MYASTHENIA GRAVIS: Muscle Pathology
|
NMJs Normal Limb muscles Ultrastructure EOM Proteins Myasthenia gravis NMJs: Abnormal Congenital AChE deficiency AChR mutation Agrin mutations Immune Chronic, Undertreated Diagram Lymphorrhages Rippling muscles & Thymoma Pathologic features Pathophysiology |
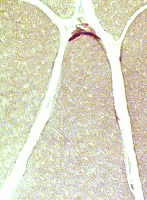 Esterase stain Congenital MG
AChR deficiency Small, pale NMJ |
Neuromuscular junctions: Normal
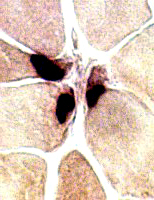
 Esterase stain |
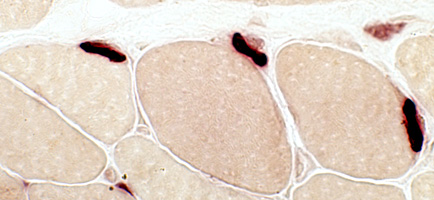
Neuromuscular Junctions: Myasthenia Gravis, Acquired
| Also see MG chronic Esterase deficiency |
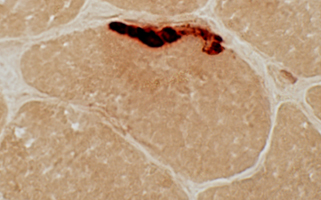
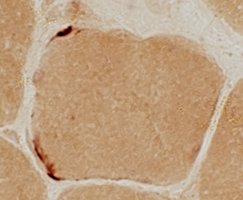 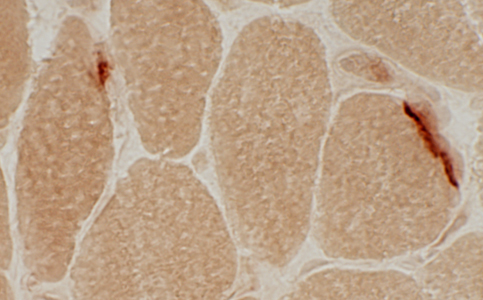
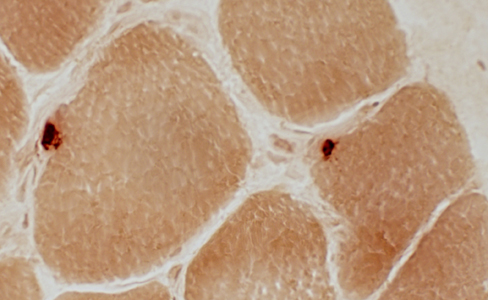 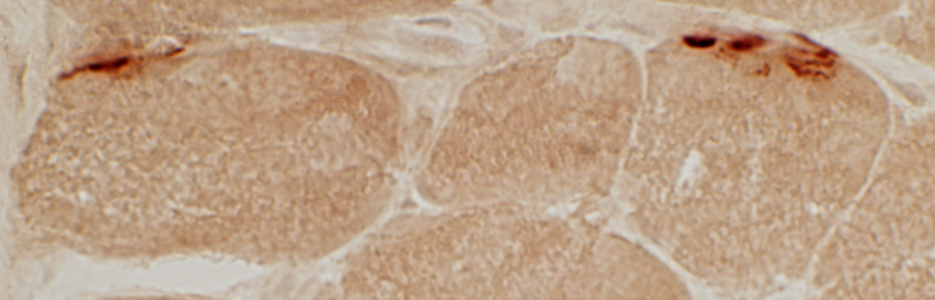 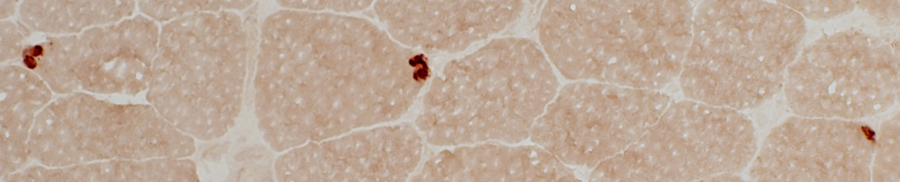 Esterase stain |
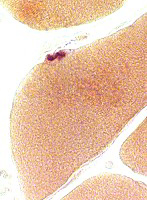
Myasthenia Gravis, AChR antibody positive
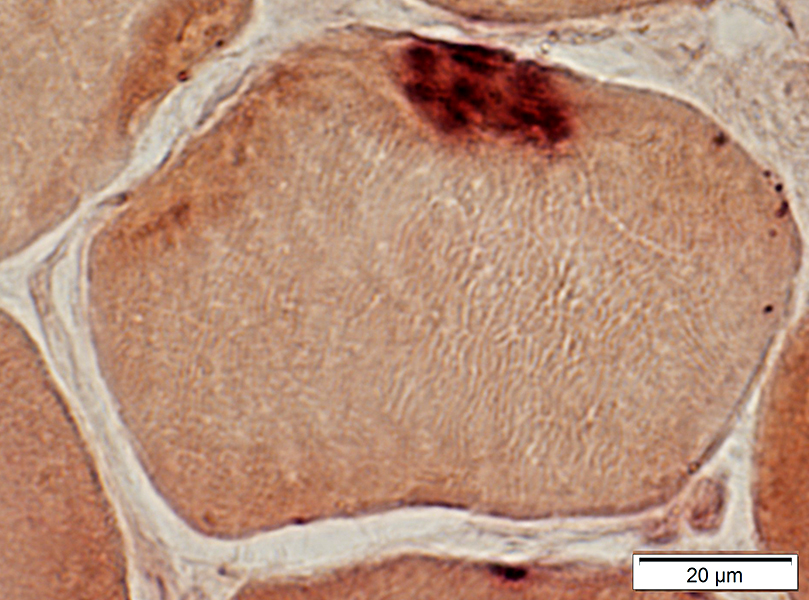 Esterase stain |
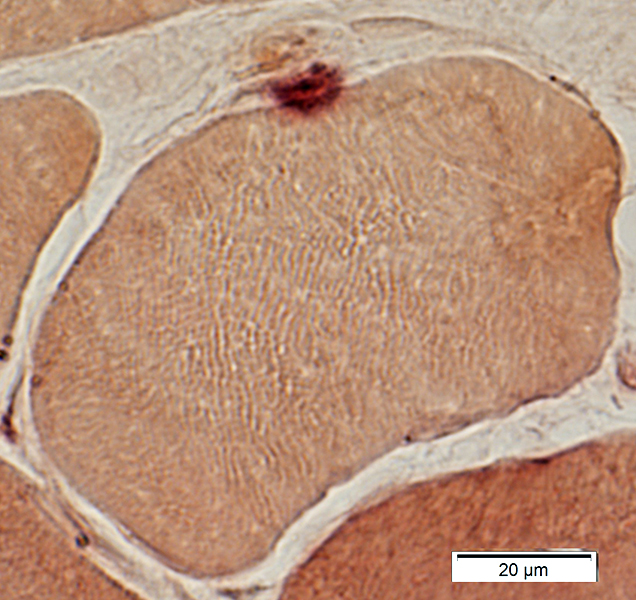 Esterase stain |
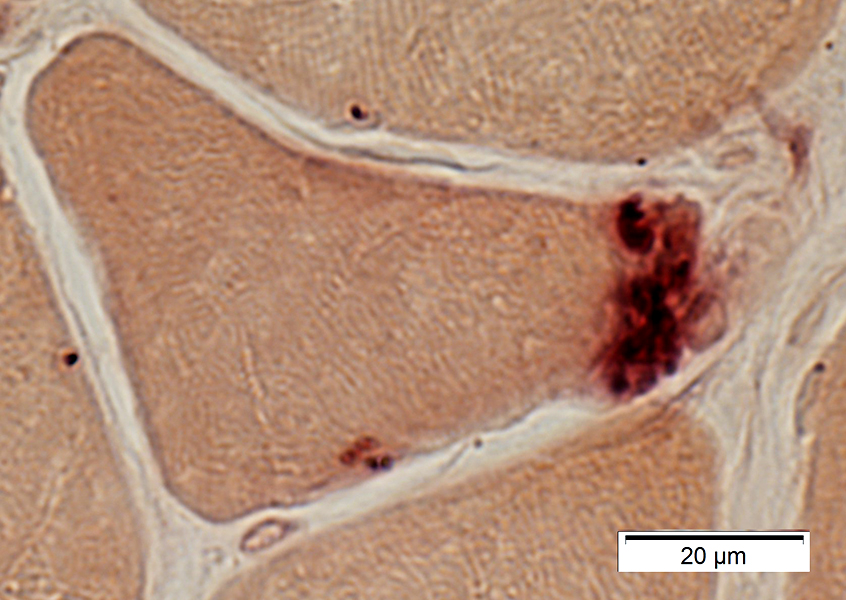 Esterase stain |
Lymphorrhages
LymphorrhagesFrom patients with myasthenia gravis & thymoma.
