Extraocular Muscles (EOM)
|
Normal Dysthyroid Orbital Myositis PEO |
Rectus EOM: Structure 1
- Layers
- Global
- Location: Internal; Near eye globe
- Insertion: Globe
- Orbital
- Location: Near orbital region
- Insertion: Pulley
- Marginal zone: External
- Global
- Other contents: Spindle fibers; Golgi tendon organs
- Axon innervation
- Twitch: May drive eye movements
- Non-twitch: Tonic muscle activity
- Innervation types
- All have innervation by single axon
- 2 types of NMJ contact: Single & Multiple NMJ regions
- EOM Muscle fiber types
- Orbital
- Single NMJ (Single-innervated)
- Frequency: 80% of fibers in orbital layer
- ATPase stain: 4.3 pale; 9.4 dark
- Myosin isoforms: Fast in entire length; Neonatal/Embryonic (developmental) in distal & proximal segments
- Mitochondrial stains (COX & SDH): Dark, Clustered
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum structure: Coarse
- AChR types: Adult & Fetal
- Physiology: Fast, Fatigue resistant
- Multiple NMJ (Multi-innervated)
- Frequency: 20% of fibers in orbital layer
- ATPase stain: Ends 4.3 dark, 9.4 intermediate; Center 4.3 pale
- Myosin isoforms: Fast in center; Neonatal/Embryonic (developmental) in distal & proximal segments
- Mitochondrial stains (COX & SDH): Dark, Clustered
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum structure: Fine in distal & proximal segments
- AChR types: Adult & Fetal
- Physiology: Fatigue resistant in center; Slow at ends
- Single NMJ (Single-innervated)
- Global
- Red, Single NMJ
- Frequency: 30% of fibers in global layer
- ATPase stain: 4.3 pale; 9.4 dark
- Myosin isoforms: IIA-like
- Mitochondrial stains (COX & SDH): Dark, Clustered
