MUSCLE FIBER NECROSIS
|
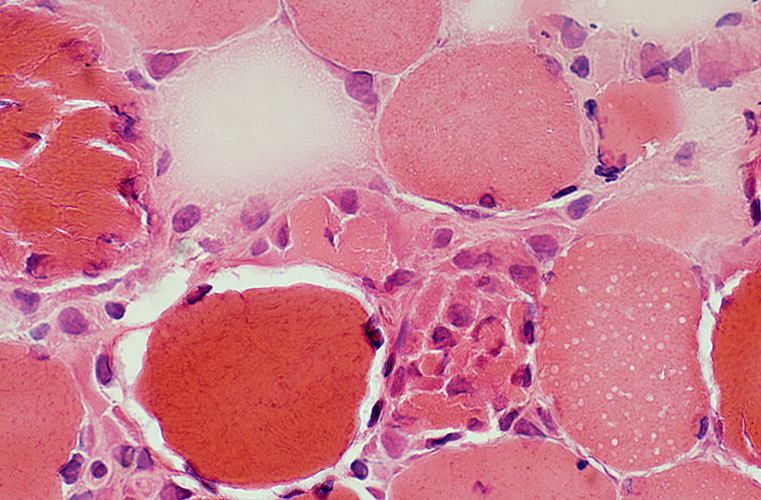 Segmental Necrosis of Muscle fibers: Varied stages
|
Necrosis: General features & Stages 1
|
Cell & Metabolic Conparative features Morphology Dark Metabolic failure Membrane damage Large Histiocyte Phagocytosis |
Necrosis, Early Stages: Muscle Fiber Patterns of Pathology |
|||
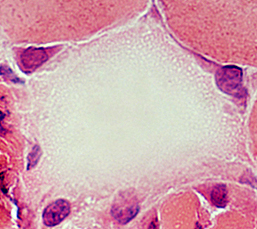 Myofiber Necrosis Metabolic Muscle Fiber cytoplasm Pale stain: Diffuse Myonuclei: Lose staining |
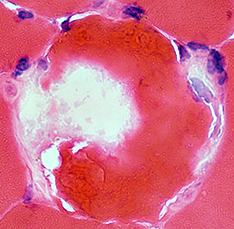 Myofiber Necrosis Sarcolemmal Membrane Δ Muscle Fiber Cytoplasm Pale stain: "C" or Δ Lesion Dark stain: Around C-region Myonuclei: Lose staining |
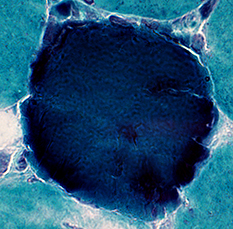 Myofiber Necrosis Dark Necrosis Muscle Fiber Cytoplasm Dark stain: Diffuse Myonuclei: Lose staining |
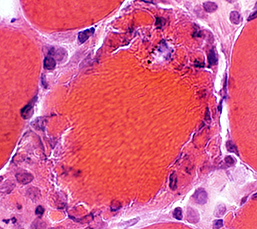 Myofiber Necrosis Histiocyte-Associated Neighboring histiocytes Around edge of fiber Muscle Fiber Cytoplasm Stain: Present |
|
| Later Stages: Histiocyte Invasion & Phagocytosis of Muscle fibers |
Later stage: Fiber Degeneration | |||
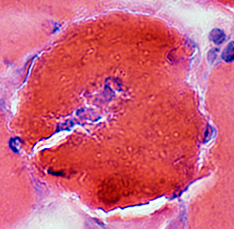 Myofiber Necrosis Cell invasion Stage: Intermediate Muscle Fiber Macrophage invasion |
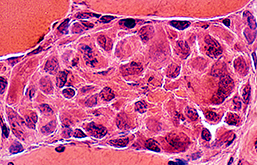 Myofiber Necrosis Phagocytic Stage: Late Muscle Fiber No cytoplasm remaining Replaced by histiocytes |
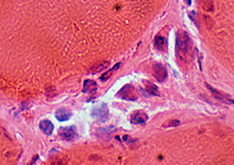 Myofiber Necrosis Collapse Stage: Very Late Muscle Fiber Space: Collapsed Histiocytes Few remaining Many have migrated away |
 Myofiber Necrosis Primary Fiber Degeneration Stage: Late Muscle fiber Cytoplasm: Fragmented; Lost Histiocytes: Few or None |
|
- Necrosis: Cellular & Metabolic changes
- Cytoplasmic swelling (oncosis)
- Rupture of plasma membrane
- Cytoplasmic organelles: Swelling; Loss
- Chromatin: Condensation, moderate
- Absent: Apoptotic & Autophagic markers
- Necrosis in muscle
- Associated with either
- Metabolic failure: Ca++ leak into cytoplasm
- Break in, or loss of, muscle surface fiber membrane
- Results in: Irreversible damage to whole, or segment of, muscle fiber
- All organelles involved
- Associated with either
- Associated metabolic alterations
