|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
SENSORY DISORDERS: Small Fiber
|
Definition Differential Diagnosis Features |
Anatomic definition
Small Fiber Neuropathy Features: Symptoms, Signs, Laboratory 7
|
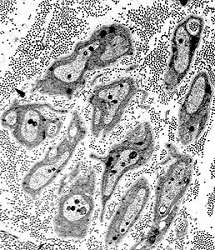 Unmyelinated axons |
Differential Diagnosis
|
Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy I (HSAN I; HSN I)
● HSAN IA
● HSAN IC
- SPTLC Genetics
- SPTLC1
- Misense mutations identified: C133Y, C133W, V144D, Ala352Val +
- S331F: Severe, early onset disease
- Founder effect in Australian & English families
- Frequency in HSAN families: 19%
- Allelic disorders
- SPTLC2 5
- Mutations: A182P; G382V; V359M; I504F
- Frequency in HSAN families: 7%
- Allelic disorders
- SPTLC3
 : HMSN, Dominant
: HMSN, Dominant
- SPTLC1
- Serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) enzyme: Sphingolipid biosynthesis
- Subunits: SPTLC1; SPTLC2; SPTLC3
- SPTLC2: Colocalizes with ER marker calreticulin
- Associated regulatory proteins: ORMDL3, ssSPTa, ssSPTb
- Function
- Catalyzes pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent condensation of L-serine & palmitoyl-CoA to 3-oxosphinganine
- Rate limiting step in de novo biosynthesis of sphingolipids
- Mutation effects
- Increased Glucosyl ceramide synthesis: ? Leads to apoptosis
- Reduced serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) activity
- Shift SPT amino acid usage from serine to alanine → Elevated levels of deoxysphingolipids
- Normal levels of protein
- Accumulation of abnormal toxic metabolites4
- Deoxy-sphingoid bases (DSB): 1-deoxy-sphinganine (1-deoxy-SA) & 1-deoxymethyl-sphinganine
- DSBs have neurotoxic effects on neurite formation in vitro
- Clinical features
- Features similar in: SPTLC1 & SPTLC2 mutations
- Onset age
- Usual: 2nd to 3rd decade; Average 25 years; Up to 52 years
- Occasional mutations: < 10 years
- Males may develop symptoms earlier than females
- Sensory
- Loss
- Pain & Temperature (Small fiber)
- Large fiber loss also occurs
- Legs earlier (10 years) than arms
- Distribution
- Distal > Proximal
- Symmetric
- Legs > Arms
- Sensory, Autonomic & Tendon reflex loss
- Balance disorders: After 10 years of disease
- Course: Progressive
- Spontaneous sensations
- Paresthesias: Rare to Occasional
- Lancinating pains: Some kindreds
- Burning pain: Some
- Loss
- Charcot joints (Neurogenic osteoarthropathy) & Skin ulceration
- Ulcero-Mutilation
- Progression: Succession of exacerbations
- Location: Feet, Severe mutilation & shortening; Occasional hands, Thickened fingers
- X-rays: Distal demineralization; Metatarsal tapering (Licked candy-stick)
- Weakness
- Common late in course
- Distal
- Autonomic involvement
- Rare
- Occasional: Horner syndrome
- Sensorineural deafness: Variably present
- Skin: Blistering; Edema & discoloration of foot; Chronic ulcers; Painless injuries
- Eye: Macular telangiectasia type 2
- Parafoveal telangiectatic retinal vessels
- 'Right angle' venules
- Retina: Opacification, Pigment clumping, Macular carotenoid pigment low
- Leakage on fluorescein angiography,
- Blue light-reflectance abnormalities
- Intraretinal cysts & ellipsoid zone defects
- Time course: Slow progression
- Possible treatment
- L-serine: High dose (400 mg/kg/day in divided doses)
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- Loss of C > Aδ & Aα axons
- Nerve conduction velocities: Normal or Intermediate (< 38 m/s in arms)
- Axon loss: legs more severe than arms
- Skin biopsy: Axon loss, distal & proximal
- Immune: Increased Synthesis of IgA
- Plasma 1-deoxysphingolipids (1-deoxySLs): High
- Electrophysiology
- Pathology
- Loss of dorsal root ganglion cells & later motor neurons
- Predominant loss of small myelinated & unmyelinated axons
- No CNS changes
- SPTLC variant syndrome: HSAN 1 + Motor, Child onset
22
- Epidemiology: 8 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutations
- SPTLC1 Exon 11; S331F & S331Y
- SPTLC2 I504F
- SPTLC1 protein
- Mutations: Increased SPT activity
- Clinical
