|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
MITOCHONDRIAL DISORDERS
|
|
Mitochondria: General 33
|
Axon transport Biogenesis Fission & Fusion DNA Functions Origin Proteins Structure |
Mitochondrial Origins
- Primordial eukaryotic cells lacked ability to use oxygen metabolically
- Colonized by aerobic bacteria: ? Related to typhus
- Intracellular aerobic bacteria
- Added oxidative metabolism to cells
- Evolved into mitochondria
- Time: > 109 years ago
-
Structural features: 4 Compartments
- Outer membrane
- Intermembrane space: Between outer & inner membranes
- Inner membrane
- Matrix: Region inside inner membrane
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
- Metals
- Iron
- Most prevalent
- Involved in maintaining normal mitochondrial functions
- Mitochondria are important regulators of ferroptosis
- Iron
- Number: ~ 1,200 to 1,500
- Primary mitochondrial disease frequency: 1:4,000
- Nuclear DNA related diseases: ~ 500
- High energy needs
- Non-replicative tissues
- CNS: Especially common
|
General Biogenesis Intermembrane space (IMS) Matrix Membrane Inner Outer Solute carriers Mitoribosome Nucleoids Submitochondrial Other mtRNA-related |
- General
- 1500 mitochondrial proteins
- Mitochondrial genes
- Code for 13 peptides (mRNA)
- Pathways
- Synthesized in mitochondrial matrix
- Sorted to matrix or inner membrane
- Oxidase assembly (OXA) pathway
- Specialized for MTCO2 & few nuclear proteins to inner membrane
- Protein components: Oxa1; COX18; Mba1
- Disorders: Mitochondrial-encoded peptides
- Mutations in most can produce: LHON
- Various other different syndromes associated with mutations in individual peptides
- Most (> 99%) mitochondrial proteins are nuclear encoded
- Precursors synthesized in cytoplasm with mitochondrial targeting sequence
- Protein types: Based on mitochondrial targeting sequence
- N-terminal targeting presequence
- Internal targeting signal in mature protein
- No cleavable presequence
- Protein locations: Inner membrane (Polytopic); IMS (soluble); Outer membrane
- Transported into mitochondria
96
- Translocation through outer membrane: Translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane (TOM40 complex)
- Receptor subunits: TOMM20 (MAS20P)
 ,
TOMM22
,
TOMM22
 ,
TOMM70
,
TOMM70

- Channel forming subunit: TOMM40
 ; 2 or 3 pores per TOM40 complex
; 2 or 3 pores per TOM40 complex
- TOMM70 chaperones: HSP90
 &
HSP70
&
HSP70

- TOM5
 :
Integral membrane protein; Transfers proteins from receptor to pore
:
Integral membrane protein; Transfers proteins from receptor to pore
- TOM6
 : Stabilizes TOM40 complex
: Stabilizes TOM40 complex
- trans receptor site of TOM40 complex: Binds proteins on intermembrane-space side of outer membrane
- Receptor subunits: TOMM20 (MAS20P)
- Transfer from TOM40 to TIM23 complex
- Proteins with presequence destined for mitochondrial matrix: Recognized by TIMM50
 of the TIM23 complex
of the TIM23 complex
- Proteins with no presequence
- Recognized in IMS by
- Small Tim proteins
- Tim9-Tim10 complex and/or
- Tom8-Tim13 complex in the IMS
- Substrate proteins forwarded to
- Recognized in IMS by
- Proteins with presequence destined for mitochondrial matrix: Recognized by TIMM50
- Translocation through inner membrane: Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane (TIM23 complex)
- Protein signal: N-terminal; Directs proteins to TIM23 complex
- Positively charged
- Mitochondrial matrix-targeting
- TIM23 complex: Transport from IMS to matrix
- At least 10 subunits
- Partly membrane-embedded
- TIMM17

 , TIMM23
, TIMM23
 & TIMM50
& TIMM50
 : Make up translocation channel & receptors
: Make up translocation channel & receptors - Maintenance factors: Tam41; Ups1; Ups2/Gep4
- Complete translocation of precursors into matrix
- Requires repeated cycles of binding & release from mitochondrial heat shock protein 70 (mtHsp70)
- mtHsp70

- Other subunits: Modulate activity of translocase in antagonistic manner
- Protein signal: N-terminal; Directs proteins to TIM23 complex
- Disorders
- Deafness-Dystonia-Dementia: TIMM8A
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Ataxia (DCMA): DNAJC19
- Encephalopathy: TIMM22
- Translocation through outer membrane: Translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane (TOM40 complex)
- Intermembrane space (IMS) proteins
94
- Transport of soluble IMS proteins: Different mechanisms
- Proteins with bipartite presequences
- Features of presequence
- N-terminal matrix-targeting signals, followed by
- Hydrophobic sorting domains
- Transport mechanisms
- TOM & TIM23 complexes
- Reaction depends on: Membrane potential &, often, ATP
- Insertion into inner membrane
- Mature part of released into IMS by proteolytic cleavage event
- Protein examples
- Apoptosis-inducing factor (Programmed cell death 8; PDCD8; AIF)

- Cytochrome c peroxidase

- Cytochrome b2

- Endonuclease G (ENDOG)

- DIABLO (SMAC)

- Apoptosis-inducing factor (Programmed cell death 8; PDCD8; AIF)
- Features of presequence
- Small proteins
- Properties: Single folding unit
- Unfolded state: Pass through TOM pore
- Folded conformation
- Trapped in IMS space
- Folding related to
- Cofactor binding
- Disulfide bonds between cysteinyl thiols: Common in IMS proteins
- IMS proteins with disulfide bonds
- Copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase (CCS)

- Cox11

- Cox12
 (COX6B1
(COX6B1
 )
)
- Cox17

- Erv1
 : See homologous protein GFER
: See homologous protein GFER
- Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 4 (CHCHD4; Mia40)

- Qcr8 (UQCRQ)

- Rieske iron sulfur protein (UQCRFS1)

- SCO1

- SOD1
 : Binds to CCS in IMS; Import independent of Mia40
: Binds to CCS in IMS; Import independent of Mia40 - Small Tim proteins
- Copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase (CCS)
- Disulfide Relay System: "Oxidative" protein folding
- Mia40: Intramitochondrial IMS import receptor; Interacts via disulfide bond
- Erv1: Sulfhydryl oxidase: Reoxidizes Mia40
- Posible function: Oxygen sensing
- IMS proteins with disulfide bonds
- Functions: IMS proteins
- Transport of metabolites, proteins, or metal ions between mitochondrial membranes
- Detoxification of reactive oxygen species
- Pro-apoptotic components: Stored until programmed cell death is induced
- Proteins with bipartite presequences
- IMS protein disorders
- Deafness
- Muscle +..
- Encephalomyopathy: GATM (AGAT)
- Myopathy + Cataracts: GFER
- Myopathy (IMMD): CHCHD10
- FTD-ALS2: CHCHD10
- Basal ganglia
- Encephalopathy
- Porphyria, variegate: PPOX
- Transport of soluble IMS proteins: Different mechanisms
- Matrix proteins
- Synthesized in cytosol
- Targeting signals
- Amino terminal extensions
- Recognized by receptors on mitochondrial surface
- Proteolytically removed in matrix
- Pathway of import: 2 membrane embedded protein complexes
- Translocase of outer membrane (TOM40)
- Translocase of the inner membrane (TIM23)
- Transportation driven by: 2 sources of energy
- Membrane potential across inner membrane
- Hydrolysis of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) in matrix
- Matrix proteins: Disorders
AARS2: Cardiac
ACAD8
 : Encephalopathy
: Encephalopathy
ACAD9: Fatigue
ACADM: Fatigue + CNS
ACADS: CNS; PEO
ACADSB
 : Hypotonia
: Hypotonia
ACAT1
 : Ketoacidosis
: Ketoacidosis
ALAS2: Anemia
ALDH2
 : EtOH sensitive
: EtOH sensitive
ALDH4A1
 : Seizures
: Seizures
ALDH5A1
 : Encephalopathy
: Encephalopathy
ALDH6A1

AMT
 : Encephalopathy
: Encephalopathy
ATP5F1D: Encephalopathy
ATPAF2: Dysmorphic, Cardiac
AUH

BCAT2
BCKDHA
BCKDHB: Maple syrup urine
BCS1L: GRACILE
C1QPB: Cardiomyopathy; PEO
c8orf38: Leigh
c10orf2: PEO; SANDO
c12orf65: Leigh+
c20orf7: Leigh+
CA5A: Encephalopathy
CARS2: Encephalopathy
CLPP : Perrault 3
: Perrault 3
COA5: Cardiomyopathy
COA6: Cardiomyopathy
COA7: SCAN3
COASY: NBIA
COX10: Encephalopathy
COX15: Leigh+
COX20 (FAM36A): Ataxia
CPS1
D2HGDH
DARS2: LBSL
DBT
DECR1
DGUOK: Hepatocerebral
DLD: Encephalopathy
DLAT: Encephalopathy
DMGDH
DNA2: Myopathy + PEO
EARS2: Leukoencephalopathy
ECHS1: Leigh-like
ETFA: Myopathy
ETFB: Glutaricaciduria
FARS2: Alpers
FASTKD5: Leigh-like
FH: Encephalopathy
FOXRED1: Leigh
FDX1L: Myopathy + Rhabdo
GCDH : Encephalopathy
: Encephalopathy
GCSH
GFM1: Hepatoencephalopathy
GLUD1
HADH
HARS2: Perrault 2
HIBCH: Leigh-like
HMGCS2: Encephalopathy
HMGCL
HSD17B10: Retardation
HSPD1: SPG13
IDH2
IDH3B
ISCU: Myopathy
IVD
KARS: Neuropathy
LARS2: Diabetes; Perrault; HLASA
LONP1: CODAS; Encephalopathy
LYRM7: Encephalopathy
MARS2: Spastic ataxia
MCCC1
MCCC2
MCEE 
MDH2: Encephalopathy
ME2
MGME1: PEO + Myopathy
MRPL3: Cardiomyopathy
MRPL12: CNS & Growth retardation
MRPL39: Leigh/Cardiomyopathy
MRPL44: Cardiomyopathy
MRPS2: Deaf & Hypoglycemia
MRPS7: Deafness + Systemic
MRPS14: Cardiomyopathy & CNS
MRPS16: Acidosis
MRPS22: Cardiomyopathy
MRPS23: Hepatic disease
MRPS25: Encephalomyopathy
MRPS28: Multisystem
MRPS29 (DAP3): Perrault 7
MRPS34: Leigh
MTFMT: Leigh
MTPAP: SPAX4
MUT
NAGS
NDUFAF1: Cardiomyopathy+
NDUFAF2: Leukoencephalopathy
NDUFAF3: Encephalopathy
NDUFAF4: Encephalopathy
NDUFAF8: Leigh-like
NDUFB8: Leigh-like
NDUFS6: Lethal infantile
NSUN3: Encephalomyopathy
NUBPL: Encephalomyopathy
OAT: Gyrate atrophy
OGDH : OGDHD
: OGDHD

OGDHL: YOBELN
OTC
OXCT1
PC: Ataxia+
PCCA: Biotinidase deficiency
PCCB
PCK2
PDHA1: Encephalopathy
PDHB: Encephalopathy
PDHX: Leigh
PDK3: CMTX6
PDP1: Encephalopathy
PET117: Encephalopathy
PITRM1: Ataxia + Retardation
POLG: PEO
POLG2: PEO
PRDX3: SCAR32
PRORP: COXPD54
PYCR1
PYCR2
RARS2: PCH6
RMRP: Cartilage-hair hypoplasia
SARDH
SARS2: Metabolic
SCO1: Hepatoencephalopathy
SCO2: Cardioencephalomyopathy
SDHAF1: Leukoencephalopathy
SDHAF2: Paraganglioma 2
SOD2
SUCLA2: Encephalomyopathy
SUCLG1: Neonatal lactic acidosis
SUPV3L1: ASOASH
SURF1: Leigh; CMT4
TACO1: Leigh
TEFM: Encephalopathy; Myopathy
TK2: Myopathy
TMEM70: Encephalocardiomyopathy
TOP3A: PEOB5
TRMT5: Exercise intolerance; Multisystem disorder
TRMU: Hepatic failure
TSFM: Cardioencephalomyopathy
TTC19: Ataxia & Encephalopathy
TUFM: Encephalopathy
TXN2: Neurodegeneration
UNG
XPNPEP3
YARS2: Myopathy + Anemia
- Outer membrane proteins
- Structure
- Non-cleavable internal mitochondrial signal
- No cleavable N-terminal presequence
- Imported into membrane via TOM40 & TOB complexes
- TOM complex: 7 proteins
- Translocation pores: Tom5/6/7/40
- Surface receptors: Tom20/22/70
- Examples
- β-barrel proteins (Tob55; Porin)
- VDAC1

- VDAC2

- Outer mitochondrial membrane protein disorders
- Macular degeneration 7
 : ARMS2
: ARMS2

- Myopathy & Fatigue (COXPD49): MIEF2
- Neoplasms
- Neuropathy
- Optic atrophy
- Encephalopathy
- Glycemic disorders
 :
Glucokinase (GCK)
:
Glucokinase (GCK)

- Wolfram syndrome 2: CISD2
- Brunner syndrome
 : MAOA
: MAOA

- Parkinson disease 6
 : PINK1
: PINK1

- Macular degeneration 7
- Structure
- Inner membrane (IMM)
- Definition
- Inner, lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of mitochondrial envelope
- Highly folded regions: Form Cristae
- Composition
- Proteins: Protein-rich membrane
- Lipids
- Cardiolipin: 15% to 20% of phospholipids; Higher in IMM than OMM
- Phosphatidylcholine (PC) (Most abundant) & Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
- Only trace amounts of sterols & sphingolipids
- Domains
- Inner boundary membrane (IBM)
- Cristae
334
- Folds in inner mitochondrial membrane
- 50% of cone-shaped lipids
- Undergo continuous cycles of membrane remodeling
- Structure regulation
- ATP synthase dimers
- Mitochondrial Contact Site and Cristae Organization System (MICOS)
- OPA1
- Connected by: Cristae junctions (CJs)
- Separate cristae from the rest of IMM
- CJs contain: Mitochondrial Contact site & Organizing system (MICOS)
- MICOS function: Maintains Inner mitochondrial membrane architecture
- Component anatomy
- Embedded in inner membrane
- Integrated into hydrophobic region of membrane
- Electron transport chain (Respiratory chain): 5 multicomplex proteins
- Respiratory chain function: ATP generation
- Extrinsic
- Gene products & protein complexes loosely bound to one of the inner membrane surfaces
- Not integrated into hydrophobic region of membrane
- Embedded in inner membrane
- Disorders
ABCB7: Ataxia + Anemia
ACADVL: Myopathy
ADCK3: SCAR9
AFG3L2: SCA28; OPA12; SPAX5
AGK: Sengers
ATP5A1: Encephalopathy, neonatal
ATP5E: Retardation + Neuropathy
ATP5MC3: Dystonia/Spasticity
ATP5MD: Encephalopathy, child
BRP44L: Encephalopathy
c12orf62: Encephalocardiomyopathy
Cardiolipin: Barth
COA3: Neuropathy + Fatigue
COQ4: Encephalopathy + Systemic
COQ5: Ataxia +
COX4I1: Encephalopathy
COX4I2: Pancreas + Anemia
COX5A: Systemic
COX6A1: CMT
COX6A2: Myopathy
COX6B1: Encephalomyopathy
COX7B : Microphthalmia + Skin Δ
: Microphthalmia + Skin Δ
COX8A: Leigh + Epilepsy
COX11: Encephalopathy, Infant
COX16: Encephalopathy
COX18: Encephaloneuropathy
COXFA4: Encephalopathy
CPT2: Myopathy
CRAT: Encephalomyopathy
- CRLS1: Encephalopathy +
CYC1: Hyperglycemia & Encephalopathy
CYCS : Thrombocytopenia 4
: Thrombocytopenia 4
CYP11A1 : Adrenal ↓ & 46 XY Δ
: Adrenal ↓ & 46 XY Δ
CYP11B1 : Adrenal hyperplasia
: Adrenal hyperplasia
CYP11B2 : Hypoaldosteronism
: Hypoaldosteronism
CYP24A1 : Hypercalcemia
: Hypercalcemia
CYP27A1: Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis
CYP27B1 : Vit D dep Rickets
: Vit D dep Rickets
DHODH : Miller syndrome (Dysostosis)
: Miller syndrome (Dysostosis)
DNAJC19: Cardiac + Ataxia
DNAJC30: LHON
ENDOG: PEO +
ETFDH: Myopathy
FASTKD2: Encephalomyopathy
GPD2 : Type 2 diabetes susceptible
: Type 2 diabetes susceptible
HADHA: Multisystem; Myopathy
HADHB: Encephalomyopathy
HCCS: MIDAS
IMMT: Encephalopathy
L2HGDH: Encephalopathy
LETM1: Encephalopathy
LONP1: CODAS
MMAA : Methylmalonic aciduria
: Methylmalonic aciduria
MICOS10: Hepato-Encephalopathy
MICOS13: Encephalopathy
MICU1: Myopathy + Movement
MICU2: Encephalopathy
MPV17: Hepatocerebral
NDUFA1: Encephalopathy
NDUFA2: Leigh + Cardiac
NDUFA4: Leigh
NDUFA6: Encephalopathy
NDUFA8: Encephalopathy
NDUFA9: Leigh; Dystonia
NDUFA10: Leigh
NDUFA11: Encephalocardiomyopathy
NDUFA12: Leigh
NDUFA13: Encephalopathy + Optic
NDUFB3: Lethal infantile
NDUFB9: Encephalopathy
NDUFB10: Lethal neonatal
NDUFB11: MLS
NDUFV1: Encephalopathy
NDUFV2: Encephalopathy + Cardiac
NDUFS1: Leukodystrophy
NDUFS2: Encephalopathy + Cardiac
NDUFS3: Dystonia
NDUFS4: Encephalopathy
NDUFS7: Encephalopathy
NDUFS8: CNS + Cardiac
OPA1: Optic atrophy
OPA3: Optic atrophy
Paraplegin: SPG7
PDSS1: Coenzyme Q10 deficiency
PET100: Leigh
PMPCA: Ataxia
PMPCB: Encephalopathy
PTCD3: Leigh-like; Spastic ataxia
PTPMT1: Neurodevelopmental
RMND1: Encephaloneuropathy
SDHA: Leigh; Cardiac; Paraganglioma
SDHB: Paraganglioma; Leukoencephalopathy
SDHC: Paraganglioma
SDHD: Paraganglioma
SFXN4: Anemia + CNS
SLC25A carriers 250
SLC25A1: Epileptic encephalopathy, CMS23
SLC25A3: Cardiac; Exercise intolerance
SLC25A4: PEOA2
SLC25A8 (UCP2)
SLC25A9 (UCP3)
SLC25A10 (DIC): Epileptic Encephalopathy + Complex I deficiency
SLC25A12: Hypomyelination
SLC25A13: Citrullinemia
SLC25A15: HHH
SLC25A16: Fingernail dysplasia
SLC25A19: Microcephaly
SLC25A20: Encephalocardiomyopathy
SLC25A21 (ODC): MTDPS18, SMA-Like disorder
SLC25A22: Myoclonic epilepsy
SLC25A24: Progeroid syndrome
SLC25A26: Encephalomyopathy
SLC25A32: Exercise intolerance
SLC25A38: Anemia
SLC25A42: Myopathy
Also see: SLC25A46 (Outer membrane)
TAMM41: Encephalomyopathy
TMEM65: Encephalopathy
TMEM126B: Fatigue & Exercise intolerance
TIMM8A: Deaf-Dystonia-Dementia
TIMM22: Encephalopathy
TIMM29: Sengers
TIMM50: Encephalopathy (MGCA9)
UCP1
UQCC2: Encephalopathy
UQCC3: Encephalopathy
UQCRB: Hypoglycemia, Hepatic
UQCRC1: Parkinson + PN
UQCRC2: Episodic metabolic encephalopathy
UQCRH: Episodic metabolic encephalopathy
UQCRQ: Encephalopathy
YME1l1: Optic atrophy +
- CRLS1: Encephalopathy +
- Definition
- Submitochondrial (around mitochondria) protein disorders
- CNS system disorders
- CoQ10 deficiency
- Systemic disorders
- Anemia
- Sideroblastic (SIDBA3)
 : Glutaredoxin 5 (GLRX5)
: Glutaredoxin 5 (GLRX5)

- Sideroblastic + Myopathy: PUS1
- Sideroblastic (SIDBA3)
- Lipoid adrenal hyperplasia
 : STAR
: STAR

- Anemia
- Metabolic disorders
- Iron-sulfur complex related
- ACO2: Cerebellar-Retinal degeneration
- BOLA3 (MMDS2): Encephalopathy, infantile
- GLRX5: SPAHGC
- ISCA2 (MMDS4): Encephalopathy, infantile
- LYRM4: Encephalopathy, infantile
- LYRM7: Encephalopathy, infantile
- Iron-sulfur cluster scaffold protein (HIRIP5, NFU1): Encephalopathy, infantile
- IBA57 (MMDS3): Encephalopathy; SPG74
- mtDNA Nucleoids: Disorders
- MTNAP1: Neurodegenerative disorder
- mtSSB
- OPA1: Optic atrophy
- SSBP1: Optic neuropathy +
- TFAM: Hepatopathy
- Twinkle: PEO
- Other mitochondrial-related proteins: Disorders
- Encephalopathy
- Encephalocardiomyopathy + Rhabdomyolysis: TANGO2
- Encephalocardiomyopathy: MTO1
- Encephalocardiomyopathy: GTPBP3
- Encephalopathy: TRIT1
- Encephalomyopathy: Apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion associated (AIFM1)
- Encephalomyopathy (MMLA): PNPLA8
- Encephalopathy: NADK2
- Encephalopathy, Cataracts, Neutropenia: CLPB
- Encephalopathy, ethylmalonic (EE): ETHE1
- Leukodystrophy, Cavitating: APOPT1
- Leigh syndrome: Leucine-rich PPR motif-containing protein (LRPPRC)
- CNS system disorders
- ALS/PD2: PARK7
- ALS-FTD: CHCHD10
- AOA: Aprataxin (APTX)
- PEBEL2: NAXD
- Ataxia, Myelopathy & Skin disease (PEBEL1): NAXE
- Biotinidase deficiency: Holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS)
- Dystonia & Optic atrophy (MEPAN): MECR
- Friedreich ataxia: Frataxin (FXN)
- IMNEPD: PTRH2
- Microcephaly, Simplified gyral pattern & Insulin-dependent diabetes: Mitochondrial elongation factor G2 (GFM2)
- Parkinson disease, juvenile, type 2
 : Parkin 2 (PARK2)
: Parkin 2 (PARK2)

- Parkinson disease 8
 : Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2)
: Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2)

- Spastic ataxia
- Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR)
- Charlevoix-Saguenay: Sacsin (SACS)
- VPS13D
- SPG20 (Troyer): Spartin
- CMT
- Systemic
- Cardiac conduction defect, susceptibility
 : A kinase anchor protein 10 (AKAP10)
: A kinase anchor protein 10 (AKAP10)

- Cardiomyopathy + Acidosis
 :
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase (MLYCD)
:
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase (MLYCD)

- Cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic: ELAC2
- Sudden death & Cardiomyopathy: PPA2
- Cardiac conduction defect, susceptibility
- Neoplasm
- Metabolic syndromes
- Myopathy
- Encephalopathy
- External link: MitoCarta
- Stimulated by
- Differentiation of myoblasts into mature myotubes
- Increasing concentrations of extracellular pyruvate
- Energy demand exceeding oxidative capacity: Endurance training
- Reduced by
- Cessation of exercise
- Aging
- Fusion & Fission molecules
299
- Regulate morphology of mitochondrial network
- Pro-fusion
- Mediators: Dynamin-related GTPases
- THG1L: Disorder - Ataxia + Spasticity
- ATAD3A: Disorder - Developmental delay; Optic atrophy; Polyneuropathy
- MSTO1: Myopathy + Ataxia
- YME1L1: Optic atrophy
- FBXL4: MTDPS13
- OMA1

- Fission
- DNM1L: MOM; Disorder - Encephalopathy with defect of mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission
- GDAP1: CMT
- SLC25A46: Disorder - HMSN6B: Optic atrophy & Neuropathy, Axonal (HMSN VIB)
- Mitochondrial Fission Factor (MFF): Disorder - Leigh-like encephalopathy, Optic atrophy & Peripheral neuropathy
- MIEF1: Optic atrophy
- MIEF2: Myopathy + Fatigue
- VPS13D: Movement disorder & Spastic Ataxia, Childhood onset
- Regulation
- Peroxisomal proliferator activator receptor gamma co-activator 1α (PGC-1α)

- High levels in skeletal muscle
- Acts through coactivation of transcription factors
- PPAR
- NRF: Nuclear respiratory factors
- ERR: Estrogen related receptor
- Coactivates peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs): Upregulation of fatty acid oxidation
- Induces
- Transcription of oxidative phosphorylation genes: Coactivates nuclear respiratory factor (NRF) 1 & 2
- Mitochondrial biogenesis
- Fatty acid oxidation
- Brown fat thermogenesis
- Expression of clock genes: BMAL1 (ARNTL)
 &
Rev-erb-alpha (NR1D1)
&
Rev-erb-alpha (NR1D1)

- Peroxisomal proliferator activator receptor gamma co-activator 1α (PGC-1α)
- Pyruvate
- Increases mitochondrial mass & functionality
- Not dependent on PGC-1α
- Pyruvate disorders
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial (TFAM; TCF6)

- Activator of mitochondrial transcription
- Regulation of mtDNA copy number
- Disorder: MTDPS15
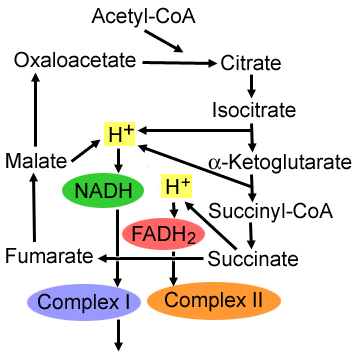
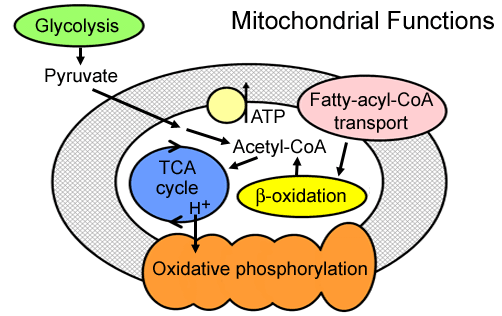
Mitochondria: Functions
- Pyruvate oxidation: Disorders
- Krebs cycle: Liver
- Metabolism: Amino acids; Fatty acids; Steroids
- Generation of energy as adenosine triphosphate (ATP): Via
- Electron-transport chain
- Oxidative-phosphorylation system (Respiratory chain)
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Gluconeogenesis: Liver & Kidney
- Calcium: Homeostasis
- Cell death mediation: Apoptosis
- Axon transport
Calcium (Ca++) Homeostasis: Mitochondria
- Ca++ concentrations: Different Locations & Reservoirs
- Extracellular: 12 mM
- Endoplasmic reticulum: 50500 μM
- Mitochondria
- Rest: 100 nM
- Cellular signalling: 10500 μM
- Ca++ stimulation
- Excess cytosolic Ca++: Sequestered into ER, Mitochondria, Other organelles
- Calcium homeostasis regulation
- Store-Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE): Components
- Sarco/Endoplasmic reticulum Ca++-ATPase (SERCA)
- Pumps Ca++ back into ER & Mitochondria
- Receptors
- Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R; ITPR1): Mediate Ca++ release into cytosol or mitochondria
- Ryanodine receptor (RyR): Mediate Ca++ release into cytosol or mitochondria
- Locations: ER; Mitochondria; ER-mitochondrial contact sites
- Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1)-Orai1 complex
- STIM: Senses Ca++ depletion & activates Orai1 channels for Ca++ influx
- Sarco/Endoplasmic reticulum Ca++-ATPase (SERCA)
- Mitochondrial Ca++ uptake: Mechanisms
- Mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex
- Intermembrane space: MICU 1/2/3
- Inner mitochondrial membrane: MCU
 ; EMRE (SMDT1)
; EMRE (SMDT1)

- Mediates Ca++ entry into mitochondrial matrix from cytosol
- Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (PYK2; PTK2B)
 :
Modulates Ca++ handling by phosphorylating MCU
:
Modulates Ca++ handling by phosphorylating MCU
- mtNa+/Ca++ exchanger (mtNCLX; SLC8B1)

- Mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex
- Cyclophilin D (CypD; PPID)

- Mitochondrial chaperone
- Component of mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP)
- Facilitates Ca++-sensitive opening of mPTP
- Maintains mitochondrial membrane potential
- MitochondriaER contact sites (MERCs)
356
- General function
- Enable efficient ER-Mitochondria molecular exchanges
- Mitochondrial MERC Proteins
- Mitofusin 2 (Mfn2)
- Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein (VDAC)
- Mitochondrial fission 1 (FIS1)
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51 (PTPIP51)
- MERC Functions
- Ca++ shuttling
- From ER to mitochondria
- Protein complexes: IP3RGRP75VDAC1, MCU
- Regulatory proteins: MFN2, PDZD8, DJ-1, BCL2
- Sigma-1 receptor (Sig-1R): ER protein; Regulates Ca++ release from ER to mitochondria
- Lipid exchange
- Protein trafficking
- ROS signalling
- Ca++ shuttling
- General function
- Store-Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE): Components
- Mitochondrial Ca++-related disorders
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA): General features
|
Differences from Nuclear DNA Inheritance mtDNA variation Mutations & Disorders Pathogenic mechanisms Replication Structure Transcription & Translation |
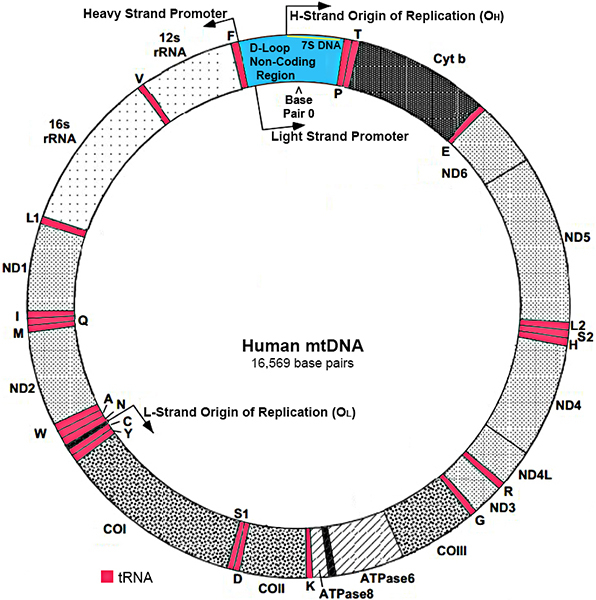 Modified from: www.mitomap.org |
- mtDNA General
- Mitochondria: Only organelle other than nucleus with own DNA
- Genes
- Number: 37
- Code for 13 proteins: 0.9% of 1,500 proteins in mitochondria
- Different structure than nuclear DNA
- Length: Short; 16,569 base pairs
- Location
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Nucleoids
- 70110 nm ellipsoid DNA protein complexes
- Associated protein component = TFAM
- Copy numbers
- Somatic cells: 100s to 1,000s
- Sperm: 100s
- Oocytes: > 100,000
- Inheritance: Maternal
- Mutations
- Rates: 10x higher than nuclear DNA
- Mechanism with aging: Replication errors
- Repair mechanisms: Fewer than nuclear DNA
- Individual muations can increase in frequency: via Clonal expansion
- More mutations: Tissues with high energetic demand (Brain, Skeletal muscle) or high proliferation (Liver)
- Less common: Oocytes
- Common mutation location: Short tandem repeats
- Diseases: Related to most mtDNA genes
- Structure
- Double-stranded, circular molecule
- Exception: D-loop is triple stranded (Contains extra 7S DNA)
- Nucleotide pair number: 16,569
- Copies
- 2 to 10 in each mitochondrion
- Polyplasmy: > 1,000 in each cell
- Strands
- Heavy (H) strand
- Rich in guanines
- 28 genes
- Light (L) strand
- Rich in cytosines
- 9 genes: ND6; 8 tRNAs
- Heavy (H) strand
- Nucleoids: mtDNA packaging
359
- Anatomy
- mtDNA arranged in nucleoprotein macromolecular complexes
- Physically interact with: Inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM)
- Interspersed between IMM cristae: Semi-regularly distributed
- Associated function: mtDNA transcription
- Contents
- mtDNA molecules
- Mitochondrial DNA replication
- Twinkle: Unwinding, Strand annealing
- TOP1MT
 : Mitochondria specific; Releases negative supercoils
: Mitochondria specific; Releases negative supercoils
- TOP3A;: Resolve & Segregate mtDNA hemi-catenanes; mtDNA replication
- POLG1: mtDNA polymerase activity
- POLG2: Assists POLG1 activity
- RAD51C
 : Homologous recombination-mediated mtDNA Repair
: Homologous recombination-mediated mtDNA Repair
- SSBP1 (mtSSB): Replication, 7S DNA maintenance
- XRCC3
 : Homologous recombination-mediated mtDNA Repair
: Homologous recombination-mediated mtDNA Repair
- Mitochondrial DNA transcription
- Transcription Factor A Mitochondrial (TFAM)

- TFB2M

- Transcription initiation for open transcription complex formation
- rRNA methyltransferase activity
- POLRMT: Transcription
- Transcription Factor A Mitochondrial (TFAM)
- Mitochondrial DNA translation
- Mitochondrial DNA maintenance & quality control
- LONP1: mtDNA quality control, TFAM degradation
- PHB

- Holdase-unholdase chaperone of membrane proteins
- Cristae morphogenesis
- PHB2

- Maintains mitochondrial integrity in inner mitochondrial membrane
- Associated with PHB1
- CLPX
 : mtDNA quality control
: mtDNA quality control
- MTNAP1: Maintains mtDNA abundance
- Mitochondrial fission
- Nucleoids segregate to daughter mitochondria
- Disorders
- Anatomy
- Double-stranded, circular molecule
- Genes & Functions: mtDNA
- mtDNA: Encodes 37 genes
- mRNA: Peptides
- Encodes 13 mitochondrial peptide subunits
- All 13 peptides are in mitochondrial respiratory-chain complex (OXPHOS)
- Remaining > 67 OXPHOS subunits are nuclear encoded
- rRNAs: 2
- tRNAs: 22; Genes located between rRNA or Protein coding genes
- mRNA: Peptides
- mtDNA: Non coding region
- Triple stranded (D) displacement-loop
- Produced from additional synthesis of strand of mitochondrial DNA: 7S DNA
- Contains: Conserved sequence elements
- Promoter region
- Origins of replication for H and L strand replication
- Contains elements for initiation of leading strand replication
- Promoter region
- Other mitochondrial proteins encoded by: Nuclear DNA
- Mitochondrial genes: External links
- mtDNA: Encodes 37 genes
- Inheritance of mtDNA
- Maternal
- Usual pattern
- Sperm mtDNA is actively degraded
- Paternal
- Transmission of mtDNA in skeletal muscle (but not in other tissues) reported 34: MTND2 mutation
- Maternal
- Transcription & Translation of mtDNA
- Promoters: Controlled by nucleus
- 3 Promoters
- H1: H-strand; Produces complete symmetric transcription of heavy strand of mtDNA
- L: L-strand; Produces complete symmetric transcription of light strand of mtDNA
- H2: Synthesis of 2 rRNAs; Acts with factor, mTERF
- Promoters started by: Mitochondrial RNA polymerase + Specificity factor (mtTFA)
- Promoter location: D-loop; Only non-coding region of mtDNA
- 7% of mtDNA length
- Contains cis elements involved in mtDNA replication & transcription
- Transcripts: Large
- Produced by H1- & L-strand
- Subsequently cleaved into individual genes
- mtRNAs
- Require extensive posttranscriptional modifications before achieving translation competency
- Disorders
- Mitoribosomes
261
- Structure: 55S particles
- Subunits coded for by 80 nuclear genes
- Mitochondrial ribosomal Small (28S) subunit
- Decodes mRNA & Mediates tRNA delivery of required amino acids
- Small subunit proteins (MRPSs)
- Number: 30
- Assemble with 12S mt-rRNA to form small 28S subunit
- 12S rRNA
- Mitochondrial ribosomal Large (39S) subunit
- Catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids
- Large subunit proteins (MRPLs)
- Number: 52
- Assemble with 16S mt-rRNA & mt-tRNAVal to form large 39S subunit
- 16S rRNA
- Structural tRNA (tRNAVal in human cells)
- Contain a much higher protein:RNA ratio (less RNA) than bacterial 70S ribosome
- Assembly factors
- RNA processing & modification enzymes
- Guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases)
- DEAD-box RNA helicases
- Kinases
- Function: Synthesis (Translation) of 13 mitochondrial-encoded proteins
- Disorders
- General: Metabolic
- Defect produced: Combined OXPHOS deficiency, Especially complexes IV & I
- Subunits
- MRPS2: Sensorineural hearing loss & Hypoglycemia
- MRPS6
 : Myocardial infarction risk
: Myocardial infarction risk
- MRPS7: Deafness, Hepatic & Renal failure, Lactic acidemia (COXPD)
- MRPS9
 : Intellectual disability & Development delay
: Intellectual disability & Development delay
- MRPS11
 : Ankylosing spondylitis
: Ankylosing spondylitis
- MRPS14: Developmental delay & Cardiomyopathy
- MRPS16: Metabolic acidosis (COXPD2)
- MRPS22: Encephalopathy (COXPD5)
- MRPS23
 : Hepatic disease (COXPD46)
224
: Hepatic disease (COXPD46)
224
- MRPS25: Encephalomyopathy
- MRPS28: Multisystem + Hepatic disease (COXPD47)
- MRPS29 (DAP3): Perrault 7
- MRPS34: Leigh-like disease (COXPD32)
- MRPS39 (PTCD3): Leigh-like (COXPD51)
- MRPL3: Cardiomyopathy + Mental retardation (COXPD9)
- MRPL12: Growth retardation & Neurological deterioration (COXPD)
- MRPL24
 : Movement disorder & Intellectual disability
: Movement disorder & Intellectual disability
- MRPL39: Leigh/Cardiomyopathy
- MRPL44: Cardiomyopathy (COXPD16)
- MRPL49: Encephalopathy (COXPD60)
- MRPL50
 : Ovarian insufficiency & Complex I deficiency
: Ovarian insufficiency & Complex I deficiency
- Mitoribosome RNA
- 12S rRNA (MTRNR1)
- 16S rRNA (MTRNR2)

- COXPD + Myopathy (G3090A)
- Cardiomyopathy (T2336C)
- Rett + PEO (C2835T)
- tRNAVal
- rRNA processing & stability
- rRNA maturation
- MRM2: MELAS-like
- TFB1M
 : Hearing loss; Type 2 diabetes risk
: Hearing loss; Type 2 diabetes risk
- Assembly chaparone
- ERAL1: Perrault syndrome
- CLPP: Perrault syndrome
- c1QBP/p32: Cardiomyopathy; PEO
- DHX30
 : Neurodevelopmental disorder; Cytosolic stress RNA granule accumulation
: Neurodevelopmental disorder; Cytosolic stress RNA granule accumulation
- GTPBP5
 : VACTERL
: VACTERL
- Other
- General: Metabolic
- Structure: 55S particles
- Promoters: Controlled by nucleus
- mtDNA Replication: Asynchronic & Asymmetric mechanism
277
- DNA synthesis
- POLγ
- POLRMT
- Synthesis of primers needed to initiate mtDNA synthesis
- H-strand Synthesis
- Starts: In origin of replication of heavy strand (OH)
- Procedes: Unidirectionally: To origin of replication of light strand (OL)
- 2/3 of way around genome
- Between cluster of 5 tRNA genes
- When OL is single strand mtDNA: Synthesis starts in opposite direction
- Factors in mtDNA replication
- Primer for H-strand replication: Small RNA synthesized from L-strand promoter
- Transition between mtDNA replication & transcription: Produced by ribonucleoprotein, RNase MRP
- Polymerase for mtDNA replication: DNA polymerase γ (pol γ)
- Mitochondrial single-stranded binding protein (mtSSB)
 : Binds to parental H-strand
: Binds to parental H-strand
- Twinkle: Unwinds dsDNA at replication fork
- All factors involved in maintenance, replication & expression of mtDNA: Nuclear encoded
- Other mitochondrial DNA polymerases
- Muscle molecular pathology: Disorders can produce
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Reduced amounts of mtDNA (mtDNA depletion)
- DNA synthesis
- mtDNA Repair
- Related proteins
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 & 2 (TDP1, TDP2)
- Topoisomerases
- RAD51C
- XRCC3
- Molecules & Disorders
- TDP1
- Function: Clearance of Top1mtcc & other 3'-DNA lesions
- Disease: SCAN1
- TDP2
- Function: Clearance of mitochondrial Top2cc
- Disorder: SCAR23
- PNKP
- Function: Repair of 3'-P ends generated by TDP1
- Disorders: MCSZ; AOA4; Epilepsy; CMT2B2
- Lig3
- Functions: XRCCl-independent nick ligation of 3'OH & 5'P
- Disorders: Reduced in Ataxia-Telangectasia; MTDP20
- APTX
- Functions: Removes 5'-AMP arising from aborted DNA ligation
- Disorders: AOA1; EAOH
- APEX1
- Function: Excises 5' or 3' to abasic site during base excision repair (BER)
- Disorder: ALS Predisposition
- Polγ
- Functions: Single strand gap filling
- Disorders: AHS; MELAS; MEMSA; SANDO
- TDP1
- Related proteins
- Mitochondrial DNA variation
- Normal: Homoplasmy; All copies of mtDNA are identical within coding region
- Heteroplasmy: Different single cells contain varied mtDNA populations
- Occurs with some mtDNA mutations
- Due to presence of multiple mitochondria in one cell, each containing several mtDNA copies
- Produces tissue variation
- Post-mitotic tissues
- Usually contain highest levels of mutated mtDNA
- Neurons; Skeletal & Cardiac muscle; Endocrine tissue
- Mutations in mtDNA
- % vs normal in mtDNA can vary widely among tissues in an individual
- Mutational loads may change over time
- Tissues are differentially sensitive to levels of mtDNA mutations: ? Related to oxidative energy requirements
- Pathogenic heteroplasmic mutations: Severity of related symptoms
- Increase with higher proportion of mutated mtDNA
- Relation to severity not necessarily linear
- Pathogenic heteroplasmic mutations: Transmission
- Initial variance among offspring: Prenatal germline without selection
- Protein-coding genes: Purifying selection; Preferentially eliminated within a few generations
- mtRNA genes: No oocyte selection over successive generations
- Progressive accumulation of mutation occurs in some non-dividing post-mitotic tissues
- Frequency of mtDNA-related disorders: 6 to 17 per 100,000 population
- mtDNA: Differences from nuclear DNA
- Circular structure
- No introns
- Intergenic spacing
- Small
- Coding sequences of most genes are contiguous or separated by 1 or 2 bases
- Codon sequences
- Different start, stop & arginine, tryptophan, isoleucine
- Some mitochondrial genes lack termination codon: Insertion of UAA at the transcriptional level instead
- Replication of mtDNA
- Rapid rate
- Lacks proofreading
- Mutation rate 10 to 100x > than nuclear DNA
- Packaged in nucleoids
- DNA-repair mechanisms
- Not fully adequate
- No association with: Protective histones
- Mode of inheritance: mtDNA inherited maternally
- External links
Mitochondrial disorders: General pathogenic mechanisms 7
- Mitochondrial disorders: Mutation types
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations: General features
- Mutation effects
- Often cause deficient function in respiratory-chain
- Abnormal Oxidative-phosphorylation enzymes
- Threshold effect
- % of mutant mtDNAs must be above a threshold to produce clinical manifestations
- % of mutant mtDNAs needed to cause cell dysfunction varies according to tissue oxidative requirements
- Disease signs especially manifest in
- Tissues with a high energy expenditure: Dependent on oxidative metabolism
- Specific tissues: Brain, Heart & Muscle
- Mitotic segregation
- % of mutant mtDNAs in daughter cells can shift at cell division
- Produces rapid changes of genotype that may lead to crossing of threshold
- Skewed heteroplasmy
- mtDNA mutation surpasses pathogenic threshold in 1 tissue
- Examples: A3243G may produce only cardiomyopathy; Myopathy with early respiratory involvement
- Inheritance
- During fertilization mtDNA is derived only from the oocyte
- Maternal inheritance: mtDNA mutations transmitted only from mother
- Mutations transmitted to all offspring, Male & Female
- Increased Mutant mtDNA in the mothers' blood → Increased Frequency of affected offspring
- Monozygotic twins: Similar clinical phenotypes & degrees of heteroplasmy 205
- Risks of having affected offspring differ between different mtDNA mutations
- Mutation effects
- Mutations in nuclear DNA coding for mitochondrial components
- Some identified mutations cause defects in oxidative-phosphorylation
- Defects of intergenomic communication
- Probably nuclear DNA mutations
- Alter control of replication & expression of mitochondrial genome leading to
- Mutation distribution
- Homoplasmic: Similar distribution of mtDNA mutation in all tissues
- Heteroplasmic: Variable distribution of mtDNA mutation in different cells or tissues
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations: General features
- Mitochondrial gene disorders: Effects on protein synthesis
- Disorders of general protein synthesis
- Mutations: Single deletions & point mutations in rRNA or tRNA genes
- Clinical features
- Typical: Multisystem disorders
- Other: Myopathy
- Laboratory: Lactic acidosis
- Muscle: Mitochondrial proliferation; COX negative ragged red fibers
- Mutations in Protein-coding genes
- Clinical syndromes: LHON; NARP/MILS; Exercise intolerance
- Inheritance: Maternal or Sporadic
- Mitochondrial proliferation: Absent in LHON & NARP; Present with Complex III deficiency
- Disorders of general protein synthesis
- Mitochondrial disorders: Biochemical & Genetic abnormalities of mitochondrial function
Mitochondrial Disorders: mtDNA-related mutations
|
General Point mutations mtRNA mtDNA Deletions Multiple IBM MNGIE Single, Large Quantitiative changes Specific disorders 2° to Nuclear mutations |
- mtDNA: General disease features
- Laboratory: Lactic acidosis
- Pathology: Mitochondrial proliferation in muscle
- Massive
- Produces ragged-red fibers
- Mutant mtDNAs accumulate preferentially in ragged-red fibers
- Ragged-red fibers are typically negative for cytochrome c oxidase activity
- Genetics
- Relatively few mutations in rRNA genes: All confined to 12s RNA
- Heteroplasmy: Pathogenic threshold of mtDNA mutations
- Phenotype changes when threshold in a previously unaffected tissue is surpassed
- Threshold for disease is lower in tissues highly dependent on oxidative metabolism
- Brain, Heart, Skeletal muscle, Retina, Renal tubules, Endocrine glands
- Mutation effects on protein synthesis
- Impairment of all mitochondrial protein synthesis
- mtDNA rearrangements (deletions or duplications)
- Mutations in mtRNA genes
- Mutations in rRNA genes
- Altered activity of specific respiratory chain complex
- Mutation of individual gene encoding protein subunits of complex
- Impairment of all mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Mutations in mtDNA & Related nuclear genes
199
- Many different point mutations identified in mtDNA related genes
- May occur in mtDNA genes for mtRNA, rRNA or Proteins
- Most common in mtRNA genes
- Hot spots
mtRNALeu [UUR] (MTTL1) ;
mtRNAIle (MTTI)
;
mtRNAIle (MTTI)
 ;
mtRNALys (MTTK)
;
mtRNALys (MTTK)

- Other mtRNA gene mutations
mtRNAAla (MTTA) ;
mtRNACys (MTTC)
;
mtRNACys (MTTC)
 ;
mtRNAAsp (MTTD)
;
mtRNAAsp (MTTD)
 ;
mtRNAGlu (MTTE)
;
mtRNAGlu (MTTE)
 ;
;
mtRNAPhe (MTTF) ;
mtRNALeu (MTTL2)
;
mtRNALeu (MTTL2)
 ;
mtRNAMet (MTTM)
;
mtRNAMet (MTTM)
 ;
mtRNAAsn (MTTN)
;
mtRNAAsn (MTTN)
 ;
;
mtRNAPro (MTTP) ;
mtRNAGln (MTTQ)
;
mtRNAGln (MTTQ)
 ;
mtRNASer (MTTS1)
;
mtRNASer (MTTS1)
 ;
mtRNASer (MTTS2)
;
mtRNASer (MTTS2)
 ;
;
mtRNAThr (MTTT) ;
mtRNAVal (MTTV)
;
mtRNAVal (MTTV)
 ;
mtRNATrp (MTTW)
;
mtRNATrp (MTTW)
 ;
mtRNATyr (MTTY)
;
mtRNATyr (MTTY)

- Hot spots
- mtRNA processing disorders
- mt-mRNA maturation disorders
- mtRNA post-translational modification disorders (maturation)
- GTPBP3: 5-taurinomethyluridine (τm5U) modification
- MFMFT: Formylation of Met-tRNA
- MTO1: 5-taurinomethyluridine (τm5U) modification
- NSUN2
 : MRT5
: MRT5

- NSUN3: Methylation of mt-tRNAMet
- PRORP
- PUS1: Pseudouridine
- TRIT1: i6A37
- TRMT5: G37
- TRMT10C: Encephalopathy, Infantile
- TRMU (MTU1): 5-taurinomethyl-2-thiouridine (τm5s2U)
- TRNT1
- YRDC
 : Galloway-Mowat 10 (GAMOS 10)
: Galloway-Mowat 10 (GAMOS 10)

- Skeletal muscle restricted mtDNA point mutations
- Associated with 652 base pair duplication in D-loop (control region) of mtDNA 43
- External links: Mutations
- Clinical: Point mutations associated with wide variety of syndromes
- Gene types with point mutations
- Genes needed for mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Usually tRNA genes
- Mutations generally impair mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Mutations produce defects in all respiratory chain complexes except Complex II (Nuclear encoded)
- Genes encoding proteins
- Respiratory chain subunits
- Mutations produce defects in single respiratory chain complex
- Genes needed for mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Example of tRNA mtDNA gene mutation: A-to-G mutation at nucleotide 3243 (A3243G)
- Most frequent mtDNA mutation
- > 16/100,000 in the adult population (Finland)
- Varied clinical presentations
- Leigh syndrome
- MELAS
- Oligosymptomatic
- Systemic: Diabetes, Short stature, Pigmentary retinopathy
- Neural: Migraine, Hearing loss, Cognitive decline,
Occipital infarction (Young patients)
- Higher levels of mutated mtDNA: More severe disease
- Leigh > MELAS > Oligosymptomatic
- Most frequent mtDNA mutation
- Example of mutation in protein encoding mtDNA gene: Nucleotide 8993 in gene for ATPase6, T-to-G & T-to-C
- General correlations
- 8993C clinically milder than 8993G
- Mutant loads: Similar in Different fetal and adult tissues; No age-related variation
- Greater Median % mutant load with Increased Severity of symptoms.
- Threshold effect: Severe symptoms Increased when mutant load reaches
- 60% to 70% for 8993G mutation
- 80% to 90% for 8993C mutation
- Disturbs H+-translocating, membrane spanning F0 region of ATPase complex
- Syndrome correlations
- NARP with intermediate levels of mutated mtDNA
- Maternally inherited Leigh's Syndrome with high (> 95%) levels of mutated mtDNA
- General correlations
- Many different point mutations identified in mtDNA related genes
- mtDNA: Single, Large Deletions (SLSMD)
- Epidemiology
- Frequency of single large mtDNA deletions: 1.5 to 1.6 per 100,000
- Single, large mtDNA deletions: Properties & Features
- Large size
- Common (50%): 4977 bp (m.8470_13446del4977)
- Range: 1.3 to 10 kB
- Common deletion region within mtDNA
- Range: ATPase 6 to ND5
- Both tRNA & Protein encoding mitochondrial genes
- Common protein gene deleted: COIII
- Origin
- Common: de novo mutation
- Inherited from mother: 4%
- Due to SSBP1 mutation: Rare
- Heteroplasmic
- Tissues containing mutations: Most
- mtDNA changes
- DNA break point locations
- May differ in disorders with single or multiple DNA deletions
- 4977 bp deletion: Common in both 357
- Patients with mtDNA deletions also often have small mtDNA duplication
- Duplication corresponds mtDNA in deleted region
- DNA break point locations
- Inheritance
- Deletions: Usually sporadic; 4% maternal
- Duplications: May be maternally inherited
- Large size
- Associations: Clinical & Metabolic
- Single large deletions
- General
235
- Larger mtDNA deletion sizes: Possible correlations
- More severe disease
- Earlier disease onset
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain profiles
- General pattern: Combined Complex I ± Complex IV deficiency
- More severe: Complex I & Complex IV deficiency
- Increased mtDNA Deletion Level
- Increased Total & Decreased Wild-Type mtDNA copy number
- Complex IV > Complex I deficiency: Complex IV genes (MT-CO1, MT-CO2 & MT-CO3) in deleted region
- Complex I & IV deficiency similar: Only MT-CO3 deleted
- Complex I > Complex IV deficiency: Complex IV genes preserved
- Muscle fiber type: More Ox-Phos deficiency in Type II than Type I fibers
- Larger mtDNA deletion sizes: Possible correlations
- Disease syndrome associations
303
- Kearns-Sayre
- Ocular Myopathy (PEO) (Sporadic types): Later onset
- Pearson's syndrome: Child onset
- Some syndromes: MNGIE & Leigh syndrome
- Specific clinical features
- Male:Female = 2:1
- Earliest onset: Anemia
- Later onset: PEO (Ptosis most common); Cardiac conduction block
- Other common
- Muscle: Weakness & Exercise intolerance
- Neurologic: Ataxia; Deafness; Vision loss
- Systemic: Pigmentary retinopathy; Renal; Diabetes
- Laboratory
- Muscle histology
- COX- or SDH+ muscle fibers
- Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency
- Serum or CSF lactate high: 60%
- Brain MRI: Globus pallidus & White matter Δ
- Muscle histology
- General
235
- Tissue dysfunction
- Correlates better with number of deleted mtDNA molecules
- Less correlation with location or size of deletion in mtDNA
- Single large deletions
- Also see: mtDNA, Multiple different deletions
- Multiple different mtDNA deletions occur in single individuals with
- Autosomal dominant PEO
- Inclusion body myositis
- Normal aging
- Multiple different mtDNA deletions occur in single individuals with
- External link: mtDNA Deletions
- Epidemiology
- Quantitative loss of entire mtDNA molecules occurs in some syndromes.
- mtDNA regulation
- Disorders
- Inherited mitochondrial deletion disorders: Usually autosomal recessive
- Toxins may also cause mtDNA depletion: AZT
- Specific disorders with mtDNA mutations
mtDNA Point mutations
Cardiomyopathy
Leber's optic neuropathy
Leigh's syndrome
MELAS
MERRF
NARP/MILS
Single deletion or duplication
Ataxia, Leukodystrophy
Diabetes: Maternal inheritance
Kearns-Sayre
Pearson's
PEO: Sporadic
Multiple deletions
Aging
Myositis
Inclusion body
COX- muscle fibers
MNGIE
PEO
Wolfram
Depletion of mtDNA
Infantile myopathy
Fatal
"Later-onset"
AZT treatment
Several types of mtDNA defect
Deafness
Diabetes
External ophthalmoplegia (PEO)
Sporadic
Maternal
Dominant
Recessive
Leigh's
Myopathy
Rhabdomyolysis
Sensory neuropathy
Systemic disorders
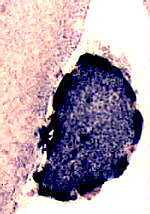
Intense SDH staining
of a muscle fiber with
mitochondrial proliferation
Nuclear encoded mitochondrial proteins
- General features
- Synthesized in cytoplasm
- Imported into mitochondria
- Respiratory chain molecules targeted to inner mitochondrial membrane
- 67 nuclear encoded proteins in respiratory chain
- ~ 1,000 mitochondrial peptides not involved in the respiratory chain
- Nuclear mutations causing Mitochondrial disorders
- Inheritance: Dominant or Recessive
- Proteins
- General clinical feature
- Onset age: Infant onset more common than in mtDNA disorders
- Respiratory chain elements: Structural
- Mutations found only in complexes I & II: ? Complex III-V mutations lethal
- Clinical associations of mutations
- Severe neurologic disorders of childhood: Leighs syndrome; Leukodystrophy
- Neoplasms: Paraganglioma; Pheochromocytoma
- Ancillary proteins of respiratory chain
- Function: Needed for assembly or insertion of cofactors
- Mutations: Cause defects in Complexes I, III, IV & V
- Disease: General clinical features
- Multisystem syndromes: Usually involve muscle
- No isolated myopathies described
- Disorders may be tissue specific
- Defects in intergenomic signaling: Nuclear mutations affect mtDNA quantitatively or qualitatively
- Quantitative: mtDNA depletion syndromes
- Qualitative: Multiple mtDNA deletion syndromes
- Acquired
- Aging
- Myositis: IM-VAMP
- Hereditary
- Acquired
- Types of genes
- mtDNA replication (Replisome)
349
- Products functioning at mtDNA replication fork
- Products supplying mitochondria with deoxynucleotide triphosphate pools needed for DNA replication
- Other
- Possible treatment: Elamipretide 348
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARS)
158
- Disease mechanisms
- ARSs provide specific attachment of amino acids to 3'-ends of their cognate tRNA
- Mitochondrial ARS
- 17
- Encoded by genes different from cytoplasmic AARS
- GARS & KARS1: Encoded by same loci as cytoplasmic enzymes
- GARS mitochondrial isoform: Generated by alternative translation initiation
- KARS mitochondrial isoform: Generated by alternative splicing
- Variants associated with: Peripheral neuropathy
- Mitochondria have no AARS for tRNAGln: tRNAGln charged by indirect pathway
- Mutations: Adversely affect mitochondrial translation with deranged synthesis of mitochondrial proteins
- Genes: Mitochondrial
- General inheritance: Recessive
- AARS2: Cardiomyopathy, Infantile; Leukoencephalopathy & Ovarian failure
- CARS2: Epileptic encephalopathy
- DARS2: Leukoencephalopathy (LBSL)
- EARS2: Leukoencephalopathy
- FARS2: Alpers fatal infantile encephalopathy; SPG77
- GARS
- Dominant: CMT 2D; dHMN
- Recessive: Cardiomyopathy; Systemic 328
- HARS2
 : Perrault syndrome 2 (Ovarian dysgenesis & Sensorineural hearing loss)
: Perrault syndrome 2 (Ovarian dysgenesis & Sensorineural hearing loss)

- IARS2: Multisystem disorder (CAGSSS); Leigh
- KARS1: CMT-RIB; Deafness; Encephalopathy; Encephalohepatopathy
- LARS2

- MARS2: Portneuf spastic ataxia with leukoencephalopathy
- NARS2: Encephalopathy or Myopathy
- PARS2: Developmental & Epileptic Encephalopathy-75 (DEE75)

- RARS2: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia 6 (PCH6)
- SARS2: Hyperuricemia, Pulmonary Hypertension, Renal Failure in Infancy and Alkalosis (HUPRA)
- TARS2: Axial hypotonia & Psychomotor delay
- VARS2: Microcephaly & Epilepsy
- WARS2: Neurodevelopmental disorder (NEMMLAS)
- YARS2: Myopathy with lactic acidosis & sideroblastic anemia (MLASA2)
- Also see
- Disease mechanisms
- mtDNA replication (Replisome)
349
- Other types of mitochondrial dysfunction caused by nuclear defects
- Respiratory Chain
- Transport
- Protein importation into mitochondria: Deafness-Dystonia syndrome (TIMM8A)
- ATP & ADP: ANT1
- Solute carriers (Thiamine; Phosphate): SLC19A3, SLC25A3, SLC25A19
- Iron-sulfur proteins & assembly
- Mitochondrial protein synthesis: COXPD11 Encephaloneuromyopathy (RMND1)
- mtRNA
- Metabolism
- Deoxynucleotide triphosphate synthesis: DGUOK, TK2, TYMP, MGME1, SUCLG1, SUCLA2, RNASEH1, c10orf2, POLG, POLG2, DNA2, RRM2B
- Elongation factors: TUFM, TSFM, GFM1
- Mitoribosomal proteins
- Protein quality control & degradation: FBXL4, AFG3L2, SPG7
- Phospholipid metabolism & Membrane structure: AGK, SERAC1, TAZ (Barth)
- Metabolism of toxic compounds: HIBCH, ECHS1, ETHE1, MPV17
- Mitochondrial motility, fission & fusion
- Optic neuropathy: OPA1
- CMT 2A: MFN2, Kinesin
- SPG 10: KIF5A
- Encephalopathy: TRAK1
- Neurodegenerative disorders: Friedreich ataxia; Spastic paraparesis (7; 13); Wilson's
- Non-human changes: Mutations often found in highly conserved subunits also found in simpler complex I in yeast
- Mitochondrial disorders with nuclear mutations
- Myopathies
- PEO
- Myopathy
- MNGIE
- Congenital muscular dystrophy: CHKB; 2q13
- Carnitine disorders
- Encephalopathies
- Leigh: SURF-1; NDUFS7; NDUFS8; NDUFV1; SDHA; Pyruvate carboxylase; PDHC
- Infantile & Childhood
- Wilson's disease
 :
ATP7B
:
ATP7B
- COX10
- Deafness-Dystonia syndrome: DDP protein
- Other systemic disorders
- Cardiomyopathies: SCO2
- DIDMOAD
- Friedreich ataxia: FRDA
- HHH syndrome: SLC25A15
- Optic neuropathy
- Paraganglioma
- Sideroblastic anemia & Ataxia: ABCB7
- Spastic paraparesis: 7; 13
- Stuve-Wiedemann syndrome: LIFR
- Triosephosphate isomerase: TPI1
- Mitochondrial disorders due to mutations in non-mitochondrial proteins
- MNGIE: Thymidine phosphorylase
- Huntington's disease: Huntingtin

- Also see: Mitochondrial proteins
- Myopathies
- Nuclear genes affecting multiple mitochondrial enzymes
- Lon proteases

- Import proteins
- Deafness-Dystonia syndrome: DDP protein
- Infantile encephalopathy: NFU1
- mtDNA Depletion syndromes
- Lon proteases
Mitochondrial disorders: Clinical features & Syndromes
|
Onset CNS Course Eye Myopathy Neoplasms Polyneuropathy Systemic |
- Onset
- Infancy: Infantile with COX- Fibers; Encephalopathy; Leigh's
- Childhood
- Adult: CNS; PEO
- CNS: Mitochondrial syndromes
- Leukoencephalopathies: Brain MRI
- Usual involvement: Periventricular & deep white matter; Central corpus callosum
- Other patterns
- Kearns-Sayre: Subcortical U-fibers; Not periventricular
- NUBPL
- SDH complex
- LYRM7
- APOPT1
- Ataxia
- Seizures: MELAS; MERRF; MILS; Myoclonic epilepsy
- Movement disorders
- Spinal
- Nuclear DNA
- SPG
- HHH syndrome: ORNT1
- SPAX4: MTPAP
- NBIA
- PEBEL2: NAXD
- Ataxia, Myelopathy & Skin disease (PEBEL1): NAXE
- Spastic dystonia
- LBSL: DARS2
- Charlevoix-Saguenay spastic ataxia (ARSACS): Sacsin
- Portneuf spastic ataxia: MARS2
- MEGDEL: SERAC1
- Movement disorder & Spastic Ataxia, Childhood onset: VPS13D
- NEDCASB: SHMT2
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Nuclear DNA
- Migraine: MELAS; Myopathy
- Cognitive disorders
- Striatal necrosis: ATPase 6 (Leigh's) mutation
- Retardation: Leigh's, Maternal (MILS)
- Psychomotor regression: MELAS; Kearns-Sayre; Infantile encephalopathies
- Dementia: MELAS; MERRF; Kearns-Sayre; PEO 3; Cytochrome b; ND3
- Episodic encephalopathy: MELAS; MERRF; Myopathy; Infantile; Leigh's
- Septo-optic dysplasia
- Encephalopathies
- Leukoencephalopathies: Brain MRI
- Myopathy
- Weakness
- Rhabdomyolysis: Recessive syndromes
- Fatigue: Associated with high serum lactate at rest in PEO
- External ophthalmoplegia (PEO)
- Polyneuropathy
296
- General
- PN involvement in mitochondrial disorders is often sub-clinical or asymptomatic
- Muscle biopsy: Denervation features (small angular fibers) common in systemic mitochondrial myopathies
- Mitochondrial DNA
- NARP
- MERRF
- MELAS: Small fiber neuropathy in 40%
- MTTV: CMTMA1
- MTTE: Myopathy + Diabetes
- MT-ATP6
- Kearns-Sayre: Sensory; 10%
- Leigh: Often subclinical
- Autosomal +
- General
- Ophthalmologic
- Ophthalmoplegia & Ptosis
- Ptosis: FOXK2
- Visual loss
- Cortical: MELAS
- Pigmentary retinopathy: Kearns-Sayre; NARP; MNGIE; Leigh's; MELAS
- Optic neuropathy: Leber's; NARP; Leigh's
- Hearing loss: Kearns-Sayre; Other
- Systemic
- Short stature: MELAS; MERRF; Kearns-Sayre; COA3
- Diabetes
- Heart
- Conduction block: Kearns-Sayre
- Cardiomyopathy
- Gastrointestinal & Hepatic
- Pseudoobstruction: MELAS; Cartilage-Hair hypoplasia
- Hepatic failure, infantile: SCO1
- Hepato-Cerebral syndrome
- Hepatoencephalopathy
- Alpers-Huttenlocher disease
- Cartilage-Hair hypoplasia
- Neoplasms
- Paraganglionoma: SDH subunits B, C, D
- Leiomyomatosis: Fumarate hydratase
- Renal cell cancer: Fumarate hydratase
- B-cell lymphoma: BCL2 overexpression

- Lymphoma: Cartilage-Hair hypoplasia
- Course
- Survival
336
- Shortest: Hepatocerebral syndrome; Mitochondrial cardiomyopathy; Pearson
- Longest: PEO: SANDO
- Causes of death: Respiratory failure; Pulmonary infections
- Aerobic training
- Exercise tolerance: Increased
- Serum lactate: Reduced
- Survival
336
Laboratory evaluation of mitochondrial disorders
|
Imaging Molecular genetics Muscle biopsy Serum Urine |
- Serum
- Lactate & Pyruvate
- Source
- Arterial better than venous
- CSF may be abnormal when blood normal
- Usually elevated in children
- Lactate/Pyruvate ratio
- High (> 50:1): Suggests metabolic block in respiratory chain
- Normal: Metabolic block is upstream, e.g. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- High lactate at rest
- Rare with pure CPEO
- Common (80%) with A3243G and A8344G mutations
- Suggests fatigue is likely
- Normal values do not exclude mitochondrial disorders
- Source
- Creatine kinase (CK)
- Usually: Normal or Mildly elevated
- High: Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) & Ptosis; Limb weakness
- Very high: Mitochondrial DNA depletion
- Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF-21)

- Commonly high: Mitochondrial disorders, especially with muscle weakness & COX- muscle fibers
- Also increased in: Diabetes, Obesity, Nonalcoholic fatty liver
- GDF-15
 , serum
335
, serum
335
- 1° mitochondrial phenotypes: High in most
- Frequency: 86%
- Course: Slow increase over time
- May correlate with: Disease activity; Lactate levels
- Also high in
- Inflammatory myopathies, especially IBM
- Increased age
- Cachexia, cancer & Weight loss
- Organ failure: Renal; Heart
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Less elevated in: Muscular dystrophy; Myopathies with necrosis
- 1° mitochondrial phenotypes: High in most
- Creatine: Reduced in serum
- Lactate & Pyruvate
- Urine: 3-Methylglutaconic Acid (3-MGA)
- Branched-chain organic acid
- Intermediate of leucine degradation
- Mevalonate shunt pathway
- Disorders
- MGCA
- MICOS13: Encephalopathy
- MC5DN1: ATPAF2
- Metabolic encephalopathy: ATP5F1D
- Encephalocardiomyopathy: TMEM70
- Senger: AGK
- Developmenat delay, Optic atrophy, Polyneuropathy: ATAD3A
- Encephalopathy, Early onset: MDH2
- Muscle biopsy: Distinctive features of mitochondrial disorders
COX stain
SDH stain
Other stains
Oxidative phosphorylation
Ultrastructure
- Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) stain: Pathology patterns
- Increased staining of muscle fibers
- Common abnormality in mitochondrial disorders:
- Most sensitive & specific stain for mitochondrial proliferation in muscle fibers
- Specific confirmation of mitochondrial dysfunction & proliferation
- Muscle fibers with increased staining: Disorders
- Mitochondrial disease: Mitochondrial proliferation
- Other: Regenerating muscle fibers
- SDH positive (Ragged red) muscle fibers with prominent lipid accumulation: Coenzyme Q10 deficiency
- SDH+ COX+ muscle fibers
- Reduced staining of muscle fibers
- Fe-S disorders
- ISCU
- Sertraline-related lipid myopathy
- SDH reactive blood vessels (Dark stain)
- Increased staining of muscle fibers
- Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain: Pathology patterns
- General
- Usual pathologies
- Absent or reduced staining of muscle fibers
- Reduced COX activity distribution: May be diffuse or in scattered fibers
- Degree of reduced COX activity in SDH+ fibers: Variable with multiple mtDNA mutations
- Increased staining of fibers
- Mitochondrial proliferation
- Variably present depending on syndrome
- Absent or reduced staining of muscle fibers
- May identify patients with mitochondrial disorders not detected by SDH stains
- Usual pathologies
- Scattered abnormal muscle fibers: Properties
- COX-negative but normal SDH staining: Suggests
- mtDNA mutation affecting mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Mutations in COX I, COX II, or COX III genes
- Heteroplasmic mutation
- Both COX-positive & SDH increased fibers: Suggests specific mutations
- SDH-Increased, COX-negative fibers
- May have reduced immunocytochemical detection of cytochrome oxidase II
- Suggests mutations affecting mitochondrial protein synthesis generally
- Perimysial vessels in MERRF: May also be SDH+ & COX-
- Reduced mtDNA-encoded COX subunits I and II in COX-deficient muscle fibres: mtDNA mutations
- Reduction of all COX subunits in all muscle fibers: ? Nuclear mutations
- COX-negative but normal SDH staining: Suggests
- Diffuse change: COX reduction
- Severe: Sparing Spindles & Smooth muscles of vessels
- Moderate: Including Spindles & Smooth muscles of vessels
- Leigh syndrome with COX deficiency
- Mitochondria large
- ATPase pH 4.3
- Type 2C muscle fibers with normal morphology > 5% in infants
- Coenzyme Q10 deficiency
- Zellweger (PEX16)
- Type 2C muscle fibers with normal morphology > 5% in infants
- General
- Other histochemistry
- Gomori trichrome stain
- Stains "Ragged red" muscle fibers
- Much less specific & sensitive for mitochondrial proliferation than SDH
- Sudan black: Increased lipid in muscle fibers
- Lipid pattern: Droplets enlarged
- Lipid increase: Muscle fiber patterns
- Scattered fibers with mitochondrial proliferation (SDH+)
- Selectively increased: Type I muscle fibers
- Increased in all muscle fibers
- Nile Red: Neutral lipid stained in muscle fibers
- Inflammation
- Uncommon in most mitochondrial disorders
- Present with: Inclusion body myositis; PM/COX-
- Muscle fiber necrosis & regeneration: Uncommon
- Perimysial vessels, Intermediate-sized
- Mitochondrial enzyme immunohistochemistry
- mtDNA-encoded respiratory chain subunits
- COX II (Subunit II of Complex IV)
- ND1 (Subunit I of Complex I)
- nDNA-encoded respiratory chain subunits
- COX IV (Subunit IV of Complex IV)
- FeS (Iron-Sulfur subunit of Complex III)
- Anti-DNA antibodies
- mtDNA-encoded respiratory chain subunits
- Gomori trichrome stain
- Oxidative phosphorylation enzymes: Biochemistry analysis
- Muscle preferable to cultured fibroblasts
- Fresh or Frozen muscle may be used
- Methods of measurement
- Interpretation
- Citrate synthase: Measure of mitochondrial abundance
- Individual complex defects
- Combined partial defects of respiratory enzymes
- I, III & IV (Containing mtDNA-encoded subunits): Suggests mtDNA mutations
- I,II & III: Fe/S disorders
- Can be normal in mitochondrial disorders: Especially with multiple mtDNA deletion syndromes
- Antibody stains for OXPHOS complexes
144
- Antibody targets for OXPHOS complex identification
- Patterns of staining: Variable among fibers
- Electron microscopy
53
- Usually not specific or sensitive in adults with non-diagnostic histochemistry results
- Children
- Ultrastructure may be only evidence of mitochondrial pathology in 6%
- No data regarding specificity of these morphologic changes for mitochondrial disease
- May be helpful in confirming mild pathologic changes on histochemistry
- Not helpful in mitochondrial differential diagnosis
- Also see: Mitochondrial pathology
- Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) stain: Pathology patterns
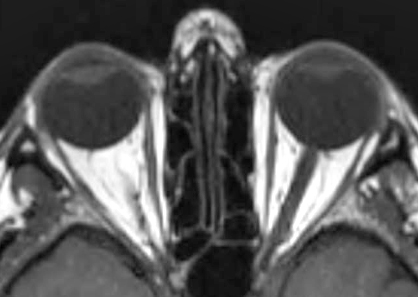
- Neuroradiology (MRI)
106
- General patterns
- Specificity for mitochondrial disorders: Symmetric involvement of deep gray structures in absence of hypoxia
- Hyperintensity: T2 & FLAIR images
- Hypointensity: T1
- Common in many mitochondrial disorders: White matter signal Δ Delayed myelination
- Specificity for mitochondrial disorders: Symmetric involvement of deep gray structures in absence of hypoxia
- Basal ganglia
- Bilateral signal intensities in putamen, globus pallidus, & caudate: Leigh's; MEGDEL
- Calcifications: Kearns-Sayre; MELAS
- Thalamus signal (T2): KSS; Leigh; LTBL (COXPD12); POLG
- Posterior cerebral hemisphere
- White matter
- Diffuse signal change in central subcortical white matter (U-fibers): Kearns-Sayre
- Leukoencephalopathy with spared corpus callosum: MNGIE
- Diffuse white matter changes: Some electron transport chain disorders (I-IV)
- Macrocystic lesions: Complex I disorders
- Malformations (Cortical & Callosal, Subependymal cysts): PDHC
- Optic nerve: LHON; OPA+
- Spinal cord signal: KSS; LBSL; SURF1
- Brainstem signal: Complex I; Complex III; KSS; LBSL; Leigh; LTBL; SURF1
- General patterns
- Molecular genetics: Mutation screening
- Positive result: Confirms diagnosis
- Screen for most common mutations associated with syndrome
- Blood DNA: Adequate for
- Muscle DNA: Required for
- Multiple deletions
- Single mtDNA deletions in PEO & other localized disorders
- MELAS point mutation in oligo- or asymptomatic relatives
- Some point mutations in structural genes
| MITOCHONDRIAL DISORDERS: CLINICAL SYNDROMES | ||||
| ||||
|
Classifications of Mitochondrial Disorders Biochemical Clinical Genetic: mtDNA; Nuclear | ||||
Neuropathy; Ataxia; Retinitis Pigmentosa (NARP)

