Limb Muscles: Control
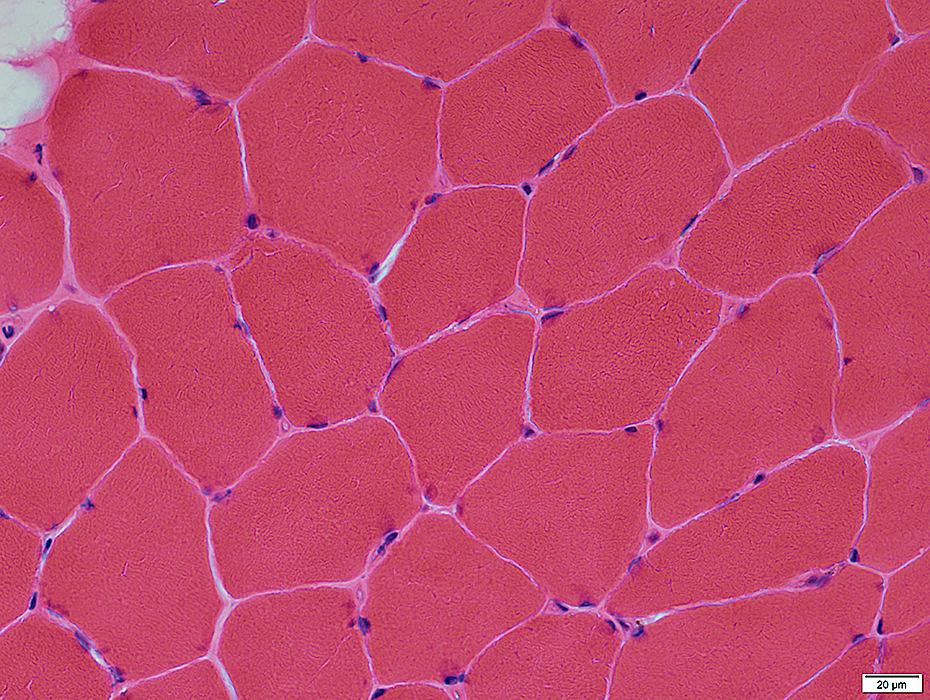 H&E stain |
Myonuclei: Dark-stained; Normally present at periphery of muscle fibers
Endomysial connective tissue: Normal
Capillaries, Endomysial: Small, Between muscle fibers
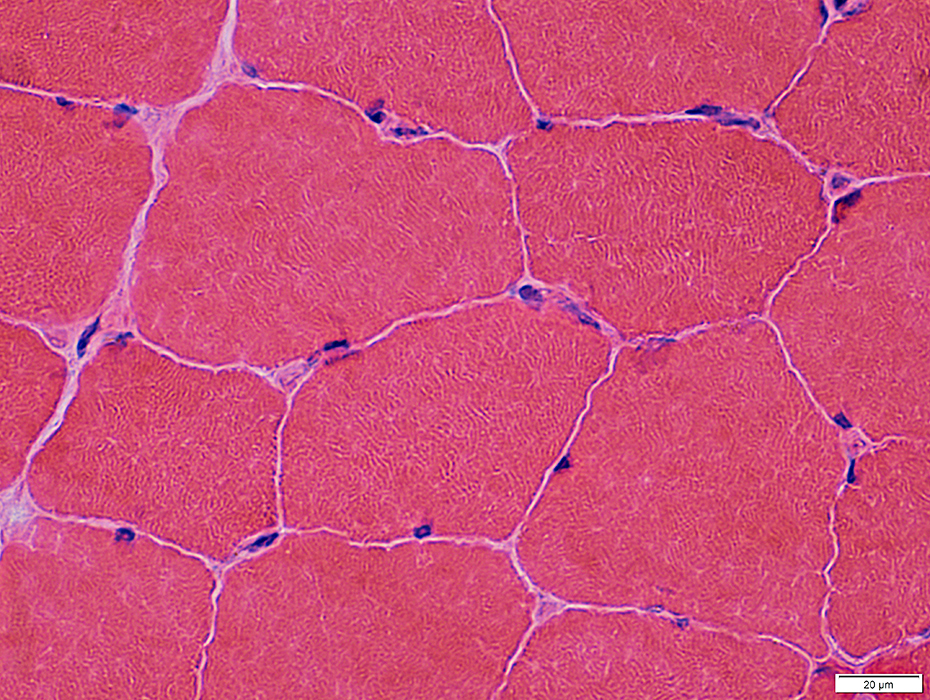 H&E stain |
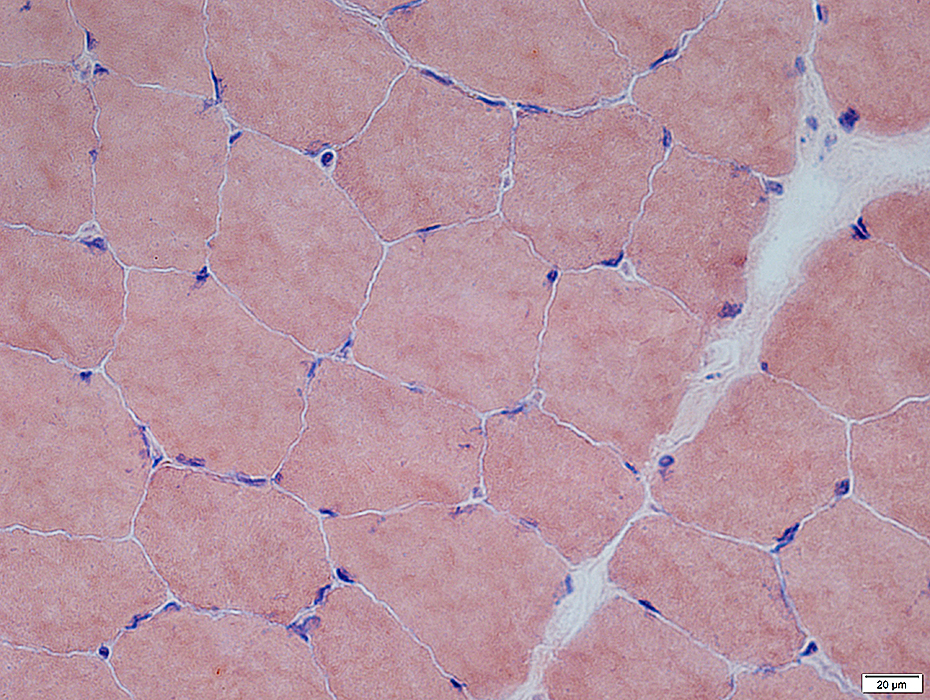 Congo red stain |
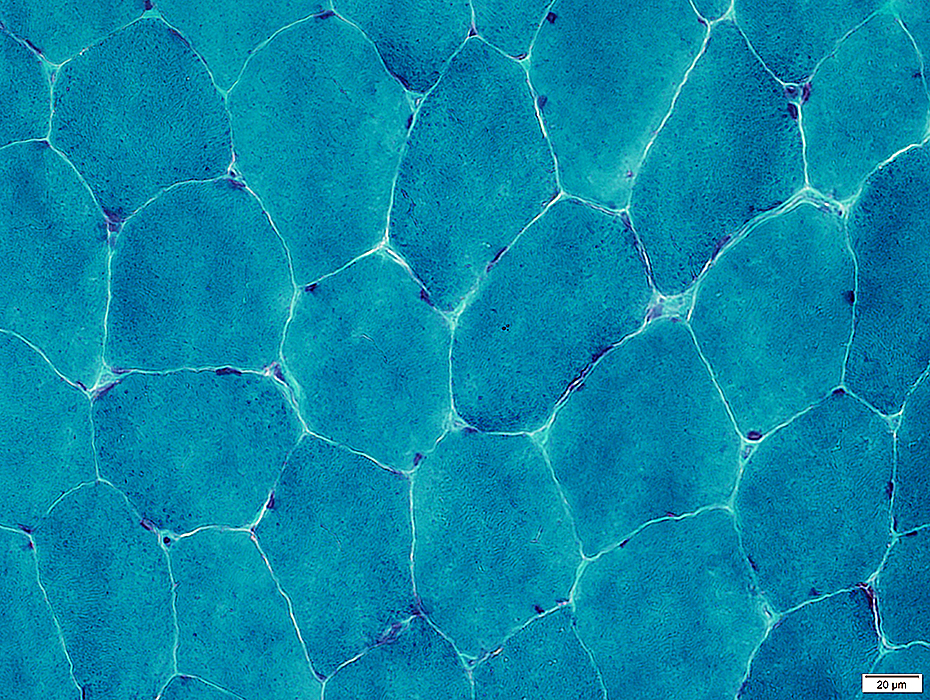 Gomori trichrome stain |
Connective tissue: Stains Green
Lipid membranes: Stain red
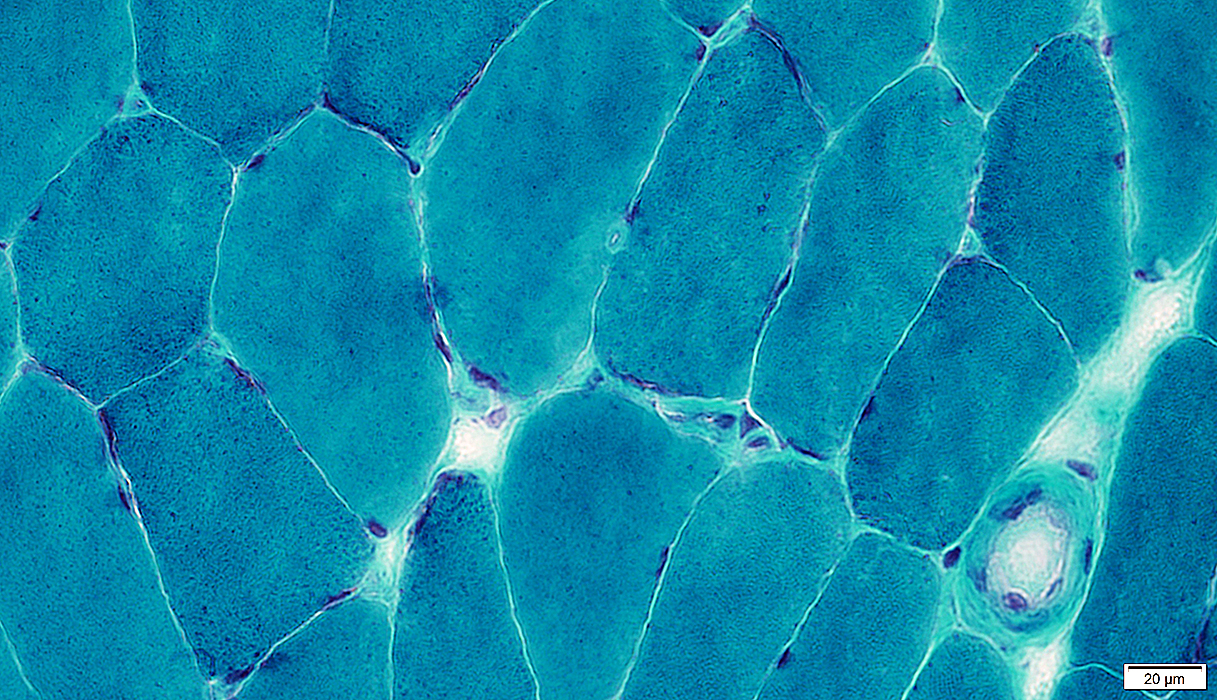 Gomori trichrome stain |
