Terminal Motor Axons & Neuromuscular Junctions
|
Acrylamide Age Atrophy Axon Regrowth Ultraterminal sprouts (Botulinum toxin) Collateral sprouts ALS Regeneration Demyelination CIDP MMN Dimethyaminopropionitrile (DMAPN) Myasthenia Gravis Normal Ultrastructure |
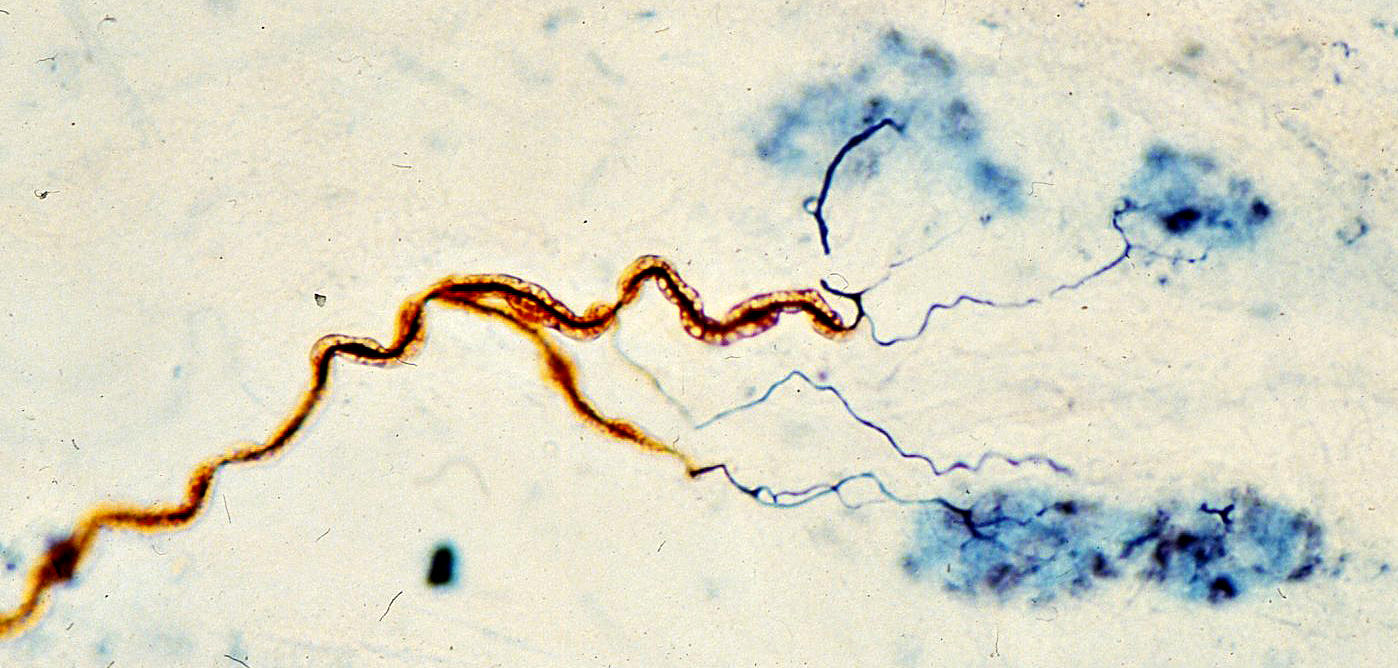
Normal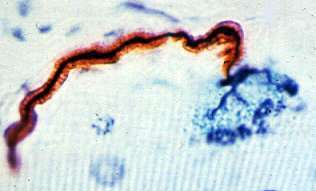 Human: Silver-P0-Esterase stain |
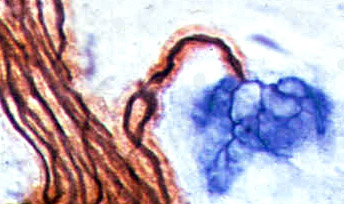 Rat: Silver-P0-Esterase stain |
- Axon stained black (Silver), innervates a single NMJ
- Terminal axon: Branches within NMJ (Blue) area
- Myelin is rust colored (P0 antibody)
- NMJ region is blue (Esterase stain)
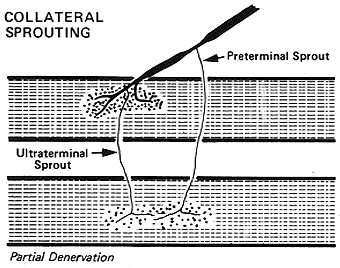
Collateral Sprouting
|
Collateral Sprouting: Features
- Nerve Sprouts
- New growth: Terminal branches to different NMJs from a single preterminal axon
- Diameter: Narrow
- Surrounding myelin: None or Thin
- Sprout Origin
- Ultraterminal: From terminal axon branches within NMJ