●
ATP synthase 6 (MTATP6)
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Maternal
- Load of mutations: May differ in different tissues
- Same mutations in maternally inherited Leigh's syndrome (MILS)
- Others in same family may have MILS syndromes
- MTATP6 mtDNA point mutations
- Common: T8993G; T8993C
- Other: G8989C; T9032C; Some Kearns-Sayre
- % of abnormal mtDNA: Correlates with clinical severity
- Heteroplasmy of 70% to 90%: Associated with NARP syndromes
- Heteroplasmy > 90%; Leigh's syndromes (MILS) & more clinical severity
- Allelic disorders
- Other causes of NARP syndromes
- MTATP6 protein
300
- Transport of protons across the membrane domain (FO) of ATP synthase
- Hydrophilic pocket: Binds protons from intermembrane space
- Transfers protons to mitochondrial matrix
- Complex V
- Disease mechanism
- ? Inefficient coupling between proton transport & ATP synthesis
- Reduced ATP synthesis rate
- Clinical
- Severity: Intrafamilial variability
- Onset
- Age: Childhood (2nd decade) or Adult
- Sensory neuropathy
- Pan modal loss: Reduced vibration
- Distal > Proximal
- Legs > Arms
- Weakness: Proximal & Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- May be presenting feature
- Reduced night vision
- May primarily affect cones or rods
- Retina
- Bull's eye maculopathy
- Pigment in posterior pole & mid-periphery
- Small retinal scars
- Vascular narrowing
- Perimetry: Central & paracentral scotomas
- ERG: Reduced amplitude of photopic b wave
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Gait disorder
- Dysarthria
- Other CNS
- Dementia
- Seizures
- More common with early onset NARP
- Later: EEG abnormalities; Tonic-Clonic seizures
- Developmental delay
- Pyramidal signs
- Dystonia
- Hearing loss
- Cardiac
- Mostly with MILS syndromes: Infantile hypertrophic
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Normal or Mildly elevated
- Muscle pathology
- No ragged red or COX- fibers
- Denervation: Type groups; Atrophic angular muscle fibers
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory > Motor
- Brain MRI
- Cerebral: Atrophy; Periventricular white matter pathology
- Cerebellar: Cortical atrophy; Dilation of 4th ventricle
- Lenticular nuclei: High T2 signal
- CNS pathology: Similar to Leigh syndrome
64
- Focal cystic necrosis
- Pathways: Visual, Auditory & Olfactory pathways,
- Cerebellar system: Inferior olive; Dentate nucleus
- Striatum: Especially putamen
- Electroretinogram: Rod or Cone dysfunction
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: CMT Type 2, Mitochondrial Inheritance
142
- Nosology: Distal Hereditary Motor Neuropathy (dHMN) in some patients
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- MTATP6 mutation
- T9185C
- High mutant loads (92%) to Homoplasmic
- Lower mutant loads (< 64%): Often asymptomatic
- Intermediate mutant loads (64% to 91%): Upper motor neuron features; No neuropathy
- Also see: Episodic weakness with Motor neuropathy: T9185C mutation
- Allelic disorders
- MTATP6 mutation
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Usual 1st or 2nd decade
- Gait disorder: Falling; Unsteadiness
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Proximal (Mild): 10%; May be early in course
- Sensory loss: 30%; Distal; More with increasing age
- Upper motor neuron: 30%
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Plantar reflex: Extensor
- Skeletal
- Pes cavus: 50%
- Kyphoscoliosis: 10%
- Course
- Progressive
- Wheelchair: 2nd to 6th decade in some
- Decompensation in affected individuals after viral or septic illness
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Motor axon loss: Most
- Sensory axon loss: Some
- Complex V: Activity reduced; Unstable
- NCV
- Asymptomatic relatives: May have upper motor neuron signs
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: Neuropathy + Ataxia, Adult Onset

- Epidemiology: 2 families, 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: 8993T-C; Heteroplasmic (80% to 90%)
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood to Adult
- Cerebellar
- Ataxia: Gait disorder; Dysmetria
- Dysarthria
- Nystagmus: Gaze-evoked; Horizontal
- Intermittent exacerbations: Few patients
- Course: Slow progression
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Distal; some normal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent at ankles
- Plantar reflex: Extensor in some
- Weakness: Distal legs
- Other: Migraine; Optic atrophy
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss
- Muscle histology: Denervation; No mitochondrial pathology
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: CNS & Motor
185
- Epidemiology: 2 patients, 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homoplasmic T9185C
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2nd or 3rd decade
- Cognitive impairment
- Exercise intolerance
- Motor: Weakness, proximal; Hypotonia
- Ataxia
- Tendon reflexes: Normal or Reduced
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
- EMG: Neurogenic, chronic
- Muscle: Neurogenic (SMA); Mitochondrial changes
MELAS
 340
340
|
Clinical Genetics Laboratory Pathology |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MERRF
 66
66
(Myoclonic Epilepsy; Ragged Red Fibers)
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Maternal
- mtDNA point mutations: Heteroplasmic
- mtRNA Lys (MTTK)
 :
A8344G (Frequent); T8356C; G8363A; G8361A
:
A8344G (Frequent); T8356C; G8363A; G8361A
- Syndromes: MERRF or MERRF/MELAS overlap
- More likely inheritance: High mutation frequency in mother
- Other mitochondrial mtRNA Lys syndromes
- Cardiomyopathy (G8363A)
- PEO with myoclonus (G8342A)
- Deafness & Diabetes (A8296G)
- Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis (A8344G)
- Leigh syndrome (A8344G)
- Parkinson syndrome, Neuropathy & Myopathy (A8344G)
- MELAS
- MNGIE (G8313A)
- Myopathy (MIMECK) (A8291G)
- ?? Madras MND (A8302)
- Genetic counseling: G8344A mutation
- Mutant load < 35% in maternal blood: Transmission risk < 5%
- No correlation of heteroplasmy level in blood with onset age or clinical phenotype
- Prognosis: Possibly related to heteroplasmy level in blood
- mtRNA Ser (MTTS1)

- Syndromes: MERRF/MELAS overlap; Epilepsia Partialis Continua; HAM
- 7472-insertion mutation in tRNASer (UCN): May have MERRF or Pure myopathy
- mtRNA Ser (MTTS2)
 : MELAS/MERRF overlap syndrome
: MELAS/MERRF overlap syndrome
- mtRNA Leu (MTTL1)

- mtRNA Phe (MTTF)

- mtRNA Ile (MTTI)

- mtRNA His (MTTH)
 : MERRF/MELAS overlap
: MERRF/MELAS overlap
- mtRNA Pro (MTTP)

- Mutation: G15967A; Heteroplasmic
- Clinical
- Myoclonic epilepsy
- Myopathy: Proximal
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Pigmentary retinopathy
- Clinical syndrome (A8344G mutation): Also see HAM syndrome
- General
- Intrafamilial variability: Common
- Overlap with other mitochondrial syndromes
- Onset age: Mean 24 years; Range 6 to 48 years
- CNS
- Myoclonus (60%)
- Treatments: Levetiracetam 1500 mg; Valproate
- Epilepsy (45% to 60%): Types
- Generalized
- Focal
- Absence
- ± Myoclonus
- Cerebellar dysfunction (70%)
- Ataxia
- Gait disorder
- Stroke-like episodes (MERRF+)
- Eye
- Optic atrophy (20%)
- Ptosis
- Pigmentary retinopathy
- No ophthalmoplegia
- Dementia
- Psychiatric disorders (54%)
- Myoclonus (60%)
- Polyneuropathy (20% to 30%)
- Distal sensory loss (Large fiber modalities)
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs (45%)
- Hearing loss (40% to 72%)
- Migraine (52%)
- Myopathy
- Weakness (60%)
- Proximal
- Arms & Legs
- Respiratory dysfunction: FVC < 85% in 45% to 65%
- Bulbar (40%): Dysarthria; Dysphagia
- Muscle pain: Resting or Exercise-related
- Cramps
- Fatigue
- Weakness (60%)
- Systemic
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (38%)
- Short stature (10%)
- Lipomata (10%)
- Cardiac: Myopathy; Dysrhythmias
- Diabetes mellitus
- General
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal or Mildly high
- Lactic acidosis: High in 54%
- Brain MRI: Cerebral or Cerebellar atrophy (43%)
- Muscle Pathology
- Ragged red fibers (60%): SDH +, COX -
- Vacuoles in small fibers (A8344G mutation): Some patients
- Rimmed or Autophagic
- LC3 aggregates
- Muscle may be morphologically normal
- Oxidative enzymes: Complexes I, III & IV may have reduced activity
- EEG abnormal (80%)
MNGIE (MTDPS1)
 10
10
(Myopathy and external ophthalmoplegia; Neuropathy;
Gastro-Intestinal; Encephalopathy)● Thymidine phosphorylase (TP; TYMP; Endothelial cell growth factor 1 (ECGF1))
|
Clinical Genetics Laboratory mtDNA TP protein Pathology Variants Late onset MNGIE syndromes: Other LIG3 MTDPS4B: POLG No encephalopathy mtRNA Trp mtRNA Val PEO + Myopathy: MGME1 |
- Nosology: POLIP, OGMID, MEPOP
- Epidemiology
- Diverse ethnic populations
- ~ 200 patients
- 1/1,000,000 in Europe
- Thymidine phosphorylase genetics: MNGIE mutations
- Type
- Most common: Missense mutations
- Occasional: Insertions, Deletions, Stop or Splice acceptor change in intron
- > 50 Different mutations identified
- Location
- More than 1 family with A3371C, G1419A, c.1160-1G>A
- More in Exons 4 & 7
- Mild, late onset disease without neuropathy: E379K + c.1160-1G>A
- Geographic
- c.C392T Mediterranian
- c.A866G Europe
- c.T518G Dominican Republic
- Type
- Thymidine phosphorylase protein (Endothelial cell growth factor, platelet derived (ECGF1))
- Thymidine phosphorylasethymine phosphorylase
- Not present in muscle
- Functions
- Mutations: Loss of function of thymidine phosphorylase
- MNGIE patients
- Most patients: Absent, or nearly complete loss of, TP function
- Milder patients may have residual activity
- Measured in leukocytes
- Carriers: ~ 35% of normal activity; Range 15% to 60%
- MNGIE patients
- Clinical features
- General
- Often: Homogeneous
- Intra- & inter-familial clinical variability: Reported
- Poor genotypephenotype correlation
- Onset
- Age
- Often < 20 years (75%)
- Mean 18 years; Range 5 mo to 53 years
- Majority with 1st symptoms < 12 years
- Signs
- Gastric (57%)
- Dysmotility (45%): Diarrhea; Nausea & vomiting
- Abdominal pain & cramps
- Extraocular (26%): Ptosis; External ophthalmoplegia
- Polyneuropathy: Foot drop
- Gastric (57%)
- Age
- Visceral neuropathy (100%)
- Diarrhea
- Obstipation
- Episodic intestinal pseudo-obstruction & Gastroparesis
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
- Malabsorption
- Borborygmi 96%
- Early satiety
- Diverticulae: In duodenum & jejunum
- Abdominal pain
- Cachexia
- Ocular
- External ophthalmoplegia (100%)
- Ptosis (100%)
- Retinal degeneration (6% to 25%)
- Optic atrophy
- Musculoskeletal
- Thin body habitus & Cachexia: Weight loss (100%)
- Short stature (70%)
- Neuropathy (87%)
- Sensory predominant
- Distal loss
- Pain
- Sensory ataxia
- Weakness
- Distal: Early
- Proximal with disease progression
- Symmetric
- Tendon reflexes: Absent (45%)
- Course: Progressive
- Nerve conduction testing
- Axon loss
- Demyelinating features: Some patients
38
- Conduction velocity: Reduced (<80% of lower limit of normal)
- Conduction block & temporal dispersion in some patients
- Sensory predominant
- Myopathy
- Proximal weakness (14%)
- Exercise intolerance (8%)
- CNS
- Hearing loss (60%)
- Cognition
- Normal intelligence in most
- Cognitive impairment or Dementia (9%)
- Other occasional
- Seizures
- Headaches
- Cardiac: Occasional; Incomplete right bundle branch block
- Pancreas: Diabetes or Glucose intolerance; Amylase increase; Exocrine insufficiency
- Neoplasms (3%)
- Disease course
- Progressive: Months to Years
- Spontaneous fluctuations may occur: Associated with acute medical events
- Early death
- Ages: Mean 35 to 38 years, Range 18 to 53 years
- Associated with infections + other systemic disorders
- Treatment
- Liver transplantation
255
- Clinical improvement: Limited
- dThd & dUrd levels: Reduced
- Allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Clinical improvement: Limited
- Mortality: High
- Liver transplantation
255
- General
- Laboratory
- Serum
- Lactic acidosis (64%)
- Plasma thymidine levels: Increased 20-fold
- Plasma deoxyuridine & deoxythymidine levels: Increased
- Hypokalemia: Tetany; Cardiac arrhythmia
- Thrombocytosis
- EKG: Abnormal in 18% to 35%
- CSF: High protein (89%)
- MRI
- Leukoencephalopathy: Very common
- Symmetric
- Spares corpus callosum
- Widespread
- T2: Hyperintense
- T1w: Hypointense
- Brain atrophy: Not prominent early in course; May be severe late
- Leukoencephalopathy: Very common
- MRS
- Reduced N-acetylaspartate (NAA) & choline in severely affected areas
- No lactate peak
- EMG
- Neurogenic only: 61%
- Neurogenic + Myogenic: 39%
- Muscle pathology
- Mitochondrial changes in muscle fibers
- Mitochondrial proliferation
- COX - fibers (80% to 90%)
- SDH + fibers (60%)
- Oxidative enzyme levels: May be normal
- Eye muscles: Myopathic changes
- Neurogenic changes
- Grouped atrophy
- Fiber type grouping
- Target/targetoid fibers
- Mitochondrial changes in muscle fibers
- MNGIE: mtDNA changes
35
- Multiple deletions without duplications (62%)
- Microdeletions occur at
- Imperfectly homologous breakpoints (Similar but not identical mtDNA sequences)
- Perfect direct sequence repeats
- Five major species of mtDNA deletions
- Hot-spot for mtDNA rearrangements
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase 5 (ND5) gene
- Occurs in 4 of 5 species of deletions
- Deletions in tissue: Most prominent in skeletal muscle; Not present in intestine
- Microdeletions occur at
- Somatic point mutations: High frequency of 5-ATT to 5-GTT
- mtDNA abnormalities may be produced by
- Increased intracellular Thymidine & Deoxyuridine that may cause
- Imbalances of mitochondrial nucleotide pools
- Homologous recombination
- mtDNA depletion (MTDPS1
 ): Variable
): Variable
- 6% to 20% of normal total mtDNA, especially in liver
- ? Secondary to mtDNA point mutations & multiple deletions
- Multiple deletions without duplications (62%)
- Biochemistry: Thymidine phosphorylase activity < 5% of normal in leukocytes
- Serum
- MNGIE variant: Late onset with TP mutations
- Partial loss of thymidine phosphorylase activity: 10% to 15% residual
- Clinical
- Late onset: 5th decade
- Eye: Ophthalmoplegia; Ptosis
- Gastrointestinal features
- Neuropathy: Axon loss ± Demyelination
- Pathology
- Muscle: COX- muscle fibers, scattered
- Nerve: Axon loss
- MNGIE variant: MNGIM syndrome, No encephalopathy
36
- Genetics: No thymidine phosphorylase or dNT-2 mutations
- Onset: 2nd decade
- Clinical
- Gastrointestinal malabsorption
- Diarrhea
- Borborygmia,
- Abdominal pain
- GI pseudo-obstruction
- Weight loss
- Parenteral nutrition eventually needed
- Eye
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Ptosis: Mild
- Weakness
- Diffuse
- Associated with cachexia
- Polyneuropathy
- Pain
- Gait disorder: Sensory ataxia
- Axonal loss: Sensory > Motor
- CNS: Normal
- Disease course: Death in 4th decade
- Gastrointestinal malabsorption
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal
- Serum Lactate: Normal
- Plasma thymidine: Normal
- CSF protein: High
- MRI: Normal brain
- Muscle
- COX negative muscle fibers: 5%
- Raged red fibers: Occasional
- Complex IIV activities: 24% of normal
- MNGIE variant: POLG mutation
- MNGIE variant: Neurogastrointestinal syndrome
● mtRNA Trp ;
Sporadic
;
Sporadic
- Mutation
- G5532A
- Heteroplasmic
- Present in all tissues: Highest in muscle (92%)
- Low levels of mutation (7% to 9%) found in patient's unaffected mother & brother
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 year
- Early: Recurrent vomiting; Failure to thrive
- Later features
- Leg discomfort
- Eye: Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, Pigmentary retinopathy, Constricted visual fields, Blindness
- Ear: Sensorineural deafness
- Muscle: Wasting
- CNS: Cognitive regression, Seizures
- GU: Incontinence
- GI: Feeding difficulties; Constipation; Diarrhea; Colitis
- Skeletal: Short stature
- Onset
- Muscle
- SDH positive fibers: COX-negative & -positive
- Complexes I & IV: Reduced activity (< 20% of normal)
- COX- fibers have highest levels of mutation
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in Blood & CSF
- MRI of brain: General atrophy; Periventricular white matter changes
- Mutation
- MNGIE variant: Neurogastrointestinal syndrome
88
● mtRNA Val (MTTV) ;
Sporadic
;
Sporadic
- Genetics
- Mutation: Heteroplasmic; A1630G
- Allelic disorders
- MNGIE variant (A1630G)
- Ataxia, Seizures & Hearing loss (G1606A)
- Leigh syndrome (Homoplasmic C1624T & Heteroplasmic G1644T)
- MELAS (A1630G, G1642A)
- ? Seizures, childhood onset (A1630G; Low heteroplasmy level) 339
- Learning difficulties, Hemiplegia & Movement disorder (Heteroplasmic T1659C)
- CMT syndrome, Axonal (A1661G)
- Spastic paraplegia, Mitochondrial (SPGM)
- Genetics
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Cachexia
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal motility problems: Ileus, Abdominal pain; Megacolon
- Hearing loss: High frequency
- Developmental delay
- Eye movements: Normal
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Muscle biopsy: COX-, SDH+ muscle fibers; Complex I & IV deficiency
- MTTV variant: CMT syndrome, Axonal (CMTMA1)
 256
256
- Epidemiology: Chinese & Venezuelan families, > 100 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: m.1661A>G, Homoplasmic
- Inheritance: Maternal
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 68 years; Mean 15 years
- Weakness
- Common: Distal legs
- Other: Distal arms, finger extension & wrist flexion
- Tendon reflexes: Increased or Decreased
- Sensory loss: Large fiber modalities
- Foot: Pes cavus
- Myelopathy: Paraparesis in 5 patients
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Chronic denervation; mt-tRNAVal reduced
- Nerve: Mitochondrial hyperplasia, Hypertrophy, Crystalline arrays
- NCV: Axon loss, Motor & Sensory
- EMG: Denervation, distal
- Brain MRI: Normal
- MTTV variant: Spastic paraplegia, Mitochondrial

- Epidemiology: 1 Chinese family; 10 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.1661A>G; Homoplasmic
- Inheritance: Matrilineal; Varied expressivity
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st 2 decades; Anticipation
- 1st generation: Mean 19 years
- 4th generation: Mean 6 years
- Spastic paraparesis
- Legs only
- DTRs increased
- Gait disorder
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Onset age: 1st 2 decades; Anticipation
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Spinal cord atrophy; Cerebral hemisphere atrophy
- NCV: Conduction block; Temporal dispersion
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss; Myelin sheaths thin
- mtDNA copy number: More reduced with earlier disease onset
● Ligase III, DNA, ATP-Dependent (LIG3)
- Nosology: Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome (MNGIE type) 20
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 7 patients
- Genetics
- Gene contains mitochondrial splice variant
- Mutations: Missense & 1 stop; K537N, P609L, G964R, C999Y, R811Ter
- LIG3 protein
- mtDNA ligase
- Role in mtDNA Maintenance, Repair & Replication
- Overexpression: Resistance to oxidative damage in mitochondria
- Interactions: POLG
- Mutations: mtDNA depletion
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy to Adult
- Autonomic
- Gut: Dysmotility; Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO)
- Neurogenic bladder
- CNS: More severe than TYMP mutations
- Epilepsy
- Migraine
- Stroke-like episodes
- Developmental delay
- Some patients
- Spasticity
- Involuntary movements
- Eye: Macular degeneration
- Course
- Progressive
- Severe disease: Death in childhood
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Leukoencephalopathy; Cortical atrophy
- Muscle
- COX- & SDH+ muscle fibers
- Ultrastructure: Morphologic changes
- GI pathology: Fibrosis; Elastin levels increased; Myenteric neurons reduced
- Lactate/Pyruvate ratio: Increased in CSF
● Guanylate kinase 1 (GUK1)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Splice, Stop, Insertion
- GUK1 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to 16 years
- Fatigue, Chronic
- Eyes: Ptosis; Ophthalmoparesis
- Weakness: Proximal
- CNS: Some patients; Seizures; MRI WM Δ
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High
- Muscle
- SDH+; COX- muscle fibers
- mtDNA deletions & depletion
- Ultrastructure: Paracrystalline mitochondrial inclusions
- Multiple complex deficiencies
- CD4 lymphocytes: Reduced
- Liver enzymes: High
● 4-Aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- ABAT protein
- Catalysis of GABA
- Maintenance of nucleoside pools in mitochondria
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Development delay
- Hypotonia
- Seizures: Some patients
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Atrophy; Signal abnormalities internal capsule, dentate nucleus
- Muscle biopsy
- Normal morphology
- Ultrastructure: Increased lipid & glycogen
- Mitochondria: Complex activities generally reduced; citrate synthetase high
- Fibroblasts: mtDNA copy number low
Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
 30
30
|
Epidemiology Genetics Mitochondrial MTND1 MTND3 MTND4 MTND6 Recessive (LHONAR) 1: DNAJC30 2: NDUFS2 Other Clinical Laboratory Optic neuropathy Other Also see: LHON, Recessive |
- LHON: Epidemiology
280
- Prevalence: Northern Europe 1 in 30,000 to 50,000; Australia 1:63,000; Japan 1:100,000
- Sex & Family relations
- Male predominance
- Vision loss with mutation: 17.5% to 50%
- Generational loss in prevalence
- No relation to any X-linked genes
- Females
- Vision loss with mutation: 5.4%
- Age: Risk constant over lifetime
- Children of
- Affected mothers: More frequent vision loss (29% to 33%)
- Mothers with Affected brothers: More frequent vision loss
- Male predominance
- Genetics: Many different mtDNA
point mutations
- Inheritance: Maternal
- Genetic-Clinical correlations
- Recurrence risks: Brother 30%; Sister 8%; Nephew 46%; Niece 10%; Male cousin 31%; Female cousin 6%
- 40% of patients with commonest mutation (G11778A) have negative family history
- Large families with maternal inheritance: G11778 & T14484C mutations
- Each mutation has a characteristic degree of severity
- Manifestations of severity include
- Mutations
- General
- 3 Mutations account for 96% of cases
- All in Complex I genes
- Mutations
- Western: ND4 (G11778A) (64% to 69%), ND1 (G3460A) (3% to 13%), ND6 (T14484C) (14% to 20%)
- Chinese: ND1 (G3460A; G3635A); ND5; mtRNAThr (G15927A)
- Associated haplogroups: 3x More vision loss with Haplogroup J than H
- Mutation pattern
- Most patient's mutations are homoplasmic
- Some patients in each family may be heteroplasmic
- 3 Mutations account for 96% of cases
- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 4 (MTND4)
 :
Complex I
:
Complex I
- Genetics
- Mutation: G11778A
- Missense: R340H
- Most common LHON mutation
- Mutation load in an individual's blood: Correlations
- Higher mutation load: Frequency of blindness in males greater
- Frequency of clinically affected sons: Related to mutant mtDNA in mother's blood
- Mothers with < 80% less likely than Mothers with 100%
- Changes in mutation load from one generation to the next
- Largely determined by random genetic drift
- Disease modifier
- Allelic MTND4 disorders
- LHON + Dystonia
- MELAS: Typical & Later onset
- Leigh
- Mutation: G11778A
- Clinical features: LHON
- Most severe syndrome
- No light perception
- Visual recovery in 4% after 36 months
- Other occasional CNS
- Ataxia syndrome: Adult-onset
- Paraparesis: Spastic
- Genetics
- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 1 (MTND1)
 : Complex I
: Complex I
- ND1 encoding
- mtDNA
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 3307 & 4262
- ND1 peptide: Complex I subunit
- mtDNA
- Mutation: G3460A (p.A52T)
- Clinical: LHON
- Moderate severity
- Recovery in 22%
- Clinical: LHON
- Mutation: G3376A
- Clinical syndromes: LHON; MELAS; LHON/MELAS overlap
- Mutation: T3394C
136
- Clinical
- Variable effects depending on haplogroup & environmental context
- Low altitude: Increased LHON risk
- Biochemical
- Complex I activity reduced: B4c & F1 haplogroups
- Complex I activity increased: M9 haplogroup
- Clinical
- Other MTND1 mutations: Clinical syndromes
- ND1 encoding
- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 6 (MTND6)
 : Complex I
: Complex I
- Mutation: T14484C
- Epidemiology
- French-Canadians: Common; Introduced in 17th century introduction by female founder 48
- Han Chinese: Low penetrance (10%)
- Genetics
- Mutation type: Missense (M64V); May be homoplasmic
- Often occurs in association with other LHON mutations
- Clinical: LHON
- Best prognosis
- Recovery in 37% at 16 months
- Epidemiology
- Mutation: A14495G
11
- Genetics: Heteroplasmic
- Clinical: LHON
- Onset age: 17 to 30 years
- Improvement in visual acuity after event in some patients
- Other mutations causing LHON ± Dystonia
- G14459A/A72V; C14482G/M64I; C14498T/Y59C; C14568T/G36S; T14596A/I26M
- Hotspot in hydrophobic cleft
- Other MTND6 mutations
- Mutation: T14484C
- Other mutations
- MTND 4L

- ND4L encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of the mtDNA
- Location between nucleotide pairs 10470 & 10766
- LHON
- Mutation: T10663C; Homoplasmic
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficit, partial
- Other disorders: Colorectal cancer
- ND4L encoding
- NADH dehydrogenase (MTND) (Subunits 2
 or 5
or 5
 ): Complex I
): Complex I
- Cytochrome c Oxidase (MTCO) (Subunits 1
 or 3
or 3
 ):
Complex IV
):
Complex IV
- Cytochrome b (MTCYB)
 : Complex III
: Complex III
- ATP Synthase 6 (MTATP6)
 : Complex V
: Complex V
- LHON, Autosomal Recessive (LHONAR)
- mtRNAThr: LHON in Chinese patients
- Malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT): OPA15

- MTND 4L
- General
- Clinical features: General
- Onset
- Midlife: 15 to 35 years; Range 1 to 87 years
- Visual loss: Unilateral; Painless
- Course: Subacute (Weeks to Months)
- Visual loss
- Clinical features
- Pain: Usually none; Present in 20%
- Visual loss pattern
- Severity: May deteriorate to 20/200 or less
- Progression to other eye: Mean 4 months; Range 1 to 24 months
- Tendency to recover: Depends on mutation; Often little recovery; Better with 14484 mutation
- Pupillary reactions: May be relatively spared for degree of visual loss
- May be precipitated by: Ethambutol
- Ocular pathology
- Early
- Earliest changes: Macula
- Disc microangiopathy
- Optic disc
- Pseudo disc edema
- Hyperemia
- Peripapillary telangiectasias
- Swelling of retinal nerve fiber layer
- Vessels: Tortuosity
- May be normal
- Late: Optic atrophy
- Early
- Clinical features
- Other features: Some families
- Cardiac conduction defects: Pre-excitation syndromes
- Spastic paraparesis 55
- Spastic dystonia: Complex I, Subunit ND4 (MTND4)

- Dystonia
 92
92
- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 1 (MTND1, Complex I)

- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 3 (MTND3, Complex I)

- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 4 (MTND4, Complex I)

- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 6 (MTND6, Complex I)

- NADH-Dehydrogenase Subunit 1 (MTND1, Complex I)
- Other CNS syndromes
- "Multiple sclerosis-like" disorder
- Increased association between LHON & MS
- Brain MRI: May look like MS
- Encephalopathy
- "Multiple sclerosis-like" disorder
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology
49
- No ragged red fibers
- EOM mitochondria: Diffuse increase in number and size; Disorganized cristae
- Preservation of myofibrils
- MRI: Optic nerve may enhance on T2 weighted images
- Muscle pathology
49
Single, Large-Scale Mitochondrial DNA Deletions (SLSMD) 302, 314
|
SLSMD: General Features Clinical Syndromes Kearns-Sayre (KSS) Pearson's Marrow Syndrome Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (PEO) |
Kearns-Sayre Syndrome "Spectrum" (KSS)
- Definition
- Eye: Ptosis or Ophthalmoparesis
- mtDNA: Single large-scale deletion (SLSMD)
- One or more of
- Retinopathy
- Ataxia
- Cardiac: Conduction defects; Cardiomyopathy
- Hearing loss
- Short stature
- Cognitive involvement
- Tremor
- Common
- Onset < 20 years
- Epidemiology
- Frequency: 1.6/100,000 in Finnish population
- Genetics
- Family history
- Inheritance: Sporadic in 90%
- Familial cases
37
- Rare
- Mother to Offspring: 4%
- mtDNA mutation types
- Single large mtDNA deletion (SLSMD)
- Different patients: Varied sizes & locations
- Size range: 1.1 to 10 kB
- Individiual patients: all cells with same mutation
- Deletion: Most common mutation general type (80%) for KSS clinical syndrome
- Heteroplasmic: 40% to 84%
- Clinical correlations
- Common deletions
- Most common
- 4977 base pairs from 8488 to 13460
- DNA feature: 13 base pair repeats at mutation break points (60% of patients)
- Thailand: 3558 bp deletion; 10204 to 13761, or 10208 to 13765
- China: 8470_13446 deletion
- Most common
- Most deletions preserve
- Promoters of transcription of heavy & light strands
- 12S & 16S ribosomal RNA genes
- Origin of heavy strand replication
- Change in number of deleted mtDNA copies over time
- Increased: Muscle
- Reduced: Rapidly turning over cells (hematopoetic)
- Different patients: Varied sizes & locations
- Large scale tandem duplication: Rare
- Also: Few KS clinical syndrome patients with missense mtDNA mutations
- Single large mtDNA deletion (SLSMD)
- Family history
- Clinical features
- General
- Characteristic signs
- PEO
- Pigmentary degeneration of retina
- Heart block
- Mitochondrial myopathy
- Partial expression of signs common
- Characteristic signs
- Onset
- Age: < 20 years
- Later onset patients: May have only PEO
- Ocular
- External Ophthalmoplegia (80%)
- Progressive
- Limitation, or absence, of movement in all fields of gaze
- Ptosis (100%)
- Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration (Retinitis pigmentosa)
- Peripheral > Central Retina
- Salt-and-Pepper appearance
- Pathology
- Atrophy of retinal pigment epithelium & outer retina
- Aberrant pigment in all layers of the sensory retina: Most posteriorly
- Vision often remains good
- External Ophthalmoplegia (80%)
- Dysphagia: 50% of adults symptomatic
- Regurgitation of liquids
- Problems with solids also
- Weight loss
- Most commonly associated with cricopharyngeal achalasia 17
- Treatment: ? Cricopharyngeal myotomy
- Myopathy
- Weakness (90%)
- Proximal > Distal
- Symmetric
- Face: Some patients
- Occasional
- Fatigue
- Pain on exertion
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Weakness (90%)
- Polyneuropathy (10%): Sensory-Motor
- CNS
- Respiratory drive: Reduced
- Hearing loss (95%)
- Ataxia (90%)
- Dementia, or impaired intellect (85%)
- Upper motor neuron: Spasticity; Increased Tendon reflexes
- Stroke (8%)
- Systemic features
- Cardiac: Conduction Block
- Onset age: May develop in childhood
- Rapid progression
- Sudden death
- Endocrinopathies (35% to 67%)
- Diabetes mellitus & Glucose Intolerance (15%)
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypoparathyroidism (6%)
- Growth hormone insufficiency
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Skeletal: Short stature
- Cardiac: Conduction Block
- Prognosis: Death common in 3rd or 4th decade
- Treatment: ? Folinic acid
- General
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology
- Ragged red fibers (98%): COX - & some COX +
- Variation in muscle fiber size
- Lactic acidosis (50% to 80%)
- CSF
- Protein: High
- 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF)
- Very Low
- Lower with higher CSF protein
- Higher with increasing age
- Homovanillic acid (HVA): High
- ? Abnormal choroid plexus function
- Head CT: Basal ganglia calcifications (5%)
- MRI
- Atrophy: Cerebrum & Cerebellum
- T2 hyperintensity in
- White matter: Subcortical U-fibers; Not periventricular
- Variable: Basal ganglia; Thalamus
- Brain pathology
- Status spongiosis: Gray & White matter
- Regions involved: Brainstem; Basal ganglia; White matter of cerebrum & cerebellum
- Muscle pathology
- Variant SLSMD syndromes
- Pearson Marrow-Pancreas Syndrome

- Sideroblastic anemia
- Pancytopenic crises
- Macrocytic
- Bone marrow: Normal cellularity; Vacuolization
- Pancreatic insufficiency
- Exocrine: Malabsorption; Steatorrhea
- Endocrine: Insulin-dependent diabetes; Later in disease course
- Infancy: Low birth weight; Death; Metabolic & lactic acidosis
- Course
- Often fatal in early childhood
- May precede development of Kearns-Sayre syndrome if survival past infancy
- Treatment
- Chronic transfusions
- Replacement of pancreatic enzymes
- Laboratory
- mtDNA deletions often found in leukocytes
- Sideroblastic anemia
- 2-Oxoadipic aciduria & 2-Aminoadipic aciduria

- Onset: 2 years
- Organic acidemia
- Episodes of ketosis & acidosis
- Progressive to coma
- Resolution of clinical & metabolic features
- Kearns-Sayre syndrome may develop later in childhood
- Leukodystrophy
- Genetics: Large mtDNA deletion
- Clinical
- Ataxia, progressive
- Bulbar palsy
- Laboratory
- CNS imaging: Diffuse white-matter lesions in occipital to parietal lobes
- Lactate: Slightly high in CSF
- Muscle biopsy: SDH+ & COX- muscle fibers
- PEO
- Syndromic deafness
- Diabetes
- Pearson Marrow-Pancreas Syndrome
PEO + (Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia)
| PEO: General features | |||
|
Dominant PEO Mitochondrial DNA Δ Multiple mtDNA deletions Nuclear DNA mutations (PEOA) POLG (PEOA1): 15q25 SANDO MIRAS MSCAE Alpers Parkinsons ANT1 (PEOA2): 4q35 Twinkle (PEOA3): 10q23 POLG2 (PEOA4): 17q RRM2B (PEOA5): 8q23 DNA2 (PEOA6): 10q21 GMPR: 6p22 OPA1: 3q28 POLRMT: 19p13 RRM1: 11p15 Hypogonadism SCA28: AFG3L2; 18p11 |
Recessive PEO Mitochondrial DNA Δ mtDNA depletion, or Multiple mtDNA deletions Nuclear DNA mutations (PEOB) ENDOG: 9q34 Leigh, PEO, OA: c12orf65; 12q24 MNGIE: TYMP; 22q13 POLG1: 15q26 HSN + PEO (SANDO) PEOB1 PEO + Cardiomyopathy PEO+ CNS PEOB2: RNASEH1; 2p25 PEOB4: DGUOK; 2p13 PEOB5: TOP3A; 17p11 PEOB6: RRM1; 11p15 POLRMT: 19p13 Myopathy MGME1; 20p11 PEOB3; TK2 16q21 TEFM: 17q11 Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy POLG1 C1QBP Myopathy & Parkinsonism Sensory neuropathy SPG7 variant: Paraplegin; 16q24 |
Maternal PEO Mitochondrial DNA Δ mtDNA point mutations May be sporadic mtRNALeu(UUR) MELAS PEO mtRNALeu(CUN) mtRNAAsn mtRNAGln: PEO-plus mtRNAAla: PEO-plus mtRNATyr: PEO-plus mtRNALys: PEO-plus mtRNAIle mtRNAPro |
Sporadic PEO Mitochondrial DNA changes Single, Large mtDNA deletion, or Multiple mtDNA deletions Kearns-Sayre: Large mtDNA deletion PEO + Proximal myopathy Sensory ataxic neuropathy ? Immune (HyperThyroid) 
EOM pathology |
Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (PEO): General Features 257
- Clinical
- Gaze limitation: All directions
- Eye movement speed: Slow
- Bilateral
- Associated with
- Ptosis
- Normal orbicularis oculi strength
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Disease syndromes
- PEO
- PEO ± Myopathy or Bulbar
- Kearns-Sayre (KSS)
- DNA features
- Lab & Pathology
- Skeletal muscle
- Mitochondrial changes in 95%
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Normal
- Extraocular muscles
49
- Mosaic pattern of muscle fiber pathology
- Myofibril disorganization
- Serum CK: Normal in 50%
- Skeletal muscle
- Differential diagnosis: Congenital ophthalmoplegia
Sporadic PEO
|
|
- tRNAGln (MTTQ)

mtDNA disorders
PEO: 4366insA
Deafness & Migraine: A4336G
MELAS: A4332G
Nuclear DNA disorders
QRSL1: COXPD40
GATB: COXPD41
GATC: COXPD42
- PEO
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetic
- Inheritance: Sporadic
- Mutation
- 1 base-pair insertion, 4366insA
- Heteroplasmic
- Location: Most in skeletal muscle; Some in fibroblasts
- Clinical
- Onset: 5 years; Weakness; Ptosis
- Cranial nerves
- Face weakness
- Dysphonia; Dysphagia
- Ptosis: Bilateral; Symmetric; Severe
- Ophthalomoplegia
- Weakness: Mild; Extremity
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- No signs of cardiac, cerebellar, or retinal disorders
- Laboratory
- NCV: Normal
- EMG: Myopathic
- Muscle pathology
- Ragged red fibers
- Many COX- muscle fibers (89%)
- Impairment in mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Mutated DNA: Skeletal muscle (87%); EOM (61%)
- tRNAGln: Other disorders
- mtDNA disorders
- Sensorineural Deafness & Migraine: A4336G
- MELAS: A4332G
- COXPD40: Disorder of Gln-tRNAGln formation
 224
224
● QRSL1 (GATA) ; Chromosome 6q21; Recessive
; Chromosome 6q21; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 6 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Protein
- Subunit of glutamyl-tRNAGln amidotransferase protein complex
- Aminoacylation of mitochondrial glutaminyl mt-tRNA (mt-tRNA(Gln))
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth
- Tachypnea
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Hepatomegaly
- Hearing loss
- Course: Death in 1st year
- Laboratory
- Mitochondrial function: COXPD
- Hyperglycemia
- Lactic acidosis
- COXPD41: Disorder of Gln-tRNAGln formation

● Glutamyl-tRNA Amidotransferase, subunit B (GATB) ; Chromosome 4q31.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 4q31.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 siblings
- Genetics
- Mutations: 2 bp deletion & Phe136Leu
- GATB protein
- Subunit of glutamyl-tRNAGln amidotransferase protein complex
- Aminoacylation of mitochondrial glutaminyl mt-tRNA (mt-tRNA(Gln))
- Clinical
- Birth: Premature
- Cardiomyopathy
- Respiratory failure
- Death in 1st week
- Laboratory
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Lactic acidosis
- Hypoglycemia
- Fibroblasts: OXPHOS deficiencies of complexes I, III & IV (COXPD)
- COXPD42: Disorder of Gln-tRNAGln formation

● Glutamyl-tRNA Amidotransferase, subunit C (GATC) ; Chromosome 12q24.31; Recessive
; Chromosome 12q24.31; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 Druze families, 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense; Met78Arg
- GATC protein
- Subunit of glutamyl-tRNAGln amidotransferase protein complex
- Aminoacylation of mitochondrial glutaminyl mt-tRNA (mt-tRNA(Gln))
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 to 3 months
- Failure to thrive
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic or Dilated
- Death: 6 months
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Serum creatine kinase: High
- Serum alanine: High
- Anemia
- Liver enzymes: Abnormal
- Muscle: OXPHOS deficiencies of complexes I, III & IV (COXPD)
- mtDNA disorders
- PEO
- mtRNAAla (MTTA)
 16:
PEO+
16:
PEO+
- Genetics
- Mutation: T5628C
- Inheritance: Mitochondrial
- Clinical
- Onset
- 6th decade
- Ptosis
- Family history: Negative
- Eye movements: Decreased in horizontal direction
- Weakness: Proximal; Symmetric; Mild
- Dysphagia
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Many COX negative muscle fibers ± Mitochondrial proliferation
- Biochemistry: Partial defect of Complex I
- EMG: Myopathic
- Serum CK: Normal
- Muscle
- Genetics
- mtRNALeu(UUR) (MTTL1)
 : PEO
: PEO
- Genetics
- Clinical
- Onset
- 5th decade
- Ptosis
- Family history: Migraines
- Eye movements: Decreased L > R
- Exercise intolerance
- Short stature
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Many COX negative, ragged red muscle fibers
- Biochemistry: Partial defects of Complex I & IV
- Mutant mtDNA: RRF with 99%; Normal fibers 88%
- Lactate: Normal
- Serum CK: Mildly elevated
- Muscle
- mtRNATyr (MTTY)
 20:
PEO
20:
PEO
- Genetics
- Mutation: T5885del
- Inheritance: Mitochondrial
- mtRNATyr: Allelic disorders
- Exercise intolerance with Complex III deficiency: A5874G
- Sensory ataxic neuropathy in Golden Retriever dogs: 5304delA 97
- Childhood-onset severe multi-system disorder: A5889G
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis & Dilated cardiomyopathy: A5843G (Homoplasmic, May not be pathogenic)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 4th decade
- Ptosis
- Exercise intolerance: Muscle pain
- Family history: Negative
- Eye movements: Ophthalmoplegia
- Exercise intolerance: Muscle pain
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Myopathy: Varied fiber size; Increased connective tissue
- Many COX negative muscle fibers with increased SDh staining
- Biochemistry: Partial defect of Complex I & IV
- Mutation load: COX+ fibers 20%; COX- fibers 79%
- EMG: Myopathic
- Serum lactate: Abnormal increase after exercise
- Serum CK: Normal
- Muscle
- mtRNATyr variant: Childhood-onset severe multi-system disorder
259
- Epidemilogy: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: A5889G heteroplasmic
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood; Learning delay
- Failure-to-thrive
- Ataxia
- Seizures
- Cognitive decline
- Myopathy: Weakness & Wasting
- Neuropathy: Tendon reflexes absent; Sensory loss
- Hearing loss
- Vision loss
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Progressive atrophy; Basal ganglia calcification
- Serum: Lactate & GDF15 increased
- Muscle histology: Non-diagnostic
- Respiratory chain enzyme complexes: Reduced Complex I activity
- Genetics
- mtRNAAsn (MTTN)
 257:
PEO
257:
PEO
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: A5692G; A5702G; G5703A
- Inheritance: Mitochondrial
- Other disorder: MC1DM2 (A5728G)
- Clinical
- PEO: Pure
- Multisystem disorder: One patient (A5692G)
Maternal PEO
- mtDNA Point mutations
PEO: Autosomal Dominant
| Autosomal Dominant PEO: Clinical features | |||
|
Triple furrowed tongue
|
||
|
PEO: Differential diagnosis |
|||
- Mitochondrial DNA breakage syndromes: Autosomal dominant PEO
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, autosomal dominant 3 (PEOA3; PEO 1)

● Twinkle mtDNA Helicase (TWNK; c10orf2) ; Chromosome 10q24.31; Dominant
; Chromosome 10q24.31; Dominant
- Epidemiology
- Multiple families & sporadic cases with different ethnic origins
- 15% of Italian PEO with multiple mtDNA deletions
- TWNK mutations common: PEO onset after 4th decade
- Genetics
- Gene mutations
- Missense most common
- Locations
- Cluster in region of protein involved in subunit interactions
- Amino acids 303 to 508
- Hot spot: Ala504Thr
- No mutations in N-terminal half of gene
- Homozygotes: Ala359Thr more severe than heterozygotes
- Other mutations: In-frame duplication
- Severe CNS phenotype with polyneuropathy: 39 bp duplication
- Muscle effect: Multiple mtDNA deletions
- May occur in similar patterns in different patients
- No strong correlation between deletion load & clinical severity
- mtDNA copy number: Not reduced
- Allelic syndromes
- IOSCA
- MTDPS7
- PEOA3
- PEO + Dementia
- PEO + Parkinson
- Perrault 5
- SANDO
- Dystonia + Rigidity & Bradykinesia
- Cerebellar ataxia: Adult onset, Recessive with Sensory neuropathy & Hearing loss
- Auditory neuropathy, Recessive: Hearing loss ± Perrault 346
- Dwarf Chicken: Runting & Stunting Syndrome
- Gene mutations
- Twinkle protein
293
- Structural similarity to phage T7 gene 4 primase/helicase
- Colocalizes with mtDNA in mitochondrial nucleoids (units of mtDNA segregation)
- Not dependent on DNA binding
- Heptamer & Octamer
- Binds to: β-subunit of polymerase-γ (POLG)
- Component of: Mitochondrial replisome
- Functions
- Unwinds DNA substrates with 5'3' polarity
- Structure relations
- Forms hexamer
- Initiation of unwinding requires
- Fork structure with single-stranded 5'-DNA loading site
- Short 3'-tail
- DNA helicase, adenine nucleotide dependent: Essential replication helicase of mtDNA
- mtDNA maintenance: Regulates mtDNA copy number
- Catalyzes nucleoside 5'-triphosphate (NTP) hydrolysis
- Functional domains
- 3' Helicase region
- Linker region: Involved in oligomerization into a hexamer required for helicase activity
- 5' primase domain
- Mutation actions
342
- ? Alter subunit interactions: ? Dominant negative action
- ? Gain of function: Alter nucleotide metabolism
- Reduced conformational changes after nucleoside triphosphate binding
- ↓ Flexibility of linker region
- ↓ Ring closure
- ↓ Subunits in helicase ring
- May produce
- Increased mtDNA copy number
- mtDNA depletion
- Accumulation of replication intermediates
- No effect on Twinkle localization or multimerization
- Splice variant: Twinky
- Present diffusely in mitochondria
- ? Function
- Clinical features
90
- Onset age
- Average = Early 20's to early 30's;
- Variable within families
- Range: 17 top 73 years
- Eye (96% to 100%)
- Ptosis: Bilateral
- External opththalmoplegia
- Myopathy (50% to 70%)
- Weakness: Proximal (45%)
- Cramps
- Respiratory failure: Occasional
- Occasional
- Bulbar weakness (18%): Dysarthria; Dysphagia; Dysphonia
- Muscle pain
- Polyneuropathy (15%): Sensory; Axon loss
- CNS
- Parkinsonism (13%)
- Ataxia (9%)
- Depression (13%)
- Avoidant personality traits
- Memory loss
- Systemic
- Cardiac (20%): Mild; LVH & Arrhythmias
- Hypothyroid
- Cataracts (5%)
- Hearing loss (4%)
- Onset age
- Laboratory
- Muscle Pathology
- SDH+ muscle fibers
- COX- muscle fibers
- Ragged red fibers
- mtDNA depletion: Mild
- Mutant mtDNA: Brain > Muscle & Heart
- Ketoacidosis: Occasional
- Serum CK: High (36%) or Normal
- Serum lactate: Normal or High (17%)
- Brain MRI: Normal, Cortical atrophy or White matter lesions
- Muscle Pathology
- Twinkle Variant syndrome: SANDO with Ataxic sensory neuropathy
52
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Twinkle (C10ORF2)
- Missense: Lys319Glu
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutations
- Also see: SANDO with POLG mutations
- Genetics
- Twinkle Variant syndrome: PEO + Parkinsonism
73
- Mutation: R374Q
- Some families with same mutation do not have Parkinsonism
- Twinkle Variant syndrome: PEO + Late-onset Dementia
- Mutation: R374W
- Clinical
- PEO: Ptosis & Ophthalmoparesis; Bilateral
- Dementia: Late-onset; Alzheimer-like
- Hearing loss
- Myopathy
- Weakness: Proximal; Mild to Severe
- Bulbar: Dysphagia, Dysphonia
- Neuropathy: Sensory
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal
- Serum Lactate: Normal
- Muscle: COX+ & COX- muscle fibers
- Twinkle Variant syndrome: Encephalopathy with mtDNA depletion (MTDPS7
 )
74
)
74
- Epidemiology: 4 patients; 2 families
- Genetics (Twinkle; c10orf2)
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations
- Missense: Common
- Compound heterozygous
- A318T & Y508C; Asn399Ser, Arg285Gln
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 6 months
- Hypotonia
- Cranial nerves
- Hearing deficit
- Eye: Ophthalmoplegia, Downbeating movements
- Neuropathy: Sensory
- CNS
- Epilepsy: Intractable
- Movements: Athetosis; Orobuccofacial dyskinesias; Myoclonus
- Ataxia
- Systemic
- Renal: Nephrocalcinosis; Proximal tubulopathy
- Hepatic: Microvesicular steatosis; Cirrhosis; Hemosiderosis
- Course: Progerssive
- Laboratory
- Serum transaminases: High
- mtDNA depletion: Liver & Brain > Muscle
- Sural nerve: Reduced numbers of large myelinated axons
- Spinal cord: Loss of axons in posterior columns
- Twinkle variant syndrome: Perrault 5
 180
180
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Arg391His, Trp441Gly, Val507Ile, Asn585Ser
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Allelic disorders
- Twinkle protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: 7 to 13 years
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Female hypogonadism
- CNS
- Ataxia: Nystagmus; Gait disorder
- Epilepsy in some
- Cognition normal
- Polyneuropathy: Panmodal sensory loss; Romberg sign
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
- Serum CK: Normal or mildly high
- Muscle: Type 2 atrophy; Oxidative enzymes normal
- Brain MRI: Non-specific changes
- Epidemiology
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, autosomal dominant 2 (PEOA2; PEO 2; PEO 2/PEO 3)

● Adenine nucleotide translocator 1; (ANT1; SLC25A4) ;
Chromosome 4q35.1; Dominant
;
Chromosome 4q35.1; Dominant
- Epidemiology: Italian & Greek families
- Genetics mutations
- Mutation type: Missense
- Familial patients: Ala114Pro; Leu98Pro
- Sporadic patient: Val289Met
- Mutation effects
- Structural: Alter α-helix of protein
- Alters oxidative metabolism
- mtDNA mutations
- Disease associations
- Allelic disorders
- Dominant: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia 2
- Recessive: Cardiomyopathy + Myopathy (MTDPS12B)
- de novo Dominant: Severe Early-Onset Mitochondrial Disease & Loss of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number (MTDPS12A)
- Possible relation: FSH dystrophy
- Gene location: Near FSH locus on 4q35
- Over-expression of ANT1 in FSH dystrophy muscle
- Allelic disorders
- SLC25A4 protein
- Class: Mitochondrial solute carrier
- Adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT1)
- Most abundant protein in inner mitochondrial membrane
- Mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier AAC1
- Clinical
- Onset age: 20 to 35 years
- Ocular: Ophthalmoplegia & Ptosis
- Severity: Milder than PEO-Twinkle
- Weakness: Variable
- Some patients: No fatigue or generalized muscle weakness
- Occasional: Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Face, Proximal & Respiratory
- Cataracts: After 40 years
- Other changes in some patients
- Sensorineural hypoacusia
- Goiter
- Dementia
- Bipolar affective disorder 28
- Laboratory
- Serum: High lactic acid
- Muscle mtDNA: Multiple deletions
- Respiratory-chain enzymes with mtDNA-encoded subunits: Mild deficiency of some
- SLC25A4 variant syndrome: Severe Early-Onset Mitochondrial Disease & Loss of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number (MTDPS12A)
 212
212
- Epidemiology: 6 families, 7 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo; Dominant
- Mutations: 2 Hot spots; c.239G>A (p.Arg80His), 4 patients; c.703C>G (p.Arg235Gly), 3 patients
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Hypotonia
- Ventilator dependent
- Limb movements: Reduced
- Tongue: Fasciculations
- Dysphagia
- Death < 3 months in 70%
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX stain: Global deficiency
- Lipid: Increased
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain: Severe combined deficiencies; I, III & IV < 20%
- Mitochondrial DNA copy number: Marked loss; 0% to 20%
- Ultrastructure: Increased glycogen & lipid; Abnormal mitochondria
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Echocardiography: Left ventricle enlargement
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Muscle
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, Autosomal Dominant 1 (PEOA1; PEO 1)
 25 or Recessive
25 or Recessive
● Polymerase, DNA γ (POLG; POLG1; POLγ; POLGA) ;
Chromosome 15q26.1; Dominant
;
Chromosome 15q26.1; Dominant
 or Recessive
or Recessive

- Epidemiology
- > 300 mutations described
- Common cause of
- PEO with multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions, Dominant (45%)
- Ataxia, Recessive
- Genetics
- Mutations general
- Effects: mtDNA deletions (Multiple) or mtDNA depletion
- Linker or Polymerase domains: More severe phenotype
- Exonuclease domain: Milder disease
- Dominant mutations
- Tyr955Cys: Most common mutation
- Other: G923D; R943H; Arg953Cys; A957S; Asn468Asp; Ala1105Thr; S1176L; G268A; R1146C
- Some dominant mutations (G923D; A957S) may have
- Low penetrance
- Severe phenotype & more mtDNA mutations if homozygous
- Clinical syndromes
- Recessive mutations (PEOB1
 ): Usually missense
): Usually missense
- Mutations
- Homozygous: Ala467Thr; Leu304Arg; Arg3Pro; G848S
- Compound heterozygotes: T251I & R309L; P587L & R853W; T251I+P587L & M603L; D1184N & N468D
- Absence of ten-repeat polyglutamine tract encoded by CAG repeat: Associated with male infertility
- Allelic syndromes
- Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome (AHS) (Severe phenotype)
- Childhood myocerebrohepatopathy spectrum (MCHS)
- Myoclonic epilepsy, Myopathy, Sensory ataxia (MEMSA; MSCAE)
- Ataxia neuropathy spectrum (ANS): SANDO; MIRAS
- Progressive Ataxia & Palatal Tremor (PAPT)
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia, Autosomal recessive (arPEO)
- MTDPS4B-MNGIE
- Parkinsons
- MELAS-like
- Mutations
- External link: Mutation database
- Mutations general
- POLG protein
- Catalytic subunit of mitochondrial DNA polymerase
- Function
- Required for mitochondrial DNA replication and repair
- C-terminal domain: DNA polymerase responsible for mtDNA replication
- N-terminal exonuclease (exo) domain: Increases the fidelity of mtDNA replication
- Location: Diffusely in mitochondria
- Binds to: Twinkle
- Accessory subunit of DNA polymerase: POLG2
- Clinical features: PEO syndrome (PEO AD1
 )
)
- Onset: 16 to 39 years
- Ophthalmoplegia, Progressive external
- Muscle
- Weakness: Proximal
- Exercise intolerance
- Neuropathy
- Sensory loss: Vibration
- Tendon reflexes: Often absent
- Endocrine
- Poorly formed 2° sex characteristics: Breasts; Pubic hair
- Early menopause: < 35 years
- Testicular atrophy
- Parkinsonism
45
- Increased association with POLG pol-domain mutations
- Onset: After PEO
- Onset age: 4th to 8th decade
- PET scan: Dopaminergic neuron loss
- Levodopa responsive
- Severe disease
- Proximal weakness & wasting: May be severe
- Cranial nerves: Dysphagia; Dysphonia; Facial diplegia
- Abnormal gait: Due to spinal ataxia or distal weakness
- Depression,
- Extrapyramidal syndrome: Also seen in recessive syndrome
- Pathology
- Muscle
- Ragged red fibers
- COX- & SDH + fibers: Numerous
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- mtDNA copy number: Normal or reduced in affected tissues
- Muscle
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Serum Lactate: Mildly elevated
- EMG
- Denervation: Distal
- Myopathy: Proximal
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: Sporadic mitochondrial myopathy syndromes with multiple mtDNA deletions
- Onset: 20 to 62 years
- PEO: All patients
- Myopathy: Most patients
- Dysphagia: 2 patients
- Neuropathy: Sensory-Motor; 1 patient
- MNGIE-like syndrome
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: SANDO (Hereditary sensory neuropathy)
- Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy, Dysarthria & Ophthalmoparesis
- Recessive inheritance
- POLG1 mutations in exo-domain: Lys319Glu 47; W748S; A467T
- Ataxic sensory neuropathy
- No Parkinsonism
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: Sensory neuropathy, PEO & Tremor
- Dominant inheritance
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: PEO + Severe axonal and demyelinating sensorymotor neuropathy
58
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous G763R
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset: 2nd decade
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal; Face
- Sensory loss: Distal legs; Panmodal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- PEO + Ptosis
- Bulbar: Dysphonia; Dysphagia
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axonal loss
- Nerve pathology: Axonal loss; Thin myelin sheaths
- Muscle: Ragged red fibers; COX- fibers
- Mitochondrial (Muscle): Complexes I, III & IV partially reduced
- Genetics
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: MIRAS
51
- Mitochondrial Recessive Ataxia Syndrome
- Epidemiology: Common in Finland (Carrier frequency 1:125), Russia & Europeans
- Genetics
- POLG1 mutations
- W748S + E1143G in cis
- Homozygous W748S or A467T
- Similar seen in MSCAE
- Inheritance
- Recessive
- Many sporadic cases
- POLG1 mutations
- Clinical: Hetergeneous
- Onset
- Age: Range 5 to 38 years
- Balance disorder
- Epilepsy
- Ataxia
- Gait & Limb
- Dysarthria
- Nystagmus (60%)
- Polyneuropathy
- Tendon reflexes in legs: Reduced or Absent
- Vibration sense: Reduced
- Pain: Some patients
- Electrodiagnostic changes (100%): Sensory neuropathy; Axonal loss
- Muscle: Strength reduced (30%); Cramps (25%)
- Epilepsy (50%)
- Cognitive impairmnent (80%): Mental retardation; Psychiatric
- Involuntary movements: Athetosis; Tremor
- Obesity (70%)
- Eye movement disorders: Mainly CNS; No PEO
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy
- White matter hyperintensity
- Olive hypertrophy
- Muscle: Denervation; Mitochondrial changes rare
- EEG: Abnormal background
- Brain MRI
- Carriers
- No prominent clinical phenotype
- Subclinical: Sensory polyneuropathy in majority
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: SCA + Epilepsy (MSCAE) 77
- POLG1 genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Homozygous: A467T; Gln497His; W748S
- Similar seen in MIRAS
- Clinical
- Onset: 2nd & 3rd decade
- Migraine
- Myoclonus or Myoclonic seizures
- Seizures
- Often presenting symptom
- Occipital lobe
- Scotomas
- Flickering
- Visual loss
- Visual hallucinations
- Simple partial: Motor; Involves arm or head
- Complex partial
- Secondary generalized epilepsy & Status epilepticus
- Treatment
- Sodium channel blocker + Benzodiazepine
- NOT Valproate
- Lamotrigine & Gabapentin: May increase myoclonus
- Ataxia
- Cerebellar
- Nystagmus
- Posterior column lesions
- Course: Chronic + Acute episodes
- Differential diagnosis
- Laboratory
- EEG: Seizure activity, Occipital
- MRI
- T2 high signal: Thalamus; Occipital cortex; Cerebellum
- Cerebellar: Atrophy; Dentate
- Olives: Enlarged
- Stroke-like lesions
- CNS pathology: Neurons
- Neurons
- mtDNA depletion
- Complex I (NDUFB8 stain): Progressively reduced
- Stroke-like lesions
- Neuron loss
- Correlate with epileptic foci
- Neurons
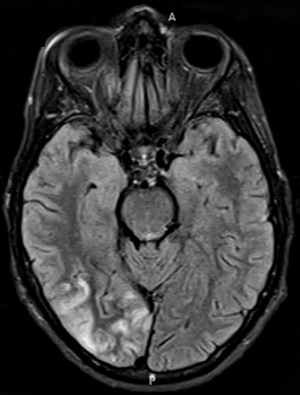
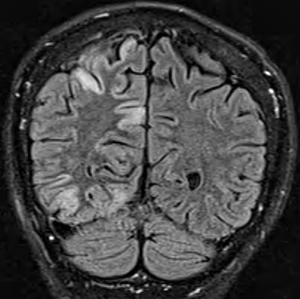
MSCAE - POLG1 Variant syndrome: Alpers
- Genetics
- POLG protein: Very low residual POLG activity
- Clinical
- Progressive neurological disorder
- Liver failure
- Laboratory
- mtDNA depletion in some patients (MTDPS4A)
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: Parkinsonism without External ophthalmoplegia
57
- Epidemiology: 2 Sisters
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Heterozygous; G737R & R853W
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 3rd decade
- Extrapyramidal: Parkinsonism or Dystonia
- Parkinsonism
- Weakness (50%): Distal, Mild
- EOM: Full
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum Lactate: High in one patient
- Serum CK: Normal
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers
- Oxidative metabolism: Reduced (50%) enzymes with mitochondrial subunits
- Nerve conduction studies: Polyneuropathy
- Axonal
- Sensory > Motor
- MRI: Moderate generalized cerebral & cerebellar atrophy
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: MELAS
- Mutations: Heterozygous missense; R627Q, G848S
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: MNGIE variant (MTDPS4B
 )
)
- Epidemiology: 5 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- POLG1 Mutations: Missense; P1073L; A467T; G848S
- Clinical
- Congenital myopathy
- Gastrointestinal pseudoobstruction
- Cachexia
- Neuropathy: Sensory, Ataxic
- Laboratory
- Muscle: mtDNA depletion
- Brain MRI: Basal ganglia & Thalamus Δ
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: PEO + Hypogonadism

- Epidemiology: Swedish family
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Hypogonadism
- Delayed sexual maturation
- 1° Amenorrhea
- Early menopause
- Testicular atrophy
- Cataracts
- CNS
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Tremor
- Parkinsonism
- Depression
- Mental retardation
- Polyneuropathy
- Vibratory loss: Distal; Symmetric
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Muscle
- PEO
- Bulbar: Dysarthria; Dysphonia
- Proximal weakness
- Rhabdomyolysis precipitated by alcohol: 1 patient
- Hypoacusis
- Pes cavus
- Hypogonadism
- Laboratory
- EMG: Myopathic
- Muscle biopsy
- Ragged-red fibers
- Cytochrome c oxidase negative muscle fibers
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: PEO + Cardiomyopathy

- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recesive
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st decade
- PEO
- Cardiomyopathy: Dilated
- Proximal weakness
- Course: Fatal in 2nd decade
- Pathology: Multiple mtDNA deletions; Ragged red fibers
- Genetics
- POLG1 Variant syndrome: Distal myopathy, Cachexia & PEO
143
● POLG1; Chromosome 15q26.1; Dominant or Sporadic- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Mutations: Leu896Arg (de novo); Tyr951His
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3rd or 4th decade
- Weakness
- Distal predominant
- Arms > Legs
- Bulbar: Dysarthria; Dysphgagia
- Cachexia: 1 patient
- Eyes
- Ptosis
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Cataracts
- Laboratory
- CK: Mildly high
- EMG: Myopathic
- NCV: Normal
- Muscle: Ragged red & COX- muscle fibers
- Muscle MRI: Fatty replacement
- Distal > Proximal
- Superficial > Deep
- Other family members
- No strong positive family history
- 1 with cataracts
- Epidemiology
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, Autosomal Dominant 4 (PEOA4; PEO 4)

● POLG2 (POLGB; POLGβ) ;
Chromosome 17q23.3; Dominant
;
Chromosome 17q23.3; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 2 generation family + Sporadic patient
- Genetics
- POLG2 protein
- Accessory subunit of DNA polymerase
- Catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase: POLG
- Component of mitochondrial replication machinery
- Dimer contains distinct sites for POLGA binding, dimerization, & DNA binding
- Mutated protein: Promotes mtDNA deletions by stalling DNA replication fork
- Accessory subunit of DNA polymerase
- Clinical: PEO + Systemic
- Variable severity
- Onset
- Age: Infancy to 30 to 40 years
- Ptosis
- Ocular
- Ptosis
- External ophthalmoplegia
- Muscle
- Exercise intolerance
- Pain
- Weakness: Mild
- Face
- Limbs
- CNS: Seizures & Hypotonia in younger onset patients
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Glucose tolerance: Impaired
- Cardiac conduction defect: Left bundle branch block; Intermittent bigeminy
- Lactate: High
- Serum CK: 664
- Muscle
- Histology: COX- muscle fibers or Normal
- Oxidative enzyme activity: Normal
- Mitochondria: Abnormal morphology
- CNS: Younger onset patients
- Cerebellar atrophy
- POLG2 variant syndrome: Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 16A (Hepatic type) (MTDPS16A)

- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Homozygous; Arg182Trp
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 months
- Poor feeding
- Difficulty breathing
- Abdominal distention
- Hepatic failure
- Death: 9 months
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- Lactate: High
- Liver enzymes & Bilirubin: High
- Coagulopathy
- Carnitine profile: Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Muscle biopsy: Histology normal
- Liver biopsy: Microvesicular steatosis, Cholestasis, Panlobular fibrosis, Mitochondria abnormal
- mtDNA depletion (20% to 25%): Liver & Muscle
- Brain MRI: Thin corpus callosum
- POLG2 variant syndrome: Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 16B (Neuroophthalmic type) (MTDPS16B)

- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Missense; D433Y
- Clinical
- Headaches
- Eye
- Vision loss: Progressive to severe
- Optic atrophy
- CNS
- Ataxia
- Chorea
- Peripheral neuropathy: Axonal
- Ovarian failure
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cortical & Cerebellar atrophy
- Retina: Thin
- Mitochondrial DNA to nuclear DNA ratio in Blood: Reduced
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, Autosomal Dominant (PEOA6)
 156
156
● DNA replication helicase 2, yeast, homolog of (DNA2) ;
Chromosome 10q21.3; Dominant
;
Chromosome 10q21.3; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 9 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Ala221Gly; Arg284His; Lys313Glu; Ser552Leu; Ser640Leu; Val723Ile;
p.Asn568Ilefs*4 (c.1703delA); p.Gln630ter, Arg956His - Clinical correlations
- Mutations: Ala221Gly; Arg284His; Lys313Glu; Ser552Leu; Ser640Leu; Val723Ile;
- DNA2 protein
- Location: Mitochondria ? + other
- Helicase/nuclease family
- Interacts with: POLG1
- Functions: Probably involved in
- mtDNA replication
- Long-patch base-excision repair (LP-BER)
- Contains ATPase domain
- Common mutation effects
- Nuclease & ATPase activities: Abnormal
- mtDNA maintenance: Impaired
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital to 7th decade
- Weakness
- Proximal > Distal
- Legs ± Arms
- Muscle features, other
- Hypotonia
- Myalgia
- Exertional dyspnea
- Small size
- Eye: Ptosis or Ophthalmoplegia (75%)
- Skeletal
- Lordosis
- Arthrogryposis: Early onset patients
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX- or SDH+ fibers (0.2% to 5%)
- mtDNA deletions
- Type 2 atrophy (1 patient)
- Serum CK: Normal or Mildly high
- EMG: Normal or Myopathic
- Muscle
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, Autosomal Dominant (PEOA)
316
● Guanosine monophosphate reductase (GMPR) ;
Chromosome 6p22.3; Dominant
;
Chromosome 6p22.3; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.547G>C, Causes abnormal splicing
- GMPR protein
- Cytosolic
- Purine metabolism enzyme
- Catalyses conversion of ribonucleotide GMP to IMP
- Clinical
- Onset age: 7th decade
- Eyes: Ophthalmoplegia; Ptosis
- Orbicularis oris: Mildly weak
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology: SDH+ & COX- fibers; Multiple mtDNA deletions
- PEO 2/3
- Disorder mistakenly localized to Chromosome 3p
- See PEO 2/3
- Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions, autosomal dominant 3 (PEOA3; PEO 1)
PEO: Autosomal Recessive
- Differential diagnosis
- PEO + Myopathy & Parkinsonism
22
● Autosomal Recessive- Epidemiology: Libyan Sephardic Jewish family
- Onset
- 30 to 74 years
- Ptosis or Extrapyramidal signs
- Clinical
- Extrapyramidal: Akinesia; Rigidity; Rest tremor
- Eyes: Ptosis; Ophthalmoplegia
- Myopathy: Proximal & Facial weakness: Occasional distal leg weakenss
- Hearing loss (50%)
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Mitochondrial proliferaion: SDH +, COX - muscle fibers
- Biochemistry: Reduced complex III + Varied other complexes
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Muscle
- PEOB1: POLG mutations
- Hereditary sensory neuropathy + Ophthalmoplegia (SANDO)
 1
1
● Polymerase, DNA, Gamma (POLG; POLG1) ; Chromosome 15q26.1; Recessive or Dominant
; Chromosome 15q26.1; Recessive or Dominant
- Nosology: SANDO (Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy Dysarthria Ophthalmoparesis)
- Epidemiology
- > 63 patients
- 10% to 15% of sporadic & recessive ataxias: Many also with PEO
- Male 55%
- Genetics: Recessive syndromes
- Common mutation: A467T
- Compound heterozygotes or homozygotes
- May be associated with other clinical syndromes
- Other mutations: Missense; N468D, G517V, G737R, W748S, R1138C, E1143G
- Gene locations: Exons 2 to 21
- Recessive POLG disorder mutation features
- > 35 described
- Compound Heterozygous
- Missense
- One in linker region
- One in polymerase region
- More common than dominant mutations
- Full SANDO syndrome: POLG Mutation frequency 78%
- Allelic disorders
- SANDO syndromes also produced by
- Common mutation: A467T
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 5 to 73 years; Mean 4th decade
- Exercise intolerance
- Ptosis
- Paresthesias
- Neuropathy: 1st manifestation
- Sensory loss
- Large & Small fiber: Vibration; JP; Temperature
- Sensory ataxia: Ataxic gait; Pseudoathetosis
- Small fiber modality loss may be earliest feature
- Strength: Variable
- Normal, Distal weakness or Diffuse weakness
- Gait: Unsteady; Sensory ataxia
- Tendon reflexes: Absent or Reduced
- Sensory loss
- Later signs
- PEO: Ptosis; Ophthalmoplegia
- Ataxia
- Other cranial nerves: Dysarthria; Facial weakness
- CNS: Myoclonic epilepsy; Depression; Parkinsonism
- Course
- Progressive
- Death
- Age: As early as 4th decade
- Due to epileptic status in some patients
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Axonal neuropathy or Neuronopathy
- SNAPs: Absent or Reduced amplitude
- EMG
- Denervation (90%): Distal ± Proximal
- Myopathy (40%): Proximal
- Lactate: High in CSF & Serum in some patients
- Serum CK: Normal or Mildly elevated
- CNS: Some patients
- Brain MRI: Abnormal in 70%
- Degeneration: Spinocerebellar & dDorsal column tracts
- Thalamic lesions in some patients
- Cerebellum (40%): Atrophy or White matter changes
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Muscle Pathology: Variable
- Ragged red fibers: COX + and COX -
- SDH+ muscle fibers
- May be Normal
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzyme activities: Often normal
- Citrate synthase: May be increased
- Nerve pathology
- Loss of myelinated & unmyelinated axons
- Axonal regeneration
- CNS pathology
127
- Spinal cord: Posterior column atrophy
- Dorsal root ganglia: Neuron loss
- Mitochondrial DNA copy number: Reduced in affected neurons
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Reduced activity of Complexes I & IV
- Electrophysiology: Axonal neuropathy or Neuronopathy
- Variant syndrome: Sensory neuropathy with Dominant POLG mutation
- Mutations: Ala889Thr missense in cis with Glu1143Gly polymorphism
- Sensory neuropathy
- Tremor
- PEO
- Variant syndrome: Ataxia + Sensory neuropathy, Recessive
105
- POLG mutations
- Frequency: 23% of patients with clinical syndrome
- Type: Homozygous intronic; Homozygous W748S; Heterozygous missense
- Onset age: 18 to 39 years
- Sensory neuropathy: Axonal
- No ophthalmoplegia
- POLG mutations
- Also see
- PEO + Myopathy & Respiratory failure (MTDPS11)
 154
154
● Mitochondrial genome maintenance exonuclease 1 (MGME1; c20orf72)
 ; Chromosome 20p11.23; Recessive
; Chromosome 20p11.23; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Trp152X; Tyr233Cys
- MGME1 protein
- Mitochondrial RecB-type exonuclease
- PD(D/E)XK nuclease superfamily
- Cleaves single-stranded DNA
- Processes DNA flap substrates
- Essential for mitochondrial genome maintenance
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: < 20 years
- Ptosis
- Eye
- Ptosis
- Ophthalmoplegia, External
- Muscle
- Weakness
- Proximal
- Respiratory failure: With disease progression
- Face
- Dysphonia
- Dysphagia
- Course: Slow progression
- Wasting
- Progressive to emaciation
- Scapular winging
- Weakness
- CNS: Mental retardation; Memory defecits
- Spinal deformities: Rigid; Lourdosis; Kyphosis
- Cardiac: Myopathy or Arrythmias
- Gastrointestinal (GI): Nausea, Flatulence, Abdominal fullness, Diarrhea - recurrent, Loss of appetite
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Histochemistry: SDH+ & COX- fibers
- mtDNA
- Multiple deletions: Larger size than with POLG1 mutations
- Depletion: Reduced copy number
- 7S DNA (single-stranded component of the mtDNA displacement loop (D loop)): Increased
- Respiratory chain: Complex I or I+IV deficiencies
- MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
- Muscle
- External ophthalmoplegia, Exercise intolerance & Encephalopathy (PEOB2)
 196
196
● Ribonuclease 1 (RNASEH1) ; Chromosome 2p25.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 2p25.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 6 families; 13 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.G424A, p.Val142Ile; c.C469T, p.Arg157*; c.C554T, p.Ala185Val
- RNASEH1 protein
- Endonuclease
- Present in nucleus & mitochondria
- Digests RNA component of RNA-DNA hybrids
- Nuclei, but not mitochondria, have 2nd ribonuclease: RNase H2
- mtDNA replication
- Clinical
- Onset age: 13 to 45 years
- Eye movement limitation
- Onset: Early in disease course
- External ophthalmoplegia: Progressive
- Ptosis
- Muscle
- Exercise intolerance
- Myalgias
- Weakness: Truncal > Limb
- Dysphagia
- Respiratory: Late
- Some patients: Face; Posterior neck
- Tendon reflexes: Increased or Decreased
- Ataxia: Gait disorder, Dysmetria, Dysarthria
- Other CNS: Some patients
- Cognitive impairment
- Spastic paraparesis
- Differential diagnosis: SANDO syndromes
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- SDH+, COX- muscle fibers
- Oxidative enzyme abnormalitites: Complexes I & IV reduced
- mtDNA: Multiple different abnormalities or Reduced
- Ultrastructure: Elongated, hyperfused mitochondria
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar > Bulbar atrophy
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
- NCV: Mild neuropathy, ? demyelinating features
- EMG: Denervation
- Muscle
● Topoisomerase, DNA, III, ALPHA (TOP3A)
- Epidemiology: 13 patients
- Genetics
- TOP3A protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix & Nucleus
- Topoisomerase
- Forms complex with: Helicase BLM; OB-fold proteins RMI1 & RMI2
- Function
- Unlinking of parental strands at final stage of nuclear & mitochondrial DNA replication
- ssDNA decatenation activity
- Break one strand of DNA: Allows relaxation of negatively supercoiled DNA & separation of hemicatenated molecules
- Loss of mitochondrial TOP3A activity: DNA replication stalling throughout mtDNA
- PEOB5: Moderate loss of TOP3A activity
- Clinical
- Onset age: 15 years to 7th decade
- Eyes: Ptosis; External ophthalmoplegia
- Weakness: Neck; Proximal, Distal or Generalized
- Fatigue & Myalgia
- Sensory loss
- Ataxia: Dysmetria; Dysarthria; Gait
- Tendon reflexes: Normal
- Mood disorder
- Cardiac: Arrhythmias; Pacemaker
- Hearing loss: High frequency
- Short stature
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 251 to 2,000
- NCV: Sensory or Sensory-Motor Neuropathy; Axon loss
- EKG: Tachycardia; LVEF reduced
- Muscle
- Histology: COX- fibers; Complex I negative fibers
- Small duplications in mtDNA non-coding region (NCR)
- mtDNA deletions: Prominent breakpoints at end of NCR
- Cardiac: A-V conduction block
- Muscle CT: Posterior thigh muscles small
- Diabetes
- Brain MRI: cerebellar atrophy
● Ribonucleotide reductase catalytic subunit M1 (RRM1)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients; 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Homozygous; Arg381His, Arg381Cys
- Allelic disorder: PEO, Dominant
- RRM1 protein

- Large subunit (R1) of ribonucleotide reductase: Substrate-binding catalytic site
- Ribonucleotide reductase
- Catalyzes biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides
- Rate-limiting step for for DNA synthesis
- Nucleotide salvage disorders with Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Clinical
- Onset age: 7 to 61 years
- GI: Dysmotility; Nausea & Vomiting
- Dysphagia: Cachexia
- PEO: Ophthalmoplegia; Ptosis
- Myopathy: Weakness; Gait disorder; Face
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Usually normal; May be milldly high
- Muscle pathology
- Frequent COX- & SDH+ muscle fibers
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Limb MRI: Muscle atrophy
- RRM1 variant disorder: PEO, Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: N427K (Catalytic site)
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Onset age: 40 years
- Eye: Ptosis; Ophthalmoplegia
- Dysphagia
- Hearing loss
- Muscle: Atrophy
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology
- Frequent COX- & SDH+ muscle fibers
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Muscle pathology
● Endponuclease G, Mitochondrial (ENDOG)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.61delG; Arg245Leu + Thr246Ile
- ENDOG protein
- Nuclease
- Activated by apoptotic stimuli
- Induces nucleosomal fragmentation of DNA
- Mitochondrion-specific
- Intermembrane space & bound to Inner membrane
- Translocates to nucleus during apoptosis
- Cleaves chromatin DNA into nucleosomal fragments independently of caspases
- Other functions
- Paternal mitochondrial elimination in early embryogenesis
- Autophagy
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- Eyes: External ophthalmoplegia; Ptosis
- Weakness: Face; Limbs, Proximal > Distal; Gait disorders; Dysphagia
- Fatigue
- Muscle cramps
- Exercise intolerance
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle
- mtDNA deletions
- Complexes I, III & IV activities reduced
- ENDOG protein: Absent
Myopathy, Myoglobinuria & Fatigue: Mitochondrial Disorders
|
Autosomal Dominant Autosomal Recessive Maternal Sporadic Myoglobinuria |
Mitochondrial disorders: Sporadic Myopathy & Fatigue syndromes
- Myopathy with large mtDNA mutations
- Kearns-Sayre: Single large mtDNA deletion
- Large scale tandem mtDNA duplication
- Myopathy with point mutations in tRNA genes: No eye signs
- tRNALeu (UUR) (A3243G): Myoglobinuria; Multiple other presentations (MELAS)
- tRNALeu (UUR) (T3250C): Riboflavin responsive myopathy/ SIDS
- tRNALeu (UUR) (A3302G): Myopathy
- tRNAPro (G15990A): Myopathy, childhood
- tRNAPhe (T618C): Myopathy
- tRNAMet (T4409C)
 : Myopathy; Exercise intolerance; Growth retardation
: Myopathy; Exercise intolerance; Growth retardation - tRNASer (UCN) (G7497A; A7480G): Myopathy; Deafness; Dementia; Ataxia
- tRNAAsp (A7526G): Exercise intolerance & Fatigue
- Also see: Maternal myopathies
- Myopathy with point mutations in tRNA genes: Eye signs present
- Exercise intolerance
- Myopathy, Exercise intolerance, Encephalopathy, Lactic acidemia

● Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit III (Complex IV)
- Exercise intolerance, Proximal weakness ± Myoglobinuria
● Cytochrome b (MTCYB; Complex III)
- Exercise intolerance ± Mild weakness:
Several mitochondrial genes identified
-
●
mtRNA Trp
 : T5543C
: T5543C
● Cytochrome b (Complex III) : A14846G
: A14846G
● MTND1 (Complex I) :
Inversion of 7 nucleotides; Preserves reading frame
:
Inversion of 7 nucleotides; Preserves reading frame
● MTND2 (Complex I) : 2 bp deletion
: 2 bp deletion
● MTND4 (Complex I) : G11832
: G11832
- Coenzyme Q10 deficiency
- Also see: Myopathies with Pain & Myalgias
- Myopathy, Exercise intolerance, Encephalopathy, Lactic acidemia
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Inflammatory myopathies
- Myopathy with aging
- Other
- Myopathy, Exercise intolerance, Encephalopathy, Lactic acidemia
● Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit III (MTCO3) (Complex IV) ; Mitochondrial
; Mitochondrial
- MTCO3 encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 9207 & 9990
- MTCO3 Mutations
- G9952A point mutation at 3' end of gene
- Stop codon
- Heteroplasmic
- Sporadic: Not maternally inherited
- Deletion: 5 amino acids, in frame
- Insertion: 1 base pair
- Missense: T9789C (S195P), Probably maternally inherited
- G9952A point mutation at 3' end of gene
- COX III protein
- Forms catalytic core of Cytochrome c oxidase with COX I & COX II subunits
- Associated 10 nuclear subunits: Modify or stabilize complex; No mutations found
- Clinical
- Onset: 4 to 20 years
- Muscle
- Weakness: Proximal; Some patients
- Myalgia & Fatigue
- Myoglobinuria
355
- Mutations
- Deletion & Missense mutations
- Heteroplasmy: High in muscle
- Associated with
- Exercise, prolonged
- Also: Fever; Fasting; Medication
- Muscle pathology: COX- muscle fibers
- Mutations
- CNS syndromes
- Encephalopathy: Recurrent
- Migraine
- Spastic paraparesis, Mental retardation & Ophthalmoplegia: 1-base pair insertion (9537C)
- Lab
- Serum CK: High or Normal
- Serum lactate: High
- Biochemistry: Isolated COX deficiency
- Pathology
- Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) activity: Reduced in 90% of muscle fibers
- SDH positive fibers: Few; Many in patient with deletion
- Lipid accumulation in type I fibers
- Severe reduction in COX activity (10% to 20% residual)
- Immunohistochemistry: Reduced COX II & COX III subunits in COX- fibers
- Variant: Isolated myopathy
- Somatic nonsense mutation: G9379A
- Clinical
- Childhood: Severe weakness
- Course: Improvement in teens to near normal
- Pathology
- Childhood: Severe diffuse COX deficiency; Mutation load 93%
- 20 years: Persistent RRF (47%) & COX+ fibers (14%); Reduced mutation load (50%)
- Other COX III syndromes
- Myoglobinuria
- Maternally inherited myopathies
- MELAS-like disorder
- Leigh-like: Homoplasmic m.C9537insC frameshift
- Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)-Myoclonic epilepsy: Homoplasmic T9957C
- MTCO3 encoding
- Myoglobinuria & Exercise intolerance
● Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit I (MTCO1) (Complex IV) ; Mitochondrial
; Mitochondrial
- Genetics
- Encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 5904 & 7444
- Mutation: G5920A
- Nonsense
- Heteroplasmic: Especially abundant in COX negative muscle fibers
- Sporadic: Not maternally inherited
- Also see
- Encoding
- Onset
- Childhood
- Exercise intolerance
- Clinical
- Myoglobinuria: Recurrent
- Exercise intolerance: Fatigue
- Strength between episodes: Normal
- Lab at rest
- Serum CK: Normal
- Serum lactate: Normal
- EMG: Normal
- Exercise testing: Low oxygen use by muscle
- Biochemistry: COX deficiency; Mild defects in complex I & III
- Muscle Pathology
- Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) immunostaining
- Reduced for mitochondrial encoded COX I & COX II
- Normal for nuclear encoded COX IV & VIc
- SDH positive fibers: COX reduced
- Many muscle fibers with reduced COX staining
- Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) immunostaining
- Other Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit I clinical syndromes
- Acquired sideroblastic anemia
- Deafness, Ataxia, Blindness, Myopathy
- Epilepsy partialis continua: C6489A
- Motor neuron disease: m.6020del5
- LHON
- Myopathy, Cardiomyopathy, Stroke: Homoplasmic C6328T
- MELAS-like: C6597A; G7023A
- ? Myopathy: Proximal, Adult onset; Inflammation; A7222G, Only 24% Heteroplasmy
- Genetics
- Exercise intolerance, Proximal weakness ± Myoglobinuria
● Cytochrome b (MTCYB; Complex III) ; Mitochondrial
; Mitochondrial
- Genetics: Sporadic syndromes; Also see Familial myalgias
- MTCYB encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 14747 & 15887
- Heteroplasmic: Muscle specific mutations in mtDNA
- Mutation types: Most point; G to A
- Nonsense: G15059A; G15084A; G15168A; G15723A; G15762A
- Missense: G14846A
- Deletion: 24-bp; Nucleotides 15498 to 15521
- ? Frequency of mutations in this gene related to oxidative damage
- MTCYB encoding
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- Exercise intolerance
- Progressive with age
- Sensation of cramps, myalgias or fatigue
- Precipitants: Normal daily activities; Chewing
- Weakness
- Proximal limb: Mild
- Face: Occasional
- EOM: Normal
- Myoglobinuria: Some patients (28%)
- CNS: Septo-optic dysplasia; Retardation; Encephalopathy & Seizures
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Serum CK: Normal at rest
- EMG: Mildly myopathic
- Muscle biochemistry: Deficient Complex III activity
- Muscle morphology
- Ragged red fibers (5% to 22%); All SDH + & COX +
- Some mutations: Reduced Complex III staining in some muscle fibers
- Cytochrome b (MTCYB) mutations: Variant syndromes
- Encephalopathy & Seizures
- Mutation: G15242A
- Clinical
- Onset
- 9 to 13 years
- Exercise intolerance
- Lactic acidosis
- Encephalopathy
- Episodic
- Poor balance
- Seizures: Complex partial
- Visual hallucinations
- Psychiatric problems: Depression, Emotional lability
- Onset
- Laboratory
- EEG: Abnormal
- Muscle: Ragged red fibers
- Treatment: Menadione + Ascorbate
- Septo-optic dysplasia
 21
21
- Mutation: T14849C; Heteroplasmic
- Clinical
- Mental retardation
- Motor: Delayed walking; Exercise intolerance
- Eye: Retinitis pigmentosa; Optic atrophy
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; Wolff-Parkinson-White
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI: Septo-optic dysplasia; Cerebellar hypoplasia
- Familial myalgia syndrome
5
- Mutation: Missense T15747C; Homoplasmic
- Myalgias
- Muscle pathology: Lipid storage
- Also see: Sporadic exercise intolerance
- Exercise intolerance: A14846G
- LHON
- Colon cancer
- Cardiomyopathy: Noncompaction of left ventricular myocardium (LVNC)
- MELAS
- Migraine, Epilepsy, Polyneuropathy, Stroke-like episodes: T14864C, Heteroplasmic
- Parkinsonism overlap: 4-BP Del, 14787TTAA
- Obesity, susceptibility to: Gly251Ser
- Encephalopathy & Seizures
- Genetics: Sporadic syndromes; Also see Familial myalgias
- Exercise intolerance ± Mild weakness
9
- Mutations in several mitochondrial genes identified
● mtRNA Trp : T5543C
: T5543C
● Cytochrome b (Complex III) : A14846G
: A14846G
● MTND1 (Complex I) :
Inversion of 7 nucleotides; Preserves reading frame
:
Inversion of 7 nucleotides; Preserves reading frame
● MTND2 (Complex I) :
2 bp deletion
:
2 bp deletion
● MTND4 (Complex I) : G11832
: G11832
- Genetics
- Usual mutations: Heteroplasmic
- MTND2 mutation
187
- Homoplasmic
- Tissue distribution: Only present in muscle
- Paternal inheritance
- Clinical features
- Onset: Childhood
- Examination
- Weakness: Mild; Proximal
- May be Normal
- Exercise: Dyspnea; Tachycardia; Intolerance
- Mutations in several mitochondrial genes identified
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High, especially with exercise
- Biochemistry
- ND2 mutation: Complex I deficiency, Isolated
- Working muscle not able to extract available O2
- Muscle: Ragged red fibers, Some are COX +
- Serum CK: Mildly high
● mtRNA Met (MTTM)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Heteroplasmic; G4403A, T4409C; G4450A
- Other MTTM mutations
- A4415G + COX III mutation; Heteroplasmic: Exercise intolerance & Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy + Lactic acidosis
- A4435G: LHON modulator/Hypertension risk factor:
- G4412A
274
- Childhood onset, High heteroplasmy: Seizures, Myopathy, Basal Ganglia Δ
- Adult onset, Low heteroplasmy: Hearing Δ, Ataxia, Dementia, Myopathy
- Clinical
- Onset age: 10 to 56 years
- Myopathy
- Weakness: Proximal & Distal
- Exercise intolerance
- Muscle atrophy
- Ptosis: Mild; Asymmetric
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in arms
- Growth retardation: Some patients
- Mental retardation: Some patients
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Serum CK: High (600)
- EMG
- Myopathic
- Complex repetitive discharges
- Positive sharp waves
- NCV: Normal
- Muscle
- Mitochondrial
- Ragged red fibers
- COX negative fibers
- Dystrophic
- Muscle fibers
- Internal nuclei
- Size: Varied
- Necrosis
- Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
- Muscle fibers
- Mitochondrial
- Brain MRI: Cortical atrophy
- C-spine MRI: Myelomalacia
● mtRNA Lys (MTTK)
- Epidemiology: Japanese patients
- Genetics
- Homoplasmic
- A8291G mutation reported in few healthy controls
- Patients all had other similar mtDNA polymorphisms
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Adult; 15 to 69 years
- May be acute or subacute
- Myopathy
- Weakness
- Proximal
- Symmetric
- Mild
- Dysphagia: Some
- Myalgias: Episodic
- Weakness
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High, episodic
- Usual: 67 to 320
- Episodic: 200 to 11,000
- Muscle biopsy: SDH+ & COX- muscle fibers
- Serum CK: High, episodic
- Other MTTK mutations
Mitochondrial myopathy: Maternal; mtDNA Point Mutations
|
Cytochrome c Oxidase: Subunit 2 Mitochondrial tRNA mutations Sporadic myopathies |
- tRNAs
- Leu (MTTL1)
 : Cramps & Weakness (A3288G)
: Cramps & Weakness (A3288G)
- Leu (MTTL2)
 : Isolated myopathy (A12320G)
: Isolated myopathy (A12320G)
- Pro
 : Myopathy
: Myopathy
- Met
 : Myopathy; Exercise intolerance (T5543C)
: Myopathy; Exercise intolerance (T5543C)
- Ser
 : Myopathy; Exercise intolerance (G7497A + other)
: Myopathy; Exercise intolerance (G7497A + other)
- Gln
 : 1st decade; Weakness; Ptosis; dysphonia; Dysphagia (4366insA)
: 1st decade; Weakness; Ptosis; dysphonia; Dysphagia (4366insA)
- Glu
 : With diabetes (T14709C)
: With diabetes (T14709C)
- Trp
 : Encephalomyopathy (G5521A)
: Encephalomyopathy (G5521A)
- Asp
 : 1st decade; Exercise intolerance & Fatigue (A7526G)
: 1st decade; Exercise intolerance & Fatigue (A7526G)
- Phe
 : Late onset (G622A)
: Late onset (G622A)
- Leu (MTTL1)
- Myopathy
- Clinical
- Weakness
- Distribution: Proximal > Distal; Symmetric; ± PEO
- May be normal strength with subclinical myopathy on EMG or biopsy
- Respiratory, Episodic
- Exercise intolerance
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Riboflavin sensitive: tRNA Leu mutation (T3250C)
- Weakness
- Laboratory
- Serum CK
- Normal or high
- Especially increased with tRNAMet mutation
- Lactate (serum): Increased at rest or after exercise
- Serum CK
- Muscle pathology
- Myopathy
- Fiber size variability
- Connective tissue: Especially increased with tRNAMet (U4409C) mutation
- Mitochondrial proliferation: Ragged red fibers (GT stain); Dark SDH stain
- Cytochrome oxidase - (COX-) muscle fibers
- Frequency: Up to 50%; greater with increased age
- Mutant DNA more abundant than in normal fibers
- Electron microscopy
- Abnormal mitochondrial morphology
- Paracrystalline inclusions
- Usually not diagnostically useful with normal light microscopic histochemistry
- Myopathy
- Clinical
- Associated systemic syndromes
- MELAS
- MERRF
- Encephalopathy


- PEO and sudden death

- Cardiomyopathy

- Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit II (COX II; COX2; MTCO2) (Complex IV)

- Encoded by
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 7586 & 8294
- COX II protein
- Clinical syndromes: General
54
- Variable syndromes
- High mutation load: Associated with Multi-organ involvement, MELAS & Early onset
- Severity: Less than with recessive mutations in nuclear encoded COX assembly genes
- Myopathy
- Onset: Childhood to Teens
- Weakness: Distal or Proximal predominant
- Fatigue & Exercise intolerance
- May occur in isolation or with CNS signs
- Rhabdomyolysis: Some patients; T7989C
- CNS: Ataxia; Retinopathy; Optic atrophy
- Variable syndromes
- Genetic associations
- Mutations generally heteroplasmic
- T7587C
- Maternal inheritance
- Myopathy + CNS
- T7671A mutation
- 90% of DNA in muscle; 5% in blood
- Sporadic
- Myopathy
- Mechanism
- Reduced Assembly of COX enzyme
- Reduced Anchoring of COX II in mitochondrial membrane
- G7970T mutation (E129X)
- Myopathy
- Many COX- fibers
- Severe reduction in COX activity (10% to 20% residual)
- Lipid in type I fibers
- Fiber size: Mild variation
- Many COX- fibers
- Cataracts
- Hearing loss: Sensory-neural
- Ataxia
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Depression
- Short stature
- Lactic acidosis
- Myopathy
- G8009A: Somatic mutation found in colorectal cancer
- Biochemistry
- Lactate: Mildly increased in serum or CSF
- Oxidative enzymes: Selective reduction in COX activity
- Muscle pathology
- COX deficiency in 97% of muscle fibers: All COX subunits reduced
- Mitochondrial proliferation: Increased SDH stain, mild to moderate
- Encoded by
- Myopathy, Deafness & CNS disorders
41
● Mitochondrial tRNASer(UCN) (MTTS1) ; Sporadic
; Sporadic
- Genetics
- Mutation: A7480G; Heteroplasmic
- Mutation location: Anticodon loop sequence A36A37A38 recognised by TRIT1
- Causes a loss of i6A37 mtRNA modification
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical: Mitochondrial myopathy +, Sporadic
- Onset
- Age: 1st decade
- Gait disorder: Weakness or Contractures
- Weakness: Proximal
- Fatigue: Exertional
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Ataxia: Limb & Trunk
- Cognitive impairment
- Eye: Optic atrophy
- Contractures: Ankle
- Dystonic movements: Face
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Myopathy: Fiber size variation
- Lipid; Increased in some fibers
- Mitochondrial pathology: Proliferation; COX- fibers (30%)
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I & IV reduced
- May be normal early in disease course
- COX- muscle fibers
- Heteroplasmic mutation
- Brain CT: Basal ganglia calcification; General atrophy
- NCV: Sensory axon loss
- EMG: Myopathic
- EEG: Low voltage
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Muscle
- mtRNASer(UCN) allelic disorders
- MELAS/MERRF overlap: T7512C; Heteroplasmic
- 7472insC mutation: Several syndromes
- Hearing loss, Ataxia & Myoclonus (HAM)
- Hearing loss (Heteroplasmy; High levels (90%)): T7445C; T7510C; T7511C
- Encephalopathy with cytochrome c oxidase deficiency
- Myoclonus, epilepsy, cerebellar ataxia & progressive hearing loss
- Skeletal myopathy, isolated: With exercise intolerance; Teen onset
- Muscle: G7497A mutation
- Myopathy: In family
- Exercise intolerance: Young female
- Muscle: G7453A
260
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth
- Muscle: Weakness & Fatigue
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Muscle: COX- muscle fibers (70%)
- Keratoderma, palmoplantar, with deafness: A7445G
- Sensorineural hearing loss
- Maternal inheritance
- Mutations: T7510C, T7511C & T7445C
- Heteroplasmic: High levels (90%); ? Low pathogenicity
- Some aminoglycoside induced: G7444A
- Genetics
● Mitochondrial tRNATrp (MTTW)
- Mutation
- G5521A
- Heteroplasmic in muscle (98%)
- Absent in leukocytes
- Clinical
- Onset: 50 years
- Eyes: Ptosis; No ophthalmoplegia
- Myopathy
- Weakness: Proximal; Mild
- Fatigue
- Muscle
- Histochemistry: SDH+, COX- muscle fibers
- Biochemistry: Cytochrome c oxidase reduction
● Mitochondrial tRNAGlu (MTTE)
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; T14709C
- Distribution of mutated mtDNA
- Homoplasmic or Heteroplasmic
- Most tissues
- Clinical correlations
- Symptoms in patients with mutation level > 80%
- Some homoplasmic patients (blood) are asymptomatic
- General: MTTE disorders
- Mutations: Very high level of heteroplasmy or homoplasmy in skeletal muscle
- Muscle: Constant & predominant involvement
- Allelic with
- Benign infantile mitochondrial myopathy with reversible cytochrome c oxidase (COX) deficiency
- Diabetes-deafness syndrome
- LHON: Helper mutation (A14692G)
- Mitochondrial myopathy with respiratory failure (A14687G)
- MELAS/LHON/DEAF: Helper mutation (A14693G)
- Progressive Encephalopathy (A14696G)
- Encephalomyopathy + Retinopathy (G14740A)
- Leukoencephalopathy (G14724A)
- Exercise intolerance (G14739A)
- Mitochondrial myopathy: Lipid type
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Teens or Adult; Occasional congenital
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Myopathy
- Weakness
- Proximal
- Orbicularis oculi
- Late: Respiratory failure
- Some patients described with FSH phenotype
- Progression: Slow
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory-Motor; Mild
- CNS: Some patients
- Cerebellar: Ataxia; Nystagmus
- Congenital encephalopathy
- Diabetes
- Onset
- Laboratory
- EMG: Myopathy
- NCV: Sensory-motor axonal neuropathy
- Muscle
- Myopathy: Endomysial fibrosis; Varied fiber size
- Mitochondrial morphology: Proliferation; COX- muscle fibers
- Biochemistry: Reduced Complex I & IV activity
- Cardiac muscle: Focal COX reductions, especially in left ventricle
- Mitochondrial myopathy: Lipid type

- Genetics: MTTE
 mutations
mutations
- Clinical
- Myopathy: Facioscapulohumeral (FSH) distribution
- Cerebellar disorder
- Diabetes
- Genetics: MTTE
- Other Mitochondrial tRNAGlu (MTTE)
 mutations
mutations
- C14680A
- Age: 14-year-old boy
- Clinical
- Myopathy: Exercise intolerance, Weakness (Face & Proximal)
- Ataxia
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Serum CK: High
- Muscle biopsy: SDH+ & COX- muscle fiberw
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complexes I, III & IV with reduced activity
- Mutant load: Highest in urine sediment & cheek mucosa
- T14687C
- Age: 16-year-old boy
- Clinical: Retinopathy, Severe myopathy with respiratory failure
- G14710A
- Age: 41-year-old woman
- Clinical: Ptosis, PEO, Pigmentary retinopathy, Migraine, Life-long exercise intolerance
- G14724A
- Age: 4-year-old boy
- Clinical: Mitochondrial myopathy, Leukodystrophy
- C14680A
Mitochondrial Myopathy: Autosomal Recessive disorders
- Benign "later-onset" myopathy with moderate reduction in mtDNA
- Congenital muscular dystrophy with mitochondrial structural abnormalities: CHKB; 2q13
- Cytochrome c Oxidase I
- Coenzyme Q10 deficiency
- Fatal infantile myopathies with severe mtDNA depletion

- TK2
- DGUOK (Hepatocerebral syndrome)
- Succinyl-CoA synthase (SUCLA2)
- Fatigue & Exercise Intolerance syndromes
- ACAD9
- COX6A2
- FLAD1 (MADD)
- Glutaricaciduria IIA (MADD)
- MIEF2 (MID49)
- SLC25A32: Riboflavin responsive exercise intolerance (RREI)
- TMEM126B
- TRMT5: COXPD26
- Iron-Sulfur Complex disorders: Myopathy + Rhabdomyolysis
- Myalgia syndrome, Familial
 :
Cytochrome b
(MTCYB; Complex III)
:
Cytochrome b
(MTCYB; Complex III)
- Myoglobinuria, Recurrent
- Metabolic
- Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase/3-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase/Enoyl-CoA Hydratase
- Alpha subunit (HADHA): Trifunctional protein, alpha subunit

- Beta subunit (HADHB): Trifunctional protein, beta subunit

- Alpha subunit (HADHA): Trifunctional protein, alpha subunit
- Ornithine aminotransferase deficiency
- Succinic Dehydrogenase deficiency: Biochemical defects
- SDH (Complex II) deficiency

- Succinic Dehydrogenase + Aconitase (Chromosome 12)

- SDH (Complex II) deficiency
- Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase/3-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase/Enoyl-CoA Hydratase
- mtDNA
- Myopathy with
- Abnormal Mitochondrial Translation
- Ataxia: MSTO1
- Cataracts & Combined Respiratory-Chain Deficiency: GFER
- CNS Δ: CIAO1
- Extrapyramidal Disorders: MICU1
- Lactic acidosis & Sideroblastic anemia (MLASA)
mtDNA Depletion Syndromes
- Fatal infantile myopathy with severe mtDNA depletion
 : General features
: General features
- Inheritance: Usually recessive
- Specific syndromes
- TK2: Onset 8 to 24 months
- DGUOK (Hepatocerebral syndrome): Onset 0 to 6 months
- Succinyl-CoA synthase (SUCLA2)
- Clinical
- Onset: birth to 14 months
- Death: 60% < 1 year
- Clinical: Weakness & hypotonia
- Family history positive in 50%
- Lactic acidosis in more severe cases
- Serum CK: Mildly, or Prominently elevated to > 1,000
- Some with renal dysfunction
- Muscle
- Ragged red fibers in 88%
- Cytochrome oxidase
- Activity: Very reduced or absent in extrafusil fibers
- Normal in spindles & arteries
- Most mitochondrial peptides absent
- COX VIIa,b selectively reduced
- Other nuclear-encoded mitochondrial enzymes normal
- Differential diagnosis
- Mitochondrial DNA depletion myopathy (MTDPS2)
 153
153
● Thymidine kinase, Mitochondrial (TK2) ;
Chromosome 16q21; Recessive
;
Chromosome 16q21; Recessive
- Epidemiology
- ~ 100 patients
- Geography: Moslem; Ashkenazi Jewish; Hispanic; Brazil
- Frequency of TK2 mutation in mtDNA depletion syndromes: 11%
- TK2 Mutations
- Missense: Most common; Asp11Gly, Ile22Met, Thr77Met, His90Asn, Thr108Met, Ile181Asn
- Exon 5: Hotspot for mutations
- Common mutations: Thr108Met, His121Asn
- Late onset: Lys202del
- Severe: Arg130Trp
- Allelic disorders: Same mutations may produce pediatric or adult disease
- TK2 protein
- Location: Mitochondria
- Tissue expression: Ubiquitous
- Phosphorylates nucleotides
- Deoxythymidine, deoxycytidine & deoxyuridine to monophosphate form
- Phosphate source: ATP
- Pyrimidine Nucleoside salvage pathway disorders
- Biosynthesis of DNA precursors necessary for
- Mitochondrial DNA replication
- Regulating levels of deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate pools
- Clinical
- Disease severity: Intra-familial variability
- Onset
- Age: Mean 11 months; Range 8 to 24 months
- Motor: Gait impairment; Hypotonia; Proximal weakness
- Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Proximal & Axial > Distal
- Respiratory failure: By 2 to 3 years
- Bulbar & Facial
- Exercise intolerance
- Eye: Ptosis; PEO in some patients
- Other: Hearing loss
- CNS: Early onset syndromes
- Seizures: Migrating focal
- Cognitive impairment
- Course: Progressive or Episodic
- Signs triggered by fever in some
- Severe cases
- Complete paralysis by 12 to 36 months
- Death: Childhood; Mean 3.5 years
- Treatment trial: Pyrimidine nucleoside
- Milder variants
- Weakness onset in childhood or adult: Slow progression
- Rapid worsening as adult
- Involvement of systems other than muscle & nerve: Rare
- Gynecomastia: 1 patient
- Probable treatment
- Laboratory: Myopathy & SMA-like changes
- Serum CK: High; 750 to 4,000
- Serum GDF15: High
- Muscle histology
- Partial denervation, chronic: Grouped atrophy (SMA-like)
- Myopathy: Active; Varied fiber size; Some patients
- Reduced COX staining, diffuse: May vary among muscle fibers
- SDH+ & COX- muscle fibers
- Lipid storage: Scattered fibers
- Mitochondrial changes in muscle
- Muscle MRI
310
- Involvement: Gluteus maximus, Sartorius, Gracilis, Gastrocnemius medial
- Plasma lactate: Normal or Elevated
- EMG
- Myopathic: Early in course
- Denervation changes: Develop in occasional patient 27
- Brain MRI: Atrophy in more severe syndromes
- Variant TK2 syndromes
- Milder clinical course: Onset > 12 years: Normal mtDNA amount
- Spinal muscular atrophy syndrome
- Rigid spine syndrome
- Severe myopathy with motor regression
- Myopathy: Adult onset
- Genetics
- Mutation: T108M; Homozygous
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4th decade (Mild symptoms in childhood)
- Weakness: Distal; Proximal; Respiratory; Face; Ptosis
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers
- mtDNA 30%
- Complex I, III & IV deficiency
- Genetics
- TK2 variant: PEOB3
 : Progressive external ophthalmoplegia, Adult onset
: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia, Adult onset
- Genetics
- Mutations: R225W; T230A
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5th decade
- Weakness: Proximal; Dysphagia; External ophthalmoplegia; Scapular winging, some
- Muscle: COX- muscle fibers
- Genetics
- Epidemiology
- Benign infantile mitochondrial myopathy with reversible cytochrome c oxidase (COX) deficiency
 103
103
● mt-tRNAGlu (MTTE) ;
Maternal
;
Maternal
- Nosology: Mitochondrial myopathy, infantile, transient (MMIT)
- Epidemiology: 12 familes
- Genetics
- Mutation: T14674C
- Homoplasmic
- Maternally inherited
- General: MTTE disorders
- Mutations: Very high level of heteroplasmy or homoplasmy in skeletal muscle
- Muscle: Constant & predominant involvement
- T14674C mutation: Only reversible phenotype
- Allelic disorders
- Myopathy, mitochondrial, with diabetes mellitus (T14709C)
- Diabetes-deafness syndrome
- LHON: Helper mutation (A14692G)
- Mitochondrial myopathy with respiratory failure (A14687G)
- MELAS/LHON/DEAF: Helper mutation (A14693G)
- Progressive Encephalopathy (A14696G)
- Encephalomyopathy + Retinopathy (G14740A)
- Leukoencephalopathy (G14724A)
- Exercise intolerance (G14739A)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Usually 1st weeks to 2.5 months
- Muscle weakness & Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Proximal > Distal
- Face
- Respiratory failure
- Dysphagia
- ± Ophthalmoplegia
- Hypotonia
- Macroglossia
- Neuropathy (40%): Axonal ± Demyelinating; Sensory > Motor; May be subclinical
- CNS: Seizures; Encephalopathy
- Liver: Hepatomegaly
- Course
- Spontaneous improvement: Common
- Begins at 5 to 20 months
- Normal by 2 to 3 years
- Residual features: Mild myopathy in some patients
- Survival: > 26 years; Pneumonia; Respiratory failure
- Spontaneous improvement: Common
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: All
- Serum CK: High in 60% to 1400
- MRI: Delayed myelination; Variable other changes
- Muscle pathology
- Ragged red fibers: SDH+; Early COX-; Later some COX+
- Cytochrome oxidase
- Early (1 to 4 months)
- COX activity 6% to 66%: Diagnostic < 30% of control
- COX VIIa,b & COX II selectively reduced
- Reduced in mosaic pattern
- Late: COX activity returns toward normal
- Early (1 to 4 months)
- Complex I: Reduced activity in some patients
- Fiber size: Variable
- Other: Increased lipid or glycogen in muscle fibers
- Occasional: Degeneration & Regeneration; Inflammation; Lipid droplets in fibers
- mtDNA: Moderate reduction
- Myopathy + Exercise intolerance
 78
78
● Iron-Sulfur Cluster Scaffold Protein (ISCU)
 ; Chromosome 12q23.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 12q23.3; Recessive
- Nosology: Myopathy with Lactic acidosis (HML)
- Epidemiology: Northern Swedish families
- Mutations
- g.G7044C (IVS5 + 382G>C)
- Homozygous
- Intronic
- Induces abnormal gene splicing
- ISCU transcripts with exon 4A more abundant in muscle
- Reduction of normal mitochondrial isoform (m-ISCU)
- Highest levels of abnormal mRNA in muscle
- Missense: Gly50Glu; Heterozygous with intronic splice mutation
- ISCU knockout mouse: Embryonic lethal
- Allelic disorders
- Mitochondrial myopathy, de novo, Dominant: Gly96Val
- Myopathy + Cardiomyopathy
- ISCU protein
- Primary scaffold on which Iron-Sulfur (Fe-S) clusters are assembled
- 2 isoforms in humans
- Cytosolic (ISCU1): Full length
- Mitochondrial (ISCU2): Exon 2 spliced out
- Regulation of cellular iron trafficking
- Iron-sulfur-cluster proteins
- Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters: Essential components of enzymes involved in
- DNA: Synthesis, Replication & Repair
- Chromosome segregation
- Ribosomes: Biogenesis & Protein translocation
- Mitochondria: Maturation of subunits of complexes I, II & III; Aconitases
- Heme & Cofactors: Synthesis of enzyme-bound cofactor lipoate in 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases
- Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster synthesis
- Assembly machinery: Protein Complex
- Fe-S Synthesis: Locations
- Fe-S Synthesis: Steps
- Formation of [2Fe2S] cluster by proteins forming core ISC assembly components
- Transfer to monothiol glutaredoxin 5 (GRX5) (Fe/S cluster transfer protein)
- Inserts [2Fe2S] cluster into mitochondrial [2Fe2S]-requiring proteins
- Generation of [4Fe4S] components
- Requires ISCA1 & ISCA2
- Integration into required metalloproteins
- Export of some Fe-S clusters to form cytosolic & nuclear proteins
- Post-Assembly: Nascent clusters
- ISCU scaffold protein binds to Co-chaperone/chaperone system
- System components: HSC20 (HSCB); HSPA9
- Complex enhances ISC transfer from the main scaffold ISCU
- Recipients: Proteins; Secondary carriers
- Fe-S cofactors delivered to recipient apoproteins
- Fe-S cluster disorders
- Mitochondria: Muscle biochemistry
- Common disorder: Complex II ± I or III deficiency
- Fe-S cluster containing proteins
- ACO2: Cerebellar-Retinal Degeneration, Infantile (ICRD)
- BOLA3: Infantile encephalopathy with multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions 2
- CISD2: Wolfram 2
- FDX1L (FDX2): Myopathy + Myoglobinuria (MEOAL)
- Frataxin: Friedreich ataxia
- ISCU (Aconitase deficiency): Myopathy ± Myoglobinuria
- NFU1: Infantile encephalopathy with multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions 1
- NUBPL: Encephalomyopathy (Complex I deficiency)
- Complex I core
- Biosynthesis of mitochondrial iron-sulfur [4Fe-4S] proteins
- ABCB7: Sideroblastic anemia & Spinocerebellar ataxia
- FDXR: Optic + Auditory neuropathy
- GFER: MPMCD
- GLRX5: Glycine encephalopathy with spasticity (SPAHGC); Sideroblastic anemia
- HSCB
 : Sideroblastic anemia
: Sideroblastic anemia
- HSPA9
 : Sideroblastic anemia 4
: Sideroblastic anemia 4
 ; Even-plus
; Even-plus

- IBA57: Encephalopathy
- ISCA1: Encephalopathy/Leukodystrophy
- ISCA2: Leukodystrophy
- LYRM4: Encephalopathy
- LYRM7: Encephalopathy
- PMPCB: Encephalopathy
- Fe-S cluster formation
- Mitochondria: Muscle biochemistry
- Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters: Essential components of enzymes involved in
- ISCU Clinical features: Homozygous splice site mutations
- Onset: Life long
- Fatigue
- Episodes: After minor exertion
- Shortness of breath
- Tachycardia
- Weakness
- Rhabdomyolysis: Some patients
- Muscle swelling
- Myalgias
- Cardiac: Mild hypertrophy
- Course: Non-progressive
- Exercise physiology
- Low maximal muscle oxygen extraction
- Exaggerated circulatory responses
- Exercise: Cardiac output/Oxygen utilization 2 to 4 times normal
- Biochemical defects
- SDH (Complex II) deficiency

- Succinic Dehydrogenase + Aconitase

 : Reduced
: Reduced
- Abnormality of muscle mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster-containing proteins
- Mature Rieske iron-sulfur protein of complex III
- Several subunits of Complex I
- SDH (Complex II) deficiency
- Serum lactate: High
- Pathology
- SDH staining in muscle fibers: Variably, but generally, reduced
- COX staining in muscle fibers: Reduced in some
- Iron: Increased (Prussian Blue) staining in SDH deficient muscle fibers
- Mitochondrial inclusions: Electron dense, Iron-rich
- ISCU protein: Severely reduced
- ISCU Variant syndrome: Myopathy + Cardiomyopathy
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Heterozygous splice site & missense mutations
- Clinical
- Muscle weakness: Severe; Proximal > Distal
- Exercise intolerance: Severe
- Slowly progressive
- Cardiomyopathy
- Laboratory
- EMG: Myopathic
- Muscle biopsy
- Internal nuclei
- Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
- ISCU protein: Moderately reduced
- Genetics
- MMDS8: Myopathy + Rhabdomyolysis with Reversible Leukoencephalopathy (MEOAL)
 169
169
● Ferredoxin 1-like protein (FDX1L; Feredoxin 2; FDX2) ; Chromosome 19p13.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 19p13.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Jewish-Moroccan & Brazilian patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.1A>T; c.431C>T (p.P144L)
- Feredoxin 2 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Adolescent
- Development: Normal or Optic atrophy
- Myopathy
- Weakness
- Episodic: Proximal; Dyspnea
- None between episodes
- Distal: May appear with neuropathy
- Myoglobinuria
- After exercise
- Resolution: Over days to weeks
- Muscle, other
- Fatigue
- Cramps
- Weakness
- Polyneuropathy
- Onset age: > 10 years
- Weakness: Distal
- Sensory loss: Ataxia; Reduced Vibration & Joint position sense
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Pes cavus
- CNS
- Optic neuropathy: Visual loss
- Nystagmus
- Pyramidal: Tendon reflexes brisk; Plantar response extensor; Spasticity, mild
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal at rest; 31,000 during episode
- Serum Lactate: High
- Serum FGF 21: Borderline high
- CBC: Anemia; Neutropenia
- MRI: Leukoencephalopathy
- NCV: Axon loss
- Muscle
- Ultrastructure: Normal
- Complex I, II & III activities reduced
- Levels: 6% to 36% of normal
- Complex II: Most severely reduced
- Aconitase: Reduced activity
- Citrate synthase: High
- Iron accumulation: In SDH- & COX- muscle fibers
- Complex II
- SDHA proteins: Reduced
- SDH stain: Regionally reduced
- COX stain: Regionally reduced
- Urinary organic acids: High Lactate, 3-Methyl glutaconic acid, Ketones & Krebs cycle metabolites
- Myopathy + Cataracts & Combined Respiratory Chain Defects (MPMCD)
 91
91
● Growth Factor, augmenter of liver regeneration ERV1-Like (GFER) ; Chromosome 16p13.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 16p13.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 7 patients, 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or Stop; R194H, c.217delG, c.219delC, c.259-25_259-24delCA
- GFER protein
- Nosology: Augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR)
- Iron-sulphur cluster assembly gene
- Function: Mitochondrial Disulfide Relay System
- ERV1/ALR protein family
- Expression: Ubiquitous; Low in muscle; High in testes & liver
- Small cysteine-containing
- Localization
- Long isoform: Intermembrane mitochondrial space (IMS)
- Short isoform: Nucleus
- Intramitochondrial import
- Requires cooperation of translocase of mitochondrial outer membrane (TOM) complex
- With Mia40-Erv1 disulfide relay system (DRS)
- Sulfhydryl oxidases
- Mutation effects in muscle & fibroblasts
- Reduction in activity of Complexes I, II, and IV activity
- Lower cysteine-rich protein content
- Enlargement of the IMS space
- Accelerated time-dependent accumulation of multiple mtDNA deletions
- Reduced co-localization with COX17, TIMM13 & COX6B1
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st month
- Cataract, congenital
- CNS
- Developmental (Psychomotor) delay ± Regression
- Epilepsy
- Dystonia & Chorea
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Muscle smallness
- Strength: Normal or Reduced
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Dysautonomia: Some patients; Absent tears, Polypneic crises, Unstable thermoregulation
- Skeletal: Scoliosis; Claw hand; Face dysmorphism
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers, scattered
- SDH+ muscle fibers, scattered
- Complex IV ± I & II: Reduced activity by 33% to 50%
- Ultrastructure: Abnormal mitochondria
- EMG: Myopathic or Normal
- Nerve: Axon loss in some patients
- Serum lactate: High
- Serum CK: Mildly elevated or Normal
- Brain MRI: Thin corpus callosum; Cerebellar & Brain atrophy
- Serum ferritin: Low
- Serum amylase: High
- Excretion of 3-methylglutaconic acid & 3-methylglutaric acid.
- Muscle
- Myopathy + Ataxia (MMYAT)
 219
219
● MISATO Mitochondrial distribution & morphology regulator 1 (MSTO1)
 ; Chromosome 1q22; Recessive
; Chromosome 1q22; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 30 families
- Genetics
- Mutations Loss of function: Missense, Splice site, Deletion, Stop Missense in tubulin domains
- ? Allelic disorder: Myopathy + Ataxia, Dominant
- MSTO1 protein
- Location
- Cytoplasmic
- Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Functions: Mitochondrial
- Morphology, intracellular distribution & fusion
- mtDNA regulation
- Location
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Most < 2 years; Oldest 53 years
- Motor delay
- Weakness: Proximal > Distal; Respiratory
- Cerebellar: Gait disorder; Intention tremor; Dysdiadochokinesis; Dysarthria
- Corticospinal tract: Spasticity; Tendon reflexes brisk
- Cognition: Normal or Learning difficulties
- Skeletal: Growth impairment; Scoliosis; Pes planus
- Eye: Optic neuropathy; Retinitis pigmentosa
- Liver disease
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar hypoplasia or atrophy
- Muscle MRI
- Diffuse thigh involvement
- Gracilis, Semimembranosus, Adductor longus & Biceps femoris: May be spared
- Serum CK: High; 300 to 5,000
- EMG: Myopathic
- Serum lactate: Normal
- Plasma citrullin: Reduced
- Muscle pathology
- Fiber size: Varied
- Endomysial connective tissue: Increased
- Vacuoles: Scattered muscle fibers
- COX stain: Reduced intensity
- Complex II: 52% to normal residual activity
- Citrate synthase: Reduced
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondrial aggregates & morphological changes
- Echocardiogram: Normal
- MSTO1 variant: ? Myopathy + Ataxia, Dominant
220
- Epidemiology: 1 Hungarian family; 4 patients
- Mutation: Val8Met (Located in MSTO2p pseudogene)
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Weakness & Atrophy: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Myalgia
- Cognitive dysfunction: Delayed motor & verbal development
- Ataxia: Trunk & Arms
- Skeletal
- Bone age: Delayed
- Joint hyperlaxity
- Short stature
- Lipomatosis
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal
- Muscle
- Fiber sizes: Varied
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondrial number increased
- Vitamin D3 levels: Low
- Serum lactate: Normal at rest; Increased after exercise
- Familial myalgia syndrome
● Cytochrome b (MTCYB; Complex III)
- Myopathy with abnormal mitochondrial translation
24
● Autosomal- Epidemiology: Two sporadic patients
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood
- Motor: Weakness or Fatiguability
- Weakness
- Proximal > Distal
- Fatiguability
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Hypotonia
- Ocular (50%): Ptosis & Ophthalmoplegia
- Short stature (50%)
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Sideroblastic anemia (50%)
- Muscle
- Mitochondrial proliferation: All muscle fibers
- COX activity: Severely reduced
- Biochemistry: Complexes I and IV (5% of control); Complex II+III (41% of control)
- Immunoblot: Complexes I, III and IV 90% reduced; Nuclear complexes II and V normal
- Mitochondrial translation defect: Generalized
- Fatigue & Exercise Intolerance
 (Complex I)
116
(Complex I)
116
● Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase family, member 9 (ACAD9) ; Chromosome 3q21.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 3q21.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 27 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense: Arg532Trp; Arg127Glut; Arg469Trp
- Also stop & trunctation
- Allelic disorders
- Episodic hepatic
- Infant multisystem (MC1DN20)
- Mutations
- ACAD9 protein
- Catalyzes initial rate-limiting step in β-oxidation of fatty acyl-CoA
- Belongs to group of ACADs that act on fatty acids containing 14 to 20 carbons
- Homodimer
- Oxidative phosphorylation complex I biogenesis
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4 years
- Fatigue syndrome
- Exercise intolerance
- Urge to vomit
- Sense of mental slowness
- Duration: 1 hour
- Cardiomyopathy
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Cardiomyopathy, Dilated or Hypertrophic
- Treatment: Riboflavin, high dose 300 mg/day
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Complex I activity reduced (6% to 40%)
- Serum lactate: High
- Serum acylcarnitine profile: Normal
- ACAD9 Variant: Episodic hepatic disorder
- Onset age: 1st 2 decades
- Precipitated by minor illnesses
- Hepatic dysfunction
- Cardiomyopathy: Some patients
- Brain MRI: Edema
- ACAD9 Variant: Infant onset disorder (MC1DN20)

- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Hypotonia
- Encephalopathy
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Lactic acidosis
- Treatment: ? Riboflavin
- Genetics
- COXPD 49: Fatigue & Exercise Intolerance (Complex I & IV)
232
● Mitochondrial elongation factor 2 (MIEF2; MID49; SMCR7) ; Chromosome 17p11.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 17p11.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Nonsense; p.Q92*
- MIEF2 protein
- Location: Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Function: Mitochondrial fission
- Adaptor
- Recruits DRP1 (large GTPase) to outer mitochondrial membrane
- Other associated adaptors: MFF & MID51 (MIEF1)
- Adaptor
- Mutation: Increased fusion
- Clinical
- Onset age: 6 years
- Weakness
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Possible treatment
- Riboflavin (100 mg/day p. o.) & Coenzyme Q10 (120 mg/day)
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- SDH+ & COX- muscle fibers
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Reduced Complexes I & IV
- MID49 protein: Reduced
- Serum CK: 377 to 1996
- Muscle
- Fatigue & Exercise Intolerance (MC1DN29) (Complex I)
 206
206
● Transmembrane protein 126B (TMEM126B) ; Chromosome 11q14.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 11q14.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 7 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Nonsense or Deletion
- Allelic disorder: Infant onset multisystem disease
- TMEM126B protein
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Complex I assembly factor
- Forms complex with other assembly factors: NDUFAF1, ACAD9, ECSIT

- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 38 years
- Fatigue
- Exercise intolerance
- Myalgia
- Vomiting
- Weakness: Proximal
- Laboratory
- Lactate & Alanine: High in cerum
- Serum CK: Normal
- Muscle
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondria large & Inclusions
- Complex I deficiency
- TMEM126B variant syndrome: Infant onset multisystem syndrome
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Homozygous Gly212Val
- Clinical
- Failure to thrive
- Renal failure
- Cardiomyopathy
- Respiratory failure
- COXPD26: CNS Δ, Demyelinating Neuropathy + Myopathy with Exercise Intolerance (PNSED)
 198
198
● tRNA Methyltransferase 5, S. cerevisiae, homolog of (TRMT5) ; Chromosome 14q23.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 14q23.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense & Stop
- Common: c.312_315del
- Other: 872G>A; Arg291His; Ile222Thr; Met386Val
- Allelic disorders
- Cardiomyopathy, Childhood-onset
- CNS Δ, Short stature, Demyelinating neuropathy 289
- Mutations
- TRMT5 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Class I-like methyltransferase superfamily
- Function
- Post-transcriptional methylation of mitochondrial tRNAs
- Methylation location: N1 position of guanosine at residue 37 (G37) of mitochondrial tRNAs
- Enhances translational efficiency
- Mutation effect
- Hypomodification of guanosine residue at position 37 (G37) of mitochondrial tRNA
- Prominent in skeletal muscle
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital to Early childhood
- Muscle
- Exercise intolerance
- Exertional dyspnea
- Weakness: Legs
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss: Vibration
- Pyramidal signs
- Onset age: Adult
- Gait disorder
- Spasticity
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Other CNS
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Developmental delay
- Intellectual disability
- Systemic
- Pancreas: Glucose intolerance
- Renal: Tubulopathy
- Hepatic: Cirrhosis
- Short stature
- Course: Progressive through adulthood
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Denervation: Distal
- COX staining diffusely reduced: Some patients
- Oxidative enzymes: Mildly reduced I & IV ± III activities
- Mitochondria: Enlarged; Abnormal shapes
- Nerve pathology
- Myelinated axons: Reduced numbers
- Myelin: Thin sheath; Split lamellae; Folding
- Mitochondria: Large
- Lactic acidosis: Exercise-induced
- Serum FGF21 levels: High
- NCV
- Demyelinating neuropathy
- Axon loss; SNAPs absent
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy; White matter foci
- Muscle MRI: Peropneus longus fatty replacement
- Muscle
- TRMT5 variant syndrome: Cardiomyopathy, Childhood onset
- Epidemiology: 1 male
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: c.[312_315del; 1156A>G], p.[Ile105Serfs*4; Met386Val]
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- General
- Premature delivery
- Hypotonia & Hypertonia
- Failure to thrive
- Growth retardation
- Intestinal pseudo-obstruction
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; Non-obstructive
- Polyneuropathy: Demyelinating
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Brain MRI: Brain atrophy; Myelination delayed
- Hypercalcemia: Mild
- Muscle: Lipid droplets; Mild myopathy
- Riboflavin responsive exercise intolerance (RREI)

● Solute carrier family 25, member 32 (SLC25A32; MFT) ; Chromosome 8q22.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 8q22.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Trp142X; Arg147His
- Polymorphism: Bone fractures in Japanese postmenopausal females
- Allelic disorder: Ataxia, Myoclonus, Exercise intolerance
- SLC25A32 protein
- Nosology: Mitochondrial folate transporter (MFT)
- Folate transporter: Cytoplasm to Mitochondria
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2nd decade
- Exercise intolerance: Recurrent
- Treatment: Riboflavin
- Laboratory
- Biochemistry: Multiple acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) pattern
- Muscle
- Lipid: Type I fibers, Mild increase
- Type II fibers: ? Small
- Succinate dehydrogenase: ? Immunostaining reduced
- SLC25A32 variant: Ataxia, Myoclonus, Exercise intolerance
217
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Homozygous; c.-264_31delinsCTCACAAATGCTCA
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 3 years
- Weakness after influenza
- Weakness: Intermittent whelchair
- Bulbar: Dysarthria; Dysphagia
- Exercise intolerance
- Ataxia
- Myoclonus
- Treatment: Riboflavin
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum lactare: High
- Muscle
- Histochemistry: Ragged red & COX negative fibers
- Oxidative enzymes: Mild changes in complex II
- Metabolic crises, Motor delay with Myalgias (MECREN)
201

● Solute carrier family 25, member 42 (SLC25A42) ; Chromosome 19p13.11; Recessive
; Chromosome 19p13.11; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 13 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Saudi: Homozygous; Missense; c.A871G, p.N291D
- Other: Splice site; IVS5DS, T-A, +2
- Mutations
- SLC25A42 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Coenzyme A importer from cytoplasm: Exchanged for
- (deoxy)adenine nucleotides
- Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate
- Carrier family: Transport substrates between cytosol & mitochondrial matrix
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Clinical: Varied severity with same founder mutation
- Onset age: Most < 1 year; Range 6 months to 10 years
- Motor: Delay; Fatigue; Falling; Dysarthria
- Muscle mass: Reduced
- Myalgias: After exercise
- Tendon reflexes: Normal
- CNS: Some patients with more severe disease
- Cognition: Normal to Developmental regression
- Epilepsy
- Movements: Dystonia; Choreoathetosis
- Exacerbations by: Intercurrent illness
- Progression: Slow or None
- Laboratory
- Serum
- CK: Normal
- Lactate: High
- Ammonia: High in 20%
- NCV: Normal
- Brain MRI: Normal or Basal ganglia changes, including iron in 1 patient
- Muscle biopsy
- Fiber size: Varied
- SDH+ & COX- muscle fibers
- Serum
- Myopathy with Extrapyramidal Movement Disorders (MPXPS)
 172
172
● Calcium-binding atopy-related autoantigen 1 (MICU1; CBARA1; CALC; EFHA3) ; Chromosome 10q22.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 10q22.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 20 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Loss of function; Stop
- MICU1 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Location: Inner membrane
- EF hand protein
- Subunit of: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter
- Function: High-capacity mitochondrial Ca++ uptake
- Ca++ sensing regulator: Mitochondrial Ca++ uniporter complex (mtCU)
- Main pathway for mitochondrial Ca++ entry
- Delivers Ca++ ions to mitochondrial matrix
- Loss of MICU1 protein: Abnormal neuronal mitochondrial Ca++ homeostasis
285
- Mitochondrial Ca++ load: Increased
- Cytoplasmic Ca++ transients: Reduced
- Mitochondrial membrane potential: Normal
- Mitochondrial calcium uptake: Uncontrolled
- Excitotoxicity
- Type I allergy: Serum IgE binding to CBARA1
- Mitochondrial
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood; 1 to 8 years
- Weakness
- Developmental delay: Motor & Learning
- Muscle
- Weakness: Proximal ± Distal; Static course
- Cramps (30%)
- Muscle size: Calf hypertrophy; General atrophy
- Extrapyramidal: Involuntary movement, variable
- Chorea
- Tremor
- Dystonia
- Orofacial dyskinesia
- CNS: Other
- Cognitive impairment
- Depression,
- Insomnia
- Seizures
- Ataxia
- Skeletal
- Head: Microcephaly/Dolichocephaly; Hypertelorism, High arched palate, Low-set ears
- Extremities: Clinodactyly, Radioulnar synostosis, Pes cavus, Hyperextensible joints
- Scapular winging
- Spine: Lordosis, Kyphosis
- Other occasional
- Eye: Ophthalmoplegia, Ptosis, Optic atrophy
- Peripheral neuropathy: Axonal
- No: Diabetes mellitus, Deafness, Cardiomyopathy
- Course: Slow progression or Static
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High; Up to 6,000
- Muscle pathology
- Varied fiber size
- Internal nuclei
- Myopathic groups
- Necrosis: Few muscle fibers, Clusters & Individual
- Regenerating & Immature fibers: Clusters & Individual
- Fiber typing: Preserved, Clustered 2C fibers
- Minicores: Types I & 2 fibers
- Respiratory chain enzymes: Normal
- Muscle MRI: Early leg adductor involvement; Anterolateral (Quadriceps) spared
- Brain MRI: Globus pallidus increased signal; Polymicrogyria
- Myopathy
(MC4DN18)
 (Complex IV)
246
(Complex IV)
246
● Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit 6A2 (COX6A2) ; Chromosome 16p11.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 16p11.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 Japanese patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Ser39Arg, Cys43Arg
- COX6A2 protein
- Tissues: Skeletal & Cardiac muscle
- Structural subunit of complex IV (COX)
- Assembly & stabilization of COX enzyme
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth or Infancy
- Hypotonia
- Weakness: General; Face; Respiratory (1 patient)
- Palate: High arched
- Cardiomyopathy: 1 patient
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal
- Lactate: High
- Muscle pathology: COX stain reduced; Lipid increased
- EMG: Myopathic
Mitochondrial Myopathy: Autosomal Dominant
- Myopathy with focal depletion of mitochondria
- Mitochondrial DNA breakage syndrome: PEO + Myopathy
- LGMD 1H
- Mitochondrial myopathy with exercise intolerance (IMMD)

● Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 10, mitochondrial (CHCHD10)
 ; Chromosome 22q11.23; Dominant
19
; Chromosome 22q11.23; Dominant
19
- Nosology: Myopathy, isolated mitochondrial, autosomal dominant
- Epidemiology: Puerto Rican family
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense in cis: Arg15Ser & Gly58Arg
- Other disorders: Missense common; 1 stop Q82X
- Allelic disorders
- FTD-ALS 2
- Fronto-Temporal Dementia: Exon 2; 8% in China
- SMAJ
- Myopathy (IMMD)
- Axonal neuropathy, Hereditary
- Ataxia
- Parkinsonism
- Mutations
- CHCHD10 protein: Mitochondrial
- Locations
- Intermembrane space
- Enriched at cristae junctions
- CX9C motifs
- Tissue expression: Ubiquitous
- Mitophagy
- Mitochondrial cristae morphology maintenance
- Upregulation: Stress conditions
- Mutant allele: Expression
- Mitochondrial network: Fragmentation
- Mitochondrial cristae: Loss, disorganization & dilatation
- CHCHD2

- Locations
- Clinical
- Onset
- First decade
- Exercise intolerance
- Leg weakness
- Weakness
- Early: Proximal; Legs > Arms
- 2nd decade: Neck flexor; Shoulder; Distal legs
- 3rd & 4th decade: Mild face weakness
- Pulmonary function: Restrictive deficits
- Progression: Slow
- Subjective improvement with methylprednisolone treatment
- EOM: Unaffected
- CNS: Normal cognition, sensation, cerebellar
- Systemic: Short stature
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 287 to 984
- Serum lactate: High
- Serum pyruvate: High
- EMG: Myopathic
- Muscle pathology
- Ragged red fibers
- Biochemistry
- Cytochrome c oxidase (Complex IV): Reduced
- Succinate cytochrome c reductase (Complex II & III): Reduced
- NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I): Normal
- CHCHD10 variant syndrome: FTD-ALS + Ataxia & Myopathy (FTDALS2)
 175,
351
175,
351
- Epidemiology
- 0.6% to 3% of FTD-ALS
- China: 7.7% of FTD
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant or Sporadic
- Mutations
- General: N-terminal half of protein
- Common locations: Exon 2
- Specific mutations
- P12S
- Arg15Leu: ALS phenotype; Common German ancestor in some; 81% penetrance
- Ser59Leu: Varied Ataxia, FTD, Myopathy
- Gly66Val
- P80L
- P34S: Present in ALS & controls
- Allelic disorders
- CHCHD10 protein
- Clinical: Variable
- Onset
- Age: 49 to 65 years
- Bulbar, Spinal or Cognitive
- Motor neuron disease
- Bulbar
- Dysarthria
- Dysphagia
- Limb weakness
- Some patients
- Arms > Legs
- Proximal > Distal
- R15L mutation: Flail Arm Syndrome (Brachial amyotrophic diplegia)
- Fasciculations
- Course: Slow progression; May be > 10 years
- Bulbar
- Cognitive decline (Frontotemporal dementia): 70%
- May occur without motor neuron disease: P23T; A35D; Q82X
- Cerebellar ataxia: 80%
- Reflexes
- Tendon: Absent or Brisk
- Plantar response: Extensor
- Myopathy
- Weakness: Proximal
- Ptosis & Face weak: 1 patient
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Muscle fibers: Ragged-red; Cytochrome c oxidase-negative
- Combined respiratory chain deficiency: I, III & IV
- Complex V: Abnormal assembly
- Multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions
- Lipid: Increased
- Glycogen: Increased
- Lactate: Normal
- EMG: Denervation, Active & Chronic
- CNS
- Motor neurons: Reduced anterior horn & hypoglossal
- Corticospinal tract: Mild pathology
- CHCHD10 aggregates: Anterior horns; Corkscrew shaped; Extracellular
- TDP43 pathology: Relatively little
- Muscle
- Epidemiology
- Also see: Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia, Dominant
Systemic Mitochondrial Syndromes
|
Adult onset Anemia Ataxia Cardiac Deafness Diabetes Infantile encephalopathies Multiple symmetric lipomatosis Optic atrophy |
Infantile encephalopathies: Mitochondrial disorders
- Fatal multisystemic complex I deficiency: NADH Dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) Fe-S Protein 4 (NDUFS4)
- Finnish neonatal metabolic syndrome: BCS1L; 2q33
- Fumarate hydratase
- Lipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency (α-ketoglutaric dehydrogenase)
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria (HHH syndrome)
- Leigh's
- Also see: Infantile disorders
Cardiomyopathy: Mitochondrial disorders
|
- Mitochondrial Cardiomyopathy: General
- Common in mitochondrial disorders
- May increase likelihood of mortality
- Hypertrophic: Most common form
- Cardiomyopathy: Mitochondrial DNA mutations
- General
- Often infantile onset
- Skeletal Muscle Pathology with mtRNA mutations: Ragged red fibers (COX -)
- Noncompaction of left ventricular myocardium ± congenital heart defects (LVNC)
- Fatal cardiomyopathy, infantile onset
● mtRNA Ile (MTTI)
- Genetics
- Mutation: A4317G; A4269G
- Also see: Other tRNA Ile mutations
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Heart: Dilated & Hypertrophic
- Other: Some features of MELAS; Short stature; Deafness
- Death due to cardiac failure: Childhood to 18 years
- mtRNA Ile syndromes
- Cardiomyopathy
- Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (A4295G; A4300G)
- Homoplasmic
- Maternal inheritance
- Cardiac muscle: Low mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Fatal cardiomyopathy, infantile onset
- Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (A4295G; A4300G)
- Encephalopathy, Familial progressive necrotizing (T4290C)
- Homoplasmic
- Onset age: 6 to 16 years
- Lab: Impaired glucose tolerance, Hyperlipidemia, Hyperuricemia
- Muscle: No mitochondrial changes
- Leigh
- Myoclonus epilepsy, Progressive (MERRF)
- Mutation: m.4279A>G
- Onset age: 4th decade
- Muscle: Ragged red fibers
- Spastic paraparesis; Ataxia; PEO; Retardation (G4284A)
- Heteroplasmic: Mutation load 55% to 90%
- Variable syndromes within family
- Spastic paraparesis: Isolated
- Cardiomyopathy + Multisystem disorders
- Ataxia, Hearing loss, Mental regression, PEO, Diabetes mellitus
- Muscle biopsy: Normal histology
- Hypomagnesemia, Hypokalemia, Hypertension, & Hypercholesterolemia, Mitochondrial (T4291C)

- Genetics
- Maternal inheritance
- Homoplasmic mutation
- Clinical
- Variable phenotype: ~50% penetrance of each feature; More signs with increasing age
- Increased prevalence: Migraine headache, Sensorineural hearing loss, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Muscle biopsy: Fibers with increased SDH staining
- Genetics
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Cardiomyopathy
- Genetics
- Cardiomyopathy (Hypertrophic)
● mtRNA Lys (MTTK)
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Death in infancy
- Lab: High serum Lactate & Pyruvate
- General
- Cardiomyopathy (Hypertrophic)
● mtRNA Leu (MTTL1)
- Mutations: A3243G; A3260G; C3303T
- Up to 10% of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Morbidity & Mortality: High
- Onset age: 24 to 40 years; Mean 30 years
- Other MTTL1 mutations
- Barth-like syndrome: Dilated cardiomyopathy
- MELAS
- Left ventricular noncompaction
- Conduction defects: Wolff-Parkinson-White or Other
- Cardiomyopathy (Dilated)
● mtRNA Leu (MTTL2)
- Mutation: C12297T
- Cardiomyopathy: Adult onset; Dilated
- Other MTTL2 mutations
- Myopathy: A12320G mutation in skeletal muscle
- Encephalomyopathy: PEO+; G12315A mutation, heteroplasmic
- Leigh syndrome
- Cardiomyopathy (Dilated)
● mtRNA His (Histidine; MTTH)
- Genetics
- Mutations: G12192A ± A16318T substitutions
- Homoplasmic
- Clinical syndromes
- Genetics
- Cardiomyopathy (Hypertrophic)
● mtRNA Gly (MTTG)
- Genetics
- Mutation: T9997C
- Heteroplasmic: Correlates with severity of cardiomyopathy
- Clinical syndromes
- Nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Onset age: Neonatal to childhood
- Enzyme deficiencies: Complex IV & Complexes II + III
- Exercise intolerance: T10010C
- Sudden death: A10044G
- Nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Genetics
- Cardiomyopathy (Apical hypertrophic) + Neuropathy
75
● ATP synthase 8 (MT-ATP8) ;
Mitochondrial
;
Mitochondrial
- Epidemiology: Sporadic; Caucasian male
- Genetics
- Encoding: mtDNA nucleotides 8366-8572
- Mutation
- Nonsense mutation: G8529A (Trp55X)
- Homoplasmic
- Other MT-ATP8 mutations
- C8393T: Valproate-induced encephalopathy
- MT-ATP8 protein: Complex V
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infancy
- Motor development: Slow
- Motor
- Delayed milestones
- Cerebellar
- Gait & Balance disorder
- Speech: Dysarthric
- Reflexes
- Tendon: Reduced
- Plantar: Extensor
- Eyes: External ophthalmoplegia, mild
- Cardiomyopathy
- Exercise intolerance
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea) during exercise
- Angina
- Left ventricular hypertrophy, apical
- Neuropathy
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Complex V: Reduced activity & protein complex
- Lactate: High in CSF; Normal in serum
- NCV
- SNAPs: Absent in legs
- CMAPs: Reduced amplitude in legs
- Muscle
- Variant syndrome: Valproate-induced encephalopathy
- Mutation: C8383T
- Course: Reversible
- Infantile histiocytoid Cardiomyopathy

