MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE: Megaconial Myopathy
|
Enlarged mitochondria: Causes Congenital Myopathy: CHKB Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome 1: BRAF Immune Myopathy Selenium deficiency Large mitochondria: Zellweger PEX12 PEX16 |
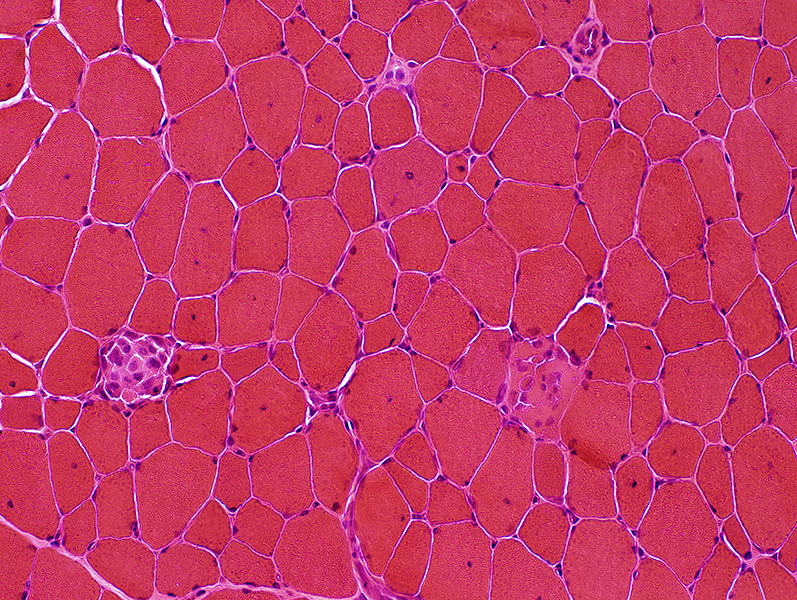 H&E stain |
