|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
INFLAMMATORY MYOPATHIES: PATTERNS OF PATHOLOGY
|
Focal inflammation Focal invasion of muscle fiber Granuloma Perimysial (IMPP) MHC-I expression Muscle fiber necrosis Myositis |
Also see: Dermatomyositis Inclusion body myositis Inflammation: Cellular Patterns Lymphorrhages Trichinosis: Acute; Chronic Vasculitis: Small & Large vessel |
Patterns of inflammation
|
Perivascular
Lymphocyte inflammation 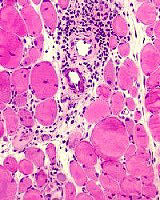
 H&E Lymphocytes: Perivascular May extend into perimysium Common in BCIM |
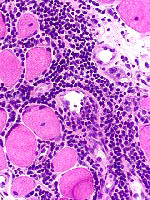
Endomysial
inflammation 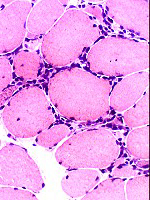 H&E Lymphocytes: Often associated with focal invasion of muscle fibers Common in IM-VAMP |
Perimysial
inflammation 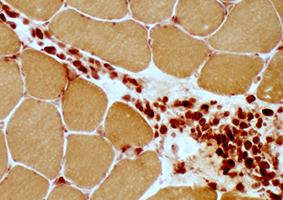 Histiocytes Location: Perimysium Stain for acid phosphatase Common in IMPP |
Granulomatous
inflammation 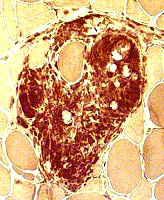 Histiocytes Focal clusters Endomysium or Perimysium Granulomatous disorders |
Focal invasion of non-necrotic muscle fibers by inflammatory cells
|
Morphology Endomysial inflammation Histiocytes MHC Class I General features Ultrastructure |
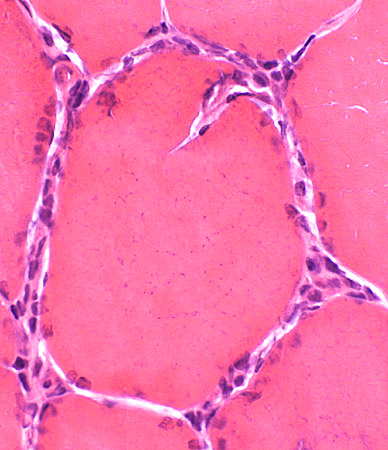
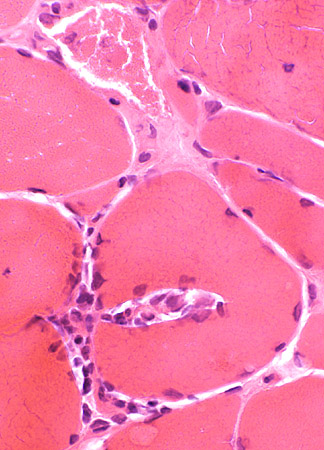 H&E stain |
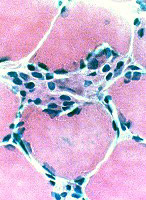
