Axons, Myelin & Schwann Cells: Molecular Features 1
Normal Peripheral Nerve: Molecular Features of Schwann cells & Myelin
| Axon associations Large axons Myelin components 3 most abundant myelin proteins: Myelin Basic Protein (MBP); P0 (MPZ); Periaxin (PRX) Small axons Non-myelinating Schwann cells: Marker = Nerve Cell Adhesion Molecule (NCAM) Myelin: Two types Large myelinated axons: Myelin contains both P0 & MBP Smaller myelinated axons: Myelin contains P0 but little MBP Schwann cells Types: Several Development: Changes |
|
MBP = Myelin Basic Protein P0 = P0 protein NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
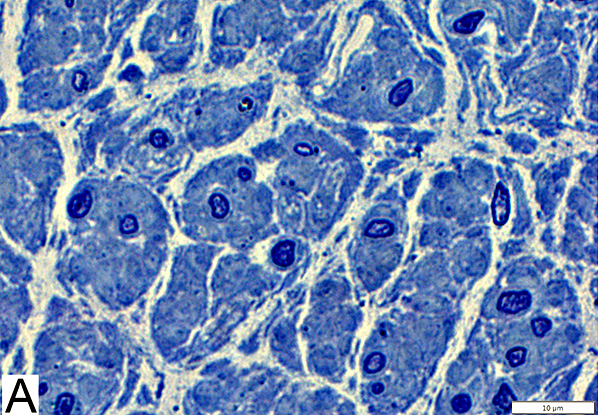
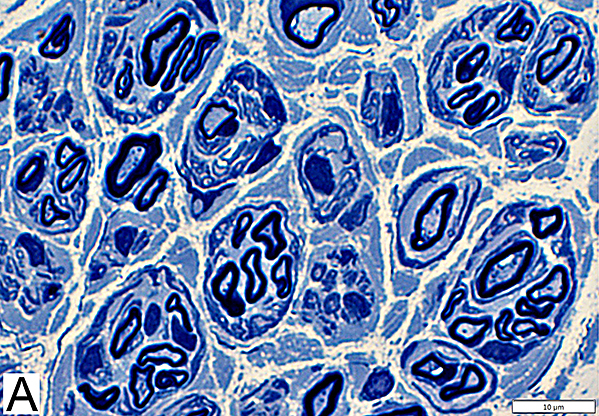
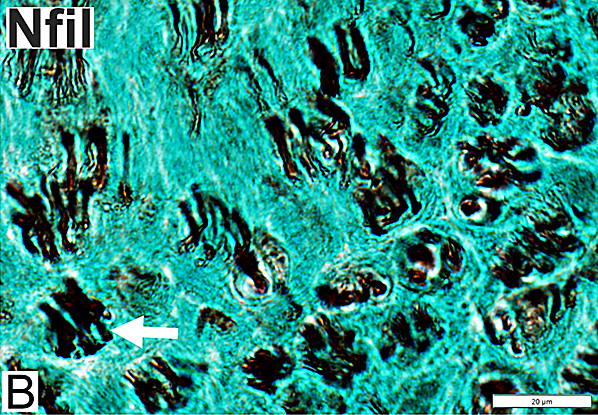
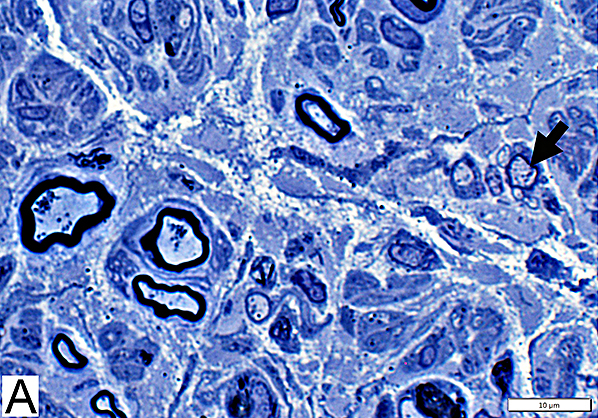
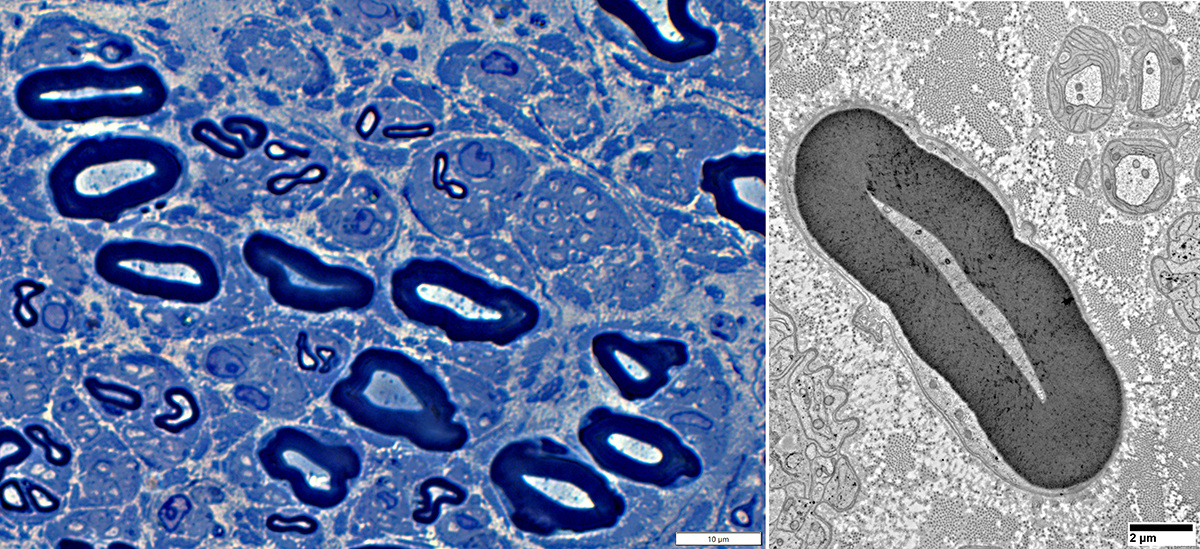
Axon Types: Normal Adult Nerve
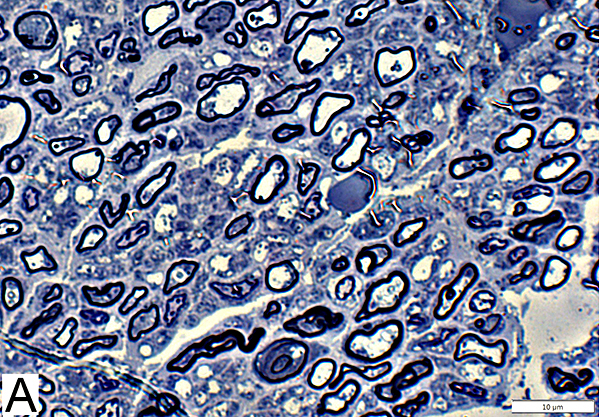
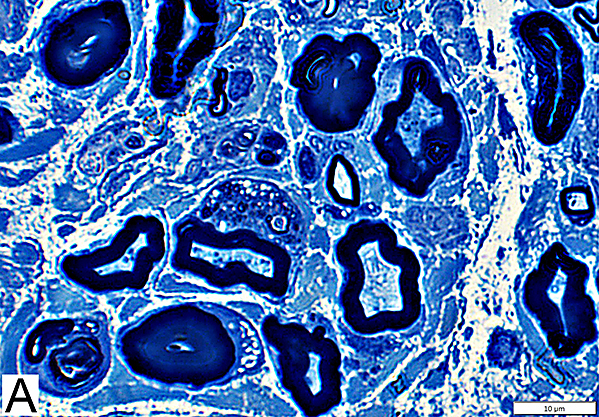
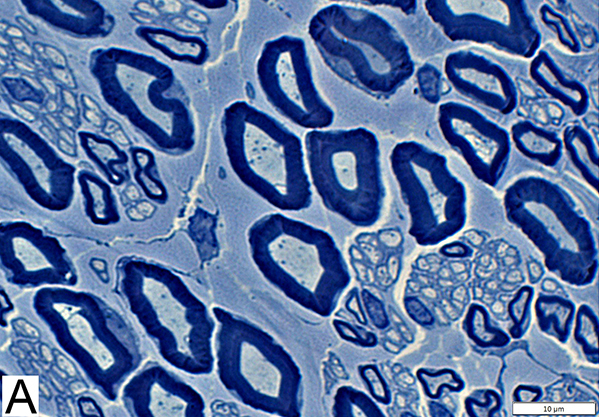 Toluidine blue stain Normal Adult Nerve: 3 Axon Populations Myelinated axons Large size; Thick myelin Intermediate-size; Thinner myelin Unmyelinated axons: Small size; Grouped |
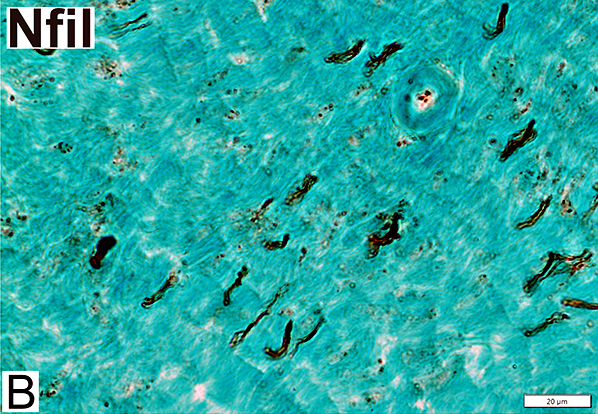
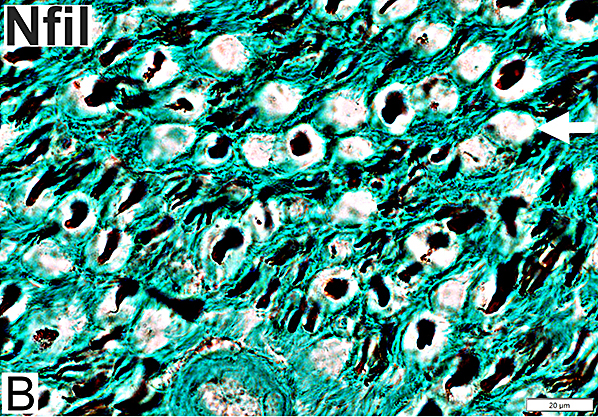
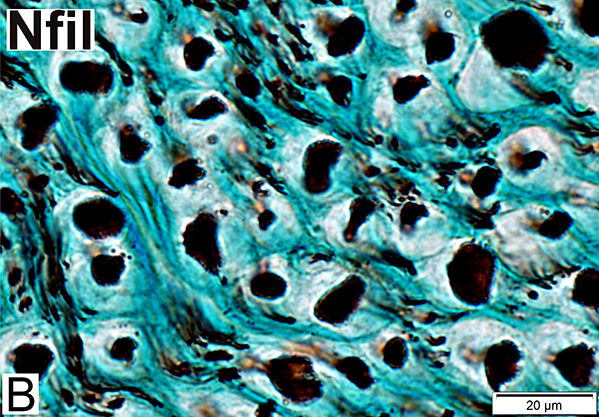 Nfil = Neurofilaments Normal Adult Nerve: 3 Axon Populations Sizes Large Intermediate Small: Grouped; Not cut in cross section |
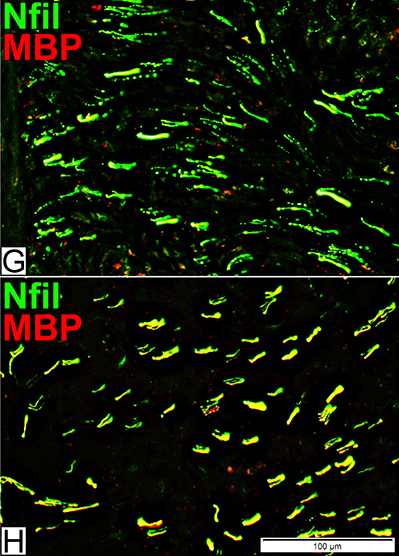
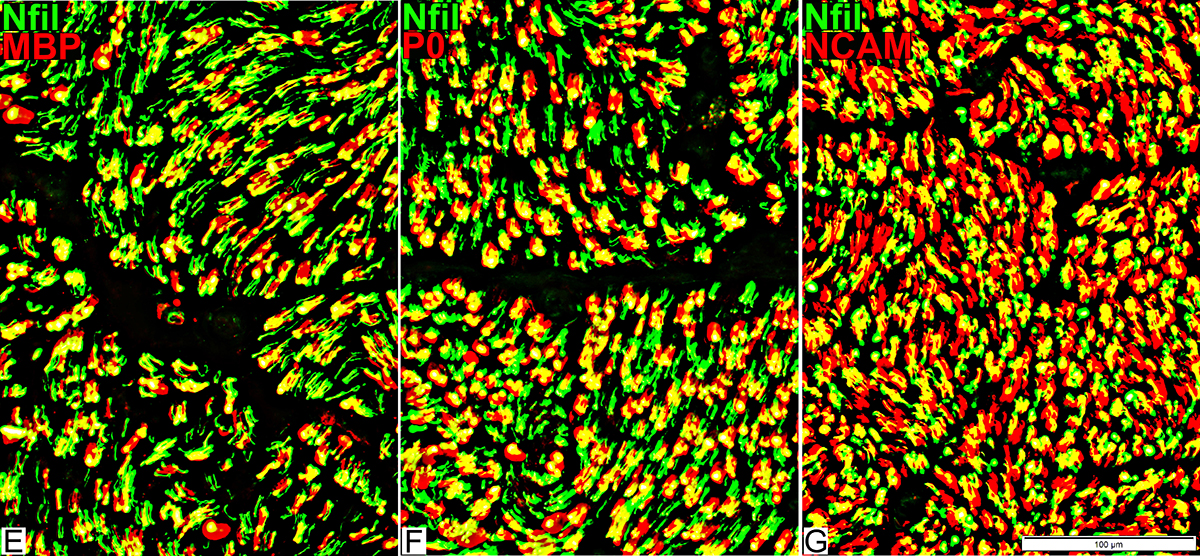
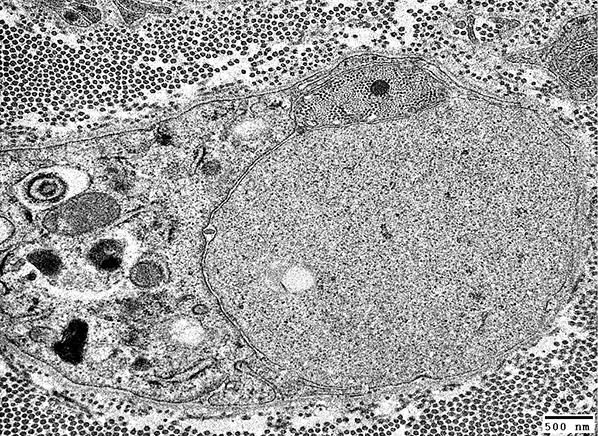
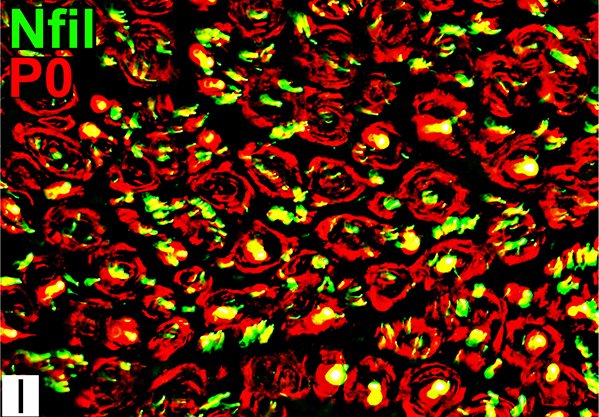
Axons & Schwann cells/Myelin: Normal
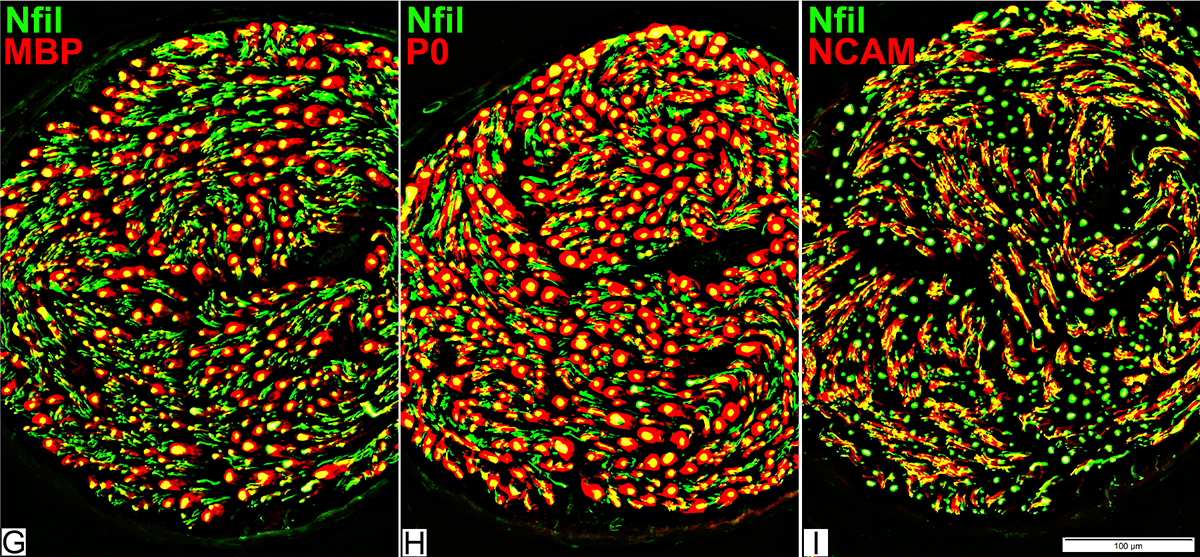 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
Myelinated axons
Large size
Myelin has both Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) & P0 protein (P0)
Intermediate-size
Myelin has mainly P0 with little MBP
Small, Unmyelinated
Schwann cells have NCAM but no P0 or MBP
Note: MBP is never present alone in normal adult Myelin or Schwann cells: See below
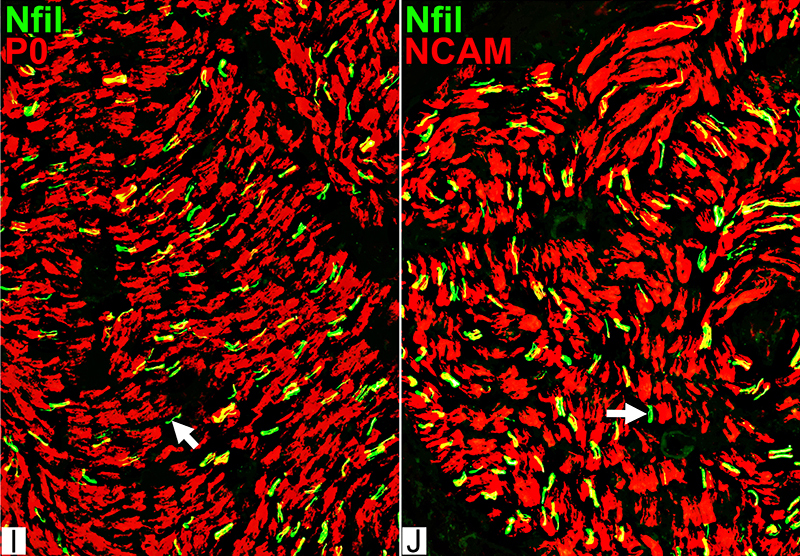
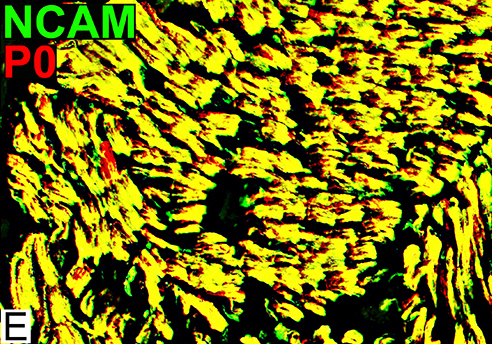
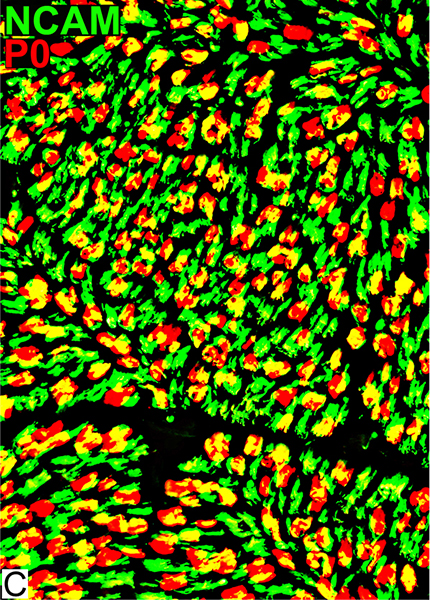
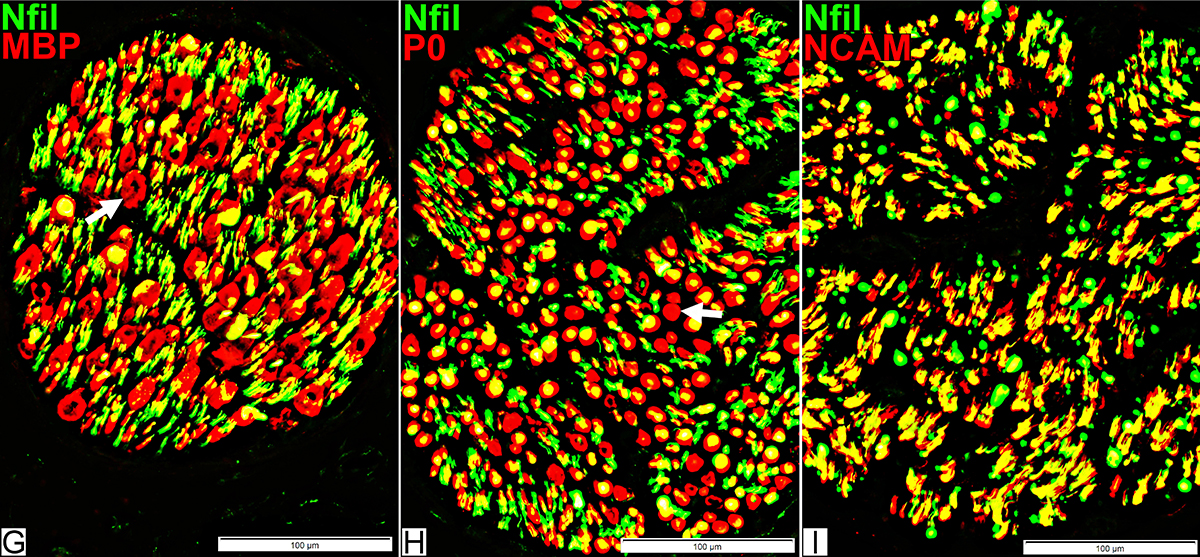
