DIFFERENTIAL FASCICULAR LOSS OF AXONS
Axon loss: Patchy or Variable
Patchy axon loss is associated with
- Vasculopathies: Small & Large vessel
- Multifocal demyelination
- Perineuritis
- Leprosy
- Subperineurial edema
- Neoplasm: Lymphoma
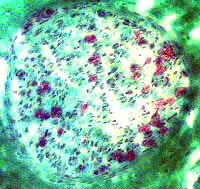
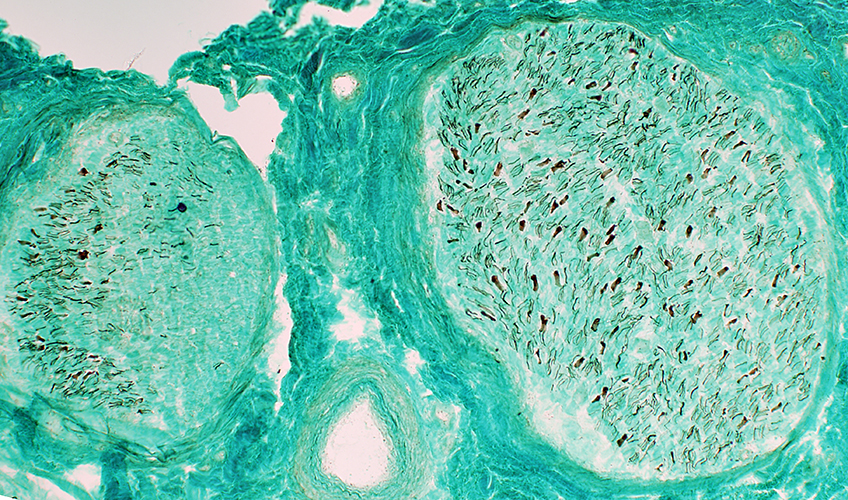
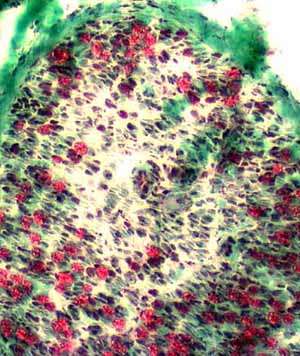
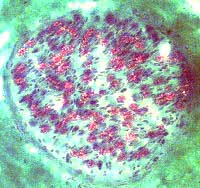 Gomori trichrome stain |
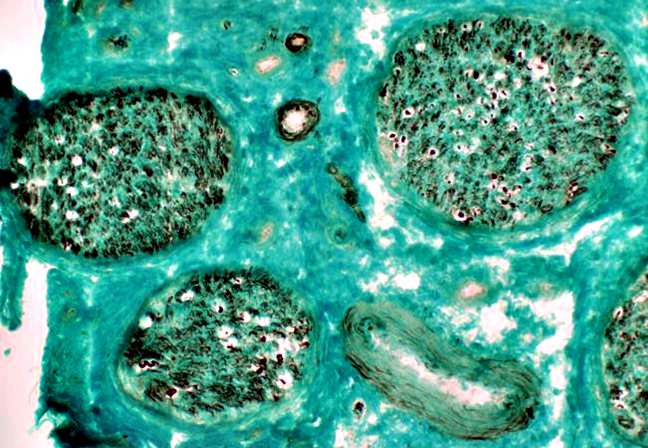
 Gomori trichrome stain |
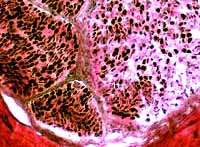 VvG stain |
|
