PERIPHERAL NERVE: Chronic Demyelination
|
CIDP Demyelination Active Demyelinated axons Focal, Persistent Segmental Hypomyelination Large nerves MMN Onion bulbs Subperineurial edema: CIDP Teased fibers Tomaculae |
MYELIN PATHOLOGY
Myelin Loss: On Preserved Larger Axons
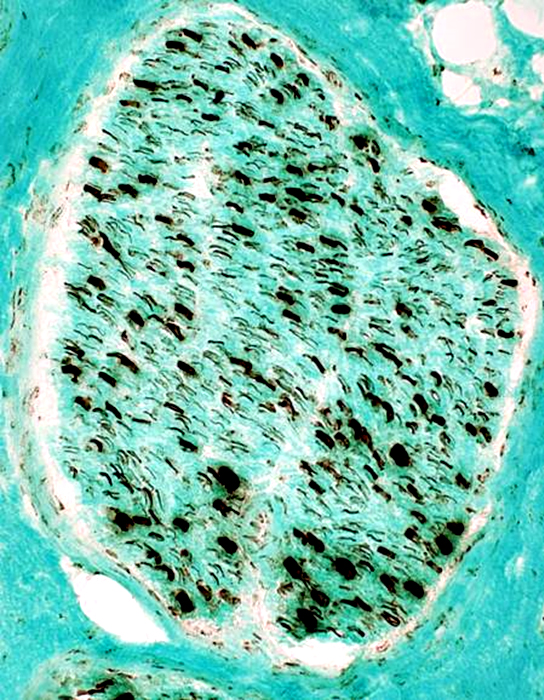 Neurofilament stain Large & Small axons: Present; Reduced numbers
|
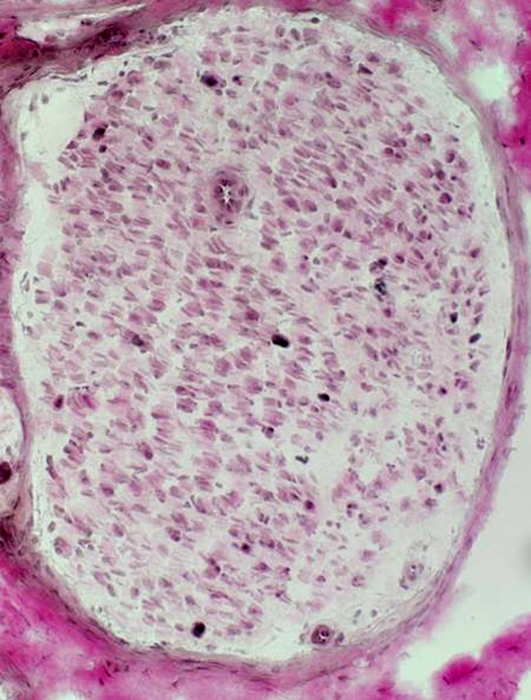 VvG stain Myelin: Mostly absent
|
|
Myelin loss: From preserved larger axons Few remaining myelinated axons are small with thin myelin sheath 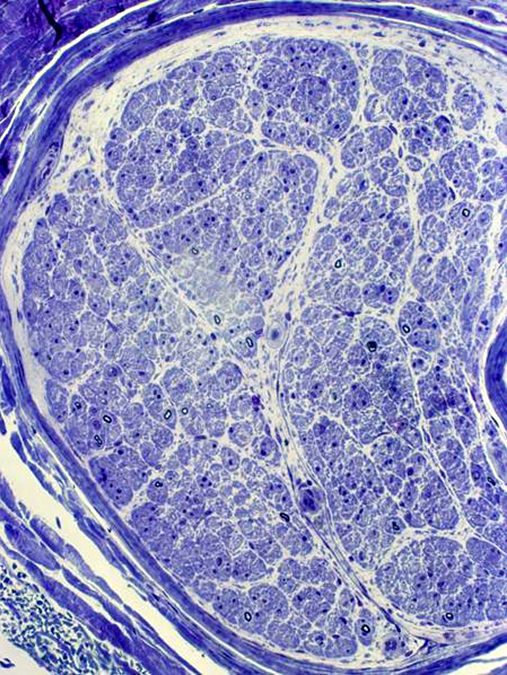 Toluidine blue stain Few myelinated axons
|
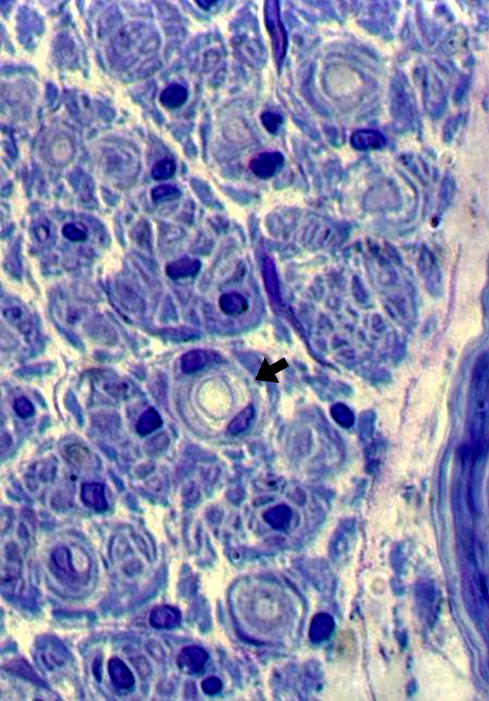 Toluidine blue stain Demyelinated large axons, Scattered (Arrow)
Demyelinated axons often have surrrounding Schwann cells |
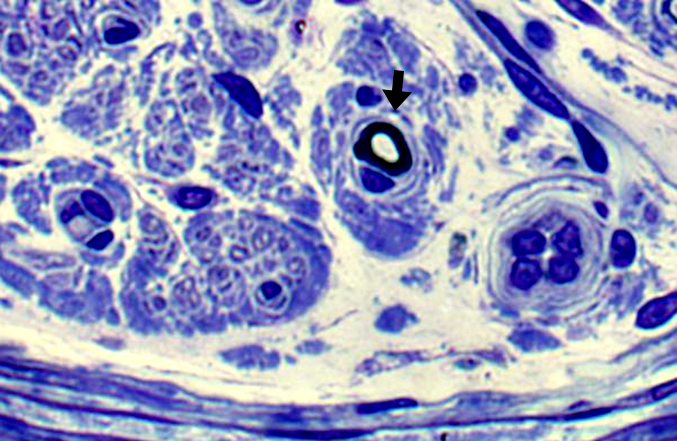 Toluidine blue stain Onion bulb, Early (Arrow): Reduplicated basal lamina |
|
Segmental Demyelination & Remyelination
Segmental Demyelination with Remyelination (Top)Internodes (3)
Short
Different
Lengths
Thicknesses
Control Myelinated Axon (Bottom)
Myelin internode
Long
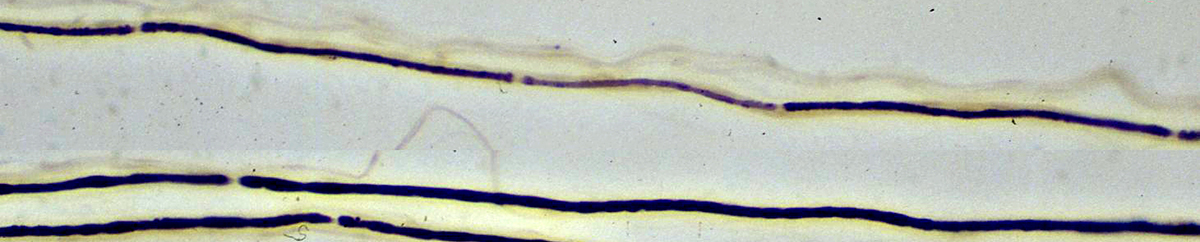 Teased Axons |
Myelinated Axons: Segmental Demyelination
Myelination is absent or thin in some internodes but not others
  Teased Axons |
Myelinated Axons: Segmental Demyelination
Myelination of internode is thin to the left of the Node of Ranvier but normal on the right side
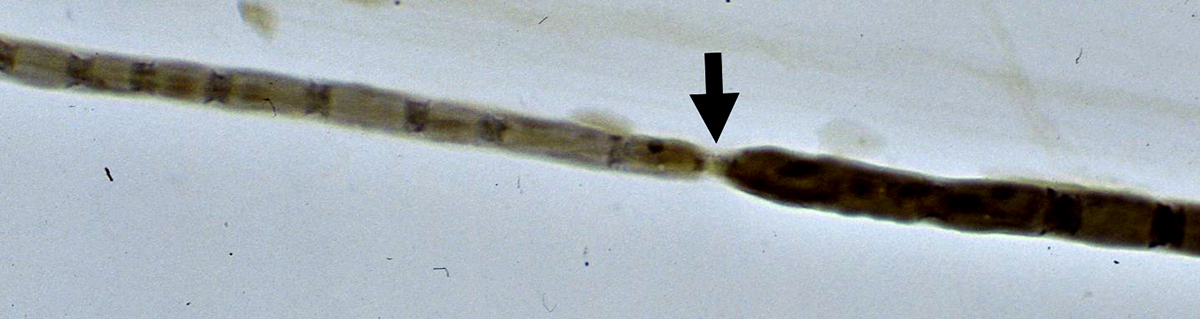 Teased Axons |
CIDP: Distal Motor Axons
Segmental Demyalination
Internode widening
Distal Axons
Thin
Absent myelin
Collateral sprouts: Reinnervate denervated NMJs
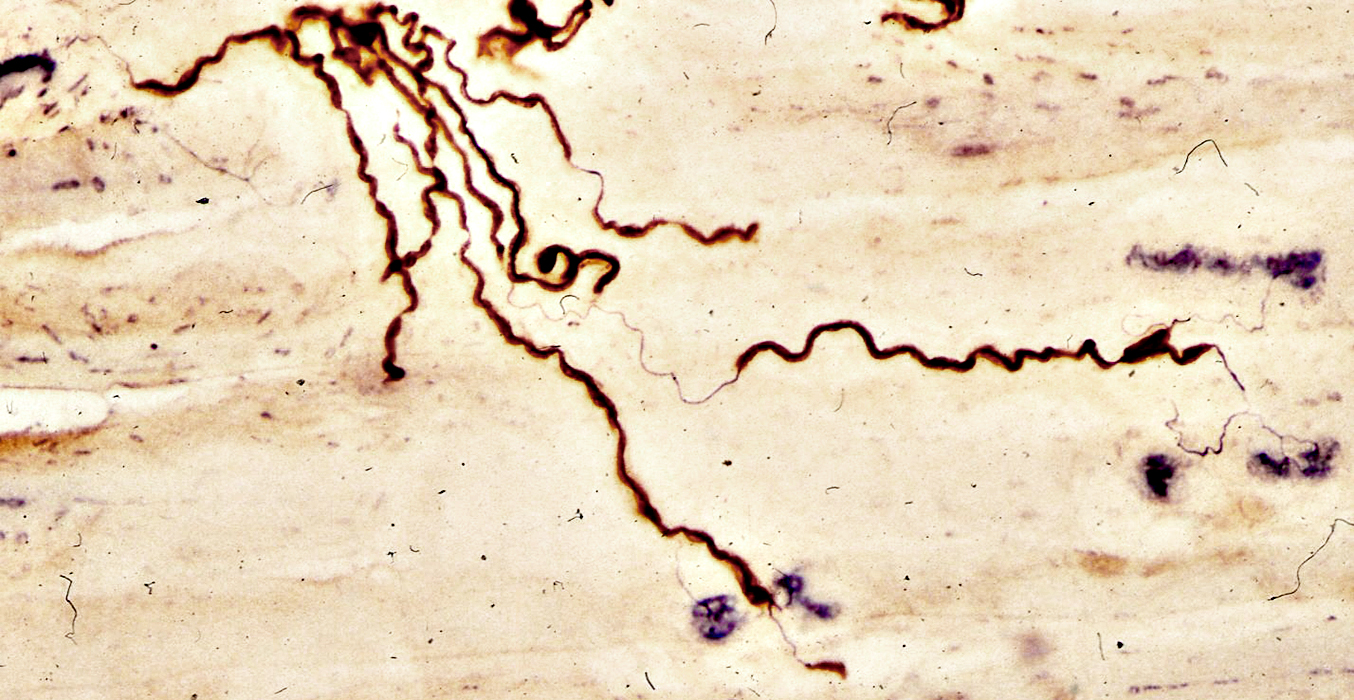 P0-Silver-Esterase stain |
Myelin pathology: Multifocal Motor Neuropathy
 P0-Silver-Esterase stain |
Arrow points to small region of myelin in area of segemental demyelination
Fragment of neuromuscular junction (Blue stain) is at left
Below: Normally myelinated distal motor axon in muscle
Arrow points normal short myelin internode on distal motor axon
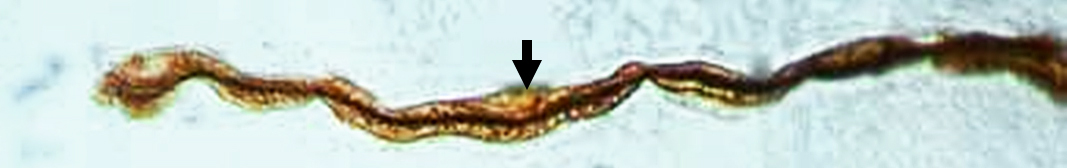 P0-Silver-Esterase stain |
Hypomyelinated Axons
