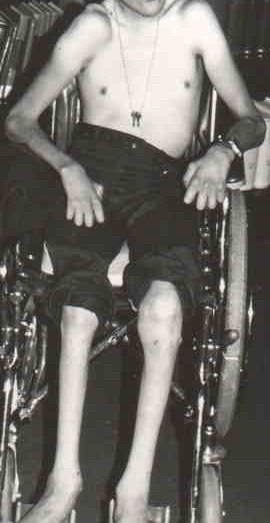
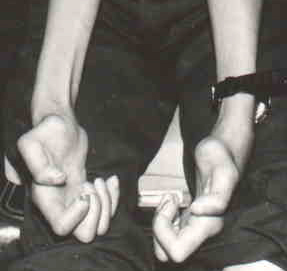
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
Childhood-Onset Polyneuropathies
| STORAGE INCLUSIONS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Disease | Cellular localization |
| Osmophilic with periodicity  Bilbao |
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy | Schwann cell Macrophage Axon |
| Fabry's | Vascular Perineurial Schwann cell, non-myelinating | |
| Niemann-Pick, Type 1 | All except axon | |
| Batten-Kufs | Schwann cell Vascular Fibroblast | |
| Toxic (Lysosomal) Amiodarone Chloroquine Perhexiline Similar inclusions: Cockayne |
Vascular: Endothelial & smooth muscle Nerve: Perineurial; Schwann cells (Non-myelinating) | |
| Zebra bodies | Metachromatic Leukodystrophy | Schwann cell Macrophage |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis | Schwann cell-myelinating Fibroblast | |
| Fabry's | Vascular Perineurial | |
| Niemann-Pick | Schwann cell Endothelial Macrophage | |
| Pi granules | Schwann cell | |
| Membrane-bound cleft or polygonal space | Krabbe | Schwann cell Macrophage |
| Adrenoleukodystrophy | Schwann cell Macrophage | |
| Farber's disease | Endothelial cell | |
| Empty vacuoles | Tangier disease | Schwann cell, non-myelinating |
| GM1 gangliosidosis | Vascular Fibroblast | |
| I-cell disease | Schwann cell, non-myelinating Fibroblast Perineurial | |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis | Fibroblast Vascular Schwann cell | |
| Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis | Schwann cell | |
| Wolman's disease | All | |
| Sialidosis, type 1 | Schwann cell | |
Farber's disease (Lipogranulomatosis; FRBRL)
● Acid ceramidase (ASAH)
- Clinical
- Nerve: Hypotonia; Distal atrophy
- Skin: Lipogranulomatosis; Nodules: Periarticular subcutaneous
- CNS: Mental & motor retardation; Hoarse cry
- Systemic: Hepatomegaly; Splenomegaly; Nephropathy
- Joints: Painful, Swollen
- Eyes: Macular cherry-red spots
- Prognosis: Respiratory insufficiency; Death 2 to 20 years
- Lab
- Neuronal & glial storage of nonsulfonated acid mucopolysaccharide
- Elevated urine ceramide levels
- N-laurylsphingosine deacylase deficiency
- Ceramidase deficiency
- Electrophysiology
- Nerve conduction velocities: Slow
- Pathology
10
- Systemic: Granulomatous infiltration of liver, spleen, lungs, and thymus
- Farber bodies: Curved, tubular; Vacuolar & cytoplasmic; Ceramide
- Nerve
- Hypomyelination
- Schwann cells: Inclusions
- Myelinating: Electron-lucent membrane-bound clefts
- Non-myelinating: Membrane bound, elongated bodies
- Myelinating: Electron-lucent membrane-bound clefts
Giant Axonal Neuropathy 1 (GAN1)
● Gigaxonin (GAN; GAN1; KLHL16)
|
|
HMSN2 with Giant Axons (GAN2)
● DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor 8 (DCAF8)
- Epidemiology: German family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg317Cys
- DCAF8 protein
- Substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood
- Pes cavus
- Polyneuropathy
- Weakness
- Distal
- Symmetric
- Legs > Arms
- Cramps
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Pan-modal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles
- Gait disorder
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Weakness
- Cardiomyopathy: Some patients
- LVH
- Conduction abnormalities
- Onset
- Laboratory
- EMG: Denervation
- Chronic: Large motor unit potentials
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- NCV
- Velocity: Normal or Mildly slowed
- CMAP amplitudes: Reduced or absent distally
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss: Large > Small
- Large axons
- Contain: Neurofilament accumulations
- Scattered
- Myelin sheaths: Thin
- Onion bulbs: Occasional; Small
- EMG: Denervation
- Differential diagnosis: GAN1, Recessive
Neuroaxonal Dystrophy (Late infantile; NBIA2A)
● Phospholipase A2, Group VI (PLA2G6)
- Nosology: Seitelberger’s disease; Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 2A
- Epidemiology: Multiple families
- Genetics
- PLA2G6 mutations: V691del; Tyr790Ter; Lys545Thr; Val310Glu; Arg632Trp (Karak syndrome)
- Allelic disorders
- Atypical Neuroaxonal Dystrophy: Childhood onset
- Karak syndrome (NBIA2B)

- Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 2 (NBIA2A)

- Parkinson Disease 14, Recessive (PARK14; Dystonia-Parkinson, Adult)

- Spastic-Ataxia
- PLA2 enzymes
- General: Catalyze release of fatty acids from phospholipids
- PLA2G6 activity high in brain
- PLA2G6 mutations: Most probably cause loss of function
- Clinical features: Typical syndrome
- Onset
- 1 to 2 years
- Gait difficulties
- CNS
- Cognitive
- Mental & Motor milestones: Loss
- Neuropsychiatric: Autistic; Disordered social communication
- Cognitive decline: Progressive
- Seizures
- Tone: Increased
- Extrapyramidal: Dystonia; Rigidity
- Spasticity: Tetraparesis; Some patients
- Gait disorder
- Ataxia
- Deafness
- Cognitive
- Neuropathy: Poorly defined by EMG or Pathology
- Limb mutilation
- Hypotonia
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or reduced
- Autonomic
- Loss of tears (keratitis)
- Poor temperature regulation
- Urinary retention
- Myopathy
- No clinical signs
- Serum CK: Mildly elevated in some cases
- Muscle pathology
- Necrosis
- Fiber splitting
- Endomysial macrophage activation
- Axonal swellings in intramuscular nerves & terminals
- Endocrine
- Diabetes insipidus
- Hypothalamic hypothyroid
- Course: Death < 10 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Diagnosis: Swellings may be present on conjuctival, skin or muscle biopsy
- Brain MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy
- Iron accumulation in globus pallidum & substantia nigra
- Pathology
- Spheroids: In CNS & Peripheral nerves
- Contents: Membranes & abnormal mitochondria
- Staining: PAS positive
- Peripheral nerve
- Swellings may be present
- Little axonal loss or Wallerian degeneration
- Ultrastructure: Tubulovesicular profiles; Mitochondrial aggregates
- CNS
- Iron deposition
- Cerebellar atrophy
- Optic nerve atrophy
- Spheroids: In CNS & Peripheral nerves
- Infantile variant
8
- Clinical
- Movements: Hyperkinetic; Tonic spasms
- Seizures
- Apneic spells
- Course: Progressive to hypotonia or plateau at 3 years
- Laboratory
- Skin nerves: Thin myelin; Condensed axonal filaments
- Brain: Axon terminal degeneration in cortex, basal ganglia & cerebellum
- Clinical
- Differential Diagnosis: Overlaps clinically with
- Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN; NBIA1)