Foci of lymphocytes with dark nuclei & little cytoplasm
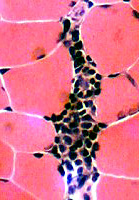 H&E stain |
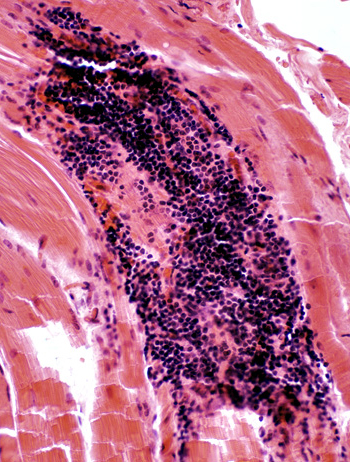 H&E stain |
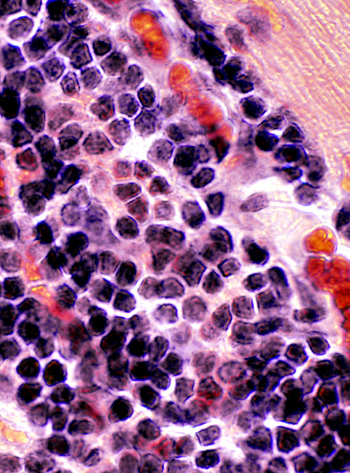 H&E stain |
Myasthenia Gravis, Immune: Muscle pathology 1
- AChR Ab+
- Muscle fiber atrophy: Type I & II
- Pyknotic nuclear clumps: More without adequate treatment
- Muscle fiber type grouping: Some patients
- Internal architecture: Disordered; Minicores
- Neuromuscular junctions: Small or multisegmented
- MuSK Ab+
- COX- muscle fibers: Present in < 2% of fibers
- Internal architecture: Disordered; Minicores
NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION ANATOMY: NORMAL & MYASTHENIA GRAVIS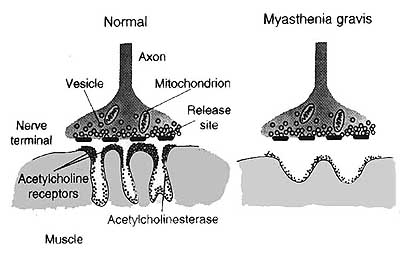 From Drachman |
Myasthenia gravis: Chronic, Undertreated
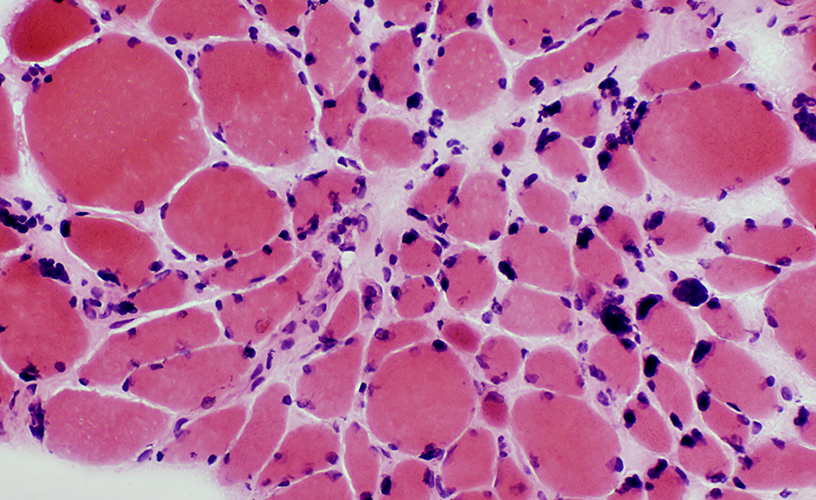 H&E stain |
|
Varied muscle fiber size: Atrophy & Hypertrophy Pyknotic nuclear clumps |
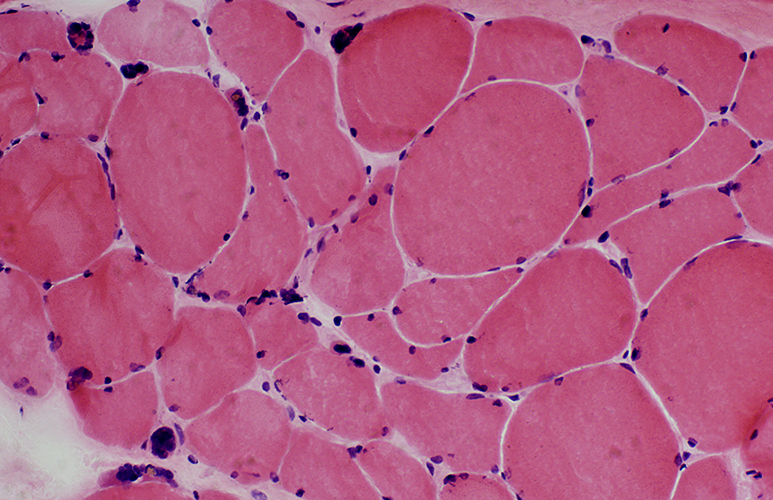 H&E stain |
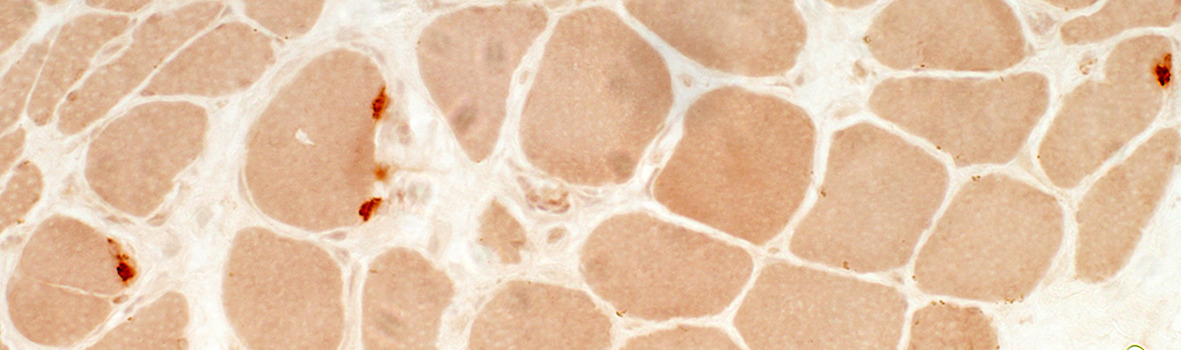 Esterase stain |
|
Neuromuscular Junctions: Small, Irregular & Pale stained |
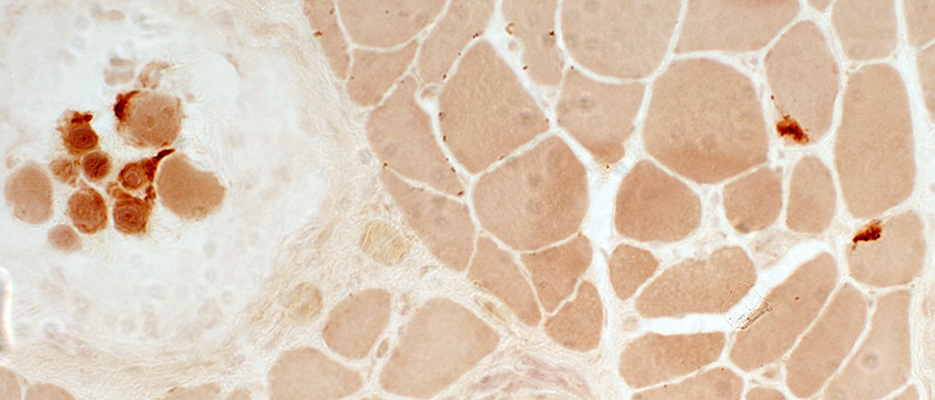 Esterase stain |
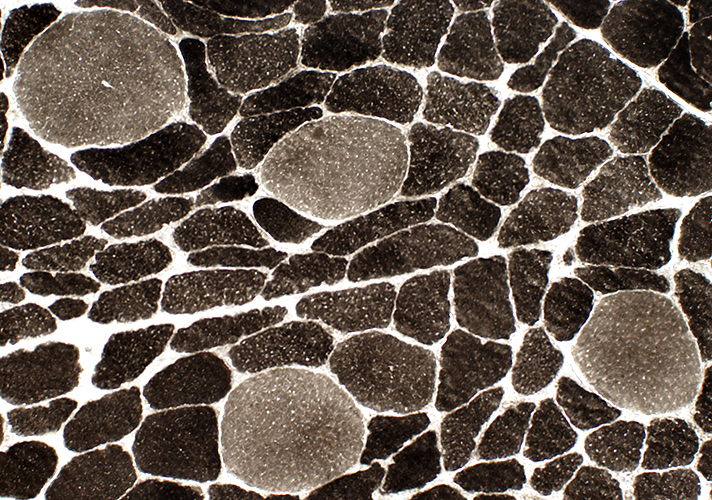 ATP pH 9.4 stain |
|
Fiber types Type 2 predominance Small are type 2 Large are type 1 (Above) or 2 (Below) |