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum structure: Coarse (C)
- AChR types: Adult
- Physiology: Fast, Fatigue resistant
- Intermediate/Pale Single NMJ
- Frequency: 60% of fibers in global layer
- ATPase stain: 4.3 pale; 9.4 dark
- Myosin stain: IIB-like
- Mitochondrial stains (COX & SDH): Dark, Clustered
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum structure: Granular (G)
- AChR types: Adult
- Physiology: Fast, Fatigue resistant
- Multiple NMJ
- Frequency: 10% of fibers in global layer
- ATPase stain: Ends 4.3 dark, 9.4 intermediate
- Myosin isoforms: Slow
- Mitochondrial stains (COX & SDH): Dark, Clustered
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum structure: Fine (F)
- AChR types: Adult & Fetal
- Physiology: Slow
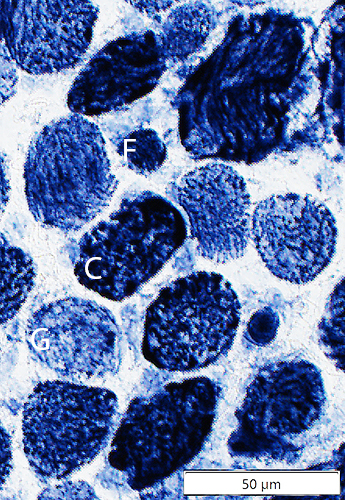
