Immune Myopathies with Perimysial Pathology (IMPP) 1
|
Clinical syndromes Dermatomyositis: Adult > Child onset Graft-vs-Host Myopathies with Anti-Jo-1 Antibodies Other tRNA synthetase antibodies High Aldolase & Normal CK Scleroderma Enterovirus Sarcoidosis Drug-related Minocycline Anti-TNF-α Dermatomyositis vs IMPP IMPP muscle pathology Adult-onset IMPP HMGCR antibody Jo-1 antibody + pathology PL-12 antibody + pathology Enterovirus (EVIM) |
 H&E stain |
IMPP: General
Clinical Features
Immune Dermatomyopathies: Comparative Features
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dermatomyopathies, General: Neoplasm associations 3
IMPP Muscle Pathology (Jo-1 antibody positive)
|
Perimysial Pathology Cellularity Endomysial Perimysial Structure: Damage Alkaline phosphatase staining Muscle fiber pathology |
Jo-1 myopathy: Perimysial Pathology
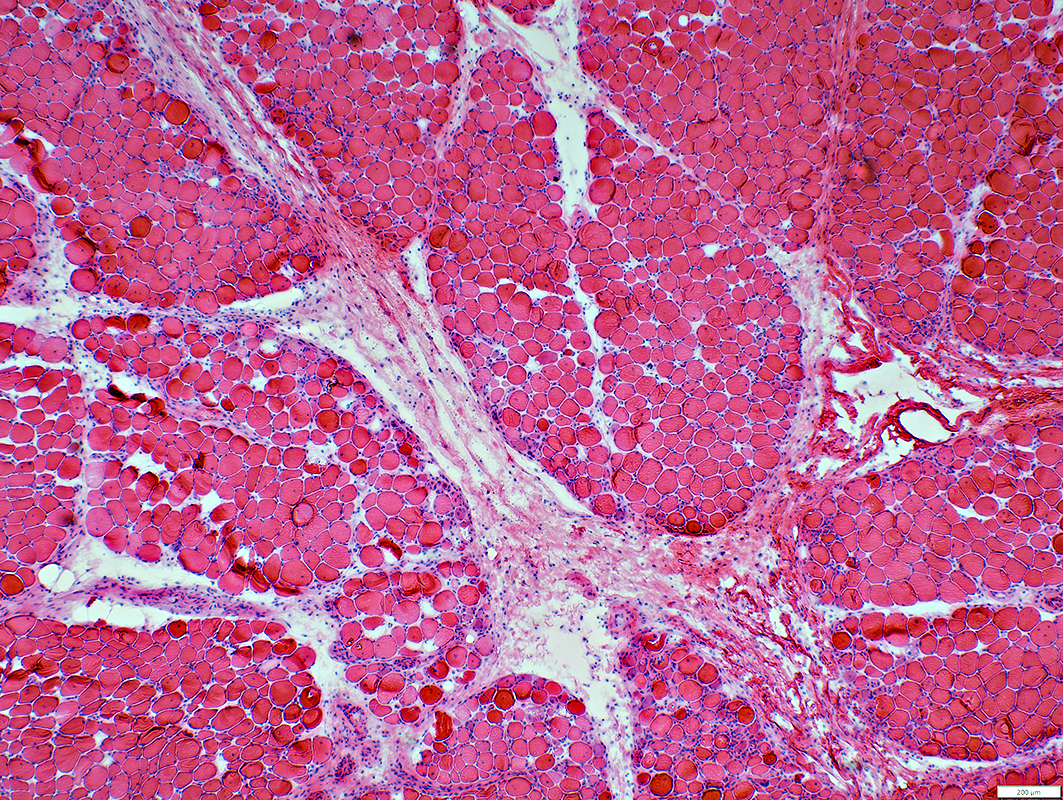 H&E stain |
- Perimysium
- Rarified (Pale)
- Fragmented
- Loculated: Many focal clear and darker areas
- Wide
- Cells: Most frequently macrophages
- Large nuclei
- Prominent cytoplasm
- Staining for Acid Phosphatase, Esterase and CD-68
- Muscle fibers Adjacent to Perimysium
- Perifascicular myopathy
- Regeneration (Immaturity): Large nuclei; Basophilic cytoplasm
