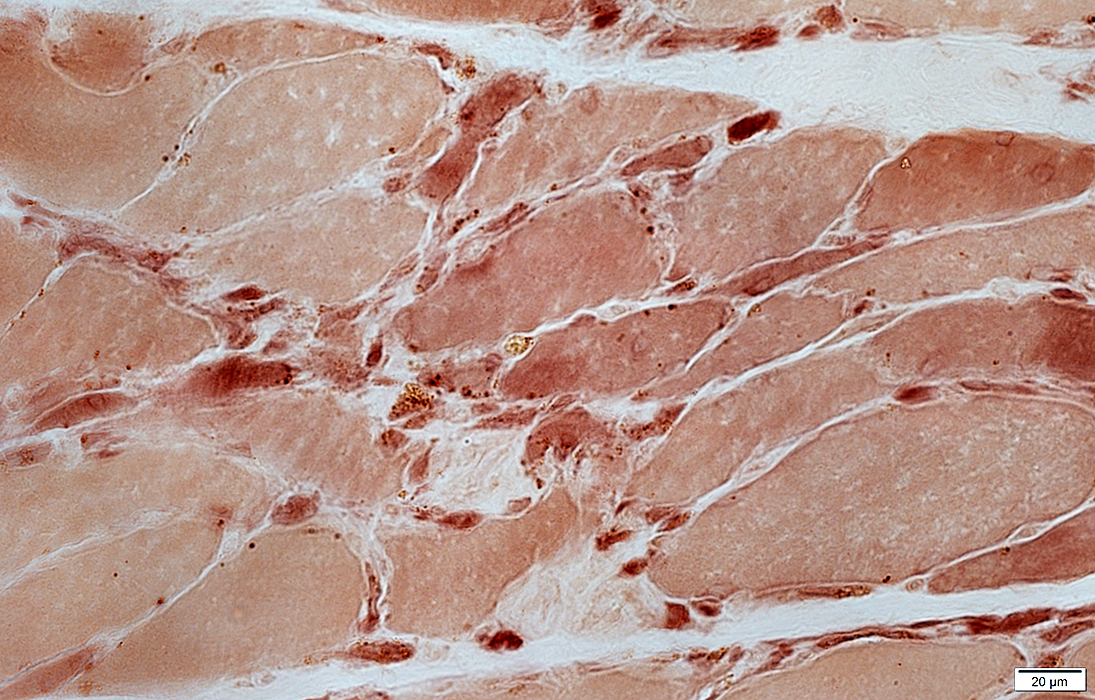 Esterase stain |
Dark on esterase & NADH stains
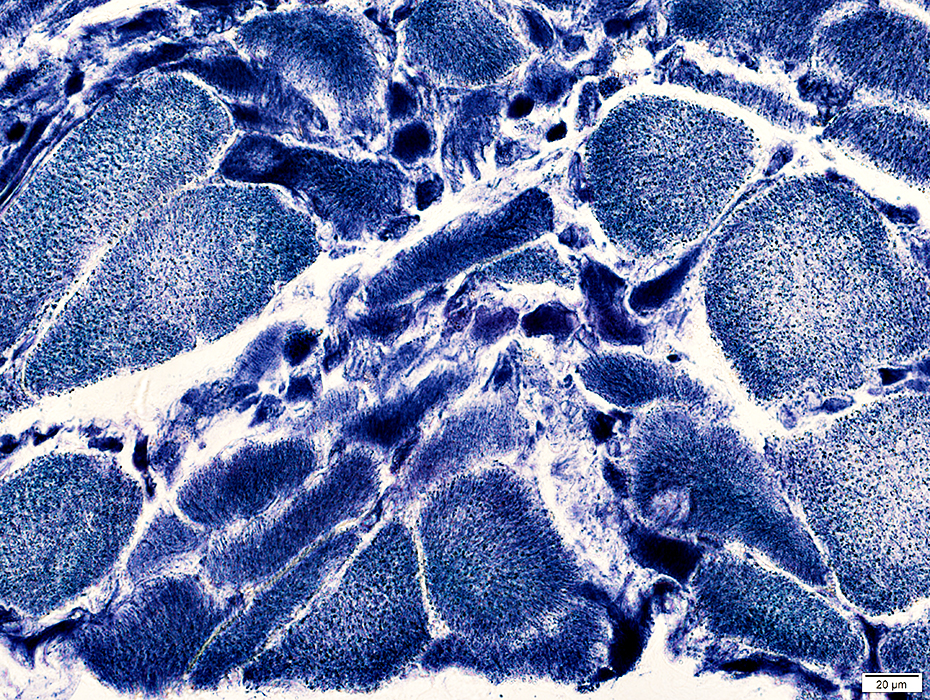 NADH stain |
ALS SOD1: Muscle
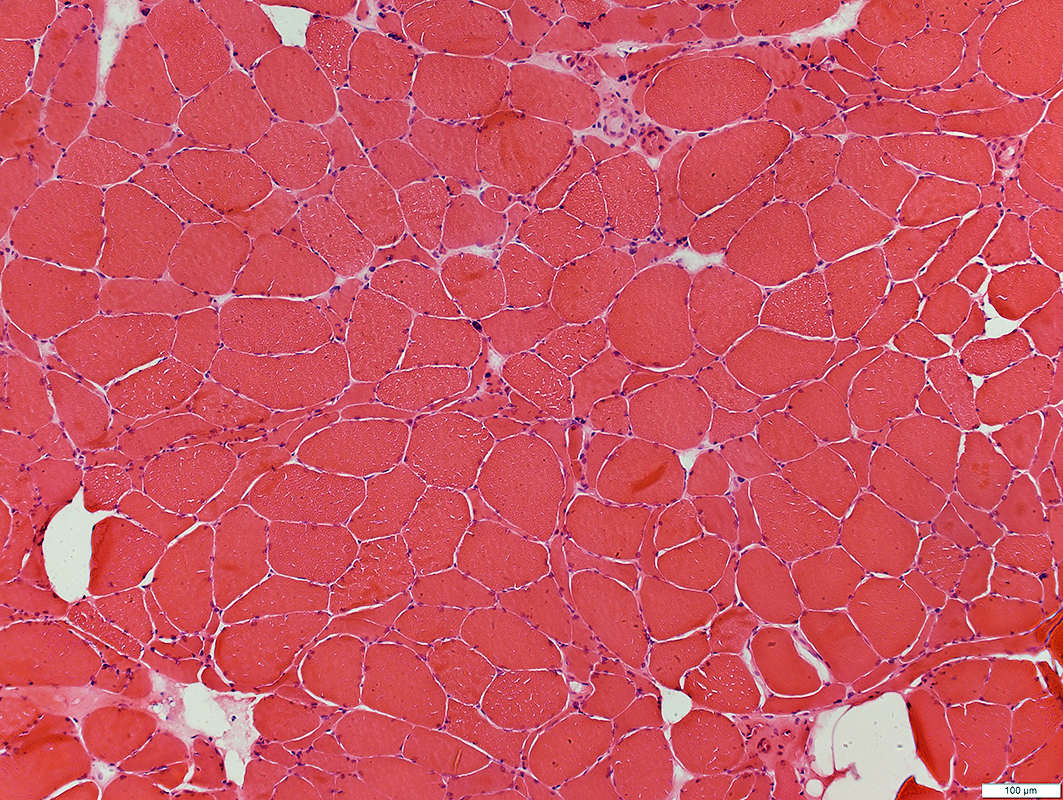 H & E stain |
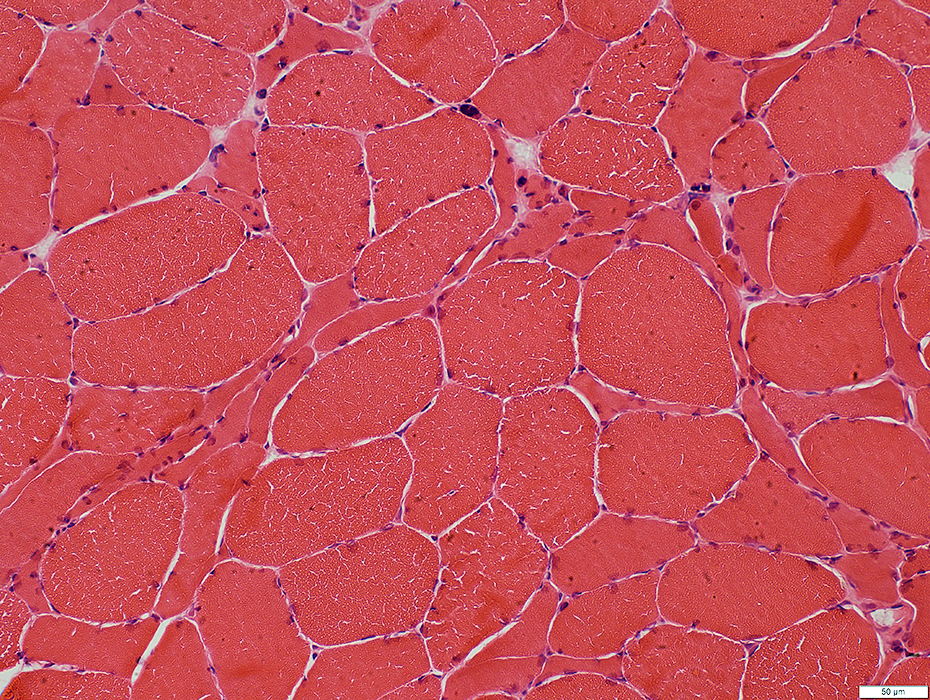 H & E stain |
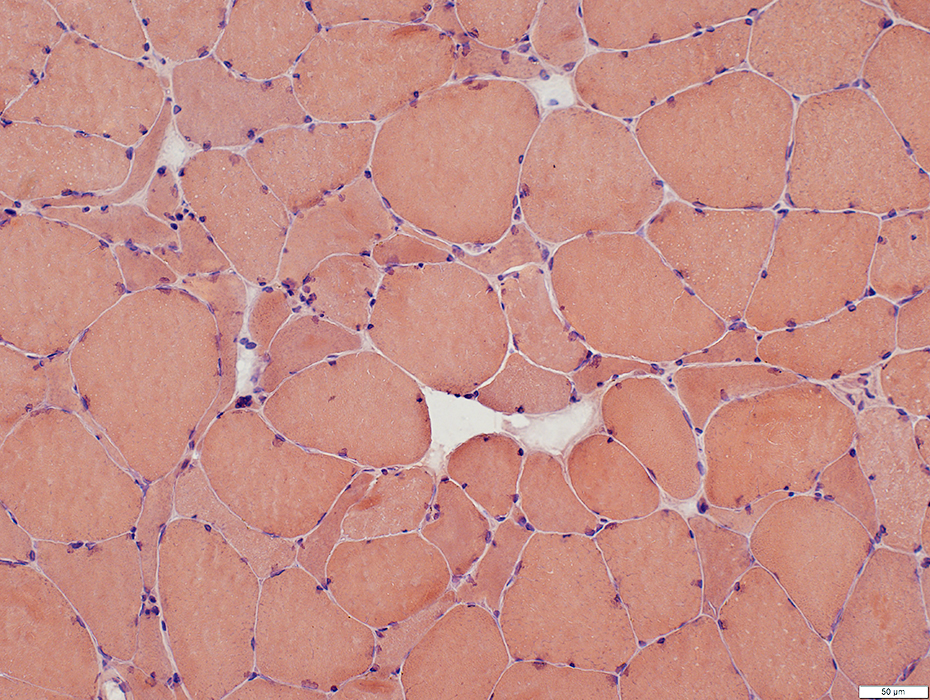 Congo red stain |
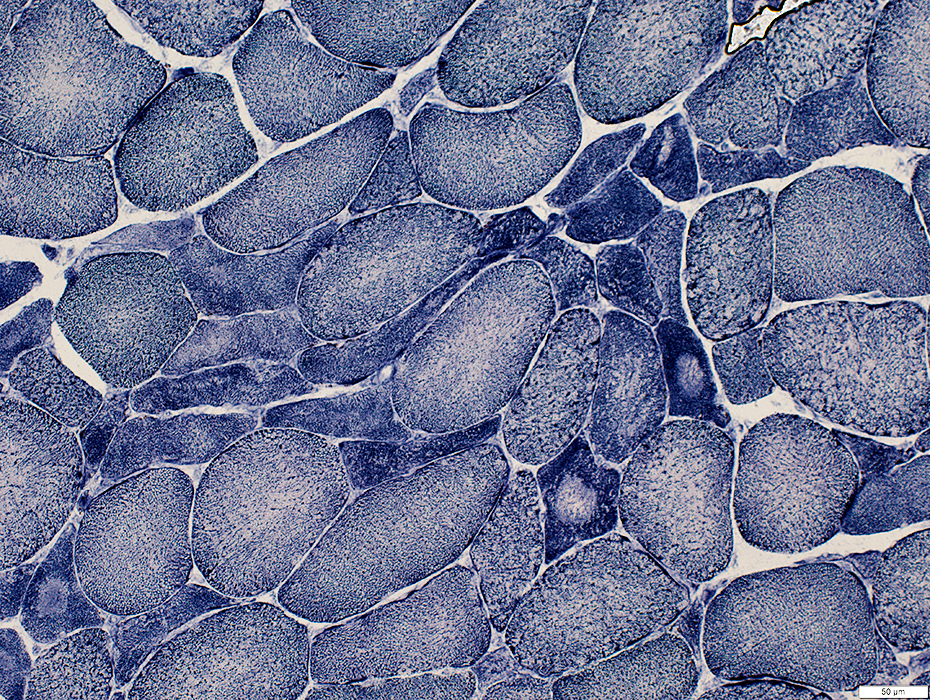 NADH stain |
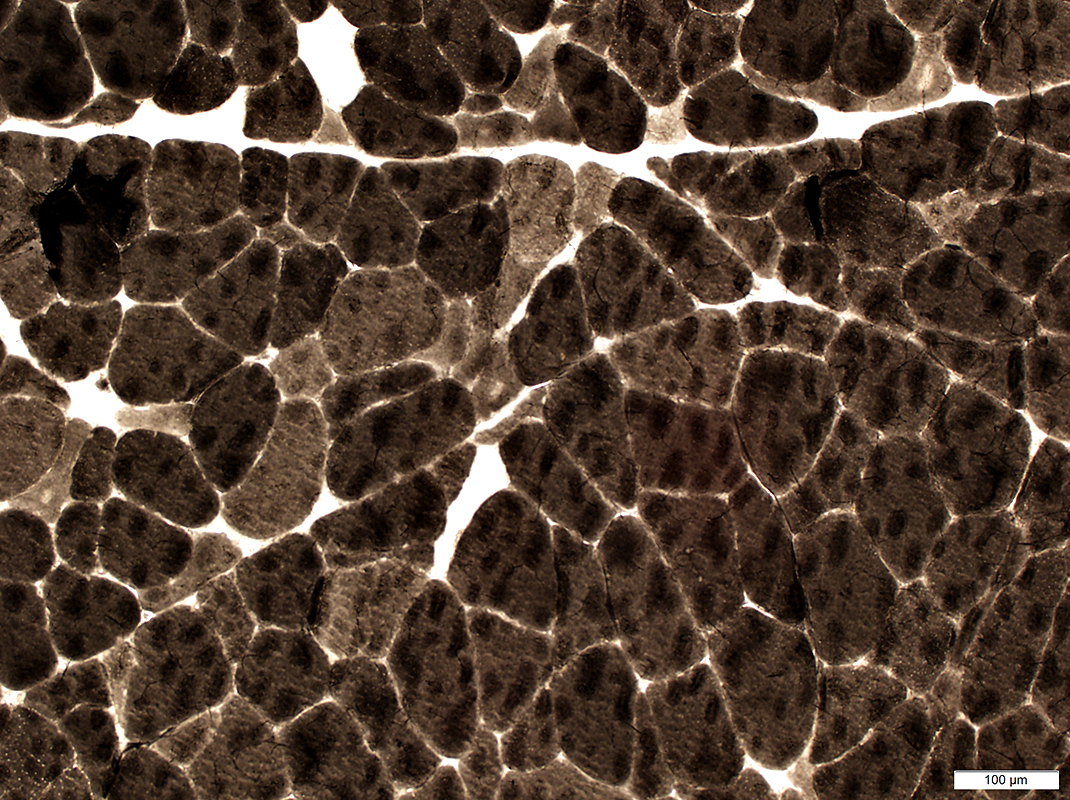 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