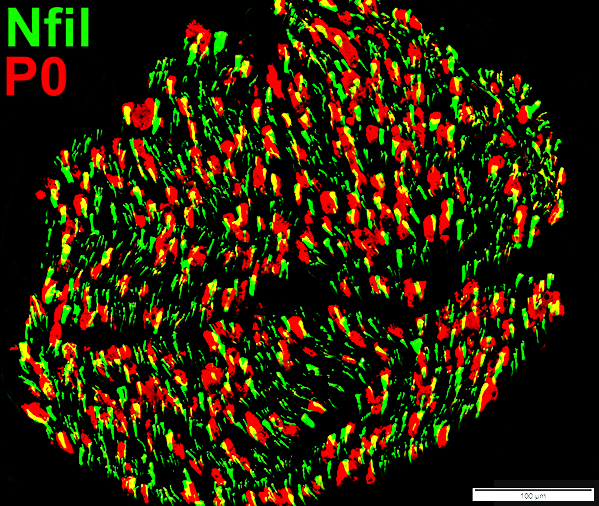
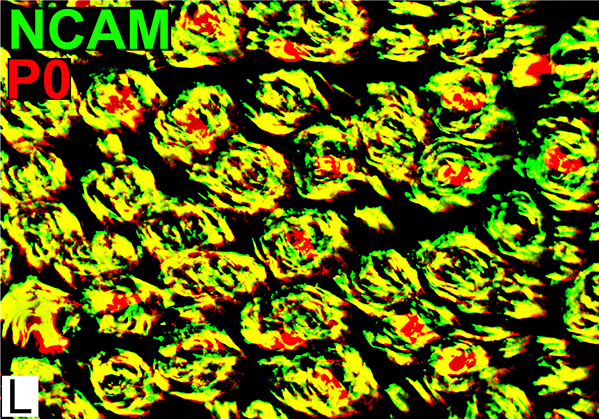
Schwann cells & Myelin: Normal
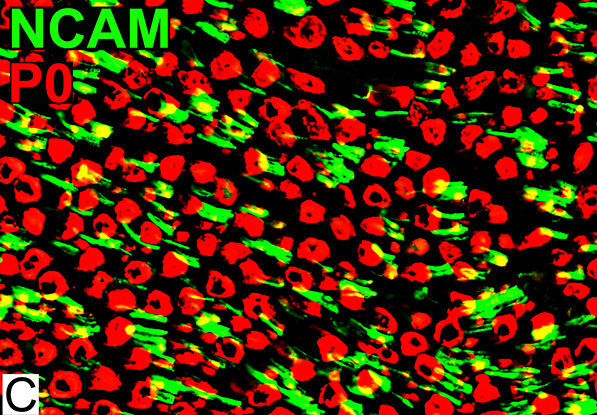 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Normal Adult Nerve: Myelin/Schwann cell Populations Non-myelinating Schwann cells Stain for NCAM (Green), but not P0 or MBP Surround: Several, clustered small axons Myelin Most, or all, sheaths stain for P0 (Red) Few cells stain for both NCAM & P0 (No Yellow) |
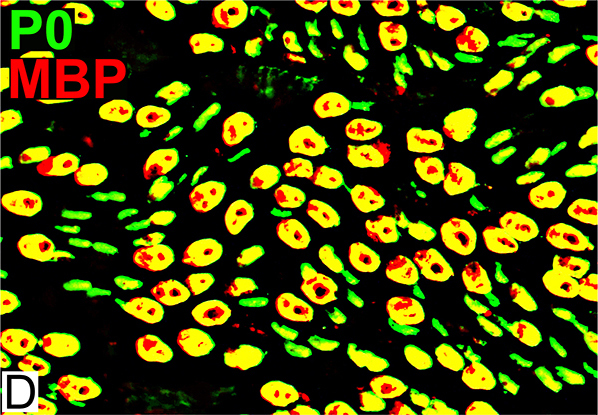 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Normal Adult Nerve: 2 Myelin Populations Large (Thick) Myelin sheaths: Myelin has abundant MBP & P0 (Yellow) Small (Thinner) Myelin sheaths: Myelin has mainly P0 (Green), but little MBP No sheaths have only MBP (Red) |
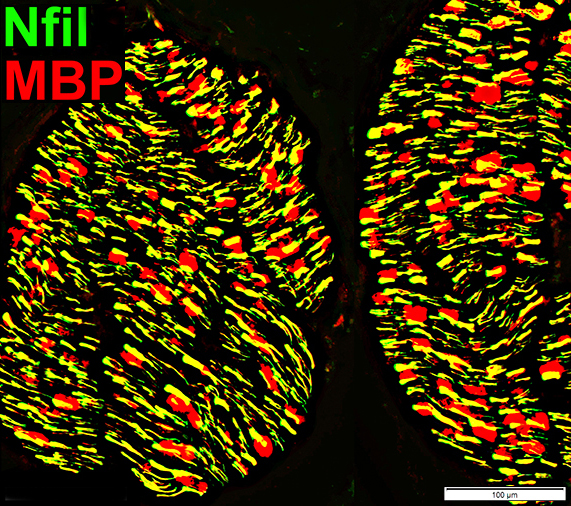
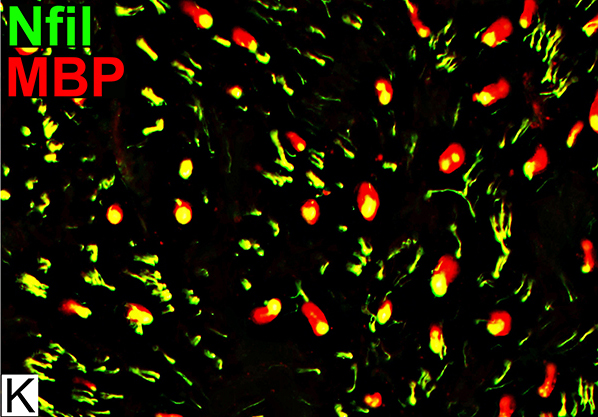
Myelin & Periaxin: Normal Nerve
3 Most abundant myelin proteins in peripheral nerveMBP
P0
Periaxin
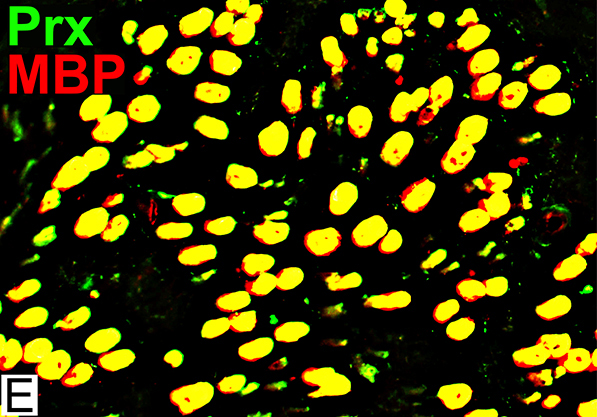 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; Prx = Periaxin Normal Adult Nerve: Myelin Populations Periaxin (Green) colocalizes (Yellow) mostly with MBP around large axons |
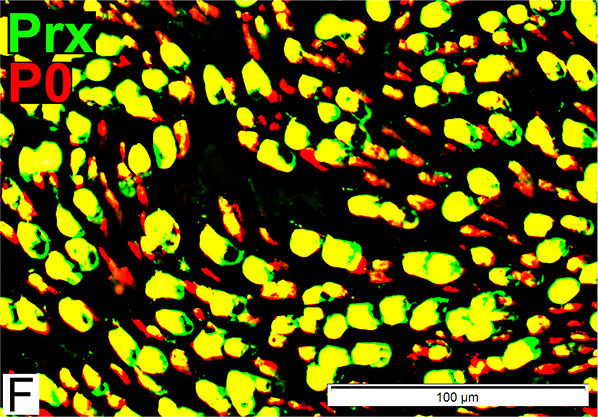 P0 = P0 protein; Prx = Periaxin Normal Adult Nerve: Myelin Populations P0 (Red) has some, patchy associated Periaxin |
Infant Sural Nerve: Normal
Axon Sizes: Smaller than adultsImmature Schwann cells: Contain MBP
Myelin: 1 population, Contains P0 & MBP
Axon types: Normal Infant
 Toluidine blue stain Infant Nerve: Axon Populations Large Myelinated: Smaller than adult large axons; Thin myelin sheath Intermediate-sized: Thinly Myelinated or Unmyelinated |
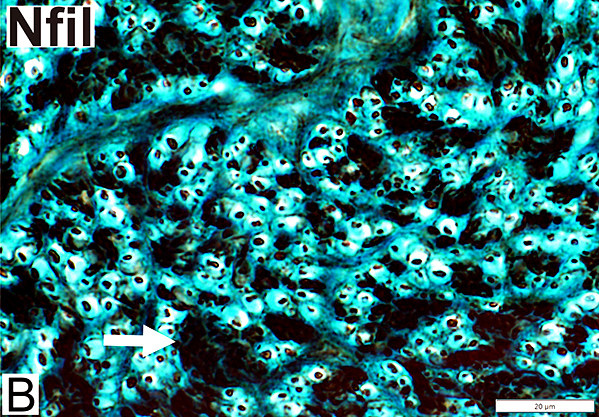 Nfil = Neurofilaments Infant Nerve: Axon Populations Large (Myelinated): Smaller than adult large axons Small Unmyelinated (Arrow): Present in clusters |
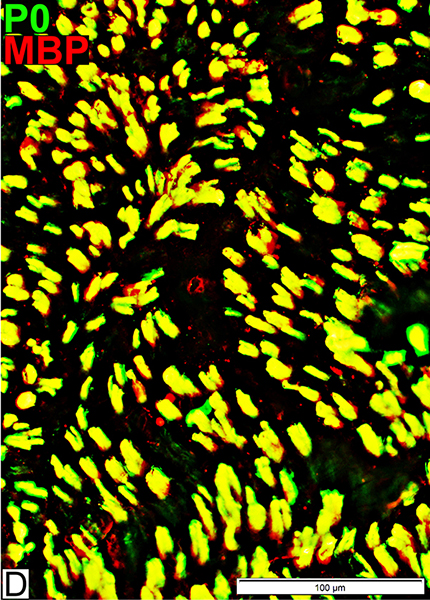
Axons & Schwann cells/Myelin: Normal Infant
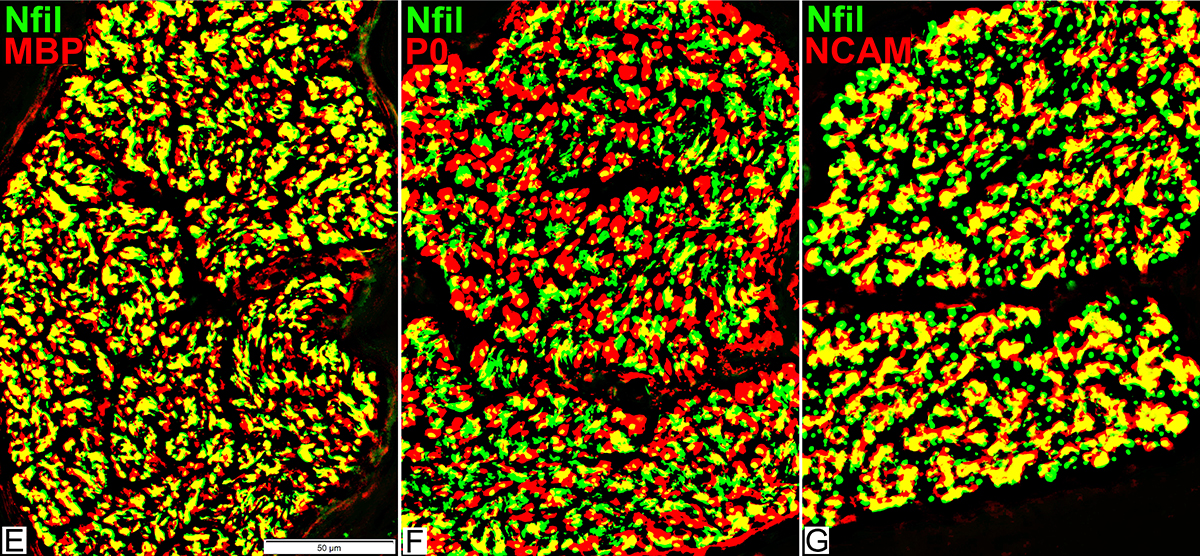 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
| Largest Axons (F & G) Smaller than in adults MBP (Left; E) (Red or Yellow): Present In most Schwann cells Alone, without P0, in some cells |
