|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
DYSTROPHINOPATHIES: Duchenne
|
Early age Mild Myopathic groups Regeneration Severe Later age Dystrophin Revertants Post gene transfer General features |
|
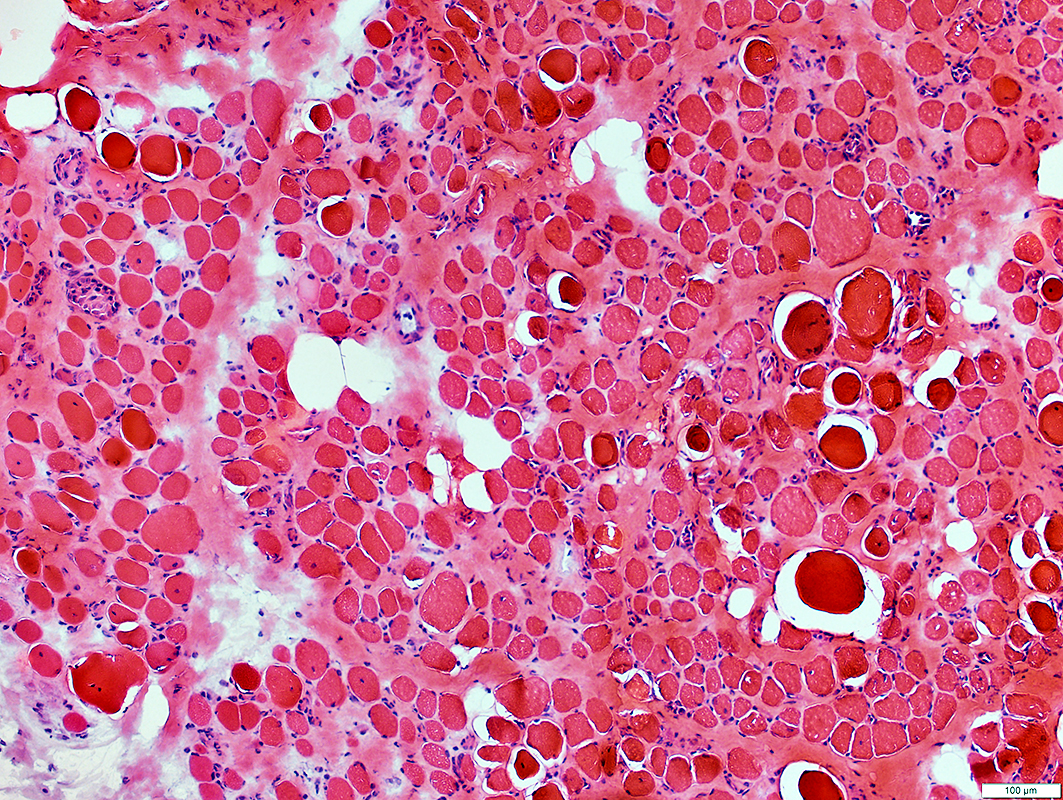
DMD Muscle pathology: General features
|
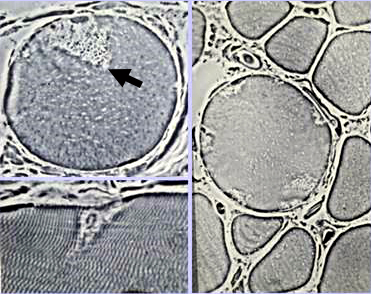 From: AG Engel Delta Lesions (Arrow)
Description: Focal wedge-shaped lesions Locations: Subsarcolemmal regions of muscle fibers |
|
Muscle fibers
Size: Varied
Shape: Small fibers round or polygonal
Internal nuclei
Hypercontracted
Necrosis
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased between muscle fibers
Fat: Increased in endomysium & preimysium
 H&E stain |
DMD
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased between muscle fibers
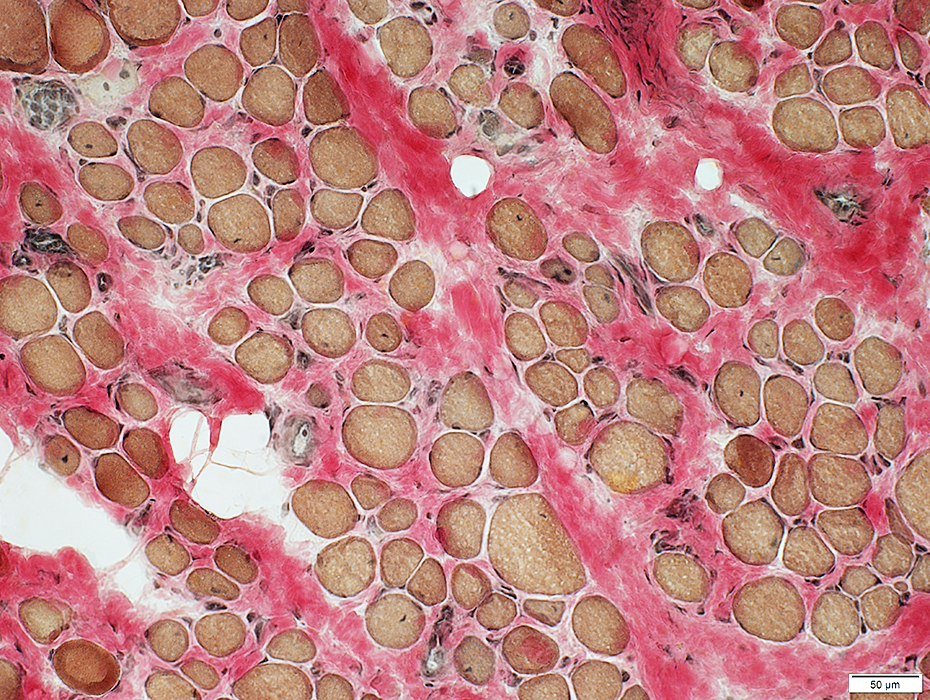 VvG stain |
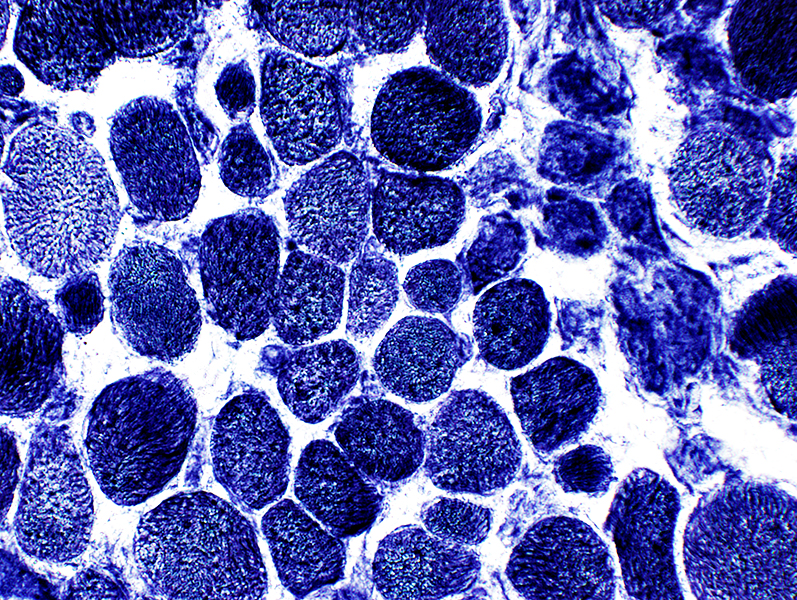 NADH stain |
Coarse internal architecture on NADH (Above)
2C fibers: Intermediate staining on ATPase pH 4.3 (Below)
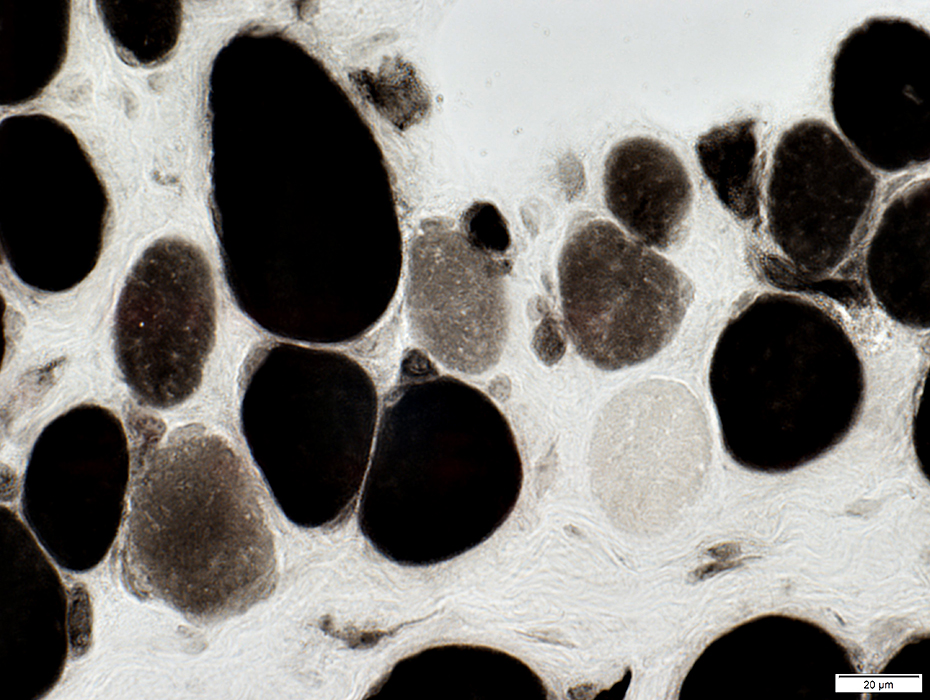 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
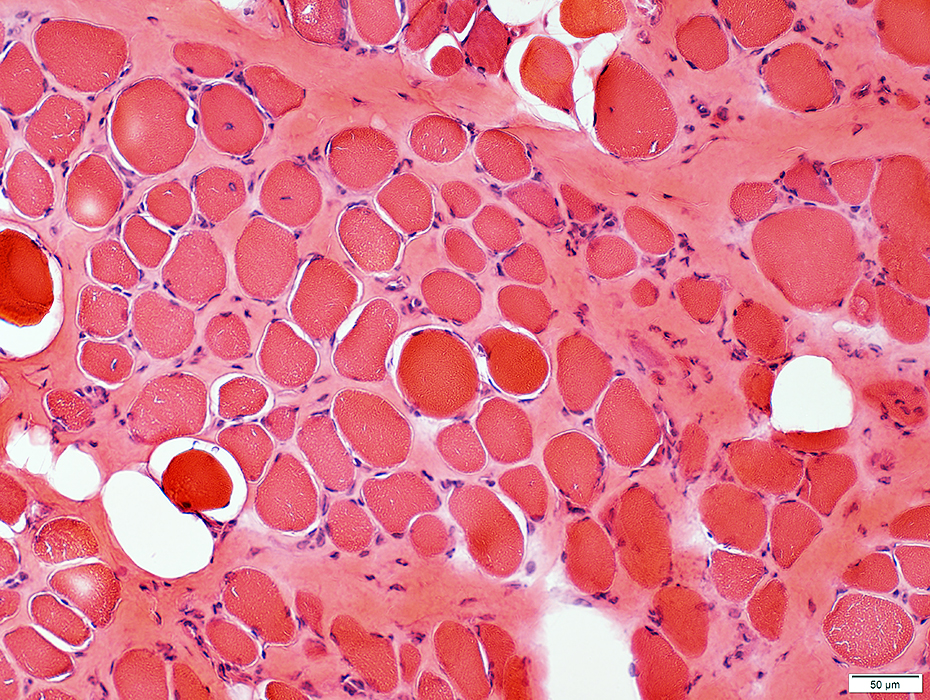
