Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
General topics Antibodies ANCA Cytoplasmic DNA Myositis-Overlap Myositis-Specific Nuclear Nucleolar Ribonucleoproteins Striational tRNA synthetases Types Complement Connective tissue disorders Lambert-Eaton myasthenia M-protein Amyloid: Light chain Anti-Decorin myopathy: IgM Scleromyxedema: IgG Myasthenia gravis Neuropathy Scleroderma |
Specific antibodies |
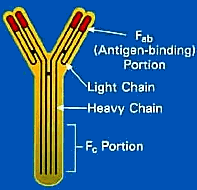 |
|
Antibody types Cytoplasmic Nuclear Nucleolar Phospholipid Myositis-associated tRNA synthetase Juvenile Other Myositis overlap |
MYOSITIS-ASSOCIATED ANTIBODIES: General
8
|
| MYOSITIS-ASSOCIATED ANTIBODIES | ||||
| Aminoacyl t-RNA synthetase Antibodies: IMPP syndromes | ||||
| Autoantibody | tRNA-Synthetase Antigen | Antigen function | Clinical associations | HEp-2 IIF pattern |
|
Jo-1
|
Histidyl |
Protein synthesis Intracytoplasmic Amino acid binding to cognate tRNA |
PM 15%-30%; DM-like 13% Lung fibrosis (ILD) Skin rash: Mechanics hands Raynauds Arthritis Fever Specificity > 95% HLA: DRw52; DRB1*0301 |
Cytoplasm: Speckled |
| PL-7
|
Threonyl | PM/DM 3%-5% of cases Antibody +: ILD > 90% Milder than Jo-1 |
Cytoplasm: Speckled | |
| PL-12
|
Alanyl | PM/DM 3% Antibody +: ILD > 90% Skin lesions |
Cytoplasm Speckled (dense) |
|
|
EJ
|
Glycyl | Antibody +: ILD > 90%; DM 10% to 80% |
Cytoplasm | |
| OJ
|
Isoleucyl | PM/DM <3% Antibody +: ILD > 90% Skin lesions |
Cytoplasm | |
| KS
|
Asparaginyl 12 | Antibody +: ILD > 90% Myositis: 25% Skin lesions Japanese |
Cytoplasm | |
| Zo
|
Phenylalanyl | Myopathy + ILD | Cytoplasm | |
| Ha (YRS)
|
Tyrosyl | Antisynthetase syndrome | Cytoplasm | |
| Other Antibodies | ||||
| Autoantibody | Antigen | Antigen function | Clinical associations | HEp-2 IIF pattern |
| SRP | Signal recognition particle 54 kD protein In 7SL-RNA complex |
Protein translocation Intracytoplasmic (Endoplasmic reticulum) |
Immune polymyopathy Specificity 93% Acute onset; Severe HLA DRw52 |
Cytoplasm: Speckled Nucleolus |
| Mi-2
|
Helicase protein part of NuRD complex |
Nuclear transcription | DM 5% -35%; PM 5%-9% HLA DRw53 Rash: V- & Shawl-sign Cuticular overgrowth |
Nucleoplasm Fine speckled |
| PMS1
|
PMS1 | DNA mismatch repair enzyme |
Immune myopathy (7%) DM/PM/Fasciitis |
|
|
TIF1γ/TIF1α p155/p140 14 |
Transcriptional intermediary factors (TIF; TRIM33): p155 = 1γ |
Nuclear transcription Cellular differentiation |
Dermatomyositis (20%) JDM (32%) Skin ulceration & edema Cancer-associated DM (75%) |
Nucleus |