NADH stain - Red, Single NMJ
- Orbital
Muscle patterns: Normal Adult EOM
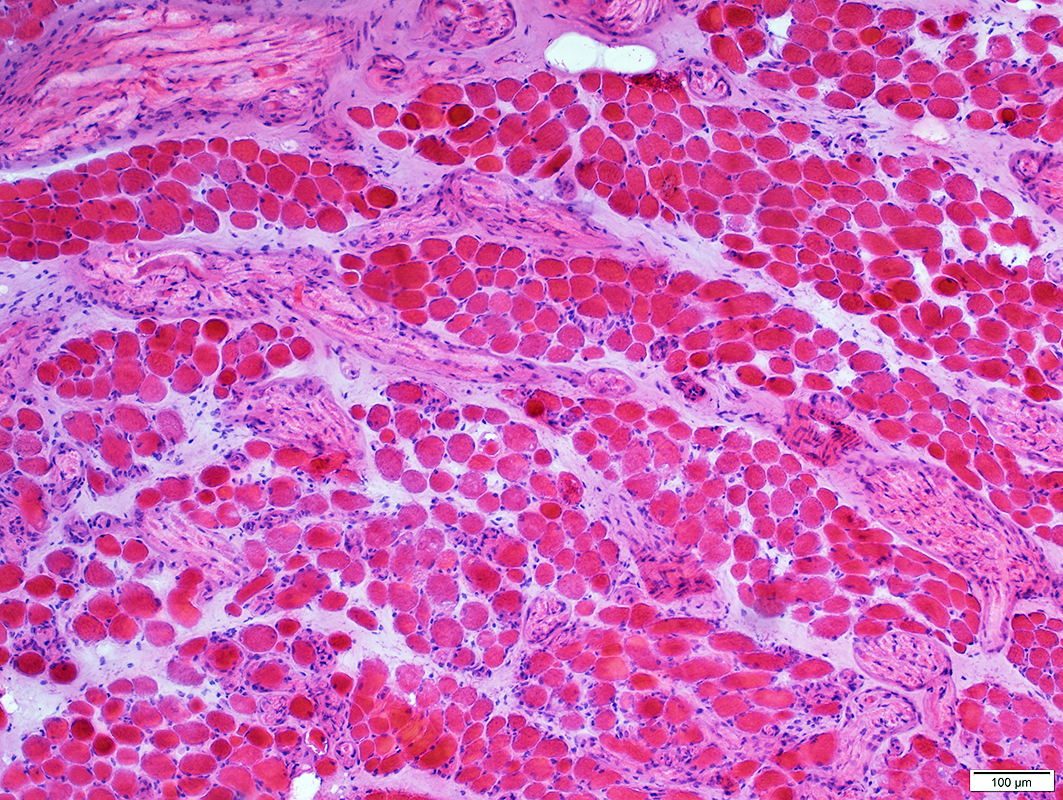 H&E stain |
Fascicles: Smaller than limb or trunk muscles
Endomysial connective tissue
More between muscle fibers than limb or trunk muscles
Especially in regions with intramuscular nerves
Perimysial Vessels: Normal structure
Intramuscular nerves: May be abundant
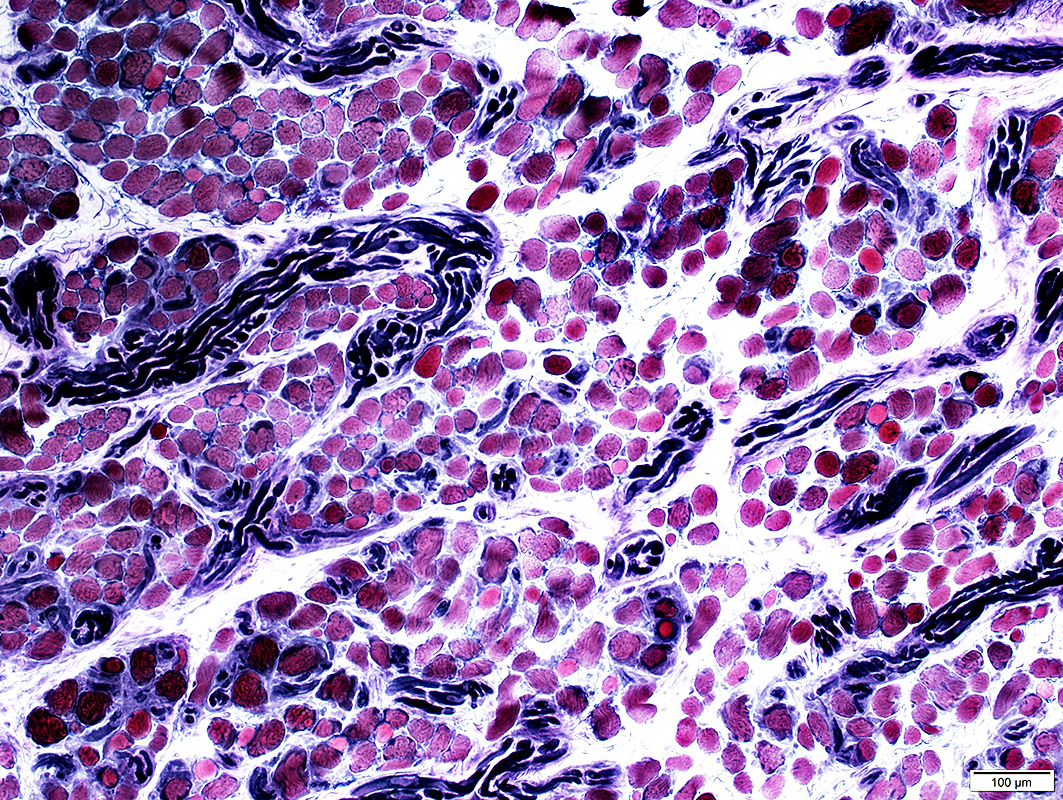 VvG stain |
Muscle fibers: Sizes & Regional patterns
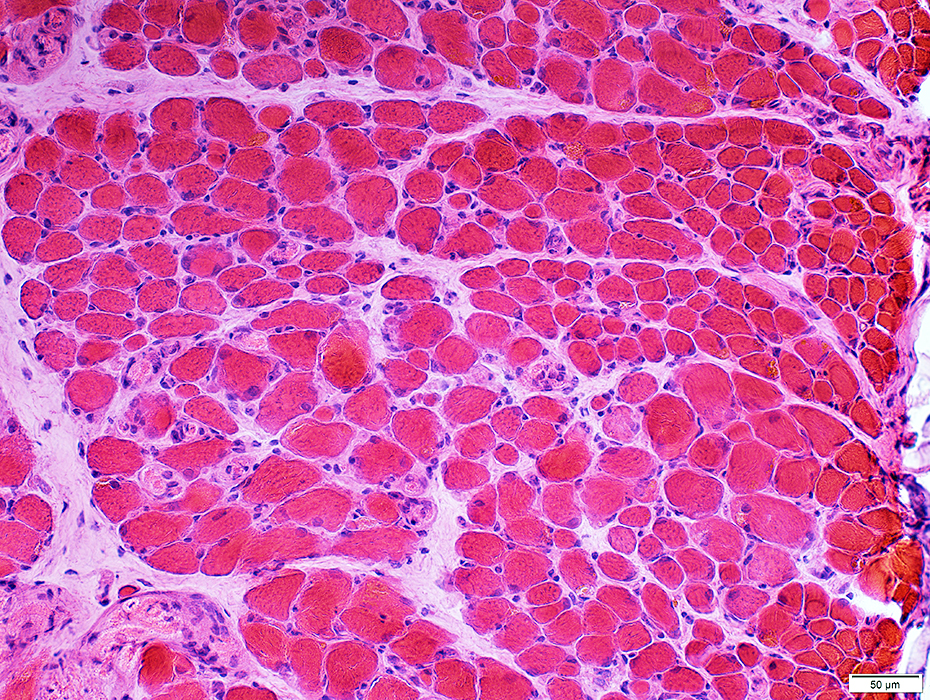 H&E stain |
Varied: Among, & within, fascicles
May be smaller at surface of muscle (Above)
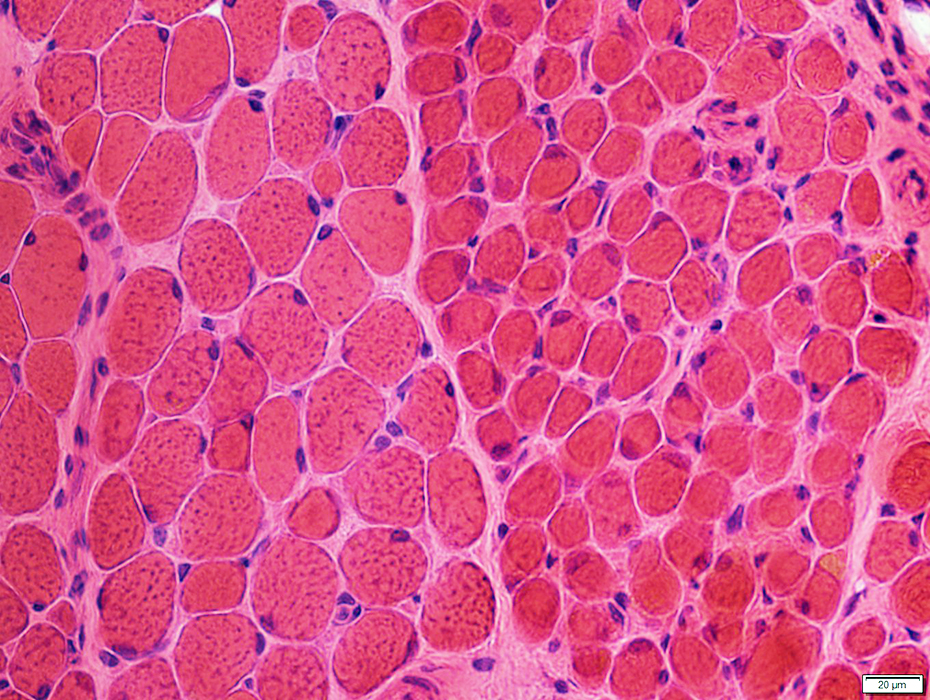 H&E stain |
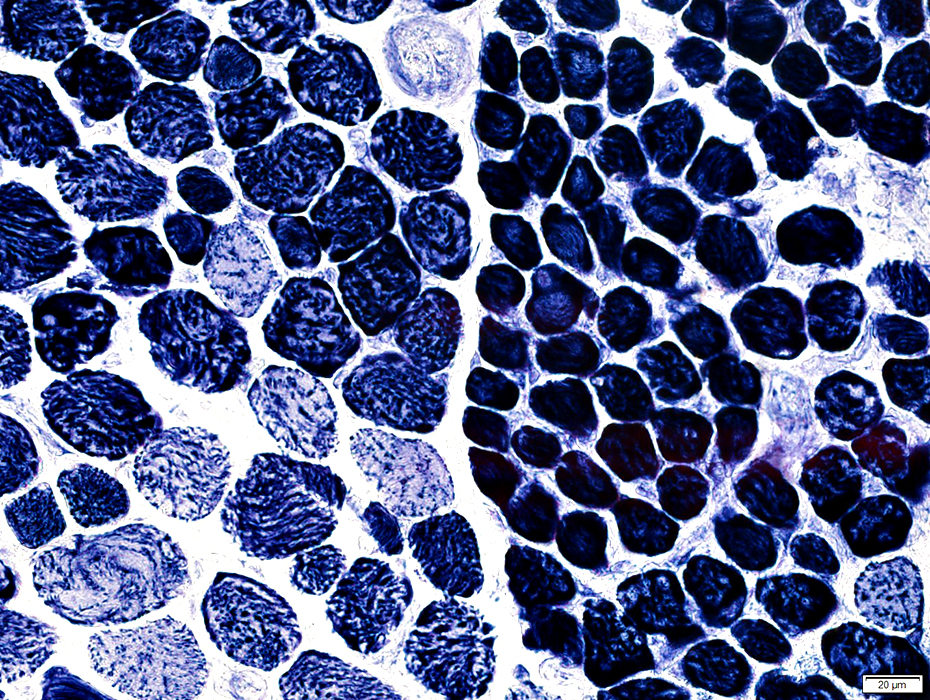 NADH stain |
Muscle fibers: Morphology
Muscle fibersSize: Varied; 10 to 50 μM in diameter
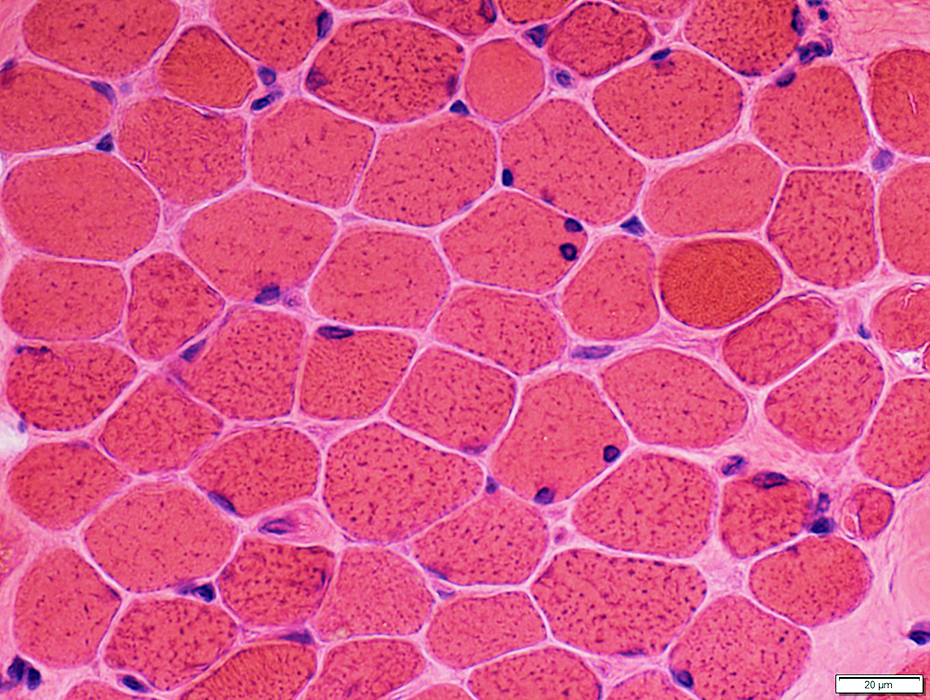 H&E stain |