● PANK2 ; Chromosome 20p13-p12.3;
Recessive
; Chromosome 20p13-p12.3;
Recessive
- Later onset
- Extrapyramidal: Dystonia; Chorioathetosis
- Schindler
 &
Kanzaki
&
Kanzaki
 diseases
diseases
● N-acetyl-α-D-galactosaminidase (NAGA) ; Chromosome 22q11;
Recessive
; Chromosome 22q11;
Recessive
- Lysosomal storage disorder presenting as INAD
- Psychomotor retardation
- Myoclonic seizures
- Decorticate posture: Long-tract signs
- Optic atrophy: blindness, marked
- Loss of contact with environment by age 3–4 years
- Also see: NBIA3
 (FTL gene
(FTL gene
 )
)
- INAD 2
- Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN; NBIA1)
Neuroaxonal Dystrophy 2 19
● Recessive
- Epidemiology: Roma family; 3 infants
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Motor
- Hypotonia: Predominantly axial
- Difficulty swallowing
- Respiratory failure
- Myoclonic seizures
- Dysmorphic features: Micrognathia
- Course: Death in 5th month; Respiratory insufficiency
- Laboratory
- EEG: Focal epileptiform abnormalities
- CNS MRI: Normal
- EMG: Chronic denervation in some
- Muscle: Fiber type grouping
- Pathology
- Brains: Small without malformation
- Axonal spheroids
- Locations: Most prominent in
- Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Anterior thalamic reticular nuclei
- Spinal cord: Anterior horns & columns
- Lower motor neurons
- Size: Especially large
- Proximal, Not in anterior roots or distal motor axons
- Contents
- Neurofilaments
- NCAM: On surface
- Vesicles: At center
- Ubiquitin & Calretinin: Some spheroids; Less in motor neurons
- No synuclein
- PAS: Negative
- Axon Sprouting: From surface of many spheroids
- Locations: Most prominent in
Infantile Neuroaxonal Degeneration with Facial Dysmorphism (INNFD; IHPRF1)
● Sodium leak channel, nonselective (NALCN)
- Epidemiology
- > 10 families
- Male > Female
- Genetics
- Mutations: Biallelic; Loss-of-function; Truncating; Gln642X, Trp1287Leul 1-BP Del, 1489T
- Allelic disorder
- CLIFAHDD (Dominant): DA2A arthrogryposis
- Pancreatic cancer: Somatic mutations
- NALCN protein
39
- Expressed in: Brain & Spinal cord
- Channel associated
- Cation leak channel
- Voltage-independent
- Nonselective
- Non-inactivating
- Permeable to Na+, K+, and Ca++
- Responsible for: Neuronal background sodium leak conductance
- NALCN channelosome: Composed of NALCN & 3 auxiliary subunits
- UNC79
 38
38
- UNC80

- FAM155A (NALF1)