P0 Present in sheaths around most myelinated axons (Center; F) Patchy presence in Schwann cells around unmyelinated axons NCAM (Right; G) Present with most unmyelinated, but not myelinated axons |
Schwann cells & Myelin: Normal Infant
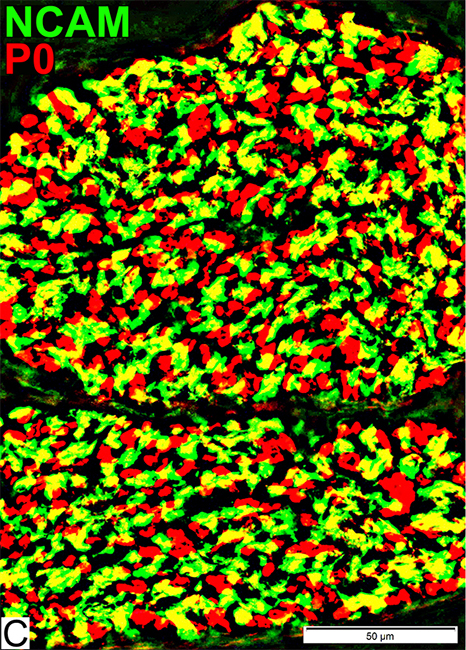 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells Stain for NCAM (Green; Yellow) Also contain patchy regions of P0 (Yellow), different from adults Myelin Stains for P0 (Red) |
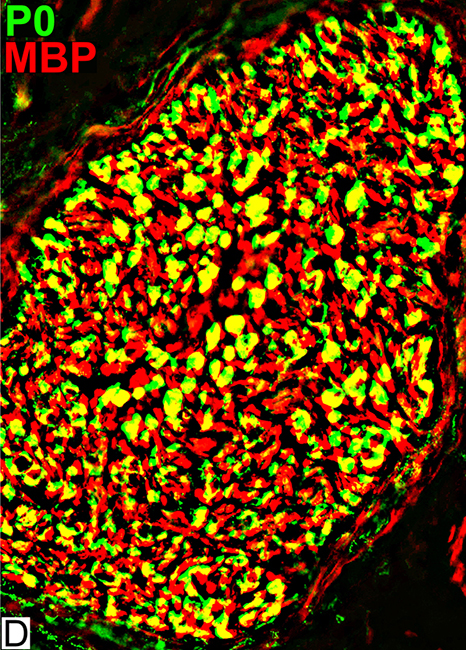 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Schwann cells MBP (Red; Yellow) Present in all Schwann cells & Myelin Present in Schwann cells without P0 (Red) Myelin Contents: MBP & P0 |
Axon loss, Severe, Chronic: Adult Sural Nerve
|
Remaining Axons Small Structure Continuous or Beaded Unmyelinated Axon/SC ratio: 1:1 Single axon in a Schwann cell "Singletons" Schwann cells associated with Singleton axons Immature Molecular components Contain MBP without myelin May have no NCAM or P0 Regenerated Often occur in clusters Myelin: Thin Other non-myelinating Schwann cell processes Concentric or within cluster Components: Small interdigitated SC processes Denervated Schwann cells Schwann cells with no associated axons Büngner bands Clusters of thin SC processes May contain both NCAM & P0 or only P0 Collagen pockets Figure legend Regenerated axon cluster (Top Left) Axon contents Thinly myelinated axons: Two Unmyelinated axon: One Collagen pocket (Between myelinated axons) Schwann cell processes Multiple closely apposed small processes Locations Around & within cluster Surround collagen pocket Singleton axons (Right) Unmyelinated Surrounded by Interdigitated small SC processes Büngner band (Small) Contains interdigitated SC processes Collagen pocket (Top right) Schwann cell (Bottom left) Surrounds 3 small unmyelinated axons Fibroblast processes: Thin; Dark Collagen Clusters of uniformly sized small dots |
|
Axon loss: Morphology
 Toluidine blue stain Severe axon loss Few, or No axons, are visible |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments Neurofilament stain A few, scattered clusters of small axons are visualized |