● Mitochondrial cytochrome b (MTCYB) ; Often sporadic
; Often sporadic
- Genetics
- Mutation: G15498A (Gly251Asp)
- Other disorders with MTCYB mutations
- Exercise intolerance
- Myopathy
- Leber optic atrophy
- Colorectal cancer
- Encephalomyopathy
- Parkinsonism
- Obesity, susceptibility
- Onset: < 2 years
- Females > Males
- Clinical
- Cardiac
- Dysrhythmia
- Cardiac arrest
- CNS & Eye anomalies
- Course
- Usually fulminant
- May simulate sudden infant death syndrome
- Treatment: Cardiac transplantation
- Cardiac
- Pathology
- Pale granular foamy histiocyte-like cells in myocardium
- Mitochondrial proliferation
- Biochemistry: Isolated complex III deficiency
- Genetics
- Cardioencephalomyopathy with Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency (CEMCOX1; MC4DN2)

● SCO2 ;
Chromosome 22q13.33; Recessive
;
Chromosome 22q13.33; Recessive
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Types: Missense & Nonsense
- Many patients heterozygous for E140K mutation: Severe disease
- Some patients homozygous for E140K mutation: Modreately severe disease
- Allelic disorders
- Myopia 6, Dominant

- CMT: Axonal, Recessive, Early onset
- Leigh syndrome
- Ataxia + Neuronopathy, Adult onset
- Myopia 6, Dominant
- Mutations
- SCO2 protein
- COX assembly gene: Enables incorporation of subunits 1 and 2 into holoprotein
- Complex IV
- Mutated protein: Impaired copper incorporation into holoenzyme
- Clinical: Heterozygous for E140K mutation; Fatal infantile
- Onset: Infantile (1st 3 months); Male = Female
- Motor: Hypotonia; Respiratory failure
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; COX deficiency
- Encephalopathy
- Course: Fatal by 6 months
- Clinical: Homozygous for E140K mutation
18
- Onset age: 3 to 10 months
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Respiratory
- Insufficiency
- Inspiratory stridor
- Limb spasticity
- Muscle: Denervation
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- CNS
- Leigh-like syndrome
- Psychomotor retardation
- Seizures
- Ocular
- Ptosis
- Ophthalmoplegia
- PNS
- ? Motor neuropathy
- EMG: Denervation in some patients
- Encephalopathy: Especially white matter lesions
- Survival: 4 to > 24 months
- Residual COX activity: 0% to Normal
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX deficiency (Moderate to Severe)
- COX (Complex IV) activity: Low or Normal; 0% to Normal
- More reduction in mitochondrial COX I & II; than nuclear COX IV & Va
- Other complexes & SDH: Normal
- COX staining: Reduced
- Morphology: Atrophic muscle fibers; Denervation (SMA-like)
- May have denervation pattern similar to SMA
- COX deficiency (Moderate to Severe)
- CNS pathology: Gliosis
- Biochemistry
- Lactic acid: High or Normal in serum or CSF
- Increased copper uptake by fibroblasts
- Neutropenia
- Muscle
- SCO2 variant: CMT, Axonal, Early Onset
231
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense; Near copper binding motif; E140K, D135G, P169T, R171Q
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy & 12 years
- Weakness
- Distal > Proximal
- Legs & Arms
- Symmetric
- Sensory loss
- Distal
- Vibration
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Normal or High
- Serum copper: Normal
- NCV: CMAPs & SNAPS small amplitude; Velocities normal
- SCO2 variant: Ataxia + Neuronopathy, Adult onset
281
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Arg60Gln, Gly193Ser
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: > 40 years
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Sensory: Neuronopathy
- Deafness
- Eye: Pigmentary retinopathy; Cataract; Hemeralopia
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: Sensory neuronopathy; Axon loss
- Brain MRI: Supratentorial white matter Δ; Cortical atrophy
- Audiometry: Perceptive hypoacusis, bilateral
- ERG: Abnormal
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Muscle
- Lipid droplets
- COX- fibers: Scattered
- Complex IV activity reduced
- Genetics
- Encephalocardiomyopathy with cytochrome c oxidase deficiency: Fatal neonatal lactic acidosis (MC4DN10)
 130
130
● COX14 (c12orf62)
 ;
Chromosome 12q13.12; Recessive
;
Chromosome 12q13.12; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Portuguese family, 3 siblings
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense; Met19Ile
- c12orf62 protein
- Clinical
- Prenatal: Oligoamnios; Septum-lucidum cysts
- Dysmorphism: Hypotelorism, Microphthalmia, Ogival palate, Single palmar crease
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Hepatomegaly
- Renal: Hypoplasia
- Adrenal: Hyperplasia
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: Blood; CSF
- Brain pathology
- Hypertrophy, diffuse alteration
- White-matter myelination: Diffuse pathology, and numerous
- Cavities: Parieto-occipital, Brainstem, Cerebellum
- COX
- Activity: 30% to 40% of control fibroblasts
- Fully assembled complex: Reduced
- COX assembly defect: Reduced levels of COX I, II & IV
- Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein Deficiency, Type 2 (MTPD2)
 267
267
● Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase/enoyl-CoA hydratase, β subunit (HADHB) ;
Chromosome 2p23.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 2p23.3; Recessive
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Inframe deletion
- Outer loop mutations: Alter protein stability; Milder disease forms
- Allelic disorders
- Cardiomyopathy: Early onset & death
- Hypoketotic hypoglycemia, Recurrent: Intermediate form
- Hepatic with recurrent Hypoketotic hypoglycemia
- Sensorimotor neuropathy ± Episodic rhabdomyolysis: Small amounts of residual enzyme activity
- Axonal sensory neuropathy, Later-onset ± Episodic myoglobinuria
- Deficiency (MTPD) also caused by mutations in: HADHA (α-subunit)
- Trifunctional Protein
- Nosology
- Trifunctional protein, β subunit
- Long-chain 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase
- Long-chain keto acyl-CoA thiolase (LCKAT)
- Function
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- See: Lipid disorders
- Nosology
- Clinical: Severe neonatal
- Cardiomyopathy
- Myopathy
- Liver dysfunction
- Encephalopathy
- Neuropathy: Axonal
- Variant syndrome: Axonal sensory neuropathy, Early-onset
170
- Epidemiology: Korean family
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- HADHB mutations: Arg229Leu; c.210-1G>C causing splicing loss of exon 5
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5 to 6 years
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Steppage gait
- Sensory: Pansensory loss
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Morphology
- Distal leg wasting
- Pes cavus
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- NCV
- Motor: CMAPs small amplitude; NCV mildly slow
- SNAPs: Absent
- F-wave latencies: Prolonged
- EMG: Denervation
- Sural nerve
- Large myelinated axons: Absent
- Small myelinated axons: Reduced
- Regeneration: Axon clusters; Thinly myelinated axons
- Pseudo onion bulbs: Occasional
- Axon swellings: Occasional
- Leg MRI
- Distal: Wasting except soleus
- Thigh: Wasting sparing vastus & adductors
- Metabolic
- Carnitine (Total & Free) & Acylcarnitine: Low
- NCV
- Genetics
- Cardiomyopathy + Encephalomyopathy (MC1DN6)
 13
13
● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase Fe-S Protein 2 (NDUFS2) ;
Chromosome 1q23.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 1q23.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- NDUFS2 Mutations: Missense; Homozygous
- Allelic disorder: Hereditary Optic Atrophy (LHONAR2)
- NDUFS2 protein
- Complex I
- Extramembranous near membrane domain
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- ? Role in protein transport
- Q-binding
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Birth to 7 months
- Hypotonia or Failure to thrive
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Hypotonia: Axial
- Pyramidal signs: Limb hyperreflexia
- Ocular: Optic atrophy; Nystagmus
- CNS: Progressive encephalopathy; Sleep apnea
- Course: Death < 2 to 3 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in CSF & Blood
- Brain CT: Hypodensities in basal ganglia; Generalized atrophy
- Echocardiogram: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Biochemistry: Selective Complex I deficiency
- Riboflavin reverses adenosine triphosphate production deficit in fibroblasts
- NDUFS2 variant syndrome: Hereditary Optic Atrophy (LHONAR2)
 214
214
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Tyr53Cys; Tyr308Cys
- Allelic disorder
- Clinical
- Onset age: 6 to 22 years
- Visual loss: LHON-like
- Subacute
- Painless
- Bilateral: Simultaneous or Sequential (1 month)
- Cecocentral scotoma
- Papillary pseudoedema: Non-hemorrhagic
- Laboratory
- Mitochondrial phosphate carrier deficiency (MPCD)
 62
62
● SLC25A3 ; Chromosome 12q23.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 12q23.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 7 patients
- Genetics: Mutations
- Missense Gly72Glu, Leu200Trp; Intron c.158-9A>G; Deletion/Insertion
- Located in, or near, Exon 3A: Specific expression in heart & muscle
- SLC25A3 protein
- Mitochondrial solute carrier
- Import of inorganic phosphate into mitochondrial matrix
- Functions in ATP synthesis
- Other causes of: TPP deficiency
- Copper transporter
- Into mitochondrial matrix
- Role in COX synthesis
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; Progressive
- Respiratory failure
- Hypotonia
- Course
- Death in 1st year: Some patients
- Survival to adulthood: Exercise intolerance; Proximal weakness
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle biopsy
- Lipid accumulation: More in type I muscle fibers
- Mitochondria: Large
- SDH & COX histochemistry: Abnormal mitochondrial network; No proliferation
- Respiratory chain enzyme activities: No significant abnormalities
- Defective ATP synthesis: Requires fresh tissue for measurement
- Mitochondrial phosphate carrier: Reduced
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Fatal infantile or Leigh syndrome (CEMCOX2; MC4DN6)

● COX15 ;
Chromosome 10q24.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 10q24.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Single patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Null allele (Exon 4 deletion) + Arg217Trp
- Allelic syndrome: Leigh (Homozygous Arg217Trp)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Shortly after birth
- Seizures
- Midface hypoplasia
- Hypotonia
- Death: < 1 month
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Autopsy: Biventricular hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Complex IV (COX) deficiency
- Leigh syndrome + Epilepsy (MC4DN15)
 (Complex IV)
202
(Complex IV)
202
● Cytochrome c Oxidase, subunit VIII A (COX8A)
 ;
Chromosome 11q13.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11q13.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 Turkish patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Splice site; Homozygous; c.115-1G>C splice acceptor site
- COX8A protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Complex IV: Nuclear-encoded structural subunit
- Expression: Ubiquitous
- Other mutations in Complex IV structural proteins
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth, Skeletal
- Skeletal: Congenital scoliosis + Thoracolumbar kyphosis; Pes planovalgus, bilateral; Short stature; Microcephaly
- GI: Malutrition; Vomiting; Childhood cachexia
- CNS
- Seizures: Generalized; Childhood onset; Tonic-clonic & Hypotonic
- Encephalopathy
- Psychomotor retardation
- Hypotonia: Proximal
- Spasticity: Distal; arms & Legs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Pigmentary retinopathy
- Death: 12 years
- Laboratory
- EEG: Generalized slowing; Multifocal spike-and-wave activity,continuous
- Lactic acidosis: Serum & CSF
- High citric acid cycle metabolites, Glycine & Alanine
- Brain MRI: Patchy; Thalamic, Cerebellar & White matter changes
- Muscle: Absent COX staining; Isolated reduced COX activity, severe
- Leigh syndrome (MC4DN24)
 (Complex IV)
(Complex IV)
● Fast kinase domains 5 (FASTKD5)
 ;
Chromosome 20p13; Recessive
;
Chromosome 20p13; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Stop
- FASTKD5 protein
- Clinical: Leigh-like
- Onset age: Early childhood to Adult
- Developmental delay
- Exercise intolerance
- Face: Dysmorphic
- Adult
- Monophasic encephalopathy
- Extrapyramidal features
- Fatigue
- Vision loss
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle
- Myopathic
- Cytochrome C oxidase deficiency, diffuse
- Complex IV activity reduced
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
- Brain MRI: Basal ganglia, Thalamus & Brainstem lesions
- Leigh syndrome
● NDUFA4 ;
Chromosome 7p21.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 7p21.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Mutation: Splice site; c.4211G>C
- NDUFA4 protein
- Expression highest in: Heart, Skeletal muscle & Brain
- ? Subunit of Complex I or IV
- Clinical: Leigh syndrome
- Laboratory: Complex IV (COX) deficiency
- Cardiomyopathy, Fatal Infantile (CEMCOX3; MC4DN9)
 (Complex IV defects
(Complex IV defects
 )
121
)
121
● Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 5 (COA5; C2orf64)
 ;
Chromosome 2q11.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 2q11.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Turkish family; 2 siblings
- Genetics
- Mutation: Ala53Pro; Homozygous
- C2orf64 protein
- Mitochondrial intermembrane
- Twin Cx9C motif protein
- Early step of Complex IV assembly process
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 month or in utero
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic restrictive
- Brain: Normal
- Muscle
- Lipid droplets
- Mitochondrial proliferation
- Complex IV deficiency
- Cardiomyopathy, Fatal Infantile, Hypertrophic (CEMCOX4; MC4DN13)
 (Complex I & Complex IV defects
(Complex I & Complex IV defects
 )
178
)
178
● Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 6 (COA6; c1orf31) ;
Chromosome 1q42.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 1q42.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Trp59Cys; Trp66Arg; Glu87Ter
- COA6 protein
- Cytochrome c oxidase assembly
- Copper homeostasis & transport to complex IV
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Hypotonia
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Face: Chin small; Orbital ridges flat
- Episodes: Hypothermia; Tachycardia
- Death: < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Respiratory chain defects: Multiple; Reduced complexes I & IV in cardiac tissue
- Cardiomyopathy (COXPD8) (Complex I &
Complex IV defects)
 122
122
● Alanyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 (AARS2) ;
Chromosome 6p21.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 6p21.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Finnish patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense common; Leu155Arg; Arg592Trp
- Allelic disorder: Leukoencephalopathy, progressive, with ovarian failure (LKENP), Recessive

- AARS2 protein
- Location: Mitochondria
- Amino acid tRNA synthetase
- Mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Mutation: Deficiency of respiratory complexes
- Clinical
- Onset: Infantile
- Cardiomyopathy: Dilated & Hypertrophic
- Death: < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX- & SDH+ muscle fibers
- Fiber size: Varied
- Oxidative enzymes: Multiple defects
- Serum CK: Normal
- Muscle
- AARS2 variant: Leukoencephalopathy, progressive, with Ovarian failure (LKENP), Recessive

- Epidemiology: 46 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Arg521Ter; Gly965Arg; Glu405Lys
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Early childhood to Adult; Mean 23 years; Males < Females
- Delayed development
- Ataxia
- Upper motor neuron
- Spasticity
- Pseudobulbar palsy
- Cortical
- Cognitive decline
- Psychiatric disorders
- Seizures: With younger onset
- Ovarian failure: 3rd to 5th decade
- Course: Progressive
- Loss of motor skills, speech & cognition by 5th decade
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- No ragged red fibers
- Oxidative enzymes: Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency (15% to 33%)
- Brain MRI
- Cerebral white matter abnormal: Frontal; Parietal periventricular; Deep white matter tracts; Corpus callosum
- DWI: Deep white matter diffusion dots
- Cerebellar atrophy: Variable
- Muscle
● Mitochondrial translation optimization 1 homolog (MTO1)
- Epidemiology: > 70 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense (Most)
- Truncating: Some in one allele; More severe phenotype; None with 2 truncating
- Mutations
- MTO1 protein
- Mitochondrial-tRNA (mtRNA) modifier
- Location: Tissues with high metabolic rate; Skeletal muscle, Liver, Heart
- Clinical
- Onset: Mean 10 months; Range Prenatal to 8 years
- Oligohydramnios
- Hypotonia
- Cardiomyopathy (80%): Hypertrophic
- CNS
- Psychomotor delay
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Dystonia
- Eye
- Optic atrophy (30% to 50%)
- Visual acuity: Reduced in some
- Ataxia (20%)
- Feeding difficulties
- Course
- Death: < 2 months to Teens
- Longer survival in patients treated with dichloroacetate (DCA) for lactic acidosis
- Hypoglycemia
- Metabolic acidosis
- Serum Lactate: High
- Oxidative enzymes: Complex I, III & IV activity moderately reduced
- VER: Reduced P100 amplitude
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Gly59Ala, Thr308Ala
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 3 months
- Seizure
- CNS
- Infantile spasms: Poor response to treatment
- Delayed development: Motor & Cognitive
- Tone: Distal increased; Axial hypotonia
- Chorio-Athetoid movements
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX negative muscle fibers
- Complex IV deficiency
- Lipid increased
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Muscle
- Genetics
- Disorders of nuclear genetic origin
- See: Other disorders of mitochondrial Complex V
- General defect
- Decreased content of structurally & functionally normal enzyme
- Primary cause: Defect at early stage of enzyme assembly; Involves formation of F1 catalytic region
- Gene defects
- ATP12: 1 case
- ATP synthase 8
- Others undefined
- Onset
- Age: Neonatal
- Low APGAR & Birth weight
- Premature birth (50%)
- Clinical
- Laboratory
- Plasma lactate: High
- 3-methyl-glutaconic aciduria
- ATP synthase complex reduced on Western blot
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L44 (MRPL44)
- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Missense; Leu156Arg common; Other c.481_484delinsTC, Leu156Pro
- MRPL44 protein
- Structural subunit of Mitochondrial ribosome, large (39S) subunit
- Role in assembly & stability of subunit
- Mutations: Reduced mitochondrial DNA encoded protein synthesis affecting oxidative subunits
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 months to Adolescence
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Fatigue
- Liver: Steatosis
- Course: Variable
- Infantile death
- Stable in teens
- Laboratory
- Liver transaminases: High
- Hypoglycemia
- Serum lactate: Normal or High
- Muscle
- COX staining: Normal or Mildly reduced
- Oxidative enzymes
- Activities: Complexes I & IV reduced
- Assembled respiratory chain complexes in muscle: I & IV reduced
- Cardiac > Skeletasl muscle involvement
- Mitochondrial morphology: Abnormal
- Fibroblasts: Complex IV deficient
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like lesions in 1 patient
● Complement component C1q-binding protein (C1QBP, p32)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- C1QBP protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Expression: Ubiquitously expressed multifunctional
- Functions: Multiple
- Mitochondrial homeostasis
- Inflammation & Infection processes
- Mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis
- Apoptosis regulation
- Nuclear transcription
- pre-mRNA splicing
- Clinical: Several syndromes
- Infantile lactic acidosis
- Clinical
- Prenatal: Oligohydramnios
- Cardiac: Ventricular cardiomyopathy, asymmetric; Cardiomegaly
- Congenital nephrosis
- Hypothyroidism
- Encephalopathy with multiple hemorrhagic events
- Laboratory
- EEG: Suppression bursts; Subclinical seizures
- Metabolic acidosis: Lactate very high
- Death: 4 to 18 days
- Clinical
- Cardiomyopathy +: Childhood
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5 years
- Cardiac: Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory
- Muscle: Exercise intolerance with fatigue & vomiting
- Eye: Ptosis; Progressive external opthalmoplegia
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
- Serum CK: 566
- Clinical
- Adult-onset: Myopathy & PEO
- Onset age: 57 years
- Muscle: Exercise intolerance; Weakness, Proximal
- Eye: Ptosis; Progressive external opthalmoplegia
- Psychiatric disorder
- Diabetes
- EMG: Neurogenic
- Infantile lactic acidosis
- Laboratory
- OXPHOS deficiencies
- Multiple: Complexes I, III & IV
- Citrate synthase: Increased
- OXPHOS deficiencies
● Ubiquinol-Cytochrome C Reductase, Rieske Iron-Sulfur (UQCRFS1)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- UQCRFS1 Protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital
- Perinatal: Feeding difficulty; Hypothermia; Hyperventilation
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; Bradycardia
- Alopecia totalis
- Episodes: Metabolic during febrile infection
- Muscle: Hypotonia; Weakness
- Course: Death at 4 months in 1 patient
- Other: Papilledema
- Laboratory
- Thrombocytopenia
- Serum CK: High
- Serum Lactate: High
- Sengers syndrome: Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic & Cataracts
(MTDPS10)
 131
131
● Acylglycerol Kinase (Multisubstrate lipid kinase) (AGK; MULK) ; Chromosome 7q34; Recessive
; Chromosome 7q34; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 43 patients
- Genetics
- AGK protein
- Mitochondrial
- Phosphorylates diacylglycerol, ceramide & 1-acylglycerol
- Assembly of ANT & Respiratory chain complexes
- Component of TIMM22
 complex with TIMM29
complex with TIMM29

- Facilitates insertion of hydrophobic proteins into inner mitochondrial membrane
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 week to 4 years
- Hypotonia
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic (88%)
- Exercise intolerance
- Myopathy (74%): Hypotonia; Motor delay
- Mental development: Normal
- Cataracts (98%): Birth in 61%
- Course
- Severe forms: Infantile death
- Cardiomyopathy
- Benign form: Survival into adulthood
- Severe forms: Infantile death
- Muscle: Skeletal & Cardiac
- Lipid: Small droplets
- Glycogen: Increased
- AGK protein: May be absent
- SDH+ fibers: Some patients
- Biochemistry
- Lactic acidosis (88%)
- OXPHOS defect (91%)
- mtDNA levels: Reduced in some patients
- Adenine nucleotide translocator 1 (ANT1): Levels in muscle reduced; No mutations
- Urine organic acids: Methylglutaconic aciduria
- Sengers syndrome 2: Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic & Cataracts
338
● Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 29 (TIMM29) ; Chromosome 19p13.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 19p13.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 family; 17 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Trp172Arg; Homozygous
- TIMM29 protein
- Subunit of TIM22 complex with AGK
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Interacts with TOMM40
- Clinical: Sengers syndrome, Severe
- Onset age: Birth & Infancy
- Cataracts
- Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic
- Hypotonia
- Copurse: Death < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: High; 920 to 6,800
- Pyruvate-dehydrogenase complex activity: Reduced
- Adenine nucleotide translocator 1 protein: Reduced
- Serum Lactate: High
- Muscle
- Mitochondria: Proliferation; Electron lucent mitochondria; Cristae loss
- Mitochondrial-respiratory-chain-complexes: Combined deficiency, especially Complexes I & IV
- COX- & SDH+ fibers
- TIMM29 protein: Reduced
- Lipid droplets
- Fiber sizes: Varied
- Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 1 (CFC1)

● V-RAF murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF) ; Chromosome 7q34; Dominant or Sporadic
; Chromosome 7q34; Dominant or Sporadic
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Especially in exon 6
- Allelic disorders
- Noonan syndrome 7

- Somatic mutations (V600E): Neoplasms (Melanoma; Erdheim-Chester)
- BRAFV600E mutation: Induces oncogene-induced senescence via pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
- Noonan syndrome 7
- BRAF protein
- May be associated with: PDK1
 &
PDP2
&
PDP2

- May alter
- Pyruvate in tricarboxylic acid cycle
- Oxidative Metabolism: Suppression via PGC1α & MITF
- May be associated with: PDK1
- Clinical
- Skin
- Atopic dermatitis
- Ichthyosis
- Hyperkeratosis (Extensor surfaces)
- Keratosis pilaris
- Multiple palmar creases
- Multiple lentigines
- Hair: Sparse, Curly, Slow-growing; Absent Eyebrows & Eyelashes
- CNS
- Optic nerve dysplasia
- Corticospinal: Tendon reflexes increased; Extensor plantar response
- Sensitive to light touch
- Mental retardation: Global development delay
- Seizures (40%)
- Cortical atrophy
- Hypoplasia: Frontal lobe; Corpus callosum ; Brain stem
- Eyes
- Ptosis
- Strabismus
- Oculomotor apraxia
- Nystagmus
- Hypertelorism
- Exophthalmos
- Face
- Forehead: Prominent; Bitemporal narrowing
- Orbital ridges: Shallow
- Philtrum: Prominent
- Micrognathia
- Macrocephaly
- Skeletal
- Joints: Hyperextensibility
- Osteopenia
- Clinodactyly
- Pectus excavatum or carinatum
- Short stature
- Heart
- Atrial septal defects
- Pulmonic stenosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- GI
- Dysmotility
- Splenomegaly
- Cancer risk: Normal
- Skin
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology
- Fiber morphology: Normal
- Mitochondria: Enlarged
- 2C fibers: Increased frequency
- Coenzyme Q10 levels: May be reduced
- MRI: Ventriculomegaly
- EEG: Spikes/slow waves, Hypsarrhythmia; Focal epileptiform discharges
- Muscle pathology
- Genetics
- Cardiac Arrest, Infancy
 208
208
● Pyrophosphatase, inorganic, 2 (PPA2) Chromosome 4q24; Recessive
Chromosome 4q24; Recessive
- Nosology: Sudden cardiac failure, infantile (SCFI)
- Epidemiology: 7 families, 12 patients
- Genetics
- PPA2 protein
- Location: Mitochondria
- Catalyzes hydrolysis of inorganic pyrophosphates
- Inorganic Pyrophosphate (PPi) + H2O → 2 Orthophsphates (Pi)
- Produces: 2 organic phosphates, which are then exported across cell membrane
- Next step in process: Pi + ADP → ATP (Catalyzed by ATP synthase)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Death: 4 to 20 months
- Cardiac: Some patients with cardiac disorders before death
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Arhythmias
- Pathology: Inflammation; Fat replacement; Fibrosis
- Some patients
- Seizures
- Hypotonia
- Laboratory
- Cardiac MRI: Endomyocardial fibrosis
- Oxidative enzymes: Normal to reduced Complexes I & IV
- Lactic acidosis: Some patients
- Encephalopathy & Cardiomyopathy
● NDUFA11 ; Chromosome 19p13.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 19p13.3; Recessive
- Leigh + Cardiomyopathy
● NDUFA2 ; Chromosome 5q31.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 5q31.3; Recessive
- Cardiomyopathy, Congenital Hypertrophic
● TRMT5 ; Chromosome 14q23.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 14q23.1; Recessive
- COXPD5
● MRPS22 ; Chromosome 3q23; Recessive
; Chromosome 3q23; Recessive
- Encephalopathy with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
● NDUFV2 ;
Chromosome 18p11.22; Recessive
;
Chromosome 18p11.22; Recessive
- Cardiomyopathy + Mental retardation (COXPD9)

● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein, Large 3 (MRPL3) ;
Chromosome 3q22.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 3q22.1; Recessive
- Cardiomyopathy (hypertrophic); Brain swelling & Macrocephaly
- Familial
- Onset: 1st month
- Lab: Complex I deficiency; High lactate
- CNS Pathology: Small vessel proliferation & gliosis
- Cardiomyopathy with PEO
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Ataxia (DCMA)
● DNAJC19 (TIM14); Recessive
- Cardiomyopathy + Mild Myopathy (MTDPS12B)

● Adenine nucleotide translocator 1 (ANT1; SLC25A4) ;
Chromosome 4q35.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 4q35.1; Recessive
- Nosology: Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 12 (Cardiomyopathic type)
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense (Ala123Asp; R236P) or Null (c.523delC)
- U mtDNA haplogroup: Disease severity worse
157
- More rapid & severe cardiomyopathy than haplogroup H
- Creatine kinase MB & Troponin I higher
- Allelic disorders
- Mutations
- ANT1 protein (SLC25A4)
- Mutations: Causes loss of function
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood
- Fatigue & Exercise intolerance
- Muscle pain
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic, symmetric & concentric
- Myopathy
- Mild
- Exercise intolerance
- No ophthalmoplegia
- Headache episodes: Often with nausea & vomiting
- Contractures: Ankle
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Moderately high
- Lactic acidosis
- Hyperalaninemia
- Muscle
- Mitochondrial proliferation; SDH-positive muscle fibers
- mtDNA: Multiple deletions or Depletion
- Ultrastructure: Abnormal mitochondria containing paracrystalline inclusions
- Ox-Phos
- Partial reductions in Complexes I, III, IV & V
- Citrate synthase: High
- SLC25A4 protein: Reduced or Absent
- EMG: Myopathic
- NCV: Normal
- Cardiac
- Hypertrophy
- Cardiomyocyte degeneration
- Mitochondria: Overabundant & Structurally abnormal
- Subendocardial interstitial fibrosis
- Arteriolar smooth muscle: Hypertrophy
- Disease pathophysiology
- May be related to excess of reactive-oxygen species (ROS)
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 162
162
● ELAC, E. Coli, Homolog of, 2 (ELAC2) ;
Chromosome 17p12; Recessive
;
Chromosome 17p12; Recessive
- Nosology: Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 17 (COXPD17)
- Epidemiology: 5 patients in 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop & Missense
- Allelic: Low-penetrance susceptibility markers of prostate cancer (Ser217Leu & Ala541Thr)
- ELAC2 protein
- Expression: Ubiquitous
- Subcellular location: Nucleus; Mitochondria
- Homodimer
- Interacts with PTCD1
- mtRNA processing: RNase Z
- Endonucleolytic cleavage at 3' termini of mitochondrial tRNAs
- Zinc phosphodiesterase
- Mutation: Impaired mitochondrial translation
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy; Failure to thrive at 3 to 4 months
- Fetal growth: Reduced; Microcephaly
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Hypotonia
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Course: Death in 1st year for some; Others alive at 13 years
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Amino acids: High alanine & glutamine
- BAER: Mild central hearing impairment
- Levels of mtRNA precursors: Greatly increased
- Muscle
- Histochemistry
- Mitochondria: Large & abnormal cristae
- COX- fibers: In older patients
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Complex I deficiency: Mild to moderate
- Complex IV deficiency: Some patients
- Histochemistry
- CNS MRI: Hyperintensities in pallida
- Cardiomyopathy + Encephalopathy
● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 alpha subcomplex, assembly factor 1 (NDUFAF1; CIA30) ; Chromosome 15q15.1
; Chromosome 15q15.1
- Barth syndrome: Allelic with Familial dilated cardiomyopathy 3A
- Right ventricular dilated cardiomyopathies (ARVD): ? Mitochondrial disorder
Deafness: Mitochondrial disorders
|
Autosomal Recessive inheritance, Syndromic Wolfram (DIDMOAD): WFS1; WFS2 Deafness-Dystonia syndrome Maternal (mitochondrial) inheritance Non-syndromic Syndromic Sporadic syndromic |
- Deafness: Maternal & Non-syndromic (mtDNA Point mutations)

- 12s rRNA (MTRNR1)

- Mitoribosome
- Mutations: A1555G; C1494T
- Clinical: Aminoglycoside-induced
 & Non-syndromic deafness
& Non-syndromic deafness
- May be more severe with associated mutants
- GJB2 (Connexin 26) allele (heterozygous)
- TRMU
- MTTS1

- MTCO1

- MTRNR1
- 12s rRNA (MTRNR1)
- Deafness: Maternal ± Syndromic
- Point mutations: Mitochondrial DNA
- mtRNALeu (MTTL1)
 : Isolated hearing loss or Syndromic
: Isolated hearing loss or Syndromic
- Mutation: A3243G
- Frequency
- 7% of patients with matrilinear sensorineural hearing loss
- Overall: 1%
- More severe in males
- Onset: Teens to 5th decade
- Progression of deafness: Increases with age
- Syndromic features
- MELAS: Hearing loss present in many patients
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cardiomyopathy
- A3243G: Mutation features
- Heteroplasmic
- Most commonly found in muscle or hair follicles
- Less common in leukocytes with increasing age
- MERRF
- mtRNA Ser (MTTS1)
 : Hearing loss, Syndromic
: Hearing loss, Syndromic
- A7445G mutation
- Sensorineural hearing loss: May be homoplasmic
- Palmoplantar keratoderma
- 7472 insC (1 base pair insertion) & T7512C
- Hearing loss; Ataxia; Myoclonus (HAM Syndrome)
- Neurologic feature, other: Epilepsia partialis continua; With high levels of mutation
- Pathology: COX deficiency; No ragged red fibers
- Biochemistry: Complex IV deficiency
- Disease mechanism
- ? Mutations produce functional insufficiency of mitochondrial mtRNA-Ser
- Also related to MELAS/MERRF overlap syndrome
- A7445G mutation
- mtRNA Ser (MTTS2)
 : Hearing loss, Syndromic
: Hearing loss, Syndromic
- Genetics
- Mutation: C12258A
- Same mutation produces: Ataxia, Cataract & Diabetes
- Other mutations MTTS2 produce
- MELAS/MERRF overlap syndrome
- Other CNS
- Encephalopathy
- Neurodevelopmental delay
- Seizures
- Diabetes mellitus
- Myopathy
- Mutation: C12258A
- Clinical
- Sensorineural hearing loss: Progressive
- Recruitment: Distortion & physical discomfort as a result of loud noise
- Persistent tinnitus
- Similar to Usher syndromes, Type III but with maternal (dominant) inheritance
- Retinitis Pigmentosa
- Sensorineural hearing loss: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Mitochondrial proliferation
- EKG: Right-axis deviation
- Genetics
- tRNA Leu: with Diabetes

- tRNA Lys
 :
with Diabetes or Cardiomyopathy
:
with Diabetes or Cardiomyopathy
- tRNA Gln
 :
Increased risk of sensorineural hearing loss & migraine
14
:
Increased risk of sensorineural hearing loss & migraine
14
- mtRNALeu (MTTL1)
- Large (> 1 kb) heteroplasmic deletion:
Kearns-Sayre
 ;
PEO; Diabetes
;
PEO; Diabetes

- Large (> 1 kb) heteroplasmic partial duplication: Kearns-Sayre; Diabetes; Ataxia; Tubulopathy
- Wolfram syndrome: ? Mitochondrial form
- Point mutations: Mitochondrial DNA
- Sporadic syndromic deafness
- Single large mtDNA deletion: with Optic Atrophy, Diabetes
- Cytochrome c oxidase 1 (MTCO1) (Complex IV)

- Genetics
- Mitochondrial DNA encoded
- Mutations: G6930A, Stop codon; G6480A
- Disrupts assembly of respiratory-chain complex IV
- Biochemical correlates with the amount of mutant G6930A mtDNA
- Differs from high threshold effect in mitochondrial tRNA point mutations
- Other COX 1 (MTCO1) mutations: Sideroblastic anemia & Leber's
- Clinical
- Onset: 3 years; Cataracts
- Hearing loss: 7 years; Sensorineural; Progressive
- Myopathy
- CNS: Ataxia; Myoclonic epilepsy
- Ocular: Visual loss; Optic atrophy
- Muscle biopsy
- Mitochondrial enzymes: 90% reduction in COX; Normal SDH
- No ragged red fibers
- MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy: Diffuse
- Basal ganglia: Bilateral small symmetrical nodular hyperintensities
- Also see: MTCO1 Exercise intolerance
- Genetics
- Recessive syndromic deafness
- CODAS: LONP1
- Wolfram syndrome (DIDMOAD)

- Major diagnostic features
- Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- Optic atrophy: Progressive
- Diabetes Insipidus, Diabetes Mellitus, Optic Atrophy, Deafness
- Subtypes
- Wolframin (WFS1): Chromosome 4p16
- WFS2: Chromosome 4q22-24
- ? Mitochondrial
- Wolfram syndrome 1

● Wolframin (WFS1) ;
WFS1; Chromosome 4p16.1; Recessive (or Semi-Dominant)
;
WFS1; Chromosome 4p16.1; Recessive (or Semi-Dominant)
- WFS1 gene mutations
- ~24 mutations identified: Nonsense, Missense...
- Most mutations in exon 8
- Most patients compound heterozygotes
- Carrier frequency: 1/350
- mtDNA
- Multiple mtDNA deletions common
- Up to 90%
- Location: Affected tissues such as brain
- Few deletions in muscle or leukocytes
- Multiple mtDNA deletions common
- Wolframin protein

- Endoglycosidase H-sensitive glycoprotein
- Location
- Subcellular
- Location: Transmembrane; Endoplasmic reticulum
- Not in mitochondria
- CNS (Neurons): Hippocampus CA1, Amygdaloid areas,
Olfactory tubercle & Allocortex (Superficial layer)
- Subcellular
- Expressed in heart, brain, pancreas, liver, kidney, skeletal muscle
- Mutations: Loss of function
- Clinical
- Prevalence: 1:100,000 to 1:700,000
- Onset
- Age: 95% by age 15
- Diabetes mellitus
- Optic atrophy
- CNS: > 60% by 4th decade
- Deafness
- Optic atrophy
- Onset Mean 15 years, Range 6 weeks to 30 years
- Usually begins after diabetes mellitus
- Ocular: Occasional patient with Parinaud's
- Cerebellar: Ataxia; Nystagmus (50%)
- Myoclonus
- Cortical
- Seizures
- Psychiatric: Depression; Psychosis
- Cognitive: Encephalopathy; Retardation; Dementia
- Central respiratory failure: Some patients
- PNS
- Autonomic dysfunction:
- Urinary tract atony
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Gastroparesis
- Polyneuropathy
- Autonomic dysfunction:
- Systemic
- Diabetes mellitus
- Diabetes insipidus (Onset 5 to 10 years)
- Renal tract change: Distended bladder
- Course: Progressive
- Heterozygous carriers: Predisposition to
- Psychiatric disease (?26x)
- Diabetes
- Lab
- Hematology: Anemia; Low WBC; Low Platelets
- Reduced
- Vasopressin
- Erythrocyte thiamine pyrophosphate activity
- Thiamine pyrophosphokinase activity
- Muscle: Multiple heteroplasmic mtDNA deletions
- MRI: Brain atrophy
- CNS pathology
- Optic nerve degeneration
- Neuron loss: Lateral geniculate; Basis pontis;
Paraventricular & Supraoptic nuclei - Axonal dystrophy: Swellings; ? Frequency

Posterior pituitary "bright signal": Absent
Atrophy: Brainstem, Cerebellum
From: B Trikamji

Pons: T2 signal Δ
Optic radiation: T2 signal
Atrophy: Cerebellum
Middle cerebellar peduncles
- Major diagnostic features
- Wolfram syndrome 2

● CDGSH iron sulfur domain protein 2 (CISD2; ERIS; ZCD2) ; Chromosome 4q24; Recessive
; Chromosome 4q24; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Deletion, Splice
- ERIS (Endoplasmic Reticulum Intermembrane Small protein) protein
- Zinc finger protein
- Localization
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Expression: Pancreas, Brain & Other tissues
- Regulates: Cellular Ca++ homeostasis: Mitochondrial integrity
- Clinical
- Typical features
- Diabetes mellitus
- Optic atrophy
- Hearing loss: Sensory-neural
- Urinary tract dilatation
- Distinctive features
- Diabetes insipidus: Milder or absent
- Bleeding tendency: Defective platelet aggregation with collagen
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Typical features
- Wolfram syndrome
● Mitochondrial form
- Deafness-Dystonia-Dementia syndromes

● DDP protein (TIMM8A) ; Chromosome Xq22.1; Recessive
; Chromosome Xq22.1; Recessive
- TIMM8A gene mutations: Missense; Stop; Small deletion
- DDP protein (Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 8)
- Location: Mitochondrial intermembrane space
- Homology to yeast Tim (Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane) mitochondrial proteins
- Function: ? Import of metabolite transporters from Cytoplasm to Mitochondrial inner membrane
- ? Mutations cause defect in mitochondrial protein import system
- Other TIM protein disorder: Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Ataxia (DCMA)
- Clinical: Mohr-Tranebjaerg syndrome; Deafness-dystonia syndrome
- Sensory-neural hearing loss: Progressive
- Eye: Myopia; Reduced visual acuity; Constricted visual fields; Retinal change
- CNS: Dystonia; Mental deficiency; Cortical blindness
- Clinical: Jensen syndrome

- Eye: Blindness; Optic atrophy
- Ear: Sensorineural hearing loss
- CNS: Dementia; CNS calcifications
- Muscle: Wasting
- Differential diagnosis: Other mitochondrial dystonia syndromes
- LHON + Dystonia
- Some patients: MELAS; NARP; POLG1; Leigh
- Leukoencephalopathy with Complex II deficiency
- TPK1
- Dystonia, Deafness with Leigh-like syndrome (MEGDEL; MGCA6)
 139
139
● Serine active site containing 1 (SERAC1)
 ; Chromosome 6q25.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 6q25.3; Recessive
- MEGDEL: 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria, Sensori-neural Deafness, Encephalopathy, & Leigh-like syndrome
- Epidemiology: > 70 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Frameshift; Splice site
- SERAC1 protein
- Mitochondrial membrane protein
- Location: Interface between mitochondria & endoplasmic reticulum
- Tissues: High in muscle & brain; Ubiquitous
- Functions: Phospholipid exchange; Intracellular cholesterol trafficking; Lipase
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 day to 6 years, Median 6 months
- Hypotonia
- Encephalopathy
- Leigh-like syndrome
- Intellectual disability & Retardation
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Muscle tone
- Early: Hypotonia
- Spasticity, Progressive
- Dystonia
- Hepatopathy
- Course: Progressive; Most never walk
- Milder phenotype in rare patients
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
- Alanine: High
- Hyperammonemia
- 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
- Transaminases: High
- Cardiolipin: Normal amounts; Abnormal
- Coagulopathy
- Serum α-fetoprotein: High
- Oxidative phosphorylation defects: Variable; I, IV or II+III
- MRI: Leigh-like; Putamen lesions; Atrophy
- Muscle: Mitochondrial ultrastructure pathology
- Filipin staining: Abnormal
- Dystonia, early-onset and/or Spastic paraplegia (DYTSPG)

● ATP Synthase membrane subunit C, Locus 3 (ATP5MC3; ATP5G3) ; Chromosome 2q31.1; Dominant
; Chromosome 2q31.1; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 large American family + 1 other patient
- Genetics
- ATP5MC3 protein
- Mitochondrial ATP synthase
 subunit (Transmembrane)
subunit (Transmembrane)
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Transports protons across mitochondrial inner membrane to F1-ATPase
- Mitochondrial ATP synthase
- Clinical
- Onset: 1 to 51 years
- Dystonia
- More in younger patients
- ± Spasmodic
- Spasticity
- More in older patients
- Leg dysfunction
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Reticular dysgenesis

● Adenylate kinase 2 (AK2) ; Chromosome 1p35.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 1p35.1; Recessive
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- Early differentiation arrest in the lineage
- Impaired lymphoid maturation
- Sensorineural deafness, bilateral
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome & Sensorineural hearing loss (COQ10D6)

● Ubiquinone biosynthesis monooxygenase COQ6 (COQ6)
 ; Chromosome 14q24.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 14q24.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 5 families, 11 patients
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- COQ6 protein: Coenzyme Q10 synthesis
- Clinical
- Onset age: 0 to 7 years
- Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome
- Sensorineural deafness, bilateral
- Other CNS
- Ataxia
- Seizures
- Face: Dysmorphism
- Course: Some patients die in early childhood
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: White matter changes
- Deafness, Cataracts, Skeletal dysplasia, Polyneuropathy (CAGSSS)
 177
177
● Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase 2 (IARS2) ; Chromosome 1q41; Recessive
; Chromosome 1q41; Recessive
- Nosology: Cataracts, Growth hormone deficiency, Sensory neuropathy, Sensorineural hearing loss, Skeletal dysplasia
- Epidemiology: 3 French-Canadian patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: P909L
- Allelic with: Leigh syndrome
- IARS2 protein
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- Mitochondrial
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Cataracts: Congenital
- Skeletal dysplasia
- Face dysmorphism: Thick eyebrows, Prominent forehead, Small mouth
- Short stature
- Hip disorders
- Scoliosis
- Spine: Cervical stenosis; C2-odontoid hypoplasia
- Spondylo-epiphyseal dysplasia
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory loss
- Distal
- Pin & Temperature
- Vibration: Preserved
- Laboratory
- Growth hormone: Deficiency
- MRI: Pituitary adenohypophysis atrophy
- IARS2 variant syndrome: Leigh
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4 weeks
- Developmental delay
- Death: 18 months
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Diffuse atrophy; T2 hyperintensities in basalganglia & thalami
- Deafness + Optic neuropathy: FDXR
- PTCD3
- CODAS: LONP1
- Non-syndromic deafness
- Deafness, Autosomal dominant 64
 : DIABLO
: DIABLO

- PNPT1
- Deafness, Autosomal dominant 64
Ataxia: Mitochondrial disorders
- Mitochondrial DNA: Ataxia is usually single part of multi-component syndrome
- Leukodystrophy: Sporadic; Single large mtDNA deletion
- MELAS (MTTL1)
- MERRF
- ATP synthase 6 (MTATP6)
- HAM: MTTS1
- Ataxia, Cataract & Diabetes mellitus: tRNA Serine 2 (MTTS2)

- Same mutation produces: Progressive sensorineural deafness & retinitis pigmentosa
- Cytochrome c Oxidase I (MTCO1)
- Cytochrome c Oxidase II (MTCO2)
 :
Ataxia; Distal weakness; Retinopathy & Optic atrophy
:
Ataxia; Distal weakness; Retinopathy & Optic atrophy
- Recessive
- Ataxia + Spasticity: SPG7
- Ataxia, Myelopathy & Skin disease (PEBEL1): NAXE
- Cerebellar-Retinal Degeneration: ACO2
- Charlevoix-Saguenay spastic ataxia (ARSACS)
- Coenzyme Q10 deficiency syndromes
- Complex IV deficiency
- COX10 (Heme A:farnesyltransferase)
- COX20 (FAM36A)
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Ataxia (DCMA): DNAJC19
- Friedreich ataxia: Frataxin
- IOSCA: Twinkle
- L-2 Hydroxyglutaric acidemia: L2HGDH
- Leukoencephalopathy
- LONP1
- Maple syrup urine: BCKDHB
- MMYAT: MSTO1
- MTPAP
- NUBPL
- OPA11: YME1L1
- OTC
- PEBEL2: NAXD
- PITRM1
- PMPCA
- PTRH2: IMNEPD
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase: Episodic ataxia; Leigh syndrome
- RRM2B
- SCAN3: COA7
- SCAR32: PRDX3
- Sensory ataxia (POLG1): MIRAS, MSCAE, SANDO
- Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (SSADHD): ALDH5A1
- TTC19
- TPK1
- TWNK (c10orf2): Perault syndrome 5; MTDPS7
- Dominant: Variable, or incomplete, connections between ataxia & mitochondrial disorders
- SCA 28
- Cerebellar ataxia, Deafness & Narcolepsy
- OPA1: Occasional patients (ADOAD)
- AD-PEO: Rare patients
- RRM2B
- X-linked
- Other: Variable or Uncertain
Diabetes & Pancreas: Mitochondrial disorders
- Diabetes
- General syndrome: Maternally Inherited Diabetes & Deafness (MIDD)
 284
284
- Diabetes: Young onset
- BMI: Low or Normal
- Maternal inheritance
- Multisystem
- Hearing loss (85%)
- Myopathy (23%)
- Neuropathy (17%)
- Cardiac (24%)
- Common mutation: m.3243A>G
- Blood heteroplasmy range: 12% to 55%
- Higher heteroplasmy: Lower diabetes onset age
- Other mutations
- D-loop mutation (T16189C): Overweight; More iron loading in hemochromatosis
- A3426A: Later onset diabetes; No hearing loss; BMI high
- mtDNA
- Myopathy: mtDNA Point mutation tRNA Glu: Heteroplasmic or Homoplasmic

- mtRNA Leu (MTTL1)

- See MELAS
- A3243G mutation
- Frequency: 0.9% in unselected DM; 2% to 5% in inherited
- mtRNA Lys

- Kearns-Sayre
- Single large mtDNA deletion
- Large scale mtDNA tandem duplication: Maternally transmitted; Deafness
- Myopathy: mtDNA Point mutation tRNA Glu: Heteroplasmic or Homoplasmic
- Wolfram syndrome
- Friedreich ataxia
- Ataxia, Cataract & Diabetes mellitus: tRNA Serine 2 (MTTS2)

- Type 2 diabetes association: PPARG mutation
- Metabolic syndrome in obesity
- Microcephaly, Simplified gyral pattern & Insulin-dependent diabetes: GFM2
- General syndrome: Maternally Inherited Diabetes & Deafness (MIDD)
- Pancreas, Other
Hypoglycemia: Mitochondrial disorders
- E3: Lipoamide (α-ketoglutaric) dehydrogenase deficiency
- FOXRED1
- SCO1
- HADHA
- HMG-CoA lyase deficiency
- Deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK)
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2
- Ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase-binding protein
Anemia & Hematologic
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Ring sideroblasts
- Bone marrow erythroid precursors (erythroblasts) with iron loaded mitochondria
- Visualized as perinuclear ring: Pearls stain
- Ataxia: ABCB7; Xq13
- Sideroblastic anemia, pyridoxine-refractory 3 (SIDBA3)

● Glutaredoxin 5 (GLRX5) ; 14q32.13; Recessive
; 14q32.13; Recessive - Sideroblastic anemia, congenital, non syndromic

● SLC25A38 (Glycine transporter) ;
Chromosome 3p22.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 3p22.1; Recessive
- MLASA2: YARS2; 12p11
- MLASA3: MTATP6
- TRNT1
- mtDNA deletion: Sporadic, large-scale, Single
- Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia

● SLC19A2 (Thiamine transporter) ; 1q24.2; Recessive
; 1q24.2; Recessive
- Iron disorders
- Myopathy with lactic acidosis & sideroblastic anemia
- MLASA1: PUS1; 12q24
- Sideroblastic anemia, congenital, non syndromic 1 (SIDBA1)

● δ-Aminolevulinate synthase 2 (ALAS2) ;
Chromosome Xp11.21; Dominant
;
Chromosome Xp11.21; Dominant
- Myopathy with lactic acidosis & sideroblastic anemia
- Myopathy with abnormal mitochondrial translation
- GRACILE (Toxic iron overload): BCS1L; 2q35
- MELAS: MTTL2
- Myoglobinuria & Exercise intolerance: MTCO1
- Wolfram syndrome (Deafness): WFS1; 4p16
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, Dyserythropoietic anemia & Calvarial hyperostosis: COX4I2; 20q11
- Anemia & Mitochondriopathy: SFXN4; 10q26
Myopathy with lactic acidosis & sideroblastic anemia 1 (MLASA1)
● Pseudouridine synthase 1 (PUS1)
- Epidemiology
- Common: Jewish families of Shiraz, Iranian extraction
- Other: Italian & Turkish patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Nonsense; Arg116Trp, Glu220X, c.487delA, Arg295Trp, Gln301Arg
- Mutation effect: Reduced tRNA pseudouridylation
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood & Teens
- Weakness
- Myopathy
- Weakness
- Proximal
- Progressive
- Respiratory: Later in course
- Exercise intolerance: Fatigue; Nausea & Vomiting
- Ptosis: Mild; Occasional patient
- Weakness
- Skeletal
- Short stature
- Kyphoscoliosis
- Intelligence: Normal
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Anemia
- Sideroblastic
- Blood transfusions may be necessary
- Lactic acidosis: At rest
- Ferretin: High
- Muscle
- Histology: Varied fiber sizes; No SDH+ or COX- muscle fibers
- Biochemistry: Reduced mitochondrial oxidative enzyme activities
- Anemia
Myopathy with lactic acidosis & sideroblastic anemia 2 (MLASA2)
● Tyrosyl-tRNA Synthetase (YARS2)
- Epidemiology: Lebanese, French, Turkish & other families
- Genetics: Mutations
- Homozygous or Heterozygous
- Missense or Stop
- Gly46Asp, Phe52Leu, Pro122Arg, Gly191Asp, Leu208Arg, Arg360X, Ser435Gly
- YARS2 protein
- Catalyzes covalent binding of tyrosine to its cognate tRNA
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) family
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infancy or Childhood
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Delayed milestones
- Weakness
- Fixed weakness
- General: Mild
- Respiratory failure
- Exercise intolerance
- GI: Feeding difficulties; Dysphagia
- Fixed weakness
- Cognition: Normal; Some encephalopathy
- Systemic
- Short stature
- Cardiomyopathy: 3 patients
- Renal tubulopathy: 1 patient
- Course
- Progressive
- May be worse with pregnancy
- Severe forms
- Encephalopathy: Lethargy
- Death in early childhood
- Milder patients: Survive to ≥ 3rd decade
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Anemia, Sideroblastic
- Serum lactate: High
- Other metabolic: Ketosis; Hyperammonemia
- Muscle
- Morphology: May be normal
- Lipid storage
- SDH+ muscle fibers
- COX reduced: Muscle fibers
- Scattered or Diffuse
- Complex I: May be reduced in same fibers
- Oxidative enzymes
- Reduced: Complex I, III, & IV activity & protein complex
- Increased: Complex II & Citrate synthase
Exocrine Pancreatic insufficiency, Dyserythropoietic Anemia & Calvarial hyperostosis
● Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit IV, Isoform 2 (COX4I2)
- Epidemiology: 5 Arab Muslim patients
- Genetics: Glu138Lys mutation
- COX4I2 protein
- Expression: Lung
- COX4: COX activity regulation
- Complex IV
- May stimulate angiogenesis
- Oncogenic in colorectal cancer
- Hypoxia-associated upregulation: Hypoxia-induced release of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species
- Clinical
- GI: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
- Steatorrhea
- Malabsorption of lipid-soluble vitamins
- Skeletal
- Calvarial hyperostosis
- Bone age: delayed
- Osteopenia
- GI: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
- Blood: Dyserythropoietic, megaloblastic anemia
MTDPS19: Epileptic encephalopathy + Anemia + Complex I deficiency
● Solute Carrier Family 25 (Mitochondrial carrier), Member 10 (SLC25A10)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop & Splice; Loss of function
- SLC25A10 protein: Dicarboxylate carrier
- Clinical: Epileptic encephalopthy
- Onset age: Birth
- Morphology: Hypospadias; Hydrocele
- Epilepsy: Infantile spasms; Onset at 3 months
- Hypotonia
- Spastic quadriparesis
- Dyskinesias
- Growth & Intellect: Normal
- Laboratory
- Muscle: mtDNA depletion (60% of control); Complex I deficiency
- Anemia: Iron deficient
- Brain MRI: White matter pathology; corpus callosum thin
Hepatic: Mitochondrial
Acute Infantile Liver Failure (LFIT)
● tRNA 5-methylaminomethyl-2-thiouridylate methyltransferase (TRMU)
- Epidemiology: > 25 patients; Some Yemenite Jewish
- Genetics
- TRMU protein
- Mitochondria-specific
- mtRNA-modifying enzyme
- Role in mitochondrial DNA translation
- Thiolates mitochondrial tRNA
- Mutation effects
- Amount of thio-modified mitochondrial tRNAs is severely reduced
- mtDNA depletion
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 to 4 months
- Irritability, Poor feeding, Vomiting
- Hepatic failure
- Jaundiced sclerae
- Distended abdomen
- Hepatomegaly
- Lethargy
- Other syndromes
- Leigh
- Myopathy
- Cardiomyopathy
- Course
- Death during acute episode, or
- Resolution without recurrence
- Improvement starts: After 2 to 3 weeks
- Liver functions normal: After 3 to 4 months
- Liver size normal: 3 months to 3 years
- Treatment
- N-acetylcysteine (70 to 150 mg/kg/day) + L-cysteine (85 to 300mg/kg/day)
- Liver transplant
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Coagulopathy: Low factor 5 & 11; Not corrected by vitamin K supplementation
- Albumin: Low
- Direct hyperbilirubinemia
- Metabolic acidosis
- Serum lactic acid: High
- Hypoglycemia
- α-fetoprotein: High
- Blood ammonia: Normal or Slightly elevated
- Plasma amino acids: High phenylalanine, tyrosine, methionine, glutamine & alanine
- Urinary organic acids: High lactate, phenylalanine & tyrosine metabolites; Ketotic dicarboxylic & 3-hydroxydicarboxylic aciduria
- Liver biopsy
- Histology: Abnormal
- Enzyme analysis: Complexes I, III & IV low; Complex II normal
- Serum CK: Normal or up to 4,000
- EMG: Normal
- Muscle biopsy: Normal histology
- Differential diagnosis: Hepatic failure + Hyperlactatemia
COXPD46: Liver disease
● Mitochondrial Ribosoml Protein 23 (MRPS23)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Pro40Arg
- MRPS23 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosome component
- Clinical
- Hepatic disease
- Laboratory
- Fibroblasts: Complex I & IV activities reduced
COXPD47: Multisystem disorder + Liver disease
● Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein 28 (MRPS28; MRPS35)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients, 1 family
- Genetics
- Mutations: Lys119Arg; 182-bp intragenic deletion
- MRPS28 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosome component
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Hepatomegaly
- Dysmorphism: Microcephaly
 , Round face, Short neck, Ptosis, Long philtrum
, Round face, Short neck, Ptosis, Long philtrum

- Extremities: Short hands; Cone-shaped terminal phalanges; Camptodactyly
 ; Toe syndactyly
; Toe syndactyly - Eyes: Cataracts; Ptosis
- Ears: Low-set & posteriorly rotated; Sensorineural deafness
- Cryptorchidism
- CNS: Hypotonia; Global intellectual delay
- Survival: 2 to 30 years
- Laboratory
- Complex I, III, IV & V activities reduced
- Retinogram abnormal
- Vertebrae flat
- Brain imaging: Bilateral lesions in Globus pallidus; Cerebellar atrophy
- Metabolic: Lactic acidosis; Alanine high
- Liver enzymes: High
COXPD48: Encephalomyopathy
● NOP2/SUN RNA Methyltransferase family, member 3 (NSUN3)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.295C4T (Arg99X); c.123-615_466+2155del; Cys152Ser; Ala141Pro
- Allelic disorder: Optic neuropathy 320
- NSUN3 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Mitochondrial translation
- Required for deposition of m(5)C at the anticodon loop in mt-tRNAMet
- 5-formylcytosine generation from 5-methylcytosine (m(5)C)
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 6 months
- CNS
- Developmental delay: Global
- Seizures
- Hypotonia
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Weakness: Proximal
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: episodic
- Brain imaging: Cerebral atrophy; Cerebral hemisphere white matter hyperintensities
- Muscle
- mtDNA levels: Normal
- Oxidative enzyme activity: Complexes I, III, IV reduced
Multiple symmetric lipomatosis
Optic Neuropathy: Mitochondrial 353
|
Mitochondrial DNA LHON Nuclear DNA Complex I genes 353
|
General
- Optic disk atrophy: Predominant loss of temporal retinal nerve fiber bundle by OCT examination
- Recessive forms: Commonly syndromic
- Leber's (LHON)
- Genetics: Various mitochondrial gene mutations
- Onset age: Mid-adult
- Clinical: Subacute loss of vision; Central scotoma
- MC1DN38: LHON, Recessive (LHONAR1)
 263
263
● DNAJC30 ;
Chromosome 7q11.23; Recessive
;
Chromosome 7q11.23; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 33 patients, 29 families, Mostly Eastern European
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense or Stop
- c.152A>G (p.Tyr51Cys) common; J domain
- Penetrance: Incomplete; 97% in males, 43% in females
- Allelic disorders
- Leigh syndrome
- LHON+
- May contribute to Williams-Beuren syndrome

- Mutations
- DNAJC30 protein
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Chaperone
- Complex I repair
- Clinical
- Male predominance
- Onset
- Age: Young adults; Mean 20 years, 10 years younger than mtLHON
- Subacute: Mean time to nadir 8 weeks
- Vision loss: Central
- Treatment: Idebenone
- Recovery: Poor; 68% of patients with spontaneous recovery
- Laboratory
- Muscle biopsy: Complex I deficiency
- Eye
- Circumpapillary telangiectatic microangiopathy
- Central retinal vessel tortuosity without leakage on fluorescein angiography
- Subacute swelling (pseudoedema) of retinal nerve fiber layer
- Brain MRI: Normal or Deep gray matter lesions
- Serum lactate: May be high
- DNAJC30 variant: Leigh syndrome
308
- 2 patients
- Mutation: May be truncating
- Disease onset: Earlier
- DNAJC30 variant: LHON+
- Optic Atrophy (OPA1; ADOA)
 76
76
● OPA1 protein ;
Chromosome 3q29; Dominant
;
Chromosome 3q29; Dominant
- Genetics: OPA1 mutations
- Mutations: General
- > 100 different mutations
- ~50% cause premature truncation
- Locations
- Spread through gene coding sequence
- Most in
- GTPase domain: Exons 8-16
- 3 end of coding region: Exons 27-28; GED domain
- Relatively few mutations in: Exons 1 to 7
- Mutation types
- Missense mutations: Linked to
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) instability
- Accumulation of multiple mtDNA deletions in skeletal muscle
- Truncation mutations: Cause reduced levels of OPA1 in tissues
- Missense mutations: Linked to
- Disease mechanism: ? Haploinsufficiency of OPA1 protein
- Allelic disorders
- OPA1
- Optic Atrophy + (ODOAD; ADOA+): GTPase domain mutations
- Behr syndrome: Recessive
- MTDPS14B: Recessive
- MTDPS14A: Dominant de novo
- Glaucoma, normal tension, susceptibility

- External link: Mutation data base
- Mutations: General
- OPA1 protein
- Cellular location: Mitochondrial
- Anchored to inner membrane facing intermembrane space
- Tissue location: Widely expressed; Most abundant in retina; Also brain, testis, heart, skeletal muscle
- Functions
- Maintenance & stability of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
- Mitochondrial fusion
- Mitochondrial dynamics & Maintenance of structural integrity of cristae
- Regulates apoptotic processes: Through control of cytochrome c redistribution
- Mitochondrial Ca++ uptake
- Dynamin-related GTPase
- OPA1 directly interacts with: Subunits of complexes I, II & III; Apoptosis inducing factor
- 8 isoforms from alternative splicing
- Processing associated with m-AAA protease AFG3L2
- Substrate of SPG7
- Mutation effects
- Oxidative phosphorylation defect at level of complex I: Similar to LHON mutations
- Impairment in mitochondrial ATP synthesis driven by complex I substrates
- OPA1 mutant fibroblasts: More prone to cell death
- Abnormal mitochondrial morphology
333
- Altered distribution of nucleoids in mitochondria
- Cristae: None or Loss of periodicity
- OPA1 loss: No nucleoids (Empty mitochondria)
- Cellular location: Mitochondrial
- Clinical: Heterogeneous
- Onset
- 60% < 10 years
- Common ages: 18-35 yrs
- Sudden onset of visual loss
- Both eyes: Asynchronously
- Visual acuity: Variably reduced
- Progressive decrease in visual acuity
- Color vision defect: Blue-yellow hues
- Loss of sensitivity in central visual field
- Optic nerve pallor
- May be exacerbated by: Ethambutol
- Deafness: R445H & G439V mutations
- Ataxia: G439V mutation
- Onset
- Pathology & Biochemistry
- Retinal ganglion cells: Degeneration
- Muscle
- Impaired oxidative phosphorylation
- Reduced ATP synthesis
- mtDNA: Multiple different deletions
- WBC mtDNA
- Increased in amount (2x to 4x): Some patients normal
- No correlation with disease severity
- OPA1 Variant syndrome: Complex phenotype; Optic atrophy +... (ODOAD)

- OPA1 Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Common mutations: R445H, G488R, A495V
- Increased risk with mutations
- Missense
- Located in GTPase region
- Clinical
- Optic atrophy
- Visual loss
- Progressive
- Abnormal electroretinogram
- No retinal pigment changes
- Deafness (62%)
- Sensorineural
- Progressive
- Onset age: 1st or 2nd decade
- Myopathy (30%)
- Ptosis
- External ophthalmoplegia (45%)
- Progressive
- Onset age: 3rd decade
- Polyneuropathy (30%)
- CNS
- Ataxia
- Spastic paraparesis
- Parkinsonism
- Optic atrophy
- Laboratory
- Macrocytic anemia
- Hypogonadism
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers
- mtDNA deletions
- Retina
- Loss of ganglion cells
- OPA1 Genetics
- OPA1 Variant syndrome: MTDPS14A, Encephalomyopathy

- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo; Dominant
- Mutations: Heterozygous; Missense
- Clinical
- Onset: Prenatal to 3 months
- Eyes: Optic atrophy; Nystagmus
- CNS: Psychomotor delay; Seizures
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Abnormal basal ganglia & white matter
- Polyneuropathy: Axon loss
- Fibroblasts: mtDNA reduced
- OPA1 Variant syndrome: MTDPS14B, Cardioencephalomyopathy

- Epidemiology: 1 Arab Muslim family, 2 sisters
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Leu534Arg; Missense; Homozygous
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 days to 2 months
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Cranial nerves
- Eye: Optic atrophy; Nystagmus
- Deafness: Sensorineural; 1 patient
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Peripheral hypertonia: Opisthotonic posturing
- Feeding difficulties
- Muscle wasting
- Neurodevelopmental delay
- Course: Rapid progression; Death at < 1 year with apnea
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Muscle
- Morphology: Normal
- mtDNA levels: 78% reduced
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Complexes I & IV: 21% to 24% of normal
- Complex II: 64% of normal
- Ultrastructure: Large mitochondria
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Genetics: OPA1 mutations
- Optic atrophy 3 (OPA3; MGCA3)

● OPA3 ; Chromosome 19q13.32; Recessive or Dominant
; Chromosome 19q13.32; Recessive or Dominant
- Nosology
- Recessive disorders: 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria, Type III; Iraqi-Jewish 'Optic atrophy plus'; Costeff syndrome
- Genetics
- Recessive syndromes: Loss of function mutations
- Allelic disorder: ADOAC, Dominant
- OPA3 expression: High in muscle
- Clinical
- Eye
- Optic atrophy
- Cataracts
- Extrapyramidal: Chorea; Early onset
- Spastic paraparesis: 50%; Onset 2nd decade
- Ataxia: Mild
- Cognitive defects: Mild
- Eye
- Laboratory
- OPA3 variant: Autosomal Dominant Optic Atrophy & Cataract (ADOAC)
245
- Epidemiology: 6 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominmant
- Mutations: c.23T>C (Met8Thr); c.313>G (p.Gln105Glu)
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st 2 decades
- Eye
- Optic atrophy
- Cataracts
- Peripheral nerve
- Autonomic
- Gastrointestinal dysmotility
- Other: Orthostatic tachycardia or hypotension; Episodic hypertension
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss: Distal; Arms & Legs
- Weakness: Mild or None
- Hearing loss
- Autonomic
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory ≥ Motor
- Nerve biopsy: Loss of myelinated axons
- Muscle biopsy
- Few angular muscle fibers
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondria enlarged & abnormal structure
- Nosology
- Optic atrophy 7 ± Auditory (OPA7)
 89
89
● TMEM126A
 ; Chromosome 11q14.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 11q14.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Algerian & Maghreb families
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg55X
- TMEM126A protein
- Mitochondrial: Co-localizes with SDHA; MTCO1; ATP5A; ATP5B
- Transmembrane
- Expressed in brain, muscle, retina
- ? Mitochondria-localized mRNA (MLR) protein
- TMEM70 mutation: Encephalocardiomyopathy
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4 to 6 years
- Visual loss: Severe; Bilateral; Central scotoma; Peripheral fields spared
- Optic disc: Pallor
- Other occasional features
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hearing loss
- Laboratory
- Complex I activity: Reduced in fibroblasts in 1 patient
- MMDS 9A: Optic + Auditory Neuropathy (ANOA)
 229
229
● Ferredoxin reductase (FDXR) ; Chromosome 17q25.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 17q25.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 47 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- Allelic disorder
- MMDS 9B: Neurodevelopmental Disorder + Mitochondrial Abnormalities, Optic Atrophy & Developmental Regression (NEDMADR)

- MMDS 9B: Neurodevelopmental Disorder + Mitochondrial Abnormalities, Optic Atrophy & Developmental Regression (NEDMADR)
- FDXR protein
- Mitochondrial
- Flavoprotein
- Facilitates the transfer of electron from NADPH to ferredoxin 1 (FDX1) & ferredoxin 2 (FDX2)
- Biosynthesis of
- Iron-sulfur clusters (ISCs)
- Heme
- Steroids
- Mutation effects
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Iron overload
- Ferroptosis susceptibility
- Lipid peroxidation
- Clinical
- Onset age: Typical 2nd decade; Range 2 to 20 years
- Auditory neuropathy
- Optic neuropathy: Optic atrophy; Retinal pigment changes
- Other CNS
- Motor delay: Some patients
- Ataxia (40%)
- Pyramidal signs
- Seizures
- Polyneuropathy (20%)
- Weakness: Distal
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Laboratory
- ERG: Absent responses
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Muscle
- Mitochondria: Small with increased number; Reduced cristae
- Sarcomere structure: Disrupted
- Nuclei: Irregular shapes
- Oxidative enzymes: Complexes I, II, III reduced
- Ferrous iron: Increased
- Reactive oxygen species: Increased
- Nerve: Axon loss; Mitochondria with absent cristae
Optic atrophy (OPA): Other
- OPA2

● Chromosome Xp11.4-p11.21; Recessive- Epidemiology: Dutch & Idaho families
- Onset: early childhood
- Clinical
- Visual acuity: Reduced; 20/30 to 20/100
- Optic nerve pallor
- Progresion: Slow
- OPA4

● Chromosome 18q12.2q12.3; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 1 German family from West Virginia
- Clinical
- Visual acuity & Color discrimination: Reduced
- Optic nerve: Atrophy
- OPA14
 266
266
● Mitochondrial elongation factor 1 (MIEF1; MID51) ; Chromosome 22q13.1; Dominant
; Chromosome 22q13.1; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 2 French families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Y240N, R146W
- MIEF1 protein
- Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Adaptor protein: Regulates mitochondrial fission
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3rd or 4th decade
- Optic nerve pallor
- Visual
- Acuity: Decreased
- Course: Slow or Sudden loss
- May be asymmetric
- Central scotoma: Bilateral superior altitudinal defect
- Color: Moderately impaired; Varies from normal to blue-yellow dyschromatopsia
- Acuity: Decreased
- Laboratory
- VEP: Reduced
- Optic disk: Pale
- RNFL: Collapsed
- OPA6

● Chromosome 8q21-q22; Recessive- Epidemiology: French family
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 to 6 years
- Optic atrophy
- Visual acuity: Decreased slowly
- Color vision: Dyschromatopsia for red-green
- Photophobia
- Optic neuropathy ± Ataxia (OPA10)

● Reticulon 4-interacting protein 1 (RTN4IP1) ; Chromosome 6q21; Recessive
; Chromosome 6q21; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics: Stop & Missense mutations
- RTN4IP1 protein
- Mitochondrial: Outer membrane
- Mitochondrial ubiquinol oxydo-reductase
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Optic
- Neuropathy: Acuity reduced; Color blindness; Constricted visual fields
- Disks: Small & Pale
- Congenital nystagmus
- Some patients
- Ataxia: Stato-kinetic; Nystagmus
- Learning disability
- Seizures
- Laboratory
- Eye: Reduced thickness of temporal retinal nerve fiber layer
- Brain MRI: Optic tracts thin
- Fibroblasts: Complex I & IV activities reduced
- Serum lactate: May be high or normal
- Optic atrophy 11 (OPA11)

● Mitochondrial escape 1-like 1 (YME1L1) ; Chromosome 10p12.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 10p12.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 Saudi Arabian family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg149Trp; Homozygous
- YME1L1 protein
- AAA ATPase family
- Processing of OPA1
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Protease domain faces intermembrane space (IMS) (i-AAA protease)
- Interacts with: Mitochondrial processing peptidase
(A
 ;
B
;
B
 )
)
- Proteolytic processing: Cleaves off mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS)
- Import into mitochondria
- Degrades intermembrane space & inner mitochondrial membrane proteins
- Mutated protein
- Proliferation defect
- Mitochondrial network fragmentation
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonate or Infant
- Psychomotor development
- Delay: Motor & Speech
- Intellectual disability: IQ 38 to 49
- Eyes
- Optic atrophy: Vision loss
- Myopia
- Amblyopia
- Hearing loss
- Other: Some patients
- Ataxia (75%): Dysmetria
- Head size change: Microcephaly or Macrocephaly
- Movement: Hyperkinetic; Athetosis
- GI: Constipation
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Leukoencephalopathy
- Muscle
- Fiber size: varied
- Fiber type groups
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondria with altered cristae parking lots)& Paracristalline inclusions
- No ragged red fibers
- OPA13: Optic atrophy + Retinal & Foveal Δ (MTDPS)

