Axon Regeneration: Peripheral Nerve
|
Axons Regeneration Sprouts Post-regeneration Regenerated Axon Clusters Thin myelination Schwann cells Pseudo-onion bulb Muscle pathology Fiber type groups Regenerated motor axon Also see Collateral Sprouting |
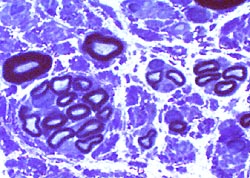
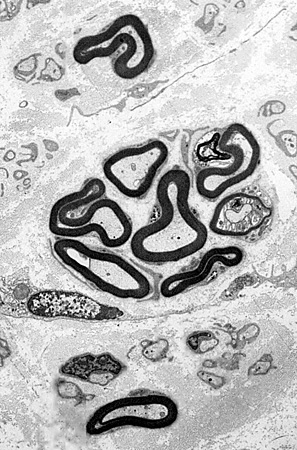
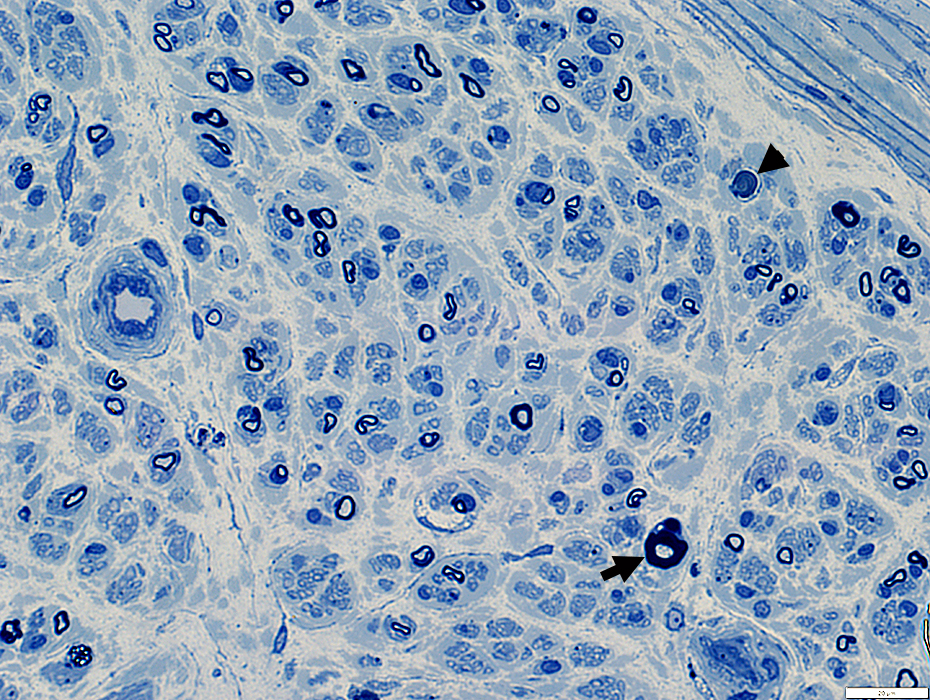
Regenerated Axon Clusters
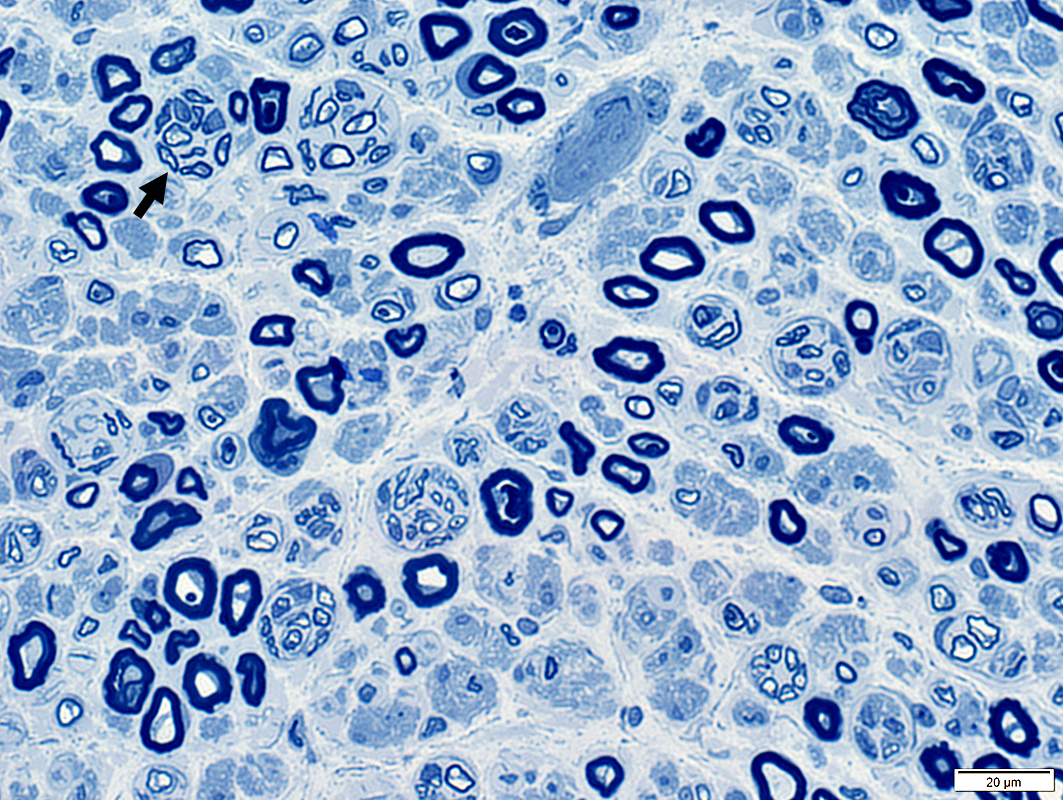 Toluidine blue stain |
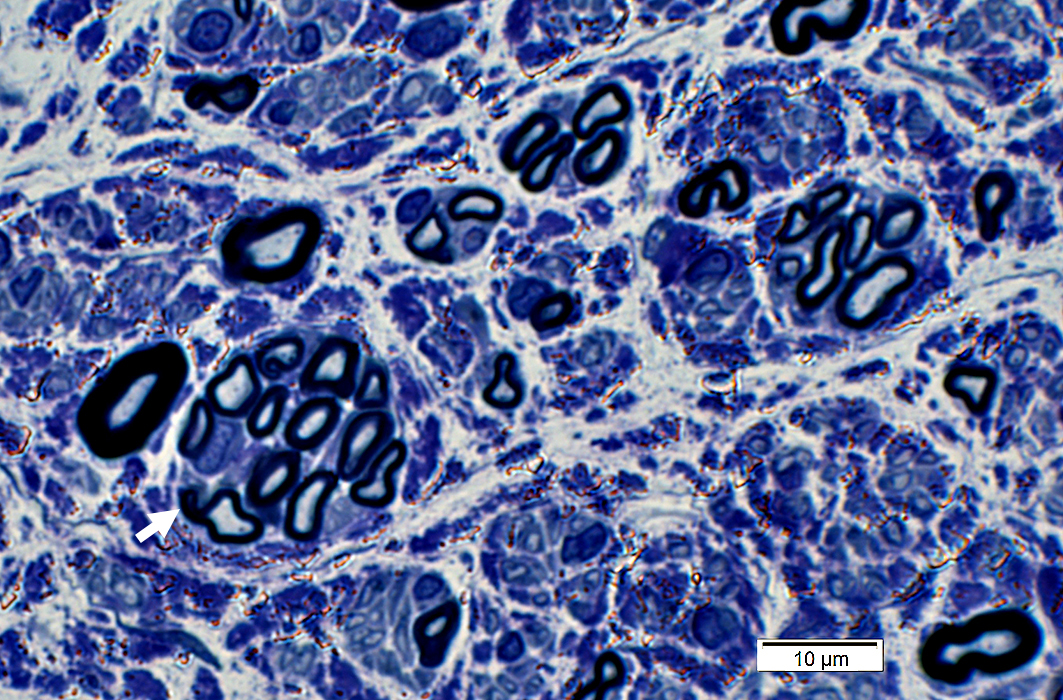
Clusters of 2 to 12 axons
Myelin thickness
Thin for axon size
Similar for all axons in cluster
Associated axon loss: Features
Reduced numbers of large & small myelinated axons
Büngner band development