Muscle Fibers: Necrosis & Regeneration, Scattered damage
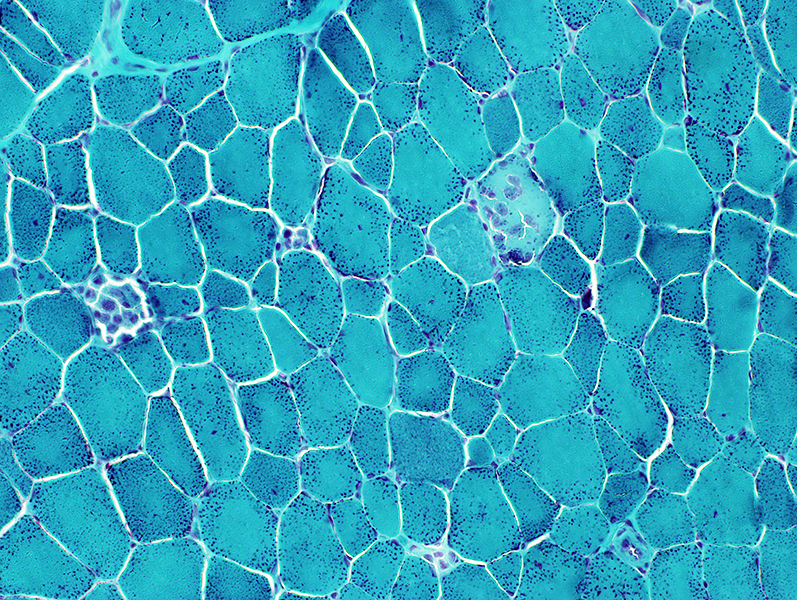 Gomori trichrome stain |
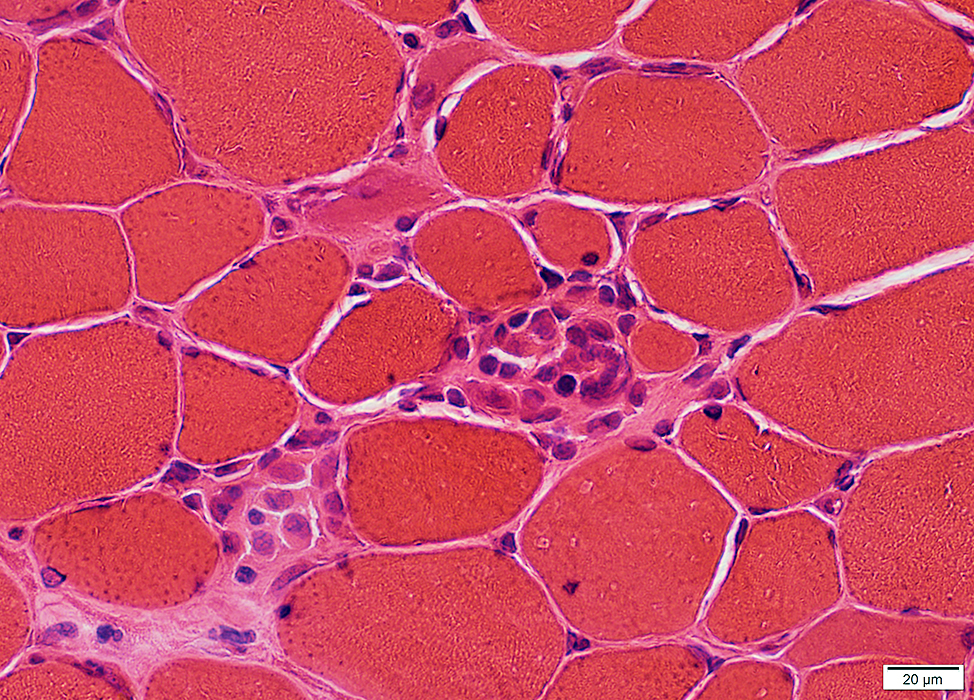 H&E stain |
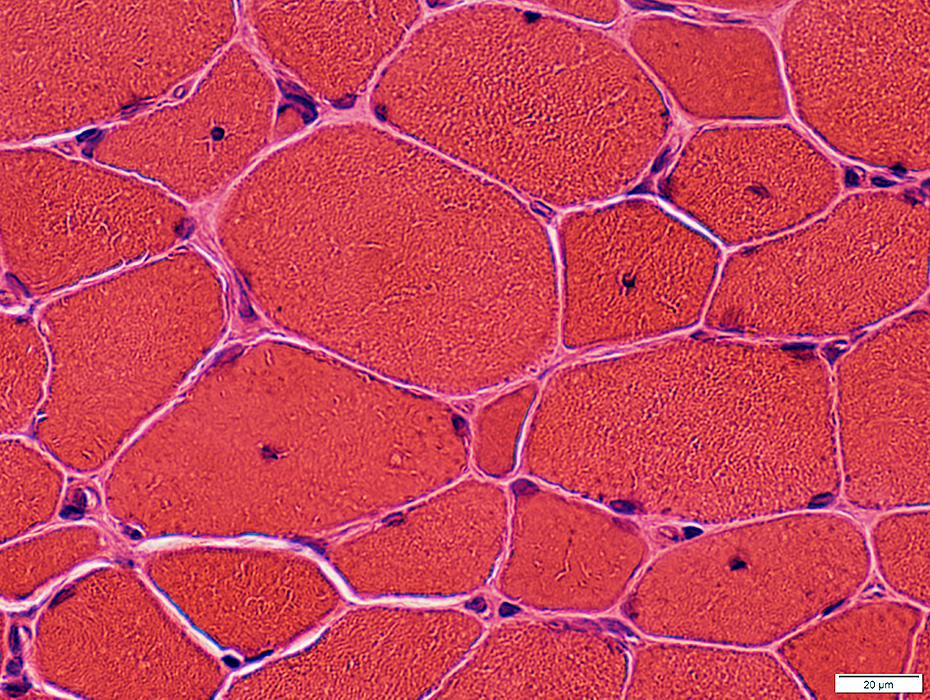 H&E stain |
Muscle fibers size: Varied
Internal nuclei: Often Single & Central