See: PMP-22 point mutation
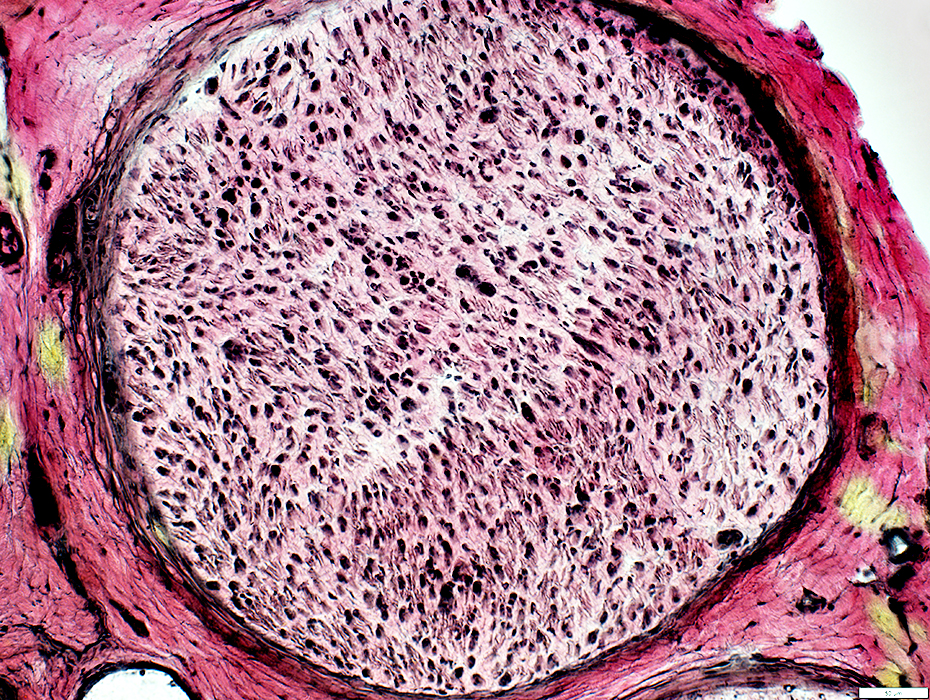 VvG stain |
Cellular
Some increased connective tissue space
No myelin
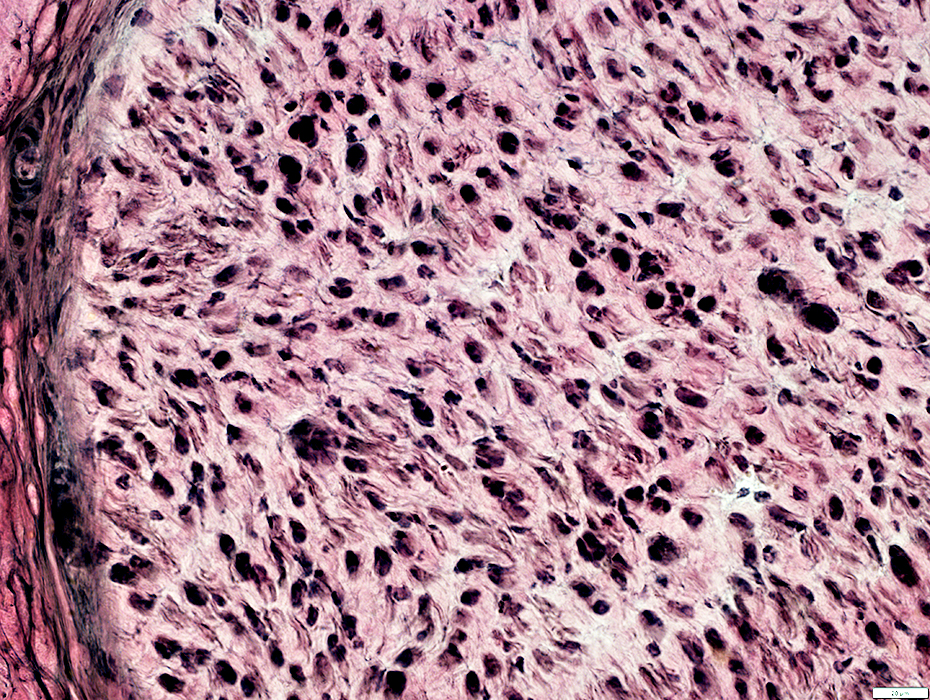 VvG stain |
Large axons: Many present with no surrounding myelin space
Small axons: Mildly reduced numbers
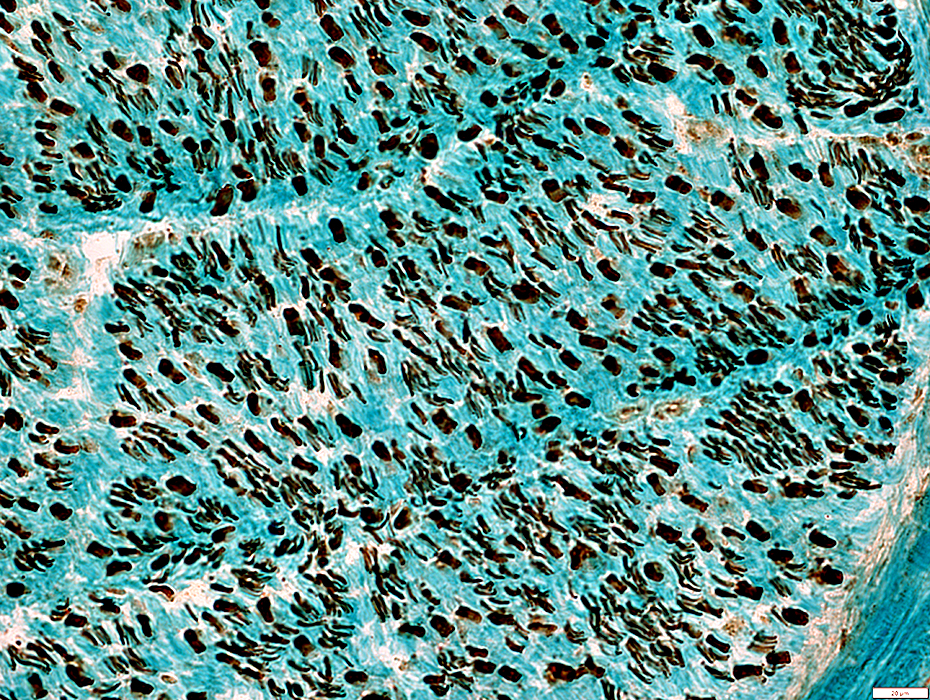 Neurofilament stain |
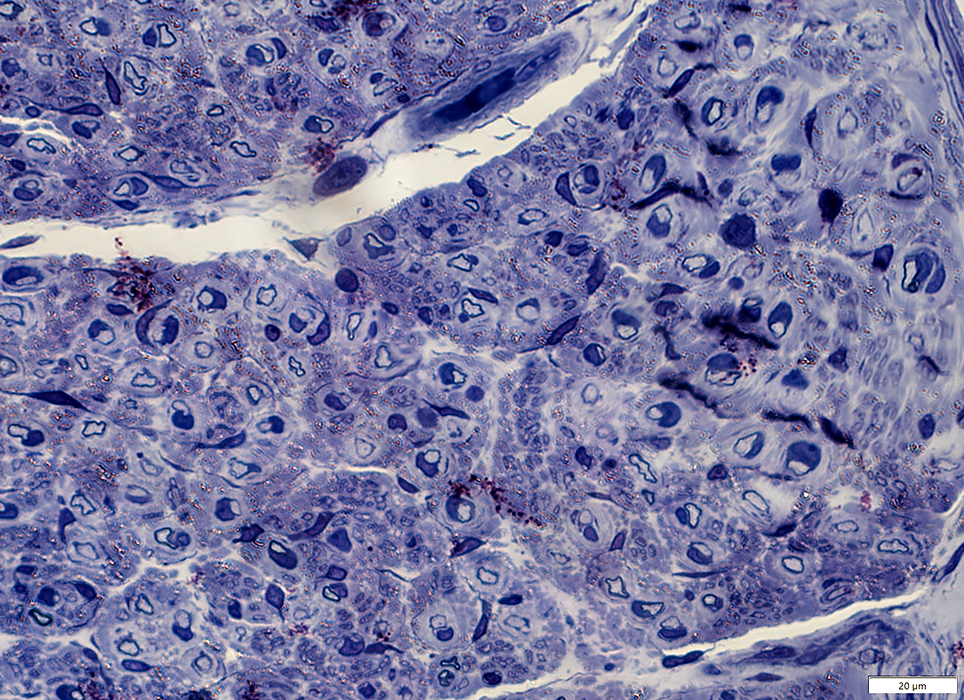 Toluidine blue stain |
Many with very thin surrounding myelin
Schwann cell nuclei often directly neighbor thinly myelinated axons
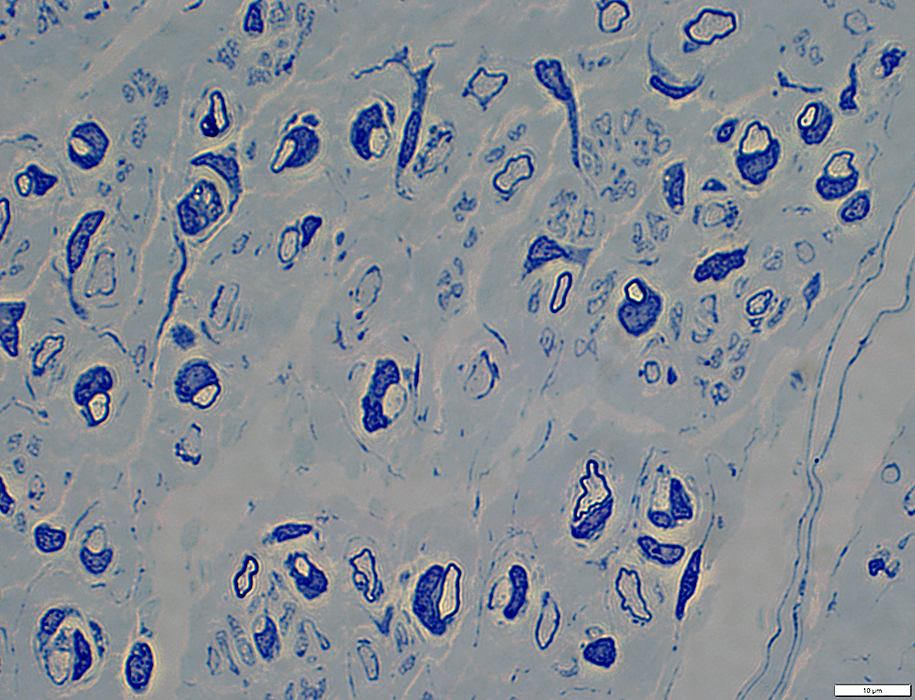 Toluidine blue stain |
Many with very thin surrounding myelin
Schwann cell nuclei often directly neighbor thinly myelinated axons
Endomysial connective tissue
Increased between axons
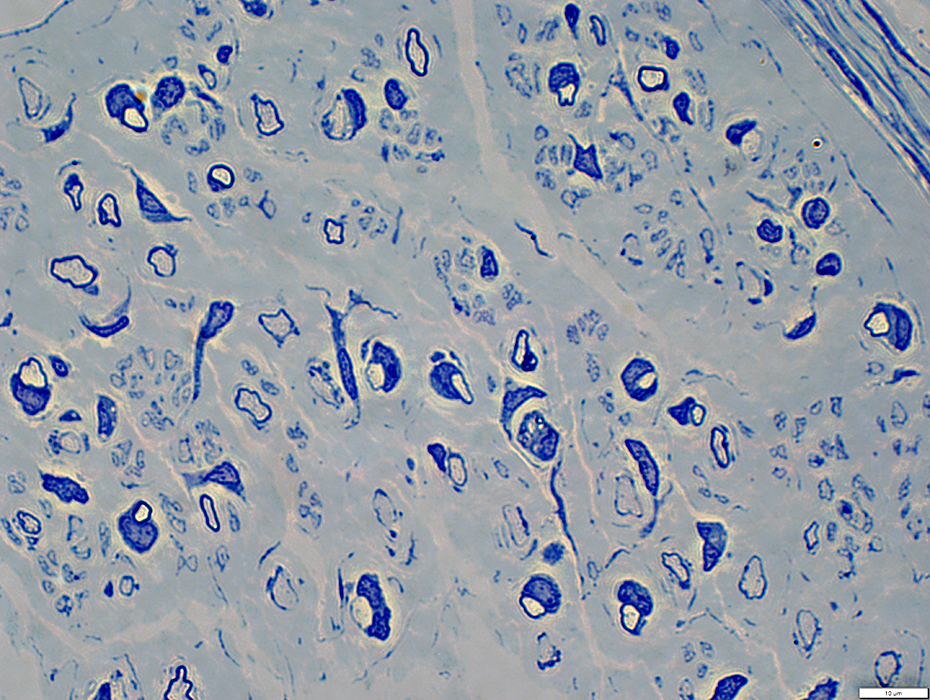 Toluidine blue stain |
ONION & ONION-LIKE BULBS
Onion Bulbs
- Definition
- Circumferentially arranged layers of
- Schwann cell processes
- Schwann cell Basal lamina
- Collagen
- Location: Around axon, or region of axon loss
- Circumferentially arranged layers of
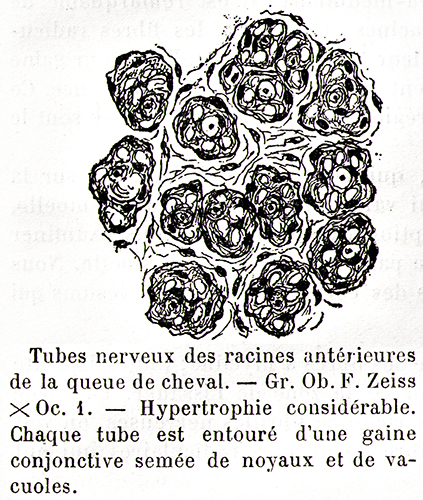
- History
- Early illustrations: Gombault (1889) & Dejerine + Sottas (1893) (Above)
- Cause
- Demyelination & Remyelination: Repeated episodes
- Schwann cell proliferation
- Development
- Remyelination: New Schwann cells add to, or replace, residual Schwann cell
- Onion bulb formation
- Source: Schwann cells & Processes
- Detatch from axon
- Generate cells & processes that form onion bulb layers
- Source: Schwann cells & Processes
- Structures within onion bulb
- General Orientation
- Circumferential
- Around axon, if one is present
- Components
- Schwann cell processes: Contain NCAM & P0 protein; "Denervated"
- Basal lamina: Stains for Collagen IV; Between Schwann cell processes
- Collagen
- Fibroblast processes: May surround onion bulb
- General Orientation
- Associated axon
- Location: In center of onion bulb
- Size: Larger size; or May be several, smaller regenerated axons
- Myelin sheath: Around axon; Inside onion bulb; Often thin for axon size, or absent
- Some onion bulbs have no central axon = "Obsolete onion bulbs"