- UNC79
- NALCN modulation: G-protein–coupled receptors
- Positive: Src family kinase–dependent pathways
- Negative: G-protein–dependent pathways
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy or Prenatal
- Prenatal
- Intrauterine growth restriction
- Oligohydramnios
- CNS
- Psychomotor regression, severe
- Retardation: No eye contact, speech or cognitive development
- Spastic tetraparaplegia
- Truncal hypotonia
- Rspiratory: Central sleep apnea (65%)
- Seizures (71%)
- Dyskinetic movements
- Strabismus
- Skeletal
- Contractures
- Microcephaly
- Facial dysmorphism: Prominent forehead; Micrognathia; Large, low-set ears
- Course
- Failure to thrive (88%)
- Some alive at 2 decades
- Laboratory
- Sural nerve: Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy
- Unmyelinated axons
- Spheroids
- Edema: Endoneurial & Perineurial; Generalized
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
- NCV: Lower limit of normal
- EMG: Normal
- Sural nerve: Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy
- NALCN variant syndrome: Congenital contractures of limbs & face, Hypotonia & Global developmental delay (CLIFAHDD)
 26
26
- Nosology: DA2A arthrogryposis syndrome
- Epidemiology: > 30 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense (97%)
- Location: In or near S5 & S6 pore-forming segments of NALCN
- Gain-of-function
- Premature death, Epilepsy, Paroxysmal dystonia, Worse prognosis: Variants in NALCN pore domains (DII-S6 region)
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Allelic disorders
- Mutations
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital
- Prenatal
- Polyhydramnios
- Clubfoot
- Eyes
- Downslanting palpebral fissures
- Strabismus
- Esotropia
- Face
- Broad nasal bridge
- Anteverted nasal tip
- Large nares
- Short columella
- Long philtrum
- Micrognathia
- Pursed lips
- H-shaped dimpled chin
- Deep nasolabial folds
- Full cheeks
- Limb contractures: Distal arthrogryposis (77%)
- Camptodactyly
- Ulnar deviation
- Adducted thumbs
- Clubfoot
- Calcaneovalgus deformity
- Other contractures: Hip; Elbow; Knee
- Other skeletal: Scoliosis; Neck short
- CNS
- Cognitive & Speech delay
- Ataxia, Episodic (41%)
- Precipitants = Physical activity, Heat, Excitement
- Onset age: 1st decade; Mean = 6.5 years
- Acetazolamide responsive
- Associated with: Motor skill decline
- Mutations: Ile322Thr, Arg1181Gln, Ala1185Thr; DIII-DIV linker
- Dystonia, paroxysmal (12%)
- Respiratory: Insufficiency; Periodic pattern with apnea
- Hypotonia
- Seizures: 1 patient
- GERD
- Course
- Progressive
- Death in childhood in some
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebral or Cerebellar atrophy; May be normal
- EMG: Normal
Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Movement Abnormalities, Abnormal gait & Autistic features (NEDMAGA)
● Zinc finger swim domain-containing protein 6 (ZSWIM6)
- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: de novo; Heterozygous; c.C2737T (R913X)
- Allelic disorder: Acromelic frontonasal dysostosis
- ZSWIM6 protein
- Expression: CNS; Lens
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Developmental delay: Global; Severe; Absent speech; autism
- Walking: Delayed; Broad based
- Seizures (50%): Mild, some patients
- Spasticity (50%)
- Movements: Tongue; Hands
- Peripheral neuropathy
- High pain threshold
- Weakness (1 patient): Distal; Legs
- Face: Dysmorphic features
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal or Mild cortical atrophy
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss; Neurofilament accumulation
Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Central & Peripheral Motor Dysfunction (NEDCPMD)
● Neurofascin (NFASC)
- Epidemiology: 9 families, 15 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Stop or Missense: N124D; Arg370Pro, P705T; S831P; Arg846X, V1077A (Nf186); Val1122Glu
- Homozygous
- Mutations
- NFASC protein
- Development: Nodes of Ranvier (CNS & PNS) & Initial segment
- L1 family immunoglobulin cell adhesion molecule
- Mutation effects
- Other disorders: Immune neuropathies & other disorders
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 0 to Infancy
- Prenatal: Reduced movements (Some patients)
- CNS
- Developmental delay
- Behavioral: Aggression; Anxiety
- Polyneuropathy, Demyelinating
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Respiratory distress
- Amyotrophy
- Dysmorphic features
- Later features
- Ataxia
- Eyes: Saccadic pursuit
- Limbs: Dysmetria
- Spasticity
- Myoclonus
- Ataxia
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy; Some WM changes
- Central conduction velocities: Slow (SSEP)
- PNS
- NCV: Length-dependent demyelination; Velocities reduced or normal
- EMG: Chronic denervation
- Muscle: Normal
Intellectual Developmental Disorder + Speech delay & Axonal Peripheral Neuropathy (IDDSAPN)
● Nuclear Export Mediator Factor (NEMF)
- Epidemiology: 11 families, 21 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Nonsense; Frameshift; Missense
- NEMF protein
- Location: Ribosome
- Resolves stalled ribosomes during translation
- Facilitates recruitment of LTN1 E3 ligase
 : Leads to proteasomal degradation
: Leads to proteasomal degradation
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 2 years
- Developmental delay
- Hypotonia
- Intellectual
- Autism
- Speech: Delay; Dysarthria
- Polyneuropathy
- Weakness: Distal; Arms & Legs
- Walking: Delayed
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Gait: Ataxic; Difficulty running
- Skeletal
- Scoliosis
- Equinovarus
- Hands: Deformities; Polydactyly
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal or Atrophy
- NCV: Axon loss
Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathies (CHN)
|
CHN 1: EGR2 2: P0 (MPZ) 3: CASPR (CNTNAP1) Other ADCY6 ARHGEF10 FAM126A GLDN LGI4 PMP-22 HMSN III (Dejerine-Sottas) Focally folded myelin sheaths SOX10 |
Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy 2 (CHN2)
● P0 protein (MPZ)
- Genetics
- Mutations: Asp61Asn, Arg98Cys, Ser111Phe, Gly123_Cys127del, Thr124Lys,
Asn131Ser, Gly167Arg, Leu184fs, Gln186X, Gln215X - Allelic disorders
- Mutations: Asp61Asn, Arg98Cys, Ser111Phe, Gly123_Cys127del, Thr124Lys,
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Birth
- Hypotonia
- Weakness: Severe generalized; Face
- Muscle bulk: Wasting or Normal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Sensory loss: Variable
- Joints: Arthrogryposis or Hyperextension
- Course
- Severe cases: Death before 3 months
- Milder cases: Static weakness; Increased disability with growth
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic
- Demyelinating: NCV Very slow; Distal latencies long; Temporal dispersion; No conduction block
- SNAPs: Absent
- Similar to HMSN III
- Pathology
- Myelin sheaths: Thin, Absent or Abnormally folded
- Axon loss: Large > Small
- Onion bulbs: Occasional small
- Muscle: Type 1 atrophy; No fiber type grouping
- MRI: Normal nerve size
- CSF protein: Mildly high
- Electrodiagnostic
Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy 1 (CHN1; CMT4E)
● Early growth response-2 (EGR2; KROX20)
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Ile268Asn (Homozygous); Ser382 Arg & Asp383Tyr (Heterozygous)
- Recessive mutations
- Repressor binding domain (R1): ? Alter transcriptional activity
- 10 kB deletion involving myelin-specific enhancer: Congenital amyelinating neuropathy
- Allelic disorcders
- Also defective in: Krox20 knockout mice; CMT1; Dejerine-Sottas
- Mutations
- Protein: Zinc finger
- Clinical
- Onset
- Infantile hypotonia
- Arthrogryposis
- Weakness: Diffuse; Distal > Proximal; Ambulation ± walker
- Wasting: Diffuse
- Onset
- Nerve conduction velocities: 3 to 8 M/s
- Nerve pathology
- Myelin: Absent or greatly reduced on most axons
- Onion bulbs: Occasional
- Axonal loss: Mild to moderate
- EGR2 Variant: Congenital Amyelinating Neuropathy, Recessive (CHN1)
20
- Epidemiology: Female Moroccan infant
- Genetics
- Mutation: 10 kB deletion involving myelin-specific enhancer
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Oligohydramnios
- Birth: Hypotonia; Respiratory failure; Reduced movements; Arthrogryposis
- Death: 7.5 months
- Nerve pathology
- Complete absence of PNS myelin
- Large axons: Ensheathed in Schwann cells
- EGR2 staining: Absent
- Parents: Normal
Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy, Asymptomatic (SNCV)
● Rho Guanine-Nucleotide Exchange Factor 10 (ARHGEF10)
- Epidemiology: Single family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Thr109Ile
- Allelic with
- Susceptibility to Paclitaxel toxic neuropathy: Heterozygous mutations
- ARHGEF10 protein
- Rho family of GTPase proteins (RhoGTPases)
- Regulate actin cytoskeleton
- Influence cell development
- Polarity; Microtubule dynamics; Membrane-transport pathways; Transcription-factor activity
- Play role in neuronal morphogenesis
- Cell migration; Axonal growth & guidance; Dendrite elaboration & plasticity; Synapse formation
- Guanine-nucleotide exchange factor (GEF): Other disorders
- FGD1
 : Faciogenital dysplasia (Aarskog-Scott)
: Faciogenital dysplasia (Aarskog-Scott)

- FGD4: CMT 4H
- ARHGEF6 (aPIX)
 : X-linked nonsyndromic mental retardation 46
: X-linked nonsyndromic mental retardation 46