- No common biochemical denominator
- Mitochondrial
- Uncoupling
- Production of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
- Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization: Often controlled by cyclophilin D
- Ca++ overload
- Lysosomal
- ROS production by Fenton reactions
- Membrane permeabilization
- Nuclear
- Lipid degradation
- Activation of phospholipases, lipoxygenases & sphingomyelinases
- Ca++
- Activation of non-caspase proteases: Calpains; Cathepsins
- Necrotic muscle fiber morphology: Patterns during necrosis
- Necrosis due to: Metabolic failure
- Myofiber changes: Sarcolemma & Cytoplasm
- H&E & Gomori Trichrome
- Cytoplasm staining: Pale
- Intermyofibrillar network: Absent
- Myonuclei: Absent or reduced staining
- Necrotic muscle fibers have reduced or absent staining with
- NADH
- Mitochondrial (SDH)
- Myosin ATPase
- Necrotic muscle fibers: Molecular & cellular markers
- Cytoplasm of necrotic muscle fibers: Stains for
- C5b-9 Complement (Membrane attack complex (MAC))
- IgM
- Ca++: Increased in necrotic muscle fibers
- Around the rim of necrotic muscle fibers: Alkaline phosphatase
- Muscle fiber phagocytosis
- Histiocytic (Phagocytic) cells stain for: Acid phosphatase; Esterase; HAM56; CD68; MHC Class I
- Cytoplasm of necrotic muscle fibers: Stains for
- Ultrastructure
- Loss of plasma membrane
- Myofibrils: Lysed or Lost
- Mitochondria: Abnormal
- Late: Granular or filamentous debris in fibers
- Rare in intrafusil muscle fibers
- H&E & Gomori Trichrome
- Myofiber changes: Sarcolemma & Cytoplasm
- Necrosis due to: Membrane damage
- Early damage pattern
- Focal susarcolemmal area: Delta (Focal, subsarcolemmal) lesion: Pale stain
- Other remaining cytoplasm: Dark stain
- Disorders
- Hereditary: Dystrophinopathy & Other sarcolemmal protein disorders
- Toxic: Statin; Lysolecithin
- Early damage pattern
- Necrosis due to: Ischemia
- Early fiber damage pattern: "Dark" necrosis
- Cytoplasm of involved muscle fibers: Diffusely dark on H&E & Gomori trichrome stains
- Later fiber damage: 2 patterns
- Pale fragmented, or No, cytoplasm staining + No, or few, associated histiocytes
- Invasion, Phagocytosis & replacement of fibers by histiocytes
