DYSTROPHINOPATHIES: Becker 1
|
Patients < 10 years Myopathic grouping Young adult: Moderate severity Older adult: Late stage Dystrophin staining patterns Neuromuscular Junctions |
Becker MD: 7 year old male
Muscle FibersSizes: Varied
Internal nuclei: Few
Myopathic groups
Early: Clusters of muscle fibers in similar stages of necrosis or regeneration (Black arrow)
Late: Focal regions with small muscle fibers & increased endomysial connective tissue (White arrow)
Endomysial Connective Tissue: Increased in some areas
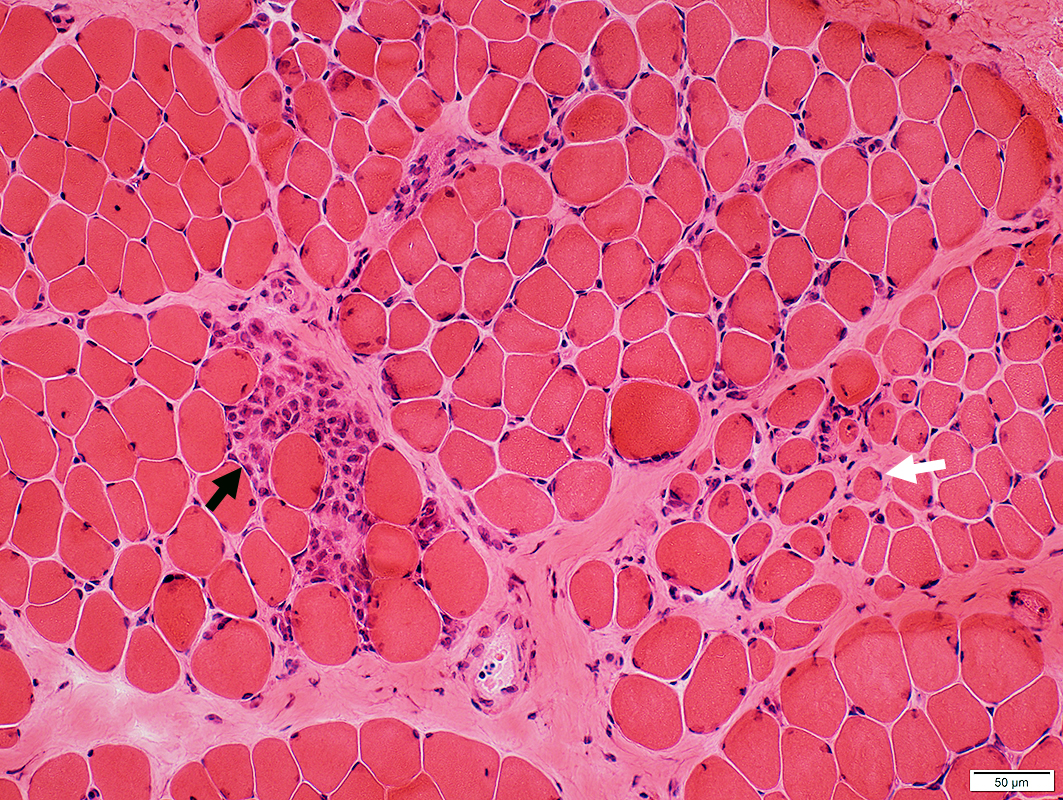 H&E stain |
Myopathic Grouping
|
Myopathic Grouping
 Gomori trichrome stain |
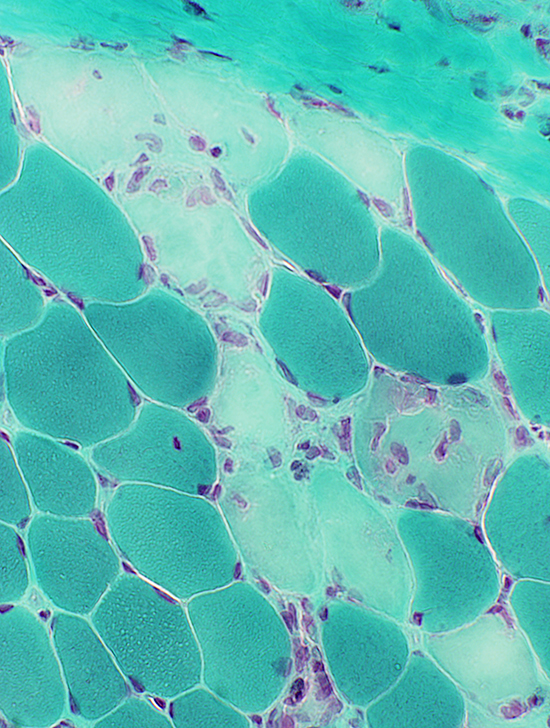 Gomori trichrome stain |
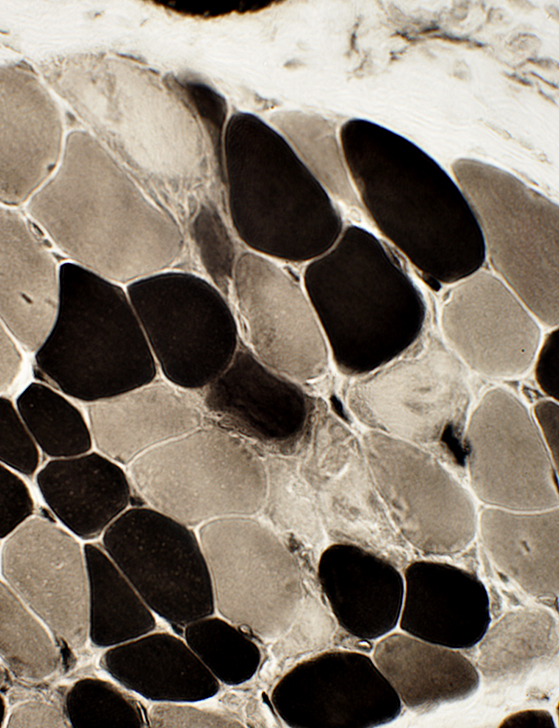 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
- Necrotic muscle fibers: Pale on Gomori trichrome, ATPase, NADH
- Phagocytic cells: Near or within necrotic muscle fibers on Esterase & Acid phosphatase