- Preterminal: From Node of Ranvier or most distal part of axon before NMJ
- Sprout Target: Neighboring neuromuscular junctions
- Effects of sprouting on Muscle
- Fiber type grouping
- Occurs with reinnervation by intact axons
- Collateral sprouts: Produce small regions of type grouping
- Regenerating axons: Produce larger regions of type grouping
- ALS: More common with slowly progressive or chronic disease
- Grouped atrophy
- Occurs when axon that has reinnervated a group of neighboring muscle fibers degenerates, or becomes less active
- ALS: Regions of grouped atrophy may contain mixed fiber types
- Fiber type grouping
Terminal (Collateral) sprouting in ALS
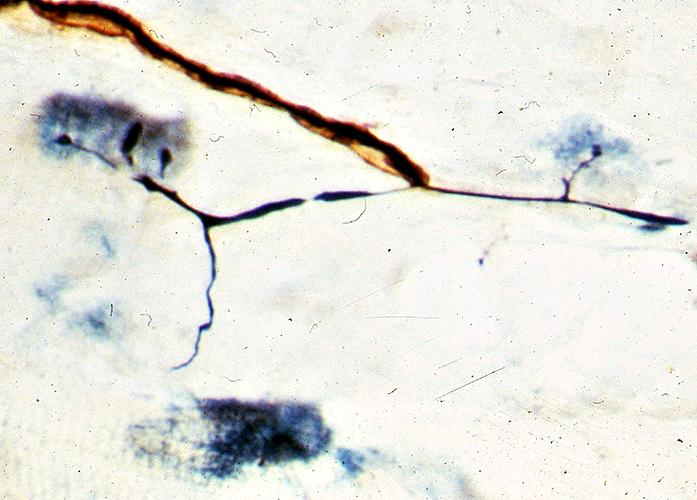 Silver-P0-Esterase stain |
Terminal (Collateral) Sprouts after Partial Denervation of rat muscle
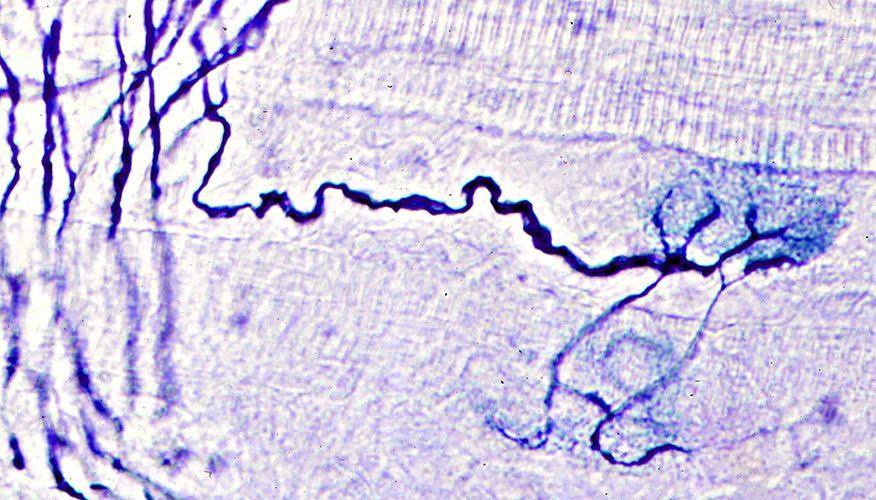 Silver (Black)-Esterase (Blue) stain: Rat muscle |
Collateral sprouts: Several sprouts reinnervate one NMJ
From Intact axons to Denervated NMJ (Arrow)