- Necrosis
- Small size
- Perifascicular myopathy
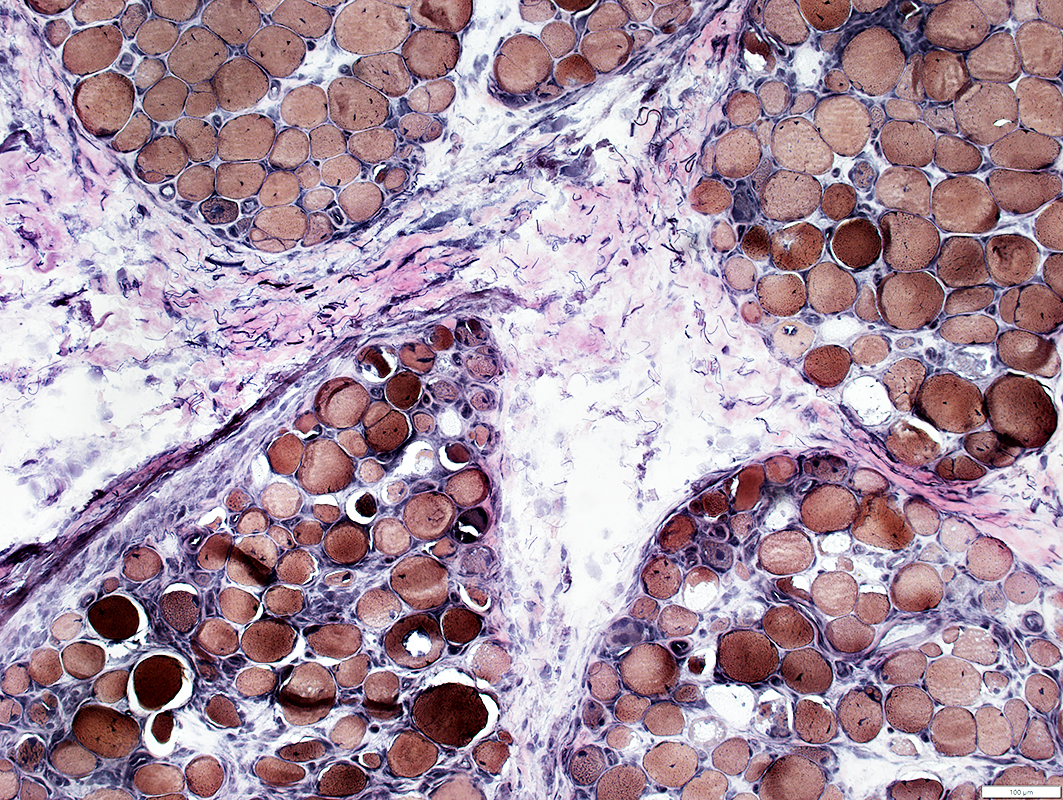 VvG stain |
 H&E stain |
 H&E stain |
Loculation: Small & Large holes (Above)
Pallor (Below)
Cells: Many scattered histiocytes (Cells with large nuclei)
Muscle Fibers
Small or Immature: In regions neighboring perimysial pathology
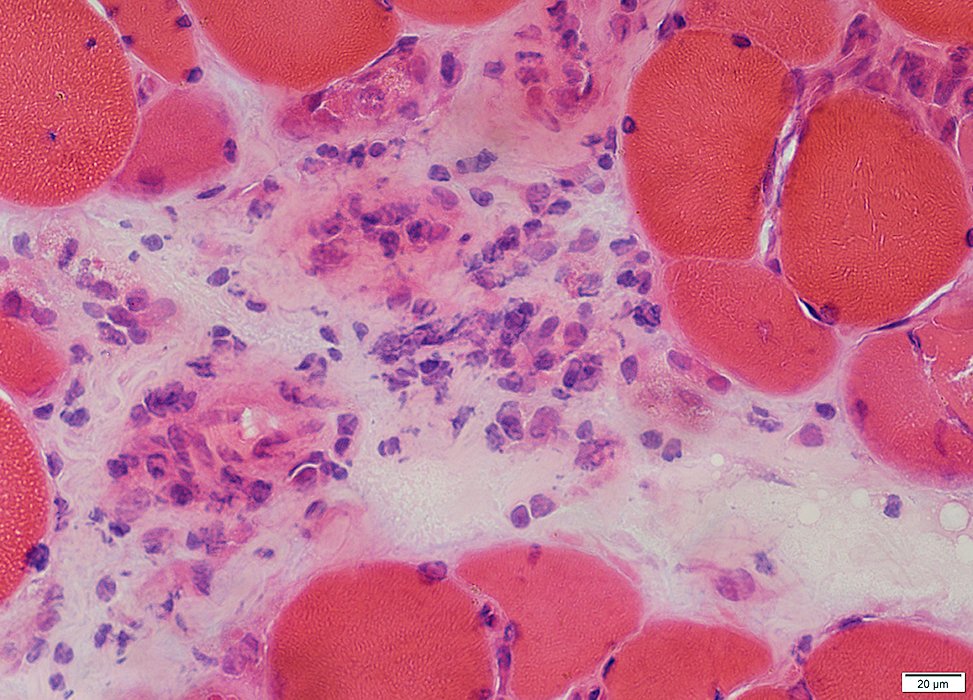
|
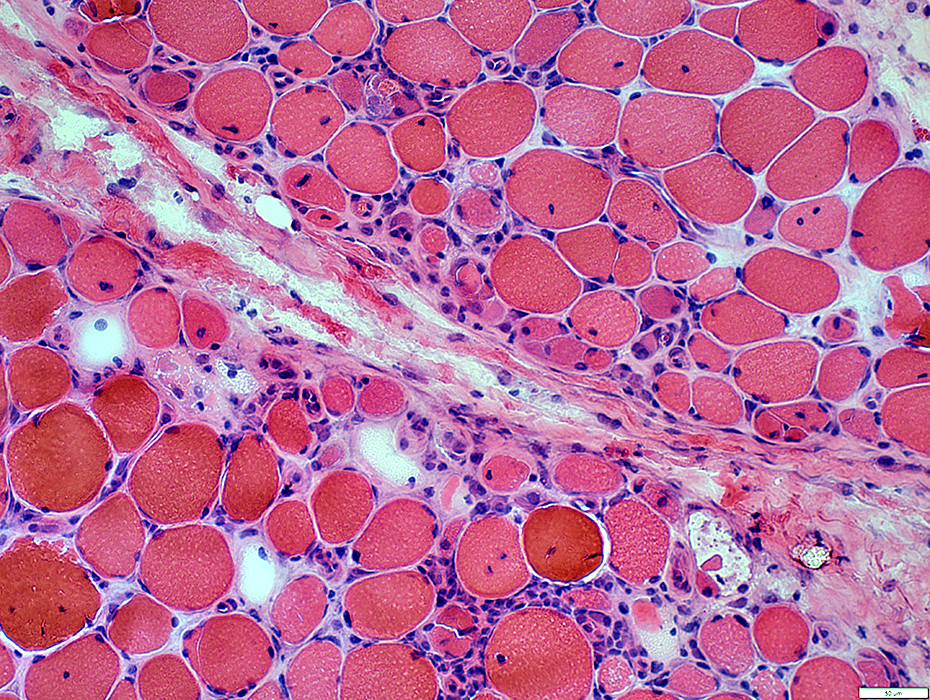