- Other features
- Individual onion bulb distribution
- Often separated from each other by increased endomysial connective tissue
- Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathies
- BLOBs: Onion bulbs have more Schwann cell basal lamina & fewer Schwann cell processes
- Obsolete (Burnt-out) onion bulbs
- Loss of central axon within onion bulb
- Eventual loss of associated Schwann cells
- Nerve size
- Often large: Due to presence of onion bulb & increased endomysial connective tissue
- Often similar in hereditary & immune, acquired demyelinating disorders
- Individual onion bulb distribution
- Differential Diagnosis
- Acquired vs Inherited disorders: Patterns of OB distribution
1
- Around most axons: More common with inherited neuropathies
- Around scattered axons: Common with acquired neuropathies
- Clustered in regions of nerve: Acquired or inherited neuropathies
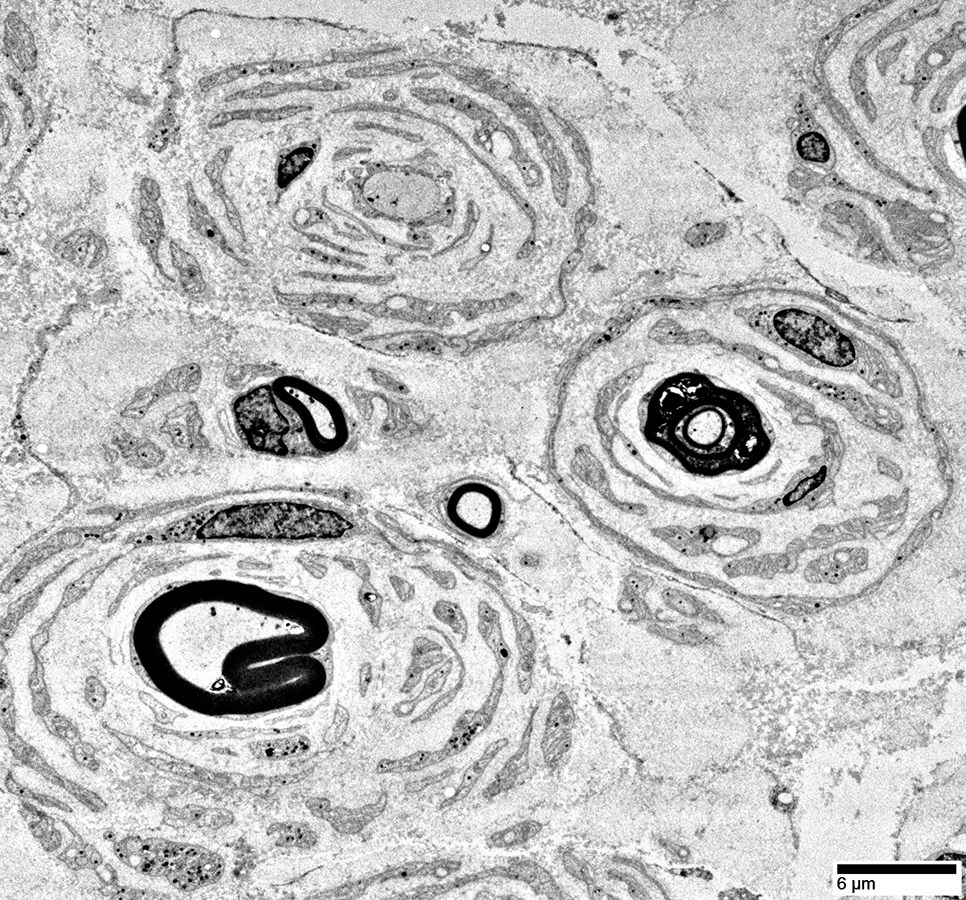 Electron micrograph: From Robert Schmidt MD |
|
Onion Bulbs: Circumferential Layer Components Schwann cell processes Schwann cell basal lamina Collagen: Between Schwann cell components Fibroblast processes: May form outer layer Axons in Onion Bulbs General location: Central Sizes: Large or Intermediate Absent: See obsolete onion bulbs Myelination: Varied Normal Thin or Abnormal None 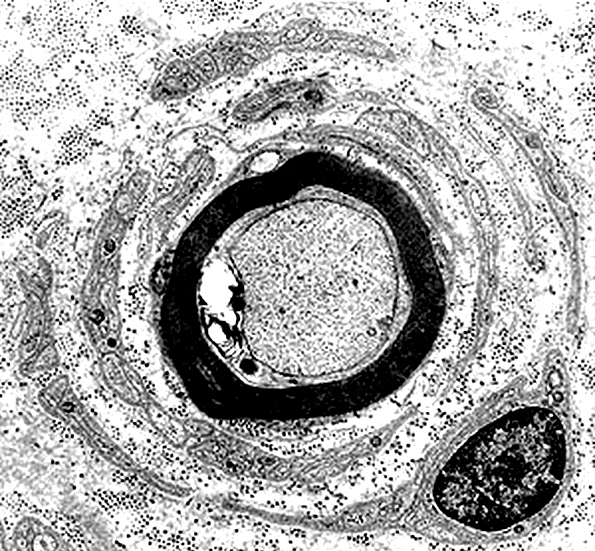 Electron micrograph: From Robert Schmidt MD |
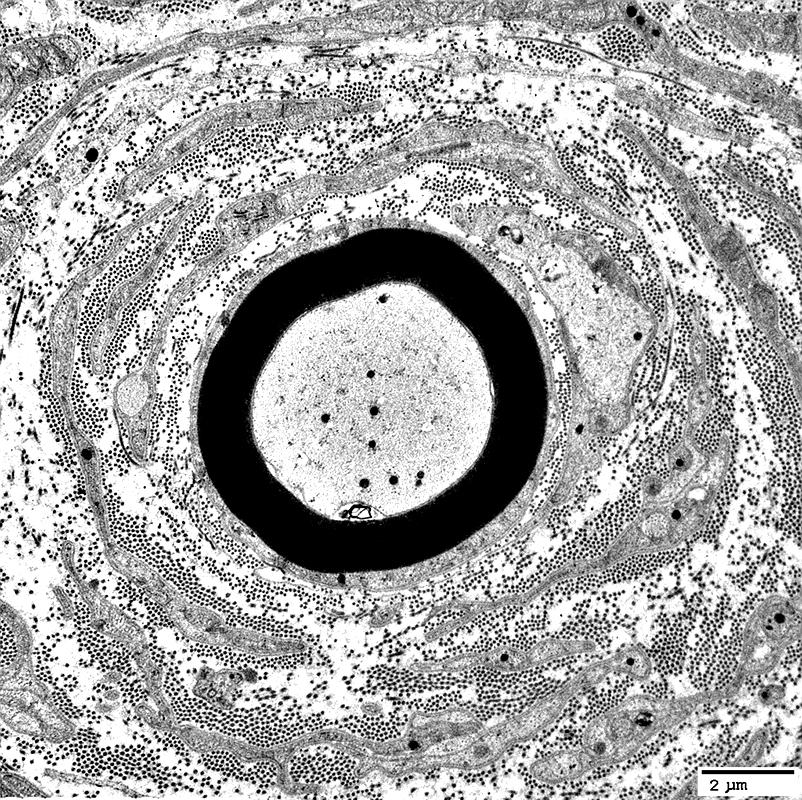 Electron micrograph: From Robert Schmidt MD |
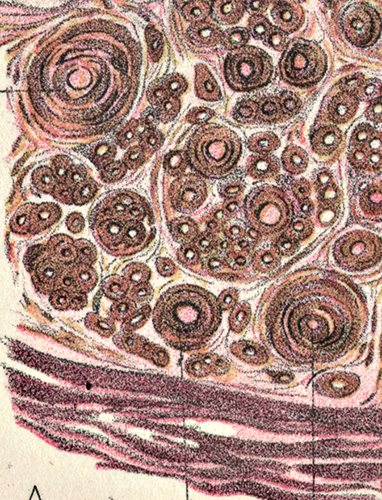
Onion Bulbs: Large, Late
|
Also see: CMT1A |
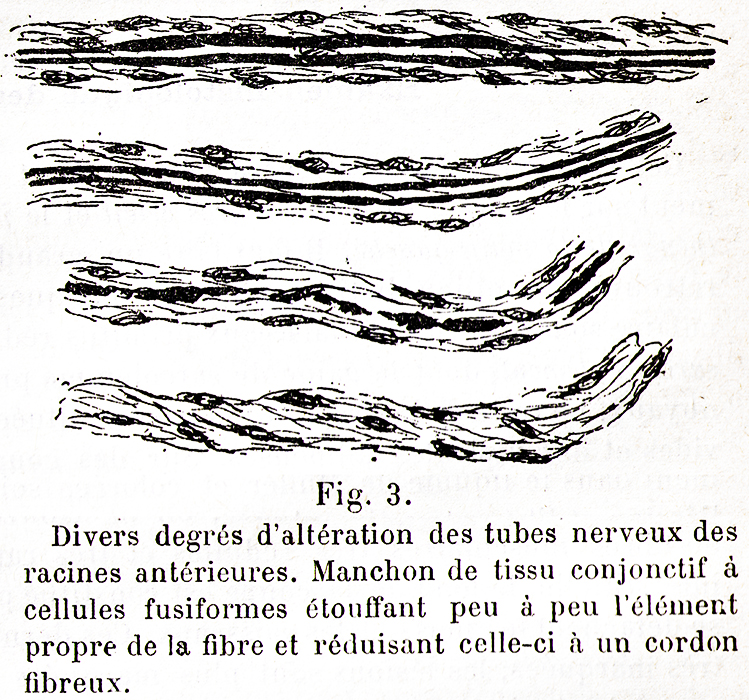 Dejerine & Sottas 1893 |
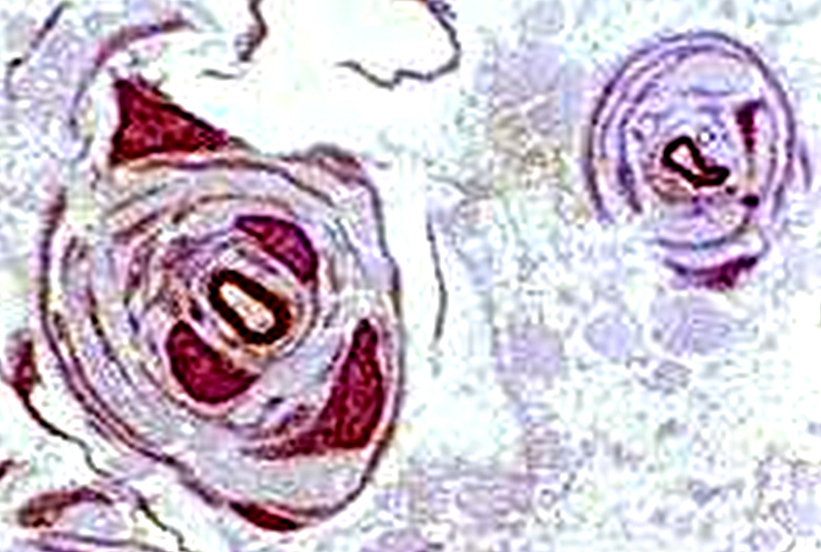 Toluidine blue stains of plastic nerve sections |
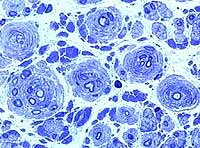 Onion bulbs, Large Multiple Connective tissue layers & Schwann cell processes around thinly myelinated axons. Onion bulbs may contain 0, 1, or several, axons. 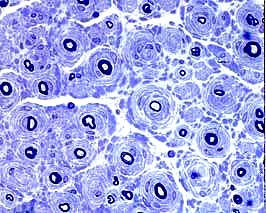 Toluidine blue stains of plastic nerve sections |
Several layers of Basal lamina, Connective tissue & Schwann cell processess around thinly myelinated axons.