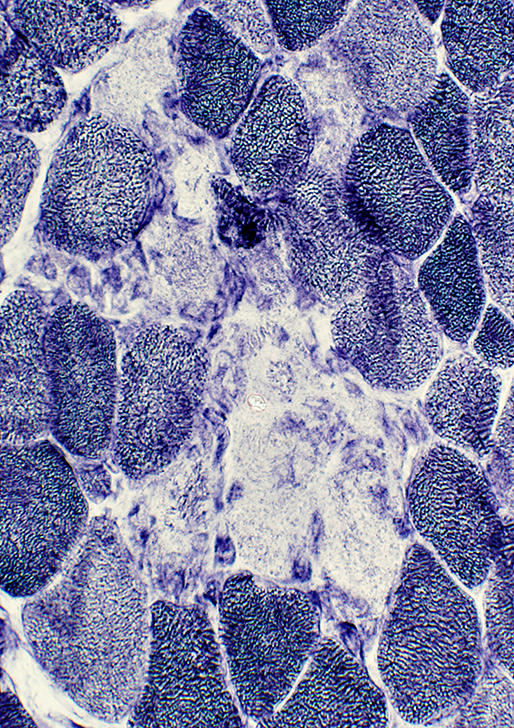 NADH stain |
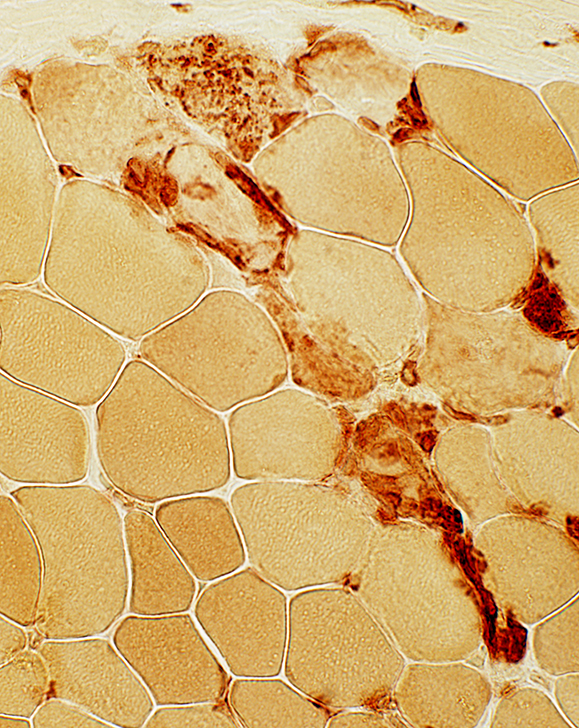 Esterase stain |
Myopathic Groups: After muscle fiber necrosis
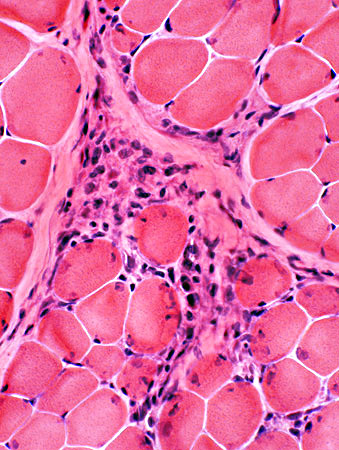 H & E stain |
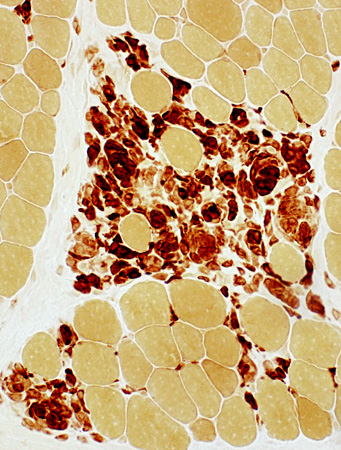 Esterase stain |
|
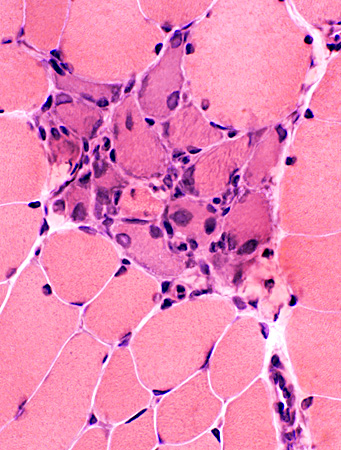
Post-Phagocytosis (Biopsy from BMD child (< 10 years) Clusters of cells (esterase positive) replacing necrotic muscle fibers Cells may include: Histiocytes; Muscle fiber precursors 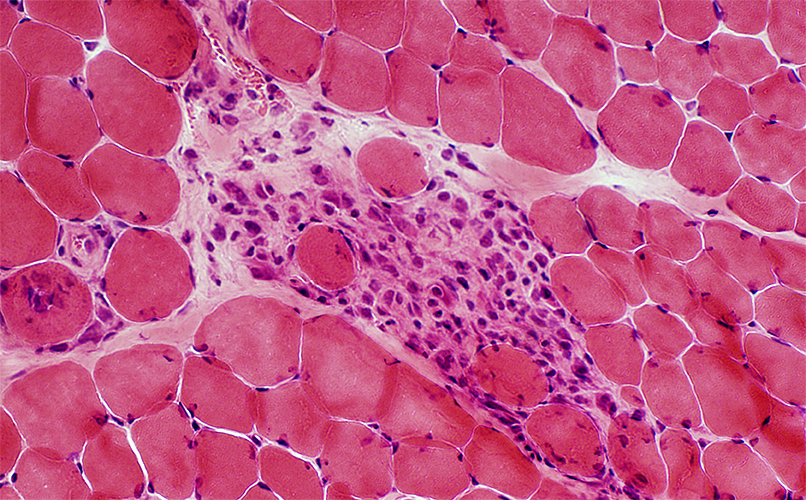 H & E stain |
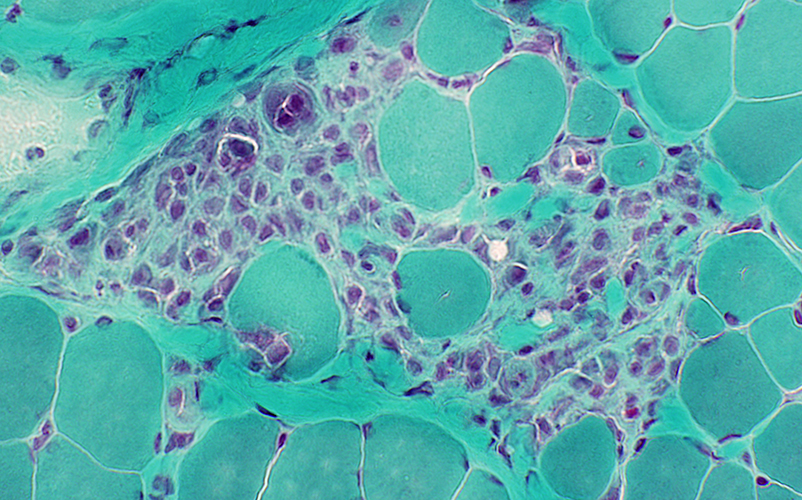 Gomori trichrome stain |
Clusters of cells replacing group of neighboring necrotic muscle fibers
Cells may include: Histiocytes; Muscle fiber precursors
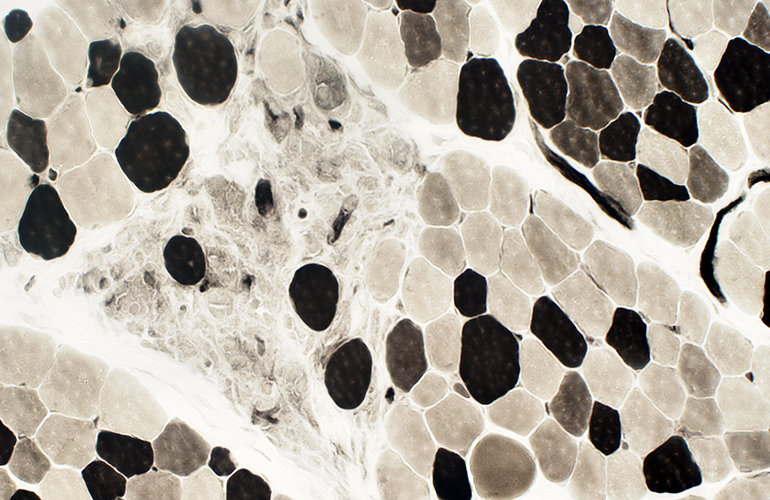 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Myopathic Groups: Clusters of Muscle Fibers all in same stage of Regeneration
