VASCULITIS
|
Pathology features Axons Differential fascicular loss Wallerian Degeneration Connective tissue Early lesion Fibrinoid necrosis Hemosiderin Inflammation Other Vessels Artery wall damage Larger vessels: 1; 2 Intimal proliferation Normal Occluded Neovascularization Epineural Vessel Recanalization Types Behçet Cryoglobulin Eosinophilic Histiocytic Granulomatous pANCA Rheumatoid Nerve Specific (Non-Systemic) Syphilis Also see HIEM (Non-inflammatory) Differential diagnosis |
Vein & Artery: Occluded Nerve showed: Differential fascicular loss of axons 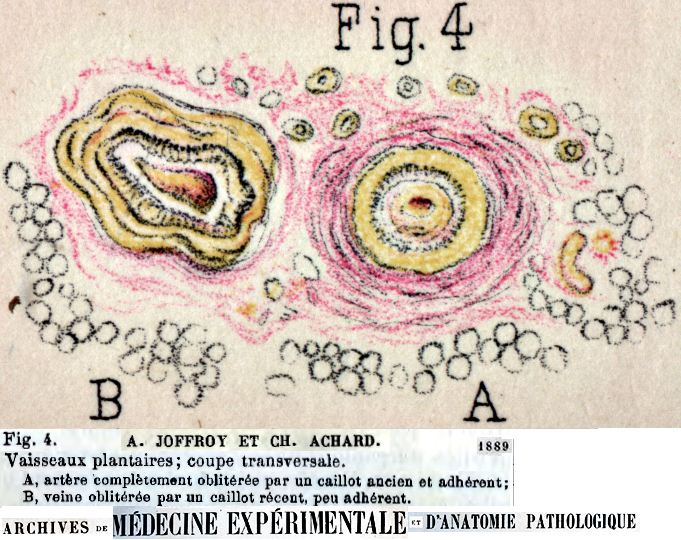 |
VASCULITIC LESION: EARLY
- Inflammation around vessel wall
- Macrophage inflammation (acid phosphatase positive) in vessel endothelium
- Relatively intact structure of vessel wall
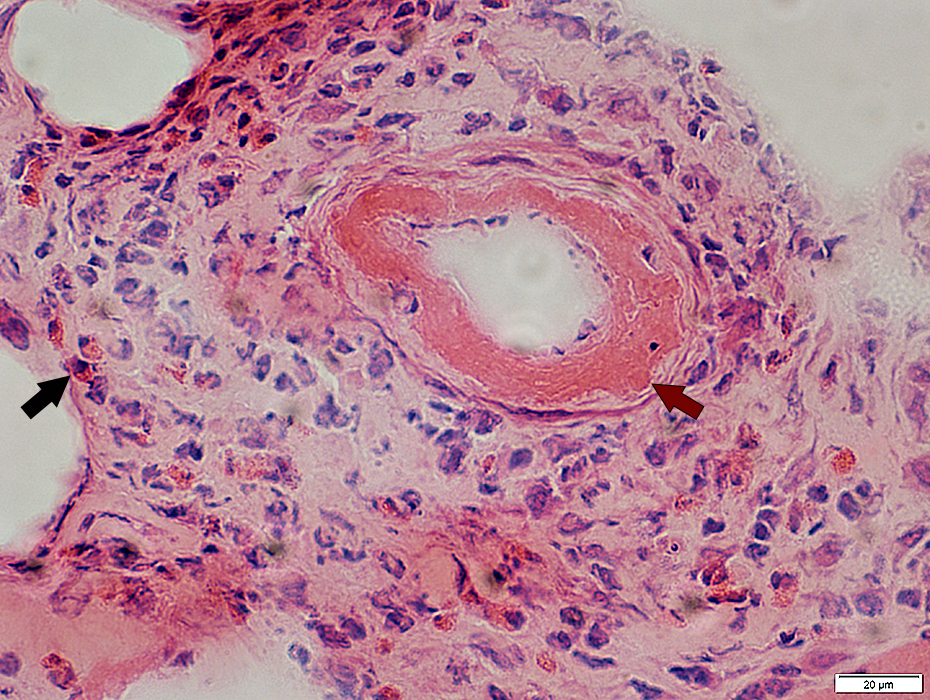
- ANCA+ vasculitis: Neutrophil-associated lesions
1
- Attachment of neutrophils to epineurial vascular endothelial cells
- Migration of neutrophils to extravascular space via the penetration of endothelial layer
- Release of neutrophil components into extracellular space
- Not present in NSVN
 H&E stain |
 Acid phosphatase stain |
 Acid phosphatase stain |
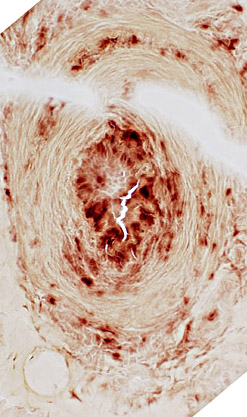
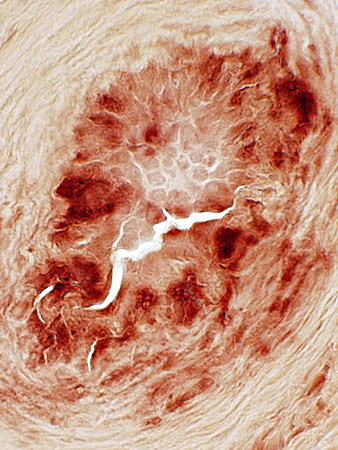
FIBRINOID NECROSIS
Definition: Accumulation of Fibrin layer in Vessel (Below; Brown arrow)Properties: Non-cellular
Location: On luminal side of vessel wall; Inside fibril layer
 H&E stain |
- Eosinophilic, homogenous, & refractile staining in inner regions of vessel wall
- Endothelial components
- Can be seen inside the layer of fibrinoid necrosis
- Endothelial cell nuclei may be enlarged
- Inner ring of elastin is incomplete, damaged & irregular (VvG)
- Fibrin is deposited inside elastin ring (VvG)