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Early Pathology
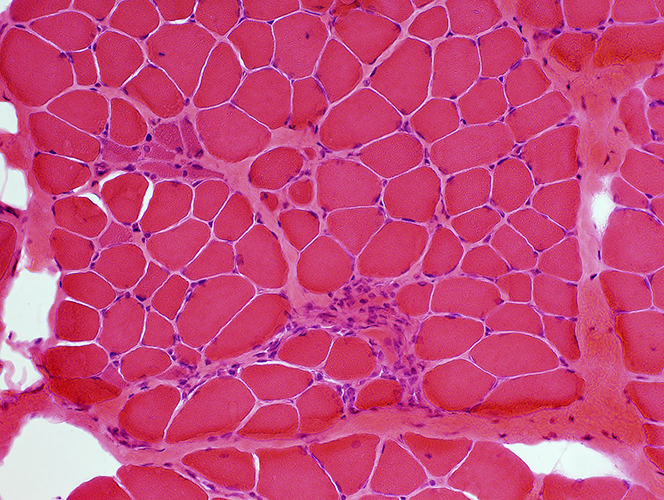 H & E stain |
|
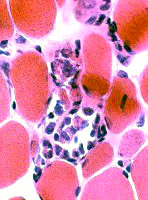
Muscle fibers Sizes: Varied; Small fibers are rounded or polygonal; Occasional hypertrophic fiber Necrosis (Left): Fibers scattered & in small groups Myopathic groups (Below): Clusters of small necrotic (Black arrow) & regenerating (White arrow) muscle fibers Internal nuclei: Occasional Endomysial connective tissue: Normal to mildly increased Perimysium: Early replacement by fat |
|
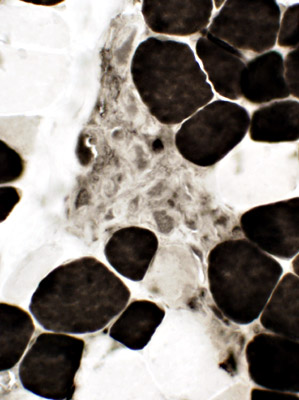
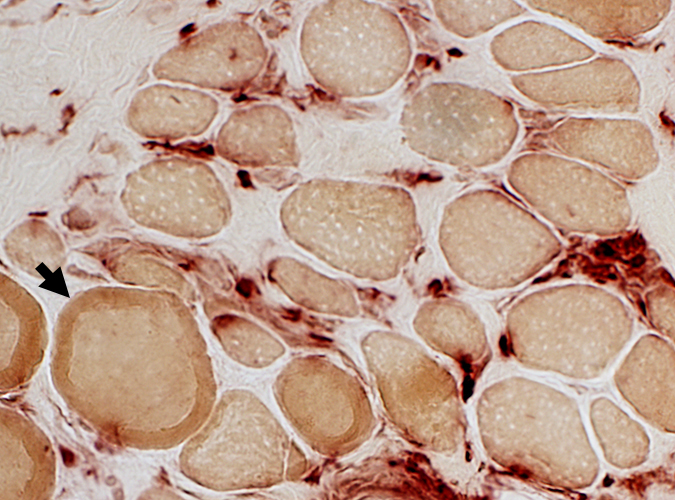 Acid phosphatase stain Acid phosphatase + cells Endomysium: Small Scattered cells Necrotic muscle fibers: Clusters of phagocytic cells Ring fibers (Arrow) |
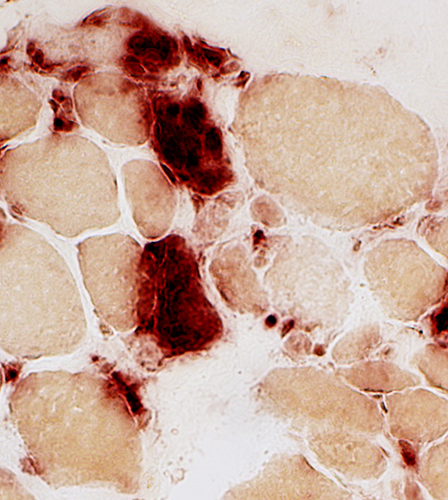 Acid phosphatase stain Acid phosphatase + cells Necrotic muscle fibers: Clusters of phagocytic cells |
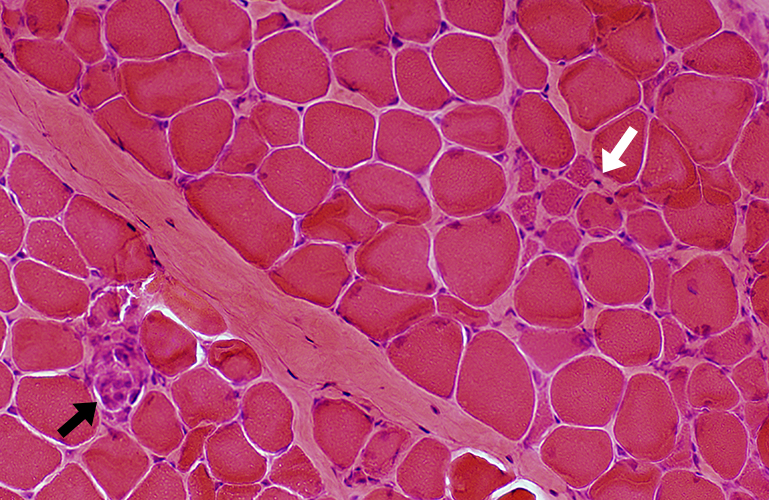
DMD: Muscle Fiber Necrosis
Necrotic Fibers: Scattered; Varied stages
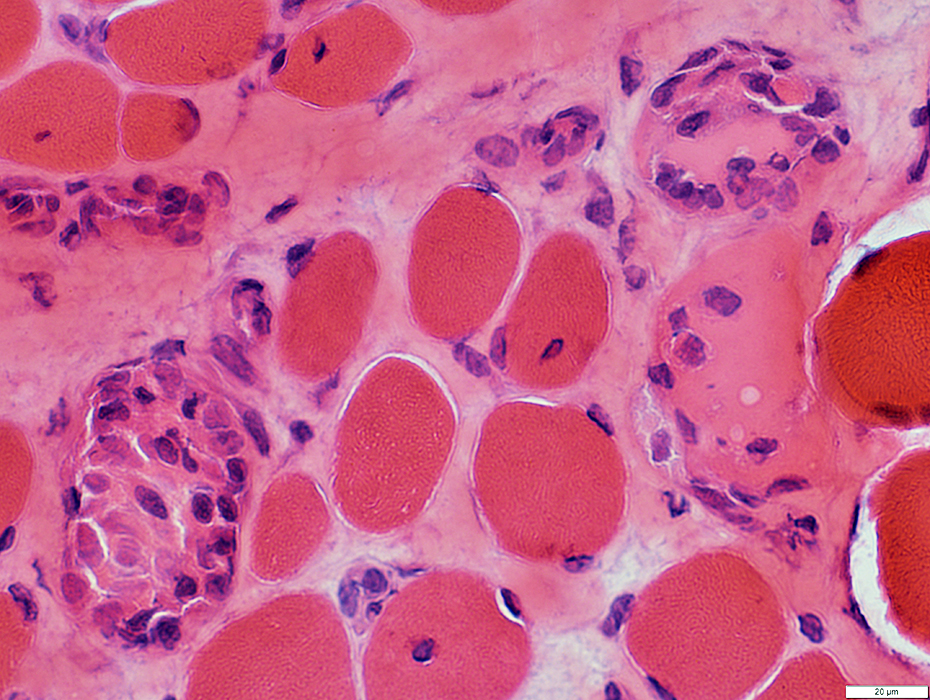 H&E stain |
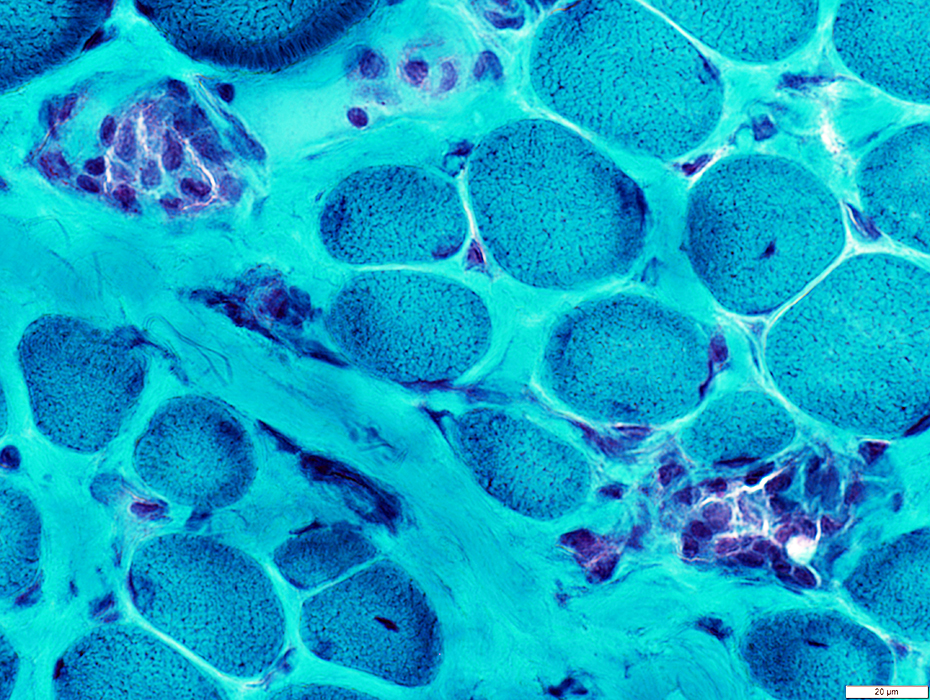 Gomori trichrome stain |
