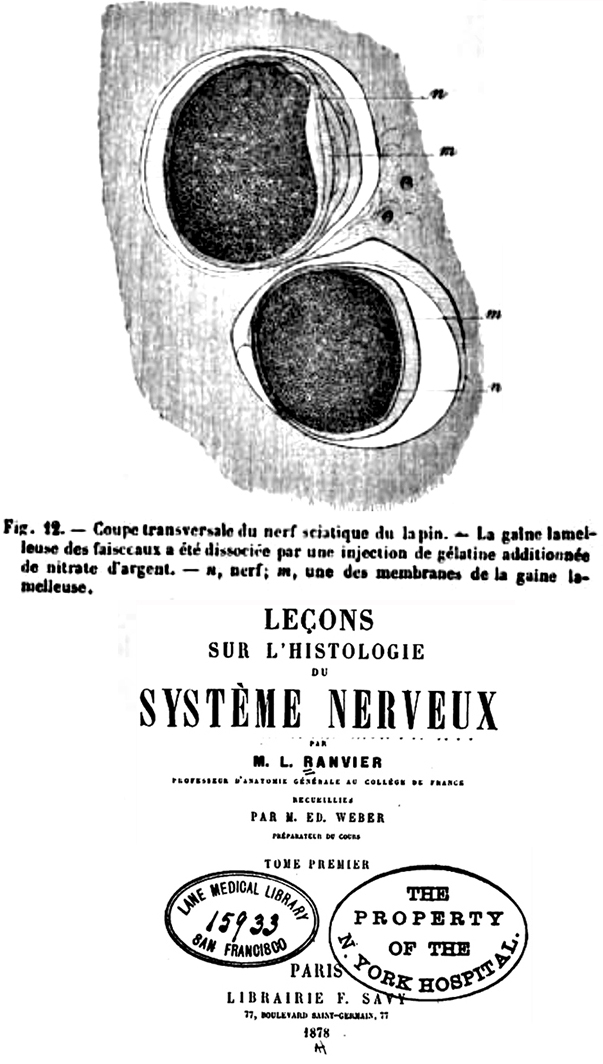
PERIPHERAL NERVE: Normal features
|
Age changes Pi granules Blood-Nerve barrier Elzholz body Endoneurium Epineurium Perineurium Stains Morphology Sural nerve Adults Axons Unmyelinated Myelinated Schmidt-Lanterman Cleft Morphology Node of Raniver Ultrastructure Epineurium Perineurium Schwann cells Vessels Endoneurial Epineurial Children Infraorbital nerve Sciatic nerve (Adult) Myelin Sciatic Sural Mouse |
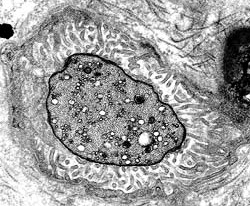
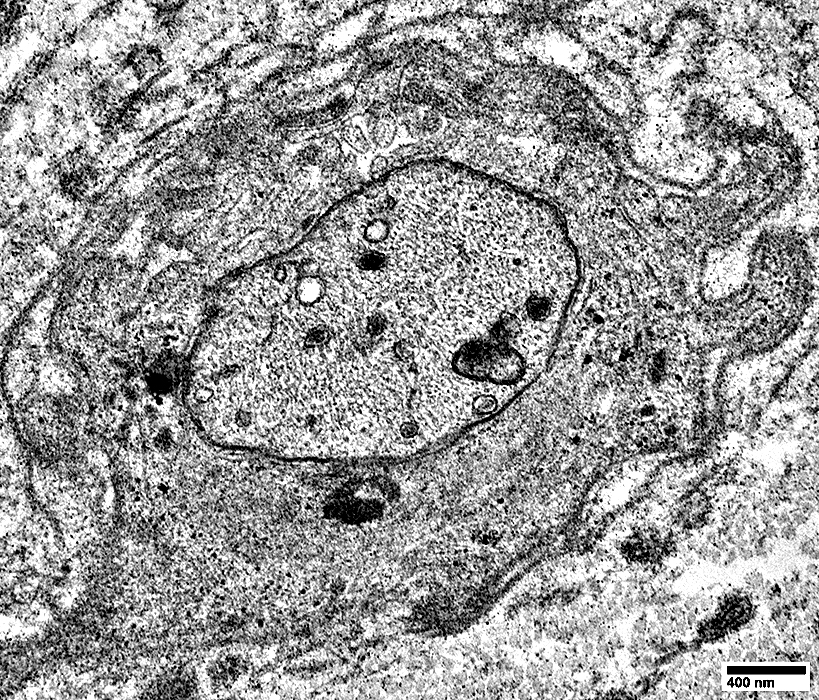
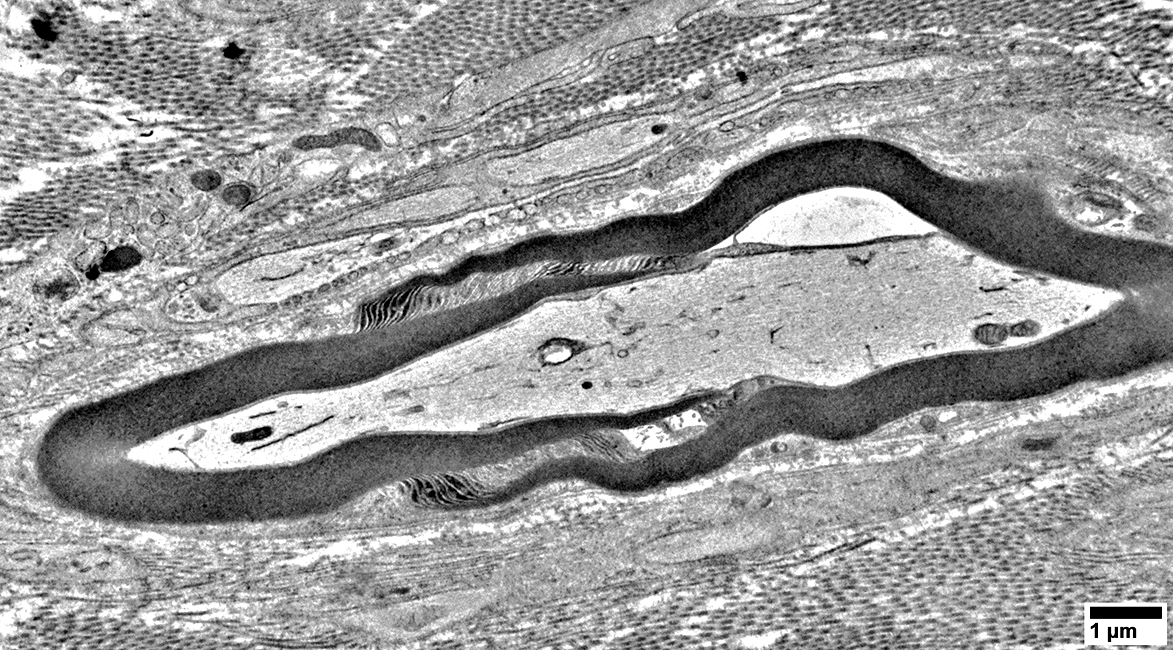
 Myelinated Axon
Filaments & Tubules are visible in the Axoplasm A Schmidt-Lanterman cleft divides the myelin sheath |
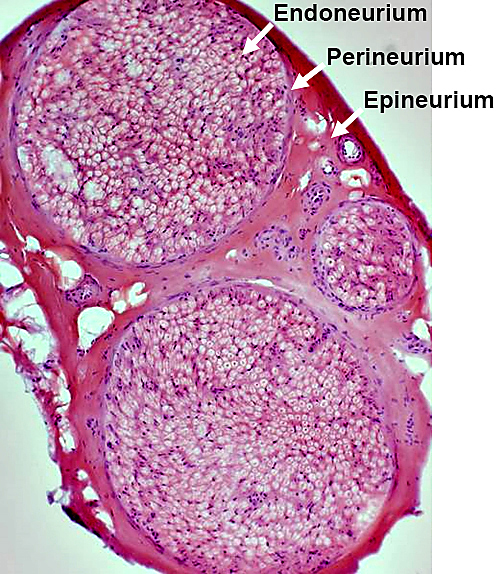
Epineurium
- Connective tissue & vessels surrounding nerve fascicles
- Collagen
- Bundles: Oriented longitudinally
- More dense near fascicles
- Fibril width: 60 to 110 nM diameter
- Type I > III
- Vessels (Vasa nervorum)
- Arteries
- Veins
- Lymphatics
- Nerves
- Axons: Small, unmyelinated; In vessel walls, Artery >> Vein
- Non-myelinating Schwann cells: NCAM+; Surround unmyelinated axons
- Pathology: Vasculitis & Inflammatory vasculopathies
Perineurium 2
|
|
Endoneurium
- Anatomy
- Region inside perineurium
- Contiguous with sub-arachnoid space
- Contents
- Axons
- Schwann cells & Myelin
- 80% to 90% of endoneurial nuclei are Schwann cells
- Collagen IV: Component of Schwann cell basement membrane