● Single-stranded DNA-binding protein 1, mitochondrial (SSBP1) ; Chromosome 7q34; Dominant & Recessive
; Chromosome 7q34; Dominant & Recessive
- Epidemiology: 10 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Usually Dominant; Recessive in 1 family
- Mutations: Missense; Recessive mutation I132V
- SSBP1 protein
- Mitochondrial nucleoids
- Coats displaced, parental H-strand during mtDNA synthesis
- Mutations: Reduced SSBP1 protein or multimerization
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Childhood to 8th decade
- Optic atrophy: Retinal macular dystrophy; Visual acuity reduced
- Deafness: Sensorineural
- Renal insufficiency
- Recessive patient: Ataxia; Growth retardation; Cardiomyopathy
- Laboratory
- mtDNA depletion: No mtDNA deletions
- Mitochondrial myopathy: COX- muscle fibers
- OPA15: Optic atrophy

● Malonyl CoA:ACP acyltransferase, mitochondrial (MCAT) ; Chromosome 22q13.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 22q13.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 families, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Loss of function
- MCAT protein
- Localization: Mitochondria
- Catalytic subunit of type II malonyl-CoA-dependent system

- Biosynthesis of fatty acids
- Catalyzes transfer of a malonyl moiety from malonyl-CoA to NDUFAB1
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood or Early adult
- Vision loss
- Asymmetric
- Bilateral
- Course: Rapid or Gradual
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Optic nerves abnormal
Leigh Syndrome
 341
341
|
Features Clinical Laboratory Types |
|
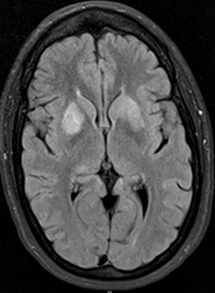 From: R Bucelli |
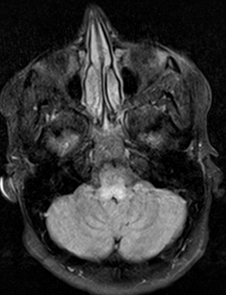 From: R Bucelli |
||||||||||||||||||
- Nosology: Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy
- Epidemiology: Prevalence 1:30,000 to 1:40,000
- Leigh syndrome: Genetics
- Multiple causes
- Clinical spectrum with NARP
- Leigh syndrome: Clinical features
- Onset age
- Usual: 1st 2 years; Most common from 3 to 12 months
- Occasionally: Later childhood or Adult
- Prodrome: Infection or illness, after initially normal development
- Hypotonia
- Episodic
- Vomiting
- Ataxia
- Choreoathetosis
- Hyperventilation
- Seizures
- Encephalopathy: Loss of verbal milestones
- Motor: Spasticity; Abnormal breathing rhythm
- Brainstem & Basal ganglia signs
- Hearing loss
- Cerebellar: Ataxia; Nystagmus
- Movement: Dystonia; Chorea
- Ophthalmologic
- Visual loss (Optic atrophy)
- Nystagmus
- Ophthalmoparesis
- Retinopathy
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Often subclinical: Prevalence by nerve conduction testing: 45%
- Pathology: Reduced Myelinated & Unmyelinated axons; ? Demyelination
- Multisystem
- Cardiac: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hepatic
- GI
- Renal tubular
- Clinical signs may become manifest with
- Stress: Intercurrent infection
- Carbohydrate intolerance
- Course
- Progression: Motor & Intellectual regression
- Death: 50% < 3 years; Often within 2 years of onset
- Distinctive features
- Clinical
- Geographic + Clinical
- Ashkenazi Jews; Typical LS: NDUFS4 (c.462delA)
- Bulgarian Roma; Cerebral palsy, Lactic acidosis newborn: PDHX (c.1336C>T)
- Europeans; Hypertrichosis; Cognitive sparing: SURF1 (c.311_312insATdel10)
- Europeans; Microcephaly: MTFMT (c.626C>T)
- Faroe Island; Dystonia, Deafness: SUCLA2 (c.534+1G>A)
- French Canadians; Face dysmorphic; Liver Δ: LRPPRC (c.1119C>T)
- Lebanese; Seizures: PET100 (c.3G>C)
- Mediterranian & Arabian; Acrocyanosis, Petechiae, GI: ETHE1 (c.487C>T)
- Treatments
- Biotin/thiamine-responsive basal ganglia disease (SLC19A3): Thiamine & Biotin (high dose)
- Biotinidase deficiency (BTD): Biotin
- Coenzyme Q10 deficiency (PDSS2): Coenzyme Q10
- Ethylmalonic encephalopathy (ETHE1): Metronidazole & N-acetylcysteine
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency (PDHA1): Thiamine & High-fat diet
- SLC39A8: Manganese
- TPK deficiency (TPK1): Thiamine
- Onset age
- Lab
- Lactate: High in CSF > blood
- Muscle biopsy
- Normal histology
- Variable oxidative enzyme deficiencies: Subunits, nuclear & mitochondrial encoded
- MRI
- Most common: High T2 signal in lentiform & caudate nuclei
- Other common abnormalities in: Thalamus, Periaquiductal gray, Tegmentum, Red & dentate nuclei
- White matter: Generally preserved
- SURF1: Lesions in Brain stem & Subthalamic nuclei
- NDUFAF2: Mammillothalamic tracts, Substantia nigra, Medial lemniscus, MLF, Spinothalamic tracts, Cerebellum
- CNS pathology
- Focal, bilaterally symmetric spongiform lesions
- Location: Especially in thalamus & brain stem
- MRI: Symmetrical hyperintense lesions on T2
- Urine: Increased methylmalonic acid or proprionic acid in some types (3-MGA)
- Common genetic cause of typical Leighs: SURF1 mutations
- General pathophysiology: Severe deficiency in mitochondrial ATP production
- Leigh syndrome (LS) & Infantile encephalopathies (IE): Genetically defined types
Nuclear mutations
Complex I
FOXRED1: 11q24
NDUFA1: Xq24
NDUFA2 (LS + Cardiac): 5q31
NDUFA6 (IE): 22q13
NDUFA9 (LS): 12p13
NDUFA10 (LS + Cardiac): 2q37
NDUFA11 (IE + Cardiac): 19p13
NDUFA12 (LS): 12q22
NDUFA13: 19p13
NDUFAF2: 5q12
NDUFAF3: 3p21
NDUFAF4 (c6orf66): 6q16
NDUFAF5 (c20orf7) (LS & IE): 20p12
NDUFAF6 (c8orf38) (LS): 8q22
NDUFAF8 (c17orf89): 17q25
NDUFB8: 10q24
NDUFC2: 11q14
NDUFS1 (LS): 2q33
NDUFS2 (LS): 1q23
NDUFS3 (LS): 11p11
NDUFS4 (LS & IE): 5q11
NDUFS7 (LS): 19p13
NDUFS8 (LS): 11q13
NDUFV1 (LS): 11q13
NDUFV2: 18p11
NUBPL: 14q12
TIMMDC1: 3q13
Complex II
PMPCB; 7q22
SDHA (LS): 5p15
SDHAF1: 19q13
Complex III
BCS1L (LS): 2q33
UQCRQ: 5q31
TTC19: 17p12
Complex IV
COX4I1: 16q24
COX8a: 11q13.1
COX10: 17p13
COX15: 10q24
ETHE1: 19q13
FASTKD5; 20p13
LRPPRC (LS): 2p16
NDUFA4 (LS): 7p21
PET100 (LS): 19p13
PET117: 20p11
Surfeit-1 (LS)*: 9q34
SCO2 (IE): 22q13
TACO1: 17q23
Complex V
ATP5MD: 10q24
Mixed defect
EARS2: 16p12
FARS2: 6p25
FBXL4: 6q16
GFM1: 3q25
GFM2: 5q13
GTPBP3: 19p13
IARS2: 1q41
MRPS34: 16p13
MTFMT: 15q22
MTRFR: 12q24
NARS2: 11q14
PNPT1: 2p15
POLG: 15q25
SUCLA2: 13q14
SUCLG1: 2p11
TRMU: 22q13
TSFM: 12q14
B-vitamin related
BTD: 3q25
SLC19A3: 2q36
SLC25A19: 17q25
TPK1: 7q35
Coenzyme Q10
COQ9: 16q13
PDSS2: 6q21
Mitochondrial Membranes
CLPB: 11q13
MFF: 2q36
SERAC1: 6q25
SLC25A46: 5q22
mtDNA maintenance
FBXL4: 6q16
GTPBP3: 19p13
POLG: 15q25
RNASEH1: 2p25
SSBP1: 7q34
SLC25A4: 4q35
SUCLA2: 13q14
SUCLG1: 2p11
Pyruvate metabolism
Pyruvate carboxylase (LS): 11q13
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
PDHA1: Xp22
PDHB: 3p14
PDHX: 11p13
DLAT: 11q23
DLD: 7q31
LIAS: 4p14
LIPT1: 2q11
LIPT2: 11q13
Valine metabolism
ECHS1: 10q26
HIBCH: 2q32
Other
ADAR: 1q21
AIFM1: Xq26
DNM1L: 12p11
HPDL: 1p34
Morc2: 22q12
NUP62: 19q13
OPA1: 3q29
RANBP2: 2q11
SCO2: 22q13
SLC39A8: 4q24
Mitochondrial mutations (MILS)
General
Complex I
MTND1
MTND2
MTND3*
MTND4
MTND5*
MTND6*
Complex IV
MTCO1
MTCO2
MTCO3
Complex V
ATPase 6 (MTATP6)*
tRNAs
MTTI (Ile)
MTTK (Lys)
MTTL1 (Leu)
MTTL2 (Leu)
MTTS2 (Ser)
MTTV (Val)
MTTW (Trp)
mtDNA deletions (LS)
* Common causes of LS
Infantile Encephalopathies
Other
- Leigh syndrome: Maternal inheritance (MILS) & other Mitochondrial DNA disorders
- Leigh syndrome (MC5DM1)

● ATP synthase 6 (MTATP6) (Complex V)
(Complex V)
- Genetics
- Encoding: mtDNA nucleotides 8527-9207
- Inheritance risk (8993 mutations)
- Mother has
- High levels of mtDNA mutant: All sibs at risk
- No detectable mtDNA mutant in blood: Low risk of sibs of proband
- Male proband: No risk to offspring
- Mother has
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Leigh syndrome
- Motor: Hypotonia; Developmental delay 50% to 90%
- Peripheral neuropathy 30%
- Severity dependent on level of mutant DNA (heteroplasmy)
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: Seizures + Ocular disorders
- Frequency: Common
- Genetics: T8993G mutation
- Clinical
- Onset: 4 to 5 months
- Seizures 67%
- Eye: Retinitis pigmentosa or Optic atrophy 33%
- Increased severity
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: Mental retardation + Ataxia
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics: T8993G mutation
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- Exercise intolerance
- Mental retardation
- Ataxia
- Plantar responses: Extensor
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle biopsy: Normal histology
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: Juvenile Leigh with Ataxia & Respiratory failure
- Frequency: Rare
- Genetics: T8993C mutation
- Clinical
- Onset age: Median = 4 years; Range = 0.5 to 56 years
- Ataxia 90%
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: Hereditary spastic paraparesis
115
- Epidemiology: 2 families; 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: T9176C (Homoplasmic), T9035C (High heteroplasmy)
- Mitochondrial haplogroup J2: J types have milder mitochondrial syndromes
- Partial penetrance
- Allelic (Same mutation) disorders
- Leigh syndrome
- Later onset: Bilateral striatal necrosis
- Clinical: Myelopathy
- Onset age: 30 to 50 years
- Spasticity
- Legs > Arms
- Hyperreflexia
- Weakness: Distal
- Sensory
- Loss: Vibration
- Pain: Legs
- Laboratory
- Lactate & Pyruvate: Normal
- Muscle histochemistry: Normal
- Oxidative enzymes: Normal
- ATP synthesis: Reduced
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy
- MTATP6 variant syndrome: Myopathy, Lactic Acidosis & Sideroblastic anemia 3 (MLASA3)

- Epidemiology: 1 male patient
- Genetics
- G8969A mutation: 96% & 88% heteroplasmy in blood & muscle
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early infancy
- Hearing loss
- Epilepsy
- Stroke-like episodes
- Head circumference: Small
- Contractures: Knees & Ankles
- Muscles: Atrophy
- Course
- Progressive
- Failure to thrive
- Developmental delay: Severe
- Laboratory
- Sideroblastic anemia: Transfusion-dependent
- EKG: Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome

- Blood lactate: High
- Urine organic acids: High fumarate, malate, beta-hydroxybutyrate
- Serum amino acids: High alanine
- Complex V dysfunction
- Genetics
- Leigh with Complex I deficiency
● MTND2
- Genetics
- ND2 encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 4470 & 5511
- Mutation: Leu71Pro
- ND2 encoding
- Clinical: Leigh syndrome
- Encephalomyopathy, progressive
- Died: Age 10 years; Respiratory failure
- ND2 mutations also cause
- Genetics
- Leigh with Complex I deficiency
● MTND5
- Genetics
- ND5 encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 12337 & 14148
- Mutation: 13730A
- Hotspot for mtDNA mutations
- ND5 encoding
- Clinical: Leigh syndrome
- Mutation: A13084T
- Combined features of Leigh & MELAS
- Course: Progressive
- Muscle pathology
- Some biopsies have muscle fibers with mitochondrial proliferation: All SDH+ & COX+
- Complex I deficiency
- MTND5 mutations also found in
- Genetics
- Leigh with Complex I deficiency
272
● MTND6
- ND6 encoding
- Cytosine-rich light (L) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 14149 & 14673
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense
- T14487C (M63V); A14597G (Ile26Thr)
- Heteroplasmic: High mutation load (> 90%)
- MTND6 allelic disorders
- Leber optic atrophy (LHON)
- MELAS
- Dementia/Dysarthria
- Mutations
- Clinical: Leigh syndrome
- Onset: 4 months to 6 years
- Clinical
- Tonic-clonic seizures
- Motor retardation
- Hypotonia
- Deafness
- Pyramidal features
- Extrapyramidal signs: Dystonia
- Course
- Episodic: Brainstem events with oculomotor palsies, strabismus & recurrent apnea
- Progressive
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidemia
- Basal ganglia lesions
- ND6 encoding
- Leigh syndrome with Complex IV deficiency
● COX III (MTCO3)
- Genetics
- COX III encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 9207 & 9990
- MTCO3 mutation: Homoplasmic m.C9537insC frameshift
- Allelic disorders: Mutations also found in
- Leber optic atrophy
- Myopathy with exercise intolerance
- Rhabdomyolysis: 15 bp in-frame deletion; T9789C
- Episodic encephalopathy
- Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)-Myoclonic epilepsy
- COX III encoding
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4 years
- Leigh syndrome
- Spastic paraparesis + Ophthalmoplegia
- Laboratory
- Lactic acid: High in serum
- Muscle: Isolated COX defecit
- MRI: Leigh-like lesions in putamen
- Genetics
- Leigh syndrome (MC5DM1)
- Leigh: Nuclear mutations
- Complex IV
- Leigh syndrome: Cytochrome oxidase deficiency (MC4DN1)
 (Complex IV)
(Complex IV)
● Surfeit-1 (SURF-1) protein ;
Chromosome 9q34.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 9q34.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology
- 10% of Leigh syndromes
- 50% of Complex IV deficient Leigh syndromes
- Genetics: SURF-1 mutations
- Small rearrangements: All predict loss of function of SURF-1 gene
- Occur in 75% of typical Leigh syndrome in Caucasians
- Rarely occur in atypical Leigh syndromes
- Allelic with: CMT4K
- Protein
- Located in inner mitochondrial membrane
- Involved in biogenesis of COX complex
- Biochemistry in disease: Reduced COX activity to ~10% of controls in fibroblasts > muscle
- Clinical: Specific for typical Leigh syndrome
- Early onset
- Encephalopathy: Rapidly progressive psychomotor regression
- Generalized hypotonia
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Ataxia: Truncal
- Oculomotor disorders: Slow saccades; Ophthalmoparesis; Irregular EOM
- Respiratory: Episodic apnea & Irregular hyperpnea
- Death: Central ventilatory failure
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
- MRI: Symmetric lesions; Scattered from basal ganglia to brain stem
- Muscle histochemistry
- COX stain: Reduced in muscle fibers & vessels
- SDH stain: Often normal
- Lipid in muscle fibers: Normal or Increased
- Fibroblasts & Muscle biochemistry: Complex IV deficiency
- SURF1 variant: CMT4K
 165
165
● Surfeit-1 (SURF-1) protein ;
Chromosome 9q34.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 9q34.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 families; 5% of CMT4
- Genetics
- Mutations: Splice site & Frame shift
- Allelic with: Encephalopathy
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- Weakness: Distal; Feet & Hands
- Sensory loss: Panmodal; Legs > Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- CNS
- Nystagmus
- Ataxia: With disease progression
- Hearing loss: Mild
- Scoliosis
- Course
- Progression: Slow
- Survival: To teens or adulthood
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology
- Cytochrome oxidase (COX) staining: Diffusely reduced
- Complex IV activity: Low
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss
- Hypomyelination
- Onion bulbs
- NCV
- Conduction velocities: Slow; 15 to 22 m/S
- Distal latencies: Mildly long
- F-wave latencies: Prolonged
- Serum CK: Normal
- Lactic acid, serum: High
- Brain MRI: Putaminal hyperintensity
- Muscle pathology
- Epidemiology
- Cytochrome oxidase deficiency: French-Canadian type (LSFC; MC4DN5)
 (Complex IV)
31
(Complex IV)
31
● LRPPRC
 ; Chromosome 2p21; Recessive
; Chromosome 2p21; Recessive
- Epidemiology
- Hot spot: Quebec families (Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean), Carrier frequency 1/23
- Other areas: 7 families, 10 patients; More severe syndromes
- Genetics: Mutations
- Type: Missense in many; Deletions
- French-Quebec: Commonly homozygous for Ala354Val
- Leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein (LRPPRC)
- mRNA-binding protein
- Likely involved with mtDNA transcript processing
- Other PPR disorder: PTCD3
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Birth to 8 months
- Developmental delay
- Hypotonia
- Facial dysmorphism: Mild
- Leigh syndrome
- Cardiomyopathy: Congenital; Hypertrophic
- Dysphagia
- Congenital malformations: Micrognathia, Polysyndactyly, Hypospadias
- Cognitive & speech impairment
- Course
- Episodic, Acute: More common than SURF1
- Mortality: Due to episodes of severe lactic acidosis & coma
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Congenital lactic acidosis: Serum & CSF
- Metabolic acidosis: Mild, Chronic, Well-compensated
- Hypoglycemia (50%)
- Brain MRI
- Abnormal: Cerebellar brainstem nuclei; Putamen
- Leukoencephalopathy
- Malformations
- Pathology
- Muscle: Fiber size variation
- CNS: Leigh disease
- Liver: Microvesicular steatosis
- Low COX activity: Muscle, Brain & Liver
- Epidemiology
- Leigh syndrome: Late onset (MC4DN8)
 (Complex IV)
98
(Complex IV)
98
● Translational activator of COX I (TACO1; CCDC44)
 ; Chromosome 17q23.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 17q23.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Mutations: Homozygous; 472insC, c.252 253delCT,
- TACO1 protein
- Mitochondrial translational activator
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Mutant: Impaired synthesis of COX subunit I
- Clinical: Leigh syndrome + Spastic ataxia
- Onset age: Childhood onset
- Cerebellar: Saccadic pursuit; Limb tremor
- Pyramidal: Spasticity; Tendon reflexes brisk; Tetraparesis
- Weakness: Proximal & Distal
- Bulbar: Dysarthria; Dysphagia
- Optic atrophy
- Learning difficulties
- Course: Slowly progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- Periventricular white matter lesions with multiple cystic defects
- Leukoencephalopathy
- EMG: Myopathic
- NCV: Axon loss later in disease course
- VEP: Prolonged P100 latency
- Muscle pathology: COX- fibers
- Serum Lactate: Normal
- Biochemistry
- Complex IV deficiency: Isolated
- Brain MRI
- Leigh syndrome (MC4DN12)
 (Complex IV)
173
(Complex IV)
173
● PET100, S. Cerevisiae, homolog of (PET100; C19orf79) ; Chromosome 19p13.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 19p13.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 6 Lebanese families
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; c.3G>C; Founder
- PET100 protein
- Size: Small (9 kDa)
- Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) assembly protein
- Copurifies with COX17

- Mitochondrial inner membrane: Exposed to Intermembrane space
- Forms a ~300 kDa subcomplex with complex IV subunits
- Mutation: Reduced Complex IV holoenzyme
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1.5 to 9 months; Earlier than SURF1 mutations
- Hypotonia
- Developmental delay: More than with SURF1 mutations
- Encephalopathy
- Seizures: More common than with SURF1 mutations
- Course
- Death 0.7 to 16 years: Some patients
- Survival: Up to 3rd decade
- Severe CNS changes: Spasticity; Mental retardation
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Biochemistry
- Complex IV deficiency: Isolated
- Muscle: 19% to 48%; Mean 29%
- Similar degree of reduction vs SURF1 mutations
- CNS imaging: Abnormal putamen, thalamus or caudate
- COX15 mutation
- Leigh syndrome: Cytochrome oxidase deficiency (MC4DN1)
- Complex I

- NDUFS4
- C20orf7
- Leigh syndrome (MC1DN26) (Complex I)
 218
218
● NDUFA9 ; Chromosome 12p13.32; Recessive
; Chromosome 12p13.32; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 12 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Missense; Arg321Pro; Hotspot Arg360
- Allelic disorder: Dystonia & Folyneuropathy, Childhood onset
- NDUFA9 protein
- Structural accessory subunit of Complex I
- Located in peripheral part of complex I
- May serve as anchor connecting peripheral arm with membrane arm
- Q-module component
- Mutation: Complex I levels reduced
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Respiratory: Insufficiency; Apnea
- Hearing loss
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Dystonia (100%)
- Pyramidal signs (80%)
- Seizures (70%)
- Intellectual disability (60%)
- Course: Progressive after 4 months of age
- Laboratory
- Acidosis: Respiratory & Metabolic
- MRI: T2 signal in basal ganglia & thalamus; White matter loss
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle: Complex I deficiency; Morphology normal
- NDUFA9 variant: Dystonia & Polyneuropathy, Childhood
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.1078C>T; p.Arg360Cys
- Clinical
- Onset age: 7 years
- Dystonia
- 1 limb spreading to all limbs
- Dysarthria
- Other CNS: No intellectual impairment
- Polyneuropathy
- Onset age: 3rd decade
- Muscle wasting: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs
- Axon loss: Motor & Sensory
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Resting normal; Post-prandial high
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like Putamen signal; Caudate atrophy
- Mitochondrial Complex I deficiency, nuclear type 8 (MC1DN8)

● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase Fe-S protein 3 (NDUFS3) ;
Chromosome 11p11.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11p11.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Compound heterozygote; R142C, N180K; Thr145Ile & Arg199Trp
- Allelic disorders: Leigh syndrome, Early & Later onset
- NDUFS3 protein
- Complex I: Core protein
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood to 9 years
- Seizures & Hypotonia: Younger patients
- Dystonia: Axial; Pharyngeal
- Optic nerve: Atrophy
- Motor: Tetraparesis; Respiratory insufficiency
- Progression: Rapid; Multisystem disorder
- Laboratory
- Cerebral MRI: High T2 signal in putamen, white matter, brain stem
- CSF lactate: High
- Muscle
- Histochemistry: Unremarkable
- Ultrastructural Morphology: Mitochondrial number increased & sizes varied
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency or Normal
- Mitochondrial Complex I deficiency, nuclear type 2 (MC1DN2)

● NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase 23-kD subunit (NDUFS8) protein ;
Chromosome 11q13.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11q13.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense
- NDUFS8 protein
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth
- Neural
- Hypotonia
- Brisk tendon reflexes
- Seizures
- Drowsiness
- Cardiomyopathy
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Increased in blood & CSF
- MRI: Hypodensity of white-matter, Putamen & Mesencephalon
- Muscle biopsy
- Histochemistry: Few Type I fibers; No ragged red fibers
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency
- Brain pathology
- Spongiform changes
- Capillary proliferation & endothelial swelling
- Demyelination
- Gliosis
- Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 3 (MC1DN3)

● NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase Fe-S Protein 7 (NDUFS7) ;
Chromosome 19p13.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 19p13.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families; 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Splice site
- Allelic disorder: Optic neuropathy
- NDUFS7 protein
- Complex I: Core protein
- Fe4S4
- Q-binding
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st year; Repeated vomiting
- Neural: Hemiparesis; Hypotonia; Hyperactive tendon reflexes
- Death: 1st decade
- Laboratory
- Pyruvate & Lactate: Normal in serum urine & CSF
- MRI: Symmetric lesions in caudate, putamen & dentate
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I deficiency
- Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 4 (MC1DN4)
 295
295
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Flavoprotein 1 (NDUFV1) (Complex 1) deficiency ;
Chromosome 11q13.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11q13.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: No patients wtih 2 null alleles
- Allelic variants
- MELAS-like
- Hepatopathy + Renal tubulopathy
- Alexander disease

- Optic neuropathy
- NDUFV1 Protein
- Complex I core protein
- NADH- & FMN-binding site of Complex I
- Fe4S4
- Clinical: Leigh-like
- Onset: 5 month to later childhood
- Repeated vomiting
- Strabismus
- Hypotonia
- Encephalopathy
- Myoclonic epilepsy
- Psychomotor regression
- Ataxia
- Macrocephaly
- Course: Progressive or episodic
- Laboratory
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency
- Spinal MRI: Dorsal column involvement
- Brain pathology: Leukoencephalopathy, Demyelinating & Cavitating
- Peripheral nerve: Normal
- Muscle
- Fiber sizes: Varied
- Mitochondria: Abnormal structure; Enlargement; Subsarcolemmal accumulation (SDH dark)
- Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 31 (MC1DN31)

● Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane domain-containing protein 1 (TIMMDC1) ;
Chromosome 3q13.33; Recessive
;
Chromosome 3q13.33; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Splicing; c.596+2146A-G
- TIMMDC1 protein
- Function: Assembly of Complex 1
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Hypotonia
- Psychomotor development: Delayed or None
- Other: Some patients
- Deafness
- Cerebellar: Dysmetria; Nystagmus
- Dyskinetic movements
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Seizures
- Course: 2 with death < 3 years
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Complex I deficiency
- Brain MRI: Maybe similar to Leigh syndrome
- Leigh syndrome (MC1DN17)
 85
85
● NDUFAF6 (C8orf38)
 ;
Chromosome 8q22.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 8q22.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 7 families
- Mutations
- Missense: Gln99Arg; A178P; Other missense
- Clinical
- Onset age: 7 months to 4 years
- Seizures: Focal right-hand
- Movement & Strength: Reduced
- Ataxia & Gait disorder
- Rigidity
- Death: Childhood
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency
- Neuroimaging: Consistent with Leigh syndrome
- Leigh syndrome (MC1DN22) (Complex 1 deficiency)
 118
118
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase 1 Alpha, Subcomplex, 10 (NDUFA10) ;
Chromosome 2q37.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 2q37.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Mutations
- Compound heterozygous: Met1? (Abnormal start codon); Gln142Arg
- NDUFA10 protein
- Probable role in biogenesis of Complex I
- Located in hydrophobic protein fraction of Complex I
- Might be involved in transfer of protons
- Mutation effects: Reduced amounts of fully expressed Complex I
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- ND2 module of complex I
- Clinical
- Onset age: Fetal distress
- Hypotonia
- Development: Retarded
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Death: 23 months
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: CSF & Blood
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency; Mild Complex III deficiency
- Neuroimaging: Consistent with Leigh syndrome; Abnormal thalamus, pons & hippocampus
- Leigh syndrome (MC1DN19)
 114
114
● FAD-dependent oxidoreductase domain-containing protein 1 (FOXRED1)
 ;
Chromosome 11q24.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11q24.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics: Mutations
- Compound heterozygous or Homozygous
- Gln232X; Asn430Ser; Arg352Trp
- FOXRED1 protein
- Function: Complex I assembly
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Neonatal
- Lactic acidosis with hypoglycemia
- Distal renal tubular acidosis
- Extrapyramidal: Limb athetosis; Cog-wheel rigidity
- Hypotonia
- Kyphoscoliosis
- Seizures
- Cognitive: No speech
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Plasma normal; CSF high
- MRI: Leigh syndrome pattern
- Abnormal putamen & cerebellum (atrophy)
- Muscle: Complex I deficiency
- Leigh syndrome + Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (MC1DN13)
 83
83
● NDUFA2 ;
Chromosome 5q31.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 5q31.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 children, 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Splice-site: c.208+5 G > A; Exon 2 skipping
- Missense: Lys45Thr; Glu57Ala
- Deletion: 1-BP del NT225
- Mutations
- NDUFA2 protein
- Complex I accessory subunit
- Molecular location: Peripheral arm of complex I
- Fe2S2 ferredoxin fold: Similar to thioredoxin
- Mutation effects
- Reduced amounts of wild type protein
- Truncated protein
- Mitochondrial depolarization
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st week
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Development: Slow
- Episodic acidosis: Seizures; Coma; Apnea
- Course: Regression; Survival through childhood in 3
- Laboratory
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency (20% of control)
- MRI
- Cerebral atrophy
- White matter: Corpus callosum hypoplasia; Periventricular pathology
- Late: Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy
- MR spectroscopy: Lactate peak
- Leigh syndrome (MC1DN23) + Dystonia
 128
128
● NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 12 (NDUFA12)
 ;
Chromosome 12q22; Recessive
;
Chromosome 12q22; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 17 patients, 11 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop (Most common) or Missense; Homozygous
- NDUFA12 protein
- Clinical: Leigh syndrome
- Onset age: Often birth
- Development
- Early motor: Delayed
- Growth: Retardation
- Decline: Beginning at 2 years
- Muscle: Atrophy; Hypotonia
- Psychomotor: Normal or Delay
- Movement disorder: Dystonia
- Spasticity
- Skeletal: Scoliosis
- Eyes: Strabismus; Nystagmus or Optic atrophy
- Course: Progression, Stability or Improvement
- Muscle
- Type 1 atrophy
- Type 1 predominance
- Complex I activity reduced
- NDUFA12 protein: Reduced or Absentr
- Other laboratory
- Cerebral MRI & MRS: Bilateral hyperintense globus pallidus; Elevated lactate in brain
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Leigh-like encephalopathy (MC1DN32)
 234
234
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase 1 beta subcomplex, 8 (NDUFB8) ;
Chromosome 10q24.31; Recessive
;
Chromosome 10q24.31; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Tyr62His; Pro76Gln; Cys144Trp; Glu63Aspfs*35
- NDUFB8 protein
- Complex I accessory subunit
- Mitochondrial matrix protein
- Clinical: Encephalo(cardio)myopathy
- Onset age: 3 to 6 months
- Hypotonia
- Cardiac hypertrophy
- Respiratory failure
- Failure to thrive
- Developmental delay
- Course: Progressive; Death at 1.5 years in one patient
- Laboratory
- Blood lactate: High
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I deficiency
- Brain MRI: T2 signal in midbrain, putamen, thalamus
- NDUFS4
- Leigh syndrome (MC1DN34)
 227
227
● NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex assembly factor 8 (NDUFAF8, C17orf89)
 ;
Chromosome 17q25.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 17q25.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Duplication, Splice
- Transcript reduced
- NDUFAF8 protein
- Function: Complex I assembly
- Mitochondrial matrix protein
- Interacts with NDUFAF5
- Clinical
- Onset age: Prenatal to Childhood
- Encephalopathy, Acute: May be related to febrile illness
- Seizures
- Spasticity
- Course: Often death < 4 years
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like (Bilateral high signal in basal ganglia & brainstem); Corpus callosum pathology
- Muscle: Complex I activity reduced (3% to 47%)
- Serum: Acidosis; Lactate high or normal
- Encephalopathy-Leigh-like (MC1DN36)

● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit C2 (NDUFC2) ;
Chromosome 11q14.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11q14.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 families, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; His58Leu, 22 bp deletion (c.346_*7del)
- NDUFC2 protein
- Clinical
- Onset: Infancy
- Global developmental delay: No ambulation; Absent speech; Impaired intellect
- Hypotonia
- Failure to thrive apparent
- Spasticity, progressive
- Other: Optic disc palor, Poor eye contact, Seizures, Congenital heart defects
- Laboratory
- Complex II: Succinate dehydrogenase, subunit A, Flavoprotein (SDHA)
 29
29
● Chromosome 5p15.33; Recessive or Dominant- Genetics: Allelic disorders
- Optic neuropathy, Syndromic, Dominant
- Leigh
- MC2DN1
- Dilated cardiomyopathy 1GG
- Paraganglioma 5
- Biochemistry of early onset SDHA disorders
- Complex II activity
- Reduced to 50% to 75% of lower limit of normals
- Other complexes normal
- Carnitine: High free & total
- Lactate & Pyruvate: High
- Krebs cycle intermediates high: Succinate > Fumarate & Malate
- Ketone: High in urine
- Complex II activity
- Clinical: Varied syndromes
- Encephalocardiomyopathy, Early or Late onset: Dominant
 265
265
- Nosology: Neurodegeneration with Ataxia & Late-onset Optic Atrophy (NDAXOA)
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- SDHA Mutation: Arg451Cys
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood to 4th decade
- Cardiopathy: Hypertrophic or Dilated
- Skeletal muscle: Myopathy
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Optic neuropathy
- Cardiomyopathy: Some patients
- Course: Progressive; Early death in severe phenotypes
- Laboratory
- Urine: 3-methylglutaconic & 3-OH-methylglutaric acid excretion
- Fibroblasts: Complex II activity 50% of normal
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
- Optic Neuropathy & Developmental delay
- Epidemiology: 1 family
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant, de novo
- SDHA Mutation: Missense; Arg662Cys
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- CNS: Developmental delay, global; Intellectual disability
- Optic atrophy
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Complex II activity in fibroblasts: Reduced
- Mitochondrial Complex II Deficiency Nuclear Type 1 (MC2DN1)

- Epidemiology: > 30 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- SDHA Mutations: Often missense
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- CNS: Leukodystrophy
- Cardiomyopathy
- Course: Progressive
- Leigh syndrome: Recessive

- SDHA Mutations
- Commonly in region of amino acids 524-555
- Action: ? Interfere with Fp-Ip molecular interaction
- Cause partial reduction in complex II activity
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset: 9 months with psychomotor delay
- Truncal ataxia: Delayed walking
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Mild increase in serum & CSF
- MRI: Necrotic lesions in basal ganglia
- SDHA Mutations
- Dilated cardiomyopathy 1GG
 29: Recessive
29: Recessive
- Paraganglioma 5, Dominant
- Encephalocardiomyopathy, Early or Late onset: Dominant
- Genetics: Allelic disorders
- Complex IV
- Leigh-like syndrome, Optic atrophy & Ophthalmoplegia
 113
113
● c12orf65
 ; Chromosome 12q24.31; Recessive
; Chromosome 12q24.31; Recessive
- Nosology: Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 7 (COXPD7)
- Epidemiology: 2 families, Turkish & Dutch
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous 1 bp deletions
- Allelic with: SPG 55
- c12orf65 protein
- Mitochondrial class I peptide release factor
- ? Recycling abortive peptidyl-tRNA species released from ribosomes during elongation phase of translation
- Mutations
- Mitochondrial protein translation deficiency
- Reduced synthesis of mtDNA encoded peptides
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 3 years
- Psychomotor retardation
- Ataxia
- Eye
- Ptosis
- Ophthalmoplegia
- Nystagmus
- Optic atrophy
- Reduced vision
- Muscle
- Atrophy: Diffuse
- Face weakness
- Bulbar: Difficulty chewing; Dysarthria
- Hypotonia
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal
- Sensory: Distal loss
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- GI: Ileus late in course
- Course
- Slower than typical Leigh
- Death in 3rd decade
- Similar to TACO1
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Variably elevated
- Oxidative enzymes
- Mixed defect
- Reduced Complex I, III, IV & V activity
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like
- Bilateral lesions in thalami, brain stem & medulla
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy
- c12orf65 variant syndrome: Spastic paraparesis with optic atrophy & neuropathy
(SPG 55)
 152
152
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- c12orf65 mutation: R132X; Homozygous
- Allelic with: COXPD7
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 7 years
- Visual loss
- Spastic paraparesis
- Legs: Spasticity
- Tendon reflexes: Increased except at ankles
- Plantar reflexes: Flexor or Extensor
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Visual loss: Optic atrophy
- Sensory loss: Distal legs; Vibration & Pain
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction
- Velocities: Mildly reduced
- CMAPs & SNAPs: Absent in legs
- EMG: Neuropathic; Large motor units
- Nerve conduction
- Genetics
- Leigh syndrome (COXPD15)
 134
134
● Methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase, mitochondrial (MTFMT) ; Chromosome 15q22.31; Recessive
; Chromosome 15q22.31; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Splice site mutation, exon 4 skipping; Stop; Missense S125L
- Allelic disorder: MC1DN27
- MTFMT protein
- Formylation of Met-tRNAMet
- Function: Mitochondrial translation
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood
- Obesity
- Short stature
- Brainstem: Eye movement disorder
- Ataxia: Gait
- Eye: Visual acuity reduced; Optic atrophy
- Developmental delay
- Course: Episodic deficits
- Laboratory
- Oxidative phosphorylation: Mixed defect
- Complexes I & IV: Most consistently reduced
- Complex III: Reduced in some patients
- Complex II: Usually normal
- Muscle histology: Normal
- MRI: High signal in putamen, globus pallidus & brainstem
- Lactate: High in CSF
- Oxidative phosphorylation: Mixed defect
- MTFMT variant: MC1DN27

- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Ser209Leu, Arg3322X
- Clinical: Leigh-like syndrome
- Laboratory: Complex I deficient
- Leigh syndrome (COXPD32)
 222
222
● Methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase, mitochondrial (MRPS34) ; Chromosome 16p13.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 16p13.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 6 patients; Puerto Rican & European
- Genetics
- Mutations: Splice-site; Missense; Nonsense
- MRPS34 protein
- Mitoribosome component: Small subunit
- Stabilizes 12S rRNA
- Stability of small mitoribosomal subunit
- Clinical
- Onset age: 10 days to 6 months
- Leigh syndrome
- Developmental delay & regression
- Microcephaly

- Dysmorphic face
- Course: Death < 1 year to Alive at 17 years
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Oxidative enzymes: Combined defects, especially Complexes I & IV
- Leigh syndrome
228
● Solute carrier family 39, Member 8 (SLC39A8; ZIP8) ; Chromosome 4q24; Recessive
; Chromosome 4q24; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Gly38Arg, Cys113Ser, Ile340Asn.....
- Allelic with: Congenital disorder of glycosylation 2n (CDG 2n)
- SLC39A8 protein
- Divalent cation transporter: Zinc, Manganese, Cadmium, Iron
- SLC39A8 disorder produces
- Reduced function of manganese transporter
- Manganese deficiency
- Results in reduced function of manganese-dependent β-1,4-galactosyltransferase
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 4 months
- Failure to thrive
- Developmental delay
- Dystonia
- Seizures
- Hypotonia
- Treatment: Manganese supplementation (20mg MnSO4/kg/Day)
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: T2 Basal ganglia hyperintensities; Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Multiple borderline abnormalities
- Manganese levels: Low or absent
- Leigh syndrome: Maternal inheritance (MILS) & other Mitochondrial DNA disorders
- Pyruvate disorders
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC): General
- Structure
- Nuclear-encoded mitochondrial matrix multienzyme complex
- Composed of multiple copies of 3 enzymes
- E1
- Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (DLAT)

- Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (DLD)

- Function
- Link between Glycolysis & Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
- Action: Catalyzes irreversible conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA
- Structure
- Disorders
- General: Common cause of encephalopathy & lactic acidosis in children
- E1
- PDHX
- PDK3: CMTX6
- PDP1
- DLAT
- DLD
- Iron-Sulfur cluster disorders
- NFU1: Infantile encephalopathy with multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions 1
- BOLA3: Infantile encephalopathy with multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions 2
- Lipoic acid disorders
- GCSH (MMDS7)
- Lipoic acid synthase (LIAS)
- Lipoyltransferase 1 (LIPT1)
- Lipoyltransferase 2 (LIPT2)
- MECR
- SLC25A26
- LONP1
- TPK1
- Pyruvate disorders: Other
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC): General
- Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency

● Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) ; Chromosome 11q13.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 11q13.2; Recessive
- Pyruvate carboxylase
- Converts pyruvate & CO2 to oxaloacetate
- Highest activity in liver and kidney
- Role in gluconeogenesis
- Location: Intramitochondrial
- Neonatal type (type B)
- Epidemiology: France & UK
- Onset age: Neonatal; 3 to 48 hours after birth
- Hypotonia
- Delayed neurologic development
- Ataxia
- Chronic lactic acidemia
- Normal lactate:pyruvate ratio
- Death in neonatal period (< 5 months)
- Muscle biopsy
- Muscle fiber size: Varied
- Type I predominance
- Rods: 1 patient
- Less severe phenotype (Type A)
- Epidemiology: North America (Canadian Indian)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Later infantile
- Hypotonia
- Developmental delay
- Seizures (50%)
- Psychomotor retardation
- Death: < 3 years
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Increased lactate:pyruvate & acetoacetate to 3-hydroxybutyrate ratios
- Benign type (Type C)
- Motor and mental abilities: Normal or mildly impaired
- Survival into childhood
- Metabolic acidosis: Episodic
- Pyruvate carboxylase
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-α deficiency (Pyruvate decarboxylase deficiency)

● Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-α (PDHA1) Chromosome Xp22.12; Recessive or Pseudo-Dominant
Chromosome Xp22.12; Recessive or Pseudo-Dominant
- Epidemiology
- Most common form of PDH deficiency
- Similar number of males & females with this diagnosis
- Genetics
- Many mutations
- Often sporadic
- Allelic disorders
- Leigh syndrome, X-linked

- Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-α deficiency
- Lactic acidosis, Neonatal or infantile
- Heterozygous females
- Leigh syndrome, X-linked
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- Nuclear-encoded mitochondrial matrix multienzyme complex
- Primary link between Glycolysis & Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
- Catalyzes irreversible conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA
- Composition: 3 enzymatic activities
- E1 (Pyruvate dehydrogenase
 )
)
- E2 (Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (DLAT)

 )
) - E3 (Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD)

 )
)
- E1 (Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Co-factor: Thiamine
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Early childhood
- Presentation pattern: Depends on functional severity of E1-α mutation
- Seizures
- Hyperventilation
- Cerebellar ataxia: Episodic
- Weakness
- Recurrent or Episodic
- May be related to polyneuropathy 304
- Choreoathetosis
- Treatment: ? Thiamine
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Carbohydrate intolerance
- Serum pyruvic acid: High
- Serum alanine: High
- E1-alpha protein: Low
- Muscle: Denervation changes; COX stain may be reduced
- Brain MRI: Basal ganglia T2 hyperintensity
- Variant syndromes: Common
- Epidemiology
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-β deficiency

● Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1-β (PDHB) Chromosome 3p14.3; Recessive
Chromosome 3p14.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics: Homozygous, Missense mutations
- PDH complex
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant
- Hypotonia
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Death: < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI: Corpus callosum agenesis, 1 patient
- PDH activity: Reduced
- PDH proteins (Fibroblast): PDHB markedly reduced; PDHA1 50% reduced
- Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency (DLDD)

● Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD) ; Chromosome 7q31.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 7q31.1; Recessive
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or Truncating
- G229C mutation in Ashkenazi Jews
- Allelic disorder: Maple Syrup Urine disease III

- DLD protein
- Component of
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex


- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex


- Branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex


- Mitochondrial glycine cleavage system

- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- DLD Mutations
- DLD activity: < 5% of control values,
- Western blot: DLD protein levels 40% of controls
- Component of
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infancy to Adulthood
- More severe with earlier onset
- Recurrent
- Vomiting & Abdominal pain
- Stroke-like episodes
- Hypothermia
- Motor retardation
- Myoglobinuria: Occasional
- Exertional fatigue: Between episodes
- Treatment: ? Lipoic acid (Oral); Reduced Branched chain amino acids in diet
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- High pyruvate, lactate, α-ketoglutarate, Branched-chain amino acids
- Hypoglycemia: Intermittent
- MRI: Symmetric basal ganglia signal
- Genetics
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase deficiency (PDHPD)

● Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase (PDP1) ;
Chromosome 8q22.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 8q22.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 10 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop comon
- PDP1 protein: PDH complex
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Hypotonia
- Developmental delay
- Seizures
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI: Posterior white matter pathology
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase E3-binding protein deficiency

● Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, component X (PDHX) ;
Chromosome 11p13; Recessive
;
Chromosome 11p13; Recessive
- PDHX protein: PDH complex
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant to 3 years
- Hypotonia
- Psychomotor retardation
- Leigh syndrome
- Optic atrophy
- Spasticity: Diplegia; Dysarthria
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI: Putaminal lesions
- Hemolytic anemia
- Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier Deviciency (MPYCD)

● Brain protein 44-Like (BRP44L; MPC1) ;
Chromosome 6q27; Recessive
;
Chromosome 6q27; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Arg97Trp; Leu79His mutation; Splicing to stop
- BRP44L
- Location: Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Pyruvate carrier protein (MPC)
- Complexes with MPC2 (BRP44)

- Substrate of: TIMM22
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital or Childhood
- Encephalopathy: 2 families
- Hypotonia
- Psychomotor retardation
- Peripheral neuropathy: 1 family
- Dysmorphic features: Face; Single palmar fold; Wide spaced nipples
- Hepatomegaly
- Course: Non-progressive; Variable; Death at 19 months to Alive at 14 years
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- Hyperlactacidemia
- Normal: Lactate/Pyruvate ratio, Sugar, Ammonia
- MRI: Periventricular cysts in severe patient
- β-Hydroxyisobutyryl CoA Deacylase deficiency (HIBCHD)

● 3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA Hydrolase (HIBCH) ;
Chromosome 2q32.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 2q32.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 children
- Genetics
- Mutations: IVS3AS, T-G, -9; Tyr122Cys; IVS2AS, C-G, -3
- HIBCH protein
- Downstream of ECHS1 in valine pathway
- Clinical: Leigh-like
- Onset
- Age: Neonatal to 6 months
- Motor: Hypotonia; Regression; Poor feeding
- Motor
- Delay & Regression
- Hypotonia
- Dystonia
- Ataxia
- Seizures
- Malformations: 1 patient
- Dysmorphic facies
- Vertebral anomalies
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Course
- Progressive or Acute encephalopathy
- Death: 75% at 3 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Lipid droplets
- Respiratory chain activities
- Multiple deficiencies (I; II+III; IV) or Normal
- Metabolite accumulation
- Methacrylyl-CoA; Acryloyl-CoA; Hydroxy-C4-carnitine
- Lactate: May be high, especially in CSF
- MRI: Basal ganglia abnormalities
- Brain pathology
- Agenesis: Cingulate gyrus; Corpus callosum
- Muscle
|
|
|
● Enoyl-CoA Hydratase, Short-chain, 1, Mitochondrial (ECHS1; Crotonase)
- Epidemiology: > 100 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Most missense, Met1Arg, Ala2Val, Asn59Ser, Ala138Val, A158D; Few splice (c.414 + 3G>C)
- China & Pacific hotspot: c.489G>A; Milder, later-onset phenotype; Reduced vision Homozygotes may be asymptomatic
- Severe phenotype: c.5C>T
- ECHS1 protein
- Catalyzes 2nd step in mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation
- Upstream of HIBCH in valine pathway
- Clinical: Leigh-like
- Onset age: Perinatal to Early childhood; Mean 13 months
- Hypotonia
- Systemic
- Respiratory: Apnea or Insufficiency in early onset disease
- Cardiomyopathy: Bradycardia
- CNS: Encephalopathy
- Developmental Delay & Regression
- Extrapyramidal
- Dystonia: Constant or Episodic in later onset patients
- Athetosis
- Orofacial dyskinesia
- Eye: Optic atrophy (20% to 30%); Strabismus; Nystagmus
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Course
- Progressive
- Later onset disease: Walk independently
- Death at 3 months to > 30 years
- Possible treatments: Valine restricted diet; Triheptanoin
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Metabolite accumulation: Methacrylyl-CoA; Acryloyl-CoA
- Urine: 2,3-dihydroxy-2-methylbutyrate, S-(2-carboxypropyl) cysteamine, N-acetyl-S-cysteine high
- Acyl-carnitine: Normal or S-(2-carboxypropyl)cysteine carnitine (SCPCC)
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like
- Atrophy, especially white matter
- T2 hyperintensity: Globus pallidus, Putamen, Caudate; White matter
- Muscle
- Morphology: Normal
- Oxidative enzymes: Normal or Mildly reduced complexes I & III
Quantitative errors in mtDNA (mtDNA depletion (MTDPS))
|
- General causes: Dysfunction of nuclear-encoded factors responsible for
- Maintenance of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) pools, or
- Replication of mtDNA: POLG1
- Biochemistry
- Complexes I, III & IV: Reduced
- Complex II: Normal
- Usual threshold for clinical manifestations: mtDNA ≤ 30%
- Autosomal Recessive syndromes
107
- Hepato-Cerebral syndromes
- MNGIE
- Myopathy (MTDPS2): Thymidine kinase 2 (TK2); 16q22
- Cardiomyopathy + Myopathy (MTDPS12): ANT1; 4q35
- PEO
- PEO + Myopathy (MTDPS11): MGME1; 20p11
- Encephalomyopathy
- Epileptic Encephalopathy
- Alpers syndromes: POLG (MTDPS4A); Twinkle (PEO1)
- IOSCA (MTDPS7): Twinkle
- Myopathy, Tubulopathy & Lactic acidosis (MTDPS8A & MTDPS8B): RRM2B; 8q23
- MTDPS10 (Sengers): AGK; 7q34
- Also see
- Fatal infantile myopathy: DGUOK; TK2; SUCLA2
- Benign infantile myopathy
- Drug toxicity: Nucleosides
- Clinical
- May manifest in single specific organ
- Other
- Categories: Overlapping
- Pathology
- mtDNA Levels in diseased tissue: 1% to 40% of normal
- Muscle: COX staining reduced
- Liver: Steatosis
Qualitative errors in mtDNA (multiple mtDNA deletions)
- Also see: Single, large mtDNA deletions
- Multiple mtDNA Deletion properties
- Multiple different mtDNA deletions: Among & within muscle fibers
- Different fiber segments: Often have different mtDNA deletions
- Disease/Deletion Mechanisms
- Defective or unreliable replication of mitochondrial genomes (mtDNA)
- Age
- More severe disorders: May produce quantitative loss of mtDNA
- Disorders with: Multiple different mtDNA deletions
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Acquired
- Aging
357: Patients > 50 years
- Frequency: > 90%
- Heteroplasmy > 10%: 10%
- Common deletion: 4977 bp
- Myositis: IM-VAMP
- Arsenic trioxide treatment
- Alcohol
- Aging
357: Patients > 50 years
- Also see
- mtDNA depletion
- Disorders with: mtDNA depletion + Multiple different mtDNA deletions
- TP: MNGIE
- Nuclear mutations altering mtDNA stability
Mitochondrial disorders: Drugs & Toxins
|
Arsenic trioxide: Myopathy Copper: CNS Doxorubicin: Cardiomyopathy Germanium: Myopathy Ixabepilone: Neuropathy Nucleosides AZT: Myopathy Clevudine: Myopathy General Neuropathy Telbivudine: Neuropathy; Myopathy Trichloroethylene (TCE): Neuropathy Valproate: Myopathy; CNS |
 AZT |
- Nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor anti-retroviral drugs (NRTIs): General
123
- Inhibit function of pol γ
- Acute effect: Moderate depletion of mtDNA (70% to 80%)
- Chronic effect: Accumulate somatic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations
- Mutation types: Similar to those caused by normal aging
- Deletions: Common mutation mt.δ4977
- Associated with: Accelerated mitochondrial turnover
- Myopathy associated with greater chronic drug dose
- AZT (3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine; Zidovudine; Azidothymidine)
- Drug history: AZT treatment for 1 to 30 months, Mean > 1 year
- Clinical: Muscle signs
- Proximal weakness
- Myalgia
- Wasting
- Course: Improves after discontinuation of drug, Usually within 3 to 4 months
- Laboratory
- EMG: Myopathic; Spontaneous activity
- Serum CK: High (2x to 11x normal)
- Myopathology
- Mitochondrial proliferation: SDH + fibers
- COX - muscle fibers: Many
- Fiber sizes: Varied
- Cytoplasmic bodies
- ± Inflammation; Necrosis
- Clevudine
109
- Onset: After 8 to 24 months
- Clinical
- Weakness
- Legs > Arms
- Proximal > Distal
- Symmetric
- Fatigue
- Myalgias
- Edema
- Course: Improvement after drug discontinuation
- Weakness
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 97% high; Normal to 6800
- Serum lactate: Often high
- LDH: Often high
- Aldolase: High in some
- Muscle: Varied fiber size; Abnormal mitochondria
- Telbivudine
110
- Drug type: Nucleoside analog
- Treatment: Hepatitis B
- Epidemiology
- Frequency: 5%
- Often in patients also on interferon treatment
- ? Some dose relation
- Clinical
- Onset: 2 to 8 weeks after treatment begun
- Myalgia: Proximal & Limbs
- Weakness: Generalized
- Numbness
- Cardiac arrhythmia: 1 patient
- Course: Reduced symptoms after drug cessation
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal to 900
- Mitochondria: Disease models
311
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number: Reduced
- Mitochondrial complex I & IV expression: Reduced
- Other nucleoside drug associated myopathies & neuropathies
- Fialuridine
- Also see: Nucleoside neuropathies
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Produce abnormal oxidative enzyne activities in cardiomyocytes
Inclusion Body Myositis
- Multiple DNA deletions
- Different deletions in each affected muscle fiber
Paragangliomas: Non-chromaffin, Hereditary
|
PGL1: SDHD; 11q23 PGL2: SDHAF2; 11q13 PGL3: SDHC; 1q21 PGL4: SDHB; 1p36 PGL5: SDHA; 5p15 PGL6: SLC25A11;17p13 PGL7: DLST; 14q24 Other SDHAF3 SDHAF4 IDH2 |
- General: Mutations in SDH related proteins
- Hereditary paraganglioma 1 (PGL1)
 : Nonchromaffin
: Nonchromaffin
● Succinate dehydrogenase complex, Subunit D, Integral membrane protein (SDHD) ; Chromosome 11q23.1; Dominant
; Chromosome 11q23.1; Dominant
- Genetics
- Mutations: Point missense & truncation
- ? Maternal imprinting of the disease gene
- Tumor inheritance: Paternal, not maternal
- Penetrance: Incomplete; Age-dependent
- Allelic disorders
- Cowden-like diseases
- MC2DN3
- Paraganglioma I
- Paraganglioma and gastric stromal sarcoma

- Pheochromocytoma

- SDHD Protein
- Small subunit (cybS) of cytochrome b in mitochondrial complex II
- Integral membrane protein
- Clinical: Benign vascularized tumors in the head and neck
- SDHD variant syndrome: MC2DN3

- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Glu69Lys, Ter164Leu, Asp92Gly
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Hypotonia
- Nystagmus
- Microcephaly, secondary
- Ataxia
- Dystonia
- Vision loss
- Catabolic episodes
- Seizures
- Cardiomyopathy
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Complex II deficiency; SDHD protein deficiency
- Genetics
- Hereditary paraganglioma 2 (PGL2): Nonchromaffin

● Succinate dehydrogenase complex assembly factor 2 (SDHAF2; SDH5) ; Chromosome 11q12.2; Dominant
; Chromosome 11q12.2; Dominant
- Epidemiology: Dutch family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Gly78Arg
- Reduced penetrance with maternal inheritance
- SDHAF2 Protein
- Flavination of SDHA
- Clinical
- Tumor location: Head & Neck; especially carotid body
- Multiplicity
- Hereditary paraganglioma 3 (PGL3)
 : Nonchromaffin
: Nonchromaffin
● Succinate dehydrogenase complex, Subunit C, Integral membrane protein (SDHC) ; Chromosome 1q23.3; Dominant
; Chromosome 1q23.3; Dominant
- Genetics
- Mutation: Point truncation
- No maternal imprinting
- SDHC Protein
- Large subunit (cybL) of cytochrome b in mitochondrial complex II
- Integral membrane protein
- Clinical: Benign vascularized tumors in the head and neck
- Genetics
- Paragangliomas 4 (PGL4)

● Succinate dehydrogenase complex, Subunit B, Iron sulfur protein (SDHB) ; Chromosome 1p36.13; Dominant or Sporadic
; Chromosome 1p36.13; Dominant or Sporadic
- Genetics
- Mutations: Germline; Truncating or Missense
- Allelic disorders
- SDHB variant syndrome: MC2DN4, Leukodystrophy

- Epidemiology: 11 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Asp48Val in many; L257V; A102T
- Clinical
- Onset: Episodic
- Age: Birth to 18 montha
- Motor skills: Subacute loss
- Motor: Hypotonia; Delay; Spasticity
- Ataxia
- Course
- Progressive or Slow improvement to age 5 years
- Some with death < 2 years
- Onset: Episodic
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Leukodystrophy in deep white matter & corpus callosum; Thalamic nuclei
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle: Complex II activity reduced
- Genetics
- Paragangliomas 5 (PGL5)

● Succinate dehydrogenase complex, Subunit A, Iron sulfur protein (SDHA) ; Chromosome 5p15.33; Dominant
; Chromosome 5p15.33; Dominant
- Mutation: Arg589Trp
- Allelic with
- NOTE: Mutations in
- SDHAF1: Infantile leukoencephalopathy
- Paragangliomas 6 (PGL6)

● Oxoglutarate/malate carrier (SLC25A11) ; Chromosome 17p13.2; Dominant
; Chromosome 17p13.2; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: P239T
- Neoplasm: Loss of heterozygosity
- SLC25A11: Mitochondrial 2-oxoglutarate/malate carrier
- Paragangliomas 7(PGL7)

● Dihydrolipoamide S-Succinyltransferase (DLST) ; Chromosome 14q24.3; Dominant, Reduced penetrance
; Chromosome 14q24.3; Dominant, Reduced penetrance
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Gly374Glu
- DLST protein
- Structural core of α-keto glutarate dehydrogenase complex
- Citric acid cycle (TCA)
- Oxidative decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids
- Mitochondria
- Clinical
- Onset: 24 to 38 years
- Paraganglioma (PGL)
- Thoracic abdominal
- Normetanephrine-secreting
- Benign
- No family history
- Laboratory
- Neoplasm: Loss of heterozygosity for DLST due to uniparental disomy (UPD) of paternal chromosome
- External links
Other Mitochondrial Syndromes & Mutations
Mitochondrial syndromes: Infantile & Childhood Onset
|
- Fumarase deficiency (FMRD)

● Fumarate hydratase (FH) ; Chromosome 1q43; Recessive
; Chromosome 1q43; Recessive
- Fumarate hydratase protein
- Conversion of fumarate to malate
- Krebs cycle
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Encephalopathy
- Clinical
- Onset: Infancy
- Hypotonia
- Microcephaly
- Delayed development
- Death < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Cerebral atrophy
- Lactic and pyruvic acidemia
- Fumaric aciduria
- Fumarase deficiency: Reduced generally or selectively in skeletal muscle
- Clinical
- Other syndromes
- Fumarate hydratase protein
- Epileptic Encephalopathy, Early infantile onset, Severe (EIEE51)
 213
213
● Malate dehydrogenase, Mitochondrial (MDH2) ; Chromosome 7q11.23; Recessive
; Chromosome 7q11.23; Recessive
- Nosology: Developmental & Epileptic Encephalopathy 51 (DEE51)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or Stop
- MDH2 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Converts malate to oxaloacetate
- Krebs cycle
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal to 5 months
- Motor
- Hypotonia: Generalized
- Weakness
- Pyramidal signs: Plantar response extensor
- CNS: Other
- Psychomotor delay
- Epilepsy
- Refractory
- May respond to ketogenic diet
- Dystonia (67%)
- Ataxia
- Systemic
- GI: Constipation
- Cardiomyopathy
- Family history: Increased cancer frequency
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in Serum & CSF
- Brain MRI
- Corpus callosum: Abnormal
- Atrophy: Cortex; Subcortical
- Muscle respiratory chain activities: Normal
- Urine organic acids
- Abnormal ketone bodies, lactate, pyruvate, malate, fumarate
- 3-Methylglutaconic acid (3-MGA)
- Encephalopathy + Dystonia (MGCA8)

● HTRA Serine peptidase 2 (HTRA2; OMI) ) ; Chromosome 2p13.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 2p13.1; Recessive
- Nosology: 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria, type VIII
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 9 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Splice site or Deletion
- Allelic Disorders
- PARK13
 ; Chromosome 2p12; Dominant or Recessive
; Chromosome 2p12; Dominant or Recessive
- Essential tremor
- Encephalopathy + Dystonia
- PARK13
- HTRA2 protein
- Mitochondrial intermembrane space protein
- Serine protease
- Mutation causes: Defective activation of protease activity & mitochondrial dysfunction
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Hypertonia
- Tremor
- Extrapyramidal: Dystonia
- Sensorineural deafness
- Seizures
- Apneic episodes
- Course: Early death
- Laboratory
- Urine: 3-MGA
- Muscle
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activities: Normal
- Immature muscle fibers
- Mitochondrial structure: Distorted cristae
- Brain MRI
- Cerebral atrophy
- Corpus callosum: Thin
- Neutropenia
- Serum lactate: High
- Metabolic Encephalopathy (MC5DN5)
 237
237
● ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, Delta subunit (ATP5F1D; ATP5D) ; Chromosome 19p13.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 19p13.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Missense; c.245C>T (p.Pro82Leu), c.317T>G (p.Val106Gly)
- ATP5F1D protein
- Mitochondrial: Complex V
- Subunit of ATP synthase
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy or Childhood
- Lethargy: Episodic; Acute onset
- Developmental delay
- Skeletal: Short stature; Ankle contractures
- Cardiomyopathy, dilated: Younger age; May resolve
- Weakness: Proximal; Mild; Exercise intolerance
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
- Hyperammonemia
- Brain MRI: Cortex swelling or WM changes during episodes
- Serum CK: 500 to 1,000 during episodes
- Fibroblasts
- Complex I-IV activities: Normal
- Complex V activity: Reduced
- Mitochondria: Reduced cristae
- Hypermetabolism due to Uncoupled Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation 2 (HUMOP2)

● ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, Beta subunit (ATP5F1B; ATP5B) ; Chromosome 12q13.3; de novo
; Chromosome 12q13.3; de novo
- Epidemiology: 1 Pair of monozygotic twins
- Genetics
- ATP5F1B protein
- Mitochondrial: Complex V
- Subunit of ATP synthase
- Catalytic core of domain F1 of complex V
- Clinical: Hypermetabolic state
- Onset: Intrauterine; Growth retardation
- Failure to thrive: Despite caloric intake in excess of calculated need
- Hyperphagia without proper weight gain
- Tachypnea, persistent
- Hyperthermia: Episodes
- Diaphoresis & Tactile warmth: Persistent
- Global developmental delay: Mild
- Laboratory
- Branched-chain amino acids: High
- Hyperammonemia: Mild
- Uremia: Mild
- Triglyceride levels: High
- Differential diagnosis
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase, E1-α Polypeptide 1

● Chromosome Xp22.12; Recessive
- Mitochondrial Complex I deficiency, nuclear type 1 (MC1DN1)

● NADH Dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) Fe-S Protein 4 (NDUFS4) ;
Chromosome 5q11.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 5q11.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Often Stop
- Allelic disorder: Leigh syndrome
- NDUFS4 protein: Complex assembly
- Clinical syndrome: Fatal multisystemic complex I deficiency
- Onset: Vomiting; Failure to thrive; Hypotonia
- Other CNS
- Psychomotor retardation
- Convulsions
- Bradypnea
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Course
- Progressive cardiorespiratory dysfunction
- Death in 2nd year
- Laboratory
- Cerebral MRI: Generalized brain atrophy; Symmetric basal ganglia change
- Serum lactate: Normal
- Muscle morphology: Normal
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency
- NDUFS4 Variant: Leigh syndrome
- Epidemiology
- Common autosomal recessive cause of complex I-associated Leigh Syndrome
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Characteristic Leigh presentation
- Course: Onset & demise typically ≤ 8 months of life: No later than 30 months
- Cardiomyopathy (33%): Hypertrophic
- Neuroradiology
- Bilateral symmetrical basal ganglia lesions: May extend to cerebral peduncles, pons and medulla
- Cerebral atrophy
- Epidemiology
- Lethal Infantile Mitochondrial Disease (MC1DN9)
 46:
Complex I
46:
Complex I
● NADH Dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) Fe-S Protein 6 (NDUFS6) ; Chromosome 5p15.33; Recessive
; Chromosome 5p15.33; Recessive
- Epidemiology
- 12 patients
- Ethnic origin: Anglo-Celtic & Turkish
- Genetics
- Types: Splicing abnormality; Deletion (Large)
- Allelic disorder: Neuropathy +
- NDUFS6 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Component of iron sulfur protein fraction of Complex I
- NDUFS6 mutation effect: Abnormal complex I assembly
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Spontaneous movements: Few
- Withdrawal to pain: Minimal
- Reflexes
- Gag: Weak
- Moro: Absent
- Grasp: Absent
- Tendon: Reduced or increased
- Eyes: Drifting movements; Nystagmus
- Hypoventilation: Central
- Death: < 2 weeks
- Laboratory
- Blood lactate: High
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I deficiency
- Neuropathology: Hypoxic
- Congestion: Basal ganglia, thalamus, & periventricular brain stem
- Chromatolysis: Many neurons
- Microvacuolation: Throughout the brain
- NDUFS6 variant: Neuropathy +
317
- Epidemiology: 5 families; 6 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: c.309+5G>A, Gln44X; Splice or Truncation; Homozygous
- Splice mutation effect: Exon 3 skipping
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 to 10 years
- Gait disorder
- Weakness
- Distal
- Legs > Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Absent at ankles
- Sensory loss
- Pan-modal: Vibration, Pin
- Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced at ankles
- Skeletal: High arched feet
- CNS
- Optic atrophy: Visual acuity reduced in some
- Nystagmus
- Intellectual dysfunction: Borderline
- Movement disorders: Some patients
- Epilepsy
- Course: Slow progression
- Onset
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axonal neuropathy; SNAP amplitudes reduced
- EMG: Denervation, distal
- Brain MRI: Normal or Basal ganglia lesions
- Serum Lactate: Normal or Mildly high
- Epidemiology
- Lethal Infantile Mitochondrial Disease (MC1DN16)
 87:
Complex I
87:
Complex I
● NDUFAF5 (C20orf7)
 ; Chromosome 20p12.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 20p12.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 9 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Leu229Pro, Met279Arg & other missense
- Allelic disorder: Leigh-like
- C20orf7 protein
- Inner-Mitochondrial-Membrane
- Complex I assembly factor
- Clinical
- Growth retardation: Intrauterine
- Failure to thrive
- Dysmorphisms: Minor facial; Unusual hair patterning, Abnormal toes, Small sacral pit
- Seizures
- Later onset: Spasticity; Extrapyramidal
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Death: 1 week to Adult survival
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Histology: Normal
- Complex I deficiency
- Serum lactate: High
- CNS: Agenesis of corpus callosum; Ventricular septation
- Urine: High alanine
- Muscle
- NDUFAF5 Variant syndrome: Leigh
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Leu159Phe
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 years
- CNS
- Spasticity: Arms & Legs
- Dystonia
- Mental delay
- Dysarthria
- Skeletal
- Ankle contractures
- Scoliosis
- Course: Progressive
- Survival: Into adulthood
- Laboratory
- Brain Imaging
- Abnormal: Caudate & Putamen; Substantia nigra; Periaqueductal grey
- Enlarged ventircles
- Lactate: Normal
- Muscle: Complex I ± IV low activity
- Brain Imaging
- Lethal Infantile Mitochondrial Disease (MC1DN25) (Complex I)

● NDUFB3 ; Chromosome 2q33.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 2q33.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Trp22Arg, Gly70Ter
- Allelic disorder: Short stature
- NDUFB3 protein
- Structural Complex I subunit
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 week
- Intrauterine growth restriction
- Failure to thrive
- Hypotonia
- Death: 4 months
- Laboratory
- Metabolic (lactic) acidosis
- Complex I deficiency: Skin, Muscle & Fibroblasts
- NDUFB3 variant
- Epidemiology: 8 families, commonly Irish
- Genetics
- Mutation: Trp22Arg, Homozygous
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset: Early life metabolic crisis
- Short stature
- Face: Prominent forehead, Smooth philtrum, Deep-set eyes
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Resolved with time
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis, Episodic
- Lethal Neonatal Multisystem Mitochondrial Disease (MC1DN35) (Complex I)

● NDUFB10 ; Chromosome 16p13.3; Recessive\
; Chromosome 16p13.3; Recessive\
- Epidemiology: 2 patients, 1 Irish-German family
- Genetics
- Mutations: Cys107Ser; 1-bp insertion, 206T
- NDUFB10 protein
- Accessory subunit for Complex I
- Located in PD part of Complex I
- Acts at late stage of assembly process
- Substrate of intermembrane space oxidoreductase CHCHD4
- Clinical
- Prenatal
- Growth retardation
- Nonimmune hydrops
- Lung hypoplasia
- Cardiomyopathy
- Nuchal skin: Excessive
- Lungs
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Pneumothorax
- Cardiomyopathy
- Death: 1 day
- Prenatal
- Laboratory
- Complex I activity: reduced in Skeletal muscle, Heart, Liver
- Lactic acidosis
- Serum alanine: High
- Urine: High organic acids
- Lipid accumulation: Cardiac & Liver
- Mitochondria: Proliferation; Abnormal cristae
- Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria (HHH syndrome)

● Ornithine transporter, Mitochondrial 1 (ORNT1; SLC25A15) ;
Chromosome 13q14.11; Recessive
;
Chromosome 13q14.11; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 120 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Loss of function
- French-Canadian: Phe188del founder
- Japanese & Middle Eastern: Arg179Ter
- Gene screen: Hyperammonemia or Urea cycle disorder multigene panel
- ORNT1 protein
- Transports ornithine across inner mitochondrial membrane
- From cytosol to mitochondrial matrix
- Component of urea cycle
- Clinical syndrome
- General
- Similar to other Urea cycle disorders
- Phenotypic variability with same mutation
- Onset
- Age
- Neonatal 8%, Infancy (10%) to 76 years
- Early & Late onset forms
- Acute
- Hyperammonemia
- Vomiting
- Ataxia
- Mental status: Lethargy, Confusion, Coma
- Age
- CNS
- Mental retardation & Learning difficulties
- Episodes
- Encephalopathy
- Triggers: Environmental; Diet change; Valproate
- Seizures: Myoclonus epilepsy
- Buccofaciolingual dyspraxia
- Ataxia (80%): Limbs, Gait, Speech
- Spastic paraparesis: Progressive
- Onset: Early adult
- Pyramidal signs
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Spasticity (30%)
- Vibration sense: Reduced or Normal
- Not diet responsive
- Weakness & Atrophy
- Distal legs
- ? 2° Motor neuron loss
- GI
- Episodic vomiting
- Aversion to protein-rich foods
- Ocular: Retinal depigmentation; Chorioretinal thinning
- Hematologic: Coagulation disorders 2° liver disorders
- Course
- Onset: Acute
- Chronic: Progressive
- 95% survive to adulthood
- Treatment
- Low protein diet
- Supplementation: Ornithine & Citrulline
- Hyperammonemic episodes: Discontinue protein intake
- Sodium phenylbutyrate
- Function: Maintain plasma ammonia, glutamine, arginine & amino acids
- Doses: 250 mg/kg (Infants & Children); 5.5 g/m2 (Other patients)
- Monitor (Especially during pregnancy): Plasma ammonia & Plasma + Urine amino acids
- Also see: GeneReviews
- General
- Laboratory
- Hyperornithinemia: Persistent
- Hyperammonemia
- Especially postprandial
- Less than in other urea cycle disorders
- Urine: Homocitrullinuria; Orotic aciduris
- Ornithine transport: Reduced into mitochondria
- Cranial MRI: White matter signal; Cortical, Corpus callosum & Spinal cord atrophy
- Liver dysfunction: AST & ALT high; Coagulopathy, mild
- Central motor conduction time: Slow or Absent
- NCV: Usually normal
- Mitochondrial Carbonic Anhydrase VA Deficiency