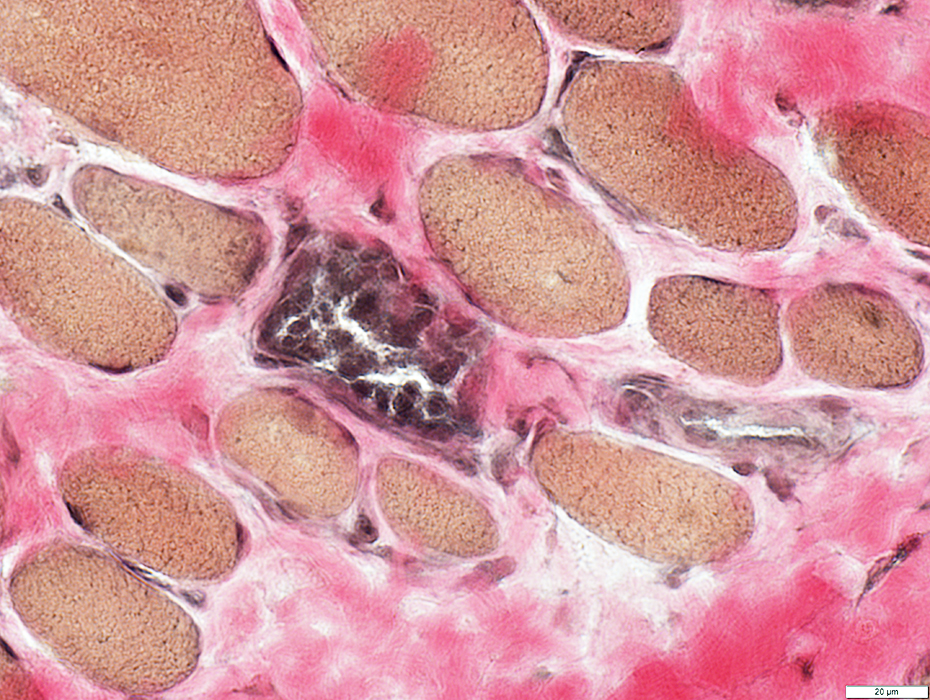 VvG stain |
Myopathic Grouping
|
Muscle fiber Stages Necrosis Regeneration Early Late |
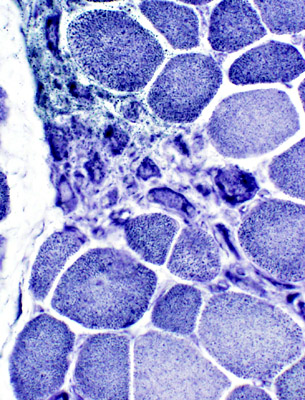
Myopathic grouping: Necrotic muscle fibers, clustered
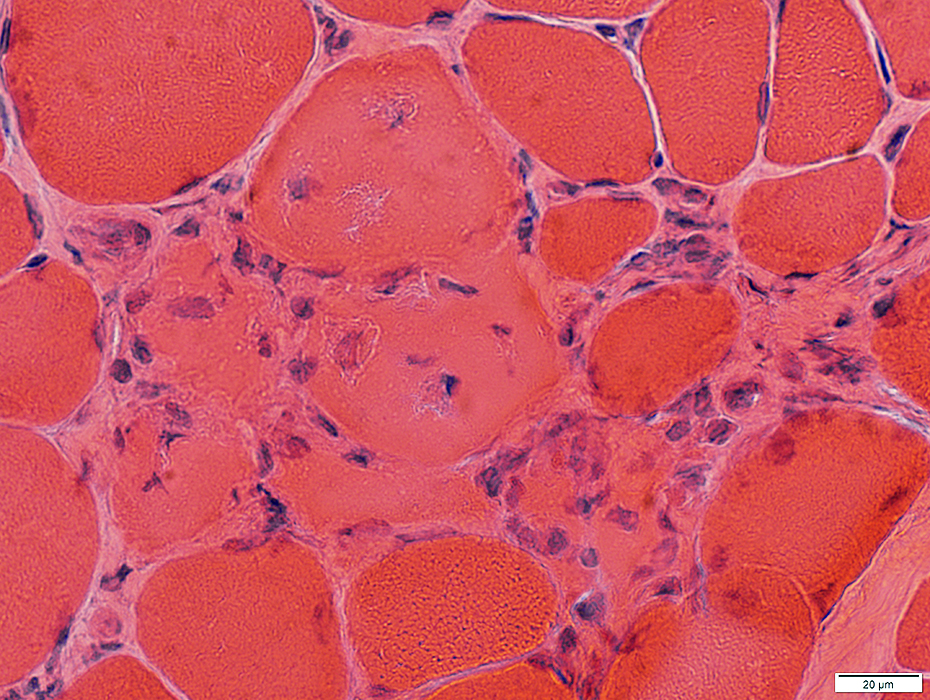 H&E stain |
Necrotic muscle fibers: Pale stained
Macrophages: Early invasion of muscle fibers
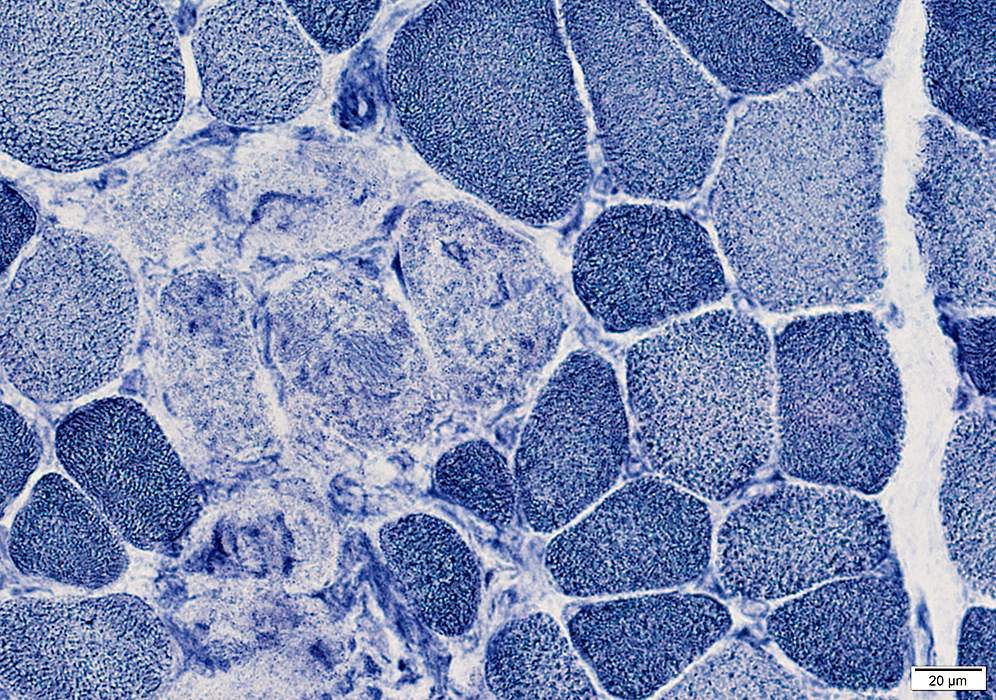 NADH stain Necrotic muscle fibers are pale on NADH stain |
Myopathic grouping: Clusters of very small regenerating muscle fibers & histiocytic cells
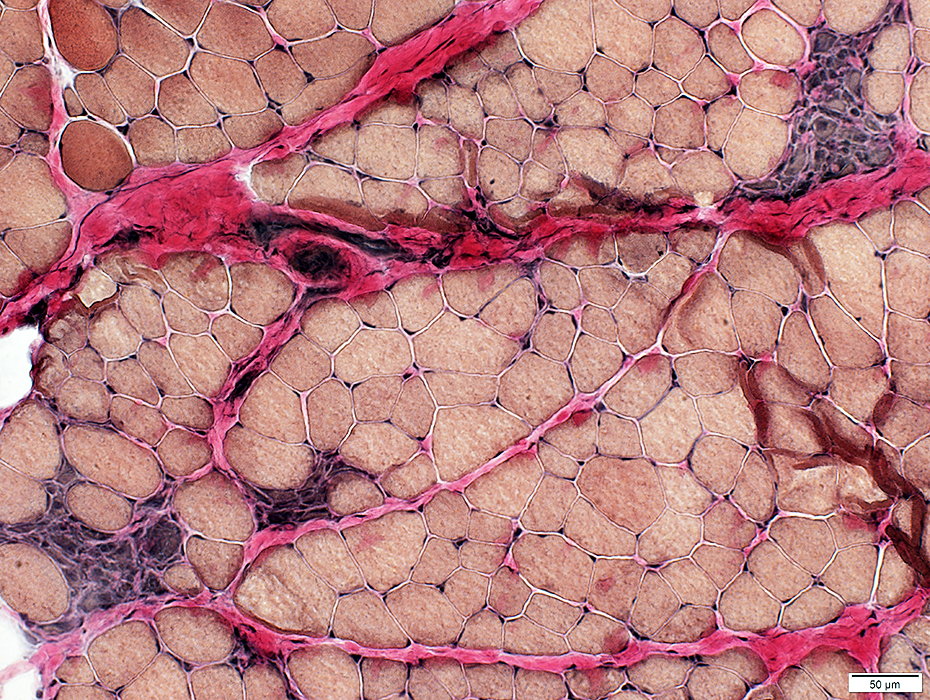 VvG stain |
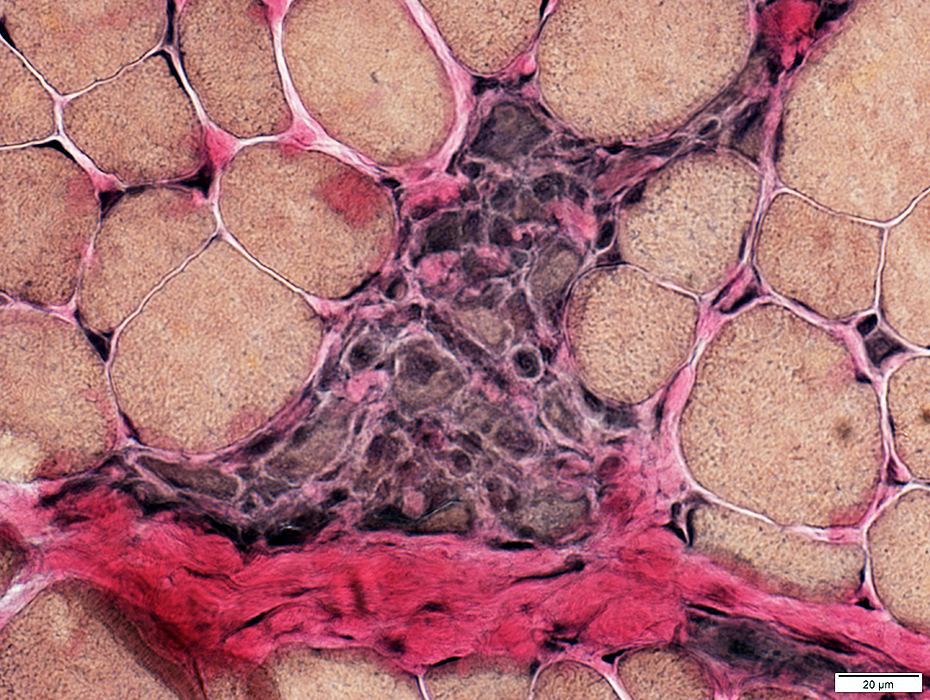 VvG stain |
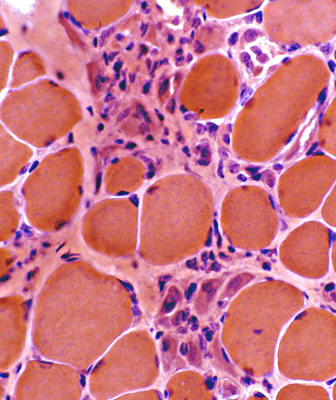 H & E stain |
 ATPase, pH 4.3 |
 NADH |
 Clusters of small cells Many stain for Acid phosphatase 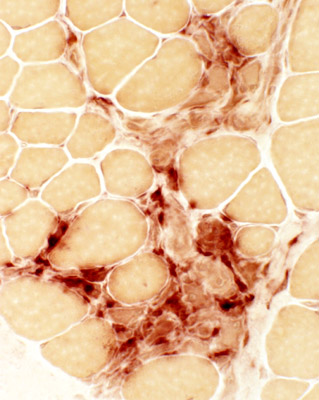 Acid phosphatase |
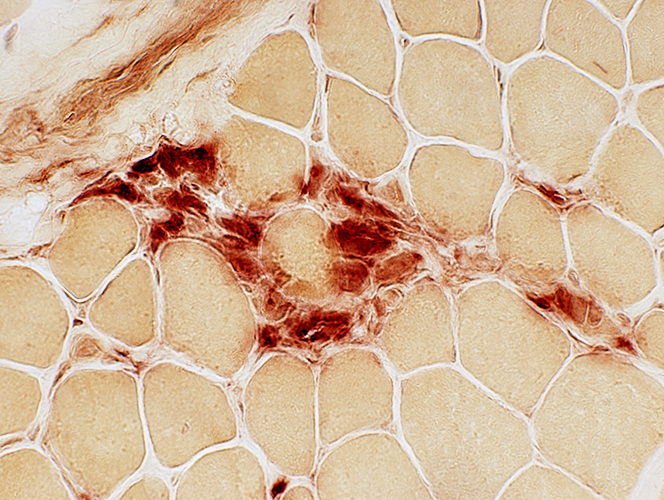 Acid phosphatase |
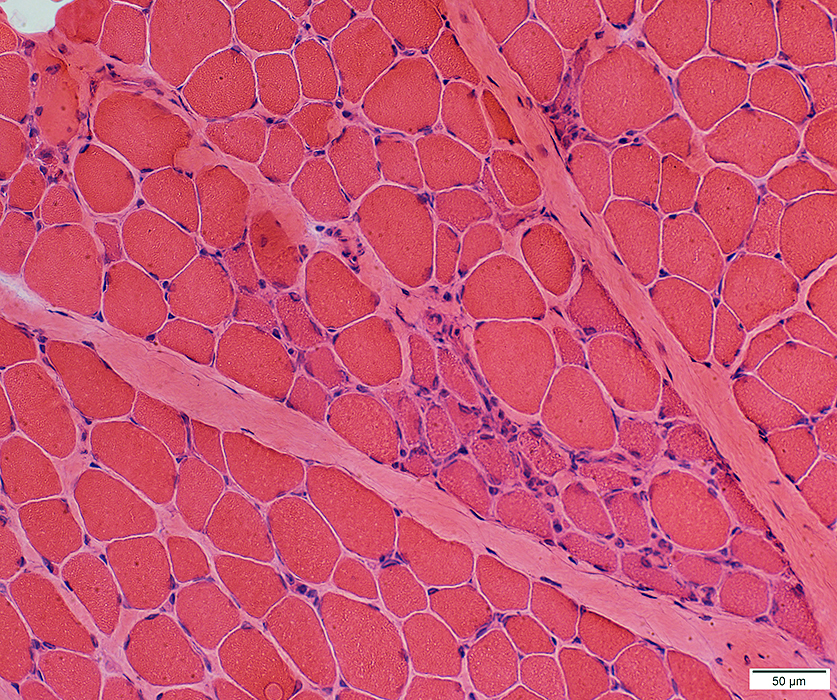 H & E stain |
Myopathic Grouping: Late
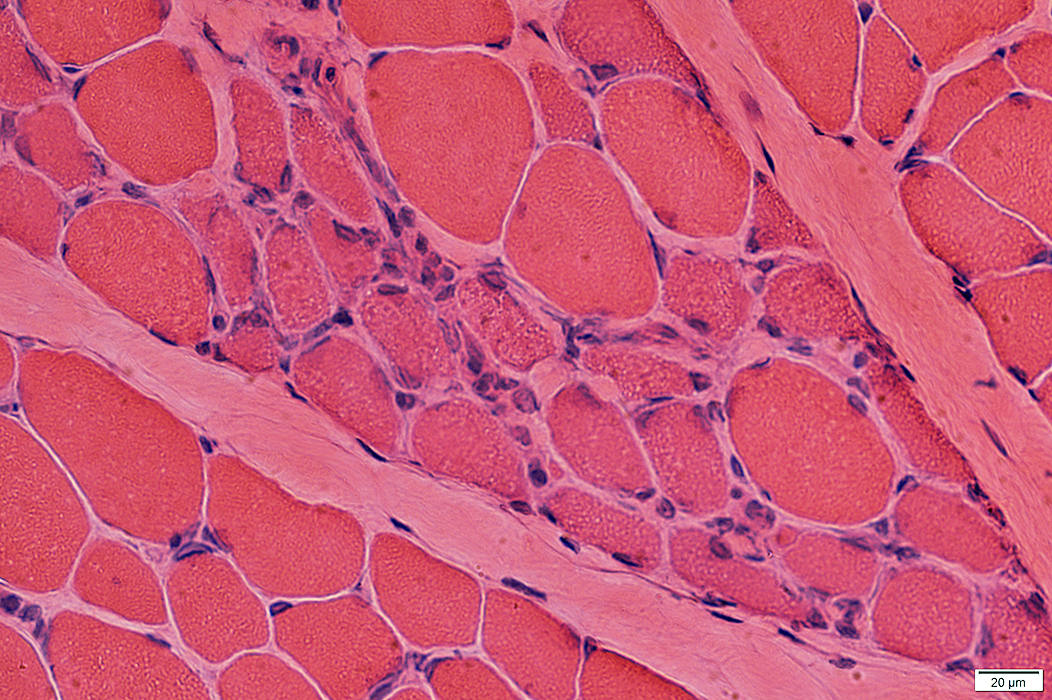 H & E stain |
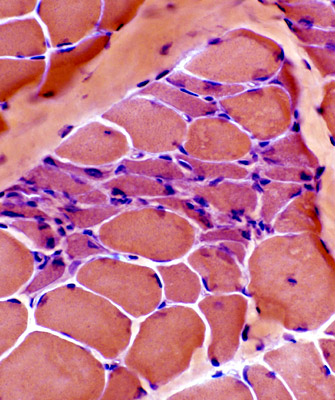 H & E stain Immature fibers are small & basophilic |