Variable loss of myelinated (red) axons in the same nerve. Severe loss of myelinated axons in a fascicle on the left. More myelinated axons remain in an adjacent fascicle (right) |
Myelinated axon loss: More severe in larger fascicle (Right). | |
Myelinated axons: Variable loss among fascicles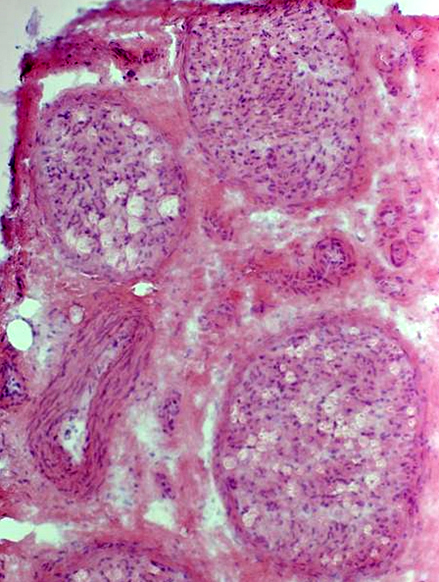 H&E stain |
Myelinated axons: Variable loss among fascicles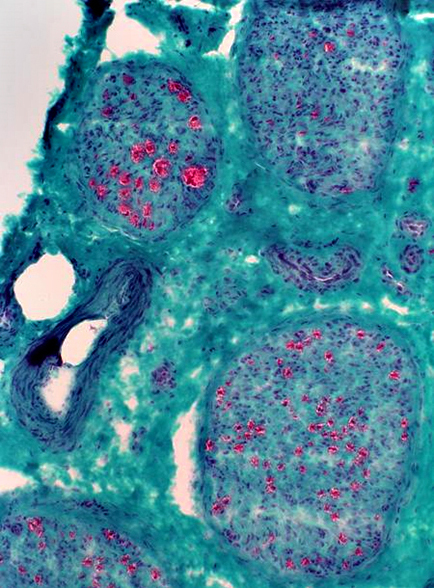 Gomori trichrome stain |
Myelinated axons: Variable loss among fascicles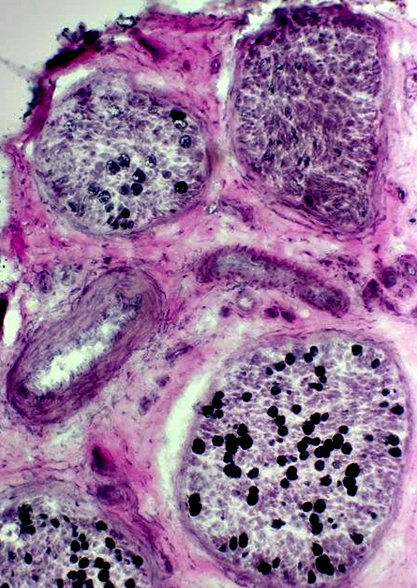 VvG stain |