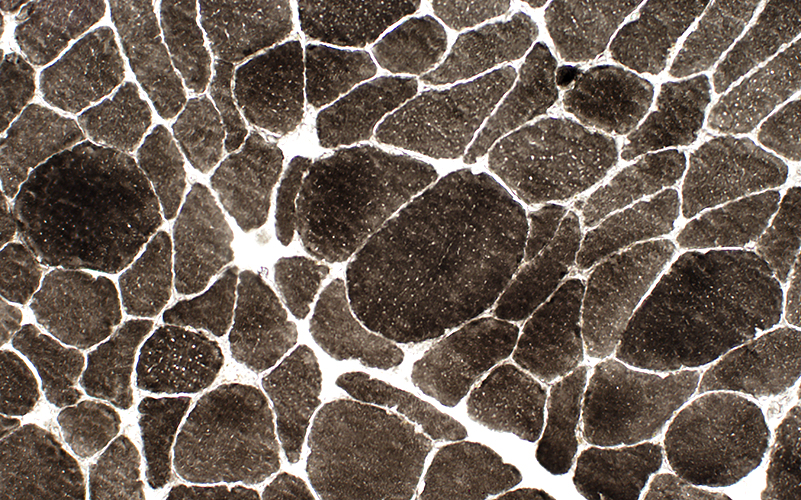 ATP pH 9.4 stain |
|
Fiber types: Scattered type 2C fibers (Intermediate staining) are present |
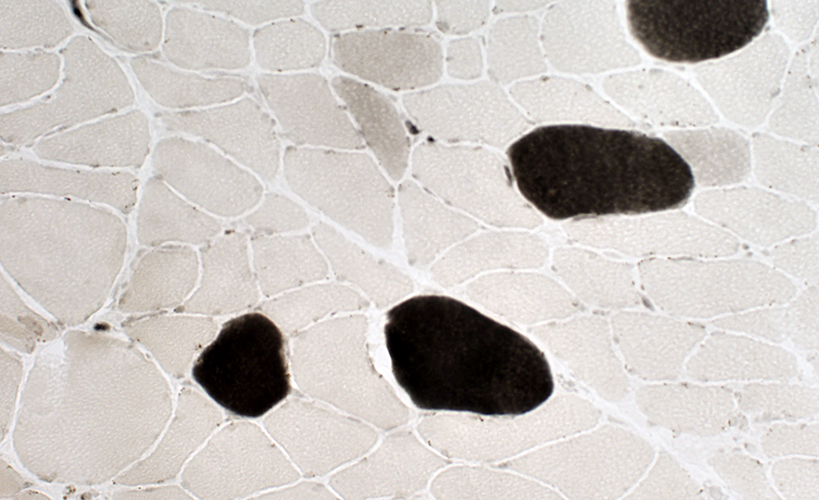 ATP pH 4.3 stain |
Myasthenia gravis, Thymoma & Rippling muscle syndrome
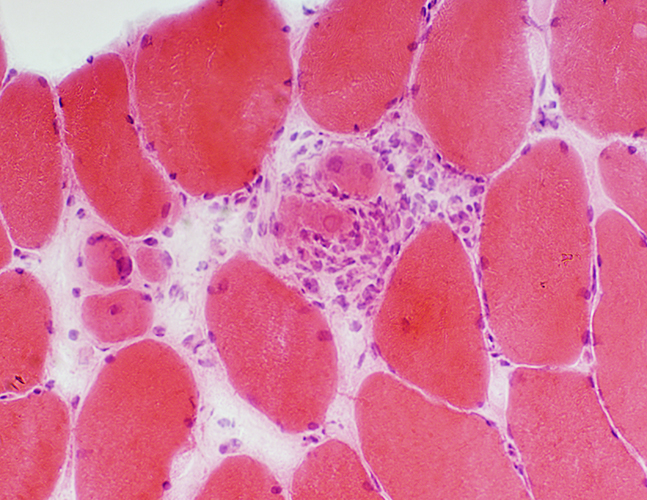 H&E stain |
|
Muscle fibers: Occasional area with regenerating muscle fibers (Above) Normal muscle fibers: In most areas (Below) |
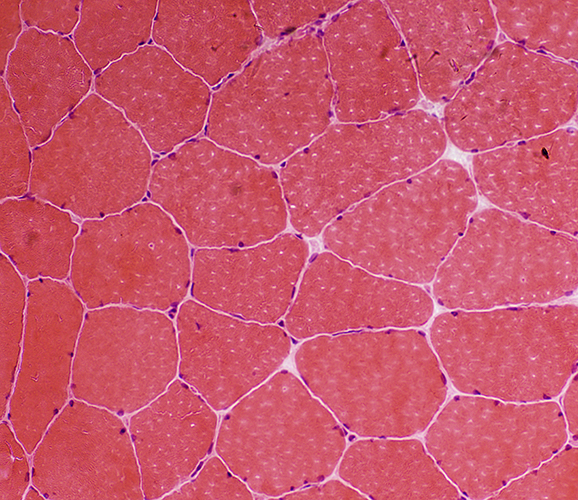 H&E stain |
|
Perimysial vessel: Associated inflammation extending into the endomysium |
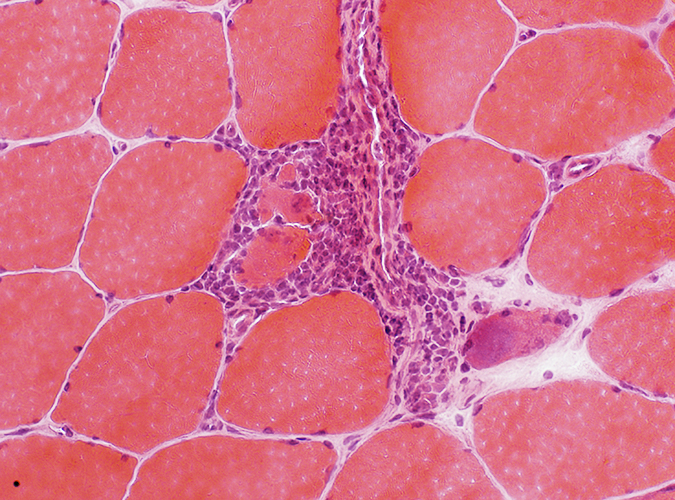 H&E stain |
|
|
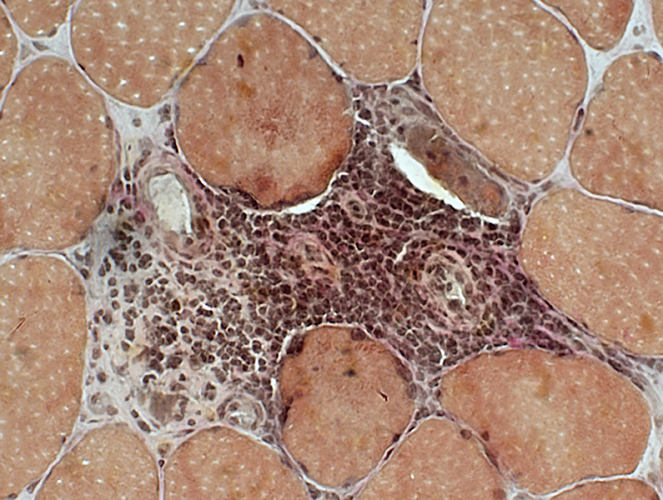 VvG stain |
|
Inflammation around intermediate-sized vessels Mostly mononuclear (probably with B-cells) Few cells stain for esterase (Below) Vessel endothelium: Stains for esterase |
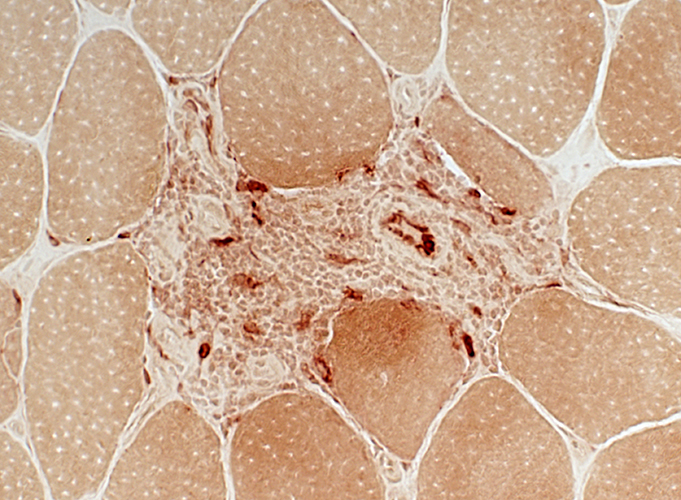 Esterase stain |
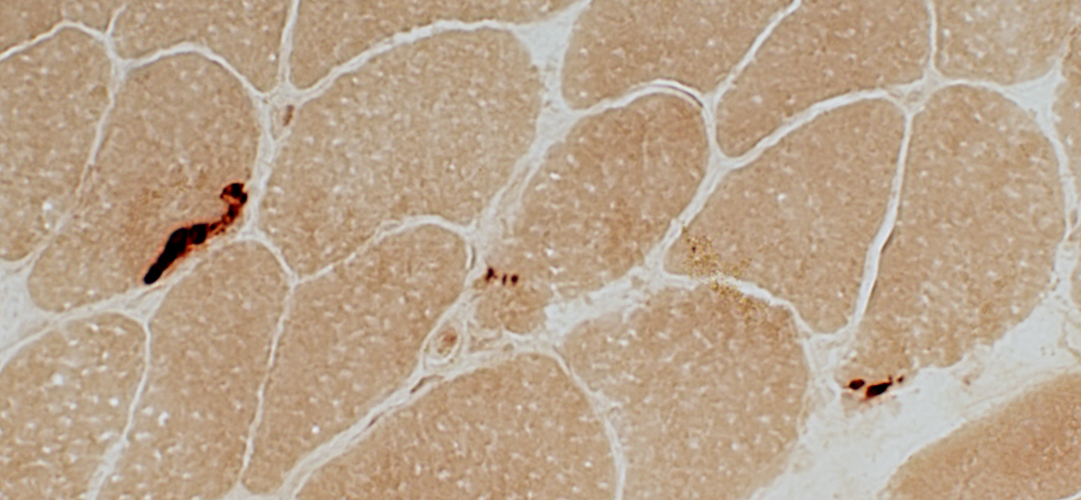 Esterase stain |
|
Neuromuscular Junctions Size: Small or Elongated Intensity of staining: Normal |
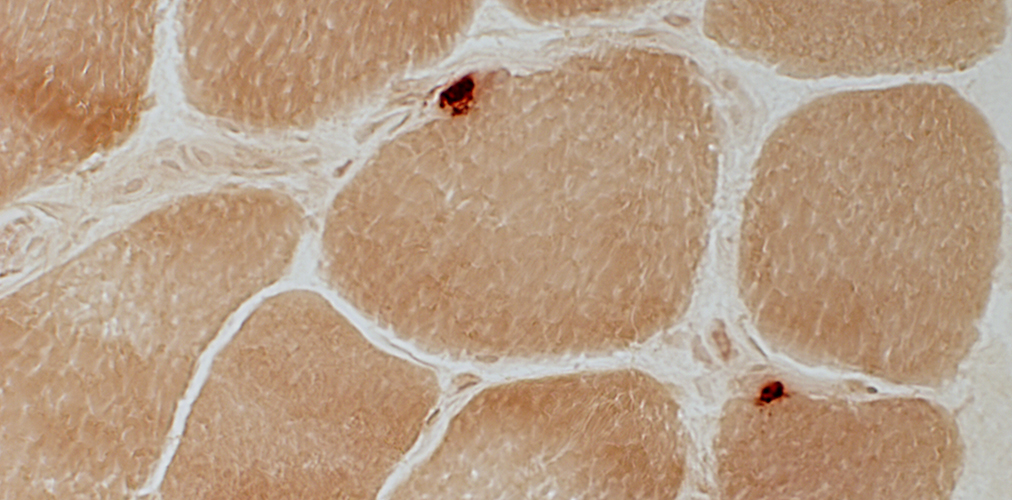 Esterase stain |
|
Caveolin-3 Variably reduced or normal on muscle fiber surfaces |
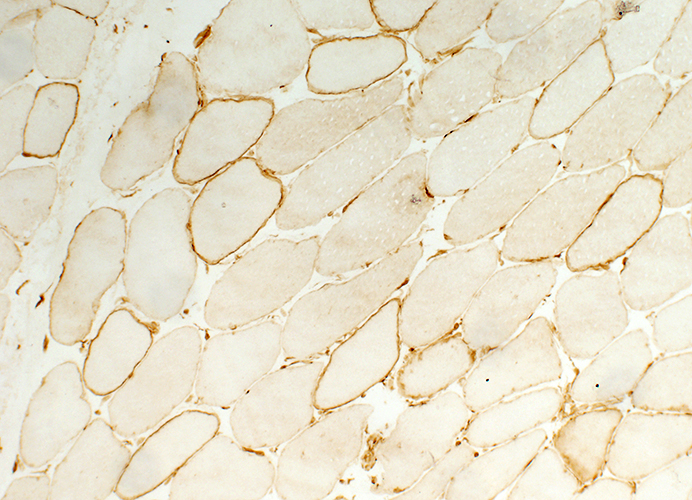 Caveolin-3 stain |
|
MHC, Class I Abnormally upregulated on muscle fiber surfaces & cytoplasm in some regions |