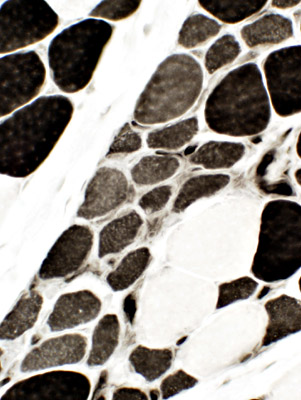 ATPase, pH 4.3 Immature fibers are: Small & 2C (Intermediate staining) |
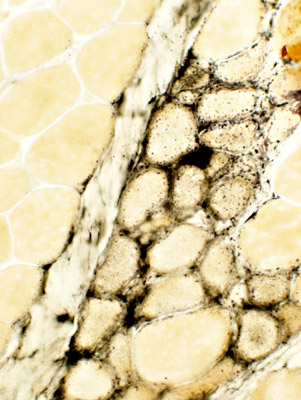 Alkaline phosphatase Immature small fibers have: Cytoplasmic staining |
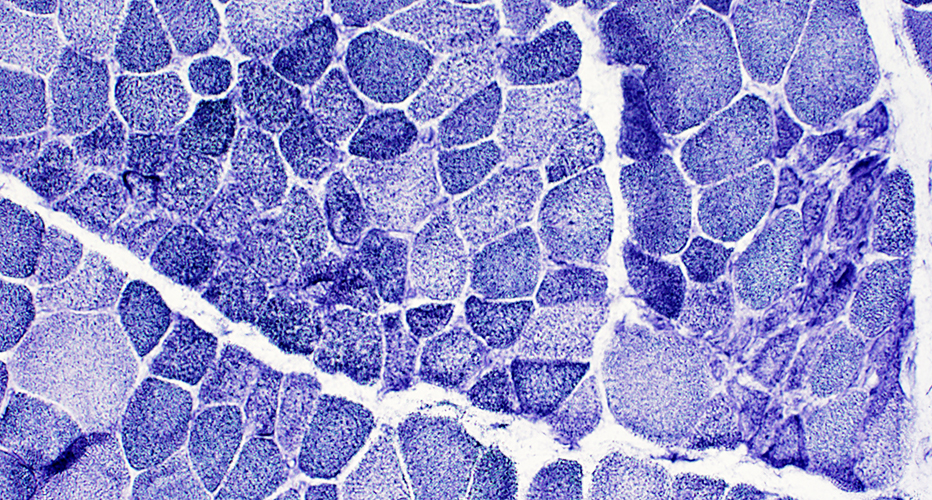 NADH Immature fibers have coarse cytoplasmic staining |
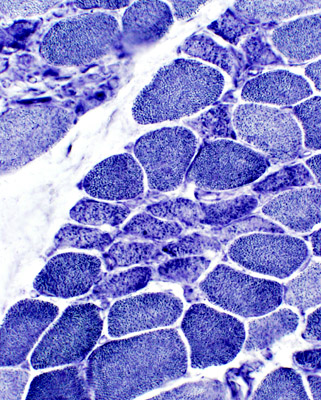 NADH |
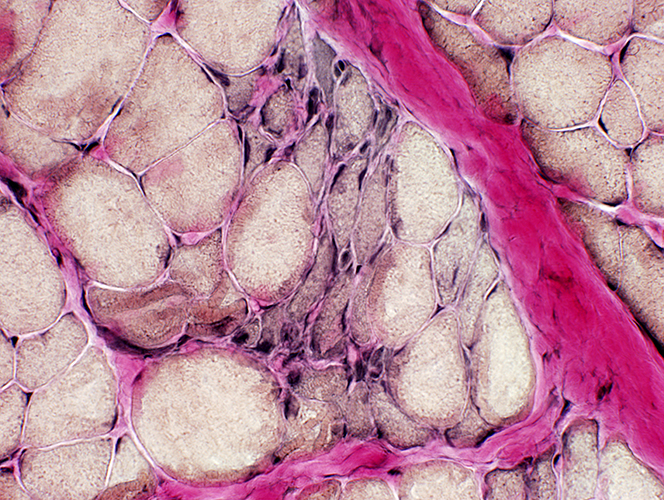 VvG Immature small fibers have coarse cytoplasmic staining |
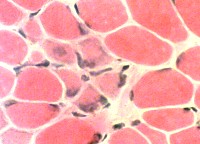
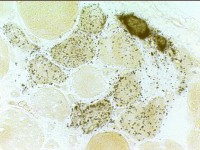
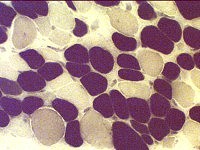
Immature muscle fibers: Many
|
|
|
Staining properties of immature muscle fibers includes: 1. H & E (left): Basophilic fibers 2. Alkaline phosphatase positive (center) 3. 2C fibers: Intermediate staining on ATPase pH 4.3 (right) | |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Severe at age 2 years
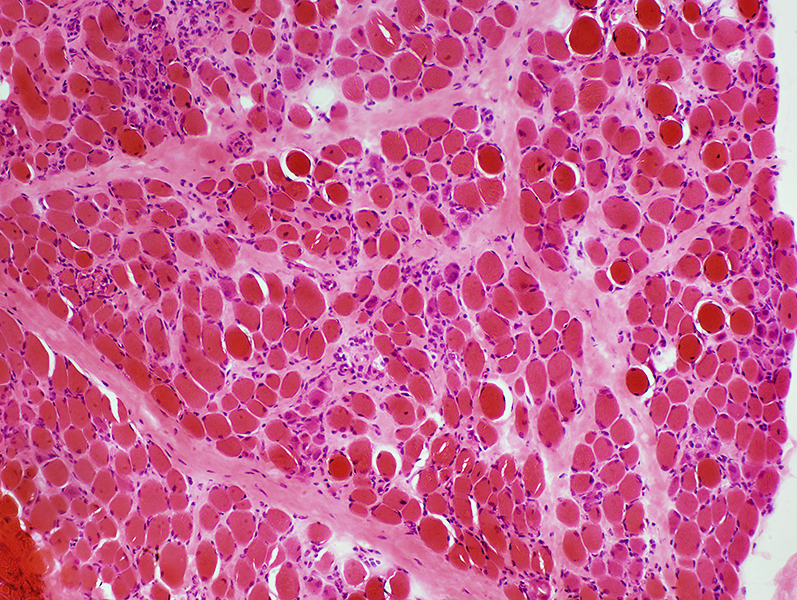 H&E stain |
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
Muscle fibers
Necrosis & Regeneration
Size: Varied
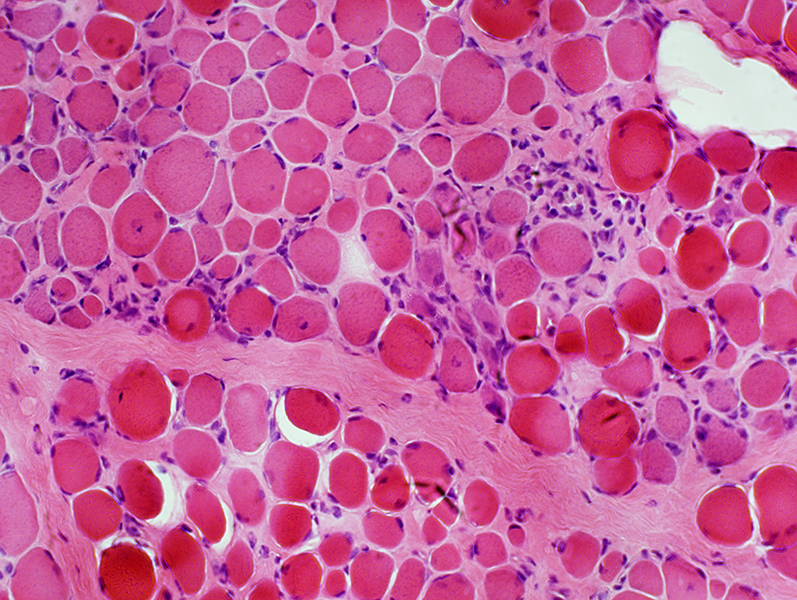 H&E stain |