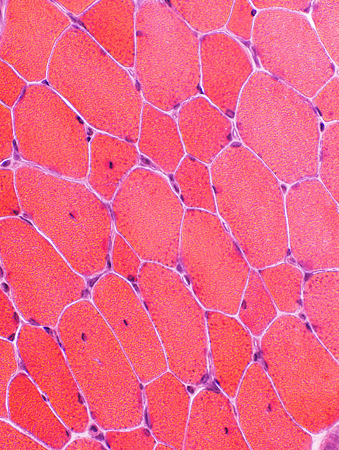 H&E stain |
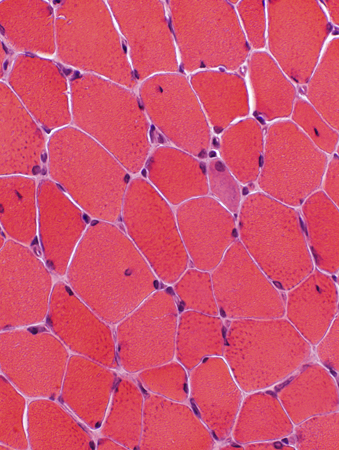 H&E stain |
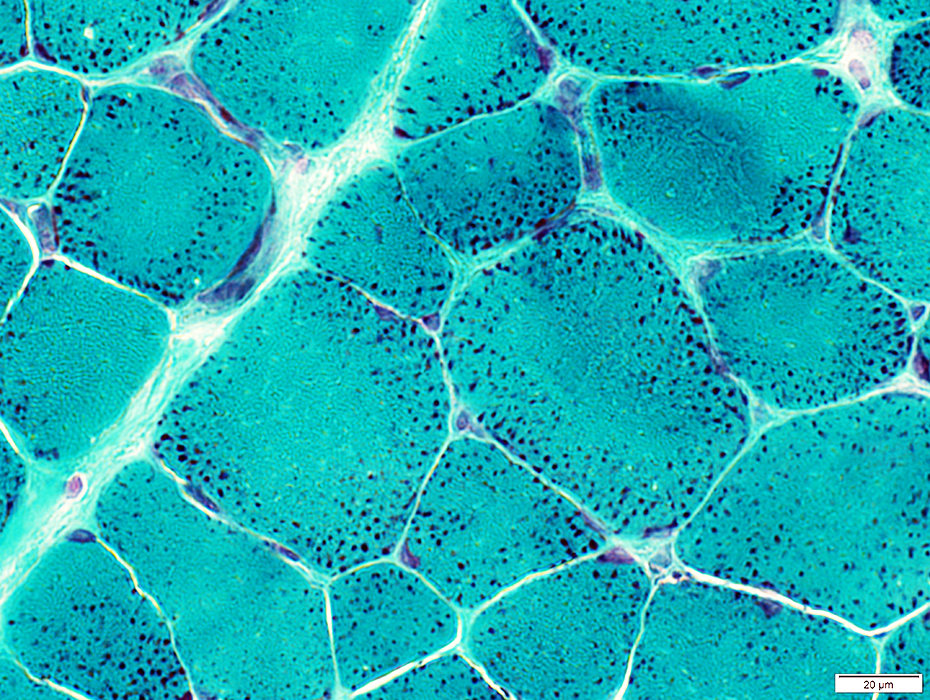 Gomori trichrome stain |
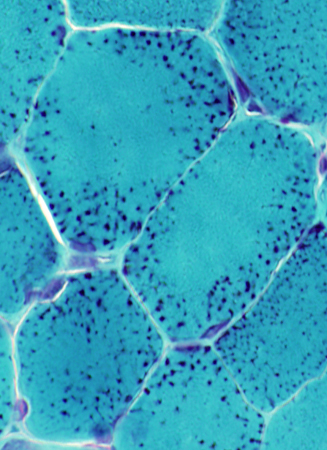 Gomori trichrome stain |
Toward periphery of muscle fibers
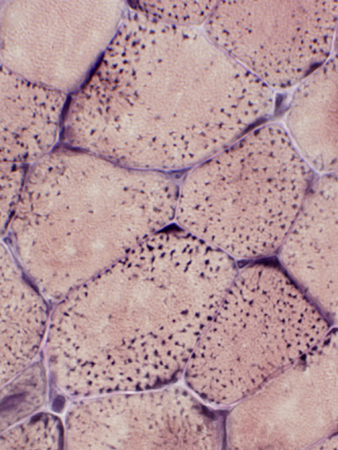 VvG stain |