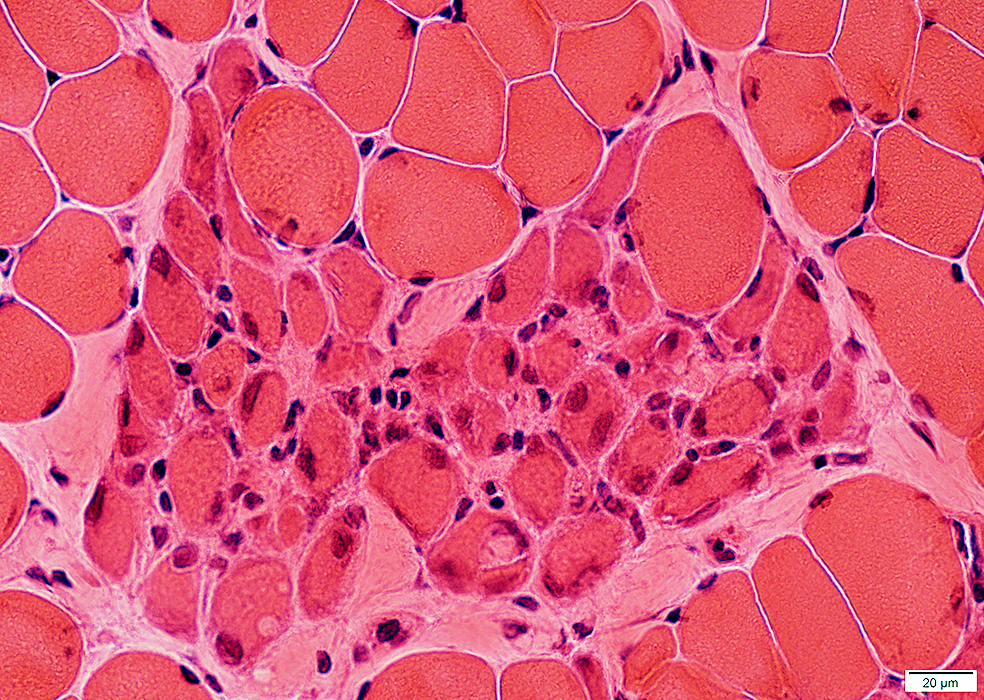 H & E stain |
Many small, immature muscle fibers with large nuclei
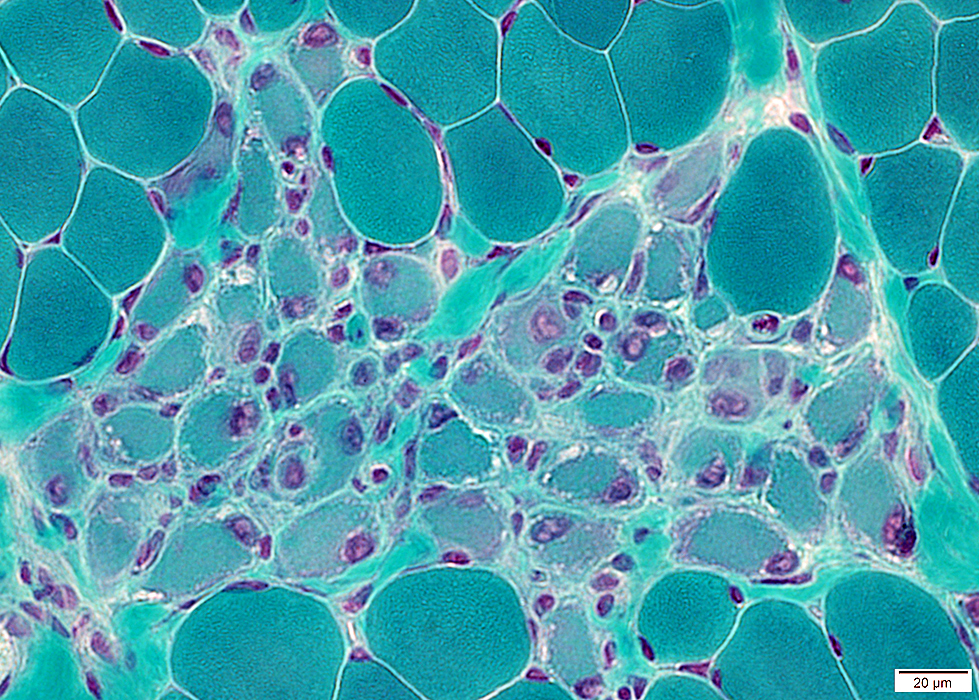 Gomori trichrome stain |
 H & E stain |
 H & E stain |
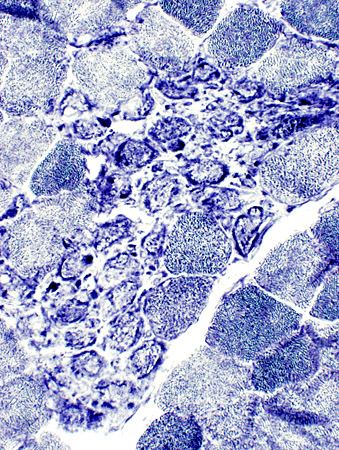 NADH stain |
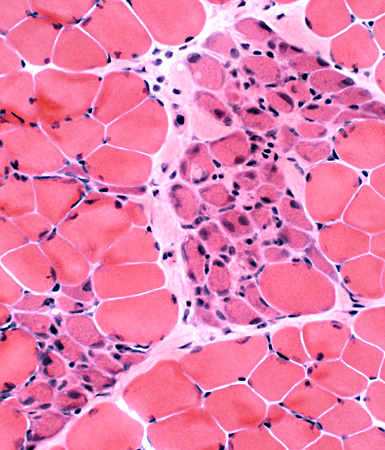
Regenerating muscle fibers: Grouped (Biopsy from child (< 10 years))
| ||
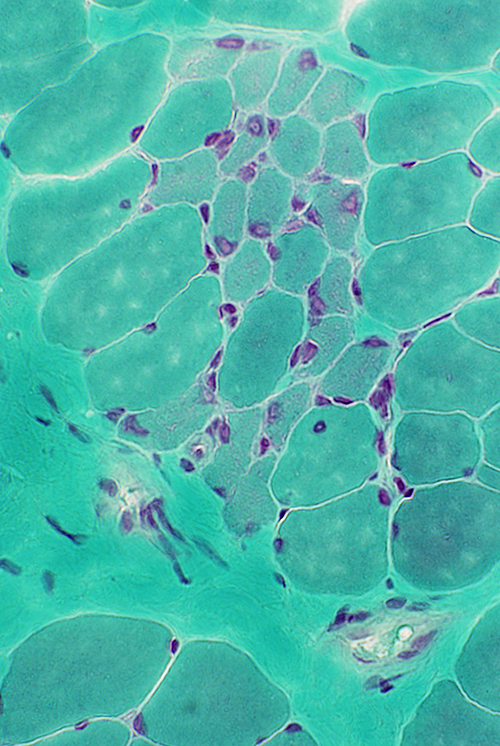 Gomori trichrome stain |
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
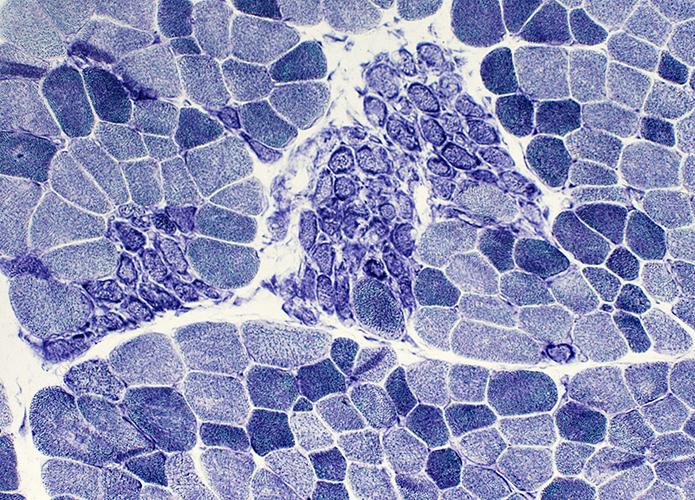 NADH stain |
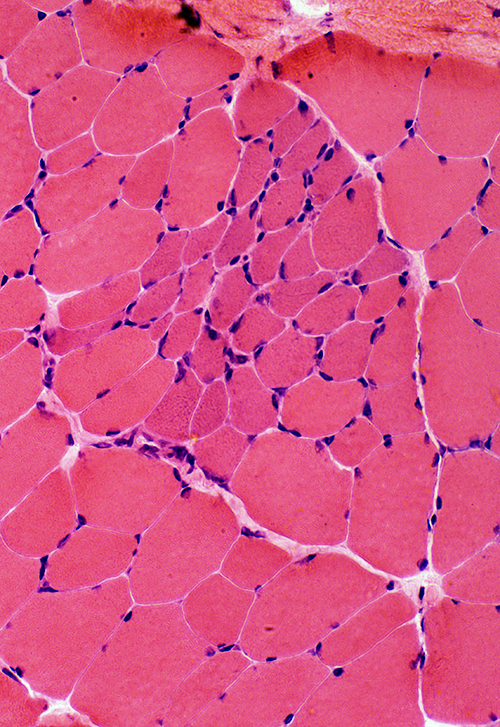 H&E stain |
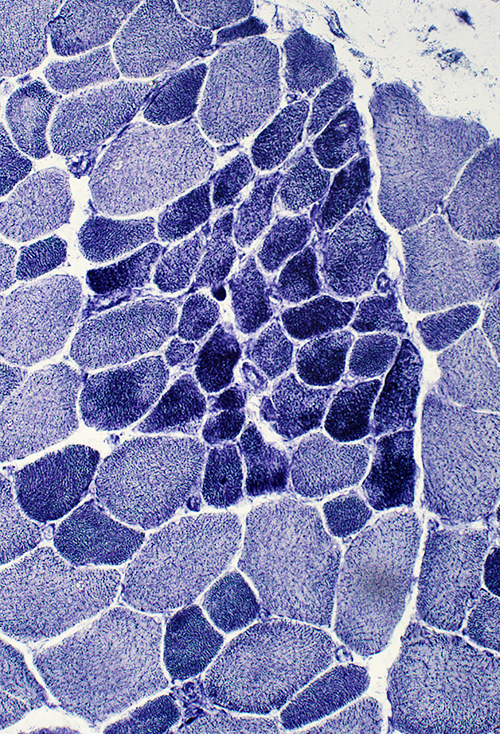 NADH stain | |
Regeneration: Grouped muscle fibers
- Immature
- Type 2C on ATPase pH 4.3
- May have reduced Dys-2 (C-teminal dystrophin) staining
- Cytoplasm
- Sizes: Intermediate
- Dystrophin stain: Less intense than more mature fibers