- Eosinophils (Above; Black arrow)): Many, Scattered
 H&E stain |
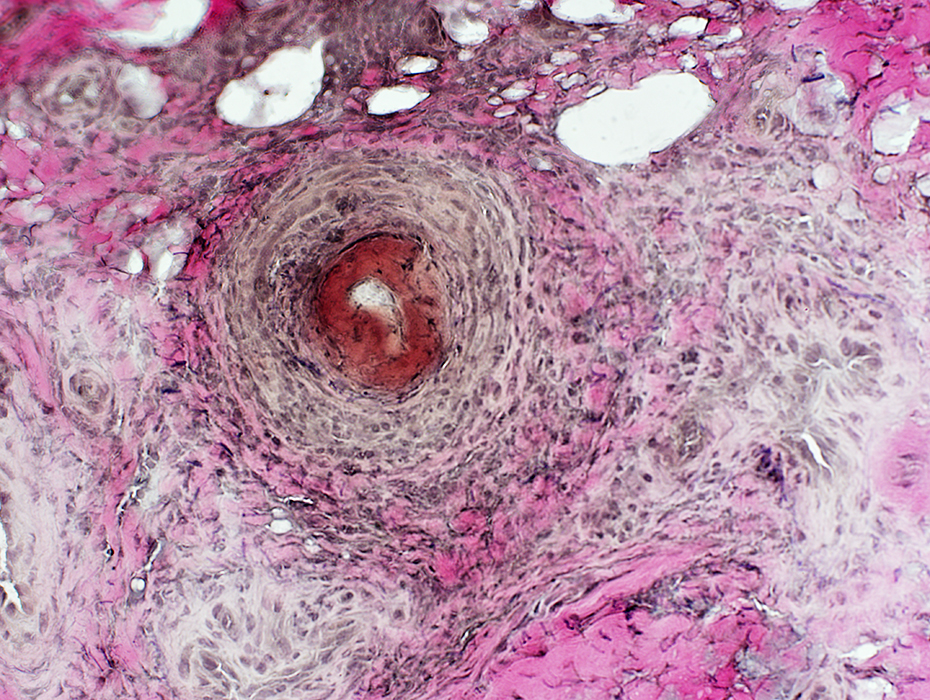 VvG stain |
Fibrinoid Necrosis: Thick orange layer within lumenal side of vessel wall
Vessel wall
Thickness: Increased
Fibril layer: Irregular or Fibrils absent
Epineurial connective tissue
Neovascularization & Irregular structure: Surrounds vessel
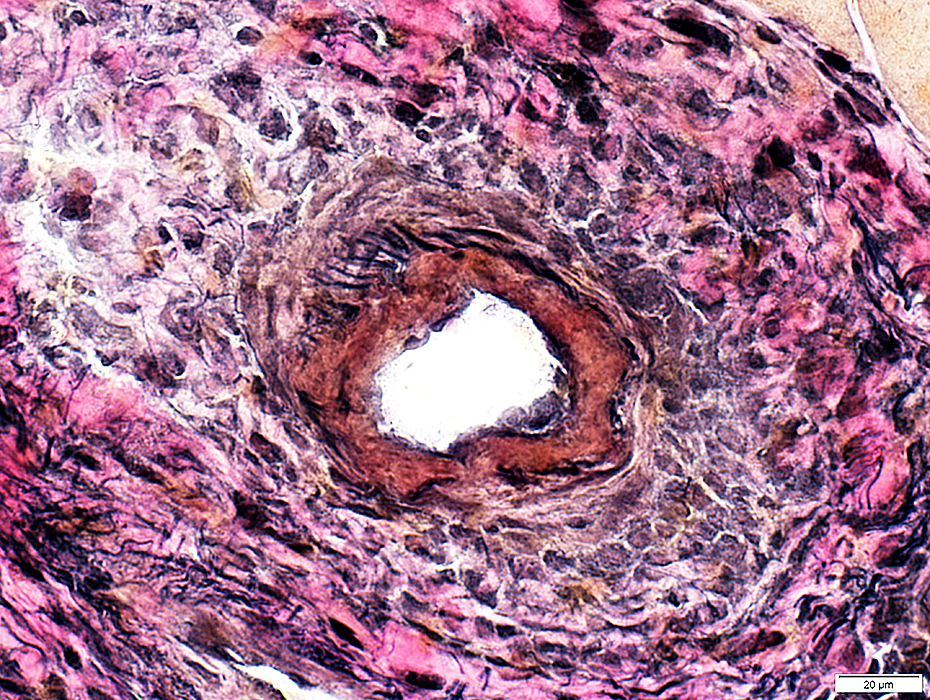 VvG stain |
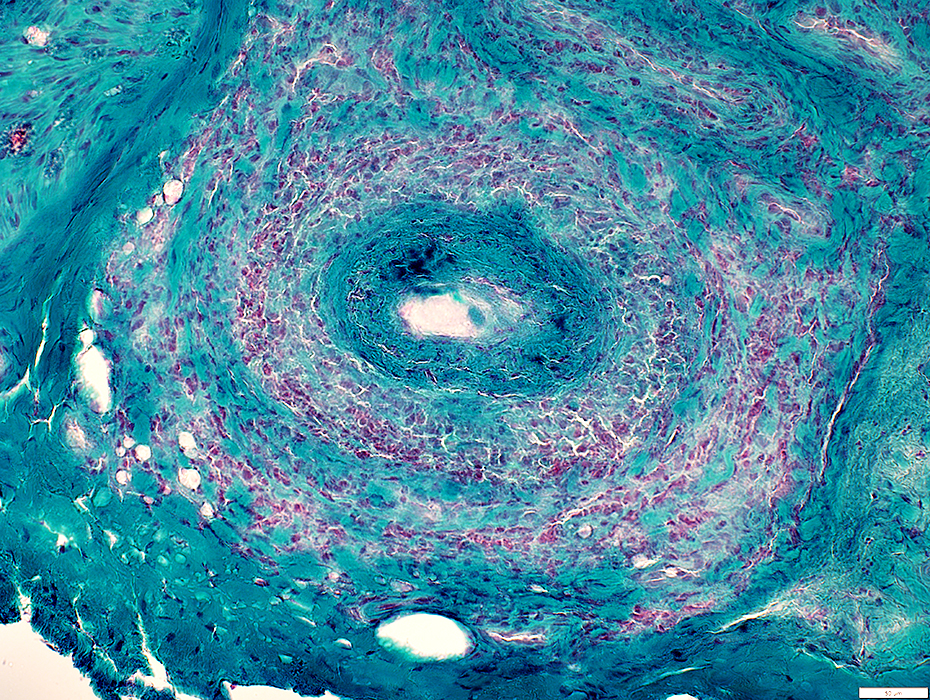 Gomori trichrome stain |
Inner layer of vessel wall
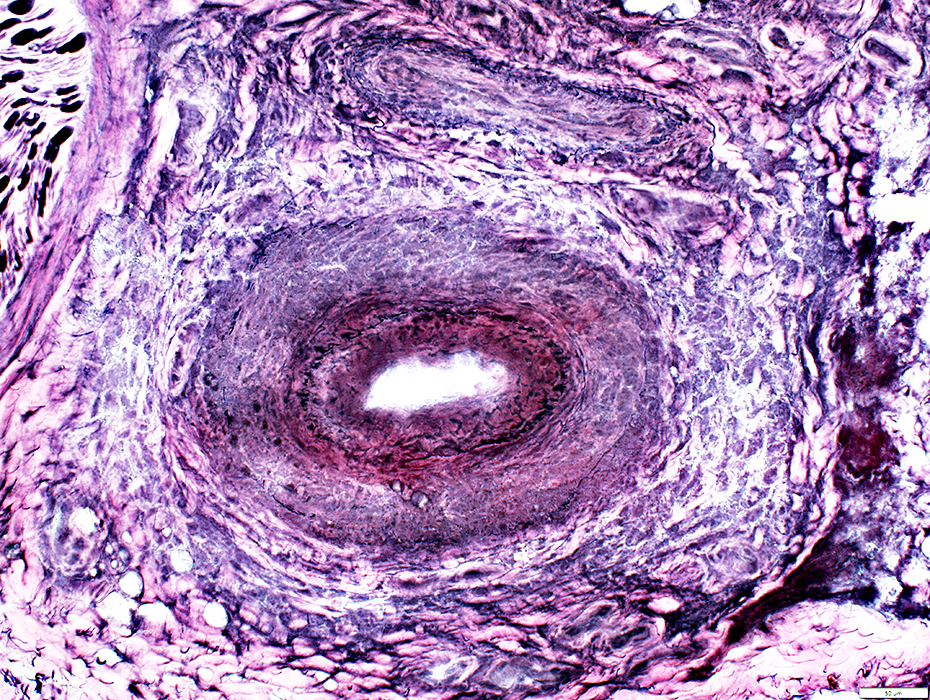 VvG stain |
Fibril layer (Above)
Thin, small, irregular fibrils
Abnormal layer within fibril layer
Lumen remains present at this level
Smooth Muscle Layer: Markedly & Irregularly reduced ATPase staining (Below; Arrow)
Lumen is lost at this section level: ATPase stains neo-vessels in area that was previously lumen
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
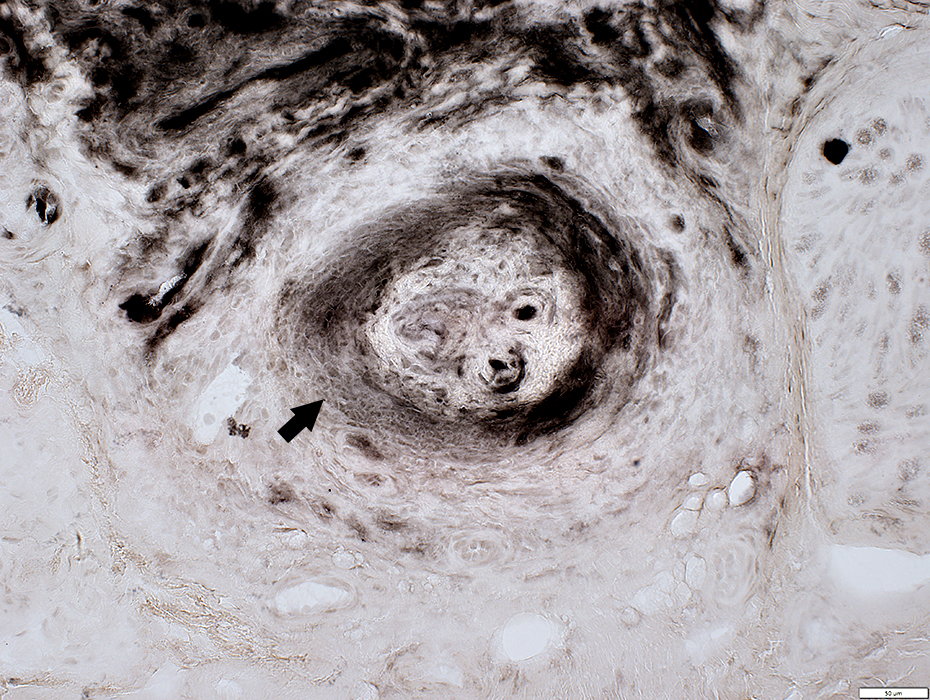
Vasculitis
Fibrinoid Necrosis: Thick, irregular layer within lumenal side of vessel wall
Vessel wall: Cellular; Reduced connective tissue
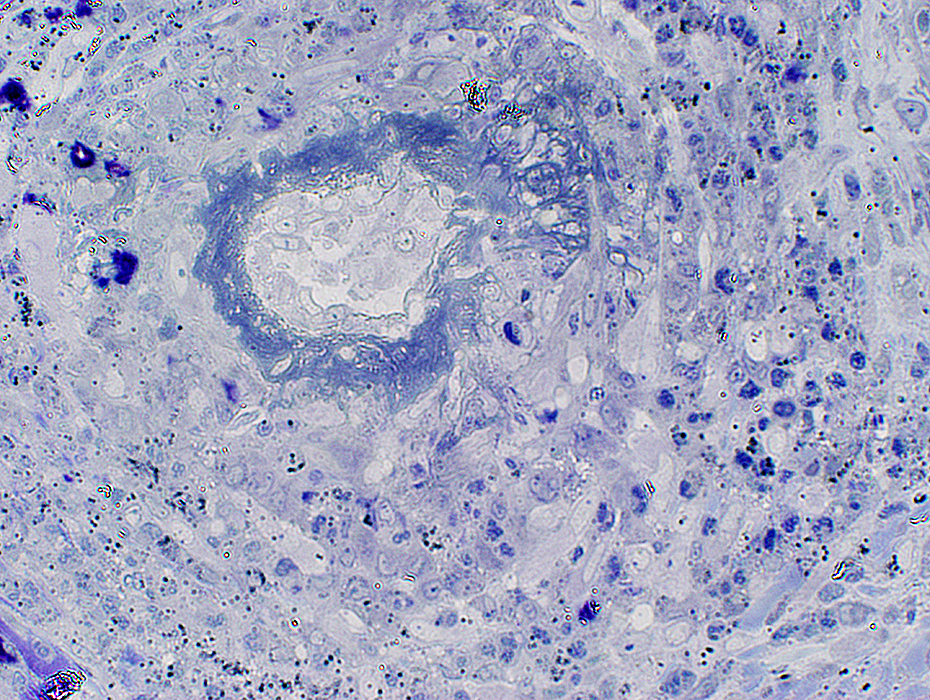 Toluidine blue stain |
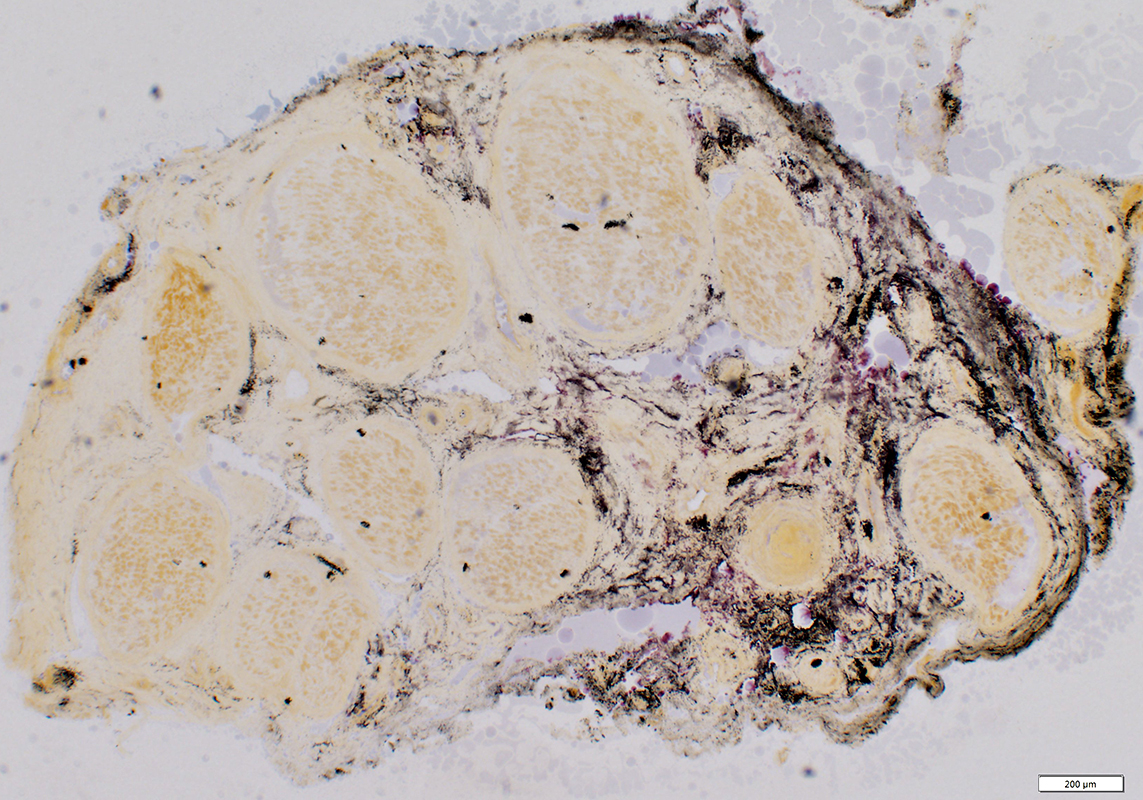
VASCULITIS: Connective Tissue (Perimysium or Epineurium) near, & far from, Vessels
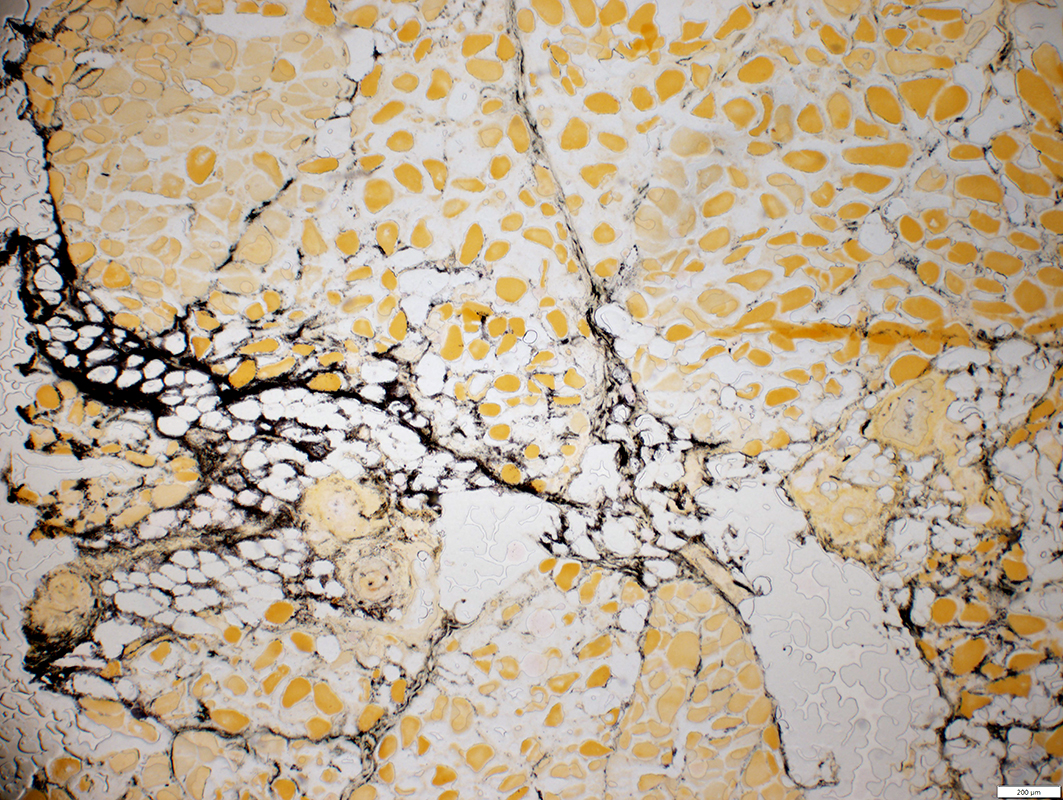 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
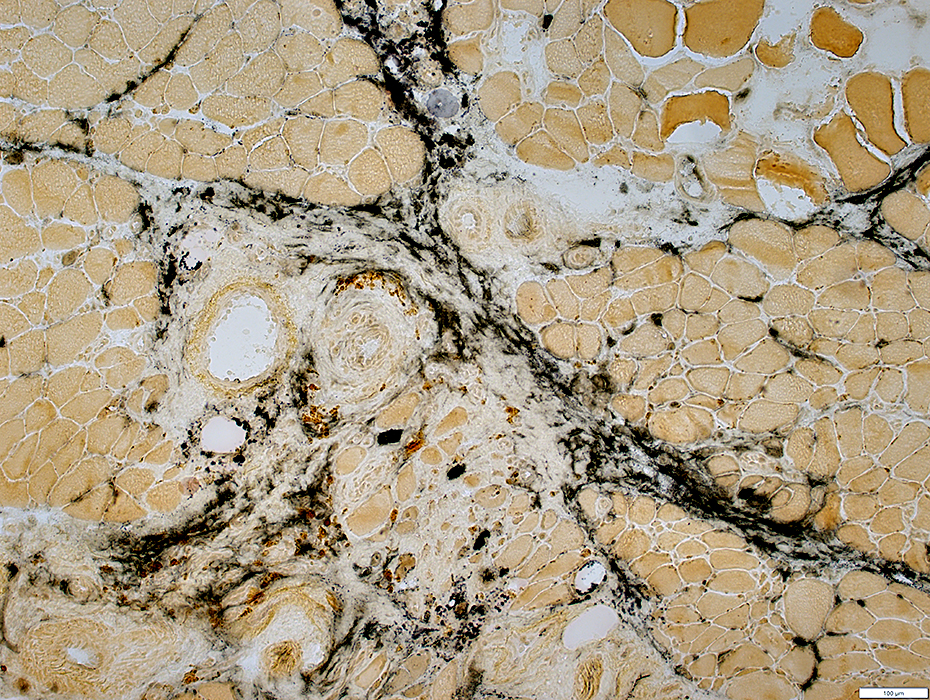 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
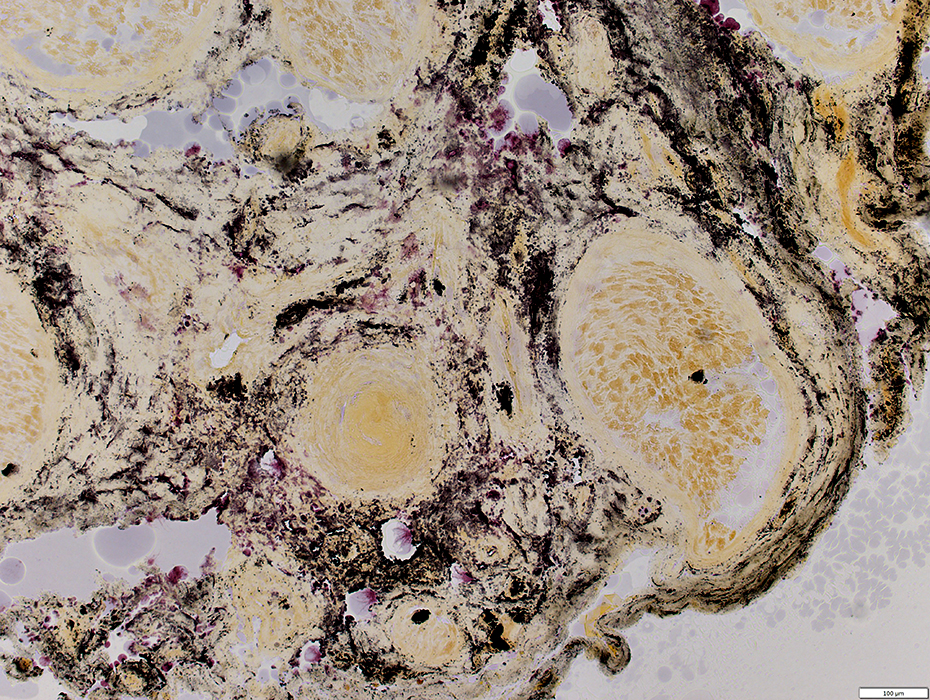 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
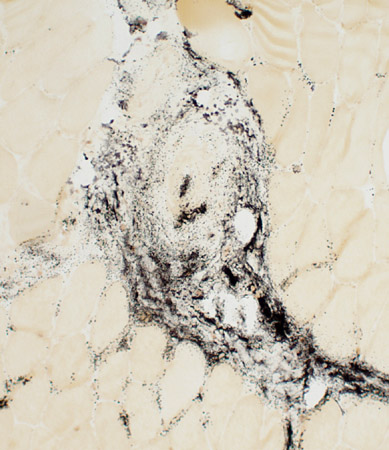 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
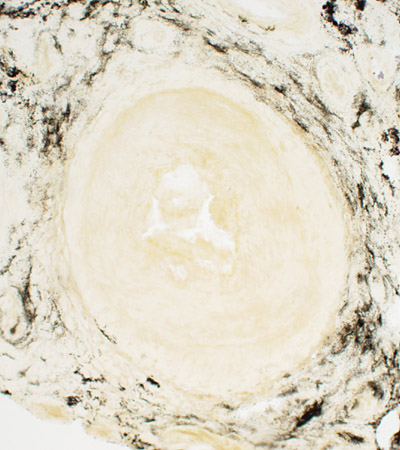 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
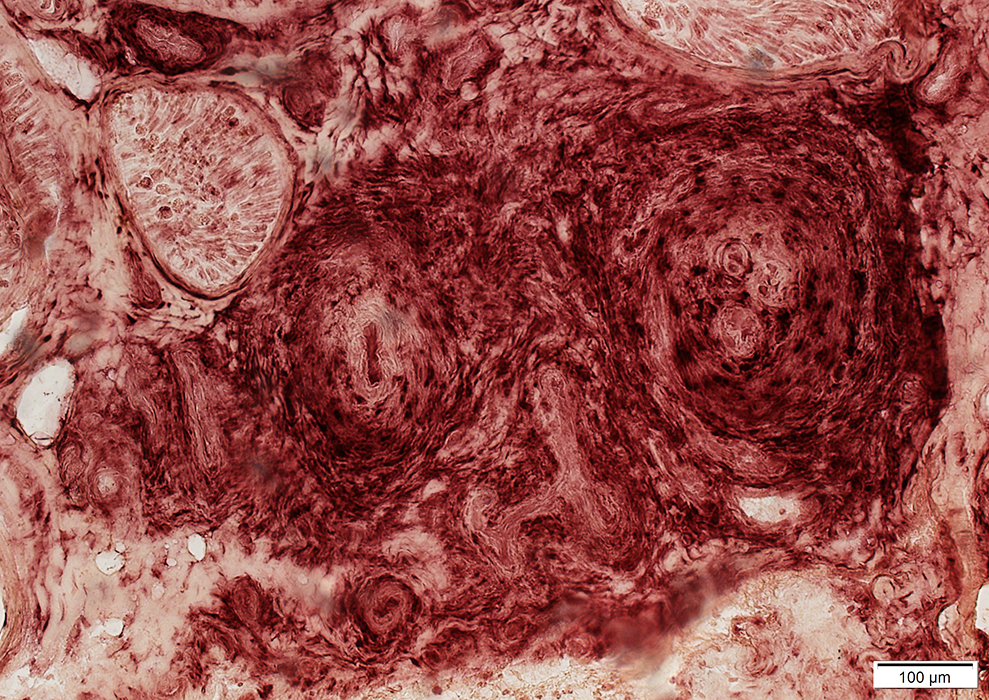