Fibroblast processes
May surround regenerated axon clusters
Clusters of regenerating axons often occur with: Chronic changes in muscle
Partial denervation
Fiber type grouping
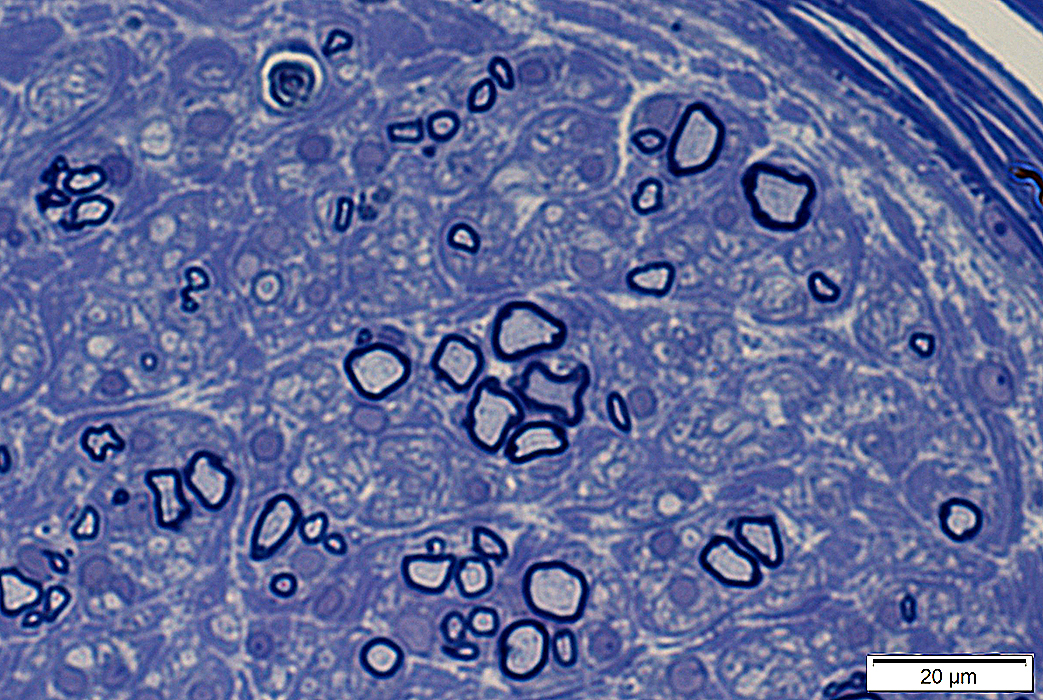
|
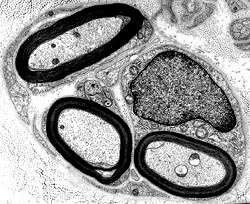
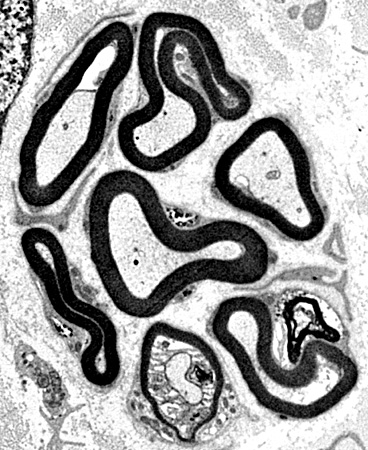
Regenerating Clusters
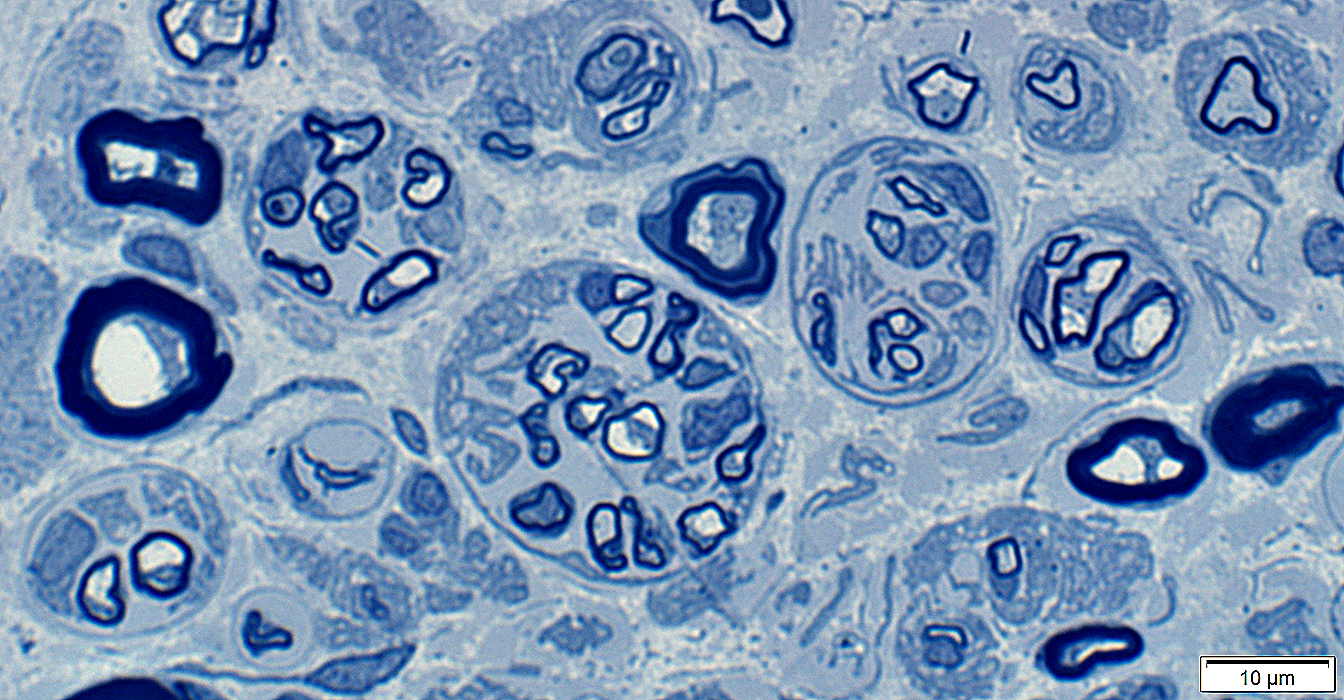
|
 From: R Schmidt |
Cluster of 3 intermediated-sized regenerated axons with similarly thin myelin sheaths
3 Unmyelinated small singleton axons are present (Left & Botom right)
Small Büngner bands with clusters of small Schwann cell process )Bottom left)
|
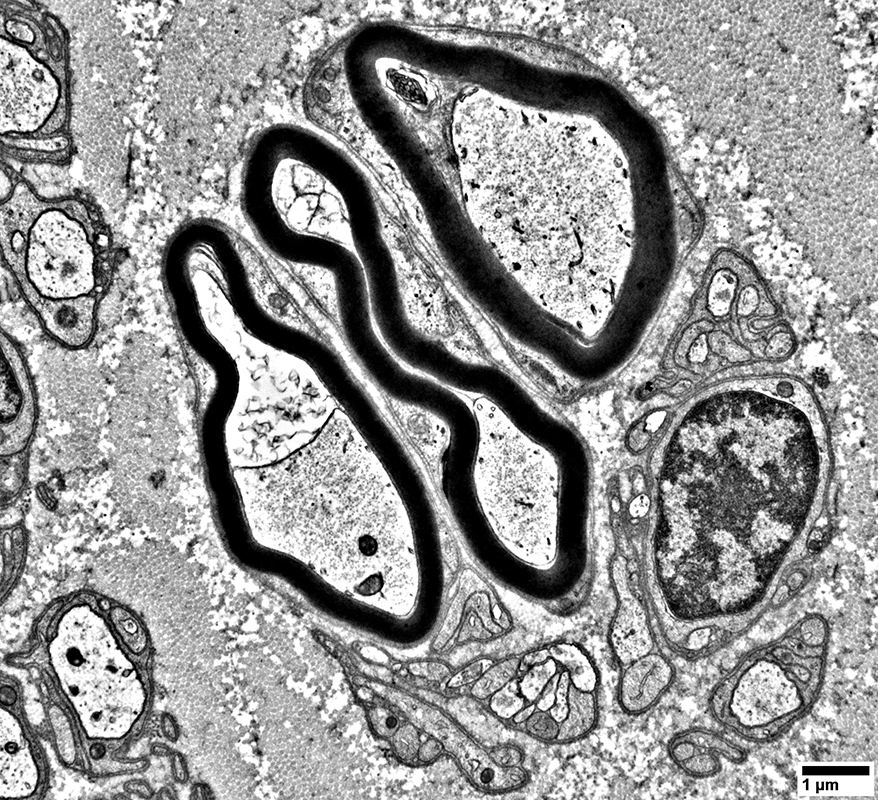
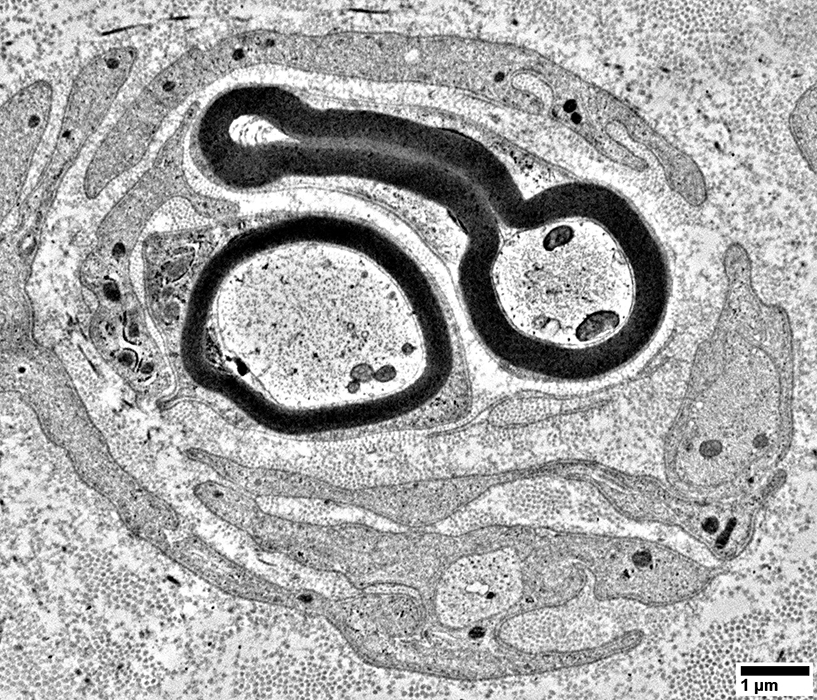