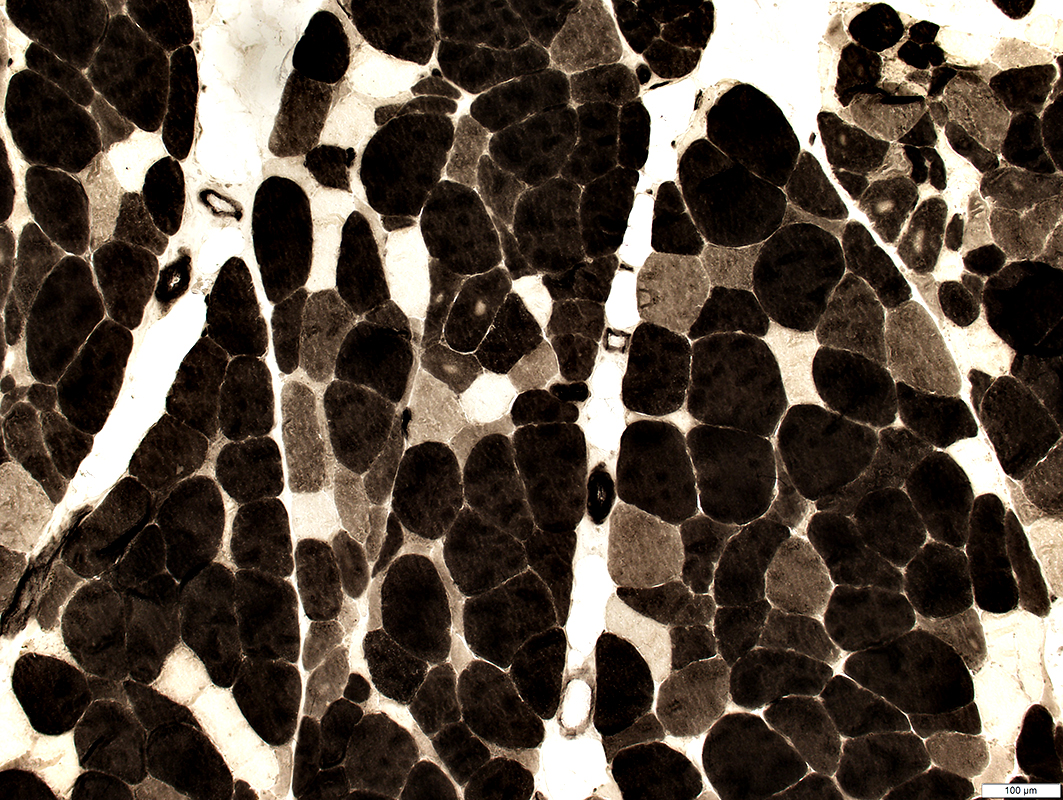 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
 VvG stain stain |
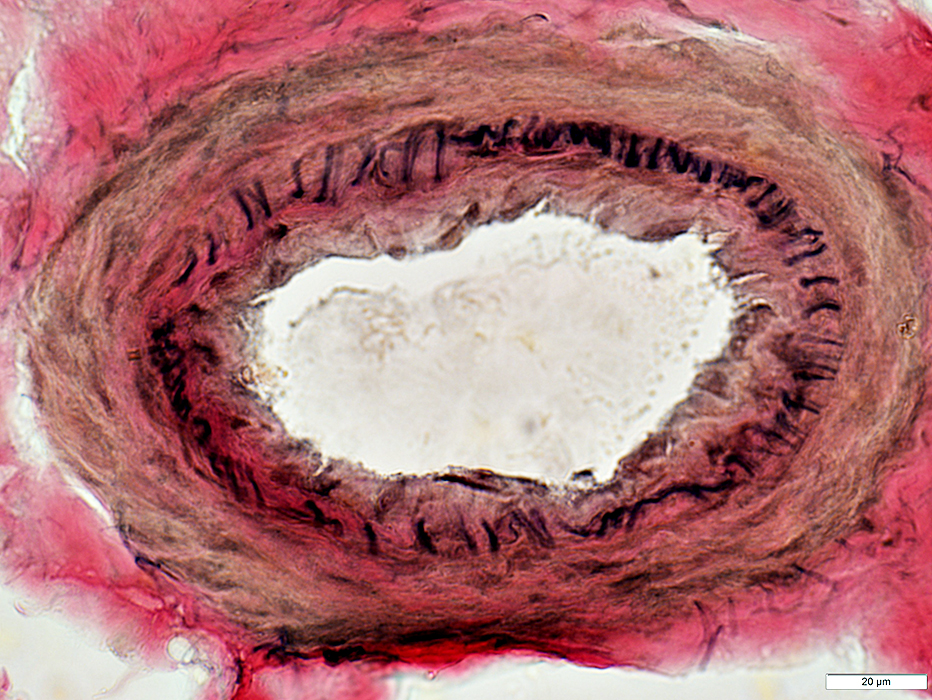
ALS: Intramuscular nerves
 VvG stain |
Loss of myelinated axons, moderate
Nodes of Ranvier: May be widened (Arrows)
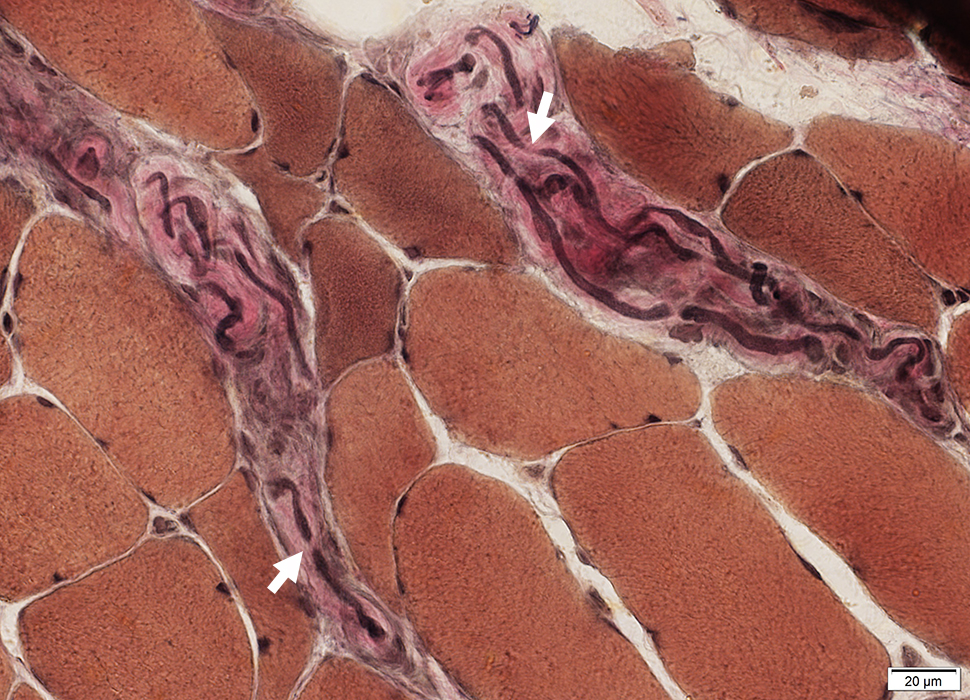 VvG stain |
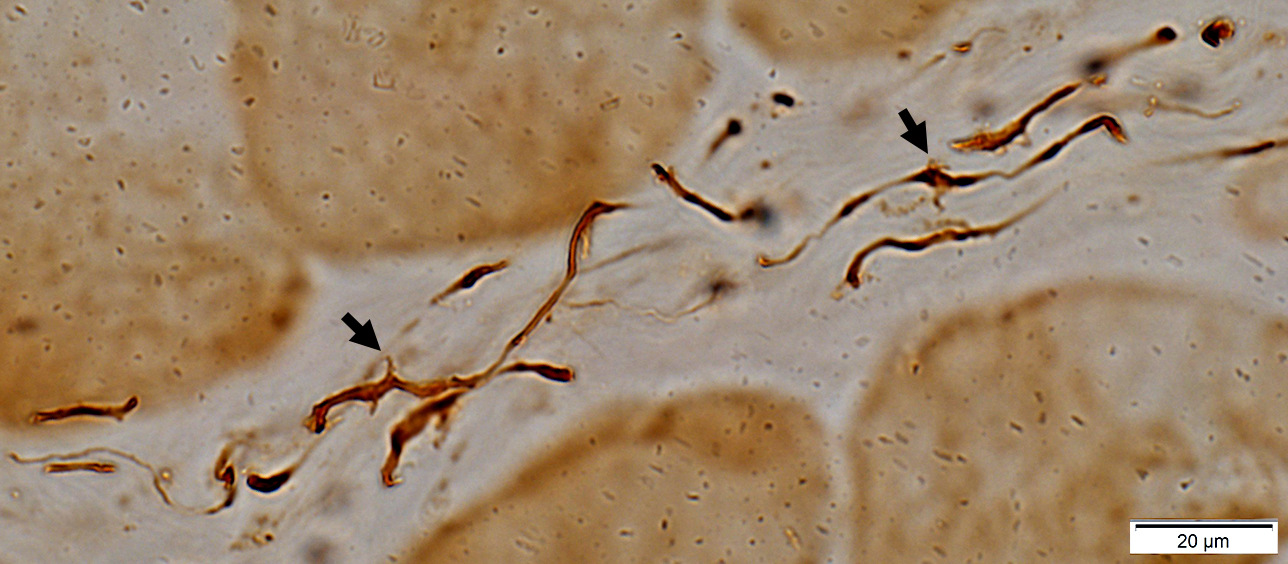 Neurofilament stain |
Abnormal branches & sprouts from intramuscular axons (Arrows)
ALS: Sciatic Nerve