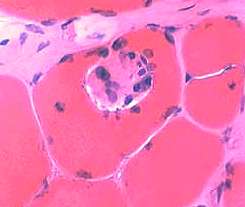  |
Mononuclear cells
Present in: Endomysium; Focal invasion of muscle fibers
Cell Types: Lymphocytes; Histiocytes
Cell Molecular markers: KLRG1; CD8 3
Muscle fiber cytoplasm: Normal color & structure
Common in
IM-VAMP syndromes: Inclusion body myositis & PM-Mito
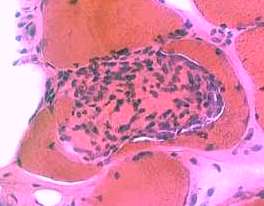
 |
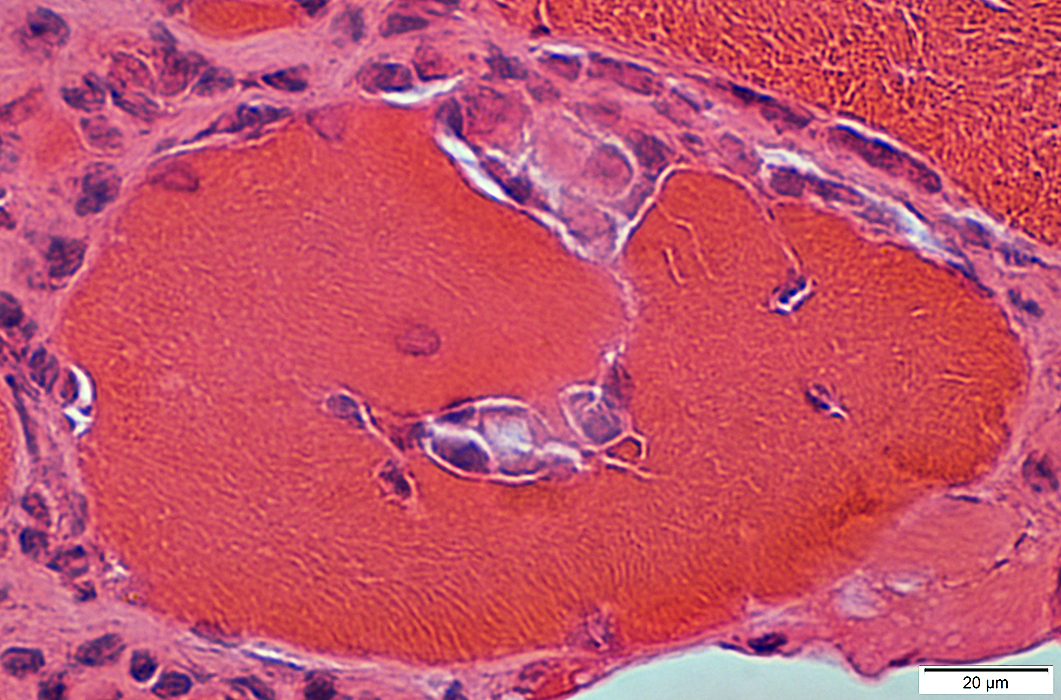 H&E stain |
Present in: Endomysium & Focally invading muscle fibers
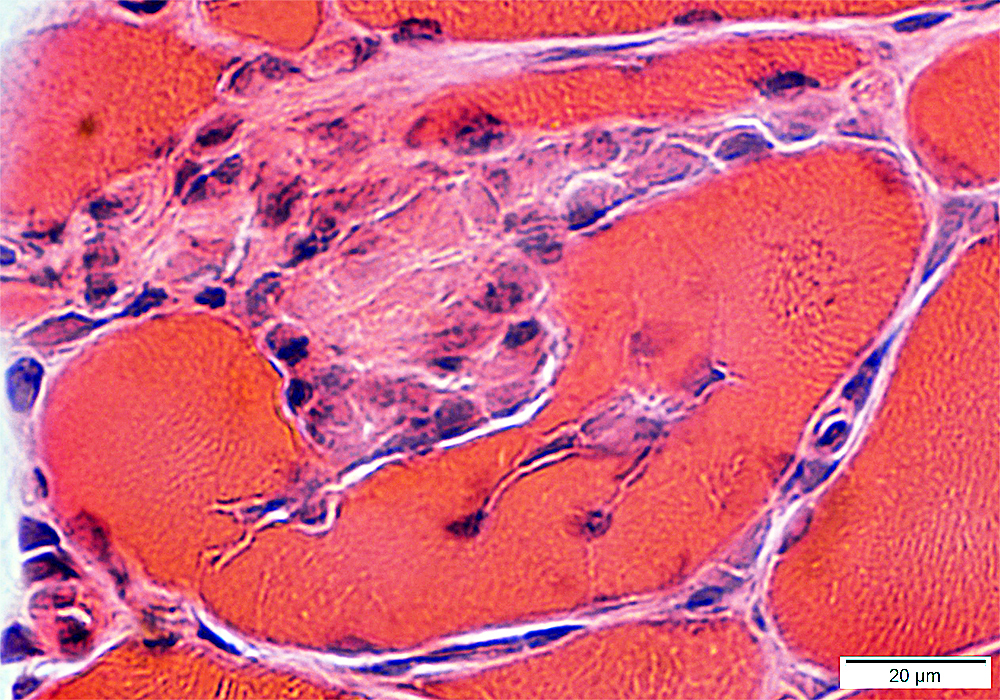 H&E stain |
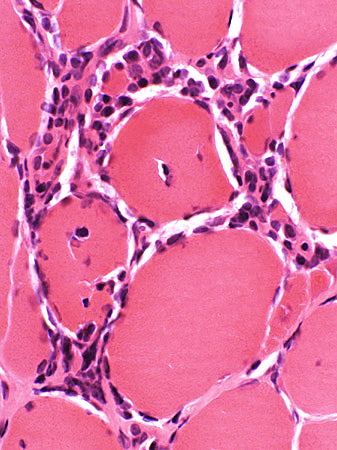
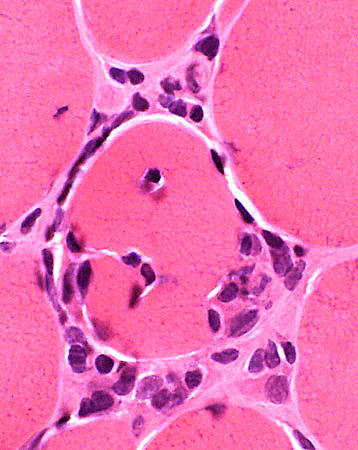
Focal invasion of muscle fibers: Stages