● Carbonic anhydrase V (CA5A) ;
Chromosome 16q24.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 16q24.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 familes, 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense (c.697T>C p.Ser233Pro); Splice site (c.555G>A); Deletion (in exon 6)
- CA5A protein
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Liver
- Provision of bicarbonate to enzymes in intermediary metabolism pathways
- Carbamoylphosphate synthetase 1 (Urea cycle)
- Pyruvate carboxylase (Anaplerosis, Gluconeogenesis)
- Propionyl-CoA carboxylase,
- 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase (Branched chain amino acid catabolism)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Lethargy
- Tachypnea
- Psychomotor delay
- Treatment
- Episodes
- Carglumic acid (Carbaglu)
- Illnesses: High-caloric & lipid-rich formula
- L-carnitine
- Vitamin C
- Coenzyme Q10
- Episodes
- Laboratory
- Hyperlactatemia
- Hyperammonemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Urine organic acids: High lactic, β-hydroxybutyric & acetoacetic acid
- Liver: Absent CA5A protein
- Acylcarnitines: Normal
- Mitochondrial ATPase (Complex V) deficiency
4

● Autosomal Recessive- Genetics
- Nuclear DNA mutations
- Mitochondrial DNA ATPase mutation
- ATP synthase 6
- ATP synthase 8
- G8529A: Cardiomyopathy + Neuropathy
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital
- Systemic: Cardiomyopathy; Hepatomegaly
- Prognosis: Death in infancy or childhood
- Lab
- Serum: Lactic Acidosis
- Tissue biochemistry
- Selective reduction in oligomycin sensitive ATPase activity (18 to 33% of normal)
- Short half-life of ATPase β subunit
- Reduced Proton leak in inner mitochondrial membrane
- Genetics
- Complex V (ATP synthase) deficiency (MC5DN1)
39

● ATP synthase F1 complex assembly factor-2 (ATPAF2; ATP 12)
 ;
Chromosome 17p11.2; Recessive
;
Chromosome 17p11.2; Recessive
- Nosology: Mitochondrial complex V (ATP synthase) deficiency, nuclear type 1
- Epidemiology: 1 patient from consanguinous family
- ATPAF2 gene mutations: W94R homozygous
- ATPAF2 protein
- Role in assembly of F1 moiety of ATP synthase
- Protects F1 subunits from forming non-productive large complexes during assembly of enzyme oligomer
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital
- Skeletal: Dysmorphic features
- Mouth: Large; Micrognathia
- Nasal bridge: Prominent
- Feet: Rocker bottom
- Contractures: Flexion; Camptodactylia
- Motor: Hypertonia; Poor suck
- Hepatomegaly
- Death: 14 months due to infection
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
- Urine: High lactate, fumarate, methylglutaconic acid, & amino acids
- Imaging
- Corticalsubcortical atrophy
- Corpus callosum: Dysgenesis; Absent anterior genu and rostrum
- White matter: Hypoplasia
- Basal ganglia & thalami: Atrophic
- Complex V
- Reduced activity
- More prominent changes in liver than muscle
- Muscle morphology
- Lipid: Increased
- No ragged red fibers
- Liver: Reduced Complex V immunoreactivity (α, β & δ subunits)
- NOTE: Other patients with similar syndrome & Complex V deficiency without ATP12 mutations
- Neonatal encephalocardiomyopathy (MC5DN2)

● Transmembrane protein 70 (TMEM70)
 ;
Chromosome 8q21.11; Recessive
;
Chromosome 8q21.11; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Roma (Gypsy) & Arab-Muslim families
- Mutations
- Homozygous or Compound heterozygous
- Nonsense
- Splice site: 317-2A>G; in splice site of intron 2 common in Roma
- Insertion or Deletion
- Varied disease severity may occur with same mutation
- TMEM70 protein
- Mitochondrial Complex V (ATP synthase) biogenesis
- Membrane protein
- TMEM126A mutations: Optic atrophy
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Neonatal
- Growth retardation: Birth weight < 3rd percentile
- Oligohydramnios
- Hypotonia
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Motor: Hypotonia; Delay
- Respiratory failure
- CNS: Variable; Microcephaly (35%); Retardation
- Face: Dysmorphism (35%)
- GI: Hepatomegaly; Pseudoobstruction
- Cataracts
- Course
- Fulminant to slowly progressive
- Death: 1st year in 50%
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: Serum & CSF
- 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
- ATP synthase (Complex V) content: Low (< 30% of control); Other Complex activities normal
- Muscle histology: Normal
- MRI: Some patients with partial agenesis of corpus callosum & basal ganglia signal change
- Neonatal hepatoencephalopathy
(MC4DN4)

● SCO1 ; Chromosome 17p13.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 17p13.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: French family
- Mutations
- Compound heterozygous
- Deletion (363GA) & Missense (Pro174Leu)
- SCO1 protein
- Location
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Intermembrane space protein
- Location
- Tissue distribution: Ubiquitious
- Role in assembly of Complex IV (Cytochrome oxidase)
- More in mitochondrial rich tissues: Skeletal muscle; Heart; Liver; Kidney
- Lower expression in brain
- Clinical
- Liver: Neonatal hepatic failure; Hepatomegaly
- Neurologic: Ketoacidotic coma; Hypotonia
- Course: Recurrent apnea & bradycardia; Death < 2 to 3 months
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyperlactatemia
- COX deficiency in liver, muscle lymphocytes
- Muscle pathology: Lipid droplets
- Mitochondrial Leucine Transfer RNA 1 (MTTL1)
 : Also see MELAS
: Also see MELAS
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 1 (MTND1)
 (Complex 1): Also see Leber's optic atrophy
(Complex 1): Also see Leber's optic atrophy
- Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase/enoyl-coa hydratase, beta subunit (HADHB)
 :
:
Trifunctional protein deficiency, type 2
● BCS1L
- Nosology: Growth retardation, Amino aciduria, Cholestasis, Iron overload, Lactic acidosis, Early death
- Epidemiology: Finnish & Turkish families
- BCS1L Genetics
- Mutation types: Usually missense; Some splice
- All Finnish patients have homozygous Ser78Gly mutation
- Other BCS1L disorders
- Björnstad syndrome
 : Sensorineural hearing loss; Pili torti
: Sensorineural hearing loss; Pili torti - Leigh syndrome

- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 1 (MC3DN1)

- Björnstad syndrome
- BCS1L protein
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Required for the expression of functional ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase (bc1) complex

- Similarity to AAA ATPase superfamily

- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy or Prenatal
- Growth retardation: Intrauterine
- Neonatal tubulopathy
- Encephalopathy
- Motor: Spasticity; Tendon reflexes increased
- Failure to thrive
- Death: Neonatally or Early infancy
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: 1st days of life
- Aminoaciduria: Fanconi-type
- Liver failure
- Iron metabolism disorder: Liver hemosiderosis
- Mitochondrial biochemistry: Complex III deficiency
● Succinate-CoA Ligase, Alpha subunit (SUCLG1)
- Epidemiology: > 20 patients
- Gene
- Encodes α-subunit of Krebs cycle enzyme succinate-CoA ligase (SUCL)
- Mutations: Missense & Truncating
- Disease severity: ? Associated with residual levels of SUCLG1 protein
- SUCLG1 protein
- Component of succinate-CoA ligase (SUCL)
- Forms heterodimer with either of its β subunits: SUCLA2 & SUCLG2
- Produces ATP/ADP-specific SUCL (A-SUCL) & GTP/GDP-specific SUCL (G-SUCL)
- Catalyze substrate-level phosphorylation in Krebs cycle
- SUCL interacts with NDPK
- Absent SUCLG1 protein: Loss of SUCLA2 protein; More severe phenotype
- Nucleotide salvage pathway disorders
- Clinical: Severe syndrome
- Mutations: 2 bp deletion in exon 2, c.113_114delAT; Tyr51fs; A209E
- Onset
- Age: 1st day of life
- Hypotonia
- Dysmature: Hypertrichosis; Low hairline
- Hepatomegaly
- Hypothermia: Severe
- Hypotonia
- Renal failure
- Death: < 1 week
- More severe phenotype than SUCLA2 mutations
- Clinical: Milder syndrome
- Mutations: Ser46Phe; Gly85Ala; Ile143Ser; Ala209Glu
- Onset age: 0 to 6 months
- Hypotonia
- Muscle atrophy
- Dystonia
- Leigh-like syndrome
- Ophthalmoplegia: 50%
- Polyneuropathy: Few patients
- Life span: Shortened
- Similar phenotype to SUCLA2 mutations
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Urine
- Lactate & Pyruvate: High
- Methylmalonate & Methylcitrate, Propionyl carnitine (C3): Elevated excretion
- Amino acids: High Taurine & Glycine
- Acyl-carnitine C4-DC: Elevation
- Muscle
- Increased lipid
- No ragged red muscle fibers
- Oxidative enzymes
- Complexes I, III and IV: Reduced activity & levels
- Complex II: Normal
- SUCLG1 protein: Absent staining
- Mitochondrial DNA depletion: Some patients; 15% to Normal
- MRI
- T2 & FLAIR hyperintensities: Bilateral caudate nuclei & putamen
- Cortical & Caudate atrophy
- Ventricular dilatation
- Fatal infantile lactic acidosis: Other causes
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency
- Deficiency of complex I of respiratory chain
- mtDNA mutations
● Transcription factor A, Mitochondrial (TFAM)
- Epidemiology: Colombian-Basque family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Pro178Leu
- TFAM protein (TCF6)
- Location: Mitochondria, Nucleoids
- Activator of mitochondrial transcription
- mtDNA: Transcription, Replication Packaging
- Interacts with: Mitochondrial single-stranded DNA-binding protein (mtSSB)

- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital or Prenatal
- Intrauterine growth retardation
- Liver
- Jaundice
- Ascites
- Course
- Progressive
- Death at 2 & 4 months
- Laboratory
- Hypoglycemia
- Liver
- Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
- Transaminases: High
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Biopsy: Cirrhosis, Microvesicular steatosis, Cholestasis, Mitochondrial pleomorphism
- Plasma: High tyrosine & methionine
- Urinary organic acids: High
- Tyrosine: High
- Coagulopathy
- Muscle
- Morphology: Sarcoplasmic irregularities
- Mitochondria
- Hyperplasia & Proliferation
- Varied shapes & sizes
- Sarcoplasmic distribution: Abnormal
- mtDNA: 21% of normal
- Citrate synthase activity: Increased
- Brain MRI: Normal
● Mitochondrial Ribosomal RNA Methyltransferase 2 (MRM2)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense; Gly189Arg
- MRM2 protein
- Methyltransferase
- S-adenosylmethionine-binding
- Clinical: MELAS-like
- Onset age: 8 months
- Developmental delay
- Febrile-triggered episodes
- Encephalopathy
- Seizures: Status epilepticus
- Liver failure: Hyperammonemia
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Death: 7 years of sepsis
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- Early: Stroke-like lesions, multiple
- Late: Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy
- Plasma citrulline: Low
- Muscle
- Complex I & IV activities low
- mtDNA copy number: 40% of control (Usual threshold for clinical manifestation ≤ 30%)
- Brain MRI
- Menkes
 :
α polypeptide
:
α polypeptide

● Chromosome Xq21.1; Recessive - Occipital horn syndrome
 :
α polypeptide
:
α polypeptide

● Chromosome Xq21.1; Recessive - Spinal muscular atrophy, distal, X-linked 3 (SMAX3)

● HIRA-interacting protein 5 (HIRIP5; NFU1)
- Nosology: Multiple Mitochondrial Dysfunctions Syndromes (MMDS)
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Disorder of systemic energy metabolism,
- Clinical: Weakness, Respiratory failure, Impaired neurologic development, Early death
- Laboratory: Lactic acidosis
- Epidemiology: 10 Spanish & Mexican families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Missense; Arg182Gln, Gly2308Cys
- Allelic disorder: SPG93
- NFU1 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial & Cytosolic
- Involved in biogenesis of Iron-Sulfur (FeS) clusters for
- Normal maturation of lipoate-containing 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases
- Assembly of the respiratory chain complexes
- Alternate scaffold to ISCU for assembly of Fe-S proteins
- Mutation effects: On both mitochondrial & cytosolic NFU1 isoforms
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st month
- Feeding difficulty
- Motor: Weakness; Hypotonia; Respiratory failure
- CNS: Lethargy; Seizures
- Hepatomegaly
- Course: Death 1 month to 1 year
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- Lactate: High in blood
- Glycine: High
- Biochemistry
- Multiple mitochondrial enzymopathies
- Complex I: 30%
- Complex II: 50%
- Complex III: 60%
- Complex IV: 50% to 100%
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc) deficiency: 5% to 10% of normal
- 2-Oxoacid Dehydrogenase enzyme deficiency: 10% of normal
- Multiple mitochondrial enzymopathies
- Pathology: White matter spongiosis
- NFU1 variant: SPG93

- Epidemiology: 12 families; 21 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Usually biallelic missense
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 2 years
- Spasticity
- Paraparesis or Tetraparesis
- Gait disorder
- Tendon reflexes: Increased in legs
- Seizures, Febrile
- Cognitive & Motor regression
- Polyneuropathy: 1 older patient
- Course
- Progressive
- Exacerbation & Progression: During febrile illness
- Early death in many
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: White matter pathology; Thalamus & Basal ganglia Δ
● BolA, E. Coli, homolog of, 3 (BOLA3)
- Nosology: MMDS
- Genetics
- Homozygous singlebase-pair duplication c.123dupA
- Stop: p.Glu42Argfs*13
- BOLA3 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial
- Involved in biogenesis of Iron-Sulfur (FeS) clusters for
- Normal maturation of lipoate-containing 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases
- Assembly of the respiratory chain complexes
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st month
- Feeding difficulty
- Motor: Weakness; Hypotonia; Respiratory failure
- CNS: Lethargy; Seizures
- Hepatomegaly
- Course: Death 1 month to 1 year
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- Lactate: High in blood
- Glycine: High
- Biochemistry
- Multiple mitochondrial enzymopathies
- Complex I: 30%
- Complex II: 50%
- Complex III: 60%
- Complex IV: 100%
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc) deficiency: 5% to 10% of normal
- 2-Oxoacid Dehydrogenase enzyme deficiency: 30% of normal
- Multiple mitochondrial enzymopathies
- Pathology: White matter spongiosis
● Hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase/3-Ketoacyl-CoA Thiolase/Enoyl-CoA Hydratase, α subunit (HADHA)
- Epidemiology
- Genetics
- Mutations
- > 59 identified
- Most loss of function: Stop; Splice; Missense
- Common mutation: Glu474Gln
- Reduces LCHAD activity
- Homozygous clinical: Neonatal death
- Allelic disorders
- Fatty liver, acute, of pregnancy

- HELLP syndrome, maternal, of pregnancy

- LCHAD deficiency

- MTPD infantile
- Myopathy & Neuropathy
- Fatty liver, acute, of pregnancy
- Mutations
- Trifunctional Protein
- Nosology: Trifunctional protein, α subunit
- Functions
- Catalyzes steps in long-chain intra-mitochondrial β-oxidation
- Source of energy: Skeletal muscle & Heart
- MTP deficiency also caused by mutations in: HADHB
- MTP components
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Common defect in MTP: LCHAD
- See: Lipid disorders
- Clinical: Several syndromes
- HADHA variant: Infant syndrome
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st 2 years
- Cardiomyopathy
- Muscle: Hypotonia
- Hepatomegaly
- Retinopathy: Pigmentary
- Course
- Recurrent metabolic crises, or Steadily progressive
- Death < 2 years
- ? Benefit from dietary management
- Mothers
- Acute fatty liver during pregnancy
- Associated severe complications
- Treatments
- Long-chain fat restricted diet
- Supplementation: Medium chain triglycerides, Triheptanoin, Carnitine
- Avoid fasting
- Laboratory
- Hypoketotic Hypoglycemia
- Lactic acidemia
- Dicarboxylic aciduria
- Acylcarnitine profile: Long-chain & 3-hydroxy long-chain acylcarnitine species high
- Carnitine: Reduced levels
- Clinical
- HADHA variants: Neuropathy ± Myopathy
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense (Gly319Ser & Others) & Stop
- Clinical
- Myopathy
- Onset ages: Infancy to 4th decade
- Episodes: Severe weakness; Precipitated by fever, vomiting, or dehydration
- Myoglobinuria: Precipitated by infection, fasting, exertion (sustained, non-vigorous), or cold exposure
- Weakness: Proximal; Symmetric
- Polyneuropathy
- Weakness: Distal; Symmetric
- Sensory loss
- Axon loss: ? 2° Demyelination
- May be present without myopathy 344
- Course: Progressive
- No hepatic or cardiac disorders
- Treatment
- Frequent feeding
- High-carbohydrate, low-fat diet
- Cornstarch: Uncooked, Oral
- ? Cod liver oil, High in Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- ? Prednisone
- Laboratory
- Muscle biopsy: Normal or Chronic denervation
- NCV: Axonal, Sensory neuropathy
- EMG: Denervation; Large motor units, Fibrillations
- Serum CK: Normal between episodes
- Acylcarnitine profile: May be normal
- Genetics
- HADHA variant: Infant syndrome
● Dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase (DLAT; Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase E2)
- Epidemiology: 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Deletion; Splice
- Allelic disorder: Neonatal death
- DLAT protein
- PDH complex
- Target of: Anti-mitochondrial antibodies
- Cuprotosis-related
- Interacts with: p-STAT3
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 weeks
- Encephalopathy
- Mental retardation
- Dystonia
- Microcephaly
- Treatment: Carbohydrate restriction; Bicarbonate supplementation
- Laboratory
- Hyperammonemia
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI: Basal ganglia pathology
- MRS: Reduced N-acetyl aspartate & choline
● HMG-CoA lyase (HMGCL)
- Epidemiology: Especially severe & common in Saudi Arabia
- Disorder of ketone synthesis
- Clinical
- Onset: First year
- Fever
- Encephalopathy
- Hepatomegaly
- Treatment: Leucine restriction; Supplementary glucose to prevent hypoglycemia
- Laboratory
- Urine: Odor resembles cat
- Metabolic acidosis
- Hypoglycemia
- Organic aciduria
- Sensitivity to dietary leucine
- Carnitine deficiency
● Deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK)
- Epidemiology: Israeli-Druze & German families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous
26
- Single nucleotide deletion in exon 2
- Nonsense mutation in exon 3
- ? Non-coding region mutations
- Allelic disorders
- Mutations: Homozygous
26
- DGUOK protein
- Expressed in all tissues
- Mitochondrial
- Function: Deoxynucleoside salvage
- Phosphorylates deoxyguanosine & deoxyadenosine
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth to 6 months
- Hepatic failure: Hepatomegaly
- Failure to thrive
- Eyes: Oscillating (Pendular) movements
- Neurological disorders
- Muscle hypotonia
- Hyperreflexia
- Irritability
- Death: < 1 year; Hepatic failure
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Hypoglycemia
- α-Fetoprotein: High in serum
- Muscle: May be morphologically normal
- Mitochondrial changes in muscle
- Low activity: Complex I, III, IV
- Normal activity: Complex II
- mtDNA depletion: 8% to 39% of control levels
- mtDNA size: Normal
- Liver: Mosaic pattern of normal and deficient cytochrome-c oxidase in hepatocytes
- DGUOK variant syndromes: Adult onset, Recessive
146
- Epidemiology
- Frequency: 5.6% of adults with multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions
- Onset ages: 20 to 69 years
- Mutations: Missense (All patients with one); Splice site; Small deletion
- Clinical syndromes
- Mitochondrial myopathy
- Variable features: Leg weakness; Fatigue; Dysphagia; PEO; Deafness
- EMG: Myopathic
- PEOB4
 :
Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions
:
Progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recesive
- Mutations: Tyr62Ter; Asn154Lys; Gln170Arg; Glu44Lys; IVS3AS, C-G, -11
- Clinical
- Onset age: Adult; 40 to 69 years
- Weakness
- Proximal & Distal
- Legs
- Dysphagia
- Episodes: Rhabdomyolysis
- Hearing loss: Sensory-Neural
- Laboratory
- Muscle biopsy: COX- muscle fibers
- Nerve biopsy: Axon loss
- Brain MRI: Cortical atrophy
- Genetics
- Rhabdomyolysis: After early hepatic failure
- Lower motor neuron syndrome
- Muscle
- Weakness: Distal & Proximal; Arms & Legs; Dysphagia
- Wasting: Limbs & Tongue
- Fasciculations
- Muscle
- Cognitive impairment: Mild
- EMG: Denervation
- Mitochondrial myopathy
- Epidemiology
- Laboratory
- Mitochondrial DNA: Multiple deletions; Normal amount
- Muscle: COX- & SDH+ muscle fibers; Myopathic, mild
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Later onset mtDNA depletion myopathy
- mtDNA depletion syndromes
- Multiple mitochondrial DNA deletion syndromes
● Glomerulosclerosis gene MPV17 (MPV17)
- Epidemiology
- Italian families
- Genetics: MPV17 mutations
- Missense: R50Q; R50W; N166K
- Deletion: 116-141del
- Allelic disorders
- MPV17 protein
- Localized to inner mitochondrial membrane
- Ubiquitous expression
- Non-selective channel: Modulates membrane potential
- Mitochondrial homeostasis
- Mitochondrial deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTP) pool homeostasis
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) maintenance
- Possible regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolism & control of oxidative phosphorylation
- Clinical: Hepatocerebral encephalopathy
- Early death due to liver failure
- Treatment: Liver transplant
- Prolongs life span
- Growth delay
- Brain lesions on MRI may develop
- MPV17 variant: Multisystem disorder (Neurohepatopathy), Juvenile or Adult onset
147
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- MPV17 mutations
- Compound heterozygous or Homozygous
- Pro98Leu; LysMet88-89MetLeu & Leu143*
- Clinical
- Onset age: 14 to 34 years
- Polyneuropathy: Distal weakness
- Weakness: Proximal; Exercise intolerance; With disease progression
- Ocular: Ptosis; Ophthalmoparesis
- Extrapyramidal: Bradykinesia; Resting hand tremor; Rigidity, mild
- Depression
- GI
- Constipation
- Liver: Fatty (Steatosis); Cirrhosis
- Course: Slowly progressive over decades
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor
- Serum CK: 700
- Lactate: High
- Anemia: Megaloblastic
- Muscle
- SDH+ & COX- or reduced fibers
- Ox-Phos activities: Normal
- mtDNA: Multiple deletions in muscle but not fibroblasts
- Nerve biopsy: Axon loss
- MRI: Leukoencephalopthy in 1 patient
- Mitochondrial pathology
- mtDNA depletion in liver
- Defects of mtDNA related respiratory chain complexes
- MPV17 variant: AR-CMT 2EE

- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense; P98L, R41Q
- MPV17 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: 9 to 23 years
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms; Gait disorder
- Joints: Finger & Ankle contractures; Pes cavus; Scoliosis
- Laboratory
- Nerve pathology: Axon loss
- Muscle: Mitochondrial pathology, mild
- NCV: CMAP & SNAP amplitudes reduced
- Muscle MRI: Fat replascement in soleus
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
● Succinate-CoA ligase, ADP-forming, β subunit (SUCLA2)
- Epidemiology: 50 patients; Muslim family, Faroe Islands, Southern Italy
- Genetics: Mutations
- Muslim: Homozygous 43 base pair deletion & 5 base pair insertion
- Gly118Arg; Arg284Cys; 534+1G-A; IVS4+1G-A
- SUCLA2 protein
- Succinyl-CoA Synthetase (SCS)
309 subunit
- Nuclear-encoded protein complex
- β-subunit of ADP-forming succinyl-CoA synthetase (SCS-A)
- Mitochondrial matrix enzyme
- Components: Heterodimeric complex
- In mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
- Catalyzes: Reversible synthesis of succinyl-CoA from succinate & CoA

- mtDNA Maintenance
- Dimerizes with SUCLG1
- Complexed with: Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK)

- SCS deficiencies: Metabolic features
- Methylmalonic aciduria
- Elevations in C3 & C4-DC acylcarnitines
- Succinyl-CoA
- Coenzyme A donor in breakdown of ketones
- Intermediate in heme synthesis
- Protein succinylation
- Nucleotide salvage pathway disorders
- Succinyl-CoA Synthetase (SCS)
309 subunit
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth to 5 months
- CNS
- Psychomotor development: Severely retarded
- Seizures: Generalized; Onset 1 year; Rx with valproate
- Dystonia: Later in course
- Motor
- Early: Severe hypotonia
- Feeding problems
- Muscle atrophy
- Areflexia
- Hearing: Impaired
- Hyperhidrosis: Some patients
- Contractures: Knee & Hip
- Respiratory infections: Frequent
- Ocular: Strabismus; Ptosis
- Growth retardation
- Course: Death in many
- Ages: < 1 year in some; > 20 years in others
- Associated with acute infections
- Milder phenotype than SUCLG1
- Onset age: 2 months vs birth
- No hepatopathy or cardiomyopathy
- More epilepsy
- Survival: Longer; 20 years vs 20 months
- Laboratory
- MRI: Leigh-like
- High T2 intensity in bilateral putamen & caudate
- Brain atrophy: Dilated lateral ventricles
- Microcytic anemia
- Serum CK: Normal
- Lactate: High but variable in plasma; Very high in CSF
- Methylmalonic acid: High in plasma ± urine
- C4-dicarboxylic carnitine: High
- Muscle
- Histology
- Fiber size: Varied
- Lipid: Increased in type I muscle fibers
- Type I muscle fiber predominance
- Oxidative enzymes
- Complexes I & IV: Especially reduced
- Complex III: Reduced in some patients
- Complex II: Normal
- SUCLA2 Western blot: Reduced or absent amount
- mtDNA depletion
- Histology
- NCV: Variable
- Normal in some
- Demyelinating neuropathy with axonal loss: Legs > Arms
- BAEP: Neurosensory deafness
- Ratio of mtDNA to nuclear DNA: Reduced to 33% of controls
- MRI: Leigh-like
● NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase Fe-S protein 1 (NDUFS1)
- Epidemiology: 8 families, 10 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Point mutations; Small Deletions
- No patients with 2 null alleles
- NDUFS1 protein
- NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase
- Subunit of Complex I core
- Iron-Sulfur: 2 Fe4S4; 1 Fe2S2
- Clinical: Leigh-like
- Onset: 2 months to 2 years
- Psychomotor retardation
- Hypotonia
- Ocular: Nystagmus; Optic atrophy
- Ataxia: Episodic; Older onset patients
- Course: Death < 1 year in early onset patients
- Laboratory
- CNS: Leukodystrophy
- Lactate: High in Blood & CSF
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I deficiency
● MYC-induced mitochondrial protein (B17.2L; Mimitin; NDUFAF2; NDUFA12L)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Stop & Missense
- Allelic disorder: LHON-AR
- Mutations
- Protein
- Molecular Chaperone
- Targeted to mitochondria
- Essential for assembly of complex I
- Ubiquitous: Relatively less in skeletal muscle
- Associates with a specific subassembly of complex I but not with mature holoenzyme
- Mutation effect: Protein is absent from cells
- Clinical
- Onset: Infancy/Childhood
- Encephalopathy: Progressive
- Respiratory failure: Episodic
- Course: Progressive: Death in childhood
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter
- Basal ganglia signal
- Complex I activity reduced: Less than 20% of control values
- Serum lactate: High
- Brain MRI
- Variant: Leigh syndrome
● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 alpha subcomplex, 13 (NDUFA13; GRIM19)
- Epidemiology: 2 families, 3 patients
- Genetics
- NDUFA13 protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Complex I assembly
- Maintenance of mitochondrial membrane potential
- Apoptosis
- Signal transduction
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- CNS
- Psychomotor retardation
- Hypotonia
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Eye: Optic atrophy; Slow saccades
- Cardiomyopathy, mild (1 patient)
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Lactate, serum: High
- BAER: Auditory neuropathy
- MRI: Normal early; Cerebellar & Optic nerve atrophy; Leigh-like lesions
- EMG: Normal
- Muscle
- Histology: Normal, or Lipid droplets in Type I fibers
- Complex I activity: Selectively reduced
● NDUFAF3 (C3ORF60)
- Epidemiology: Muslim & Jewish families
- Genetics
- Missense mutations: M1T; G77R; R122P
- Allelic with: Leigh syndrome
- NDUFAF3 protein
- Clinical
- Muscle tone: Increased or Decreased
- Weakness
- Optic disc pallor
- Respiratory failure
- Seizures
- Death: Age ≤ 6 months
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Leukomalacia
- Complex I deficiency: Activity & Protein
- NDUFAF3 variant: Leigh syndrome
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Ala165Val; Homozygous
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Eyes: Nystagmus, Horizontal; Optic atrophy
- Vomiting
- Head: Abnormal posturing; Microcephaly
- Course: Progressive loszs of motor & speech; Death at 21 months
- Laboratory
- VER: Abnormal
- Lactate: High
- Urine: Fumaric acid & Aconitic acid high
- Brain MRI: Symmetric bilateral basal ganglia & brainstem lesions
- MRS: Lactate peaks in basal ganglia & subcortical white matter
- Complex I deficiency
● SDH Assembly factor I (SDHAF1)
- Epidemiology: Turkish, Palestinian, Norwegian & Italian families
- Genetics: Mutations
- Homozygous
- Missense & Stop: Gln8X, Arg55Pro, Gly57Arg, Gly57Glu
- SDHAF1 protein
- LYR-motif protein
- Expression: Ubiquitous
- Cellular location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Function: SDH assembly factor
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 6 to 11 months
- Psychomotor regression: Acute
- Psychomotor regression
- Speech development: Poor
- Spastic quadriparesis: Severe
- Postural control: Partial loss
- Dystonia
- Growth: Delayed or Reduced
- Course: Stabilization or Progression
- Some: Survival past 1st decade
- Others: Death in childhood (2 to 11 years)
- Onset
- Laboratory
- MRI
- Leukoencephalopathy
- Spared U fibers
- Vacuolization: 1 patient
- Lactate & Pyruvate: Variably elevated in blood
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain in muscle: 2030% residual activity of SDH & SCoQR
- Protein blot analysis: Marked reduction of cII holoenzyme in muscle
- MRI
● mtRNATrp (MTTW)
- Mutation: C5545T
- Clinical
- Developmental delay: Severe
- Hypotonia
- Ataxia
- Chorea
- Seizures
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Muscle: Reduced COX activity; No ragged red muscle fibers
- Other mtRNATrp syndromes
- Encephalopathy: G5549A
- Encephalopathy or Leigh syndrome: 1-BP ins, 5537T
- Myopathy: G5521A
- Exercise intolerance: T5543C
- Neurogastrointestinal syndrome: G5532A
● SLC25A19
- Nosology: Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 3 (THMD3)
- Epidemiology: Old-Order Amish of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania
- Genetics
- Mutation: Gly177Ala
- SLC25A19 protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Thiamine-PP transporter
- ?? Mitochondrial solute carrier: Mitochondrial deoxynucleotides
- Clinical features
- Congenital microcephaly: Frontal sloping; Small cranial vault
- CNS: No orientation to light or sound
- Motor: No fine or gross development; Normal tone
- Episodic viral illnesses precipitate metabolic acidosis
- Hepatomegaly: Mild
- Progression
- Increasing irritability after 1st 2 or 3 months
- Death: Mean 24 weeks; Range 0 to 60 weeks
- Laboratory
- 2-Ketoglutaric aciduria
- Pathology: Immature brain with no gyral development; Cerebellar vermal hypoplasia, mild
- Variant syndrome: Episodic flaccid paralysis & Encephalopathy (Leigh-like)
 100
100
- Nosology
- Striatal necrosis, bilateral & Polyneuropathy
- Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 4 (THMD4)
- Epidemiology: 9 patients; Non-Amish
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- SLC25A19 Mutations: c.373G>A, c.580T>C, c.910G>A, c.869T>A, c.576G>C, c.673G>A
- Clinical
- Weakness
- Onset
- Age: 3 to 6 years
- Acute weakness: 2 to 3 days after febrile illness
- Episodes: Proximal; Distal; Bulbar; No respiratory failure
- Long term
- Progressive
- Distal Legs & Arms
- Proximal Legs
- Severity: Mild to Moderate
- Disability: May need walking aids
- Onset
- Contractures: Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Encephalopathy
- During episodes: Obtundation, Aphasia, Disorientation
- Other times: Normal
- Treatment: High-dose thiamine (600 mg/day)
- Course: Spontaneous & Nearly complete resolution beginning days later
- Weakness
- Laboratory
- CSF lactate: High
- MRI: Bilateral T2 hyperintense lesions in putamen & caudate nuclei (Striatal)
- NCV: Absent CMAPs & SNAPs
- Muscle histochemistry: Normal
- Mitochondrial oxiative enzyme activities: Normal
- Differential diagnosis of episodic striatal damage
- ATP6-related mitochondrial respiratory chain defects
- Organic acid disorders
- Wilson disease
- Juvenile Huntingtons chorea
- Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration
- Biotin responsive basal ganglia disease
- Striatal necrosis associated with NUP62 mutation
- Nosology
● SLC25A22 (GC1)
- Epidemiology: Arab Muslim family
- Genetics: Missense mutation Pro206Leu
- SLC25A22 protein
- Mitochondrial glutamate/H+ symporter
- Expression: Brain regions associated with seizures
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Seizures: Intractable
- Hypotonia
- Laboratory
- Head CT: Brain atrophy
- EEG: Myoclonic seizures, Burst suppression
● POLG
- Epidemiology
- > 60 patients
- Male prevalence: Mild
- Genetics
- Allelic disorders
- Common mutations: A467T; G848S; L966R
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Childhood; Usually < 2 years
- Epilepsia partialis continua
- Encephalopathy
- Episodic
- Precipitated by fever
- Developmental delay
- Epilepsy: Myoclonic; Focal motor
- Central visual function: Impaired
- Ataxia (50%)
- Sensory loss: Described in 1 patient with juvenile form
32
- Sensory ataxia
- Dorsal root ganglion: Loss of neurons
- Nerve pathology: Loss of myelinated axons
- Posterior columns: Loss of myelinated axons
- Liver
- Progressive failure
- Acute dysfunction precipitated by valproic acid
- Course
- Progressive over years
- Episodes of deterioration
- Death: < 11 years; Mean 4 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Mitochondrial disorder: Abnormal oxidative metabolism
- Muscle
- Occasional COX- muscle fibers
- Respiratory enzymes: Normal or Reduced I, III & IV with mtDNA depletion
- CSF: High Protein & Lactate
- EEG: Absent/slow posterior dominant rhythms; Interictal occipital discharges
- MRI
- T2/FLAIR hyperintensities
- Locations: Occipital regions, Deep cerebellar nuclei, Thalamus, Basal ganglia
- CNS pathology
- Gliosis & Neuronal loss: Occipital cortices, Cerebellar cortex (Purkinje cells)
- Necrosis: Subcortical deep nuclei, Hippocampi, Lateral geniculate, Amygdala
- Liver
- Late sign
- Pathology: Fatty; Mitochondrial pathology
● Phenylalanyl-tRNA Synthetase 2, Mitochondrial (FARS2)
- Epidemiology: Finnish & Saudi families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Tyr144Cys; Asp325Tyr; Ile329Thr; Asp391Val; Genomic deletion
- Allelic disorders
- SPG77
- Juvenile onset refractory epilepsy
- FARS2 protein
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- Mitochondrial
- Highly expressed in cerebellar Purkinje cells
- Clincial
- Onset age: 1st week
- Seizures
- Myoclonic jerks
- Developmental delay
- Death: < 2 years
- Laboratory
- EEG: Multifocal spikes
- MRI: Central & cortical brain atrophy
- Lactate: High in serum
- Muscle: COX activity reduced; Lipid dropplets
- Liver: Enlarged hepatocytes; Increased glycogen, lysosomal iron, copper
- Brain: Atrophy of brain, hippocampus, cerebellar cortex, aqueductal grey; Cortical laminar necrosis
- Mitochondrial respiratory complex activities
- Complex IV: Severe deficiency
- Complex I: Partial deficiency
- FARS2 variant: SPG77
- Epidemiology: 1 Chinese family, 4 siblings
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Homozygous, Missense; D142Y
- Clinical: Spastic paraparesis, pure
- Onset age: 1 to 5 years
- Pyramidal features
- Spasticity: Legs only
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Plantar reflex: Extensor in some
- Amyotrophy: Legs, 1 patient
- Course
- Slow progression
- Loss of ambulation in 4th or 5th decade
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Normal
- Nosology: Multiple Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (MADD)
- Types
- IIA
● Electron transfer flavoprotein, α subunit (ETFA) ;
Chromosome 15q24.2-q24.3; Recessive
;
Chromosome 15q24.2-q24.3; Recessive
- Frequency in MADD: 2%
- IIB
● Electron transfer flavoprotein, β subunit (ETFB) ;
Chromosome 19q13.41; Recessive
;
Chromosome 19q13.41; Recessive
- Frequency in MADD: 5%
- IIC
● Electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase (ETFDH) ;
Chromosome 4q32.1; Recessive
;
Chromosome 4q32.1; Recessive
- Frequency in MADD: 93%
- Allelic with: Myopathy with exercise intolerance
- Acquired
- Sertraline use 326
- Seeds with hypoglycin A (Horses): Acute, severe muscle weakness
- IIA
- Clinical
- MADD: Clinical syndromes
- General
- Type I: Neonatal onset with Congenital anomalies
- Metabolic acidosis, Servere ± Hypoglycemia & Hyperammonemia
- Anomalies: Dysmorphic face, Cystic kidneys, Hypospadias
- Type II: Neonatal onset without Congenital anomalies
- Metabolic acidosis, Servere ± Hypoglycemia & Hyperammonemia
- Type III: Later onset
- Onset age: Infancy to Adult
- Clinical: Weakness, Exercise intolerance, Myalgia, Rhabdomyolysis
- Type I: Neonatal onset with Congenital anomalies
- Glutaricaciduria Type IIA (ETFA)
- FLAD1
- Spastic ataxia: ETFA; ETFB; ETFDH
- Myopathy, later-onset
- General
- Associated with: Coenzyme Q10 deficiency
- Also see
- Brown-Vialetto-van Laere 1 & 2
- Exercise intolerance, riboflavin responsive: SLC25A32
- Treatments
- Limitation of dietary protein & fat
- Avoid prolonged fasting
- High-dose riboflavin (100-300 mg daily)
- Carnitine supplementation (50-100 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses) (If carnitine deficiency)
- Coenzyme Q10 (60-240 mg daily in 2 divided doses)
- MADD: Clinical syndromes
- Laboratory
- Plasma acylcarnitine profile: Elevated C4, C5, C5DC, C6, C8, C10, C12, C14:1, C16 & C18:1
- Urine organic acids: Elevations of multiple organic acids
- Lactic acid
- Glutaric acid
- 2-hydroxyglutaric acid
- 2-hydroxybutyric acid
- 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid
- 3-hyroxyisovaleric acid
- 5-hydroxyhexanoic acid
- Ethylmalonic acid
- Adipic acid
- Suberic acid
- Sebacic acid
- Urine acylglycine assay: High
- Isobutyrylglycine
- Isovalerylglycine
- Hexanoylglycine
- Suberylglycine
- Brain MRI
- Heterotopias: Severe disease
- T2 signal: Periventricular white matter, Basal ganglia, Corpus callosum
- Muscle
- Lipid: Increased
- SDH: Reduced
● ETHE1
- Nosology
- EPEMA: Encephalopathy, Petechiae, Ethylmalonic Aciduria
- Genetics: Mutations
- Most are loss of function: Stop, Frameshift, Deletion or Aberrant splicing
- Missense mutations: All predict amino acid changes in highly conserved positions
- Patients often homozygous
- ETHE1 protein
- Mitochondrial matrix protein (Inner compartment)
- Function: Mitochondrial homeostasis & energy metabolism
- Clinical
- Onset: Bimodal
- Age
- Neonatal (25%)
- Infantile (2 to 7 mo)
- Course
- Acute: Orthostatic acrocyanosis, petechiae, seizures, hypotonia
- Chronic: Delayed development; Cognitive dysfunction
- Age
- Skin
- Petechiae: Recurrent
- Acrocyanosis: Hands & Feet; Orthostatic
- CNS
- Developmental delay & Regression
- Hypotonia: Axial
- Seizures
- Pyramidal signs
- Extrapyramidal
- Diarrrhea: Chronic
- Course
- May be acute or chronic
- Death: 1st decade; Often 1st year
- Onset: Bimodal
- Laboratory
- MRI (FLAIR): High-intensity signal in deep gray (Caudate & Putamen)
- Muscle histochemistry: COX staining markedly reduced
- Fibroblasts: COX activity often normal
- Lactic acidemia
- C4 and C5 acylcarnitine species: High in plasma
- Urine high in
- Ethylmalonic acid (EMA)
- C46 acylglycines (Isobutyrylglycine and 2-methylbutyrylglycine)
- Differential diagnosis of high EMA
- Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
- Glutaric acidemia type 2 (Ethylmalonic adipic aciduria)
- Jamaican vomiting sickness
● Mitochondrial elongation factor G1 (EFG1; GFM1)
- Epidemiology: Lebanese & Italian families
- Genetics: Missense mutation (Asn174Ser; M496R) + Stop
- EFG1 protein
- GTPase
- Catalyzes mitochondrial protein elongation during translation
- Catalyzes translocation step of protein biosynthesis
- Allows movement of peptidyl-tRNA-mRNA complex on ribosome during protein elongation
- Transfer of nascent peptidyl-tRNA from ribosomal acceptor (amino acyl or A) site to ribosomal peptidyl site
- Abundant in heart, skeletal muscle & testis
- Onset: Congenital
- Clinical: Hepatoencephalopathy
- Growth delay
- Motor: Hypertonia; Reduced spontaneous movements
- Cardiac: Normal
- Death: 1 to 5 months
- Laboratory
- Defect in mitochondrial translation
- Muscle biopsy
- COX staining: Reduced, but not absent
- SDH: Normal
- Mildly increased lipid & glycogen
- Reduced levels of oxidative phosphorylation complexes containing mtDNA-encoded subunits (I, III & IV)
- Lactic acidosis
- Liver failure
- Pathology: Liver necrosis; Corpus callosum hypoplasia; Brain atrophy
- Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency: General
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S16 (MRPS16)
- Epidemiology: Bedouin, consanguinous parents
- Genetics: Mutation
- Stop codon: Arg111Ter
- MRPS16 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosome, small subunit
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital; Small size
- Facies: Dysmorphic
- Ears: Low-set
- Limbs: Non-pitting edema, Brachydactyly
- Redundant skin over the neck
- Death: 3 days; Intractable metabolic acidosis
- Laboratory
- Corpus callosum: Agenesis
- Lactic acidosis
- Skeletal muscle
● Ts Translation elongation factor, mitochondrial (EFTs; TSFM)
- Epidemiology: 2 families, Turkish male & Kurdish-Jewish female
- Mutation
- Homozygous Arg333Trp in both patients
- Produces defective mitochondrial translation
- May block interactions of EFTs with EFTu
- Reduced amounts of assembled ox-phos complexes, except complex II
- Clinical: 2 different syndromes
- Fatal mitochondrial encephalomyopathy
- Onset: Birth
- Hypotonia: Sucking weakness
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Seizures
- Respiratory failure
- Death at 7 weeks
- Fatal hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Onset: 1 day
- Apathy
- Irregular breathing
- Hypotonia
- Echocardiography: Concentric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Death at 7 weeks
- Fatal mitochondrial encephalomyopathy
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Skeletal muscle
- COX staining: Reduced
- Ox-phos: Combined deficiencies of Complexes I, III & IV
- Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency: General
● Mitochondrial elongation factor Tu (TUFM; EFTu)
- Epidemiology: 1 South Italian patient
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense (R339Q)
- EFTu protein: GTPase
- Clinical: Severe encephalopathy
- Episodic
- Onset: 2 days after birth
- Encephalopathy
- Persistent vomiting
- Lethargy
- Skin pallor
- Respiratory distress: Acral cyanosis
- Psychomotor regression
- Microcephaly
- Tone: Trunk reduced; Limbs spastic
- Nystagmus
- Death: 14 months
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Hepatic enzymes: Mildly elevated
- Hyperammonemia
- Brain CT: Hypodense lesions
- Brain MRI: Cystic leukodystrophy, diffuse; Micropolygyria
- Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency: General
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S22 (MRPS22; C3ORF5)
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Arg170His
- Allelic disorders
- Cornelia de Lange-like
- Primary ovarian insufficiency
- MRPS22 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosome, small subunit
- Clinical
- Onset: Antenatal
- Head: Face coarse, Microcephaly
- Edema: Generalized subcutaneous or ascites
- Hypotonia
- Death: 1st month or prenatal
- Laboratory
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Tubulopathy
- Muscle: Decreased mtDNA content
- Brain white matter: Abnormal Corpus callosum, Internal capsule, Pyramidal tract
- Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency: Complexes I, III, IV
- MRPS22 Variant syndrome: Cornelia de Lange-like
- Mutation: Missense; Homozygous; L215P
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth; Hypotonia
- Microcephaly
- Cardiomyopathy, dilated
- Dysmorphic features
- Seizures
- Spastic tetraplegia
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis, Chronic
- MRI: Corpus callosum hypoplasia, Leukoencephalopathy, Delayed myelination
- Mitochondria
- Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency: Complexes I, III, IV
- Defect in mitochondrial translation
- MRPS22 variant syndrome: Primary ovarian insufficiency
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein, Large 3 (MRPL3)
- Epidemiology: 2 families, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense (Pro317Arg) + Stop (Deletion 255 kb (entire gene) or c.49delC)
- MRPL3 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosome, small subunit
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: < 1 year
- Developmental delay
- Growth delay
- Hepatomegaly
- Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic
- Course: Death < 2 to 4 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- MRI: Hypergyria
- Plasm lactate: High
- Oxidative enzymes: Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency
- Activity: Normal or Reduced complexes I or IV
- Western blot: Reduction of of fully assembled complexes I, IV & V
● Segmental monosomy, or Mitochondrial Holocytochrome cType Synthase (HCCS)
- Nosology
- "MIDAS" (Microphthalmia, Dermal aplasia, Sclerocornea)
- Microphthalmia, syndromic 7 (MCOPS7)
- Genetics
- Chromosomal aberration: Segmental monosomy of the Xp22 chromosomal region
- Point mutations (Heterzygous females): 2 patients; R197X, R217C
- HCCS protein
- Mitochondrial holocytochrome ctype synthase ("heme lyase")
- Catalyzes covalent attachment of heme moieties to
- Heme attaches to
- Apocytochrome c: Mitochondrial CIIICIV electron shuttle
- Cytochrome c1: Component of complex III
- Leads to mature forms, holocytochrome c & c1: Necessary for functioning of mitochondrial respiratory chain
- Cytochrome c is released from mitochondria
- In response to a variety of intrinsic death-promoting stimuli
- Results in caspase-dependent cell death (apoptosis)
- Heme attaches to
- Males: Lethal in utero
- Clinical (Females): Intrafamilial variability
- Ocular
- Microphthalmia: Unilateral or Bilateral
- Sclerocornea
- Chorioretinal abnormalities
- Linear skin defects: Face & Neck; Aplastic skin; Heals with age to form hyperpigmented areas
- CNS: Agenesis of corpus callosum, Infantile seizures, Mental retardation
- Congenital heart defect
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Ocular
● Cytochrome c Oxidase, Subunit VIIb (COX7B)
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.196delC (Frameshift; p.Leu66Cysfs*48); c.41-2A>G (Splice; Intron 1); Nonsense (Gln19X)
- COX7B protein
- Subunit of Complex IV: 1 of 10 nuclear encoded
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Clinical
- Head
- Microcephaly
- Microphthalmia: Some patients
- Facial dysmorphisms
- Skeletal: Short stature (50%)
- Skin: Linear lesions on face & neck
- Psychomotor: Normal or Mildly delayed
- Cardiac: Variable
- Head
- Laboratory
- MRI: Delayed myelination
- Mutations cause reduced COX activity & protein
● NADH Dehydrogenase 1 beta subcomplex, 11 (NDUFB11)
- Epidemiology: Females; 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Females (Dominant): Nonsense & 1-bp deletion
- Male (Hemizygous): E121K
- Mutations
- NDUFB11 protein
- Mitochondrial Complex I: Assembly & Activity
- Clinical
- Skin: Linear lesions, Reduced with age
- Short stature
- Cardiomyopathy: Histiocytoid; Dilated
- CNS: Hypotonia; Seizures, 1 patient
- Death
- Females: 6 to 15 months
- Male: 2 days
- Laboratory
- MRI: Corpus callosum agenesis
- Blood lactate
- Females: Normal
- Male: Metabolic acidosis
● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 α-subcomplex, 1 (NDUFA1)
- Epidemiology: 5 patients
- Mutations: Missense; Gly8Arg; Arg31Ser
- NDUFA1 protein
- Accessory protein for Complex I
- Mutations: Reduced levels of Complex I formation
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- ND2 module of complex I
- Clinical: 2 syndromes
- Infantile encephalopathy: Leigh syndrome
- Onset
- Age: 4 to 9 months
- Developmental delay
- Clinical
- Hypotonia
- Nystagmus
- Choreoathetosis
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Death: < 2 years
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- MRI: Lesions in thalamus; Cerebral peduncles & Brainstem
- EMG & NCV: Normal
- Muscle: Normal morphology
- Myoclonic epilepsy with developmental delay
- Onset
- Age: 6 months
- Developmental delay
- Clinical
- Poor walking
- Hypotonia
- Myoclonic epilepsy
- Tendon reflexes: Present
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Normal
- MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
- EEG: Polyspike & wave bursts
- Muscle: Normal morphology; Complex I deficiency
- Onset
- Biochemistry
- Isolated Complex I deficient activity
- Reduced levels of Complex I proteins
● Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)
- Genetics: Missense mutations
- Clinical
- Megalencephaly: In infancy
- Spasticity: Bulbar & Limbs
- Seizures
- Cognitive defects
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
- Muscle
- Histology
- Infant: Unremarkable
- Later onset: Mitochondrial proliferation
- Biochemistry: Cytochrome oxidase (Complex IV) deficiency
- Histology
- CNS
- Rosenthal fibers (Eosinophilic masses): Especially in subpial, perivascular and subependymal regions
- MRI: White matter signal, frontal > occipital
- Variants
- Juvenile & Adult onset: GFAP mutations
- NDUFV1 deficiency
● Dynamin 1-like (DNM1L; DRP1; DLP1)
- Nosology: Encephalopathy due to defective Mitochondrial & Peroxisomal Fission
- Epidemiology: Multiple patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- General type: Missense; Ala395Asp, G149R
- Hotspot: Arg403Cys; Status epilepticus
- General effect: Dominant negative
- G-domain: Optic atrophy & Sensory neuropathy common
- Middle assembly domain (MSD): Developmental delay & Seizures common
- Allelic disorders: Poor genotype-phenotype correlation
- EMPF encephalopathy, Dominant 1
- Encephalopathy, Recessive
- Optic atrophy, Dominant 5 (OPA5)
 : G-domain mutations
: G-domain mutations
- Sensory neuropathy + CNS disorder
- Mutations
- Dynamin 1-like protein
- Cell location
- Cytoplasmic
- Mitochondrial: Outer membrane
- Function
- Promotes: Mitochondrial fission & normal morphology
- Severs mitochondria at endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mitochondria contact sites
- Shapes peripheral ER tubules: Facilitates ER-mitochondria interactions
- Mechano-GTPase activity
- Interactions: MIEF2; MFF; FIS1

- Mutation effects: Abnormal mitochondrial & peroxisomal morphology in cultured cells
- Dynamin-related disorders
- OPA1: Optic atrophy, autosomal dominant
- MFN2: CMT-2A2
- DNM1L: Encephalopathy
- DNM2
- Centronuclear myopathy
- CMT, Dominant-intermediate Type B (CMTD1B): Mutations in plecstrin domain
- CMT 2M
- Charlevoix-Saguenay - Spastic Ataxia
- Also see: EMPF2
- Cell location
- Clinical: Varied severity
- Onset
- Age: Prenatal to Childhood
- Reduced fetal movements
- Developmental delay: Global
- Motor: Poor feeding; Hypotonia
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Microcephaly
- Dysmorphic: Deep-set eyes; Pointed chin
- Eye: Optic atrophy & Hypoplasia; Visual acuity, Reduced
- Muscle wasting
- Seizures: Super refractory Status Epilepticus (SRSE)
- Dystonia
- Varied features
- Ataxia
- Spasticity
- Cardiomyopathy
- Polyneuropathy
- Course
- Progressive
- Death: 37 days to Long survival
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Gyral patterns abnormal; Atrophy; T2 Δ in thalamus & putamen
- Lactate: High or Normal in serum & CSF
- Very-long-chain fatty acids: Mildly elevated in plasma; Elevated cerotic acid
- EMG & NCV: Normal
- Muscle
- Cultured fibroblasts
- Peroxisomes: Reduced number & varied size
- Mitochondria: Elongated; Abnormal shapes; Concentrated around nuclei
- DNM1L variant: Sensory neuropathy + CNS disorder
262
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant, de novo
- Mutations: Missense; Ser39Gly, Asp146Asn, G149R, A192E; GTPase domain
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Hypotonia
- Developmental delay
- Muscle
- Weakness: Distal & Proximal
- Bulk: Reduced
- Sensory loss: Neuropathy; Ataxia
- Dystonia
- Seizures
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Face: Dysmorphic
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Non-diagnostic
- EEG: Slowing
- NCV: No sensory responses in arms or legs
- EMG: Neurogenic
- Serum CK: Normal
- DNM1L variant: Encephalopathy + Spastic-Ataxia, Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Truncating or Missense
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to 1 year
- Development: Delayed
- Hypotonia
- Oculomotor apraxia
- Cerebellar: Dysarthria, Dysmetria
- Pyramidal signs
- Gait disorder
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High with increased age
- Pathology
- CNS neurons: Large mitochondria or inclusions
- Peripheral nerve: Axon loss; thin myelin
- Muscle: Normal
● Mitochondrial Fission Factor (MFF)
- Nosology: Encephalopathy due to defective Mitochondrial & Peroxisomal Fission
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop; Point, Small insertion & Deletion
- Manifesting heterozygote: Ptosis, Fatigue & Weakness
- Animal disorder: Bullmastiff ataxia (Glu158Alafs*14)
- MFF protein
- Localization: Mitochondrial outer membrane
- Function: Mitochondrial fission
- Recruits Drp1 to sites of mitochondrial division
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year
- Seizures
- Developmental delay
- Microcephaly, acquired
- Dysphagia
- Spasticity
- Optic neuropathy
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: "Leigh-like"; Signal in basal ganglia and subthalamic nucleus
- Muscle: Mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes normal
- MFF heterozygote: Ptosis, Fatigue & Weakness
298
- Epidemiology: 1 patient; 1 family
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant
- Mutation: E313K
- Clinical
- Onset age: 60 years
- Ptosis
- Dysphagia
- Weakness
- Laboratory
- EMG: No myopathy
- SF-EMG: Increased jitter
- Muscle biopsy
- COX- muscle fibers
- Fiber sizes: Mildly varied
● ATPase family, AAA domain-containing, member 3A (ATAD3A)
- Nosology: Harel-Yoon Syndrome (HAYOS)
- Epidemiology: 7 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Recurrent
- Uniallelic
- de novo
- c.1582C>T; p.Arg528Trp
- Biallelic variants
- Allelic disorders
- PCH, Hypotonia, Respiratory insufficiency, Neonatal Lethal (PHRINL)
- Chromosome 1p36.33 Duplication syndrome, ATAD3 Gene cluster, Autosomal dominant

- Mutations
- ATAD3A protein
- Mitochondrial
- ATPase family: AAA domain
- Other functions
- Channeling of cholesterol for steroidogenesis
- Resistance of cancer cells to therapy
- Mutant protein: Dominant negative
- Produces small mitochondria: Trigger mitophagy
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to < 1 year
- CNS
- Developmental delay, global (100%)
- Spasticity
- Seizures (40%)
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Extremity weakness
- Eye
- Optic atrophy (30%)
- Strabismus
- Myopia
- Polyneuropathy: Axonal
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Face: Dysmorphic
- Laboratory
- Plasma lactate: Increased in some patients
- Serum CK: Normal
- 3-methylglutaconic acid: Mildly increased secretion
- MRI
- Brain: Reduced gyration; Cerebellar atrophy; Optic nerve hypoplasia
- Spinal cord: Hypoplasia
- Muscle pathology: Varied fiber size; Internal nuclei, few
- NCV: Axon loss or Normal
- ATAD3A variant disorder: PCH, Hypotonia, Respiratory insufficiency, Neonatal Lethal

- Epidemiology: 9 families
- Genetics
- Clinical
- Prenatal: Reduced movements
- Birth: Hypotonia; Respiratory distress
- Seizures: Some patients
- Death: < 7 months; Usually neonatal
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia; White matter pathology
- Plasma lactate: High
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: May be abnormal
● Ribonucleotide reductase, M2 B (RRM2B)
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Types: Nonsense, Missense, Splice-site, In-frame deletion
- Recessive: Homozygous or Compound heterozygote
- Mutations
- Allelic disorders
- MTDPS8A: Encephalomyopathic + Renal
- MTDPS8B: MNGIE-like
- Myopathy, Tubulopathy & Lactic acidosis: Milder course
- PEOA5, Dominant
- Rrm2b-/- mouse: Severe mtDNA depletion
- Cytosolic p53-inducible ribonucleotide reductase small subunit
- Other p53-interacting protein: CABC1 related ataxia
- Function: Role in nucleotide synthesis
- Mutation: RRM2B protein level reduced or normal
- Onset: < 1 month to 6 months
- Hypotonia
- CNS: Seizures
- Renal: Proximal tubulopathy
- GI: Vomiting & Diarrhea
- Motor axon loss: Some patients
- Deafness
- Course
- Severe: Death < 5 months
- Milder patients
- Survive into childhood (At least 2 to 3 years)
- May require tracheostomy & G-tube
- Muscle
- mtDNA depletion
- Severe: Reduced to 1% to 2% of normal
- Milder: Reduced to 7% to 12% of normal
- Oxidative enzymes
- Reduced Complexes I, III & IV or only Complex IV
- Complex IV: May be reduced disproportionately
- Citrate synthase: May be increased or decreased
- Milder cases: Normal
- Ragged red muscle fibers: Some patients
- COX staining: Reduced
- mtDNA depletion
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Brain MRI: White matter loss or generalized atrophy
- Myopathy, Tubulopathy & Lactic acidosis
- Milder course with survival into childhood
- Recessive
- PEO, Autosomal Dominant (PEOA5)
 102
or Recessive
102
or Recessive
- Epidemiology: North American & Hungarian families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Heterozygous
- Nonsense: Dominant; Common; R327X, Leu317X, Glu318X, Asn322LysfsX4
- Missense: Recessive (Thr144Ile, Arg211Lys, Phe202Leu, Gly273Ser) or Dominant (Arg41Gln, Gly195Arg, Gly229Val)
- Inheritance: Dominant or Recessive
- Allelic disorders
- Mutations
- Mutated RRM2B protein
- Truncated
- Interacts with ribonucleotide reductase subunit R1
- Dominant negative effect
- Clinical
- Onset age: ≥ 2nd decade
- Ophthalmoplegia: May be present without ptosis
- Ptosis
- Dysphagia
- Fatigue
- Myopathy: Proximal weakness; Some patients
- Ataxia: Some patients
- Hypoacusis: Some patients
- Encephalopathy: Occasional patient
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers
- Multiple mtDNA deletions
● NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 11 (NDUFA11)
- Epidemiology: Israeli-Bedouin patients, some from inbred families
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Splice site, G-A at intervening sequence (IVS) 1 +5
- Mutation effect: Predicted to abolish the 1st transmembrane domain
- Allelic disorder: Myopathy, Adult-onset
- NDUFA11 protein
- Accessory subunit of mitochondrial Complex I
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- ND2 module of complex I
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infancy; 1 day to months
- Neonatal: Lactic acidosis
- Later onset: Psychomotor delay & Cardiomyopathy
- CNS
- Encephalopathy
- Seizures
- Microcephaly
- Motor
- Hypotonia
- Delayed milestones
- Weakness
- Reduced voluntary movements
- Eye: Few patients with nystagmus or optic atrophy
- Cardiac: Biventricular hyperplasia
- Death: Death to 4 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Complex I reduced to 4% to 45% of control mean
- Metabolic acidosis: Severe
- Lactate: High; Increased further with intercurrent infections
- Serum CK: Normal
- NDUFA11 variant: Myopathy, Adult-onset
244
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense; c.317C>T (p.Thr106Ile; c.394G>Cv (p.Ala132Pro)
- Clinical
- Onset age: 65 years
- Weakness: Proximal legs
- Other: Hearing loss; Saccadic EOM
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: 900
- EMG: Myopathic
- Brain MRI: White mattter pathology (? Cerebrovascular)
- Muscle
- COX- & SDH+ fibers
- Connective tissue: Mldly increased
- Complex I activity: Reduced
● COX6B1
- Epidemiology: Arab family originating from Saudi-Yemeni border
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous missense; R19H
- COX6B1 protein
- Function: Complex IV structural subunit
- Mutated protein: Destabilizes muscle COX holocomplex
- Clinical
- Onset
- Birth weight: Low
- Muscle mass: Reduced
- Muscle
- Weakness in 1st decade
- CNS
- Cognitive deterioration
- Visual loss
- Course
- Death: Severe case
- Age: 10 years
- Neurological deterioration: Rapid; Seizures
- Slow progression: Milder patient
- Death: Severe case
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX activity reduced by histochemistry & quantitation (20% to 50%)
- Other respiratory complexes: Normal
- MRI: Leukodystrophic changes
- Symmetric
- Diffuse
- VER: Absent
- EMG: Lower motor neuron involvement
- EEG: Slowing
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Muscle
● COX4I1 (COX4)
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: 2-bp Del/Ins, 303TT; Pro152Thr; Nonsense
- COX4I1 protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Reduced with: Disuse-related muscle fiber atrophy
- Clinical
- Onset: 5 months to 3 years
- Low weight
- Developmental regression
- Seizures
- Short stature
- Intellectual disability
- Treatment: ? Coenzyme Q10
- Laboratory
- Chromosomal breakage
- Brain MRI: Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy; Leigh-like T2 basal ganglia signal
- Lactate & Fumarate: High in serum & CSF
- Muscle: Complex IV deficiency
● PET117 Cytochrome c oxidase chaperone (PET117)
- Epidemiology: 1 Moroccan family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: 172C-T; Homozygous
- PET117 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Biosynthesis & assembly of Complex IV
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood
- Developmental delay: Global
- Pyramidal signs
- Extrapyramidal: Bradykinesia
- Progressive: Loss of motor & cognitive skills
- Systemic: Enteropathy; Infections
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Medulla T2 signal
- Lactate, Alanine & Glycine: Mildly high
● Cytochrome c oxidase, subunit 5A (COX5A)
- Epidemiology: 1 Arab family, 2 sisters
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg107Cys; Homozygous
- COX5A protein
- Mitochondrial: Complex IV subunit
- Location: Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Assembly factor in Complex IV biogenesis
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant
- Poor feeding
- Failure to thrive
- Hypotonia
- Delayed development
- Hepatomegaly
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Death < 2 years
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
● Cytochrome c oxidase, subunit FA4 (COXFA4; NDUFA4)
- Epidemiology: 1 Pakistani family, 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous, Splice site; IVS1DS, G-C, +1
- COXFA4 protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Complex IV subunit
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Developmental delay
- Gait: Unsteady
- Ataxia
- Dystonia
- Spasticity
- Course: Episodic; 2 with death in 1st & 3rd decade
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Muscle: Lipid increased; Complex IV deficiency
- Brain imaging: Leigh-like; T2 hyperintensities in White matter, Basal ganglia, Thalamus, Brainstem
● Cytochrome c Oxidase Assembly Factor 16 (COX16)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Stop; Arg82X
- COX16 protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Interacts with: COX1; COX2
- Clinical
- Onset: Prenatal
- Encephalopathy
- Hypotonia
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Hearing loss
- Cardiac: Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Course: Death < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis: Serum & CSF
- Hypoglycemia
- Liver failure: Coagulopathy
- Brain MRI: Atrophy; Multiple infarcts
- Serum CK: High
- Muscle: Histology normal; Complex IV activity reduced
- Urine organic acids: Abnormal
● Cytochrome c Oxidase Assembly Factor 11 (COX11)
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense (Ala240Pro); Deletion/Insertion (c.35_36delinsG)
- COX11 protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Complex IV assembly
- Mediates copper delivery into COX1 CuB center
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Developmental delay
- Seizures
- Other: Dyskinesia; GI disorders
- Course: Proressive
- Laboratory
- Plasma lactate: High
- Brain MRI: Early Normal; Later Basal ganglia or Dentatelesions
- EEG: Epileptiform discharges
● NDUFV2
- Epidemiology: Family of African descent
- Genetics
- Mutation: 4 bp deletion at 5-prime end of IVS2
- Allelic disorder: Optic neuropathy
- NDUFV2 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5 days
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Hypotonia: Truncal
- Growth retardation
- Encephalopathy
- Death: < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Complex I activity: Reduced (50%)
- Variant: Parkinson's susceptibility
- Missense mutation: Ala29Val
● C6ORF66 (NDUFAF4)
- Epidemiology: Arab-Muslim family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Leu65Pro
- Allelic with: Leigh syndrome
- C6ORF66 protein
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Soon after birth
- Metabolic acidosis
- Hypotonia: Reduced movements
- CNS: Encephalopathy
- Pyramidal: Spastic; Arms & Legs
- Dystonic posturing
- Optic atrophy
- Cardiac: Cardiomyopathy in 1 patient
- Contractures
- Course: Death at 2 to 5 days to Survival to 7 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- MRI: Atrophy of grey and white matter
- Muscle mitochondria: Complex I activity reduced to 0% to 21%
- Complex I protein: Reduced
- NDUFAF4 variant: Leigh syndrome
- Epidemiology: 1 Pakistani patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Hoimozygous; Ala3Pro
- Clinical
- Onset age: 7 months
- Delayed milestones: Rolling over; Sitting; Speech
- Hypotonia
- Tendon reflexes: Present
- Seizures
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Basal ganglia & thalamus diffuse signal
- EEG: Multifocal spikes
- Lactate: High
- Complex I deficiency
● FAS activated serine-threonine kinase domains 2 (FASTKD2; KIAA0971)
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Nonsense & Missense
- FASTKD2 protein
- Mitochondrial marker: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Membrane-potential-dependent in vitro mitochondrial import
- Highest tissue expression: Muscle, Heart, Thyroid
- Clinical
- Onset: Congenital to 2nd decade
- Social & Motor development
- Normal until 7 to 12 months
- Then markedly delayed: More severe cases
- Irritability
- Seizures
- Refractory, generalized tonic-clonic convulsions
- Course: Febrile illness at onset; Persistent
- Other CNS: May be asymmetric
- Stroke-like episodes: Hemiparesis
- Optic atrophy
- Extrapyramidal movements
- Muscle tone: Reduced
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Skeletal: Hip dislocation & contractures
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging
- Atrophy: General
- T2-hyperintensities in basal ganglia & brainstem
- Mitochondria
- Plasma & CSF lactate: Mildly increased
- Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) (Complex IV): Reduced to 21%
- Other mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Normal or borderline activities
- Muscle histochemistry: Normal SDH & COX
- Brain imaging
● Apolipoprotein O (APOO; MIC26)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.350T>C (p.I117T)
- APOO protein
- Paralog MICOS subunit
- Forms: 55 kD (Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi & Extracellular space); 22kD (Mitochondrial)
- Maintains cristae structure
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 years
- Systemic: Vomiting, Fever, Diarrhea, Weight loss, Infections
- Developmental delay, progressive: Cognitive impairment
- Behavioral: Irritability, Fatigue, Autistic
- Hypotonia
- Dysautonomis: Gastrointestinal, Body temperature
- Treatment: L-Carnitine, Biotin, CoQ10
- Laboratory
- Blood: Lactate & Pyruvate high
- Carnitine profile: Increased C4, C5, C5:1, C5-OH
- Brain MRI: T2 signal in white matter
● Apoptosis-Inducing Factor mitochondrion-associated 1 (AIFM1)
- Nosology: Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 6 (COXPD6)
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Pro169Leu; Arg201 del; Gly308Glu; Gly338Glu; Met340Thr
- Allelic disorders
- AIFM1 protein
- Location: Targeted to mitochondrial intermembrane space (AIFmito)
- FAD-dependent NADH oxidase: Unknown function
- Rotenone-sensitive reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH):Ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity
- Apoptogenic stimuli
- Cause a soluble form (AIFsol) to be released by proteolytic cleavage
- AIFsol migrates to nucleus: Induces parthanatos (Caspase-independent fragmentation of chromosomal DNA)
- Cleaved fragment of AIFM1: Implicated in caspase-independent programmed cell death induction
- Mutation effects
- Cells more sensitive to apoptotic stimuli
- Cell death by caspase-independent, AIF-mediated parthanatos
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st year
- Hypotonia
- Involuntary movements: Continuous in hands & feet
- Tongue fasciculations
- Muscle wasting
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- CNS
- Psychomotor development delay: Head control; Sitting; Speech
- Seizures
- Course: Progressive regression
- Treatment: Riboflavin supplementation stabilized condition
- Laboratory
- MRI: Signal in neostriatum
- Lactate & Pyruvate: High in serum & CSF
- Electrodiagnostic
- NCV: Sensory-Motor axonal polyneuropathy
- EMG: Denervation
- Muscle biopsy
- Fiber size
- Varied
- Some with large grouped atrophy: Large fibers type I
- SDH increase in some fibers
- COX: Reduced diffusely
- Regenerating fibers
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Complex IV: Reduced
- Other Ox-Phos activities: Mild changes; Combined Ox-Phos deficiency
- TUNEL staining of muscle nuclei
- Fiber size
- mtDNA copy number: 20% of normal
- Variant: AIFM1 Intermediate syndrome
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: X-linked, Recessive
- Mutation: c.727G>T (p.Val243Leu)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 2.5 years
- Hearing loss
- Muscle atrophy: Progressive
- Ataxia
- Hearing loss
- Ophthalmoplegia, Progressive (PEO)
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Morphology: Non-specific
- COX stain: Reduced
- Oxidative enzymes: Combined Complex I & IV defect
- Muscle
- AIFM1 variant: Motor neuropathy, Distal
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: c.629T>C (p.F210S)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Weakness: Distal
- Laboratory
- NCV: Motor axon loss
- Fibroblasts: Mitochondrial network fragmented
- AIFM1 variant: Cerebellar ataxia + Polyneuropathy, Hearing loss & Intellectual disability
249
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive, X-linked; X-inactivation in Female
- Mutation: c.1195G>A; p.Gly399Ser
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- Cerebellar ataxia: Gait; Limb; Dysarthria; Hypometric saccades
- Polyneuropathy (Not in female): Tendon reflexes reduced
- Hearing loss
- Intellectual disability
- Mood & Behavior disorder
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
● ATP synthase, H+ transporting, Mitochondrial F1 complex, Epsilon subunit (ATP5E)
- Epidemiology: Single patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Tyr12Cys missense; Homozygous
- ATP5E protein
- Epsilon subunit of mitochondrial ATPase F1 catalytic part of complex
- Complex V
- Mutation
- Normal ATP synthase complex assembly
- Decreased amount of ATP synthase biosynthesis
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal; Respiratory distress; Lactate high
- Metabolic crises
- Recurrent
- Elevated plasma lactate & hyperammonemia
- Especially during infections
- CNS
- Cerebellar: Ataxia; Nystagmus
- Mental retardation: Mild
- Fatigue
- Weakness on exertion
- Reduced walking distance
- Polyneuropathy
- Severe
- Develops over time
- Cardiac: Left ventricle hypertrophy
- Survival: Adulthood
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria
- Fibroblasts
- ATP synthase activity: Low
- Respiratory chain activity: Normal
- EMG: Chronic neuropathy
- NCV: Mixed axonal-demyelinating polyneuropathy
- MRI: Transient increased signal intensity in caudate & lentiformis nuclei
● ATP synthase, H+ transporting, Mitochondrial F1 complex, Alpha subunit (ATP5F1A; ATP5A1)
- Alpha subunit of mitochondrial ATPase F1 catalytic part of complex
- Complex V
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Irritability
- Seizures
- High pitched cry
- Eyes: Nystagmus, Vertical & Horizontal
- Microcephaly
- Tone: Abnormal
- Death: 1st weeks of life to 15 months
- MRI: Hyperdense thalami; Subcortical densities; Asymmetric
- EEG: Slow waves
- Hyperalaninemia
- CNS Pathology: Cerebellum small; White matter damage
- Muscle: Complex I+III 22%; mtDNA depletion 40%
- Complex V: Reduced activity & amount in fibroblasts
- Epidemiology: Moroccan family
- Genetics: Tyr321Cys; Missense; Homozygous
- Clinical
- Onset age: Prenatal
- Hypotonia
- Microcephaly
- Cardiac: Heart failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- CNS: Seizures; Encephalopathy
- Course
- Failure to thrive
- Death < 2 years
- Laboratory
- Serum alanine: high
- Muscle
- Mitochondrial DNA depletion
- Reduced activities of mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Epidemiology
- 6 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Dominant, de novo
- Mutations: Missense; R207H, R182Q, S346F
- Clinical
- Onset: Early infancy
- Feeding difficulties
- Failure to thrive
- Developmental delay
- Spasticity
- Dystonia
- Course: Symptoms may persist or spontaneously remit
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Hyperammonemia
- Plasma alanine: High
● ATP synthase, Peripheral stalk, Subunit OSCP (ATP5PO)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients, 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Loss of function; Splice site
- ATP5PO protein
- Connects F1 & Fo domains of synthase complex
- Oligomycin sensitivity-conferring protein (OSCP)
- Complex V
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal or Early infancy
- Seizures
- Hypotonia
- Developmental delay: Intellect; Walking
- Dystonia
- Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic
- Course: Progressive; Death at 4 months to 6 years
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Atrophy, progressive; Myelination delayed
- Lactate: High in Serum & CSF
● Seryl-tRNA Synthetase, Mitochondrial (SARS2)
- Epidemiology: Palestinian children
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; p.Asp390Gly
- SARS2 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- Provides serine aminoacylation to 2 mitochondrial tRNAs
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Failure to thrive
- Renal
- Tubulopathy: Hyperuricemia, Metabolic alkalosis
- Progressive failure
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Death: ~ 1 year
- Laboratory
- Hyperuricemia
- Metabolic alkalosis: Hypochloremic
- Lactate: High
- Muscle
- Type II atrophy
- COX stain: Reduced, focal or diffuse
- Oxidative enzymes: Reduced Complex I, III & IV activity
- Ratio of mtDNA to nuclear DNA: Normal
● Lipoyltransferase 1 (LIPT1)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- LIPT1 protein
- Catalyzes second step in covalent attachment of lipoic acid to lipoate-dependent proteins