| Control Nerve |
 Neurofilament stain |
 Neurofilament stain |
Varied among fascicles
 Neurofilament stain |
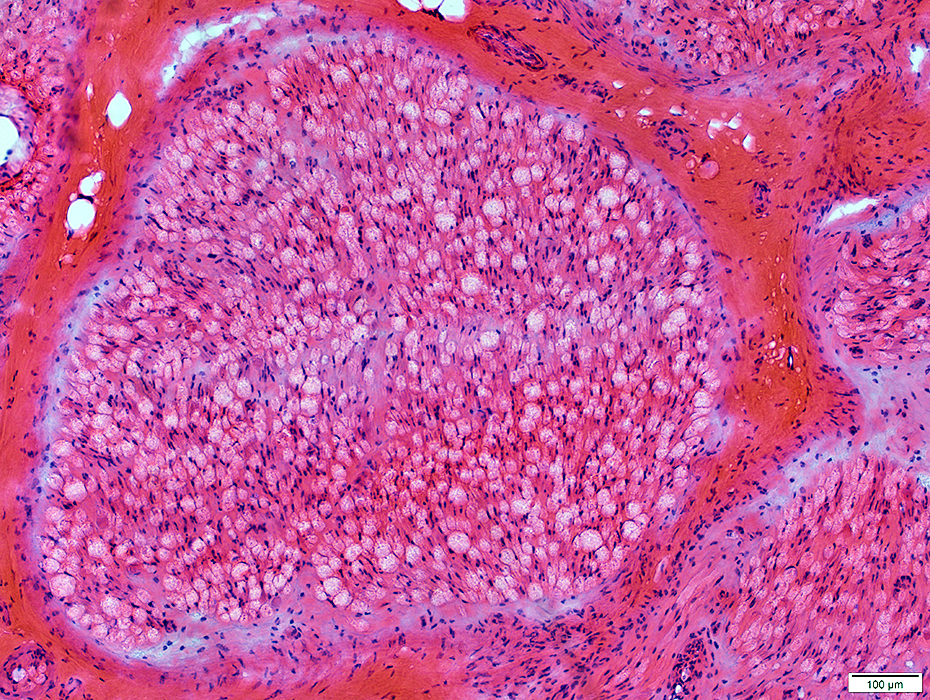 H&E stain |
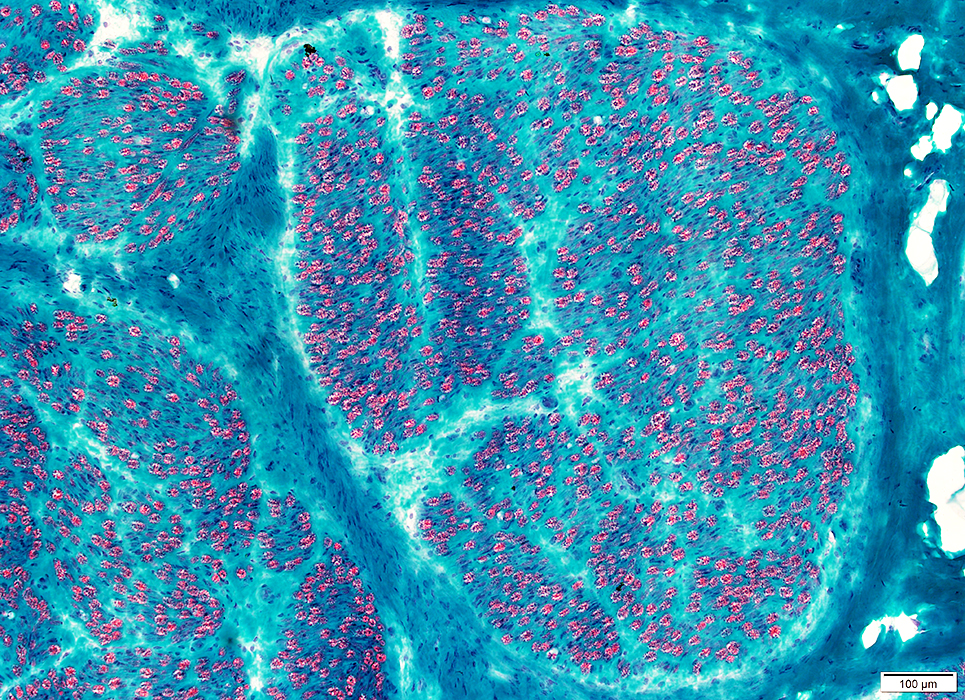 Gomori trichrome stain |
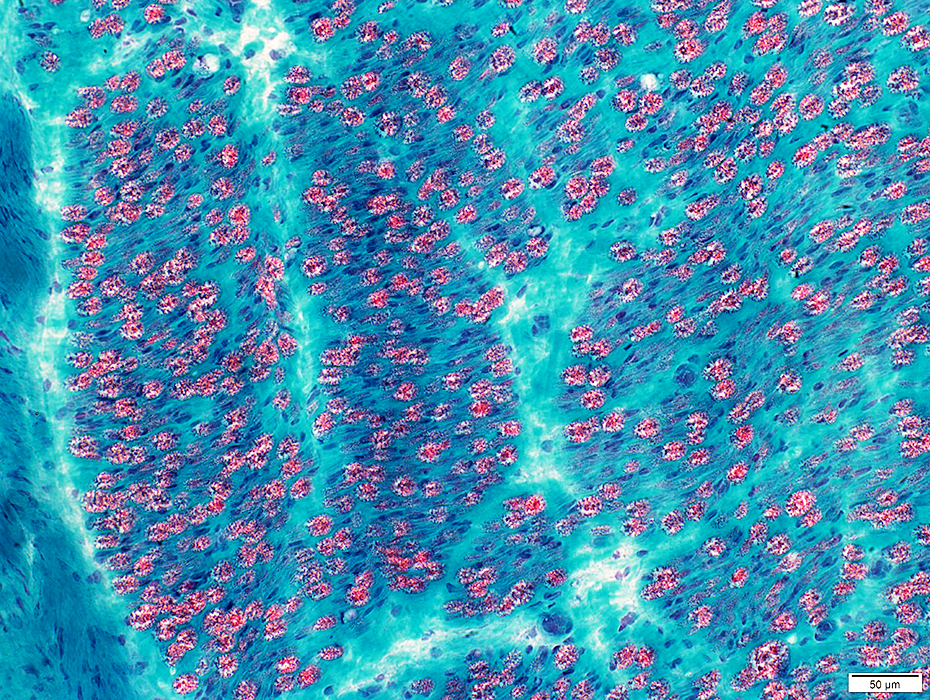 Gomori trichrome stain |
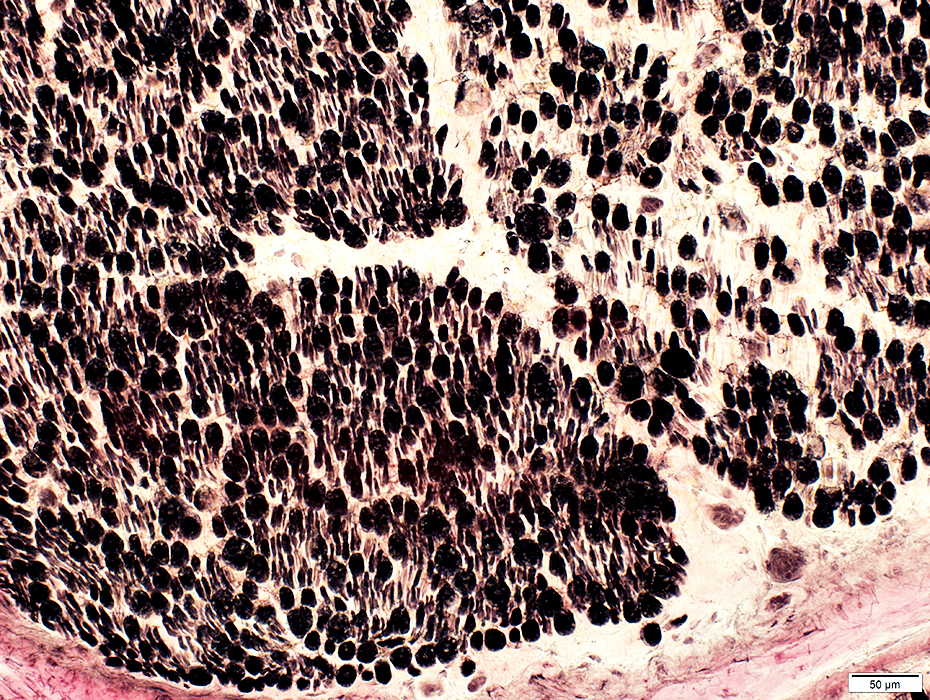 VvG stain |
Varied among fascicles
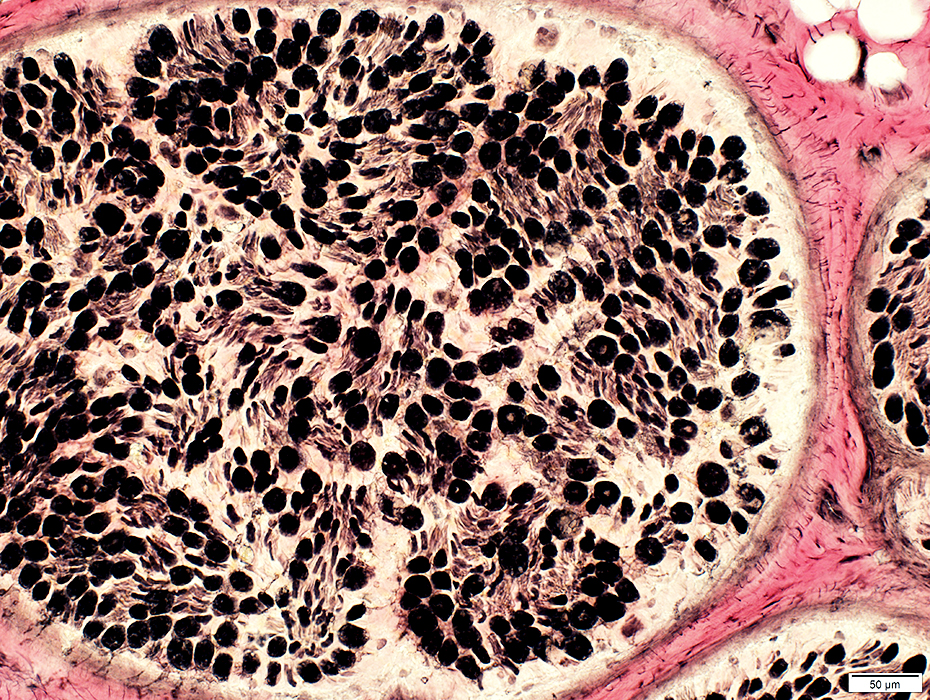 VvG stain |
ALS Nerve: Non-myelinating Schwann cells
Control