- Onset earlier: Childhood
- Autonomic: Sweating disturbances
- Sensory
- Postural instability
- Loss: Less prominent
- Muscle
- Atrophy
- Tongue: Fasciculations
- Weakness: Distal
- Respiratory dysfunction
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Stereotyped movements: Swinging; Trunk & Legs
- Growth retardation
- Skeletal
- Metacarpophalangeal joint hypermobility
- Pes cavus
- Scoliosis
- Cataracts
- Course: Wheelchair < 15 years
- Treatment: L-serine supplementation may be detrimental
- Laboratory
- NCV: Intermediate velocities; Axon loss
- Brain MRI: Normal
- SPTLC1 variant: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 27, Childhood (ALS27)
 23
23
- Epidemiology: 11 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo or Dominant
- Mutations
- General location: Membrane-spanning domain
- Exon 2; A20S (Exon 2 skipping), Ala20Thr, Y23F, L38R, L39del, F40_S41del
- Mutation mechanism
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood; 1st decade
- Spasticity: Legs; Toe walking
- Lower motor neuron
- Weakness: Loss of ambulation
- Respiratory insufficiency (50%)
- Sensory: Normal
- Course: Progressive
- Macular telangectasias
- Variant syndrome: 1 adult patient with sensory-motor neuropathy
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Denervation, Acute & Chronic
- Sural nerve: Normal
- Muscle MRI: Global atrophy
- Muscle ultrasound: Fasciculations
- Serum: Sphingolipid levels high
- SPTLC2 variant: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Childhood
27
- Epidemiology: 8 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant; de novo
- Mutation: Glu260Lys, Recurrent; T66R
- SPTLC2 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood; Congenital to 4 years
- Lower motor neuron
- Weakness: Proximal > Distal
- Tongue fasciculations
- Muscle atrophy
- Respiratory: Support neded in 60%
- Upper motor neuron
- Spasticity: Distal legs
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Loss of ambulation: 3 to 10 years
- Bulbar: Dysphagia; Dysphonia
- Sensory: Normal
- Course: Progressive; More rapid than SPTLC1-ALS
- Cognitive disorder: Some patients
- May be exacerbated by: Serine supplementation
- Laboratory
- NCS: CMAP amplitudes reduced; Sensory: Normal
- EMG: Denervation, Acute & Chronic
- Muscle pathology: Chronic neurogenic; Grouped atrophy
- Muscle Ultrasound: Fasciculations; Echogenicity increased
- Brain MRI: Normal
- See: Other Hereditary sensory neuropathies
Hereditary sensory neuropathy with loss of Pain perception (HSAN5)
● Nerve growth factor-β (NGFB)
- Epidemiology: Northern Swedish & Arab families
- Genetic: Mutations (Homozygous)
- Missense: Arg211Trp (Arg100Trp in mature NGFB)
- Null: c.[680C>A]+[681_682delGG]
- Carriers
- NGF-β protein
- Neurotrophin family
- Functions: Role in development & maintenance of sympathetic & sensory nervous systems
- Cellular location: Secreted
- Clinical: Variable degrees of severity
- Onset: Early childhood to adult
- Sensory loss
- Pain perception: Reduced; Insensitivity to pain
- Temperature: Reduced
- Skeletal: Charcot joints & Fractures
- Onset: Childhood or Adult (3rd & 4th decade)
- Lower extremities: Feet; Ankles; Knees
- Autonomic
- Sweating: Normal or Reduced
- Fainting: 1 patient
- GU & GI disorders: 1 patient
- CNS: Mental retardation (1 family)
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology
- Nerve conduction velocity: Normal
- Sensory loss: Temperature ± Vibration
- R-R interval: Normal
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss: Thinly myelinated & Unmyelinated
- Less axon loss in adult onset cases
- Electrophysiology
- NGFB variant syndrome: Heterozygote carriers
- Inheritance: Dominant, Incomplete penetrance
- Clinical: Neuropathy
- Sensory loss: Temperature
- Arthropathy: Adult onset, few patients
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- No insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis or mental retardation
- Laboratory
- Nerve: Loss of small myelinated (Aδ) & unmyelinated (C) axons