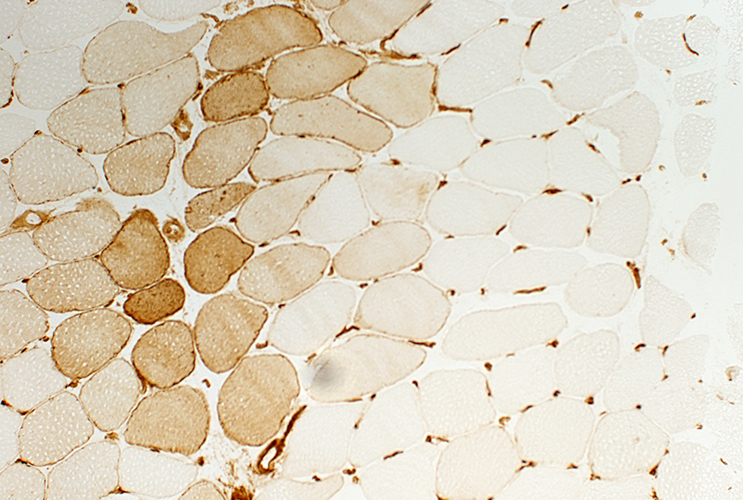 MHC Class I stain |
Myasthenia gravis, Congenital: AChE deficiency
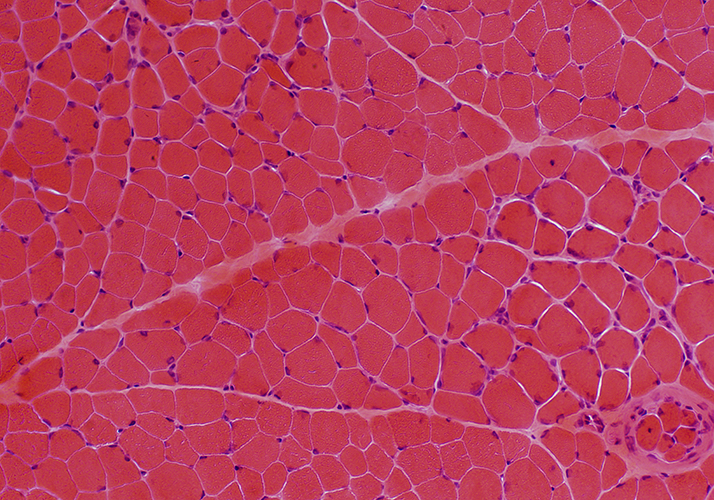 H&E stain |
|
Muscle, Motor points (Areas with NMJs; Above = Top left & Bottom right near spindle) Endomysium: Mildly increased Muscle fibers: Enlarged nuclei (Below right) |
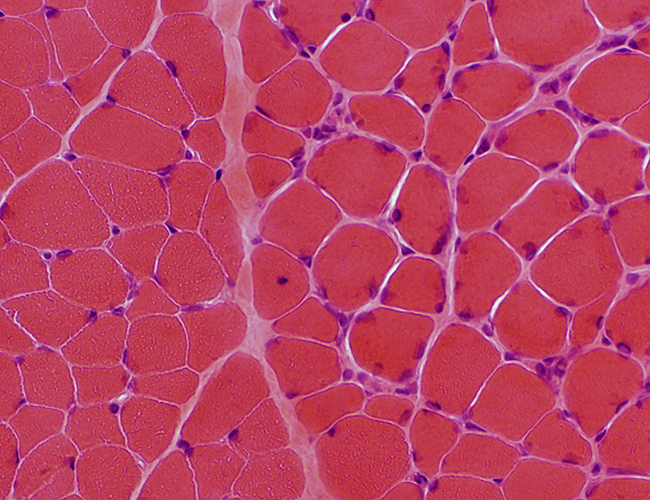 H&E stain |
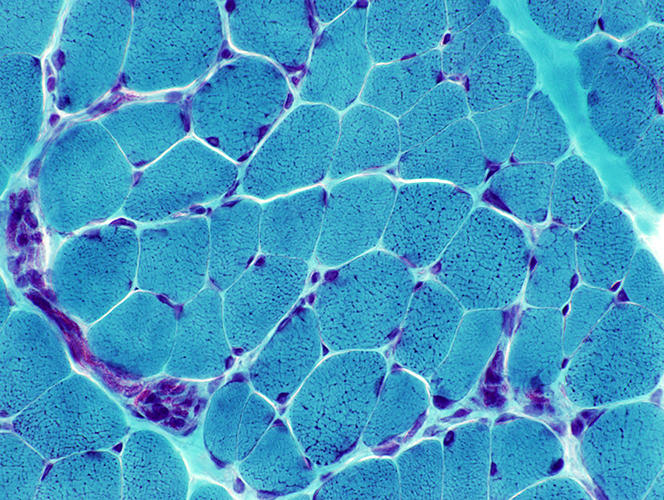 Gomori trichrome stain |
|
Muscle, Motor points Endomysium: Mildly increased Muscle fibers: Coarse internal architecture (Above) Intramuscular nerves: Normal (Below) |
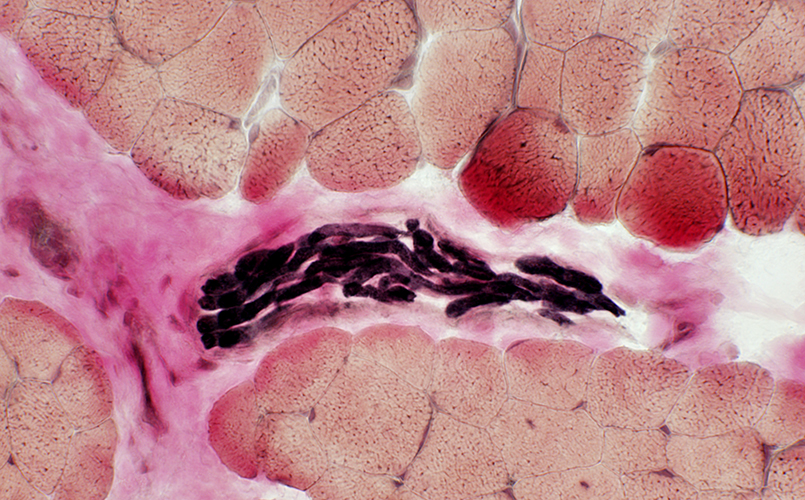 VvG stain |
|
Fiber types: Type 1 (pale) muscle fiber predominance |
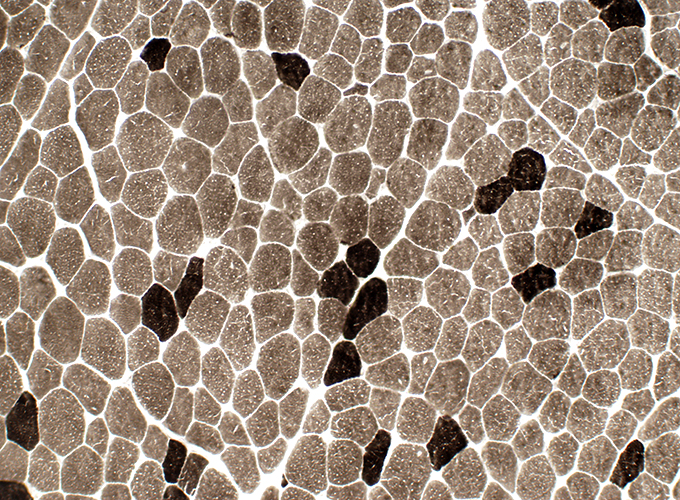 ATP pH 9.4 stain |
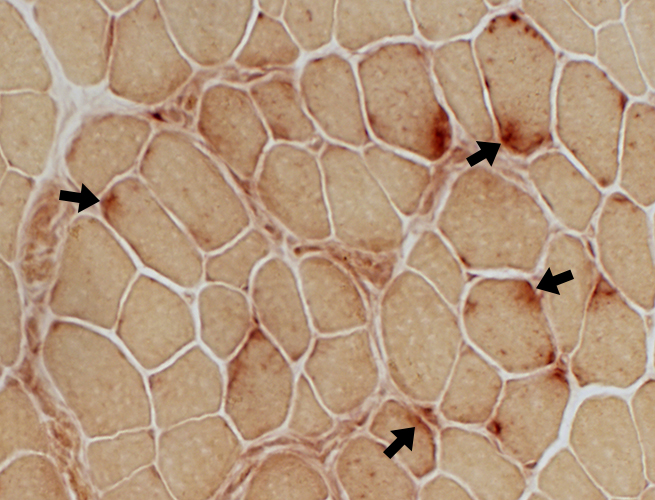
 Esterase stain |
|
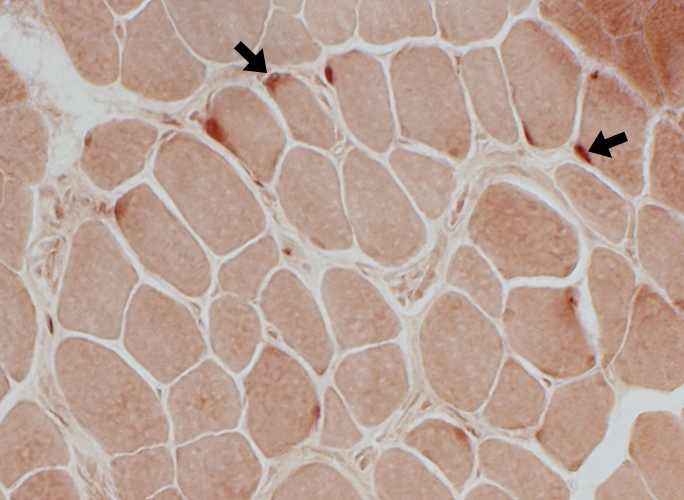
Neuromuscular Junctions Very Pale stained (Above; Arrows) Some of the palest NMJs have neighboring acid phosphatase staining (Below; Arrows) |
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Myasthenia gravis, Congenital: AChR deficiency ε-Subunit mutations
Young adult
Motor Point in Muscle
Intramuscular Nerves: Normal
Present in perimysium
Myelinated axons: Normal numbers
Endomysium: Increased space between muscle fibers compared to other areas of muscle.