- Endoneurial microvessels: Pathology
- Disease: HIEM
- Features
- Orientation: Longitudinal with many oblique & transverse anastomoses
- Size: 9 μM mean diameter; Range 5 to 22 μM
- Density: 60–100 per mm2 in human sural nerve: Lower with age
- May stain for
- Alkaline phosphatase
- UEAI lectin: Endothelial cells
- Scaffolding proteins: Link endothelial cell membranes to cytoplasmic components
- Endoneurial microvessels: Endothelial cells
- Anatomy: Single layer next to vessel lumen
- Linked by tight junctions
- Molecules: Mitogen receptors
- May contain Weibel–Palade bodies: ? Produce factor VIII-related antigen
- Surrounded by collagen
- No fenestrae or associated glial cells
- Form part of blood-nerve barrier
- Tight junction proteins in endoneurial capillaries
- Claudin-5: Endothelial; Schmidt-Lanterman incisures
- Occludin
- ZO-1
- Collagen (50 to 65 nM)
- Collagen III > I
- More tightly packed near Schwann cell basement membrane
- Interstitial space
- Other cells
- Fibroblasts: Few (10%); More frequent near endoneurial vessels; No basement membrane
- Macrophages: Resident
- Under pressure relative to epineurium
Blood-Nerve Barrier 1
- Anatomy
- Locations
- Perineurium: Very impermeable; High pinocytotic activity
- Endoneurial microvessels: More permeable than perineurium
- Tight junctions between
- Endothelial cells in microvessels
- Innermost perineurial epithelioid myofibroblast cells