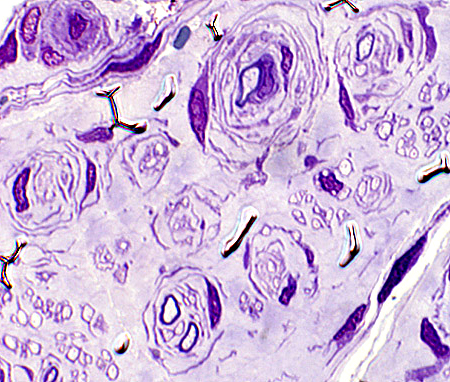
|
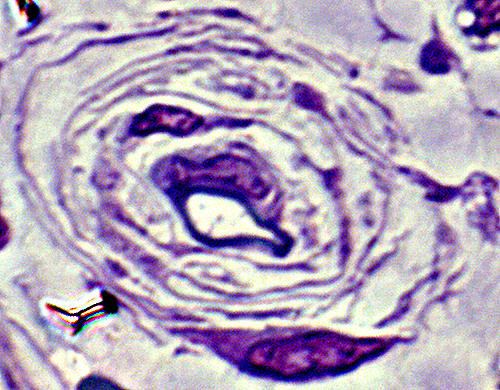
|
Onion Bulbs: Ultrastructure
CIDP, Childhood onset
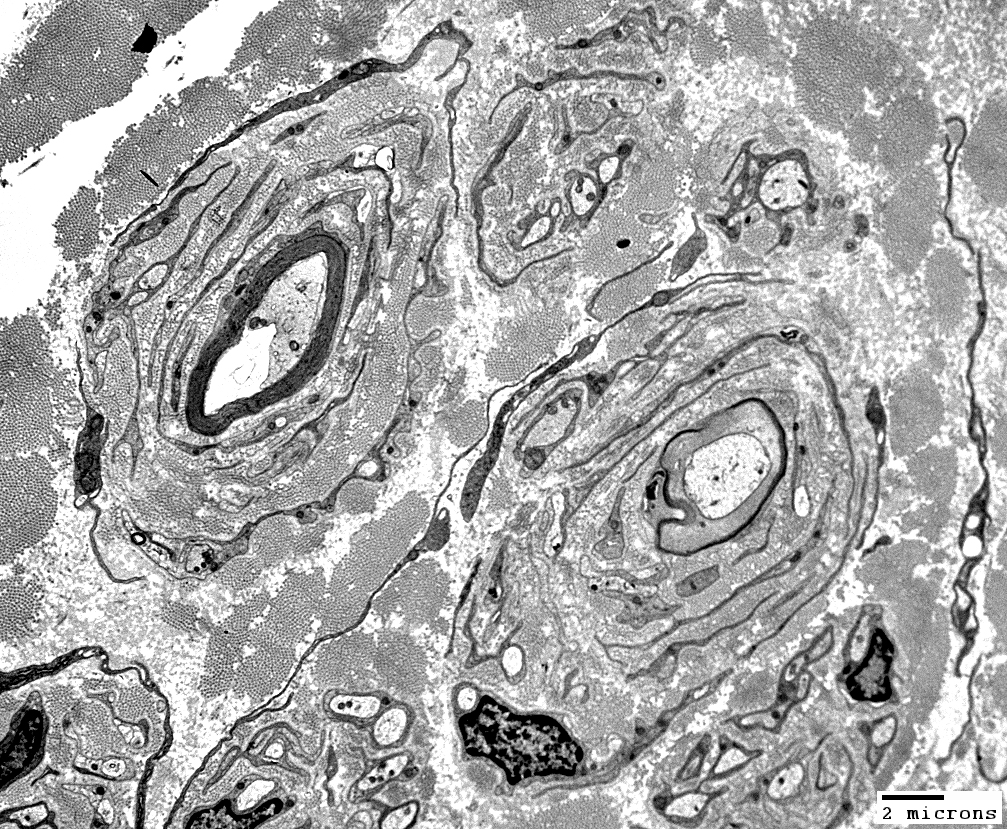 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Layers include
Schwann cell processes
Schwann cell basal lamina
Connective tissue
Outer rim: My be fibroblast process
Central axon: Thinly myelinated
Onion Bulbs: Around thinly myelinated axons
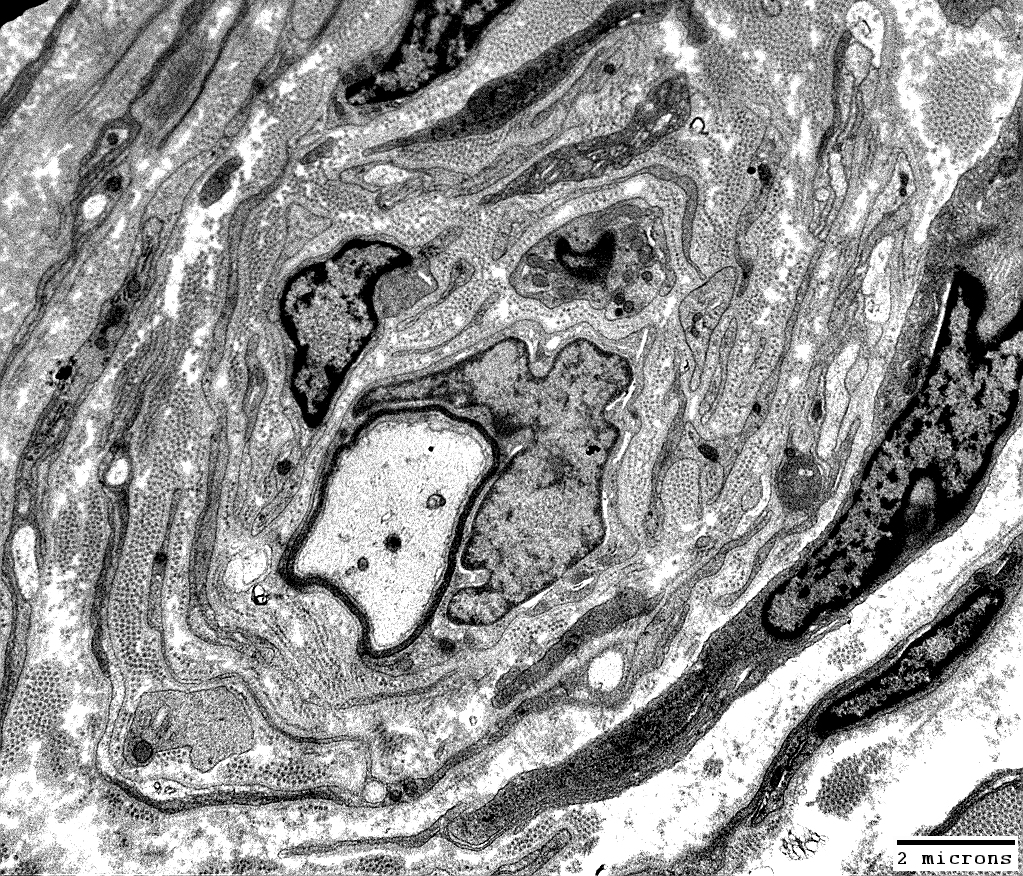 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Layers include
Schwann cell processes
Schwann cell basal lamina
Connective tissue
Outer rim: My be fibroblast process
Central axon: Thinly myelinated
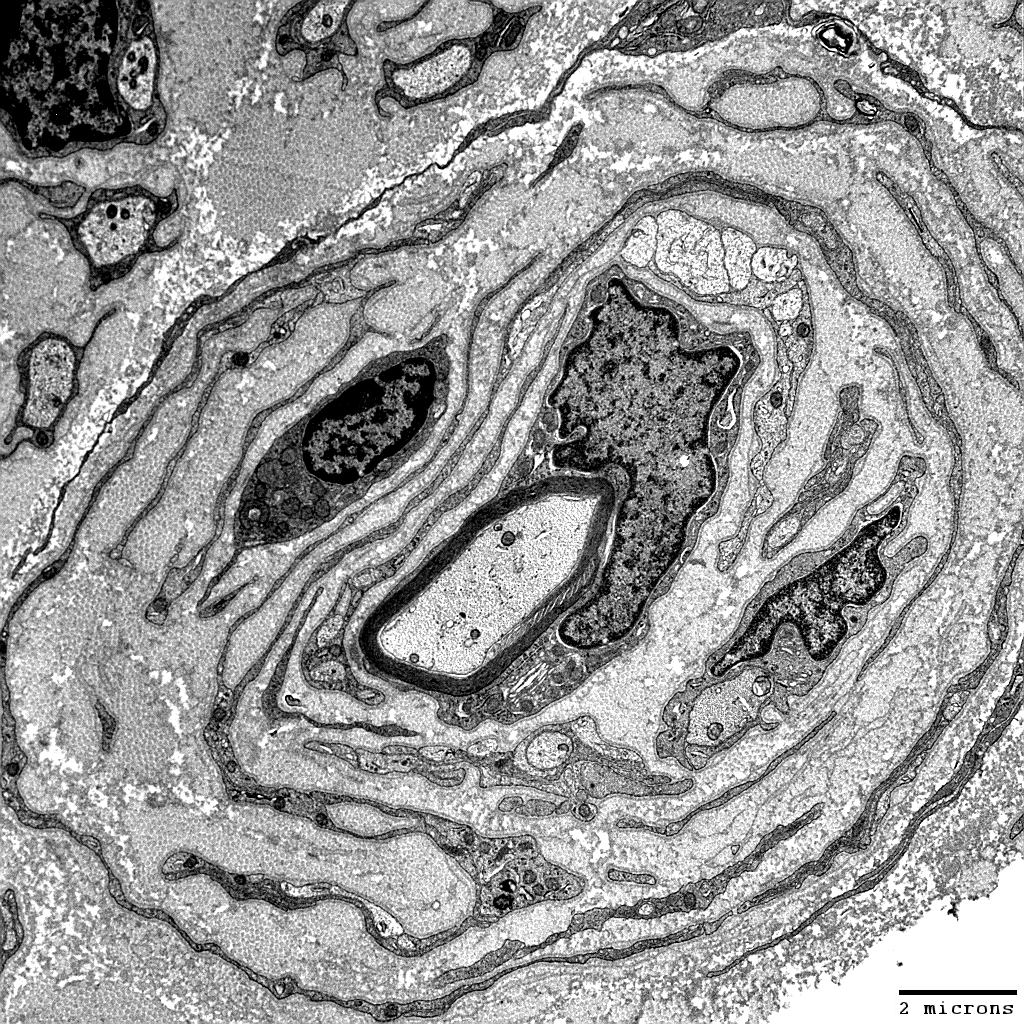 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Cells within Onion Bulbs
 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
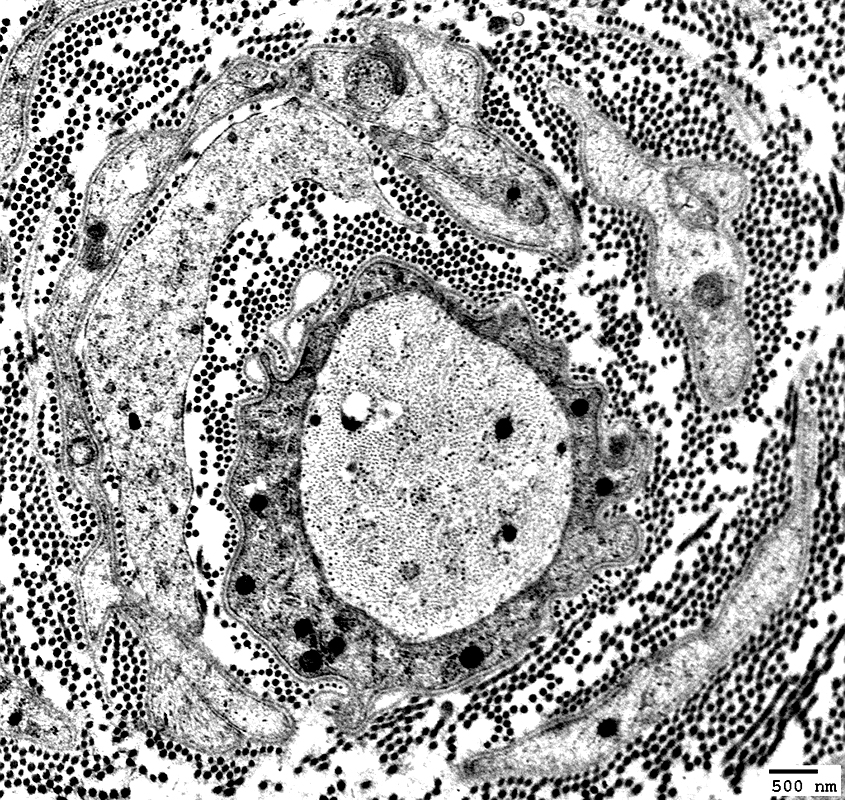 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Macrophage: Between onion bulb layers