Differential fascicular involvement: Endoneurial supporting cells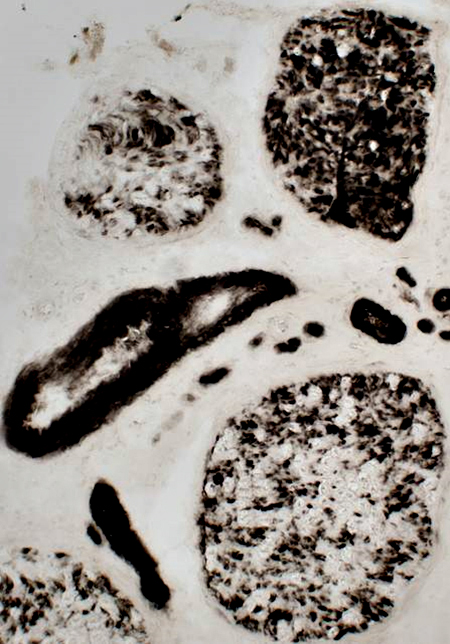 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
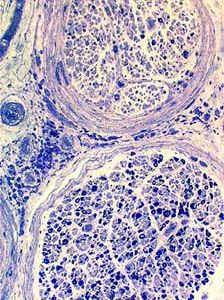
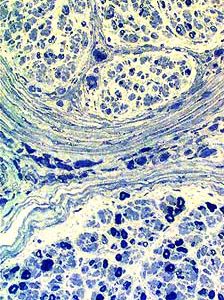 Toluidine blue stain |
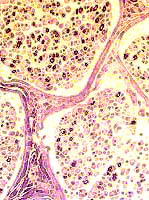 |
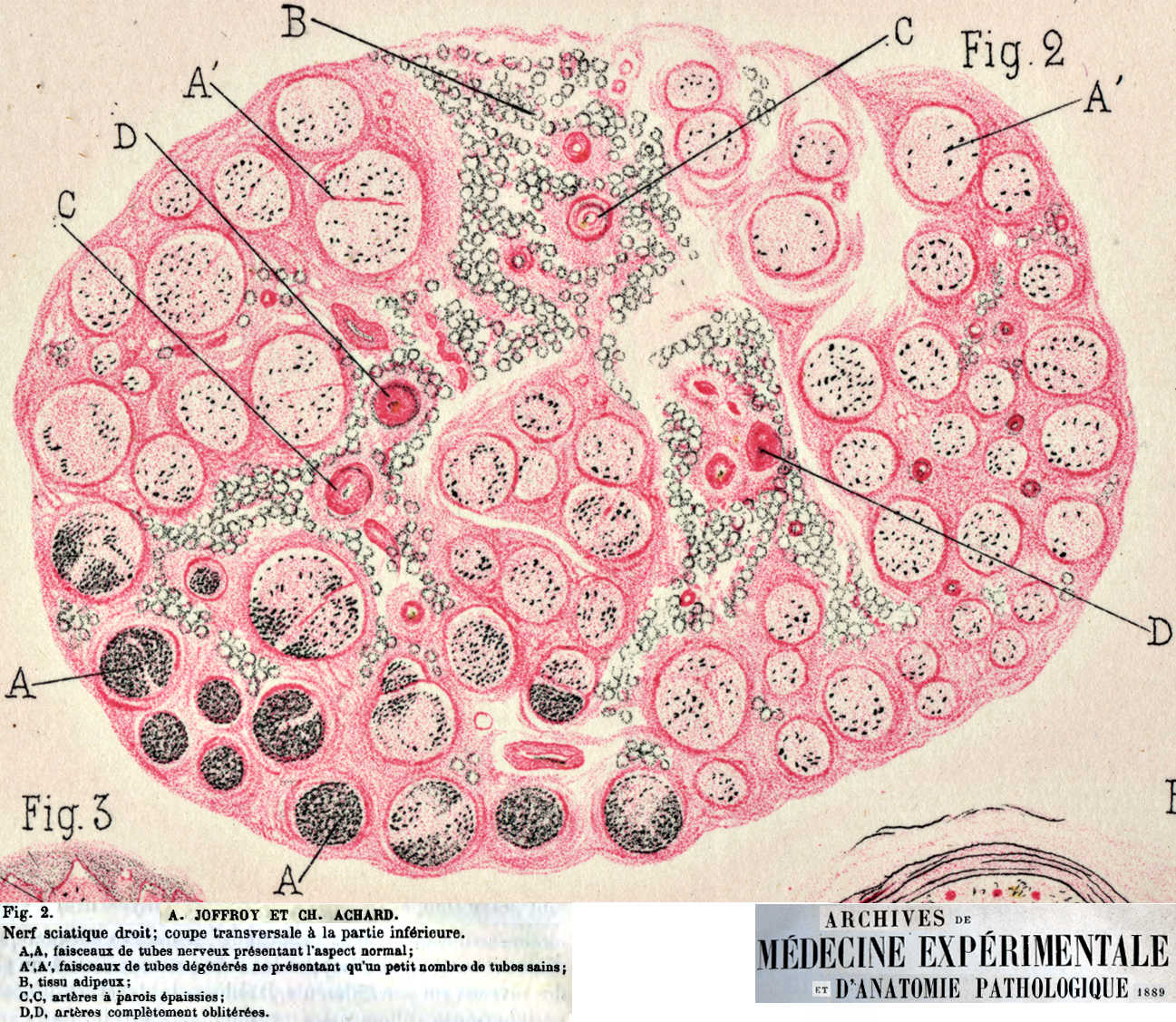
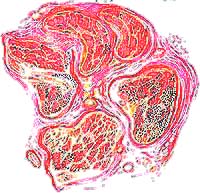 Drawing from Wiegert-Pal stain R. Cassirer (1910) Leprous polyneuropathy with differential fascicular loss of axons |
|
Myelinated axon loss: More in some fascicles than others.