Myelinated Axon Loss
Schwann Cells surround Remaining Unmyelinated Singleton Axons
Singleton Axon sizes: ~ 1μMNo surrounding myelin
Associated Schwann cells
Express MBP but no P0
One Axon/Schwann cell
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Remaining Small axons without Myelin Structure: 2 patterns Beaded (Above) Continuous: Singletons Associated Schwann cells Stain for MBP (Yellow) on axons without myelin sheath Myelin None visible around remaining singleton axons |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Remaining Small Axons Size: Small May have no staining for p0 or NCAM (Arrows) Schwann cells Abundant: Remain after axon loss Most have no associated axons Stain for: NCAM & P0 |
MBP on small axons with no myelin
Some remaining axons may appear beaded with Neurofilament/MBP stain
Normal small axons have no MBP staining
MBP(r)sm.jpg) Neurofilament = Green; MBP = Red; Co-stain = Yellow |
Singleton Unmyelinated Axons
 From: R Schmidt |
Unmyelinated axons surrounded by Schwann cell processes (Arrow; Below)
May contain small blebs (Sprouts; Right)
Associated Schwann Cells
Surround single unmyelinated axon
In normal nerve non-myelinating Schwann cells surround several small axons
Similar to: Immature SC
Stain for MBP, even without myelin
Don't stain for NCAM or P0
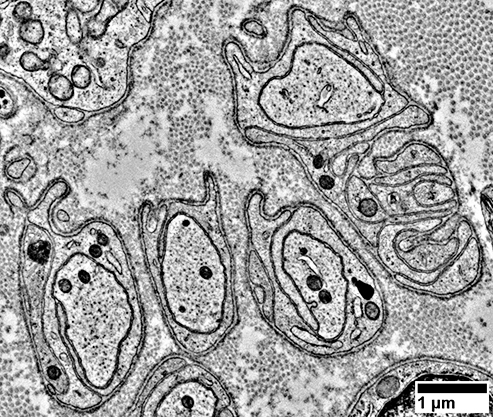 From: R Schmidt |
 From: R Schmidt |
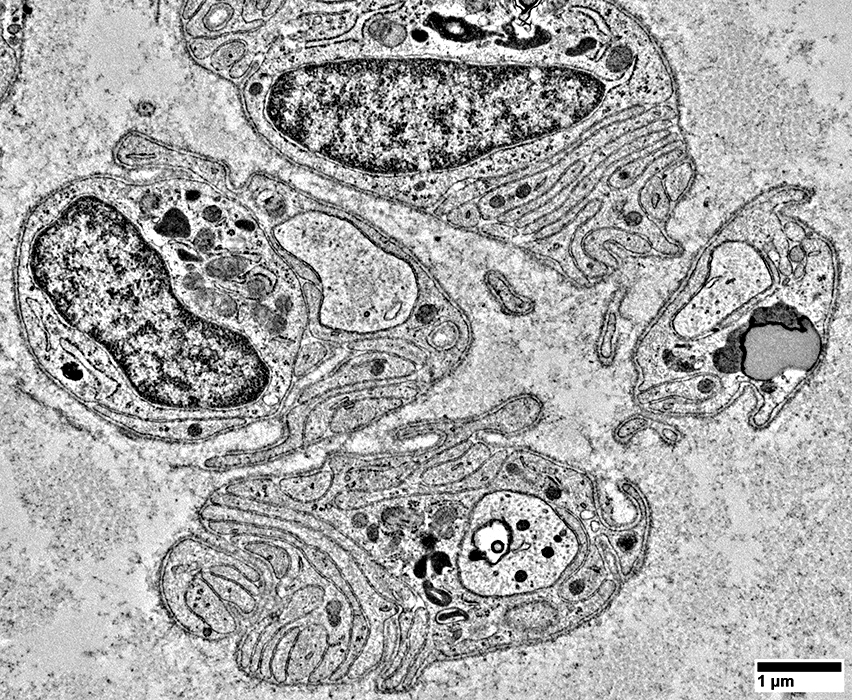 From: R Schmidt |
Unmyelinated axon surrounded by Schwann cell processes but no myelin
One unmyelinated axon per Schwann cell
 From: R Schmidt |
 From: R Schmidt |
Axon surrounded by Schwann cell processes but no myelin
One unmyelinated axon per Schwann cell
 From: R Schmidt |
Axon surrounded by Schwann cell processes but no myelin
One unmyelinated axon per Schwann cell
 From: R Schmidt |
 From: R Schmidt |
Axon surrounded by Schwann cell processes but no myelin
One unmyelinated axon per Schwann cell
Some axons have accumulations of organelles in their axoplasm
 From: R Schmidt |
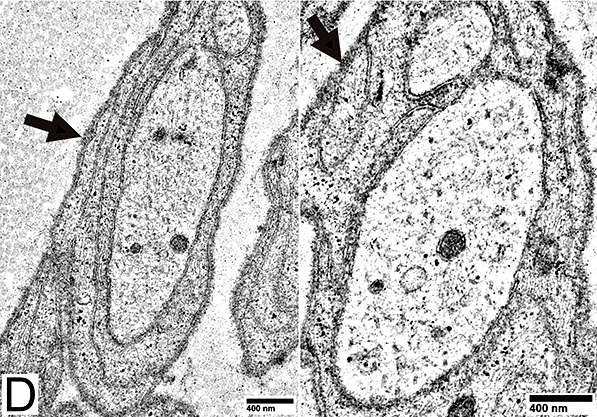
Denervated Schwann Cells (Büngner Band Cells)
 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells: Denervated No associated Axons Costain NCAM + P0 (Yellow) Also see: Onion bulb cells |