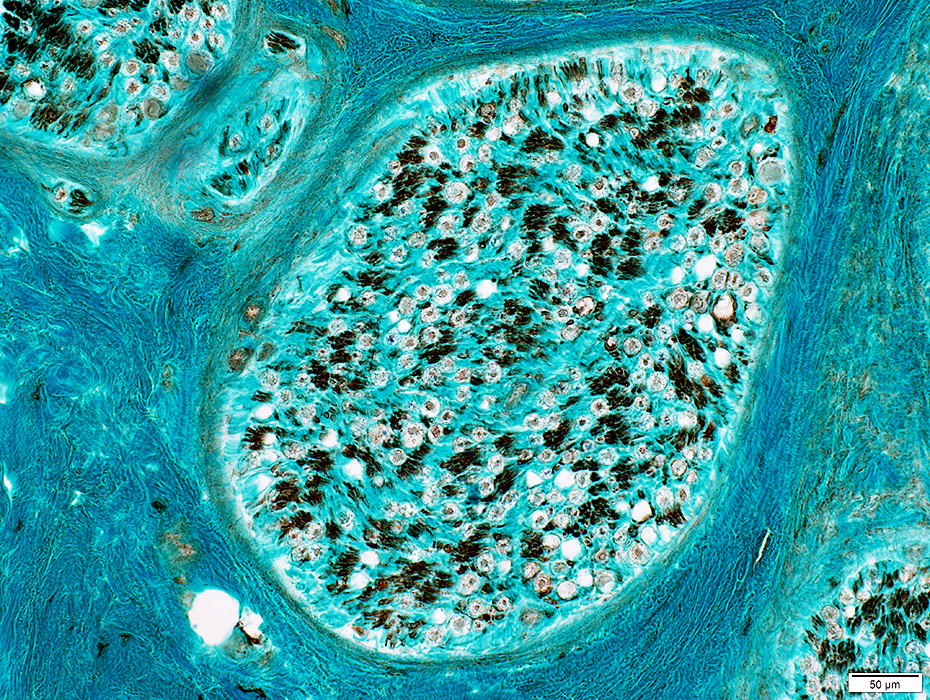 NCAM stain |
Myelin: Scattered myelin sheaths with abnormal NCAM staining (Arrow)
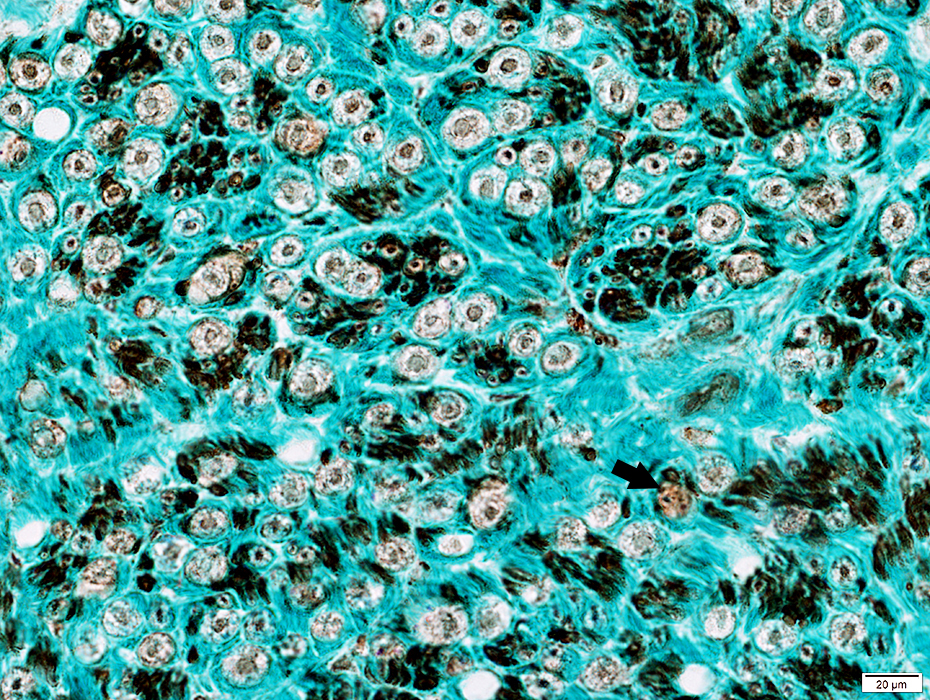 NCAM stain |
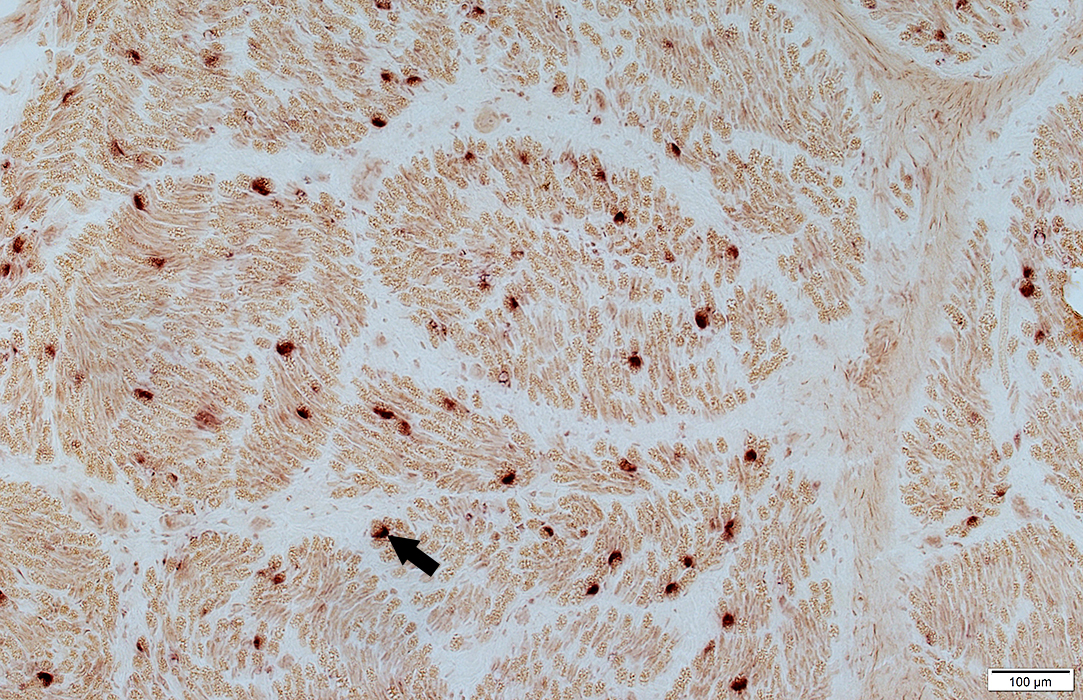 Acid phosphatase stain |
Scattered in the endoneurium
Some neighbor myelin sheaths (Arrow)
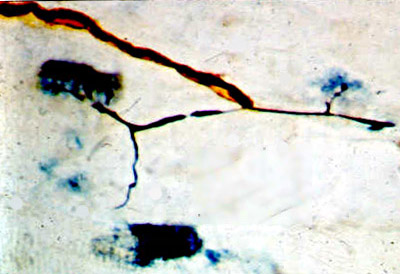
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Motor axon in ALS: Collateral sprouting of terminal axon
 |