- Disorders with "Dark" necrosis
- Early fiber damage pattern: "Dark" necrosis
- Necrosis due to: Large Histiocyte-mediation
- Necrosis due to: Necroptosis (Regulated)
2
- Programmed cell death
- Stimuli
- Pathway: Kinase RIP1 (RIPK1)

- Molecules upregulated: RIPK1
 , RIPK3
, RIPK3
 , MLKL
, MLKL

- Execution pathway
- RIP1–RIP3 necroptotic complex: Necrosome
- Production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS)
- Depletion of cell energy under apoptotic-deficient conditions
- MLKL increase
- Disrupts plasmalemma integrity
- Targets cellular organelles: Mitochondria & Endoplasmic reticulum,
- Releases: Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) from ruptured cells
- DAMPs
- Molecules: HMGB1, Nuclear DNA, Mitochondrial DNA, ATP from necroptotic cells
- Effects: Induce tissue inflammation injury; Recruit immune cells
- Caspase-independent
- Molecules upregulated: RIPK1
- Regulation
- Stimulated by: TNF-α; DUX4
- Down-regulated: Muscle fiber differentiation; Adulthood
- General effects
- Inflammation: Induced
- Cytokines, Pro-inflammatory
- Activation
- TNF-α, IL-1β, Interferons
- DAMPs: Released
- Tissue homeostasis
- Satellite cells: Activation
- During development, regeneration & cell damage
- Inhibit tumor growth
- Recruit cells to clear debris
- Histologic marker: phospho-MLKL
- Necrosis due to: Metabolic failure
- Necrosis in muscle: Stages
- Early necrosis: Patterns
- Cytoplasmic pallor: "Metabolic" pattern
- Sectoral lesion & Hypercontraction
- Subsarcolemmal lesion
- Phagocytosis (Clean-up) of necrotic muscle fibers
- Early: Infiltration of muscle fibers by histiocytic cells
- Proliferation or Migration of Phagocytic cells
- Attraction of Phagocytic cells to necrotic muscle fiber
- Phagocytosis of necrotic muscle fibers
- Associated macrophages: M1 type
- Classically activated inflammatory macrophages
- Infiltrate at early time points after injury
- Generate inflammatory cytokines
- Sustain activation & proliferation of muscle stem cells
- Late: "Collapse"
- Migration of macrophages away from necrotic muscle fiber
- "Collapse" of region with necrotic muscle fiber