- ALS2 (Alsin): Autosomal recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PLEKHG5: DSMA4; CMTRIC
- HRAS: Congenital myopathy with excess spindles (Costello syndrome)
- FGD1
- Rho family of GTPase proteins (RhoGTPases)
- Clinical
- Most patients asymptomatic
- Examination: Often normal: Normal tendon reflexes & muscle bulk
- Occasional patients with Raynaud's phenomenon
- Electrodiagnostic testing
- Nerve conduction velocities: Uniform slowing; Arms 33 to 42 m/s; Legs 27 to 36 m/s
- CMAPs: Normal amplitude
- SNAPs: Normal or mildly reduced amplitude
- Similar values at all ages: ? Non-progressive
- Pathology
- Nerve: Hypomyelination
- Reduced number of myelinated axons: 50% of normal
- Size of remaining myelinated axons: 2 to 6 μm
- Axonal sheath: Thin for axon diameter
- Onion bulbs: Rare
- Regenerating clusters: Rare
- Tomaculae: none
- Muscle: Mild denervation changes
- Nerve: Hypomyelination
Hereditary Relapsing Thermosensitive Neuropathy
● Autosomal Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 French family
- Clinical
- Onset age: 6 to 43 years (Usually < 15)
- Relapsing
- Precipitated by fever > 38 °C
- 2 to 5 attacks
- Exam normal between attacks
- ? Duration of symptoms correlated with duration of fever
- Weakness: Paraparesis or quadriparesis
- Sensory: Paresthesias & numbness
- Occasional: Dysphagia; Dysuria
- Electrophysiology: Demyelinating
- Conduction block
- Prolonged distal latencies
Lethal Neonatal Sensory-Motor Polyneuropathy
● Autosomal Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 Mississippi family
- Clinical
- Onset: Prenatal with reduced fetal movements
- Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Distal > Proximal
- Symmetric
- Diaphragm: Onset birth to 6 months
- Sensory: Pain reduced in some patients
- Contractures (75%)
- CNS: ? Changes related to hypoxia
- Prognosis
- Increasing disability
- Late static phase with no recovery
- Death < 8 months 2° Respiratory failure
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- NCV: Reduced or absent CMAPs & SNAPs
- EMG: Denervation
- Brainstem evoked potentials: Reduced wave 5 suggesting sensorineural hearing loss
- Nerve Pathology
- Loss of sensory & motor, large & medium sized, myelinated axons
- Muscle pathology: Grouped atrophy; Many small fibers
- Electrophysiology
- Rule out
Infantile Axonal Polyneuropathy with Respiratory Failure 5
● Recessive; Sporadic
- Epidemiology
- 2 families
- Male > Female
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: < 6 months; Usually < 2 to 3 months
- Hypotonia
- Apneic spells
- Weakness
- Distal > Proximal
- Symmetric
- Cranial nerves
- Feeding difficulties
- Facial weakness
- EOM: Nystagmoid eye movements
- Sensory: Pain sense preserved
- Autonomic dysfunction: Some patients
6
- Tachycardia
- Hyperhidrosis
- Hyperthermia
- Hypertension
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Prognosis
- Increasing disability: Quadriplegia & Respiratory failure
- Death < 6 months 2° Respiratory failure
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- NCV: Reduced or absent CMAPs & SNAPs
- EMG: Denervation
- Fibrillations
- Some enlarged motor units firing at rapid rates
- Brainsten evoked potentials: Reduced wave 5 suggesting sensorineural hearing loss
- CSF: Normal
- Nerve Pathology
- Loss of sensory & motor, large & medium sized, myelinated axons
- Normal myelination on remaining axons
- Ultrastructure: Büngner bands; Normal unmyelinated axons
- Muscle pathology
- Grouped atrophy: Small fibers angular
- Larger muscle fibers: Hypertrophy; Type 1 predominance in some
- Spinal cord: Mild loss of anterior horn cells
- Electrophysiology
- Differential diagnosis: SMARD
- Neuropathic
- SMARD1: IGHMBP2
- SMARD2: LAS1L
- Spinal muscular atrophy: SMN1
- Lethal neonatal axonal neuropathy
- Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy: MPZ
- Infantile Axonal Polyneuropathy with Respiratory Failure
- Axonal neuropathy & Diaphragm palsy, Congenital: REEP1
- MFN2, Recessive
- Brown-Vialetto-van Laere: SLC52A2; SLC52A3
- Myopathy
- Diaphragm weakness
- Neuropathic
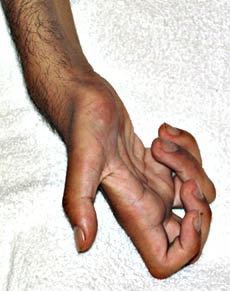
Congenital Cataracts, Facial Dysmorphism & Neuropathy Syndrome (CCFDN)
● C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II subunit A, phosphatase of, subunit 1 (CTDP1)
- Epidemiology: Wallachian Gypsies (Vlax Roma; Rudari); Bulgaria
- Genetics: Transcription syndrome
- Mutation: Single nucleotide substitution in antisense Alu element in intron 6
- Produces: Aberrant splicing; Alu insertion in processed mRNA
- Carrier rate in Rudari gypsies: 6.9%
- No mutations in Marinesco-Sjögren patients
- FCP1 Protein
- TFIIF-associating CTD phosphatase-1
- Dephosphorylates C-terminal domain of largest RNA polymerase II subunit
- Substrates are phopsphorylated serine residues
- Regulates recruitment of proteins involved in transcription & mRNA processing machinery
- Other functions
- Involved in transcription regulation: Part of elongation complex
- Opposes Srb 10 mediated repression of cell-cycle & growth control genes
- TFIIF-associating CTD phosphatase-1
- Clinical
- Skeletal
- Short stature: 100%
- Facial dysmorphism: 80%; Prominent midface; Thickened perioral tissues; Hypognathism
- Kyphoscoliosis
- Foot: Pes cavus; Pes equinovarus
- Claw hand
- Eye
- Congenital zonular cataracts: 100%
- Microcornea
- Pendular nystagmus
- Strabismus: 100%
- Neuropathy
- Motor: Predominant
- Initially lower extremities: By 8 months
- Upper extremity weakness in childhood
- Severe disability by 3rd decade
- Sensory: Distal; Loss of all modalities
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or absent, especially in lower extremities
- Nerve conduction velocities: Demyelinating
- NCV: 20 to 34 M/sec
- Distal latencies: Prolonged
- Nerve biopsy
- Hypomyelinated axons
- Axonal degeneration & regeneration in older patients
- Motor: Predominant
- Rhabdomyolysis: After viral infections
- CNS
- Upper motor neuron
- Intellectual Retardation: Mild
- Extensor plantar response: 40%
- No spasticity
- Choreiform movements: 36%; Face & Upper extremities
- Ataxia: Mild; 22%
- Tremor: 10%
- EEG: Slowing
- MRI
- Cerebral atrophy (30%)
- Ventricles: Enlarged
- Spinal cord: Atrophy (25%)
- White matter lesions: Periventricular; Progressive focal supratentorial
- Upper motor neuron
- Endocrine: Mild hypogonadism
- General anesthesia complications
- Pulmonary edema
- Epileptic seizures
- Skeletal
- Differences from Marinesco-Sjögren
13
- Present in CCFDN: Peripheral neuropathy; Facial dysmorphism; Microcornea; Linkage to 18qter
- Less in CCFDN: Mental retardation severity; Cerebellar atrophy; Chronic myopathy
Navajo Neurohepatopathy
● Glomerulosclerosis gene MPV17 (MPV17)
Navajo Sensory-Autonomic Neuropathy + Arthropathy (MTDPS6) ● Glomerulosclerosis gene MPV17 (MPV17)
|
|
Hypomyelination in CNS & PNS; Hypopigmentation & Enteric Aganglionosis (PCWH)
● SOX10
- Nosology: Waardenburg-Shah, Neurologic variant (WS4)
- SOX10 gene
- Mutations
12
- Specific mutations: 12 base pair deletion in exon 5; Q250Stop; 759delG; SOX10 deletions
- Produces intact protein with extended tail added to transactivation domain in C-terminus
- Disease Mechanisms
- Severe disorders: ? Mutated protein acts as dominant negative
- Haploinsufficiency: Milder phenotype disorders
- Allelic disorders
- Null mutations
- SPG + Hypomyelinating neuropathy & Deafness
- Dominant megacolon syndrome
- Waardenburg syndrome, type 2E ± Neurologic involvement

- Waardenburg-Shah syndrome (WS4C)

- Clinical: Intestinal aganglionosis; Pigmentation defects; Deafness, sensorineural
- Also due to mutations of:
EDNRB (Endothelin B receptor)
 ;
Endothelin-3 (EDN3)
;
Endothelin-3 (EDN3)

- Peripheral demyelinating neuropathy, central dysmyelination, Waardenburg syndrome, Hirschsprung disease (PCWH)