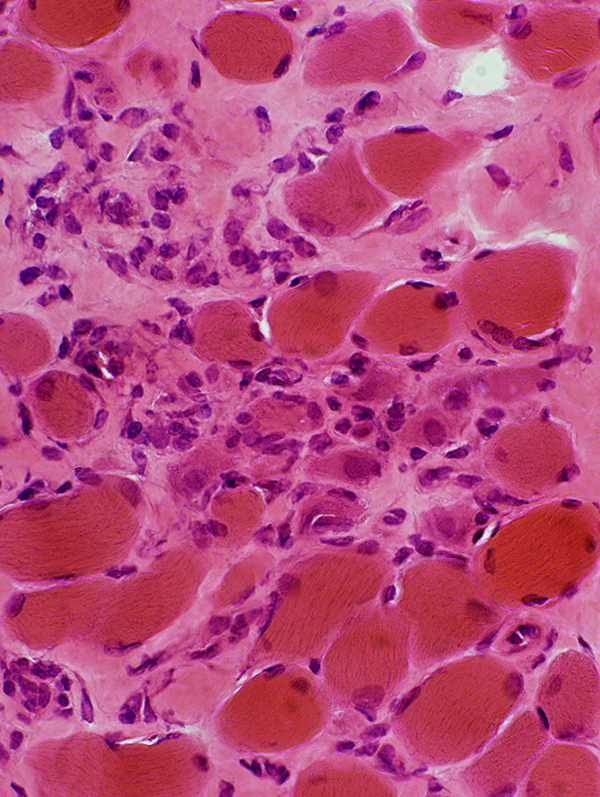
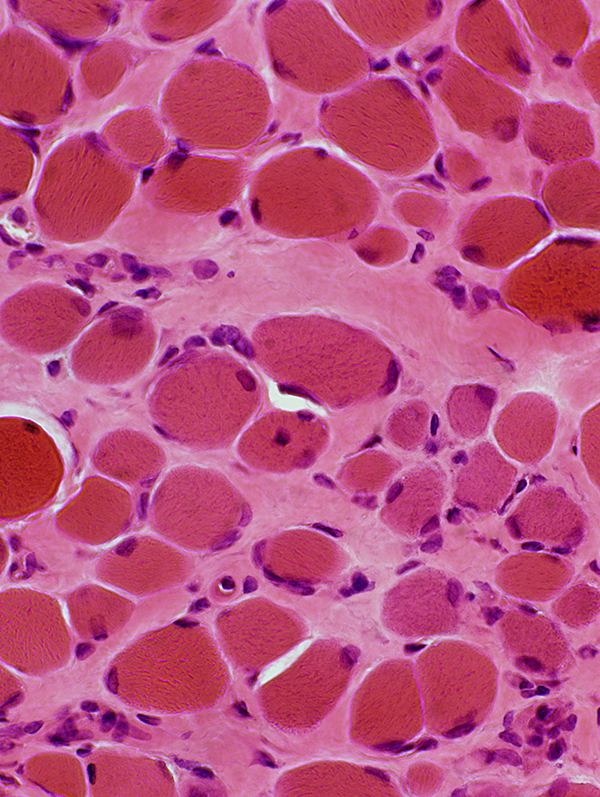 H&E stain |
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
Muscle fibers
Necrosis & Regeneration
Size: Varied
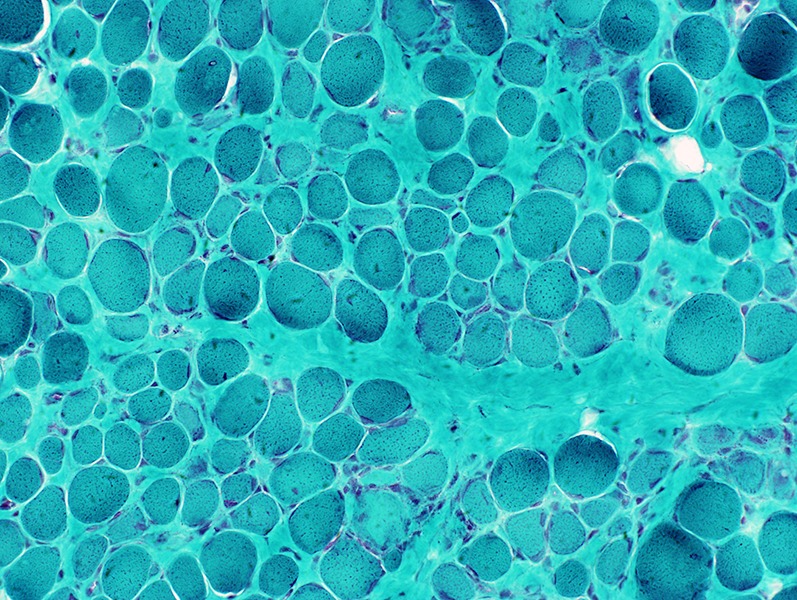 Gomori trichrome stain |
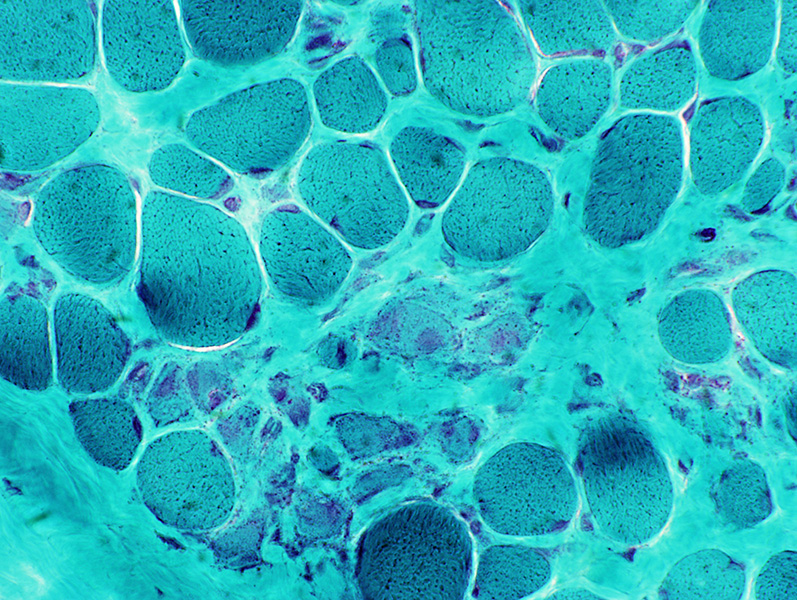 Gomori trichrome stain |
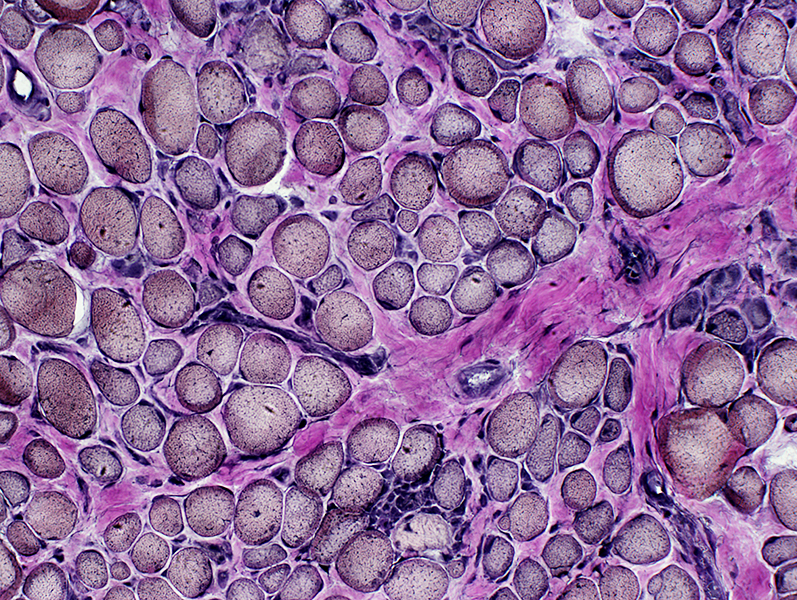 VvG stain |
DMD
Many intermediate-stained muscle fibers
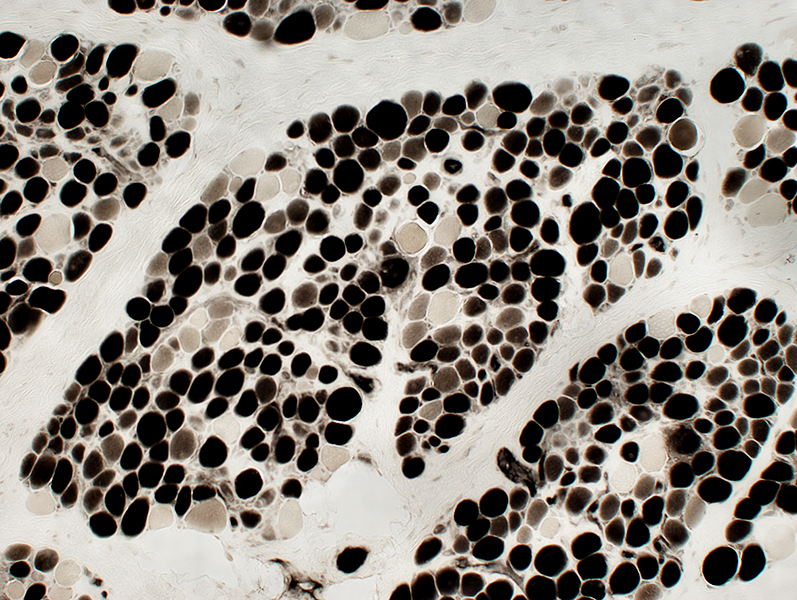 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
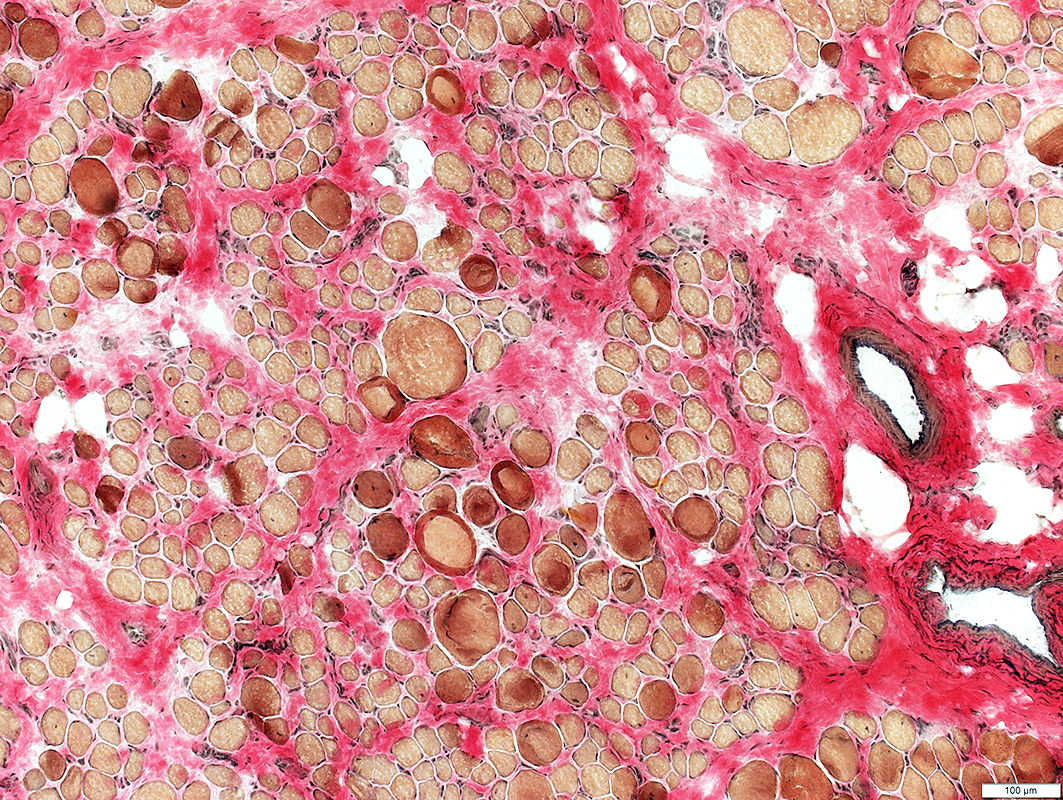
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Later Pathology (10 years)
|
Endomysial connective tissue Fat replacement Fiber types Internal architecture Necrotic fibers |
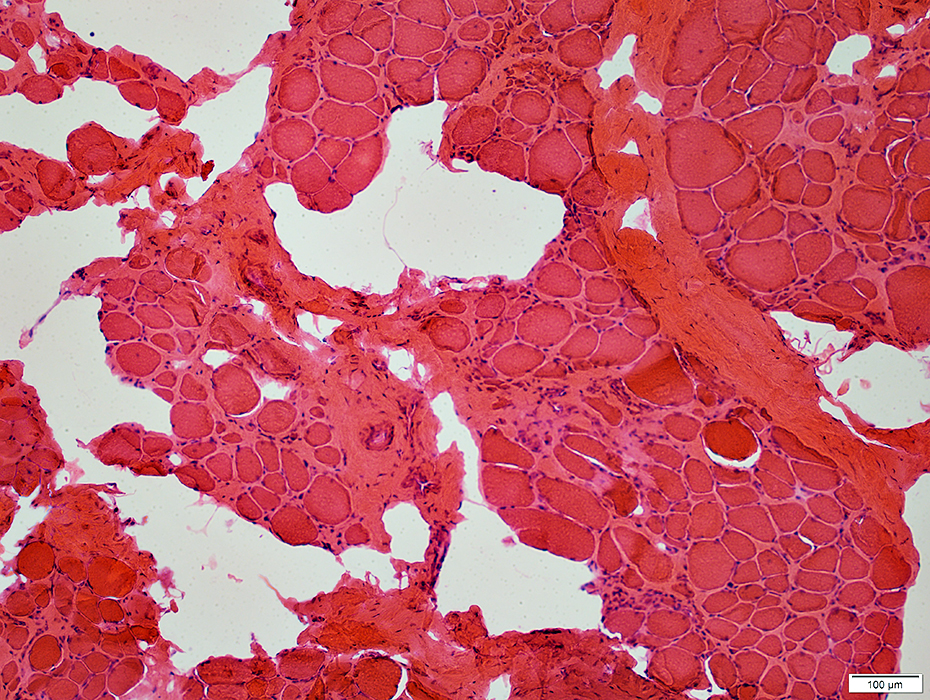 H&E stain |
Fiber size: Varied
Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
Fat replacement of muscle: Prominent
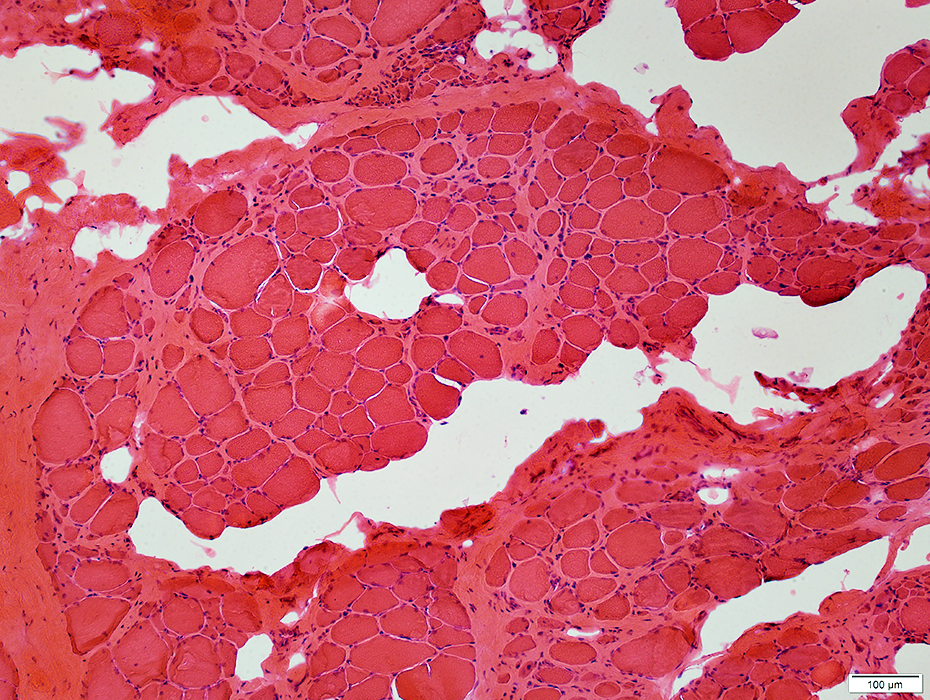 H&E stain |
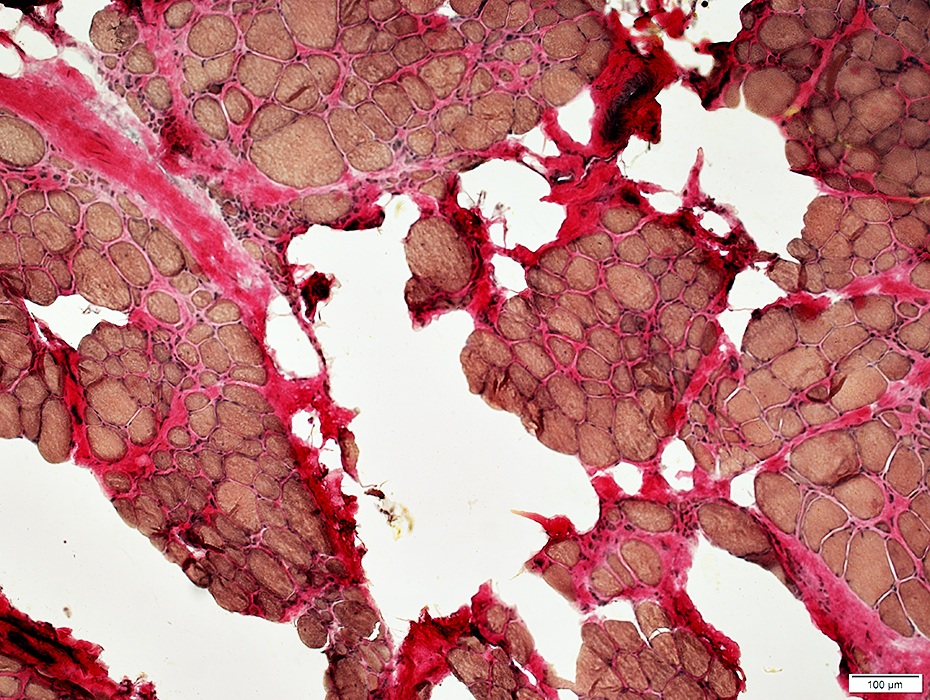 VvG stain |
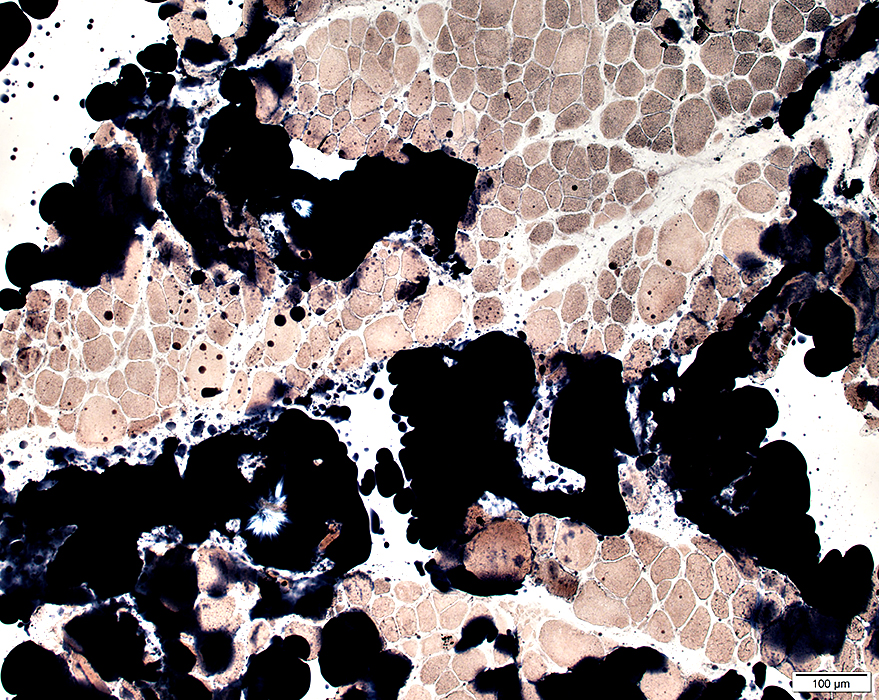 Sudan stain |
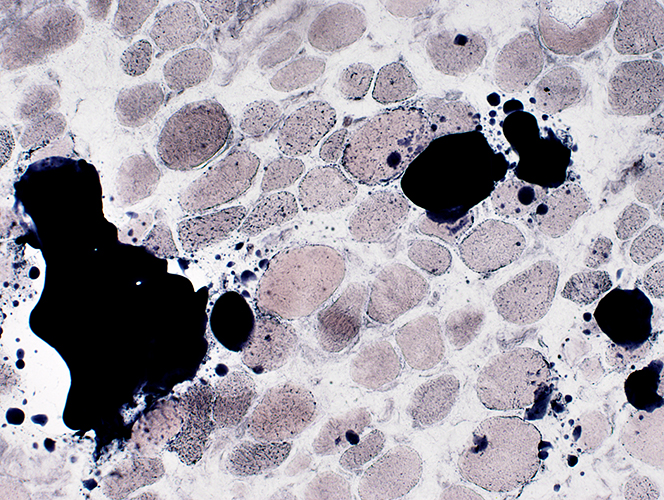 Sudan stain |