ALS spinal cord pathology: Bramwell & Charcot images
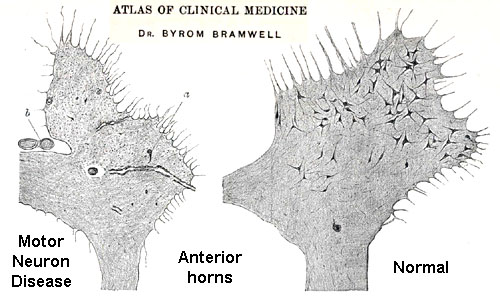
From Bramwell: Atlas of Clinical Medicine
Spinal cord: Reduced number of motor neurons in anterior horn
ALS Spinal cord pathology: Original patients of JM Charcot
Case reports:English translation from Google books
Illustrations from original article
Case 1
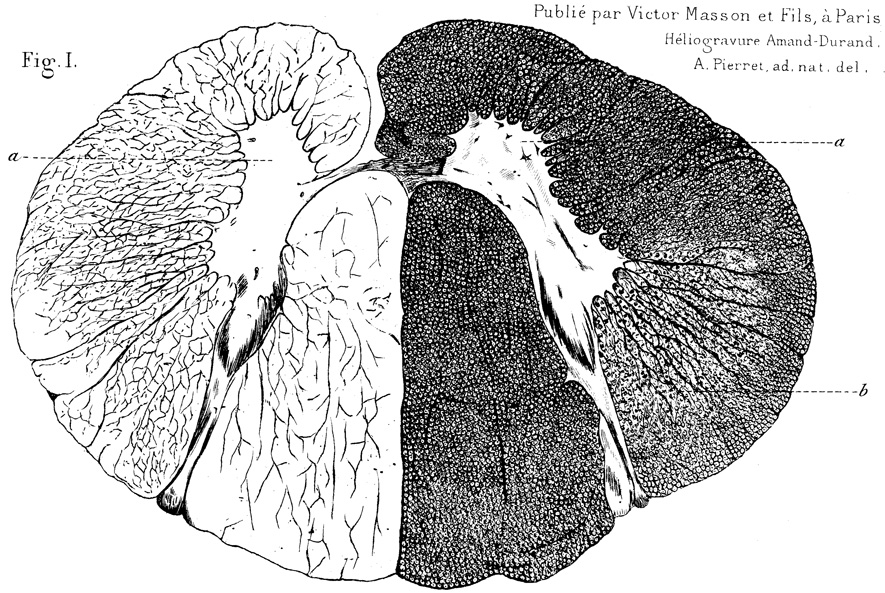
From: R Baloh
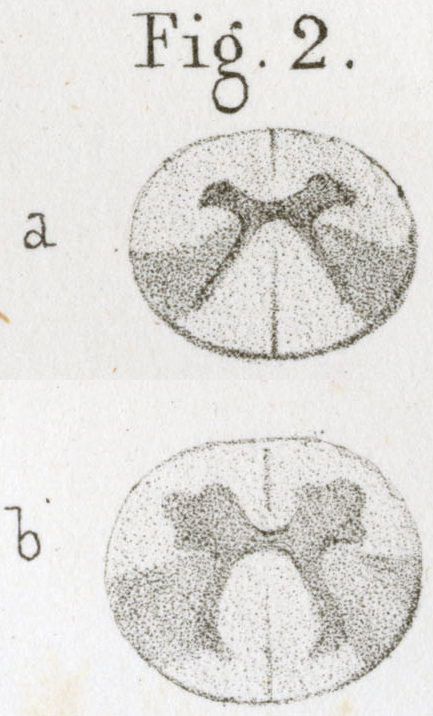