- Loss of function, Missense mutations
- Kallmann Syndrome (Anosmia & Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism) with Deafness
- Other
- Hearing loss
- Anosmia
- Neurodevelopment disorders
- Cancer progression
- Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy symptoms: SNP rs139887 36
- Dom mouse (Dominant megacolon; intestinal aganglionosis, white belly spot & white paws)
- Null mutations
- Mutations
12
- SOX10 protein
- Marker for
- Migratory multipotent Neural Crest progenitors
- Neural Crest derivatives
- Myelin-specific
transcription factor
- In Schwann cells & Oligodendroglia
- Required for Schwann cell development & Myelination
- Transition from Schwann cell precursor to Immature Schwann cell
- Modulates other myelin-related transcription factors & proteins
9
- Promotes expression of OCT6 (POU3F1)

- Triggers events enabling myelin gene transcription
- P0 protein
- Connexin-32: Activates expression by binding to promoter; Synergy with EGR2
- Other: ERBB3; PLP; MBP; SIPA1L2
- Promotes expression of OCT6 (POU3F1)
- Plays role in neural crest development: Enteric ganglion cells & Melanocytes
- Marker for
- Clinical
- Waardenburg syndrome: General features
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Pigmentation disorders: Skin, Hair, Iris
- Subtypes
- WS1: Facial dysmorphisms; PAX3

- WS2: No dystopia canthorum; SOX10; MITF

- WS3: Facial dysmorphisms, Arm Musculoskeletal; PAX3

- WS4: Hirschsprung disease; SOX10;
Endothelin-3
 , EDNRB
, EDNRB

- WS1: Facial dysmorphisms; PAX3
- Onset
- Congenital
- Hirschsprung disease
- CNS
- Clinical
- Developmental delay: Severe
- Spastic paraplegia or quadriplegia
- Seizures
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- MRI
- Semicircular canals: Agenesis or hypoplasia of one or more
- White matter: Absent myelination; Hyperintensity on T2
- Olfactory bulbs: Agenesis (88%)
- Lacrimal glands: Hypoplastic (79%)
- Parotid glands: Hypoplastic (86%)
- CSF: Protein mildly increased
- Pathology: Absent central myelin
- Clinical
- PNS
- Muscle atrophy
- ? Sensory loss
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Electrophysiology: Demyelinating neuropathy
- NCV: Slowing, Uniform
- F-waves: Preserved; Long latency
- CMAPs: Amplitude small
- Stimulation threshold: High
- Pathology: Nerve
- Large axons
- Absent or reduced myelin
- Number: Normal or Reduced
- Occasional excessively large axon
- Small axons: Reduced number
- Schwann cells: Present; Aligned with axons in 1 to 1 relationship
- Endoneurial fibroblasts: Small vacuoles
- Large axons
- Ocular
- Nystagmus
- Optic Atrophy
- Dystopia canthorum
- GI
- Hirschsprung disease
- Enteric aganglionosis
- Depigmentation
- Skin
- Heterochromia iridis
- Fundus: Depigmentation, patchy
- Course
- ? Non-progressive
- Death at 3 months in 1 patient
- Waardenburg syndrome: General features
- SOX10 variant: SPG + Hypomyelinating neuropathy & Hearing loss
28
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: c.1140C.A (p.Y380X)
- Parental mosaicism
- Clinical
- Onset: Reduced fetal movements
- Motor: Developmental delay
- Spastic paraparesis
- Legs > Arms
- Loss of ambulation
- Course: Slow progression
- Tendon reflexes: Increased at knees; Reduced at ankles
- Hearing loss
- Neuropathy: Hypomyelinating
- Sensory loss: Vibration & Pain
- Weakness: Distal legs
- Cerebellar
- Dysmetria: Arms
- Nystagmus
- GI: Constipation, mild
- Cutaneous hypopigmentation
- Face: High arched palate; Small mouth; Thin, upturned nostrils
- Eye: Macular pigment changes
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Absent semicircular canals
- NCV
- Velocities: Slowing, diffuse & symmetric (11 to 20 m/s)
- SNAPs: Reduced amplitude or Absent
- Nerve biopsy: Thin myelination; Axon loss
Tyrosinemia 1 (TYRSN1)
● Fumarylacetoacete Hydrolase (FAH)
- Epidemiology
- > 100 patients
- 1 in 100,000 births
- Unusual: Central America; Oceania
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Splice & Stop; > 40
- Geography: Mutations often common in specific regions
- Turkey: D233V
- Finland: W262X
- Asia: Gly64His
- Saudi Arabia: Met1Val
- Europeans & Caucasians: c.974C>T
- Fumarylacetoacetase protein
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal to Infant
- Peripheral neuropathy: Attacks
30
- Clinical: Porphyria-like
- Onset
- Children: Mean 1 year
- Adults: After discontinuation of, or intermittent, NTBC treatment
- Multiple attacks
- Pain: Severe; Abdomen, Extremities
- Muscle weakness
- May be severe
- Respiratory failure
- Autonomic
- Blood presure fluctuations: Hypertension
- GI: Vomiting; Ileus
- CNS: Seizures; Confusion
- Fever
- Prognosis
- Treatment: Full recovery
- Mortality: High
- Treatment
- NTBC
- 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoro-methylbenzyol)-1,3 cyclohexanedione
- Inhibitor of 4-hydroxy-phenylpyruvate dioxygenase
- Diet
- Protein restriction
- Tyrosine- & Phenylalanine-free protein substitutes
- Glucose: IV
- Liver transplantation
- NTBC
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction studies: Axon loss
- Nerve Pathology: Axon degeneration, Acute
- Hyponatremia
- Succinylacetone: Increased blood spot
- NTBC level: Below therapeutic range
- Clinical: Porphyria-like
- Myopathy: 2° Carnitine deficiency
7
- Epidemiology: Case report
- Clinical
- Onset: 2 years; Gait disorder
- Weakness: Proximal; Hypotonia
- Treatment: Carnitine, dietary supplementation
- Laboratory
- Plasma carnitine: Low
- Hypophosphatemia
- Systemic features
- Hepatic failure
- Renal: Fanconi syndrome
- Cardiomyopathy: Mild
- Natural history
- With treatment: Survival to adulthood
- No treatment: Death < 3 years
- Laboratory
- Toxic metabolite accumulation
- Succinylacetone, Maleylacetoacetate, Fumarylacetoacetate
- Succinylacetone: Competitive inhibitor of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)
- Toxic metabolite accumulation
Chediak-Higashi
● Lysosomal trafficking regulator (LYST; CHS1)
- Genetics
- Null mutations: Severe childhood forms
- Missense mutations: Later onset
- Allelic with: Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis, Complicated
- LYST (CHS1) protein
- Functions
- Interacts with N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) attachment protein receptors (SNAREs)
- Role in membrane fusion or fission
- May regulate lysosome trafficking
- Subcellular location: ? Cytoplasmic
- Tissue specificity: Thymus; Peripheral blood leukocytes; Bone marrow; Brain
- Functions
- Clinical
- Polyneuropathy
- Clinical
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal; Feet & Hands
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- EMG: Distal denervation
- Pathology: Axonal loss
- Relative sparing of smaller myelinated axons
- Loss of unmyelinated axons: Moderate
- Axon regenration
- Inflammation: Perivascular; Occasional
- Schwann cells: Giant lysosomal inclusions & Lipofuscin
- Rule out: Neoplastic infiltrative neuropathy
- Treatment: Transient improvement with corticosteroids 15
- Clinical
- Motor neuropathy
24
- Epidemiology: 2 patients in 1 family
- Mutations: Y3163C; S3475F
- Onset age: Childhood to 4th decade
- Weakness: Legs; Symmetric; Proximal & Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Sensation: Normal
- CNS
- Mental retardation
- Spinocerebellar degeneration
- Adult onset: Parkinsonism; Dementia
- Pigmentation defective (Partial oculocutaneous albinism)
- Skin: Giant melanosomes; Hypopigmentation
- Ocular: Nystagmus; Photophobia
- Systemic
- Organomegaly: Liver; Spleen; Lymph nodes
- Hematologic
- Anemia; Pancytopenia
- Hemorrhage: Platelets lack dense granules; Function is abnormal
- Reduced natural killer cell & cytotoxic T lymphocyte function
- Abnormal fusion of lysosomes
- Defective granule killing
- Bone marrow
- Eosinophilic, peroxidase-positive inclusion bodies in myeloblasts & promyelocytes
- External link: New Mexico
- Lymphoreticular (Lymphohistiocytic) malignancy (90%)
- "Accelerated phase" of CHS
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- CD8 T-cells proliferate & infiltrate tissues
- Susceptibility to infection
- Heterozygotes: Granular anomaly of lymphocytes
- Course
- Death: Often < 7 years
- If malignancy is absent
- Longer survival
- Progressive neurologic disorder
- Polyneuropathy
- Pathology: Giant lysosomal inclusions in CNS, Schwann cells & Leukocytes
- Animal model: Beige mouse
- Variant syndrome: Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis, Complicated
22
- Epidemiology: 6 Japanese families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Misense (Leu58Val; Phe1397Val); Stop & Splice
- Allelic with: Chediak-Higashi
- LYST protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2nd to 6th decade
- Spastic paraparesis: Gait disorder
- Cerebellar ataxia: Arms
- Peripheral neuropathy: Motor & Sensory axon loss
- Tendon reflexes: Increased except at ankles
- IQ: Low
- Laboratory
- MRI: Cerebellar & Thoracic spinal cord atrophy
- NCV: Velocities mildly reduced in legs; SNAP & CMAP amplitudes low
- SNAPS: Absent or Reduced amplitude
- Motor-evoked potentials: Central delay
- Granulocytes: Peroxidase stained giant granules
- Nerve biopsy: Myelinated axon loss; Axon swelling
Cerebral Dysgenesis, Neuropathy, Ichthyosis, and Palmoplantar Keratoderma (CEDNIK)
● SNAP29
- Epidemiology: > 10 families
- Genetics
- SNAP29 protein
- Modulator of vesicle trafficking
- Binds to syntaxin fusion proteins
- Disease: Levels reduced in tissues
- Other mutations in vesicle recycling genes
- Chediak Higashi