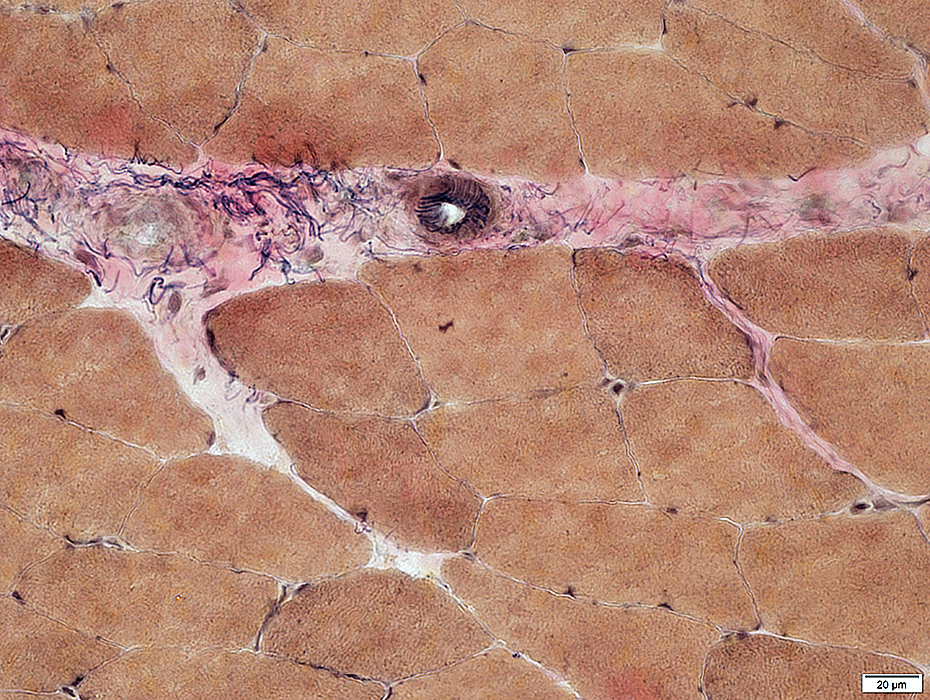 VvG stain |
Muscle fibers: Mildly varied size; Peripheral nuclei
Endomysial capillaries: Between muscle fibers; Often contain nucleated endothelial cells
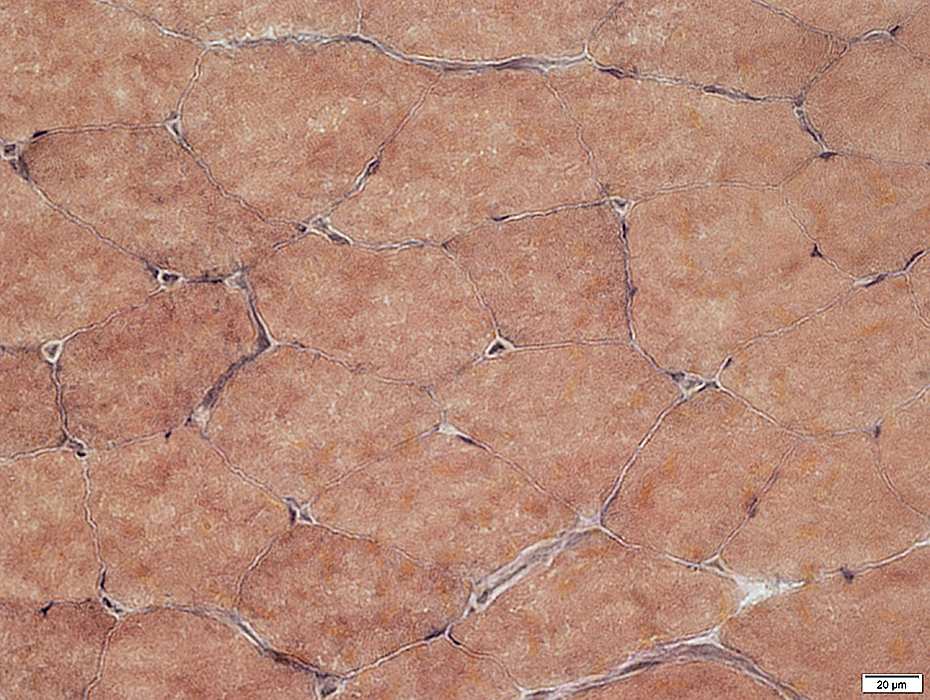 VvG stain |
Internal architecture
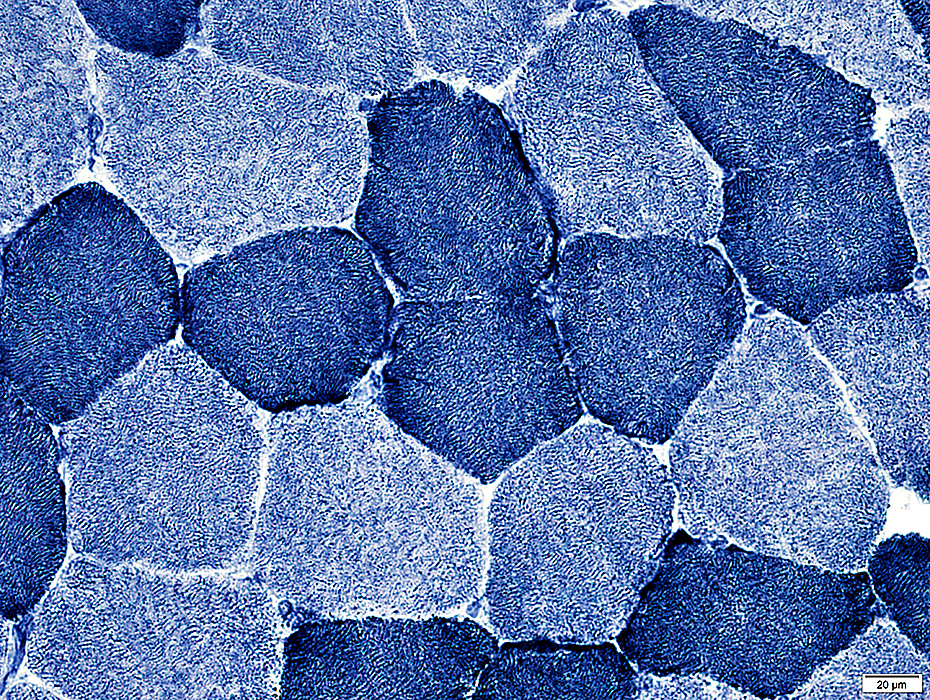 NADH stain |
Stained structures: Sarcoplasmic reticulum; Mitochondria
Type 1 muscle fibers: Darker stained
Subsarcolemmal staining
Increased in regions of some muscle fibers Reflects neighboring endomysial capillaries