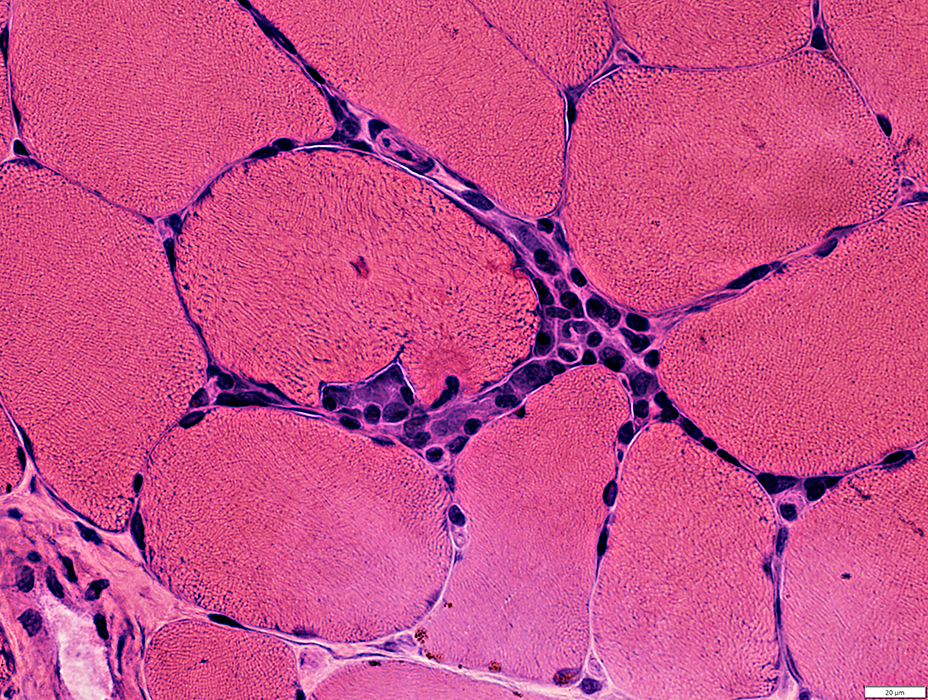 H&E stain |
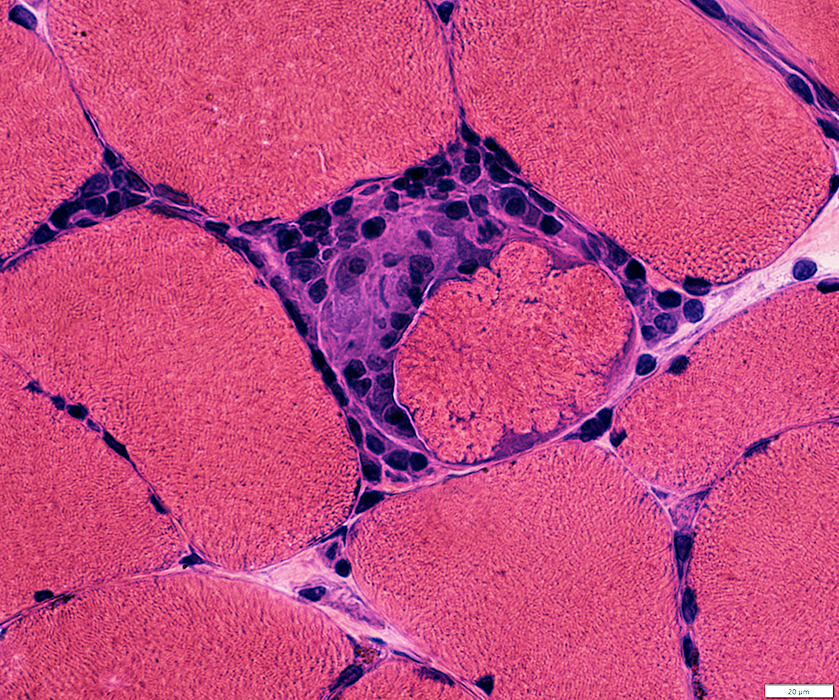 H&E stain |
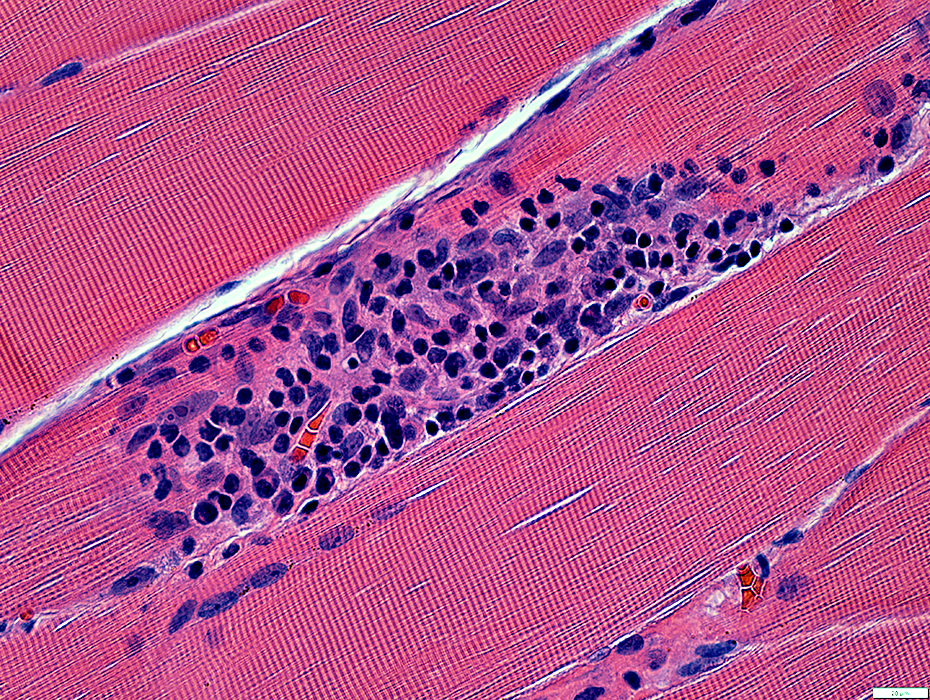 H&E stain |
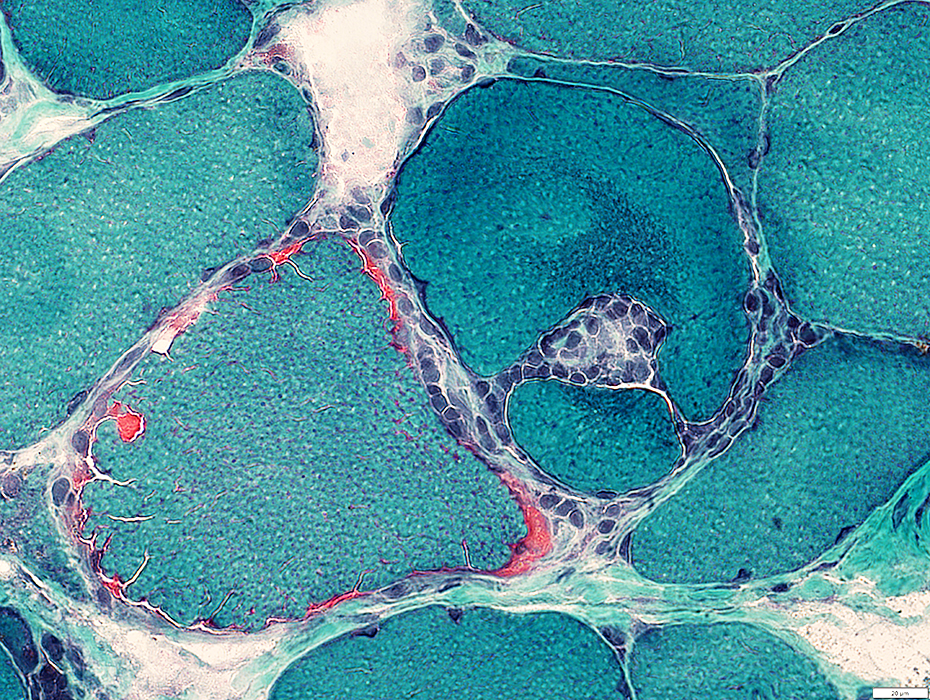 Gomori trichrome stain |
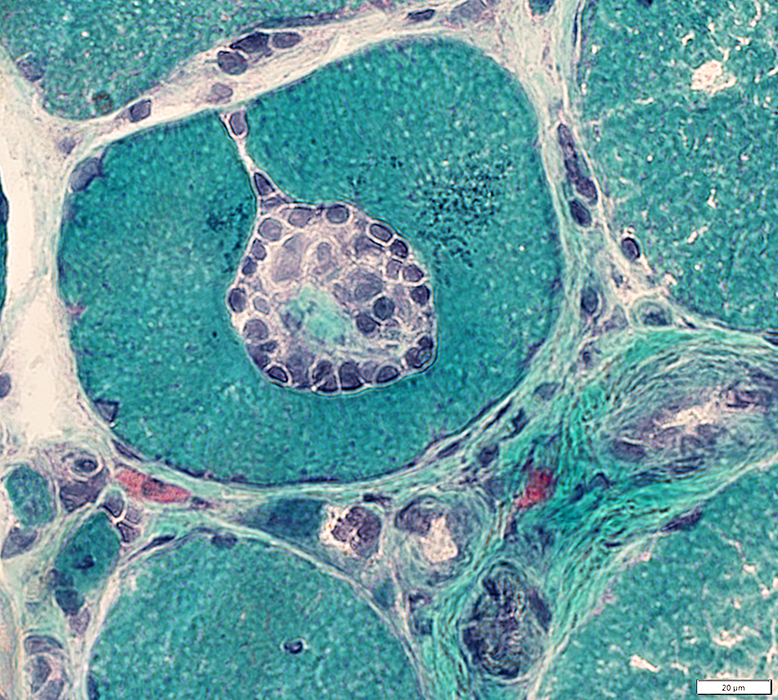 Gomori trichrome stain |
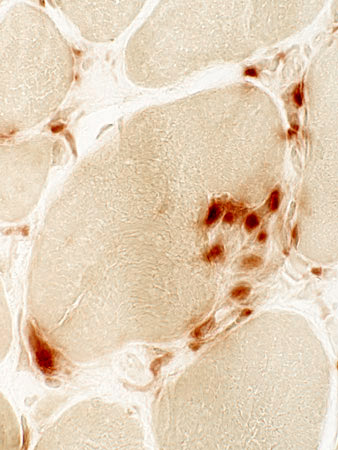
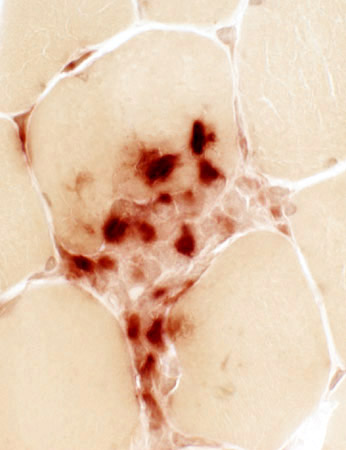 Focal invasion of muscle fibers: Histiocytic cells 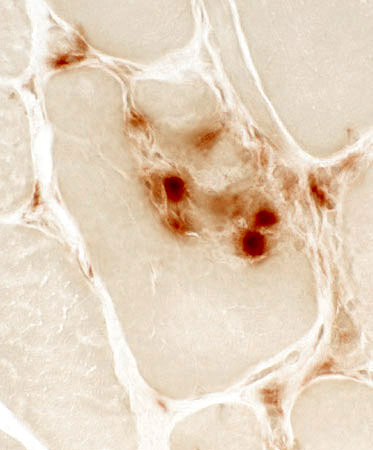
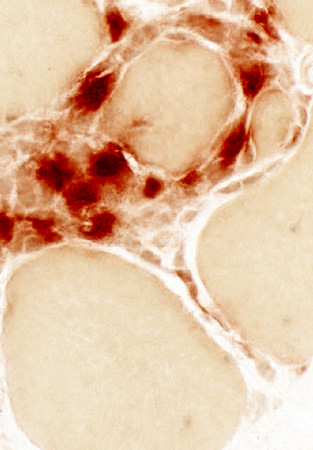 Acid phosphatase stain |
Focal invasion of muscle fibers in IM-VAMP: Histiocytic cells
Histiocytic cells invade muscle fiber (Arrow)
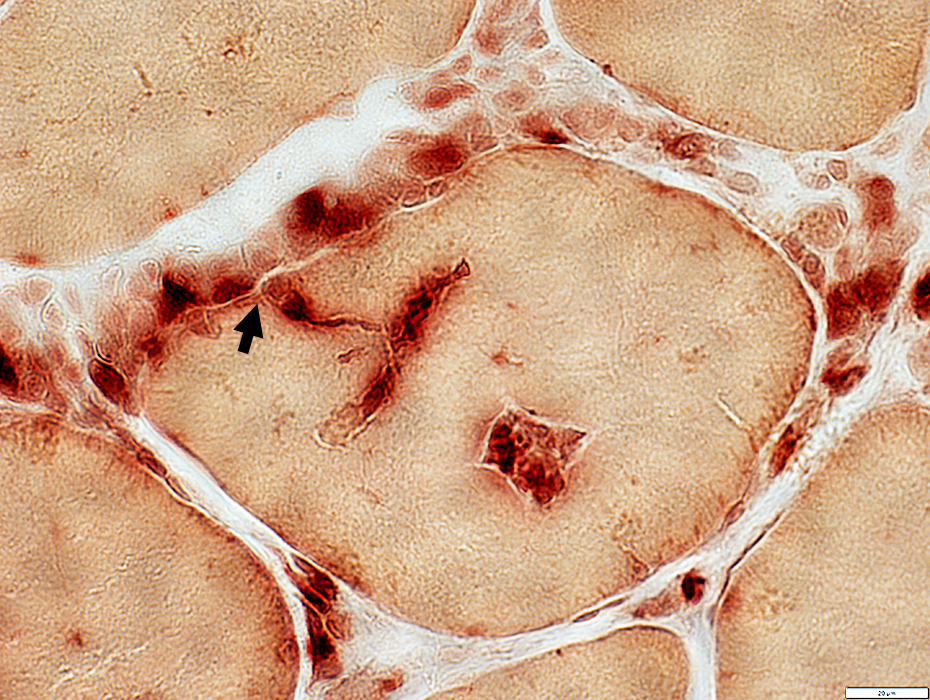 Acid phosphatase stain |
