Muscle Fiber Regeneration
5
- Features
- Pathways & Mechanisms
- General: Myogenesis; Satellite cell-muscle regeneration vs Embryonic development
- MyoD dependence: Regeneration > Embryogenesis
- Pax7: Required for satellite cell ontogeny but not embryonic precursors
- Myokines
- Side population (SP) cells
- Cells with heterogeneous hematopoetic & myogenic capacities
- CD45 positive subpopulation can develop myogenic specificity: May express Pax7
- Injured muscle: SP cells
- Stimulated by Wnt (Wingless) pathway
- May replenish satellite cell population during muscle regeneration
- Terminal differentiation: Molecular markers
- Muscle fiber self repair without stem cells
14
- Local muscle fiber repair
- Muscle cell-autonomous mechanism
- Markers of local sarcomere damage
- Molecular: Signalling cascade for repair
- Calcium
- Cdc42

- Phosphokinase C
- Subcellular organelle involved: Myonuclei
- Attracted to migrate to injury site
- Migration mechanisms: Microtubules; Dynein
- Repair Actions
- Accelerate sarcomere repair
- Locally deliver messenger RNA (mRNA) for cell reconstruction
- Stem cells, Pluripotent
2
- Functions
- Self-renewal: Capable of high proliferation
- Multipotential: May differentiate into different lineages
- Muscle, Neural, Bone, Fat, Hematopoietic or Cartilage
- Location: Beneath basal lamina of normal myofibers
- Molecular markers
- Functional characteristics
- Commonly remain quiescent
- Bmp-2: Stimulates conversion to bone pathway
- Transplantation: More effective at restoring dystrophin than satellite cells
- Immunogenicity: Relatively low
- May provide muscle fiber precursors during regeneration
- Satellite cells: General
11
- Tissue specific stem cell in mammalian limb skeletal muscle
- Location: Periphery of muscle fibers; Close to plasma membrane
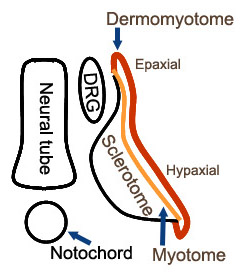
- Developmental origin: Dermomyotome
- Molecular label: Pax7
- Limb muscles
- Satellite cells quiescent
- Activated by exercise or damage
- General actions
- Muscle growth
- Fuse to muscle fibers
- Anatomy: Longitudinal & Radial
- Contribute new muscle nuclei
- Craniofacial & Extraocular muscle satellite cells
- Less quiescent
- Actively contribute to homeostasis
- General populations
- Slow-dividing: Self-renewal to maintain stem cell pool
- Fast-dividing: Differentiates into myogenic cells; Proceeds with myofiber formation
- Age effects
- Satellite cell: Quiescent
- Definition
- Quiescent myoblast
- Location
- Adjacent to muscle fiber sarcolemma
- Beneath basal lamina
- Embryonic origin unclear
- Contain endothelial cell markers
- May originate from somite or cells associated with embryonic vasculature
- Adult origins
- Other satellite cells
- Bone marrow cells
- SP cells
- Function: Repair & Regeneration of muscle
- Other features
- Multipotent
- May differentiate into: Muscle, Bone, Fibroblast or Fat
- Aged satellite cells: More likely to differentiate outside myogenic lineage
- Cell division may be asymmetric
- May generate daughter cells for renewal or differentiation
- Associated with Numb protein
- Limited capacity for replication
- SC in Aging muscle
- SC numbers
- Variably maintained or reduced
- More loss: Females
- Less loss: Exercise
- SC properties
- Formation of myogenic colonies: Reduced
- Ability to activate & proliferate: Decreased
- Capacity to differentiate & fuse into myotubes: Impaired
- Apoptosis: More likely
- Increased propensity to exit quiescent state
- FGF2 signal: Increased
- Molecules expressed
- Pax7


- PAX7 protein
- Subcellular location: Nuclear
- Can bind as heterodimer to Pax3
- Commits pluripotent stem cells to myogenic lineage
- May function in specification of satellite cells upstream of MRFs
- Animal model: Pax7 mutations
- Satellite cells: Absent
- Embryonic muscle development: Normal
- Postnatal muscle growth: None
- Pluripotent stem cells still present
- Disrupt function of embryonic, but not adult, stem cells
- PAX7 disorders
- Heparan sulfate proteoglycans
- Mnf: Responsible for timing of expression of genes for
- Myogenic determination
- Cell cycle progression
- Muscle segment homeobox 1 (Msx-1; HOX7)


