Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
Acid Maltase Deficiency (GSD2): 17q25 Aldolase A (GSD12): 16p11 Branching enzyme (GSD4): 3p12 Debrancher (GSD3): 1p21 β-Enolase (GSD13): 17p13 G6PD: Xq28 Glycogen synthase 1 (GSD0B): 19q13 Glycogenin (GSD15): 3q24 Hexokinase 1 (HMSNR): 10q22 Lactate dehydrogenase A (GSD11): 11p15 Lafora disease: Laforin, 6q24 Lamp-2 (GSD2b): Xq24 Phosphofructokinase (GSD7): 12q13 Phosphoglucomutase 1 (GSD14): 1p31 Phosphoglycerate Kinase: Xq21 Phosphoglycerate Mutase (GSD10): 7p13 Phosphorylase (McArdle's) (GSD5): 11q13 Phosphorylase b Kinase PHKA1 (GSD9D): Xq13 PHKB (GSD9B): 16q12 PRKAG2: 7q36 Polyglucosan body Branching enzyme (GBE1) Myopathy (GSD4): 3p12 Syndrome Myopathy (PGBM) 1: RBCK1; 20p13 2: GYG1; 3q24 Triosephosphate isomerase: 12p13 SMGMQTL: PRKAG3; 2q35 Acquired: MGGSM General principles Glycolytic reactions Metabolic pathways Muscle biopsy results |
 From D Driemeier 19 Glycogenosis Type 2: Brahman calf
|
|
Clinical syndromes Infant Infant treated Child Juvenile Adult Vascular & Systemic Epidemiology GAA protein Genetics Clinical-Genetic Laboratory Muscle pathology Child Adult Treatment |
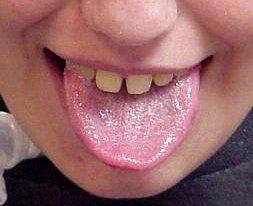 From: Anne Connolly MD Acid maltase deficiency
Mildly enlarged tongue |
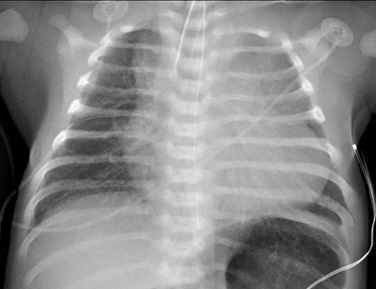
Pompe disease: Cardiomyopathy
|
 |
Debrancher deficiency (Glycogenosis type 3; GSD3)
●
Amylo-1,6-glucosidase, 4-α-Glucanotransferase (AGL; GDE)
|
|
|
Epidemiology Genetics PYGM protein Clinical Laboratory Muscle pathology PYGM: Myopathy, Dominant |