Connective tissue: Acid phosphatase stain
Most cells in epineurium & vessel walls are histiocytes
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Hemosiderin
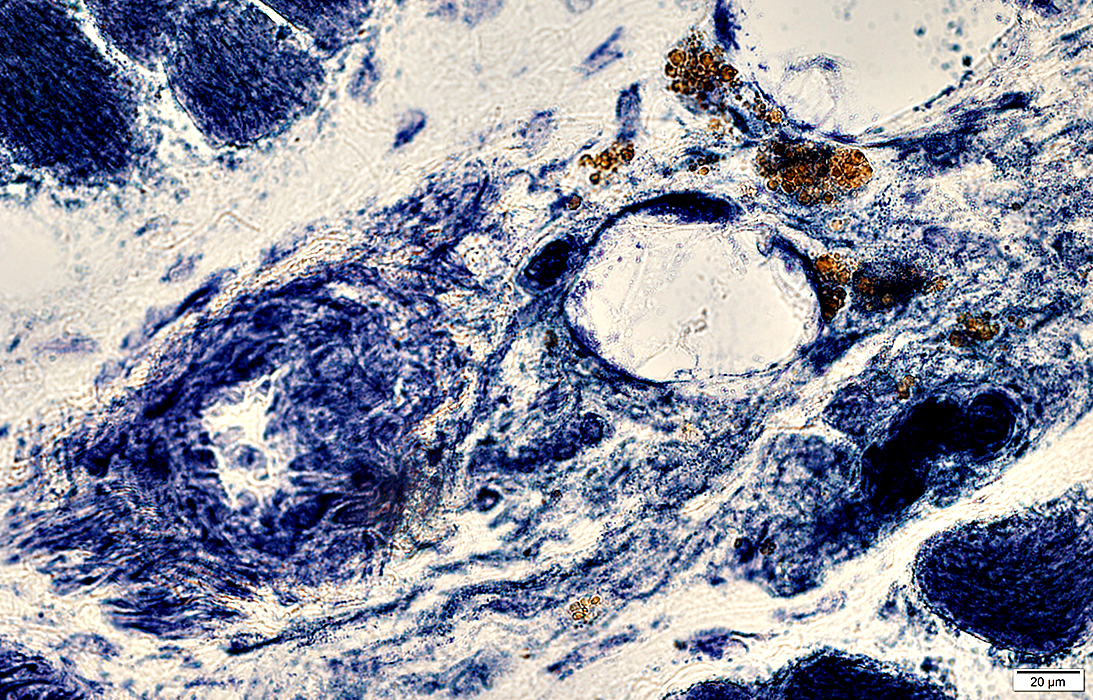 NADH stain |
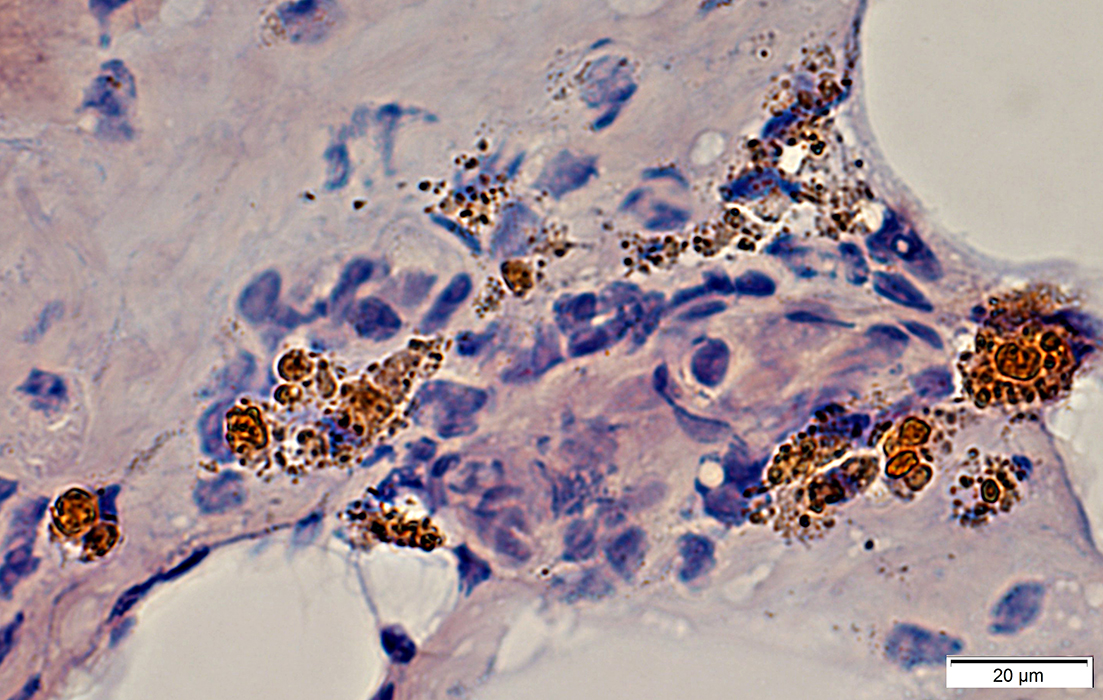 Congo red stain |
Epineurium: Hemosiderin deposits; Neovascularization
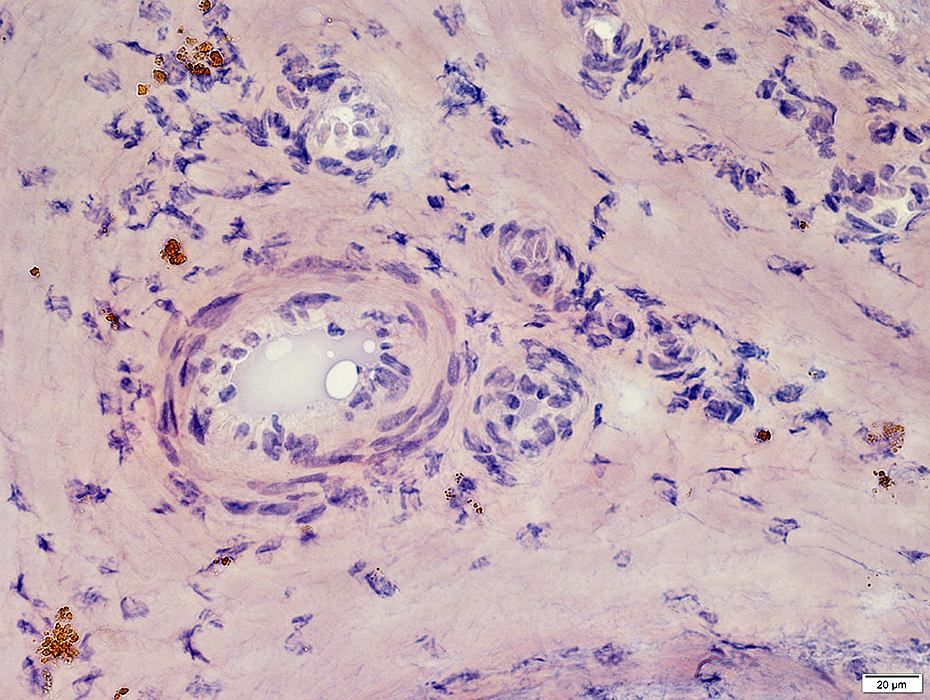 Congo red stain |
Vasculitis: Hemorrhage, Old
Hemosiderin: Brown granules in connective tissue around vessel
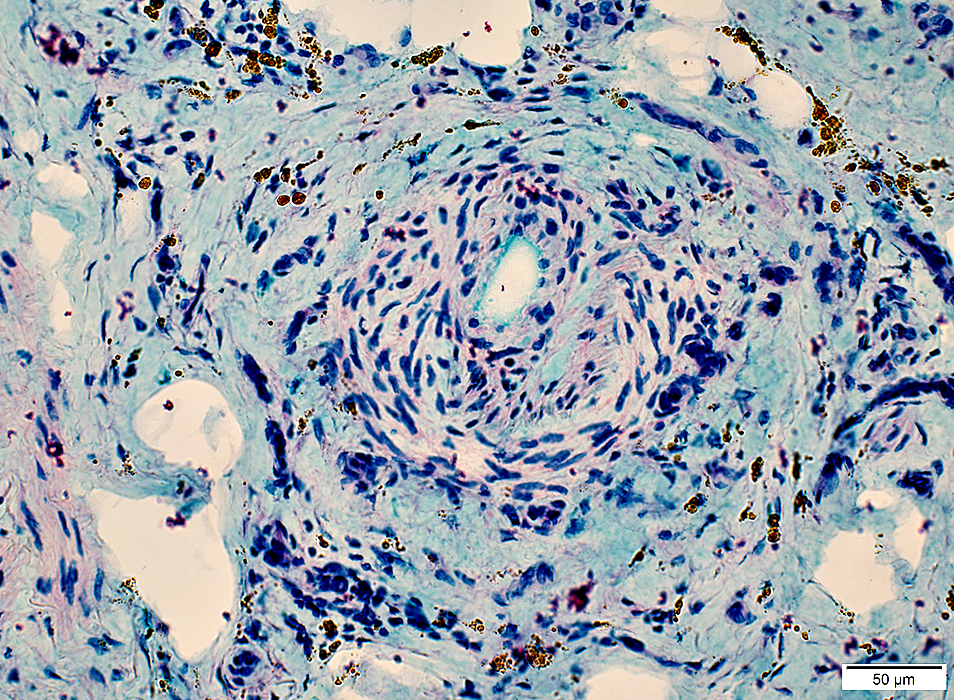 Alcian blue/Nuclear fast red |
VASCULITIS: Occluded Vessels & Lumen pathology
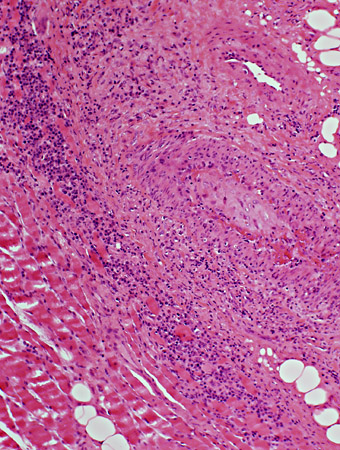 H & E stain |
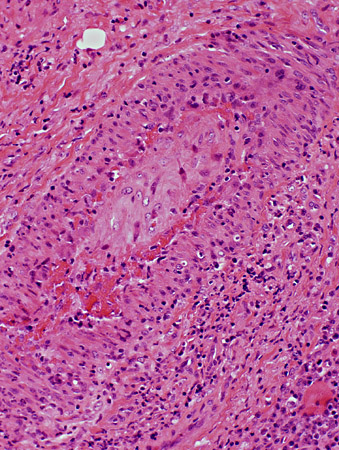 H & E stain |
- Lumen is replaced by
- Connective tissue
- Fibrin
- Neovascularization: New lumens within elastin layer
- Vessel wall: Thick; Cellular
- Inflammation may remain surrounding vessel
- Macrophages (acid phosphatase staining cells) are relatively scarce
- Alkaline phosphatase staining
- Present around vessels in connective tissue
- No endothelial structures stained
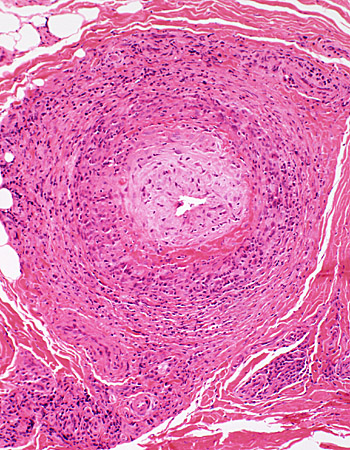 H & E stain |
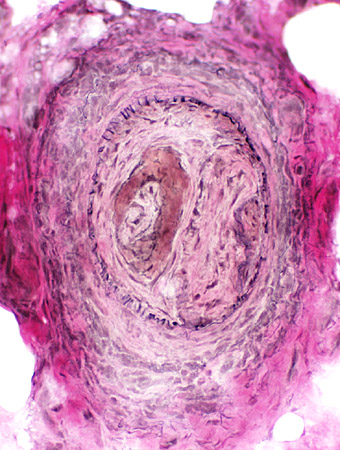 VvG stain |
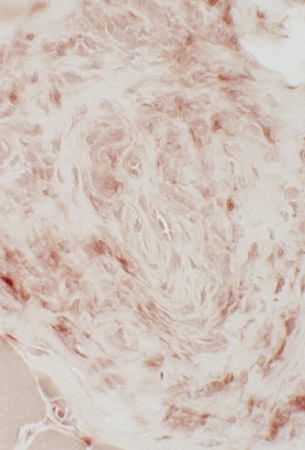 Acid phosphatase stain |
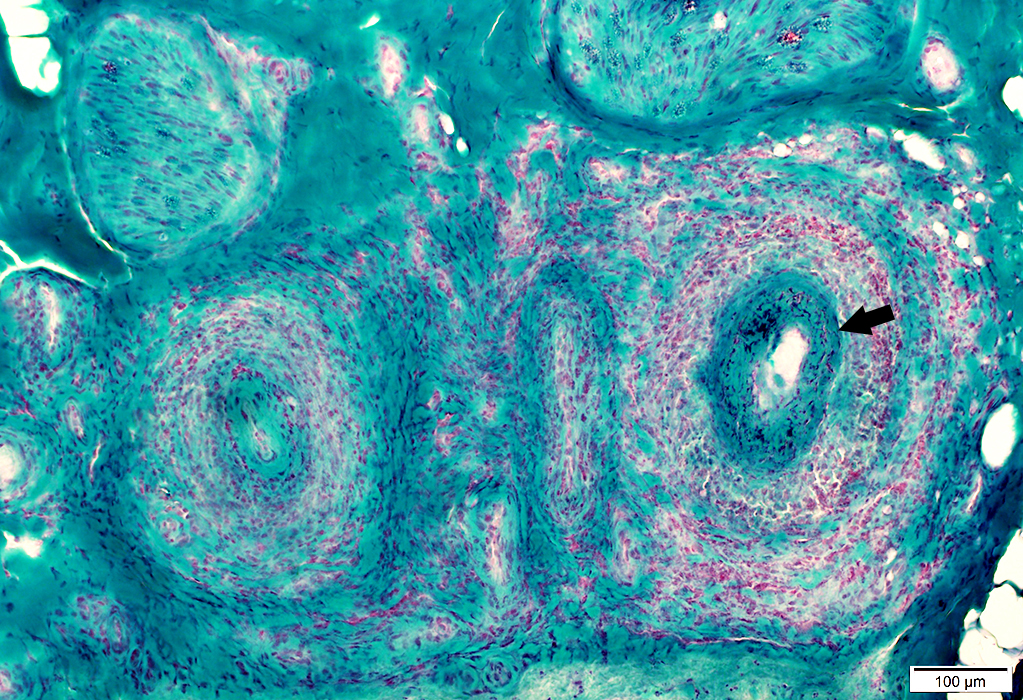 Gomori trichrome stain |
Histiocytic Cells (Acid phosphatase positive)
Locations: Artery wall & Surrounding connective tissue
Lymphocytes: Less common
Fibrinoid deposition (Arrow)
Connective tissue surrounding vessels
Damaged & Rarified
Contains histiocytic cells
Arterial Damage
Lumen: Occluded
Fibril (elastin) layer: Damaged, Irregular (Arrow)
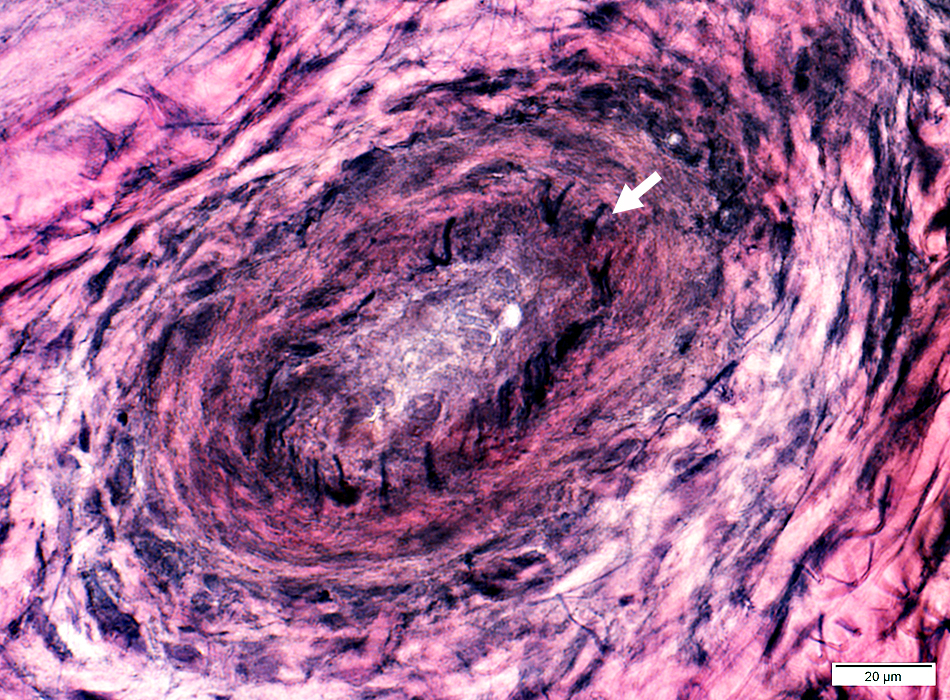 VvG stain |
Perimysial arteriole: Occluded, Early neovascularization
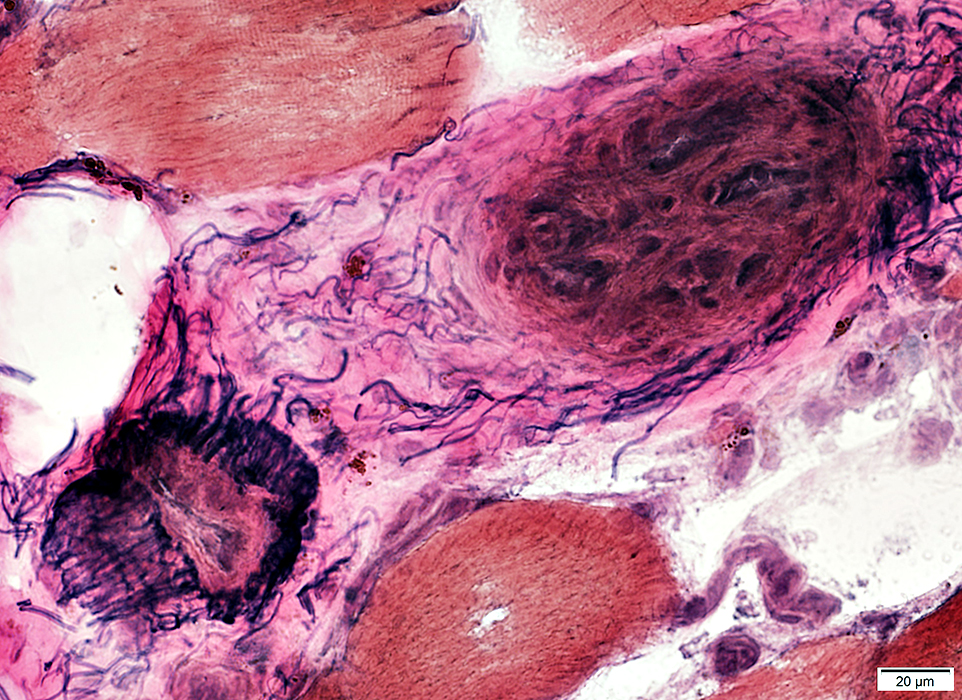 VvG stain |