- Griscelli syndrome


- Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome

- Chylomicron retention disease

- Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 4

- Chediak Higashi
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: < 4 months
- Roving eye movements
- Poor head & trunk control
- Failure to thrive
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Delayed development
- Late sitting & walking
- Polyneuropathy
- Clinical: Not well described
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Electrophysiology: Axon loss
- Muscle biopsy: Denervation; Normal mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- CNS
- Microcephaly: Progressive
- Corpus callosum: Dysgenesis
- Psychomotor retardation: Severe
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Face: Dysmorphism
- Elongated faces
- Antimongolian eye slant
- Hypertelorism: Mild
- Flat broad nasal root
- Skin
- Onset: Between 5 & 11 months
- Palmoplantar keratoderma
- Ichthyosis
- Hypopigmentation
- Progressive during 2nd year of life
- Eye
- Optic disk: Hypoplastic
- Strabismus
- Electrophysiology: Reduced conductance from peripheral retina & macular atrophy
- Skeletal
- Dislocated hips
- Contractures: Legs
- Short stature
- Ear: Sensorineural deafness, mild
- Course: Death in 40% due to pneumonia at ages 5 to 12 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- White matter
- Corpus callosum Δ
- Hypomyelination
- Optic nerve atrophy
- Cortical dysplasia: Pachygyria & Polymicrogyria
- White matter
- Skin
- Ultrastructure: Clear vesicles in spinous & granular epidermal layers
- Glucosylceramides: Retained, abnormally,in lower stratum corneum cells
- Brain MRI
Hypomyelination and Congenital cataract (HCC; HLD5)
● Hyccin (DRCTNNB1A; FAM126A)
- Nosology: Leukodystrophy, Hypomyelinating 5 (HLD5)
- Epidemiology: 6 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Type: Stop, Splice site & Missense
- All homozygous
- Missense mutations
- Milder phenotype
- May have no peripheral neuropathy
- Mutations
- Hyccin protein
- Ubiquitously expressed in brain
- Cell localization: Plasma membrane, patchy
- Mutation effects
- Absent or reduced levels of Hyccin protein
- Mildest patient, without neuropathy, had residual protein
- Onset
- Age: birth or in 1st 2 months of life
- Cataract
- Clinical
- Psychomotor
- Birth: Normal
- 1 year: Delayed
- Walking only with support
- Onset: 1 to 2 years
- Loss: 8 to 9 years
- Mental deficiency: Mild to Moderate
- Other CNS
- Pyramidal: Progressive
- Cerebellar: Progressive
- Seizures (30%)
- Muscle
- Weakness: Legs > Arms
- Wasting
- Eye: Cataracts (100%)
- Congenital
- Bilateral
- Surgery often performed
- Scoliosis (40%)
- Survival
- Most at least to 3rd decade
- 1 death in 1st decade
- Psychomotor
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Diffuse cerebral hypomyelination
- Electrophysiology: Polyneuropathy (90%)
- Motor nerve conduction velocity: Slightly to markedly slowed depending on the age
- CMAP amplitude: Reduced
- Sural nerve biopsy
- Deficiency of myelin sheath in several nerve fibers
- Axonal loss: Mild
- No active axonal degeneration
Myoclonus Epilepsy & Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (EPM4)
● Scavenger receptor class B, Member 2 (SCARB2; LIMP2)
- Nosology: Action myoclonus-Renal failure (AMRF)
- Epidemiology: EPM4 in multiple populations
- Genetics
- Mutations: Nonsense (Q288X; French Canadian), c.435_436insAG & Splice site (c11187.3insT)
- SCARB2 protein
- Lysosomal membrane
- Functions
- Endosomal/lysosomal mediated protein degradation and recycling
- Lysosomes: Cholesterol export
- Onset age: Teens
- Action myoclonus: Aggravated by action, tactile stimuli & startle
- Dysarthria
- Dysphagia
- Seizures: Generalized; Myoclonic-tonic-clonic
- Ataxia: Limb
- Intellect: Normal or Dementia
- Tendon reflexes: Present
- Hearing loss: BAER reduced
- Course: Rapid progression of renal failure
- Nerve conduction studies: Demyelinating polyneuropathy in 4 patients
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced
- F-wave latencies: Prolonged
- Conduction velocities: 30 to 40 M/s
- Renal failure: Proteinuria
- EPM4 Brain pathology: Autofluorescent pigment
Hemolytic Anemia & Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
● CD59 antigen (Protectin)
- Epidemiology: 5 North African (Libyan & Moroccan) Jewish patients
- Genetics
- CD59 mutation: Cys89Tyr, Homozygous
- Allelic with
- Hemolytic anemia & Cerebral infarction
- Early-onset chronic axonal neuropathy, Strokes & Hemolysis
- CD59 protein
- Inhibits final step of membrane attack complex (MAC) formation
- Protects cells from complement mediated lysis
- CD59 deficiency: Common in adults with Paroyysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria 1