- Locations
- Molecules
- Barrier proteins
- ZO-1 (TJP1)
- Intracellular
- Connects tight junction proteins to actin cytoskeleton
- Claudin-1 (CLDN1)

- Claudin-3 (CLDN3)

- Locations: Schmidt-Lanterman incisures; Mesaxon
- Claudin-4 (CLDN4)
 : BNB tight junctions
: BNB tight junctions - Cadherin-5 (CDH5)

- Endothelial
- Adherens junctions
- Locations: Endoneurial vessel endothelium; Schmidt-Lanterman incisures; Mesaxon
- CLDN5 knock-out: Increased permeability for molecules < 800 Da
- Occludin (OCLN)

- Tricellulin (MARVELD2)

- α1 catenin (CTNNA1)
 : F-actin cytoskeleton linking to adherens junctions
: F-actin cytoskeleton linking to adherens junctions
- ZO-1 (TJP1)
- Transporters: Influx & Efflux
- Barrier proteins
- Functions
- Endoneurial ionic microenvironment: Regulation
- Transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER): High
- Permeability to solutes & macromolecules: Low
- Transendothelial water flux (hydraulic conductivity): Low
- Possible Disorders
Adults: Sural nerve
|
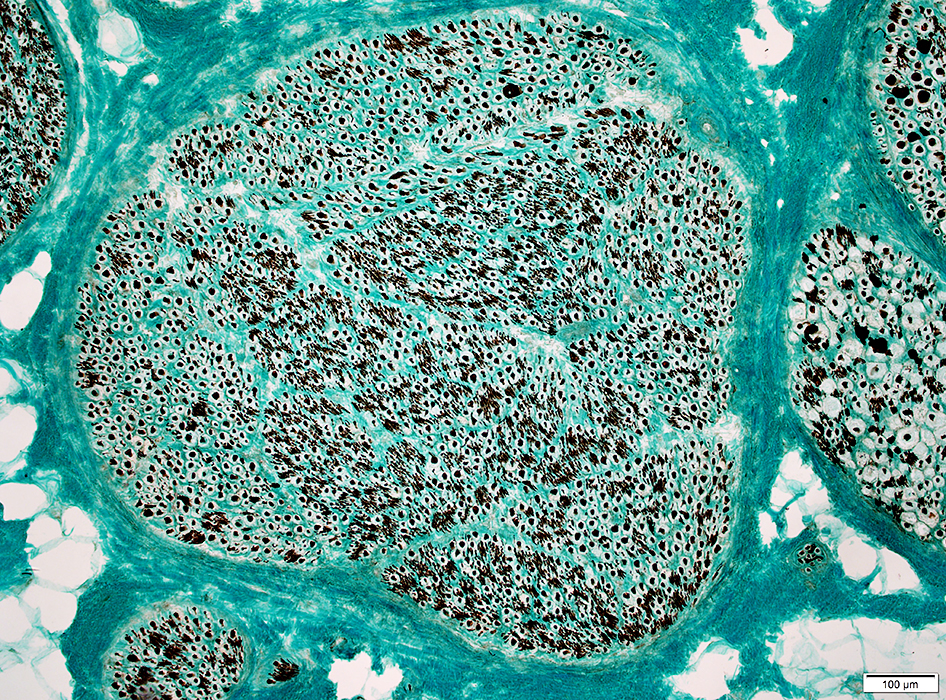
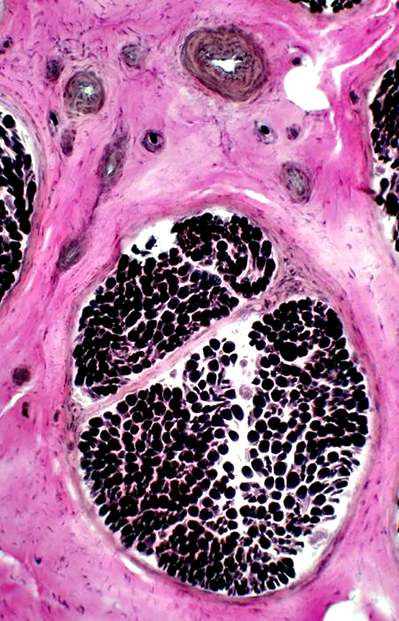
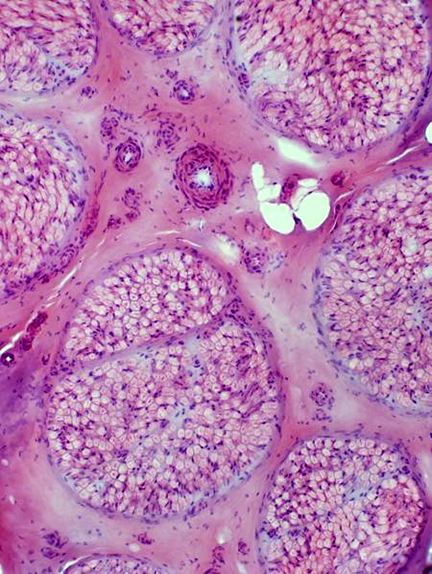
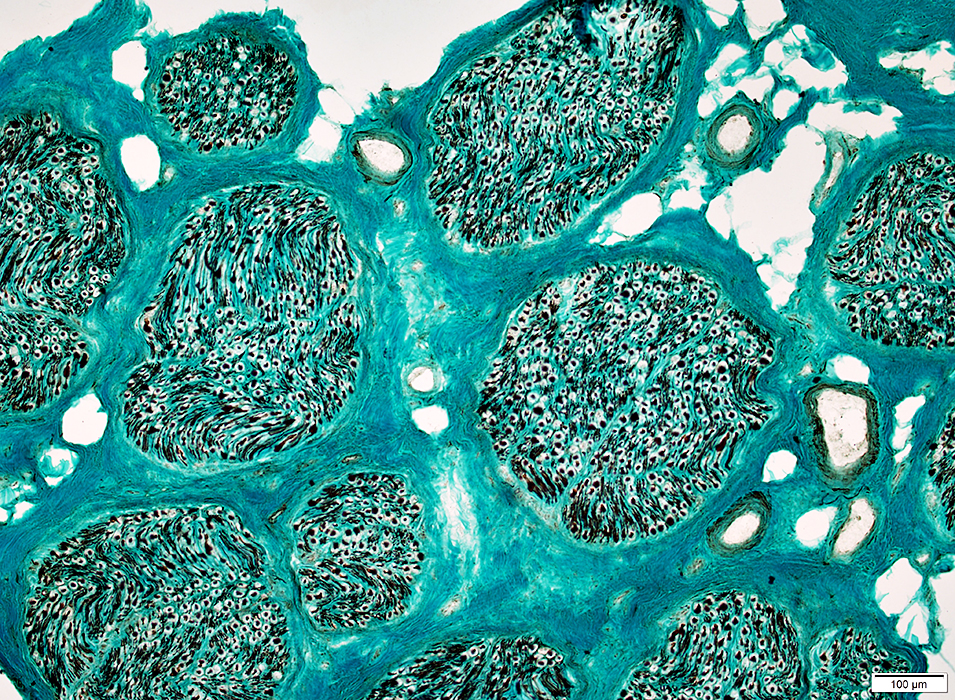
Structure Fascicles |
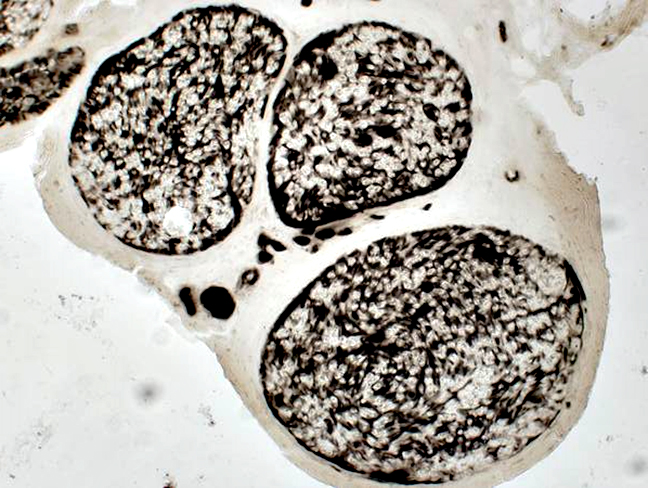
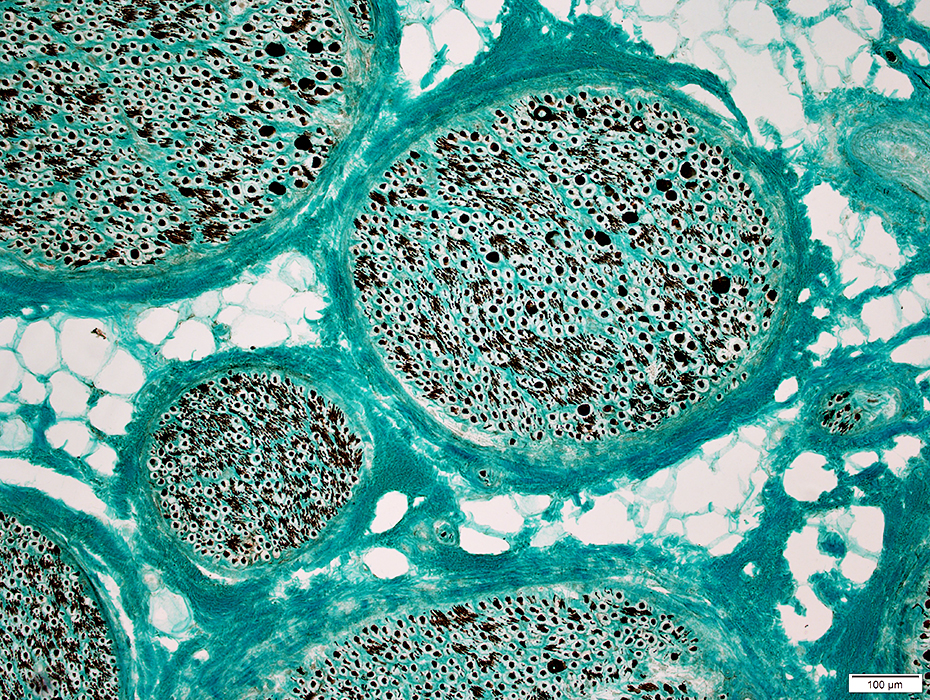
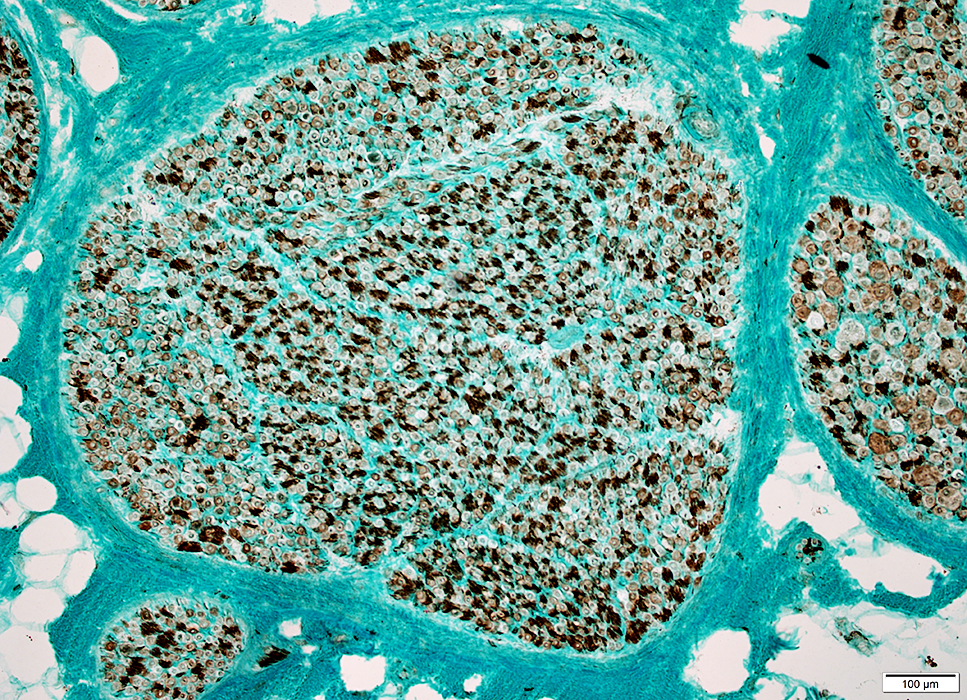
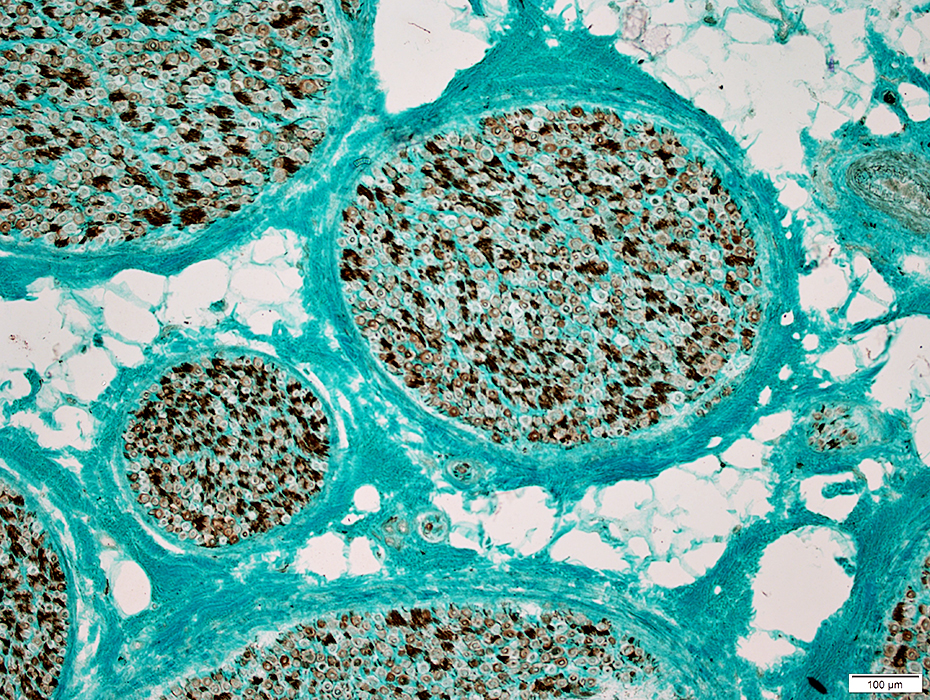
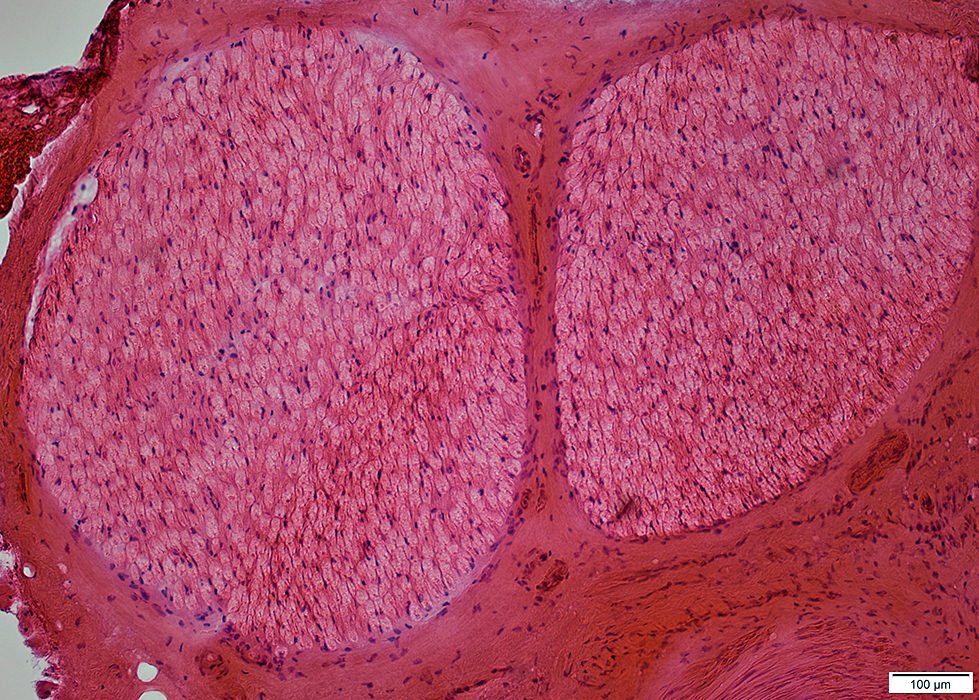