Congenital absence of pain perception (HSAN7)
● Sodium channel, voltage-gated, Type XI, alpha subunit (SCN11A)
- Epidemiology: German & Swedish patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Heterozygous
- S6 segments: Lining channel pore
- Missense: Leu811Pro, Leu1302Phe
- Allelic disorders
- HSAN7
- Familial Episodic Pain 3 (FEPS 3)
- Neuropathy, Painful & Autonomic
- Post-surgical pain sensitivity: SCN11A variants (rs33985936; rs13080116) 13
- Mutations
- SCN11A protein (Nav1.9)
- Mutated SCN11A protein (Gain of function)
- Channel activation: Left shift
- Diminished peak current densities at depolarized voltages
- Greater inward current under resting conditions
- Slow channel inactivation
- Channel activation: Left shift
- Mutated SCN11A protein (Gain of function)
- Clinical
- Sensory
- Pain perception: Absent
- Temperature: Sensation present; Intolerance of moderate cold & heat
- Pruritis
- Abnormal postures
- Autonomic
- Hyperhidrosis
- GI dysfunction: Diarrhea & Constipation; Colon enlarged
- Anosmia
- Wounds: Slow healing
- Skeletal
- Fractures: Painless; Multiple
- Charcot joints
- Self-mutilation
- Joint hypermobility
- Sensory
- Development: Motor delay
- ? Weakness
- Intellectual: Normal
- Muscle biopsy: Normal
- EMG: Normal
- NCV: Slightly slowed Motor & Sensory CV; Normal amplitudes
- Nerve biopsy: Normal numbers of large & small axons
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Intestinal biopsies: Normal
- Epidemiology: > 20 families
- Genetics
- SCN11A mutations: Missense; Arg222His, Arg225Cys, Ala808Gly, Leu811Phe, N816K, N820Y
- Inheritance: Dominant
- SCN11A protein
- Mutation effect: Gain of function
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 month to 9 years
- Pain sensation: Cold
- Pain locations
- Common: Distal legs
- Other: Upper body; Joints of fingers & Arms
- Pain episodes
- Onset: Late in day
- Duration: 5 to 20 minutes
- Cycles: Every 2 to 5 days; 9 to 19 recurrences per cycle; 1 to 24 cycles per year
- Associated with: Sweating
- Pain exacerbation: Fatigue, Infections; Exercise.
- Pain relief: Anti-inflammatory analgesics (Ibuprofen); Heat
- Course: Reduced pain with increasing age
- Examination: Normal large & small fiber sensory modalities
- GI: Constipation
- Laboratory
- NCV: Normal
- QST: Abnormal cold & warm temperature thresholds
- Nerve pathology: Mild axon loss
- Intraepidermal nerve fiber density: Often reduced
- Epidemiology
- 12 patients
- 3% of painful neuropathies
- Mutations
- Missense: Tyr66Ser
- Gain of function
- SCN11A protein
- Clinical: Neuropathy
- Sensory
- Discomfort
- Pain & Paresthesias
- Pinprick: Hyperalgesia
- Loss
- Distal; Hands & Feet
- Temperature
- Discomfort
- Autonomic
- Dry eyes
- Diarrhea
- Urinary
- Cardiac: Palpitations, Orthostatic dizziness
- Laboratory
- Axon loss: Small > Large
- Axon Hyperexctability: Involvement of CMi axons (Mechanoinsensitive C-fibers)
- Sensory
Familial Episodic Pain 2 (FEPS2)
● Sodium channel, voltage-gated, Type X, alpha subunit (SCN10A)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients; 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Leu554Pro, Ala1304Thr
- Other missense mutations: Cys1523Tyr, Gly1662Ser; Associated clinical syndrome not described
- SCN10A protein: Nav1.8
- Mutation effects in FEPS2: Gain of function
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4th to 7th decade
- Discomfort
- Pain: Burning or Shooting
- Itch: Intense paroxysmal
- Allodynia & Hyperalgesia
- Location: Distal; Feet, Some hands
- Warmth: Some relief
- Laboratory
- Skin: Loss of small axons or Normal
- NCV: Small SNAP ampltiudes or Normal
- Also see
Congential insensitivity to pain without anhidrosis (HSAN)
● Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital
- Sensory loss
- Pain
- Temperature
- Location: Extremities
- Acromutilation
- Normal: Large fiber sensation; Strength; Tendon reflexes
- Nerve pathology
- Small myelinated A-delta fibers: Absent
- Unmyelinated axons: Normal
- Differential diagnosis: Insensitivity to pain
Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Preserved Temperature sensation 11
● Clathrin, heavy polypeptide-like 1 (CLTCL1; CHC22)
- Epidemiology: Balochi (Iran) family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: p.E330K; Missense; Homozygous
- Protein
- Nosology: Clathrin heavy chain 22
- High expression: Skeletal muscle, Testis, Heart
- Functions
- Neural crest development
- Genesis of pain & touch sensing neurons
- Muscle: Formation of insulin-responsive GLUT4 compartments
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital
- Sensory
- Loss: Pain; Soft touch
- Preserved: Hot & Cold
- Mutilation
- Motor: Normal strength
- Autonomic
- Bladder distention
- Vomiting
- Sweat & Tearing: Normal
- Eyes: Strabismus; See-saw nystagmus
- Dysmorphic features: Palpebral fissures, short; Nose large
- CNS
- Developmental delay
- Learning difficulties, severe & non-progressive
- Seizures: 1 patient
- Death: 5 to 7 years in some
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Delayed myelination
- No diabetes
- Differential diagnosis: Insensitivity to pain
Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Hypohidrosis (HSAN8; HSAN VIII)
● PR domain zinc finger protein 12 (PRDM12)
- Epidemiology
- > 40 patients
- Male 70%
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Homozygous in many
- Types
- Missense: Most common
- Poly-alanine (GCC) repeat expansion: Up to 20 repeats
- Other: Splice & Frameshift
- Mutations
- PRDM12 protein
- Expressed in: Sensory neurons in Sensory spinal (dorsal root) ganglia
- Cell location: Nucleus
- Functions
- Transcriptional regulator
- Nociceptor neurogenesis
- Mutation effects: Impair histone methylation
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital to 57 years
- Sensory loss
- Pain: Acute or Inflammatory
- Temperature: Noxious Heat & Cold
- May be restricted to limbs
- Large fiber sensory: Normal
- Mutilation
- Regions: Limbs; Mouth; Tongue; Cornea
- Recurrent infections: Skin; Bones
- Autonomic
- Sweating & Tearing: Reduced but present
- Other: Normal
- Eyes
- Conjunctival hyperemia
- Tears: Reduced
- Cornea: Sensitivity Reduced; Ulcers; Reflexes reduced
- Skin: Midface toddler excoriation syndrome (Mites)
- Smell & Hearing: Normal
- CNS: Global developmental delay in some
- Laboratory
- Axon loss
- Aδ
- Small axons in skin
- Subepidermal neural plexus & autonomic sweat glands
- Axon loss
- Differential diagnosis: Insensitivity to Pain
24
- General onset age: Congenital
- CMT (HMSN): Adult onset
- HSAN: Congenital to Adult onset
- 1A: SPTLC1; Adult onset
- IC: SPTLC2; Adult onset
- ID: ATL1; Adult onset
- IE: DNMT1; Adult onset
- IF: ATL3; Adult onset
- 2A: WNK1; Child onset
- 2B: RETREG1/FAM134; Child onset
- 2C: ATSV (KIF1A); Child onset
- 2D (CIP): SCN9A (Normal intelligence; Anosmia)
- 3: ELP1/IKAP
- 4: NTRK1 (Cognitive disorder; Anhidrosis)
- 5: NGFB
- 6: DST
- 7: SCN11A (Hyperhidrosis; GI)
- 8: PRDM12 (Sensory loss more in limbs)
- 9: TECPR2
- Other
- Congenital Insensitivity to Pain (CIP)
- CIP: CLTCL1 (CHC22)
- PAINQTL1: FAAH + FAAH pseudogene (Digenic)
- MARSIS (CIP): ZFHX2
- + Preserved Temperature sensation: CLTCL1 (Cognitive disorder; Temperature preserved)
- Multisystem
- AAMR: GMPPA
- CANVAS: RFC1; Adult onset
- DEEAH: MADD
- Marbach-Schaaf Neurodevelopmental Syndrome (MASNS): PRKAR1B
- Intellectual Disability, Ataxia & Facial Dysmorphism (HADDS): EBF3
- MICPCH: CASK
- PCARP: FLVCR1
- PSATD: PSAT1
- SPG: CCT5; Child onset
- SPG61: ARL6IP1 (Spastic paraplegia)
- Also see: Hereditary Sensory Neuropathies (HSN)
Insensitivity to Pain (Marsili syndrome)
● Zinc finger homeobox protein 2 (ZFHX2)
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; R1913K; Heterozygous
- ZFHX2 protein
- Cell location: Nucleus
- Nervous system: Expressed in
- Brain
- Dorsal root ganglia: Peripherin-positive small diameter neurons
- Transcriptional regulator
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood
- Sensory loss
- Painful thermal & Capsaicin stimulation