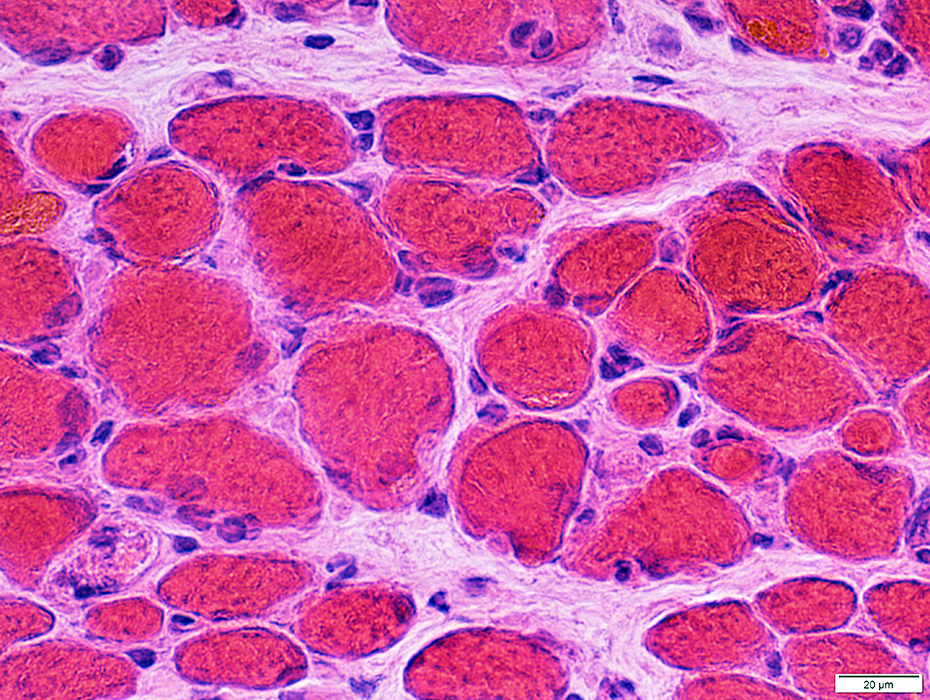 H&E stain |
Size: Varied; 10 to 50 μM in diameter
Myonuclei: Large or Small
Neuromuscular junctions: Pale regions around muscle fibers (Arrow)
Motor point: Endomysial connective tissue increased
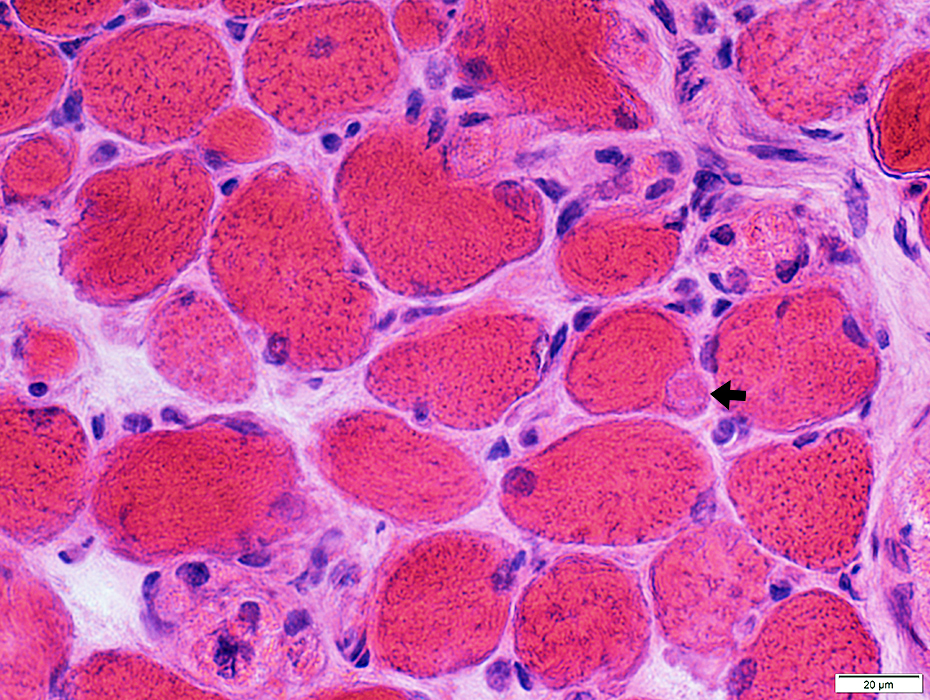 H&E stain |
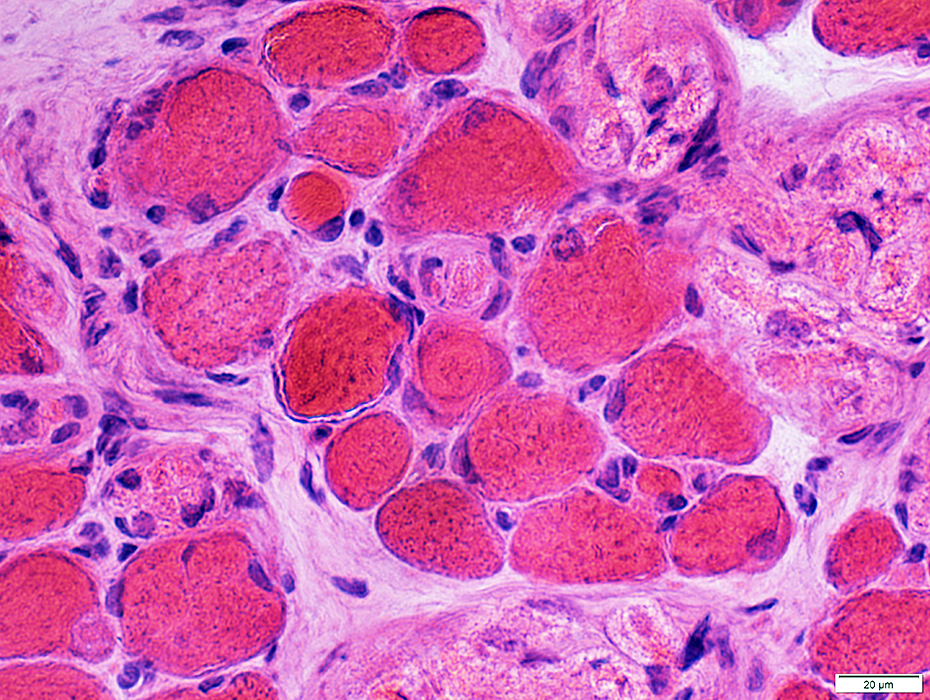 H&E stain |
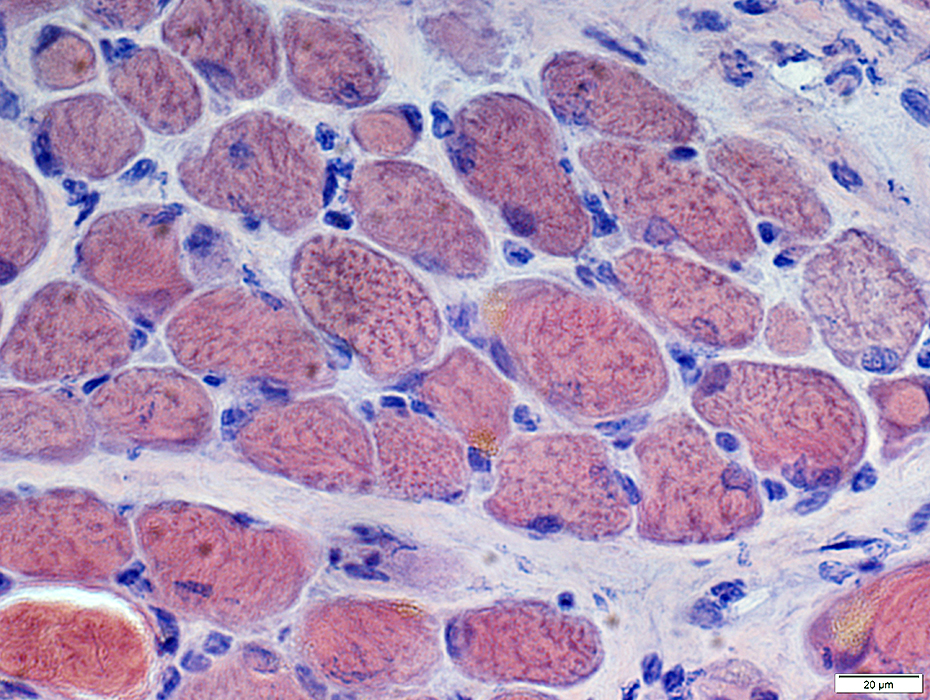 Congo red stain |
Internal architecture: Irregular
Myonuclei: Large
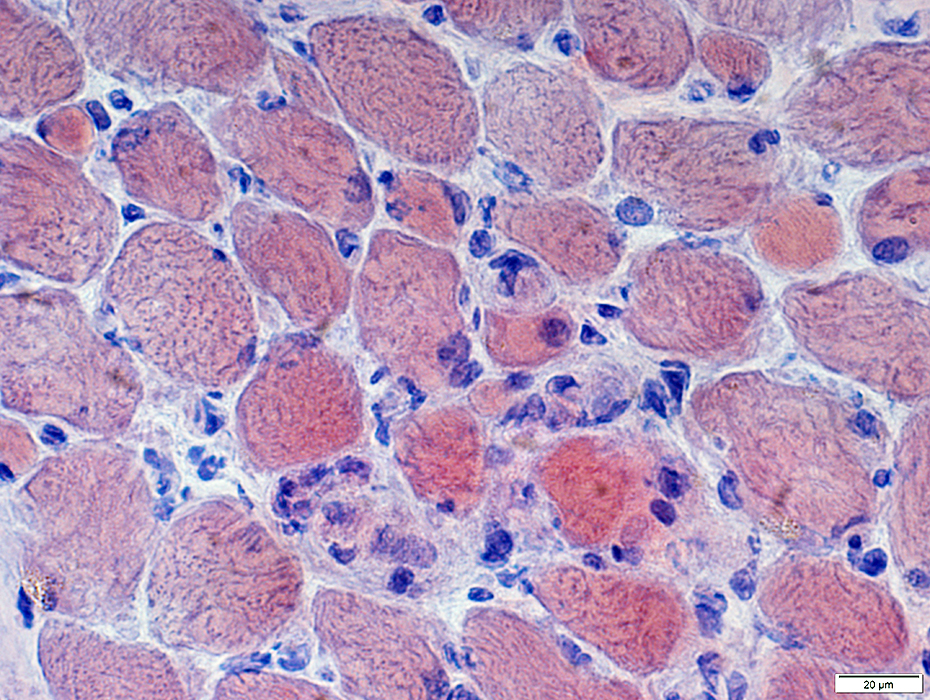 Congo red stain |
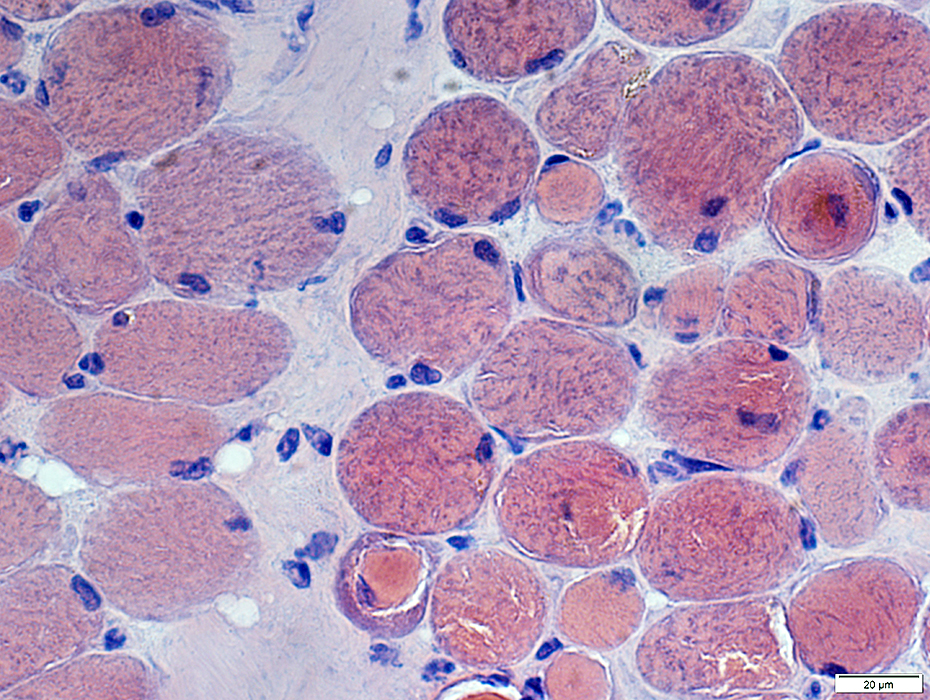 Congo red stain |
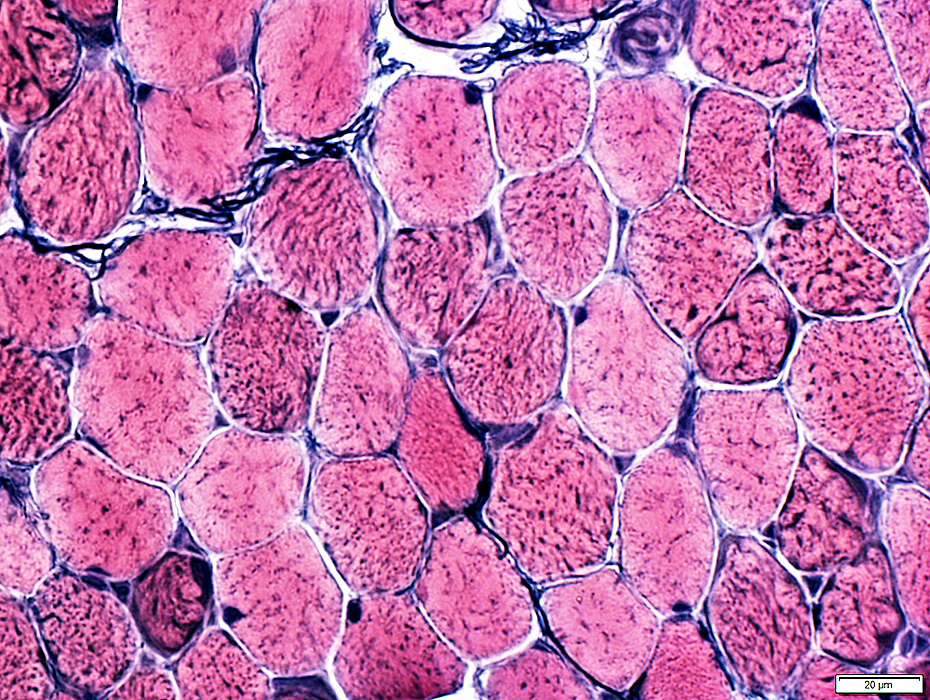 VvG stain |
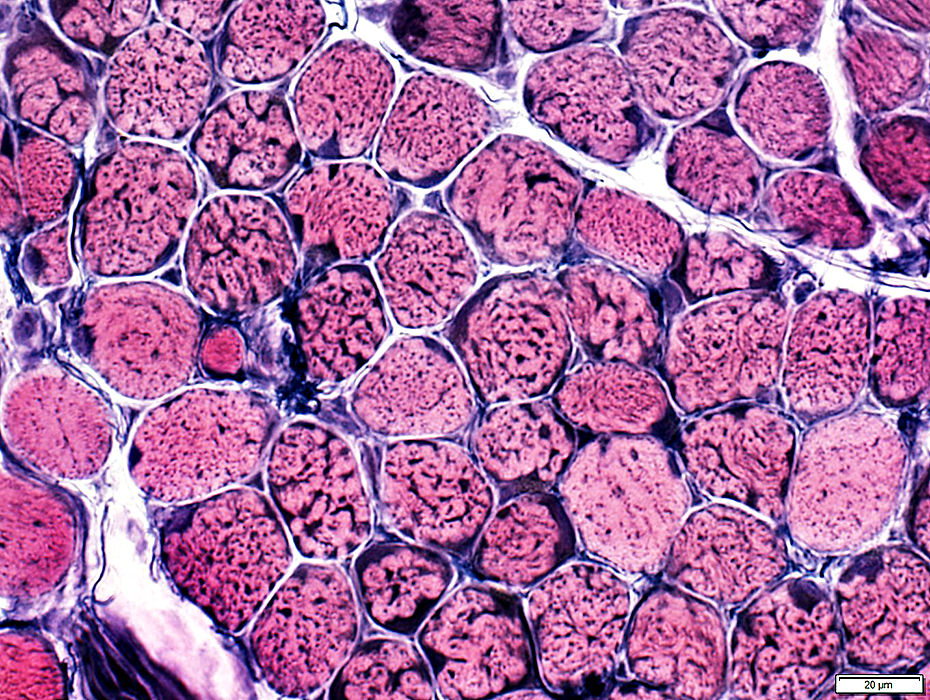 VvG stain |
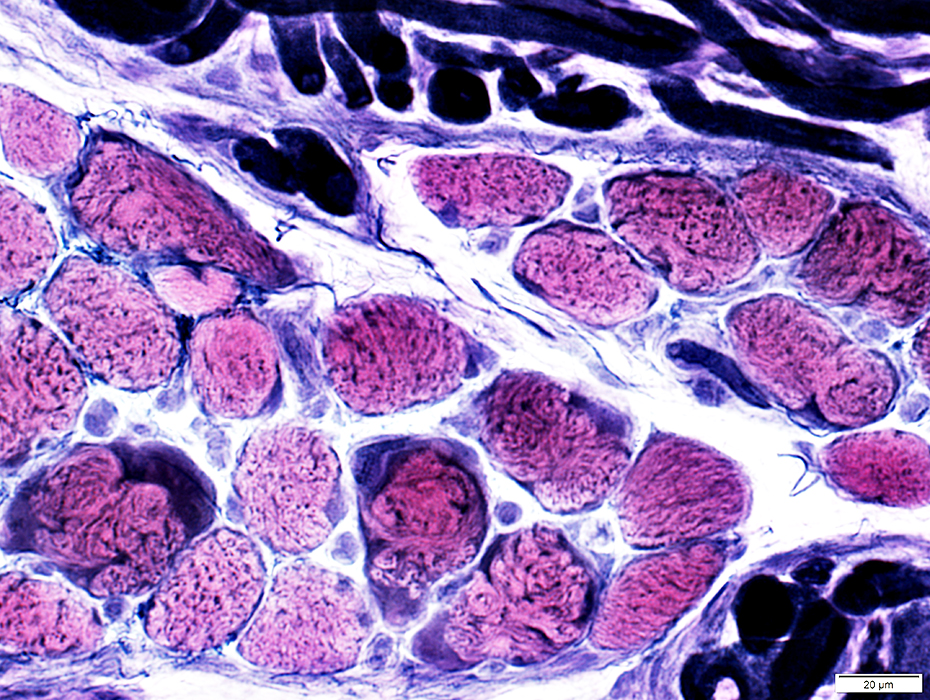 VvG stain |
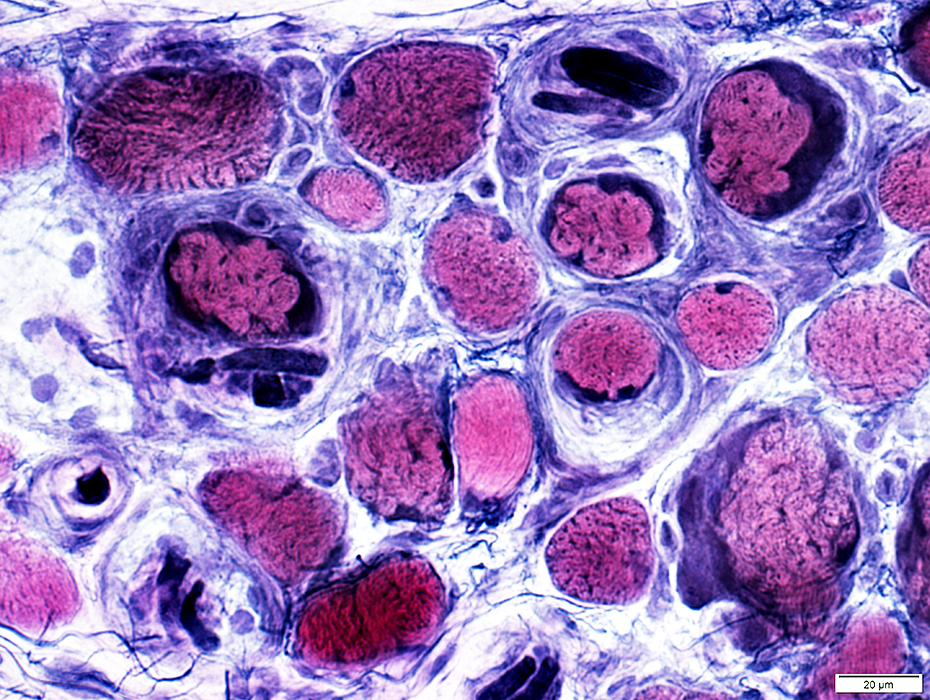 VvG stain |
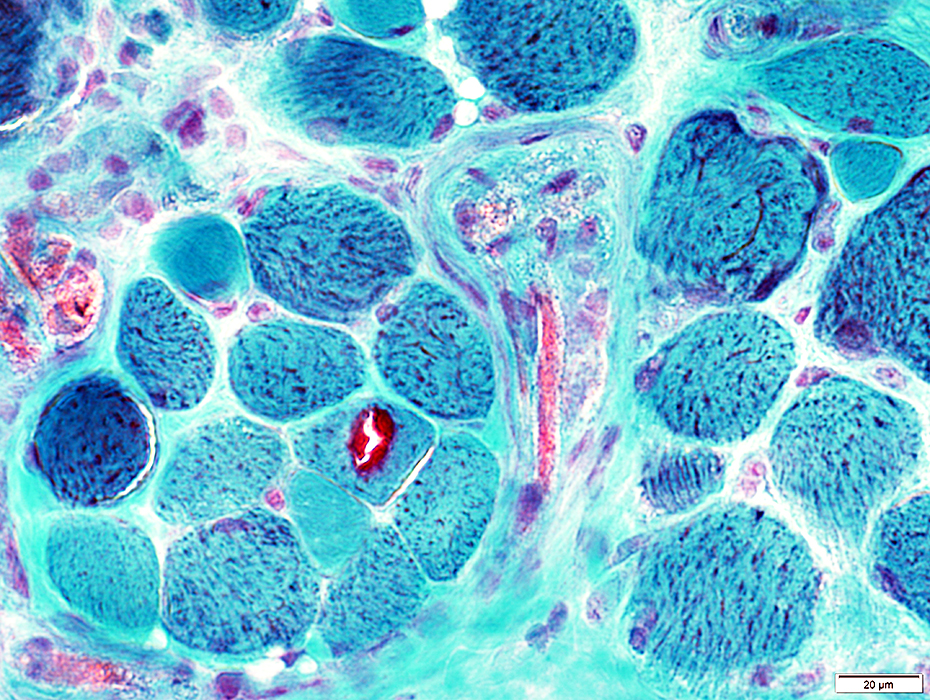 Gomori trichrome stain |