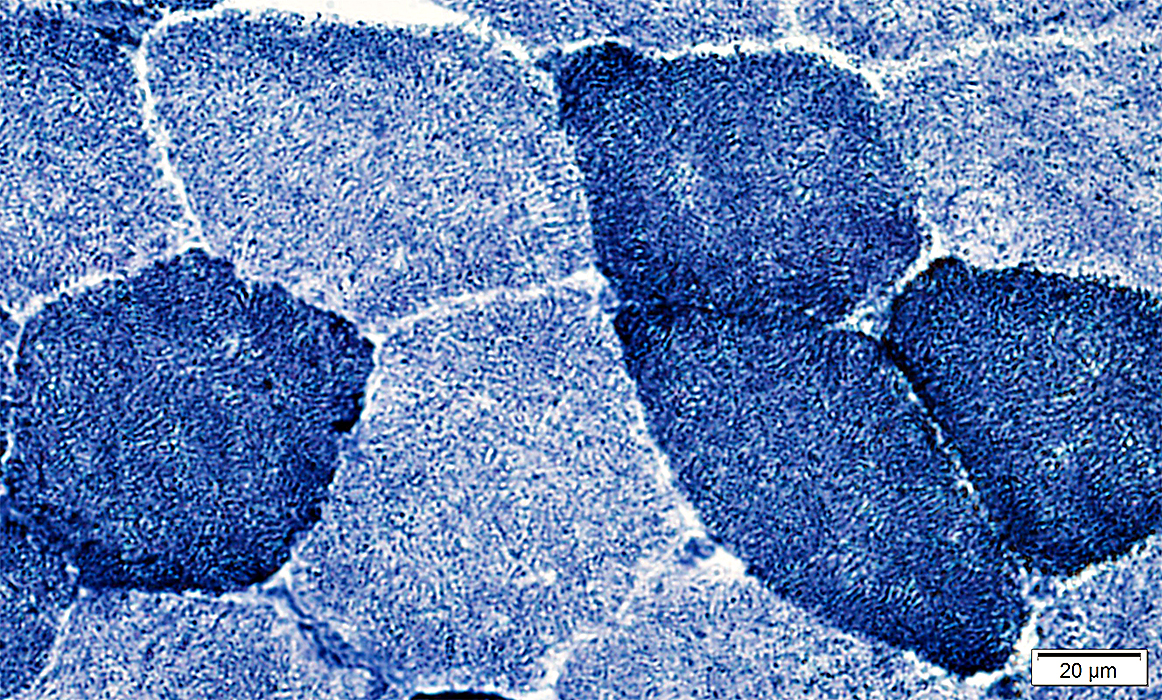 NADH stain |
Fiber Types
|
ATPase pH 9.4 pH 4.6 pH 4.3 Ultrastructure Myosin HC types Type grouping |
ATPase pH 9.4
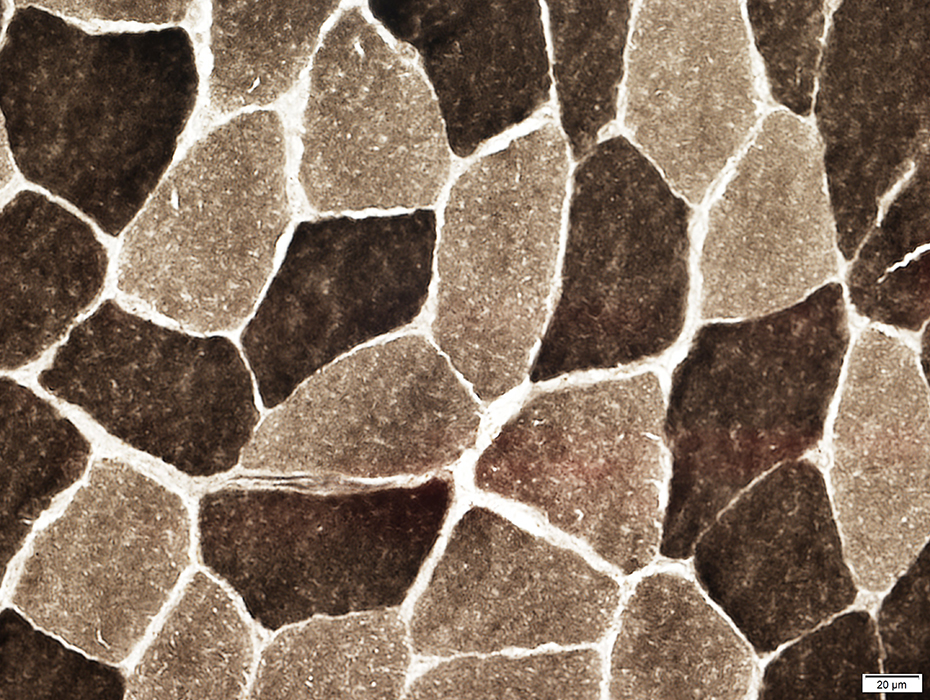 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
Type 2 fibers: Dark color
ATPase pH 4.6
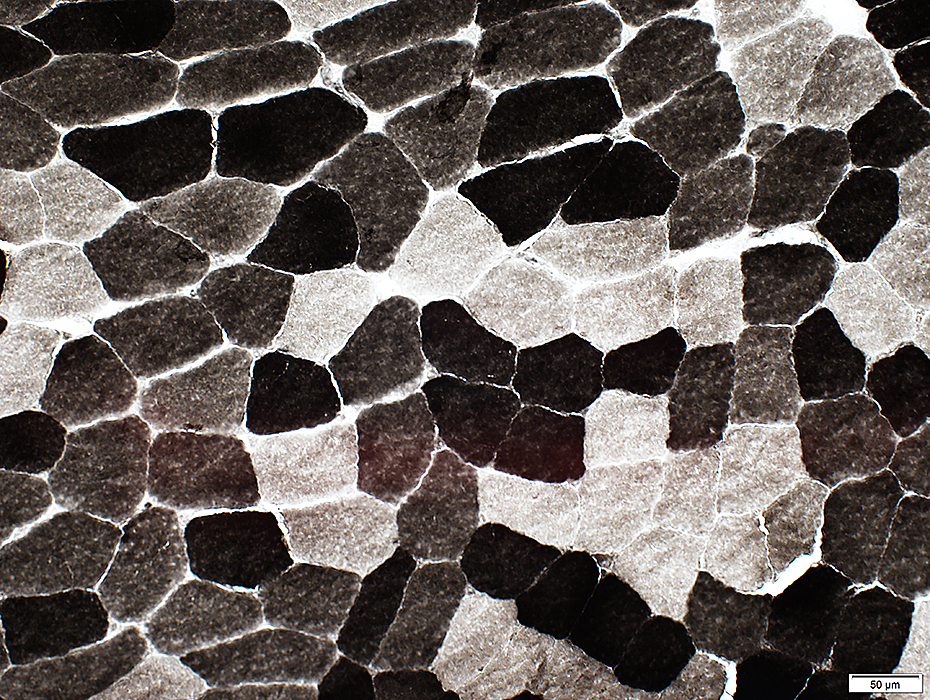 ATPase pH 4.6 stain |
Type 2A fibers: Pale
Type 2B fibers: Intermediate color
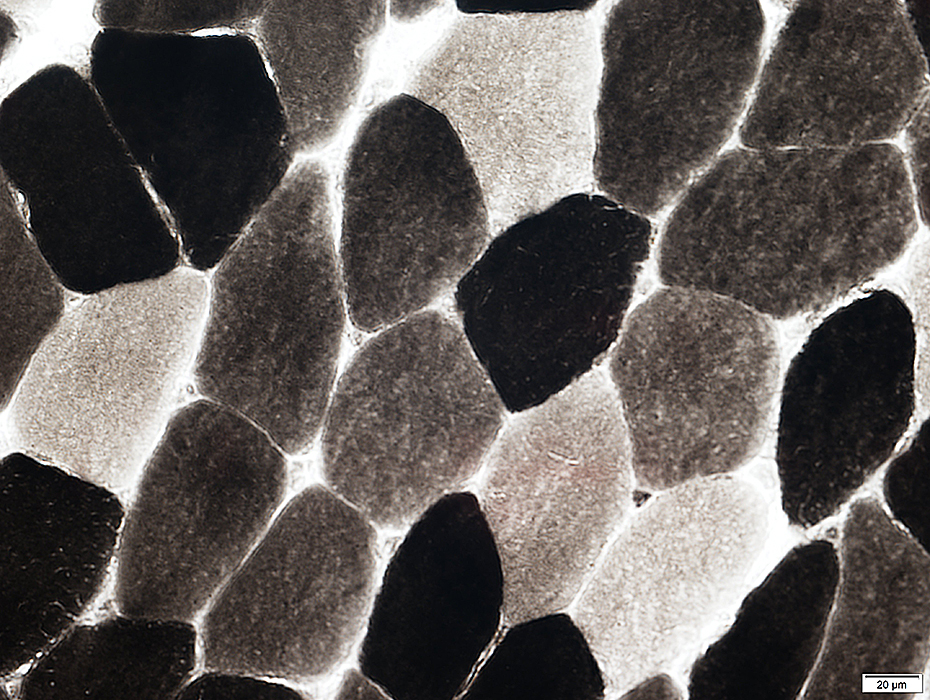 ATPase pH 4.6 stain |
ATPase pH 4.3