Pairs of axons within Schwann cell bands (Above & Below)
Also see: Pseudo-onion bulbs
Empty Büngner (Schwann cell) bands (Below)
Composed of multiple interdigitated Schwann cell processes
Axons are absent
|
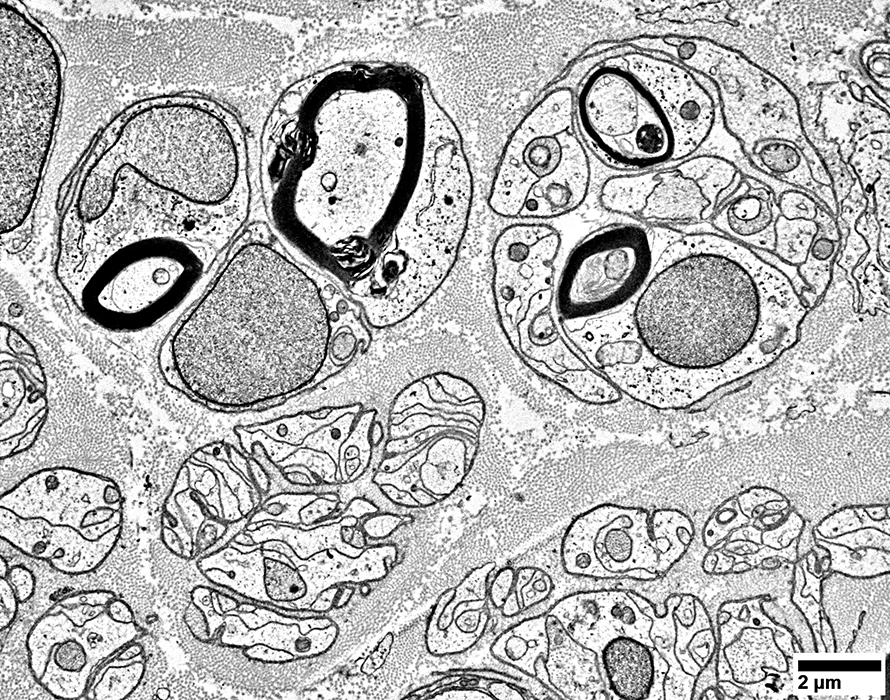
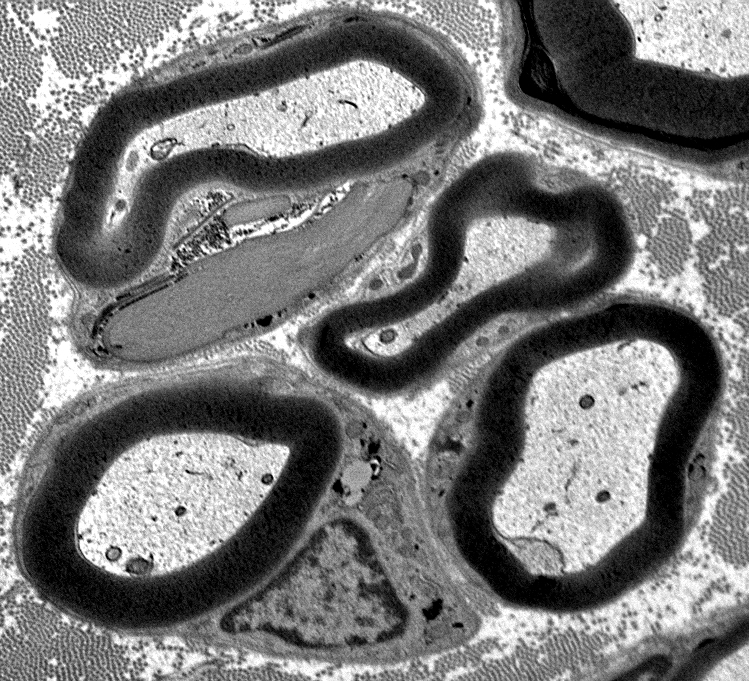
Fibroblast Processes
Long, branched, dark fibroblast process surrounds a regenerated axon cluster & Some collagen
Regenerated Axon Cluster
Two thinly myelinated axons
Surrounded by clusters of Schwann cell processes
Previously Büngner bands
Unmyelinated axons: Present within clusters of Schwann cell processes
|
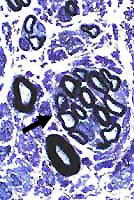
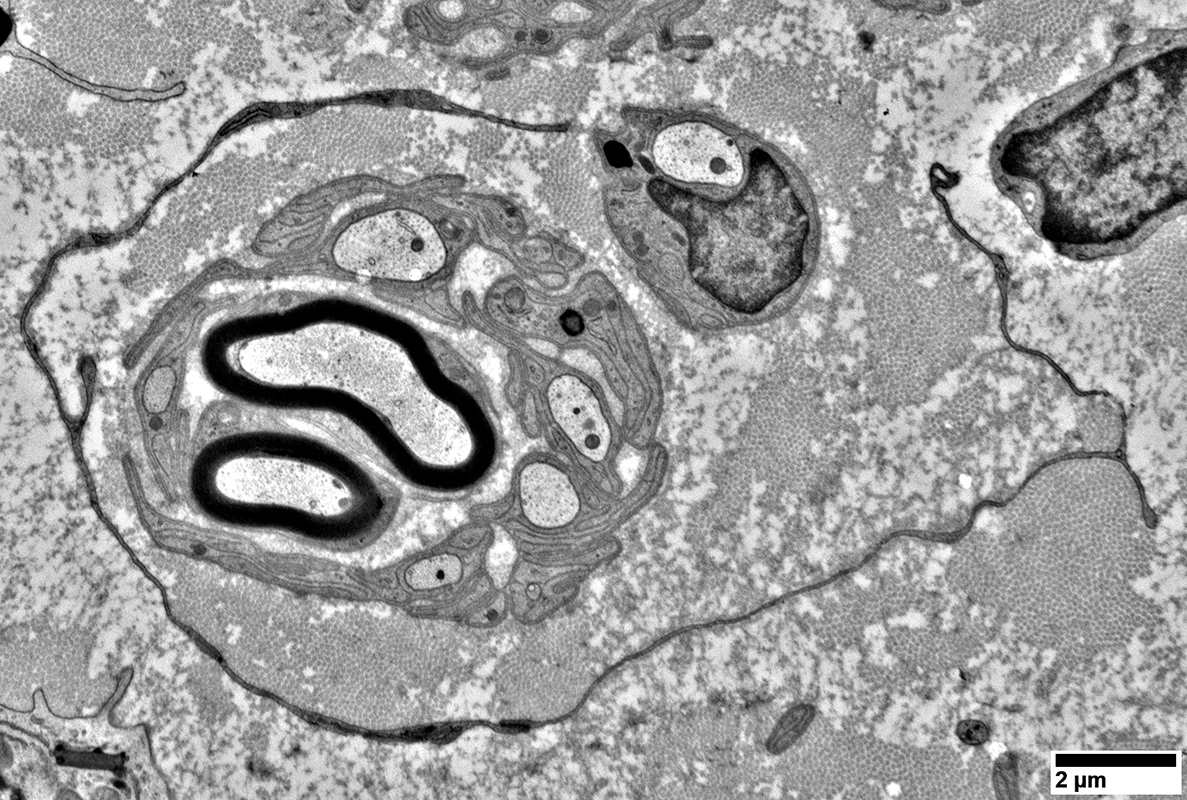
Regenerating Cluster: Late
