Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Myopathy: Distal Weakness
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
Distal Weakness in Myopathies |

|
|
DISTAL WEAKNESS Differential Dx General Features Pathology Myopathies ACTN2: 1q43 Congenital myopathies ACTA1 Centronuclear 2: DNM2; 19p13 RYR1 Cystinosis + Renal: CTNS; 17p13 Cytoplasmic body Distal dystrophy: PLIN4; 19p13 Emery-Dreifuss FSH dystrophy Glycogenoses Acid maltase Debranching Enzyme Phosphorylase b Kinase Gowers-Laing (MPD1): MYH7; 14q11 Hereditary IBM Dominant Recessive Respiratory failure LGMD variants 1A: Myotilin; 5q31 1C: Caveolin-3; 3p25 1D: DNAJB6; 7q36 2B: Dysferlin; 2p13 2G: Telethonin; 17q12 2L: ANO5; 11p14 Mitochondrial: POLG1; 15q26 Miyoshi (MMD) MMD1: Dysferlin; 2p13 MMD2: ? 10p MMD3: ANO5; 11p14 MPD 1 (Gowers-Laing): MYH7; 14q11 2 (Vocal cord): MATR3; 5q31 3: HNRNPA1; 12q13 4 (Williams): FLNC; 7q32 5 (Adolescent): ADSSL1; 14q32 6: ACTN2 7: SMPX; Xp22 Myasthenia: Agrin; 1p36 Myofibrillar αB-crystallin: 11q22 BAG3 CCDC78: 16p13 Desmin: 2q35 Filamin C (MPD4): 7q32 Myotilin Scapuloperoneal: 12q13 ZASP (LDB3): 10q23 Myofibrillary (Cytoplasmic body) Myopathy + Paget's disease of bone with Dementia: VCP/p97; 9p13 Type 2: HNRNPA2B1; 7p15 Myopathy + PEO: MYH2; 17p13 Myotonic Dystrophy 1: DMPK; 19q13 Nebulin: 2q23 Nemaline (Rod) myopathies Neutral lipid storage: PNPLA2; 11p15 Nonaka-HIBMR: GNE; 9p13 Oculopharyngodistal Ring fiber myopathy Scapuloperoneal syndromes SQSTM1: 5q35; Dominant TDP43; 1p36 Titin; 2q31 Finnish: Dominant Serbian: Recessive Welander: TIA1; 2p13 Other Myopathy or Motor Neuropathy Distal weakness: KLHL9; 9p22 Distal weakness: HSPB8; 12q24 Distal weakness: SPTAN1; 9q34 Distal, Hoarse, Deaf: MYH14; 19q13 Distal atrophy: DNAJB5; 9p13 Neuropathies Uncertain NSUN2 Acquired (Sporadic) disorders Myasthenia gravis Myopathy + Neuropathy Hyperthyroid IIM + VAMP (IBM-like) syndromes Inclusion Body Myositis |
Type | Inheritance Pattern |
Gene & Locus |
Early Weakness |
CK | Muscle | |
| Welander | Dominant |
TIA1 2p13 |
> 40 years Hands: Extensor |
Normal, or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic ± Vacuoles |
||
|
Finnish (Tibial; Udd) |
Dominant |
Titin 2q31 |
40 to 50 years Legs: Anterior |
Normal, or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
|
HMERF |
Dominant |
Titin 2q31 |
12 to 75 years Distal anterior legs Respiratory |
Normal or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic Eosin inclusions Cytoplasmic body Vacuoles |
||
|
Gowers-Laing (MPD1) |
Dominant |
MYH7 14q11 |
1.5 to 25 years Dorsiflex: Ankle; Toe |
↑ up to 3x |
Myopathic: Mild Vacuoles: Few |
||
|
Distal dystrophy + Rimmed vacuoles |
Dominant |
DNAJB6 7q36 |
10 to 50 years Legs: Distal |
Normal, or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
| HIBM1 | Dominant |
Desmin 2q35 |
25 to 40 years Legs: Distal; Quadriceps |
Normal, or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
| Oculopharyngodistal | Dominant | Autosomal |
40 years Extraocular |
3x ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