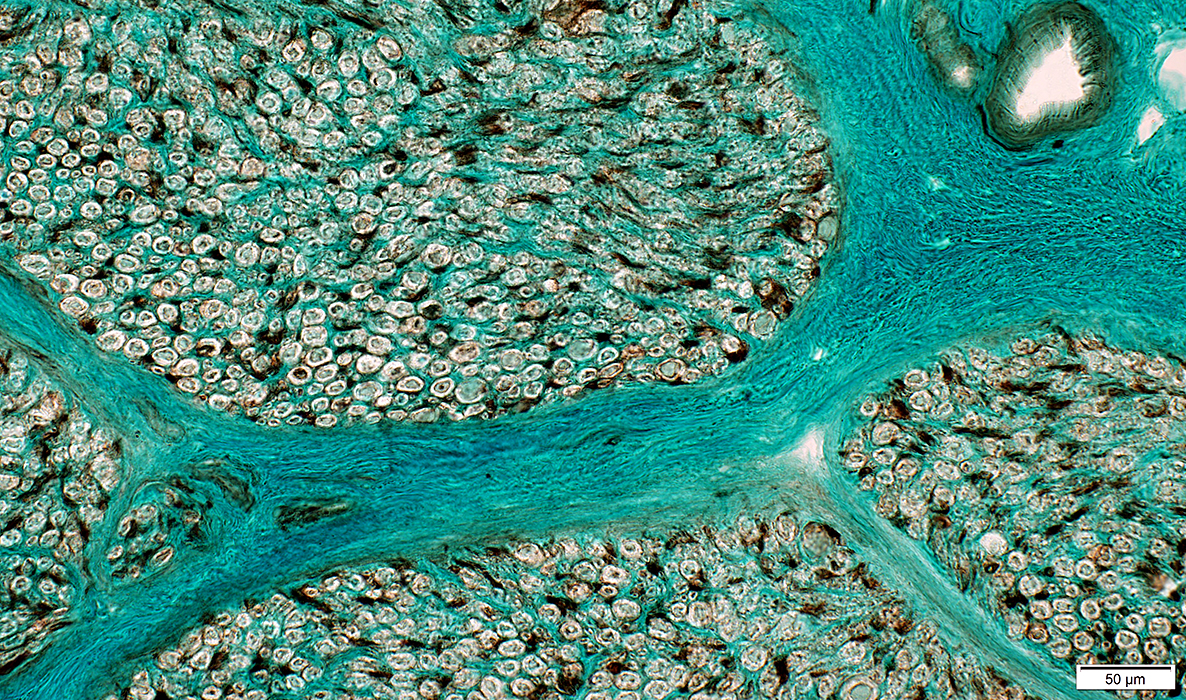
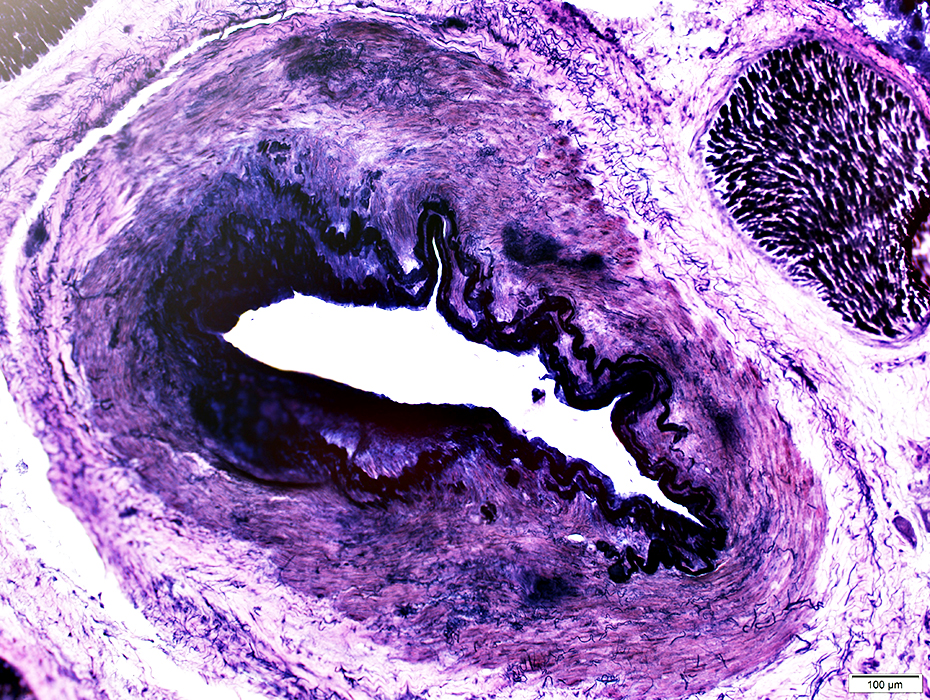
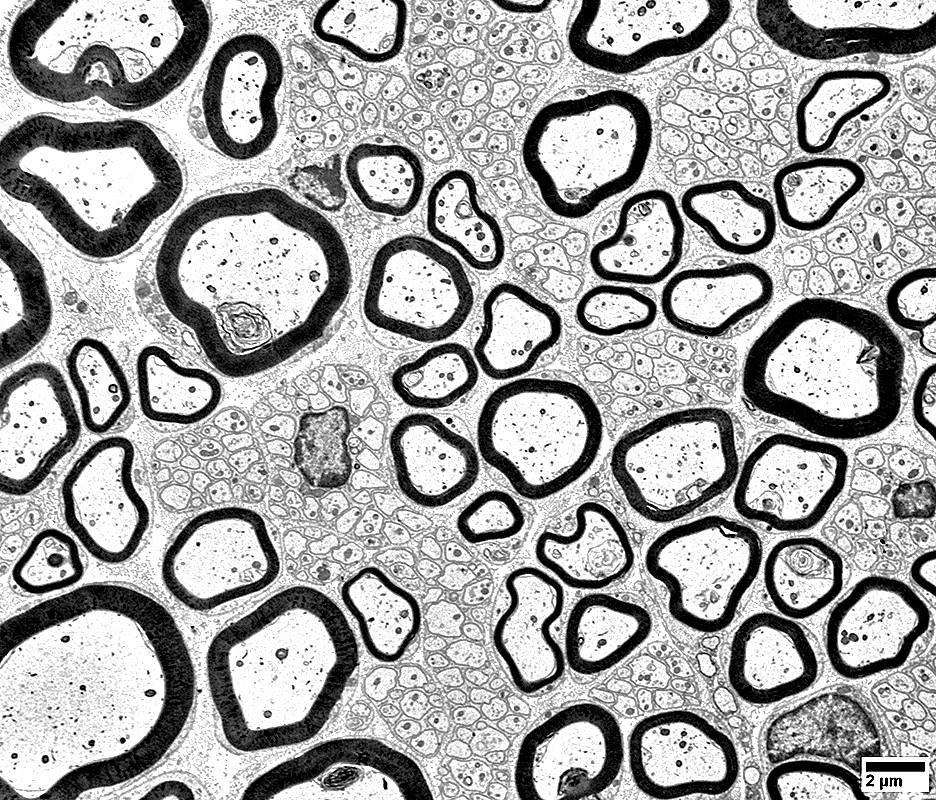
Nerve Structure
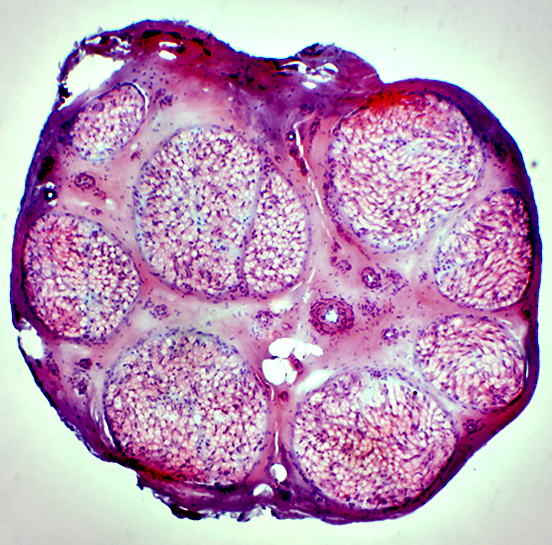 H&E stain Normal Endoneurium, Perineurium, Epineurium & Vessels |
|
|
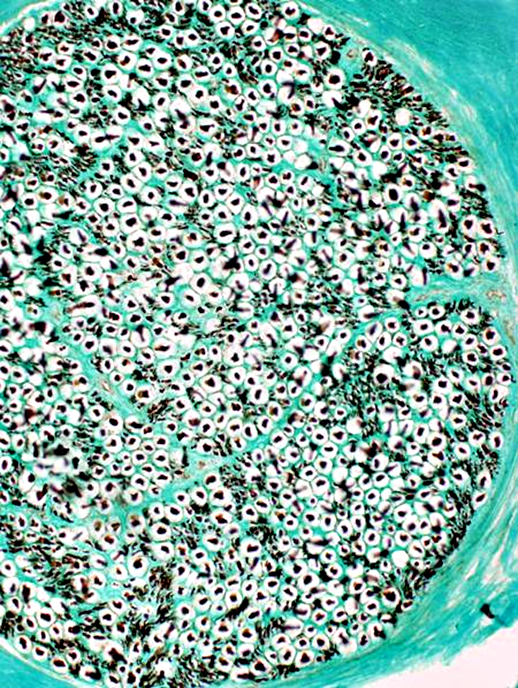
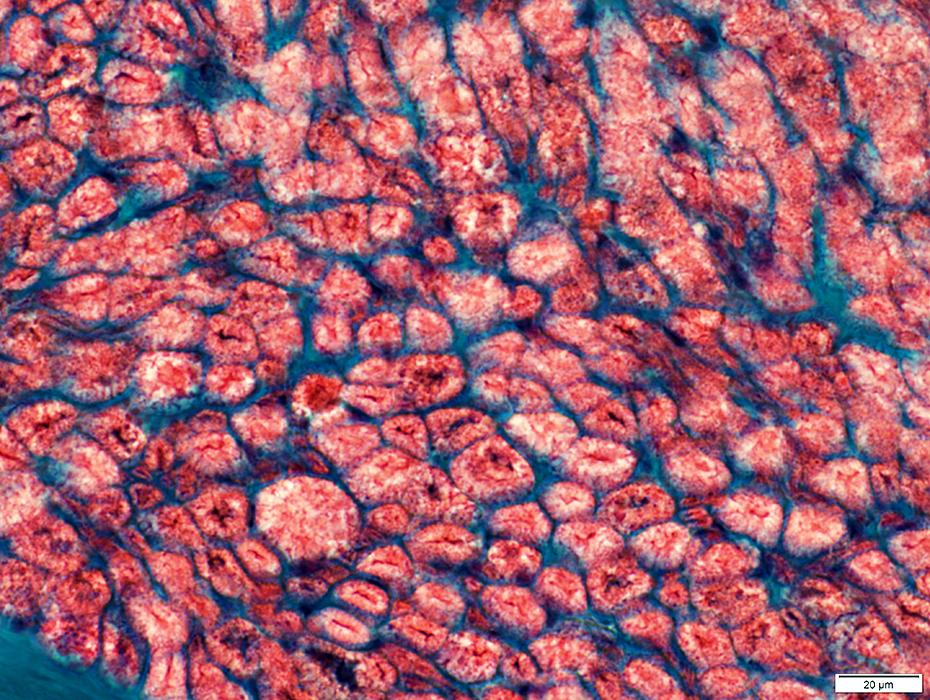
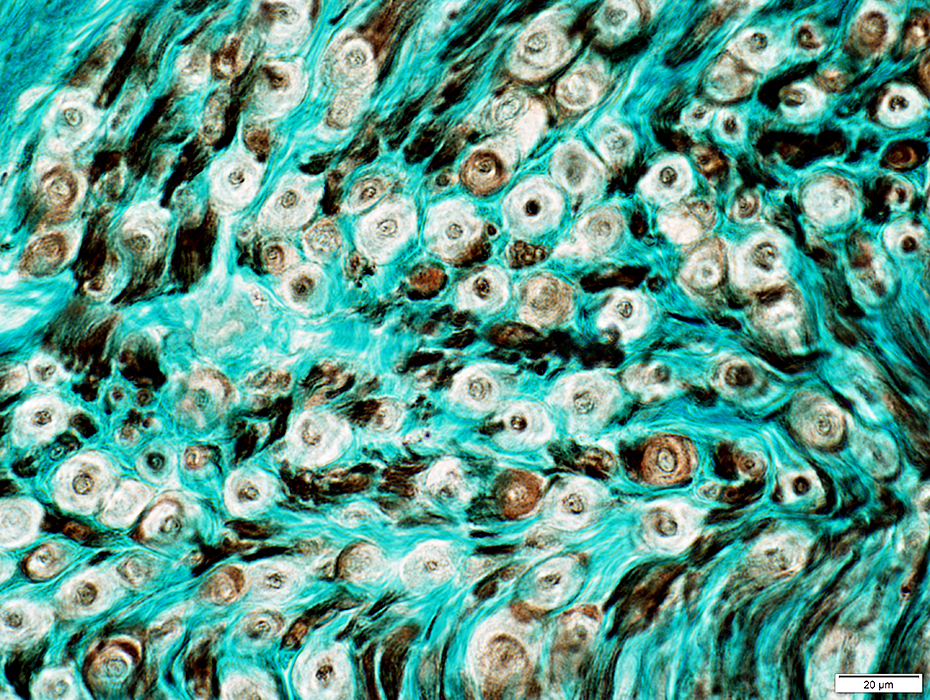
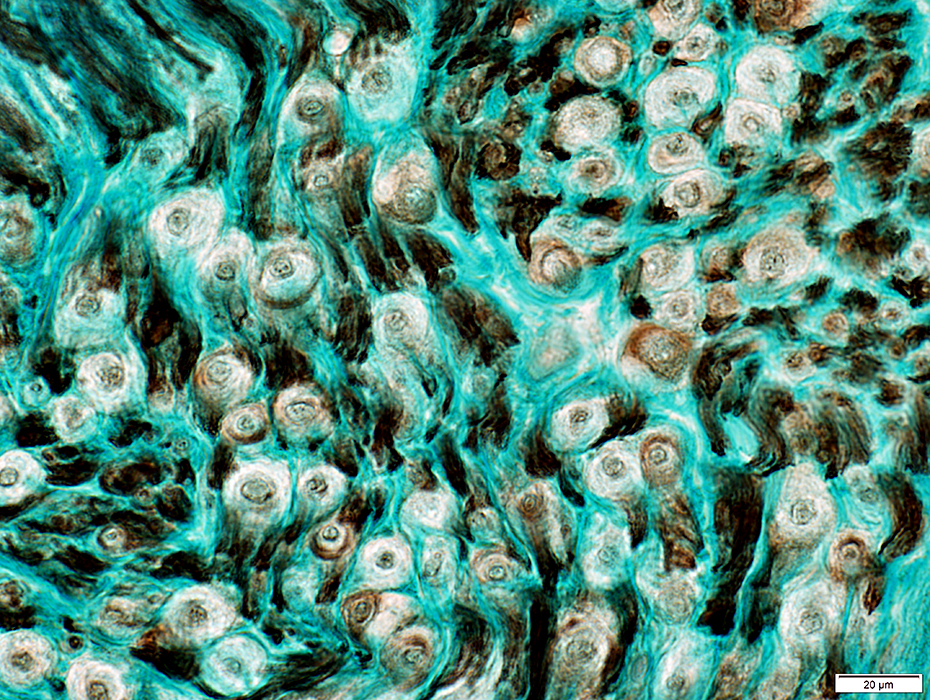
Nerve fascicles Contain normal numbers of myelinated axons in endoneurium 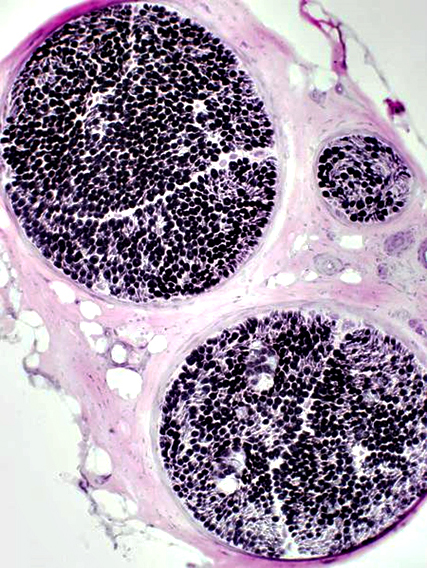 VvG stain |
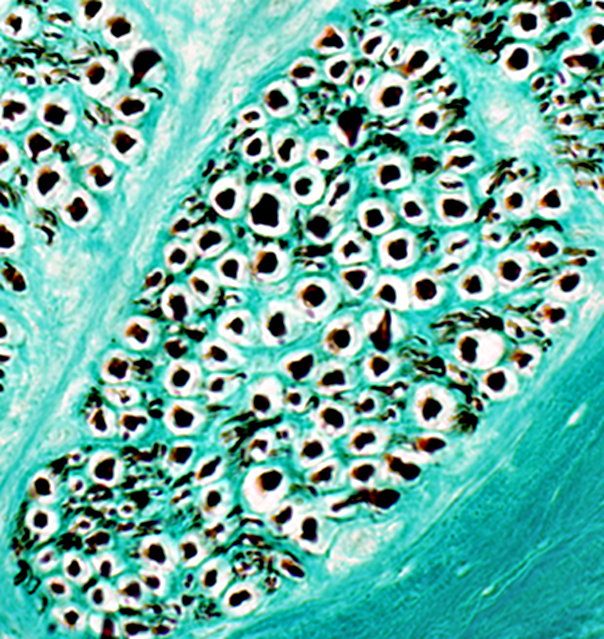
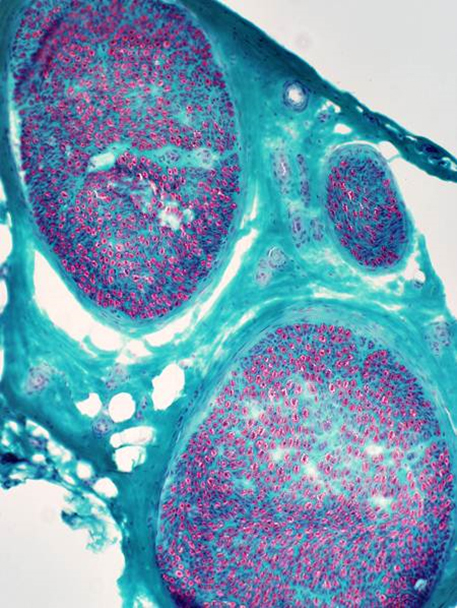 Gomori trichrome stain |
 VvG stain |
 H&E stain |
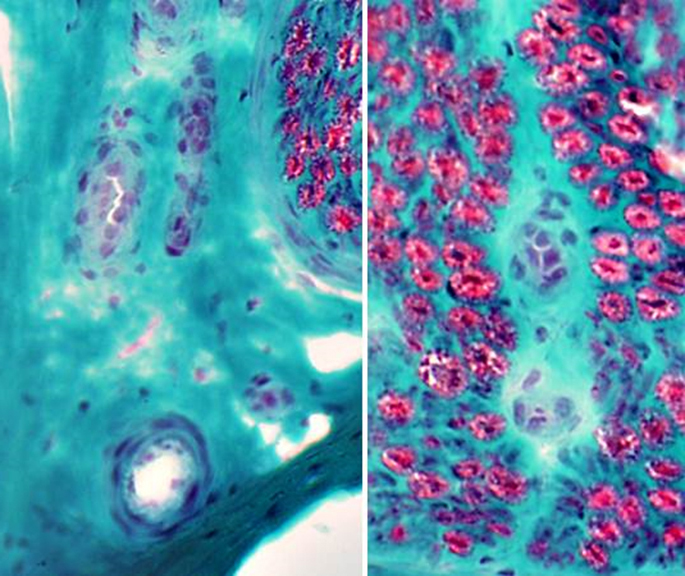
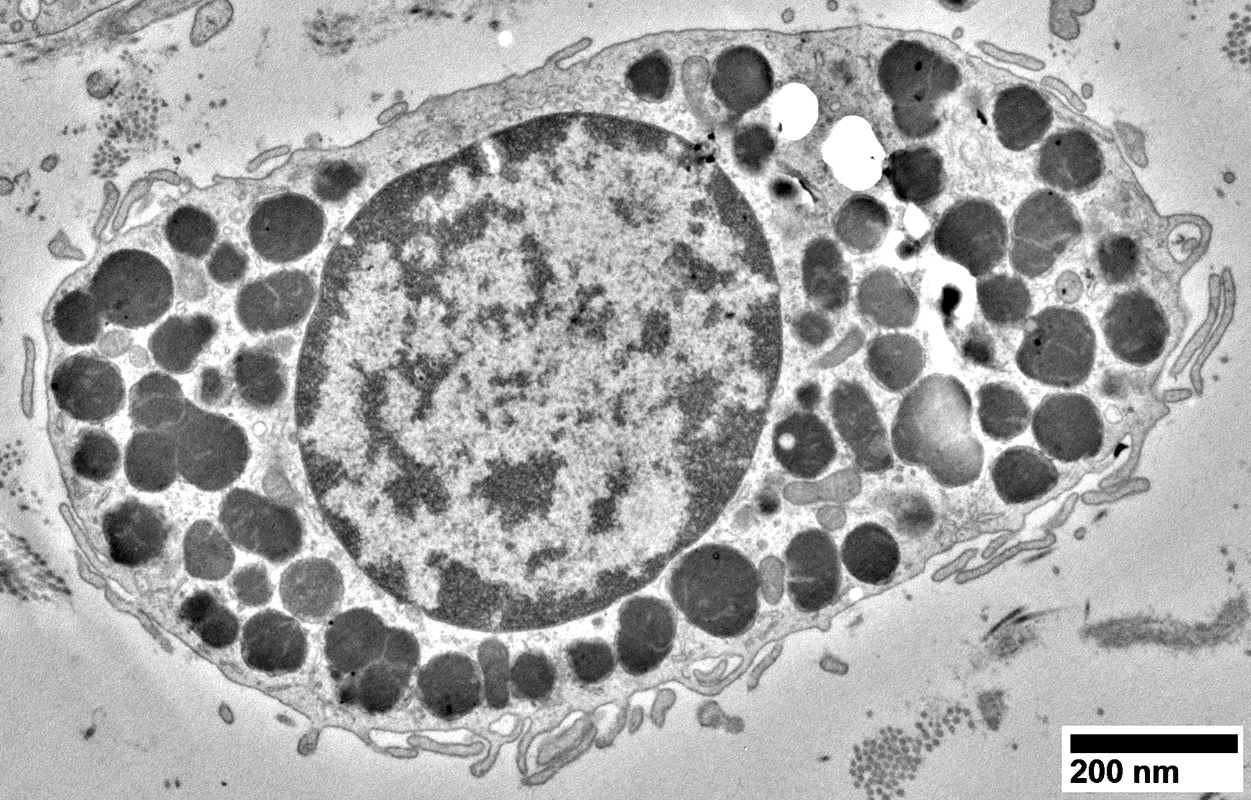
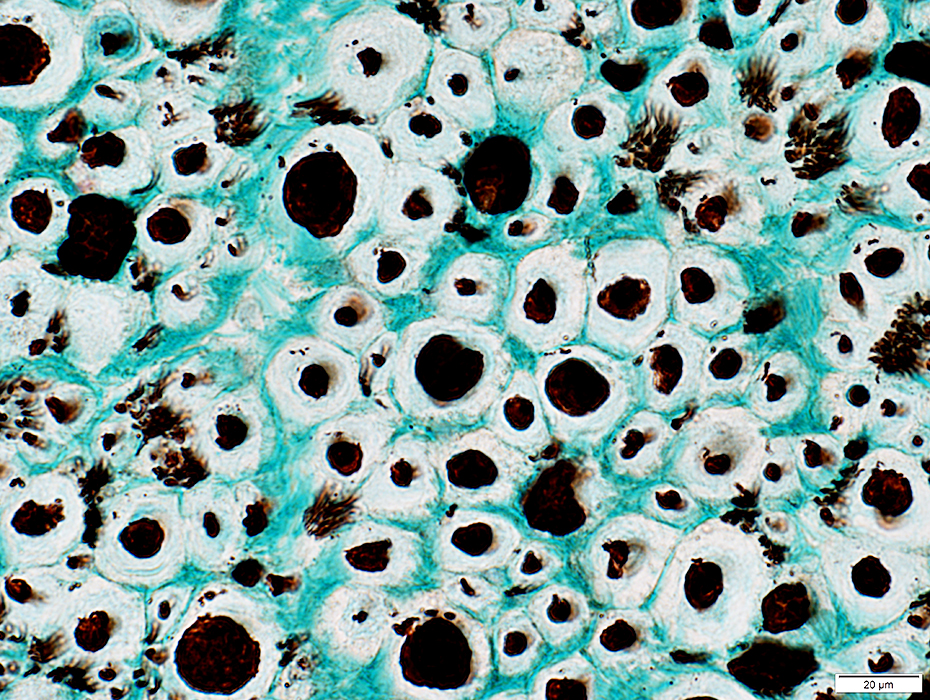
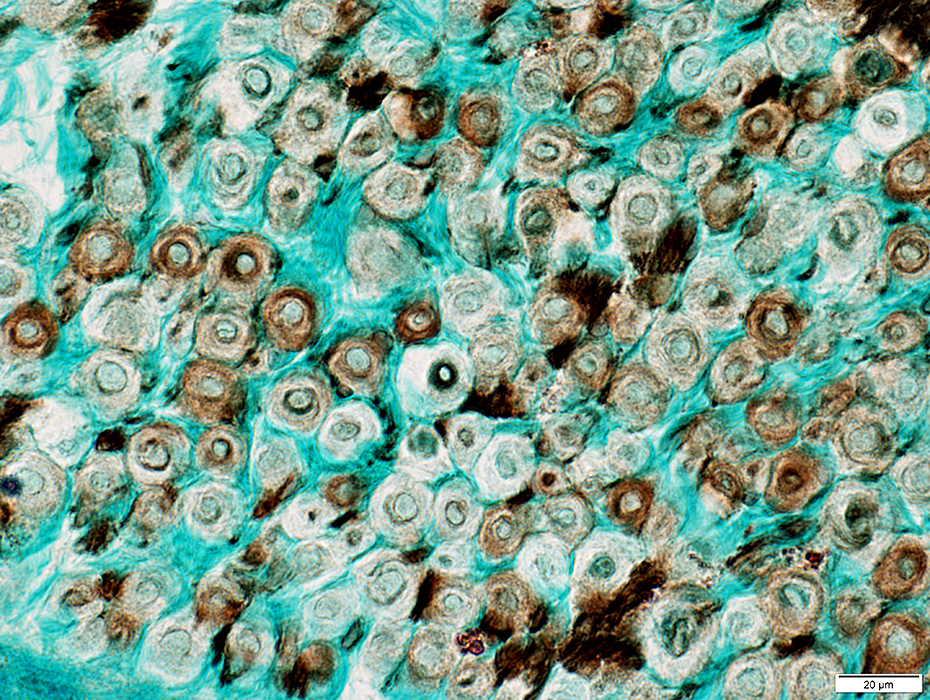
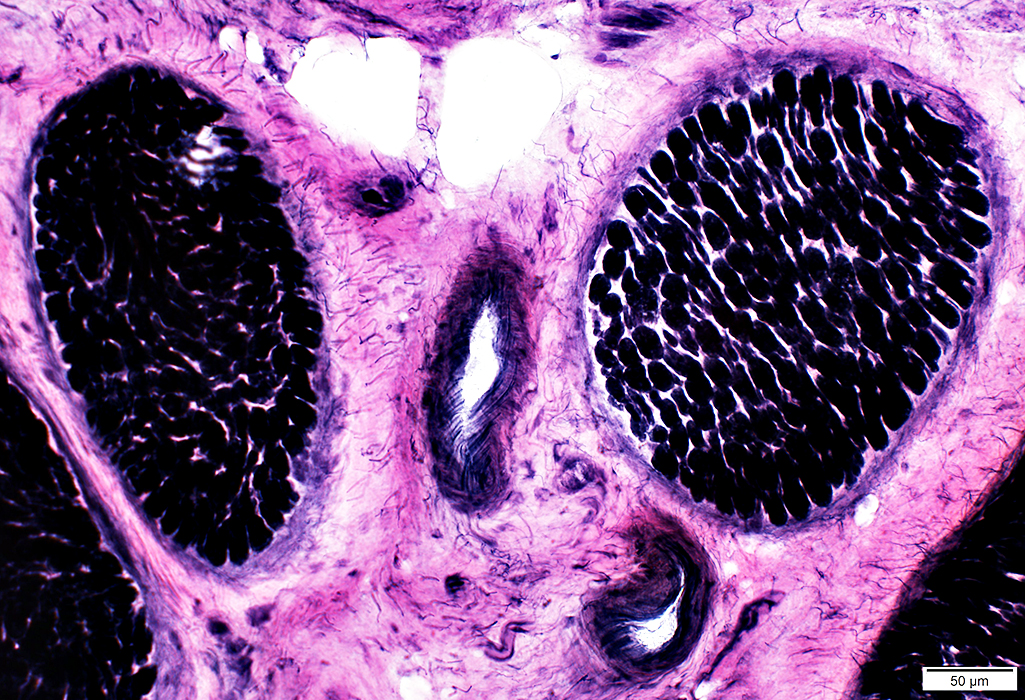
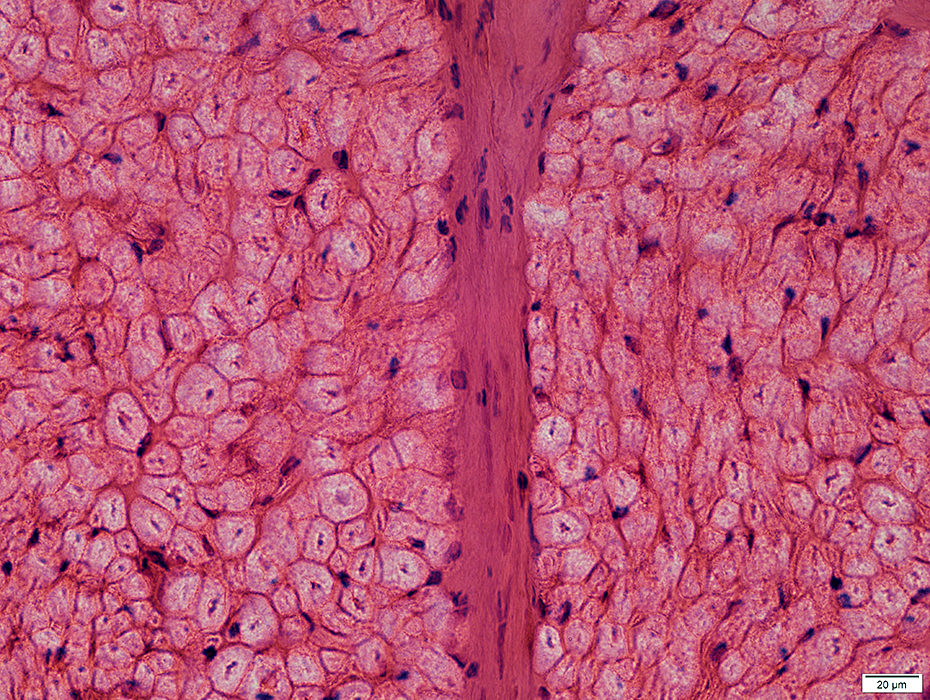
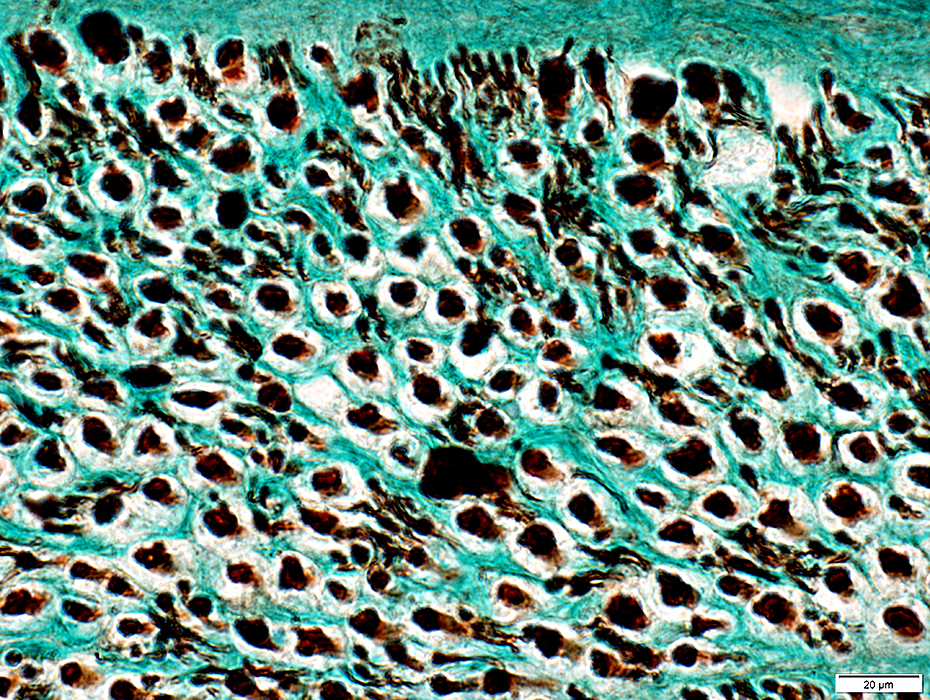
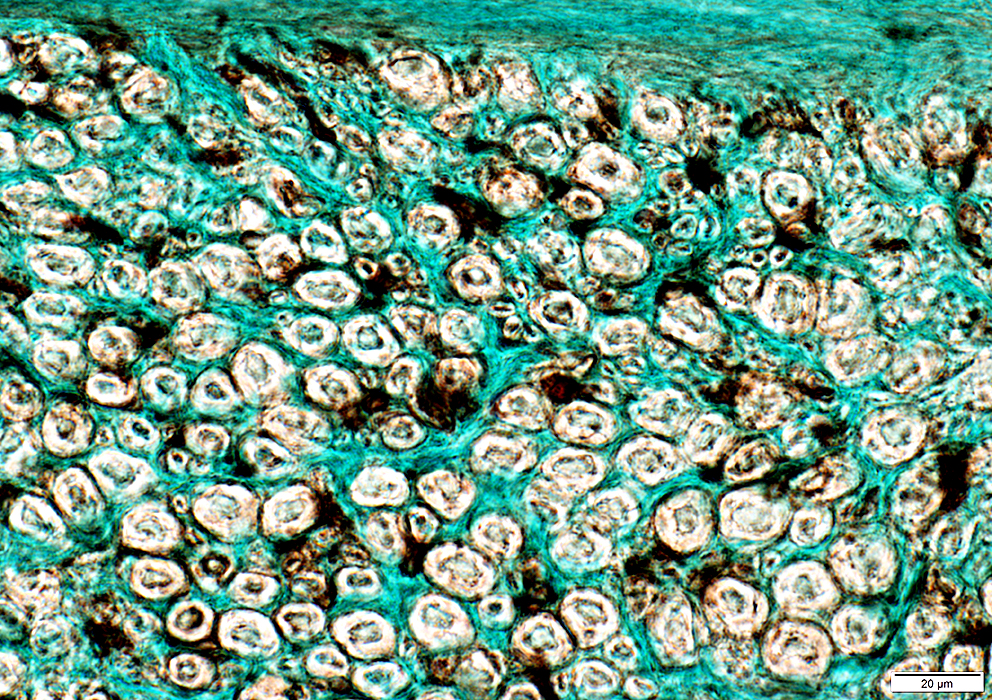
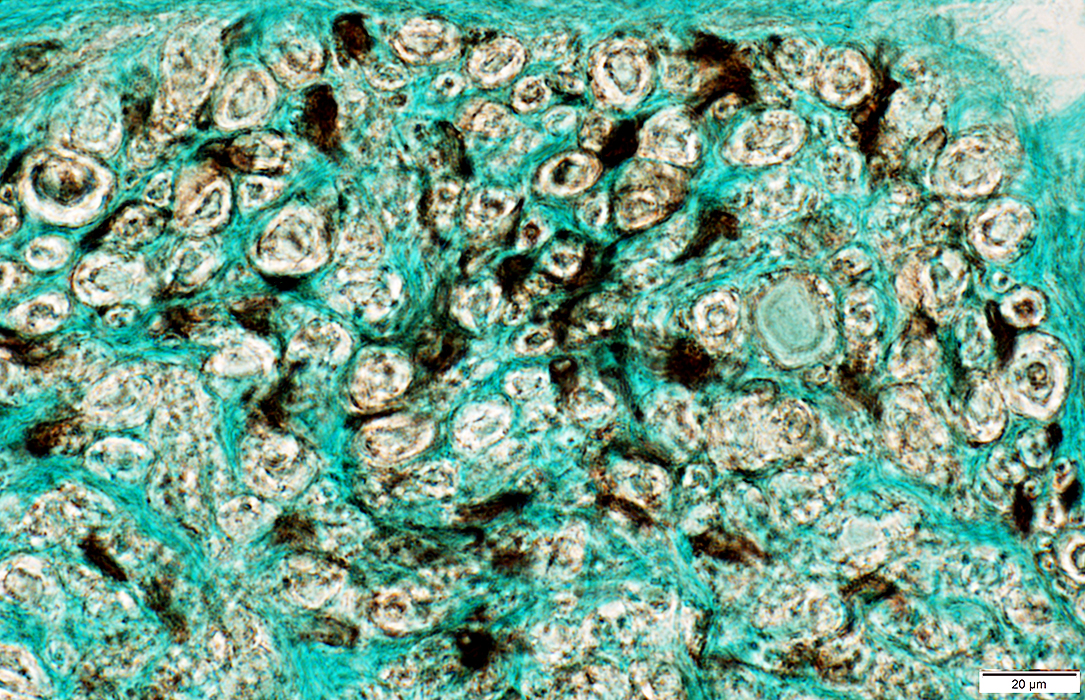
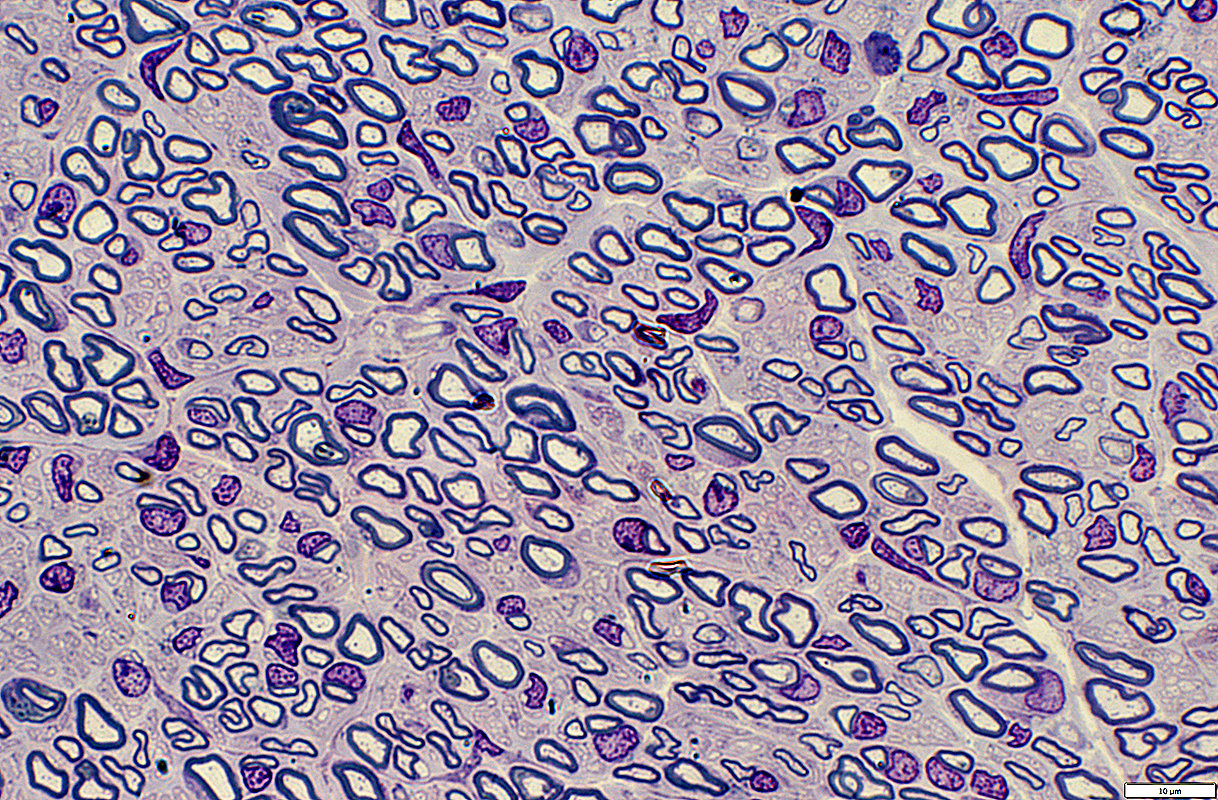
Nerve (Sural): Axons
|
Large & Small axons in endoneurium
Large axons: Surrounded by clear myelin halos
Small axons: Clustered among large myelinated axons
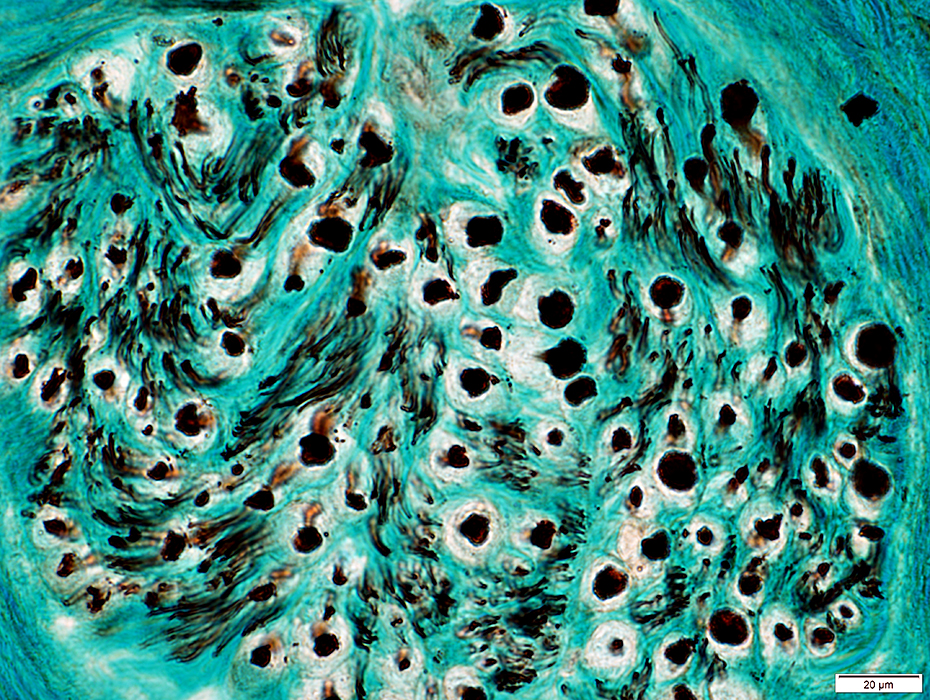 Neurofilament stain |
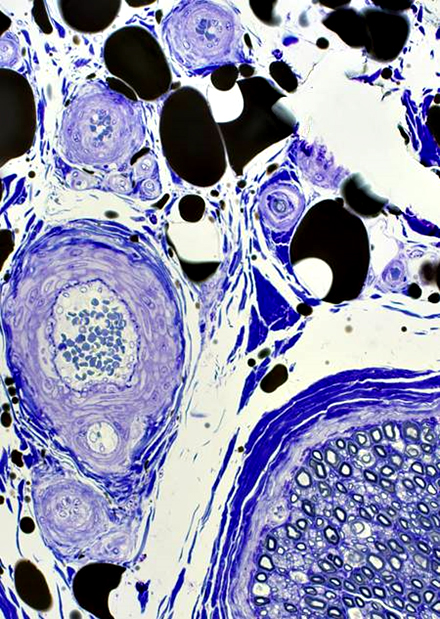
 Toluidine blue stain |
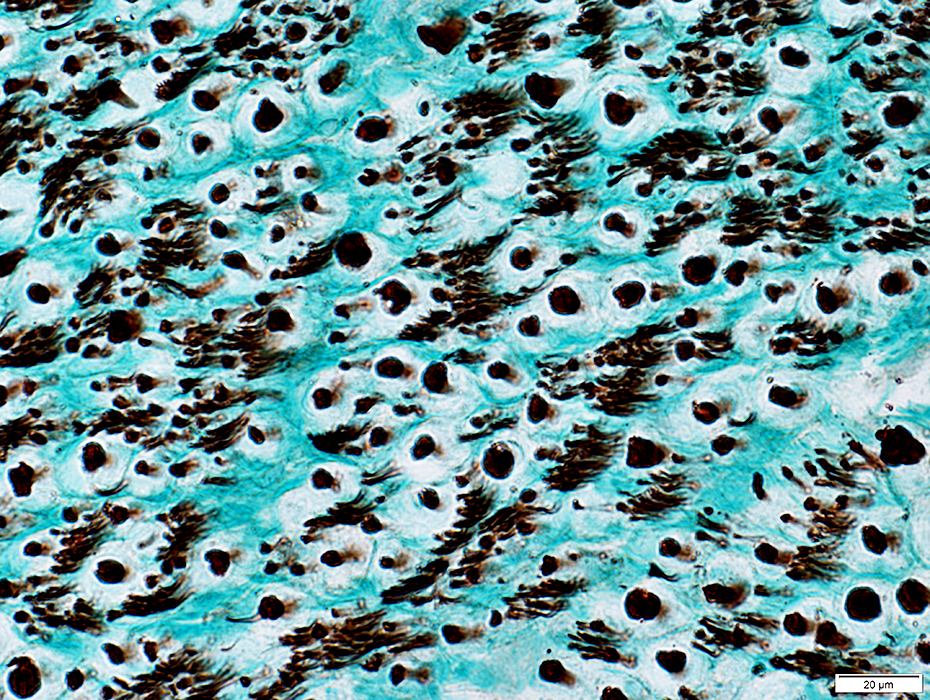
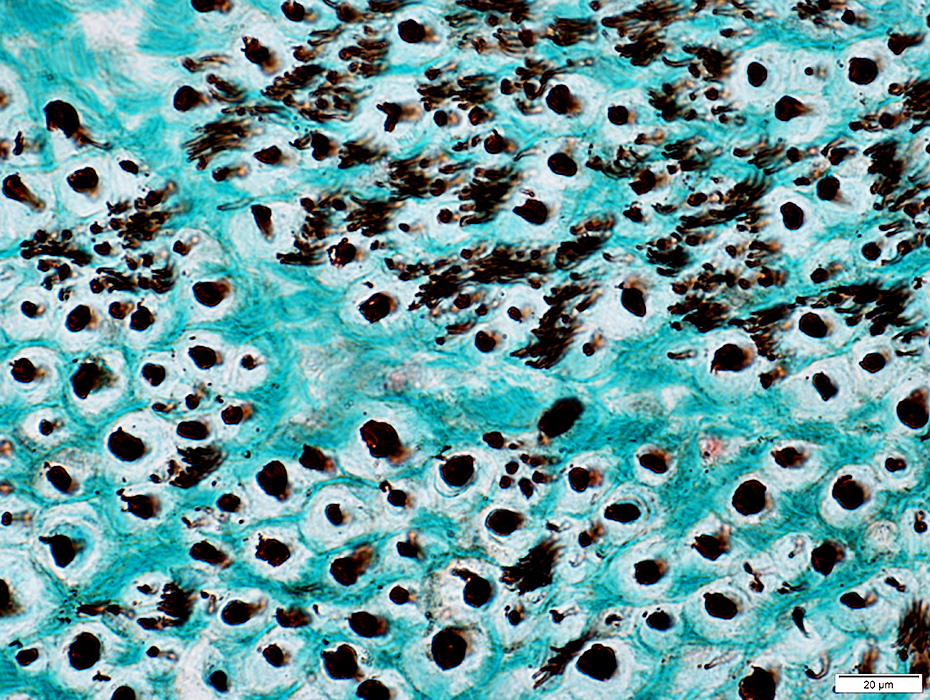