Abundant in muscle fibers
Some muscle fibers appear "ragged red"
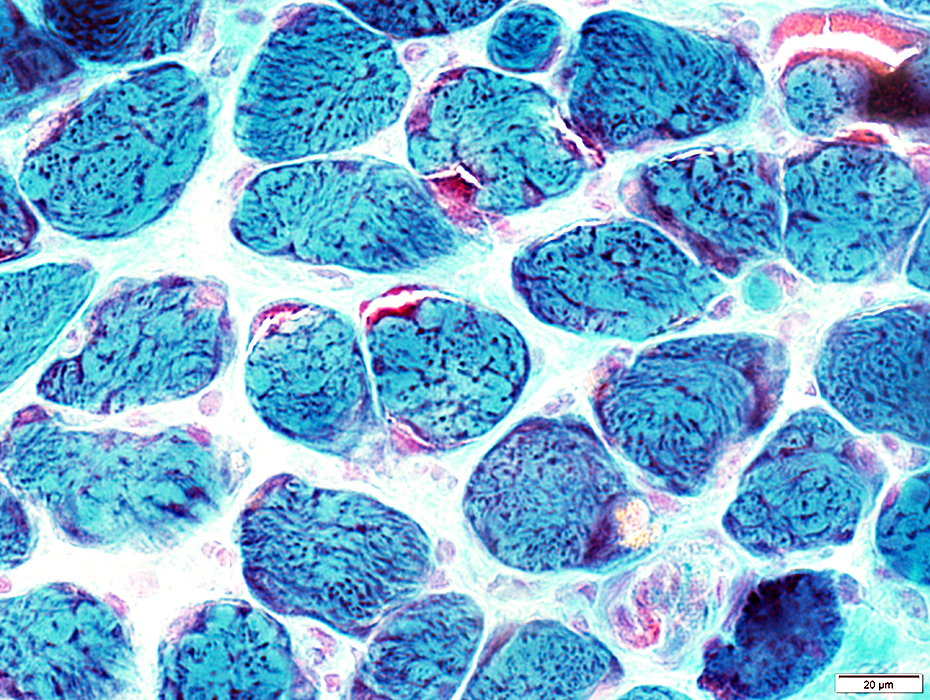 Gomori trichrome stain |
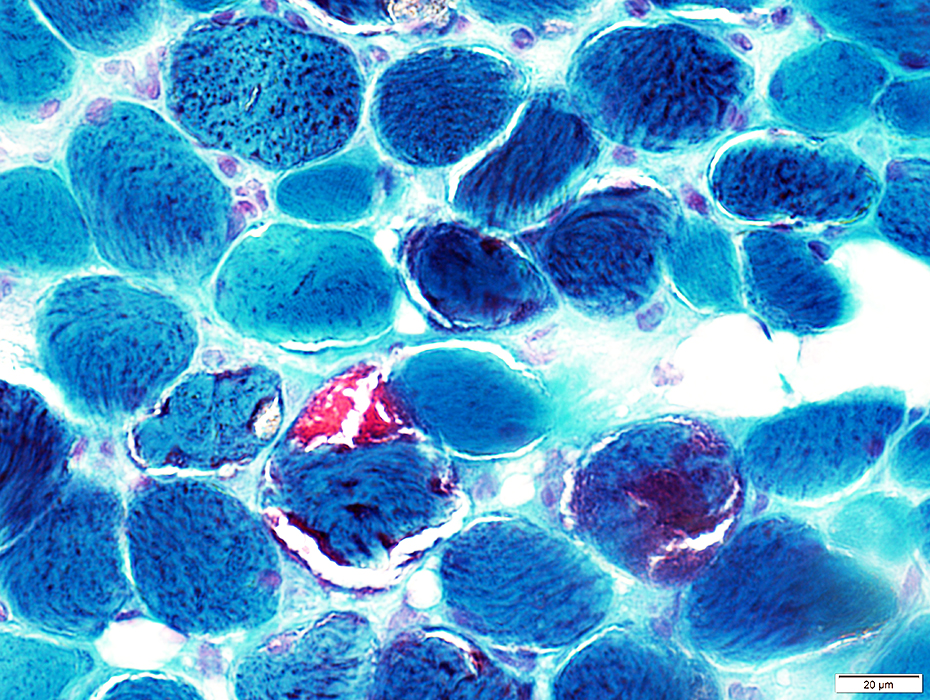 Gomori trichrome stain |
Internal architecture
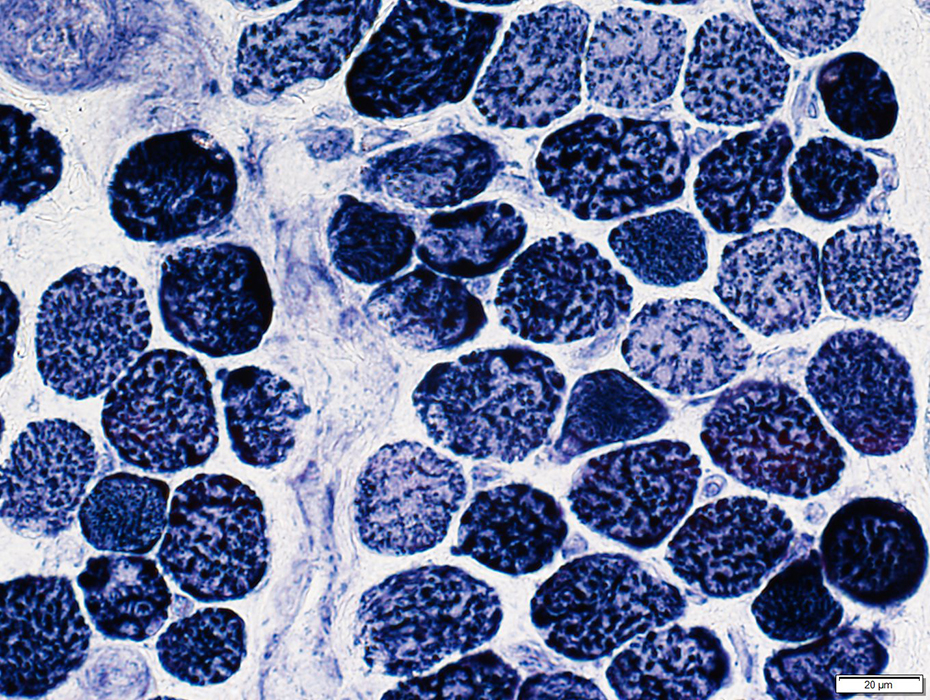 NADH stain |
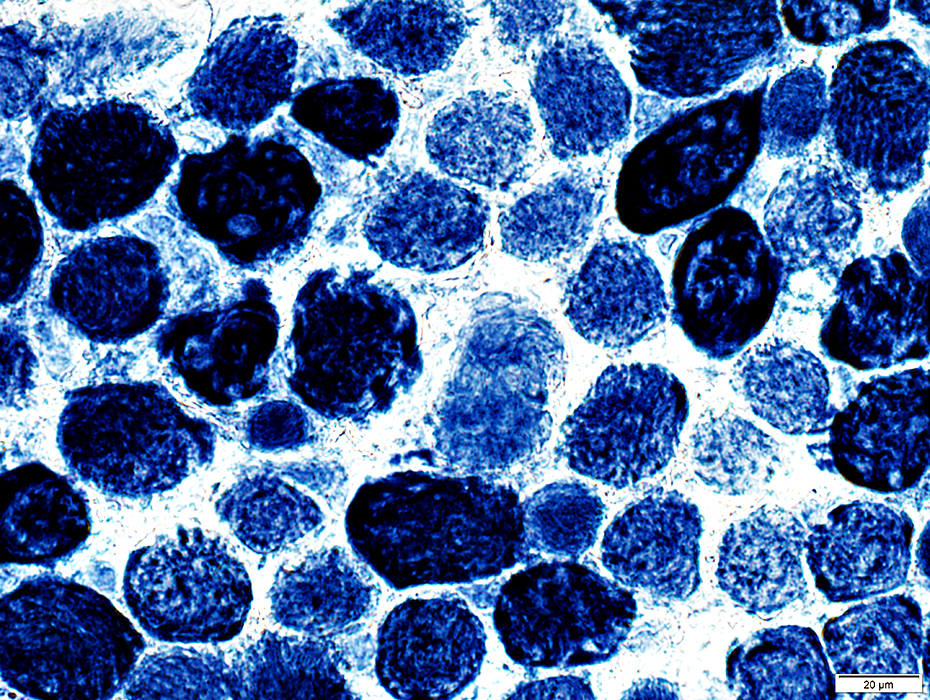 NADH stain |
Some muscle fibers are very darkly stained
Sarcoplasmic reticulum staining: Coarse; Punctate
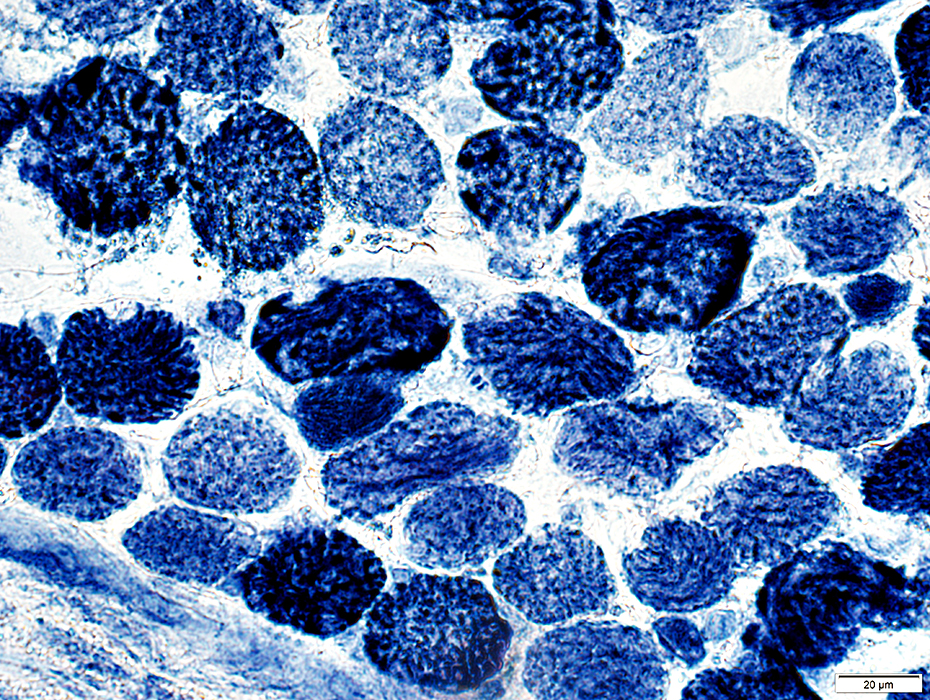 NADH stain |
EOM: Mitochondria
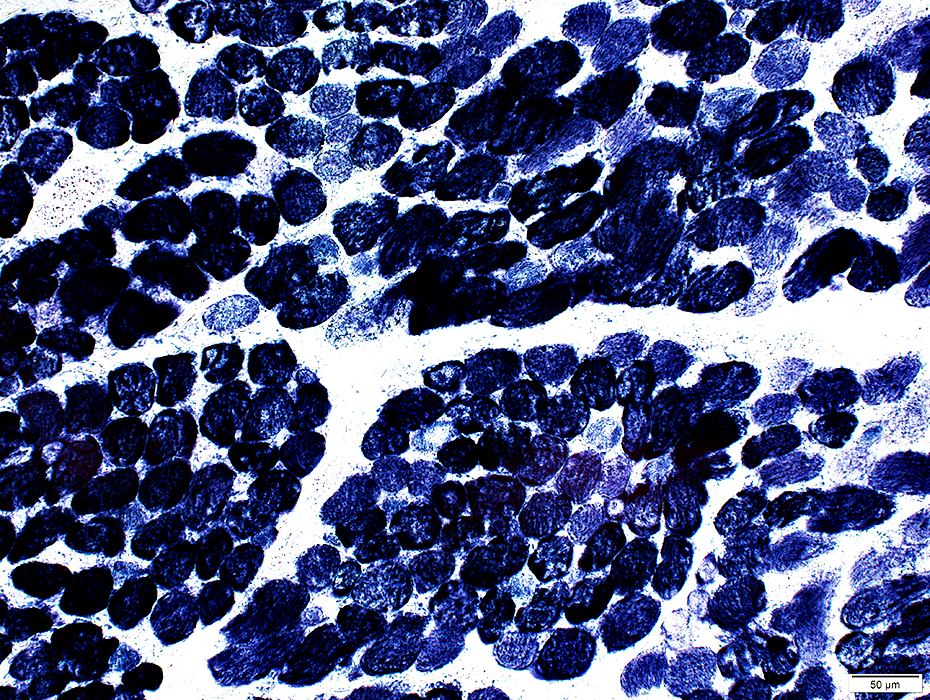 SDH stain |
Some muscle fibers are very dark stained for SDH
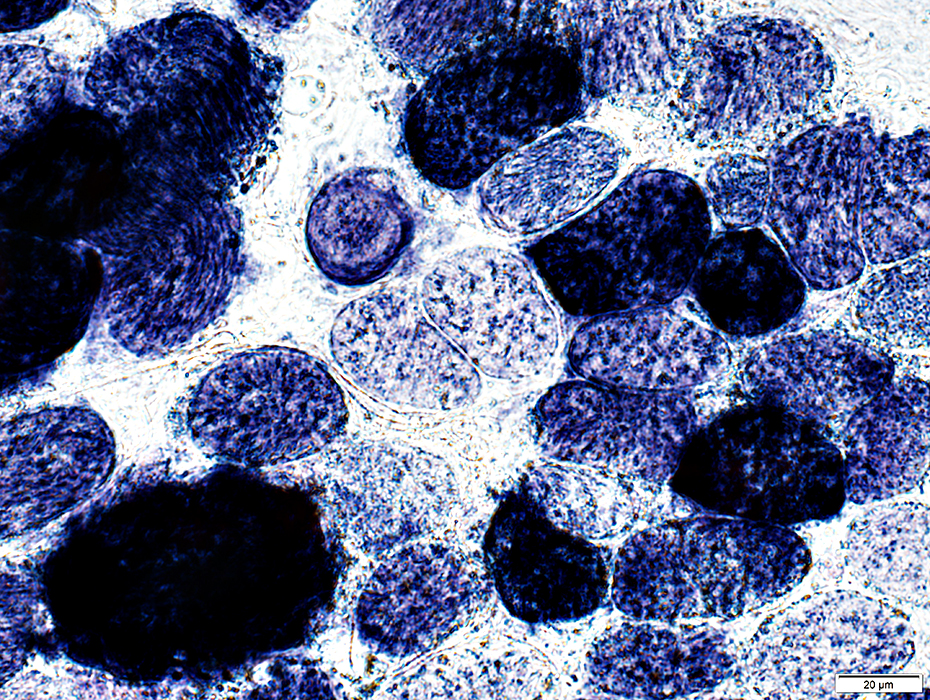 SDH stain |
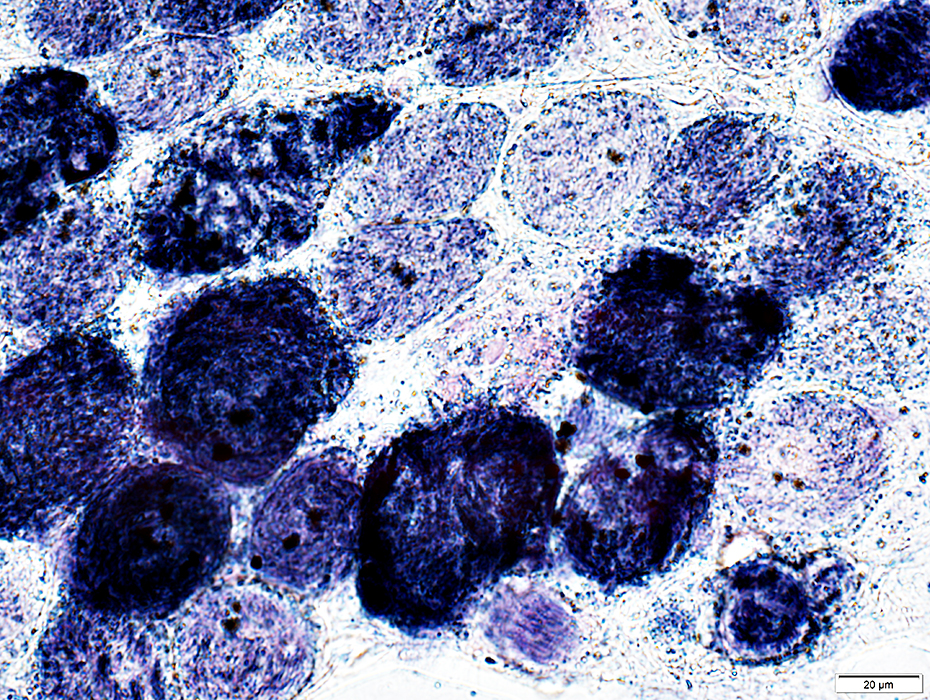 SDH stain |
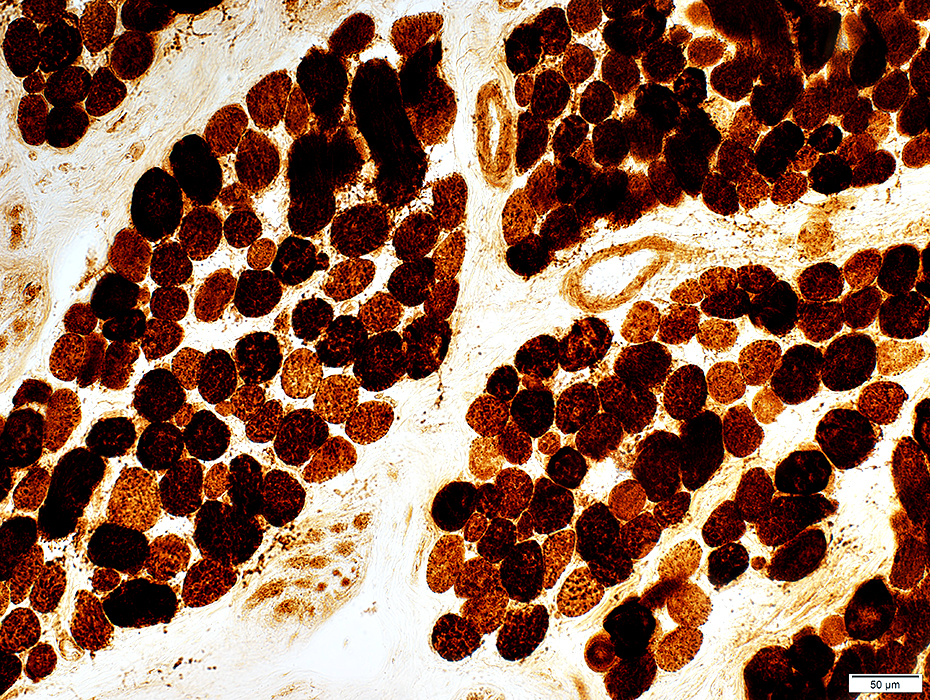 COX stain |
Some muscle fibers are very dark stained for COX