All axons in cluster (Arrow) have nearly normal myelin sheath thickness
|
|
|
|
|
Thinly myelinated large axons have similar degrees of myelination
One Schwann cell contains a large Pi granule
|
|
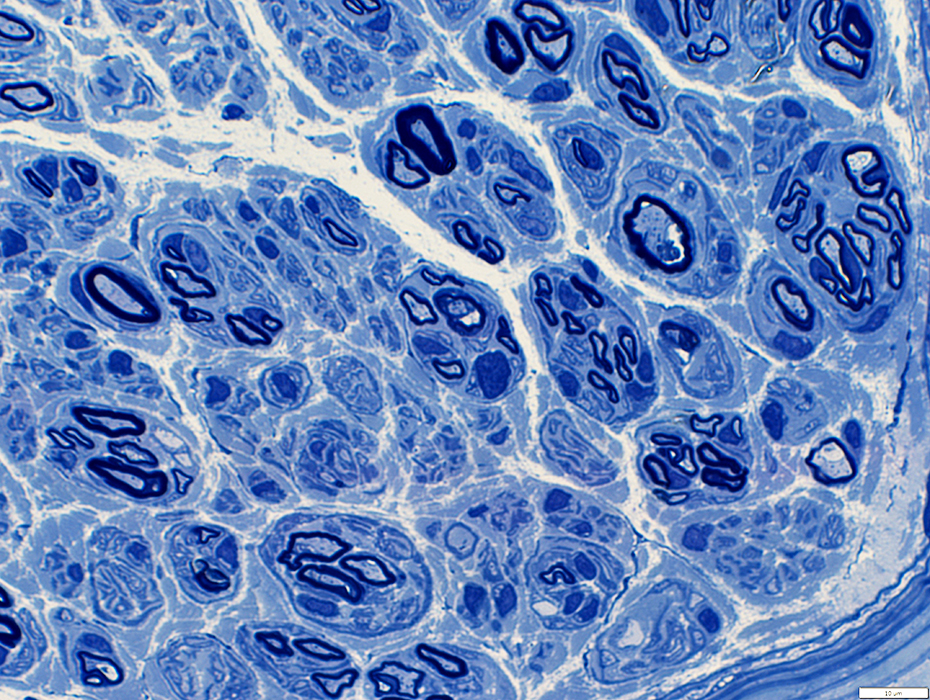
Regenerated axons
Usually thinly myelinated with short internodal length
May be distributed individually (Above), or in clusters (Below)
Thinly myelinated large axons may comprise: Most myelinated axons in a nerve
A few myelin ovoids (Arrow head) or thickly myelined axons (Arrow) remain (Below)
|
|
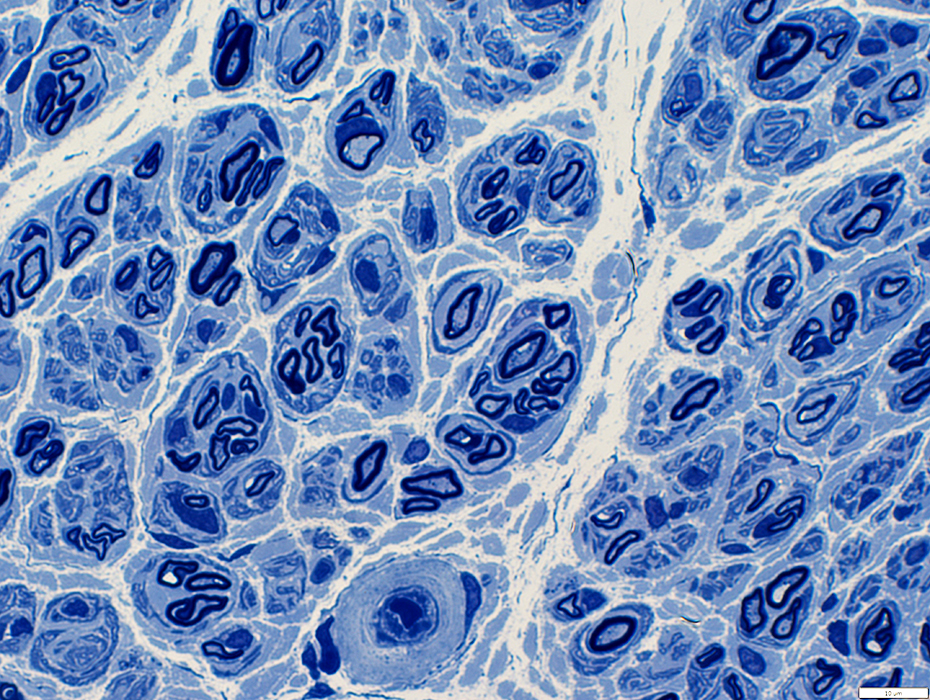
Regenerated axons
Usually thinly myelinated with short internodal length
May be distributed individually (Above), or in clusters (Below)