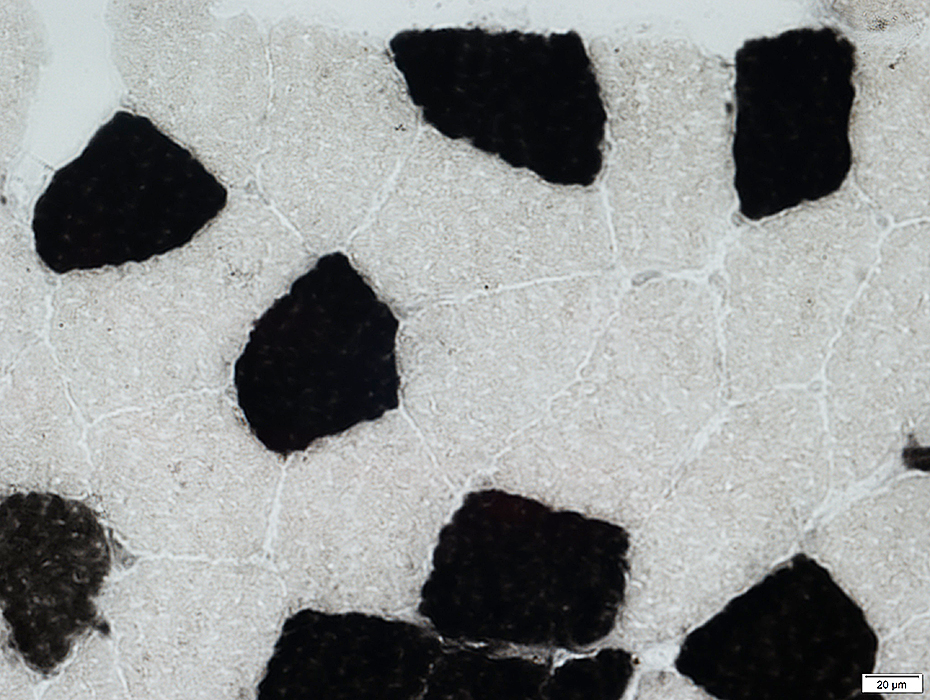 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Type 2A fibers: Pale
Type 2C fibers (Immature; Abnormal) (Below): Intermediate color
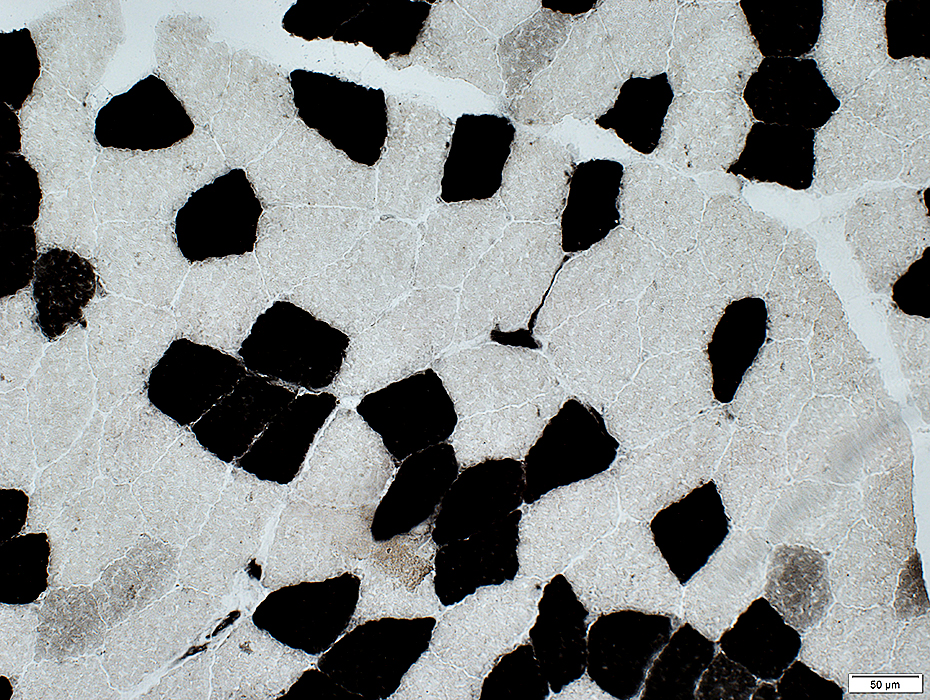 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
ATPase may also stain endomysial capillaries
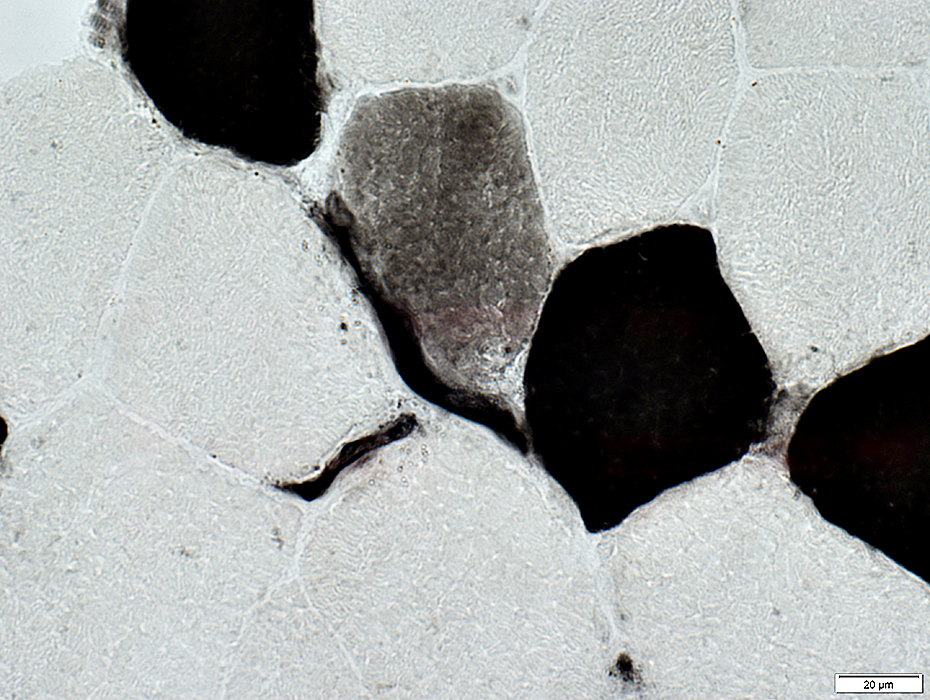 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Muscle Fiber Types: Ultrastructure
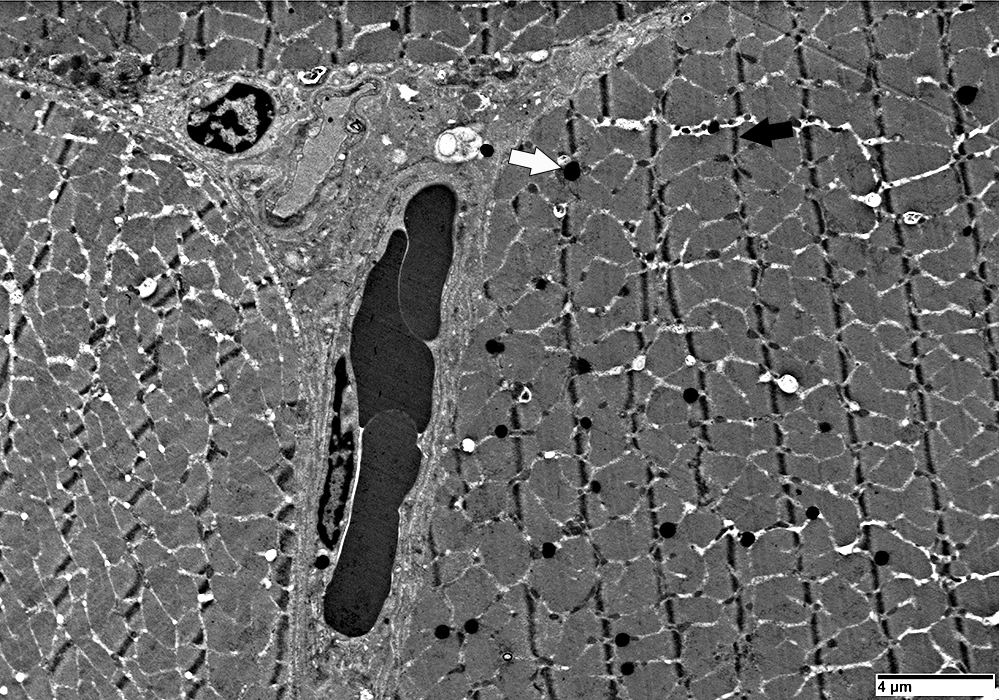 |
Z-lines (Dark arrow): Thicker
Mitochondria (Light arrow): More
Lipid bodies: More
Glycogen granules: Fewer