|
||
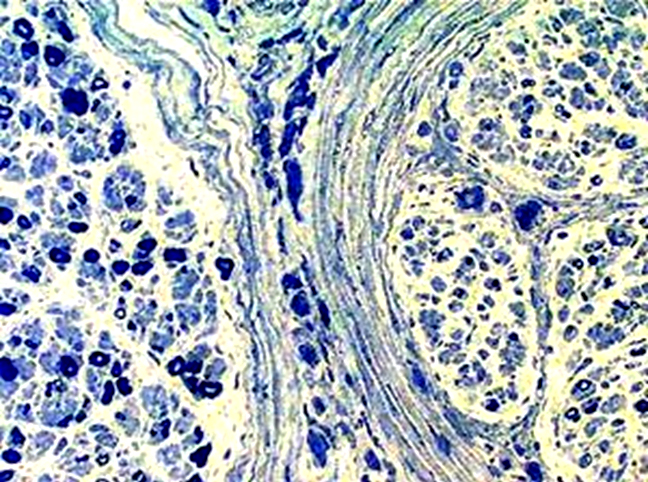
|
||
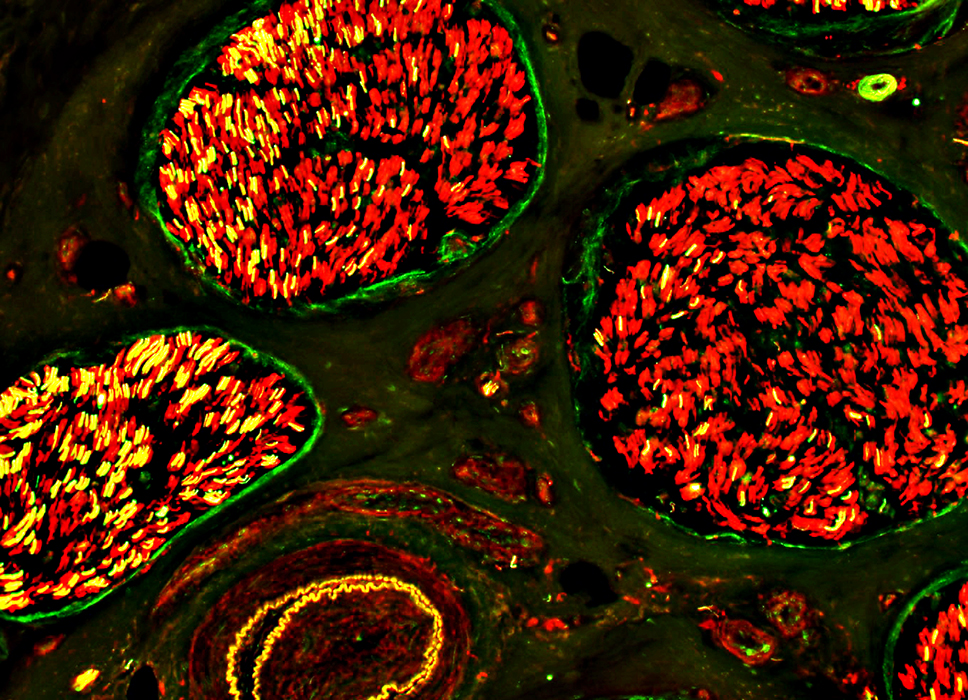
 Neurofilament stain |
|
Unmyelinated Axons: Differential Fascicular & Intrafascicular Loss
Non-myelinating Schwann cells (Red) in some areas have no associated axons (Büngner bands)
Epineurial vessel, Abnormal: Occluded lumen; Abnormal fibrillar layer
Axon loss: Varied
Large axons: Complete loss (No green stained axons)
Small axons (Yellow): Varied loss within, & among, fascicles
See: Control
 Green: Neurofilament stain Red: N-CAM stain (Non-myelinating Schwann cells) Yellow: Small unmyelinated axons surrounded by Schwann cells Photo by: Julia Sim |