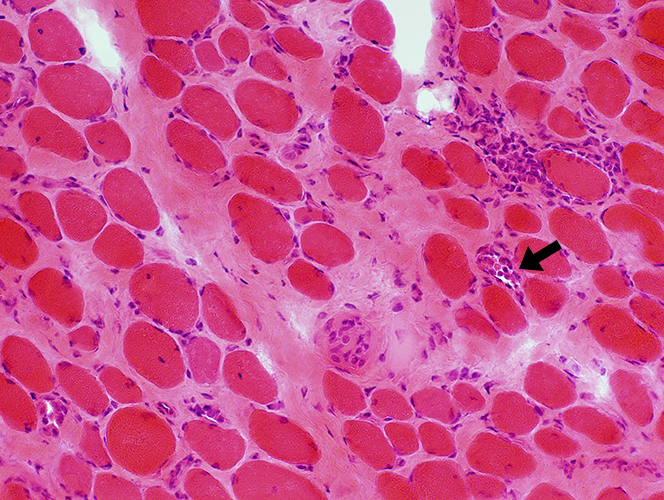 H&E stain Endomysial connective tissue: Increased Fiber size: Variable Small fibers: Rounded Large or hypercontracted muscle fibers: Scattered Necrotic fibers (Arrow): Scattered |
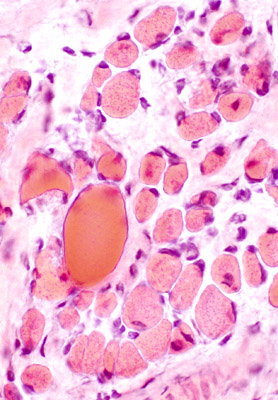
|
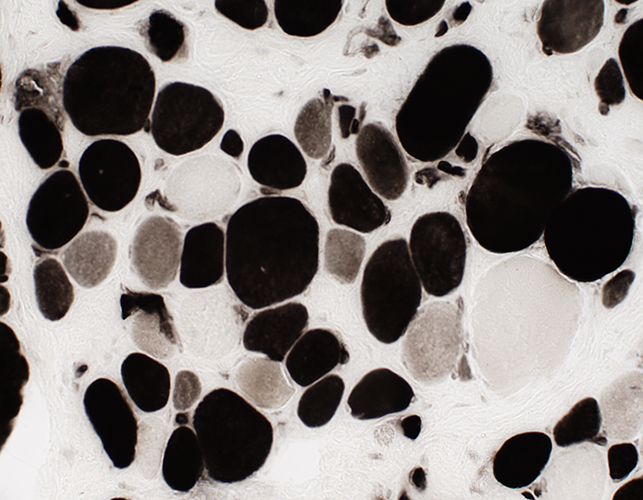
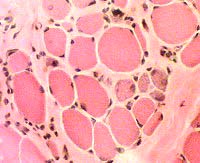 H&E stain 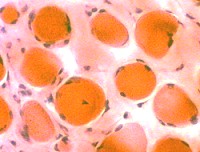 Endomysial connective tissue Increased between fibers |
|
|
Muscle fiber size: Varied
Small & Large fibers: May be are either type (I = Dark; II = Light)
Many type IIC fibers: Smaller size; Intermediate stain
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
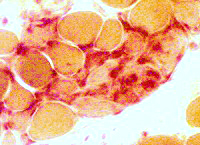
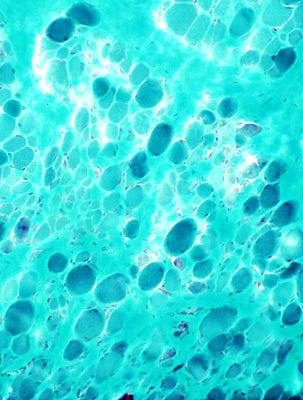
DMD late: Few necrotic muscle fibers
 Acid phosphatase stain |
Muscle fiber internal architecture: Coarse
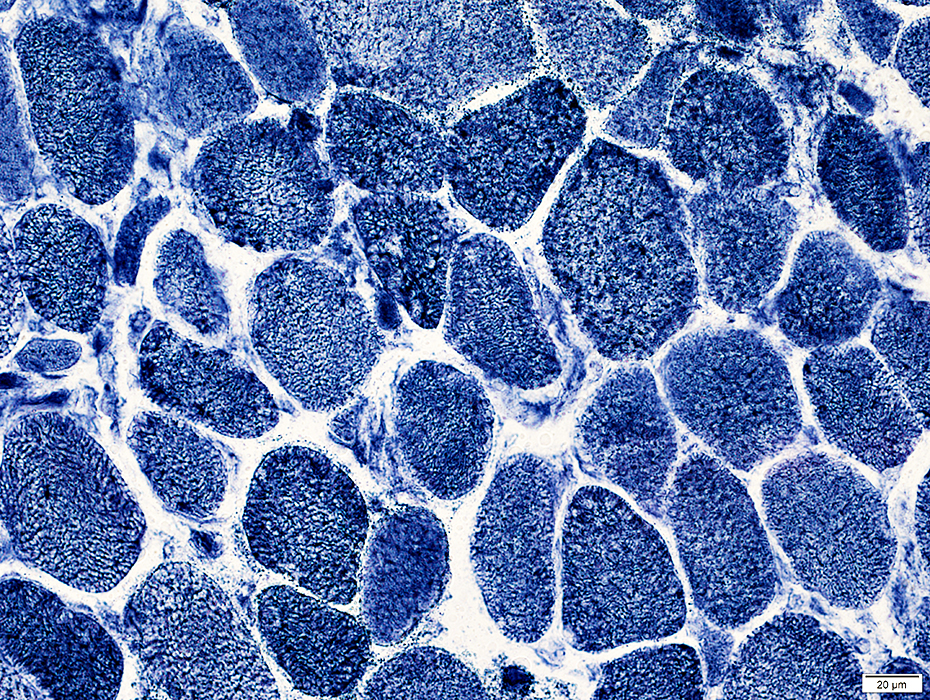 NADH stain |
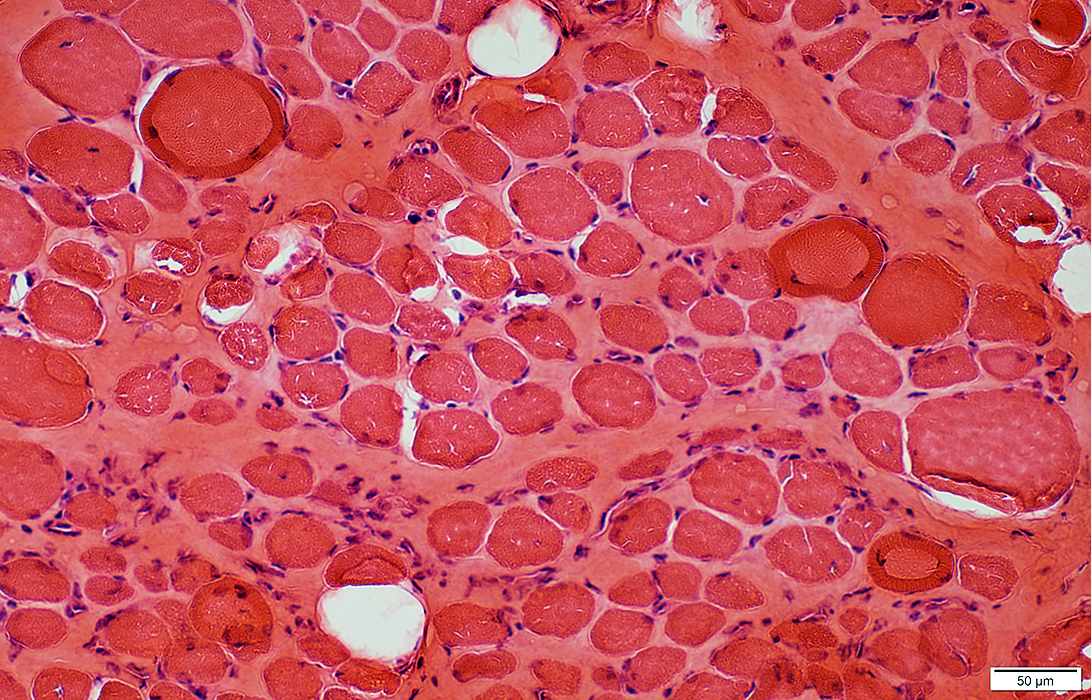 H&E stain |
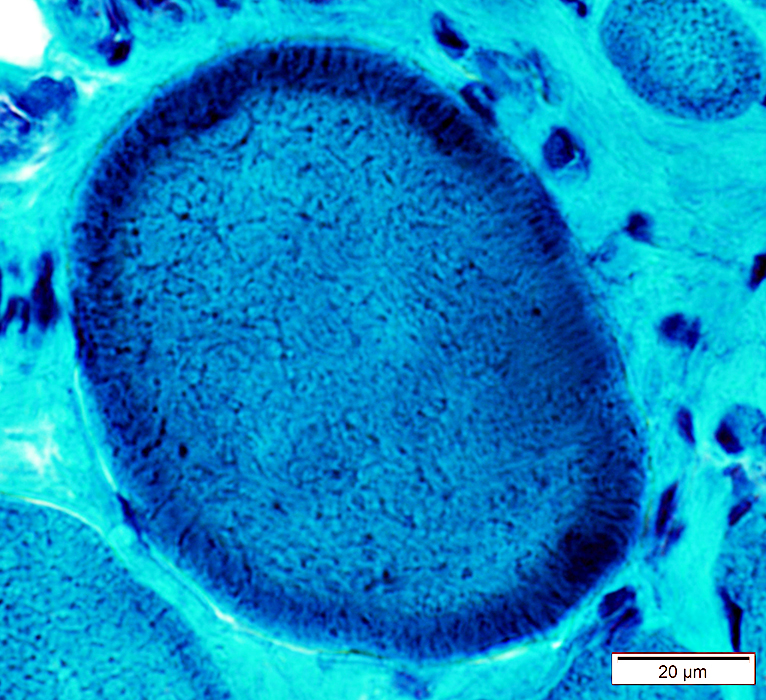 Gomori trichrome stain |
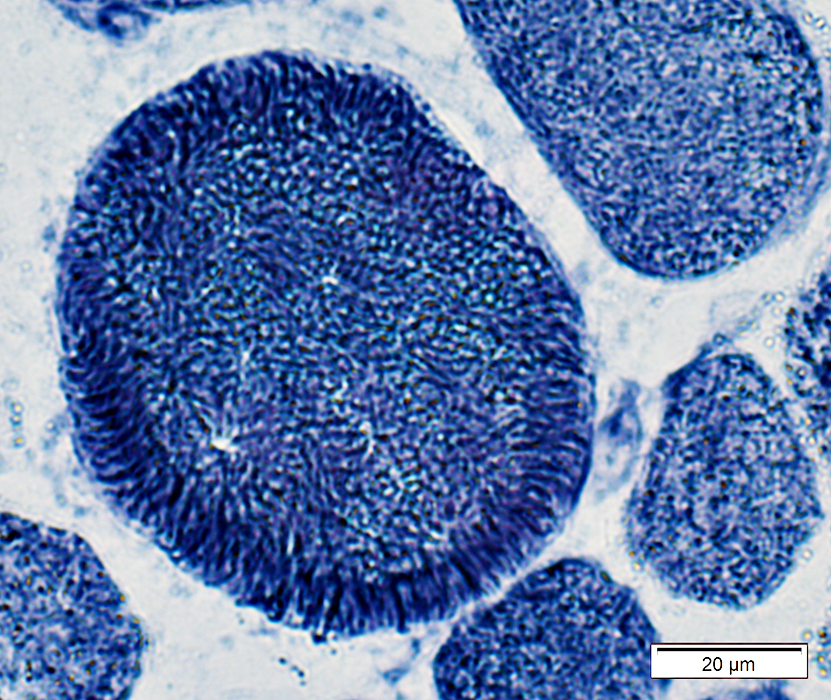 NADH stain |
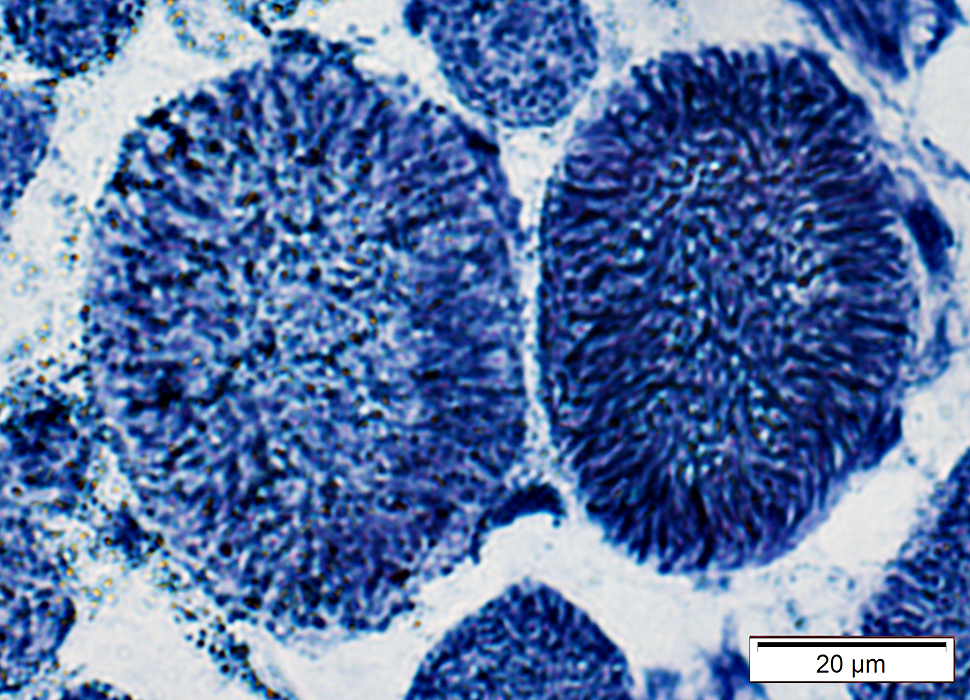 NADH stain |