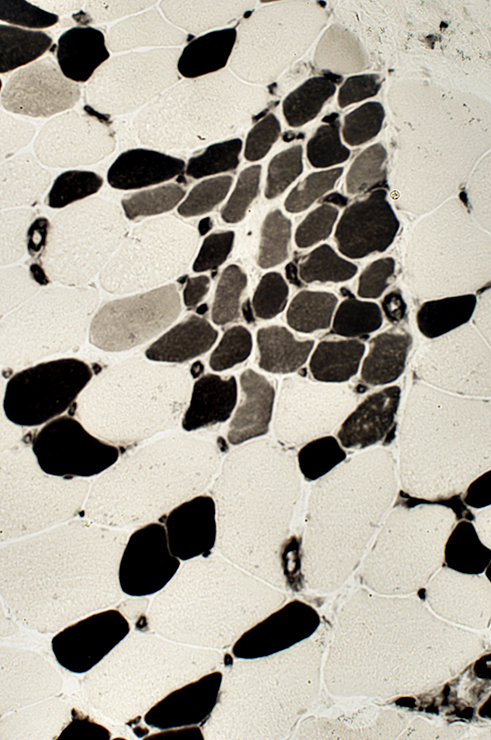 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
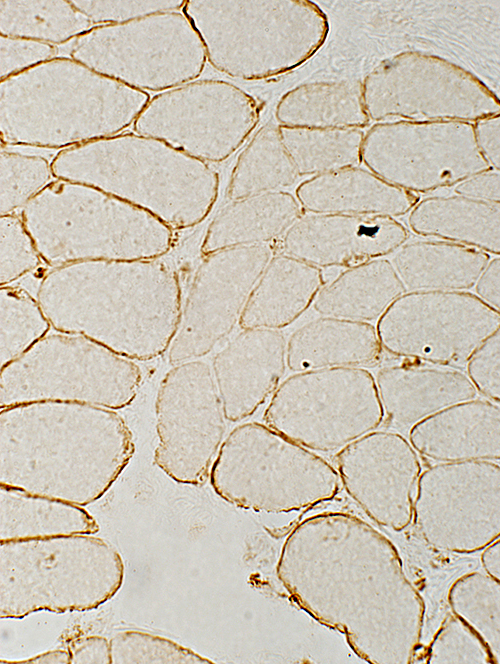 Dys-2 (Dystrophin C-terminus) stain |
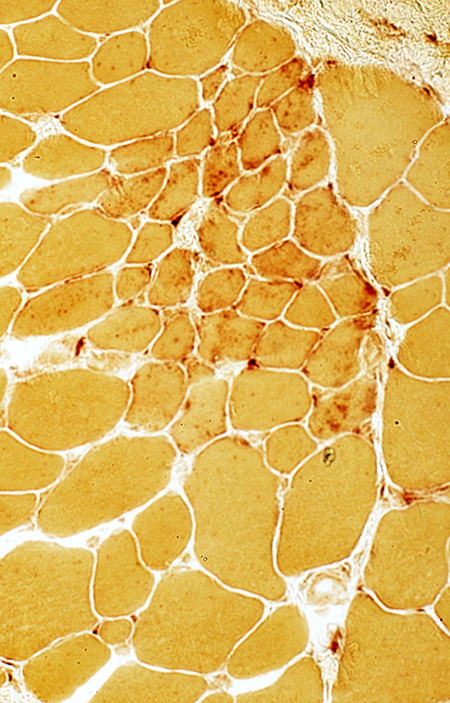 Esterase stain |
Clusters of regenerated muscle fibers Fiber cytoplasm often has increased esterase staining 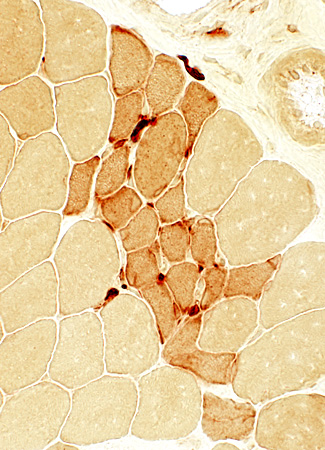 Esterase stain |
Post-Regeneration
| |
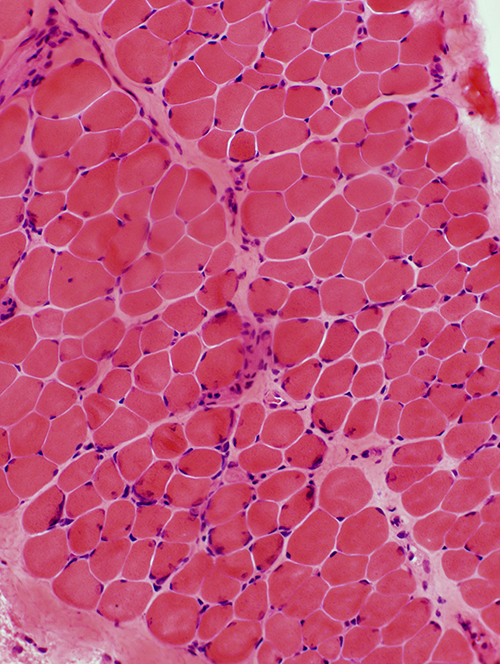 H&E stain |
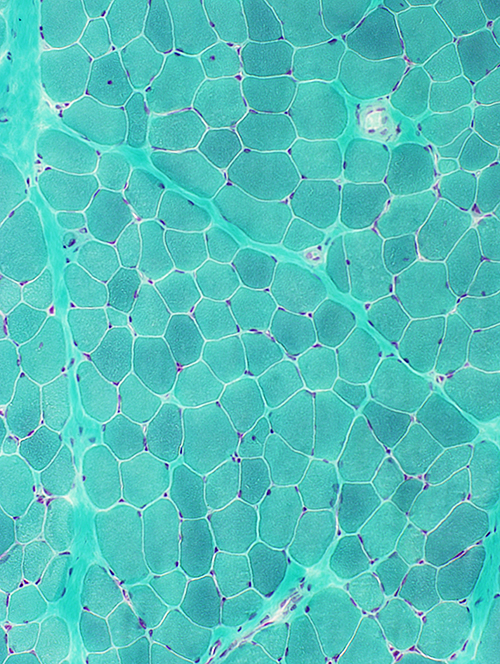 Gomori trichrome stain |
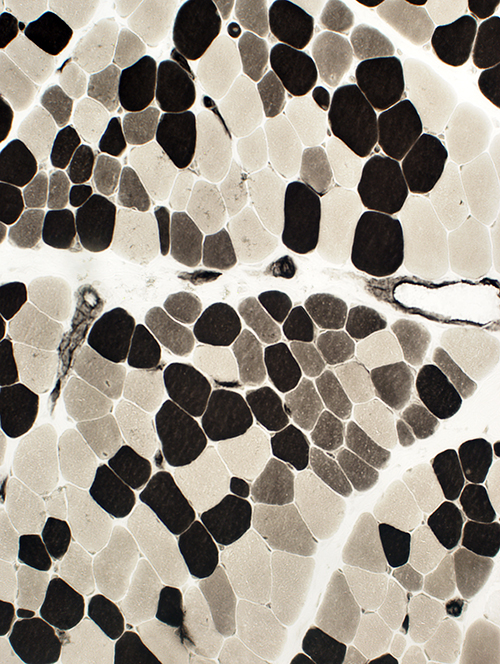 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
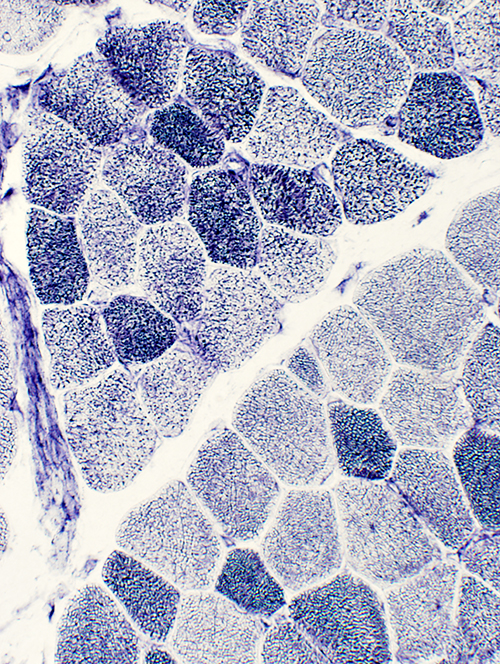 NADH stain |
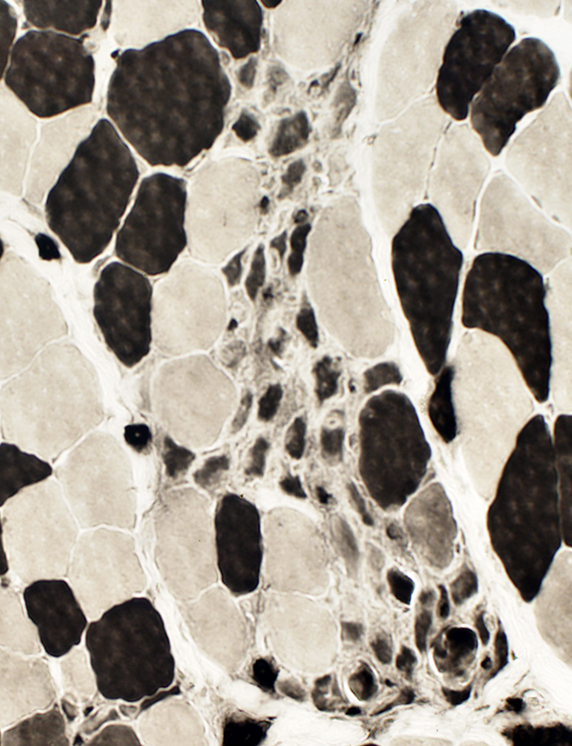
NADH stain: Mildly coarse structure of internal architecture
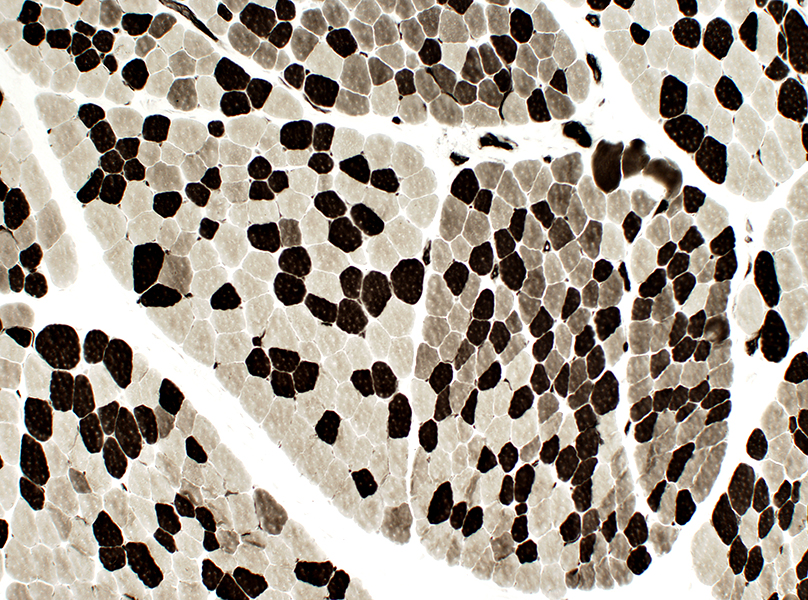 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Becker Muscular Dystrophy: Biopsy from young adult male
- Muscle fibers
- Muscle fiber size: Varied; Atrophy & Hypertrophy