Perimysial vessel: Occluded, Early neovascularization
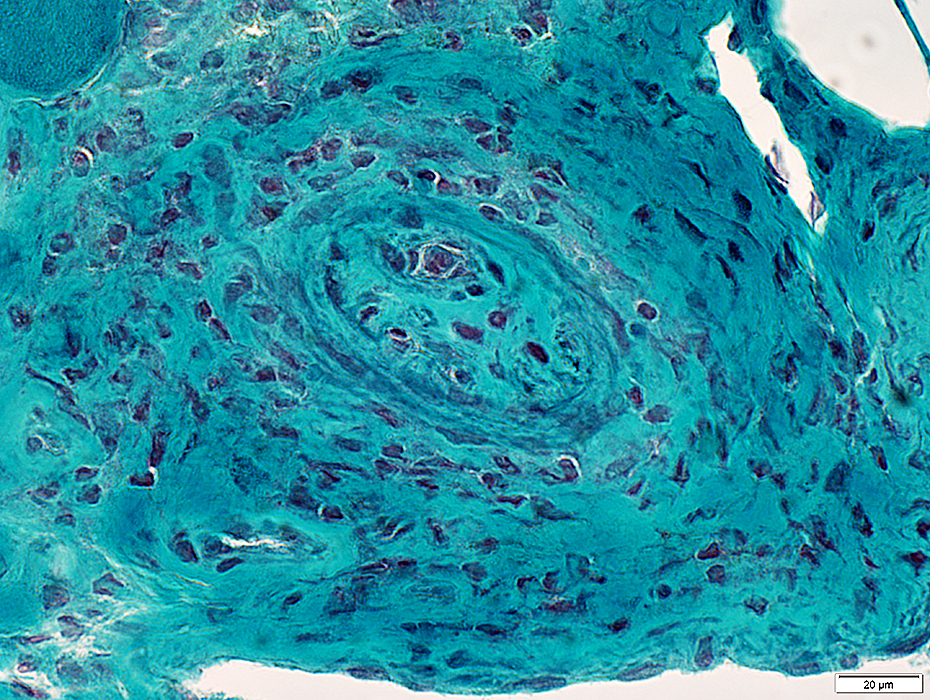 Gomori trichrome stain |
Vessel wall: Thickened around area of occlusion
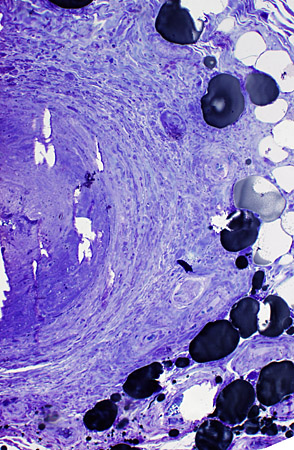 Toluidine blue stain |
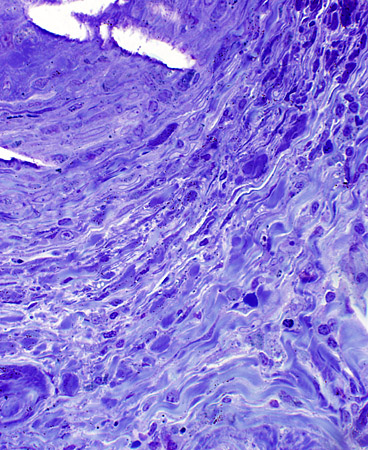 Toluidine blue stain |
VASCULITIS (Chronic): Neovascularization; Multiply recanalized Vessels
- Several small lumens surrounded by cells appear in center of intermediate-sized vessel
- New vessels also appear in connective tissue surrounding vessel intermediate-sized
- Alkaline phosphatase stains endothelium of new vessels
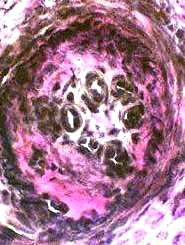 VvG stain |
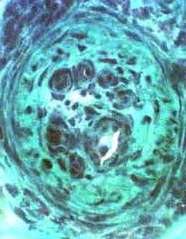 Gomori trichrome stain |
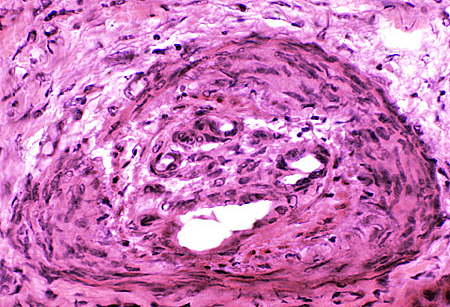 H & E stain |
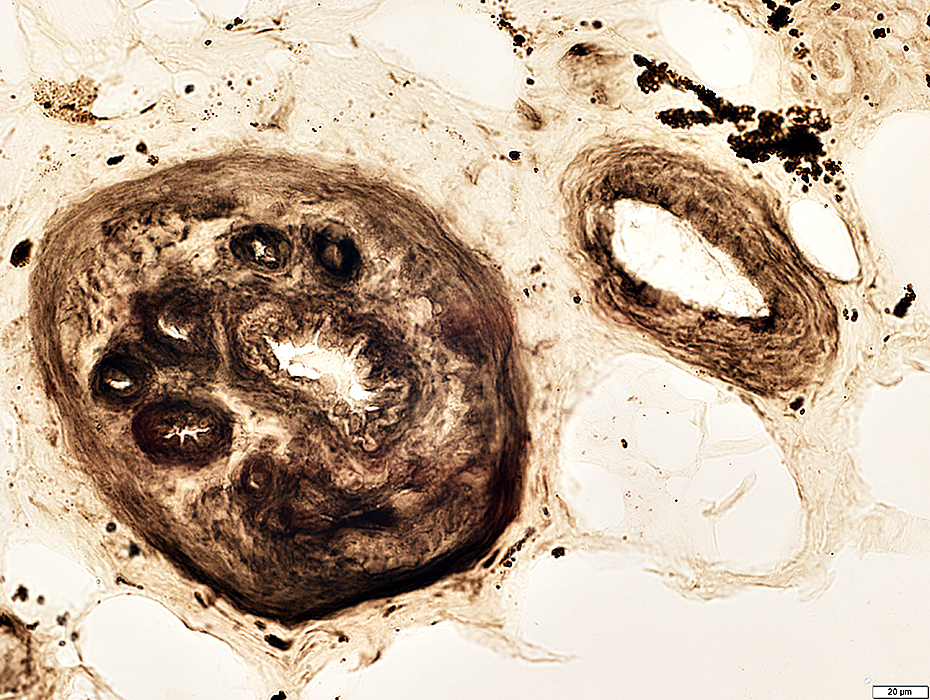 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
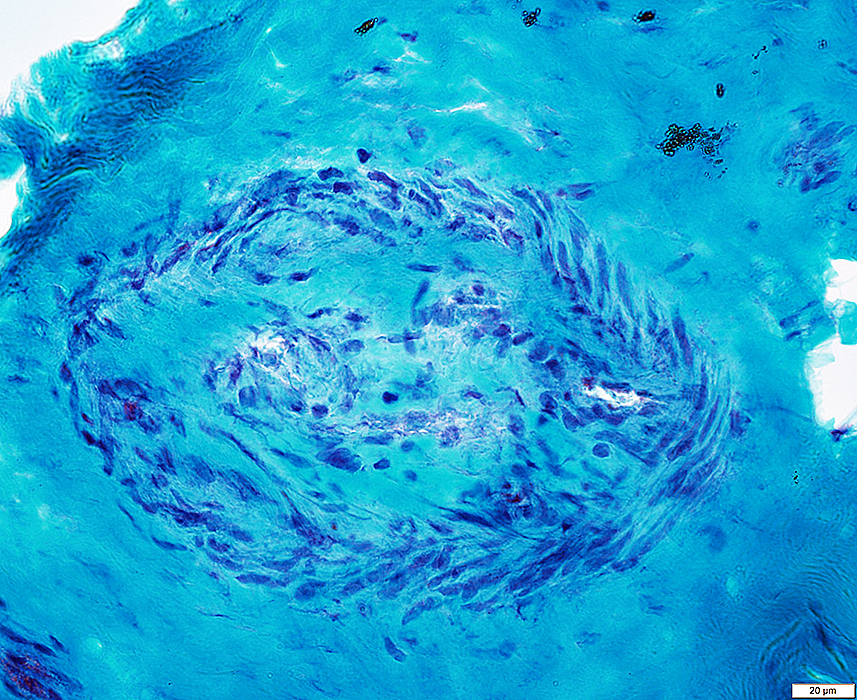 Gomori trichrome stain |
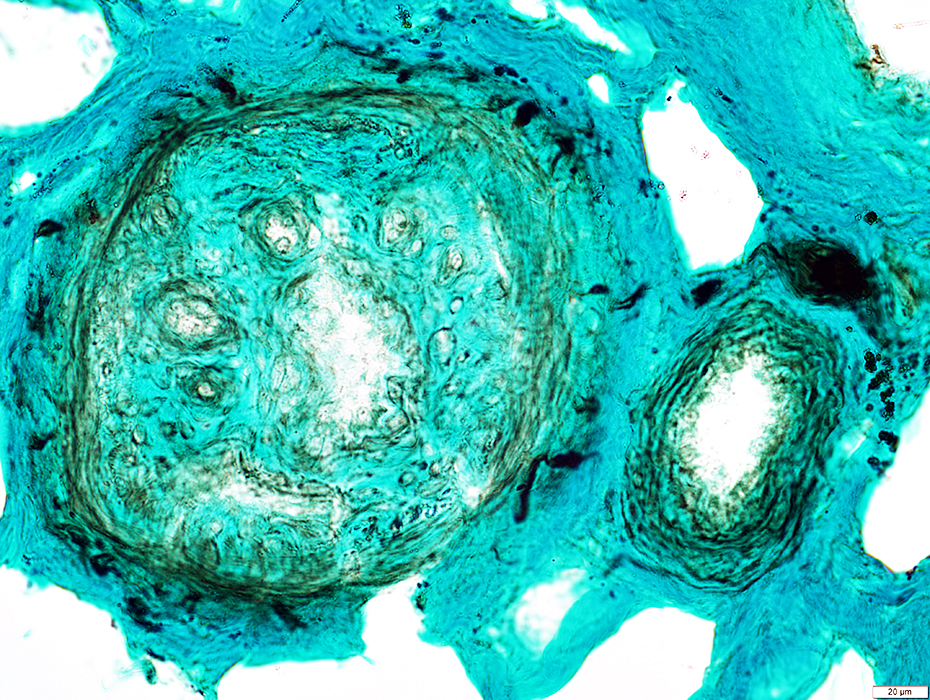 NCAM stain |
Elastin layer & fibrils: VvG stain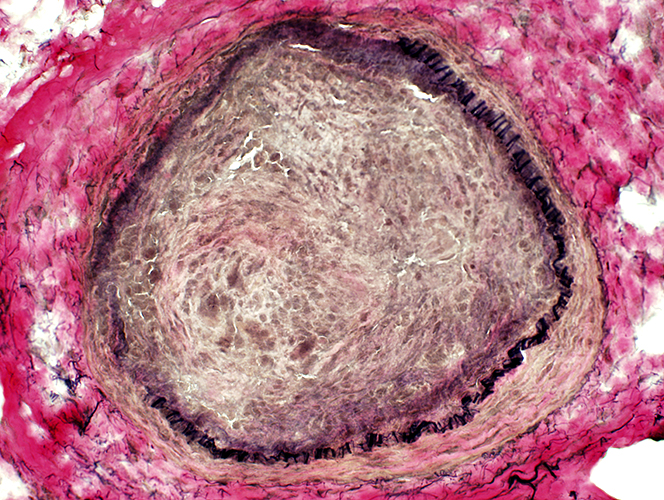 VvG stain Artery: Damage Connective tissue & Neovascularization: Proliferation inside elastin layer Elastin layer: Incomplete in a region of vessel wall |
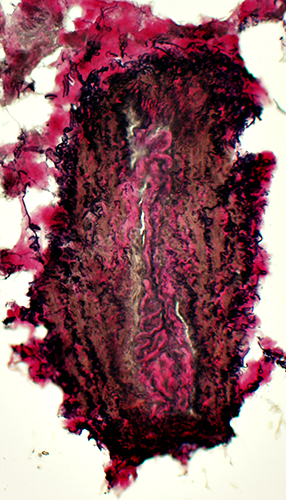 VvG stain A neighboring vein has normal wall structure |
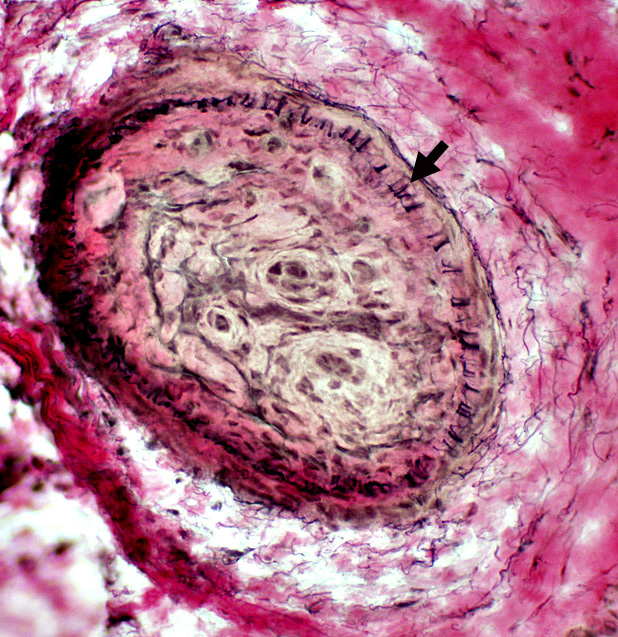 VvG stain |
Surrounding Connective Tissue: Irregular & Rarified (Above)
Structure
Elastin fibrils (Arrow): Reduced in number
Central Connective tissue: Proliferation & Recanalization inside elastin layer
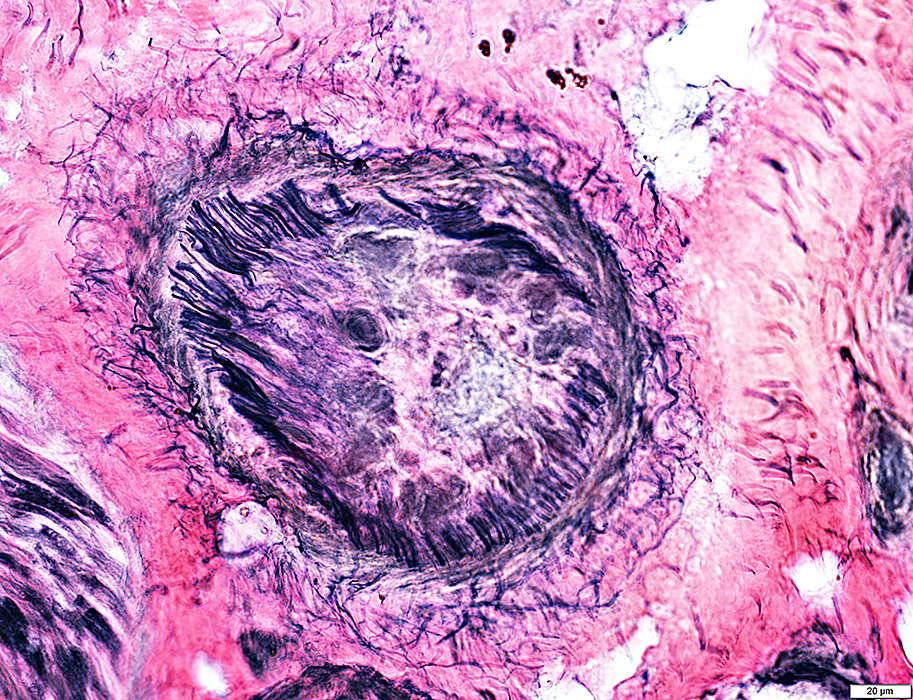 VvG stain |
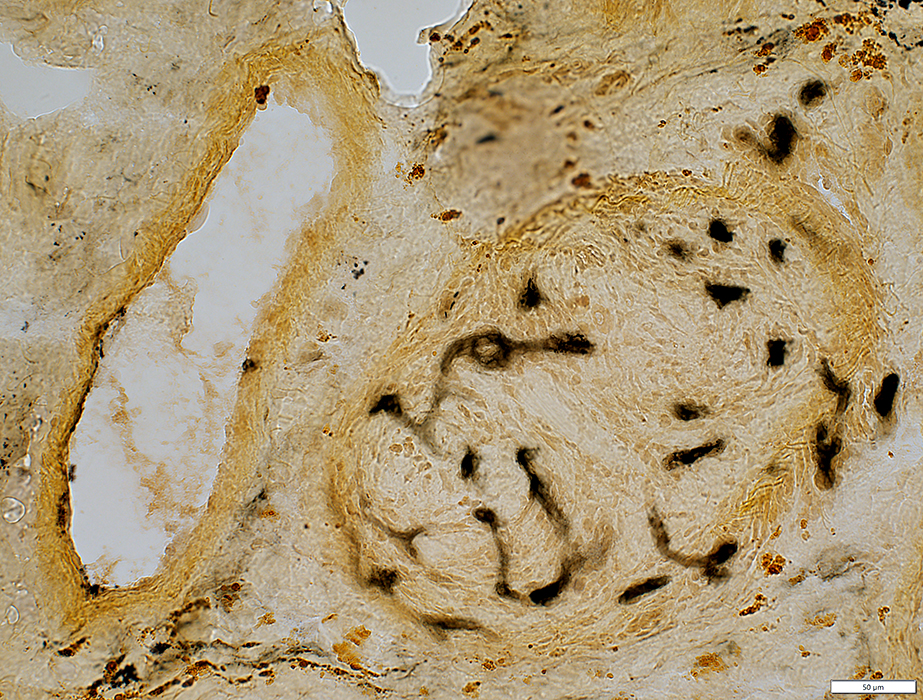 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