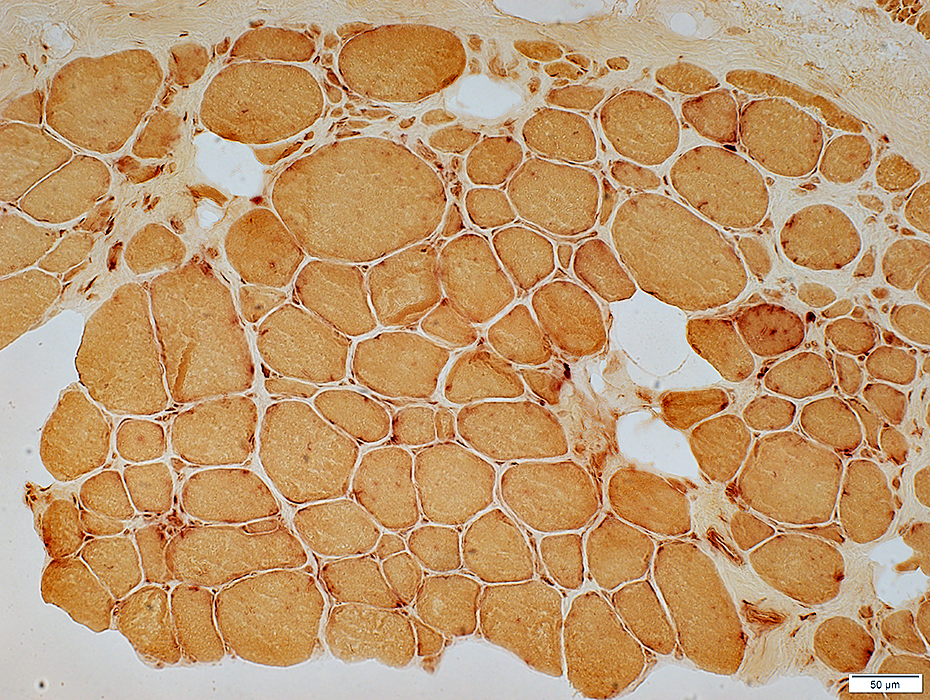
Dystrophin staining
Normal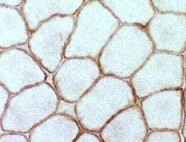
|
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: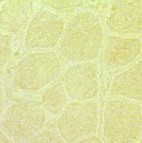
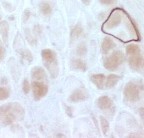
|
|
Normal dystrophin staining around the rim of muscle fibers. |
Absent dystrophin: Duchenne muscular dystrophy Left: No staining around the rim of any muscle fibers Right: No staining of most muscle fibers One "revertant" fiber with dystrophin staining. Revertant fibers reflect a somatic mutation allowing dystrophin expression |
|
Normal: Dystrophin present near surface of muscle fibers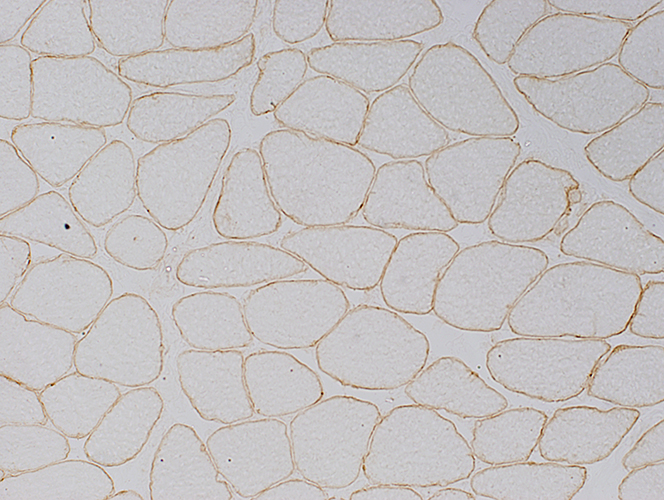  Dys1 stain Duchenne MD: Dystrophin absent from surface of muscle fibers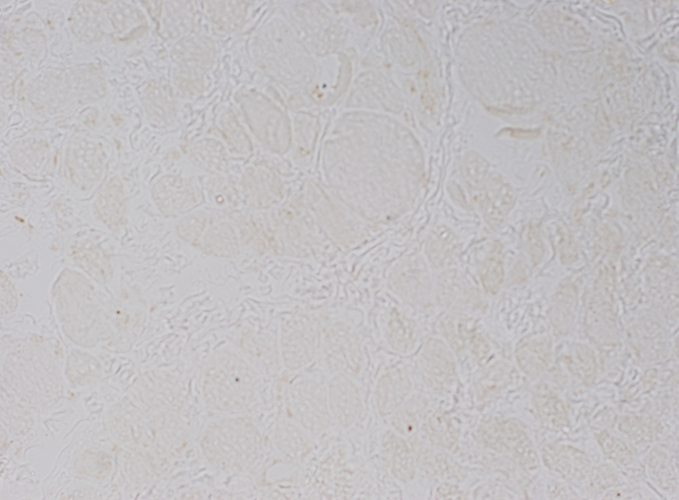  Dys1 stain |
Muscle from Duchenne MD male with large area of revertant muscle fibers
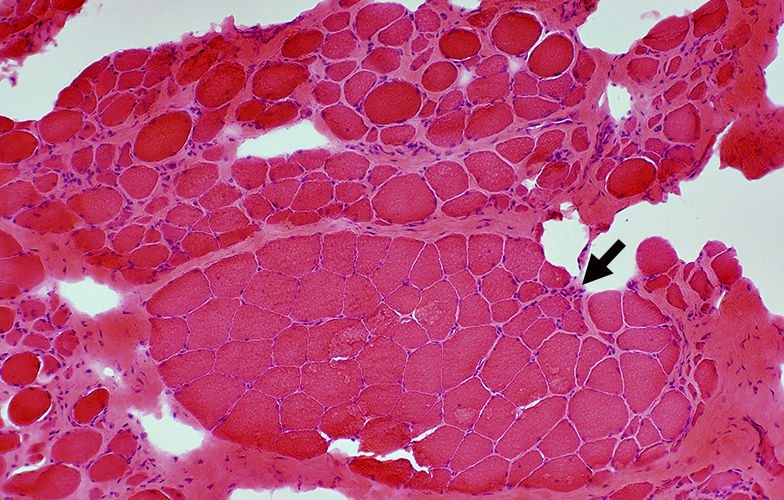
|
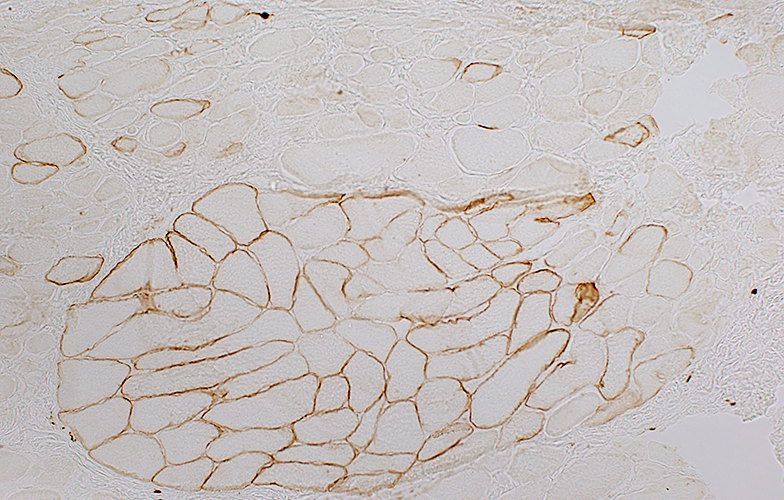
Dystrophin staining (Below): Muscle fibers in preserved fascicle are revertants with dystrophin present around their rim
Some revertant muscle fibers are present in myopathic regions as well.