- Internal nuclei: One or several in muscle fibers
- Regeneration: Scattered fibers
- Endomysial connective tissue: Moderately increased
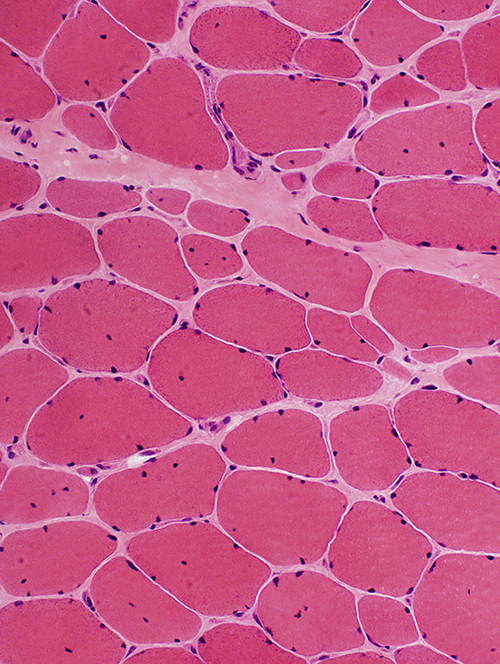 H&E stain |
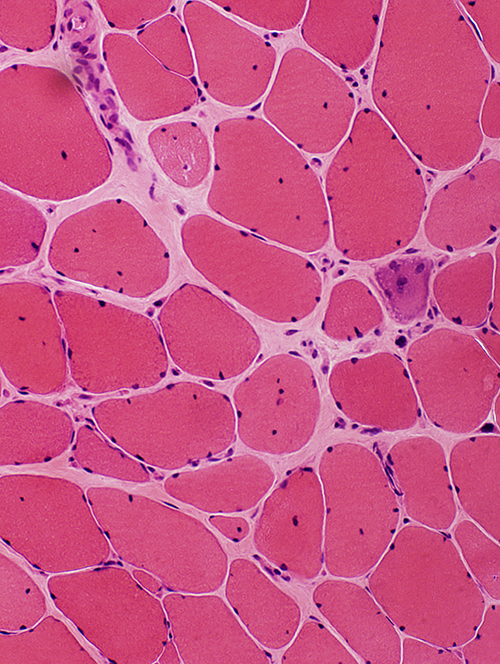 H&E stain |
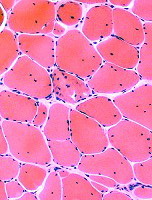 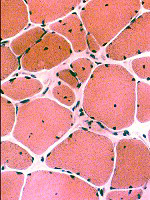
|
Becker Muscular Dystrophy: Biopsy from adult male
- Typical of chronic dystrophies or myopathies
- Endomysial connective tissue
- Increased
- Correlates with levels of muscle-specific microRNA miR-133b in serum 2
- Muscle fibers
- Fiber sizes
1
- Varied
- More large & small fibers
- Largest muscle fibers: Hypertrophied
- Mean size: Not changed
- Small muscle fibers: Round shape
- Internal nuclei
- Scattered fibers
- Necrosis & Regeneration: Less than in younger patients
- Hypercontraction
- Split
- Immature fibers
- Type 2C fibers: Scattered, Many
- MYH3 (Fetal myosin): Increased numbers of fibers stained