|
Vocal cord & Pharyngeal (MPD2) |
Dominant |
Matrin 3 5q31 |
35 to 57 years Legs, Hands or Vocal cord |
Normal to ↑ 8x |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
|
Myopathy + Paget's & Dementia |
Dominant |
VCP 9p13 |
20 to 40 years Legs Proximal & Distal |
Normal or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
| Myopathy + Paget's | Dominant |
HNRNPA2B1 7p15 |
35 to 42 years Legs: Distal Scapular |
Normal or High |
Myopathic |
||
| MPD3 | Dominant |
HNRNPA1 12q13 |
32 to 45 years Distal Legs & Hands |
Normal or Slight ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
| Cytoplasmic body | Dominant | Autosomal |
40 to 50 years Hands |
Normal or Slight ↑ |
Myofibrillary inclusions |
||
|
Myopathy with Anterior leg sparing (MPD4) |
Dominant |
Filamin C 7q32 |
0 to 30 years Distal Legs & Hands |
Normal or Slight ↑ |
Varied fiber size No vacuoles |
||
|
Nonaka-HIBMR (HIBM2) |
Recessive, or Sporadic |
GNE 9p13 |
20 to 40 years Legs: Anterior |
↑ up to 5x |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
|
Miyoshi ± LGMD 2B |
Recessive, or Sporadic |
Dysferlin 2p13 |
20 to 50 years Legs: Posterior |
10x to 150x ↑ |
Myopathic No vacuoles |
||
| LGMD 2G | Recessive |
Telethonin 17q12 |
12 years Legs: Proximal & Anterior distal |
3x to 17x ↑ |
Myopathic Vacuoles |
||
|
Miyoshi-like 3 (MMD3) |
Recessive |
Anoctamin 5 11p14.3 |
11 to 50 years Legs: Posterior |
3x to 100x ↑ |
Myopathic Sarcolemmal lesions |
||
| Nebulin | Recessive |
Nebulin 2q23 |
Child or Adult Toe & finger extensor |
Normal |
Myopathic Rods, Small |
||
| Adolescent | Recessive |
ADSSL1 14q32 |
Adolescent Posterior legs; Face |
Mildly high |
Myopathic Vacuoles, Few |
||
| Myofibrillar myopathies | |||||||
| Desmin |
Dominant or Recessive |
2q35 |
20 to 40 years Legs |
Mild ↑ |
Myopathic Desmin ↑ |
||
| αB-crystallin | Dominant | 11q22 |
Adult Distal |
Mild ↑ |
Myopathic Desmin ↑ |
||
| Scapuloperoneal | Dominant |
FHL1 Xq26 |
20 to 58 years Distal; Legs |
1.5x to 10x ↑ |
Myopathic, Focal Desmin inclusions |
||
|
ZASP, Markesbery |
Dominant |
ZASP 10q23.2 |
Child to 73 years Distal in 9% |
Normal to 6x ↑ |
Myopathic Desmin inclusions Vacuoles: Small |
||
| Distal Myopathies: Weakness & Muscle involvement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | Muscle Pathology | |||||
General Features
Myopathy: MRI Patterns |
|
Muscle Fibers
|
||||
|
Nosology Epidemiology Genetics GNE protein Clinical Laboratory Muscle Pathology Variant |
 from M Sadeh |
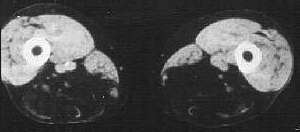
|
HIBM2: Quadriceps sparing CT of thigh |
|
Miyoshi 1 (MMD1): Dysferlin; 2p13.2 Miyoshi 2 (MMD2): ? 10p Miyoshi 3 (MMD3): ANO5; 11p14 Other: CAPN3 |
|
|
||||||
●
Myosin heavy chain 7 (MYH7)
|
|
Vocal Cord & Pharyngeal Weakness (MPD2; VCPDM; ALS21; MSP5)
●
Matrin 3 (MATR3)
|
|
|
IBMPFD (Dominant) 1: VCP; 9p13 2: HNRNPA2B1; 7p15 3: HNRNPA1; 12q13 |
Multisystem Proteinopathy (MSP) 1: VCP; 9p13 2: HNRNPA2B1; 7p15 3: HNRNPA1; 12q13 4: SQSTM1 (+TIA1); 5q35 5: MATR3; 5q31 6: ANXA11; 10q22 Other likely TIA1 HSPB8 TFG TUBA4A |
|
|