Focal Invasion of Muscle fibers: MHC Class I
Up-regulated by muscle fibers
Strongly expresed by mononuclear cells invading muscle fibers
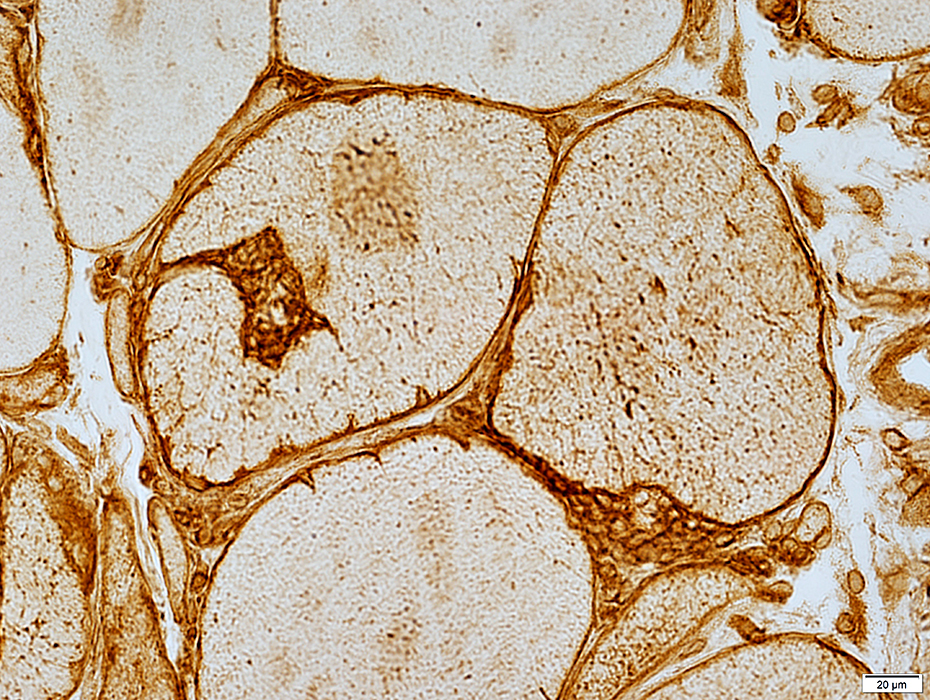 MHC Class I stain |
Features of focal invasion of muscle fibers
|
Necrotic Muscle Fibers
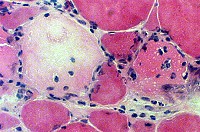 H&E stain Necrosis, Early (Left) Fiber is pale & enlarged Internal nuclei Invading macrophages |
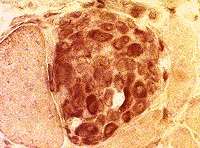 Esterase stain Necrosis, Late Fiber replaced by macrophages. |
|
Also see Muscle fiber necrosis Regional Ischemic Immune Myopathy (RIIM) |
Membrane attack complex deposition on muscle fiber surface