Thinly myelinated large axons may comprise: Most myelinated axons in a nerve
|
Regenerated axons
Size: Small
Distribution: Present in clusters
POST-REGENERATION
Myelin around Regenerated axons
Myelin sheaths (Below): Contain both P0 & MBP (Yellow)
Differs from myelin around normal smaller myelinated axons which contains mainly P0
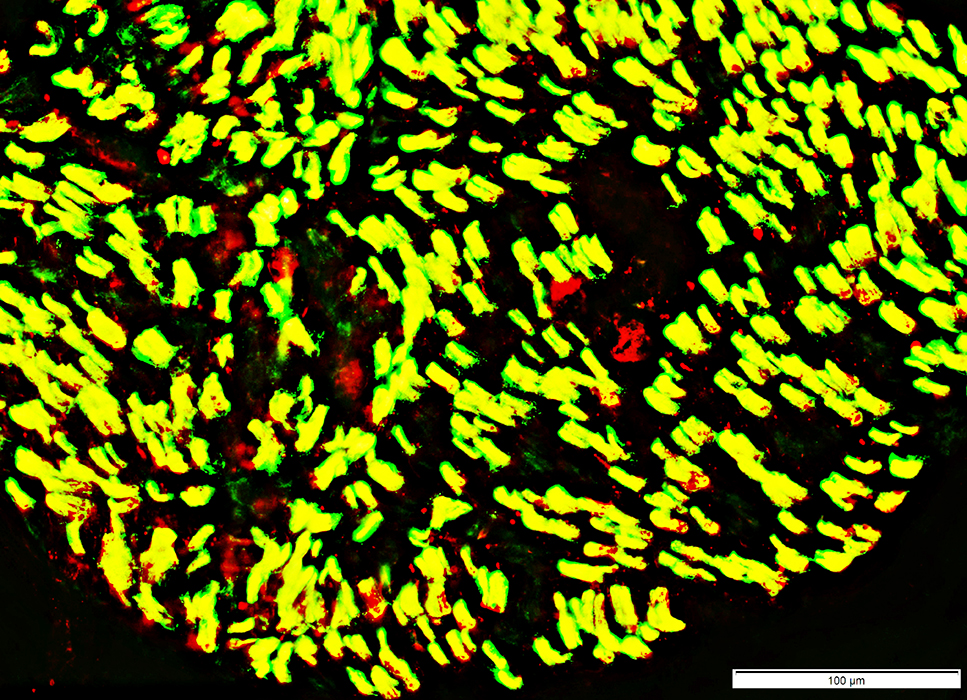 P0 green; Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) (Red); Both Yellow |
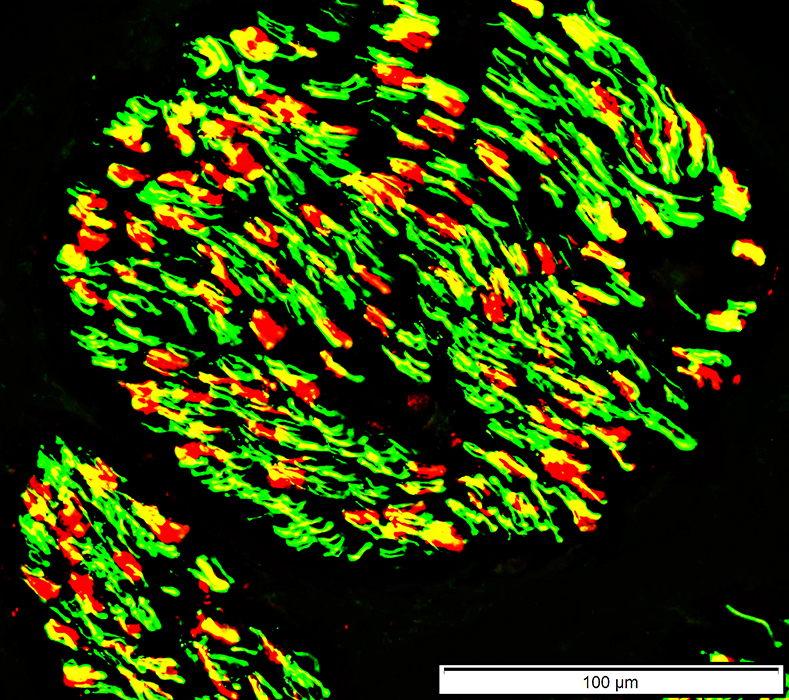 P0 (Red); Neurofilament stained axons (Green); Both Yellow |
MBP-containing Myelin around Regenerated axons
Most MBP-containing myelin sheaths
Surround small, rather than large, axons
Are smaller than in control nerves