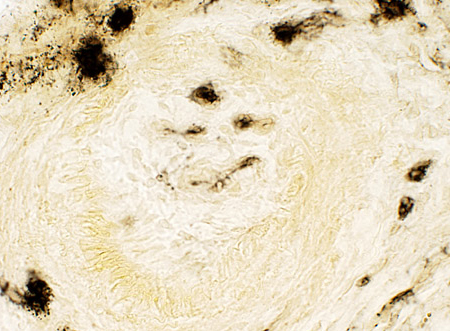 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Neovascularization New, small vessels within previous large vessel Endothelium of new vessels stains for alkaline phosphatase |
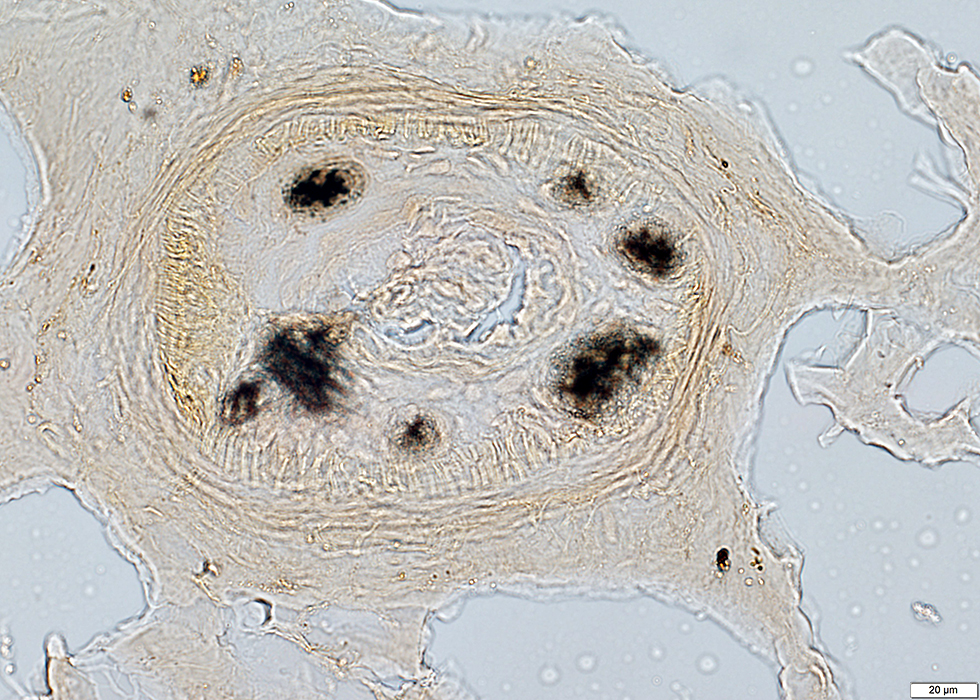 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
|
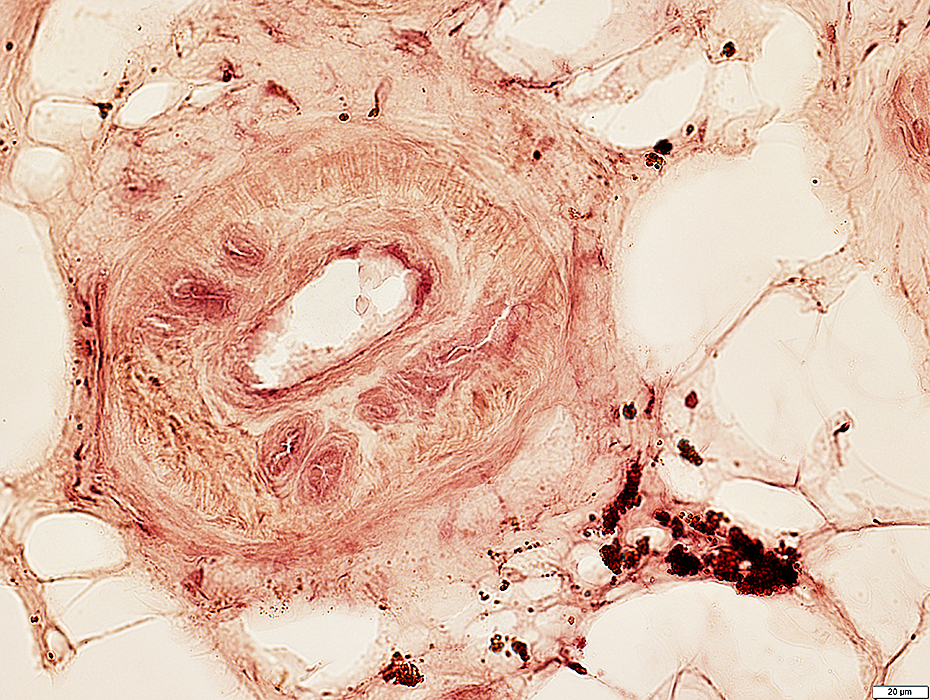 Acid phosphatase stain |
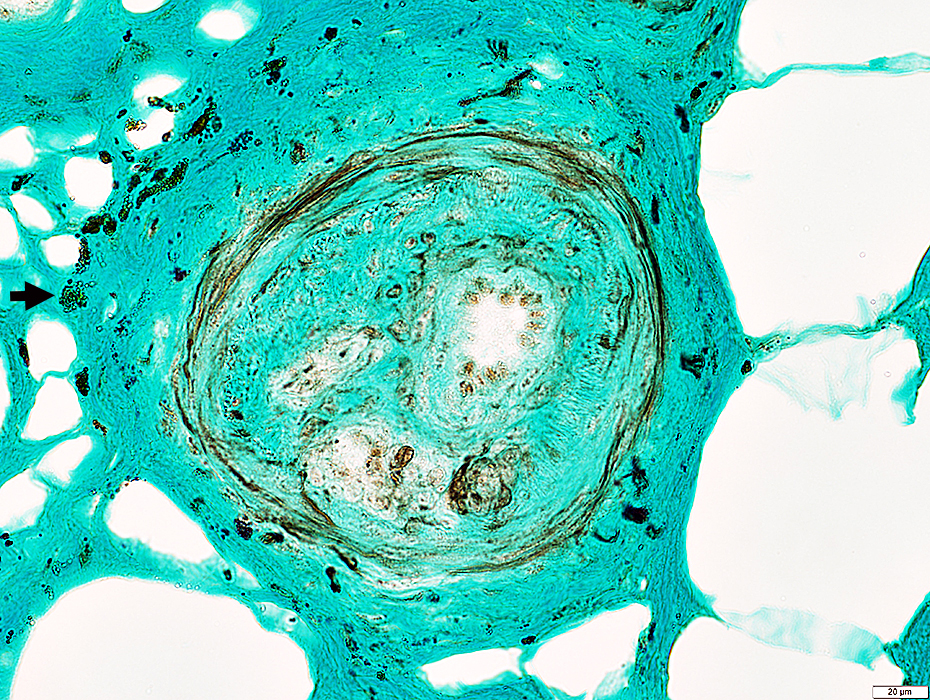 Neurofilament + Trichrome stain |
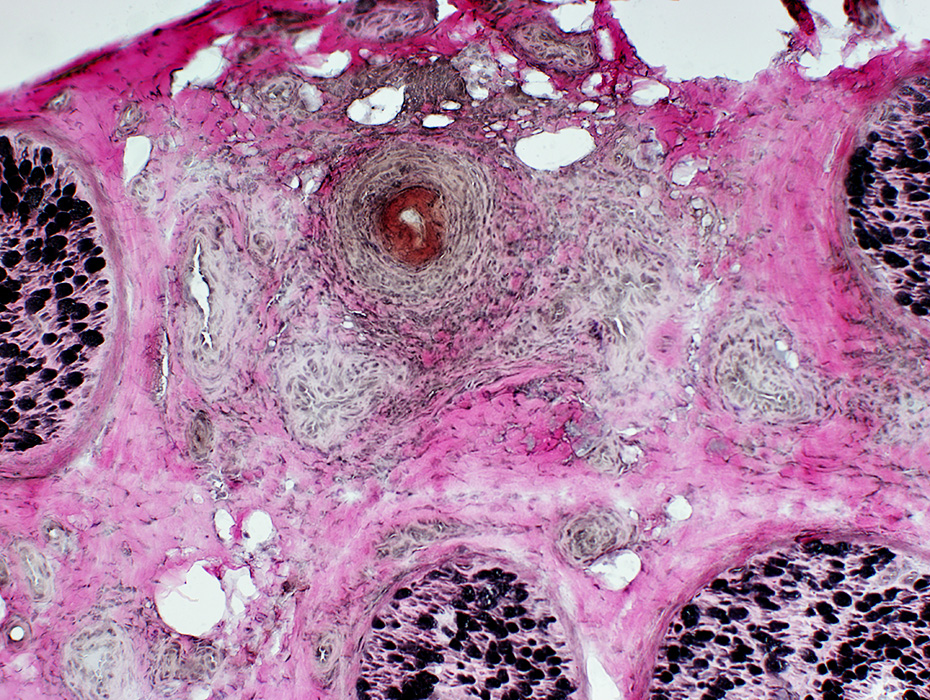
VASCULITIS (Chronic & Ongoing): Epineurial Neovascularization
Differential diagnosis- Vasculitis
- Diabetes: Mononeuritis multiplex
- Castleman disease
- Leprosy
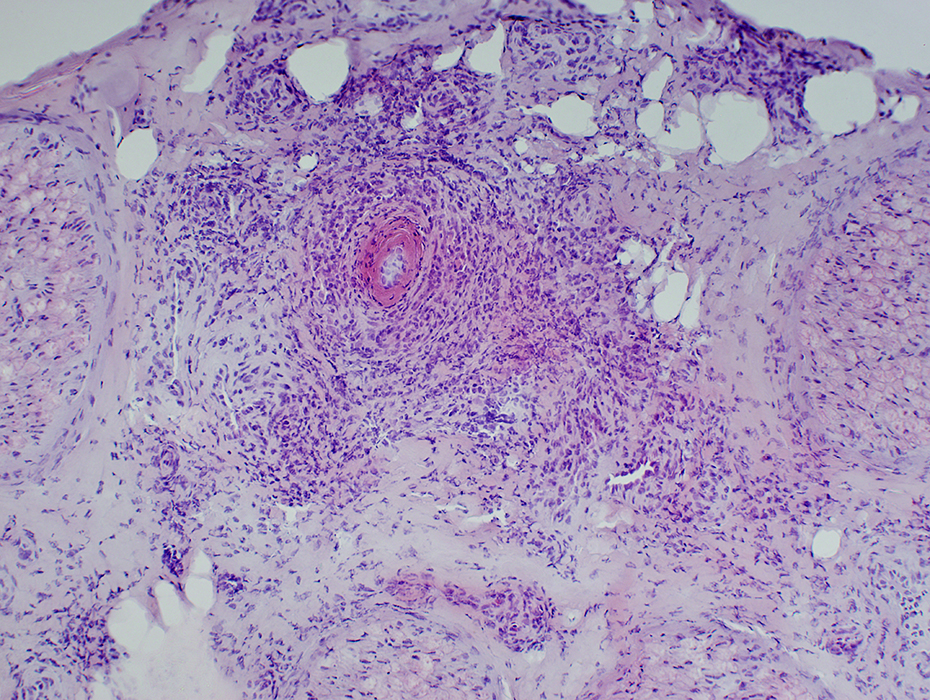 H&E stain Neovascularization: New small vessels in pale, hypercellular epineurial connective tissue around large vessels Fibrinoid necrosis: Wide-stained region around vessel lumen |
 VvG stain |
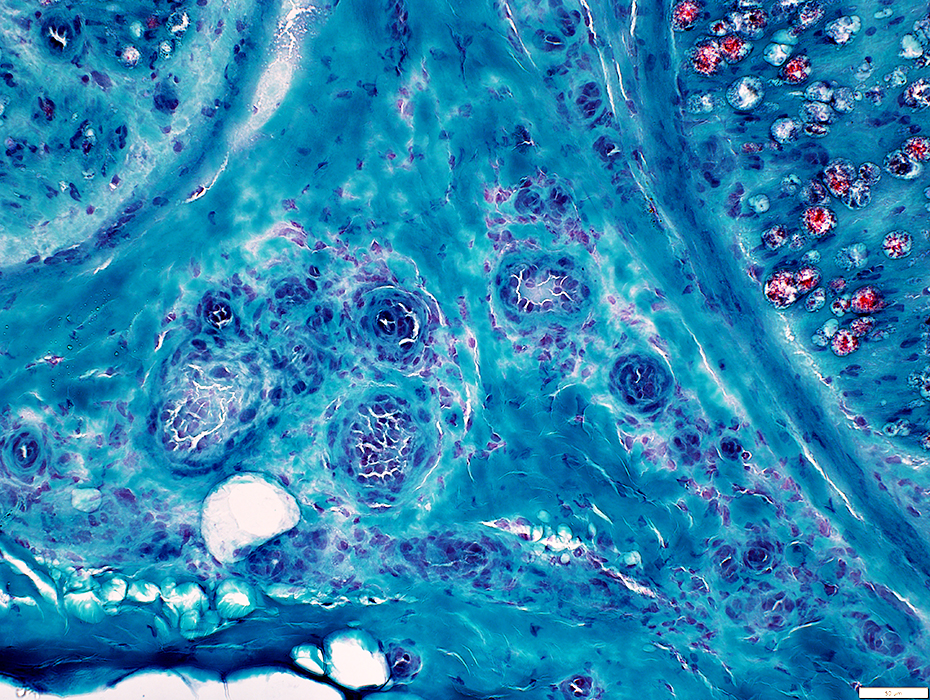 Gomori trichrome stain |
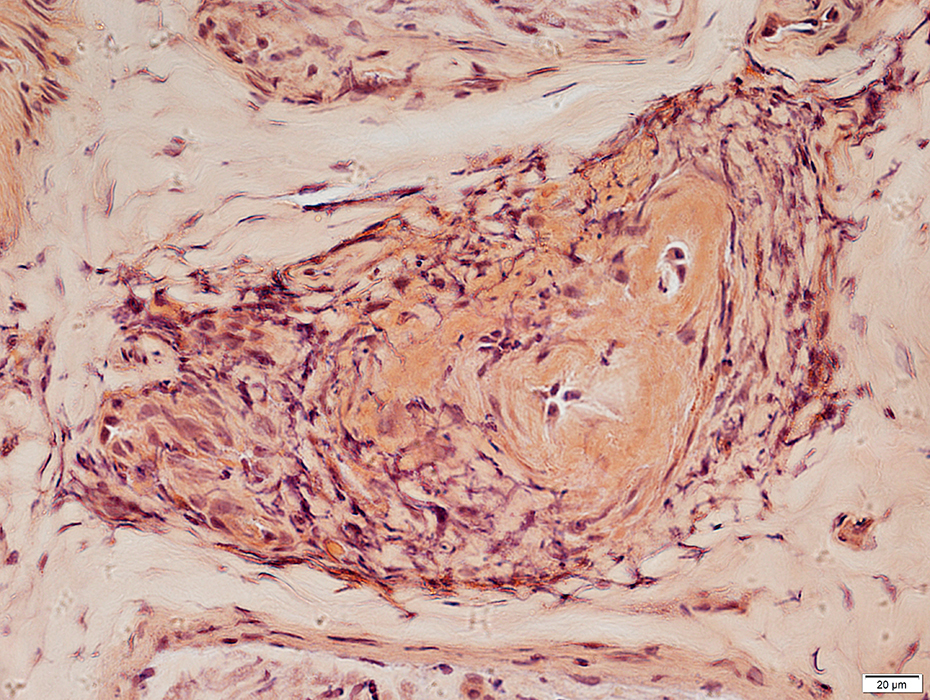 Congo Red stain |
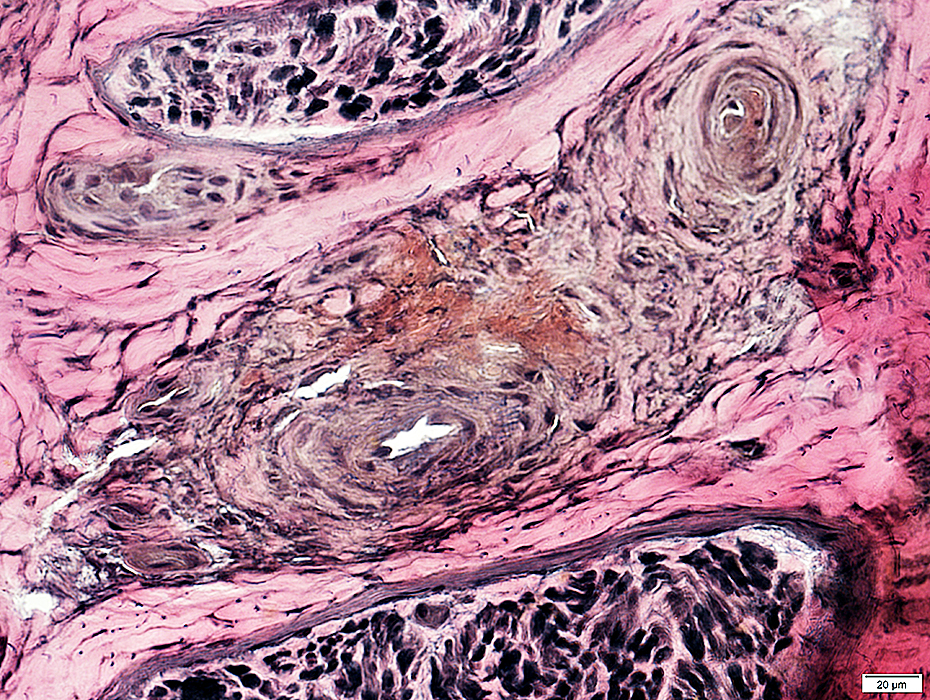 VvG stain |
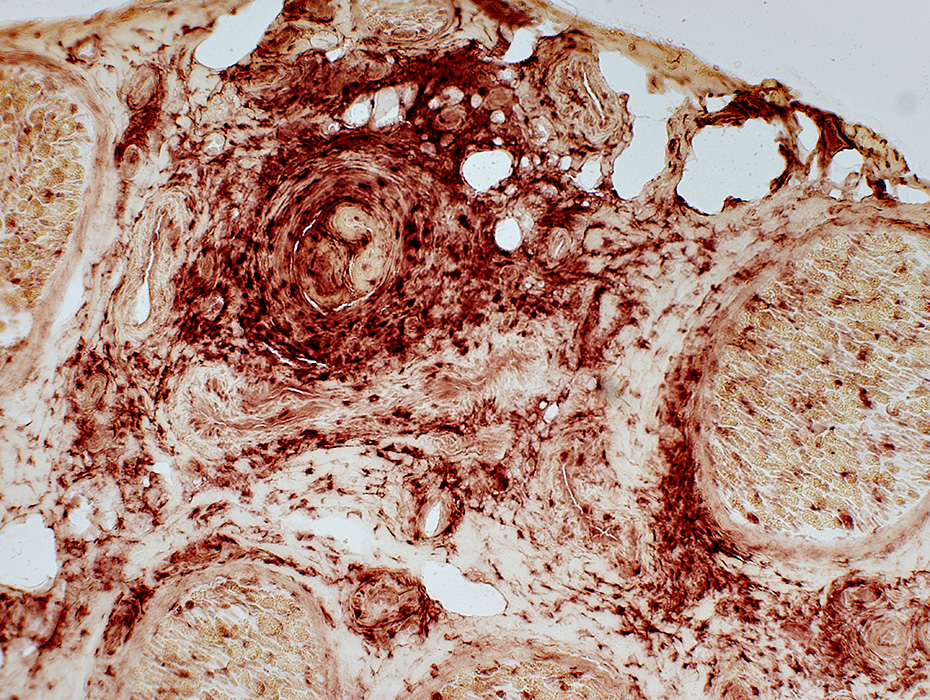 Acid Phosphatase stain |
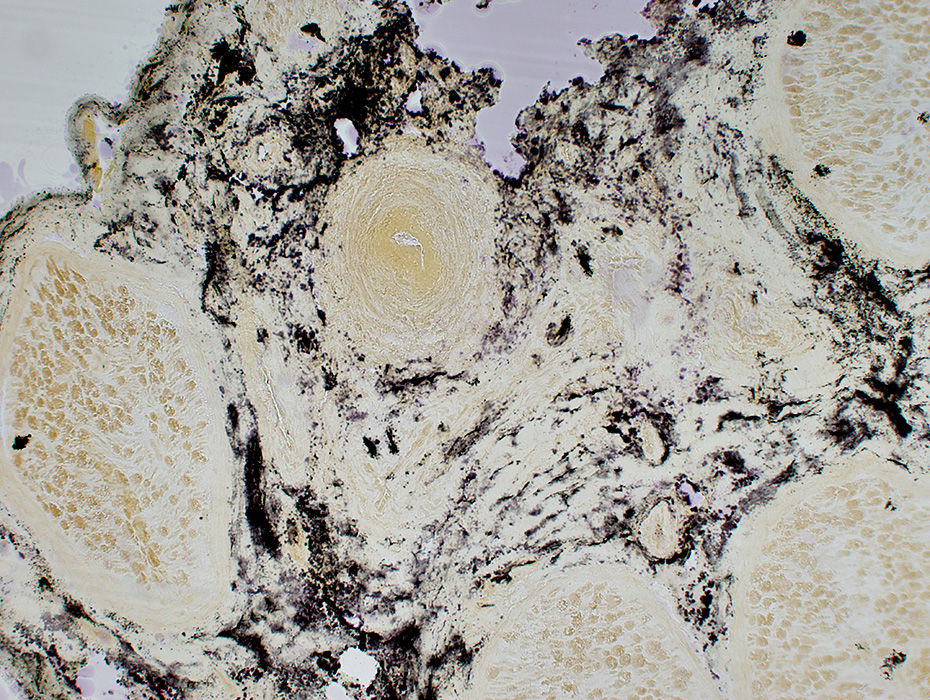 Alkaline Phosphatase stain |
Vasculitic process involves connective tissue around vessel
Alkaline phosphatase: Stains connective tissue around, & distant from, abnormal vessel
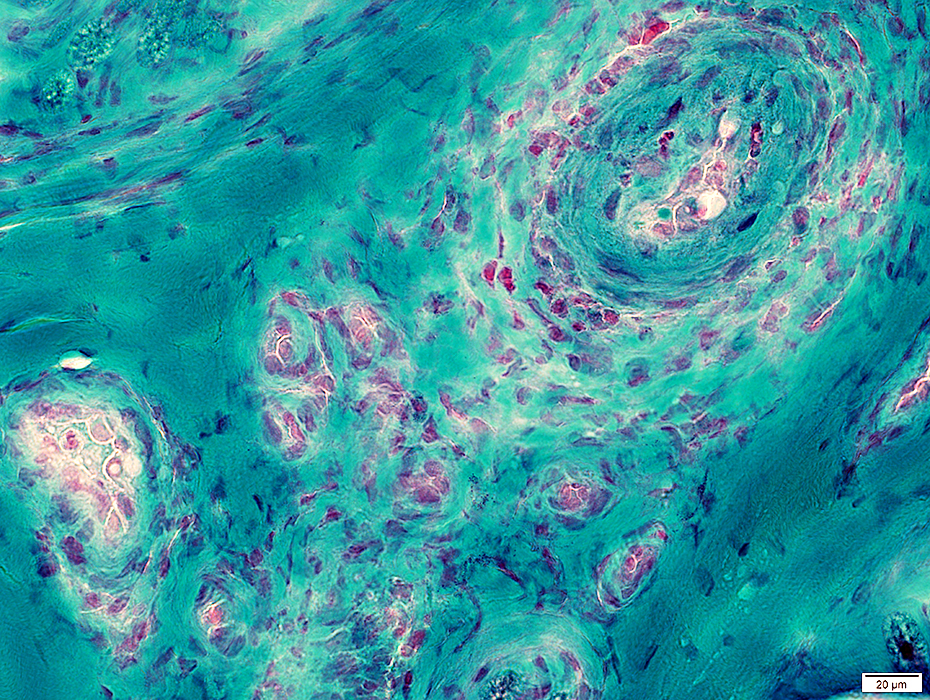 Gomori trichrome stain |
Proliferation of small vessels in epineurium near larger vessel (Above)
Many epineurial capillaries with endothelium stained by UEA-I (Below)
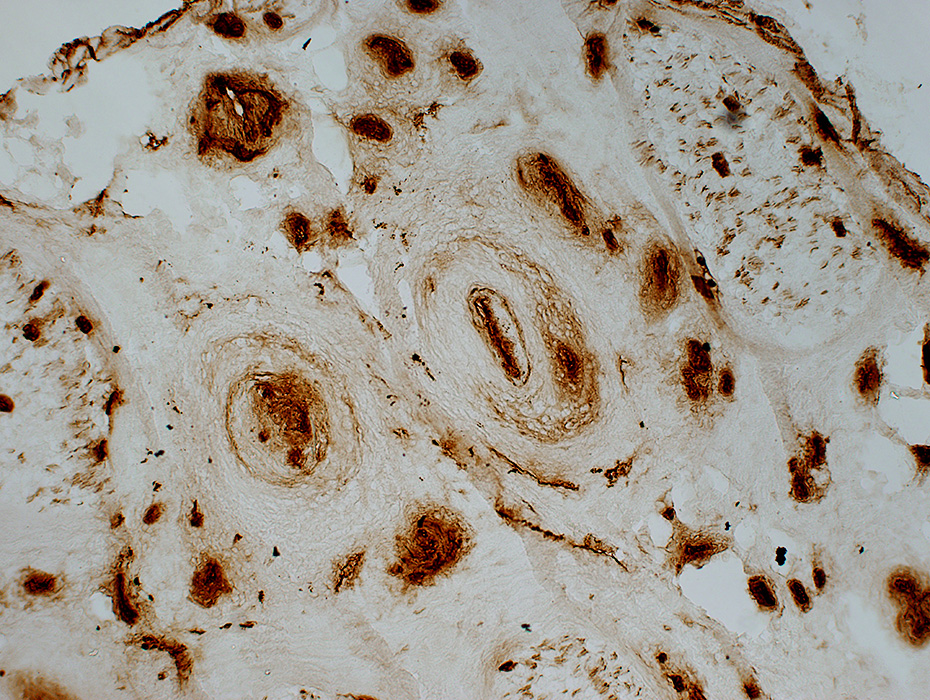 Ulex (UEA-I) stain |
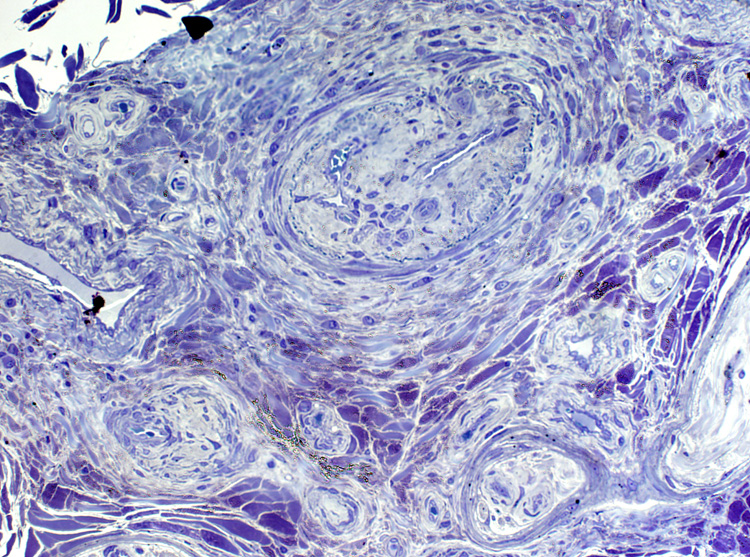 Toluidine blue stain Epineurium Vessel: Abnormal structure Connective tissue: Neovascularization & Irregular structure |
Endoneurial Microvessel Proliferation
Unusual feature of vasculopathic neuropathies