• Large: Thick myelin sheath
• Intermediate: Thin myelin sheath
• Small: Unmyelinated axons
• Compare to: Infant
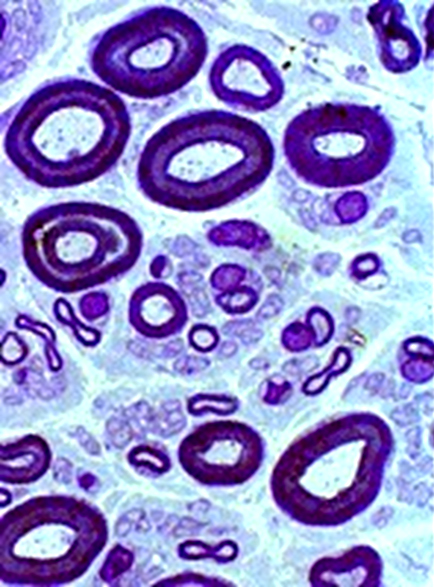 Toluidine Blue stained plastic section |
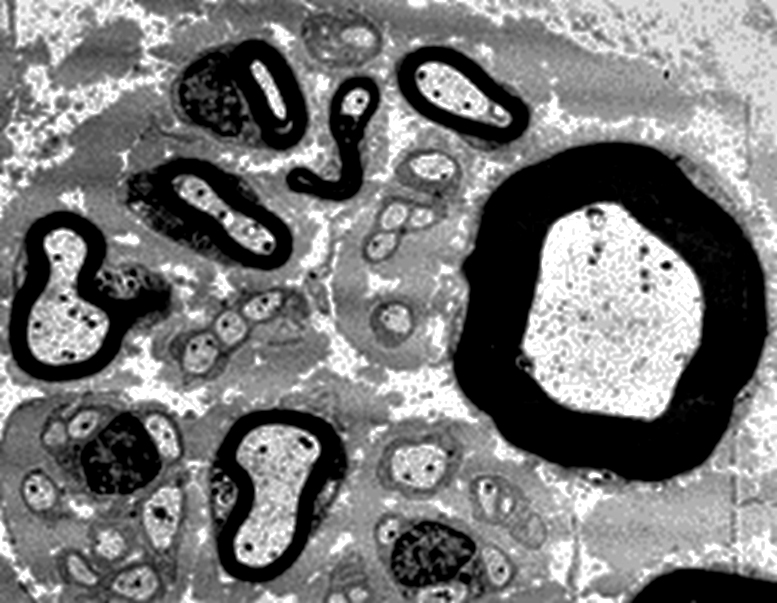 Electron micrograph (Robert E Schmidt MD) |
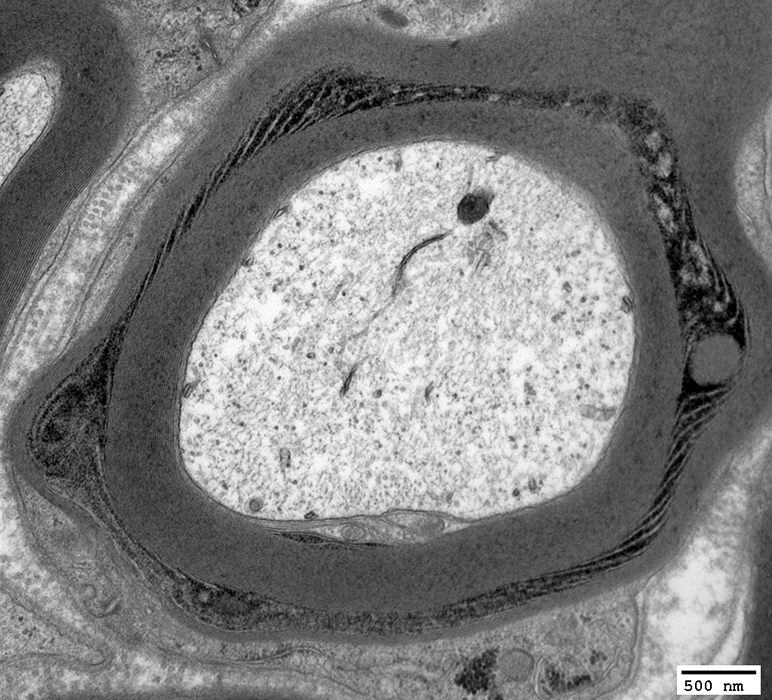
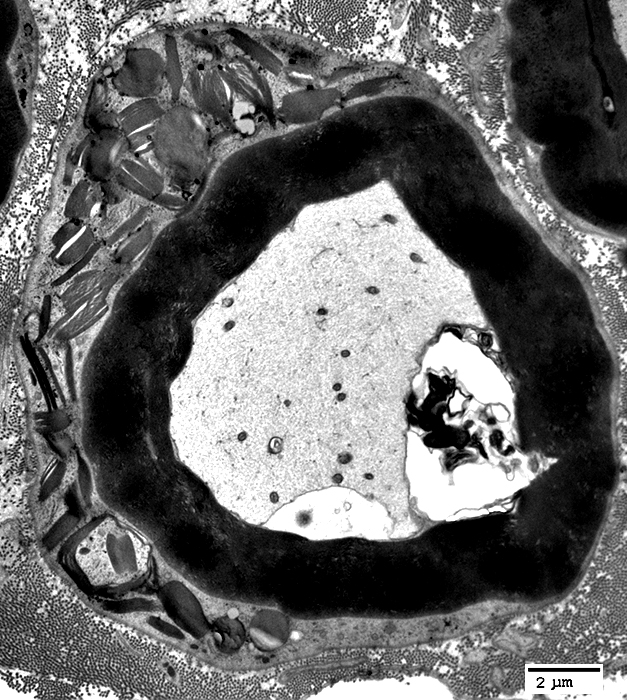
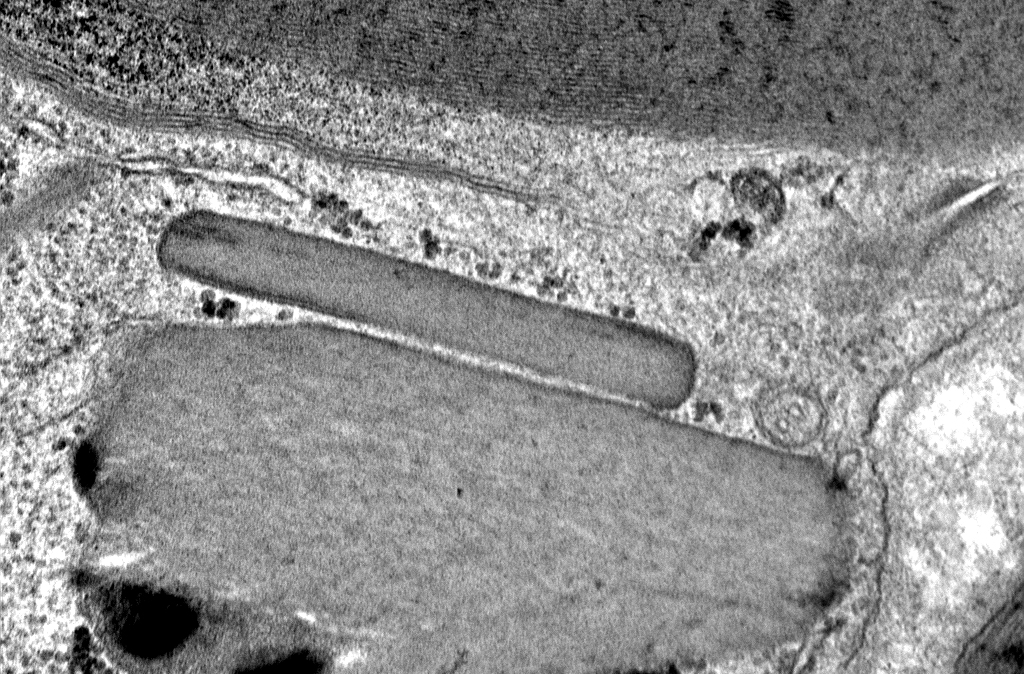
Myelinated Axon
 From Robert E Schmidt MD |
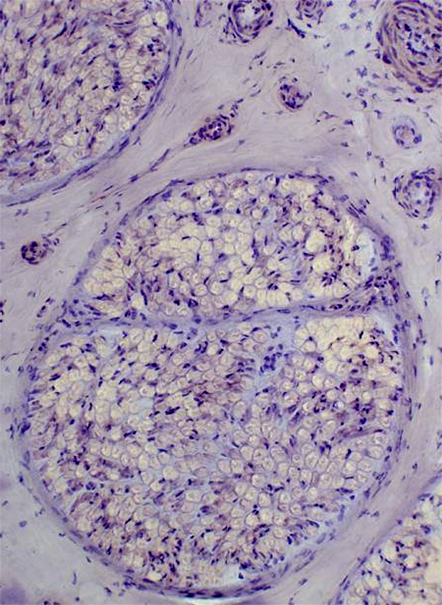
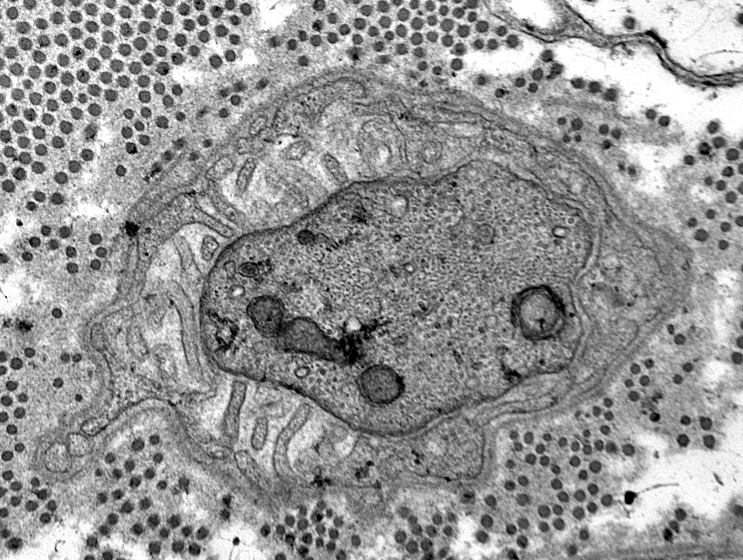
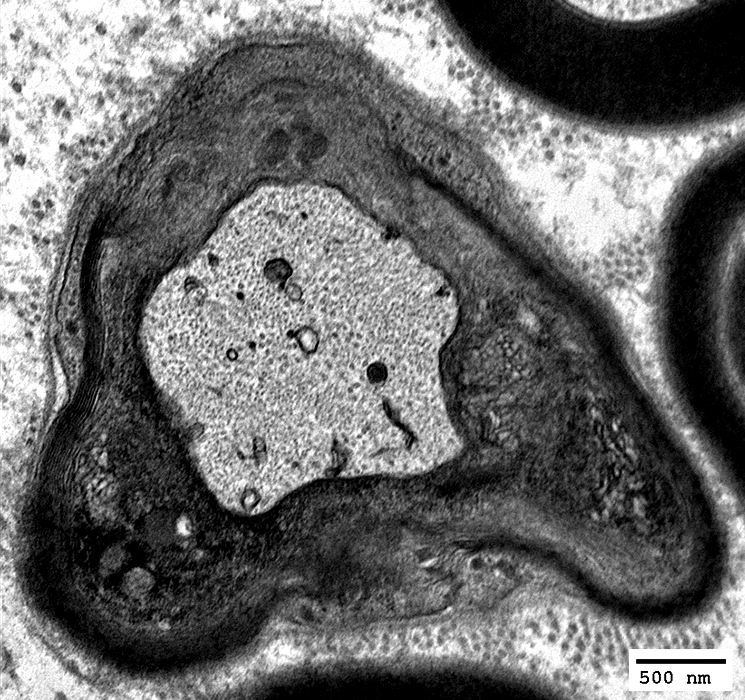
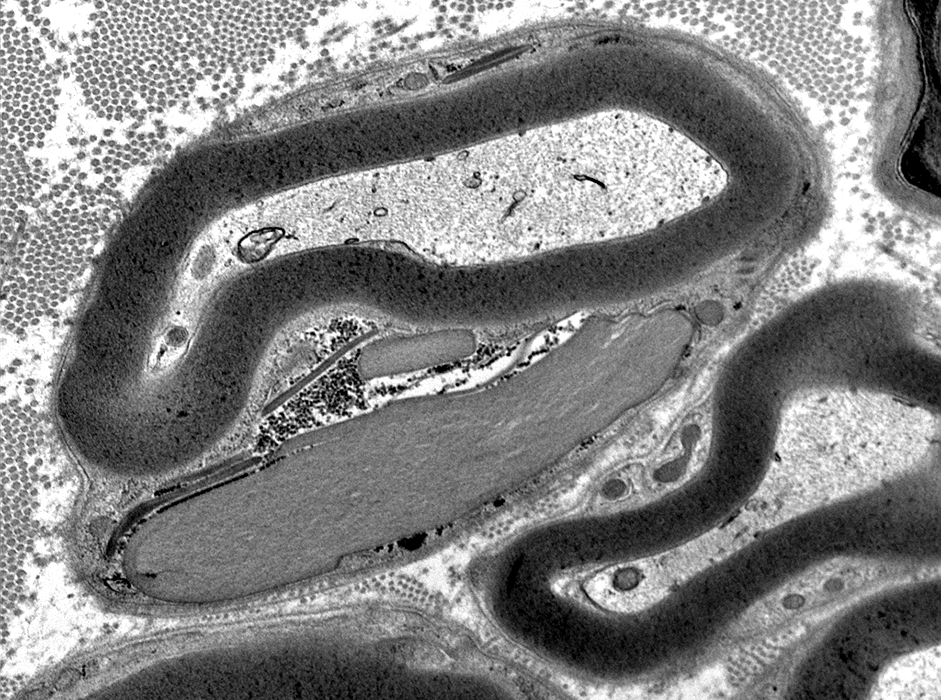
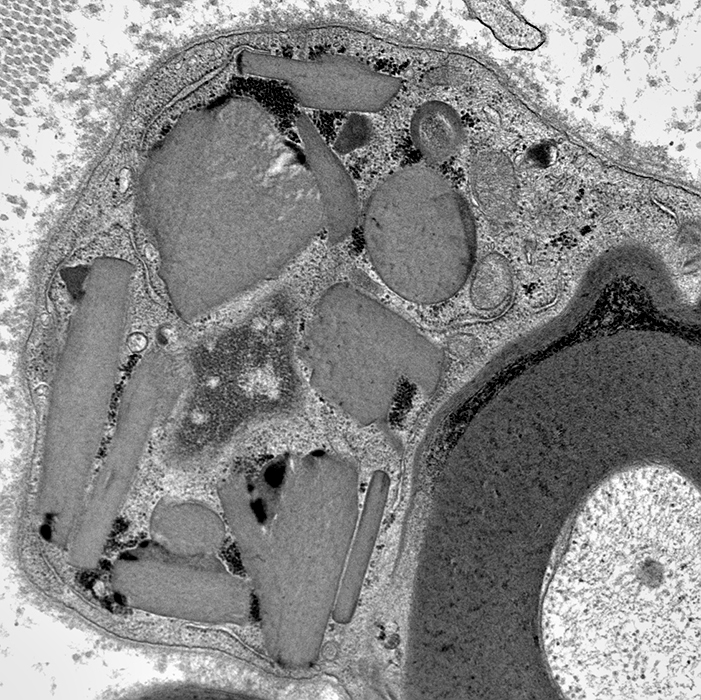
Small, Unmyelinated Axons
 From Robert E Schmidt MD |
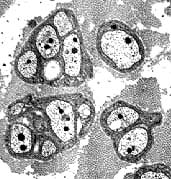 Electron micrographs (Robert E Schmidt MD) Unmyelinated axons Surrounded by Schwann cells |
Several are often surrounded by processes from single Schwann cell

|
Singletons
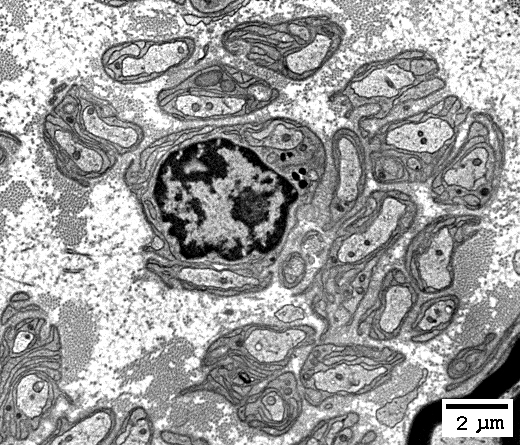
|
Singletons: 1 axon/Schwann cell
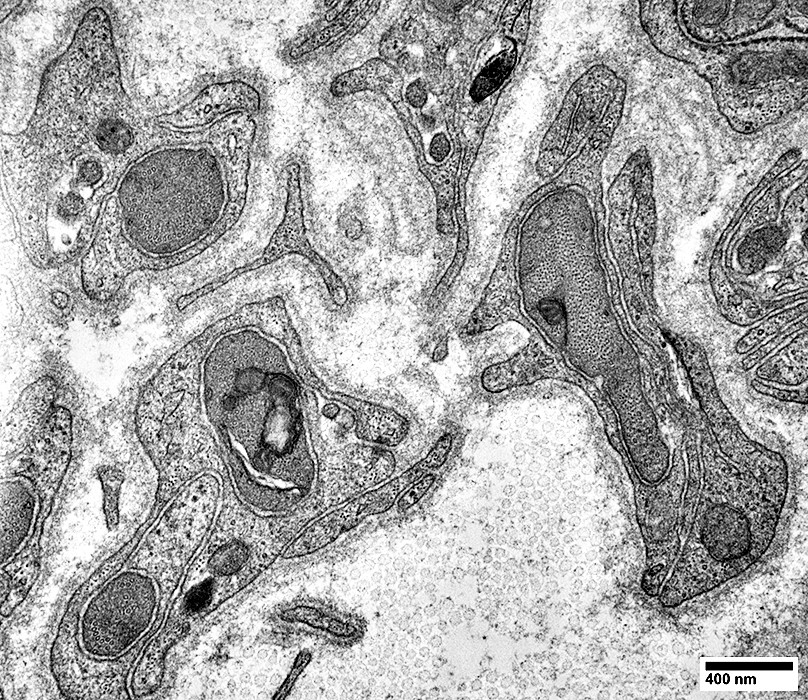
|
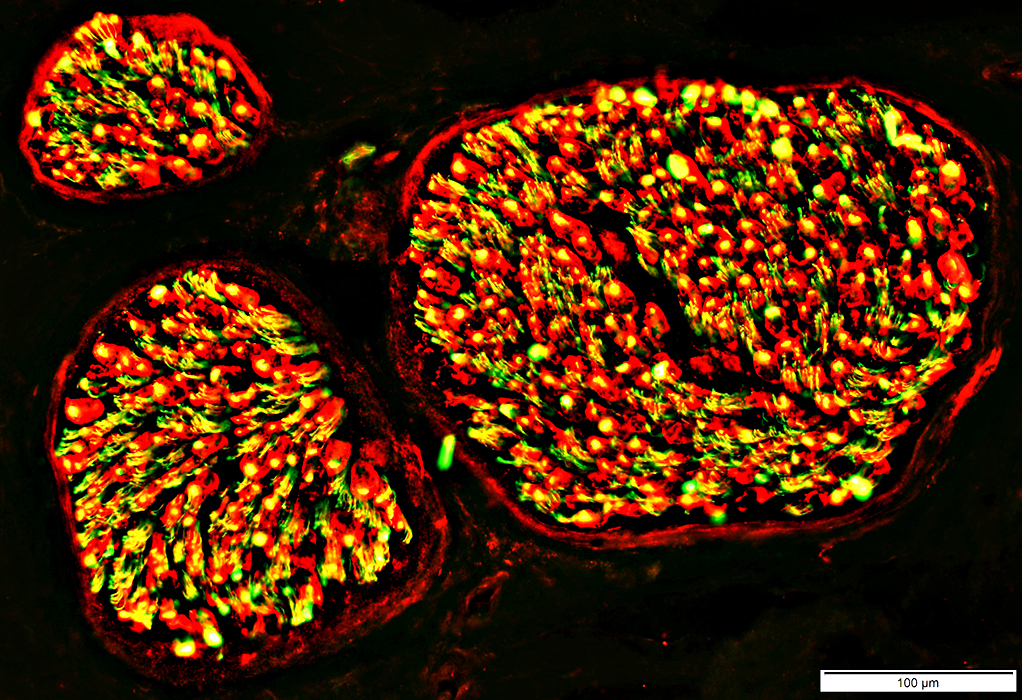
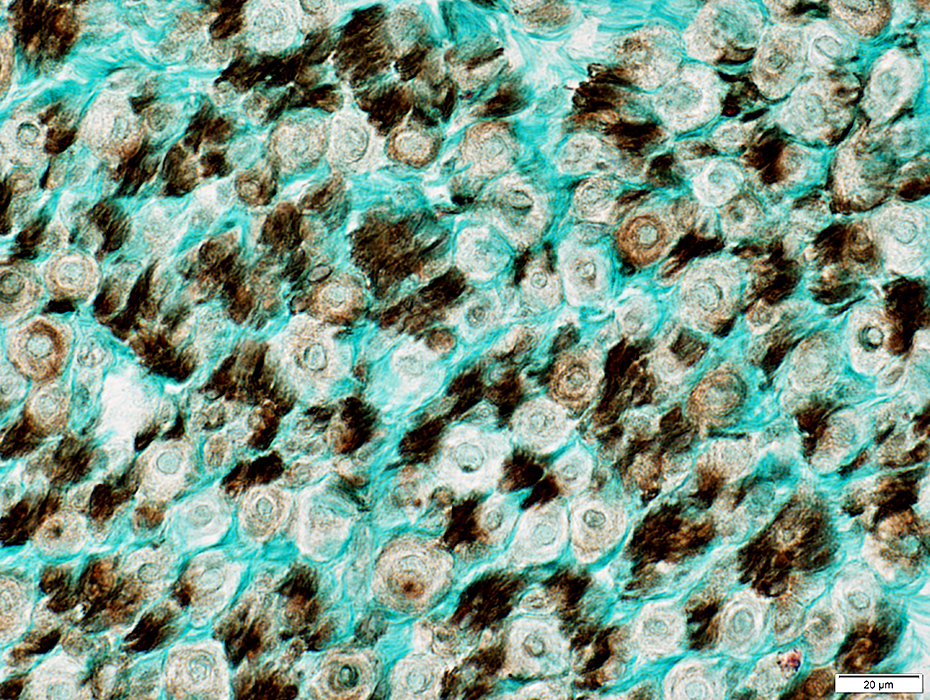
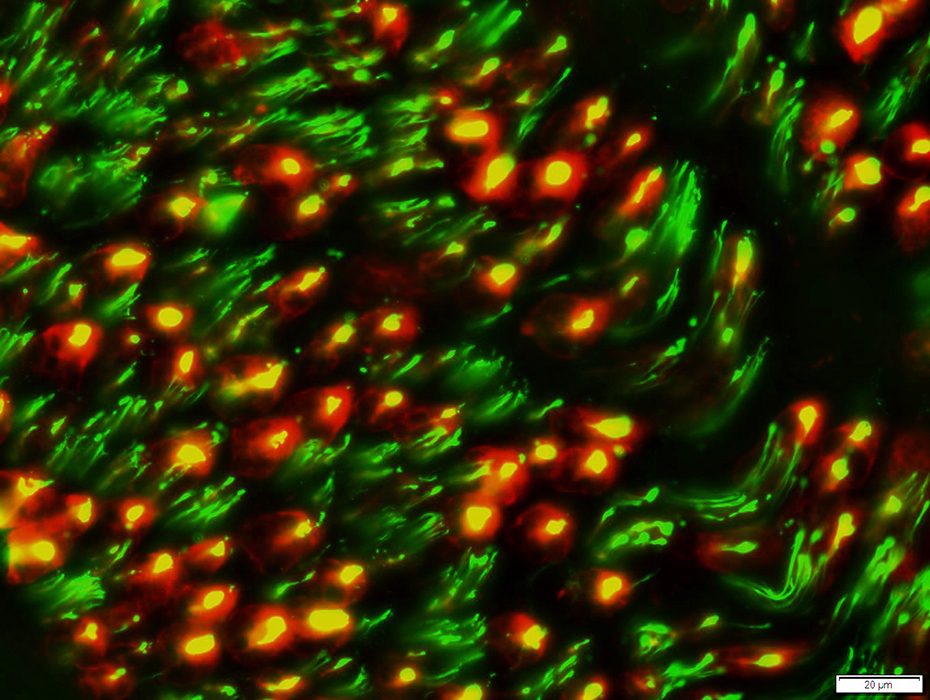
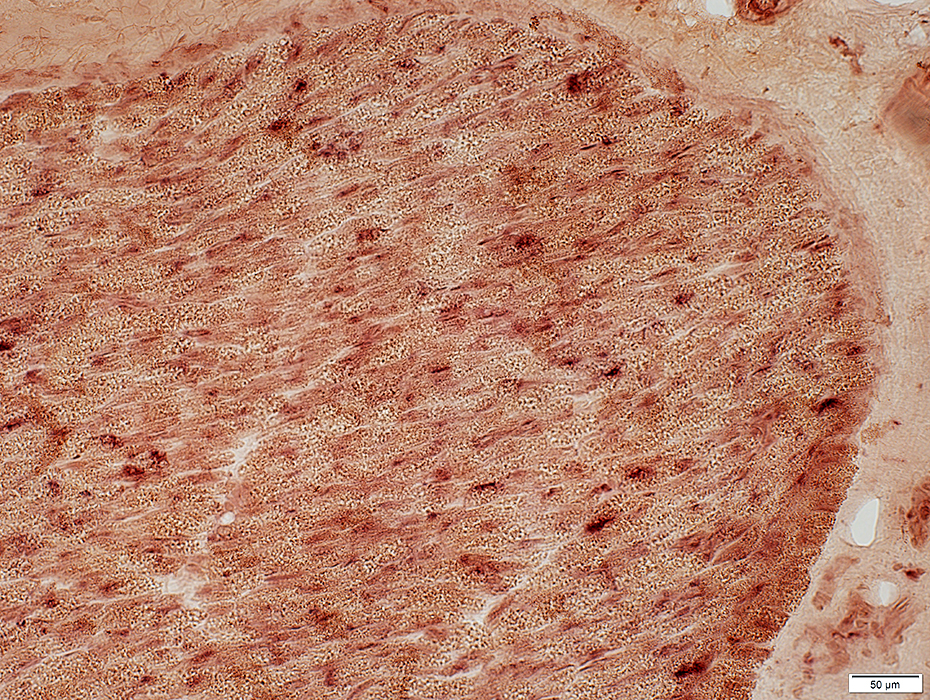
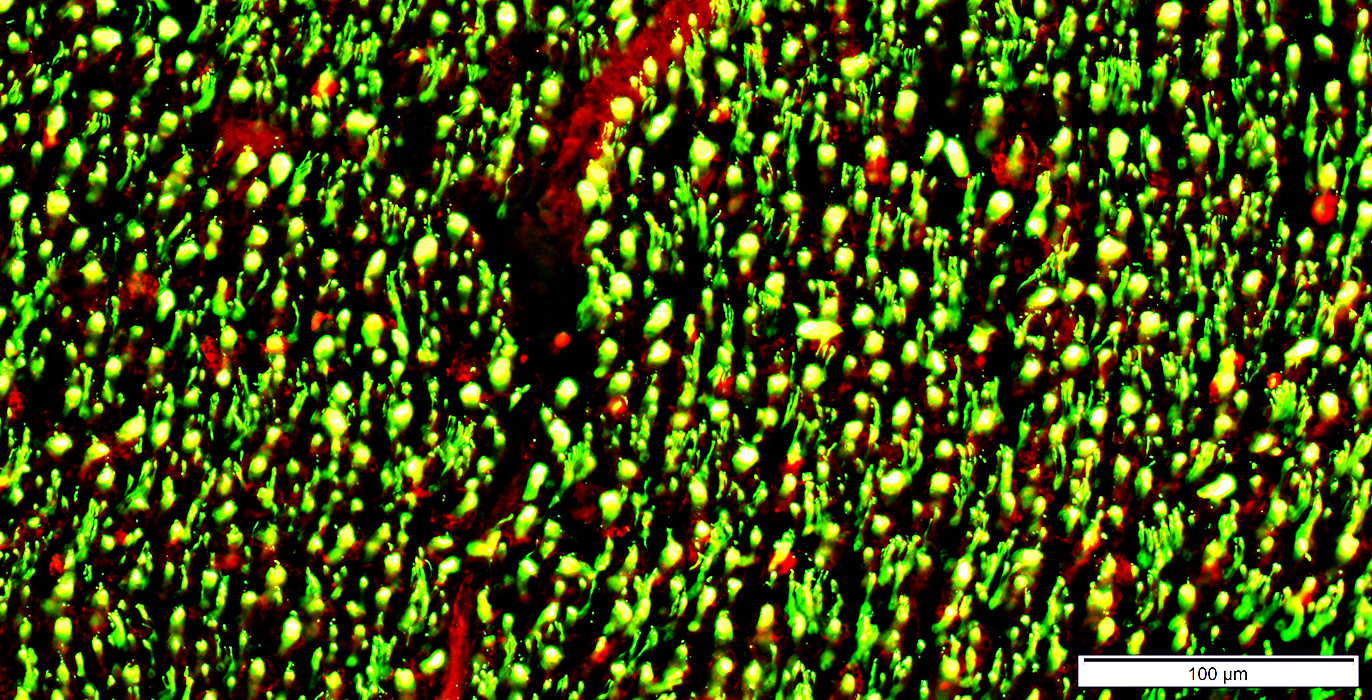
Nerve (Sural): Schwann cells, Non-myelinating
 NCAM1 stain |
NCAM is abundant in non-myelinating (Remak) Schwann cells that surround Unmyelinated axons