See: MBP myelin in control nerve, mostly associated with larger axons
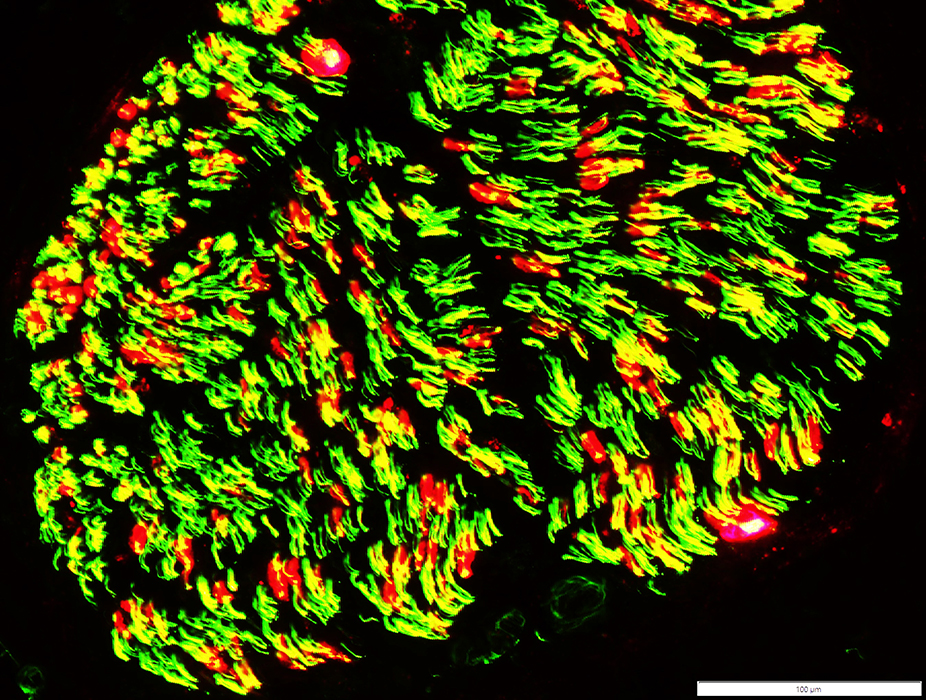 P0 (Red); Neurofilament stained axons (Green); Both Yellow |
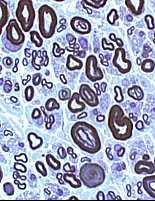
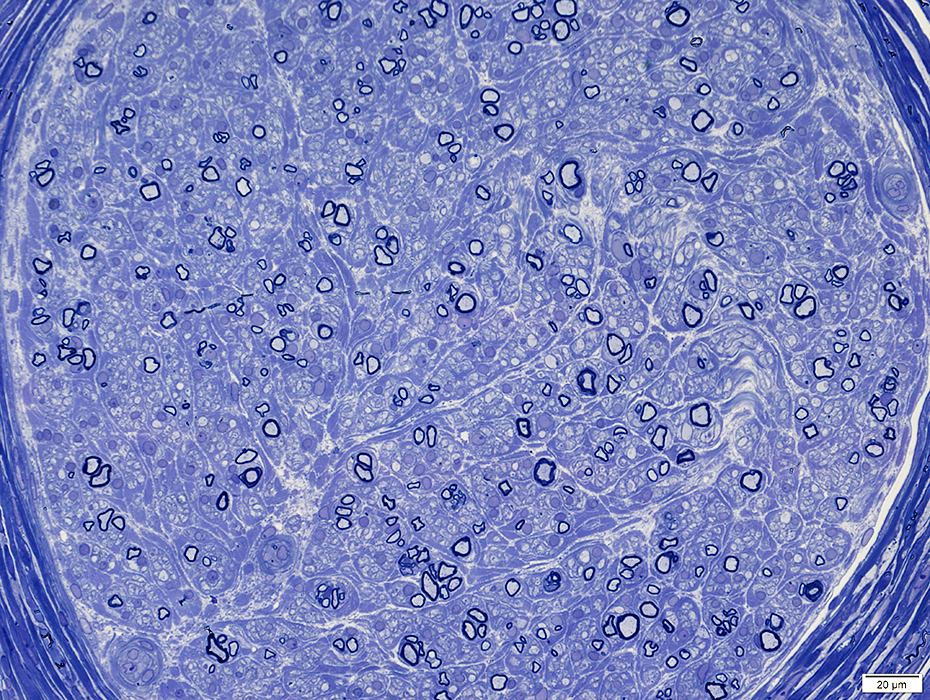
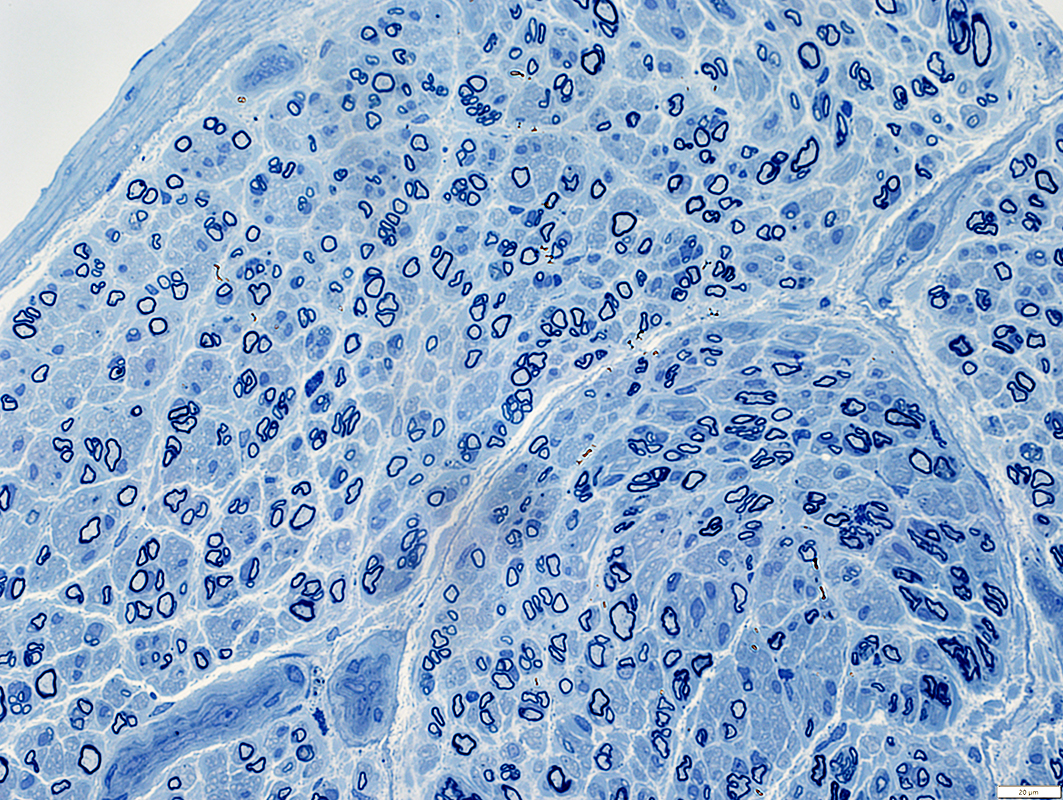 Toluidine blue stain |
Axons: Thinly myelinated, Some in small clusters
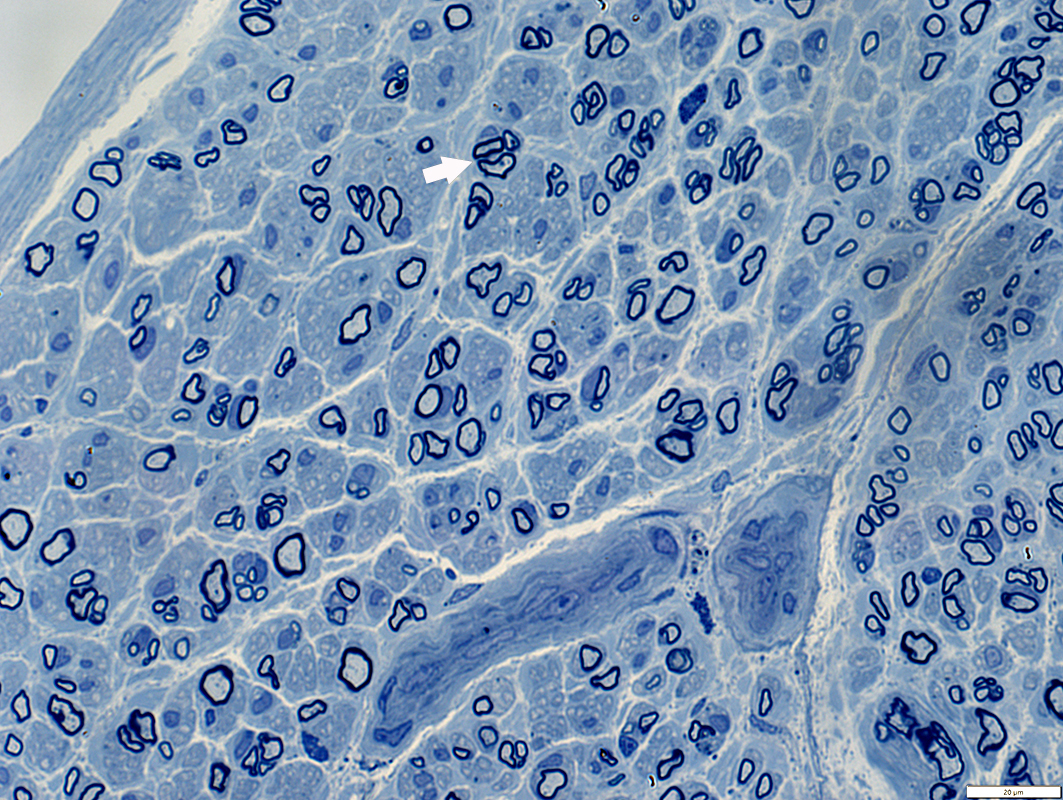 Toluidine blue stain |
Diffusely distributed in most of nerve (Above)
Many thinly myelinated large & small axons
Regenerated clusters
Groups of Small & Large thinly myelinated axons (Above; Arrow)
Scattered (Below; Dark Arrows): Thinly myelinated axons among larger axons with thicker myelin