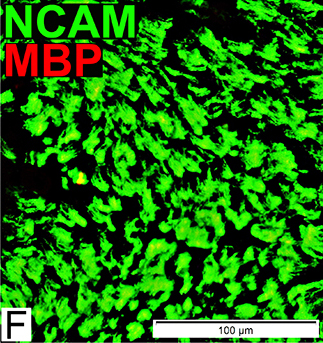 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells: Denervated No associated Axons Contain NCAM (Green) but not MBP |
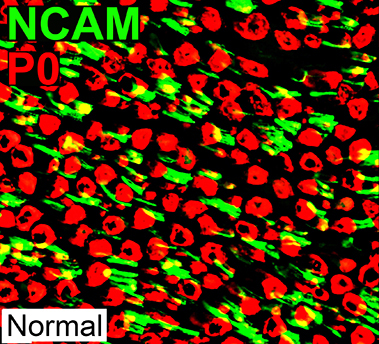 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann cells: Normal NCAM (Green) No co-staining with P0 (Red) P0 (Red) Stains myelin, not Schwann cells |
Büngner bands: Clusters of Schwann cell processes with no axons
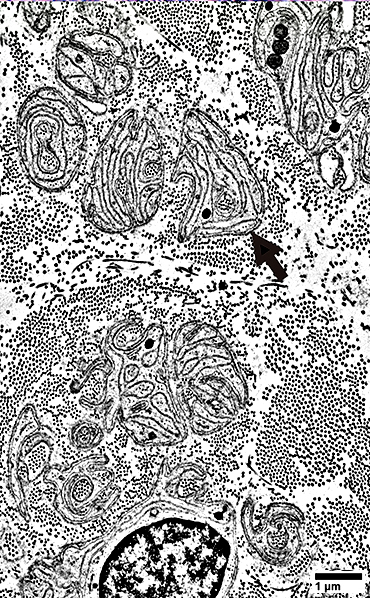 From: R Schmidt |
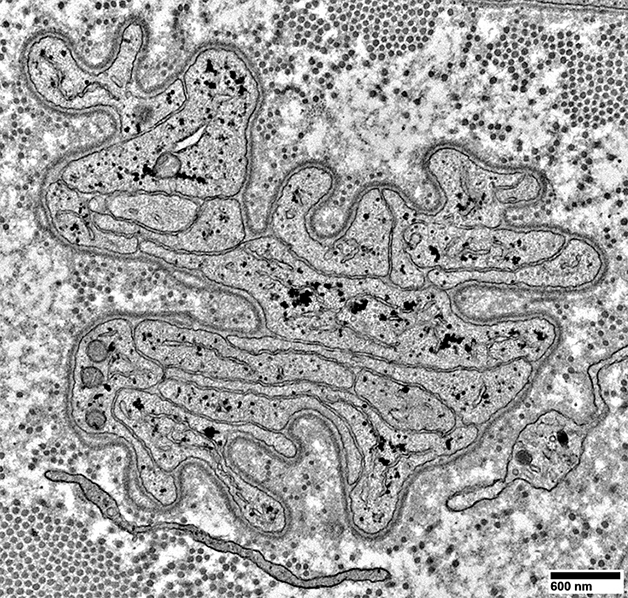
|
Interdigitated Schwann cell processes
Axon Regeneration
Regenerated Myelinated AxonsSize: Intermediate
Myelin Thickness: Thin; Similar thickness in each axon cluster
Myelin molecular components
MBP + P0 ± NCAM
Smaller myelinated axons have MBP in myelin
 Toluidine blue stain Regenerated Axons Many clusters of intermediate-sized thinly myelinated axons Axons in individual clusters have similar myelin thickness |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments Regenerated Axons (Neurofilament stain) Clusters of regenerated larger axons are present (Arrow) |
Axons & Schwann cells/Myelin: Axon Regeneration
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
P0: Stains myelin around many axons (Center; F)
NCAM (Right; G)
Stains around some, but not all, larger axons
Some NCAM profiles have no associated axon: Suggests incomplete axon regeneration with remaining denervated Schwann cells
Axon Regeneration: Myelin Features
 P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule NCAM Patchy co-stain (Yellow) with P0 (Red) in myelin sheaths Stains many non-myelinating Schwann cells (Green) |
 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Myelin Most myelin sheaths, even small, costain for both P0 & MBP |
Adult Sural Nerve: Wallerian Degeneration
Wallerian Degeneration: Active
 Toluidine blue stain Autophagic & Phagocytic Cells Cell Types Schwann cells: Autophagic Macrophages: Phagocytic Cell Contents: Myelin debris; Lipid droplets Myelin sheaths: Collapsed Autophagic Schwann cells have not completely degraded myelin |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments Degenerated axons: No neurofilament stain (Arrow) Neurofilament fragments, or Empty regions with no axon |