- Early: Infiltration of muscle fibers by histiocytic cells
- Cell remnant disposal
- Cell proliferation
- Muscle precursors
- Function: Formation of regenerating muscle fibers
- Origins
- Satellite (Stem) cells
- Vessel-associated muscle stem cells (Mesoangioblasts)
- Myogenic precursors
- Express pericyte markers
- Cross vessel walls
- Connective tissue & Fat: Fibro/adipogenic progenitors (FAPs)
- Sustain satellite cell-driven myogenesis
- May differentiate into myoblasts, adipocytes or fibroblasts
- M2 macrophages
- Presence: Associated with tissue "Inflammation"
- Late: Muscle healing
- FAPs & Stem cells undergo apoptosis
- Muscle precursors
- Early necrosis: Patterns
Differential Diagnosis: Myofiber Necrosis in Immune Myopathies |
||||||
| Syndrome | Myofiber Necrosis |
Myofibers MHC-1 expression |
Pathology Other Tissues |
Immune cells/ Location |
Antibody or Marker (Serum) |
IIM Clinical Syndromes |
| LHIM | Scattered Peripheral |
Diffuse Most fibers |
Anemia | Histiocytes/ Near myofibers |
Ferritin (50%) | Necrotic Myopathy |
| IMPP | Near Perimysium |
Fibers Near Perimysium |
Perimysium Damage |
Histiocytes/ Perimysium |
tRNA synthetase (Jo-1) |
DM/PM/ NM/ILD |
| SRP | Scattered | Immature fibers Scattered None on most fibers |
Fibrosis Endomysium & Perimysium |
No | Signal Recognition Particle 54 (SRP54) |
Necrotic Myopathy |
| RIIM | Clustered in Border zones |
Little or Diffuse | Vein damage | No | Tif1γ NXP-2 |
DM/PM/ Paraneoplastic |
| Checkpoint Inhibitors |
Clustered | Regional: Around necrotic fibers |
Mitochondrial Δ Cardiac; Eye |
Histiocytes Clustered |
Striation | Necrotic Myopathy |
| Active or Chronic Myopathy |
Scattered or Near Perimysium |
Immature fibers None on most fibers |
Perimysium | No | HMGCR | Necrotic or Dystrophy-like Myopathy |
| BCIM | Scattered |
Diffuse Most fibers |
Endomysium C5b-9 deposition |
B-lymphocyte foci/ EGC (ELS) |
ANA (Nucleolar) PM-Scl100 |
Polymyositis/ Other immune |
| Active Myopathy |
Scattered |
Diffuse Most fibers |
Capillaries | No | U1snRNP 4 | Necrotic Myopathy |
| Optimal stain for identifying Necrotic Muscle Fibers: C5b-9 complement on fiber cytoplasm | ||||||