May originate from
Terminal axon branches (Above), or
Preterminal axon (Below)
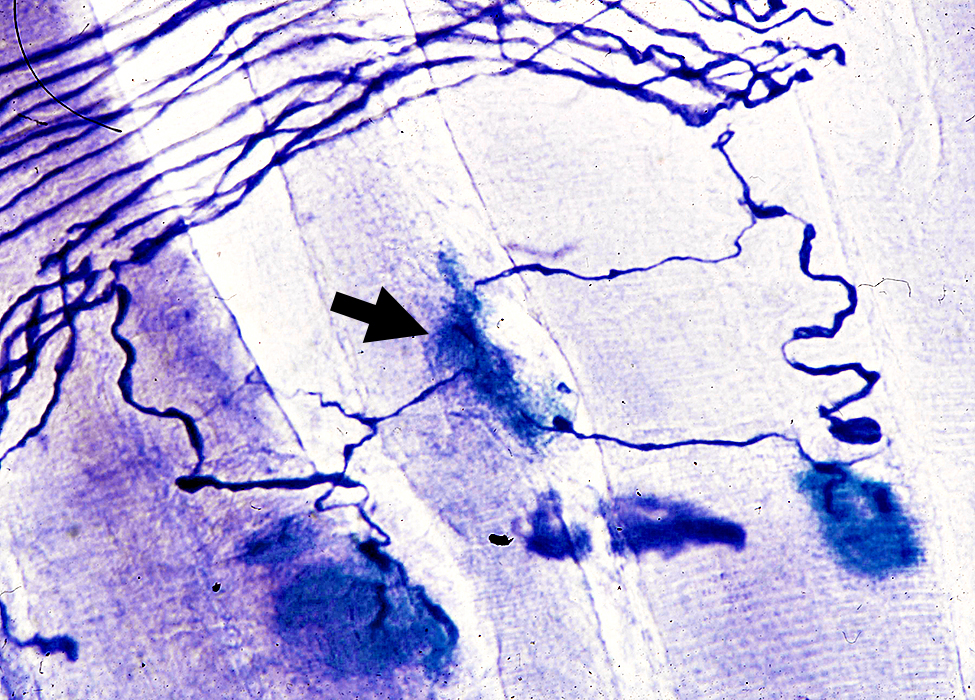 Silver (Blue)-Esterase (Blue) stain: Rat muscle |
Collateral sprouts (Arrow) after Partial Denervation of rat muscle
Preterminal axon origin: Arise from Nodes of Ranvier
Size: Thin compared to original axon
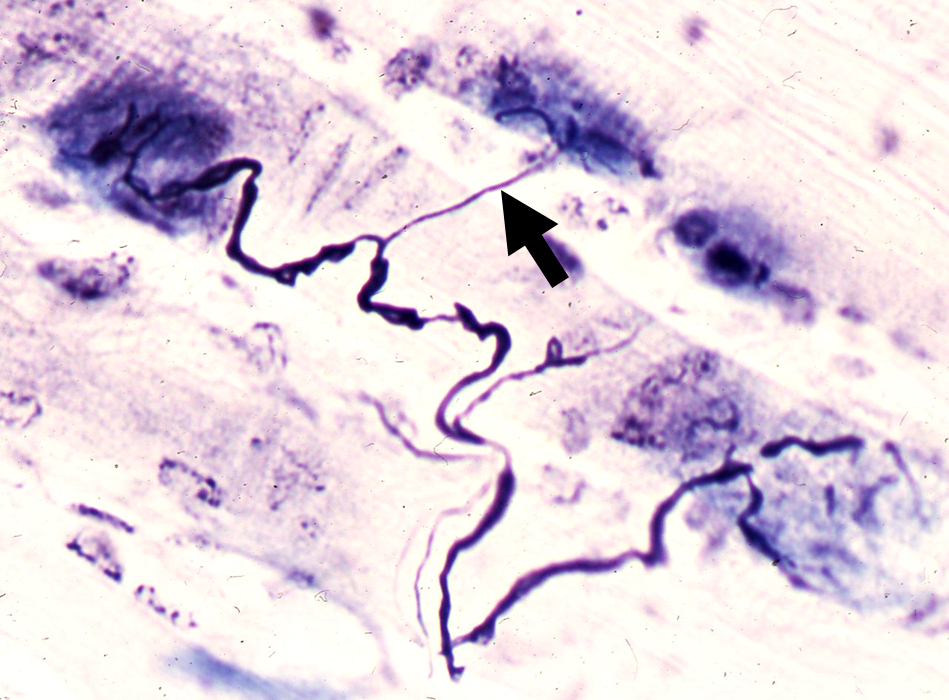 Silver (Black)-Esterase (Blue) stain: Rat muscle |
Axon Regeneration
Single Regrowing Axon (Left)- May develop several branches
- Branches
- May be myelinated or non-myelinated
- Origin:
- Often pre-terminal axon
- May appear as regenerating clusters in proximal nerve
- Single proximal axon
- Innervates several NMJs (Below)
- May, or may not, convert fiber type
- Type conversion less likely conversion in ALS
 Silver (Black)-Esterase (Blue) stain: Rat muscle |
Axon Atrophy
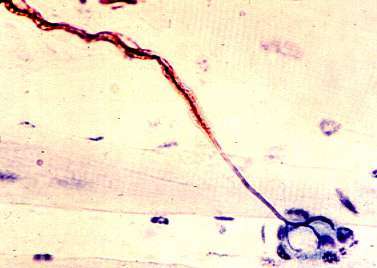
Silver-P0-Esterase stain
Loss of myelin sheath toward end of an atrophic (thin) axon