- Fiber sizes
1
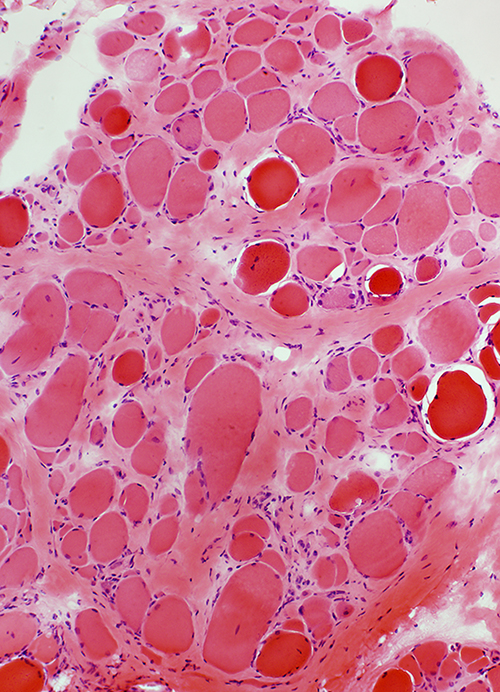 H&E stain |
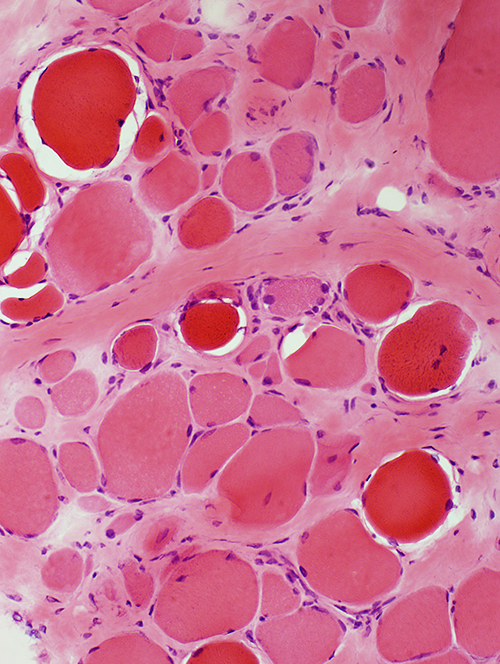 H&E stain |
Sizes: Varied
Hypercontracted: Scattered
Endomysial connective tissue
Increased
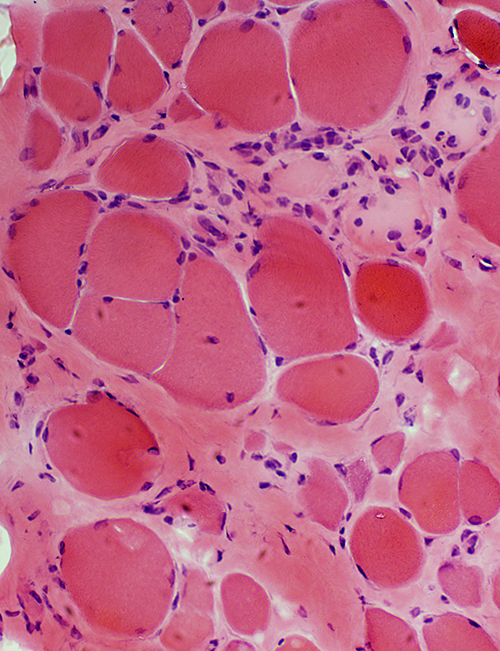 H&E stain |
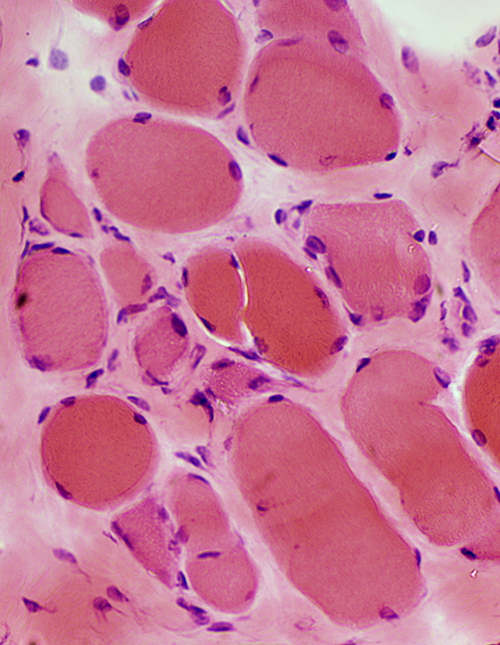 H&E stain |
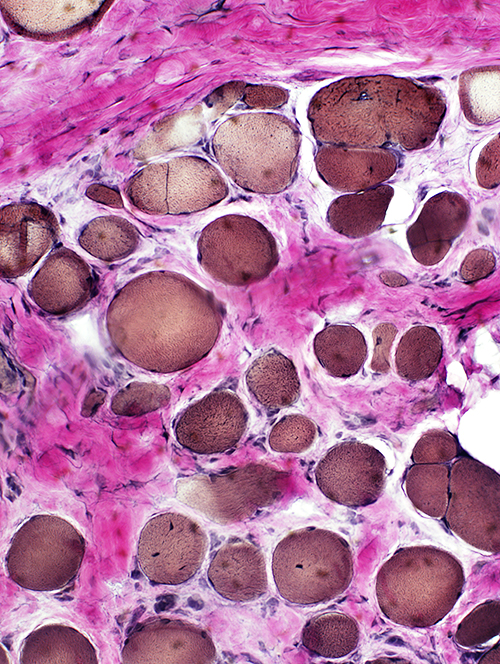 VvG stain Endomysial connective tissue: Increased |
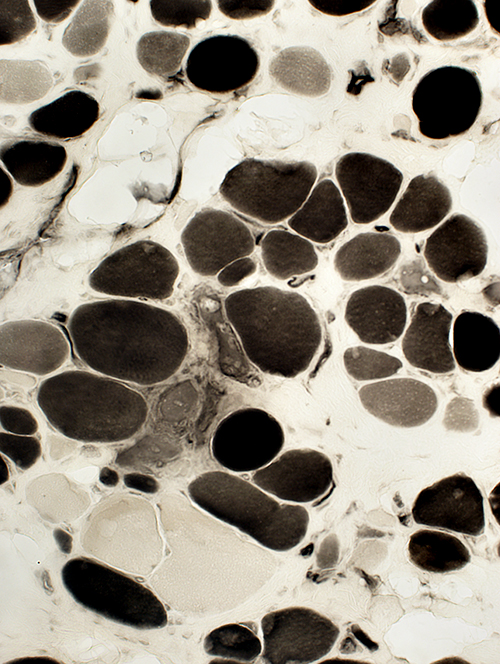 ATPase pH 4.3 stain Many scattered 2C fibers |
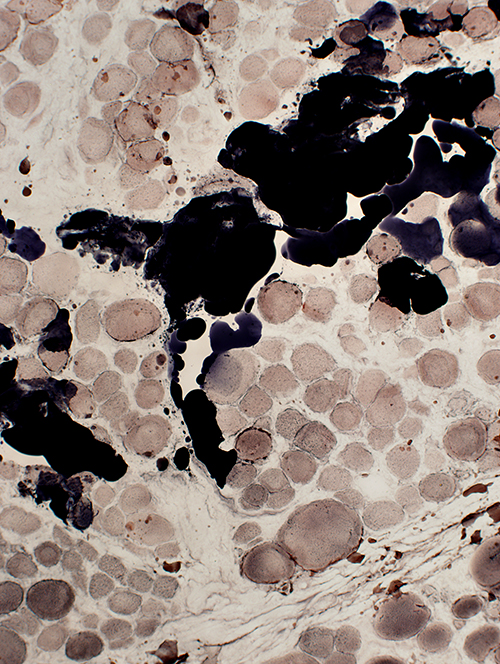 Sudan black stain Endomysium & Perimysium replaced by fat |
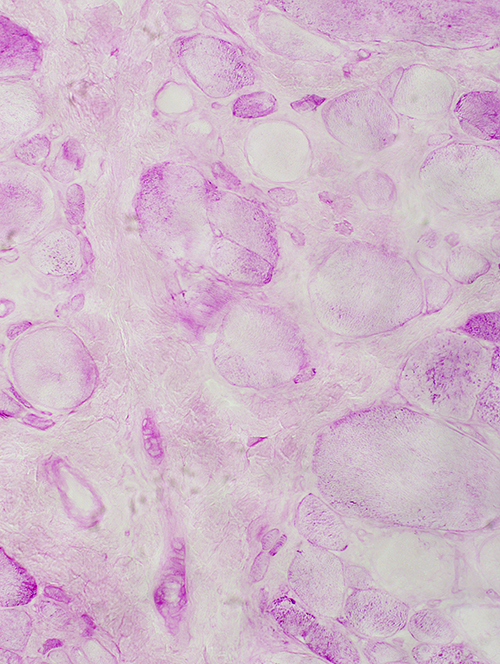 PAS stain Normal glycogen |
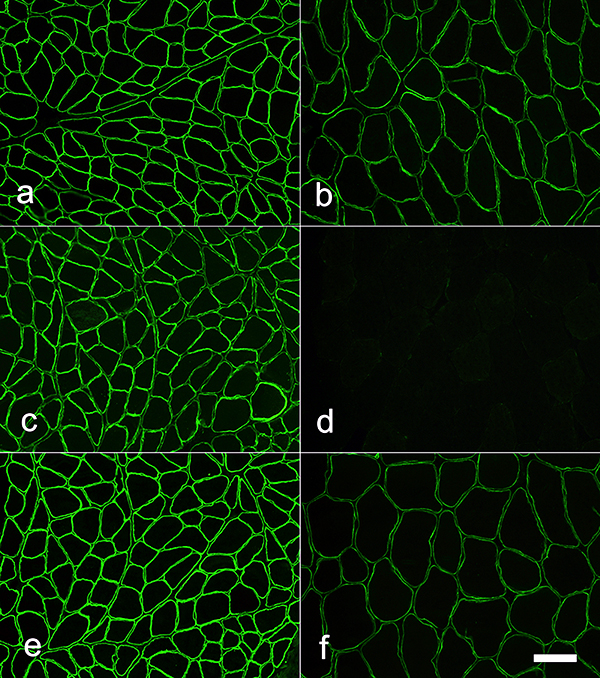
Becker Muscular Dystrophy: Dystrophin staining
Dystrophin Antibodies- Dys3 (10/12B2): N-terminus; Amino acids 321-494; Dystrophin hinge 1; Spectrin repeats
- Dys1: Rod domain; Amino acids 1181-1388