Myopathies with Abundant Muscle Fiber Necrosis: Comparative Pathology |
|||||||||||
| Myopathy Type |
Myopathy: Examples |
|
Tissue Pathology: Other |
||||||||
| Hereditary | |||||||||||
| Sarcolemma Disorders |
Dystrophin Dysferlin |
Scattered Myopathic Groups |
Ongoing | Δ lesion, or Diffuse |
Endomysium Increased |
||||||
| Rhabdomyolysis Metabolic & Membrane Disorders |
Phosphorylase Malignant Hyperthermia Membrane disorders |
Scattered, or Regional |
Monophasic ± Ongoing |
Diffuse | No | ||||||
| Toxic | |||||||||||
| Rhabdomyolysis | Statin toxicity, acute Ethanol |
Scattered | Monophasic | Δ lesion, or Diffuse, Pale |
No | ||||||
| Immune | |||||||||||
| IMPP | Jo-1 & Synthetase Ab Multisystem Δ Dermatomyopathy |
Perifascicular Predominant |
Ongoing | Diffuse | Perimysium Damage | ||||||
| HMGCR antibody |
Myopathies: Subacute or Chronic |
Scattered & Perifascicular |
Ongoing | Diffuse | Perimysium Damage Alkaline Phosphatase+ |
||||||
| SRP antibody | SRP Myopathy, Progressive, Severe |
Scattered | Ongoing | Diffuse | Endomysial Proliferation Perimysium Damage |
||||||
| LHIM | Myopathy, Subacute | Scattered | Ongoing | Peripheral | Histiocytes: Surround Myofibers |
||||||
| NXP-2 & Tif1γ antibodies |
RIIM Dermatomyopathy Paraneoplastic: ↑ Age |
Clustered: Vessel Borderzone areas |
Ongoing | Diffuse | Vessel: Veins & Capillaries Connective tissue |
||||||
| Mi-2 antibody | Dermatomyopathy | Scattered & Perifascicular |
Ongoing | Diffuse | |||||||
| Focal | |||||||||||
| Toxic | Injections Venoms |
Clustered | Monophasic | Diffuse, or Δ lesion |
|||||||
| Ischemia | Vascular Disease | Clustered | Monophasic | Diffuse | Endomysium: Edema | ||||||
| Freeze | Clustered | Monophasic Slow recovery |
Diffuse | Satellite cells Number reduced |
|||||||
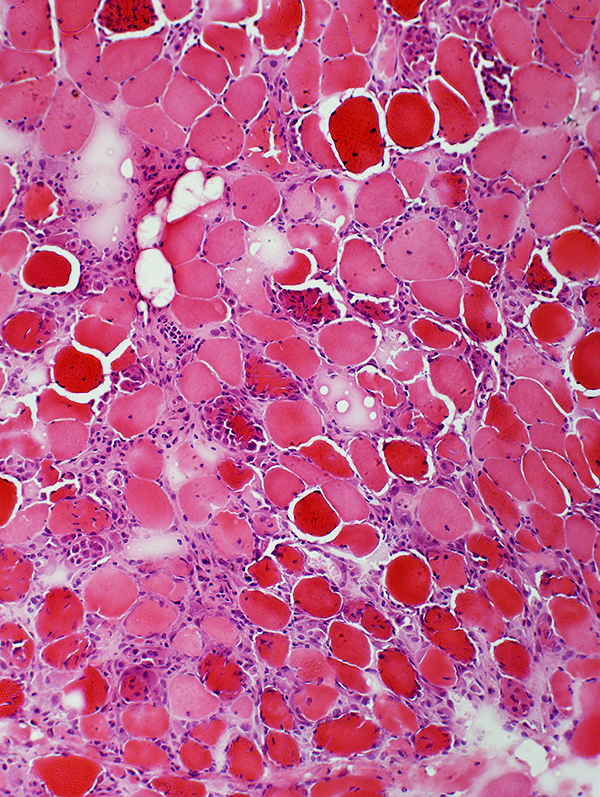
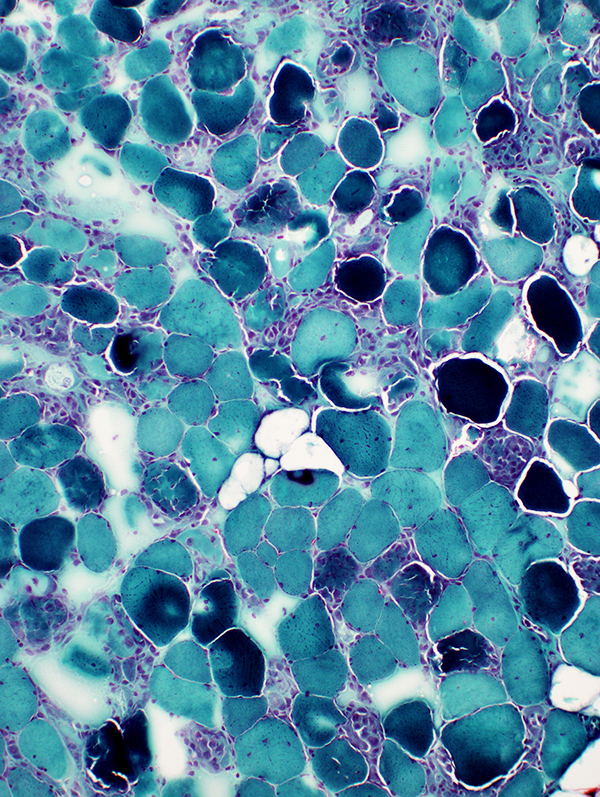
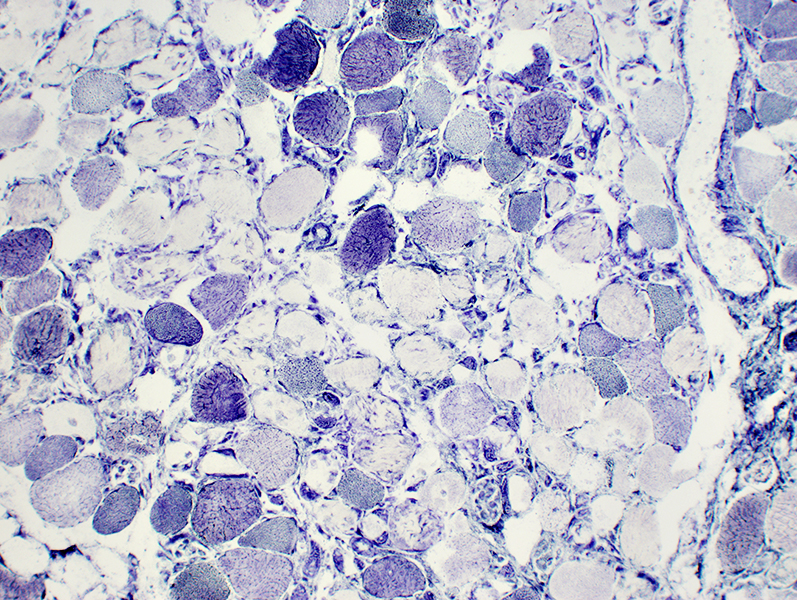
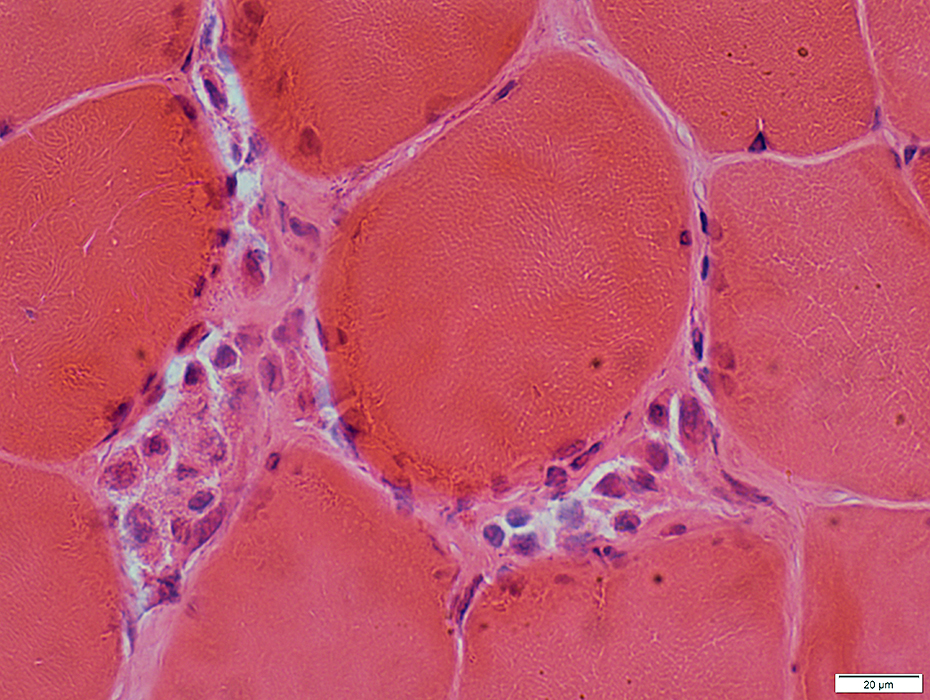
Muscle Fiber Necrosis (Rhabdomyolysis episode): Morphology
Segmental necrosis: Scattered necrotic & hypercontracted muscle fibers
|
|
 H & E Stain |
← Normal muscle fiber |
| ← Necrotic muscle fiber: Pale; Little phagocytosis | |
| ← Necrotic muscle fiber: Phagocytosis by macrophages | |