Botulinum Toxin
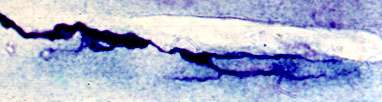 Silver-Esterase stain Botulinum treatment (Rat) NMJ: Enlarged Elongated 2 segments Motor axon terminal: Increased branching |
Botulinum Toxin Treatment (Rat): Ultraterminal sprouts
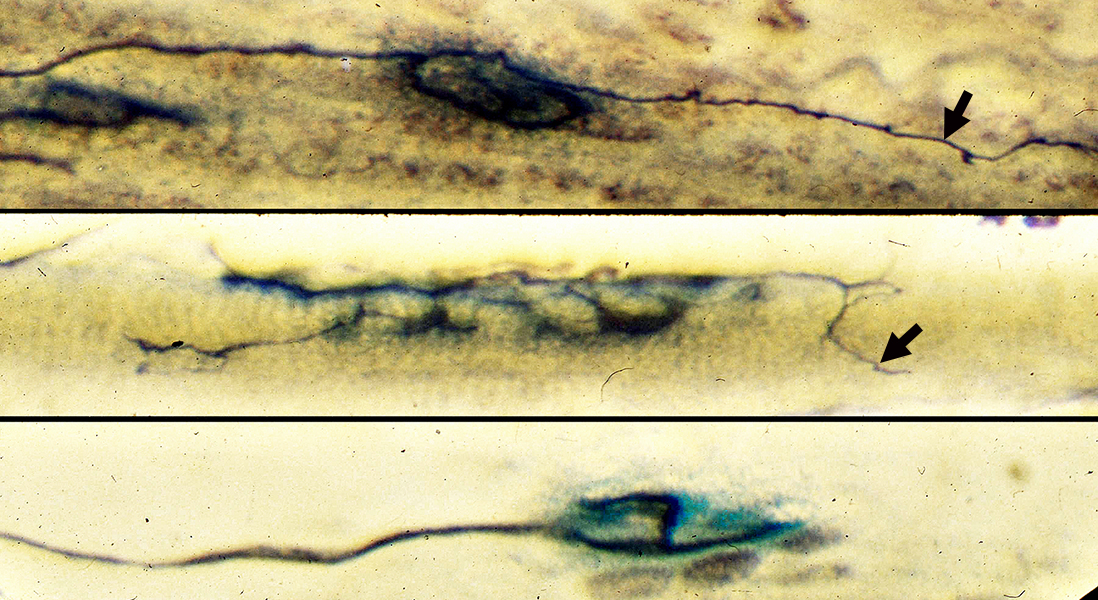
Silver-Esterase stain |
Botulinum toxin induces
Enlargement of NMJs (middle) &
Ultraterminal sprouts (Arrows) extending from nerve terminals at NMJs (middle & top)
Control NMJ (Bottom)
Acrylamide
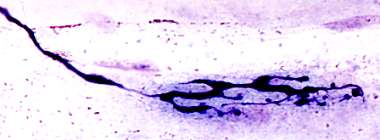 Silver-Esterase stain Acrylamide intoxication (Rat) Motor nerve terminals: Focal Enlargements |
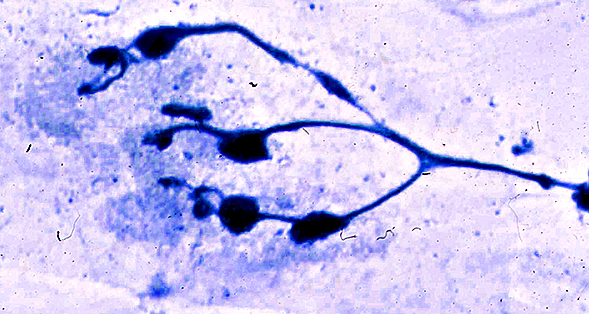
|
Dimethyaminopropionitrile
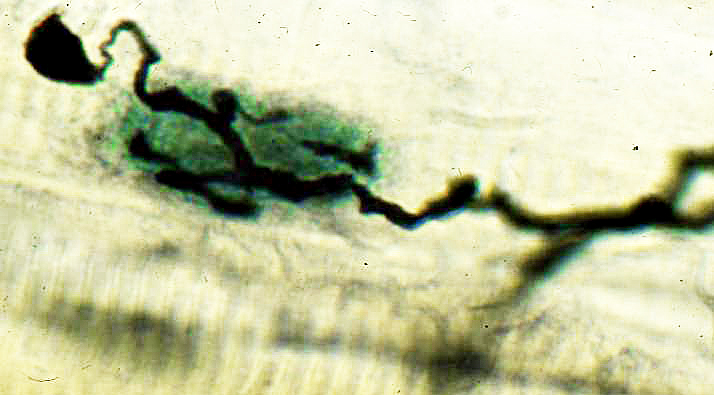 Silver-Esterase stain Dimethyaminopropionitrile (DMAPN) intoxication (Rat) Swelling in sprout & axon terminal branches in NMJ Ultraterminal sprout with swelling (Top left) |
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Myasthenia gravis
7/30/2025