- Dermatomyositis, Juvenile
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 7 months
- Polyneuropathy
- Relapsing-remitting
- Exacerbated by: Infection; Febrile episodes
- Hypotonia
- Weakness: Limbs
- Legs > Arms
- Distal > Proximal
- Symmetric
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Immunosuppression treatment
- Eculizumab
- IVIg
- Reduced relapse length & severity
- Improved arm strength
- Hemolytic anemia, Chronic
- Laboratory
- Red blood cells: Reduced CD59, especially on surface membrane
- Sural nerve
- Vessel endothelium: Loss of CD59 expression
- Axon loss
- Myelin sheath: Thin
- NCV: Demyelination; Axon loss
- CSF protein: High
- CD59 variant disorder: Early-onset chronic axonal neuropathy, Strokes & Hemolysis
27
- Epidemiology: Turkish family, 3 patients
- CD59 mutation: c.A146T (p.Asp49Val); Homozygous
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Polyneuropathy
- Axon loss
- Onset: Acute
- Course: Relapsing
- Treatment: Immunomodulation
- Strokes
- Anterior & Posterior circulation
- Cerebral venous thrombosis
- Laboratory
- CD59: Reduced expression on blood cells
- NCV: Axon loss, Motor & Sensory
- Hemolysis: Chronic & Recurrent; Coombs negative
- Indirect hyperbilirubinemia: Neonatal
Congenital Disorder of Deglycosylation 1 (CDDG1)
● N-Glycanase 1 (NGLY1)
- Nosology
- Carbohydrate deficient glycoprotein syndrome, Type 1v (CDG1V)
- Also see: Congenital disorders of glycosyation
- Epidemiology: 17 families; 43 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Cys283Trp; Glu356Gly; Arg401Ter; Arg524Ter; Small deletions & duplications
- NGLY1 protein
- Cytosolic enzyme
- Cleaves intact glycan from N-linked glycoproteins
- Proteasome
- Deglycosylation of cytoplasmic proteins
- Degrades aberrant glycoproteins synthesized in ER & translocated to cytoplasm
- Endoplasmic reticulum–associated degradation (ERAD) pathway
- Mitochondrial homeostasis
- Mutations: Accumulation of misfolded proteins in cytosol
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood or Infancy
- Intrauterine growth retardation (50%)
- CNS
- Hypotonia: Central
- Development delay (Severe): Cognitive; Motor; Speech
- Movements: Chorea & Athetosis; Lip smacking; Tremulousness
- Epilepsy: Intractable; Multifocal; Myoclonic; Drop attacks; Staring or tonic episodes
- Ocular apraxia (20%)
- Microcephaly
- Autonomic
- Absent tears
- Constipation
- Anhidrosis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Sensory loss: Especially pain
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Skeletal: Hands & Feet small; Microcephaly; Scoliosis
- Eyes: Corneal scarring & opacities; Strabismus
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Liver
- Transaminases: High
- Vacuolar amorphous cytoplasmic storage material
- EEG: Often abnormal
- Electrodiagnostic studies
- NCV: 20 to 30 M/s; Axon loss, Sensory > Motor
- EMG: Denervation, Legs > Arms
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss
- Large & Small myelinated
- Unmyelinated axons: Spared
- Myelin sheath: Thin
- Axon loss
- Muscle
- Fiber size: Varied
- Fiber type: 1 predominant
- Fiber typs grouping: Mild
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzyme activities: Individual complexes reduced in some patients
- Glycogen: May be increased
- NGLY1 protein: Absent
- Liver: Cytoplasmic accumulation of storage material in vacuoles
- EEG: Generalized spikes
- α-fetoprotein: High
- Lactate: High in 50%
- Liver
Axonal neuropathy, Optic atrophy & Cognitive deficit (ANOAC) 25
● Syntaxin binding protein 5-like (STXBP5L; LLGL4)
- Epidemiology: 1 Middle-Eastern family; 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.3127G>A, Val1043Ile
- STXBP5L protein
- Expression: CNS & PNS
- Inhibits neurotransmitter release
- Inhibits formation of SNARE complexes between synaptic vesicles & plasma membrane
- Rgulates docking & fusion of synaptic vesicles with presynaptic membrane
- Neurosecretory cells
- Insulin secretion: Negative regulator
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 3 months
- Hypotonia: Proximal & Distal
- Feeding dificulties
- Weakness
- Diffuse
- Legs > Arms
- No sitting or walking
- Bulbar dysfunction
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Sensation: Normal
- Skeletal
- Scoliosis
- Contractures: Distal
- CNS
- Optic atrophy: Progressive
- Extra-pyramidal (50%): Dystonia; Dyskinesia
- Seizures: Myoclonic & Tonic-Clonic
- Eye movements: Slow saccades; Supranuclear paresis; Ophthalmoplegia
- Cognition: Delayed
- Course
- Progressive
- Death: 3rd to 8th year; Respiratory failure
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor (Small SNAPs & CMAPs)
- EMG: Motor unit potentials large
- Muscle: Neurogenic atrophy
- Nerve: Axon loss
- EEG: Epileptic discharges with seizures
- MRI: Brain atrophy
Leukodystrophy, progressive, early childhood-onset (PLDECO)
● Alkaline ceramidase 3 (ACER3)
- Epidemiology: 1 Ashkenazi Jewish family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Gly33Gly
- ACER3 protein
- Hydrolysis of unsaturated long-chain ceramides
- Clinical
- Onset age: 6 to 13 months
- Developmental regression
- Truncal hypotonia
- Appendicular spasticity
- Dystonia
- Areflexia
- Optic discs pale
- Neurogenic bladder
- Face dysmorphism
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: White matter pathology, Cerebral atrophy, Corpus callosum thin
- Nerve biopsy: Axon loss
GPI Biosynthesis Defect with Axonal Neuropathy & Metabolic Abnormality 29
● Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class B protein (PIGB)
- Epidemiology: 11 families
- Genetics
- PIGB protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Global delay: Developmental; Intellectual
- Seizures
- Peripheral neuropathy
- More severe disorders
- Axon loss: Motor > Sensory
- Other
- Deafness
- Bone: Osteodystrophy; Terminal phalanges aplasia; Scoliosis
- Onychodystrophy
- Course: Often death < 4 years
- Laboratory
- 2-Oxoglutaric aciduria
- Alkaline phosphatase: High
- Brain MRI: Polymicrogyria 20%; Cerebral atrophy; Hypomyelination
- EEG: Spike wave discharges
Mental retardation, Enteropathy, Deafness, Peripheral Neuropathy, Ichthyosis, Keratoderma (MEDNIK)
● Adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma-1 subunit (AP1S1)
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Splice site & Insertion
- AP1S1 protein
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital
- Mental retardation: Psychomotor
- Enteropathy: Diarrhea; Hepatic fibrosis
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Skin: Ichthyosis; Keratoderma; Hypopigmentation; Laxity
- Treatment: ? Zinc acetate
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Atrophy
- Lactate: Increased
- Serum copper & ceruloplasmin: Reduced
- Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs): Increased
Deafness, Cataract, Impaired intellectual development & Polyneuropathy (DCIDP)
● Proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase, 3 (PSMC3; PRS6A)
- Epidemiology: 1 Turkish family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Intronic; c.1127+337A-G
- PSMC3 protein
- Component of 26S ATP-dependent protease
- 19S proteasome regulatory complex
- ATPase activity
- Proteasome related
- ATP-dependent degradation of ubiquitinated proteins
- Heterohexameric ring of AAA proteins
- Unfolds ubiquitinated target proteins: Concurrently translocated into proteolytic chamber & degraded into peptides
- Component of 26S ATP-dependent protease
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood
- Deafness: Rapidly progressive
- Cataract: Congenital
- Intellectual development: Severe delay
- Face: Dysmorphism
- Skin
- Subcutaneous calcifications at elbows & knees
- Hair: Depigmented (White) in legs
- Polyneuropathy
- Legs
- Distal
- Laboratory
- Auditory brainstem reflexes: Reduced
- Heat CT: Lateral semicircular canal malformations
Phosphoserine Aminotransferase Deficiency (PSATD)
● Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1)
- Epidemiology
- 31 patients
- 4 patients diagnosed as adults
- Genetics
- PSAT1 protein
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital to Childhood
- Polyneuropathy
- Weakness: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Acromutilation
- Tendon reflexes: Absent at ankles; Brisk elsewhere
- CNS
- More severepatients
- Psychomotor retardation
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Skin
- Early in disease course
- Ichthyosis
- Xerotic
- Hypertension
- Joint contractures: Distal
- Course: Progressive
- Treatment
- Serine supplementation (100 to 900 mg/kg/day)
- Glycine (300 mg/kg/day)
- Laboratory
- Serum serine: Low or Normal
- Head imaging: Microcephaly; Brain atrophy or normal
- NCV: Axon loss
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss
- Large & Small
- Severe
- Skin: Hyperkeratosis
Polyendocrine-Polyneuropathy syndrome (PEPNS)
● DMX-like 2 (DMXL2; RC3)
- Epidemiology: Senegalese family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- DMXL2 protein
- Encodes: Rabconnectin-3
- α-subunit of Rabconnectin protein complex
- Concentrates in vesicles at synapses
- Role in: Neurosecretion
- Regulates: Trafficking & activity of v-ATPase
- Encodes: Rabconnectin-3
- Clinical
- Polyneuropathy, Demyelinating
- CNS
- Mental retardation
- Ataxia
- Dysarthria
- Puberty incomplete
- Testicular volumes: Low
- Laboratory
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- Hypothyroid, Central
- Hypoglycemia → Nonautoimmune insulin-dependent Diabetes mellitus
- NCV: Diffuse slowing
- Brain MRI: Subcortical temporal white matter disease
Acute-onset Axonal Neuropathy following Infection in Children (IIAAN)
● Regulator of Chromosome Condensation 1 (RCC1)
- Epidemiology: 12 families, 24 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense
- RCC1 protein
- Chromatin bound
- GDP-to-GTP exchange activity
- Maintains homoeostatic Ran-GTP gradient across nuclear membranes
- Mutations
- Reduced thermal stability
- Defects in Ran nuclear localization
- Impaired nucleocytoplasmic transport
- TDP-43 mislocalization
- Clinical
- Onset age: Mean 22 months; Range 6 months to 5 years
- Onset course
- Acute
- Days after infection
- Illness: Often respiratory
- Weakness (100%)
- Hypotonia (100%)
- Severity: Varied
- Rapid onset & Fatal (60%)
- Motor neuropathy, mild, with inpaired gait
- Respiratory involvement: Common
- Tendon reflexes: Often absent
- Course: No improvement after treatment in many
- Laboratory
- NCV: Motor + Sensory Axonal Neuropathy in most
- Brain MRI: Cerebral atrophy (60%), progressive
- CSF: Protein may be high
Childhood Carpal tunnel syndrome: Differential daignosis
- Storage disorders: Mucopolysaccharidoses
 ;
Mucolipidoses
;
Mucolipidoses