| ← Hypercontracted necrotic muscle fiber | |
| ← Perimysium |
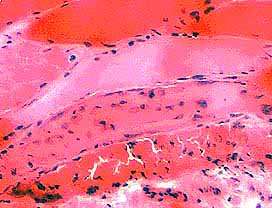
Segmental Necrosis (Arrow) in Muscle fiber
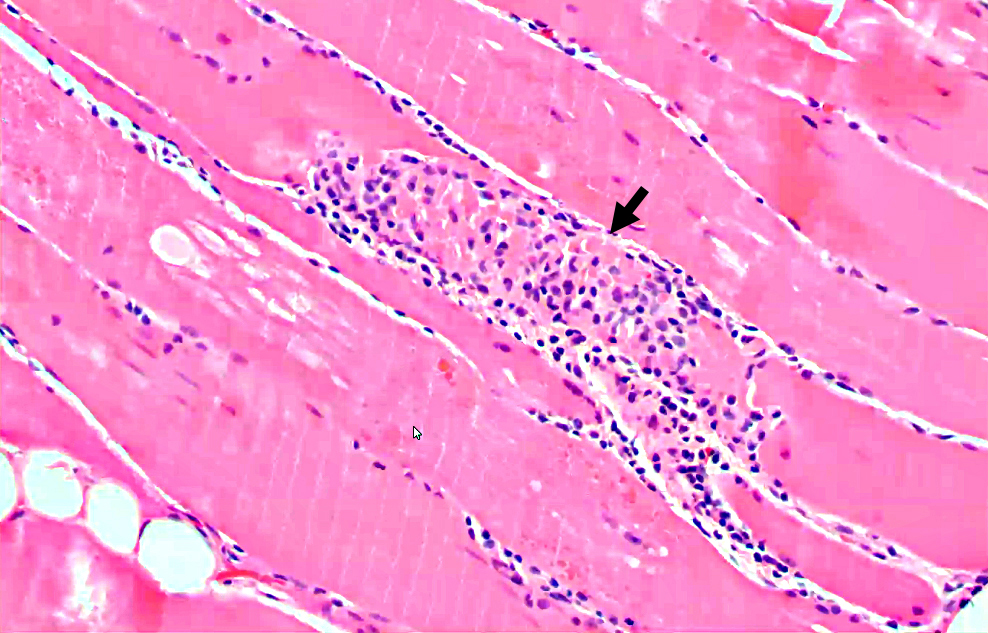 H & E Stain |
Necrosis: Early; Metabolic failure
Pale muscle fibers with loss of cytoplasmic structures & staining
 H&E stain |
|
| Necrotic muscle fibers: Pale; Little phagocytosis (Arrows) | |
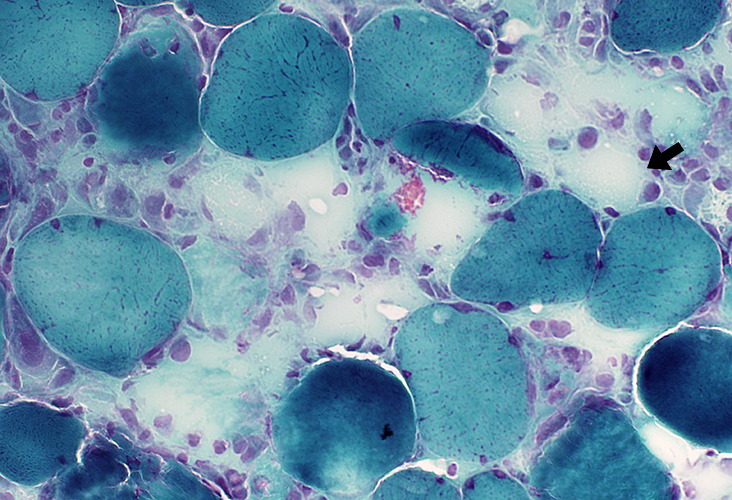 Gomori trichrome stain |
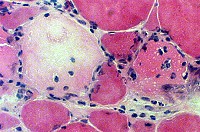 H&E Necrotic muscle fiber, Early
|
Muscle fiber cytoplasm: Pale
Nuclear staining: Absent
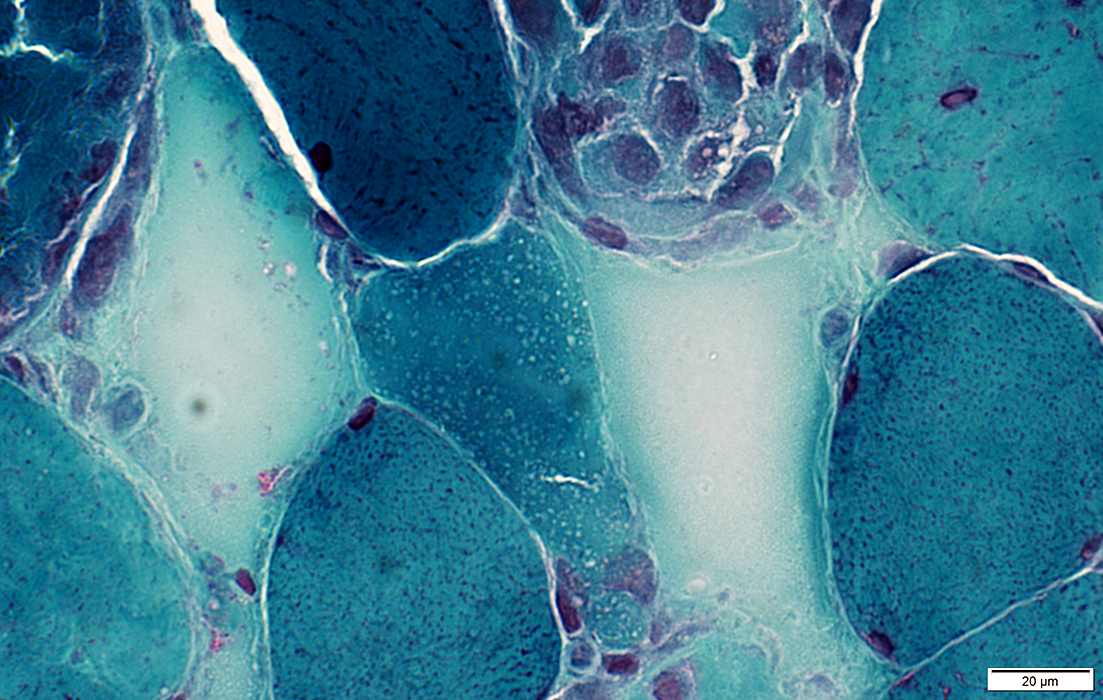 Gomori trichrome stain |
 Necrotic muscle fibers: Internal architecture has lost NADH staining (Arrow) 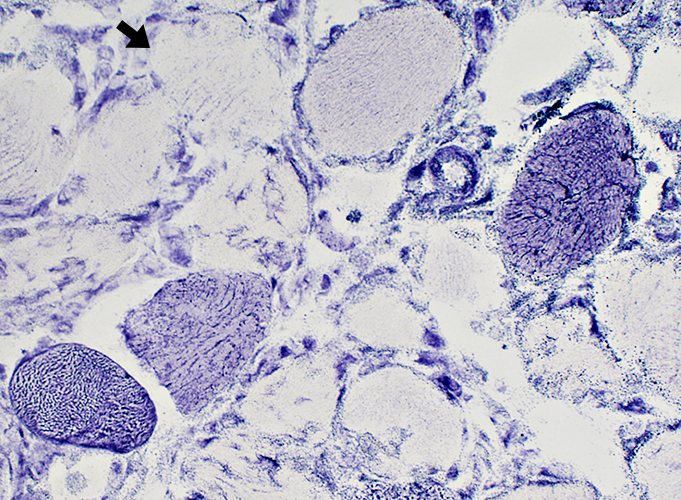 NADH stain |
Rhabdomyolysis
Some non-necrotic muscle fibers have increased lipid (Left)
Phagocytic cells have only minor staining of their cytoplasm (Right)
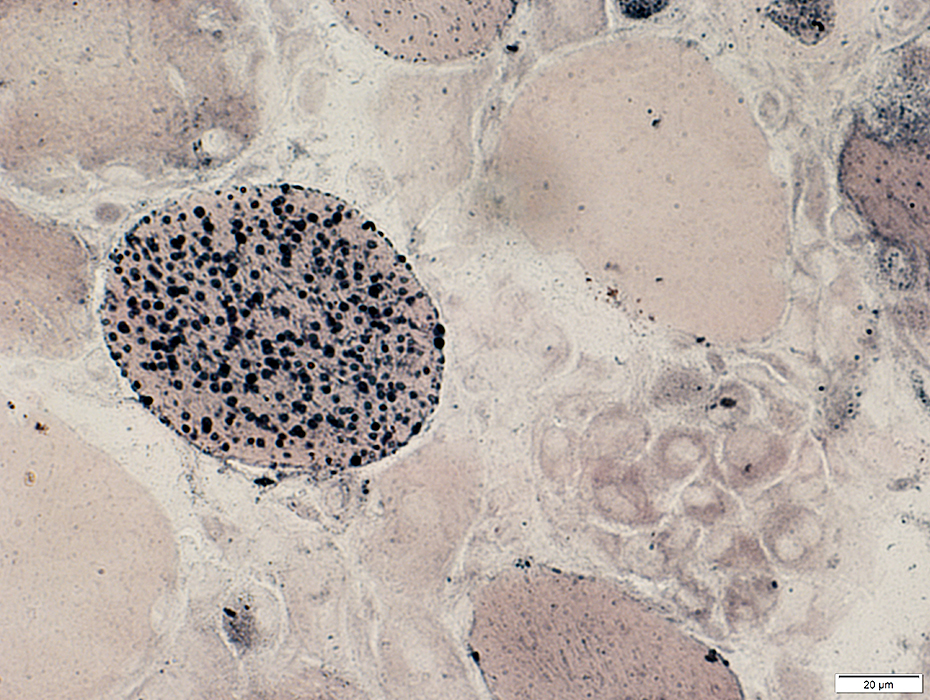 Sudan black stain |
Necrosis: Early; Membrane damage, Statin toxicity
Varied internal structure: Hypercontracted material & Palor in different areas of single fibers
 H&E stain |
|
Membrane damage at several regions of individual fibers: Associated with clear regions in cytoplasm 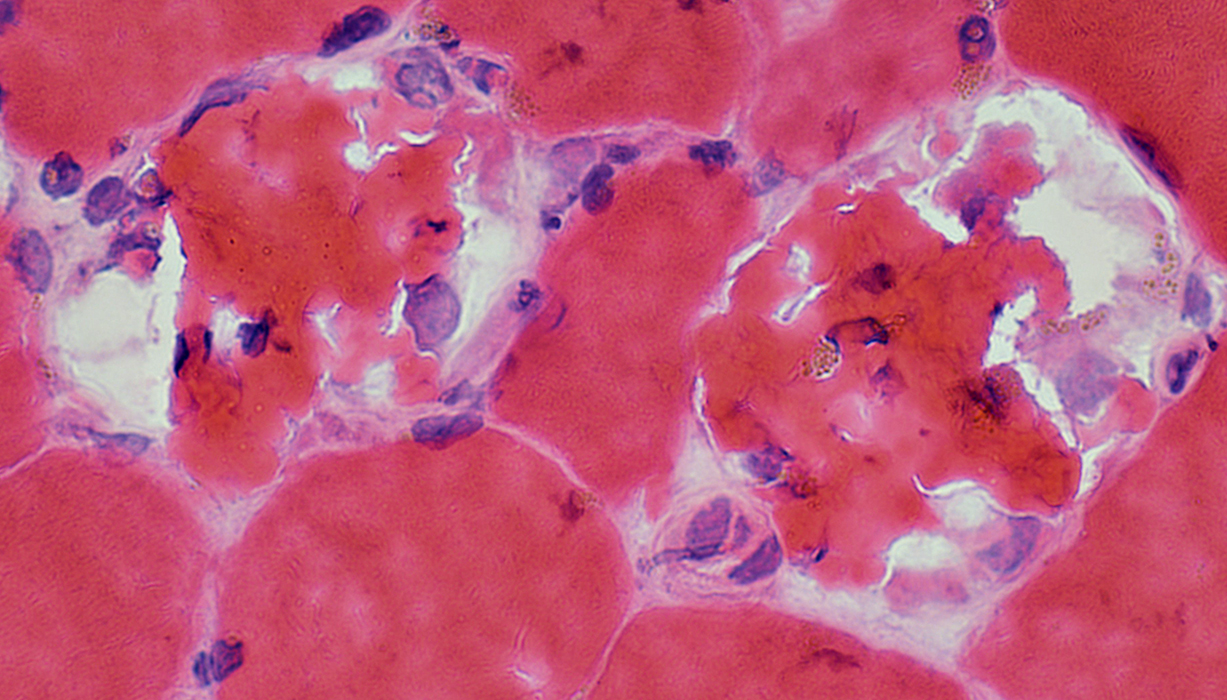 H&E stain |
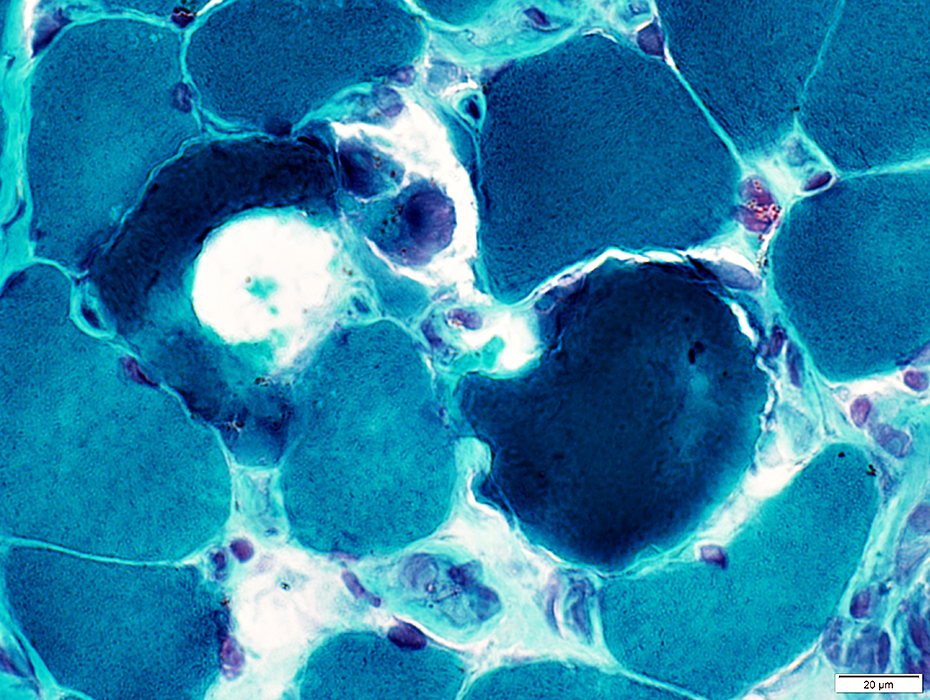 H&E stain |
Membrane & Neighboring cytoplasm damage in a focal region of individual muscle fibers: Pale staining
Cytoplasm around focal lesion stains dark
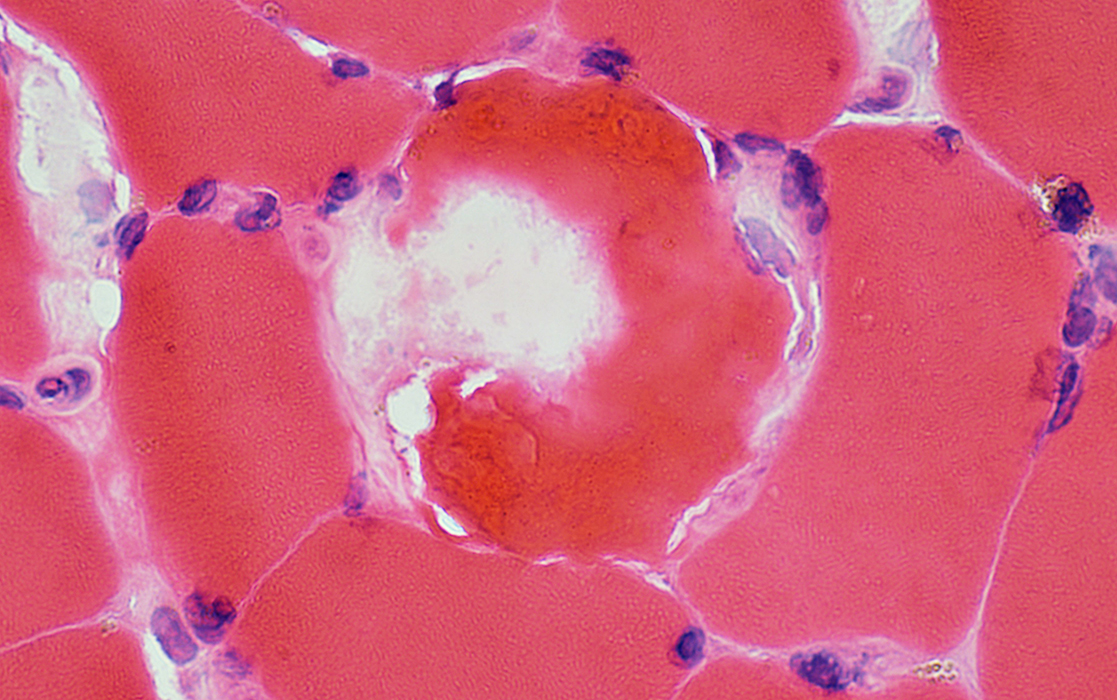 H&E stain |
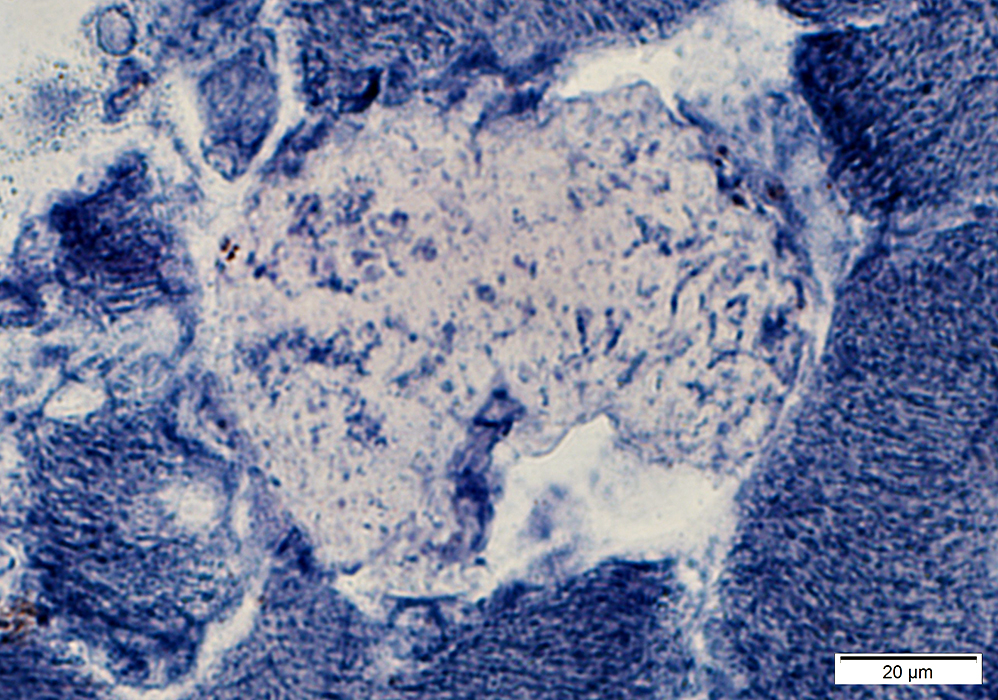 NADH stain |
Cytoplasm around focal lesion stains pale
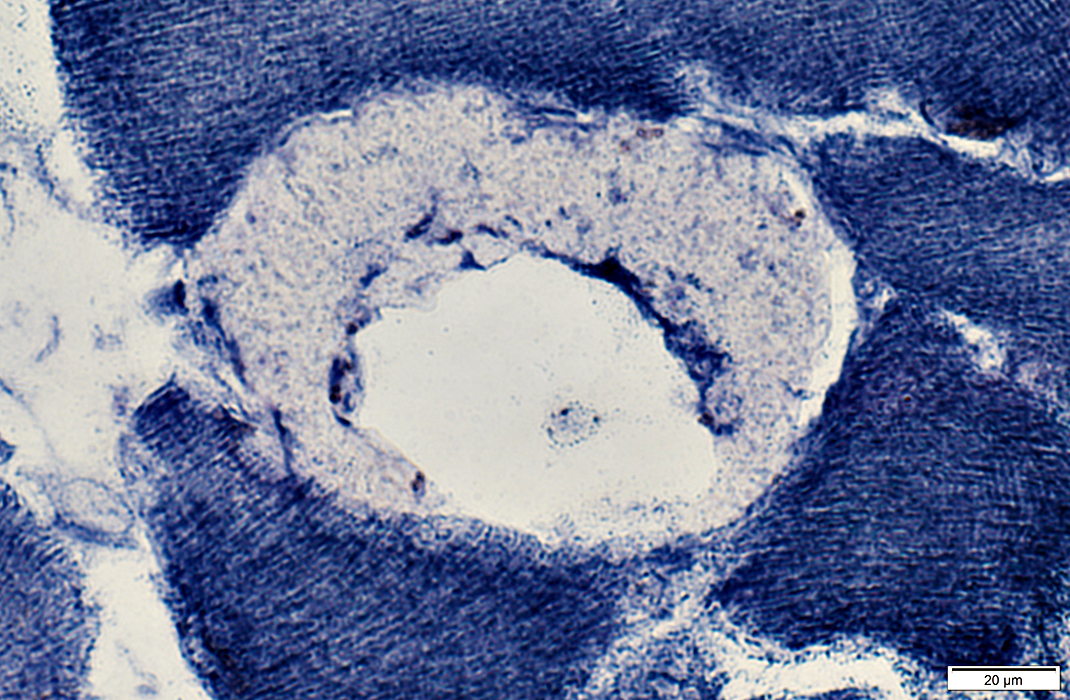 NADH stain |
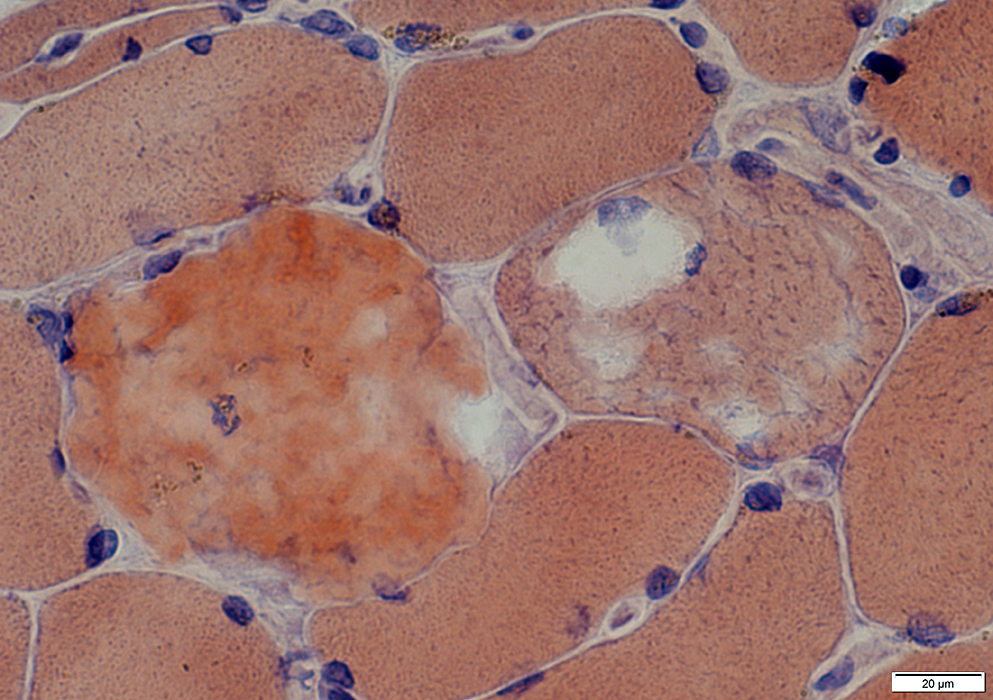 Congo red stain |
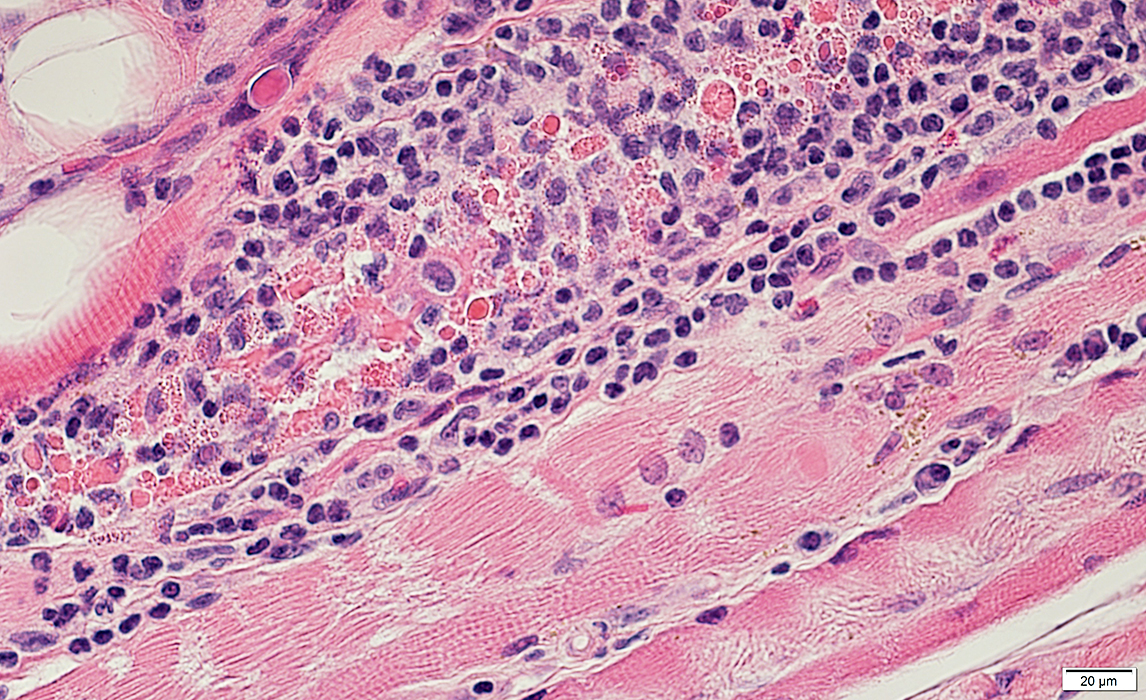
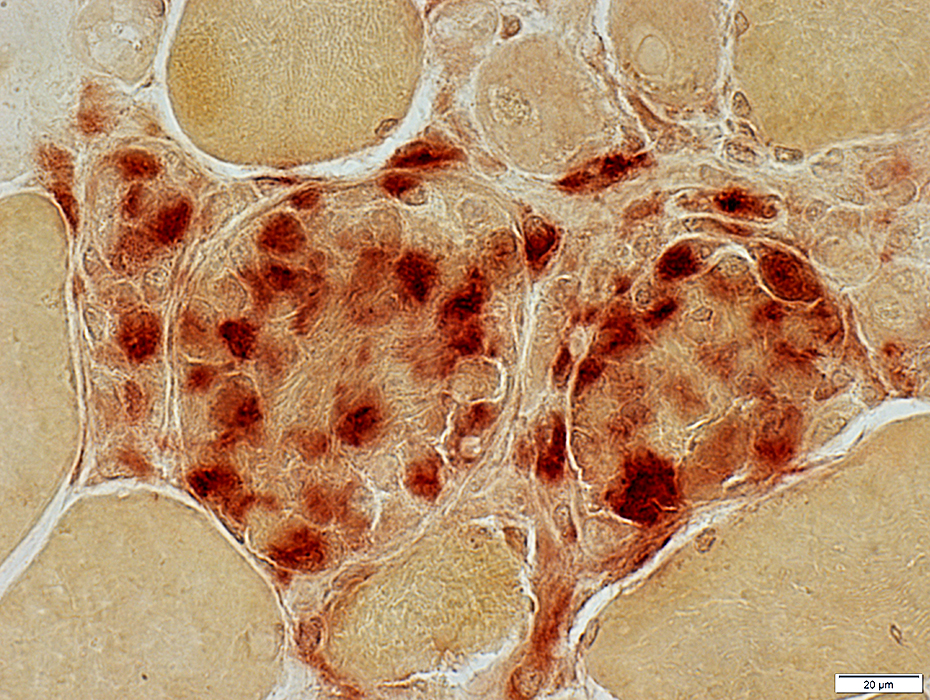
Phagocytosis of Muscle fibers
Histiocytic cells invade & replace muscle fibers
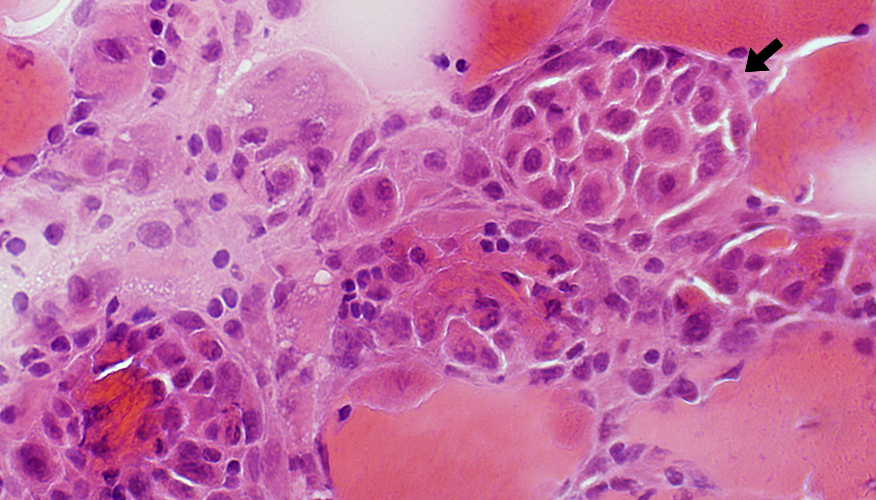 H&E stain |
|
| Necrotic muscle fibers: Phagocytosis (Arrows) | |
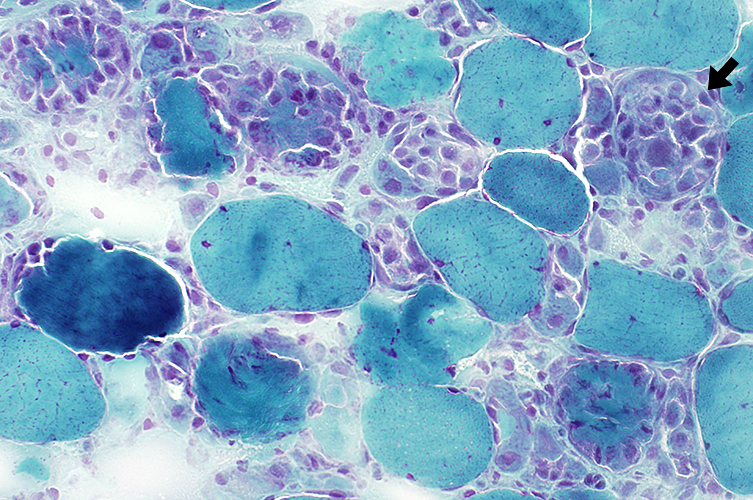 Gomori trichrome stain |
|
Necrotic muscle fiber
Largely replaced by cells
Some remaining debris