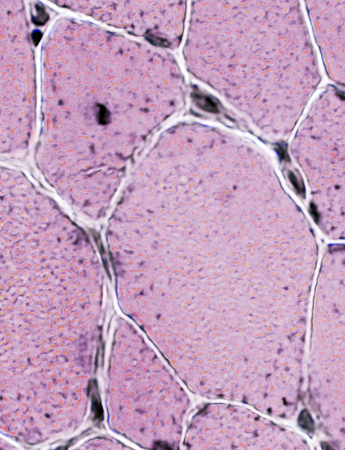 H&E stain |
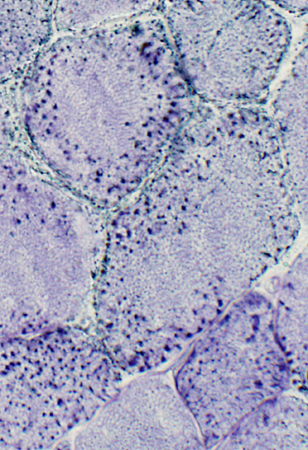 AMPDA stain |
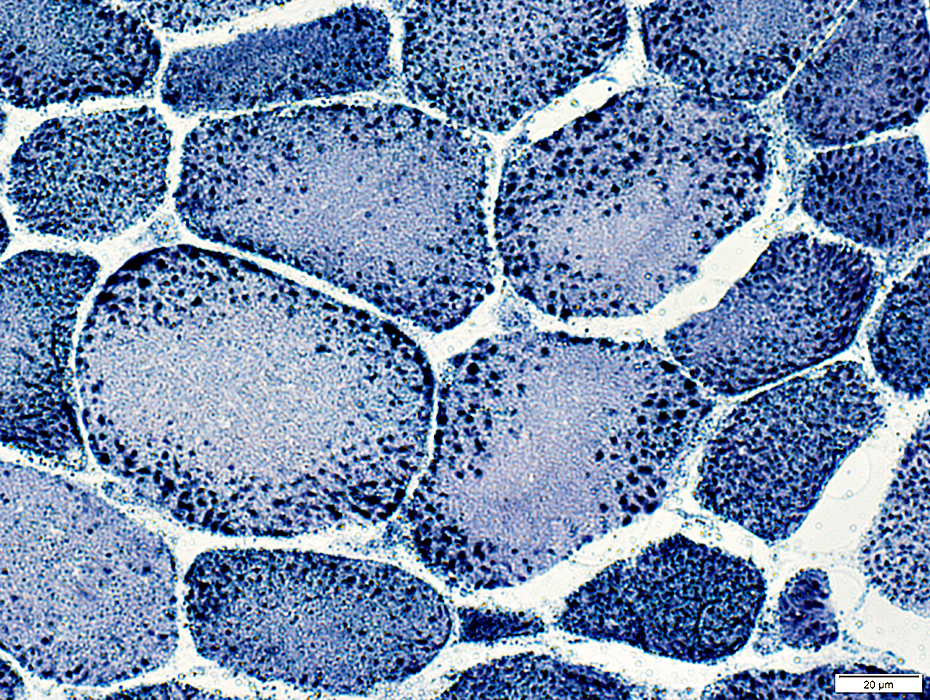 NADH stain |
Center of muscle fibers: No staining for sarcoplasmic reticulum
Periphery of muscle fibers: Punctate staining
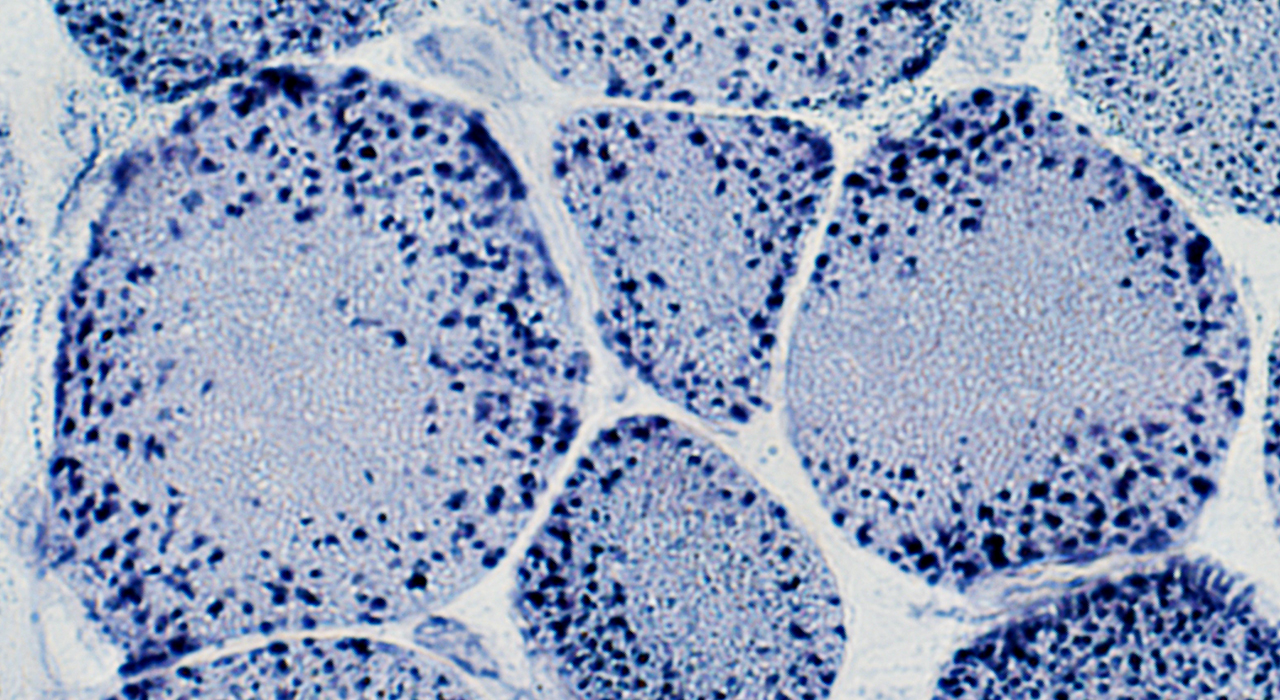 NADH stain |