- Subcellular location: Nuclear
- Homeobox transcription factor
- Expression
- Actions
- Down-regulates expression of MyoD & other muscle regulatory factors
- May interact with Pax3
- Promotes muscle cell de-differentiation & proliferation
- Ensure correct expansion of myogenic precursors before arrest & differentiation
- Mutations: Hypodontia; Witkop syndrome
- ± MyoD
- Promotes regenerative ability
- Upregulated in dystrophin deficient & inflammatory myopathies
- Mice deficient in dystrophin & MyoD: Severe phenotype
- CD34 (Hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen)

 : Truncated form : Truncated form
- V-CAM1
- c-met (Hepatocyte growth factor receptor)


- Pax3
- Present in satellite cells in some proximal muscles
- Absent from limb muscle satellite cells
- NCAM (CD56)
- No myogenic regulatory factors
- Sub-populations
- EP: Proliferate well
- LP: Slow division; Lack of fusion; 1% of satellite cells
- Satellite cell: Activated (Proliferating myogenic precursor)
- Stimuli to activation: Muscle
- Injury
- Stretch
- Mechanical load
- Molecular markers
- Development
- Arise during late stages of embryogenesis
- Highly active during postnatal growth of muscle tissue
- Provide most of myonuclei to adult muscles
- Regeneration: Stages
- Satellite cells
- Necessary for adult muscle regeneration
- Not necessary for recovery of size after disuse
- Activation: Associated with MyoD
- Proliferation
- Related to Myf-5
- Midkine: Expressed by small regenerating muscle fibers
- Fusion
- Muscle usage
7
- Muscle fiber hypertrophy
- Normally occurs with fusion of satellite cells with muscle fibers
- May occur without satellite cells: Increase of
- Myonuclear domain size
- Myonuclear size
- Increase in muscle fiber size from myostatin inhibition or Akt overexpression
- May occur without satellite cellproliferation
- Addition of new small muscle fibers
- Requires satellite cells
- Fibers have immature myosin patterns
- Differentiated product: Myoblast
- Pathology: Regenerating muscle fibers (After necrosis) (Arrow)
- Fiber size: Small
- Nuclei: Large
- Distribution: May occur individually or in clusters
- Molecular: MHC-1 & NCAM expression
- NADH Histochemistry: Dark stain; Coarse internal architecture
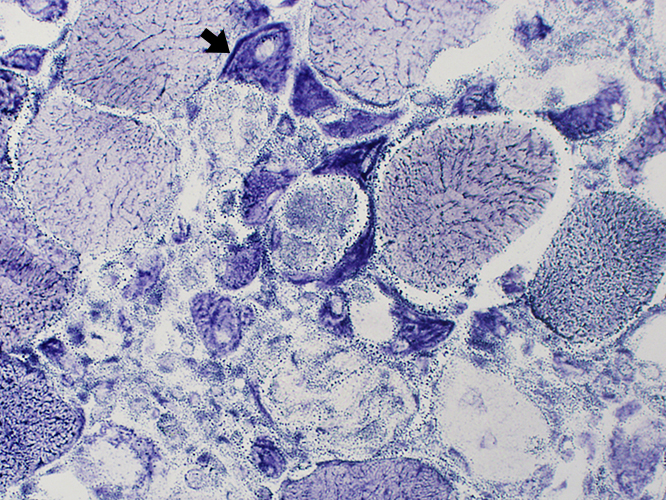
NADH stain
|
|
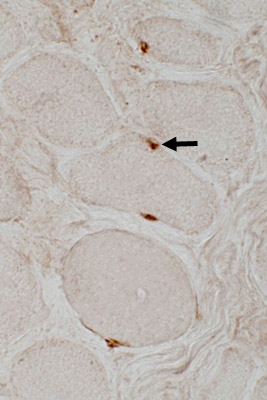
PAX 7 stain
Satellite cells in Duchenne MD
|
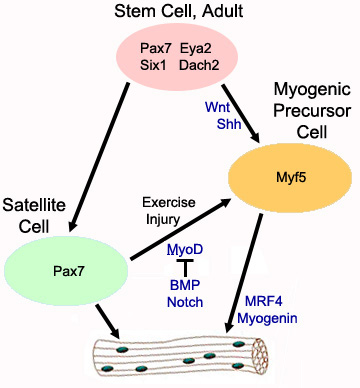
Muscle Regeneration: Pathways
|
|