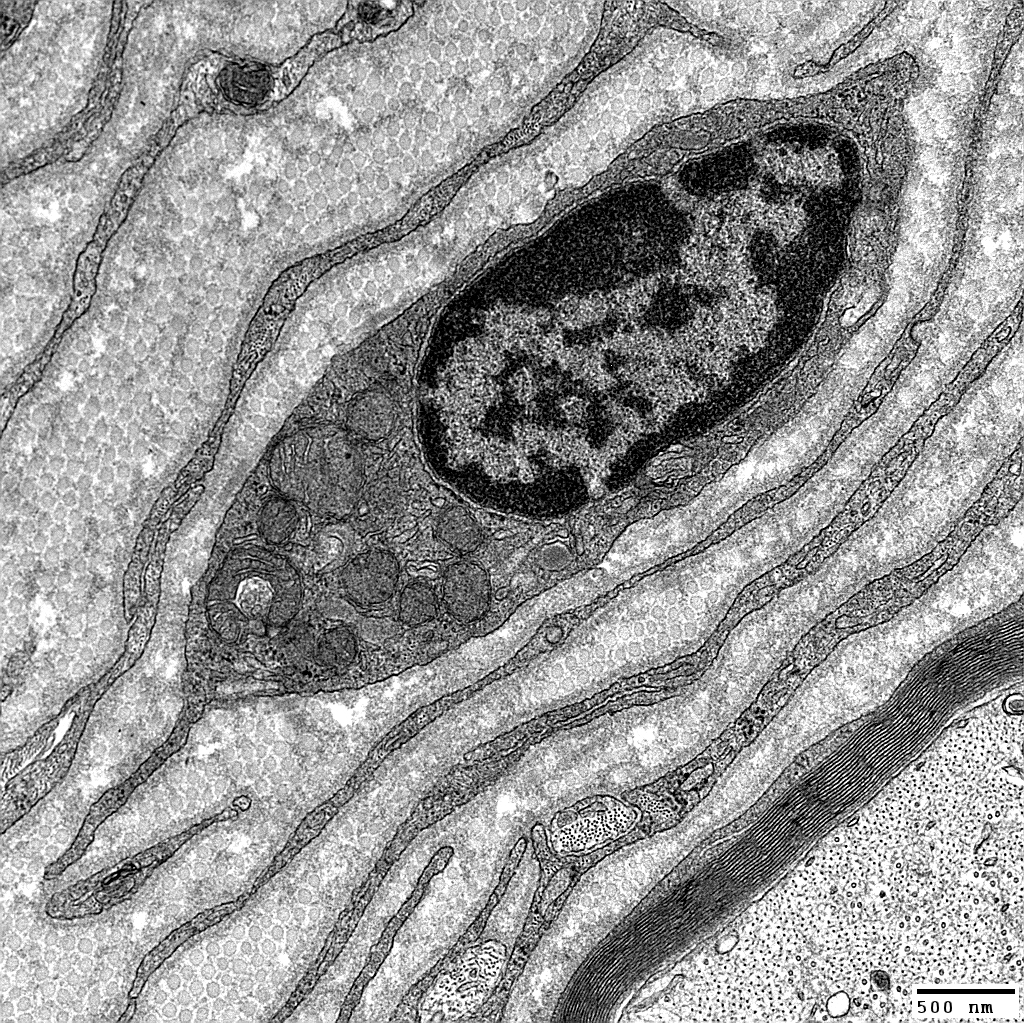 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
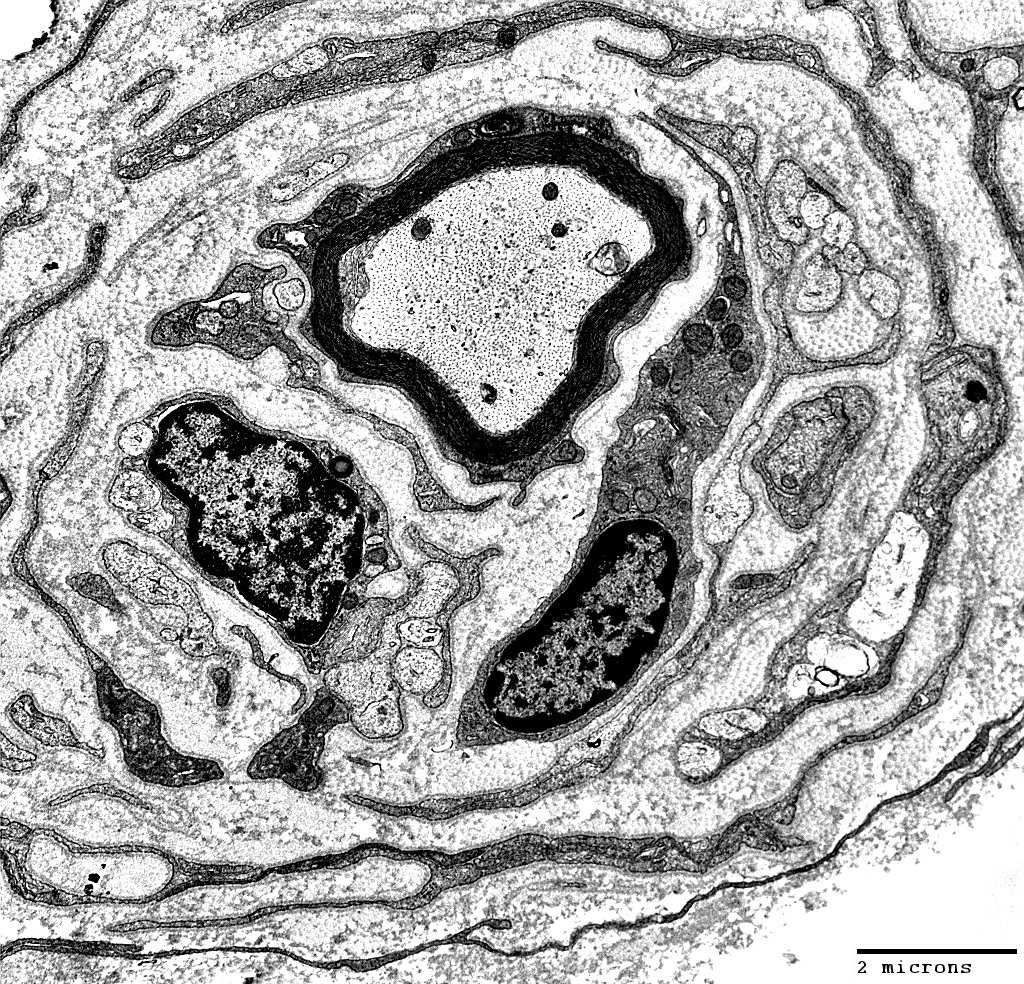
Onion Bulbs: Around demyelinated axons
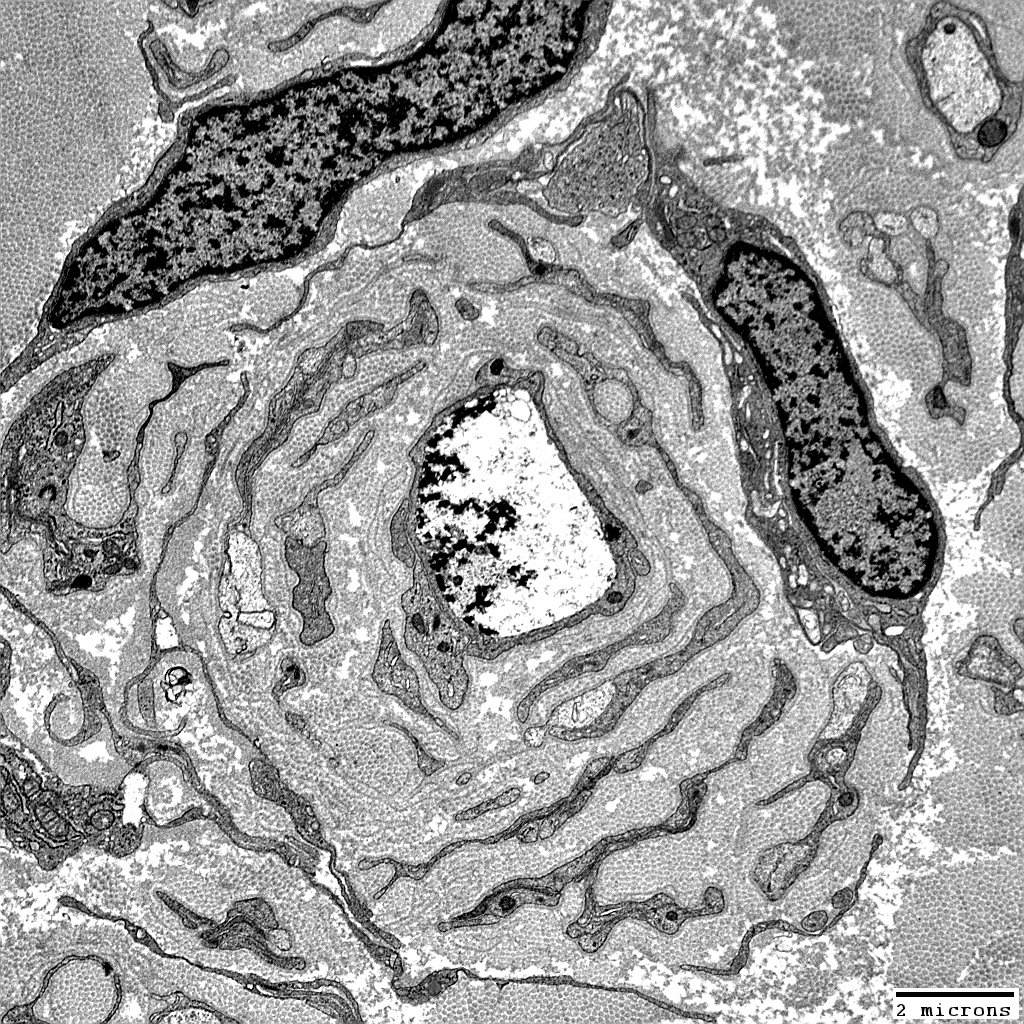 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Layers include
Schwann cell processes
Schwann cell basal lamina
Connective tissue
Outer rim: My be fibroblast process
Central axon: Unmyelinated
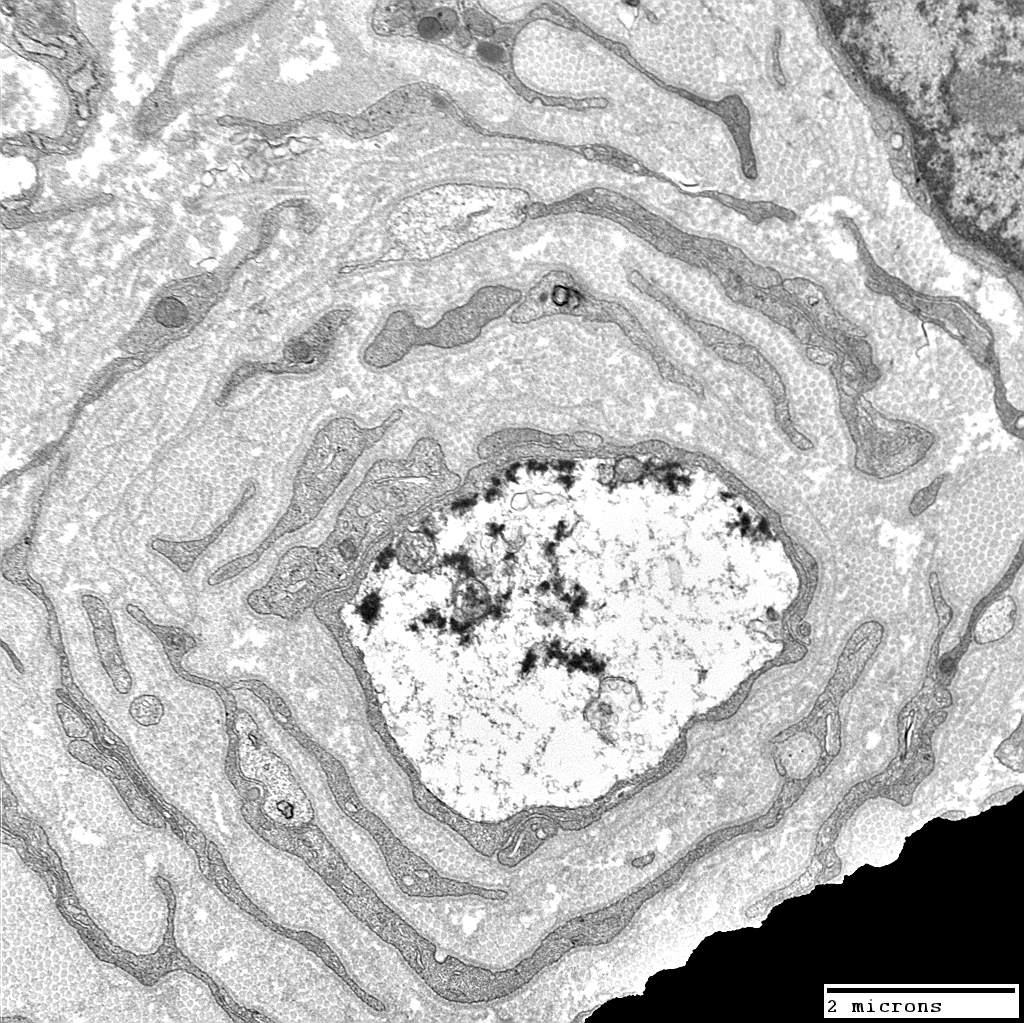 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Schwann cell processes surround demyelinated axon
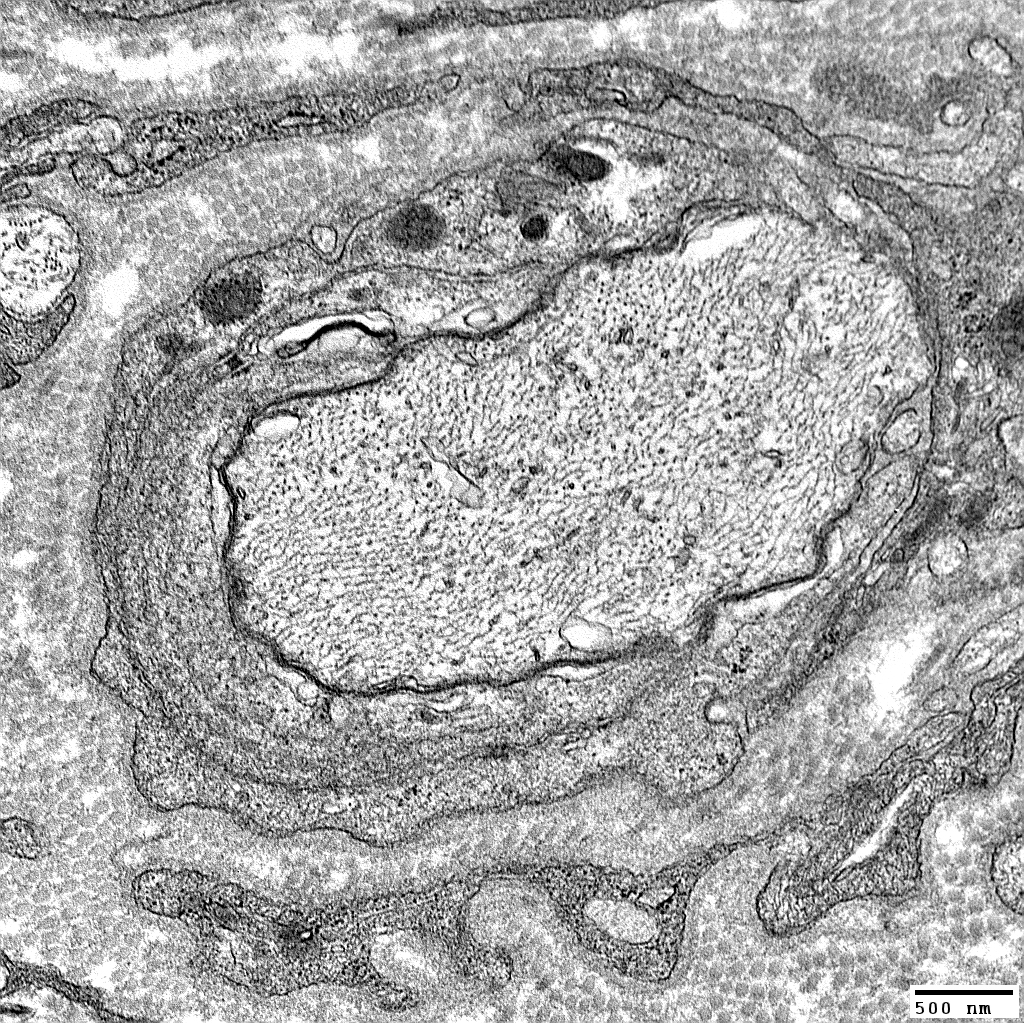 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
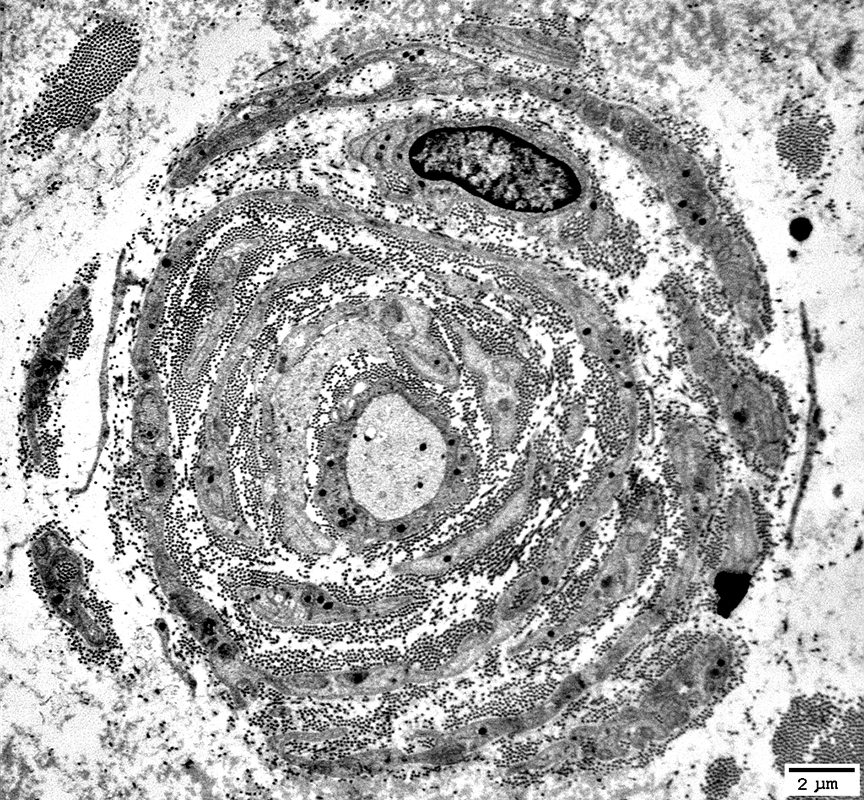 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
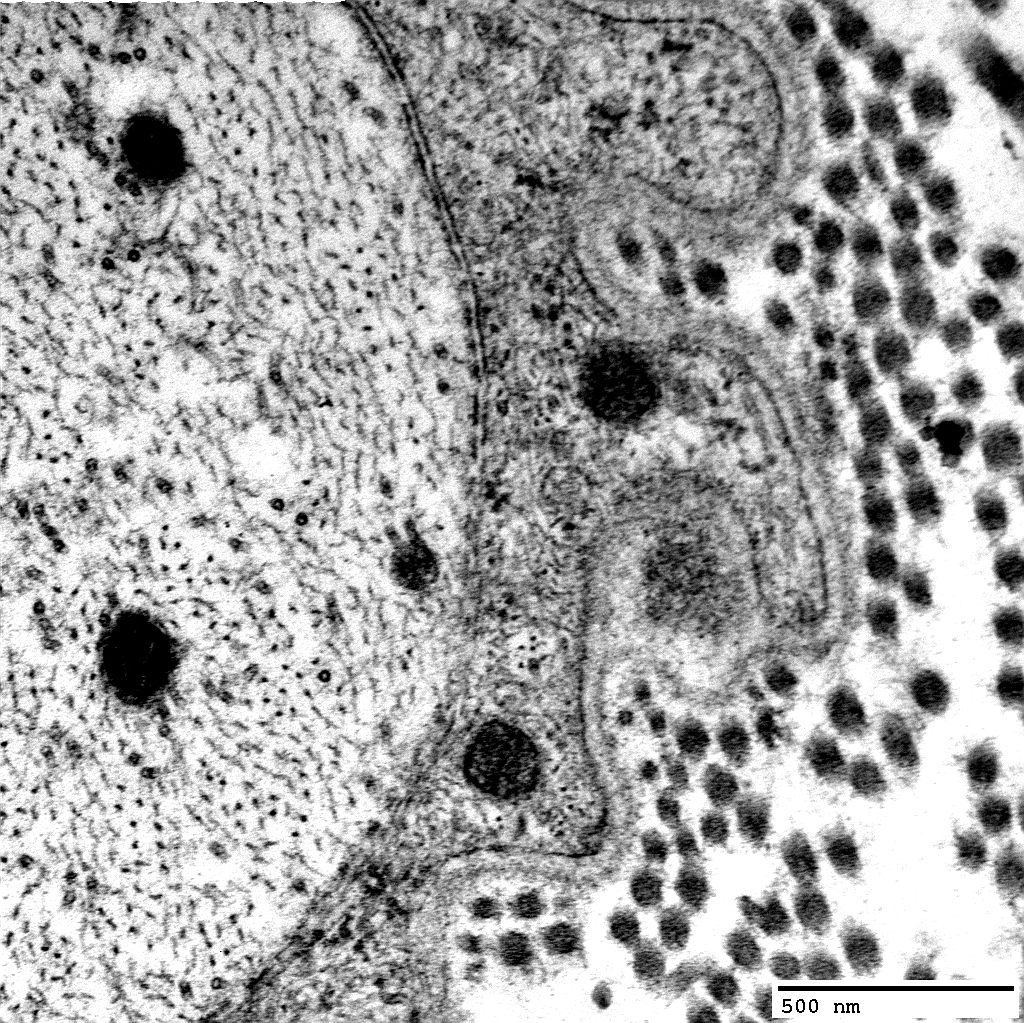 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Onion Bulbs, Obsolete: Central axons are lost (Above)
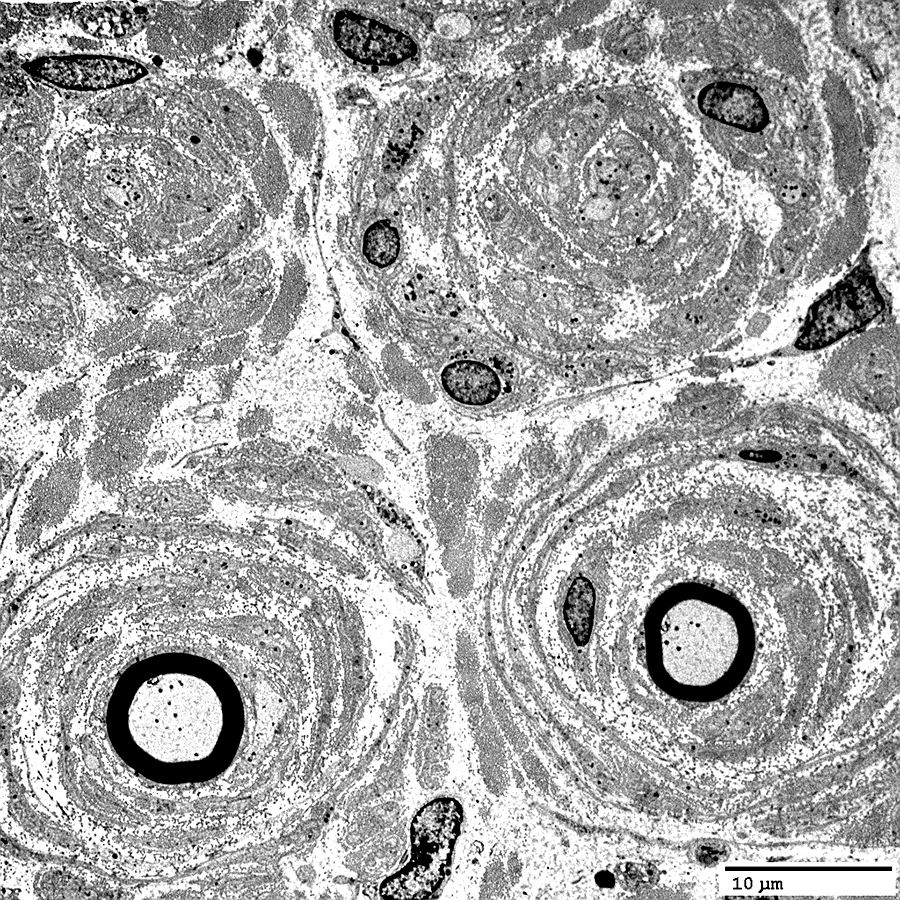 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