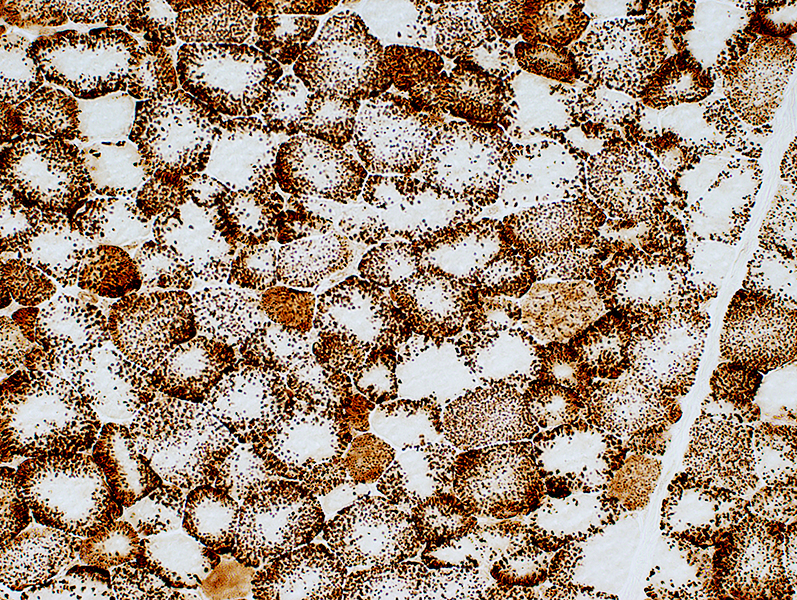
| ||
| Mitochondria: Large; Non-uniform distribution | ||
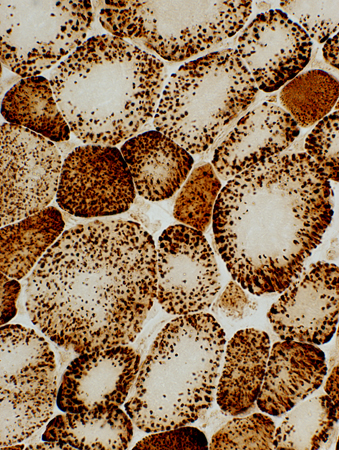 COX stain |
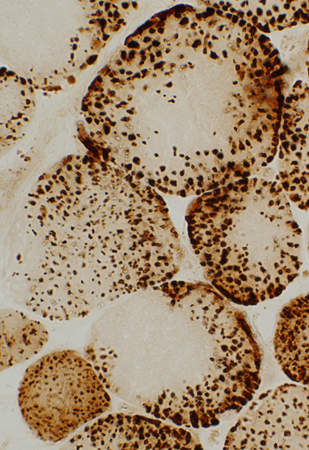 COX stain |
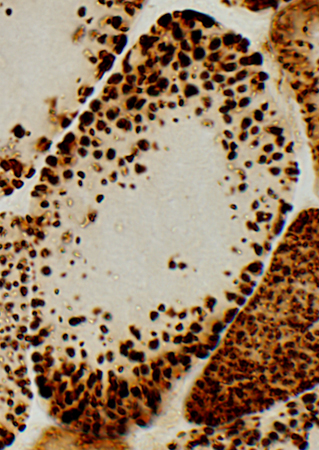 COX stain |
| Mitochondria: Large; Non-uniform distribution | ||