Muscle fibers
Fiber sizes
Bimodal distribution
Smaller fibers are often angular
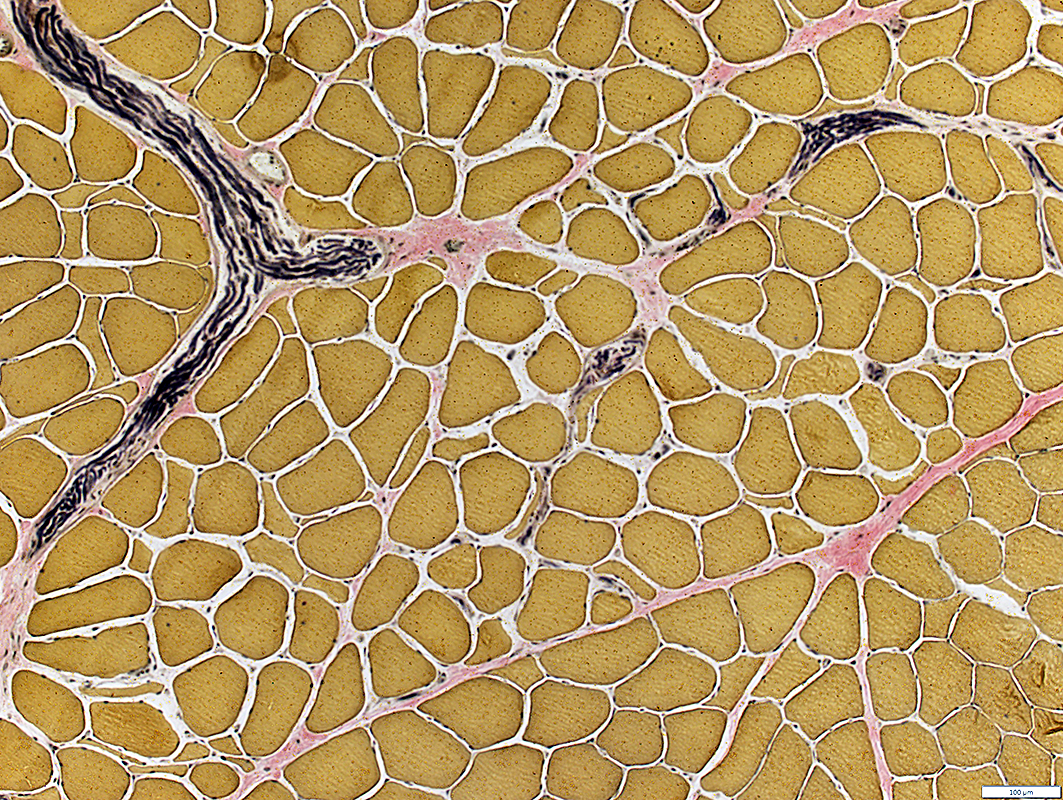 VvG stain |
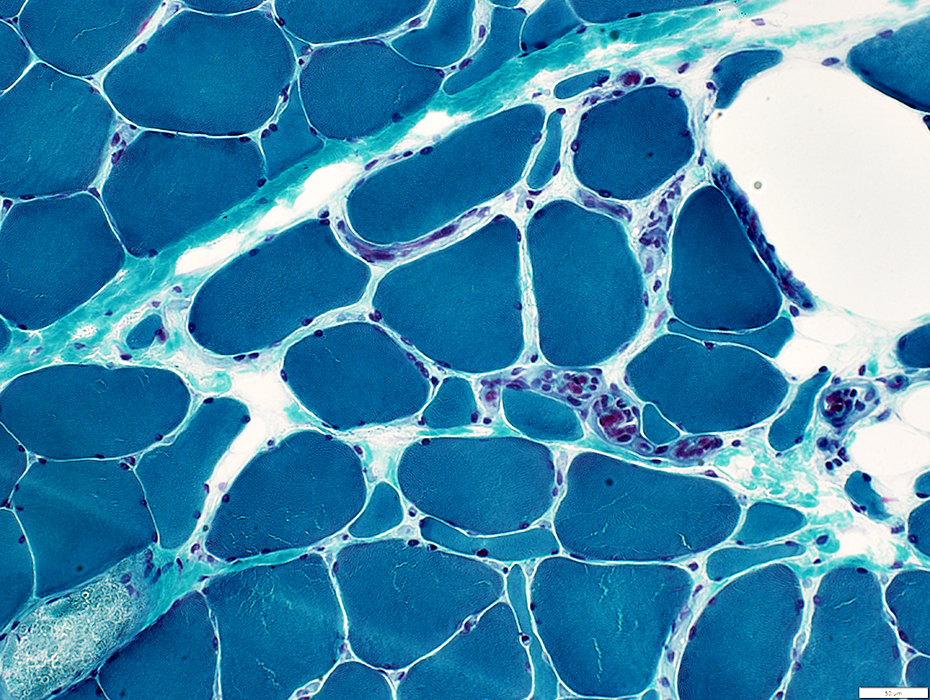 Gomori trichrome stain |
Intramuscular Nerves
Small branches: Present in endomysium
Myelinated axons: Red stained (Above)
Muscle fibers
Increased space between fibers compared to other areas of muscle.
Small fibers are often angular
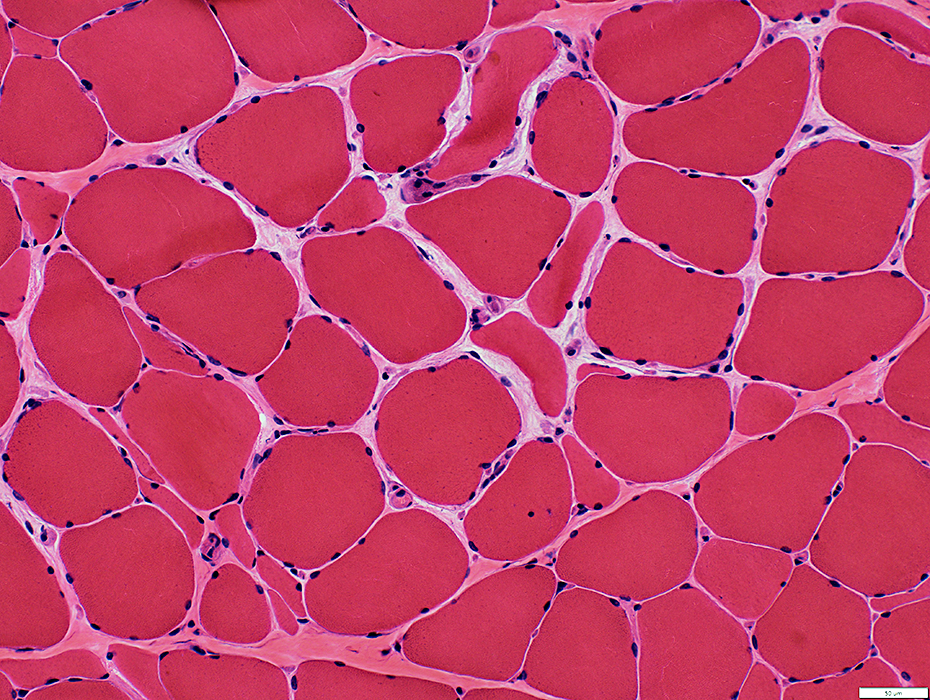 H&E stain |
Muscle Spindle: Normal