- Catalyzes second step in covalent attachment of lipoic acid to lipoate-dependent proteins
- Clinical: Leigh
- Onset age: 2 days to 15 months
- Tone
- Early: Hypotonia
- Later: Spastic tetraparesis
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Dystonia
- Course: Episodes of deterioration
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging
- Atrophy: Cerebellum & Cortex
- White matter abnormalities: Thalamic & Frontal
- Serum lactate: High
- Metabolic acidosis
- Brain imaging
● Lipoic acid synthase (LIAS)
- Nosology: Pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoic acid synthetase deficiency (PDHLD)
- Epidemiology: Turkish family
- Genetics: Arg249His mutation
- LIAS protein
- Function: Lipoic acid synthesis
- Catalysis formation of protein-bound Dihydrolipoamide
- Catalyzes addition of 2 sulfohydryl groups at positions 6 and 8 on protein-bound octanoic acid
- Lipoic acid: Coenzyme of 3 mitochondrial dehydrogenase complexes
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDHC)
- α-dehydrogenase (α-KGDH)
- Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKDH)
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st week
- Epilepsy
- Tone
- Early: Hypotonia
- Spastic tetraparesis
- Poor feeding
- Apnea: Recurrent
- Microcephaly
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Glycine: High
- Brain: Multicystic encephalopathy; Hydrocephalus ex vacuo
- Echocardiography: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Muscle biopsy
- Histochemistry: Normal
- EM: Enlarged mitochondria with electron-dense matrix
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Normal
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity: Low
- Mitochondrial substrates: Reduced reactivity with pyruvate-containing substrates
● Lipoyl (Octanoyl) transferase 2, mitochondrial (LIPT2)
- Epidemiology: 2 families; 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.89T>C (p.Leu30Pro); c.314T>G (p.Leu105Arg); c.377T>G (p.Leu126Arg)
- LIPT2 protein
- Intermediary in: Posttranslational lipoylation of proteins
- Mitochondrial lipoate synthesis with LIASl; LIPT1
- Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (Up to eight carbon length)
- Octanoic acid residues transferred to: Glycine cleavage H protein (GCSH)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Early: Hypotonia; Respiratory distress
- Childhood
- Spastic tetraparesis
- Dystonia
- Epilepsy
- Microcephaly
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Course
- Severe cases: Death < 1 year
- Mild case: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cortical atrophy; White matter Δ & cysts; Enlarged ventricles
- Plasma glycine: Mildly increased
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle
- Fiber size: Mild variation
- Respiratory chain enzyme activities: Normal
- EEG: Spikes & Waves
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase 1 beta subcomplex, 9 (NDUFB9)
- Epidemiology: 1 European patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous, Missense; Leu64Pro
- NDUFB9 protein
- Complex I ancillary protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Contribute to oligomerization of CI, CIII, and CIV
- Oncogene-like: Prognostic factor in uveal melanoma
- Genetic predisposition to Cocaine Dependence in African-Americans
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 6 months
- Hypotonia
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Serum high; CSF normal
- Brain MRI: Normal basal ganglia & brainstem
- Biochemistry: Complex I activity < 50% of normal
● Aconitase, mitochondrial (ACO2)
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Ser112Arg; Gly259Asp; Lys736Asn; 4-BP del, 2328GAAG
- Allelic with
- Optic atrophy 9 (OPA9)

- Mutations: Gly661Arg; Leu74Val
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Optic atrophy: Dominant 273
- Spastic paraplegia (SPG), complicated
- Optic atrophy 9 (OPA9)
- ACO2 protein (Aconitate hydratase (AH))
- TCA cycle
- Catalyzes reversible isomerization of citrate to isocitrate
- Fe-S protein: 4 iron-sulfur clusters
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 to 6 months
- Developmental delay: Moderate to Severe; Motor & Cognitive
- Ataxia
- Seizures
- Eye: Retinal dystrophy; Optic atrophy; Strabismus
- Athetoid movements
- Tendon reflexes: Usually reduced; Occasionally brisk
- Hearing loss: 2 patients
- Laboratory
- MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy
- Corpus callosum: Thin
- Dysmyelination
- Frontal & Temporal cortical atrophy
- Muscle: Normal histology & oxidative enzyme activities
- Blood & CSF: Normal
- Urinary organic acids: Normal
- Glutamate oxidation: Mildly reduced
- WBC aconitase activity: Reduced to 11%
- MRI
- ACO2 variant: Hereditary spastic paraplegia + Intellectual disability & Microcephaly
240
- Epidemiology: 1 Arab-Bedouin family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense; c.1240T>G p.Phe414Val
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Failure to thrive
- Encephalopathy: Episodic
- Intellectual disability: IQ 40 to 60
- Seizures: Remission in childhood
- Spasticity: Legs > arms; No, or impaired walking; Tendon reflexes increased
- Contractures
- Weakness: Legs: Distal > Proximal
- Sensory loss: Distal legs
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Mild changes
- EMG & NCV: Normal
● Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 (WARS2)
- Epidemiology: 9 patients
- Genetics
- WARS2 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- Catalyzes aminoacylation of tRNA(trp) with tryptophan
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal to Early childhood
- Delayed development: Speech; Motor
- Hypotonia, axial
- Spastic quadriplegia: Hyperreflexia
- Muscle: Diffuse atrophy
- Cerebellar: Dysmetria, Tremor,
- Eye: Nystagmus, Exotropia, Amblyopia with difficulty tracking, Optic atrophy
- Extrapyramidsl: Dystonia
- Multifocal seizures
- Course: Early death to Slow progression with intellectual disability
- Laboratory
- Serum: Lactic acidosis
- Oxidative enzymes: Variable; Normal to Complex I & IV reduction
- Brain MRI: White matter defects; Atrophy
● Required for meiotic nuclear division 1 (RMND1; c6orf96)
- Epidemiology: 7 families including Saudi Arabian & Canadian
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous, splice site or missense (Arg417Gln)
- Allelic disorders
- COXPD11: Infant onset, Severe
- Perrault syndrome: Later onset; Hearing loss; Renal disease; Ovarian dysfunction
- RMND1 protein
- Location
- Mitochondrial: Inner Membrane
- Homopolymer
- Localization
- Discrete foci in mitochondrial network
- Near RNA granules where 1° mitochondrial transcripts are processed
- Function
- Mitochondrial protein synthesis
- Assembly or maintenance of mitochondrial ribosome
- Location
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to Childhood
- CNS
- Lethargy
- Respiratory failure
- Hypotonia: Severe
- Hyporeflexia
- Seizures
- Equinus deformities
- Systemic
- Renal failure
- Pancreatitis
- Hearing loss
- Dysautonomia
- Death: < 10 years
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Anemia
- Muscle pathology: COX staining reduced
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Combined I, III & IV deficiencies
- Fibroblasts
- COX staining reduced; SDH normal
- Reduced complexes I, III, IV & V
- MRI: Hypomyelination; Prominent cortical sulci; Pachygyria
- CNS Pathology: Cortical & Spinal cord atrophy
● Glutamyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 (EARS2)
- Epidemiology: 13 patients; European, US & South American
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or Stop
- EARS2 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial
- Mitochondrial tRNA-glutamyl synthetase
- Clinical: Several phenotypes
- Mild type
- Onset age: 6 to 12 montha
- Spasticity
- Loss of milestones
- Seizures: Some patients
- Irritability: Extreme
- Course
- Initial: Rapid progression
- Later: Partial recovery of clinical & MRI features
- Onset age: 6 to 12 montha
- Severe type
- Onset: Infancy
- Psychomotor development: Absent
- Hypotonia: Early
- Spastic tetraparesis
- Dystonia
- Visual impairment
- Seizures
- Course
- Initial: Rapid progression
- Later: Clinical stagnation, Brain atrophy on MRI, Persistent lactate increase
- Hepatocerebral
- Mutation: Lys65Glu, homozygous
- Clinical
- Onset: Infantile
- Hypotonia
- Hepatomegaly
- Cardiac: Hypertrophy of cardiac interventricular septum, mild
- Course: Death in infancy
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI: Dysgenesis of posterior corpus callosum
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I & IV deficiency
- Mild type
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in body fluids
- MRI
- White matter abnormalities: Extensive; Symmetrical; Cerebral; Sparing periventricular rim
- Signal abnormalities: Symmetrical; Thalami, Midbrain, Pons, Medulla oblongata, Cerebellar white matter
- Muscle
- COX- fibers
- SDH+ fibers
- Oxidative enzyme deficiencies: Multiple; I > III & IV
● Polyribonucleotide Nucleotidyltransferase, Mitochondrial 1 (PNPT1; PNPase)
- Epidemiology: 24 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Most Missense; Few splice
- Allelic disorders
- PNPT1 protein
- Polynucleotide phosphorylase
- Mitochondrial: Intermembrane space & Matrix
- RNA import to mitochondria: Noncoding nuclear RNAs (5S rRNA, MRP RNA, some tRNAs & miRNAs)
- PNPase: Prevents abnormal accumulation of double-stranded mtRNAs in mitochondria
- Mitochondrial RNA degradation
332
- Other component: SUPV3L1
- Mutations: Destabilize protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 1 year to Adolescence
- Developmental delay
- Trunk hypotonia
- Movement disorders: Dystonia; Choreoathetosis; Facial dyskinesias
- Spasticity
- Weakness: Diffuse; Dysphagia
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs
- Optic atrophy: Fovea; Papillomacular bundle
- Hearing loss (38%)
- Ophthalmoplegia: Long surviving adult
- Course: Progressive; Early death in 10%
- Laboratory
- Muscle pathology: Type 1 predominance; Type 2 atrophy
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Combined defects of complexes I, III & IV, mild
- mtDNA: Normal
- Nerve conduction velocities: Mildly reduced (32 to 35 M/s)
- Lactate: High in CSF & Blood
- MRI
- Caudate & Putamen hyperintensities
- White matter or Corpus callosum Δ
- PNPT1 variant syndrome: Hearing loss (DFNB70)

- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- PNPT1 mutation: Missense; Glu475Gly
- PNPT1 mutated protein: Present in cochlea
- Clinical
- Onset age: Congenital or Early childhood
- Nonsyndromic hearing impairment
● IBA57 (C1orf69)
- Nosology: MMDS
- Epidemiology: > 50 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Gln314Pro; Homozygous
- Allelic disorders
- SPG74
- SPOAN phenotype
- Necrotizing myelopathy in dogs
- IBA57 protein
- Biosynthesis of mitochondrial iron-sulfur [4Fe-4S] proteins
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Prenatal to 2 years
- May be
- Subacute
- Associated with: Infection or Vaccination
- CNS
- Hypotonia & Impaired motor function: Generalized
- Psychomotor regression
- Intellectual disability
- Spasticity
- Epilepsy (30%)
- Feeding difficulty
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Arthrogryposis
- Microcephaly
- Course
- Progresseive or Episodic worsening
- Death: Perinatal to Later childhood in some
- Onset
- Laboratory
- CSF & Serum Lactate: High
- Muscle
- IBA57 protein: Reduced
- Complex I & II: Reduced
- Brain MRI
- Malformations
- White matter pathology
- Hyperglycinemia
- IBA57 Variant syndrome: Spastic paraplegia 74 (SPG74)

- Epidemiology: 11 patients with SPOAN-like syndromes
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Slice site, Homozygous; c.678A-G
- Mutation efects: Retention of intron 2; Truncated protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1st decade
- Spasticity
- Legs > Arms
- Spastic gait
- Tendon reflexes: Increased at knees; Reduced at ankles
- Plantar reflexes: Extensor
- Sensation: Distal loss
- Legs: Distal atrophy; Pes cavus
- Optic atrophy
- Cognition: Normal
- Laboratory
- Mitochondia
- IBA57 protein: 90% decreased levels
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I & II subunits & activities: 30 to 40% reduction
- Aconitase activity: Mildly reduced
- NCV: CMAPS reduced amplitude; SNAPs normal
- Brain MRI: Optic nerve atrophy
- Mitochondia
● F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 4 (FBXL4)
- Nosology: MMDS
- Epidemiology
- 36 families
- Common with: Congenital lactic acidosis
- Genetics
- Mutations: Truncating or Missense
- Null mutations: Concentrated at N-terminal
- Missense mutation affecting splicing of last exon: Milder disease
- FBXL4 protein
- Location: Mitochondria, Inner membrane space
- F-box protein
- Function: mtDNA maintenance & fusion
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Birth (Most common) to 6 years
- Birth weight: Low
- CNS
- Developmental delay: Hypotonia; Global; Often severe
- Dysphagia
- Seizures (70%)
- Dysmorphism
- Microcephaly
- Craniofacial
- Hypotonia
- Cataracts (25%)
- Cardiac
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Course
- Poor growth
- Death: More severe patients
- Survival up to 2nd decade
- Mother: Hx of miscarriages
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX stain: Diffusely reduced with nonsense mutations; Punctate staining
- mtDNA depletion: Severe in some patients; 22% to 45%
- Combined mitochondrial dysfunction (MMDS): Complexes I, III & IV reduced activity
- Ultrastructure: Occasional enlarged mitochondria
- Lactic acidosis: Congenital
- Brain MRI: Cerebral atrophy; White matter lesions
- Muscle
● Centrosomal protein of 89 kDa (CEP89; CCDC123)
- Epidemiology: 1 Turkish patient, consanguinous family
- Genetics
- CEP89 protein
- Expression: Ubiquitous; Mitochondrial inter membrane space; Cytosol
- Subsynaptic organization
- Late assembly steps of Complex IV
- Clinical
- Developmental delay
- Feeding problems
- Intellectual dysfunction: No speech
- Gait: Broad based; Legs externally rotated
- Ataxic: Arm movements
- Deafness
- Face
- Hypotelorism
- Ears: Small low-set
- Columella below alae nasi
- Micrognathia
- Neck: Short broad
- Camptodactyly: 5th fingers
- Calcinosis cutis
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High
- Muscle
- Morphology: Normal
- Complex IV deficiency; Complexes I & II at lower limit of normal
- EMG: Myopathy
- Auditory evoked potentials: Peripheral conduction dysfunction
- Cystinuria: From SLC7A9 deletion
● Sideroflexin-4 (SFXN4)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients; European origin
- Genetic
- Mutations: 233delC (Pro78Leufs*26); c.739dup (Arg247Lysfs*19); Splice site 471+1G>A
- SFXN4 protein: Inner mitochondrial mambrane
- Clinical
- Onset: Intrauterine growth retardation
- Muscles: Atrophic; Difficulty running
- Motor: Delay; Abnormal fine skills; Hypotonia
- Tremor
- Dysmetria
- Language delay
- Intellectual disability
- Visual deficit: Severe
- Hematologic
- Anemia: Macrocytic
- Neutrophils: Hypersegmented
- Blood lactate & ammonia: Increased
- Muscle biopsy
- Mitochondrial numbers: Mildly increased
- Complex I deficiency or Global activity defects
- Lipid droplets
● LYR motif-containing protein 4 (LYRM4; ISD11)
- Epidemiology: 1 Lebanese & Syrian family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg68Leu
- LYRM4 protein
- Locations: Mitochondrial & Nuclear
- Iron-sulfur cluster formation
- Forms complex with& stabilizes sulfur donor NFS1

- Clinical
- Onset age: Newborn period
- Respiratory distress
- Hypotonia
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Epilepsy (50%)
- Hepatomegaly (50%)
- Course: Variable; Death at 3 months or Survival to 3rd decade
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis, severe
- Muscle
- Lipid increased
- Ultrastructure: Abnormal mitochondria
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Complexes I, II & III ± IV reduced
- Liver: Steatosis; High iron
● Valyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 (VARS2)
- Epidemiology: 18 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: Often missense; Thr367Ile
- VARS2 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to Infancy
- Psychomotor delay
- Facial dysmorphisms
- Microcephaly
- Seizures: Partial,continuous; Status
- Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- Cerebellar atrophy
- Hyperintense periventricular regions
- Serum: Lactic acidosis
- MRS: Lactate peak
- EEG: Seizures
- Muscle CT: Quadriceps small
- Muscle pathology
- Histochemistry: Normal
- Complex I: Isolated deficiency
- Brain MRI
● Threonyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 (TARS2)
- Epidemiology: 27 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense > Stop or Splice; 30 variants
- TARS2 protein
- Mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS)
- Regulates mTORC1
 activity after changed levels of threonine
activity after changed levels of threonine
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal to > 6 months
- Hypotonia: Axial
- Hypertonia: Limbs
- Developmental delay: Absent speech
- Seizures
- Dystonia (50%)
- Eye anomalies
- Course
- Regression (36%)
- Death: Months to Adult
- Laboratory
- Blood lactate: High
- Brain MRI
- Corpus callosum: Thin
- Globus pallidum: Hyperintense
- Atrophy: Cerebrum & Cerebellum
- Muscle pathology
- Subsarcolemmal lipofuscin
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain: Multiple defects (COXPD)
● GTP-binding protein 3 (GTPBP3; MSS1)
- Epidemiology: 22 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Compound heterozygous or Homozygous
- Missense or Stop
- Mutations
- GTPBP3 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to 10 years
- Cardiomyopathy (80%)
- Hypertrophic
- Limiting factor in survival of milder phenotypes
- Encephalopathy (60%): Variable severity
- Leigh-like
- Developmental delay
- Intellectual disability
- Respiratory dysfunction
- Visual dysfunction
- Seizures
- Course: Varied
- Survival: Neonatal death to Adult
- Laboratory
- Skeletal muscle
- Oxidative enzymes:
Combined respiratory chain complex deficiency
- Complex I & IV deficiency: Some patients normal
- Oxidative enzymes:
Combined respiratory chain complex deficiency
- Lactic acidosis
- MRI Δ: Thalamus, Putamen, Brainstem
- Fibroblast mtRNA levels: Normal
- Skeletal muscle
● Asparaginyl-tRNA Synthetase, Mitochondrial (NARS2)
- Epidemiology: 13 families
- Genetics
- NARS2 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- Provides asparagine aminoacylation
- Clinical: Varied phenotypes
- Onset age: Infancy
- Myopathy
- Weakness: Proximal; Face
- Dysarthria
- Ptosis
- Amyotrophy
- Fatigability
- CNS
- Intellectual disability: Regression
- Epilepsy
- Hearing loss
- Tone
- Early: Hyoptonia
- Later: Spasticity; Tendon reflexes brisk
- Eye
- Ptosis
- Nystagmus
- Cortical blindness
- Optic atrophy
- Skeletal
- Microcephaly
- Limbs: Brachymetatarsia, Hallux valgus, Clubbed fingers
- Disease course
- Severe: Some with death in infancy or childhood
- Mild: May present with myopathy or hearing loss without CNS involvement
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Atrophic muscle fibers
- Ragged red fibers: Few
- Mitochondria: Enlarged
- Lipid: Increased in muscle fibers
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Combined complex I, III & IV deficiency
- Complex V Western blot: Subcomplexes
- NARS2 protein: Reduced
- Serum CK: Up to 1600
- Lactate: Serum & CSF high or normal
- Brain MRI: Normal or Atrophy ± White matter changes
- EEG: Seizures
- Acylcarnitine & Organic acid (Urine) profiles: Normal
- Muscle
● Cysteinyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 (CARS2)
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or other In-frame
- CARS2 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy or Childhood
- Feeding difficulties
- Motor: Hypotonia; No anti-gravity movements
- Movements: Chorea; Dystonia; Myoclonus; Opisthotonus
- Eyes: Vision loss; Oculogyric crises
- Microcephaly
- Seizures: Multifocal; Complex
- Psychomotor: Delay & Decline
- Hepatic dysfunction
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cortex & White matter atrophy & T2 signal
- EEG: Multifocal epileptiform discharges
- Serum lactate: Increased in some samples
- Muscle: Normal histology; mtDNA increased
- Oxidative enzymes (Liver): Complexes I, III & IV reduced actities
● Solute carrier family 25 (Mitochondrial carrier, adenine nucleotide translocator), Member A26 (SLC25A26; SAMC)
- Epidemiology: 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense & Splice site
- Severe disease: Transmembrane domain
- Adult onset: In repeat 2
- Mutations
- SLC25A6 protein
- Mitochondrial
- Transporter
- S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) across inner mitochondrial membrane
- SAM exchanged for S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH)
- SAM
- Synthesized in cytosol from methionine & ATP in methionine cycle
- Predominant methyl-group donor for > 200 methyltransferases
- Mitochondrial methylation: RNAs, NDUFS2, ETFB, Citrate synthase, ANT, Ubiquinone biosynthesis components
- CoQ10 & Lipoic acid: Biosynthesis
- Disease effects
- Reduced intra-mitochondrial methylation
- Reduced transport of SAM or SAH
- Mild disease: SAH levels increased in mitochondria
- Clinical
- Onset
- Ages: Neonatal to Adult
- Children: Systemic disease
- Adults: Exercise intolerance
- Respiratory failure
- Episodic: Circulatory collapse; Pulmonary hypertension
- Exercise intolerance
- Fatigue & "Weakness"
- Pain
- Weakness: Adults
- Abdominal pain
- Course: Death at 5 days to Alive at 6 years to Adult onset
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- CoQ10: Levels reduced
- Serum CK: Normal
- EMG: Mild myopathy
- Muscle
- SDH+ & COX- muscle fibers
- Complexes I & IV ± III: Reduced activity
● Thioredoxin 2 (TXN2)
- Epidemiology: 1 German patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Nonsense; Trp24X
- TXN2 protein
- Dithiol-reducing activity
- Mitochondrial: Matrix
- Thioredoxins: Control cellular redox state; Protect against oxidative damage
- Reduces peroxiredoxin dimers formed on reaction with H2O2: With TXNRD2 & PRDX3/5
- Keeps peroxiredoxins in reduced & active state.
- Efficient cycling of PRDX3

- Control of
- Mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
- Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Microcephaly
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Spasticity
- Dystonia
- Incoordination
- Epilepsy
- Optic neuropathy
- Retinopathy
- Polyneuropathy
- Peripheral: Axon loss
- Autonomic: GI hypomotility
- Treatment: ? Coenzyme Q10
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Reduced complex I & III activity (Combined complex)
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy; Delayed myelination
- TXN2 protein: Absent
- CSF: High lactate & protein
- NCV: Axon loss
● tRNA Methyltransferase 10, S. Cerevisiae, Homolog of, C (TRMT10C)
- Epidemiology: British & Kurdish patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.542G>T (p.Arg181Leu); c.814A>G (p.Thr272Ala)
- TRMT10C protein
- Mitochondrial RNase P protein 1 (MRPP1)
- Member of mitochondrial ribonuclease P (mt-RNase P) complex
- Cleaves 5' ends of mt-tRNAs from polycistronic precursor transcripts
- Stable complex of MRPP1 & MRPP2 has m1R9 methyltransferase activity
- Methylates mt-tRNAs at position 9
- Folding mt-tRNAs into correct tertiary structures
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Hypotonia
- Feeding difficulties
- Deafness
- Death: 5 months; Respiratory failure
- Laboratory
- Serum & CSF lactate: High; 5 to 10 mmol/L
- Muscle
- COX- & SDH+ fibers, Scattered
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex I, IV ± III reduced
- mtDNA: Normal copy number
● Mitochondrial intermediate peptidase (MIPEP; MIP; Oct1)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous or Compound heterozygous; Missense or Stop
- MIPEP protein
- Mitochondrial target peptide presequence cleavage
- After MPP
 cleavage
cleavage
- Removes octapeptide
- After MPP
- Maintains mitochondrial iron homeostasis
- May be related to Friedreich ataxia pathology
- Mitochondrial target peptide presequence cleavage
- Clinical
- Failure to thrive
- Hypotonia
- Cardiac
- Developmental delay, global
- Some patients
- Seizures
- Hypertonia
- GI disorders
- Laboratory
- Serum: High lactate & alanine
- Muscle
- Glycogen
- Lipid droplets
- Mitochondrial proliferation
- Oxidative enzymes: Mildly reduced Complexes I+III & IV; COXPD
- Brain pathology: Neuronal loss, diffuse; Parenchymal rarefaction; Gliosis
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S7 (MRPS7)
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 siblings
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.550A>G; Met184Val; Homozygous
- Mitochondrial location: Matrix
- Mitochondrial Ribosome protein: Small subunit
- Onset
- Congenital
- Sensorineural deafness
- Sensorineural deafness
- Systemic
- Vomiting
- Hepatic failure: Hepatomegaly
- Renal failure
- Course: More severe sib died in 2nd decade
- Oxidative enzyme deficiencies
- Liver: Complex I, III & IV
- Muscle: Borderline changes
- Serum lactate: High
- Hypoglycemia
- Urinary organic acids: 3-hydroxybutyrate peak
- Muscle
- Lipid: Increased
- SDH & COX: Normal
- Liver: Steatosis; Fibrous expansion of portal tracts
● tRNA Dimethylallyltransferase (isopentenyltransferase), mitochondrial 1 (TRIT1)
- Epidemiology: 15 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg323Gln
- Tumor suppressor: Alleles associated with poor survival from lung cancer in some ethnic groups
- TRIT1 protein
- mtRNA modification
- Transfers isopentenyl group from dimethylallyl pyrophosphate to N6 of adenine at position 37 of the tRNA
- i6A modification at position 37 in anticodon loop of subset of tRNASer(UCN)
- Mutation: Loss of i6A37 from cy-tRNASer(UGA) & mt-tRNASer(UCN)
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 14 months
- Seizures: Some with fever; May be difficult to treat
- Microcephaly, Progressive
- Developmental delay: Speech, Motor & Cognitive
- Obesity
- Strabismus
- Spasticity, Progressive (25%)
- Optic disk hypoplasia: 25%
- Liver disease
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers: Many, scattered
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Combined deficiency
- Complex I & IV deficiency
- EEG: Myoclonic epilepsy
- Endocrine: Diabetes & Hypoglycemia
- Brain MRI (60%)
- Cerebral atrophy
- Myelination: Delayed, Reduced periventricular WM
- Megacisterna magna
- Corpus callosum Δ
- DandyWalker-malformation
- Hydrocephalus,
- Polymicrogyria
- Vermis hypoplasia
- Septo-optic dysplasia
- Serum lactate: Normal
- Muscle
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S2 (MRPS2)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Arg110Cys, Asp114Asn, Arg138His
- MRPS2 protein
- Mitochondrial location: Matrix
- Mitochondrial Ribosome protein: Small subunit
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant
- Deafness
- Developmental delay
- Hypotonia
- Course: Alive after 1st decade
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Hypoglycemia
- Urine 2-oxoglutaric acid: High
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes
- Most tissues: Combined Complex Deficiencies
● Mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system, 13-kD subunit (MICOS13; QIL1)
- Epidemiology: 5 patients, 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Deletion; Splice site
- MICOS13 protein
- Localizes to: Inner mitochondrial membrane at cristae
- Required for
- Cristae junction integrity & morphology
- MICOS assembly
- Mitochondrial function
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth or 1st months
- Hypotonia
- Failure to thrive
- Neurodegeneration: Developmental milestone loss
- Liver dysfunction.
- Some patients
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Vision & Hearing loss
- Seizures
- Spasticity
- Death: 1 to 5 years
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate & alanine: High
- 3-Methylglutaconic & 3-Methylglutaric acids: High in urine
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar & vermis atrophy
- Mitochondria
- Oxidative enzymes: Complexes I, III & IV reduced in liver or muscle
- Pathology: Enlarged; Abnormal cristae; MICOS3 protein absent
● Mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system, 10-kD subunit (MICOS10)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: Cys58Ser; 19596826_19601303del
- MICOS10 protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- MICOS assembly
- Mitochondria: Positioning, distribution & replication of mtDNA.
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Liver failure: Jaundice
- Mental retardation
- Absent speech
- Apenic episodes
- Seizures
- Laboratory
- Fibroblasts: Mitochondrial cristae abnormal
- Hepatocytes: Complex I reduced < 25%
- Galactose: High
- Liver: Enzymes High; mtDNA 24%
- Liver structure: Abnormal
- Brain MRI: Delayed myelination; Cerebellar atrophy; Basal ganglia T2 signal
- Muscle MRI: Low mass
- Hypoglycemia: During fasting
- Renal failure: In teens
● Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein S14 (MRPS14; uS14m)
- Epidemiology: 2 patient2
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Arg108Cys; Asp37Asn; Asn60Asp
- MRPS14 protein
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Mitochondrial ribosomes: Small subunit
- Clinical
- Onset: Prenatal
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome
- Developmental delay: Global
- Growth retardation
- Face: Dysmorphic
- Course: Early deterioration during infections
- Father: Rhabdomyolysis, 1 episode
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Complex IV activity: Mildly reduced
- Western blot: All complexes except II reduced
- Serum lactate: High
- Muscle
● Mitochondrial elongation factor G2 (GFM2)
- Nosology
- Microcephaly, Simplified gyral pattern & Insulin-dependent diabetes
- Leigh syndrome
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, splice, Small deletion
- GFM2 protein
- Ribosome recycling
- Ribosome dissociation from mRNA
- Clinical
- Onset age: 0 to 2 years
- Development
- Delay & Regression
- Hypotonia: Axial
- Arthrogryposis: 1 family
- Spasticity
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Basal; ganglia T2 Δ Corpus callosum & Cerebellum Small
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Fibroblasts: Complex I & IV defects
● Caseinolytic peptidase B protein homolog (CLPB)
- Epidemiology: 13 families; Greenland, North Europe, Asia, US
- Genetic
- Mutations: Missense, Frameshift & Nonsense
- Nonsense mutations: More severe phenotype
- CLPB protein
- Mitochondrial chaperone
- Disaggregation of misfolded proteins due to stress (heat)
- Interacts with ATP2A2
- AAA+ domain
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infant
- Febrile episode
- Psychomotor: Regression during febrile episodes
- Muscle tone: Hypotonia to Stiff
- Epilepsy
- Movement disorder: Dystonia
- Ataxia
- Cataracts
- Microcephaly
- Infections: Frequent
- Leigh-like features
- Course: Death in infancy to Survival to 10 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Neutropenia
- Methylglutaconic aciduria
- CLPB protein: Reduced in tissues
- Serum lactate: High in some patients
- Respiratory chain enzyme activity: Normal
- Brain atrophy: Progressive
- Hypoglycemia: Neonatal
- Muscle: Type 1 predominance
● Coenzyme Q4, S. Cerevisiae, homolog of (COQ4)
- Nosology: Coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, 7
- Epidemiology: > 40 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Severe disease
- General: Exons 57; Early onset, Unresponsive to CoQ10 therapy
- Mutations: Leu52Ser; Arg141*; Arg145Gly; Arg240Cys
- Milder course
- General: Exons 1-4; Later onset, Responsive to CoQ10 Rx, Longer lifespan
- Mutations: Pro64Ser homozygous; Other missense
- East Asia: c.370G>A; Intermediate disease in homozygotes
- Severe disease
- Allelic disorder: SPAX10; Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis, Pure & Complicated, Recessive
- Mutations
- COQ4 protein
- Mitochondrial inner membrane: Matrix side
- May stabilize multiheteromeric complex containing CoQ biosynthetic enzymes
- Clinical
- Onset age: Prenatal to Childhood
- Hypotonia
- Respiratory distress
- Seizures: Some patients
- Cardiac: Cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic; Bradycardia
- Possible treatment: Ubiquinol, COQ10 high dose (1,000 to 5,000 mg/day)
- Course
- Severe disease: Often fatal in childhood
- Longer surviving patients
- Spastic ataxia
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory-Motor
- Seizures
- Neurodevelopmental disorder
- Laboratory
- Brain: Cerebellar hypoplasia or Normal
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- Serum lactate: High
- Urinary organic acids: 2-OH glutaric acid high
- Muscle
- Oxidative enzyme activites
- Complex II + III activity possibly low
- Complex I low in some; Others ≥ 30%
- CoQ10 levels: 10% to 30% of LLN
- Oxidative enzyme activites
- Brain pathology: Neuron loss; Astrocytosis
- COQ4 variant: SPAX10; Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis, Pure ± Epilepsy or Ataxia, Recessive
 313
313
- Epidemiology: 16 patients, 13 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense; Loss of Function
- Clinical
- Onset age: 8 to 55 years
- Spasticity
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Some patients
- Epilepsy
- Ataxia: Gait; Limb
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Usually normal; Cerebellar atrophy
- NCV: Usually normal
- Muscle pathology: Normal
- Fibroblasts: COQ4 low
● tRNA nucleotidyl transferase 1 (TRNT1)
- Epidemiology: 16 patients
- Genetics: Mutations
- TRNT1 protein
- tRNA modification
- Adds CCA trinucleotide to 3end of newly synthesized tRNAs
- Functions in cytoplasm & mitochondria
- Most sensitive tRNA to TRIT1 dysfunction: tRNASer(AGY)
- Neonatal onset
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 weeks
- Episodic: Lactic acidosis; Fevers
- CNS
- Hypotonia
- Central apnea
- Seizures
- Developmental delay
- Neurosensory deafness
- Ataxia (50%)
- GI: Vomiting; Esopageal dysmotility
- Microcephaly
- Death: 1 to 14 years
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Cortical atrophy, progressive
- Sideroblastic anemia
- B lymphopenia
- Brain MRI: Cerebral atrophy
- Renal Fanconi syndrome
- Generalized Aminoaciduria, Glycosuria, Hypercalciuria
- Muscle
- Large mitochondria
- Lipid droplets
- Combined oxidative phosphorylation defect
- Reduced activity of: Complexes I, II+III & IV
- Clinical
- Childhood onset
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3.5 years
- Gait ataxia
- Dysarthria
- Motor regression: Hypotonia, Dysarthric
- Hypotonia
- Eye: Ptosis; Ophthalmoplegia, horizontal
- Course: Stable or Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Abnormal brainstem & dentate nucleus
● Peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase 2 (PTRH2, BIT1)
- Epidemiology: 19 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense & Stop
- 50% at GLN85: Gln85Pro
- Mutations
- PTRH2 protein
- Mitochondria: Outer membrane
- Integrin-mediated cell survival
- Apoptosis signaling
- Interaction with focal adhesion kinase (FAK)
- PI3K-AKT-NFkB pathway
- Induces Bcl-2 transcription
- Apoptosis
- Blocks: Intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
- Promotes: Caspase-independent apoptosis by regulating transcriptional regulators, AES & TLE1
- Regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling
- Prevents accumulation of dissociated peptidyl-tRNA: Could inhibit protein synthesis
- Controls skeletal myogenesis: Caspase-mediated signaling pathway; Regulation of Bcl-2
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Prenatal: Decreased movement
- CNS
- Intellectual disability
- Motor delay (94%)
- Ataxia (75%)
- Deafness
- Seizures
- PNS (90%)
- Weakness: Distal (85%)
- Sensory loss
- Eyes: Exotropia
- Face
- Microcephaly
- Midface hypoplasia
- Hypertelorism
- Upper lip: Thin
- Endocrine: Hypothyroid
- Pancreas: Exocrine insufficiency; Steatorrhea; Diabetes
- Liver: Fibrosis
- Skeletal
- Fingers & Toes: Proximal thumb; Long; Ankle contractures
- Short stature
- Genitalia: Shawl scrotum
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy, Progressive
- EEG: Abnormal rhythmic alpha-beta-waves with high amplitudes
- Abdominal ultrasound: Organ fibrosis and/or Increased fatty tissue
- NCV: Neuropathy, Demyelinating; Uniform slowed velocities
- HbA1C: Mildly high
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- PTRH2 protein: Reduced levels in fibroblasts
- Nerve pathology: Loss of large myelinated axons
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein 12 (MRPL12)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient; Roma/Gypsy male
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; c.542C>T (p.Ala181Val)
- MRPL12 protein
- Mitoribosome component: Large subunit
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Congenital
- General hypotrophy
- Seizures
- Psychomotor retardation: No speech
- Hypotonia
- Severe
- Trunk: Inability to sit & stand unaided
- Cerebellar +
- Nystagmus: Horizontal; Intermittent
- Ataxia
- Tremor
- Dysmorphism
- Face: Round; Epicanthic folds, Arched palate, Short neck, Low-set ears
- Bilateral abnormal median palmar crease
- Tendon reflexes: Normal
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Plasma lactate: High
- MRI: T1 hyposignal & T2 hypersignal of White matter & Basal ganglia
- Oxidative enzymes: Complex I & IV deficiency
● Transmembrane protein 65 (TMEM65)
- Epidemiology: 1 Pakistani patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Splice variant; Homozygous; c.472+1G>A
- TMEM65 protein
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Mitochondrial respiratory chain function
- Clinical
- Microcephaly
- Developmental delay, Global
- Seizures
- Spasticity: Increased tone & tendon reflexes
- Dystonic posture: Legs
- Sensory: Vision & Hearing loss
- Dysmorphism
- Head: Low ears & hairline
- Feet: Polydactyly; Syndactyly; Brachydactyly; Clinodactyly
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: Variably high
- Brain MRI: Atrophy
- Muscle ultrastructure: Mitochondrial pleomorphism
● Mitochondrial calcium uptake protein 2 (MICU2)
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Truncating
- MICU2 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU): Regulatory subunit
- Interacts with MICU1
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Cognitive impairment
- Spasticity
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Periventricular white matter changes
● Peptidase, mitochondrial processing, beta (PMPCB)
- Nosology: MMDS
- Epidemiology: 4 families, 5 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense
- PMPCB protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Catalytic subunit of mitochondrial processing protease (MPP)
- Required for maturation of mitochondrial precursor proteins
- Biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters
- PMPCA: MPP binding subunit
- Other mitochondrial sequence cleavage protein: MIPEP
- Mutation: Impairs frataxin processing
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy; 4 to 12 months
- Neurodegeneration
- Developmental regression
- No speech
- No ambulation
- Seizures (80%)
- Some patients: Ataxia, Dystonia, Optic atrophy
- Course: Death in 1st decade
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High (60%)
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzymes: Complex II activity reduced
- Brain MRI
- Cerebellar & Brainstem atrophy
- Basal ganglia signal
- Leukodystrophy: More severe disease
● Glycine cleavage system H protein gene (GCSH)
- Epidemiology: 7 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Multiple types
- GCSH protein
- Functions
- Glycine cleavage system: Glycine exchange
- Lipoylation
- Location: Mitochondria
- Mutation effects: Hypomorphic on glycine exchange and/or lipoylation
- Glycine cleavage system proteins
- Functions
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal to Infantile
- Lethargy
- Poor feeding
- Developmental delay
- Hypotonia
- Seizures
- Microcephaly
- Course: Early death in most
- Laboratory
- Glycine: High in serum & CSF
- Brain MRI: Deep gray matter lesions
● Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 8 (PNPLA8; iPLA2γ)
- Epidemiology: > 25 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop (Nonsense/Frameshift; Most), Missense (Few)
- Allelic disorders
- Ataxia in Australian shepherd dogs
- Bovine progressive degenerative myeloencephalopathy (Weaver syndrome)
- PNPLA8 protein
- PNPLA8 nosology: Mitochondrial calcium-independent phospholipase A2-γ (iPLA2-γ)
- Predominant phospholipase in mammalian mitochondria
- Catalyze cleavage of acyl groups in glycerophospholipids
- Mutation effects
318
- Reduced mitochondrial membrane potential
- Remodeling of cardiolipin molecules
- Reduced weight gain during high-fat feeding
- Other PNPLA (iPLA2-specific) disorders
- PNPLA2: Neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy
- PNPLA4
 224
224
- PNPLA6: SPG39
- PLA2G6: Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy 1
- Clinical
- Onset age: Prenatal to Adolescence
- Early onset disease
- Hypotonia
- Microcephaly
- Weakness
- Proximal
- Loss of ambulation
- Distal: With later disease onset
- CNS
- Speech: Dysarthric
- Spasticity: With younger onset
- Ataxia: Dysmetria; Gait disorder
- Seizures: Complex Partial
- Dystonia: Oral
- Cognitive dysfunction: With younger onset
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced in legs
- Course: Slow Progression
- Laboratory
- Serum CK: Normal
- Serum lactate & pyruvate: High or Normal
- Muscle
- Fiber size: Varied
- Secondary lysosomes: Increased
- SDH & COX staining: Normal
- Subsarcolemmal aggregates of abnormal mitochondria
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Normal
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor in some patients
- EMG: Distal denervation in legs
- Brain MRI: General or Cerebellar atrophy; White matter loss; Ponto-Cerebellar hypoplasia
- Pathology: Reduced basal radial glia
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase 1 Alpha subcomplex, 6 (NDUFA6)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- NDUFA6 protein
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Complex I assembly
- Clinical
- Onset age: Prenatal to 2 years
- Prenatal: Growth retardation
- Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Arms & Legs
- Dysphagia
- May become severe
- Spasticity: Some patients
- Optic atrophy
- Seizures (50%)
- Course
- Progressive
- Some exacerbations with fever
- Death < 4 months in 50%
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis (75%)
- Brain MRI: Leukoencephalopathy; Atrophy
- Muscle
- Morphology: Normal
- Complex I
- Activity: Mildly reduced
- Assembly defect
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase 1 Alpha subcomplex, 8 (NDUFA8)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Arg47Cys, Arg98Leu
- NDUFA8 protein
- Mitochondrial inner membrane or intermembrane space
- Complex I assembly
- Clinical
- Onset ages: Infancy to 4 years
- Tone: Increased
- Developmental delay
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Muscle: Complex I deficiency; Citrate synthase high
- Brain MRI: Atrophy; Infarcts
● NADH-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Subunit B7 (NDUFB7)
- Epidemiology: 1 Iranian family
- Genetics
- Mutation: Intronic; IVS1, C-G, -10
- NDUFB7 protein
- Complex I subunit
- Mitochondrial intermembrane space
- Clinical
- Prenatal: Cardiomyopathy; Intrauterine anemia; Oligohydramnios
- Birth: Small for gestational age
- Cardiac: Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic; VSD & ASD
- Pulmonary hypertensioin
- Genital: Cryptorchidism; Hypospadias
- Death: 55 days
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Brain MRI: Cysts; Corpus callosum dysplasia
- Complex I deficiency
● Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 22, yeast, homolog of (TIMM22)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: Tyr25Ter; Val33Leu
- TIMM22 protein
- Inserts multispanning proteins into inner mitochondrial membrane
- Associated metabolite carriers & translocase subunits (TIM23, TIM17A/B)
- Hydrophilic, high-conductance channel
- Complex with: TIMM29; AGK
- Substrates: MPC1; MPC2
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Low birth weight
- Hypotonia
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzyme activities: Complex I, III & IV reduced
● Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein S25 (MRPS25)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; p.P72L
- MRPS25 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosomes: 28S
- Assembly or stability of the 28S subunit
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Clinical
- Onset age: 8 months
- Psychomotor delay
- Cerebral palsy: Tendon reflexes brisk
- Dyskinesia
- Weakness: Diffuse
- Skeletal: Short stature; Microcephaly
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Course: slow progression
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI
- Corpus callosum: Partial agenesis
- Under-development of frontal & parietal temporal regions
- Muscle
- COX staining reduced
- Complex IV mildly reduced
- COXPD
- Brain MRI
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
● Pentatricopeptide repeat domain-containing protein 3 (PTCD3)
- Epidemiology: 10 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Splicing (IVS6AS, A-G, -2); Stop (c.1747_1748insCT)
- Allelic disorder: Spastic ataxia with blindness
- PTCD3 protein
- Small ribosomal subunit protein mS39
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Associated with mitochondrial: 12S rRNA (MTRNR1)
 ; MRPS15
; MRPS15
- C-terminal: Consists of pentatricopeptide repeats (PPR) are necessary for interaction with RNA
- Expression: All tissues
- Functions
- Mitoribosomes
- Mitochondrial translation & respiration
- Forms entry channel of mitochondrial small (28S) ribosomal subunit (mt-SSU)
- Binds to single-stranded mRNA
- Other PPR disorder: LRPPRC
- Clinical: Leigh-like
- Onset: Intrauterine growth retardation to Infancy
- Motor
- Respiratory insufficiency
- Feeding: Disordered
- Movement disorders
- Limb rigidity
- Myoclonus
- Dystonia
- Cranial nerves
- Nystagmus
- Optic atrophy
- Deafness
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Seizures
- Hearing loss
- Death: 16 months to Teens
- Laboratory
- Fibroblasts: Complexes I & IV reduced
- Brain imaging: Lesions in medulla, cerebral peduncle, thalamus & basal ganglia
- EEG: Abnormal
- Muscle: COX- muscle fibers
- PTCD3 variant: Spastic ataxia with blindness
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop & Missense (His269Tyr)
- Clinical
- Onset: 2 years
- Eyes: Vision loss; Nystagmus, Horizontal;
- Ataxia: Gait disorder; Truncal; Tremor
- Spasticity: Tendon reflexes increased
- Non-ambulatory
- Cognitive decline
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Mildly high
- Brain MRI: Normal
- NCV: Polyneuropathy, Motor-Sensory
- Genetics
● NFS1 Cysteine Desulfurase 1 (NFS1)
- Epidemiology: 2 families; 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Arg72Gln
- NFS1 protein
- Fe-S clusters: Assembly
- Supplies inorganic sulfur in iron-sulfur clusters
- Locations: Mitochondria; Cytosol; Nucleus
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Episodic
- Encephalopathy: Lethargy; Hypotonia
- Motor delay
- Seizures
- Cardiac disorders: 2 patients
- Course: Often death < 1 year
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Liver enzymes: High
- Serum CK: High
- Hypoglycemia
- Plasma amino acids: High Alanine & Glycine + others
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Complex II & III ± I reduced
● Translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 70 yeast, homolog of A (TOMM70A)
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Heterozygous; Ile554Phe, Thr607Ile
- Allelic disorder: OXPHOS deficiencies, Recessive
- TOMM70 protein
- Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Receptor for transport of multi-spanning hydrophobic carrier proteins
- With help of cytosolic HSP70 & HSP90
- Recruits IP3R3 at ER-mitochondria contacts
- Regulates ER-mitochondrial Ca++ balance
- TOM70 complex coordinated with TIM22 complex
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 0 to 4 years
- CNS general: Developmental delay; Irritability
- Microcephaly
- Hypotonia
- Movement disorders: Choreoathetosis, Dystonia, Exaggerated startle response, Cog-wheeling
- Ataxia: Gait disorder; Dysarthria; Dysmetria
- Spasticity
- Course: Progressive decline, Associated with fever or head trauma
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Hypomyelination & White matter pathology, Cerebellar atrophy, Corpus callosum thin
- TOMM70 variant disorder: OXPHOS deficiencies, Recessive
252
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense; T265M, A582V
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Developmental delay
- Intellegence: Normal
- Skeletal: Growth reduced; Reduced head size
- Weakness: Mild
- Laboratory
- Anemia, severe
- Lactic acidosis
- Mitochondrial oxidative enzyme activities: Complex IV most reduced
● Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, mitochondrial (SHMT2)
- Epidemiology: 5 patients, 4 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Inframe deletion
- SHMT2 protein
- Transfers one-carbon units from serine to tetrahydrofolate (THF)
- Generates glycine & 5,10-methylene-THF
- Amino acid & folic acid metabolic pathways
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood
- Microcephaly
- Neurodevelopmental delay: Severe
- Spasticity: Legs
- CNS, other: Ataxia, Dystonia, Attention deficit-hyperactivity
- Eye: Strabismus; Saccades slow
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Polyneuropathy: Axonal, Distal, Sensory
- Dysmorphism: Face
- Skeletal: Low-set thumbs, Short fifth finger, 2-3 toe syndactyly
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Corpus callosum hypoplasia; Perisylvian polymicrogyria
- Muscle: Ragged red muscle fibers
● c2orf69
- Nosology: Elbracht-Isikay syndrome
- Epidemiology: 13 families; 28 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Loss-of-function; Truncating or Inframe deletion
- c2orf69 protein
- Homology: Esterases
- Mitochondrial associations
- Locations: Outer membrane (Cytosolic side) or Matrix
- Losely bound
- Affects mitochondrial membrane potential & oxidative respiration
- Interactions: SDHB; BOLA3; ETFA; KLHDC9; CMPK2
- Controls levels of glycogen branching enzyme 1 (GBE1)
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 3 months
- Failure to thrive
- CNS
- Developmental delay, global
- Seizures
- Spasticity: Some patients
- Microcephaly
- Short stature
- Muscle: Hypotonia; Wasting
- Episodes: Inflammatory
- Fever
- Osteomyelitis
- Arthritis
- Course: Lethal in early childhood (90% < 3 years)
- Laboratory
- C-reactive protein: High
- Anemia: Hypochromic; Microcytic
- Lactate: High in some patients
- Brain
- Leukoencephalopathy: CNS hypomyelination
- Cerebral atrophy
- Corpus callosum: Thin
- Muscle
- Subsarcolemmal mitochondria
- COX stain: Pale
- PAS stain
- Granular, Diastase resistant
- Polyglucosan bodies
- Similar features in liver or macrophages
- Oxidative enzyme activities reduced: Complex I, II, V ± IV
- Glycogen branching enzyme 1 (GBE1) activity: Reduced
- Reactive oxygen species (ROS): Increased
- Hepatopathy
● Inner membrane protein, Mitochondrial (IMMT; Mitofilin)
- Epidemiology: 2 cousiins
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Lys299Glu
- IMMT protein
- Mitochondrial membrane organization
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Mitochondrial inner membrane organizing system (MINOS)
- Interact with outer membrane protein complexes
- Deletion: Loss of crista junctions
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood
- Developmental encephalopathy
- Hypotonia
- Eye: Optic neuropathy; Nystagmus
- Seizures, focal
- Dystonia
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- Fiber sizes: Varied
- type 1 predominance
- SDH+ & COX- fibers
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Normal
- Ultrastructure
- Inner membrane & cristae replaced by tubular & membrane folds
- Concentric onion-bulb lamella layers
- Brain MRI: Globus pallidus small & T2 signal
- Visual evoked responses: Abnormal
- Serum lactate: High
- Urine: 3-Methylglutaconic Acid
- Muscle
● Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like protein (OGDHL)
- Epidemiology: 9 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Nonsense, Frameshift
- OGDHL protein

- Mitochondrial matrix
- OGDHC complex: OGDH, DLS2, DLD, OGDHL
- 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase
- Krebs TCA cycle
- Clinical: Spastic ataxia +
- Onset age: < 1 to 8 years
- Developmental delay: Intellect, Speech delay
- Motor: Hypotonia, Delayed walking
- Cerebellar: Gait ataxia; Tremor, Dysmetria
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Hearing loss: Some patients
- Eye: Retinopathy, Myopia, Central visual impairment, Optic atrophy, Nystagmus
- Skeletal: Scoliosis, Hip dysplasia, Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal, Thin corpus callosum, or Atrophy
● Protein only RNase P catalytic subunit (PRORP; MRPP3)
- Epidemiology: 8 patients; 4 families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Type: Missense & 1 bp duplication
- Location: Metallonuclease domain of PRORP
- Allelic disorder: Variance in posttranscriptional modification of functionally important sites in mitochondrial transfer RNAs
- Mutations
- PRORP protein
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Cell localization: Afferent & efferent synapses; Axons around inner hair cells
- Endonuclease subunit of mitochondrial ribonuclease (RNase) P complex

- tRNA maturation: Removes extra nucleotides from 5-prime termini of tRNA
- Partially co-localizes with SNAP25
- mt-RNase P complex
- Clinical
- General: Perrault-like syndrome
- Onset: Infancy
- Sensorineural hearing loss
- Primary amenorrhea + Absent ovarian tissue
- CNS
- Intellectual disability
- Seizures
- Laboratory
- Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism
- Serum lactate: Often normal
- Brain MRI: White matter pathology
● Polymerase, RNA, Mitochondrial (POLRMT; mtRNAP)
- Epidemiology: 15 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense: Common
- Allelic disorder: PEO, Dominant
- POLRMT protein
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Transcription & Replication

- Only mitochondrial primase
- Mitochondrial transcription initiation complex
- TFAM recruits POLRMT to a specific promoter
- TFB2M induces structural changes in POLRMT
- Enables promoter opening & trapping of DNA non-template strand
- TEFM: Required by POLRMT for transcription elongation stage
- Transcription & Replication
- Mutations: Imparied mRNA synthesis
- Mitochondrial DNA
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant to Early childhood
- Developmental delay: Global; Motor; Language; Social; Intellectual
- BMI: Low (70%)
- Hypotonia (60%)
- Weakness (Proximal) (40%)
- PEO (40%)
- Gastrointestinal (40%)
- Short stature (60%)
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Normal or some COX- fibers; Mild Complex I & III ↓; Lipid ↑ 1 patient
- Serum CK: Mildly high
- POLRMT variant: PEO, Dominant
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Deletion, Gly881_Lys883del, Heterozygous
- Inheritance: Dominant or de novo
- Clinical
- Onset age: 4th decade
- Eyes: PEO (All directions); Ptosis
- Course: Slow progression over 20 years
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Many COX- & some RRF; Complex I & IV reduction, mild
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Serum CK & Lactate: Normal
● Transcription elongation factor, mitochondrial (TEFM)
- Epidemiology: 5 families, 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Deletion (c.484_489del), Point
- Allelic disorder: Myopathy + NMJ disorder
- TEFM protein
- Nuclear-encoded mitochondrial protein
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Regulates transcription of mitochondrial genome
- Complexes with: Mitochondrial RNA polymerase (POLRMT)
- Enhances POLRMT processivity on single- & double-stranded DNA
- Increases mitochondrial RNA polymerase processivity
- Interacts with: DNA downstream of elongation complex; G-quadruplex region of mtRNA
- Knockdown: Reduced abundance of mitochondrial complex IV subunit COX2
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal to 2.5 years
- Disease severity: Varied within & among families
- Developmental delay: Intellectual disability
- Hypotonia (50%): Mild
- Eyes: Nystagmus; Optic atrophy (2 patients); Strabismus
- Face: Dysmorphism
- Seizures (1 patient)
- Weakness: No
- Course: Rapid progression to Stationary
- Laboratory
- Hypoglycemia
- Plasm lactate: High
- Brain MRI: Normal or Cerebellar atrophy (1 patient)
- Muscle: Complex IV ↓
- TEFM variant: Myopathy, NMJ disorder, Epilepsy
- Epidemiology: 1 family, 2 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutation: Homozygous; Pro157Ala
- Clinical
- Onset Age: 1st decade
- Hypotonia
- Weakness
- Proximal
- Eye: PEO; Ophthalmoparesis, Ptosis
- Face
- Fatigable
- Gait impaired
- Ataxia: Gait
- Cognitive Δ: 50%
- Seizures: Onset 2nd decade
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- Plasma lactate: High
- Repetitive nerve stimulation: Decrement
- Muscle pathology: COX- muscle fibers; Complex IV ↓ + Mild complex I ↓
- Brain MRI: Periventricular gliosis
- EEG: Slowing
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L 39 (MRPL39)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Misense; Splice; Stop
- Milder disease: Homozygous missense mutation
- MRPL39 protein
- Component of: Mitochondrial ribosome
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy or Early childhood
- Developmental delay
- Seizures
- Apnea
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Hypoglycemia
- Brain MRI: Basal ganglia Δ
● Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L 49 (MRPL49)
- Epidemiology: 13 patients; 9 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense, Few stop
- MRPL49 protein
- Mitochondrial ribosome, component of large subunit
- Clinical
- General
- Perrault syndrome
- Childhood leukodystrophy
- Onset age: Infancy to early childhood
- Intellectual development, impaired
- Microcephaly
- Retinal dystrophy
- Hearing loss, Sensorineural hearing loss
- Ovarian insufficiency, primary
- General
- Laboratory
- Fibroblasts: Reduced complex I & IV expression
- Brain MRI: Signal in globus pallidus, deep white matter or brainstem; Cerebellar atrophy
● 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase X (HSD17B10: HSD10; HADH2)
- Epidemiology: > 10 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense
- Female carriers: Mild phenotype
- HSD17B10 protein
- Mitochondrial matrix enzyme
- Multifunctional moonlighting protein: Involvement in multiple biochemical pathways
- Isoleucine metabolism
- Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase: Preference for short-chain methyl-branched acyl-CoA
- Subunit of mt-RNase P complex
- tRNA maturation; Removes extra nucleotides from 5-prime termini of tRNA precursors
- Disease: Defects of mitochondrial tRNA processing
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal to Childhood
- Cardiomyopathy: Hypertrophic Severe disease
- Developmental regression
- Seizures
- Choreoathetosis
- Spastic tetraplegia
- Eye: Optic atrophy; Retinal degeneration
- Laboratory
- Urine: Isoleucine metabolites high
- Lactic acidosis
● Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase, mitochondrial (TAMM41)
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- TAMM41 protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane: Extrinsic component
- CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthesis
- Phosphatidic acid → CDP-diacylglycerol
- Step in biosynthesis: Phosphatidylglycerol & Cardiolipin (1,3-bis(3-phosphatidyl)glycerol)

- Mitochondrial
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Lethargy
- Hypotonia
- Delay: Motor & Cognitive
- Weakness: Proximal ± Distal; Dysphagia
- Eyes: Ptosis ± PEO
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Muscle
- Cardiolipin: Reduced
- Mitochondrial complex activities: Complexes I, III, IV reduced
● Cardiolipin Synthase (CRLS1)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients, 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense
- CRLS1 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Catalyzes synthesis of: Cardiolipin (CL) (diphosphatidylglycerol)

- Transfers phosphatidyl group from CDP-diacylglycerol to phosphatidylglycerol (PG)
- Cardiolipin
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Encephalopathy
- Hypotonia, Central
- Extrapyramidal: Myoclonus; Dystonia
- Seizures
- Bulbar dysfunction
- Autonomic instability
- Auditory neuropathy
- Eye: Bull's eye maculopathy
- Cardiac
- Left ventricular noncompaction
- Civentricular systolic dysfunction
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebral atrophy
- Respiratory chain activities: Complex IV deficiency with milder changes in I & III
● Leucine zipper/EF-hand-containing transmembrane protein 1 (LETM1; SLC55A1)
- Nosology: Childhood-Onset Neurodegeneration + Multisystem involvement due to Mitochondrial dysfunction (CONDMIM)
- Epidemiology: 18 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Loss of function
- LETM1 protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Osmoregulatory
- K+-H+ exchanger
- Regulation of uptake or extrusion of Ca++
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant; Birth to 2 years
- Global developmental delay (94%)
- Optic atrophy (83%)
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural (78%)
- Hypotonia
- Cerebellar ataxia (78%)
- Epilepsy (67%)
- Spasticity (53%)
- Myopathy (50%)
- Skeletal: Small Weight & Height
- Peripheral neuropathy (15%)
- Course: Progression in some
- Laboratory
- Mitochondrial complex deficiencies: Multiple
- Lactic acidosis (50%)
- 3-MGA high in urine (40%)
● Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (PYCR2)
- Epidemiology: 13 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Stop; Splice
- PYCR2 protein
- Proline biosynthesis
- Reduces pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) to L-proline using NADH as cofactor
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Loss of PYCR2: Increased susceptibility to apoptosis under oxidative stress.
- Clinical
- Onset: Birth
- Failure to thrive
- Face: Dysmorphic
- Hypotonia
- Spasticity
- Hearing loss
- Seizures (50%)
- Skeletal: Arachnodactyly
- Course: Progressive; Death < 10 years
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Atrophy, General; Hypomyelination; Corpus callosum thin
● Cytochrome c Oxidase Assembly Factor COX18 (COX18)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homozygous; Missense (Asp223His), Splice site (c.598G>A)
- Allelic disorder: CMT 2MM/Peripheral Neuropathy
- COX18 protein
- Mitochondrial: Inner membrane
- Transmembrane protein: Oxa1/YidC/Alb3 family of membrane protein insertases
- Function
- Assembly factor of mitochondrial Complex IV
- Maturation of MT-CO2 (COX-II) subunit
- Facilitates export of COX2 C-terminal across inner mitochondrial membrane
- Onset age: Neonatal & 7 months
- Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic
- Myopathy: Weakness
- Neuropathy: Axonal
- Orofacial apraxia
- Muscle
- Denervation: Grouped atrophy; Nuclear clumps
- Type I: Predominance
- COX: Reduced staining, diffusely
- Complex IV: Reduced activity, moderate
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondrial pathology
- Serum CK: Normal
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor; Small CMAPs & SNAPs
- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: c.435-6A>G (Splice variant), Leu72Arg, Ala110Pro, Arg297Pro
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy to Adult
- Weakness: Distal; Legs > Arms
- Sensory loss: Pan-modal; Distal
- Tendon reflexes: Often Reduced
- Plantar response: Often mute
- Foot deformities: Pes equinovarus; Hammer toes
- Upper motor neuron features: 1 family
- Course: Slow progression
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss; SNAPs absent
- Brain MRI: Usually normal
● Protein-tyrosine phosphatase, mitochondrial, 1 (PTPMT1)
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Splice
- PTPMT1 protein
- Cardiolipin synthesis
- Mitochondrial tyrosine phosphatase
- Location: Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal/Infantile
- Developmental delay
- Microcephaly
- Face: Dysmorphism
- Epilepsy
- Spasticity
- Cerebellum: Ataxia; Nystagmus,
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural
- Optic atrophy
- Bulbar dysfunction
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: White matter Δ & Corpus callosum thin; Cerebellar atrophy
● Mitochondrial nucleoid-associated protein 1 1 (MTNAP1; c17orf80)
- Epidemiology: 2 families, 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Gly553Arg, Tyr13X; Homozygous
- MTNAP1 protein
- Mitochondria: Nucleoids; Inner Membranes; Matrix
- Maintains mtDNA abundance
- Mutations
- Aberrant aggregation
- Mitochondrial fragmentation
- Oxidative phosphorylation capacity: Reduced increased
- Reactive oxygen species: Acumulation
- Premature senescence-like stress responses
- Clinical
- Developmental delay, Global: Cognitive, Speech, Language
- Ataxia
- Spasticity
- Seizures
- Course: Progressive neurological decline
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy; Corpus callosum thin
● Cytidine Monophosphate (UMP-CMP) Kinase 2, Mitochondrial (CMPK2)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients, 2 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense (Tyr414Cys); Single nucleotide substitutions
- CMPK2 protein
- Mitochondrial UMP-CMP kinase


- Component of: Salvage pathway for nucleotide synthesis
- Nucleotide Synthesis Salvage pathway proteins: Other
- Controls mitochondrial DNA synthesis by supplying required deoxyribonucleotides
- Mediates immunomodulatory & anti-viral activities
- Mitochondrial UMP-CMP kinase
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3rd & 4th decades
- Motor: Dysfunction; Movements
- Speech disorder
- Cognition: Impaired
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain CT: Calcification in bilateral globus pallidus, thalamus & cerebellum
- Serum calcium & phosphate levels: Normal
Mitochondrial syndromes: Childhood Onset
- MC4DN11: Ataxia, Pyramidal syndrome &
Cytochrome oxidase deficiency
 151
151
● FAM36A (Cytochrome c oxidase 20; COX20) ; Chromosome 1q44; Recessive
; Chromosome 1q44; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 27 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; Homozygous; c.154A>C; Thr52Pro
- Allelic disorders
- Infant-onset hypotonia, No neuropathy
- Ataxia, Dystonia & Polyneuropathy
- Sensory Neuronopathy
- Sensory-dominant axonal neuropathy & Static encephalopathy
- COX20 (FAM36A) protein
- Mitochondrial; Complex IV
- Interacts with: MTCO2
- Stabilizes newly synthesized catalytic core subunit COX2
- Interacts with SCO1 & SCO2 metallochaperones in maturation of COX2 redox center
- Mutation: Reduced incorporation of COX2 subunit into complex IV
- Clinical: Infant-onset syndrome
- Pregnancy: Oligohydramnios; Growth retardation
- Birth weight: Low
- Hypotonia: 1 year
- Speech development: Delayed
- Ataxia: Unsteady gait; Intention tremor
- Pyramidal signs
- Short stature
- Course: Non-progressive to age 10
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Mildly high in serum & CSF
- Muscle: Complex IV deficiency
- MRI: Normal
- EEG: Normal
- COX20 variant syndrome: Ataxia, Dystonia & Polyneuropathy
167
- Epidemiology: > 10 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Thr52Pro; Trp74Cys; Lys14Arg
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood to 12 years
- Ataxia
- Dysarthria
- Gait diaorder
- Extrapyramidal
- Dystonia: Cervical & Leg; Torticollis; Dysarthria
- Choreoathetosis
- Intellectual disability
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory: Loss (Panmodal); Dysesthesias
- Weakness: Distal; Legs or Arms
- Wasting: Distal limbs
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Course
- Episodic: Worsening & Plateau phases
- Laboratory
- MRI: Cerebellar vermis atrophy, Mild
- Serum lactate: Mildly high
- Serum CK: Mildly high or Normal
- NCV: Axonal sensory-motor neuropathy
- EMG: Chronic denervation
- Muscle
- Mitochondria: Large & Abundant
- Complex IV deficiency: 25% of normal
- Coenzyme Q10: Low
- Nerve pathology
- Myelinated axons: Reduced numbers
- Axon mitochondria: Vacuolar
- COX20 variant syndrome: Sensory Neuronopathy
268
- Epidemiology: 8 Chinese families; 14 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Lys14Arg (Common; Founder), Trp74Cys, Ser33Leu, Gln87X
- Clinical
- Onset age: Mean 8 years; Range 1 to 17 years
- Sensory
- Ataxia: Impaired gait
- Vibration sensation: Reduced
- Weakness: Mild; Distal; Legs > Arms
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Pes cavus
- Laboratory
- NCV: SNAPs reduced amplitude
- Spinal MRI: Spinal cord atrophy
- Brain MRI: Usually normal
- CSF: Normal
- Serum CK: Normal
- Nerve pathology: Myelinated axon loss
- Muscle pathology: Mitochondrial ultrastructural Δ
- Ataxia, Pyramidal syndrome &
Cytochrome oxidase deficiency (MC4DN3)

● COX10 (Heme A:farnesyltransferase) ; Chromosome 17p12; Recessive
; Chromosome 17p12; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations
- Missense
- Asp204Lys; Thr196Lys; Pro225Leu; Asp336Val; Asp336Gly
- Allelic with
- Myopathy, Neuropathy & Multisystem disease
- COX10 may be mutated with HNPP deletion
- Mutations
- Protein
- Complex IV
- Functions
- Required for biogenesis of functional cytochrome c oxidase
- Farnesylates protoheme (heme B) to heme O in the heme A biosynthetic pathway
- Location: Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 2 to 18 months
- Ataxia
- General syndrome: Leigh syndrome or Encephalopathy
- Motor
- Weakness
- Hypotonia
- Pyramidal syndrome
- Other CNS
- Ataxia
- Status epilepticus
- Ptosis
- Other systemic
- Cardiomyopathy: 1 patient
- Splenomegaly
- Course: Death at 1 to 2 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Increased in Blood & CSF
- Increased Urinary amino acids: Suggests proximal renal tubulopathy
- Anemia
- Biochemistry: Isolated deficiency of cytochrome oxidase (COX)
- Tissues: Muscle, Lymphocytes, Fibroblasts
- Selective reduction of Subunit II by Western blot analysis
- MRI: Basal ganglia or Thalamic lesions
- COX10 variant syndrome: Myopathy, Neuropathy & Multisystem disease
166
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- COX 10 mutations: Missense; Asp336Val, Arg339Trp
- Clinical
- Onset
- Infancy: Poor weight gain
- Short stature
- Exercise intolerance
- Myopathy
- Exercise intolerance
- Weakness: Proximal
- Demyelinating neuropathy: Tendon reflexes absent
- Ovarian failure, premature
- Short stature
- Hearing loss: Mild; Asymmetric
- Pigmentary maculopathy
- Renal tubular dysfunction: Fanconi syndrome; Metabolic acidosis
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle COX
- Activity: Reduced
- COX holoenzyme: Absent
- Staining: Reduced in most muscle fibers
- Serum lactate: High
- Brain MRI: Normal
- EMG: Myopathic
- Nerve biopsy: Axon loss; Myelin sheaths thin; Schwann cell Golgi inclusinos
- Muscle COX
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2, mitochondrial deficiency (HMGCSD2)

● HMGCS2 ;
Chromosome 1p12; Recessive
;
Chromosome 1p12; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Stop
- HMGCS2 Protein
- Mitochondrial matrix protein
- Mediates early step in ketogenesis
- Long chain fatty acid oxidation
- Clinical
- Onset: 1st decade; 11 months & 6 years
- Encephalopathy or Seizures: Episodic
- After prolonged fasting
- Associated with hypoglycemia
- Treatment
- Carnitine
- Avoid fasting
- Laboratory
- Hypoglycemia with fasting
- No rise in ketone bodies during fasting or after long chain fat load
- Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE1; IIAE3)