 H&E stain |
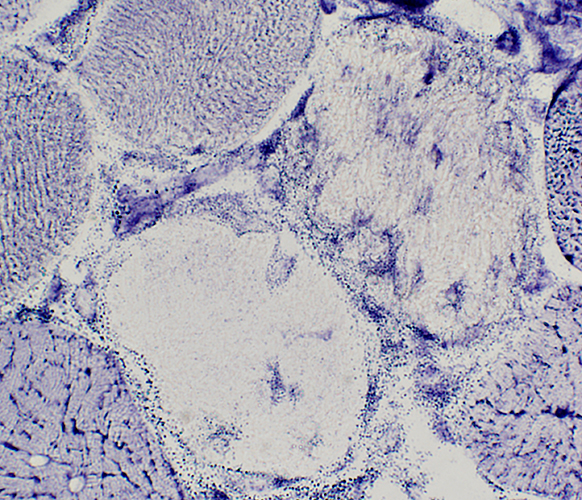 NADH stain |
Phagocytic cells have
Mild NADH staining
Strong esterase staining
Necrotic muscle fibers: Cytoplasm has little, or no, staining
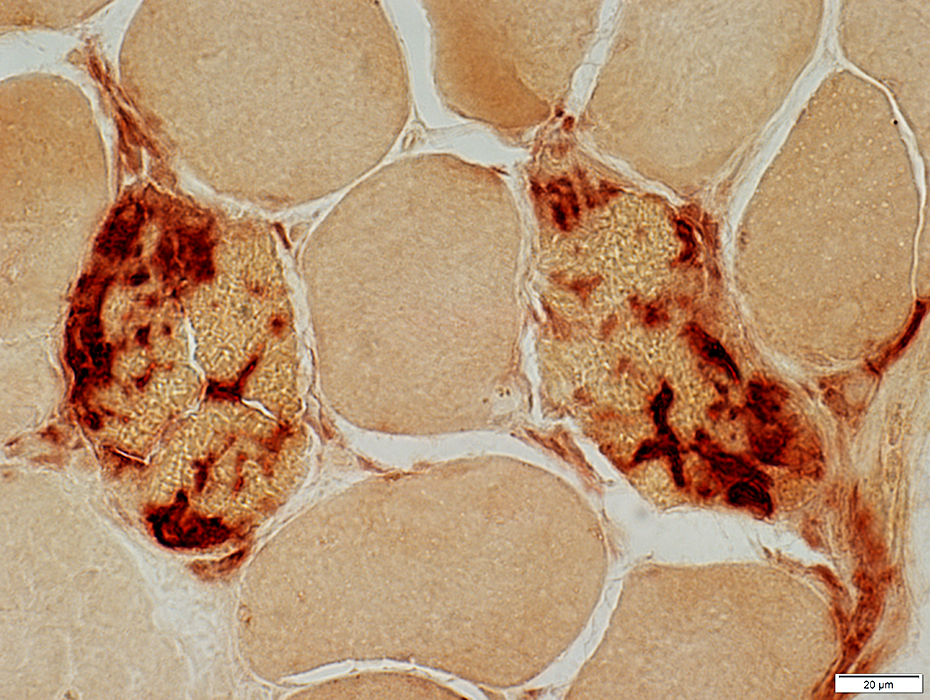 Esterase stain |
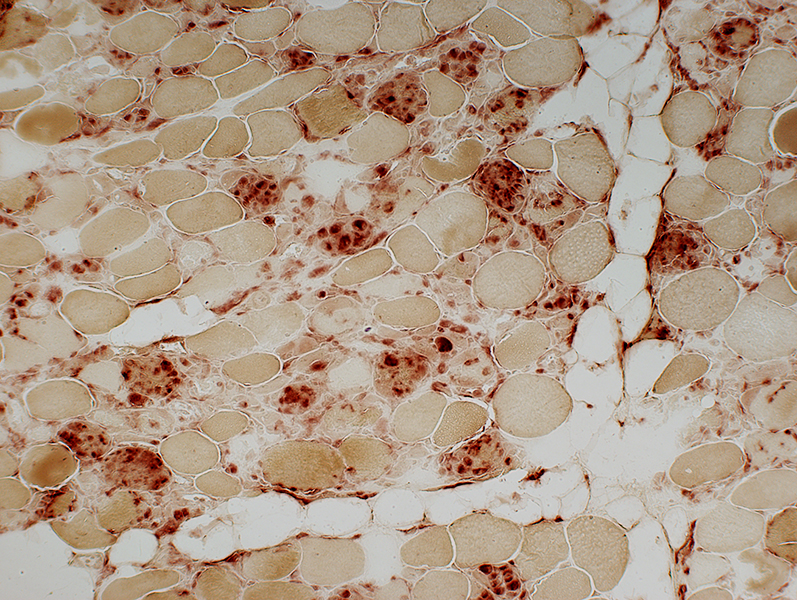 Acid phosphatase stain Necrosis: Varied Stages Early: Pale stained muscle fibers Later: Muscle fibers progressively replaced by acid phosphatase + cells (Right) 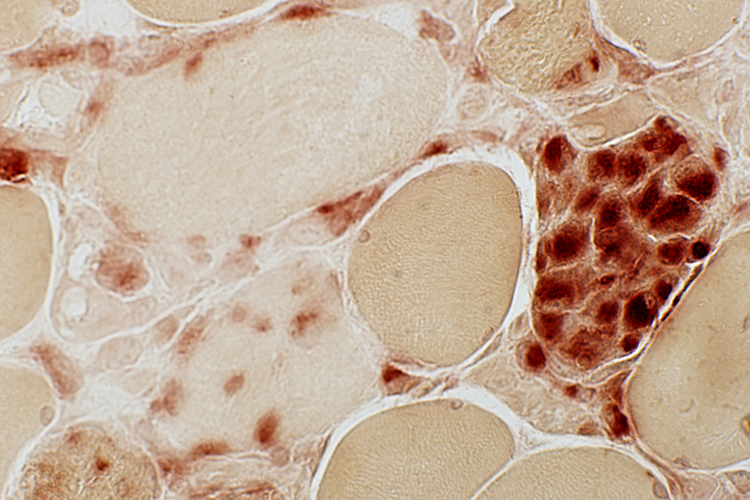 Acid phosphatasae stain |
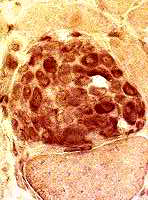 Esterase stain Necrotic muscle fiber, Late Muscle fiber is invaded and replaced by phagocytes. |
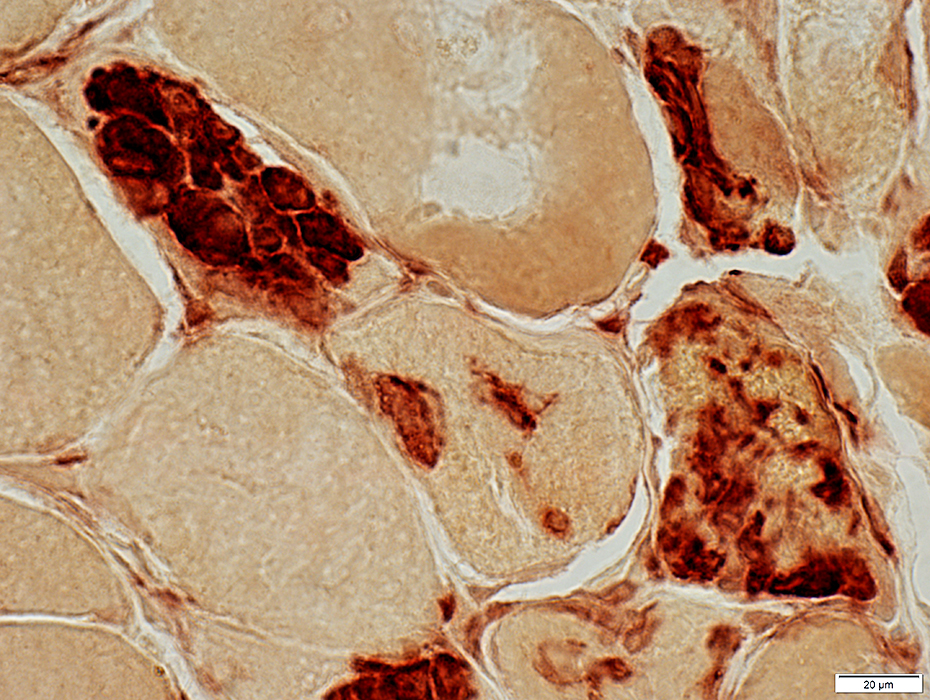 Esterase stain |
Necrosis & Phagocytosis: Late
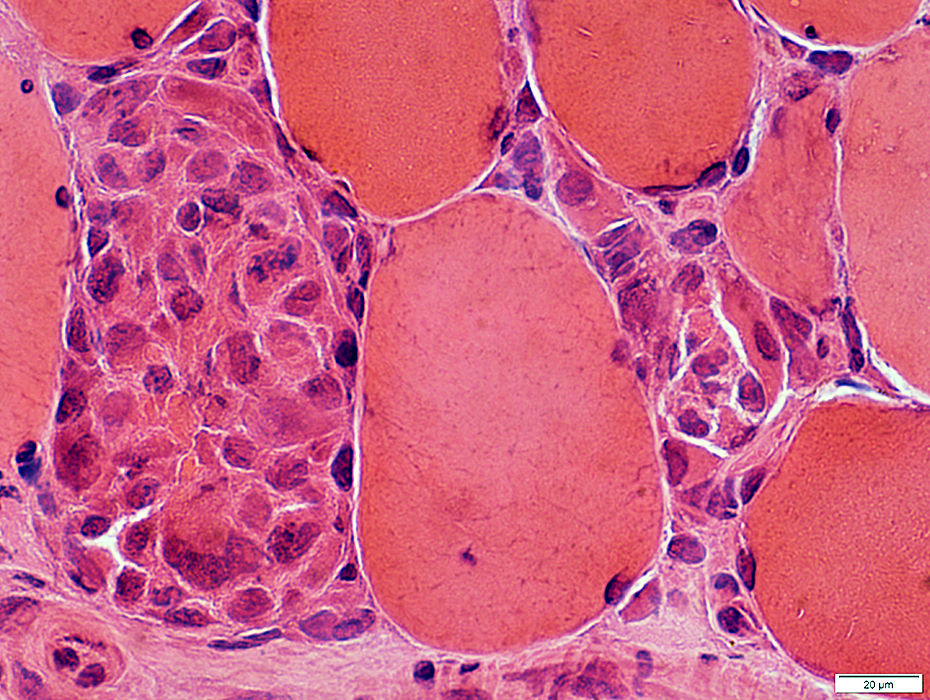 H&E stain |
Replace necrotic muscle fibers
Move out of necrotic muscle fiber areas
 Acid phosphatasae stain |
 H&E stain |
Space occupied by necrotic muscle fibers "Collapses"
Some histiocytes remain
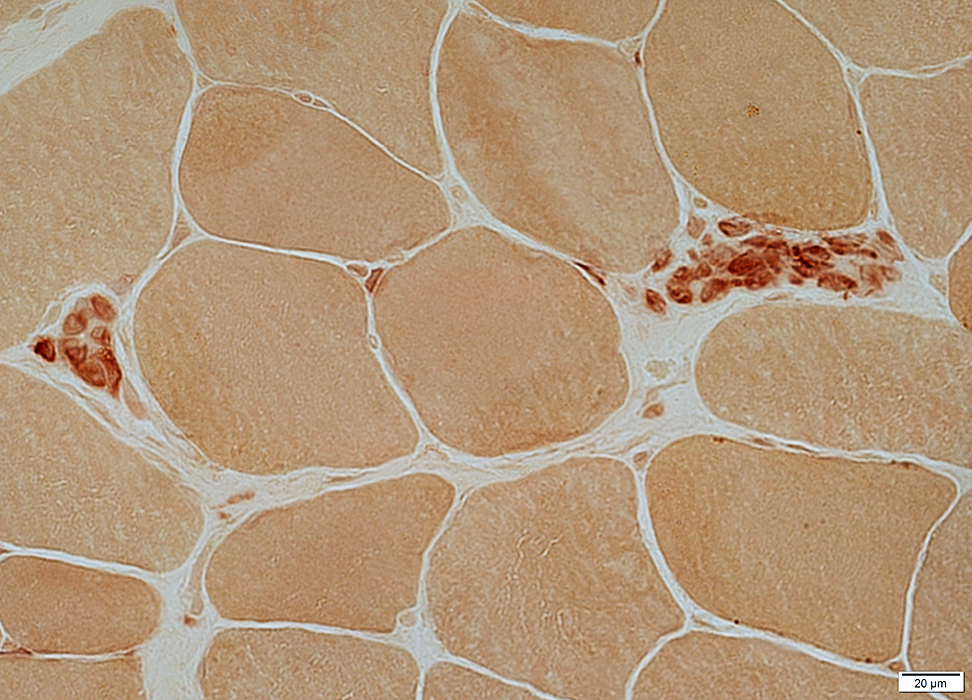 Acid phosphatase stain |
 MHC Class I stain Very late stage necrosis: MHC Class I Stains remaining cells phagocytsing collapsed muscle fibers Stains capillaries (Normal) No staining of most muscle fibers (Normal) |
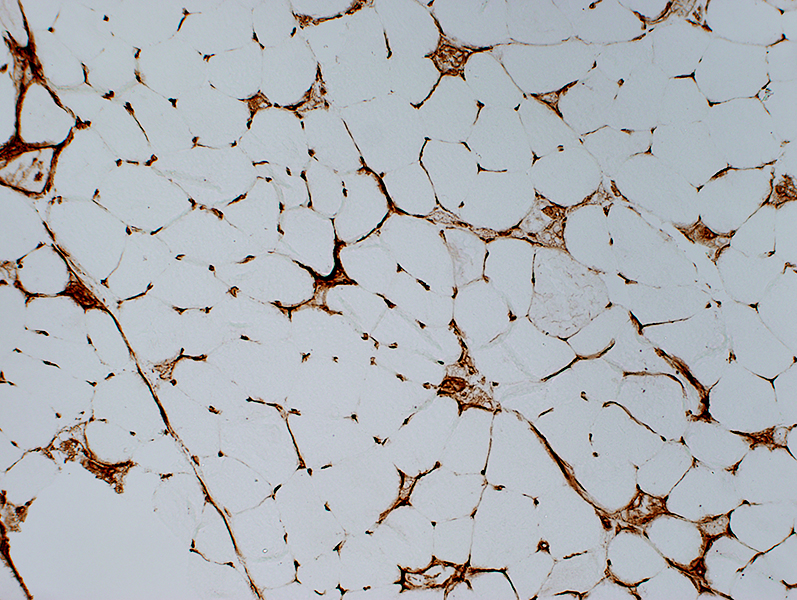
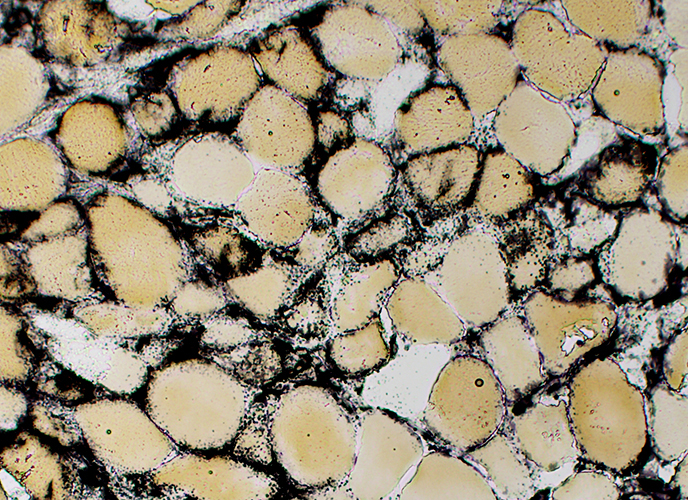 Alkaline phosphatase stain Necrosis: Alkaline phosphatase stains around the rim of muscle fibers |
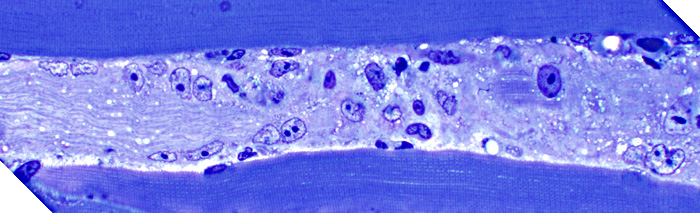 Toluidine blue stain Necrotic muscle fiber (Longitudinal section) Pale Invaded by cells |
|
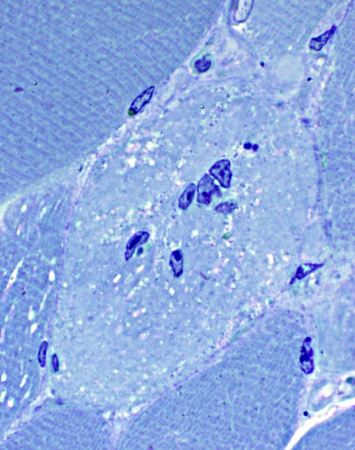 Toluidine blue stain Necrotic muscle fiber (Cross-section) Pale Invaded by cells |
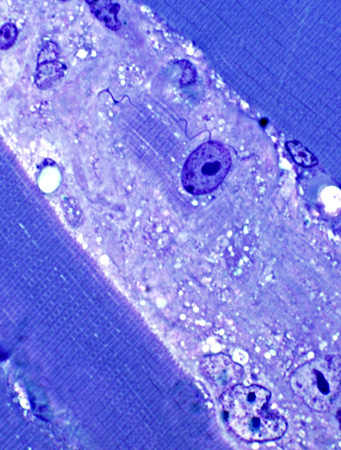 Toluidine blue stain Necrotic muscle fiber Pale Invaded by cells |
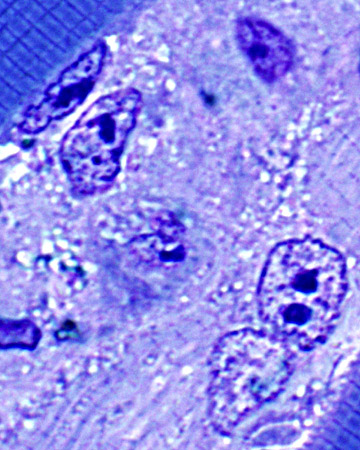 Toluidine blue stain Cells in necrotic fiber |
 Toluidine blue stain Non-necrotic, abnormal muscle fiber (Left): Dilated SR |
Necrotic muscle fibers: Complement C5b-9 (MAC) deposition
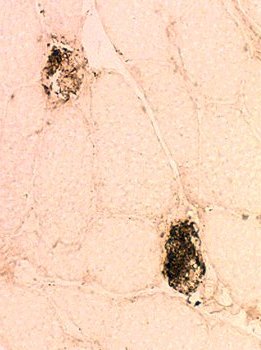
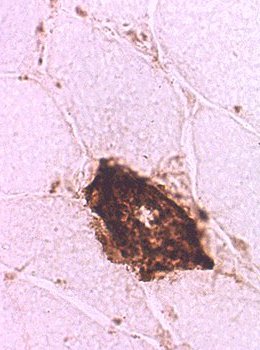 Stain: C5b-9 components of complement (Membrane attack complex (MAC)) Necrosis: C5b-9 deposition diffusely within muscle fiber cytoplasm 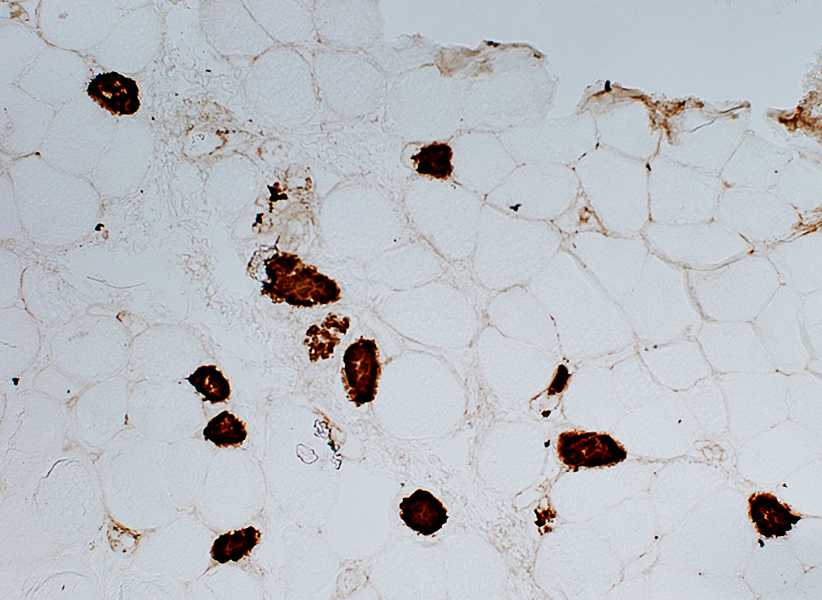