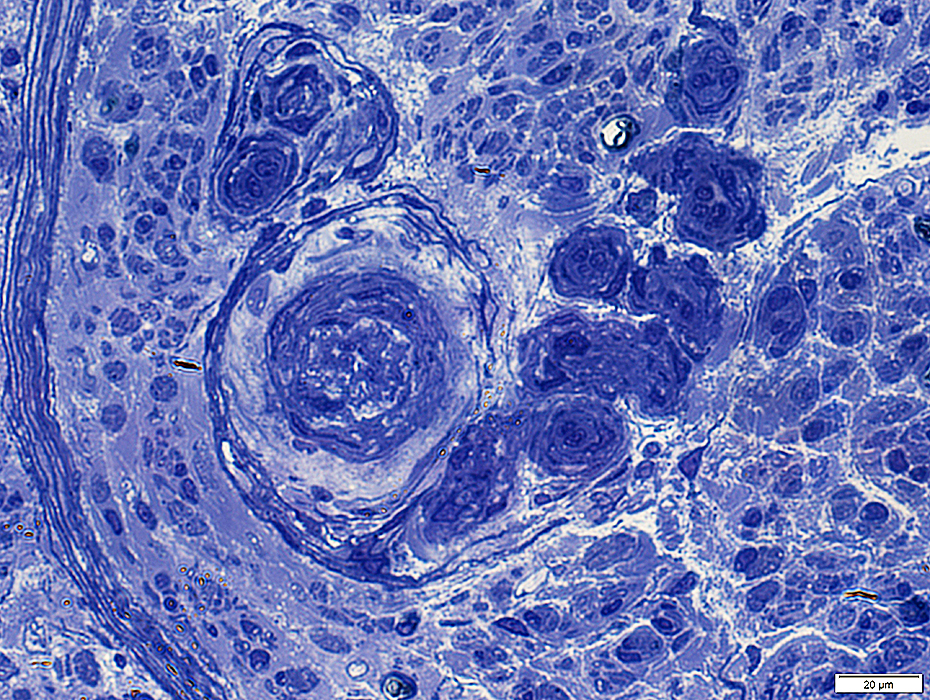 Toluidine blue stain |
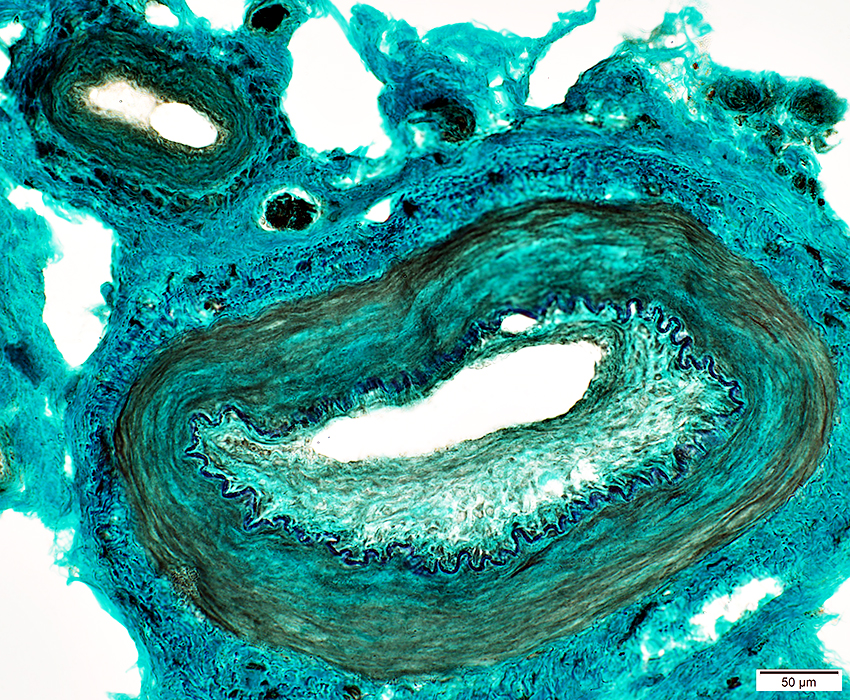
Epineurial Vessel: Intimal Proliferation
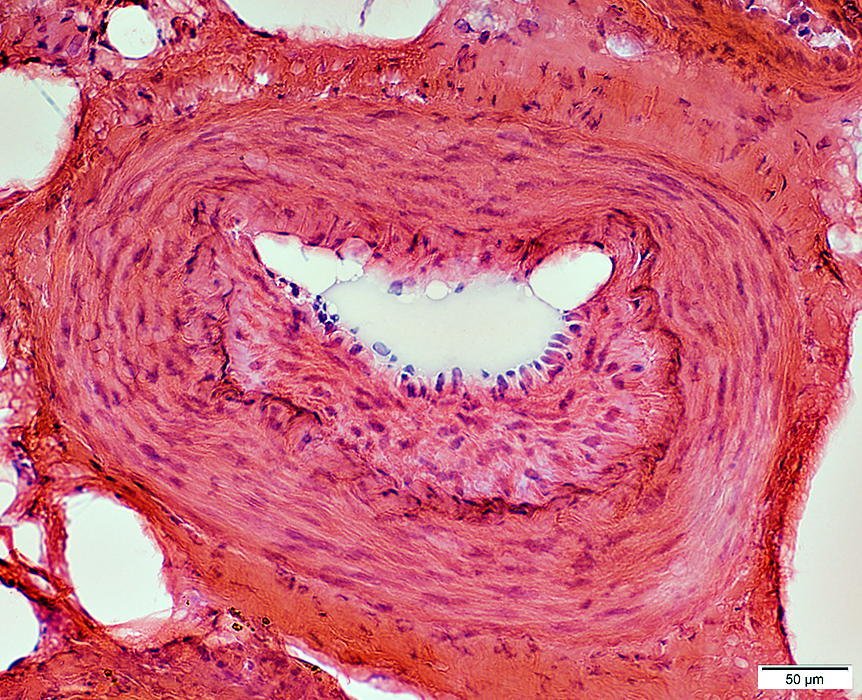 H&E stain |
Lumen: Connective tissue proliferation
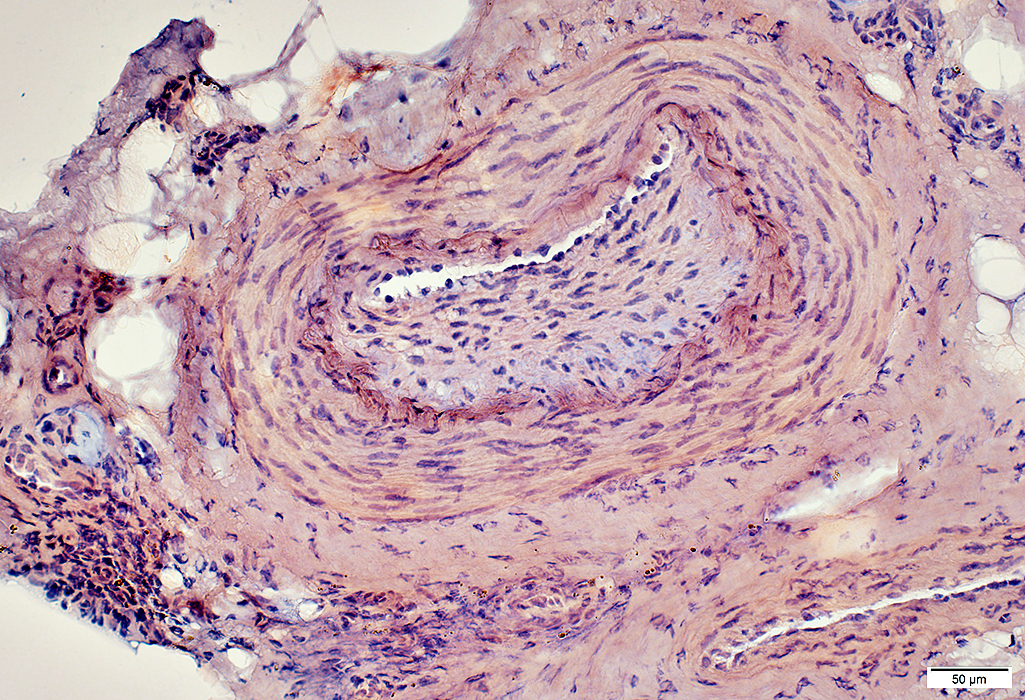 Congo red stain |
 Neurofilament stain |
Lumen: Connective tissue proliferation
Elastic lamina: Damaged & Interrupted
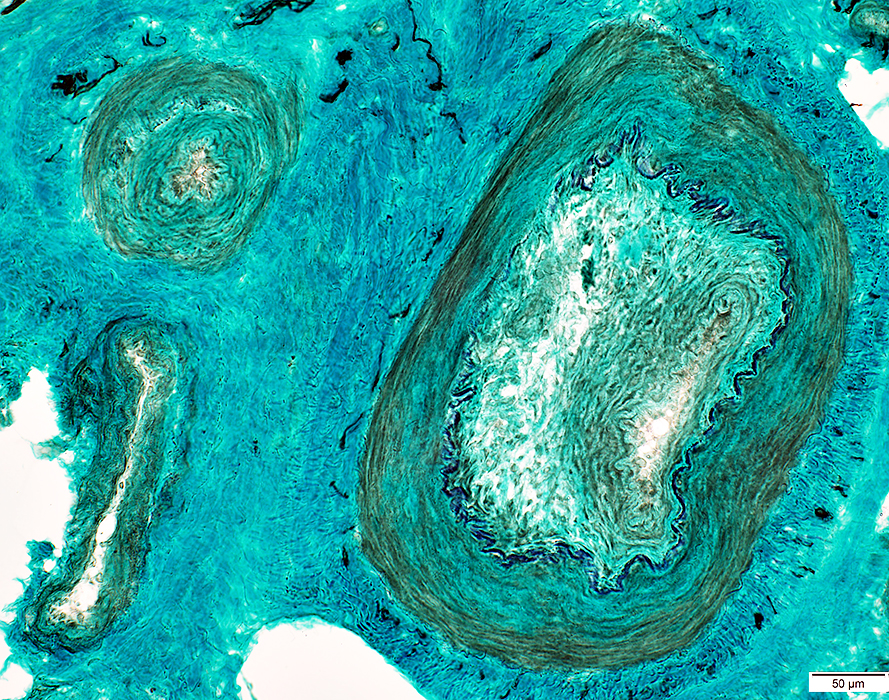 NCAM stain |
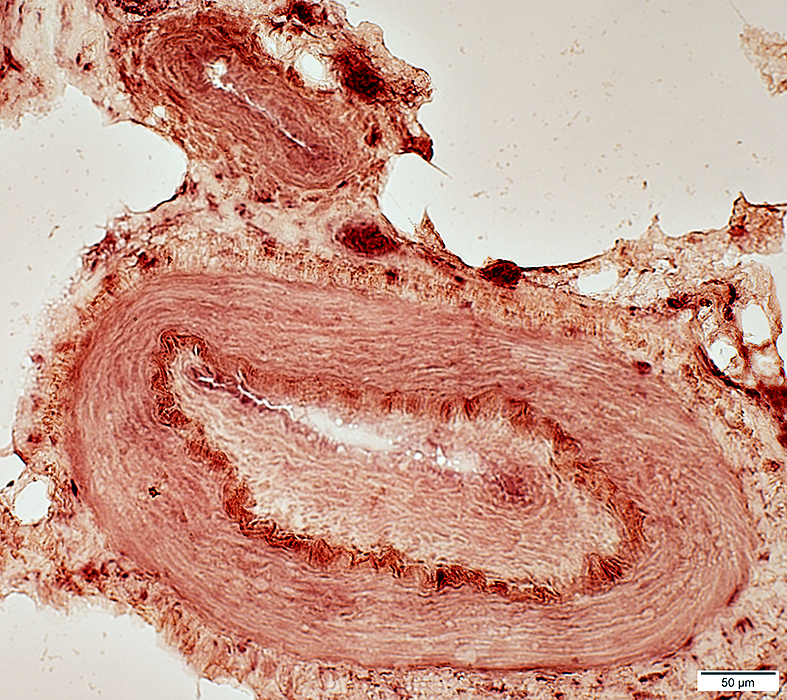 Acid phosphatase stain |
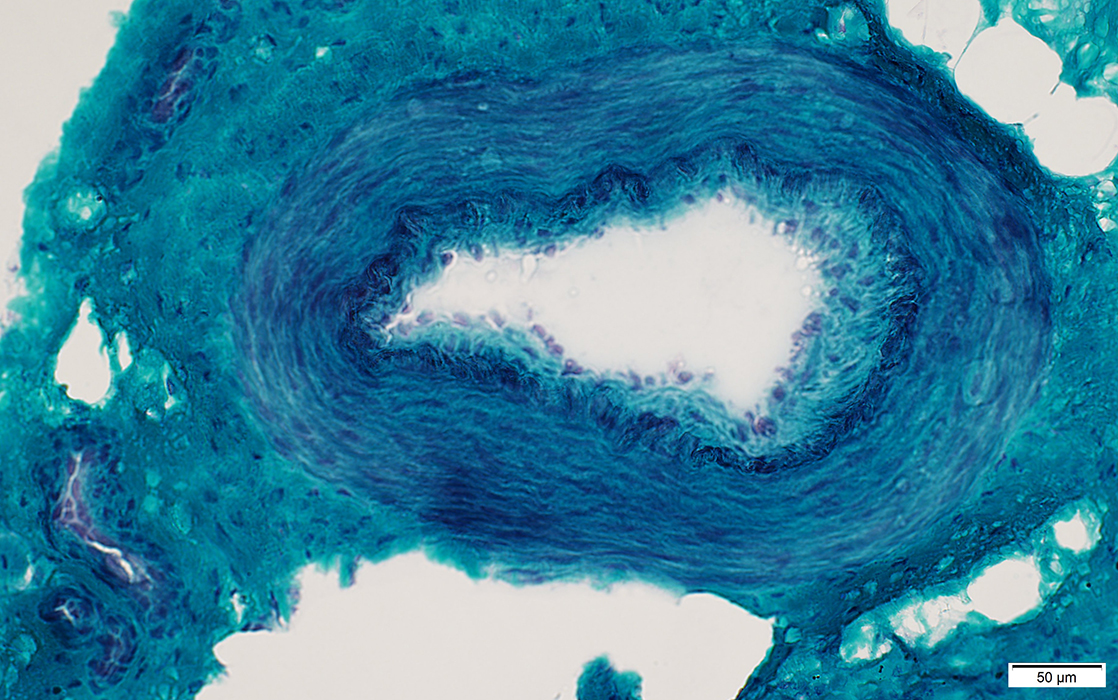 Gomori trichrome stain |
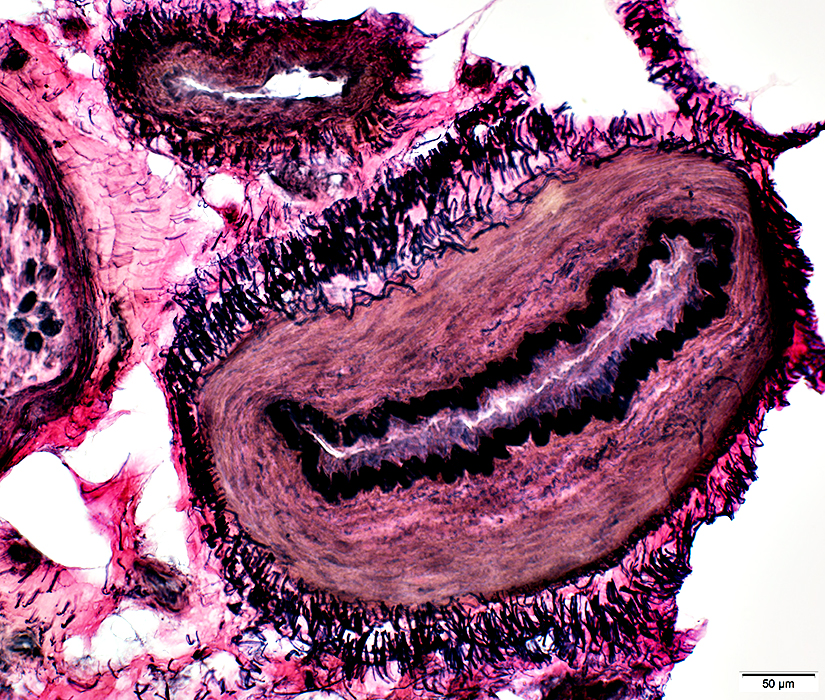 VvG stain |
Vasculitis
Damaged Artery Walls: Abnormal fibril layer in
Larger artery near nerve (Dark Arrow)
Smaller epineurial artery (White Arrow)
Axons
Myelinated axons: Severe loss
Unmyelinated, small axons: Relative preservation
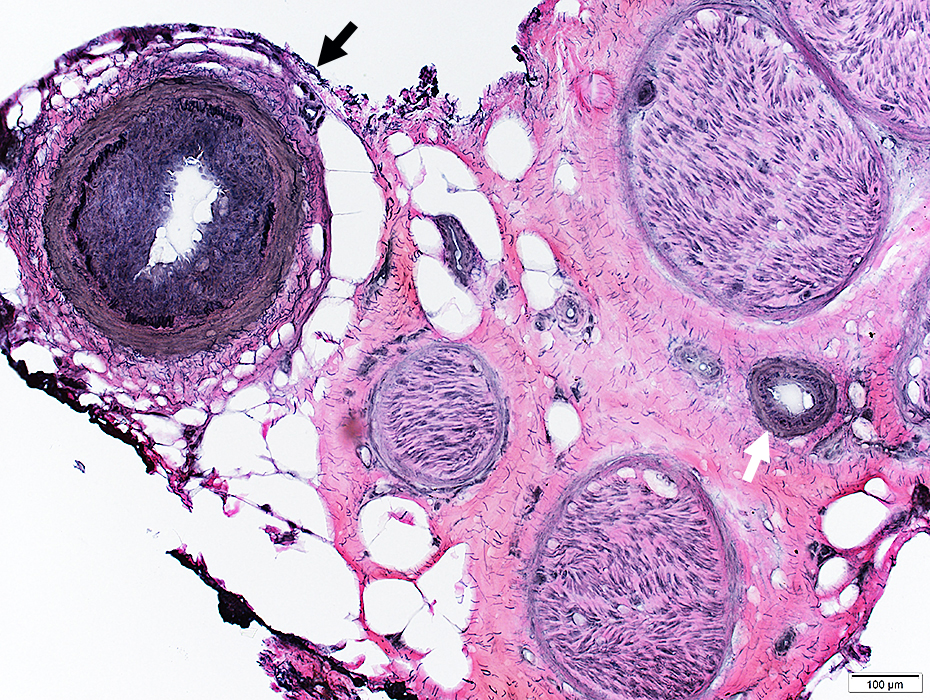 VvG stain |
Vasculitis: Larger artery
Discontinuous fibril layer
Intima proliferation
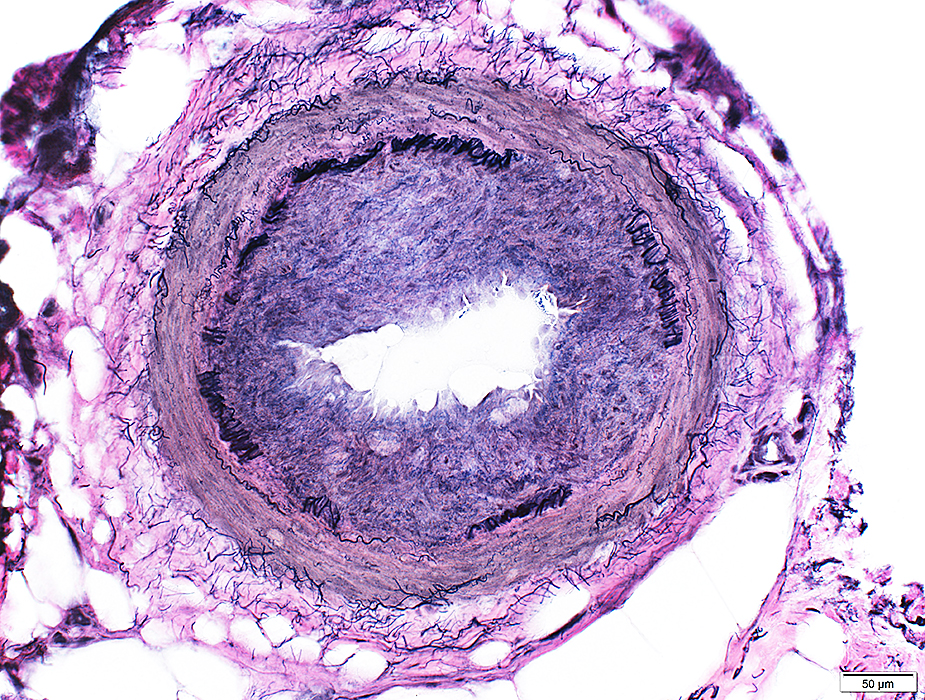 VvG stain |
Vasculitis: Epineurial artery
Abnormal fibril layer
Intima proliferation
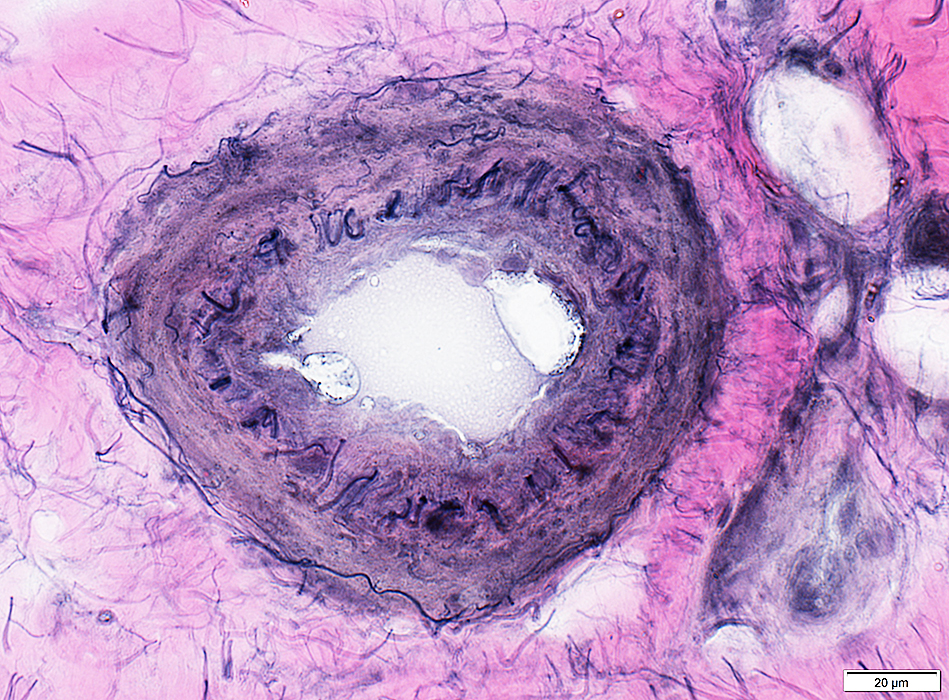 VvG stain |
Vasculopathy: Larger artery with abnormal wall
Fibril layer: Reduced number of fibrils
Intima proliferation, Mild
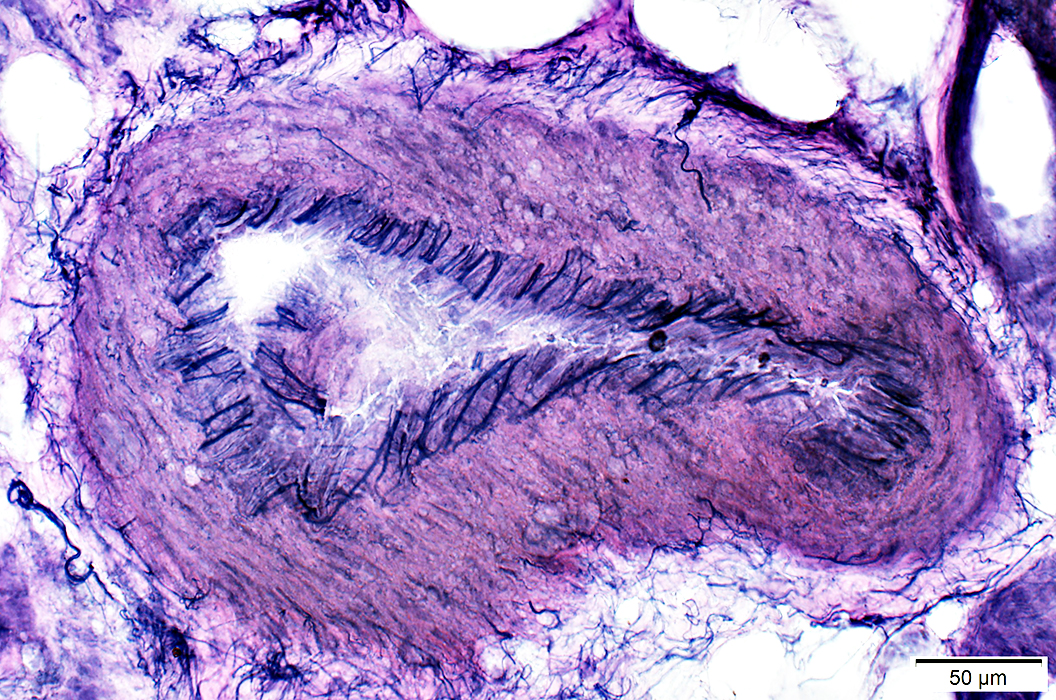 VvG stain |
Vasculitis: Axon loss
Large axons: Near complete loss
Small, unmyelinated axons: Relatively preserved
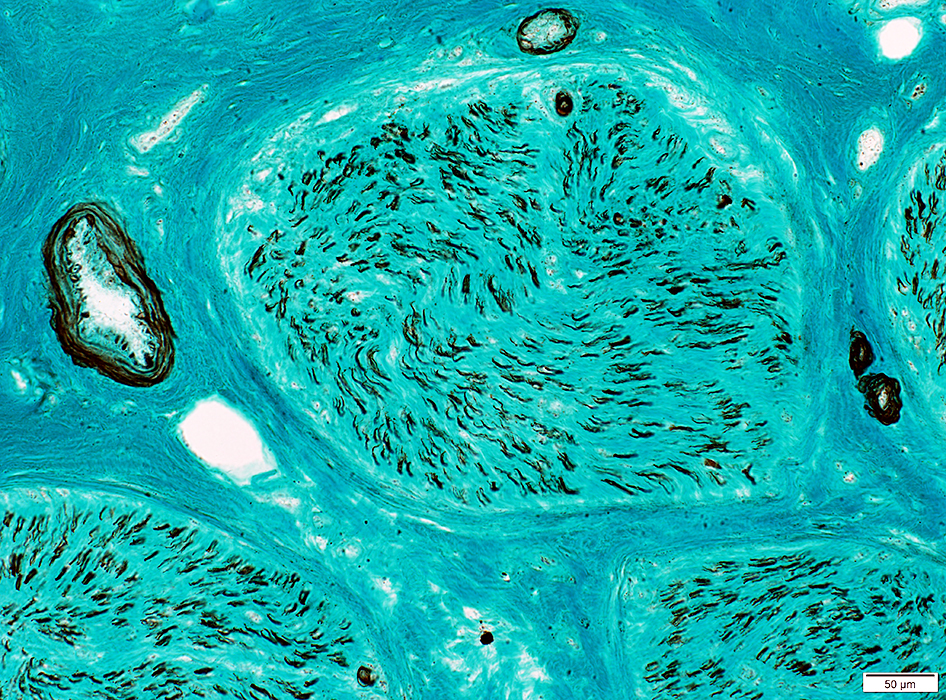 Neurofilament stain |
Vasculitis
Vessel wall: Contains blue mucinoid material inside elastin layer
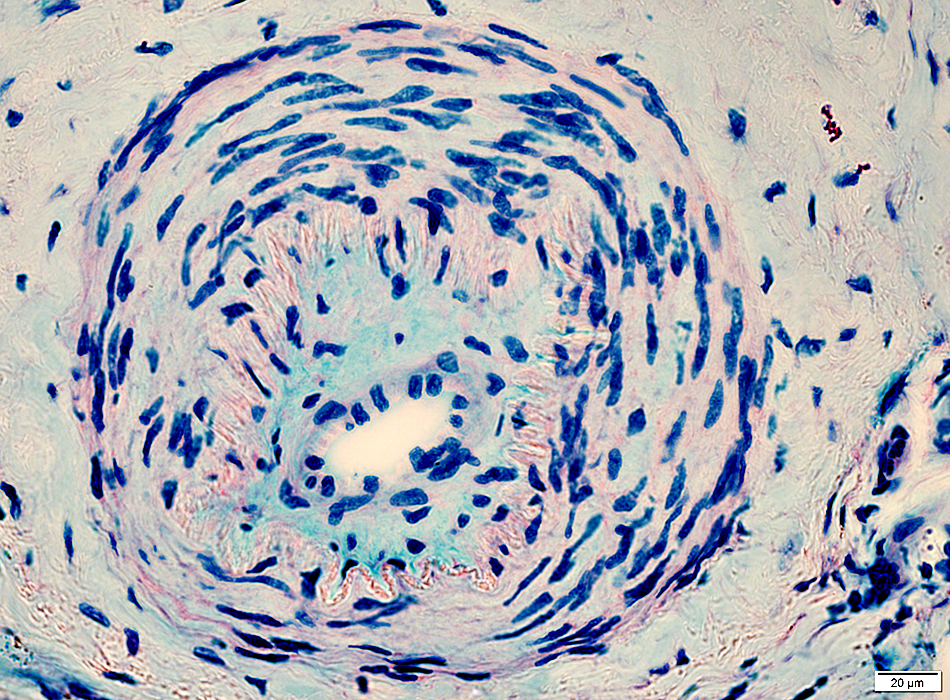 Alcian blue/Nuclear fast red |
Perivascular Inflammation
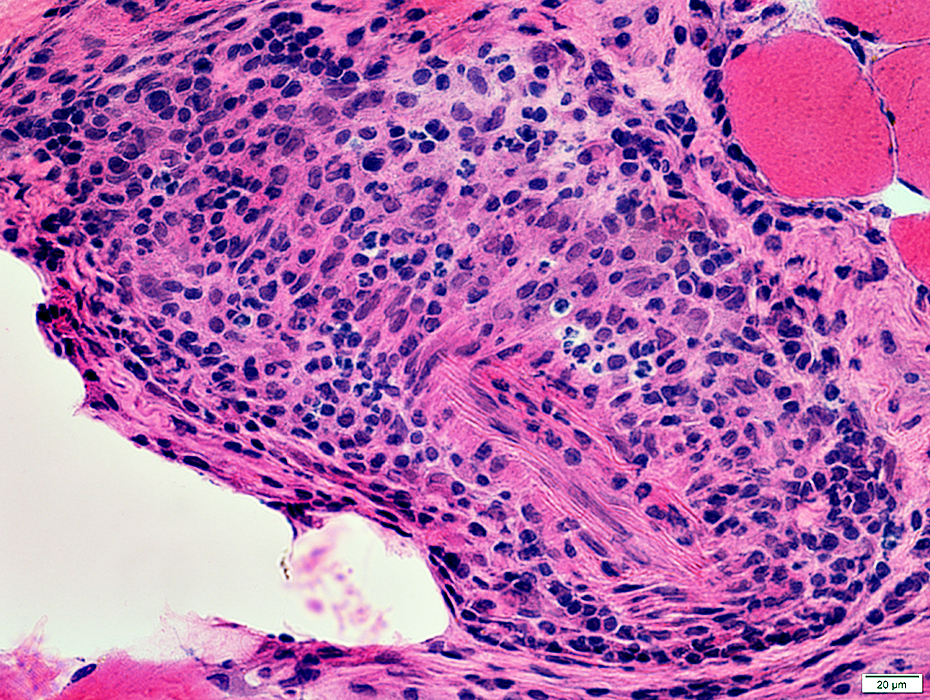 H&E stain |
Mixture of lymphocytes & histiocytes surrounds vessels