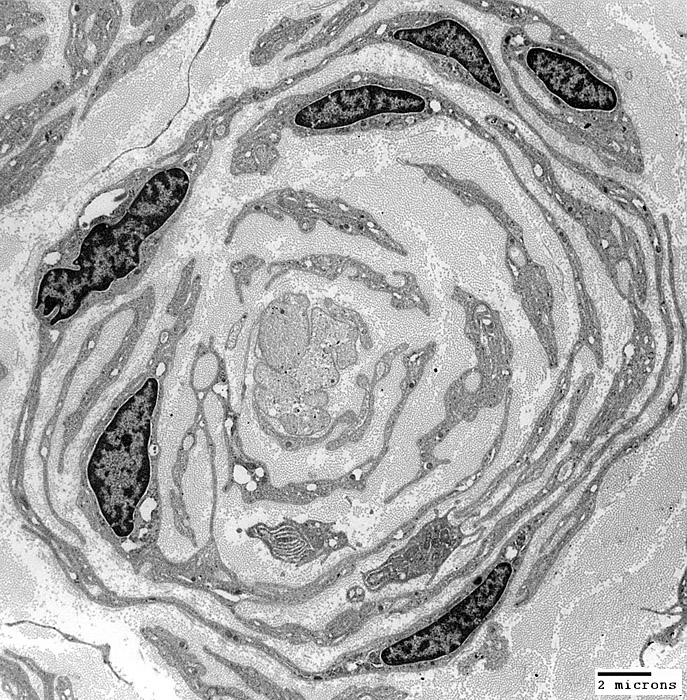 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Multiple layers contain: Schwann cells alternating with collagen
Associated central axon is: Lost
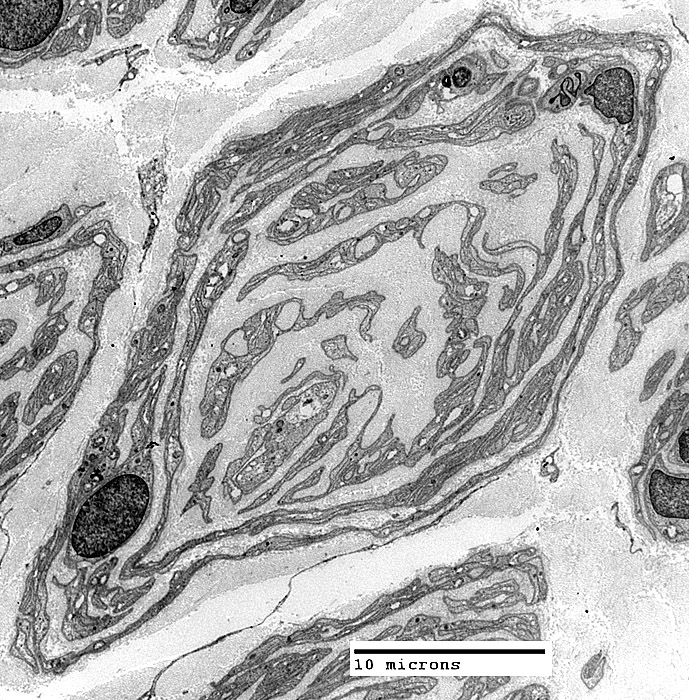 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
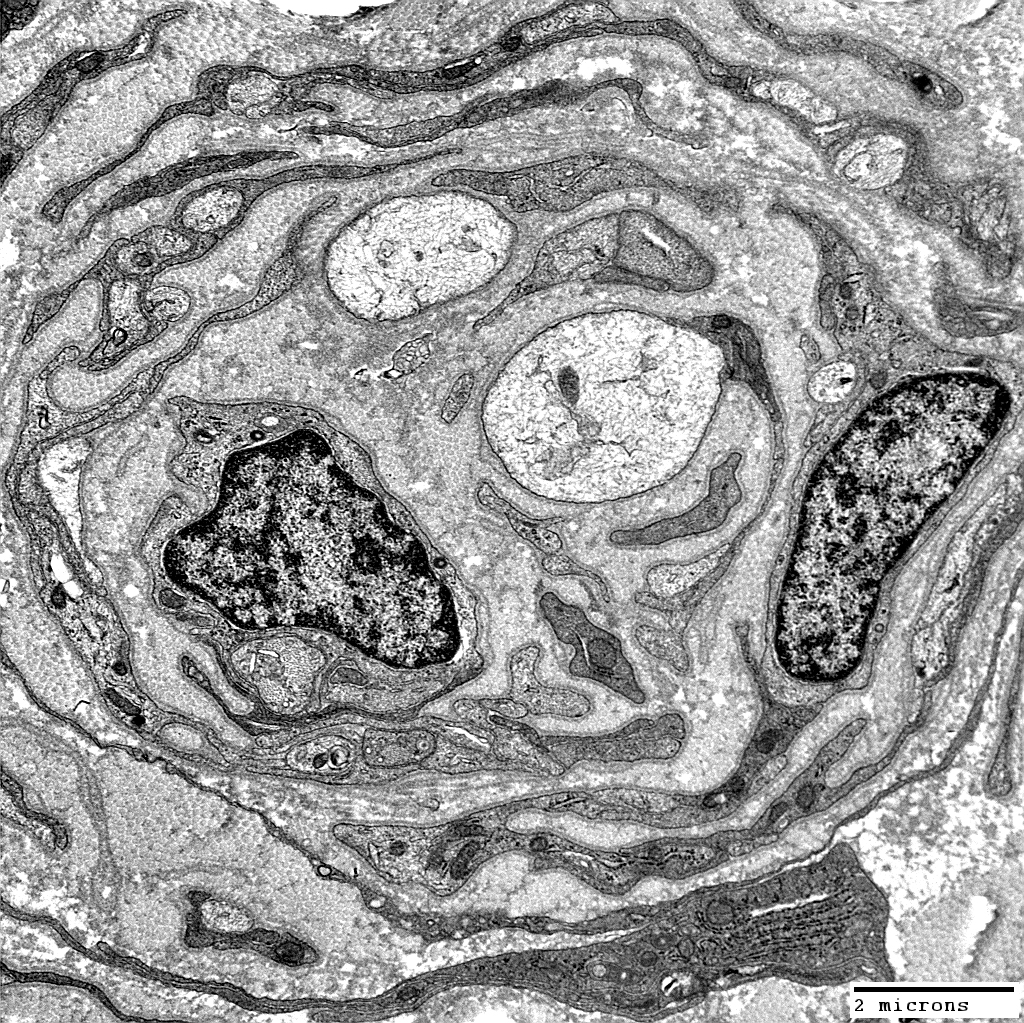 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
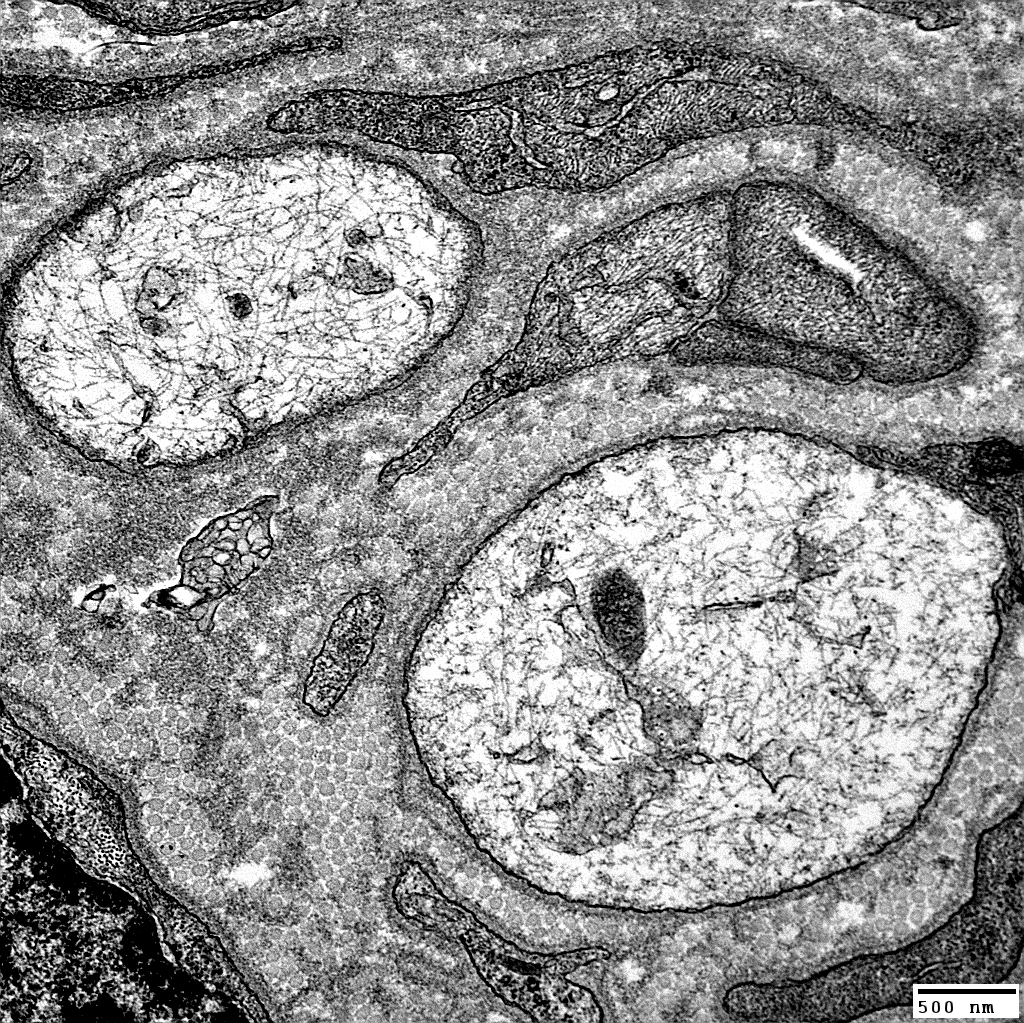 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
Onion bulbs: Molecular composition
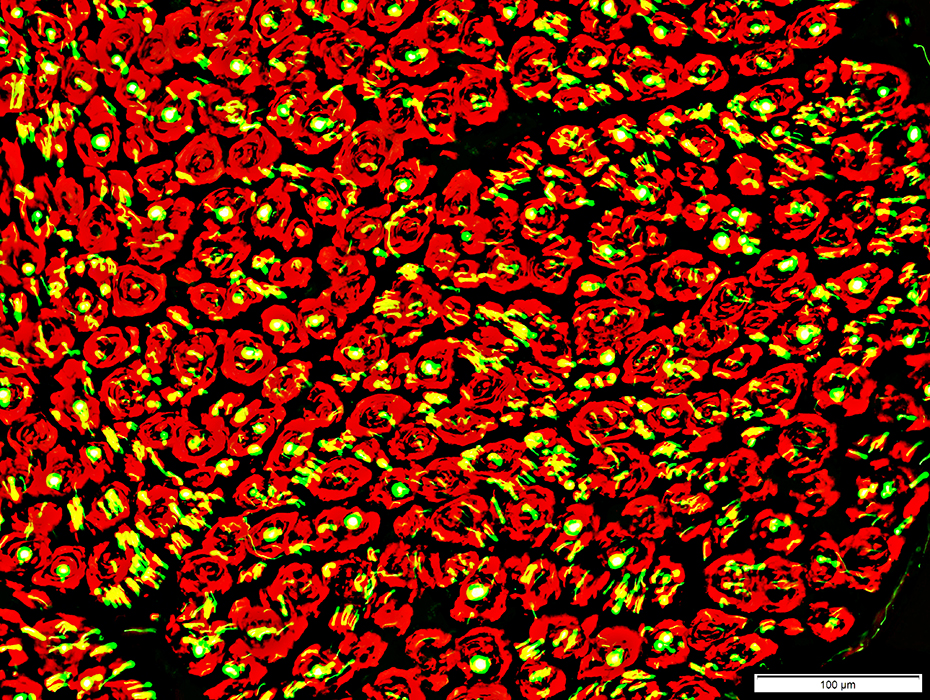 Neurofilament stain (Green) + NCAM stain (Red) |
Surrounded by NCAM containing Schwann cells
Schwann cells in Onion Bulbs
Contain both NCAM (Above) & P0 (Below) (Similar to Büngner band cells)
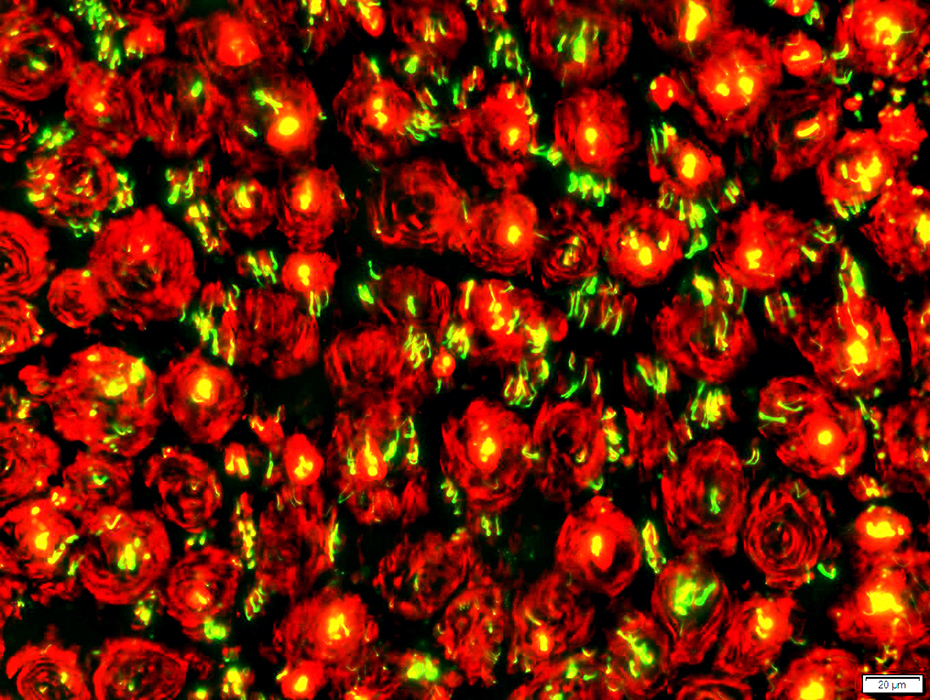 Neurofilament stain (Green) + P0 stain (Red) |
Contain both NCAM & P0 (All onion bulb cells cells costain (Below; Yellow))
Similar to Büngner band cells
P0(r).jpg) NCAM stain (Green) + P0 stain (Red) |
Onion Bulbs, Early
Onion bulbs, Incompletely formedSchwann cell processes: Long, uninterrupted
