- SLE: General Neurologic
- Most frequent: Central NS disease
- Clinical syndromes: Seizures; Cerebrovascular
- Timing of CNS disease
- Common early in disease
- May be initial presentation
- SLE: General Treatments
- 1st Line
- Hydroxychloroquine: All SLE patients; 5 mg/kg
- Corticosteroids (Prednisone)
- No major organ damage: < 7.5 mg/day
- Cerebritis, Nephritis, Thrombocytopenia: 40 to 60 mg/day
- NSAID: Joint pain
- 2nd Line
- Azathioprine: Nephritis, Severe SLE; 2 to 2.5 mg/kg/day
- Methotrexate: 7.5 to 25 mg/week
- 3rd Line: Severe SLE or Nephritis
- Cyclophosphamide
- Mycophenylate mofetil
- Rituximab
- Anifrolumab
- Belimumab
- Voclosporin
- SLE: Nerve
37
- Neuropathy: General
- Frequency
- General: 5% to 10%; Range 2% to 28%
- Increases over 1st 10 years of disease
- Rarely initial manifestation of lupus
- Multiple mononeuropathies
- Distal Symmetric Sensory-Motor
5
- Epidemiology
- Clinical
- Sensory
- Usually predominant
- Loss: Distal; Symmetric
- Pain
- Autonomic: GI reflux; Constipation
- Weakness: 40%
- Treatment: Corticosteroids
- Antibody association: Ro
- Electrodiagnostic studies
- Axon loss
- Progression
- Slow or none over years
- More in older patients
- Pathology patterns
- Small fiber neuropathies
- Frequency: 17% of neuropathies in SLE
- Onset age: Juvenile or Adult
- Patterns
- May be length, or non-length, dependent
- Some are asymmetric
- Treatment: ? Pain improved with corticosteroids
- Trigeminal neuropathy
- Distribution
- Usually 2 or more divisions affected
- Unilateral or Bilateral
- Sensory: Numbness & Pain
- Motor: Normal
- Treatment: Pain control
- Acute-onset neuropathy
- Pain
- Weakness: Diffuse
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs
- NCV: Axon loss; Distal latency long
- Course: Monophasic; May have relapses
- Treatment: ? Corticosteroids
- SLE: Muscle
36
- Clinical
- Myopathy
- Frequency in lupus: 3% to 9%
- More common in: African-Americans
- Onset: Before or after SLE onset
- Increased frequency with myositis
- Skin rash
- Pulmonary disorders: Hypertension; Fibrosis
- Gonadal failure
- Diabetes
- Cardiac: Pericarditis
- Arthritis
- CNS: Cognitive Δ
- Laboratory
- Immune myopathy: Serum antibody associations
- KL-6
- Ro-52 (75%): Active lupus
- Ku
- U1RNP (44%): Pulmonary hypertension; Raynaud"s
- dsDNA
- Serum CK: Often high
- EMG: Myopathy ± Irritability
- Muscle pathology
- Inflammation
- Frequency: 45%
- Location: Perimysial, Endomysial & Perivascular
- More in patients with perifascicular pathology
- Muscle fiber necrosis (60% to 80%)
- Fiber type changes
- Type 2 atrophy 85%
- Type 1 predominance 45%
- Capillary pathology
- SLE: Increased frequency of other autoimmune disorders
- SLE: Systemic
- Onset age: Mean 25 to 30 years
- Arthralgia
- Fatigue
- Hematologic
- Skin
- Photosensitivity
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Malar rash
- Alopecia, Non-scarring
- SLE: Autoantibodies
45
- ANA
- Frequency: 100%; Necessary for diagnosis
- Patterns: Homogeneous; Speckled
- dsDNA
- 70% of SLE
- Levels related to disease activity: Especially lupus nephritis
- Sm
- 30% of SLE
- May relate to renal & CNS lupus
- U1snRNP
- 13% of SLE
- Musculoskeletal & Lung involvement
- SLE specificity: IgM > IgG
- Ro52 (SSA)
- Histone H1: SLE disease activity
- Histone H2A-H2B: Drug-induce lupus
- β2-Glycoprotein: Thrombosis & CNS
- Ribosomal P protein
- 15% of lupus
- High specificty
- Phospholipid
- 30% of lupus
- Thrombosis & Hypertension
- N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: CNS
- Cardiolipin: Thrombosis
- C1q: Higher in SLE nephritis
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Diagnostic Evaluation (EULAR/ACR)
42
|
| Mandatory: ANA ≥ 1:80 |
| Organ |
Feature |
Dx
Points |
| Pulmonary |
Effusion
Pleural, or
Pericardial |
5 |
| Cardiac |
Pericarditis,
Acute |
6 |
| Constitutional |
Fever > 100.9°F |
2 |
| Mucosal |
Alopecia, nonscarring
Ulcers, Oral
Lupus Rash
Skin/Discoid, Subacute
Skin, Acute/Malar
|
2
2
4
6 |
| Skeletal |
Joint Δ |
6 |
| CNS |
Delerium
Psychosis
Seizure |
2
3
6 |
| Hematologic |
Leukopenia (WBC < 4,000/mm2)
Thrombocytopenia (Platelet < 100,000/mm2)
Hemolysis, Immune |
3
4
4 |
| Immune |
Cardiolipin IgG Ab
β2-Glycoprotein 1 Ab
Lupus anticoagulant
C3 or C4 low
C3 + C4 low
dsDNA or Sm Ab |
2
2
2
3
4
6 |
| Renal |
Proteinuria/24 hr > 0.5g
Renal bx Nephritis
Lupus II or V
Lupus III or IV |
4
8
10 |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Dx + =
Total points ≥ 10 + ANA ≥ 1:80
|
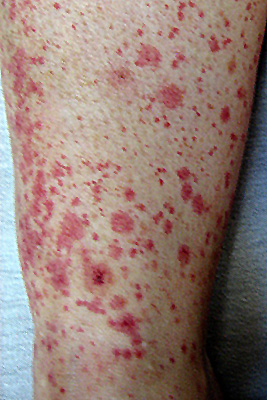
From: M Al-Lozi
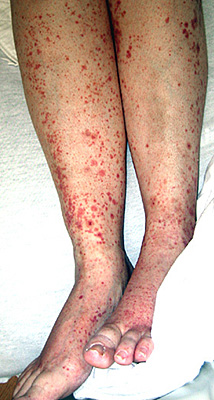
SLE vasculitis
|
|