- Dys2: C-terminus; Amino acids 3668-3684
- 6A9 (MANEX50): Exon 50
- 7G1 (MANEX46B): Exon 46
Dystrophin gene: Large deletion
Normal control on left panels; Patient on right panels
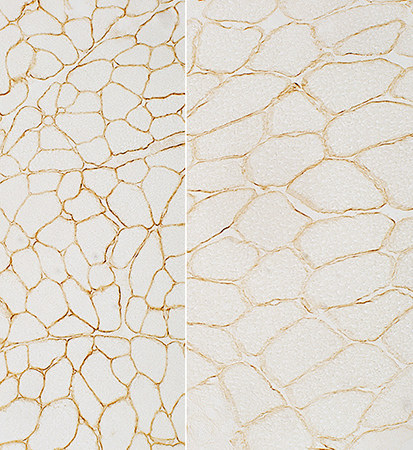 Dys-3 stain N-terminus: Staining is present but reduced |
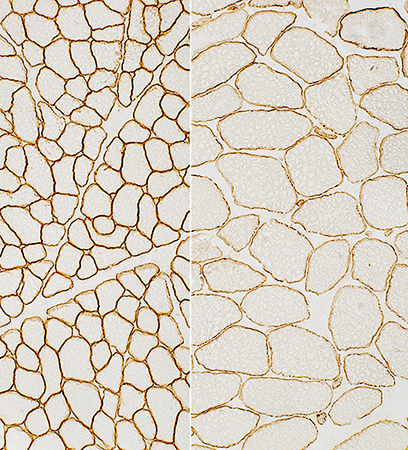 Dys-1 stain Rod domain: Staining is present but reduced |
 Dys-2 stain C-terminus: Staining is absent except on a revertant muscle fiber |
Dystrophin gene: Leaky stop mutation
Normal control on left panels; Patient on right panels
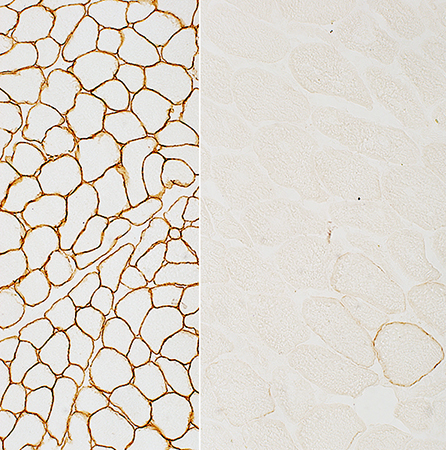
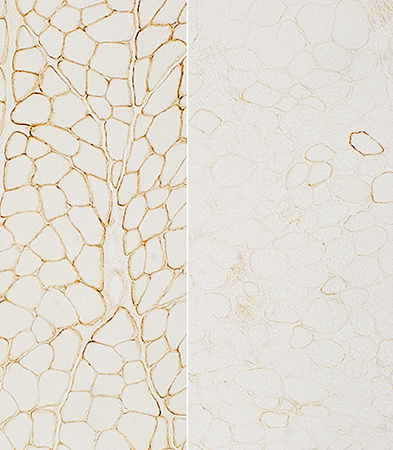 Dys-3 stain N-terminus: Staining is present but very reduced |
 Dys-1 stain Rod domain: Staining is present but reduced |
 Dys-2 stain C-terminus: Staining is present but very reduced |
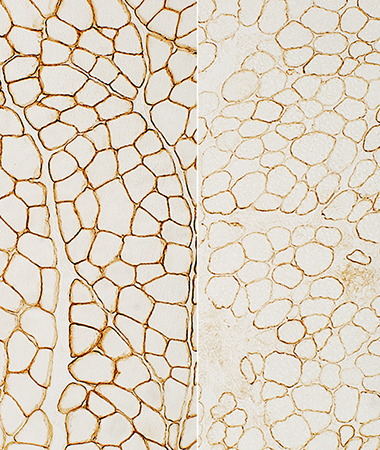
Dystrophin gene: Rod domain deletion
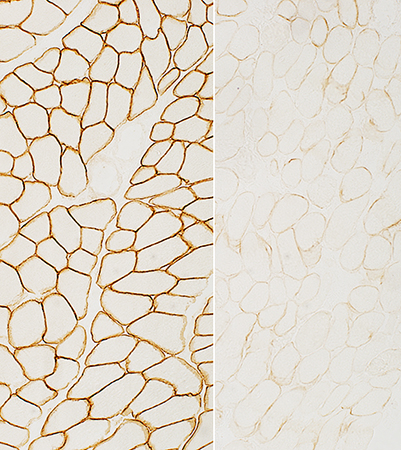