● Ran-binding protein 2 (RANBP2) ; 2q12.3; Dominant
; 2q12.3; Dominant
- Epidemiology: 13 families
- Genetic
- Dominant with incomplete penetrance
- Mutations: Heterozygous; Thr585Met; Thr653Ile; Ile656Val
- RANBP2 protein
- Onset
- Acute
- Altered mental status
- Age: Usually < 4 years; Range 8 months to 6 years
- Prodrome: Febrile illness (94%); URI (50%)
- Clinical
- Initial development: Normal
- Vomiting (30%)
- CNS
- Seizures (50%)
- Tone: Spasticity; Rigidity; Abnormal posturing,
- Altered mental status: Usually leading to coma
- Breathing patterns: Abnormal (25%); Hypopnea, Apnea, CheyneStokes
- Hemiparesis: (12%)
- Course
- Death in 20%
- Relapses
- Some patients
- Age: Usually < 6 years; Range 3 to 27 years
- Triggered by: Infections
- Time from previous episode: Usually 6 months to 3 years
- Residual disability: Common
- Full recovery in 36%
- More disability after recurrent episodes
- Types
- Weakness
- Seizures
- Gait abnormalities
- Speech disturbance
- Mental retardation
- Mood disorders
- Difference from Leigh encephalopathy: No chronic course
- Pathology
- Cerebral edema
- Hemorrhagic lesions
- Perivascular
- Thalamus; Putamen; Brain stem
- Microgliosis
- No inflammation
- MRI
- Symmetric T2-weighted hyperintensities
- Localization: Cortex; Thalamus; Brainstem
- Muscle biopsy
- Light microscopy: Normal
- Ultrastructure: Pleomorphic mitochondria
- Biochemistry
- Loose coupling of oxidative phosphorylation: High O2 consumption when ADP depleted
- Electron transport chain complexes I to IV & Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: Normal
- Leukodystrophy, Cavitating
(MC4DN17)
 (Complex IV)
179
(Complex IV)
179
● Apoptogenic protein 1, mitochondrial (APOPT1; APOP1; C14orf153)
 ; Chromosome 14q32.33; Recessive
; Chromosome 14q32.33; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 6 patients, 5 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Truncation
- APOPT1 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial
- Apoptosis regulation
- Mediates mitochondria-induced cell death in vascular smooth muscle cells
- Regulates release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
- Clinical: More severe during episodes
- Onset
- Age: 2 to 5 years
- Regression episode: Acute onset
- Spastic tetraparesis
- Ataxia
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory-Motor
- Cognition: Normal or Reduced
- Course: Episodic; 1 or several regressions
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle
- COX stain: Reduced
- SDH stain: Normal
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Complex IV reduced (3% to 25%)
- Ultrastructure: Mitochondria large with osmophilic inclusions
- Brain MRI
- Cavitating leukodystrophy: Posterior cerebral white matter; Corpus callosum
- Muscle
- Pantothenate kinaseassociated neurodegeneration (PKAN; Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome; NBIA1)
 40
40
● Pantothenate kinase 2 (PANK2) ; Chromosome 20p13; Recessive
; Chromosome 20p13; Recessive
- Nosology
- Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 1 (NBIA1)
- Also see: NBIA2A & Neuroaxonal dystrophy
- Genetics
- Early-onset, rapidly progressive disease: Associated with null mutations
- More mild disease with later age at onset: Missense mutations; Likely to retain partial enzyme function
- Pantothenate kinase (PANK2) protein
- Regulatory enzyme in biosynthesis of coenzyme A (CoA)
- CoA roles: Energy metabolism; Fatty acid synthesis & degradation; Neurotransmitter & glutathione metabolism
- PANK2 subcellular location: Mitochondrial intermembrane space
- See: Iron disorders
- Typical PKAN phenotype
- Onset
- Age: 1st decade; Mean 3 to 4 years
- Gait abnormality
- Clinical
- Extrapyramidal: Dystonia, Dysarthria, Rigidity
- Corticospinal: Spasticity, Hyperreflexia, Extensor toe signs
- Ocular
- Pigmentary retinopathy: Two thirds of childhood cases
- Optic atrophy
- Progression
- Rapid
- Lose ability to ambulate independently within 10 to 15 years of onset
- Intermittent periods of rapid, often precipitous, clinical deterioration
- Variant subgroup
- Hypoprebetalipoproteinemia, Acanthocytosis, Retinopathy & Pallidal degeneration (HARP)
- Onset
- Atypical PKAN
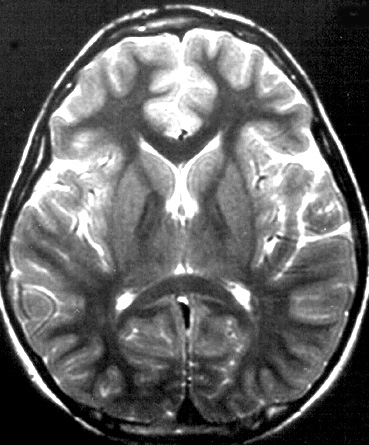
- Onset
- Mean 13 to 14 years
- Neurobehavioral disorders
- Clinical
- Behavioral
- Mood: Depression, Emotional lability
- Personality changes
- Cognitive decline
- Speech disorders
- Palilalia & Tachylalia
- Hypophonia
- Difficulty initiating speech
- Extrapyramidal
- Dystonia
- Rigidity
- Corticospinal: Spasticity
- Behavioral
- Progression
- Slower than typical form
- Loss of independent ambulation after 15 to 40 years
- Intermittent periods of rapid clinical deterioration
- Onset
- MRI: Globus pallidus on T2-weighted images
- Central region of hyperintensity
- Primary tissue insult
- Produces edema
- Surrounding hypointensity
- Region high in iron
- May be 2° process
- "Eye-of-the-tiger" sign
- Central region of hyperintensity
- Pathology
- Deposition of iron
- Especially globus pallidus & retina
- Other iron deposition disorders
- Karak syndrome

- Neuroferritinopathy
 :
FTL
:
FTL

- Aceruloplasminemia
 :
Ceruloplasmin
:
Ceruloplasmin

- Friedreich ataxia
 : Frataxin
: Frataxin - MPAN
- Karak syndrome
- Axonal spheroids: In regions of iron deposition
- Deposition of iron
- Other laboratory features
- Acanthocytosis
- Hypoprebetalipoproteinemia
- Serum CK: May be high or normal
- Muscle
- Scattered fiber necrosis
- Macrophage activation
- Mitochondrial: Reduced COX staining
- Nosology
- Mitochondrial Membrane Protein Associated Neurodegeneration (MPAN; NBIA4)
 124
124
● C19orf12
 ; Chromosome 19q12; Recessive
; Chromosome 19q12; Recessive
- Nosology: Subtype of Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation (NBIA)
- Epidemiology: Common cause of NBIA
- Genetics
- Common mutation in Poland: 11 base pair deletion (Gly69ArgfsX10)
- Other mutations: Often missense; Thr11Met
- More severe disease: Nonsense or frame-shift mutations
- Allelic disorders
- SPG43
- Distal Motor Neuropathy & Optic atrophy 270
- C19orf12 protein
- Cell location: Mitochondrial membrane
- Location: Brain, Blood cells, Adipocytes
- Possible functions
- Fatty acid biogenesis
- Valine, leucine & isoleucine degradation
- See: Iron disorders
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Range 3 to 29 years; Mean 9 years
- Gait disorder
- Speech changes: Dysarthria
- Extrapyramidal (60%)
- Dystonia: Oromandibular & Generalized
- Parkinsonism: Unresponsive to L-DOPA
- Pyramidal (80%)
- Spasticity
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Plantar reflex: Extensor
- Motor neuropathy
- Mild or Severe
- Weakness: Distal > Proximal
- Axonal
- Eye
- Optic atrophy
- Slow, saccadic movements
- Cortical (80%)
- Cognitive loss
- Psychiatric signs
- Course
- Progressive
- Loss of ambulation by 18 to 31 years
- Occasional rapid course: Death in 1 to 3 years after onset
- Onset
- Laboratory
- EMG: Motor axonopathy (40%)
- NCV: CMAP amplitudes small
- Serum CK: High
- Muscle: Grouped atrophy
- MRI (T2-weighted)
- Globus pallidus & Substantia nigra: Hypointensities
- No hyperintensity in anteromedial region of the globus pallidus ("Eye of the tiger" sign)
- Cerebellar atrophy
- Globus pallidus & Substantia nigra: Hypointensities
- Brain pathology
- Iron-containing deposits: Globus pallidus & Substantia nigra
- Axonal spheroids, numerous
- Lewy bodies: α-synuclein-positive
- Tract lesions: Pyramidal; Optic
- Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation 6 (NBIA6)
 171
171
● CoA Synthase (COASY) ; Chromosome 17q21.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 17q21.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 Italian patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Arg499Cys; Gln59*
- Allelic disorder: PCH12
- COASY protein
- Mitochondiral matrix
- Bifunctional enzyme
- Converts 4'-phosphopantetheine into Dephospho-CoA and then to Coenzyme A
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 1 to 2 lyears
- Gait difficulty
- Spastic paraparesis
- Gait disorder
- Legs > Arms
- Extrapyramidal
- Oro-mandibular dystonia
- Bradykinesia
- Rigidity
- Cognitive
- Impairment: Severe
- Obsessive-compulsive symptoms
- Depression
- Peripheral nerve
- Amyotrophy: Distal
- Tendon reflexes; Absent in legs
- Pes cavus
- Course
- Progressive
- Loss of ambulation in 2nd or 3rd decade
- Onset
- Laboratory
- EMG & NCV: Motor axonopathy
- Brain MRI
- Globus pallidus: Bilateral hypointensity; Central anteromedial hyperintensity
- COASY variant: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia 12 (PCH12)
 291
291
- Epidemiology: 7 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations
- Loss of function
- Asian Indian: c.1486-3C>G
- Clinical
- Polyhydramnios: Few patients
- Skeletal
- Arthrogryposis: Contractures, multiple
- Microcephaly
- Growth restriction
- Micrognathia
- Postnatal
- Apnea
- Seizures
- Spasticity
- Death: in utero or < 1 month
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Microcephaly, Cerebellar hypoplasia, Cortical atrophy
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 3 (MC3DN3) (Complex III)

● Ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase-binding protein (UQCRB) ; Chromosome 8q22.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 8q22.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Sporadic Turkish female
- Genetics: Homozygous 4 base pair deletion
- UQCRB protein
- Plays role in electron transfer: Complex of ubiquinone & QP-C
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 8 months
- Episode of acute gastroenteritis
- Moderate liver enlargement: Resolved over time
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Episodic hypoglycemia with metabolic acidosis: Provoked by fasting
- Complex III deficiency
- Transaminase levels: Mildly elevated
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 4 (MC3DN4) (Complex III)
 81
81
● Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase, complex III subunit VII (UQCRQ)
 ; Chromosome 5q31.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 5q31.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Israeli Bedouin kindred
- Genetics: Missense mutation; Ser45Phe
- UQCRQ protein
- Protein component of mitochondrial Complex III
- Intermembrane space protein
- Onset
- Age: Months
- Delayed development
- Clinical
- Psychomotor retardation: Severe
- Dementia: Marked; Defects in verbal & expressive communication skills
- Extrapyramidal: Dystonia, Athetosis
- Ataxia
- Tone
- Axial: Hypotonia, Mild
- Limbs: Increased
- Tendon reflexes: Increased
- Course: Not lethal
- Laboratory
- Lactate: Mildly elevated levels in blood
- MRI: Putamen increased density; Caudate & lentiform nuclei decreased density
- Muscle
- Histochemistry: Non-specific; Varied fiber size; Immature muscle fibers
- Reduced mitochondrial Complex III activity; Variable decrease in complex I
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 5 (MC3DN5) (Complex III)

● Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein II (UQCRC2) ; Chromosome 16p12.2; Recessive
; Chromosome 16p12.2; Recessive
- Epidemiology: Mexican & French-Canadian families
- Mutation: Arg183Trp
- UQCRC2 protein
- Required for Complex III assembly
- Clinical
- Onset
- Neonatal
- Episodes of metabolic acidosis
- Multiple episodes: Often associated with illness
- Poor suck
- Tachypnea
- Growth & Development: Normal to mildly delayed
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis: Lactate high during episodes
- Liver failure: Hyperammonemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Complex III deficiency
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type (Complex III):
Insulin-Responsive Hyperglycemia & Encephalopathy (MC3DN6)
 163
163
● Cytochrome C1 (CYC1) ; Chromosome 8q24.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 8q24.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Trp96Cys, Leu215Phe, Arg317Trp
- CYC1 protein
- Heme-containing component of complex III
- Mediates transfer of electrons from the Rieske iron-sulfur protein to cytochrome c
- Affected individuals: CYC1 10% of normal in skeletal muscle & fibroblasts
- Clinical
- Onset age: 5 months to 10 years
- Vomiting & Encephalopthy: Episodic
- Polypnea
- Optic neuropathy: Relapsing
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory-Motor
- Treatment: Insulin
- Laboratory
- Metabolic keto acidosis
- Lactic acidemia
- Hyperglycemia
- Hyperammonemia
- Liver failure
- Muscle
- Complex III: Reduced activity & Amount
- CSF: Protein & Lactate high
- Brain MRI: Leukoencephalopathy
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 7 (Complex III):
Encephalopathy (MC3DN7)

● Ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase complex assembly factor 2 (UQCC2) ; Chromosome 6p21.31; Recessive
; Chromosome 6p21.31; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Intron 2 splice site (IVS2AS, C-G, -3), Homozygous
- UQCC2 protein
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Mitochondrial complex III assembly factor
- Cooperates with UQCC1

- Mediates cytochrome b (MTCYB)
 protein expression
protein expression
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Encephalopathy
- Dysmorphic features, mild
- Psychomotor development: Delayed, Lack of meaningful speech
- Autistic features & Aggressive behavior
- Seizures, infrequent
- Sensorineural hearing loss, mild
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis: Severe; Increased serum & CSF lactate
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Muscle: Complex III deficiency (9% of controls)
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 8 (Complex III):
Encephalopathy (MC3DN8)
 305
305
● LYR motif-containing protein 7 (LYRM7; MZM1L) ; Chromosome 5q23; Recessive
; Chromosome 5q23; Recessive
- Epidemiology: > 20 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Asp25Asn, c.243_244 + 2del, c.25C>T; c.2T>C
- LYRM7 protein
- Soluble
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Chaperone
- Stabilizes Fe-S cluster Rieske protein (UQCRFS1
 ) in matrix
) in matrix
- Precedes UQCRFS1 translocation from matrix to inner mitochondrial membrane
- Stabilizes Fe-S cluster Rieske protein (UQCRFS1
- LYR (lysine, tyrosine, and arginine) motif
- Facilitates incorporation of Fe-S cluster within Rieske (UQCRFS1/Rip1) protein
- Interacts with co-chaperone protein HSC20 (HSCB)

- cIII assembly factor
- LYRM7-deficient mitochondria
- Temperature elevation leads to misfolding of UQCRFS1
- Clinical: Recurrent encephalopathy
- Onset
- Age: 9 months to 27 years
- Febrile illness
- Acute or Subacute
- Developmental delay
- Neurologic
- Weakness: Rapidly progressive
- Motor defecits
- Weakness (70%)
- Reduced movement
- Cranial nerves
- Dysarthria or Dysphagia: Some patients
- Face weakness
- Eyes: Ptosis; Ophthalmoplegia; Vision loss (Optic atrophy)
- Spastic
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Tone: Increased
- Gait
- Tetraparesis: Few patients
- Psychomotor: Delayed or Regression
- Polypnea
- Sensation: Normal
- Course
- Episodes
- Repeated
- Febrile prodrome
- Stroke-like
- Lactic acidosis
- Death: 2 to 7 years in 2 patients; Respiratory failure
- Episodes
- Possible treatment: Thiamine, Arginine, Carnitine, Biotin, CoQ10
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Anemia: Low iron
- Lactic acidosis
- Muscle biopsy
- Aggregates
- Complex III deficiency, Isolated: Mild to Severe
- LYRM7 protein: Reduced
- Serum CK: Normal
- Brain MRI
- White matter: Leukoencephalopathy
- Demyelination
- Vacuolization, Cysts, or Cavitations: Some patients
- Spinal cord: Abnormal signal
- Global atrophy
- Corpus callosum: Thin
- White matter: Leukoencephalopathy
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 9 (Complex III):
Encephalopathy (MC3DN9)

● Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex assembly factor 3 (C11orf83, UQCC3, CBP4) ; Chromosome 11q12.3; Recessive
; Chromosome 11q12.3; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.59T>A (p.Val20Glu); Homozygous
- UQCC3 protein
- Localization
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- C-terminus in inter-membrane space
- Cytochrome bc1 complex assembly factor
- Cytochrome b stabilization/assembly: Mayp require IMS-localized components
- Localization
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth
- Hypotonia
- Delayed development: IQ 70
- Motor: Weakness; Fatigue
- Growth delay
- Course: Slow improvement
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Hypoglycemia
- Brain MRI: Normal
- Muscle: Complex III activity reduced by 87%
- Mitochondrial complex III deficiency, nuclear type 11 (Complex III):
Encephalopathy, Episodic (MC3DN11)

● Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase, Hinge protein (UQCRH) ; Chromosome 1p33; Recessive
; Chromosome 1p33; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 1 British Pakistani family; 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Exon 2 & 3 deletion (In frame)
- UQCRH protein
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Complex III
- Minor subunit of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex
- 'Hinges' (Links) cytochrome c (CYCS)
 with cytochrome c1 (CYC1)
with cytochrome c1 (CYC1)

- Formation of cytochrome c-cytochrome c1 complex
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 to 3 years
- Encephalopathy
- Episodic
- Vomiting
- Precipitants: Upper respiratory infections
- Treatment: IV fluids
- Between episodes: Normal
- Laboratory
- During episodes
- Lactic acidosis
- Hyperammonemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Fibroblasts
- Complex III activity reduced
- UQCRH: Reduced
- During episodes
- Cardiomyopathy + Encephalopathy (MC1DN11)
 84
84
● NADH-Ubiquinone oxidoreductase 1 alpha subcomplex, assembly factor 1 (NDUFAF1; CIA30) ; Chromosome 15q15.1; Recessive
; Chromosome 15q15.1; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 2 children, Australian & French
- Genetics: Mutations
- Missense
- Thr207Pro; Lys253Arg
- NDUFAF1 protein
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 11 months
- Hypotonia
- Cardiac
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Wolff-Parkinson-White
- CNS
- Mental retardation
- Cortical visual dysfunction
- Muscle
- Atrophy
- Hypotonia
- Eye: Pigmentary retinopathy
- Skeletal: Kyphoscoliosis
- Contractures: Flexion of 5th fingers
- Skin: Hirsute
- Course: Survival to adulthood
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Serum lactate: High
- Fibroblasts: Complex I deficiency
- Encephalomyopathy/Leukoencephalopathy (MC1DN21)
 114
114
● Nucleotide-binding protein-like (NUBPL)
 ; Chromosome 14q12; Recessive
; Chromosome 14q12; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 19 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Gly56Arg; Asp105Tyr; Met117Ile; Leu193Phe; Exon 1-4 deletion; c.815-27T>C
- NUBPL protein
- Mrp/NBP35 ATP-binding protein family
- Complex I assembly factor
- Iron-sulfur cluster
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 4 months to 2 years
- Developmental delay: Some patients
- Delay: Motor; Unable to walk
- Cognitive: Normal or Reduced
- Eyes: Strabismus; Nystagmus
- Ataxia: Trunk & Limbs
- Contractures
- Spasticity
- ? Seizures
- ? Myopathy
- Other organs: Normal
- Course: Progressive, continuous or episodic
- Onset
- Laboratory
- MRI: Leukoencephalopathy with abnormal
- Cerebellar cortex: T2 & FLAIR signal; Progressive
- Cerebral white matter, deep: Spares U-fibers; May resolve
- Corpus callosum pathology: May resolve
- Basal ganglia: Some patients
- Lactate: Serum normal or high; CSF high
- Muscle biopsy
- Histology: Normal or Ragged red fibers with no COX- fibers
- Biochemistry: Complex I deficiency
- NUBPL protein: Reduced
- MRI: Leukoencephalopathy with abnormal
- Ataxia & Encephalopathy (MC3DN2) (Complex III)
 119
119
● Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 19 (TTC19)
 ; Chromosome 17p12; Recessive
; Chromosome 17p12; Recessive
- Epidemiology: 22 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Nonsense; Leu219X; Gln173X
- Allelic disorders
- CNS + Motor PN
- Diabetes: Biomarker for Nephropathy & Sarcopenia 347
- TTC19 protein
- Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Complex III association
- ? Involved in early assembly of Complex III
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Infancy to 42 years
- Ataxia: Younger patients
- Onset
- Ataxia: Dysmetria; Dysarthria; Nystagmus
- Encephalopathy: Cognitive regression
- Pyramidal
- Tendon reflexes: Brisk
- Toes: Extensor
- Skeletal: Pes cavus
- Course: Progression over decades; some with death in 3rd decade
- Laboratory
- Muscle biopsy
- Morphology: Normal
- COX stain: Few negative fibers
- Lipid increase
- Complex III deficiency
- MRI
- Leigh-like: T2 basal ganglia hyperintensities
- Necrotic lesions: Many CNS regions; Bilateral
- Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy
- Peripheral nerves: Axon loss; May be pure motor
- Lactate: Normal or Mildly high
- Muscle biopsy
- TTC19 Variant: Motor neuropathy + CNS
● Pitrilysin metallopeptidase 1 (PITRM1; KIAA1104; MP1; Presequence peptidase, mitochondrial; PreP)
- Epidemiology: Norwegian & Palestinian families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Arg183Gln, T931M; Homozygous
- PITRM1 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial matrix
- Expression: Multiple tissues; Muscle, Heart, Brain
- Metalloprotease: Peptidase
- Digests oligopeptides, especially 40 to 65 amino acids
- Substrates: Mitochondrial presequences; Short unstructured peptides; Forms of amyloid-β peptide
- Degrades amyloid beta A4 (APP) accumulating in mitochondria
- Clinical
- Onset age: Childhood
- Cortical: Mental retardation; Psychosis; Obsession; Hallucinations
- Ataxia
- Course: Slowly progressive over decades
- Laboratory
- Brain imaging: Cerebellar ± Cortical atrophy
- CSF: Low Aβ142
- Serum CK: Normal to 2900
- Serum lactate: High
- EMG & NCV: Normal
- Muscle
- Mitochondria: Few COX- muscle fibers; Citrate synthase low; Oxidative enzyme activities normal
- PITRM1: Reduced
● Thiamine Pyrophosphokinase (TPK1)
- Nosology: Thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 5 (Episodic encephalopathy type) (THMD5)
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or Truncation
- TPK1 protein
- Regulation of thiamine metabolism
- Catalyzes conversion of thiamine to thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
- TPP
- Pathways: Either
- Bound to transketolase from pentose phosphate cycle, or
- Transported into mitochondria via mitochondrial SLC25A19 TPP carrier
- Functions: Cofactor of 3 ketoacid dehydrogenases
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC)
- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH)
- Branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKDH)
- Other causes of TPP deficiency
- Pathways: Either
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 4 years
- Developmental delay
- Encephalopathy: Exacerbation during infection
- Loss of function: Episodic
- Hypotonia
- Ataxia: Gait disorder; Variable
- Dystonia: Progressive to severe in later onset patients
- Spasticity: Legs
- Microcephaly
- Epilepsy: Late
- Ophthalmoplegia: 1 patient
- Cognition: Often normal
- Death: 3 to 8 years in more severe patients
- Treatment: ? Thiamine (100200 mg/day)
- Laboratory
- Lactate: High in serum & CSF
- Urine: α-ketoglutaric acid often high
- MRI: Normal or Brain atrophy
- Muscle
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Normal or borderline low
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: Normal
- Oxidation rates of mitochondrial substrates: Reduced metabolism of pyruvate-containg substrates
● Trafficking protein, kinesin-binding 1 (TRAK1)
- Epidemiology: 3 families, 6 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; c.287-2A>C; Loss of function; Splice acceptor site in intron 3
- TRAK1 protein
- Adaptor protein: Connects KIF5 motors to mitochondria
- Interacts with KIF5A
- Mitochondrial movement in axons
- Endocytic trafficking: Shunting of receptor proteins to lysosomes
- Clinical
- Onset age: 1 to 19 months
- Myoclonus: Perioral; Hnads; Other, Multifocal
- Tone: Reduced early; Spastic later
- Seizures: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized
- Course: Progressive; Loss of all developmental milestones
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Atrophy; White matter changes in 1 patient
- Lactate: Normal in blood & CSF
● NAD(P)HX Epimerase (NAXE; APOA1BP)
- Epidemiology: 16 families, 25 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop
- NAXE protein
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 8 to 20 months
- Course: Subacute
- Trigger: Fever
- Cerebellar: Ataxia; Nystagmus
- Weakness: Hypotonia; Limbs; Respiratory
- Eye: Ptosis; Strabismus
- Skin (80%): Bullous lesions
- Course: Rapid progression; Fatal in 90%
- Possible tgreatment: NAD or nicotinic acid (vitamin B3)
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Brain atrophy; Cerebellar edema; Myelopathy
- Lactate: High in CSF
- Toxic metabolite: cyclic-NADHX
- Reduced activity of: Complex I, mild change; Pyruvate oxidation
● SUV3-LIKE 1 (SUPV3L1; SUV3)
- Epidemiology: 20 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop, Missense, Splice
- SUPV3L1 protein
- Location: Mitochondrial
- Mitochondrial RNA degradation
332
- Component of: Mitochondrial degradosome
- RNA helicase: Unwinds RNA secondary structures
- Substrates
- 3' overhang double-stranded RNA with a 3'-to-5' directionality in an ATP-dependent manner.
- Non-coding mitochondrial transcripts (MT-ncRNA)
- tRNA-like molecules
- Other component: Polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase, PNPT1)
- Clinical
- Onset age: Early childhood
- Ataxia
- Eye
- Nystagmus: Horizonal, gaze-evoked
- Optic atrophy
- Spastic paraparesis: Gait disorder
- Bulbar: Dysphagia; Dysarthria
- Cognitive deficit
- Skin: Hyper- & Hypopigmented & Ichthyotic patches
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar white matter atrophy
- Fibroblasts: Complex I increased
● NAD(P)HX Dehydratase (NAXD; CARKD)
- Epidemiology: 9 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop or Missense
- NAXD protein
- Cell location: Mitochondria, Cytoplasm
- ATP-dependent dehydratase

- Nicotinamide repair system: Cellular metabolite repair with NAXE for NADHX & NADPHX
- Prognostic marker: Renal & Endometrial cancer
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 43 months
- Trigger for deterioration: Fever
- Ataxia
- Seizures
- Cardiomyopathy
- Skin lesions
- Course: Progressive; Early death (< 5 years)
- Possible treatment: Mitochondrial cocktail
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Atrophy
- EEG: Epileptiform activity
● Aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 family, member A1 (ALDH5A1)
- Epidemiology: > 350 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Stop, Splice, Missense (Especially exon 4 or 5), Deletion
- ALDH5A1 protein
- Mitochondrial matrix
- 4-aminobutanoate degradation
- Catalyzes γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (Inhibitory neurotransmitter) degradation
- Mutated proteins: Usually low SSADH enzyme activity
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infant to 21 years
- Hypotonia
- Psychomotor retardation: Especially language
- Hyperkinesis
- Ataxia, Mitochondrial
- Seizures
- Sleep disorders
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: T2-weighted signal globus pallidus
- 4-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB): Increased in urine, plasma & CSF
● NAD Kinase 2, mitochondrial (NADK2)
- Epidemiology: 3 patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous Arg340Ter
- NADK2 Variant syndromes
- NADK2 protein
- Mitochondrial
- NAD kinase: Converts NAD & ATP to NADP+ & ADP
- Clinical: Encephalopathy
- Onset
- Age: Birth to 8 weeks
- Failure to thrive
- Hypotonia
- Microcephaly
- Dysmorphic features
- Pyramidal: Hypertonia, Clonus, Spastic quadriplegia
- Extrapyramidal: Choreoathetosis, Dystonia
- Epilepsy
- Optic neuropathy: Visual loss
- Developmental delay
- Other CNS: Central apnea, Nystagmus
- Treatment: Low lysine diet; Carnitine
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Metabolic
- 2,4-dienoyl-coenzyme A reductase (DECR1) activity: Low
- Blood & CSF lactate: Increased
- C10:2-carnitine: Increased, Abnormal polyunsaturated fatty acid oxidation
- Free carnitine: Low
- Lysine: Increased, abnormal degradation
- Proline: High
- NADPH deficiency
- Brain imaging
- Leukodystrophy
- Cerebral atrophy, generalized
- Ventricles: Enlarged ventricles
- Basal ganglia: T2 abnormalities
- Metabolic
- NADK2 variant: 2,4-Dienoyl-CoA reductase (DECR1
 ) deficiency
) deficiency

- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Recessive inheritance
- DECR1 Protein
- Mitochondrial
- Allows β-oxidation of lineolate
- Clinical
- Onset age: Neonatal
- Hypotonia
- Cardiomyopathy
- Death: 4 months
- Lab: Disorder of Fatty acid oxidation
- Hyperlysinemia
- Hypocarnitinemia
- 2-trans,4-cis-decadienoylcarnitine in urine & blood
- Normal organic acids
- DECR1 Mouse model
- Hypoglycemia
- Stress intolerance
- Ketogenesis: Unimpaired
- NADK2 variant: Multisystem CNS disorder, Childhood onset
233
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Recessive inheritance
- Mutation: Homozygous: Start loss g.36241900 T>C (p.Met1Val)
- Clinical
- Onset age: 9 years
- Optic atrophy: Reduced vision
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Ataxia: Gait disorder; Intermittent
- Intelligence: Normal
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Atrophy; Abnormal ventricles
- Plasma lysine: High
- C10:2 carnitine: Normal
● Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 50, Yeast, homolog of (TIMM50)
- Epidemiology: 2 families (Bedouin & Muslim), 4 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Arg217Trp, Thr252Met, Gly372Ser
- TIMM50 protein
- Clinical
- Onset age: 2 to 4 months
- Epilepsy
- Intellectual disability, severe
- Psychomotor development: Delayed
- Laboratory
- 3-methylglutaconic aciduria
- Lactate: Mildly high
- Mitochondrial complex V in muscle: Variable mild deficiency
- Brain MRI: Atrophy
● Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase (GCDH)
- Epidemiology: > 100 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: > 60
- GCDH protein
- Dehydrogenation & Decarboxylation of glutaryl-CoA to crotonyl-CoA
- Degradative pathway of L-lysine, L-hydroxylysine, L-tryptophan metabolism
- Homotetramer
- Mitochondrial matrix
- Clinical
- Onset: Early childhood
- Infantile encephalopathy
- Seizures
- Extrapyramidal: Dystonia; Rigidity; Choreoathetosis
- Spastic diplegia
- Treatment
- Diet: Low-lysine + Lysine-free, tryptophan-reduced, arginine-fortified amino acid supplementation
- Carnitine
- Laboratory
- Metabolic acidosis
- Glutaricaciduria
- Hypoglycemia
- Brain MRI: Striatal necrosis
- Peripheral neuropathy
354
- Subclinical
- NCV: CMAPs small; NCV slow
- MR Neurography: Abnormal
● Iron-sulfur cluster assembly 2, S. cerevisiae, homolog of (ISCA2)
- Nosology
- Encephalopathy & Leukodystrophy
- MMDS
- Epidemiology: 5 Families; 6 Patients
- Genetics
- Mutation: c.G229A; G77S; Homozygous; Founder
- ISCA2 protein
- Essential for protein assembly required for [4Fe4S] cluster maturation
- Clinical
- Onset age: 3 to 7 months
- Spasticity
- Optic atrophy
- Cognitive: Loss; No words
- Course: Progressive decline; Death at 11 mo to 5 years
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Abnormal White matter, Midbrain, Cerebellum & Pons, C-spine
- Metabolic screening: Normal
- Muscle
- Fiber size: Varied
- NADH: Moth-eaten fibers; Small dark fibers
- COX: Normal
- SDH: Small dark fibers
- Fibroblasts
- Complex I deficiency
- mtDNA depletion (Fibroblasts)
● ATP Synthase membrane subunit DAPIT (ATP5MD; USMG5)
- Epidemiology: 4 patients, 3 families; Ashkenazi Jewish
- Genetics
- Mutations: Intron, Splice, IVS3DS, G-C, +1; Homozygous
- ATP5MD protein
- Mitochondrial ATP synthase subunit
- Mitochondrial inner membrane
- Also present in lysosomes
- Expression: Insulin-sensitive cells, Epithelial cells, Neurons
- Muscle: More in slow muscle fibers
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 6 to 18 months
- Motor development: Delay
- Hypotonia
- Spasticity
- Extrapyramidal: Chorea; Bradykinesia
- Episodic regression: Related to infections
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like; Signal changes in basal ganglia & periaqueductal gray
- Brain pathology
- Neuron degeneration, gliosis amp; spongiform changes: Hypothalamus, Thalamus & brainstem
- Abnormal pigmentation in substantia nigra & locus ceruleus
● Iron-sulfur cluster assembly 1, S. cerevisiae, homolog of (ISCA1)
- Epidemiology: Indian European familes, 5 children
- Genetics
- Mutation: Homozygous; Missense; V10G (Milder phenotype), Glu87Lys
- ISCA1 protein
- Iron-sulfur cluster (ISC) assembly machinery
- Clinical
- Onset age: < 2 months
- Developmental delay: Feeding difficulty; Poor head control
- Seizures: Onset 2 to 4 months
- Spasticity
- Eye: Pigmentary retinopathy
- Course: Progressive; Death 2 to 11 years
- Laboratory
- Lactic acidosis
- Brain MRI: Leukodystrophy, vacuolating; Neuronal migration abnormalities
- Serum CK: High in 1 patient
- Fibroblast OXPHOS: ATP synthesis reduced
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Complex II most reduced
● LON Peptidase 1, Mitochondrial (LONP1; PRSS15)
- Nosology
- CODAS: Cerebral Ocular Dental Auricular Skeletal syndrome
- > 20 patients
- Pennsylvania Amish-Swiss & Canadian families
- Mutations
- At least one missense
- Missense: Arg721Gly (Amish), Ser631Tyr, Pro676Ser, Ala724Val
- In AAA+ domain: Residues near ATP-binding pocket
- c.2161C>G (Arg721Gly) allele frequency in Amish: 11.8%
- Allelic disorders
- Neonatal Encephalopathy
321
- Mutation: Missense; R301W
- Inheritance: Dominant de novo
- Mutation effects: Chaperone function loss; Proteolytic function increased
- Lactic acidosis, Severe, Congenital
- Multiple respiratory chain complex activity deficiencies
- Quantitative loss of mtDNA copy number in muscle
- Pyruvate Dehydrogenase deficiency + Progressive neurodegeneration & Cerebellar atrophy
- Neonatal Encephalopathy
321
- Mitochondrial matrix protease
- AAA+ Lon Protease
- Protease, serine 15
- Mitochondrial Lon: Multi-functional
- Elimination of misfolded & oxidatively damaged proteins
- Degradation of rate-determining mitochondrial proteins: In response to metabolic flux & cell stress
- Chaperone-like assembly of protein complexes in respiratory chain
- Regulation of mitochondrial gene expression
- Respiratory complex assembly
- Processing of mitochondrial targeting sequences: SSBP1, MTERFD3
 , FASTKD2, CLPX
, FASTKD2, CLPX

- Modulates: PINK1, phospho-PDH E1α, TFAM, COX4-1, NDUFB8, MRPL44, MRPL11
- Onset age: Congenital
- Skeletal
- Short stature
- Bone age: Delayed
- Vertebral: Coronal clefts (T11-S2); Scoliosis
- Pelvis: Square iliac bones
- Hips: Acetabular margins flat & irregular; Congenital dislocation
- Arms: Humeri, Metacarpals & Phalanges short
- Dens hypoplasia
- Genu valgus
- Cranial
- Ears: Overfolded, Rumpled
- Hearing loss: Sensorineural or Conductive
- Eyes: Cataract, congenital; Ptosis
- Nose: Median nasal groove
- Teeth: Delayed eruption; Enamel dysplasia
- Vocal cords: Atrophic; Airway complications
- Tongue hemiatrophy: 50%
- Feeding difficulty
- CNS
- Developmental delay: May be related to deafness
- Hypotonia & Motor delay
- Cell lines: Mitochondria
- Swollen
- Inclusions: Electron-dense
- Inner-membranes: Abnormal morphology
- MTCO2: Aggregated
- Spare respiratory capacity: Reduced
- Brain MRI
- Cortical atrophy
- Myelination: Delayed
- Corpus callosum: Hypoplasia
- Epidemiology: 7 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: Missense & Stop; D463N, Pro761Leu, Arg786Trp
- Clinical
- Onset: Neonatal
- Developmental delay
- Hypotonia
- Cataracts
- Cerebellar: Ataxia; Nystagmus
- Spasticity
- Weakness
- Skeletal: Epiphyseal dysplasia
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Serum Lactate: Normal
- Muscle Pathology
- COX- fibers, Scattered; Mitochondria with abnormal morphology
- Inclusions: Intra-mitochondrial, Globular, Electron dense
- Oxidative enzyme activities: Normal
- MRI: Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy, Progressive
- EMG & NCV: Normal
- Fibroblasts: PDH deficiency 2° ↑ levels of phosphorylated E1α subunit of PDH
● Cytochrome C oxidase assembly factor 3 (COA3)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutations: c.199dupC, c.215A>G
- COA3 protein
- Inner mitochondrial membrane protein: C terminus exposed to intermembrane space
- Involved in assembly of mitochondrial Complex IV (COX)
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: Early childhood
- Motor delay: Walked at 3 years
- Neuropathy
- Sensory loss: Gait disorder
- Strength: Mild weakness
- Tendon reflexes: Absent in legs
- Exercise intolerance
- Onset
- Morphology
- Obesity
- Short stature
- Face: Epicanthal folds; Deep-set eyes
- Pes cavus
- CNS: Cognitive impairment
- Muscle
- COX staining: Absent
- Complex IV activity: 17% of control
- Plasma lactate: Mildly high
- NCV
- Axon loss: Motor & Sensory
- ? Demyelination
● Solute carrier family 25, member 46 (SLC25A46)
- Epidemiology: 10 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense or Stop; Compound heterozygous
- Allelic disorders
- HMSN6B
- Atopic dermatitis
- Pontocerebellar hypoplasia (PCH)
- Leigh syndrome
- SLC25A46 protein
- Location: Outer mitochondrial membrane
- UGO1-like
- Interacting protein: Mitofilin (IMMT)

- Pro-mitochondrial fission
- Mitochondrial lipid homeostasis & cristae maintenance
- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 0 to 43 years
- Visual loss
- Optic atrophy: Vision loss
- Sensory-Motor neuropathy
- Sensory loss: Distal
- Weakness: Distal; Legs
- Muscle wasting: Distal
- Cerebellar: Ataxia
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced generally or at ankles
- Other CNS
- Spasticity
- Myoclonus
- Course: Slow progression
- Onset
- Laboratory
- Muscle: Normal; No SDH+ or COX- fibers
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory & Motor
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar ± WM changes, or Normal
- Brain MRS: Lactate high
- SLC25A46 variant syndrome: Congenital, Lethal Pontocerebellar Hypoplasia (PCH)
209
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Mutations: c.1022T>C (Leu341Pro); 1897-nucleotide deletion spanning exon 1;
- Mutations cause lower amounts of protein than HMSN 6B
- Clinical
- Polyhydramnios
- Motor: Hypotonia; Little movement; Respiratory failure
- Optic atrophy: Some patients
- Death: Infancy
- Laboratory
- NCV: Absent motor & sensory responses
- EMG: Fibrillations; Large motor units
- EEG: Global encephalopathy
- Brain MRI: Brainstem & Cerebellum small
- Serum CK: Normal
- SLC25A46 variant syndrome: PCH1E

- Epidemiology: 4 families
- Genetics
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Pregnancy: Full term; Polyhydramnios
- Weakness: Severe; No spontaneous respiration
- Eye: Optic pallor
- Death: < 1 month of life
- Laboratory
- Spinal cord: Loss & atrophy of motor neurons
- Muscle: Diffuse atrophy
- CNS imaging: PCH
- SLC25A46 variant: Leigh syndrome
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Mutation: Missense; c.425C>T (p.Thr142Ile)
- Clinical
- Oligohydramnios
- Onset age: 4 to 8 months
- Psychomotor delay
- Irritability
- Growth failure
- Spastic diplegia
- Optic atrophy
- Course: Progressive; Ventilator dependence; Death 14 months
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Lesions Cerebellar hemispheres, Periaqueductal grey, Globus pallidum
- Lactate: Normal in blood; Mildly high in CSF
- Muscle: Neurogenic atrophy
Mitochondrial syndromes: Adult onset CNS
- Parkinsonism
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 1

- Alzheimer's/Parkinsonism
- Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
- mtRNALys (MTTK)
 : A8344G
: A8344G
- Parkinson syndrome, Neuropathy & Myopathy 66
- mtRNAThr (MTTT)

- LHON (G15927A): Variant also described in 1 family with coronary heart disease
- Occasional sporadic Parkinsonism

- mtRNAPro (MTTP)
 207
207
- Occasional sporadic Parkinsonism
 : T15965C
: T15965C
- mtRNAPro mutations: Other
- Myopathy
- Genetics
- Mutations may be restricted to muscle
- C15975T: PEO; Ptosis
- G15990A anticodon mutation: Pure myopathy; 1st decade onset
- G15995A: Fatigue; Dysphagia; Unsteady gait
- A15998T: Myopathy, Proximal & Asymmetric
- T16002C: PEO; Myopathy; Exercise intolerance
- T16015C: PEO; Myopathy, Proximal; Exercise intolerance
- 16021_16022 del: Fatigue; RP; Seizeures; Small stature
- G16023A: Myopathy, proximal; Migraine; RP; Deafness; Leukoariosis (MRI)
- Muscle
- COX- muscle fibers: Common; 5% to 98%
- Raqged red fibers
- Complex I ± IV deficiency
- Genetics
- MERRF: G15967A
- Myopathy
- Occasional sporadic Parkinsonism
- Mitochondrial DNA deletion (5kb)
67
- Young-onset Parkinsonism, Tremor, Rigidity & Multiple symmetric lipomas
- POLG1
- PEO
- Parkinson syndrome
- Sensory neuropathy
- Parkin 2
 : Parkinson disease, juvenile, type 2 (PARK2)
: Parkinson disease, juvenile, type 2 (PARK2)

- PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)
 : Parkinson syndrome 6 (Recessive; Early onset)
: Parkinson syndrome 6 (Recessive; Early onset)

- LRRK2
 : Parkinson syndrome 8
: Parkinson syndrome 8

- Location: Outer mitochondrial membrane
- Mutation (G2019S) causes: Reduced mitochondrial membrane potential & total intracellular ATP levels 117
- Twinkle
- HTRA2
 : Parkinson 13; Encephalopathy
: Parkinson 13; Encephalopathy
- UQCRC1: Parkinsonism + Polyneuropathy
- Toxicity
- Trichloroethylene
- MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine)
- Pesticides
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 1
- Extrapyramidal: Other
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 4 (MTND4)

- Cu++ transporting ATPase 7B
- MTCYB
 (14787del4)
(14787del4)
- Juvenile akinetic rigid syndrome & MELAS
- MECR: Dystonia & Optic atrophy (MEPAN)
- DDP: Dystonia & Deafness
- VPS13D: Movement disorder, Childhood onset
- Huntingtin

- Huntington's chorea
● CAG repeat disorder; Chromosome 4p16.3; Dominant- Huntingtin protein: Not mitochondrial
- Mitochondrial OXPHOS defects
- Severe deficiencies of complexes II and III & moderate defect of complex IV
- Aconitase deficiency
- Locations
- Caudate > Putamen & Cortex: Similar to neuronal pathology
- Skeletal muscle
- Huntington's chorea
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 4 (MTND4)
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 2
 ; Chromosome 4q25
; Chromosome 4q25
- Increased longevity

- 5178C-A transversion: Increased frequency in Japanese centenarians
- Leber hereditary optic neuropathy
- Increased longevity
- NADH Dehydrogenase, Subunit 3 (ND3)

- Parkinsonism: Protective effect
- 10398G: Nonconservative amino acid change from threonine to alanine
- Protective effect in whites; Women > Men
- Migraine & Encephalopathy: Ser45Pro mutation
- Parkinsonism: Protective effect
- Malic enzyme 2
 :
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (adult)
:
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (adult)
- 9-SNP haplotype, homozygous: Increased risk for IGE
Parkinsonism & Polyneuropathy (PKNPY)
● Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein 1 (UQCRC1)
- Epidemiology: 3 families
- Genetics
- Mutations: Ile311Leu; Tyr314Ser; Splice (c.70-1G4A) & Frameshift insertion (c.73_74insG, p.Ala25Glyfs*27)
- Loss of function mutations: Malignant pleural mesothelioma
- UQCRC1 protein
- Mitochondrial: Complex III
- Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex function
- Catalyzes transfer of electrons from coenzyme QH2 to ferricytochrome c
- Coupled with translocation of protons across mitochondrial inner membrane
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 40 to 60 years
- Parkinsonism
- Asymmetric
- Tremor-predominant: Resting
- Bradykinesia
- Rigidity
- Levodopa responsive
- Anxiety
- Polyneuropathy
- Legs > Arms
- Distal
- Sensory loss: Panmodal
- Weakness
- Course: Progressive
- Cognition: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss
- EMG: Distal denervation
- SPECT: Loss of dopamine transporter
- Brain MRI: Atrophy, Mild & Diffuse
- Animal models: NMJ presynaptic defect
Movement disorder & Spastic Ataxia, Childhood onset 236
● Vacuolar protein sorting 13, yeast, homolog of, D (VPS13D)
- Epidemiology: 5 families, 7 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense & Deletion
- Allelic disorder: SCAR4
- VPS13D protein
- Expression: Ubiquitous
- Functions: Mitochondrial size, fission, clearance & autophagy (mitophagy)
- VPS13A mutations & VPS disorders: Chorea-Acanthocytsis
- Clinical
- Onset age: Birth to 12 years
- Developmental delay
- Hypotonia: Axial
- Movement disorders: Chorea; Dystonia; Tremor
- Spastic-Ataxia: Some with paraparesis
- Course: Progressive
- Laboratory
- Brain MRI: Leigh-like; T2 hyperintensity in basal ganglia or White matter
- Muscle biopsy: Mitochondcrial aggregates, subsarcolemmal; Lipid increased
Migraine & Encephalopathy (MC1DM1)
● Complex I, Subunit 3 (MTND3)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Genetics
- Encoding
- Guanine-rich heavy (H) strand of mtDNA
- Located between nucleotide pairs 10059 & 10404
- Mutation: Serine45Pro (T10191C)
- Heteroplasmic: Skeletal muscle 77%; Blood 14%
- Low level of mutation in mother: 3% in blood
- Allelic disorders: ND3 mutations
- Leigh 297
- LHON + Dystonia
- Protective for Parkinsonism
- MELAS-like disorder + Epilepsia partialis continua
- 10197G>A mutation: Varied syndromes
337
- > 70 patients
- Homoplasmic & Heteroplasmic
- Leigh overlap: More progression; Dystonia
- LHON overlap: Childhood &asmp; young adult onset; Higher mutation loads
- Encephalopathies/MELAS-like
- Encoding
- MT-ND3 protein
- Mitochondrial encoded Complex I component
- Binds FASTKD4 (TBRG4)

- Clinical
- Onset
- Age: 24 years
- Migraine
- Migraine
- Epilepsy: Progressive myoclonic
- Ataxia
- Eye
- Optic atrophy: Subacute painless central scotoma
- EOM: Absent upgaze & Convergence; Reduced downgaze
- Pupils: Bilateral afferent defects
- Upper motor neuron: Increased tone; Brisk tendon reflexes
- Myoclonic jerks: Occasional
- Peripheral nerve: Neuropathy on electrical studies
- Disease progression: Over 20 years
- Onset
- Laboratory
- MRI: Increased signal in midbrain
- Muscle pathology: Varied fiber size; No ragged red or COX- muscle fibers
- Respiratory enzymes: Reduced Complex I activity
- MTND3 variant: MELAS-like + Epilepsia partialis continua
99
- Epidemiology: 2 patients
- Genetics
- Mutations: Homoplasmic T10158C; Heteroplasmic T10191C
- Clinical
- Onset: Childhood
- Learning disabilities
- Migraine
- Short stature
- Epilepsia partialis continua
- Focal signs: Field defect; Ataxia
- Laboratory
- MRI: Calcarine + Rolandic lesions; Cervical cord swelling
- Muscle: Normal histology; Citrate synthase high or normal; Complex I activity normal
Germanium myopathy
- Myopathy: Proximal weakness
- Polyneuropathy: Axonal; Autonomic
- Systemic
- GI: Nausea & vomiting; Anorexia & weight loss
- Renal failure: Tubular degeneration & Interstitial fibrosis
- Myopathology
- Myopathy: Necrosis & regeneration
- Ragged red fibers
- Cytochrome oxidase: Reduced in atrophic fibers
- Lipid: Increased in muscle fibers
- Vacuoles
- Mitochondria with electron dense inclusions
Arsenic trioxide myopathy 148
- Arsenic trioxide (ATO) use: Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
- Epidemiology: 1 patient
- Mechanisms: May inhibit myogenic differentiation
- Clinical
- Myalgia: Diffuse
- Weakness: Arms & Legs; Proximal > Distal
- Course
- Progression over months
- Slow improvement after drug stopped
- Laboratory
- EMG: Myopathic
- Serum CK: Slightly high
- MRI: Muscle atrophy
- Muscle
- Lipid droplets: Especially Type I fibers
- COX stain: Reduced in all muscle fibers
- mtDNA: Multiple deletions
- Oxidative enzymes: Mild reduction of Complexes II+III & IV
- Variant syndrome: Rhabdomyolysis in few patients
Mitochondrial Solute Carriers (SLC25A family & Others)
Inner mitochondrial membrane- SLC25A family: General
250
- Transported to inner mitochondrial membrane by carrier proteins
- 6 potential transmembrane domains
- Nuclear encoded
- Types of carriers
- SLC25A1

- Tricarboxylate transporter (Citrate transport protein (CTP))
- SLC25A2

- Transporter: Ornithine; Asymmetric dimethyl L-arginine
- SLC25A3

- Phosphate carrier
- Disease: MPCD
- SLC25A4 (ANT1)

- Adenine nucleotide translocator
- Tissue: Skeletal & cardiac muscle
- Diseases: PEO2/PEO3 & Other
- Mouse knockout
- Exercise intolerance
- ATP deficiency
- Skeletal muscle: Ragged-red muscle fibers; Increased Mitochondrial number
- Cardiac: Hypertrophy with mitochondrial proliferation
- Serum Lactate: High
- SLC25A5 (ANT2)

- Catalyzes exchange of ADP & ATP
- Most abundant mitochondrial protein
- No related disease
- SLC25A6 (ANT3)

- Catalyzes exchange of ADP & ATP
- Tissue: Liver
- SLC25A8 (UCP2)

- SLC25A9 (UCP3)

- SLC25A10

- Dicarboxylate carrier
- Transports pyruvate & H+ across inner mitochondrial membrane into matrix
- Exchange for phosphate, sulfate & thiosulfate
- Supplies substrates for Krebs cycle, gluconeogenesis, urea synthesis & sulfur metabolism
- Disease
- SLC25A11

- SLC25A12

- Ca++ binding
- Expression: Heart & Skeletal muscle > Brain & kidney
- Diseases
- Hypomyelination, global cerebral (DEE39)

- Myopathy ± Ataxia: Dogs (Dutch Shepherd L349P; Nova Scotia Duck Tolling Retrievers Pro446Leu) 282
- Hypomyelination, global cerebral (DEE39)
- SLC25A13

- SLC25A14

- Expression: Brain
- Uncoupling protein: Proton channel
- SLC25A15

- Ornithine transporter: Across inner mitochondrial membrane
- Maintains NH4+ ions in non-toxic range
- Disease: HHH syndrome
- SLC25A16
 (Graves Disease Carrier Protein (GDC))
(Graves Disease Carrier Protein (GDC))
- ADP/ATP carrier protein
- Target of IgG autoantibodies in Graves disease
- Disease: Fingernail dysplasia, Recessive
- SLC25A17

- Peroxisomal membrane protein
- SLC25A19
 : Thiamine transporter
: Thiamine transporter
- Mitochondrial deoxynucleotide carrier (Deoxynucleotide diphosphates)
- Diseases: Microcephaly, Amish type; Striatal necrosis, bilateral & Polyneuropathy
- SLC25A21
 : Oxodicarboxylate transporter
: Oxodicarboxylate transporter
- Mitochondrial Oxodicarboxylate carrier
- Disease: MTDPS18, SMA-Like disorder
- SLC25A22

- Mitochondrial Glutamate/H+ symporter
- Expression: Brain regions associated with seizures
- Disease: EEIE3
- SLC25A23

- Mitochondrial Phosphate carrier
- Calcium binding
- SLC25A24

- SLC25A25

- Calcium-binding Phosphate carrier
- SLC25A26

- Mitochondrial S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) carrier
- Disease: Encephalomyopathy
- SLC25A31 (ANT4)

- ADP/ATP carrier protein
- SLC25A32
- SLC25A38
- Glycine transporter
- Disease: Anemia
- SLC25A42
- Coenzyme A transporter
- Disease: Myopathy
- SLC25A46
- Mitochondrial: Outer membrane
- Disease: HMSN6B
- Mitochondrial uncoupling protein (UCP1)

- ATPase deficiency: Reduced H+ transport
- Carnitine transport
- SLC25A1
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
Return to Neuromuscular Syndromes
References
1. Brain 1996;119:997-1010, Neuromuscular Dis 2002:Online Dec 2002, Am J Med Genet 2005; Online Apr, Neuromuscul Disord 2008 Jun 26, J Mol Neurosci 2021;71:2462-2467
2. Curr Opin Rheum 1997;9:496-503
3. AJHG 1998;63:1594-1597, Ann Neurol 2015 Oct 27
4. Hum Molec Genet 1999;8:1967-1974
5. Human Mutation 1999;14:545
6. Acta Neuropathologica 2000;99:31-38, Brain 2005;128:18611869, Ann Neurol 2008 Feb 27
7. J Child Neurol 1999;14:S23-S36
8. Neurology 1997;49:239-245
9. Neurology 2000;54 S3:A331, Am J Hum Genet 2000;66:June
10. Ann Neurol 2000;47:792-800, Neuromuscular Disorders 2001;11:7-10, Brain 2011 Online Sept, JIMD Rep. 2022;63:484-493
11. Brain 2001;124:209-218
12. Am J Hum Genet 2001;68:386-396, Am J Hum Genet 2011;89:486495
13. Ann Neurol 2001;49:195-201
14. J Med Genet 2001;38:400-405
15. Am J Hum Genet 1996;58:763-769
16. Neuromuscular Disorders 2001;11:481-484
17. Neurology 2001;56:1409-1412
18. Neurology 2001;57:1440-1446
19. Muscle Nerve 1997;20:1219-1224
20. Neurology 2001;57:2298-2301
21. Ann Neurol 2002;51:388-392
22. Neurology 2001;56:802-805
23. Neurology 2002;58:A330
24. Hum Molec Genet 2002;11:1669-1681
25. Ann Neurol 2002;On-line June
26. Ann Neurol 2002;On-line June
27. Neurology 2002;59:1197-1202, Pediatr Neurol 1996;15:153158
28. Neuromuscular Disord 2003;Online January
29. Am J Med Genet 2003;Online January
30. Curr Opin Neurol 2003:16:3543
31. PNAS 2003:Online January, Brain 2015; Online October
32. J Neurol 2003;250:702706, Ann Neurol 2005;57:921-923, Pediat Neurol 2011; 45:311-318
33. N Engl J Med 2003;348:2656-2668
34. N Engl J Med 2002;347:576-580
35. Hum Mol Genet 2003; Online November
36. Neurology 2002;59:926929
37. J Med Genet 2003;40:858-863
38. Muscle Nerve 2004; March
39. J Med Genet 2004;41:120124
40. Curr Opin Pediatr 2003;15:572577
41. Neuromuscular Disorders 2004;14:417420, 2005;15:364371
42. Ann Neurol 2004;55:478484
43. J Med Genet 2004;41:e73
44. Brain Dev 2004;26:453-458, Brain Dev 2004 Online April
45. Lancet 2004;364:875-882
46. J Clin Invest 2004;114:837-845
47. Neurology 2005;64:371373
48. Am J Hum Genet 2005; Online June
49. Br J Ophthal 2005;89:825-827
50. Ann Neurol 2004;56:631641
51. Am J Hum Genet 2005;77:430441
52. Neurology 2005;64:371-373
53. Ultrastruct Pathol 2005;29:169-174
54. Neuromuscular Disorders 2005; Online November
55. J Neurol 2005 Nov 23
56. Nature Genetics 2006; Online April 2
57. Ann Neurol 2006;59:859-862
58. J Neurol 2006; Online May
59. Am J Hum Genet 2006;79 Online September
60. Ann Neurol 2004;56:734738
61. Arch Neurol 2006;63:746-748
62. Am J Hum Genet 2006; Online December, Neuromuscular Disorders 2011; Online July
63. Neuromuscular Disorders 2006;16:821829
64. Acta Neuropathol 2006;111:610616
65. Ann Neurol 2007;61:73-83
66. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2007 Feb 9, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007;354:1058-1060, Neurology 2007;68:56-58 J Neurol 2016;263:961-972, Cureus 2025;17:e82875
67. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;71:685687
68. Brain 2007; Online Feb 7 & Feb 14, J Inherit Metab Dis 2015 Oct 16
69. Pediatr Neurol 2006;35:293-296, Neurology 2004;63:1302-1304
70. Am J Hum Genet 2007; Online April, Mitochondrion 2010;10:335-341, J Inherit Metab Dis 2015 Oct 16
71. NEJM 2007;356:1736-1741, Front Pediatr 2021;9:604105, Front Pediatr 2025:13:1672700
72. Nature Genet 2007; Online May 7
73. Arch Neurol 2007;64:998-1000
74. Brain 2007 Oct 5
75. J Med Genet 2007 Online Oct 22
76. Brain 2008;131:352-367
77. Brain 2008 Jan 30
78. Am J Human Genet 2008; Online February
79. Ann Neurol 2008; Online Feb
80. Acta Neurol Scand 2007;116:114
81. Am J Hum Genet 2008; Online May
82. Am J Hum Genet 2008; Online May
83. Am J Hum Genet 2008; Online May
84. EMBO J 2007;26:3227-3237
85. Cell 2008;134:112123
86. Am J Hum Genet 2008;83:415-423
87. American J Human Genetics 2008;83:468478, J Med Genet 2010;47:507-512
88. J Neurol 2009 Mar 1
89. American J Human Genetics 2009 Mar 25
90. Am J Med Genet A 2009 Apr 7
91. Am J Hum Genet 2009;84:594-604
92. Neurogenetics 2009; Online May 21
93. Nature Genet 2009; Online May
94. Ann NY Acad Sci 2008;1147:293302
95. Am J Hum Genet 2009 May 20
96. Biol Chem 2009 May 20
97. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000499
98. Nature Genet 2009; Online June, J Neuromuscul Dis 2020 May 16
99. Pediatr Neurol 2009;41:27-33
100. Ann Neurol 2009; Online June, J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2020;34:261-266
101. Muscle Nerve 2009;39: Online July
102. Am J Hum Genet 2009; Online Aug, Neurology 2011;76:2032-2034
103. Brain 132:3165-3174.
104. Am J Hum Genet 2009; Online Aug, Mol Genet Metab 2021 Jan 14
105. Neurology 2009;73;898-900
106. Mitochondrion 2008;8:396413, Pediatr Radiol 2025 May 2
107. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009;1792:1109-1112, Neuromuscul Disord 2010 May
108. Am J Hum Genet 2010; Online April
109. J Hepatol 2010 Apr 18
110. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:3549-3553
111. Human Molec Genet 2010; Online June
112. Am J Hum Genet 2010; Online July
113. Am J Hum Genet 2010;87:115-122
114. Nature Genet 2010; Online Sept, J Med Genet 2021;58:314-325
115. Mitochondrion 2010; Online July, J Neuromuscul Dis 2025 Nov 12
116. Brain 2010; Online October
117. Neurology 2010;75:20172020
118. European Journal of Human Genetics 2011;19:270-274
119. Nature Genetics 2011 Online January, J Peripher Nerv Syst 2025;30:e70060
120. Am J Human Genet 2011; Online January
121. Am J Human Genet 2011; Online March
122. Am J Human Genet 2011; Online May, Cerebellum 2022 Jan 27
123. Nature Genetics 2011; Online June
124. Am J Human Genet 2011;89:543-550
125. Am J Human Genet 2011;89:792-797
126. Am J Human Genet 2011;89: 806-812
127. Brain 2011; On-Line Dec
128. J Med Genet 2011;48:737-740, Hum Mutat 2021 Mar 14, Mov Disord Clin Pract 2022;9:218-228
129. J Med Genet 2011; On-line Dec
130. American J Human Genetics 2012;90:142151
131. Am J Human Genet 2012; On line Jan, Mol Genet Metab 2023;139:107626
132. Am J Human Genet 2012;90:518523
133. NEJM 2012;366:1132-1141
134. Cell Metab 2011;14:428-434
135. Brain 2012; April
136. PNAS 2012; Online April
137. Am J Human Genet 2012; Online May
138. Pediatr Int 2012 Apr 12
139. Nature Genetics 2012l Online June
140. Ann Neurol 2012;70:486-492
141. Acta Neuropathol 2011;121:775783
142. Neurology 2012;79:11451154
143. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2012 Aug 29
144. J Clin Pathol 2009;62:172176
145. Am J Human Genet 2012; Online Sept A, B
146. Brain 2012; Online October
147. Arch Neurol 2012 Sep 10: Online September, Neuromuscul Disord 2012;22:587-591
148. Blood 2012;119:4272-4274
149. Am J Hum Genet 2012;91: Online October, Am J Hum Genet 2012;91: Online October
150. Am J Hum Genet 2012;91:942-949
151. Human Molec Genet 2012; Online November
152. J Med Genet 2012;49:777-784
153. Neurology 2013; Online Jan, Orphanet J Rare Dis 2025;20:130, Sci Rep 2025;15:9013, J Inherit Metab Dis 2026;49:e70147
154. Nature Genetics 2103; Online Jan
155. J Med Genet 2013; Online Jan, Mol Genet Metab 2021 Jun 10
156. Am J Hum Genet 2012;91:942-949, Neuromuscular Disorders 2017; Apr, Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2019;6:1893-1899
157. PNAS 2013; Online Feb
158. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 2013; Online Feb
159. Hum Mol Genet 2013 Mar 5, Mol Genet Metab 2023 Oct 20
160. Brain 2013; Online April, Neurology 2103; Online April
161. Human Molecular Genetics 2013; Online April
162. Am J Hum Genet 2013; Online July
163. Am J Human Genet 2013; Online August, Mitochondrion 2021 Jul 9
164. Am J Human Genet 2013; Online August
165. Neurology 2013; Online Sept
166. JAMA Neurol 2013 Oct 7
167. J Neurol 2013; Online November
168. Am J Human Genet 2013;93:906-914
169. European Journal of Human Genetics 2013; Online November, Brain 2018; Online July
170. BMC Medical Genetics 2013;14:125
171. Am J Human Genet 2013; Online December
172. Nature Genet 2013; Online December, Cureus 2024;16:e52672
173. Am J Human Genet 2014; Online January
174. Hum Mutat 2014; Online May 14, Genet Med 2023;25:100938
175. Brain 2014; Online June, Neurol Genet 2020;6(1):e394
176. Brain 2014; Online August, Mol Genet Metab 2025;145:109158
177. Hum Mutat 2014 Aug
178. Human Molecular Genetics 2014;23:35963606
179. Am J Human Genet 2014; Online Aug
180. Neurology 2014;83: Online October
181. Hum Mutat 2014 Nov 11, Eur J Med Genet 2022;:104643
182. Am J Human Genet 2014; Online Nov, Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2024;11:819-825
183. PLoS Genet 2014;10:e1004424, J Inherit Metab Dis 2022;45:1039-1047
184. J Med Genet 2014; Online Dec
185. Case Rep Neurol Med 2014;2014:701761
186. Human Molec Genet 2015; Online Jan
187. N Engl J Med 2002;347:576-580
188. Am J Human Genet 2015;96:121135, Front Genet 2023:13:1031856
189. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online Jan 15
190. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online Feb
191. Hum Mol Genet 2015 Feb 4
192. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online Mar
193. J Med Genet 2015 Mar 18
194. Hum Mol Genet 2015 April
195. J Med Genet 2015;52:203207
196. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online June
197. Nature Genetics 2015; Online July
198. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online July
199. J Inherit Metab Dis 2015;38:655680, Int J Mol Sci 2025;26:12023
200. Am J Human Genet 2015; Online Oct, Hum Mol Genet 2022 Jan 13
201. Hum Genet 2015 Nov 5
202. Brain 2015; Online December
203. EMBO Mol Med 2015 Dec 23, J Med Genet 2018 May 15
204. Am J Human Genet 2016; Online Apr
205. JAMA Neurol 2016 Jun 20
206. Am J Human Genet 2016; Online June
207. Neurology Genetics 2016; Online June
208. Am J Human Genet 2016: A; B
209. Brain 2016; Online August
210. Am J Human Genet 2016;99:831-845
211. Am J Human Genet 2016;99:894-902
212. Am J Human Genet 2016;99:860-876
213. Am J Human Genet 2016; Online Dec
214. J Med Genet 2016 Dec 28
215. Brain 2017; Online Feb
216. Eur J Hum Genet 2017 Mar 15
217. Eur J Hum Genet 2017 Apr 26
218. Clin Genet 2017 Jul 3, Brain Commun 2025 Sep 23
219. Hum Mutat 2017;38:970-977, Acta Neuropathol 2019 Aug 29
220. EMBO Mol Med 2017;9:967-984
221. Am J Human Genet 2017; Online July
222. Am J Human Genet 2017;101:239-254
223. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013;1832:1304-1312
224. PLoS Genet. 2016;12::e1005679
225. Am J Human Genet 2017; Online Sept
226. Cell Metab 2017;25:128-139
227. Mol Cell 2016;63:621-632
228. J Inherit Metab Dis 2017;40:261-269
229. Am J Hum Genet 2017 Sep 27, Int J Dev Neurosci 2021 Mar, Free Radic Biol Med 2025 Feb 13
230. Brain 2017; Online November
231. Brain 2018; Online Jan
232. Hum Mol Genet 2018 Jan 19
233. Am J Med Genet A 2018 Feb 1
234. Am J Hum Genet 2018 Feb
235. Ann Neurol 2017 Dec 28
236. Ann Neurol 2018 Mar 8
237. Am J Hum Genet 2018 Mar
238. Am J Hum Genet 2018 Mar
239. Am J Hum Genet 2018 Mar
240. Neurol Genet 2018;4:e223
241. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2018 Apr 17
242. Am J Hum Genet 2018 Sept
243. Hum Mol Genet 2019 Apr 30
244. Muscle Nerve 2019; Online May
245. Neurol Genet 2019;5:e322
246. Ann Neurol 2019;86:193-202
247. Hum Mol Genet 2018;27:4135-4144
248. Am J Hum Genet 2019 Dec 23
249. Neurol Genet 2020 Jun;6(3):e420
250. Biomolecules 2020;10(4)
251. Hum Mol Genet 2020 Apr 30
252. J Hum Genet 2020;65:231-240
253. Med Genet 2020 May 21
254. GeneReviews, Hum Mol Genet 2021 Oct 27
255. J Neurol 2020 Jul 18
256. Ann Neurol 2020 Jul 26
257. J Med Genet 2020 Mar 11
258. Brain 2020 Nov 3
259. Mol Genet Metab 2020 Nov 24
260. Mitochondrion 2020 Dec 3
261. FEBS Lett 2020 Dec 12
262. Eur J Med Genet 2020 Dec 30
263. J Clin Invest 2021 Jan 19, J Clin Invest. 2021;131:147734
264. Front Neurol 2019;10:780
265. Am J Med Genet A 2017;173:225-230
266. Mol Neurodegener 2021;16(1):12
267. Mol Genet Metab 2021 Mar 13
268. Brain 2021 Mar 22
269. Brain 2021 Apr 15
270. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2021 Apr 20
271. Am J Hum Genet 2021 May 21
272. Sci Rep 2021;11:11123
273. Brain Commun 2021 Apr 7
274. Mitochondrion 2021 Jun 2
275. Mitochondrion 2021 Aug 11
276. Hum Mol Genet 2021;30:687-705
277. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2020;55:509-524
278. FEBS Lett. 2021 Apr;595(8):1003-1024
279. Nat Commun 2021;12:1135
280. Am J Hum Genet 2021 Oct 12
281. Neurol Genet 2021 Nov 3
282. J Neuromuscul Dis 2019;6:485501, Genes (Basel) 2022 ;13:1223
283. Clin Genet 2021 Nov 29
284. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021;12:728043
285. Sci Adv 2022 Mar 18
288. HGG Adv 2022 Mar 4;3(2):100097
289. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2022 Mar 27
290. Cells 2022;11:974
291. Am J Med Genet A 2022 May 2
292. Neurol Genet 2022;8:e200007, EMBO Mol Med 2023:e16775
293. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022 Aug 9
294. Am J Hum Genet 2022;109:1692-1712
295. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022;10:142
296. Mitochondrion 2021 Jan;56:52-61
297. Cureus 2022;14:e28986
298. J Neuromuscul Dis 2022 Oct 28
299. Membranes (Basel) 2022;12:893
300. Hum Mol Genet 2022 Nov 26
301. Neurol Genet 2021;8:e660
302. J Neurol 2015;262:1301-9, Brain Sci 2020;10:766
303. J Med Genet 2023;60:65-73
304. Neuropediatrics 2023 Jan 24
305. Am J Med Genet A 2023 Feb 9, Am J Med Genet A 2025 May 2
306. Nat Commun 2023;14:1009
307. Neurol Genet 2023 Apr 10, Clin Genet 2023 Sep 6, Brain 2024;147:3949-396
308. Genes Dis 2022;10:1165-1168
309. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24(13)
310. J Neurol 2022;269:3550-3562
311. Chem Biol Interact 2023 Aug 31;110692
312. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2023;32:107080
313. Mov Disord 2023 Nov 28
314. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2023 Nov 28;:e2328
315. Cell Metab 2015;21:417-27
316. Clin Genet 2020;97:276-286
317. J Neuromuscul Dis 2024 Jan 8, Genet Med 2024 Mar 5:101117, Int J Mol Sci 2026;27:1375
318. iScience 2023;26:106895
319. Mitochondrion 2024;76:101879
320. Genes (Basel) 2024;15(5)
321. Mitochondrion 2020:51:68-78
322. Hum Mol Genet 2019;28:290-306, Front Neurol 2019;10:981
323. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2024 Jun 14, Genes (Basel) 2024;15:1508
324. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2024 Jul 1, Eur J Hum Genet 2023;31:1414-1420
325. Brain 2025 Aug 20
326. Ann Neurol 2024 Aug 2, Mol Genet Metab Rep 2024;41:101142
327. Brain 2024 Aug 30
328. PLoS One 2017;12:e0178125
329. Liver Int 2024 Nov 7
330. JIMD Rep 2024;65:297-304
331. Genes (Basel) 2024;15:1406
332. Hum Mol Genet 2024;33(R1):R26-R33
333. Cell Death Dis 2024;15:870
334. Membranes (Basel) 2021;11:465
335. Mol Genet Metab 2025;144:109023
336. Neurology 2025;104:e209779
337. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2025;20:59
338. Hum Genomics 2025;19:21
339. Transl Pediatr 2025;14:367-372
340. J Neurol 2025;272:280
341. Biomedicines 2025;13:733
342. Hum Mol Genet 2019;28:1090-1099
343. Cureus 2025;17:e86670
344. J Child Neurol 2025 Aug 17
345. Neurology 2025;105:e213908
346. Hum Genet 2025 Sep 8
347. Front Cell Dev Biol 2025:13:1596204
348. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2024;19:431
349. Molecules 2023;28:1796
350. J Rare Dis (Berlin) 2025;4:47
351. medRxiv 2025 Sep 26
352. Mitochondrion 2025:102095
353. Brain 2025 Nov 14
354. J Inherit Metab Dis 2026;49:e70131
355. Mol Genet Metab 2026;147:109767
356. Cell Mol Biol Lett 2026;31:13
357. Front Pharmacol 2025:16:1507493
358. NPJ Genom Med 2026 Feb 20
359. J Cell Sci 2025;138:jcs263638
2/21/2026