Surround 3 thinly myelinated axons
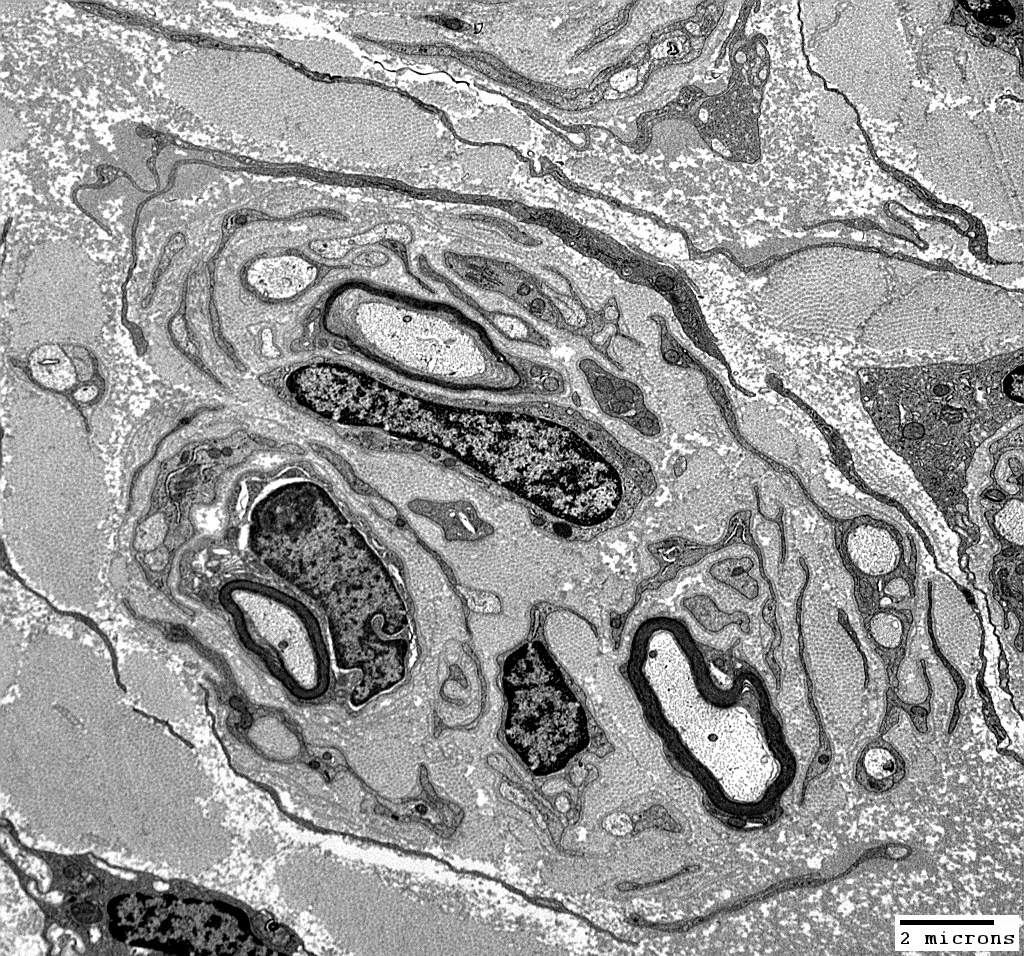 From: Robert Schmidt MD |
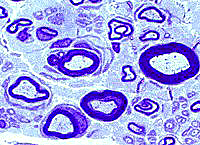 Toluidine blue Onion bulbs, Early Extra layers of Basal lamina, Collagen & Schwann cell processes around thinly or normally myelinated axons. |
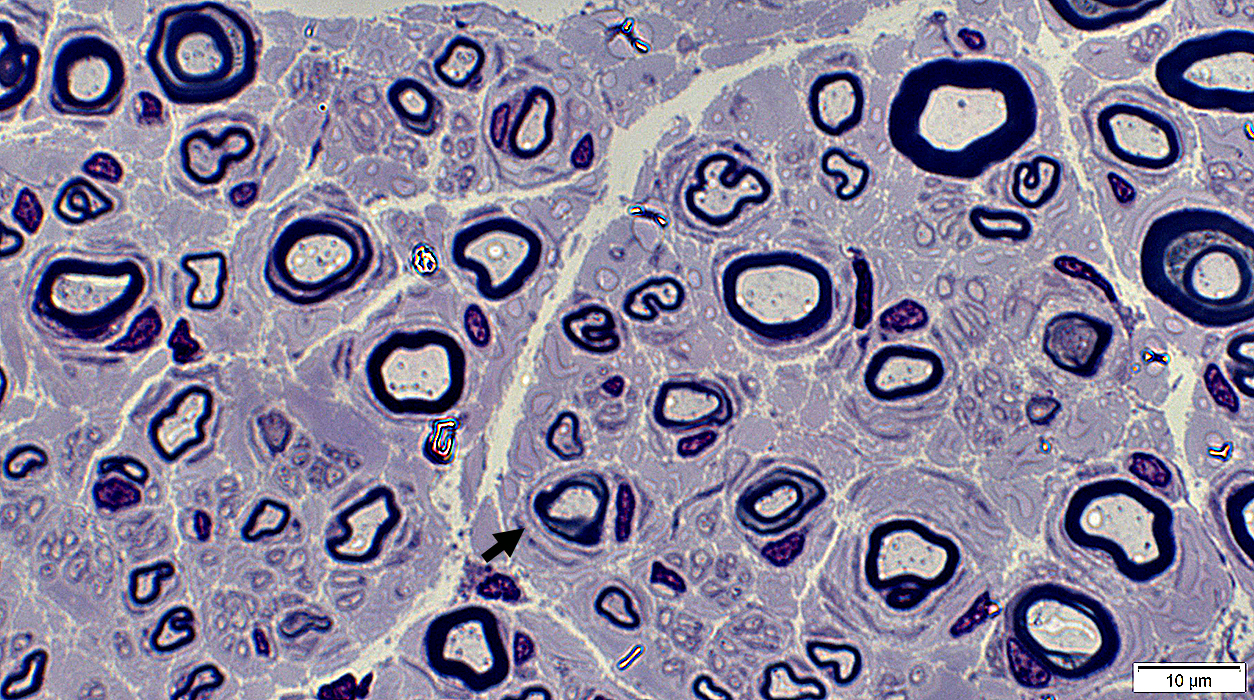 Toluidine blue |
More thickly myelinated, irregular-shaped myelinated axons (Below)
May be related to changes in axon size or regeneration
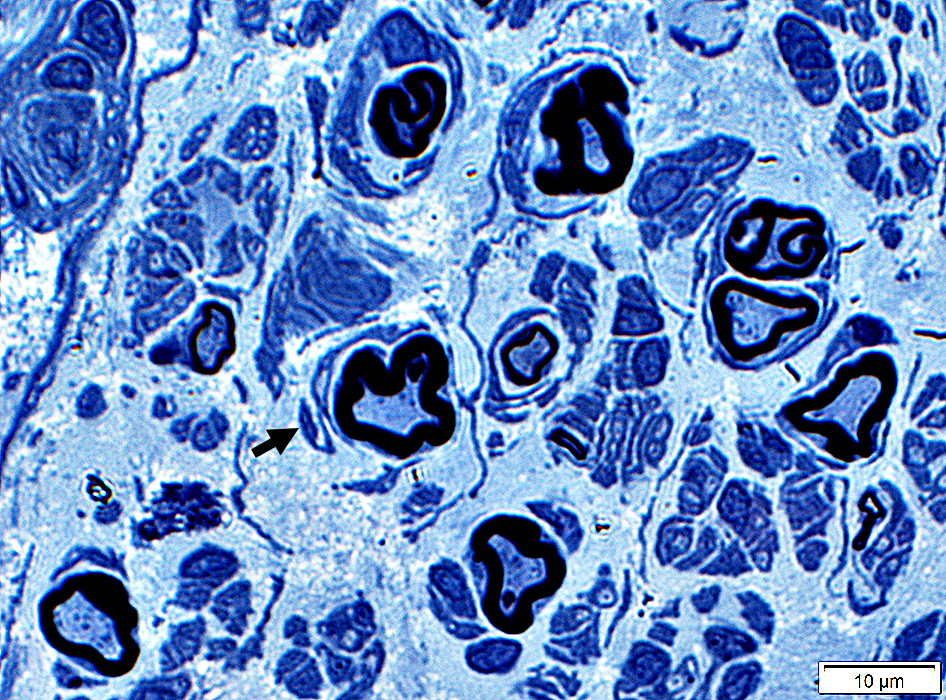 Toluidine blue |
Schwann cell processes & Collagen
May partially surround irregular-shaped myelinated axons
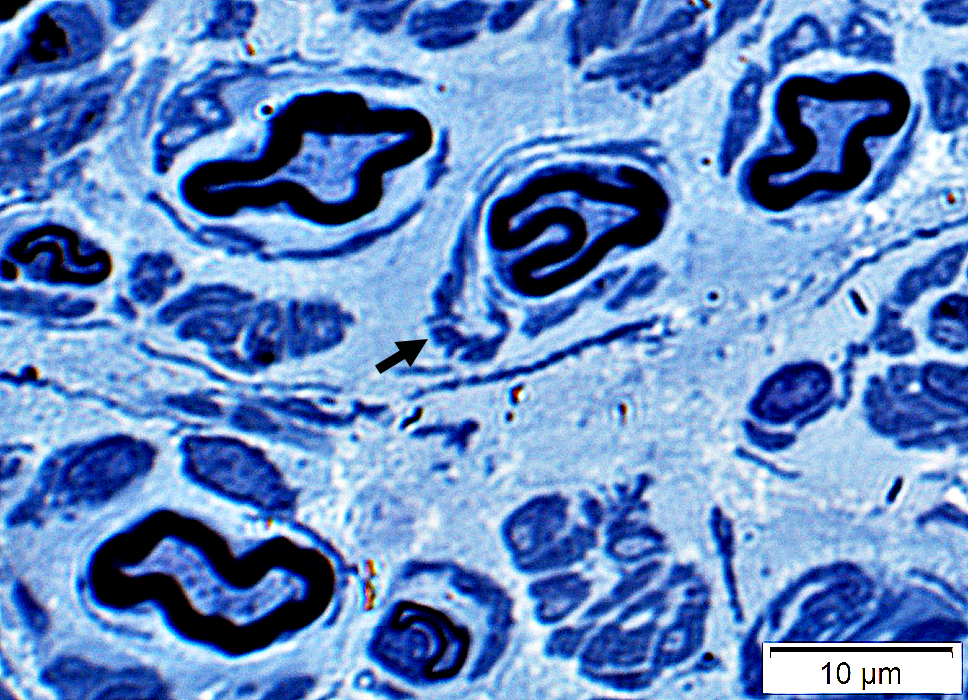 Toluidine blue |
Also see
Pseudo-onion bulbs
Perineurioma
Schwann cells & Circumferential Axon Sprouts
Chronic Immune Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP): Adult
|
Other CIDP pathology Adult Childhood Demyelinated axons Demyelination, Active Differential fascicular Δ Onion bulbs Segmental demyelination Sub-acute onset Thin myelin sheaths Tomacula |