- Painless: Bone fractures; Burning
- Cornea: Hyporeflexia
- Heat pain: Variably reduced
- Cold pain: Reduced to Hyperalgesia
- Sensory: Other
- Pain present: Back; Headache; Childbirth
- Light touch: Normal
- High force: Pleasure
- Autonomic
- Sweating: Reduced
- Hyperthermia episodes
- Recurrent infections (50%)
- Motor: Normal strength
- Cognition: Normal
- Laboratory
- Skin biopsy: Normal numbers of axons
Pain Insensitivity (PAINQTL1)
● FAAH-OUT (FAAH pseudogene; FAAH1)
● Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH)
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Genetics
- FAAH protein
- Catabolic enzyme for: Fatty-acid amides (FAAs) (Bioactive lipids)
- FAAs
- N-acyl ethanolamines: Anandamide (AEA)
- Endogenous ligands for cannabinoid receptors
- Roles in: Nociception, Fear-extinction memory, Anxiety, Depression
- Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)
- Oleoylethanolamine (OEA)
- N-acyl-taurines
- N-acyl ethanolamines: Anandamide (AEA)
- Effect of digenic mutations: Reduced FAAH \levels & activity
- FAAH inhibitor drug (BIA 10-2474); May cause acute encephalopathy
- Clinical: Digenic patient
- Onset: Childhood
- Pain after surgery or trauma: Absent
- Morphene: Causes vomiting
- Skin: Multiple scars; Normal sweating
- CNS
- Fear & Memory symptoms: Altered
- Personality: Non-anxious
- Laboratory
- Blood lipids: Increased AEA, OEA, PEA
Hereditary Ataxia with Thermoanalgesia & Loss of fungiform papillae
● ? Autosomal Dominant with incomplete penetrance or Recessive
- Epidemiology: Japanese & New Zealand families
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5th decade
- Neuropathy
- Sensory
- Pain & Temperature sensation: Lost or reduced globally
- Vibration: Reduced distally
- Unsteady gait
- Motor: Normal
- Sensory
- Ataxia: Benign
- Nystagmus
- Dysarthria
- Limb ataxia
- Autonomic
- Fungiform papillae of tongue: Absent
- Lacrimation: Reduced
- Taste: Reduced
- Temperature control: Abnormal, Fevers
- GI: Constipation/diarrhea
- Vasomotor instability
- Bladder dysfunction: Urinary frequency
- Sweating: Normal
- Sympathetic & Parasympathetic involvement
- Other
- Emotional instability
- IQ: Reduced
- Hearing loss
- Eye
- Saccadic pursuit
- Corneal sensation: Reduced
- Laboratory
- NCV
- SNAPs: Absent
- CMAPs: Normal or mildly reduced
- EMG: Chronic denervation
- Caloric responses: Absent
- CNS imaging
- CNS MRI: Atrophy of spinal cord, cerebellum, brainstem & corpus callosum
- Sural nerve biopsy
- Axon loss: Myelinated & Unmyelinated
- NCV
Hereditary Ataxia with Thermoanalgesia
● ? Autosomal Dominant with incomplete penetrance
- Epidemiology: Northeast Spanish family
- Genetics
- Not linked to known SCA loci
- Incomplete penetrance
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 4th to 7th decade
- Gait instability
- Fatigue
- Cerebellar
- Ataxia: Limbs, dysmetria; Gait imbalance
- Dysarthria
- Eye: Nystagmus (30%); Slow saccades
- Sensory
- Paresthesias: Face & Extremities
- Pain sensation: Reduced early & diffusely
- Vibration: Early preserved; Late reduced distally in legs
- Strength: Normal
- Tendon reflexes: Present
- Other CNS: Dementia (50%); Cognitive affective syndrome
- Course: Progressive ove decade
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conductions
- Sensory: SNAPs absent
- Motor: Normal
- Autonomic: Absent sudomotor response
- EMG: Denervation
- MRI: Cerebellum, Medulla & Spinal cord atrophy
- Pathology
- Cerebellum & Medulla: Atrophy
- Spinal cord: Abnormal posterior column, lateral & anterior spinothalamic & posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Nerve conductions
Sensory & Autonomic Neuropathy with Chronic Diarrhea 6
● Prion protein (PRNP)
- Epidemiology: 1 British family, 11 patients
- Genetics
- Clinical
- Onset: 4th decade
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss: Symmetric; Legs > Arms
- Weakness: Later in course; Distal legs
- Autonomic dysfunction
- Diarrhea: Chronic; Weight loss
- Urinary retention
- Impotence
- Postural hypotension
- Later features (5th to 6th decade)