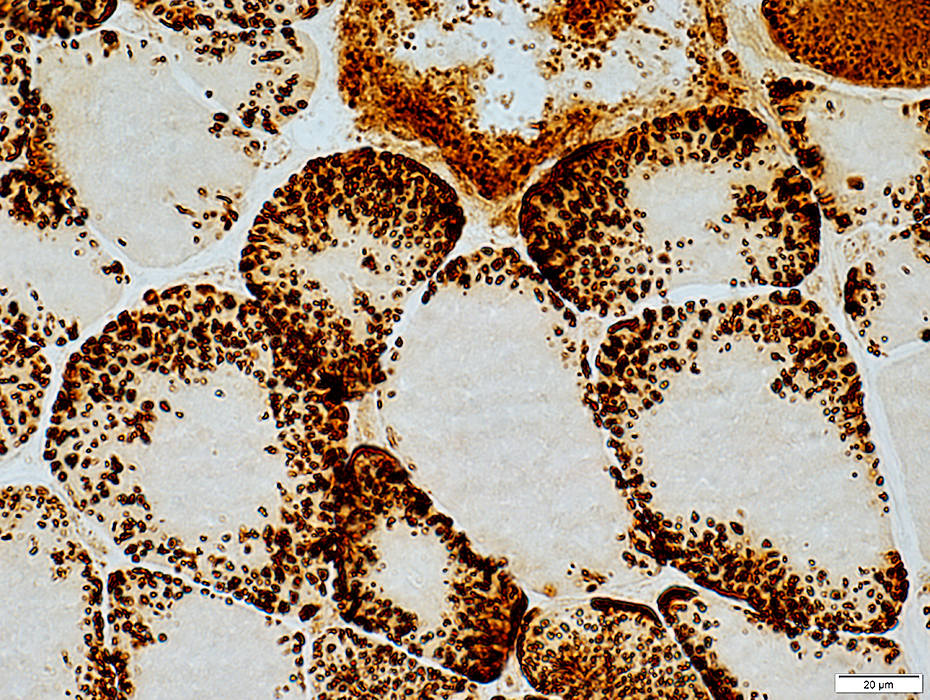 COX stain |
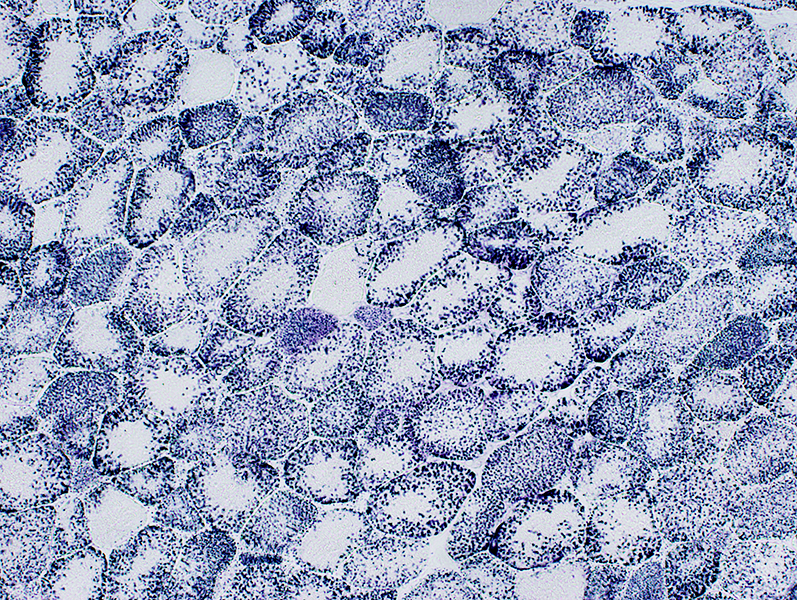 SDH stain |
|
Mitochondria Large Most in periphery of muscle fibers |
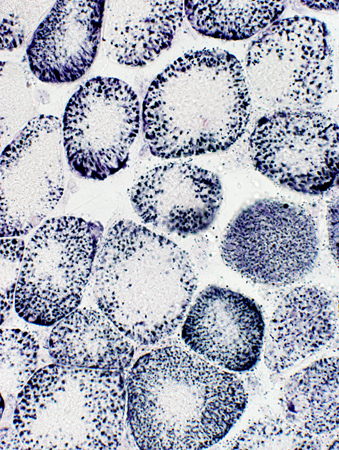 SDH stain |
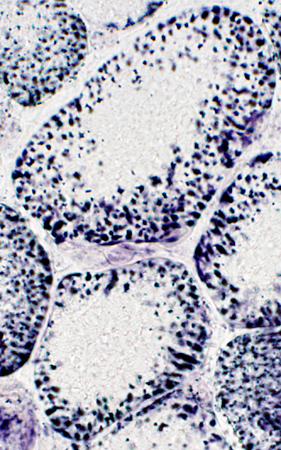 SDH stain |
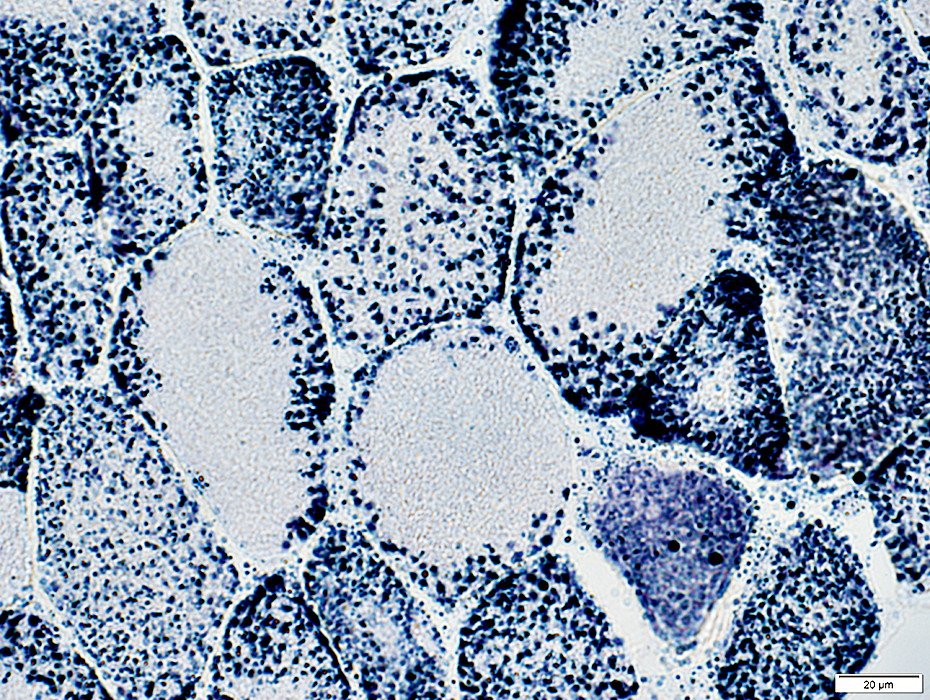 SDH stain |