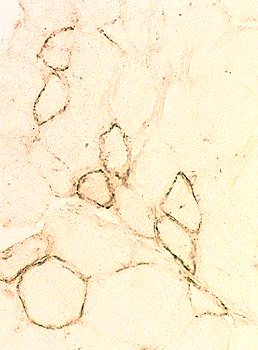
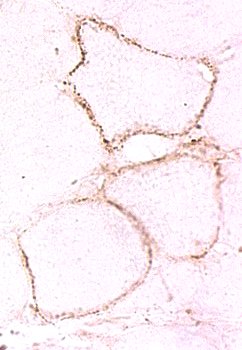 Stain: C5b-9 components of complement (Membrane attack complex (MAC)) C5b-9 deposition without muscle fiber necrosis
|
Major Histocompatibility Complex-1 (MHC-I) Expression in Muscle
General features- Molecular
- Normal muscle
- MHC-I is expressed on capillaries but not muscle fibers
- Inflammatory myopathies & MHC-I
- Upregulation: General patterns
- Muscle fibers
- Surface: Immune disorders
- Cytoplasm: Immature fibers
- Inflammatory cells
- Muscle fibers
- Inclusion body myositis, Sporadic
- Diffuse expression by all muscle fibers: > 95% of patients
- Expressed by histologically normal muscle fibers