NOTES: Image below also shows
2 atrophic muscle fibers in the center
 |
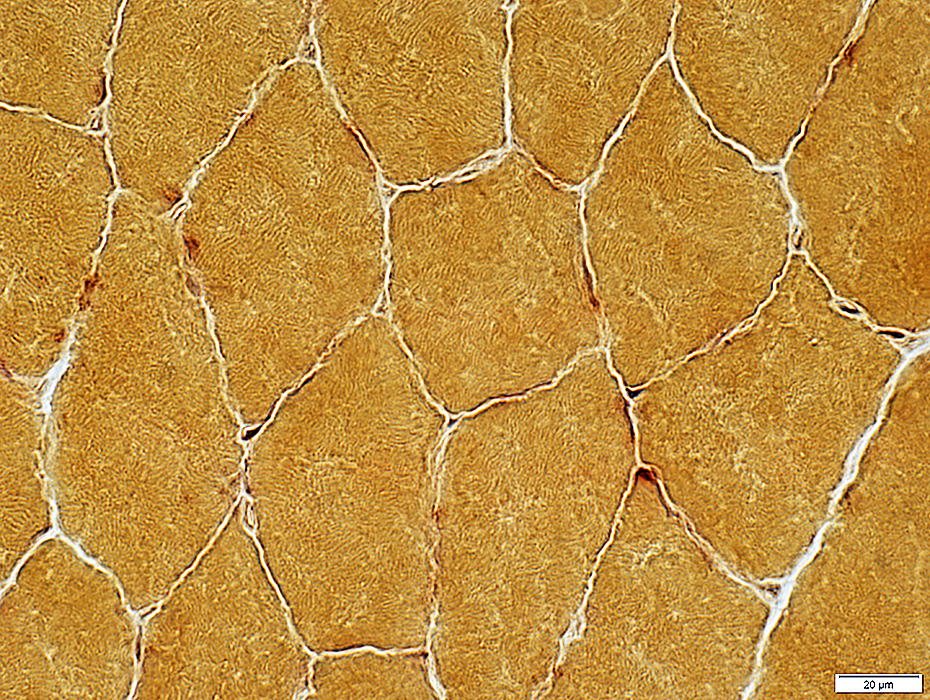
Alkaline phosphatase stain
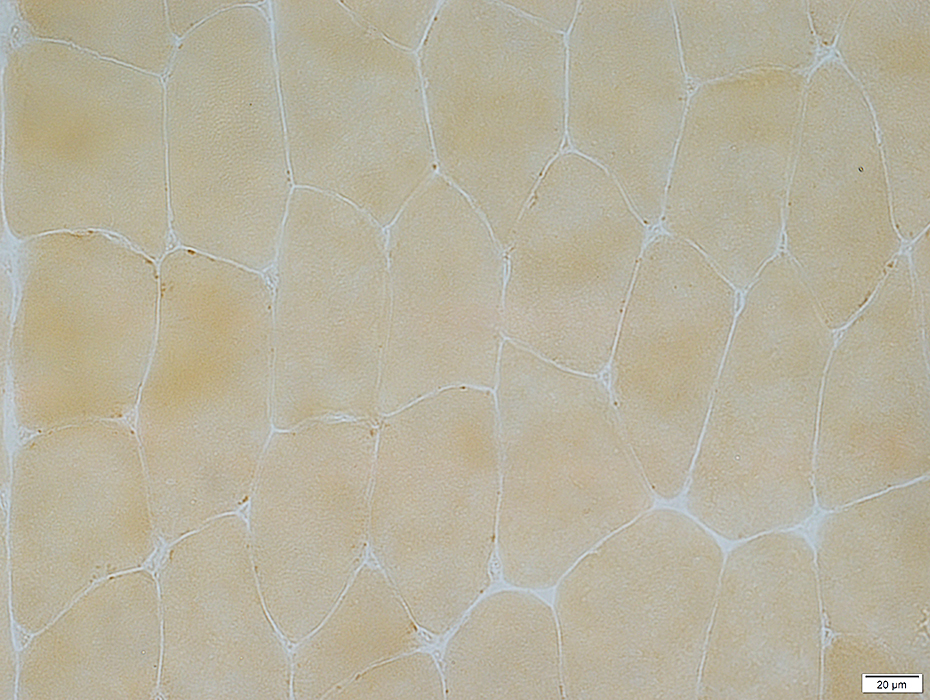 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Some penetrating vessels, more in a few areas than others, stain for alkaline phosphatase
Small endomysial capillaries do not normally show staining
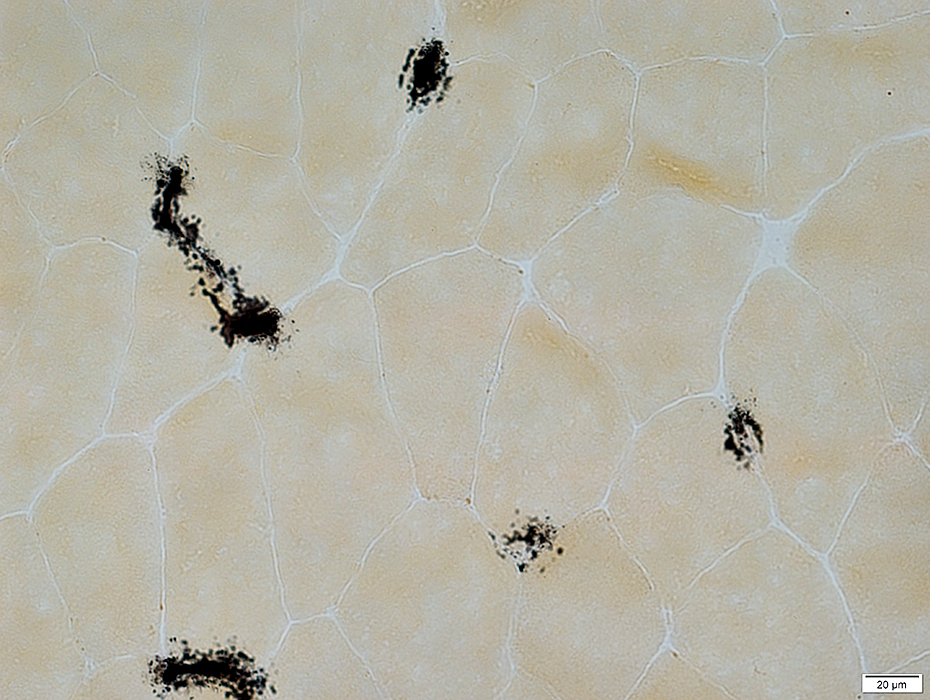 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
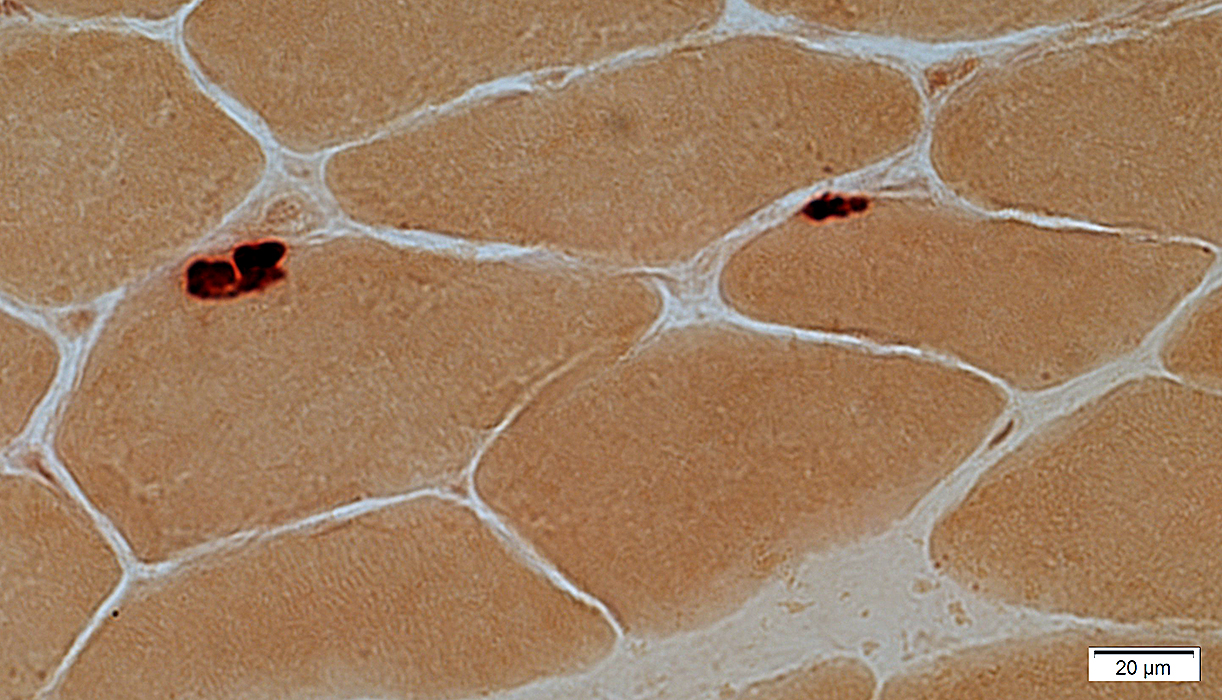
Acid phosphatase stain