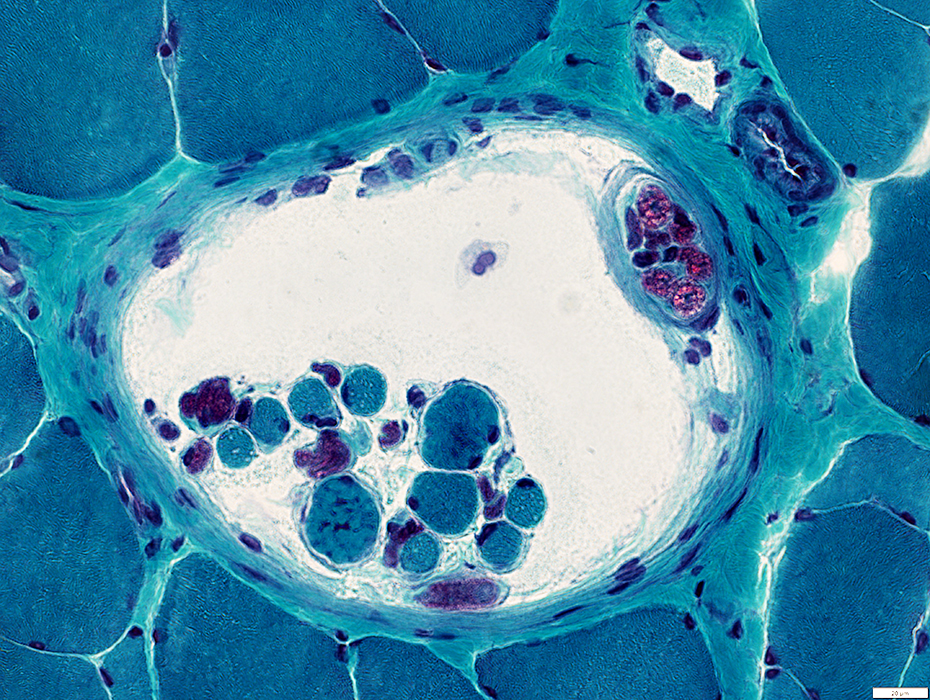 Gomori trichrome stain |
Muscle Fibers: Internal architecture
Normal distribution
Small muscle fibers: Pale stained (Probably mostly type 2)
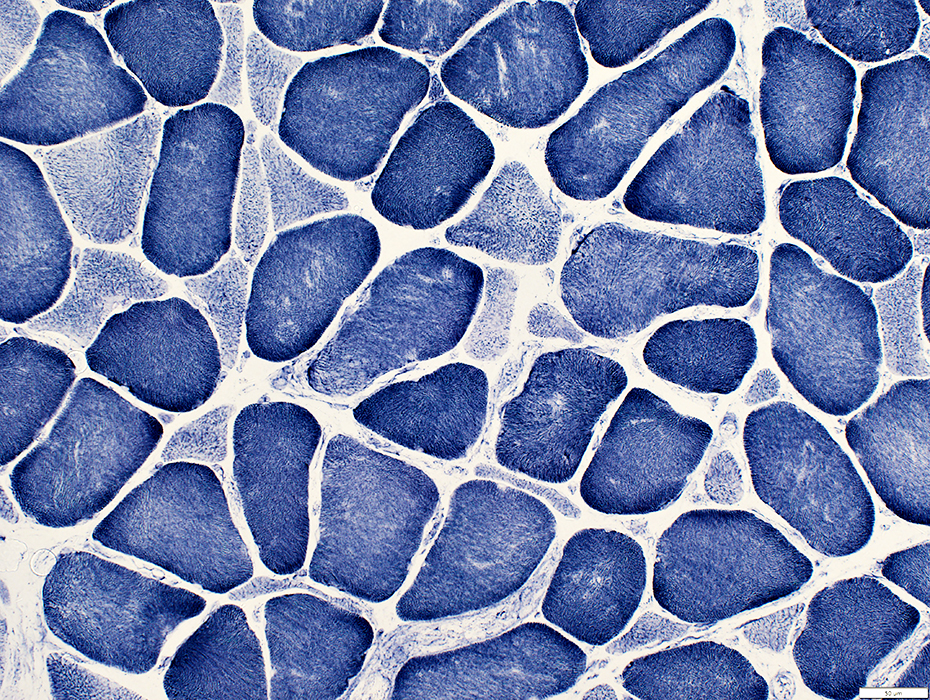 NADH stain |
Congenital MG: Neuromuscular Junctions
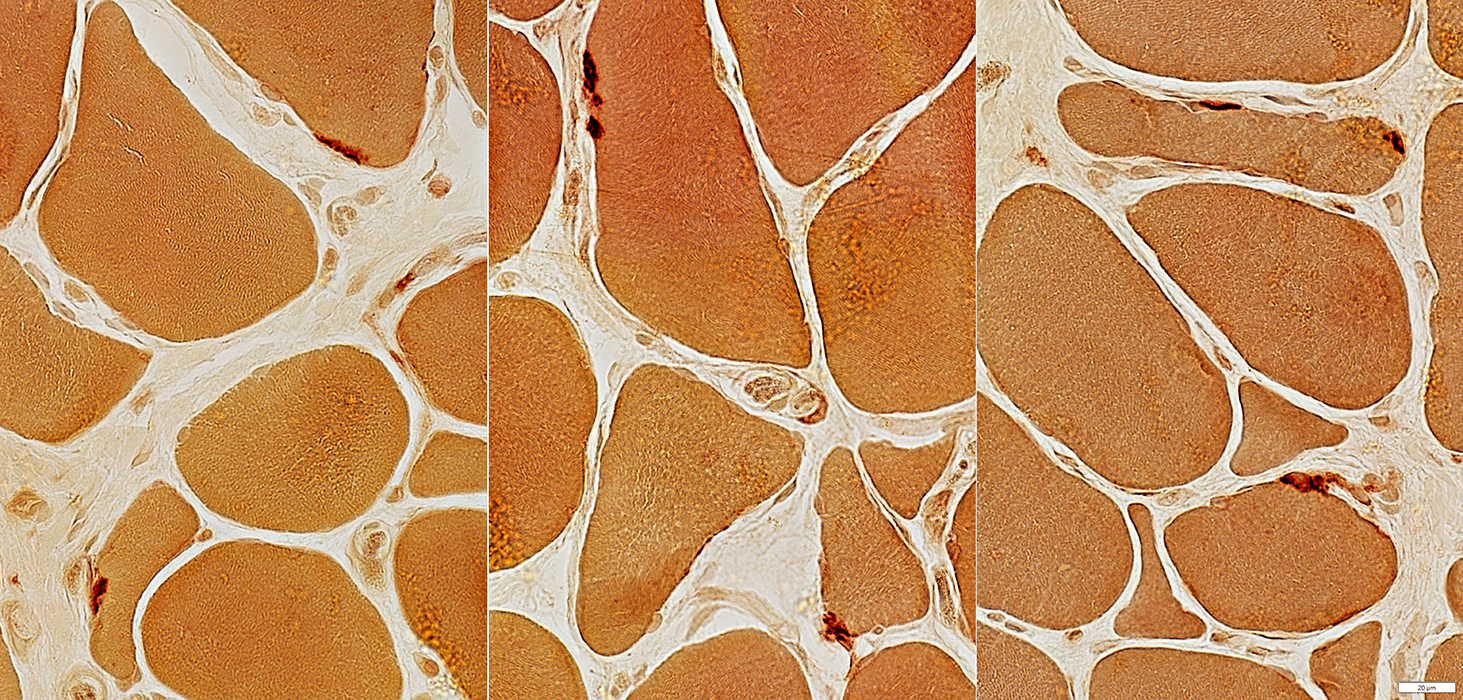 Esterase stain |
Pale stained
Small
May be multi-segmented (Above Right)
See: Control
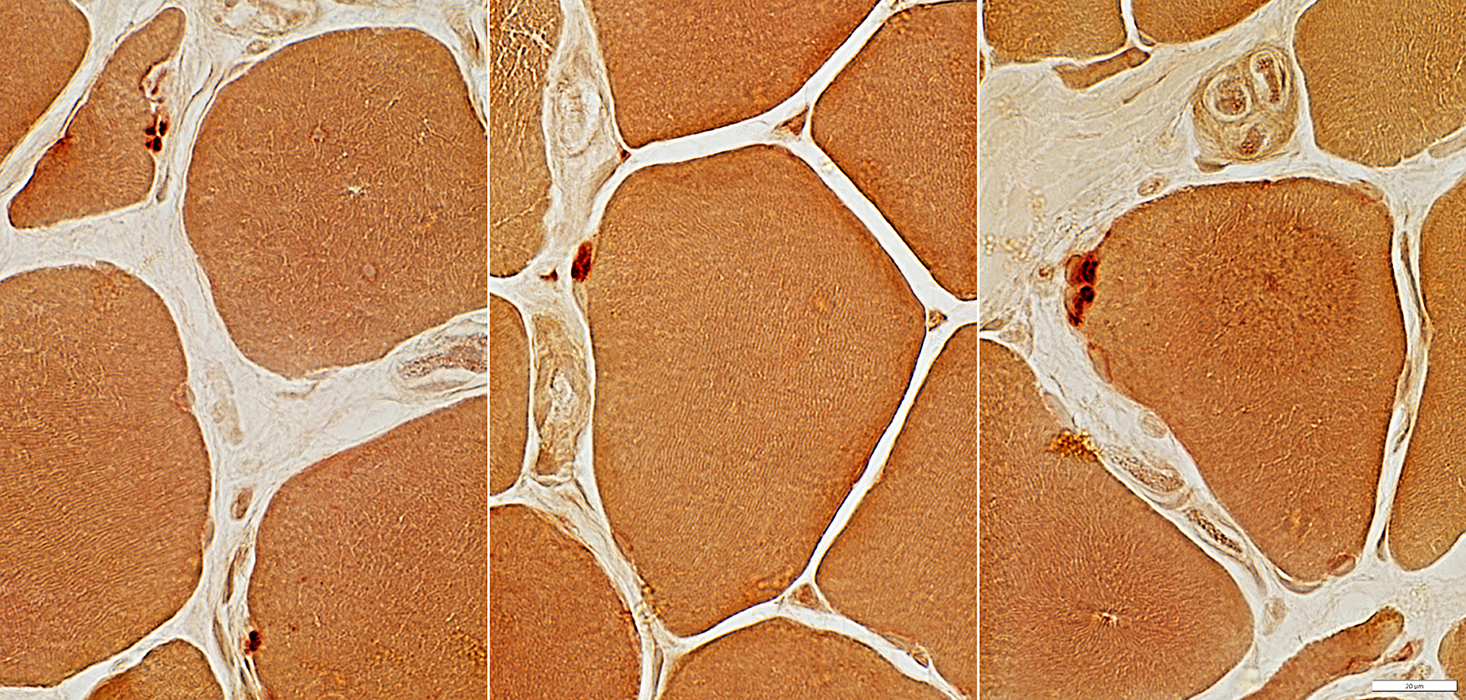 Esterase stain |
2 yo Child: AChR ε subunit mutation