|
MDA5
|
IFIH1 (CADM-140) | Immunity vs viral infection Detection of viral dsDNA |
Dermatomyositis, Amyopathic ILD: Rapid progression Skin: Ulcers; Palmar papules |
Cytoplasmic |
|
NXP-2
|
Morc3 |
Nuclear transcription | Dermatomyositis, Juvenile (23%); Calcinosis Adults: Lung Δ; Neoplasm |
Cytoplasm |
| SAE | Small-ubiquitin-like modifier enzyme (SUMO) |
Post-translational modification Nuclear transcription factors |
Dermatomyositis, Adult (< 5%) Amyopathic early |
|
| Decorin | Chondroitin sulfate | Extracellular matrix | Immune myopathy | Basal lamina |
| Ku
|
Thyroid autoantigen, 70-kD G22P1 |
DNA protein kinase regulatory subunit |
Systemic sclerosis PM/Scleroderma Japanese |
Nucleolus & Nucleus Homogeneous |
| KJ | ? Translation factor | PM < 1%; Raynaud's Lung Fibrosis |
Cytoplasm Speckled (dense) |
|
| HMGCR (200/100) |
3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl -Coenzyme A Reductase |
Cholesterol biosynthesis | Myopathy + Myalgias ? Statin use |
|
| Mup44 | NT5C1A | IM-VAMP; sIBM Systemic sclerosis; SLE |
||
| Cortactin |
CTTN | Immune myopathies | ||
| Nuclear pore |
Nuclear pore proteins | Myopathy + Systemic | ANA: Peripheral | |
| FHL1 |
FHL1 | PM > DM > IBM | ||
MYOSITIS-OVERLAP ANTIBODIES
|
|||
| Autoantibody | Antigen | Clinical associations | HEp-2 IIF pattern |
| PM-Scl | Exosome: RNA processing complex PM/Scl-100 PM/Scl-75 |
PM 8%-12% Scleroderma 25% Caucasian |
Nucleolus & Nucleus Homogeneous |
| 56 kD | RNP component | PM/DM 87% Other CTD 10% High with active disease |
|
| SSA/Ro | 2 proteins & 4 small RNAs |
PM/DM 5%-10% Sjögren's 90% |
Nucleoplasm Fine speckled |
| U1-snRNP | 3 proteins: 22, 33 & 70 kD |
PM/DM 4%-17% SLE & Scleroderma 30% MCTD 95% |
Nucleoplasm Speckled |
| U2-nRNP | Small nuclear RNP | PM/DM 4%-17% SLE & Scleroderma 30% |
Nucleoplasm Speckled |
| U3-nRNP | |||
| Fer
|
Elongation factor 1a | PM/DM (rare) | |
| MAS | tRNA bindingSer protein |
PM/DM (rare) HLA DRw53 Rhabdomyolysis Myalgias |
Diffuse cytoplasm |
| Mitochondrial | PDC-E2 | Histiocytic IM 1° Biliary cirrhosis Disease severity |
Speckled |
| HSF1 | HSF1 |
IIM + Neoplasm: 17% Other: RA, Sjögren 12% |
|
|
General Antibodies EJ Jo-1 OJ PL-7 PL-12 Other tRNA synthetases |
|
|
|
|
|
Epidemiology Antigens Adults Children Subtypes DM: DDx |
|
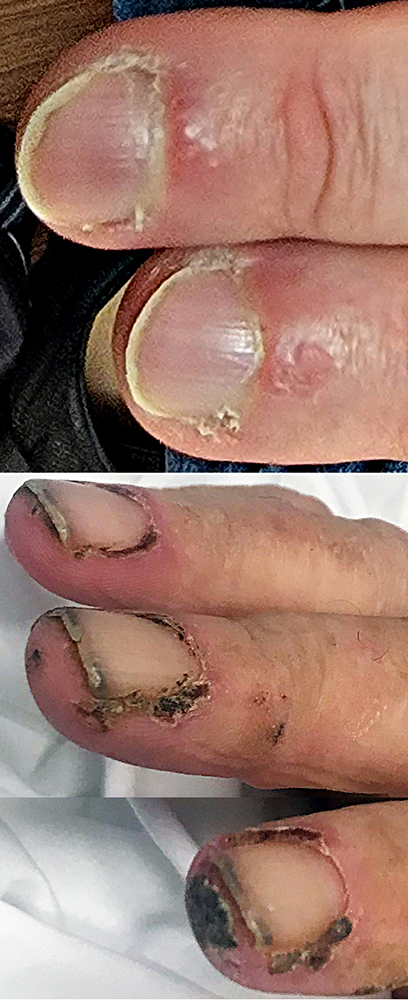
Nail & Nailbed pathology
|
|
Activation pathways Classical Alternative Lectin Functions Muscle diseases & Complement Serine proteases |
|
Complement activation: Three pathways
|