Intrafascicular axon variation
|
|
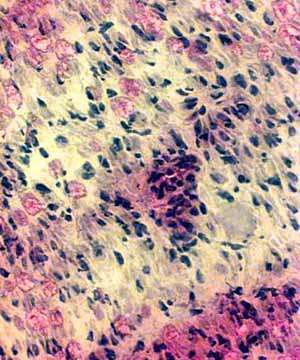
Focal inflammation around a small endoneurial vessel (Left). Localized loss of myelinated axons (red) around the vessel (Right). |
Nerve pathology associated with Vascular Occlusion
Axon Loss: More in some regions than others
Vascular pathology: Occlusion
 |
Axon loss: Varied among fascicles
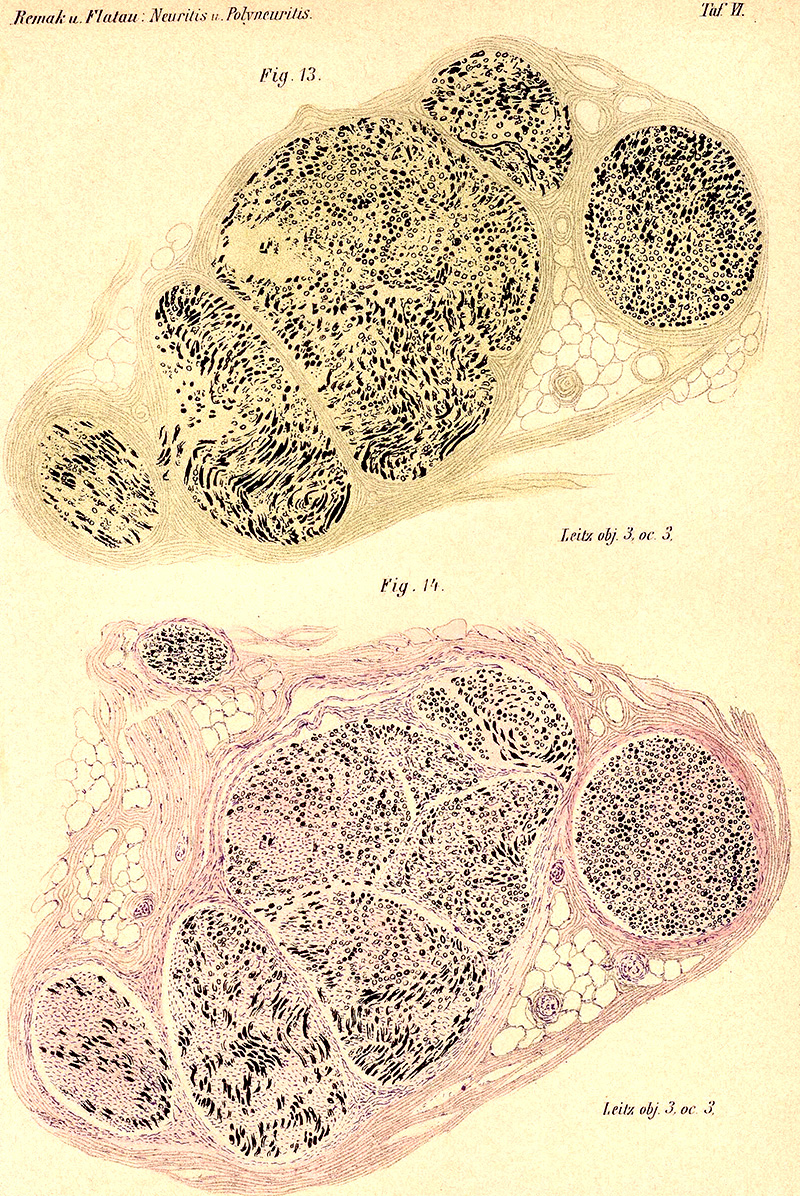
Remak
Also see: Axon loss
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Vasculitis
3/11/2019