Red, subsarcolemmal staining of regions with lipofuscin: More with increasing age
 Acid phosphatase stain |
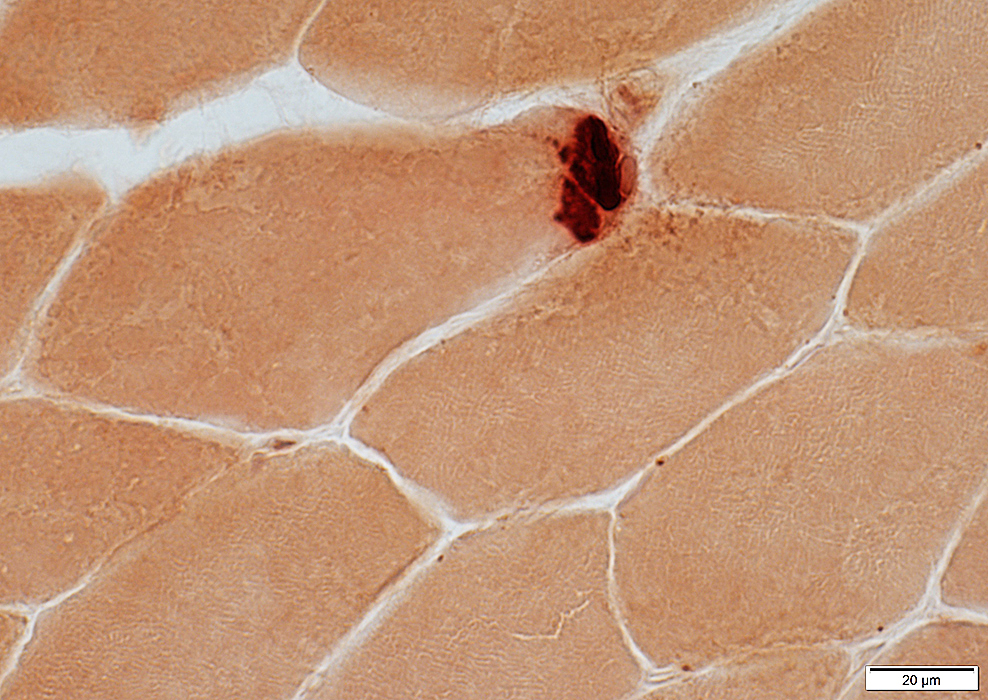
Esterase stain
 Esterase stain |
 Esterase stain |
Mitochondrial Stains
Cytochrome Oxidase (COX)
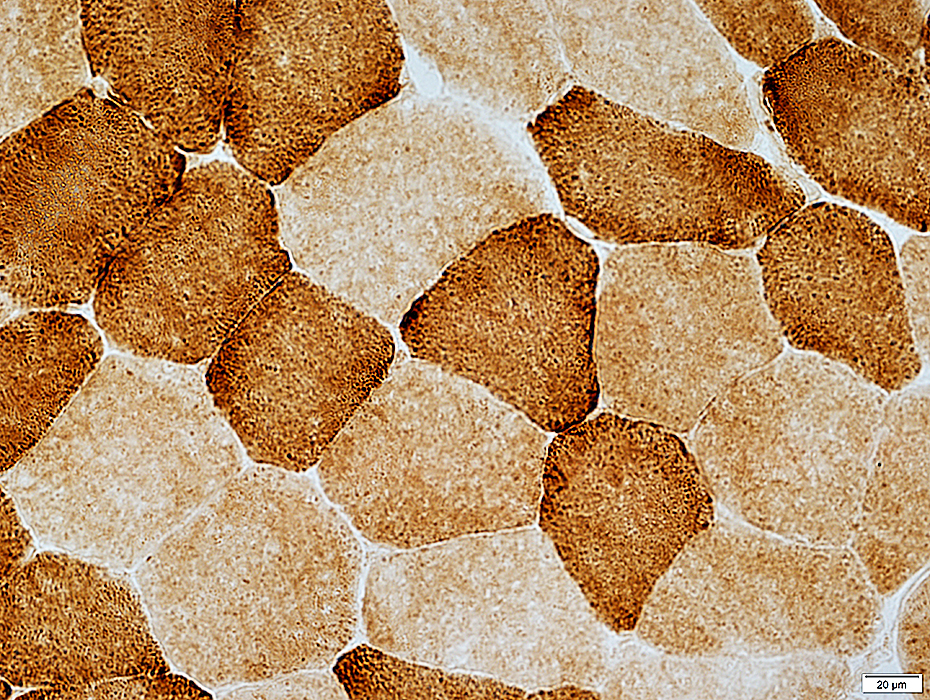 COX stain |
Fiber types
Type 1: Dark
Type 2: Intermediate or Pale
Staining pattern: Punctate
Mitochondrial disease
Dark staining: Due to mitochondrial proliferation, or
Pale staining: Due to reduced COX synthesis
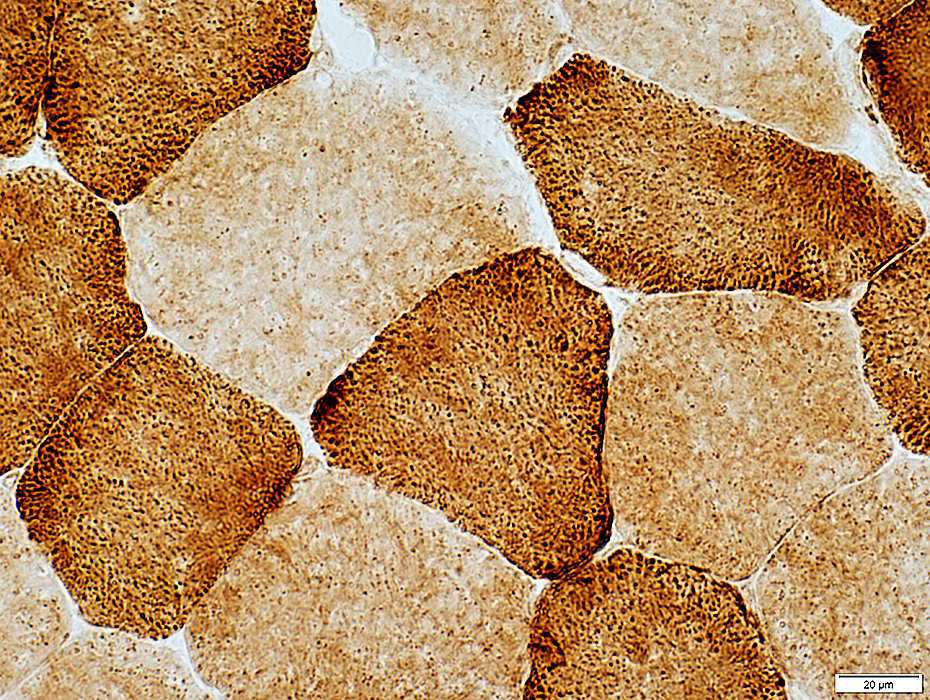 COX stain |
Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH)
 SDH stain |
Type 1: Dark
Type 2: Intermediate or Pale
Staining pattern: Reticular & Punctate
Mitochondrial disease: Dark staining due to mitochondrial proliferation
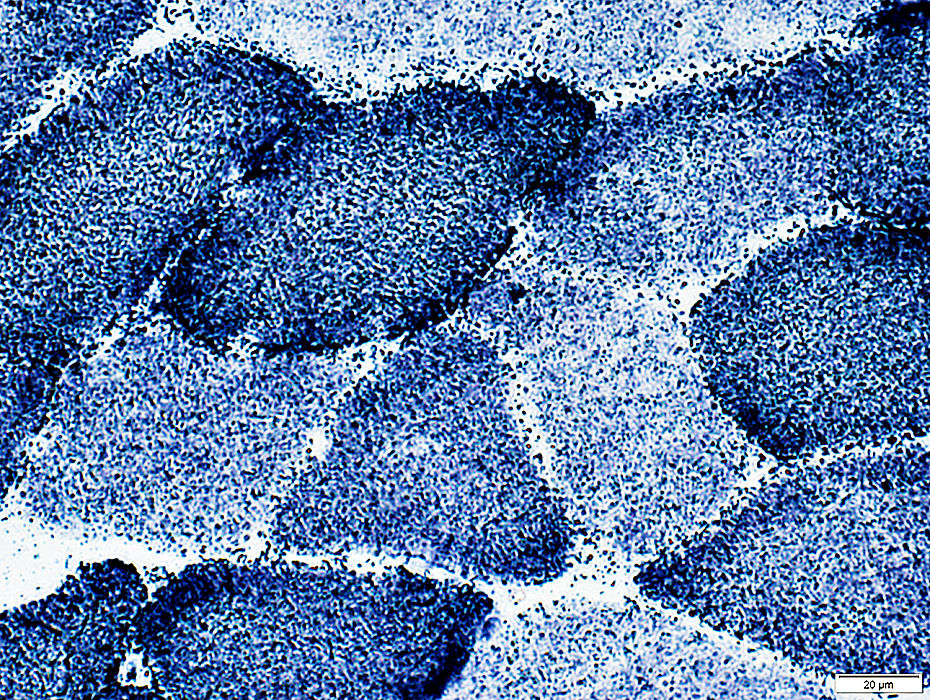 SDH stain |
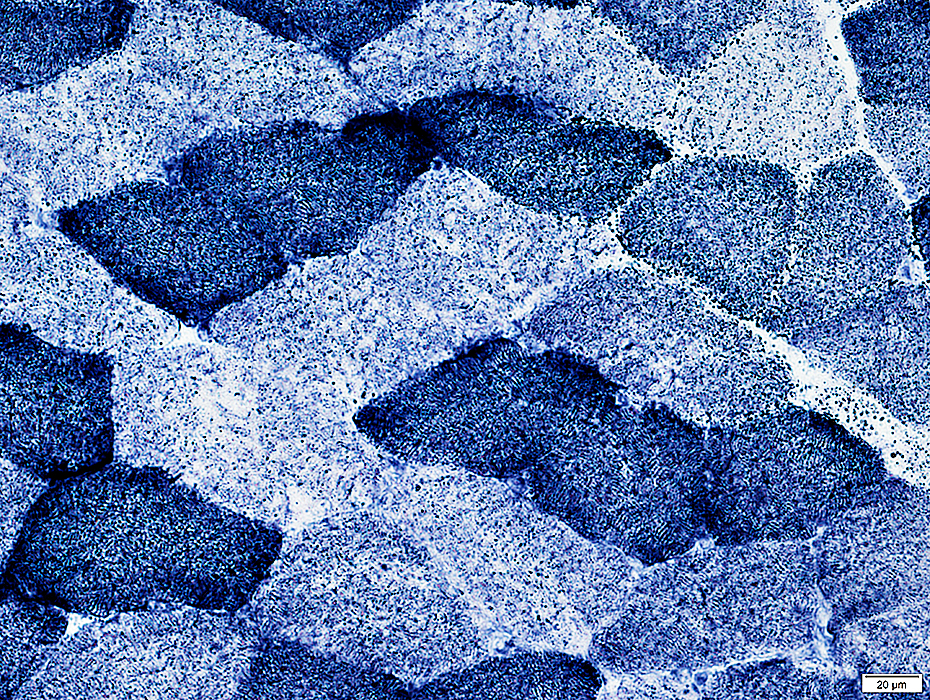
Mitochondrial Disorders
COX + SDH
COX negative muscle fibers stain blue
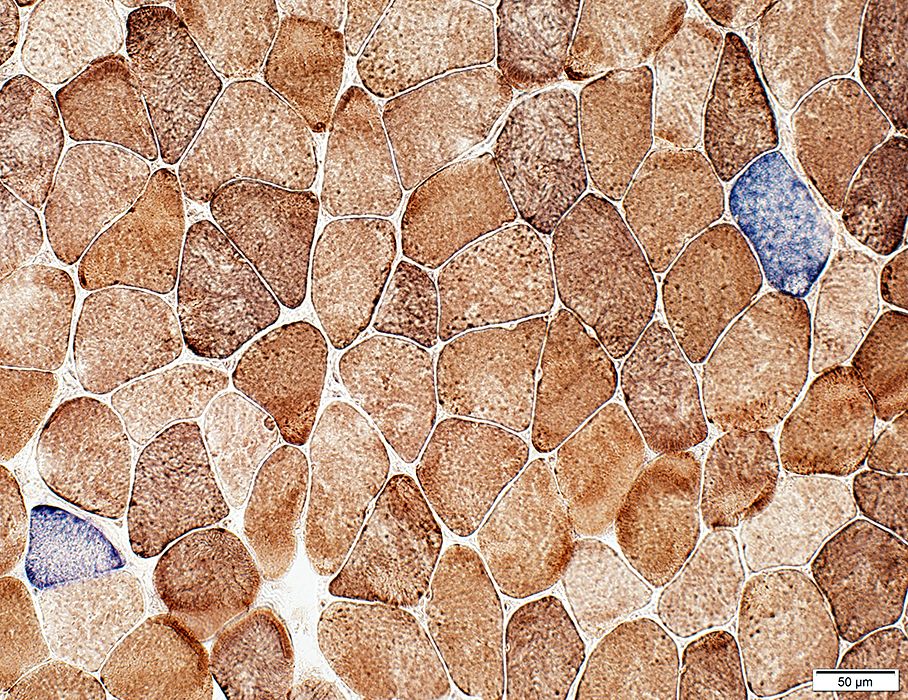 COX + SDH stain |
Lipid stain: Sudan Black
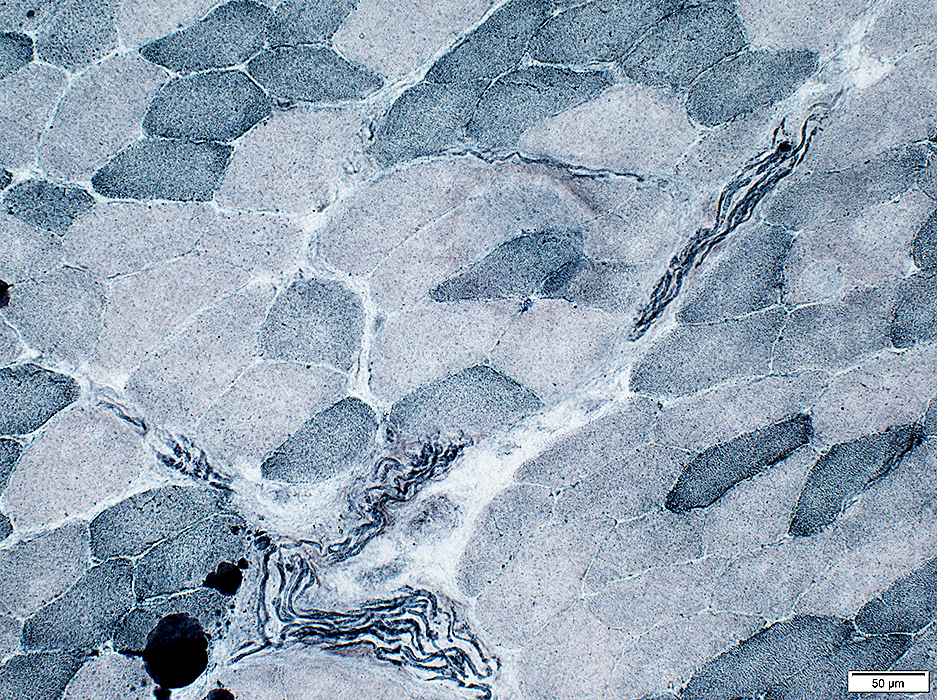 Sudan Black stain |