- Dermatomyositis & IMPP: Patterns of muscle fiber expression
- Diffuse: Expression on all fibers
- Selective: Muscle fibers near perimysium (perifascicular)
- SRP & HMGCR antibody myopathies
- Expression mainly by regenerating/immature muscle fibers
- Upregulation: General patterns
- Hereditary myopathies
- Usual: MHC-I is expressed on capillaries & scattered regenerating muscle fibers
- Up-regulation by muscle fibers more common
MHC-II expression in Muscle
- General pattern: Perifascicular muscle fibers
- Commonly present: IMPP; Ku antibody IIM
- Uncommon: DM-VP
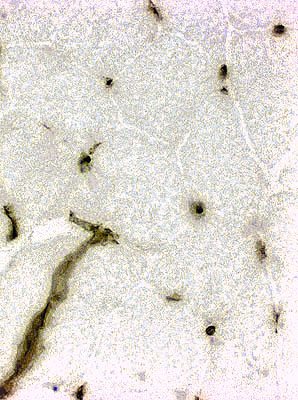 Normal
MHC-I on small vessels but not muscle fibers |
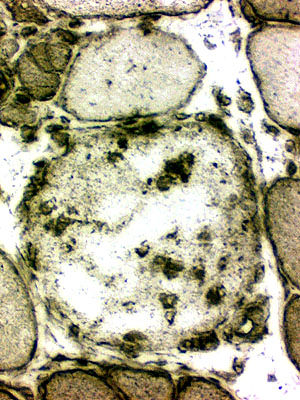 Necrosis
MHC-I on phagocytic cells in a muscle fiber |
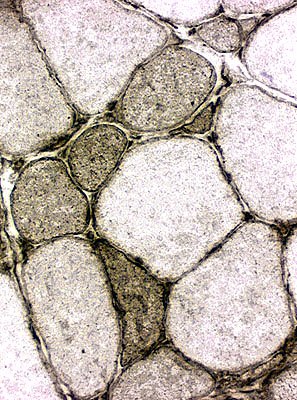
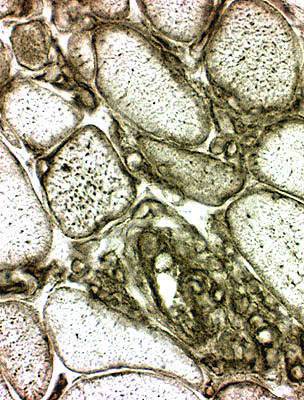 Inclusion Body
Myositis
MHC-I on surface of most or all muscle fiber MHC-I increased in cytoplasm of regenerating muscle fibers MHC-I also stains mononuclear cells in infiltrate (Right) |
|
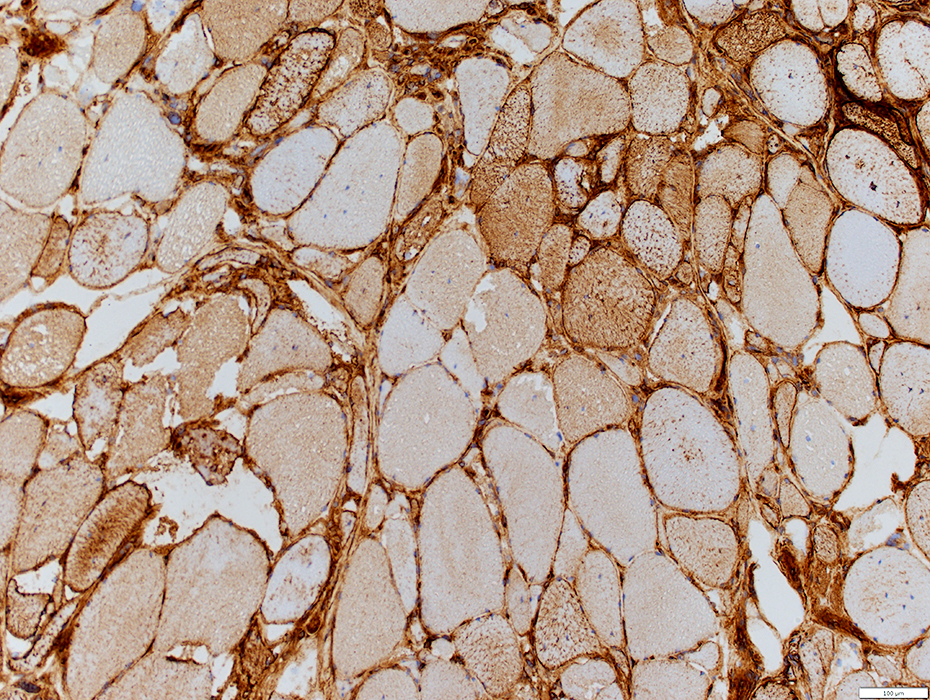 MHC Class I stain |
Return to Inflammatory myopathies
Return to Neuromuscular Syndromes
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
References
1. Neurology 2002;58:1779–1785
2. Neurology 2017 Aug 9
3. Brain 2019;142:2590-2604
12/12/2025