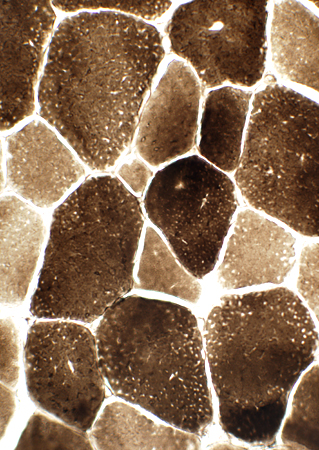 ATPase pH 9.4 stain |
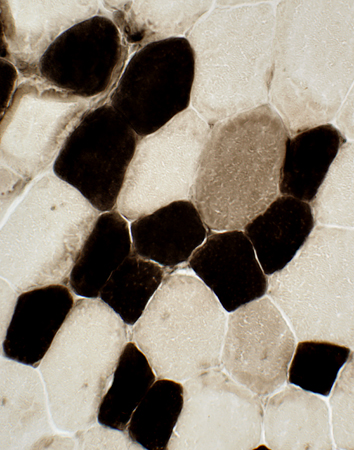 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
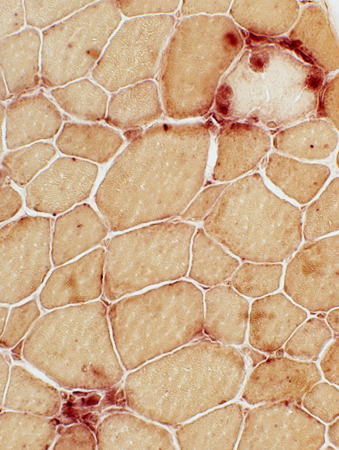 Acid Phosphatase stain |
| Type 2 fibers are larger than type 1 Large mitochondria: More common in type 2 fibers |