Myelin: In intramuscular nerves stains dark
 Sudan Black stain |
Glycogen stain: PAS
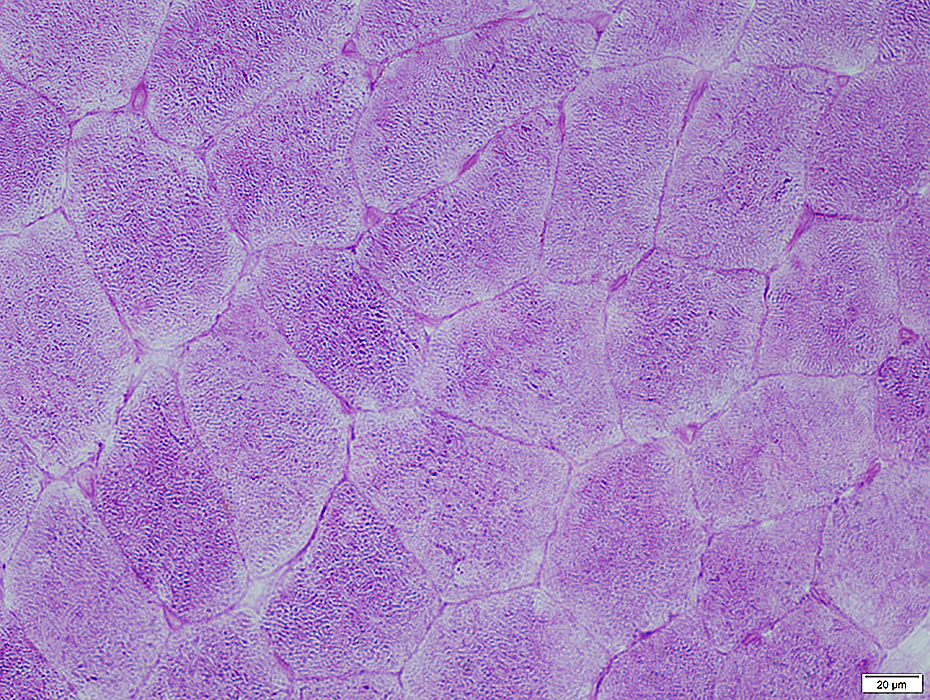 PAS stain |
Capillary basal lamina: Stains dark
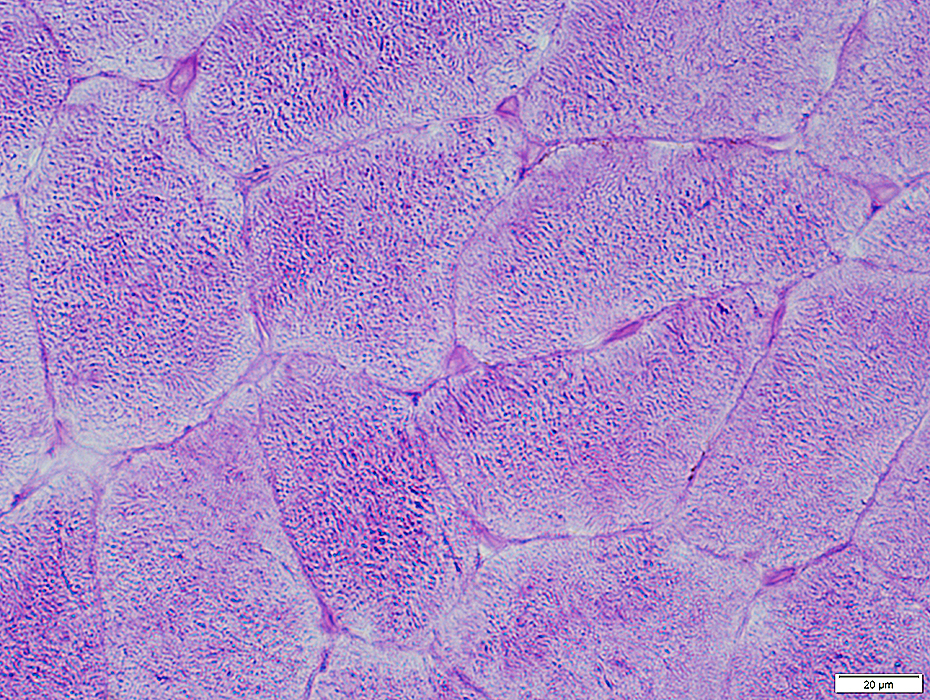 PAS stain |
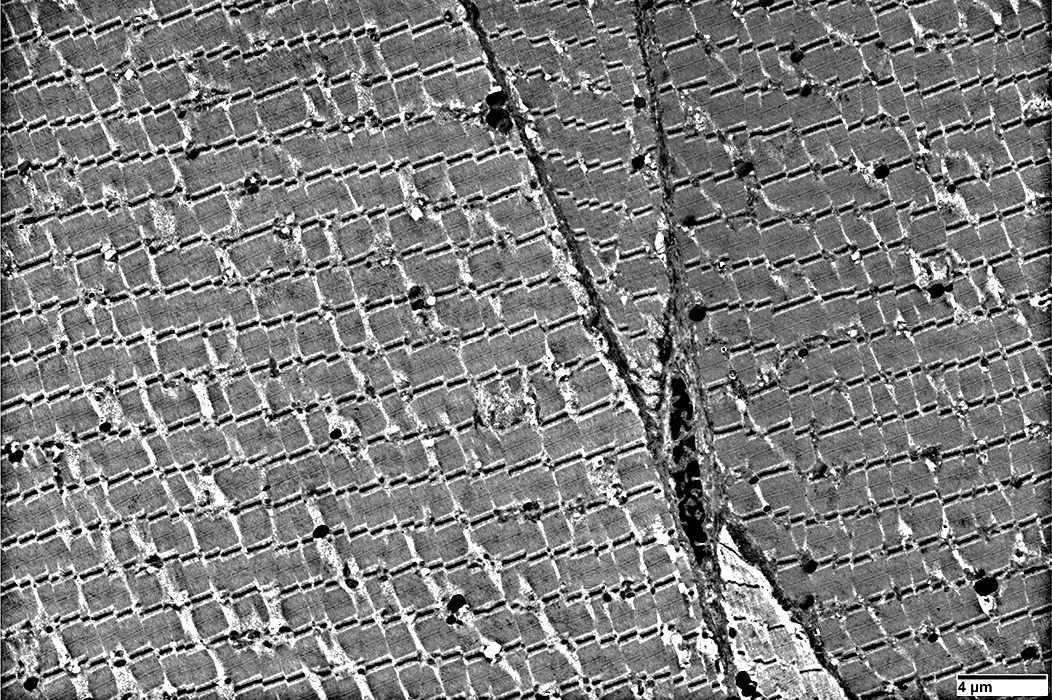
Normal Muscle: Transverse section
A band: Thick filaments surrounded by thin filamentsScattered mitochondria between fibrils
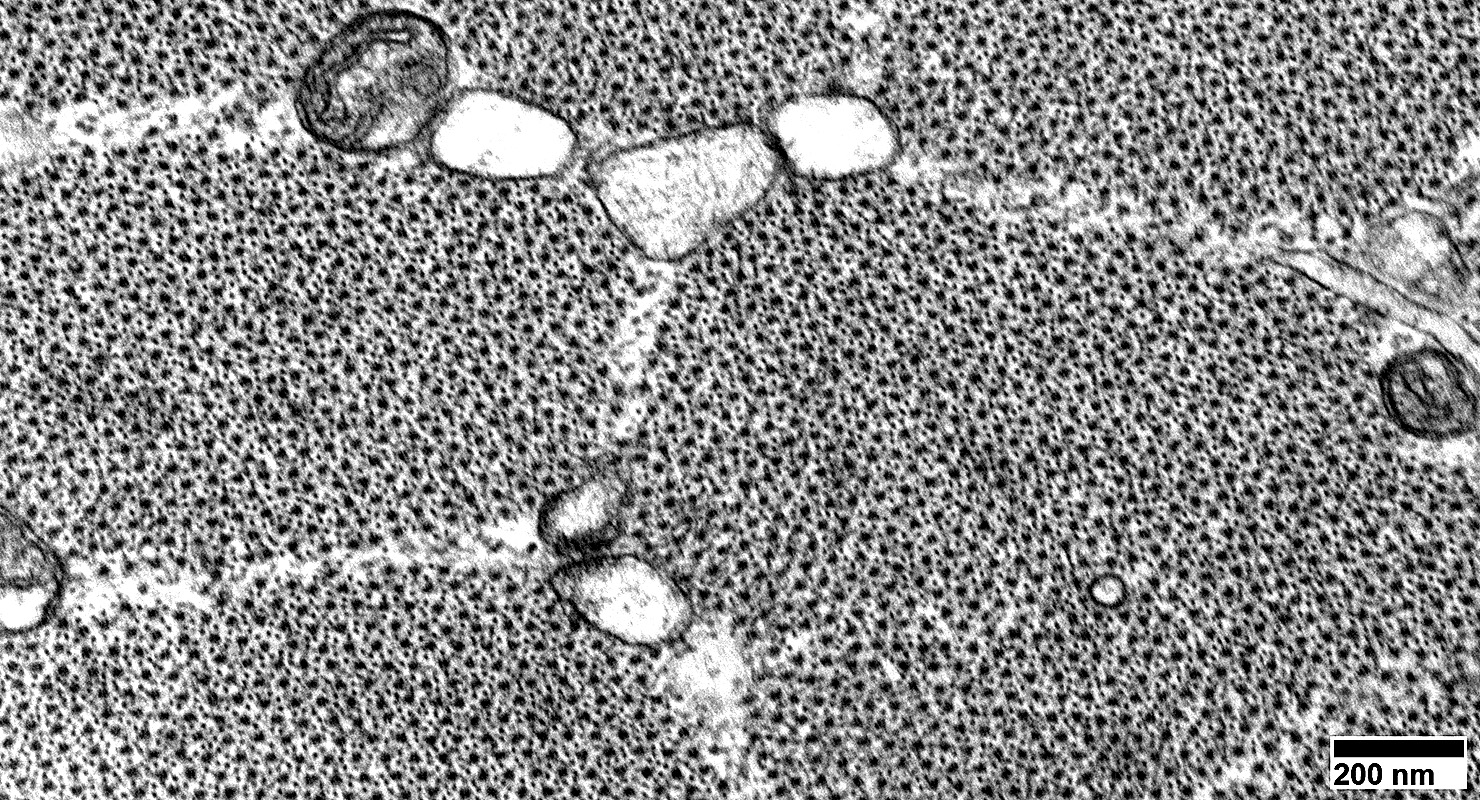
|
Return to Pathology index
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
2/5/2021