Myelinated axons: Reduced numbers
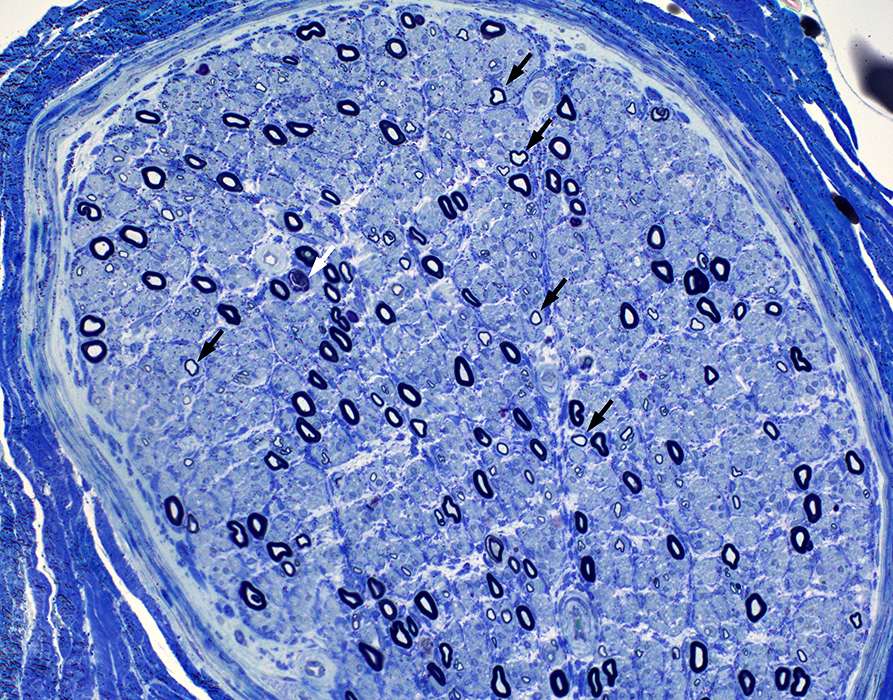 Toluidine blue stain: From Chunyu Cai |
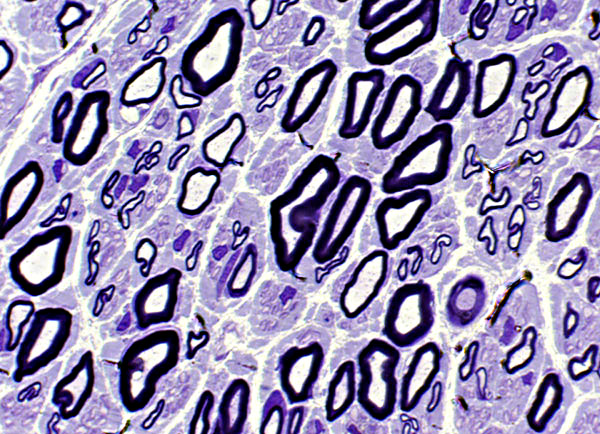 Toluidine blue stains of plastic nerve sections |
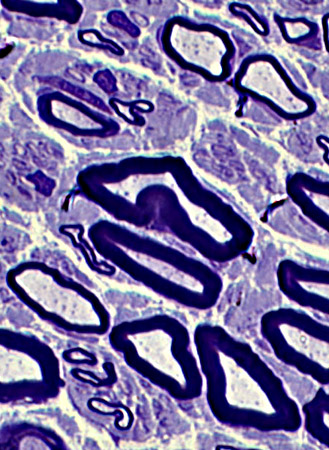 |
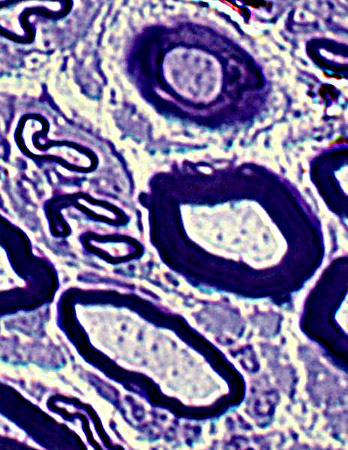 |
Post-Regeneration: Few thickly myelinated large axons
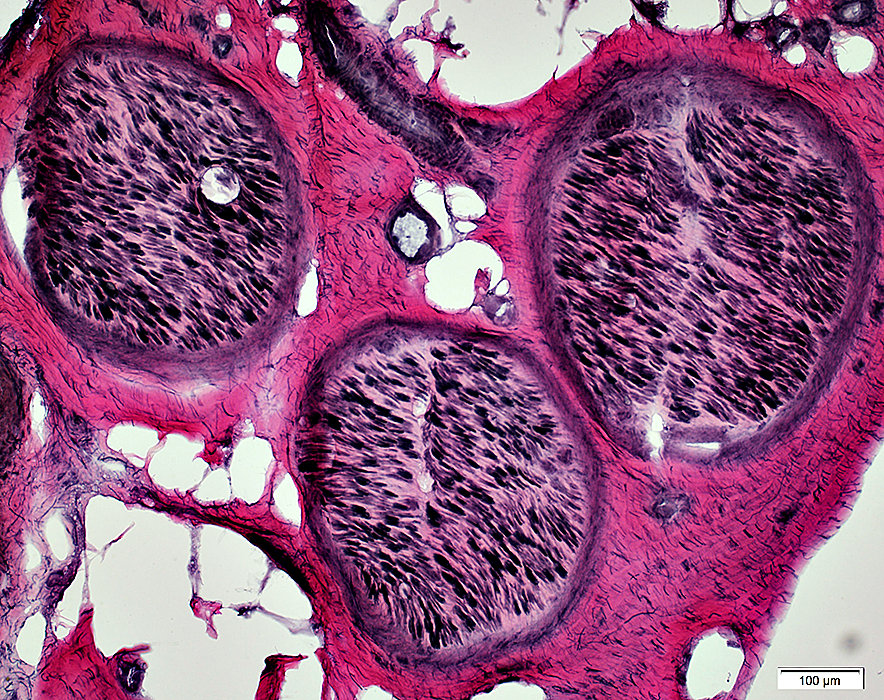 VvG stain |
POST-REGENERATION: Reduced numbers of large axons
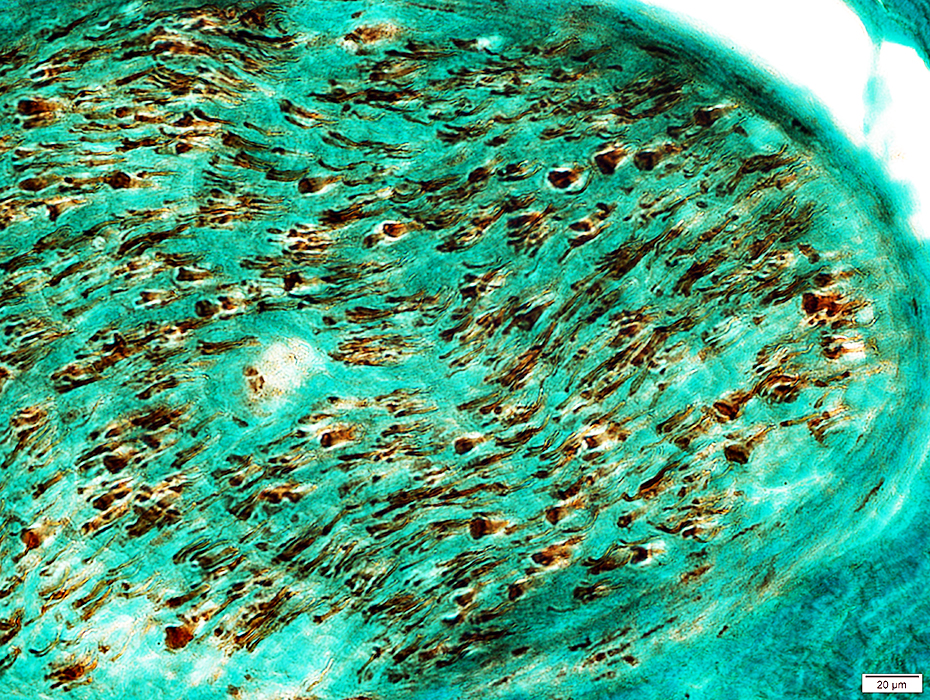 Neurofilament stain |
POST-REGENERATION
Proliferation of non-myelinating Schwann cells
Non-myelinating Schwann cells distributed all through endoneurium
NCAM staining of myelin sheaths around regenerated axons (Arrow)