 H&E stain |
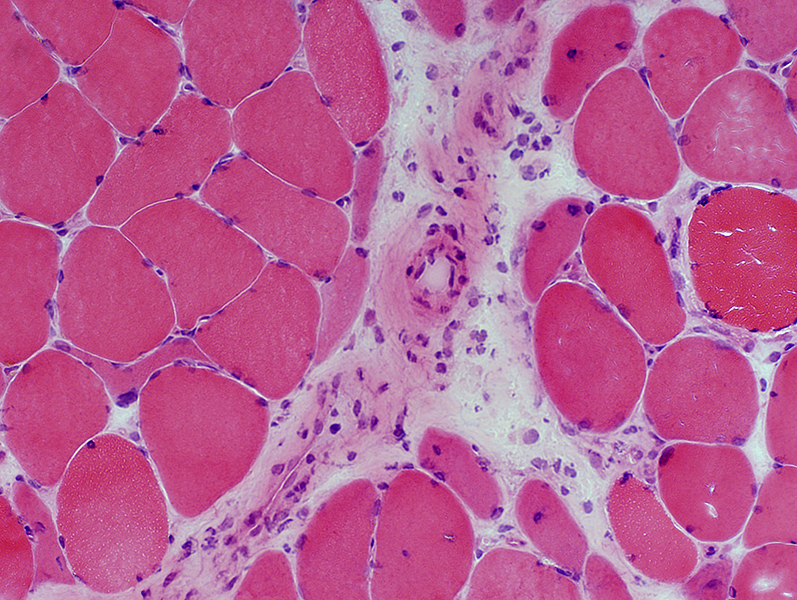
Damaged structure (Irregular, Pale regions)
Cellularity: Large cells with cytoplasm & large nuclei
Neighboring myopathology:
Muscle fibers: Necrotic & Regenerating (Small, Basophilic)
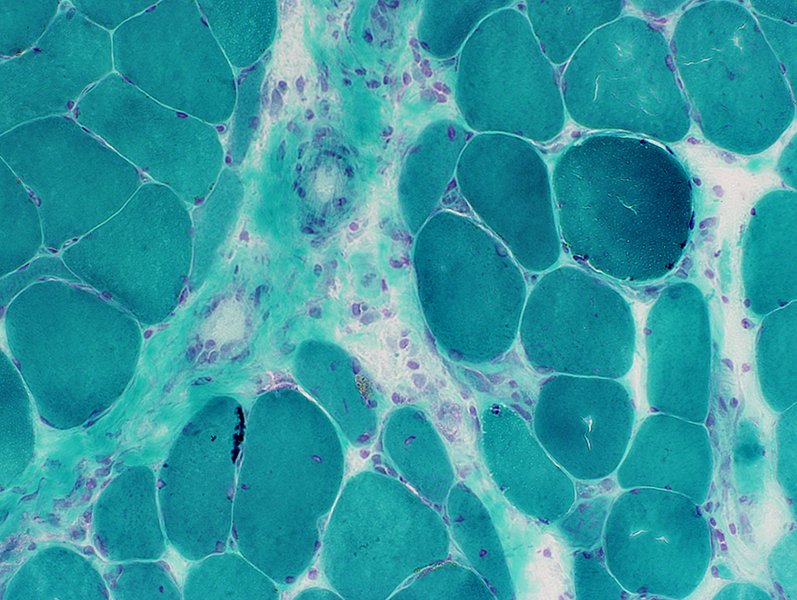 Gomori trichrome stain |
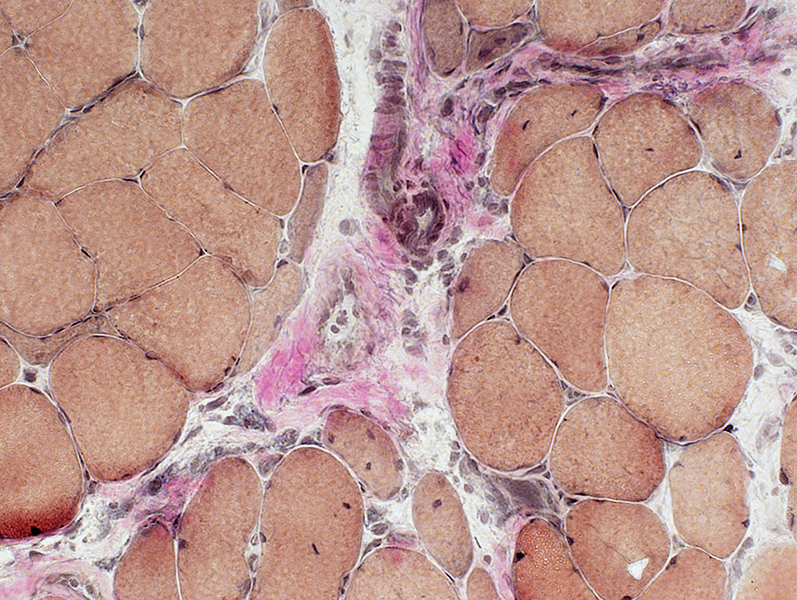 VvG stain |
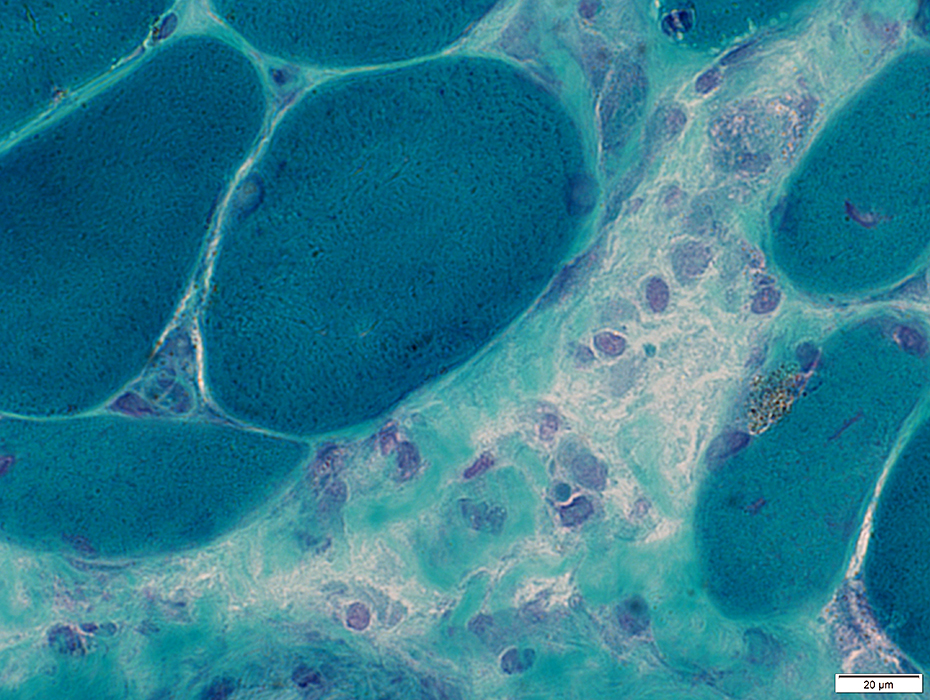 Gomori trichrome stain |