Mitochondria appear large
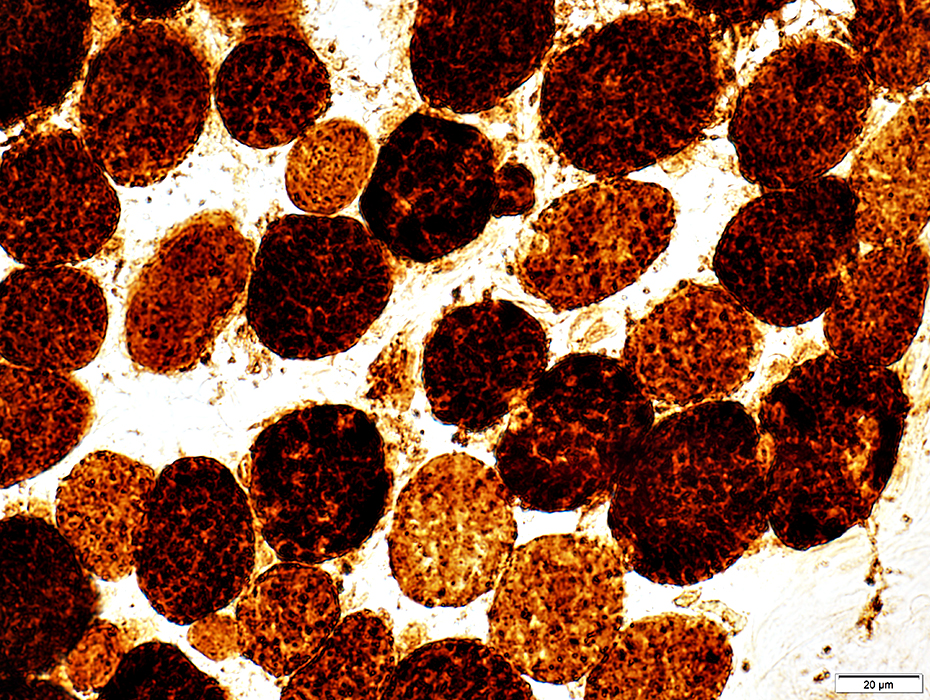 COX stain |
EOM: Fiber types
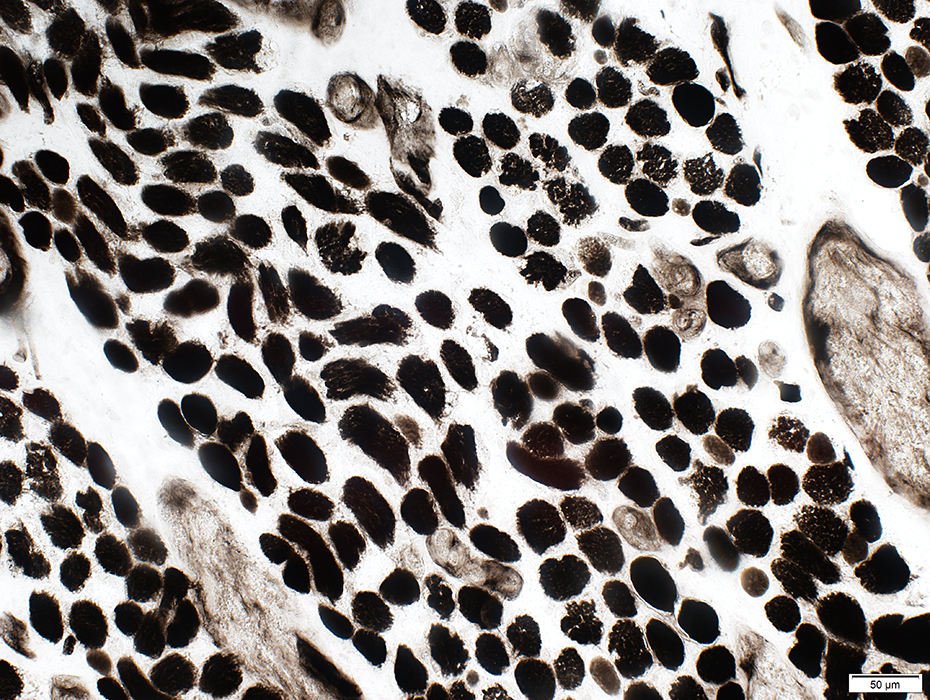 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
ATPase pH 9.4: Dark stained
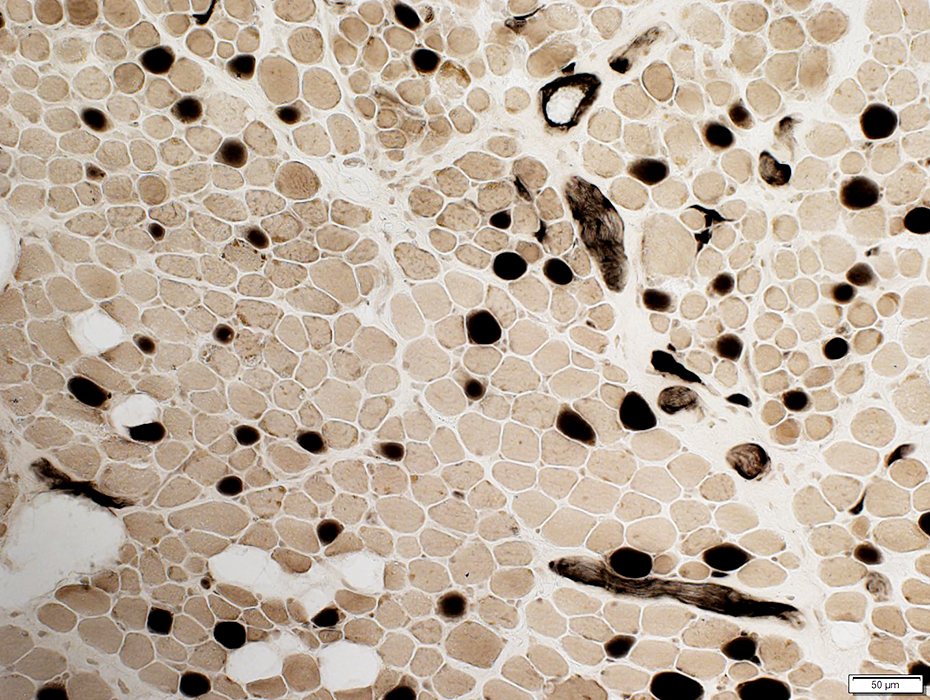 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Most similar to type 2C
ATPase pH 4.6 & 4.3: Intermediate stained
Few fibers similar to type I
ATPase pH 4.6 & 4.3: Dark stained
Often are: Muscle fibers with multiple innervation regions by individual axons
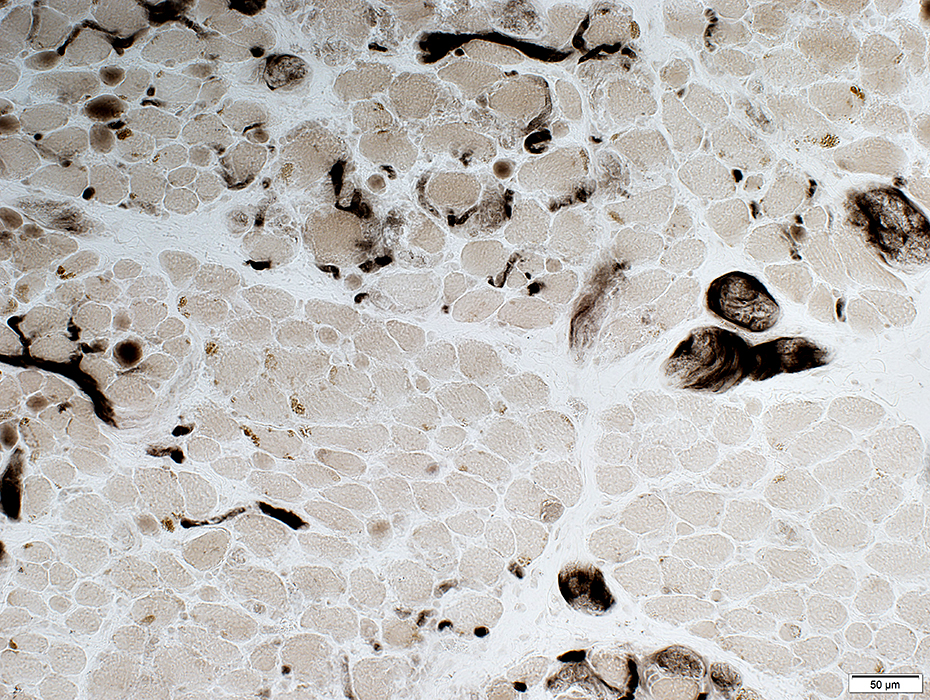 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
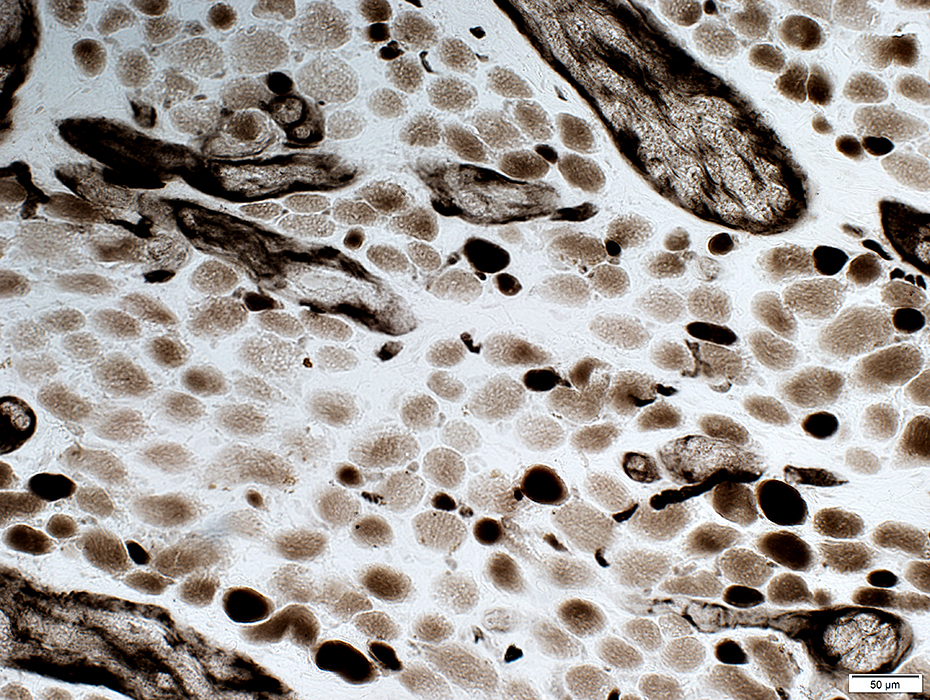 ATPase pH 4.6 stain |
EOM: Neuromuscular Junctions
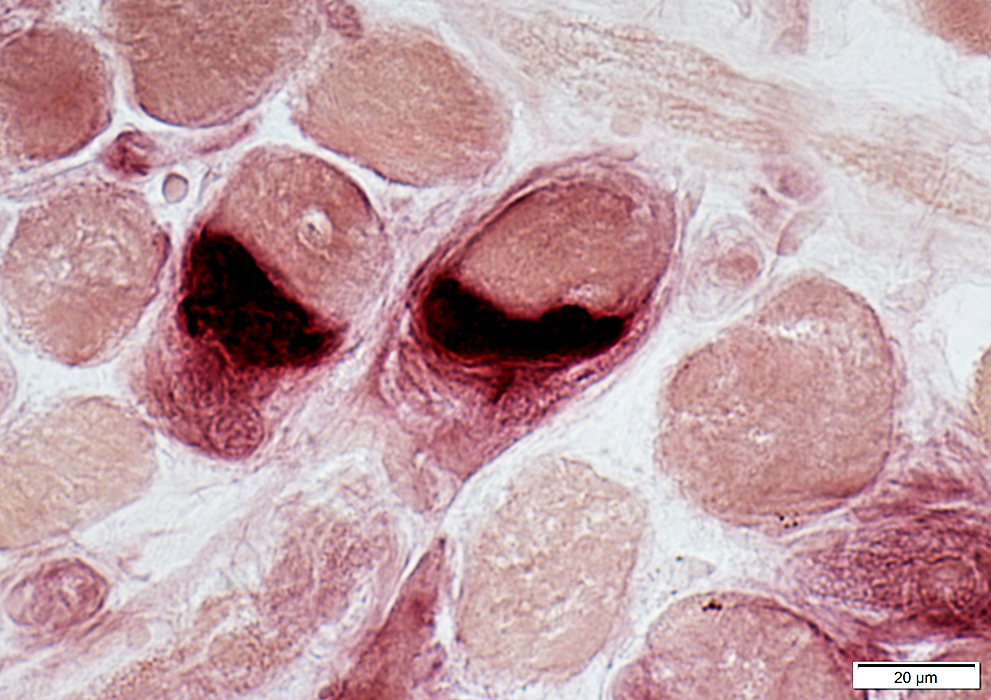 Esterase stain |
Dark stained by esterase
Large
May extend around surface of muscle fibers