Legend: "Section of the cord of Catherine A. (Case 1), taken from the superior cervical region.
In a, one can see the rare cells and cell debris in the anterior horns.
In b, sclerosis of the lateral columns, determined by the atrophy of a large number of axons."
 From: R Baloh |
Legend:
"Symmetric sclerosis of the posterior part of the lateral columns in the dorsal region (Case 2)" |
ALS: SOD1
Hyaline conglomerate inclusions (HCI)
From A Hays MD |
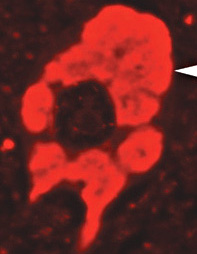 Neurofilament stain 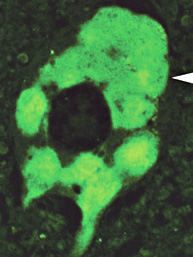 Peripherin stain |
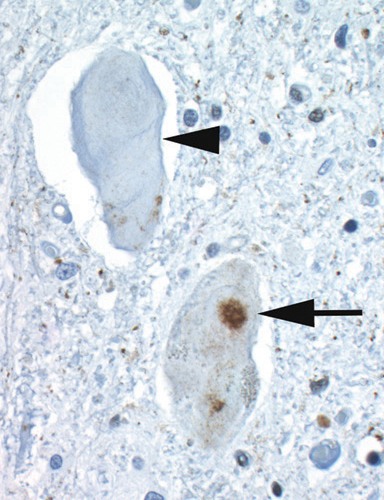 Ubiquitin stain |
- May occupy most of the neuronal cytoplasm
- Contain: Neurofilaments & peripherin but little ubiquitin
- May be more prominent with some SOD mutations
- Not present in sporadic ALS
ALS: HTT
Spinal Cord: Histiocyte (CD163) stain
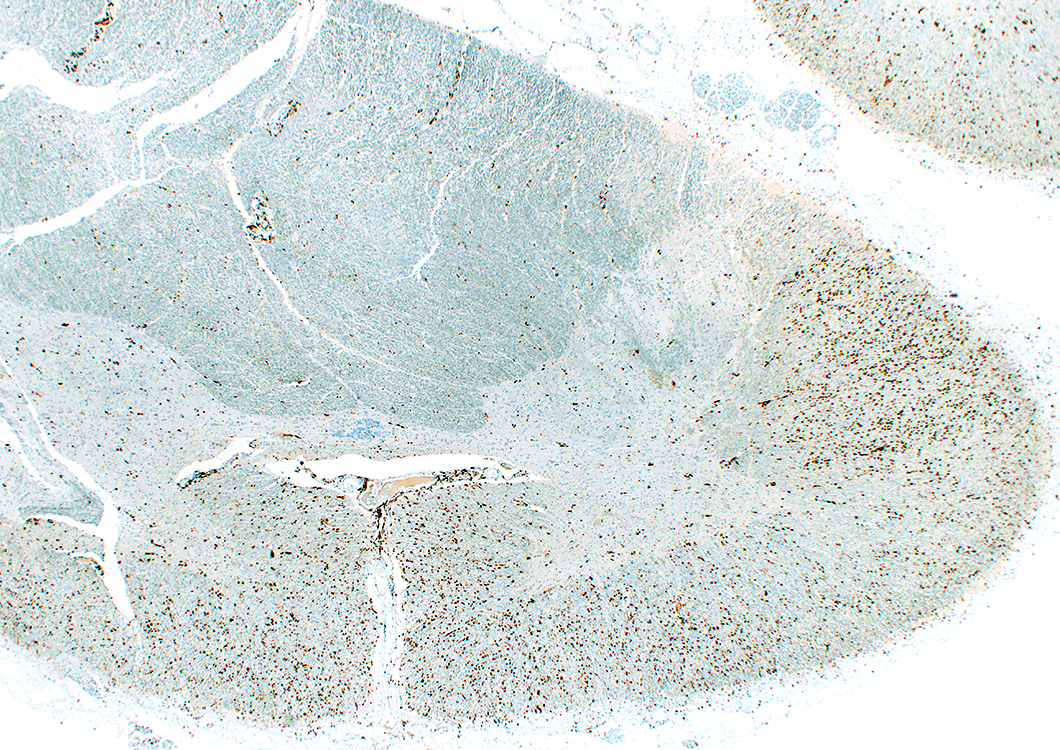 From: R Bucelli; R Schmidt |
Lateral corticospinal tract: Histiocyte (CD163) stain