NCAM is not usually present in normal adult myelin
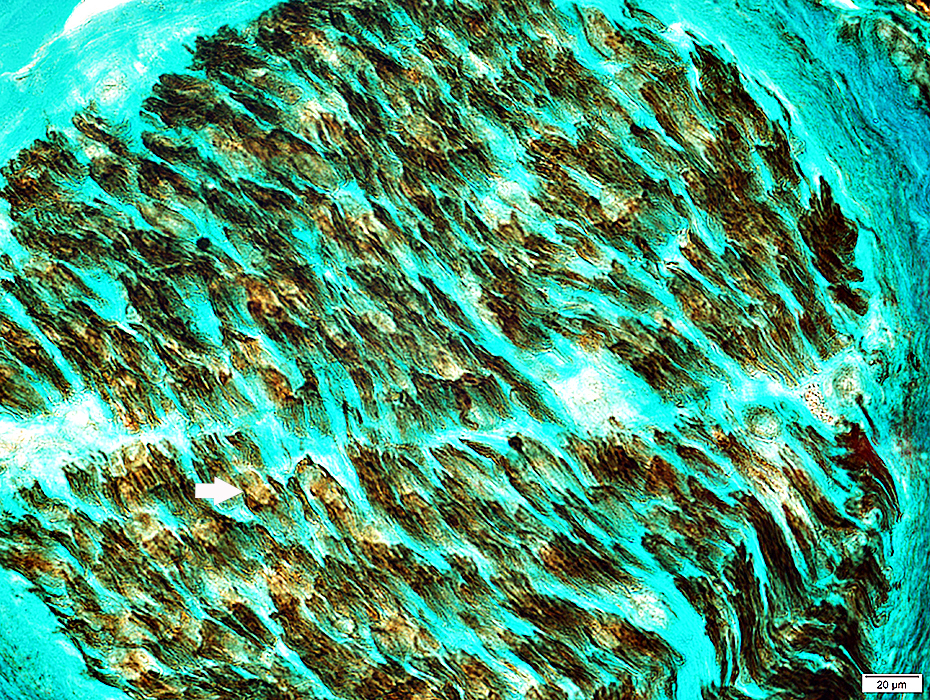 NCAM stain |
POST-REGENERATION
NCAM staining of myelin sheaths
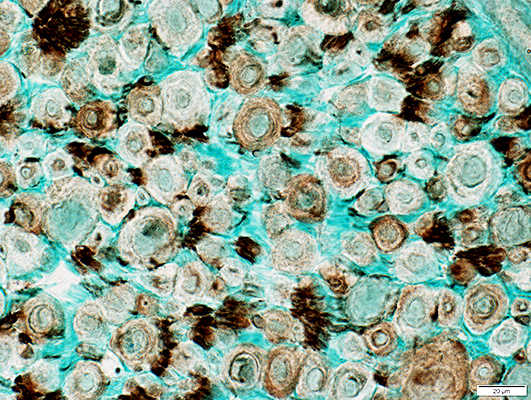 NCAM stain |
Onion Bulb-like structures (Dark Arrow) & Redundant Schwann cell processes (White arrow) around thinly myelinated axons
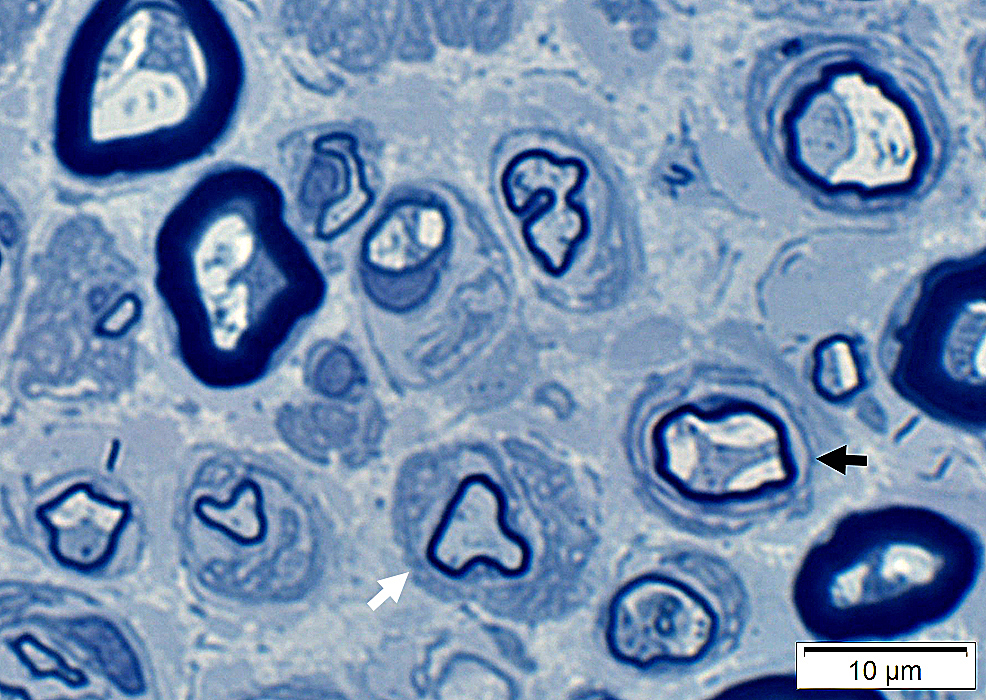
|
Pseudo Onion bulb
Center: Thinly myelinated large axon
Surround: Multiple circumferential clusters of interdigitated Schwann cell processes
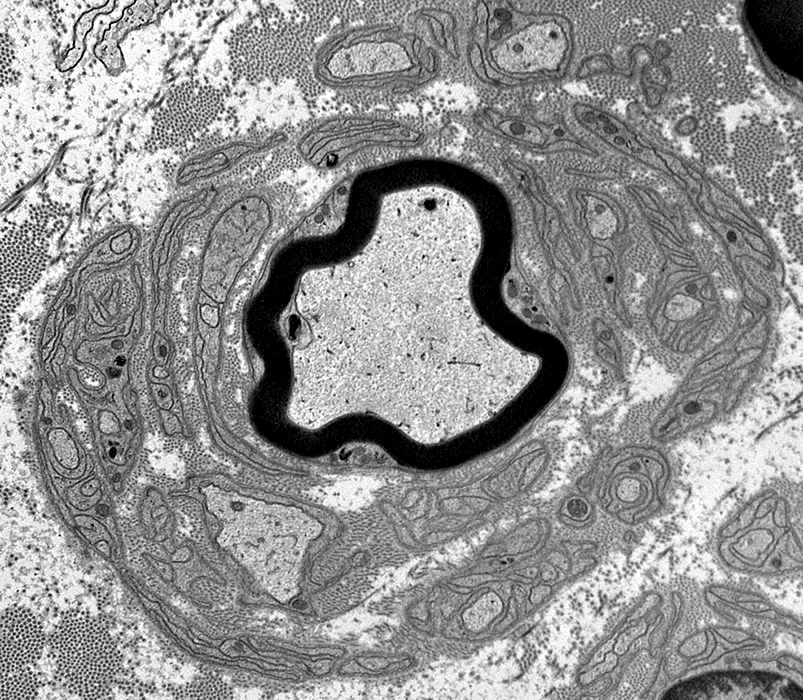
|
Return to Normal nerve
Return to Biopsy illustrations
Return to Nerve biopsy
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
9/23/2025