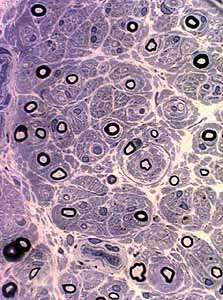 |
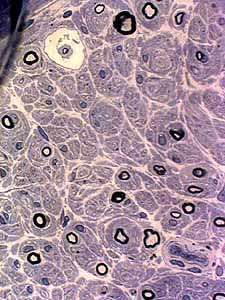 |
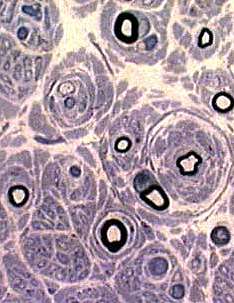 |
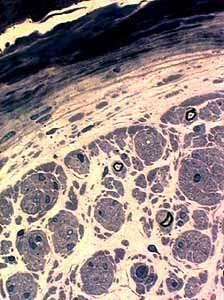 |
|
Remaining axons
Thinly myelinated Reduced numbers |
Onion bulbs: Small
|
||
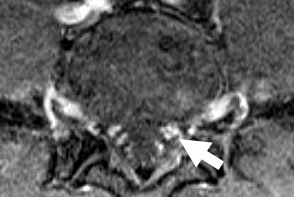
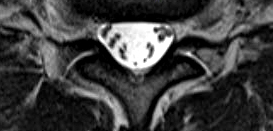
Sensory CIDP: MRI
Cervical Spinal Cord & Roots: Enlargement & Contrast enhancement of Anterior & Posterior (Arrow) Roots
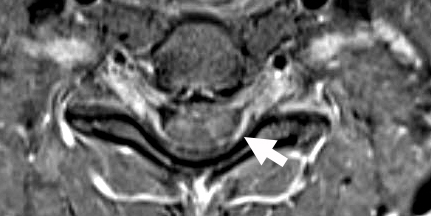 T1 with contrast |
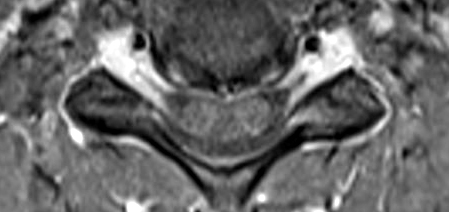 T1 with contrast |
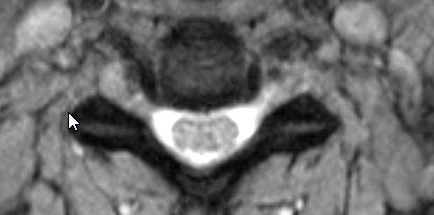 T2 |
Enlargement of Cervical Roots & Brachial plexus (Arrow)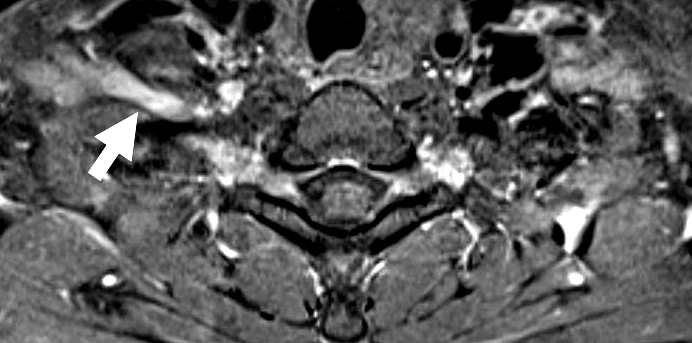 T1 with contrast |
|
Return to Normal nerve biopsies
Return to Biopsy illustrations
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Nerve biopsy
Return to Demyelinating neuropathies
Return to Active demyelination
References
1. Muscle Nerve 2019;59:665-670
1/19/2026