NCAM is also present in
Adaxonal Schwann cell cytoplasm around myelinated axons
Myelin sheaths of some larger axons
Myelinated axons: Are generally smaller than in the more proximal sciatic nerve
 NCAM stain |
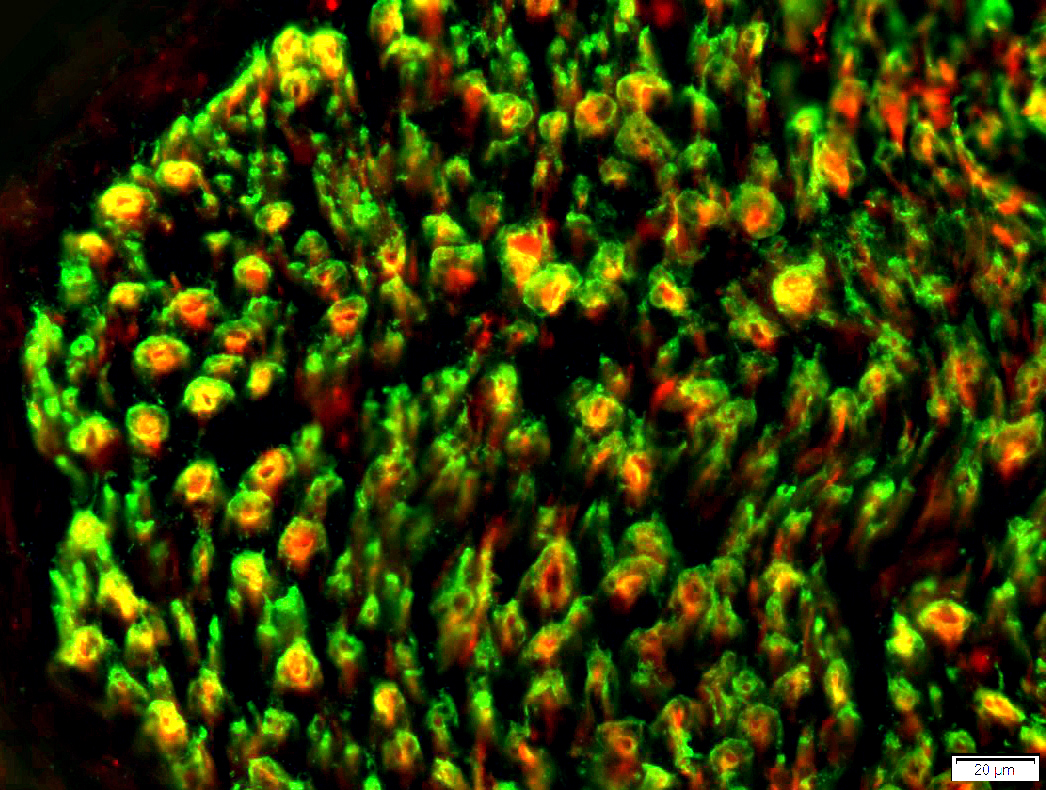
 Neurofilament stain (Green) NCAM stain (Red) Overlap (Yellow) |
Surrounds most small unmyelinated axons (Yellow)
Not present around large, myelinated axons (Green)
May occur in the center of larger axons (Yellow)
See: Loss of small axons
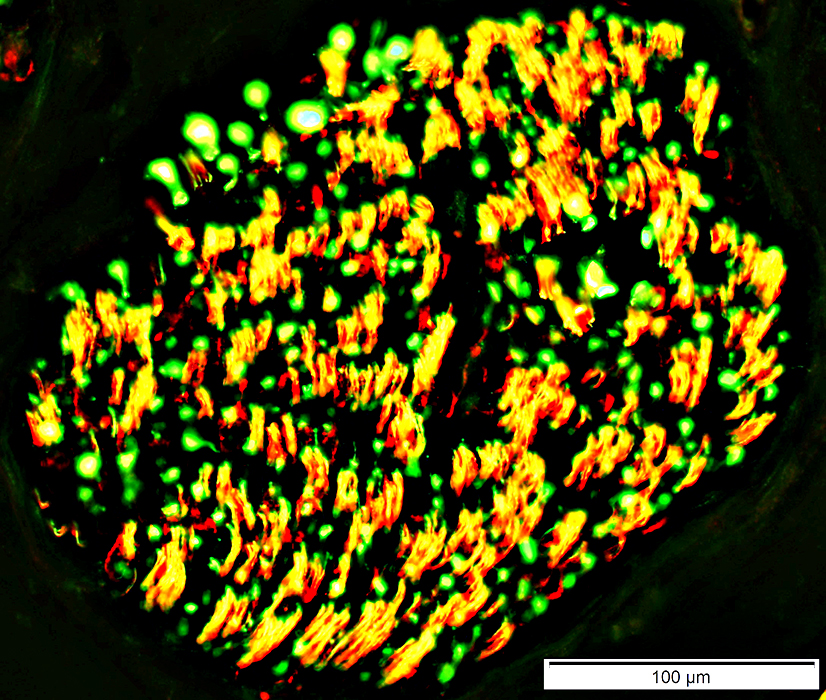 Neurofilament stain (Green) NCAM stain (Red) Overlap (Yellow) |
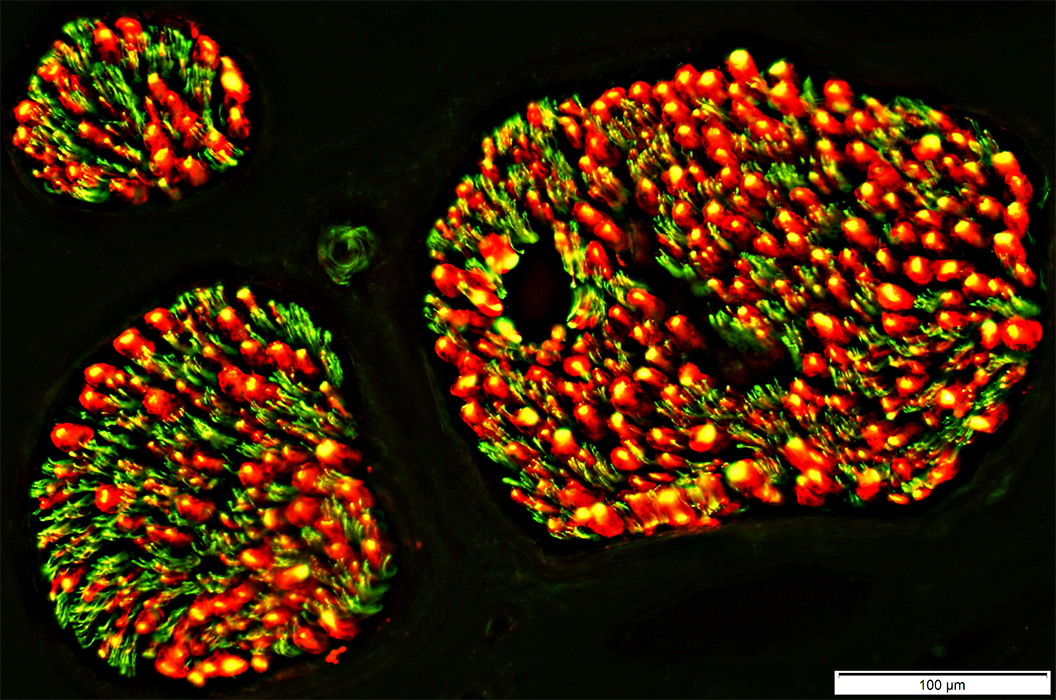
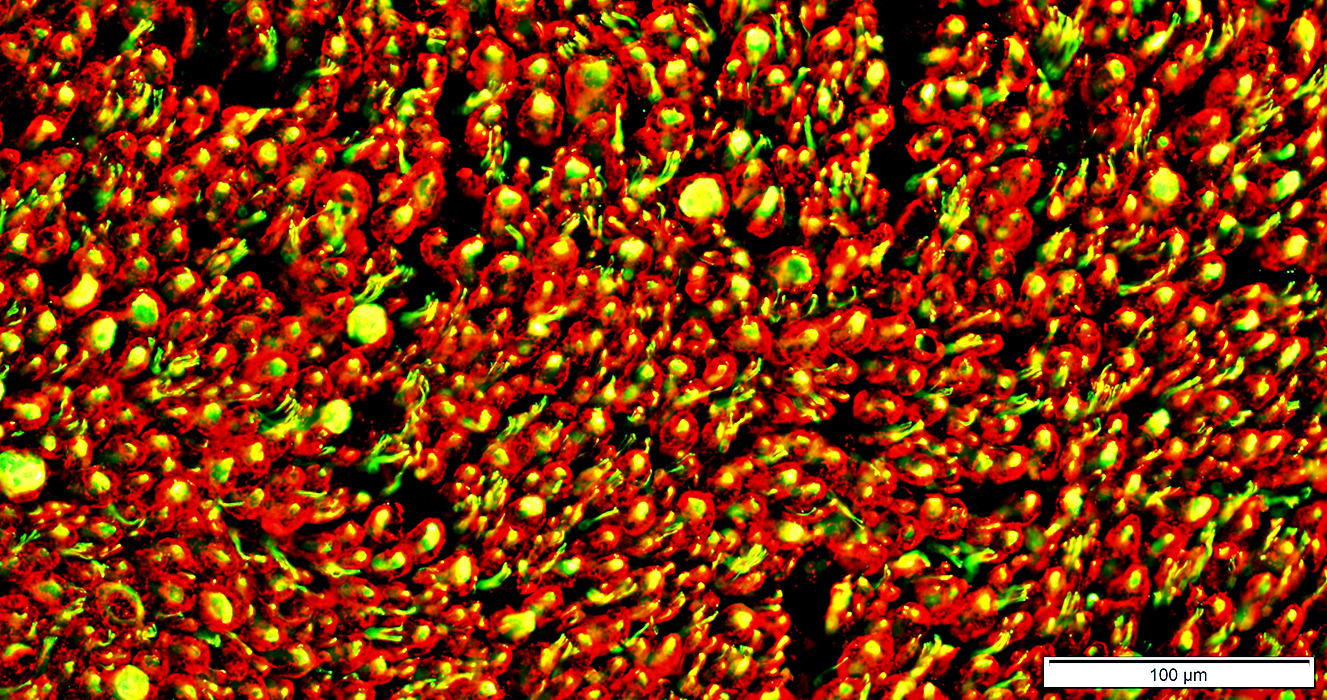
NCAM & P0
Normal: Mostly present in different endoneurial cells
NCAM
Non-myelinating Schwann cells (Green)
Small amounts in non-compacted areas of myelinating Schwann cell cytoplasm (Yellow)
P0: Myelin & Myelinating Schwann cell cytoplasm (Red)
Schwann Cell Pathology
Büngner bands: NCAM & P0 present in same Schwann cells
Onion bulbs
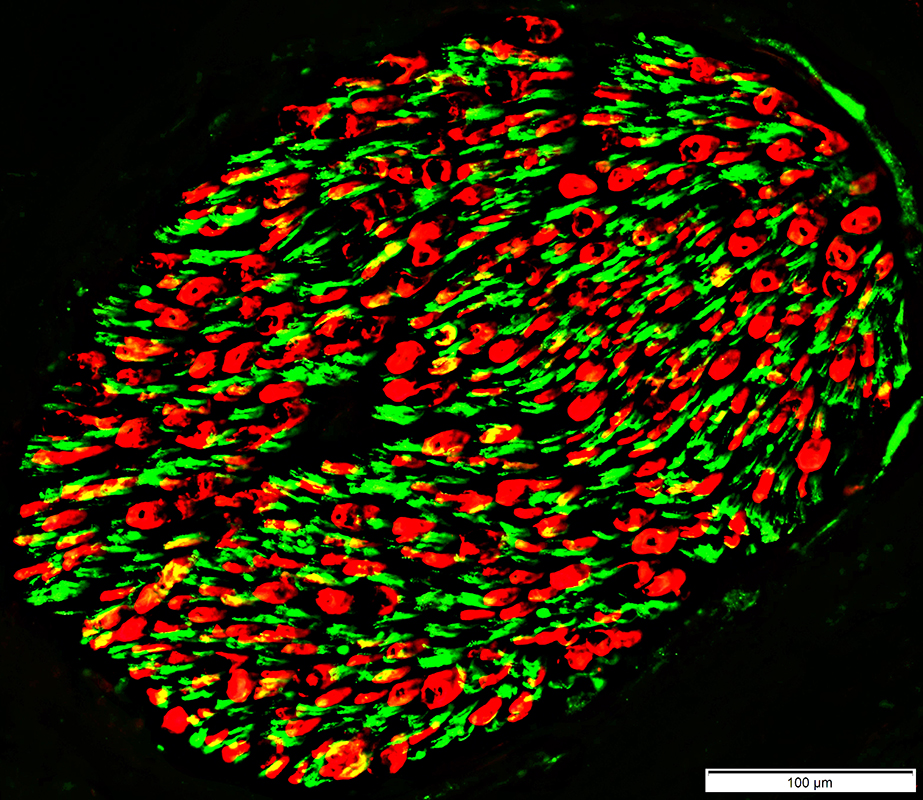 NCAM stain (Green) p0 stain (Red) |
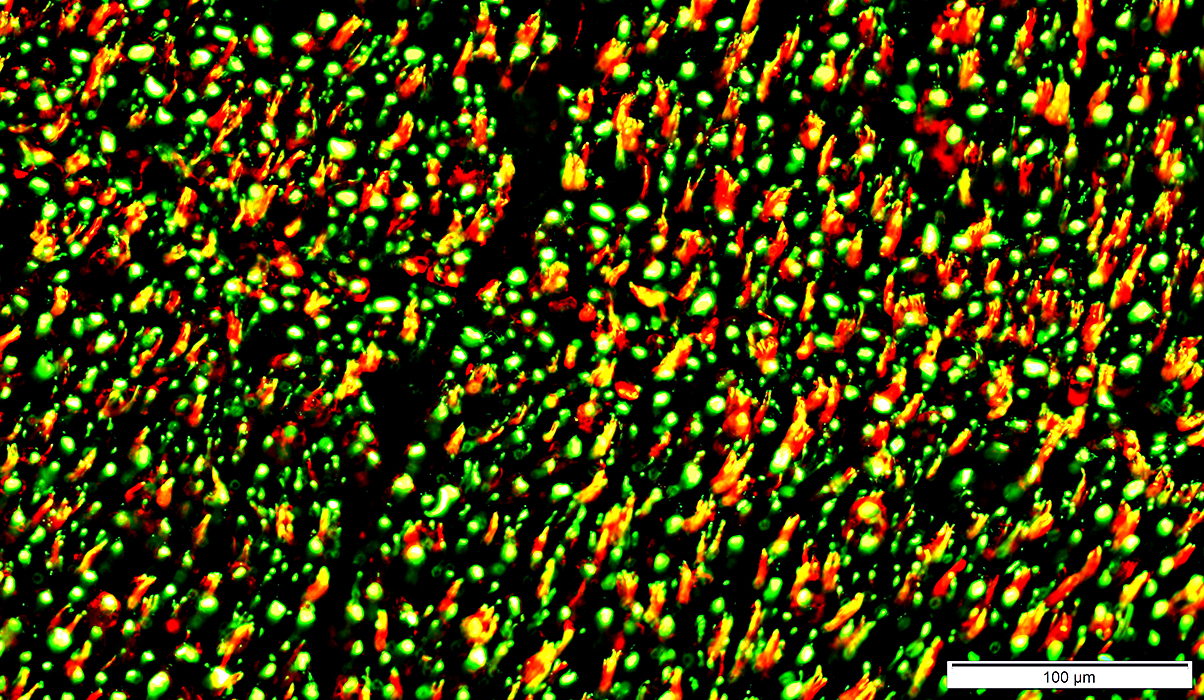
NCAM & MBP
Normal: Mostly present in different endoneurial cells
NCAM
Non-myelinating Schwann cells (Green)
Small amounts in non-compacted areas of myelinating Schwann cell cytoplasm (Yellow)
MBP: In Myelin surrounding larger axons (Red)