 From: R Bucelli; R Schmidt |
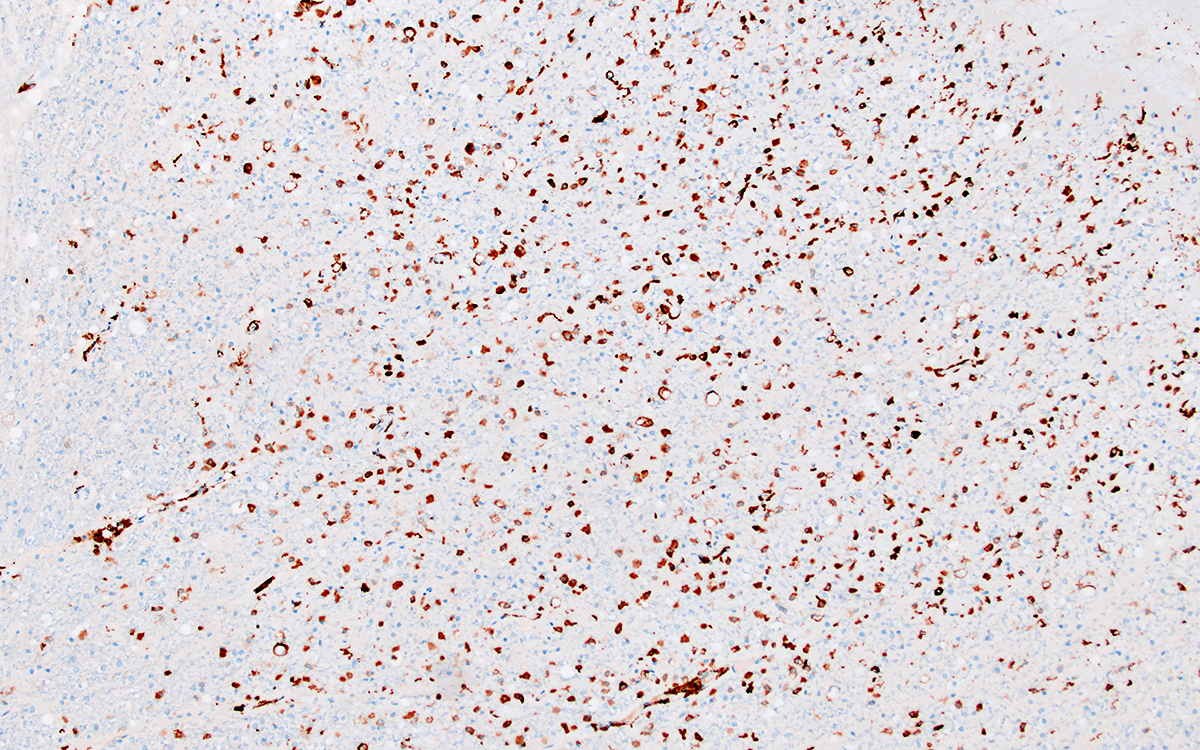
TDP43 aggregates
 From: R Bucelli; R Schmidt |
|
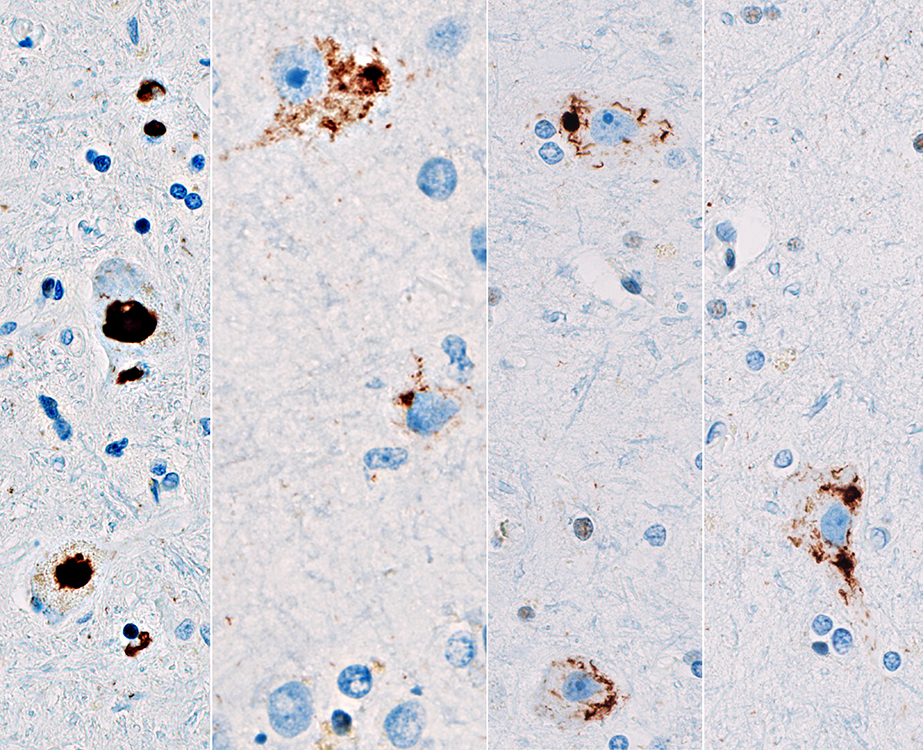
HTT (PolyQ) aggregates Not in nuclei; Motor cortex 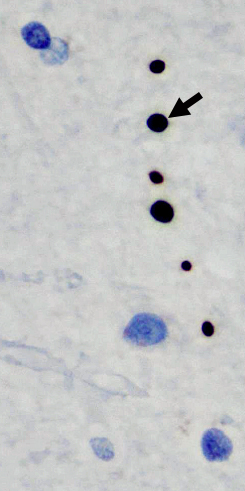 From: R Bucelli; R Hickman (Columbia, NY) |
p62 aggregates Intranuclear; Hippocampus 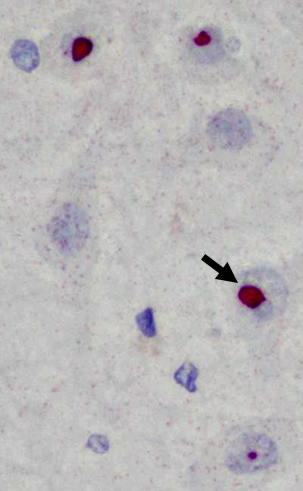
|
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Pathology index
Return to ALS
6/24/2021