|
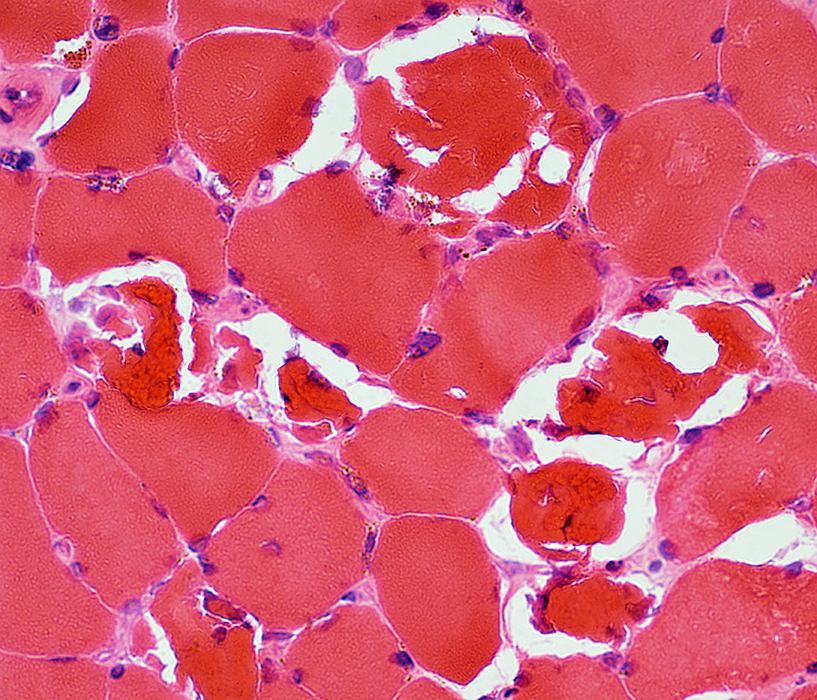
Rhabdomyolysis: PAS stain is pale in small & large muscle fibers
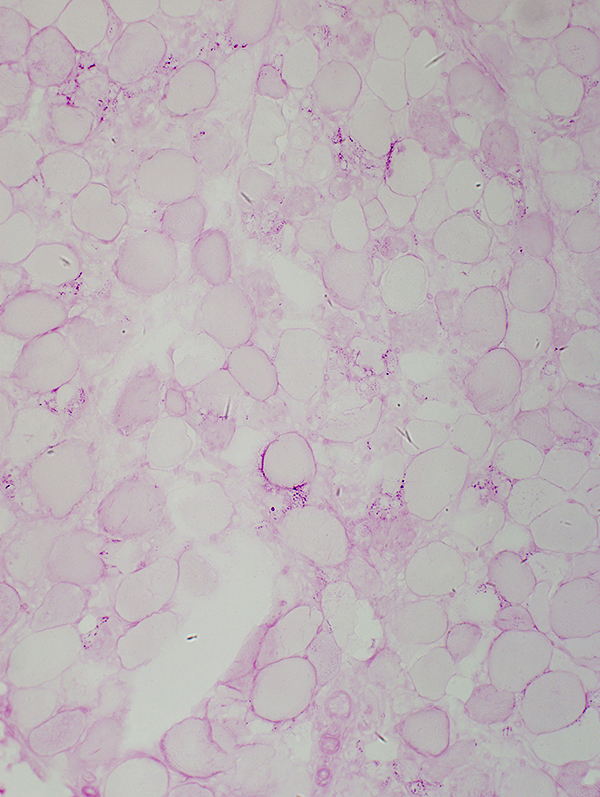
|
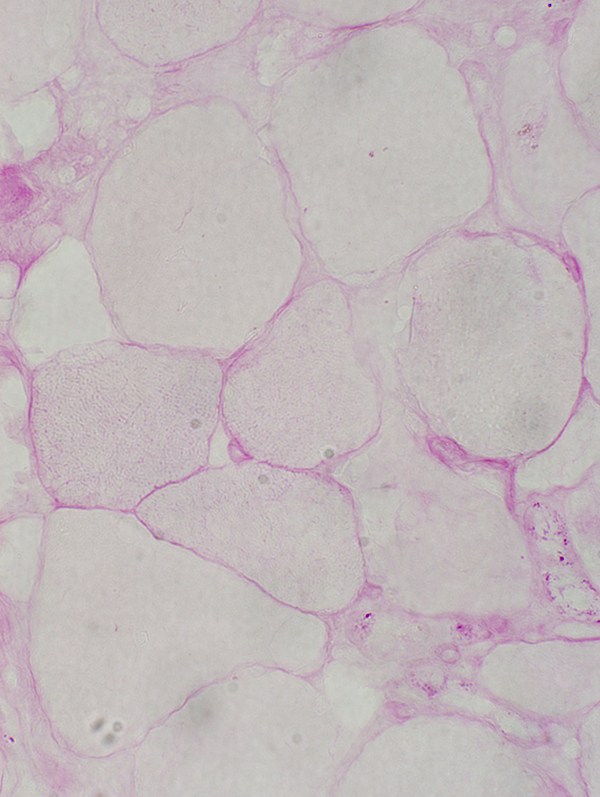
|
Necrosis: Ongoing
|
Necrosis: Early stage Pale muscle fiber cytoplasm Lipid droplets Two other muscle fibers have large lipid droplets but are not pale & necrotic 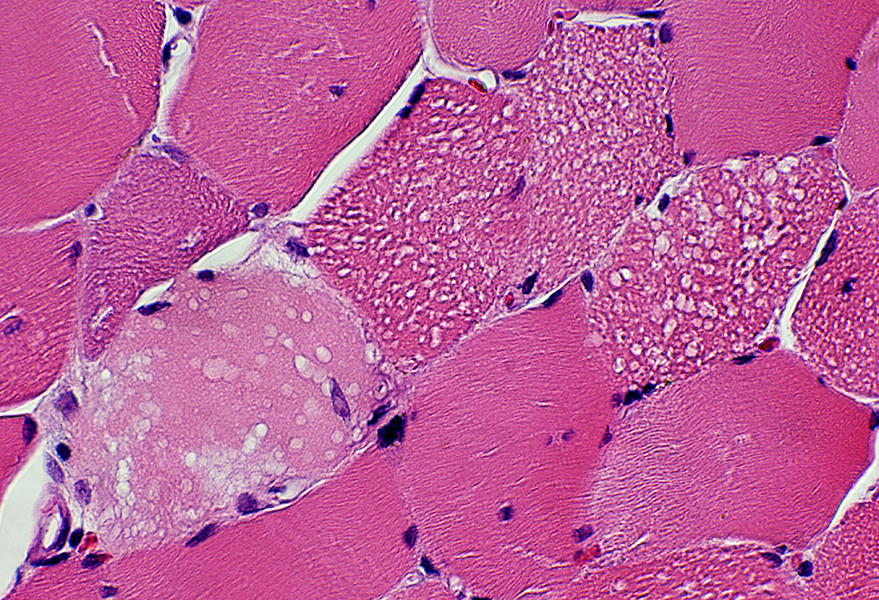 H&E stain |
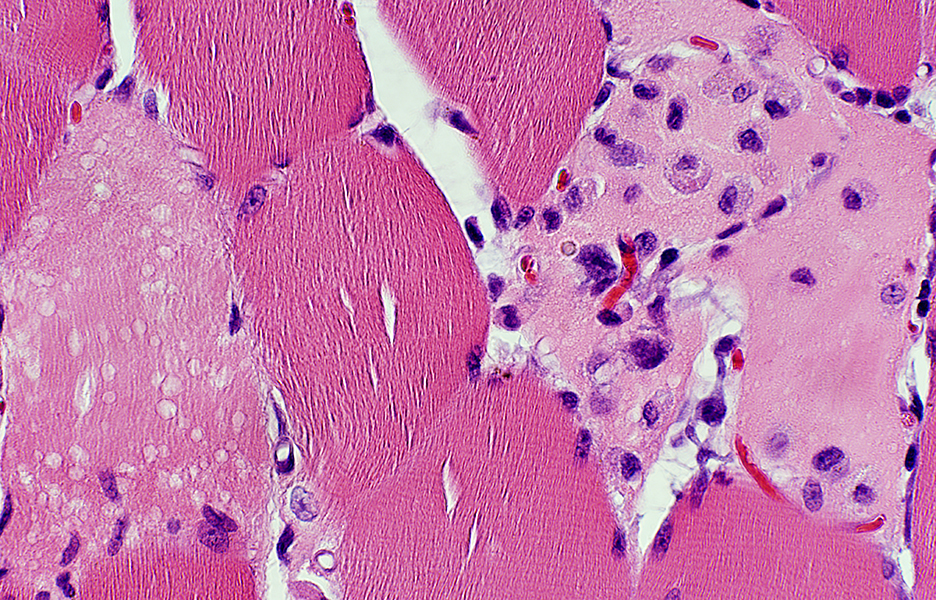 H&E stain |
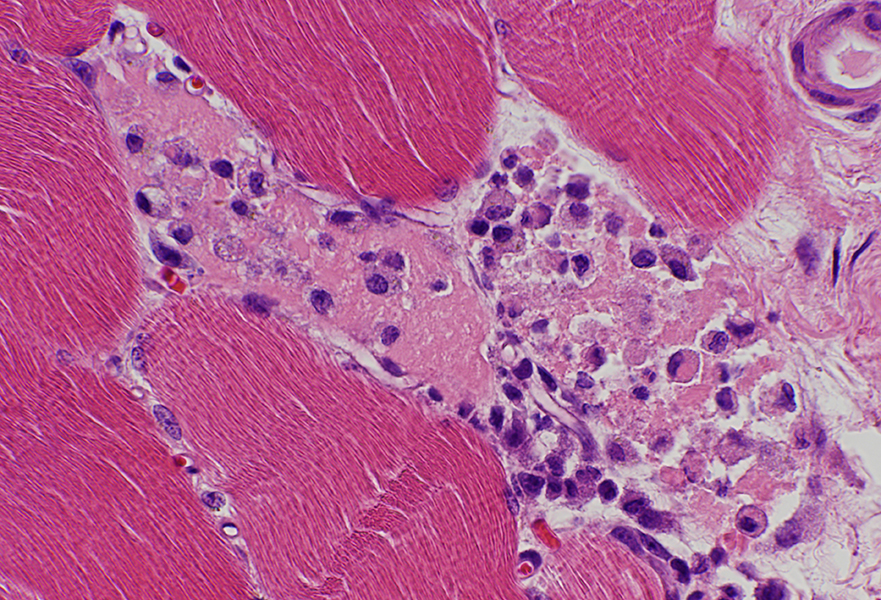 H&E stain |
Necrosis associated with Eosinophils
Unusual: Eosinophils may be a component of cells replacing necrotic muscle fibersReported with LGMD 2A (Calpain-3 mutations)
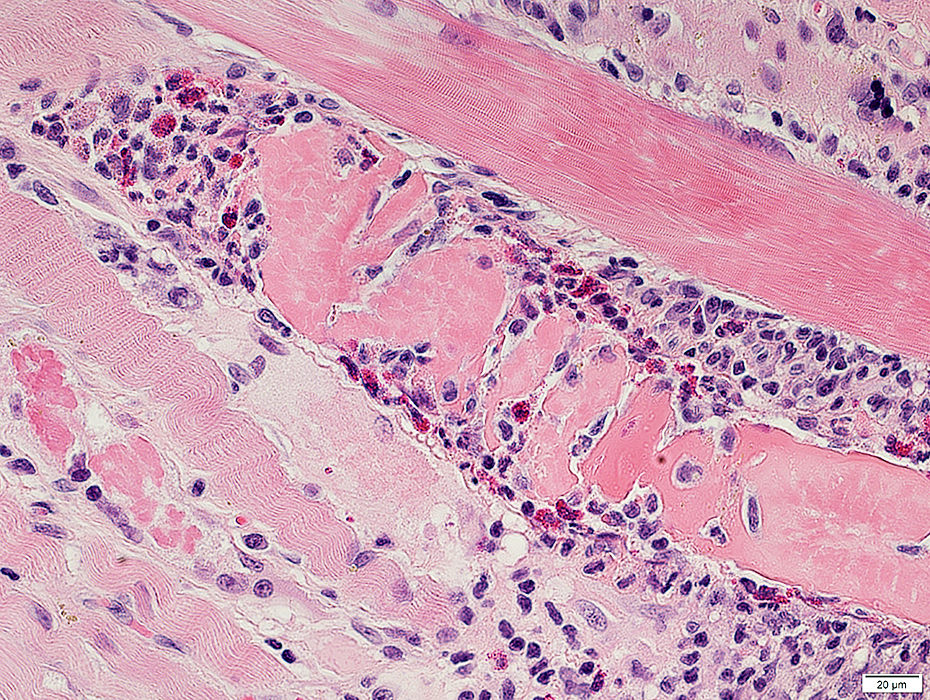 H&E stain |
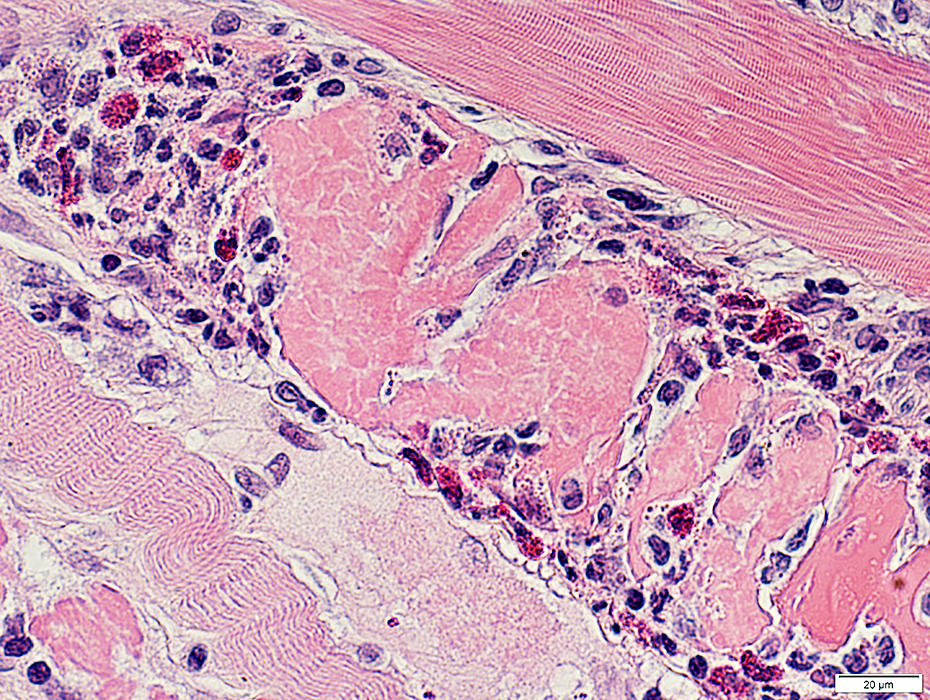 H&E stain |
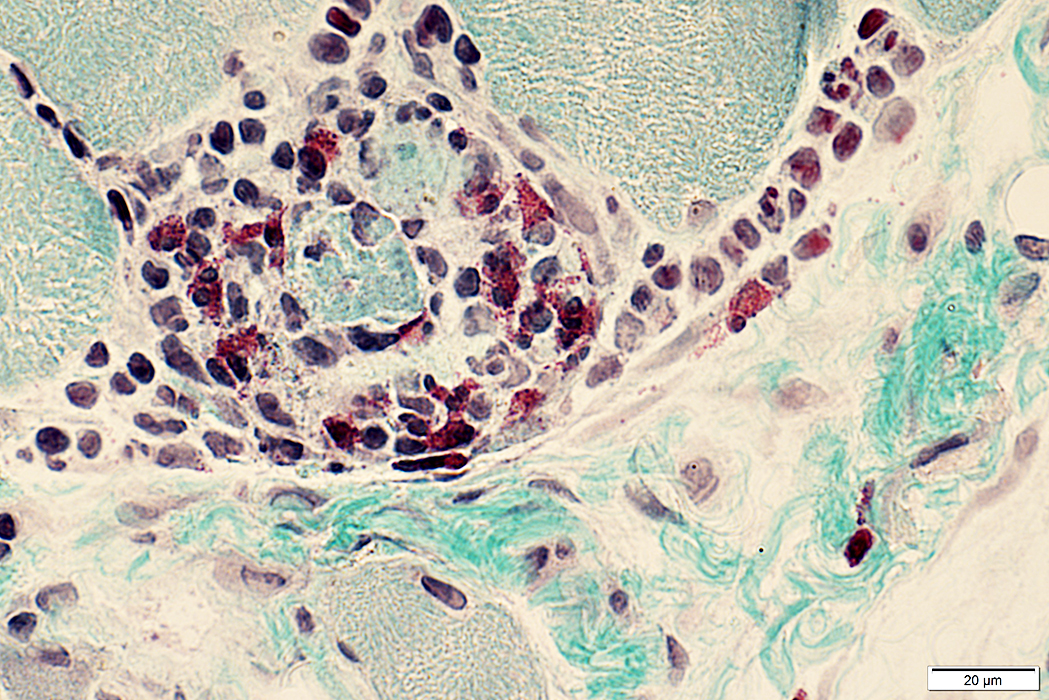 Gomori trichrome stain |
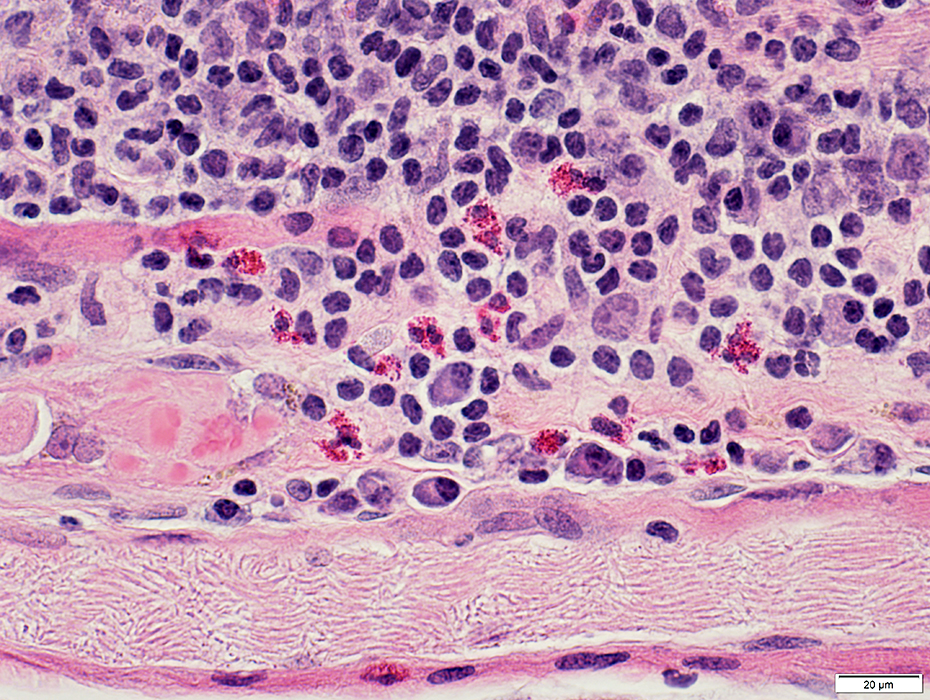 H&E stain |
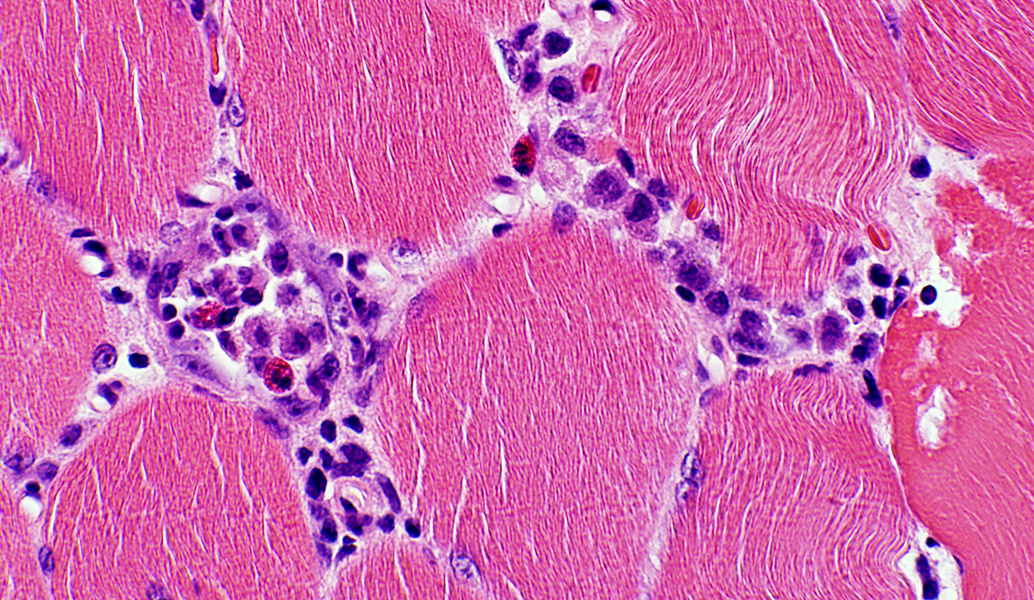 H&E stain |
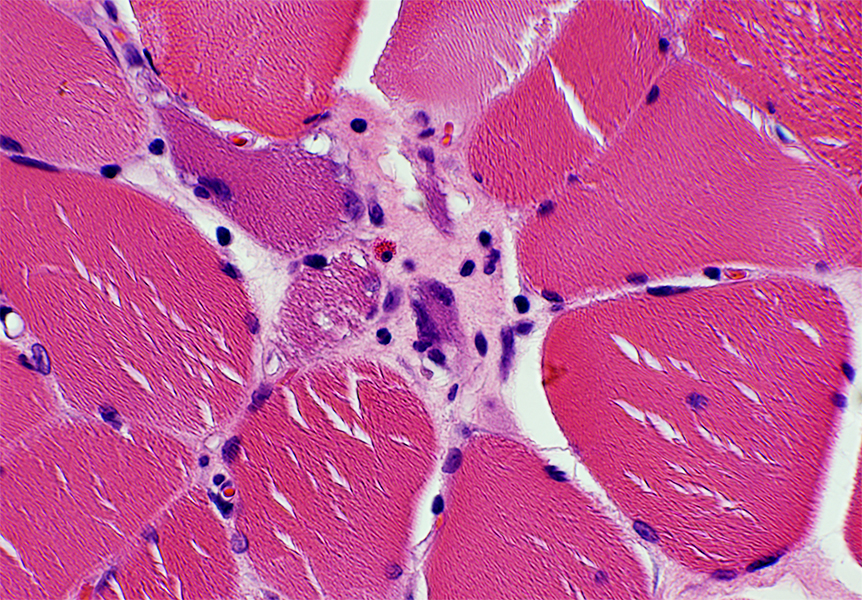 H&E stain |
Necrosis: Scattered Muscle fibers
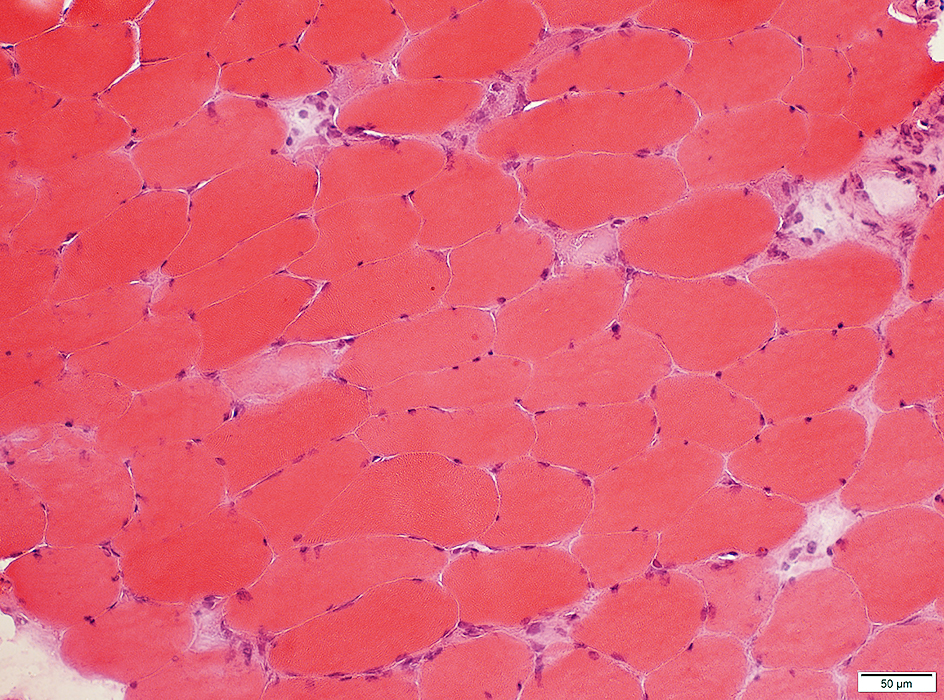 H&E stain |
Ongoing: Muscle fibers in varied stages of necrosis & regeneration
Also see: Scattered necrosis, Severe
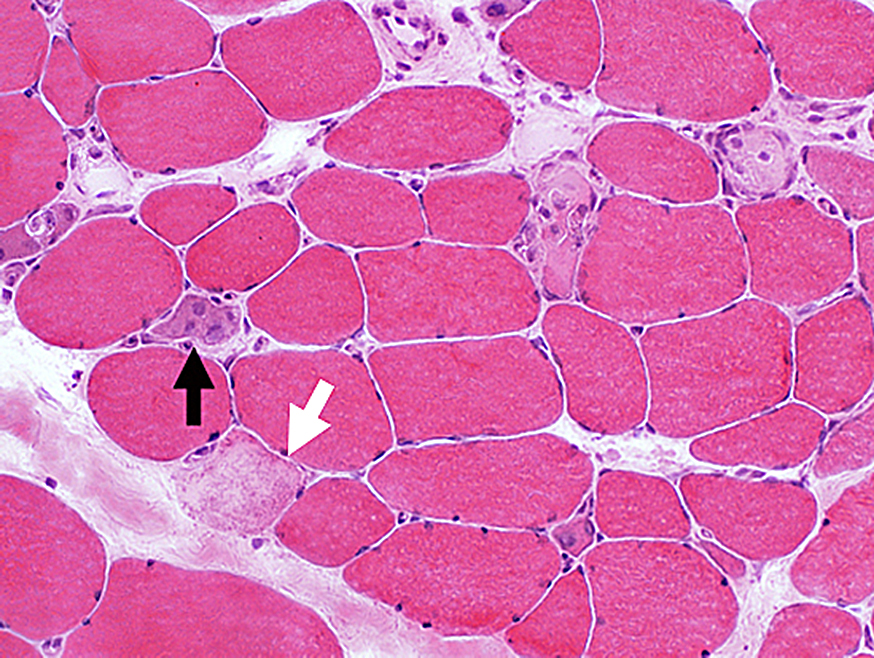 H&E stain |
Necrotic Muscle Fibers: Scattered
Monophasic: Scattered muscle fibers in early stage of necrosis
Cytoplasm of Necrotic Muscle fibers stains diffusely for C5b-9
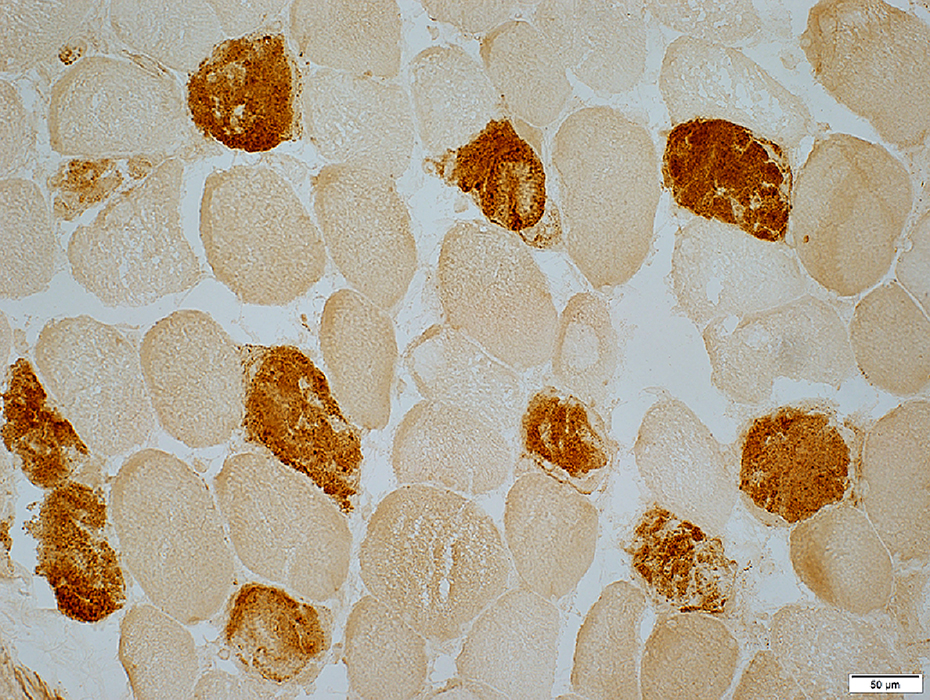 C5b-9 stain |
Necrosis, Early: Comparative Patterns
"Pale" Necrosis
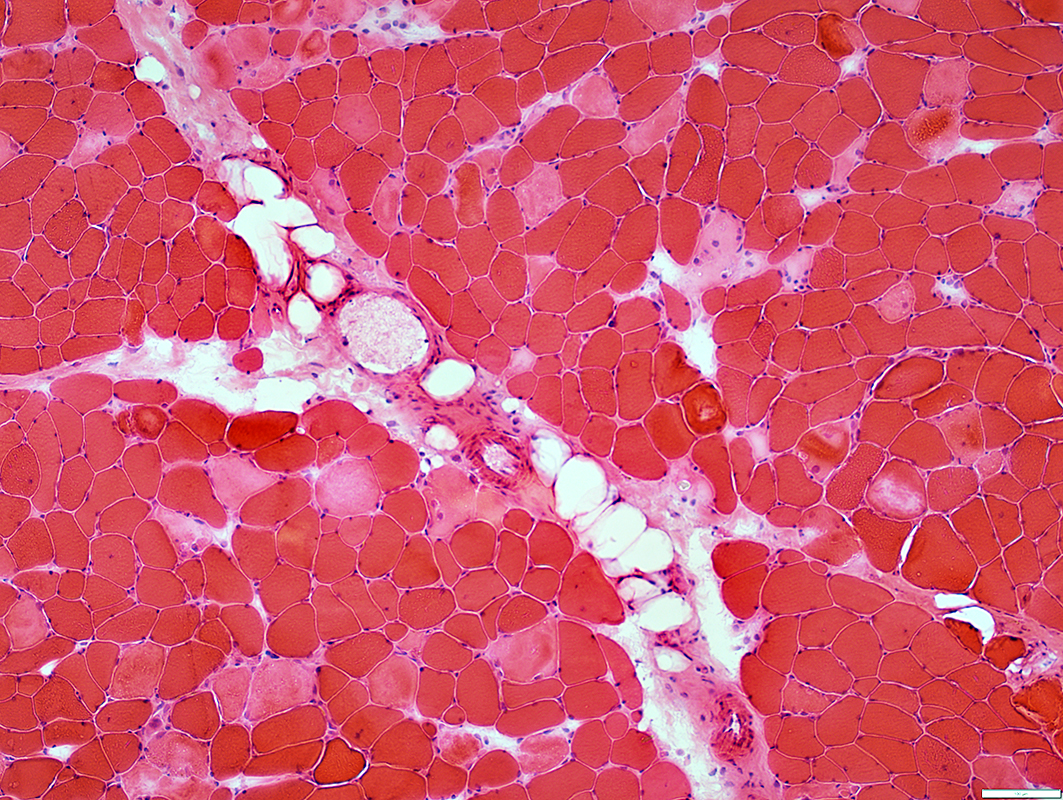 H&E stain |
"Dark" Necrosis
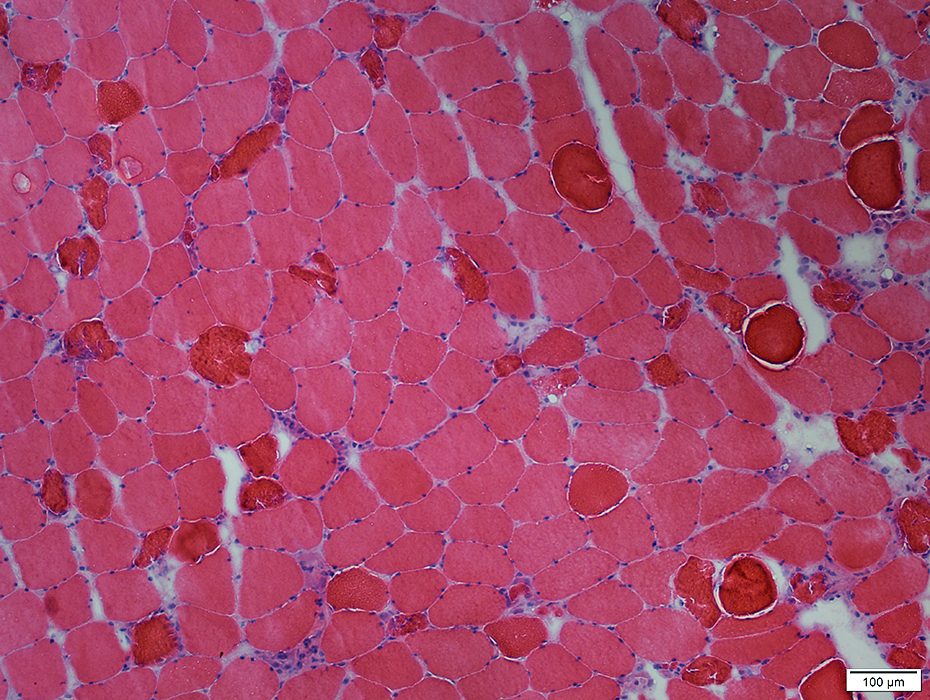 H&E stain |
"Membrane (Sarcolemma)-Related"Necrosis
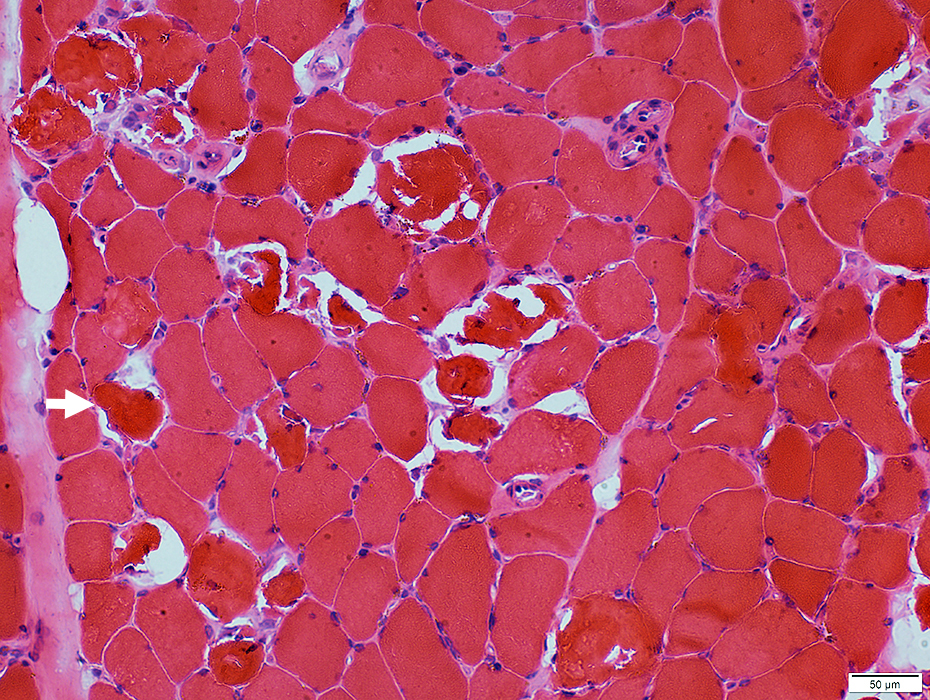 H&E stain |
Large Histiocyte-Related Necrosis
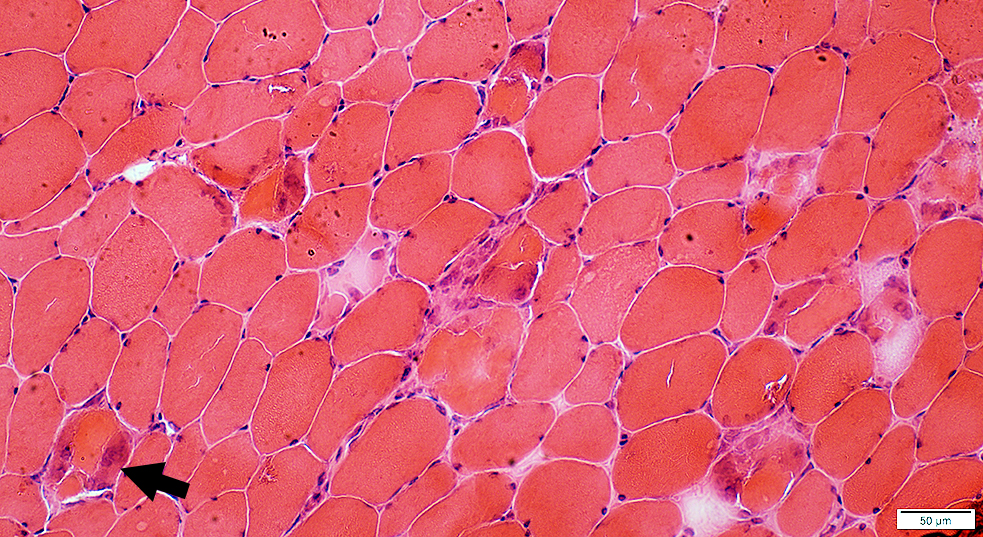 H&E stain |
Also see: Regional Ischemic Immune Myopathy
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
References
1. Cell Death Differ 2016 Feb 12
2. Pflugers Arch 2024 Jul 22
3. Neuromuscular Disorders 2025 Apr
4. Muscle Nerve 2025;71:583-592
1/21/2026