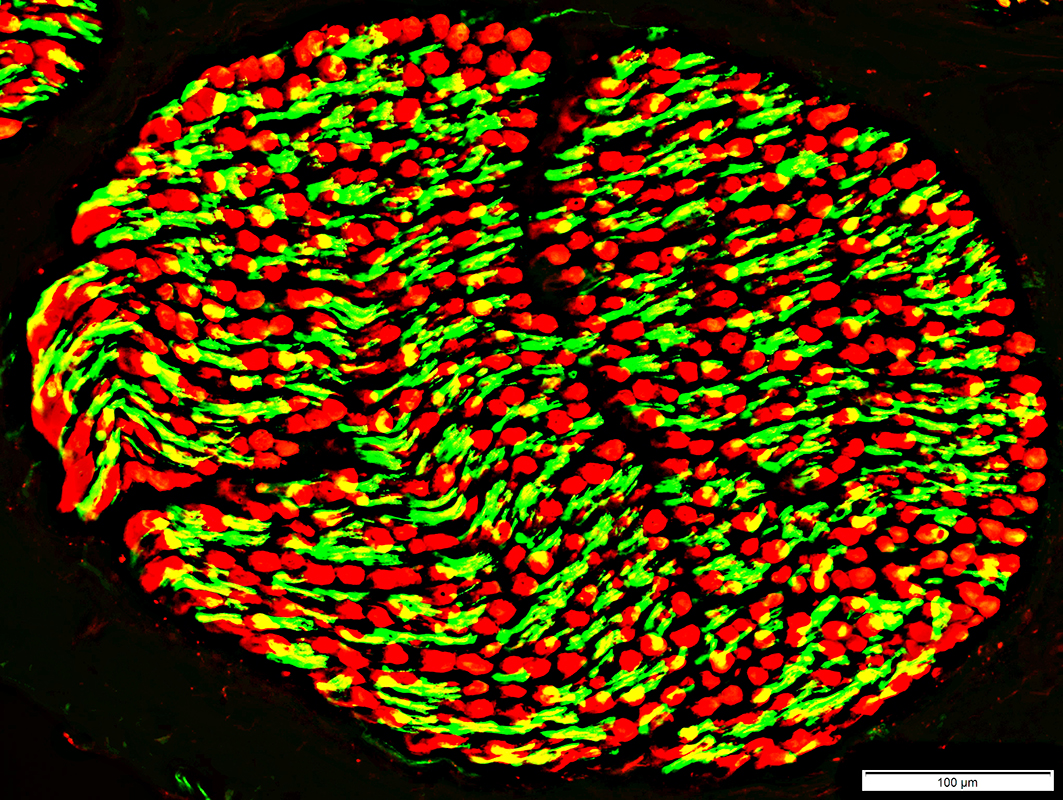 NCAM stain (Green) MBP stain (Red) Epineurial vessels & Supporting cells in endoneurium
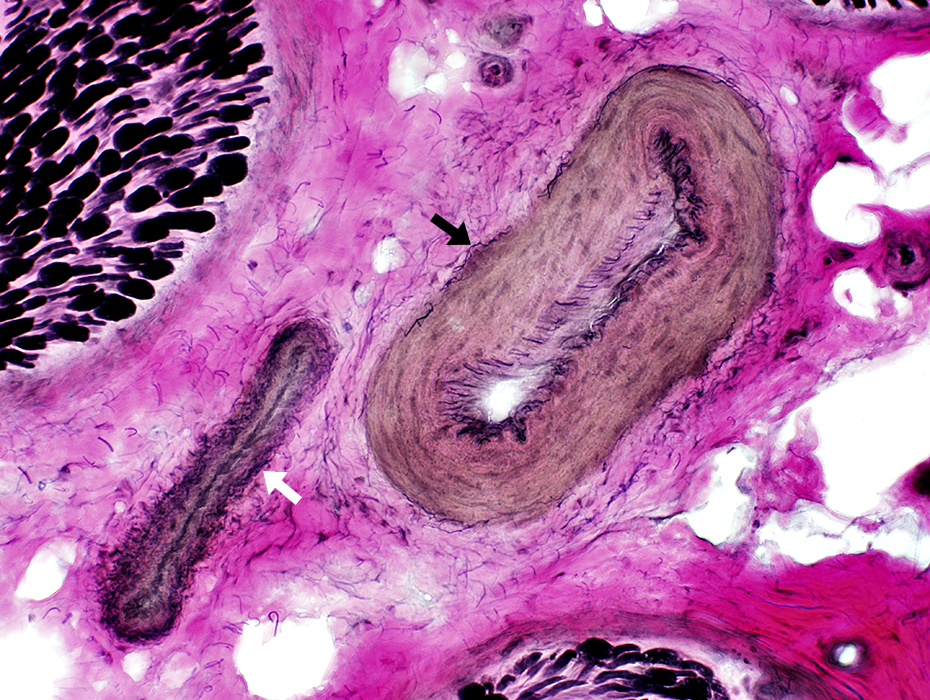
Epineurial Vessels
Artery (Black arrow): Linear fibrils near lumen; Thick wall Vein (White arrow): Interlaced, thin fibrils around outside of vessel; Thin wall
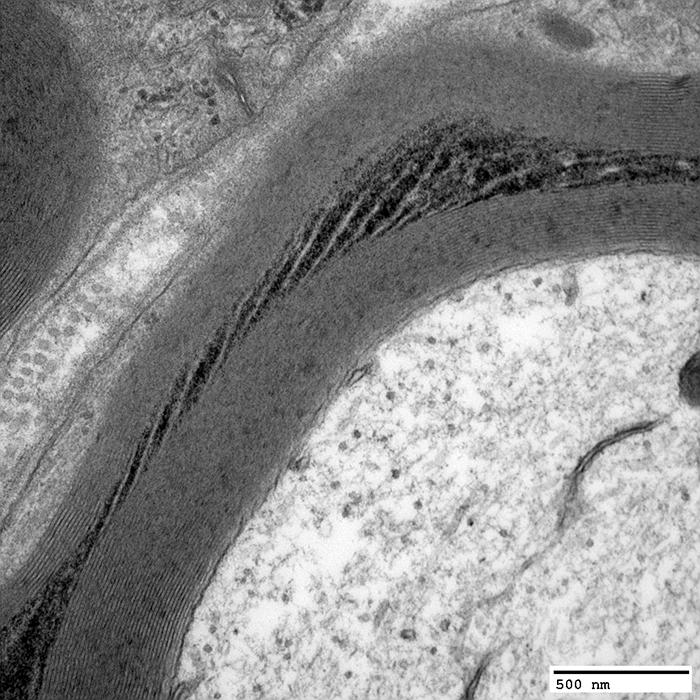
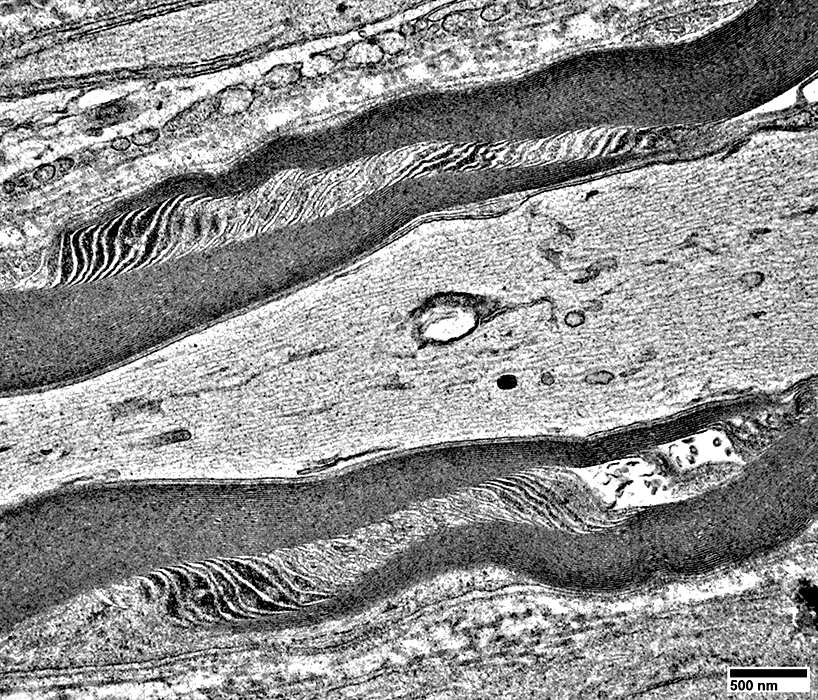
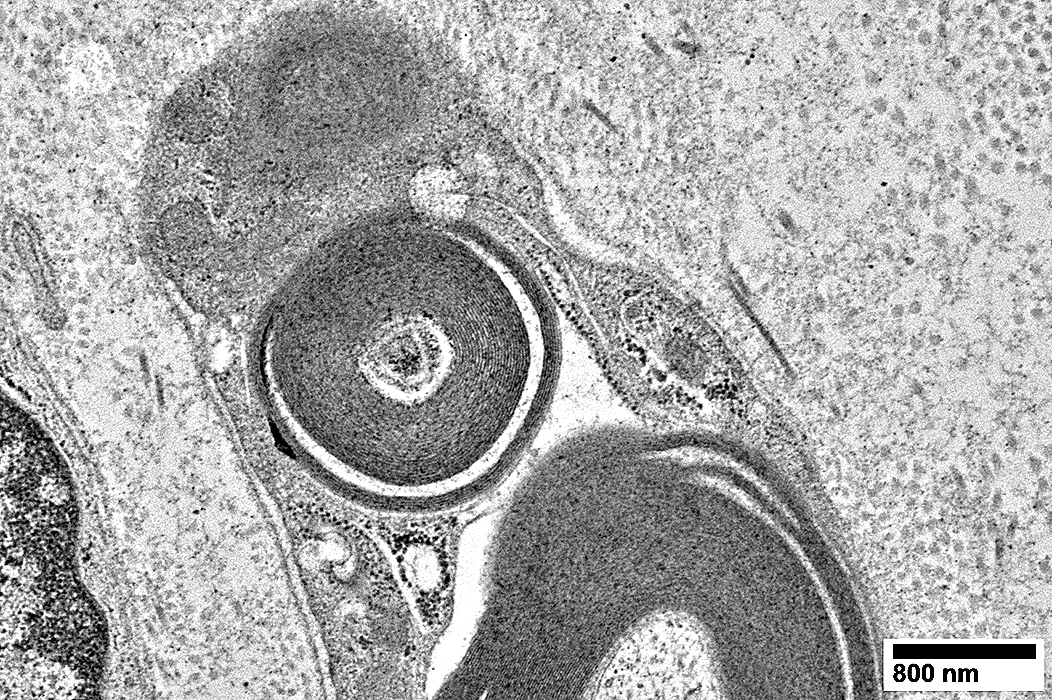
Schmidt-Lanterman Cleft (Incisure)
Schmidt-Lanterman Cleft: Extends through myelin from inside to outside
Pi (Reich) Granules
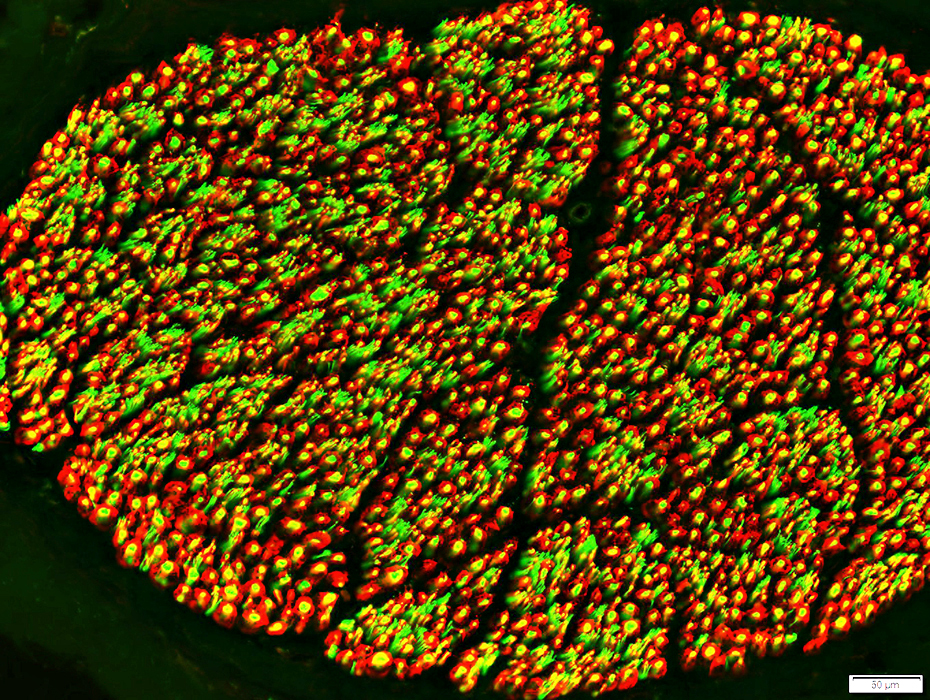
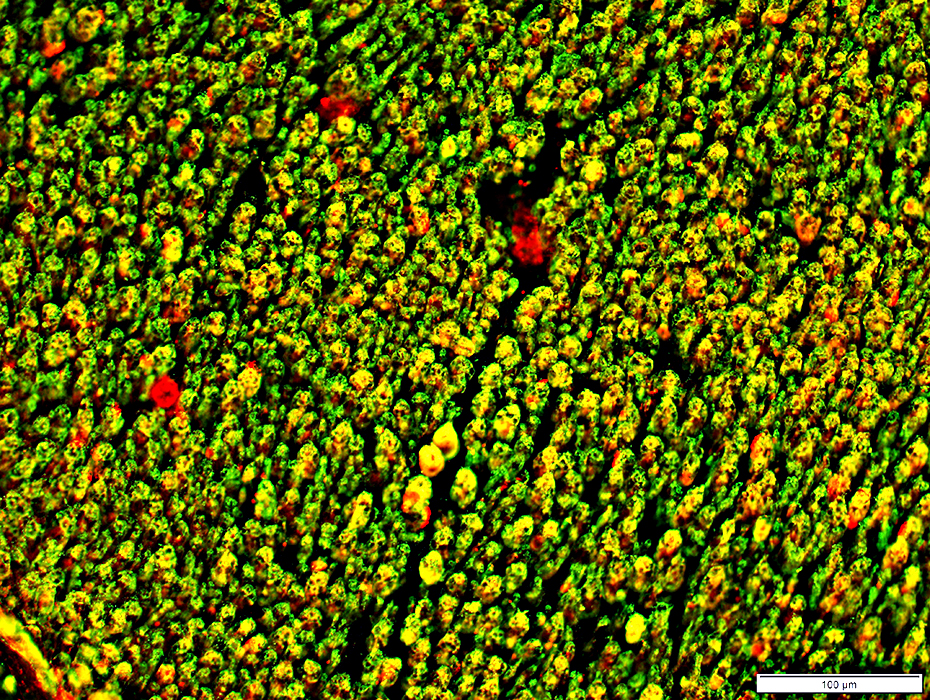
Myelin & Schwann cells: Sural nerve
Prominent in myelin around most (large & small) myelinated axons Smallest axons (Green), often in clusters, have no myelin or associated P0 staining
Most prominent in myelin around largest myelinated axons In myelin around fewer axons than P0
Non-myelinating Schwann cells Nerve: Sciatic
Non-myelinating Schwann cells
Myelin Components
Prominent in myelin around most (large & small) myelinated axons Smallest axons (Green), often in clusters, have no myelin or associated P0 staining
Myelin basic protein (MBP) (Red) Most prominent in myelin around largest myelinated axons
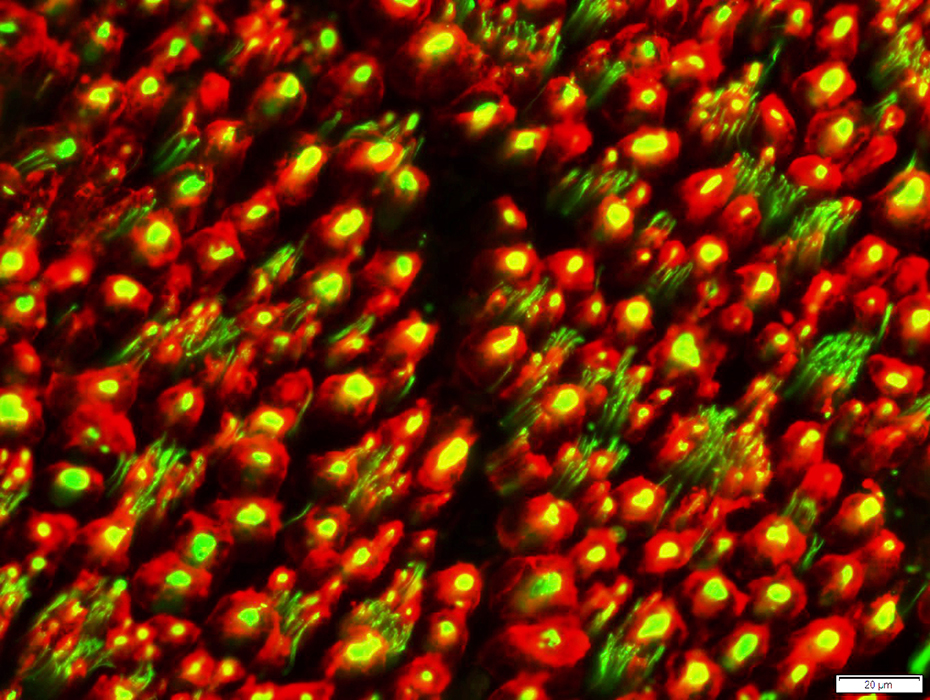
P0 vs Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) in Myelin
Associated with large & small axons More around periphery of myelin sheath Myelin basic protein Mainly associated with largest axons More toward inside of myelin sheath