Axon Degeneration: Acute
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule |
No axon staining within MBP stained myelin (Left; G) (Arrow)
No axon staining within P0 stained myelin (Center; H) (Arrow)
Minor loss of small axons: Scattered empty NCAM (Red) sheaths (Right; I)
Wallerian Degeneration: Active, Autophagic cells
Definition: Schwann cells degrading their own myelin
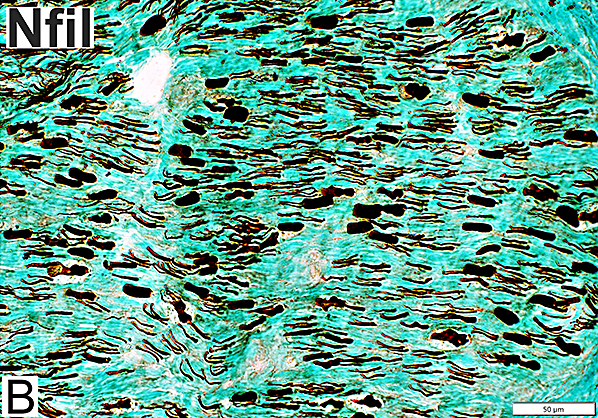
 Autophagic Cells Types Autophagic Schwann cells (Left) Macrophages (Center) Contents: Myelin debris (Left; Arrow); Lipid droplets (Center; Arrow) |
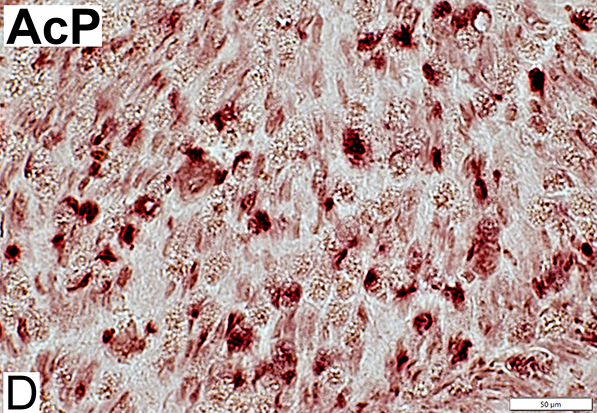 AcP = Acid Phosphatase Lysosomal Stain (Acid phosphatase): Endoneurial cells, scattered (Red) Compare to: Demyelination |
Adult Sural Nerve: Demyelination
Demyelination: Macrophage-Mediated/Associated
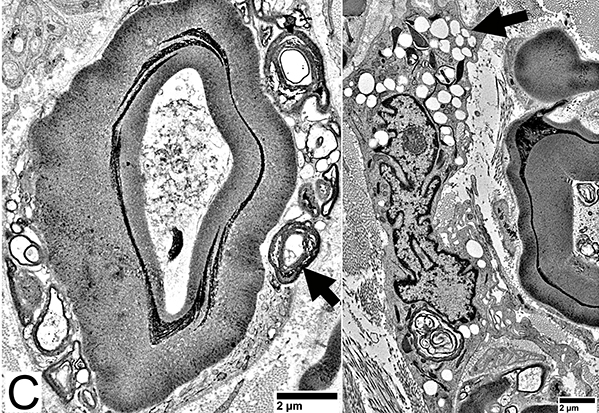
 Nfil = Neurofilaments Demyelinated Large Axons Large axons: No surrounding myelin space |
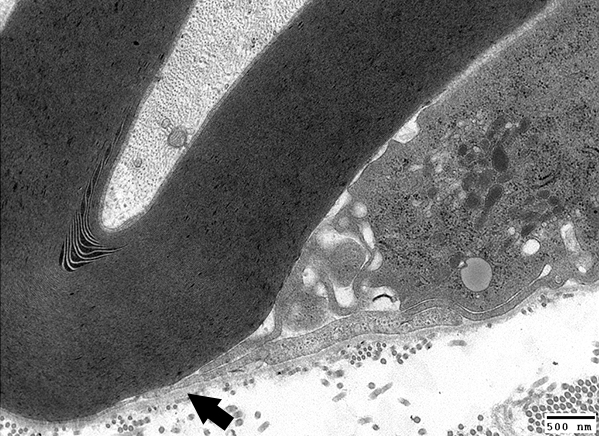 From: R Schmidt Macrophage-mediated Demyelination Macrophage process (Arrow) extends underneath Schwann cell basal lamina |
Demyelinated Axons
 Toluidine blue stain Large Demyelinated Axons (Arrow) Other axons often have thin myelin sheath for size |
 From: R Schmidt Demyelinated Axon: Surrounded by Schwann cell processes |
Demyelinated Large Axons: No surrounding Myelin sheath
Schwann cells surrounding Demyelinated axons: MBP+; P0 & NCAM-
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein Demyelinated Large Axons (P0 stain) No surrounding myelin (Arrow; Below) |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Demyelinated Large Axons Co-stain (Yellow) for MBP: Immature non-myelinating Schwann cells |
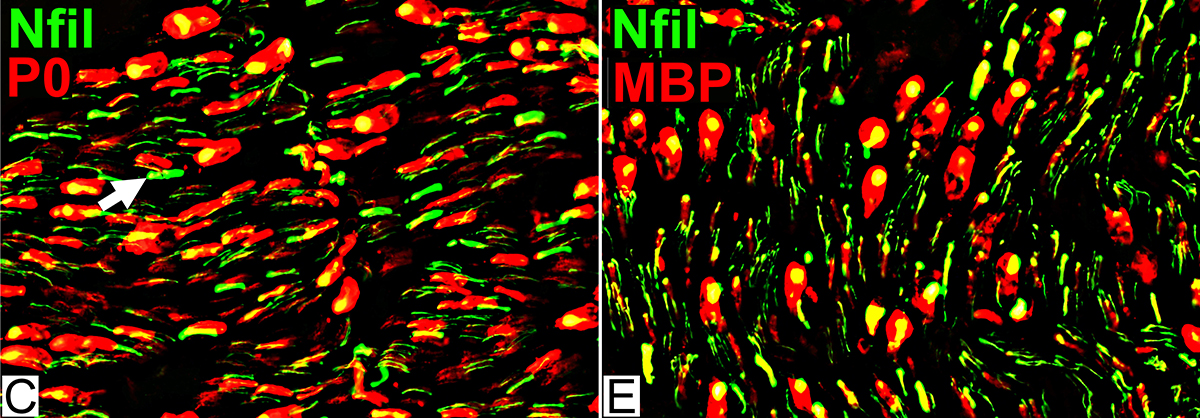 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein |
Myelin Disorders: MAG Neuropathy
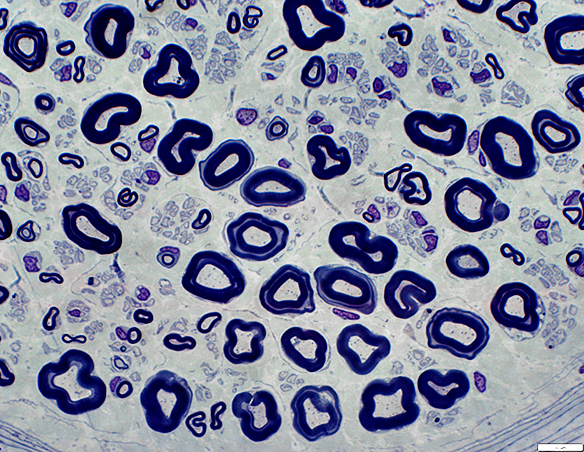 Toluidine blue stain Myelin sheaths: Irregular structure |
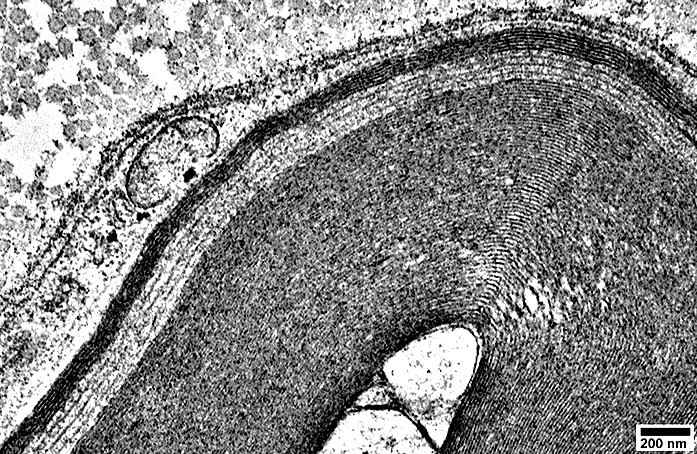 From: R Schmidt Myelin Wide-spacing Cleft, contatining a few layers, within compact myelin |