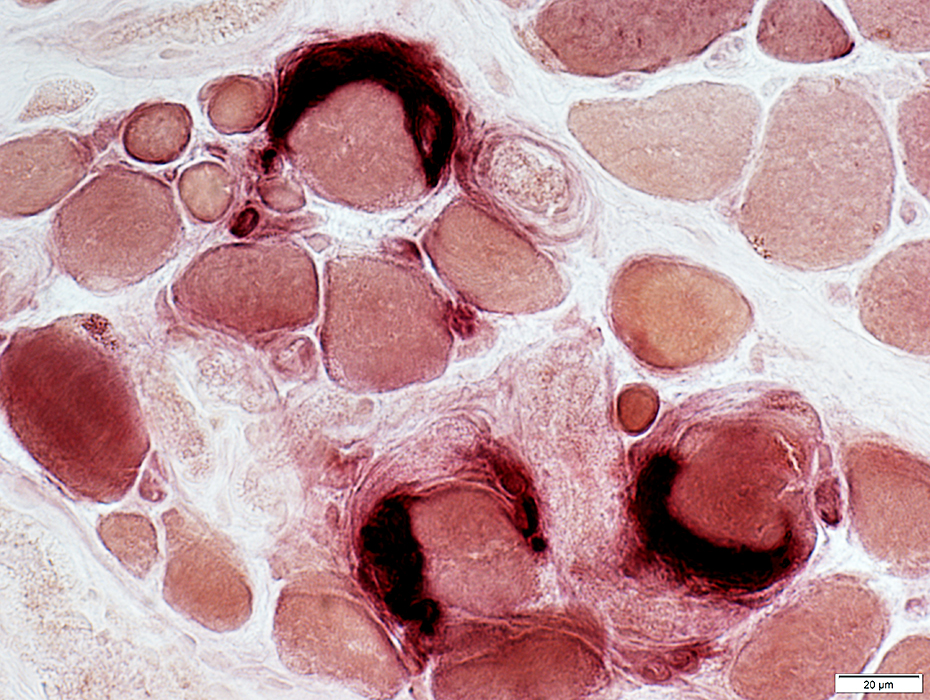 Esterase stain |
Varied sizes
Usually have 1 or 2 patches on single muscle fiber
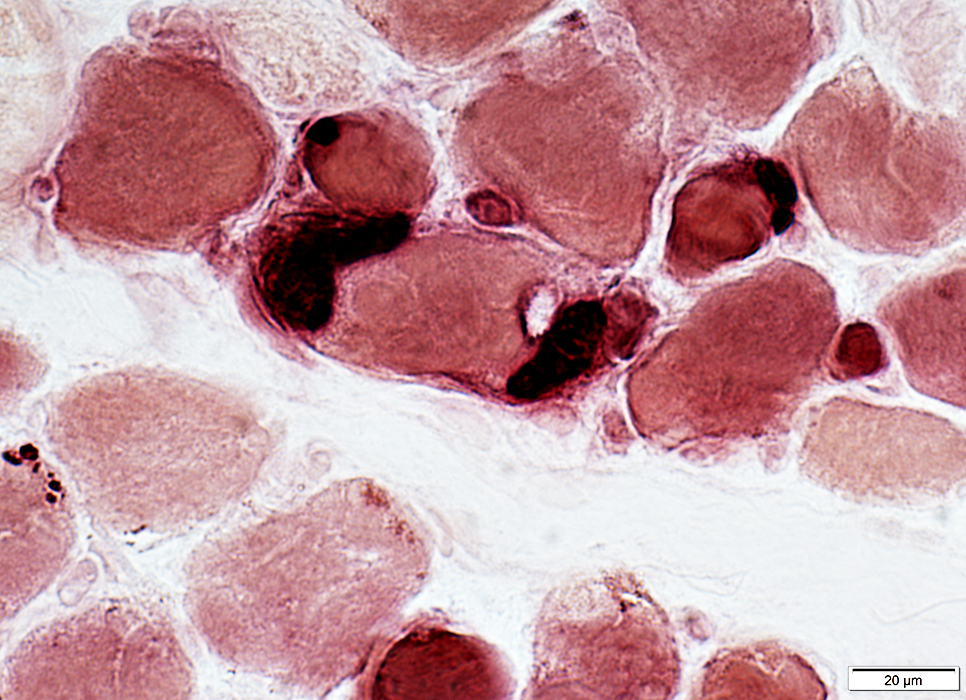 Esterase stain |
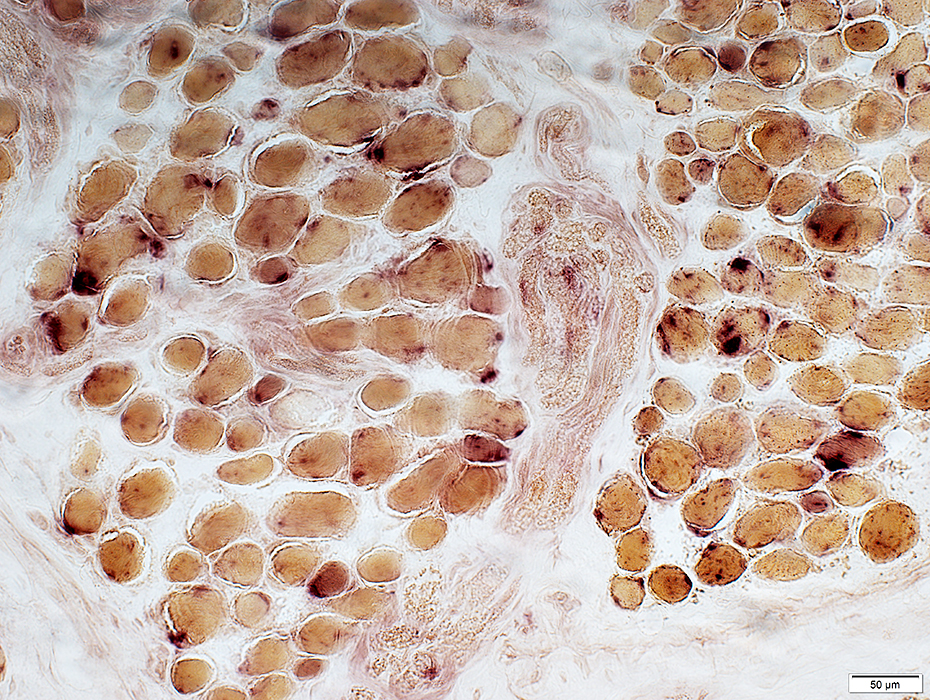 Acid phosphatase stain |
Acid phosphatase positive granules in muscle fibers
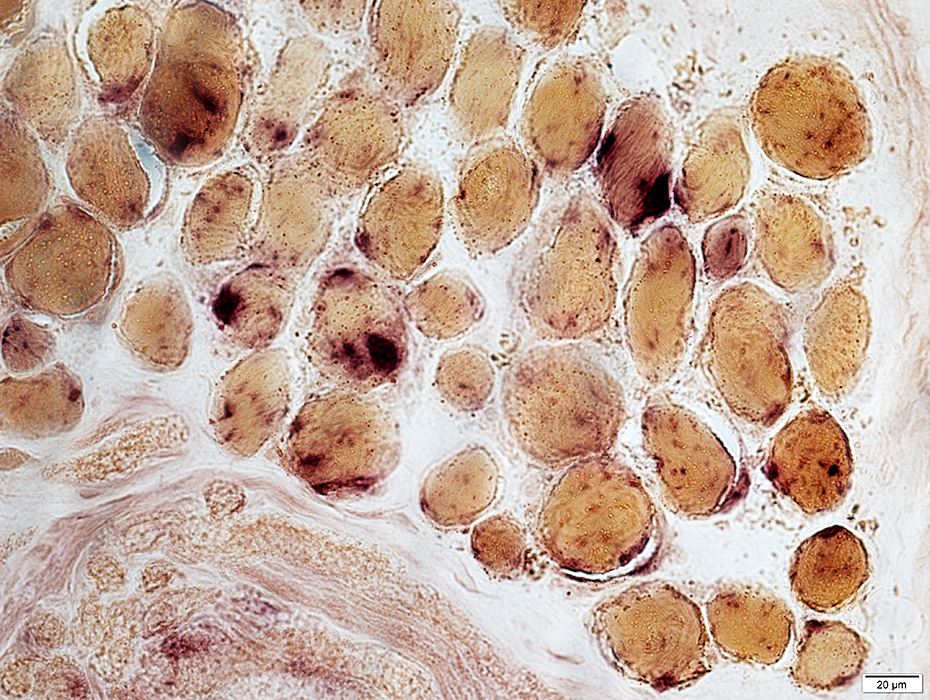 Acid phosphatase stain |
EOM: Endomysial capillaries
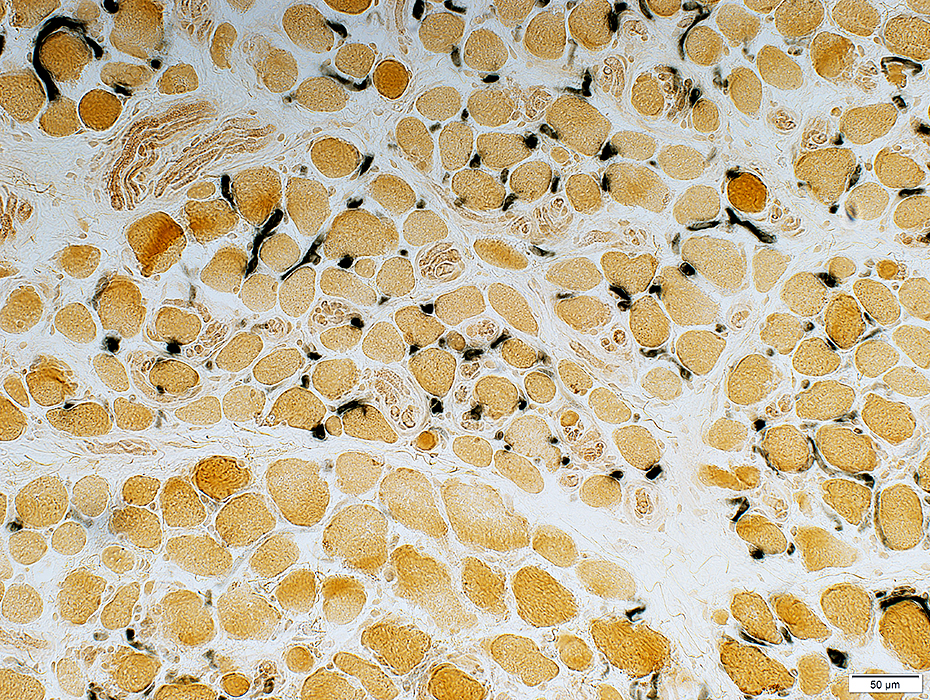 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
EOM: Lipid in muscle fibers
Muscle fibers have scattered, small, lipid droplets
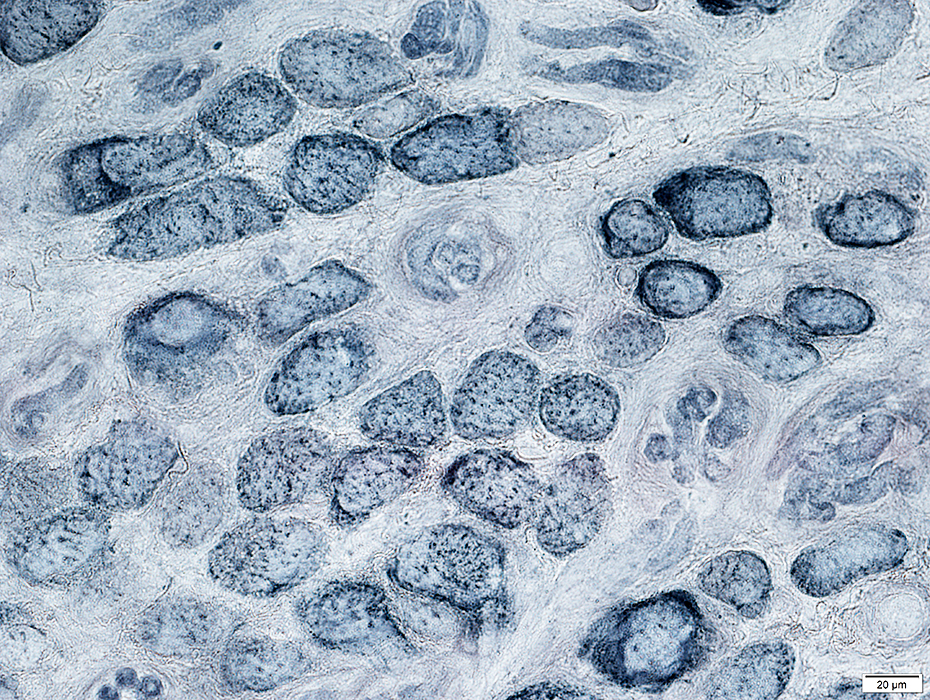 Sudan black stain |
Return to Pathology index
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
References
1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2000 Apr;41(5):980-90
11/27/2024