Muscle morphology
 H&E stain |
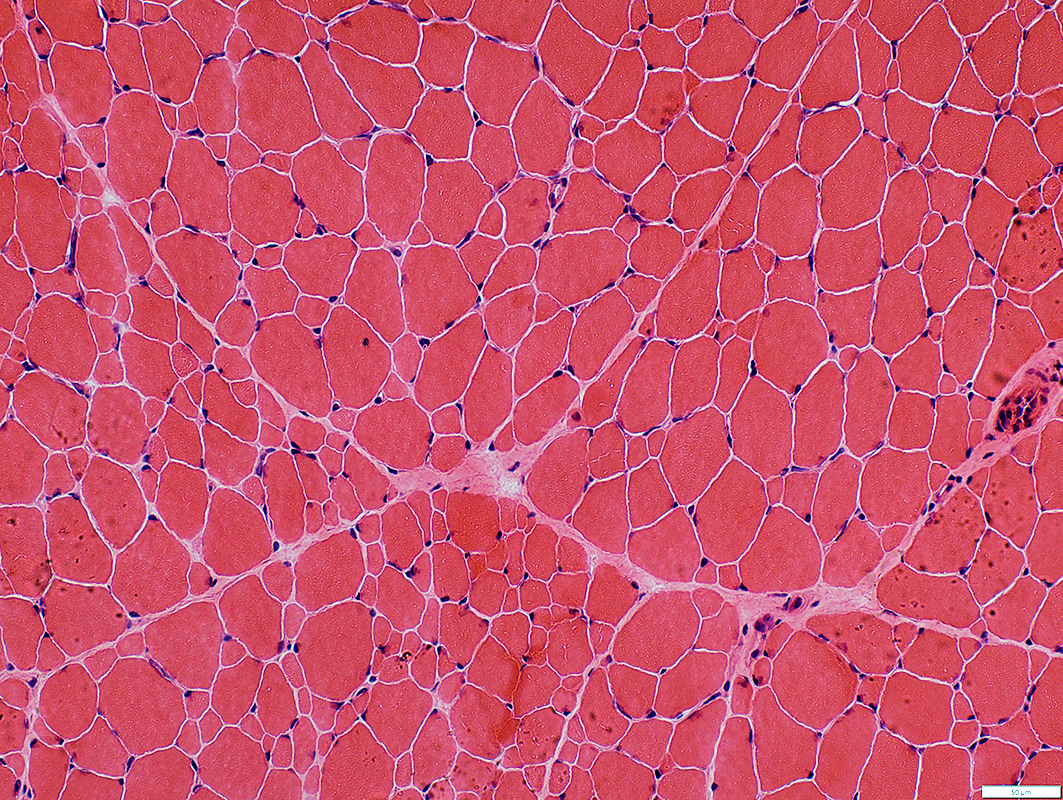
Size Distribution: Bimodal
Small fiber shapes: Polygonal or Round
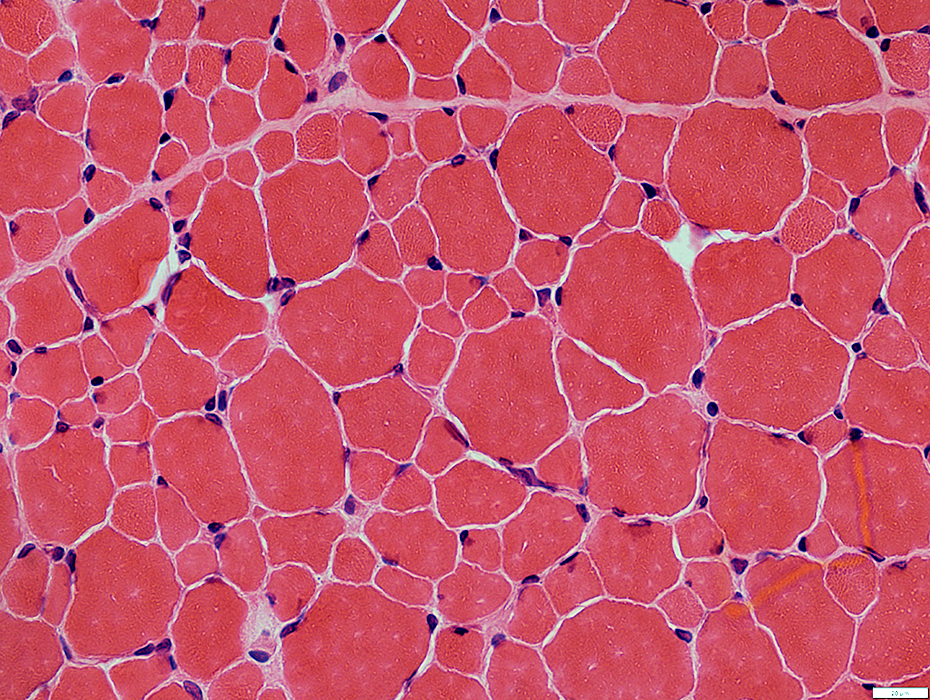 H&E stain |
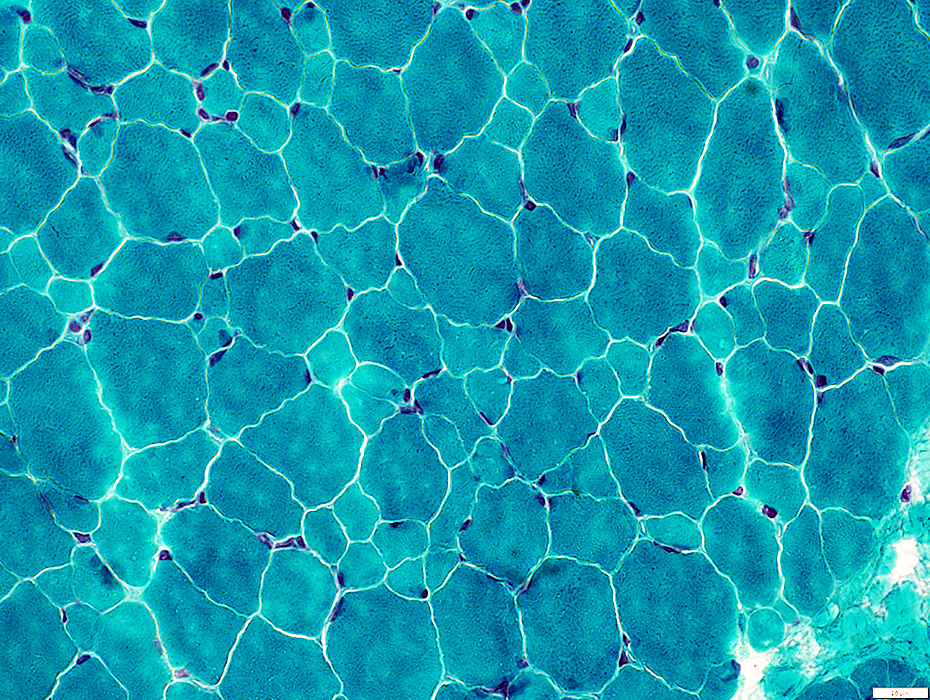 Gomori trichrome stain |
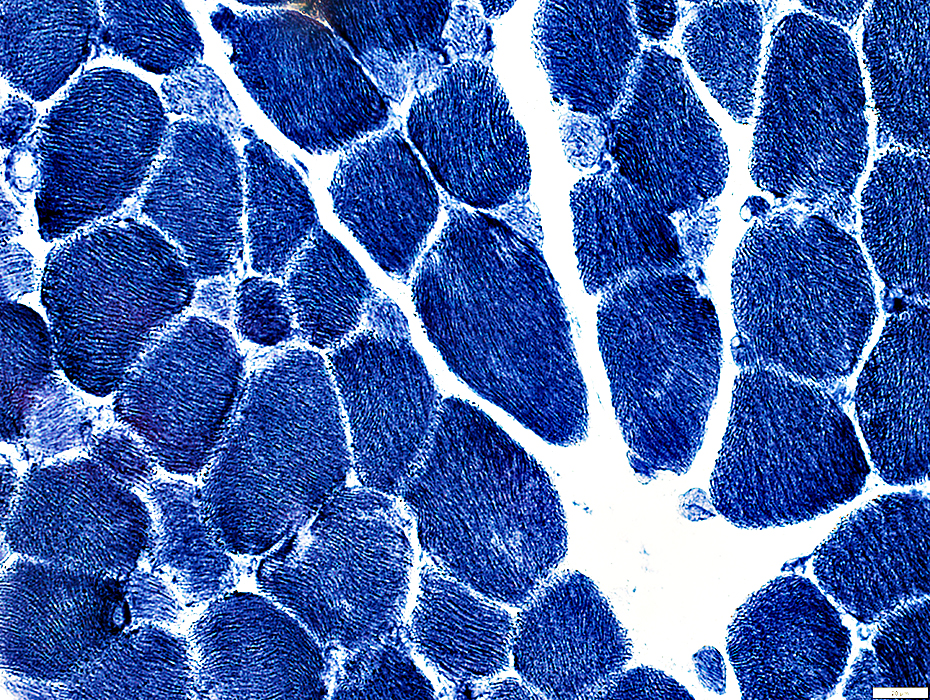 NADH stain |
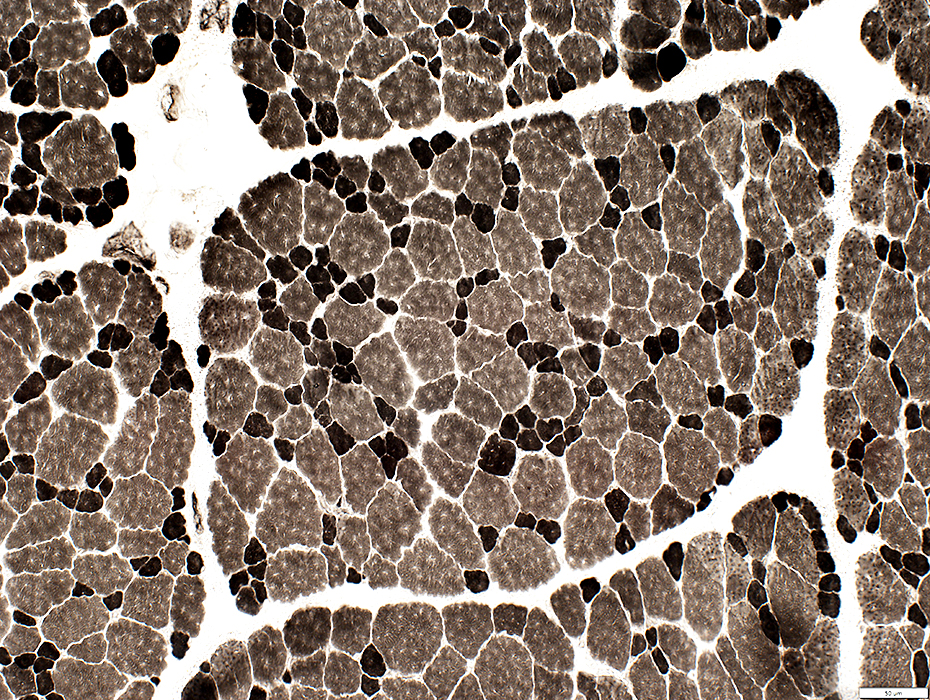 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
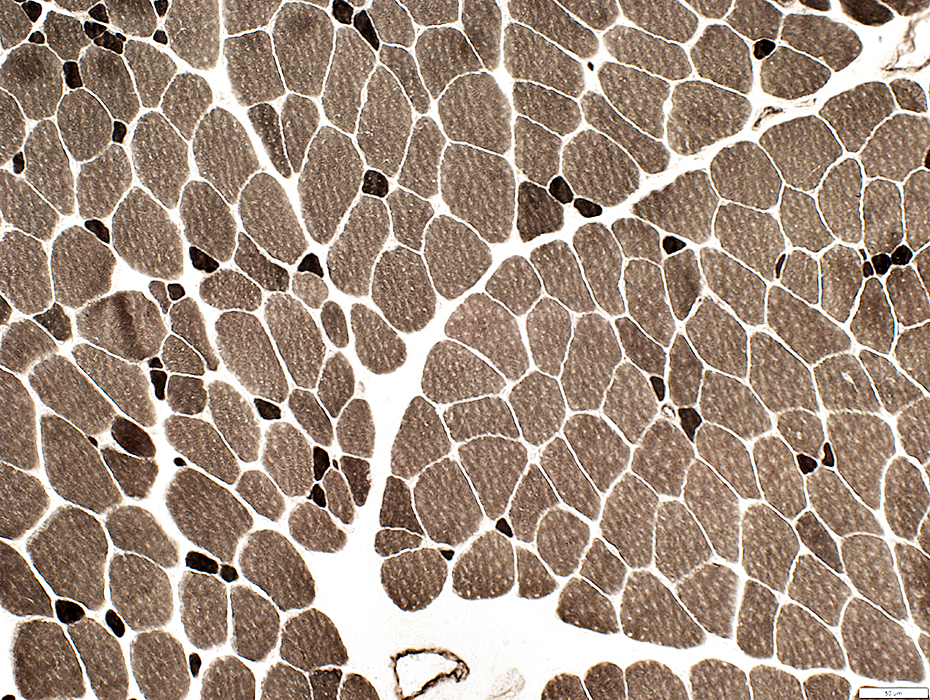 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
