- Sources
- Thespesia populnea: Cotton plant flower
- Gossypium herbaceum: Seed & Root
- Intoxication route: Ingestion of raw cottonseed oil
- Uses
- Male contraceptive
- Uterine hemorrhage (in China)
- Animal feed: Cotonseed
- Epidemiology
- Location: Common in cotton growing areas of China
- Seasonal: More common in Winter & Spring
- Clinical
- Prodrome: Nausea; Anorexia; Tingling in hands; Cramping; Weakness
- Progression: Over 1 to 2 weeks
- Polydipsia
- Polyuria
- GI: Anorexia; Nausea & vomiting
- Palpitations
- Weakness
- Proximal > Distal
- Other: Wrist weakness; Occasional respiratory
- Tone reduced
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Normal cranial nerves & sensation
- Course: Resolution over weeks
- Laboratory
- Serum K+: Low
- Urine: High K+; Distal renal tubular acidosis
- EKG: Long QT; T wave change; PVC; AV block
- Mechanism of myopathy: Hypokalemia
- Treatment
- Stop gossypol intake
- K+ supplementation: IV or oral
- Animal toxicity
- Source: Cottonseed feed
- Affected animals: Non-ruminants; Younger age
- Sudden death
- Cardiomyopathy
|
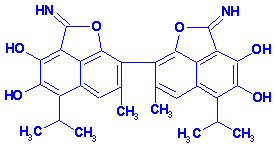
Gossypol
|
|