- Structural anomalies
- Bleeding: Hemophilia
- Mass: Hemangioma; Hamartoma; Tumors; Abscesses
- Systemic disease: Disseminated angiomatosis; Lipoid proteinosis; Scleroderma
- Local injury
- Overuse: Flexion-extension; Sustained flexion (Dystonia; Cerebral palsy)
- Trauma; Burns
- Familial

- Commonly autosomal dominant
- Onset: 1 year to 3rd decade
- Frequently bilateral or right hand
- Associated with thickened transverse carpal ligament, or digital flexor tenosynovitis
Hereditary Sensory Neuropathies
Return to Neuromuscular home page
Return to Polyneuropathy Index
1. Muscle Nerve 1998;21:1473-1477, 2001;24:760-768
2. Ann Neurol 1999;45:742-750, Nature Genetics 2003; Online Sept
3. Ann Neurol 1999;46:313-318, J Med Genet 2021 Oct 19
4. Neuromuscular Disorders 2000;10:592-598
5. J Child Neurol 2000;15:513-517
6. Neuromuscular Disorders 2001;11:395-399
7. J Child Neurol 2001;16:642-644
8. Acta Neuropathol 2001;Online June
9. Hum Molec Genet 2001;10:2783-2795
10. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2002;28:170
11. Hepatology 2001;34:116-120
12. Ann Neurol 2002;52:836–842
13. J Med Genet 2002;39:838–843
14. Am J Hum Genet 2003; October, Arch Neurol 1999;56:1283-1288
15. Eur J Ped 2000;159:300-301
16. Am J Hum Genet 2005;77: On-line June, Eur J Med Genet 2022 Jan 27
17. Nat Genet 2006;38:1111-1113
18. Arch Neurol 2011;68:812-813, Epileptic Disord 2016;18(S2):63-72
19. Eur J Ped Neurol 2011; Online Sept
20. Ann Neurol 2012; Online Jan
21. Pediatr Neurol 2013;48:59-62
22. JNNP 2014; Online Feb
23. Neurology 2014; Online March
24. J Neurol Sci 2014 Jun 21
25. Human Molec Genetics 2014; Online Dec
26. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online February
27. Neurology 2015 Feb 25
28. Neurology Genetics 2017; Online May
29. Am J Hum Genet 2019 Jun 25
30. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2020 Aug 21
31. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:4996
32. Am J Med Genet A 2021 Jun 4, Front Genet 2022;13:949038
33. Brain 2021 Jun 11, JCI Insight 2025;10(5)
34. BMC Med Genet 2016;17:82
35. Eur J Med Genet 2021;64:104146
36. Gynecol Oncol 2021 Oct 18
37. Neurology 2025;104:e213429
38. Genet Med 2023;25:100894
39. Physiol Rev 2024;104:399-472
40. Lancet Neurol 2025;24:667-680
9/27/2025