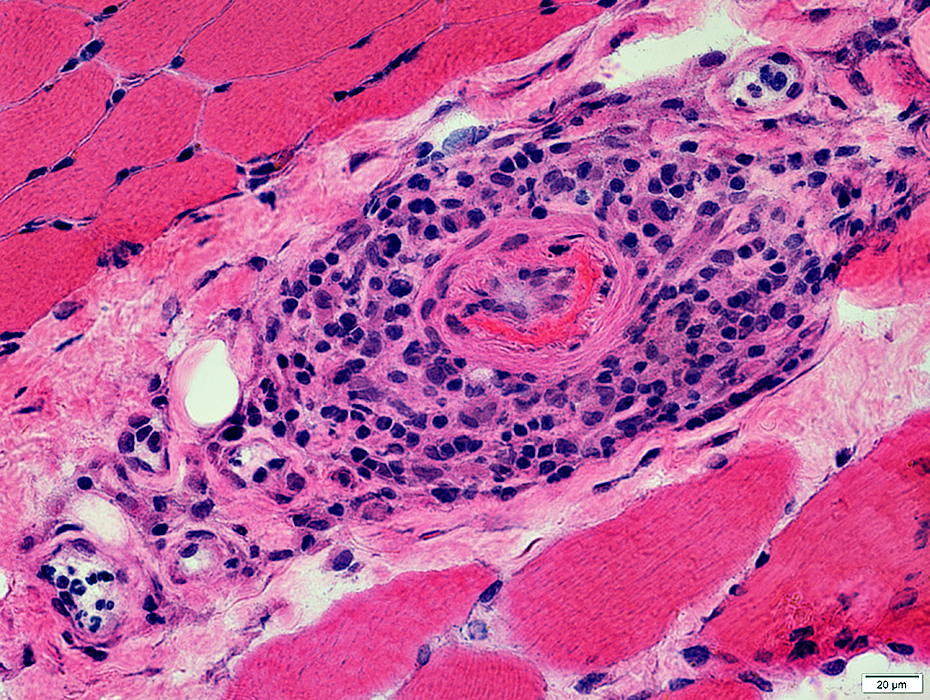 H&E stain |
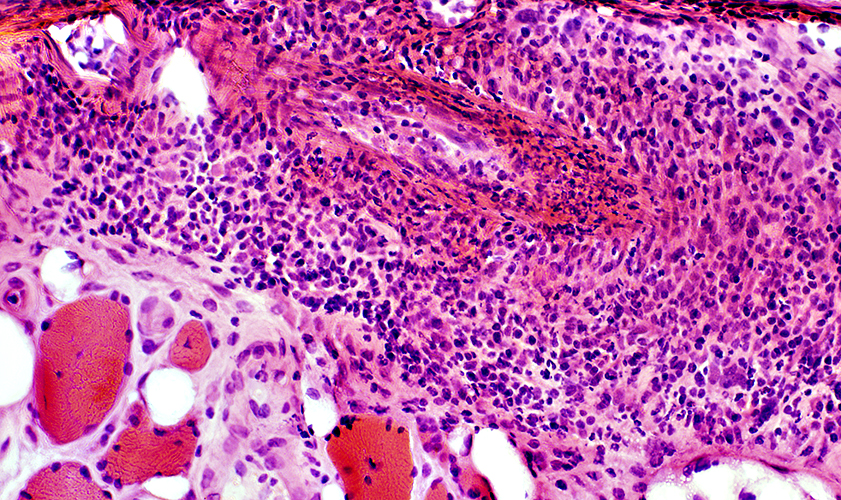 H&E stain |
VASCULITIS: Other Inflammatory features
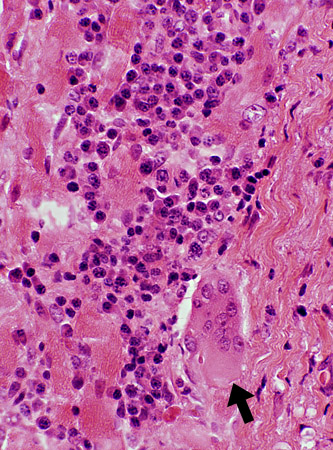 H & E stain |
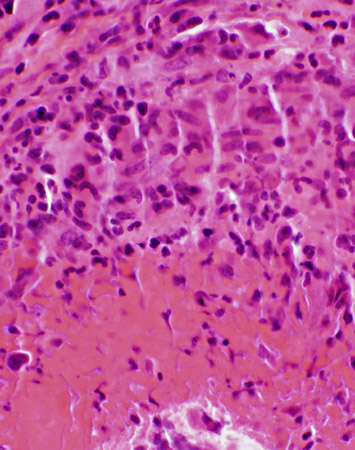 H & E stain |
Inflammation patterns
| |
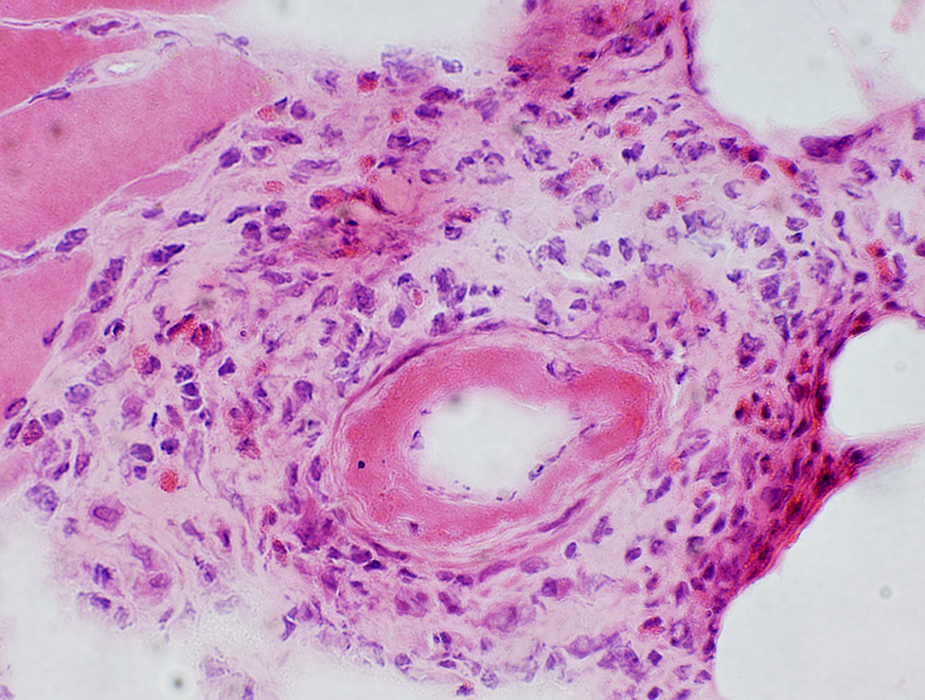 H&E stain Fibrinoid necrosis: In vessel wall Eosinophils: In perivascular inflammation |
|
Differential fascicular involvement of nerve
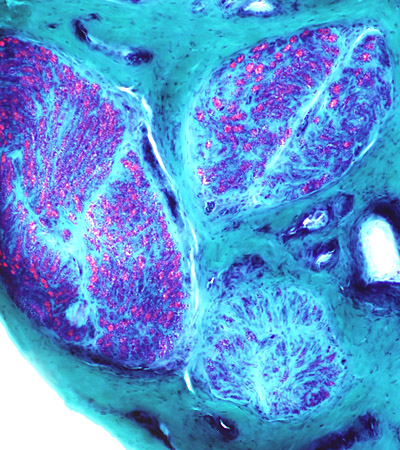 Gomori trichrome stain Different loss of myelinated axons in Different fascicles |
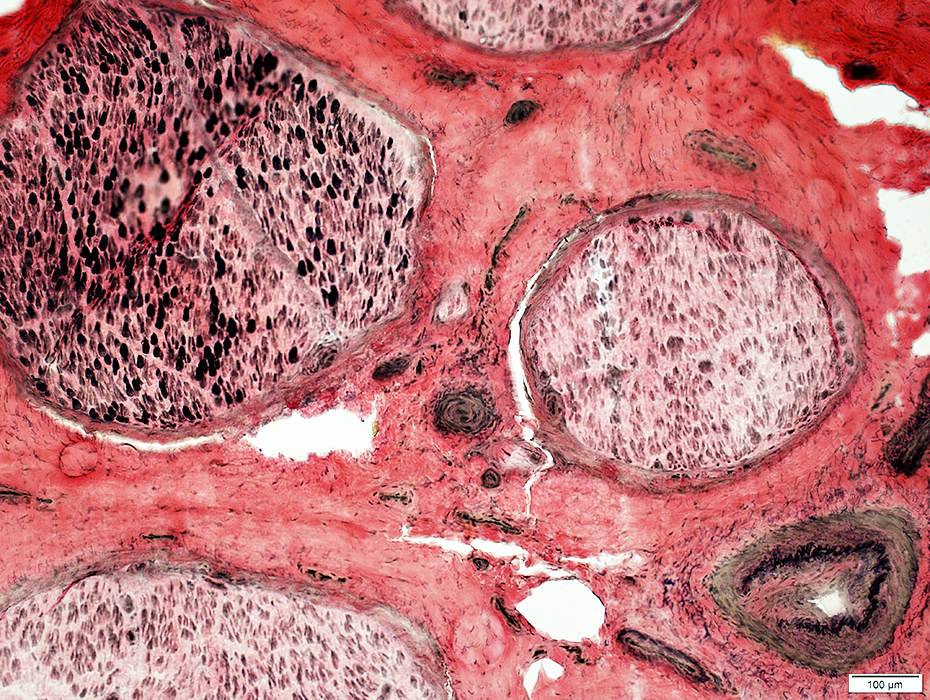 VvG stain Vessel fibril layer damage (Bottom Right) |
Vasculitis: Wallerian Degeneration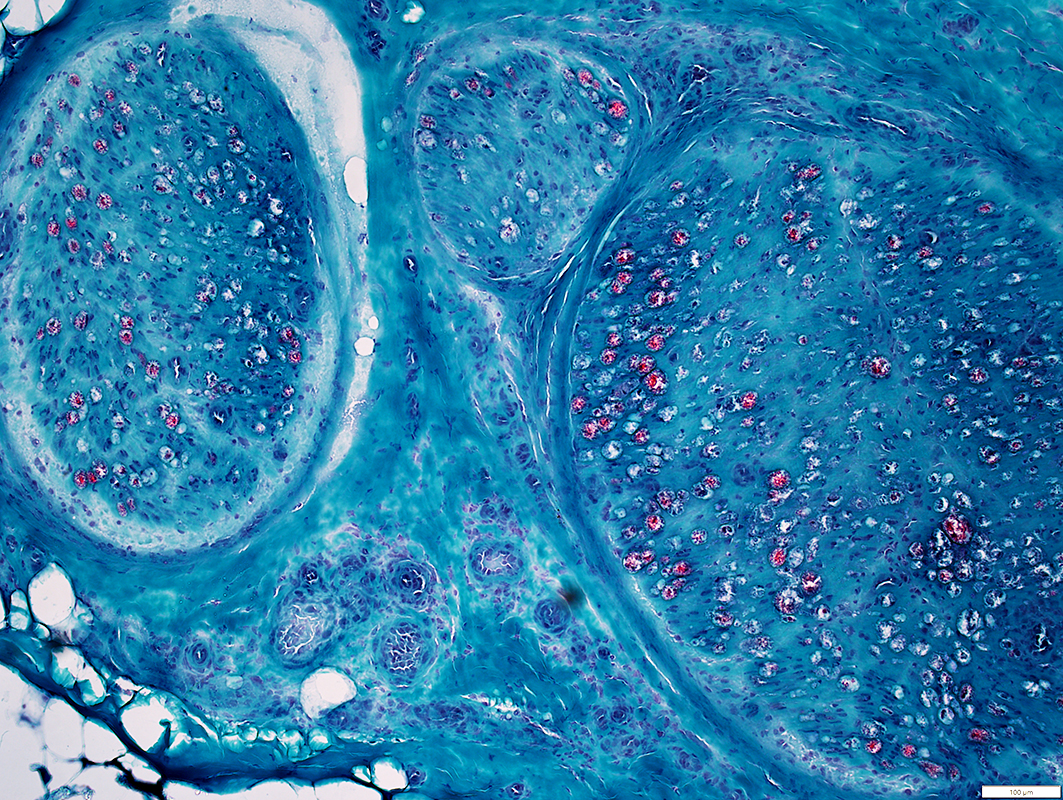
Gomori Trichrome stain |
Myelin on many axons has lost red staining properties
Vasculopathy: Larger vessels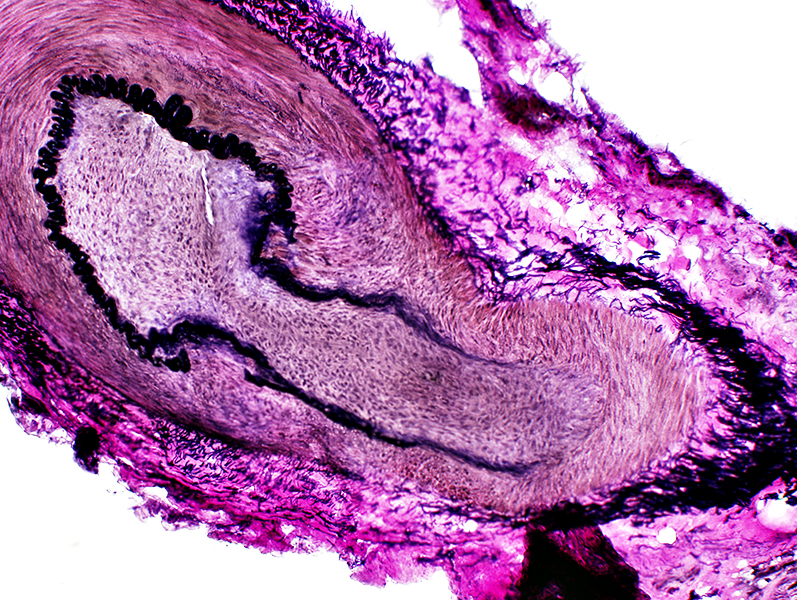 VvG stain |
Elastin fibril lamina: Interrupted
Intimal proliferation: Increased tissue inside fibril layer (See: Normal)
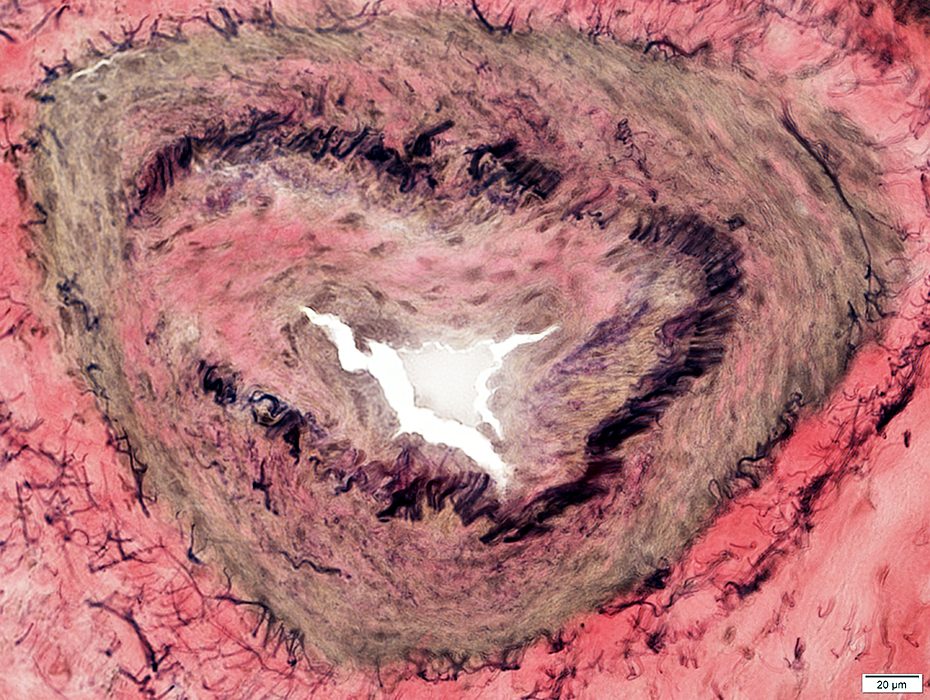 VvG stain |
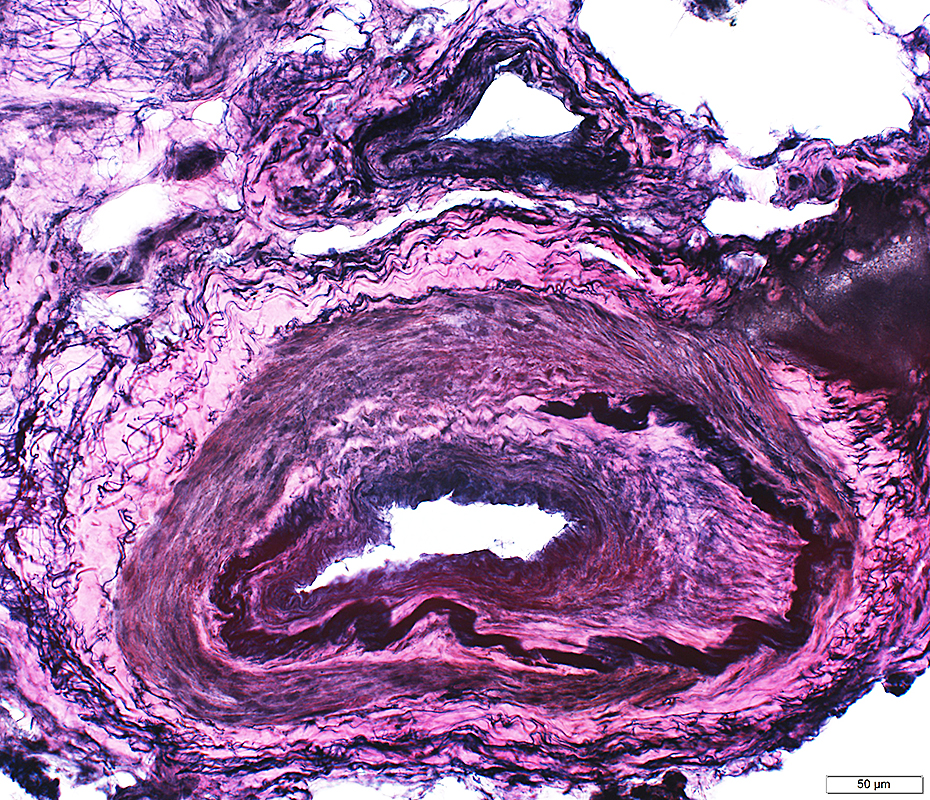 VvG stain |
Vessel wall: Contains Histiocytic cells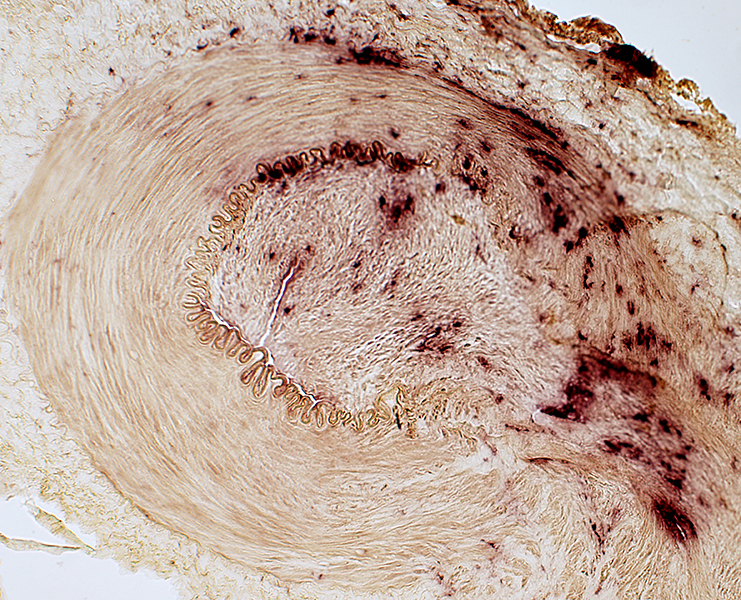 Acid phosphatase stain |
Vasculitis: Endoneurium
ATPase stain reduced except onendoneurial vessels
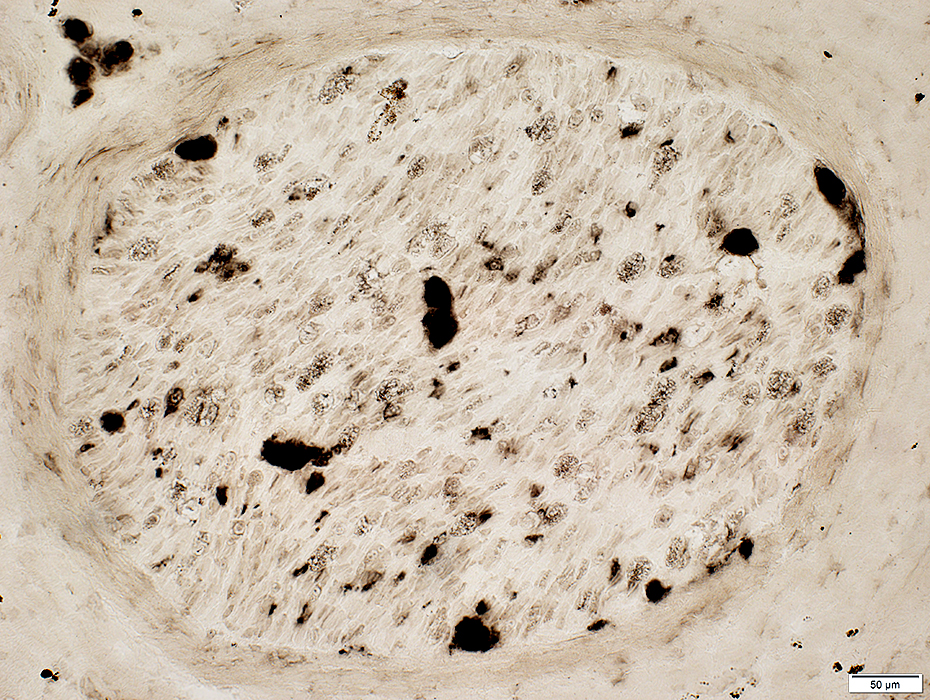 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Vessels: Intermediate-Sized
|
Normal Muscle Fetal Nerve |
Immune Myopathies DM-VP RIIM Vasculitis |
Normal Vessels
Nerve: Epineurial Veins & Arteries
|
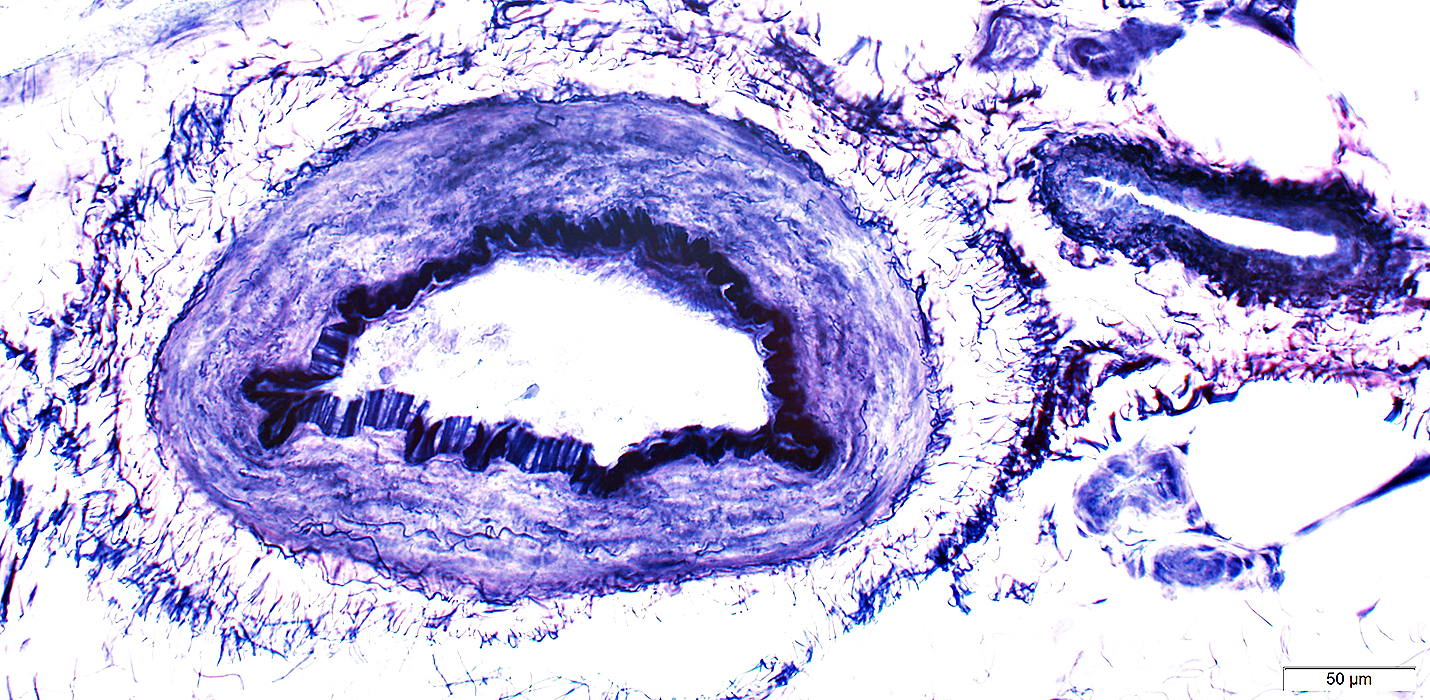
Artery (Black arrow): Linear fibrils near lumen; Thick wall Vein (White arrow): Interlaced, thin fibrils around outside of vessel; Thin wall 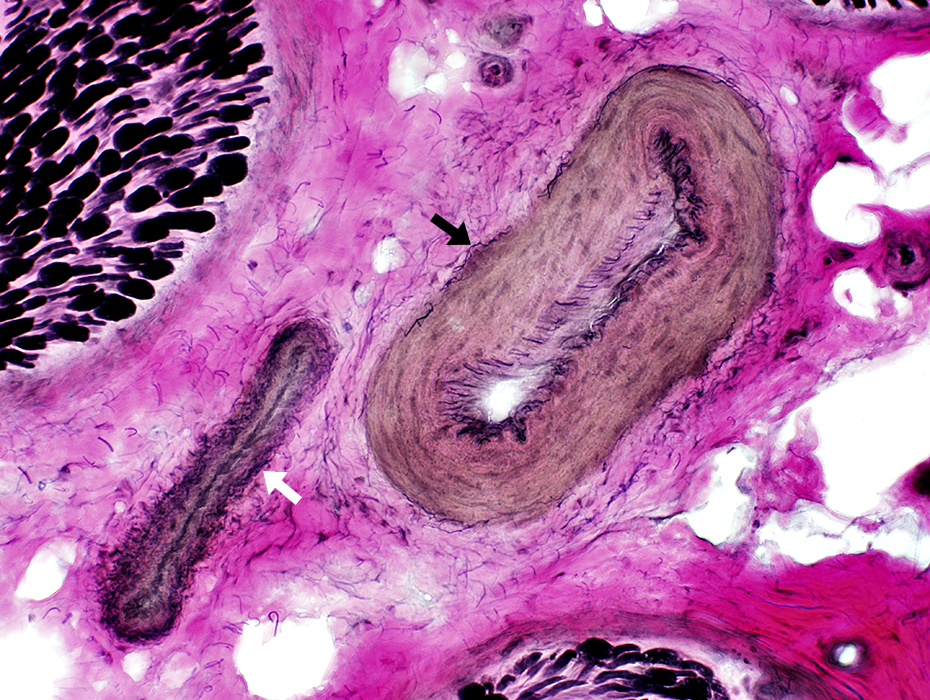 VvG stain |