Scattered type 2C muscle fibers |
Necrotic Muscle Fibers |
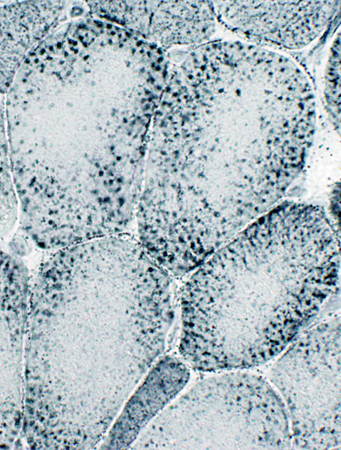 Sudan stain Lipid Droplets: Large |
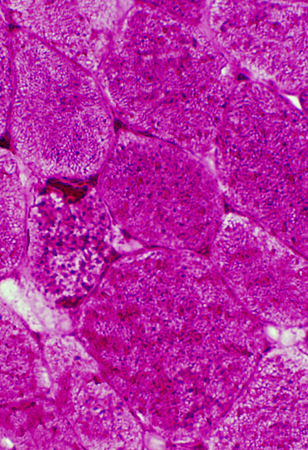 PAS stain Glycogen: Increased in muscle fiber cytoplasm |
Return to Megaconial Myopathy
Return to Mitochondrial syndromes
Return to Muscle biopsies
10/31/2024