MAG Neuropathy
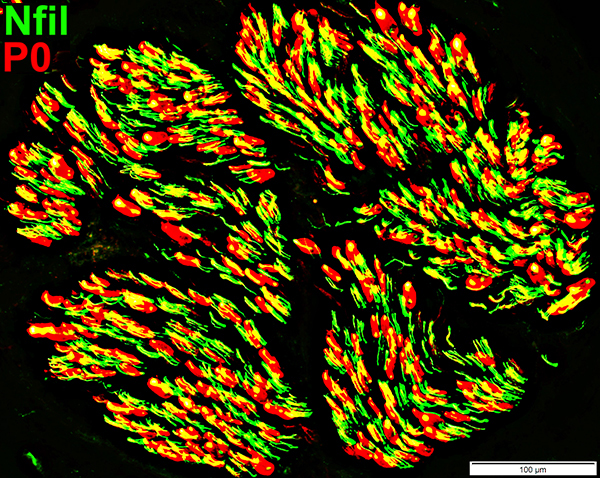 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein No demyelinated axons |
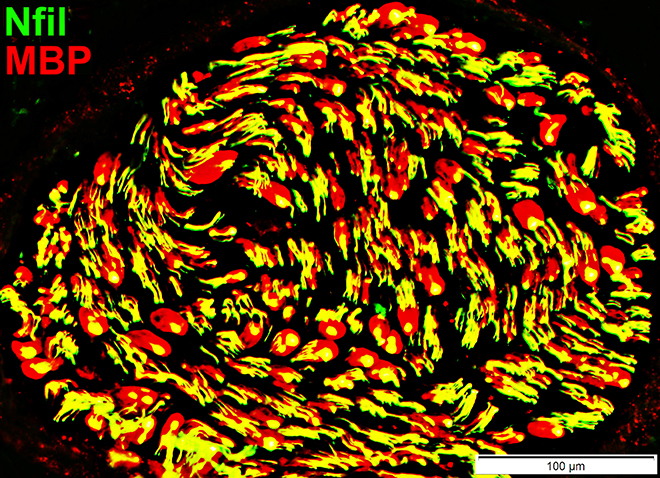 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Small axons: Many have associated MBP co-staining (Immature Schwann cells) |
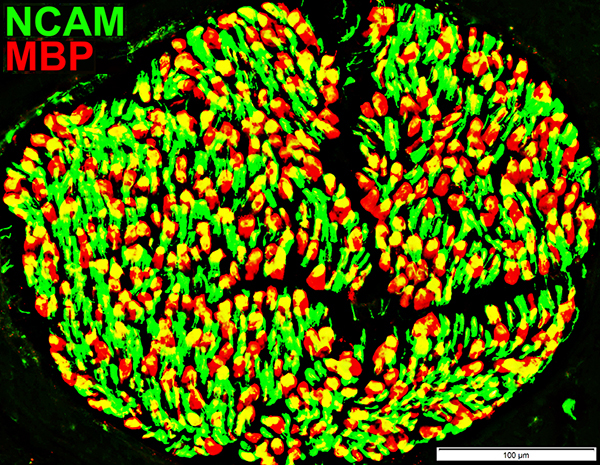 NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein NCAM (Yellow): Abnormally expressed within MBP-containing (Red) myelin sheaths |
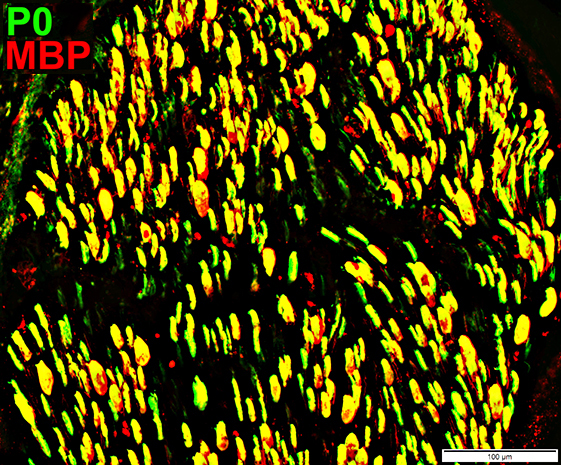 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein MBP & P0 expressed in Large & Smaller myelin sheaths Smaller myelinated axons normally have myelin that stains only for P0 |
Chronic Demyelinating Neuropathy: Onion Bulbs
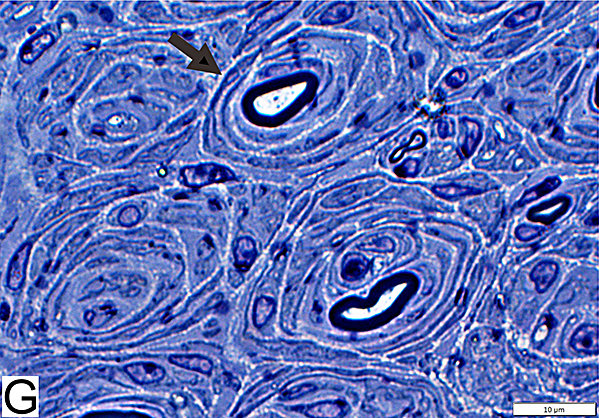 Toluidine blue stain Onion bulbs Structure: Concentric layers of Schwann cells & Collagen (Arrow) Center: Some have myelinated axon |
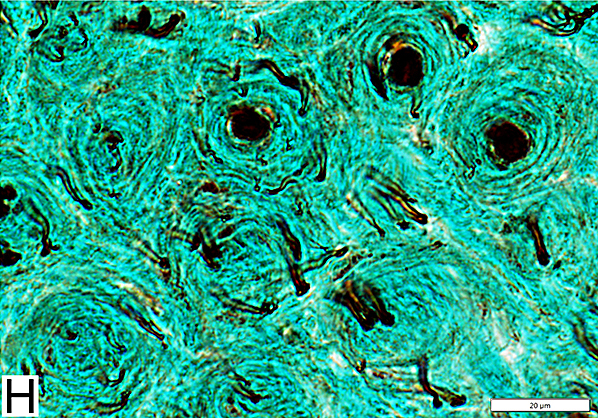 Neurofilament stain Onion bulbs (OB): Relation to axons Some have large central axon Others have no central axon Small, unmyelinated axons May be present within onion bulb layers or around OB periphery |
Onion Bulbs: Ultrastructure
Onion Bulb with Thinly Myelinated Central Axon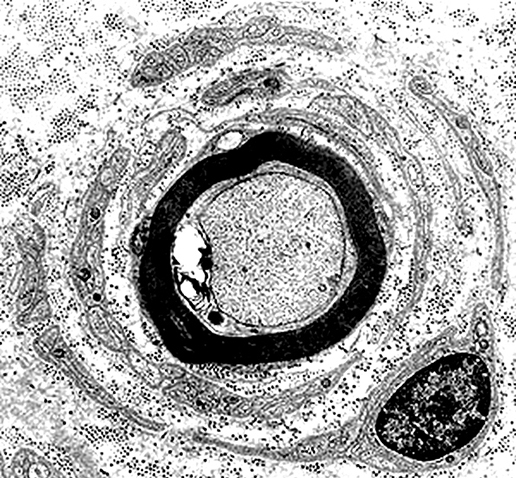 From: R Schmidt Onion Bulb structure Alternating layers of Schwann Cell processes & Collagen |
"Obsolete" Onion bulb: No remaining Central axon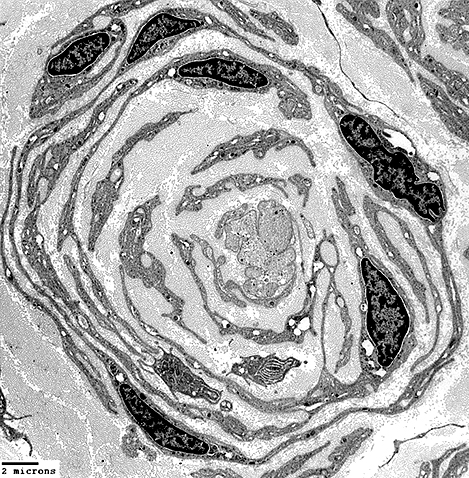 From: R Schmidt Onion Bulb structure Alternating layers of Schwann Cell processes & Collagen |
Onion Bulb Schwann cells: Molecular features
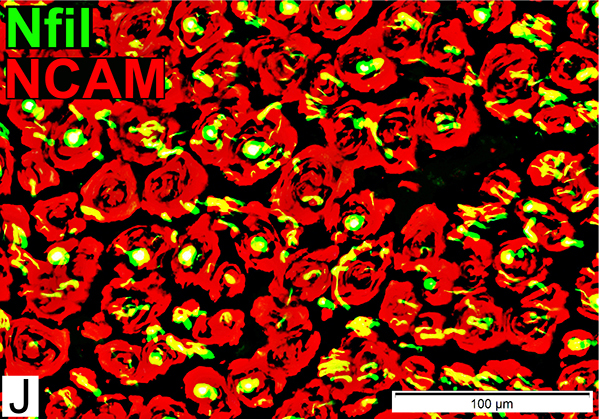 Nfil = Neurofilaments; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Onion Bulb cells NCAM Abundant in onion bulb Schwann cell processes Some onion bulbs contain central axons (Yellow) |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein Onion Bulb cells P0 Present in most onion bulb Schwann cell processes Some onion bulbs contain central axons (Yellow) |
 NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule; P0 = P0 protein Onion bulb Cells Contain both NCAM & P0 (Yellow) P0 (Red) also stains myelin around central axon in some onion bulbs |