Artery: Linear fibrils near lumen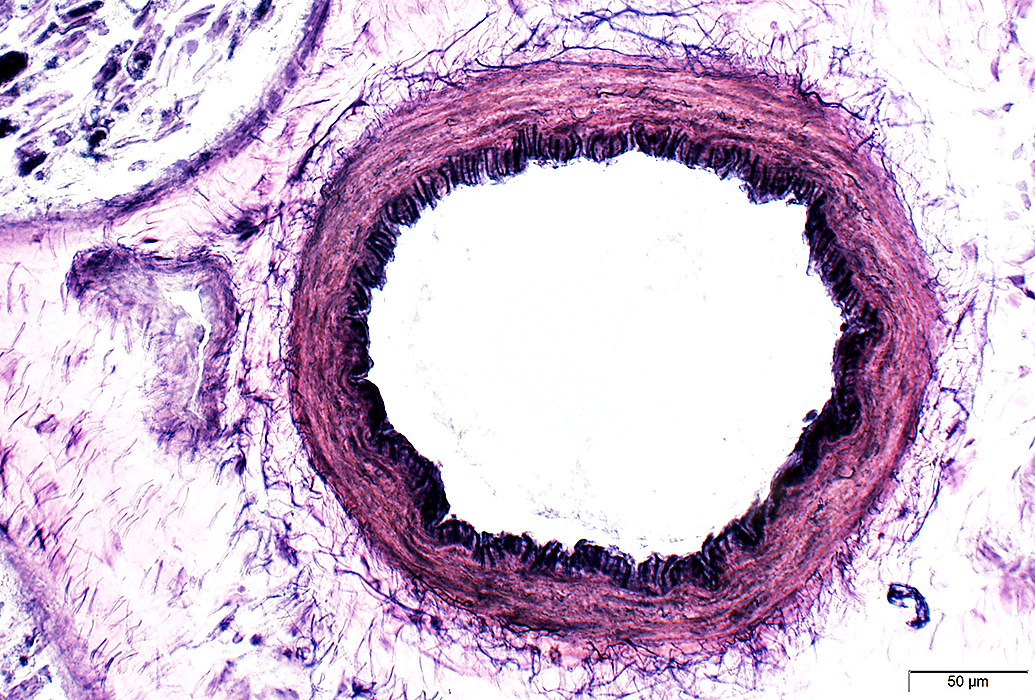 VvG stain |
Epineurial Artery: Normal
 Alcian blue stain |
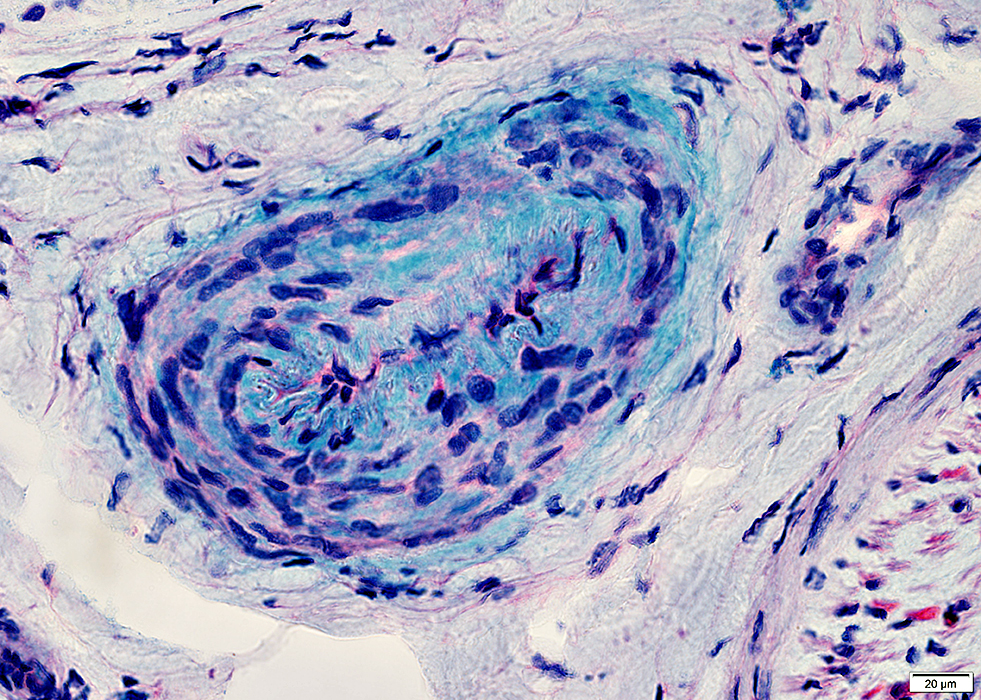
Epineurial Vein: Normal
Vein wall contains less mucopolysaccharide than artery
 Alcian blue stain |
Muscle: Perimysial Vein & Artery
Endothelial cell markers 6
Artery: SEMA3G, PCSK5, VWF
Vein: LRRC1, ACKR1, VWF
Capillary: ADGRF5, BTNL9, VWF
Artery (Top right): Linear fibrils near lumen; Thick wall
Vein (Bottom left): Interlaced, thin fibrils around outside of vessel; Thin wall
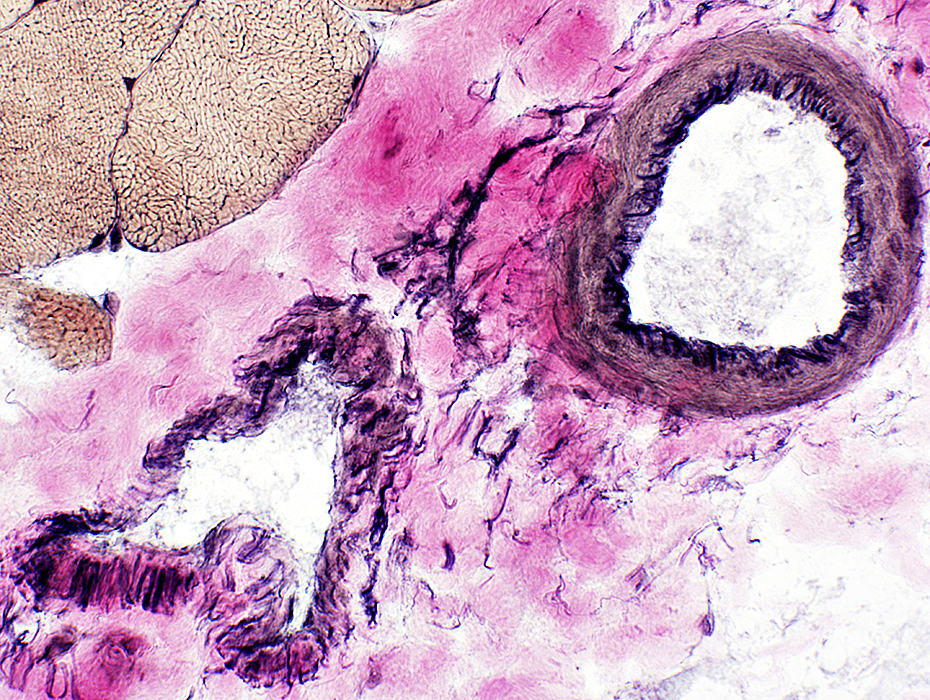 VvG stain |
Muscle: Perimysial structural variations
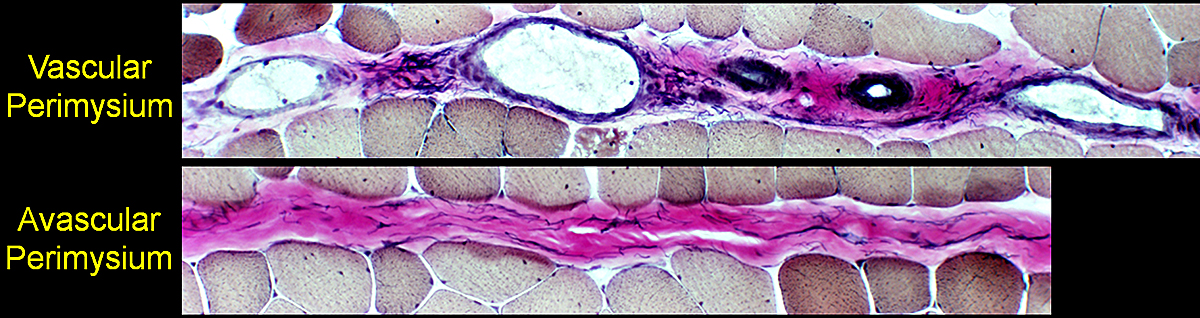
|
Avascular Perimysium: Contains connective tissue & fibrils, but no vessels
DM-VP: Muscle fiber atrophy is most often near avascular perimysium
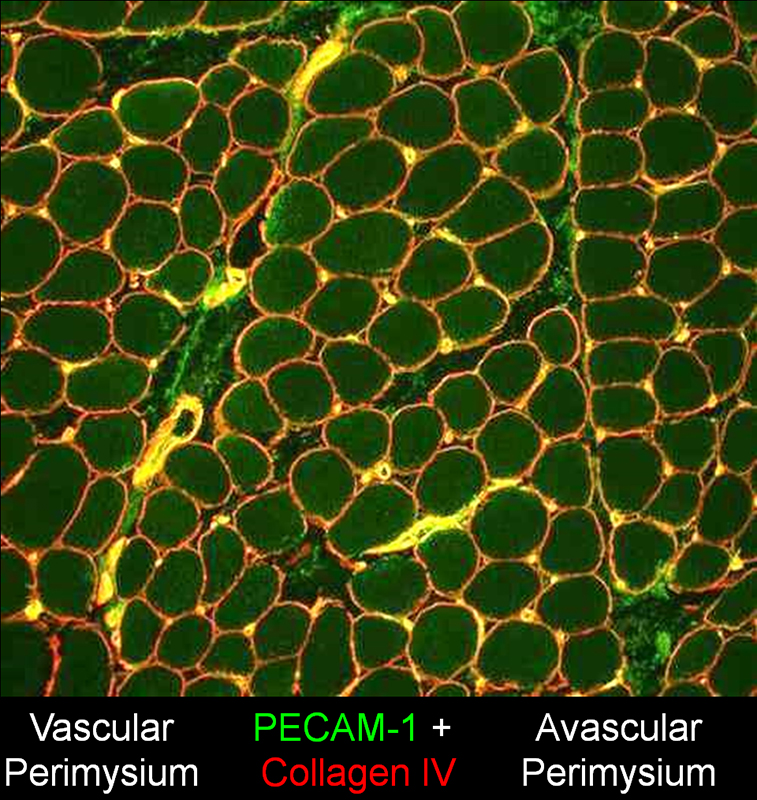
|
|
Elastin Forms a continuous ring inside the smooth muscle layer: Most prominent in artery Is present in a network outside the smooth muscle layer: Artery & Vein Vein (Bottom left) & Artery (Top right) 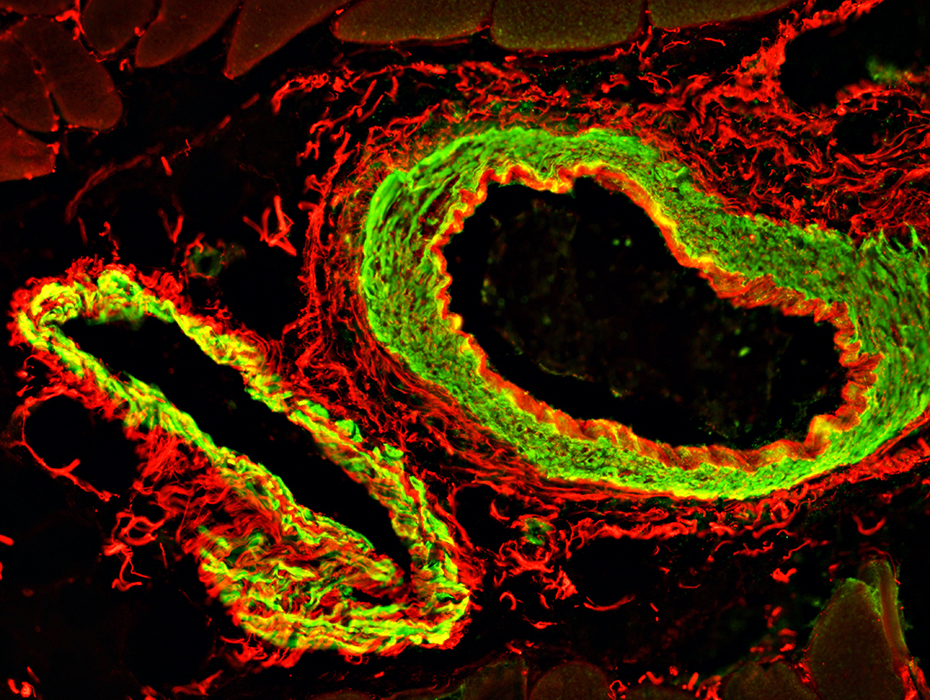 Smooth muscle actin (SMA) (Green) & Elastin (Red) stains |
|
PECAM (Endothelium marker) Fibrils inside the smooth muscle layer: Most prominent in artery Vein (Left) & Artery (Right) 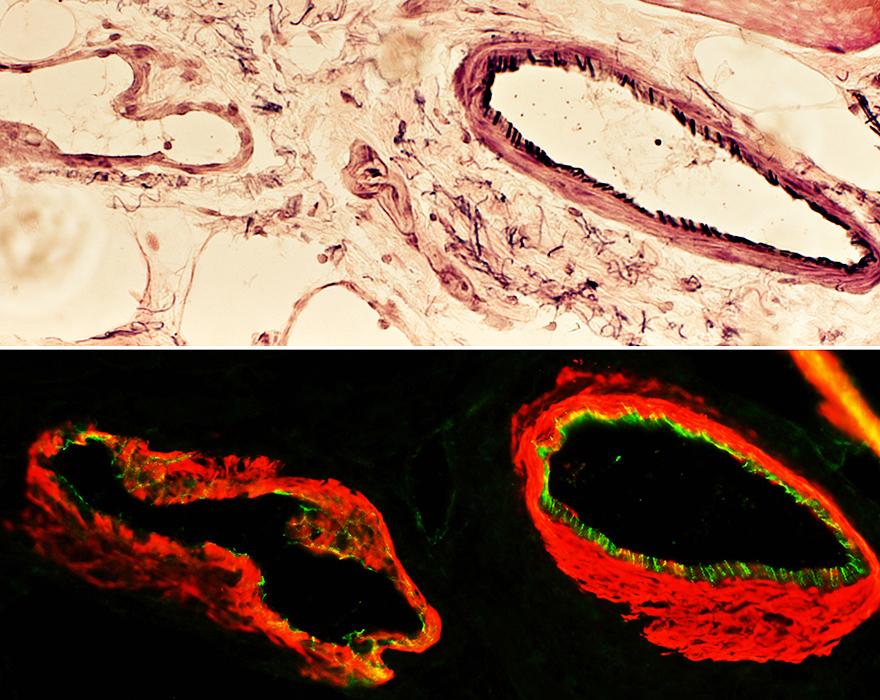 Smooth muscle actin (SMA) (Red) & PECAM (Green) stains |
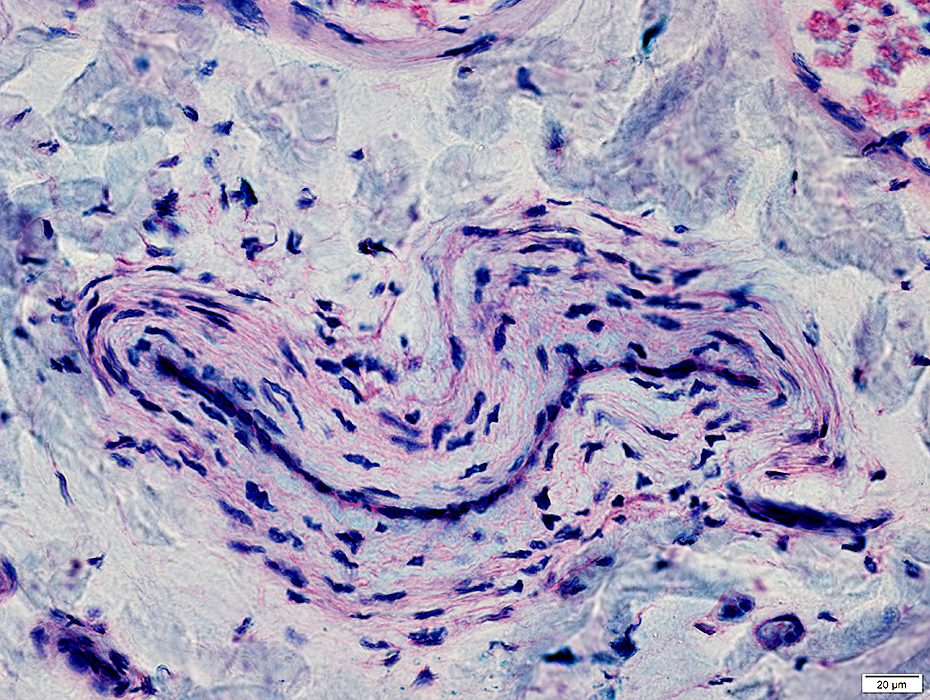
Epineurial Artery & Vein
Artery is mildly abnormal: Small cluster of connective tissue inside fibril layer
 VvG stain |
Syphilitic arteritis
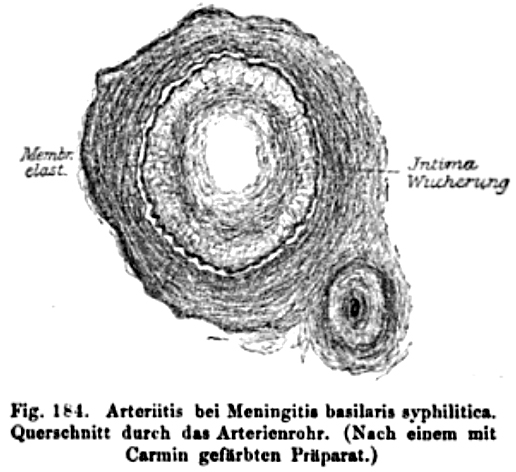 Oppenheim 1894 |
Go to Small vessel vasculopathy
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Vasculitis
References
1. Neuropathology 2022 Jun 15
10/18/2023