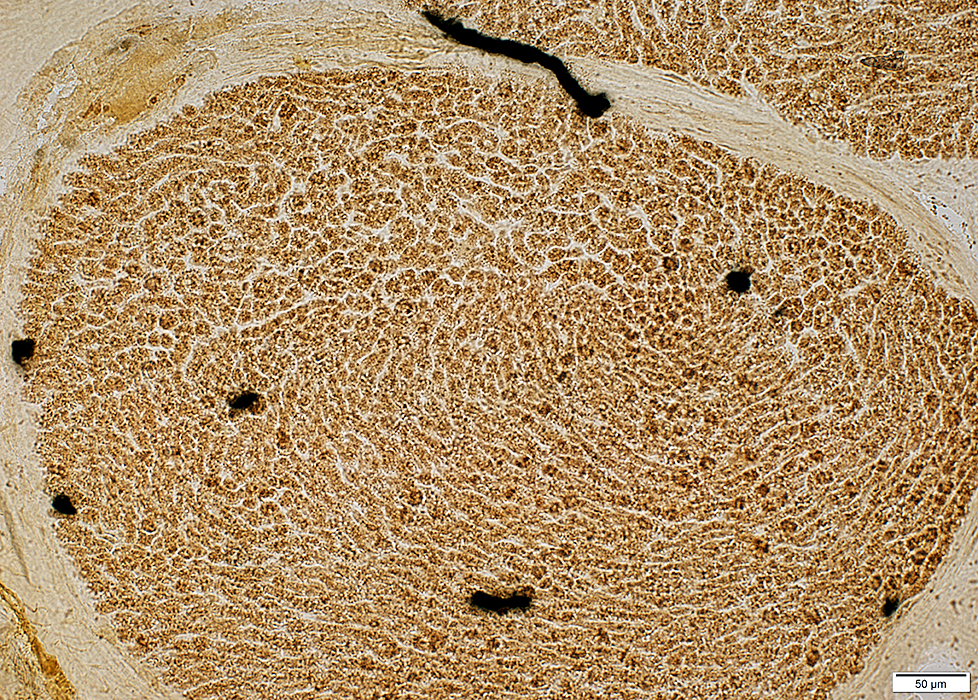
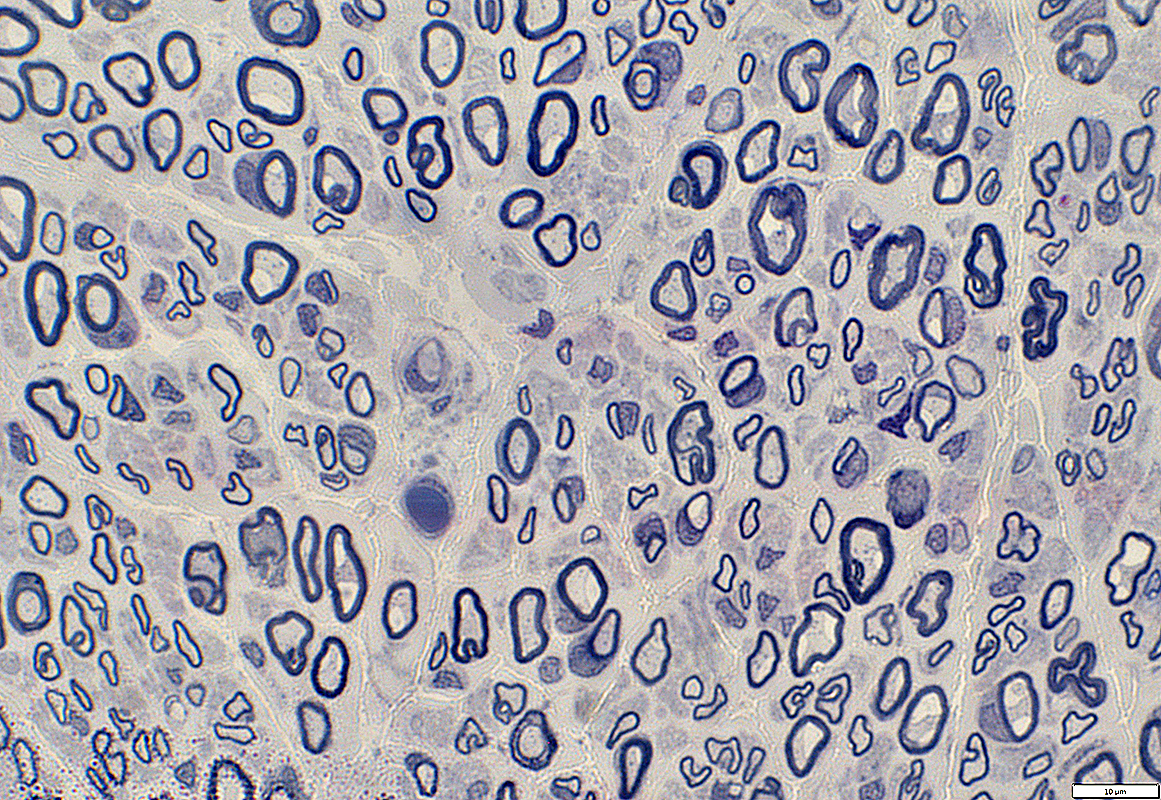
Nerve: Infraorbital (Branch of Trigeminal)
Acid phosphatase positive cells scattered in endoneurium (Above) Alkaline phosphatase positive vessels: Few in endoneurium (Below)
ATPase activity: Abundant in endoneurial cells
Infraorbital Nerve Larger myelinated axons: Many Small unmyelinated axons: Fewer than in sural nerve
Non-myelinating (Remak) Schwann cells : Fewer than in sural nerve
Non-myelinating (Remak) Schwann cells Myelinating Schwann cells: Adaxonal & Abaxonal cytoplasm
Infraorbital Nerve Larger myelinated axons (Green): No associated NCAM; Many Small unmyelinated axons (Yellow): Fewer than in sural nerve
Infraorbital Nerve: P0 (Red) Prominent in myelin (Red) around most (large & small) myelinated axons Smallest axons (Green) have no myelin or associated P0 staining
Infraorbital Nerve Myelin basic protein (MBP) is markedly reduced in myelin around axons compared to sural nerve
Nerve: Infant
Axons are mildly small Myelin sheaths around large axons are moderately thin Compare to: Adult
Normal nerve: MouseAxon populations: 3Myelinated, Large Myelinated, Small Unmyelinated
Return to Biopsy illustrations Return to Neuromuscular Home Page Return to Nerve biopsy References 1. Exp Neurol 2020 Mar 3;328:113272 2. Muscle Nerve 2023;68:696-713 12/10/2025 |