 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Onion bulb Cells MBP (Red) Present in myelin around a few large axons Not in onion bulb cells Costains unmyelinated small axons (Immature SC) |
Neurofascin-186 antibodies: Axon Atrophy & Small Axon Loss
Axon Atrophy
 Larger myelinated axons: Axon atrophy Morphology: Small & Slit-like shape Myelin sheath: Thick for axon size See: Normal |
Axon atrophy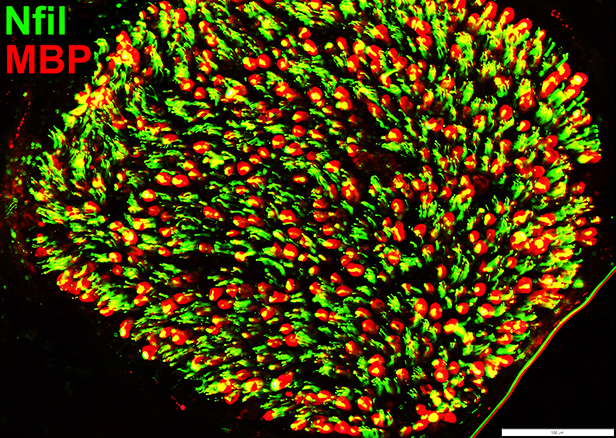 Nfil = Neurofilaments; MBP = Myelin Basic Protein Axons within MBP myelin sheaths Many are smaller than Normal |
Myelin: Irregular Structure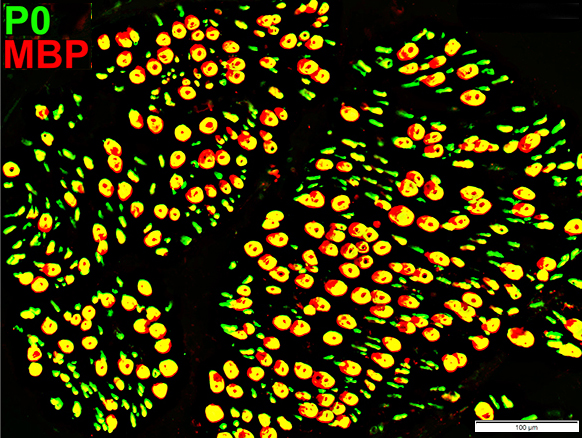 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Larger myelin sheaths Irregular co-stain for P0 & MBP |
Neurofascin-186 antibody: Reduced numbers of Non-myelinating Schwann cells & Small axons
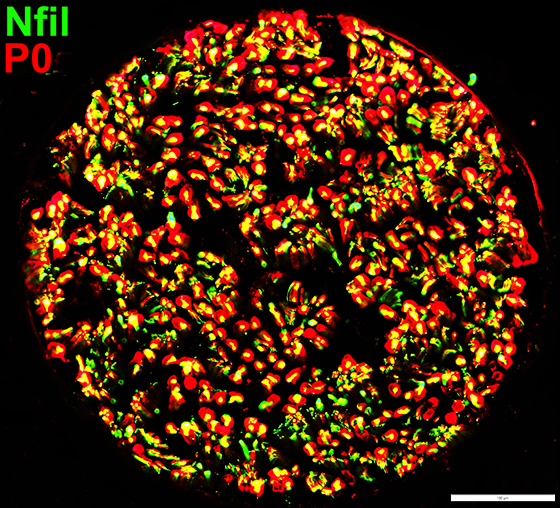 Nfil = Neurofilaments; P0 = P0 protein Small Axons (Green): Reduced numbers |
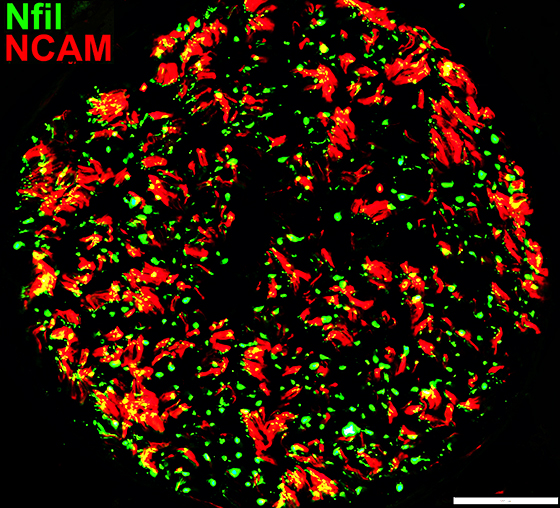 Nfil = Neurofilaments; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Non-myelinating Schwann cells (Red): Reduced numbers Small Axons: Reduced numbers (Many empty non-myelinating Schwann cells (Red)) Myelinated axons (Green): Generally small size |
Myelin Disorders: Other Pathology Patterns
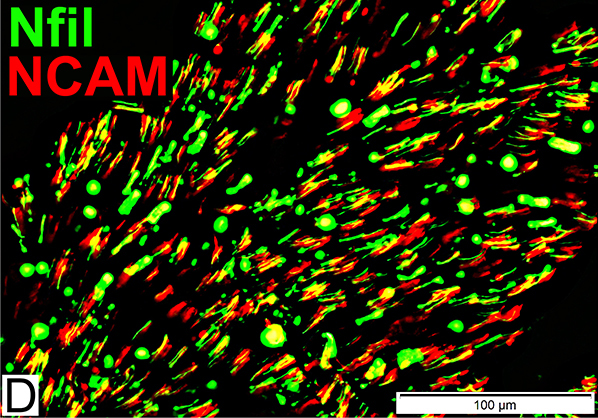 Nfil = Neurofilaments; NCAM = Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Schwann Cells (Red): Reduced numbers |
|
Abnormal Myelin Composition P0 lost from myelin on large axons; MBP (Red) remains (Arrow) Also see: PN with IgM vs MAG 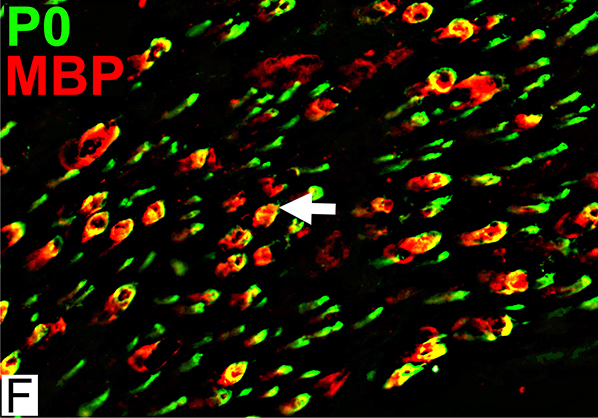 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein |
Active Demyelination: Autophagic Schwann cells & Myelin
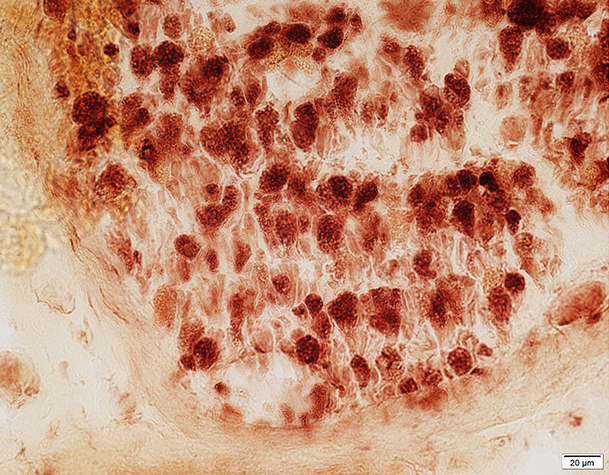 Acid phosphatase stain Most Myelin sheaths: Acid phosphatase+ Compare to: Wallerian degeneration |
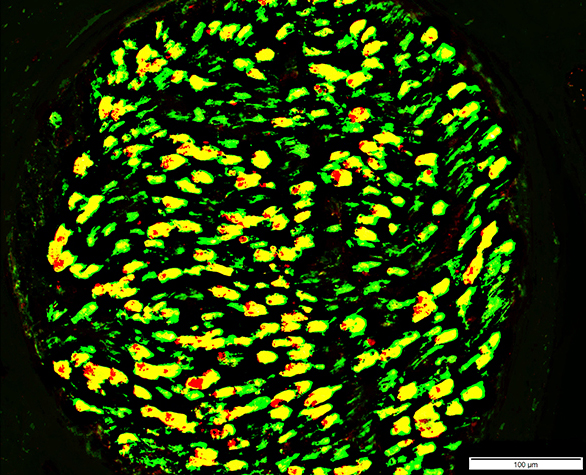 MBP = Myelin Basic Protein; P0 = P0 protein Myelin Structure: Irregular P0 & P0+MBP Sheaths |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Pathology Index
References
1. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2023;49:e12898
1/27/2026