 Normal Becker MD |
Dystrophin: Sarcolemmal staining Rod region (d): Absent N- (b) & C-terminus (f): Reduced but Present Normal control on left; Becker MD patient on right N-terminal region of dystrophin: (a & b; Dys-3 antibody) Rod region of dystrophin (c & d; Dys-1 antibody) C-terminal region of dystrophin (e & f; Dys-2 antibody) |
Becker MD (Exon 45 to 47 Deletion): NMJ Pathology
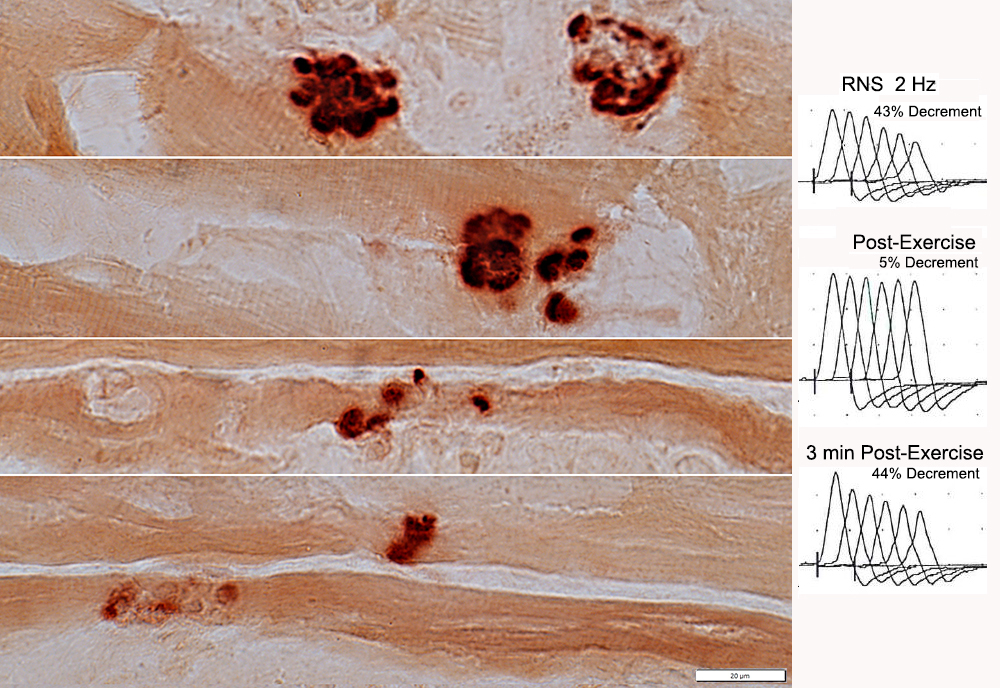 RNS from: Robert Bucelli |
Decrement: Ramp-like
NMJ features
Multi-segmented
May be small (Below)
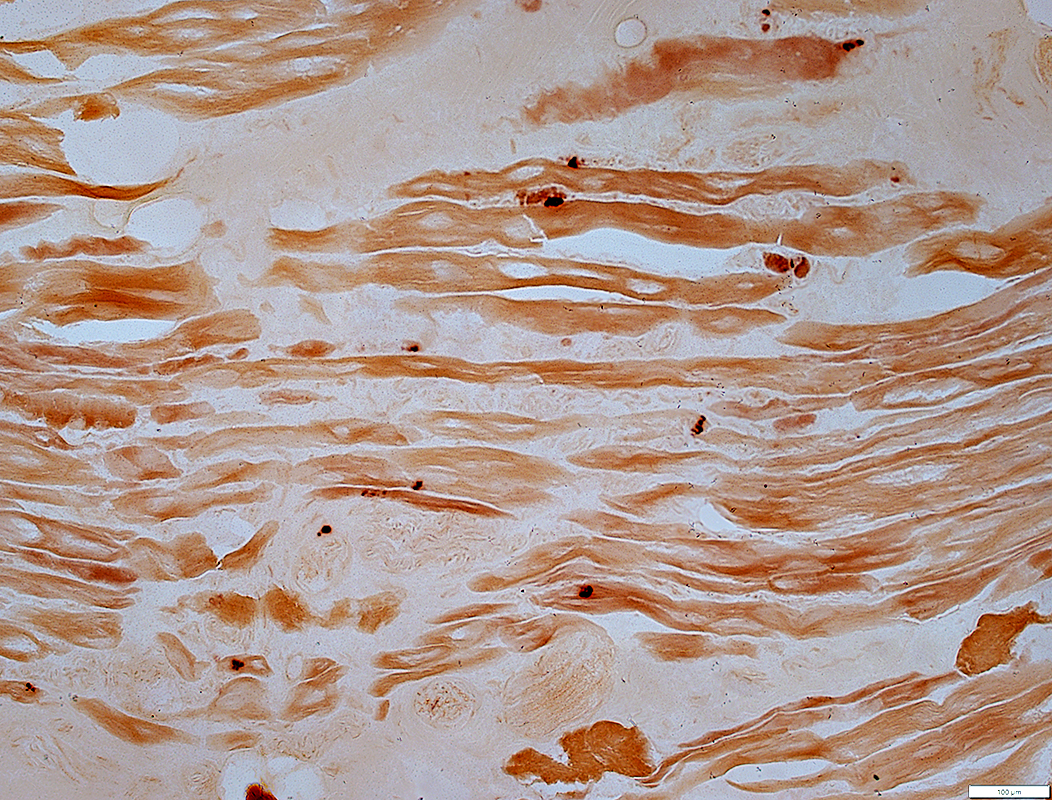 Esterase stain |
Go to Duchenne muscular dystrophy pathology
Return to Dystrophinopathies.
Return to Neuromuscular syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular home page
References
1. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:48
2. J Cell Mol Med 2022;26:4678-4685
3. Brain Research 1999;839:298–304, Neurosci Lett 2020;737:135304
12/2/2023