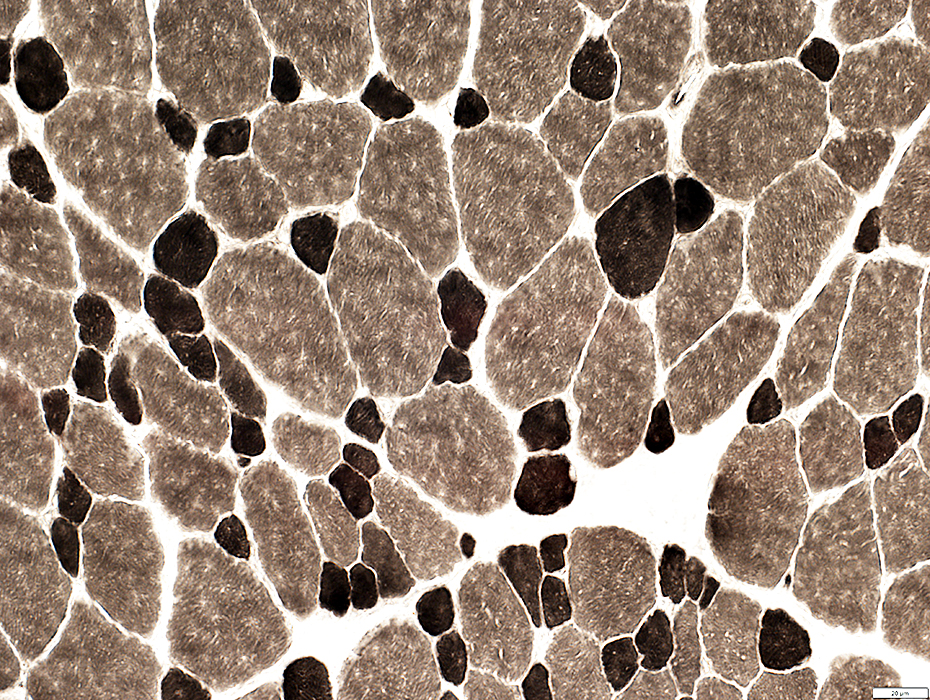 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
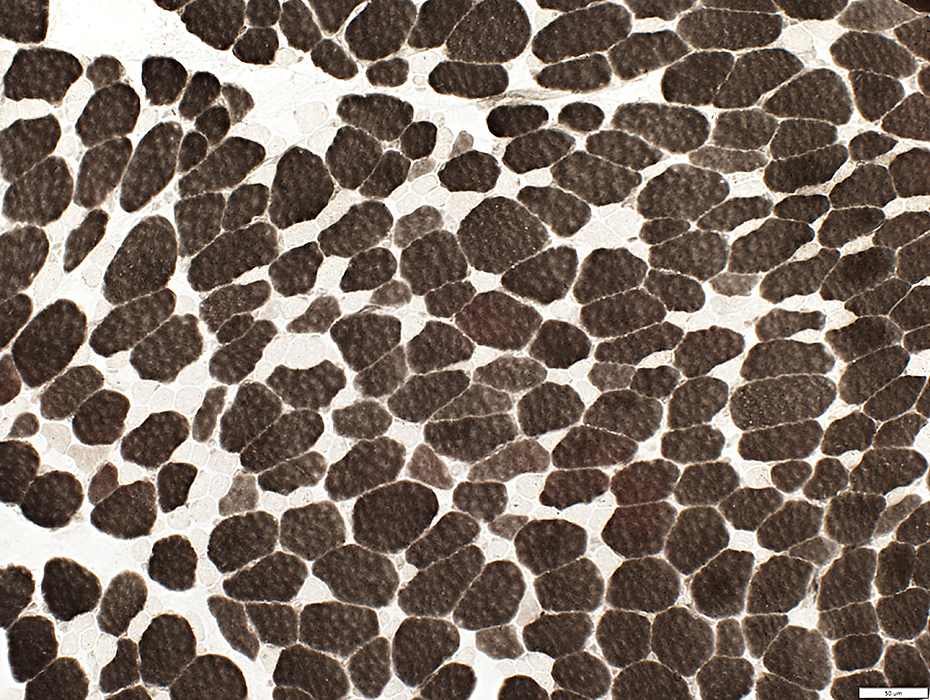 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Immature fibers (Intermediate stain; Type 2C): scattered in biopsy |
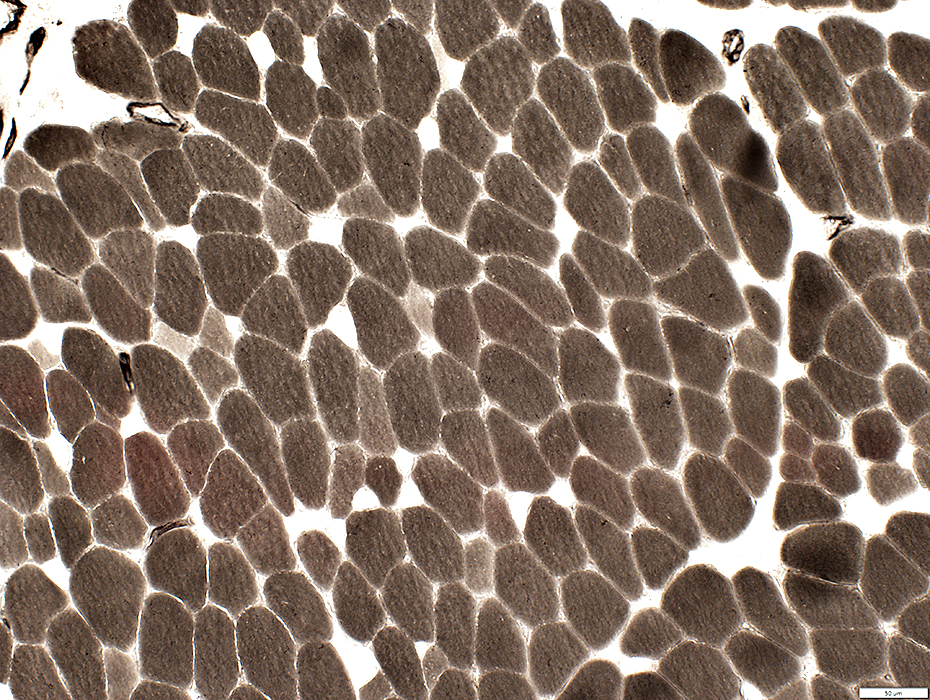 ATPase pH 4.6 stain |
References
1. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 2009;35:103–110
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Myasthenia gravis
7/22/2025