|
Western blot: Dystrophin from dystrophinopathies
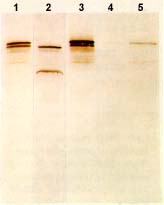 from Novocastra Lane 1: Becker dystrophy; Dystrophin has reduced abundance but normal size. Lane 2: Becker dystrophy; Dystrophin has reduced size and abundance. Lane 3: Normal; Dystrophin has normal size and amount. Lane 4: Duchenne dystrophy; Almost no protein is present. Lane 5: Duchenne outlier; Dystrophin has severely reduced abundance. |
DMD muscle: After dystrophin mini-gene transfer
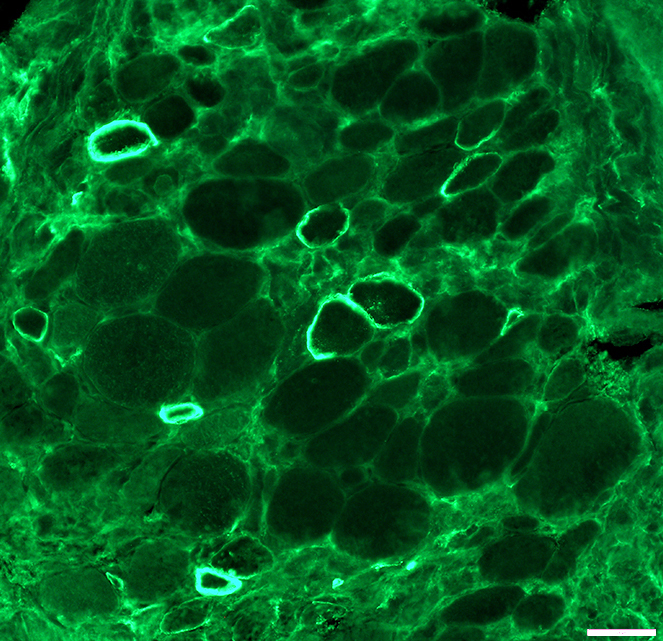 Dys3 antibody Stains dystrophin N-terminal epitope present on transferred mini-protein Present, irregularly, on surfaces of minority of muscle fibers Most dystrophin positive muscle fibers are small & intermediate sized |
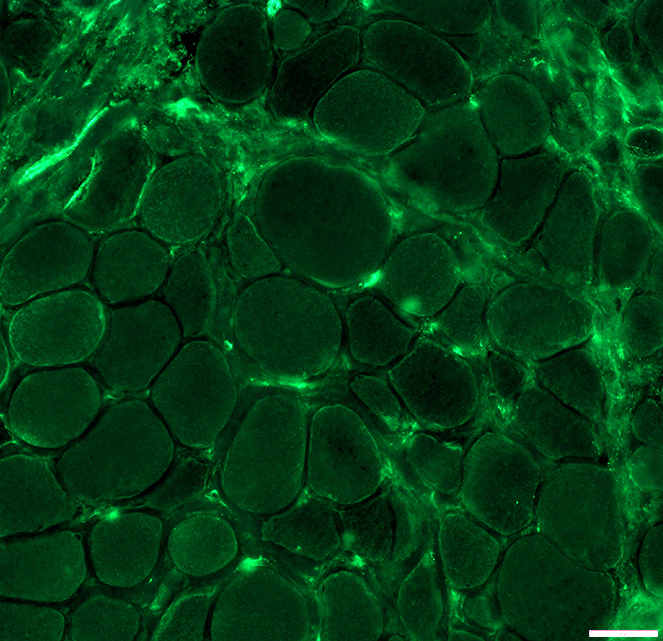 Dys2 antibody Stains dystrophin C-terminal epitope not present on transferred mini-protein Staining is generally not present on surfaces of muscle fibers |
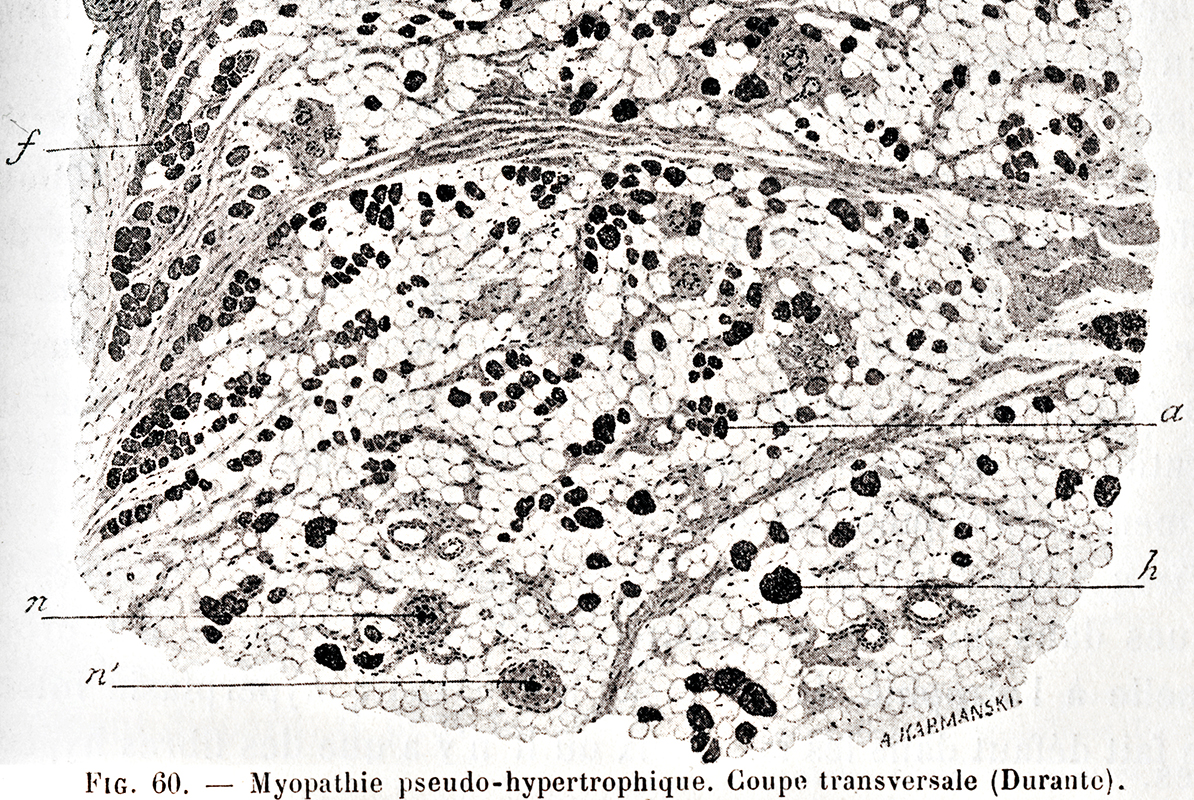 |
The muscle is almost entirely transformed into adipose tissue.
The striated fibers that persist are gathered in small bundles or scattered among adipose cells.
Some are normal volume. Others are in different degrees of atrophy a. There are still a few rare hypertrophied fibers h. n, n', neuro-muscular bundles.
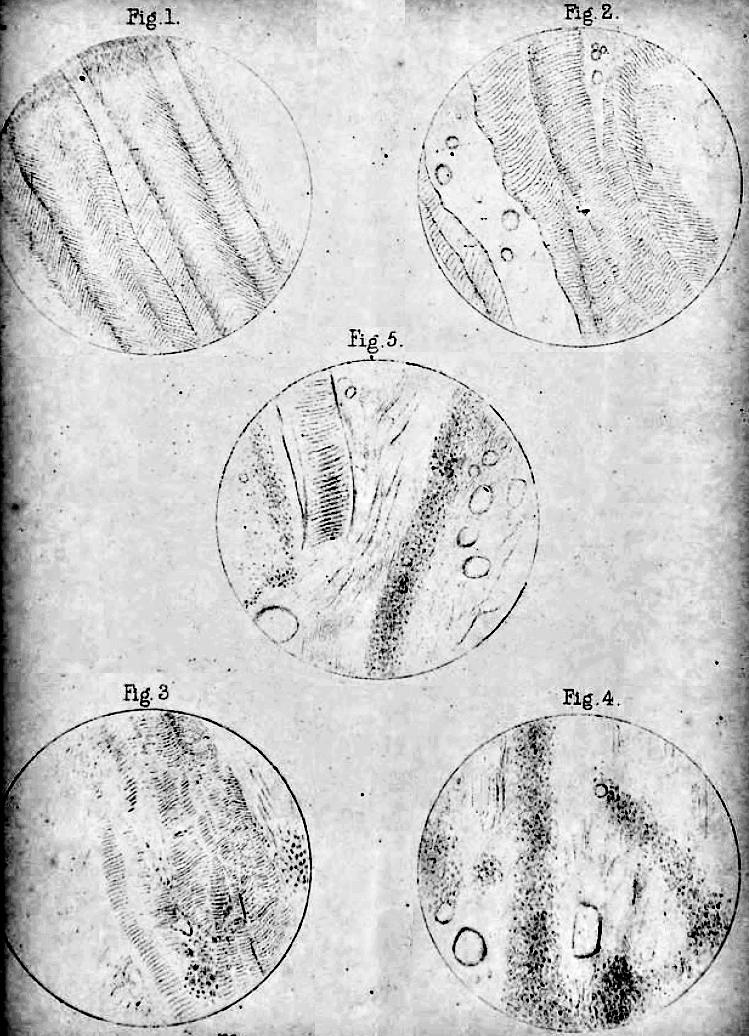 |
The accompanying illustrations are taken from the muscles of the Hon. Wm. P-, who suffered from an affection identical with that of the subjects of the present paper, and whose case is described in the thirty-fifth volume of the 'Transactions' of this Society, p. 77. DESCRIPTION OF PLATE II. 1. Rectus abdominis. (1/8 lens; low eyepiece.) 2. Spinalis dorsi. (ditto.) 3. Pectoralis major. clavicular portion. (ditto.) 4. Longissimus dorsi. (ditto.) 5. Pectoralis major. sternal portion. (ditto.) |
 |
Go to Becker muscular dystrophy pathology
Return to Dystrophinopathies.
Return to Neuromuscular syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular home page
References
1. J Gen Physiol 2022;15:e202213081
12/17/2025