- Cognitive decline: Impairment of memory & executive function
- Seizures
- Death: Mean age 57; Range 40 to 70 years
- Laboratory
- CNS
- Prion protein deposition
- Congophilic angiopathy: Prion protein in vessel walls
- Spinal cord: Posterior column axon loss
- Brain MRI
- Volume loss or Normal
- Duodenum: Prion protein deposition
- NCV: Axon loss
- Distal > Proximal
- Sensory > Motor
- Peripheral nerve pathology
- Deposition of prion protein amyloid
- CSF
- tau: High
- S100b: High
- 14-3-3: High
- CNS
Marbach-Schaaf neurodevelopmental syndrome (MASNS)
● Protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, Beta (PRKAR1B)
- Epidemiology: 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Heterozygous; Arg335Trp (Common)
- PRKAR1B protein
- RIβ Regulatory subunit of Protein kinase A (PKA) holoenzyme (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent)
- PKA: Essential enzyme in signaling pathway of cAMP
- R1β-deficient mice: Diminished nociceptive pain & inflammation
- Expressed in CNS
- Clinical
- Onset: Infancy
- BMI: Increased
- Face: Dysmorphic
- Pain: Insensitivity
- Hypotonia
- CNS
- Global developmental delay: Speech & Behavior
- Dyspraxia
- Seizures: Some patients
- Sleep disturbances
- Behavioral: Autism ADHD; Aggression
- Hyperphagia: Some patients
- Course: Progressive in some
Developmental Delay + Endocrine, Exocrine, Autonomic & Hematologic abnormalities (DEEAH)
● MAP kinase-Activating death Domain (MADD)
- Epidemiology: 34 patients
- Genetics
- MADD protein
- MAPK-activating
- Regulation of
- Vesicle trafficking
- Rab3 and Rab27 small GTPase activities
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) induced signaling
- Prevention of cell death
- TNF signalling
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early infancy
- Hypotonia
- Failure to thrive
- Sensory: Loss; Pain insensitivity; Mutilation
- Autonomic: Hypohidrosis
- CNS
- Intellectual development: Impaired
- Seizures
- Hearing loss
- Eyes: Strabismus
- Systemic
- Respiratory: Distress; Apnea
- GI: Feeding disorders, GE reflux, Hepatosplenomegaly, Exocrine pancreas insufficiency
- Endocrine: Hypoglycemia, Thyroid Δ, Growth hormone ↓, Panhypopituitarism
- Skeletal: Arthrogryposis, Distal; Face dysmorphism
- Cardiac: Congenital
- Genital anomalies
- Course: Some with death < 3 years
- Laboratory
- Hemoglobin: Low
- Brain MRI: Often normal
Return to Polyneuropathy Index
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
References
1. Brain 1996;119:1011-1021
2. Hum Mol Genet 2004; April 2004, J Med Genet 2010 Oct 26
3. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009;80:518-523
4. J Biol Chem 2010; Online Jan
5. American Journal of Human Genetics 2010;87:513–522
6. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1904-1914
7. Nat Rev Neurol 2012 May 29
8. Nature Genet 2013; Online Sept
9. Brain 2014 Apr 27, J Gen Physiol 2025;157:e202413691
10. Nature Genetics 2015; May 25, Front Genet 2023;14:1139161, Neurol Genet 2026;12:e200346
11. Brain 2015; Online June
12. Brain 2017; Online Dec
13. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8149
14. Brit J Anaesthesia 2019; March
15. Muscle Nerve 2020 Feb 7
16. Muscle Nerve 2015;51:514-521
17. Muscle Nerve 2013 Aug;48(2):252-255
18. Muscle Nerve 2019 Oct 25
19. Muscle Nerve 2020 Feb 3
20. Lancet Neurol 2017;16:144-157, Muscle Nerve 2020 Jan 14
21. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2021 Jan 9
22. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2020;25:308-311, Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2022;e12842
23. Nat Med 2021 May 31, J Neurol 2024;272:36
24. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2022;8:41, Brain 2023;146:4880-4890
25. Muscle Nerve 2022 Nov 30
26. J Pain Res 2022:15:2505-2515
27. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2023 Nov 24, J Neuromuscul Dis 2025 Aug 23
28. J Hum Genet 2024 Mar 8
29. World J Diabetes 2025;16:94861
30. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2025;30:e70041
8/24/2025