 Gomori trichrome stain |
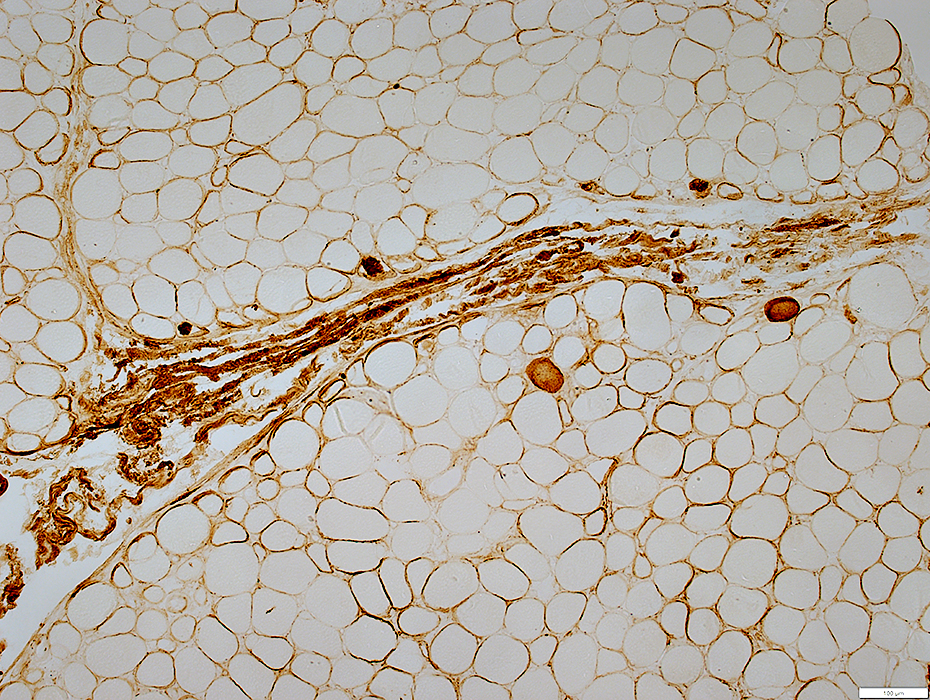 C5b-9 stain |
C5b-9 may also stain
Neighboring endomysial connective tissue around muscle fibers
Surface of muscle fibers
Cytoplasm of nearby necrotic muscle fibers
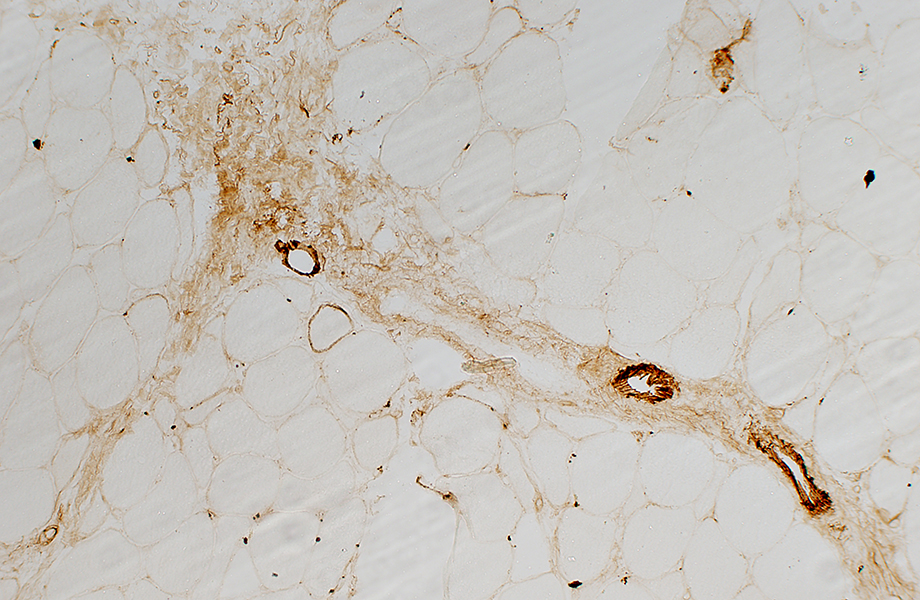 C5b-9 stain |
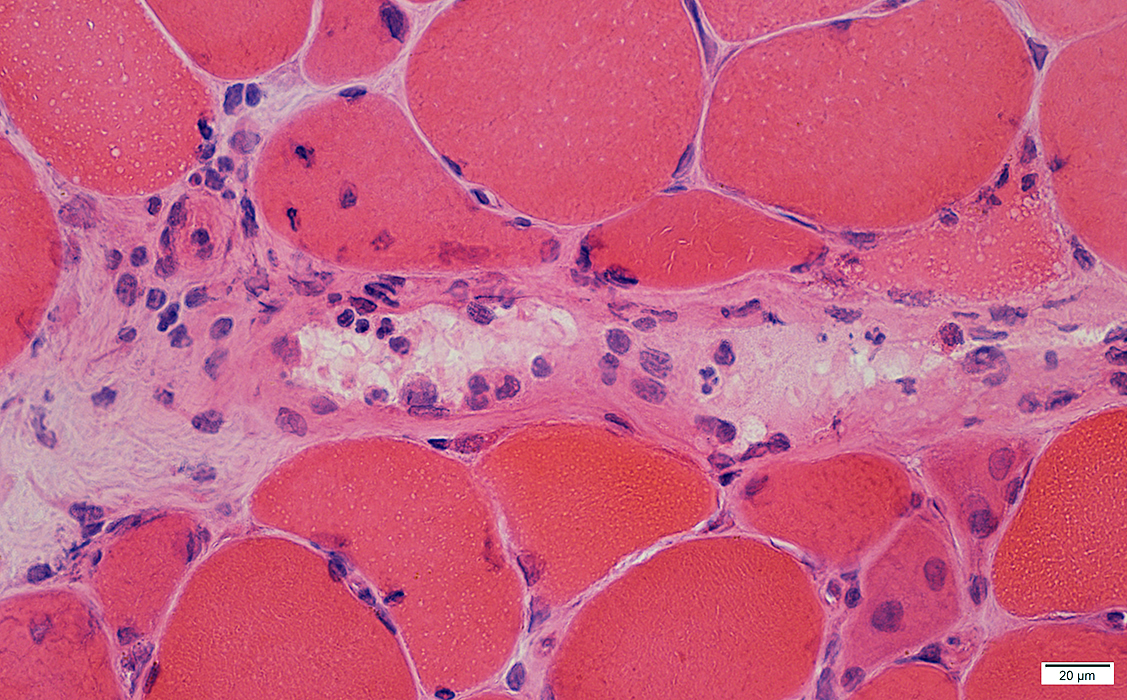
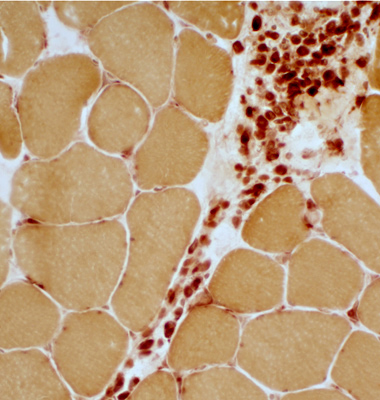
Perimysium: Inflammation, Usually histiocytic
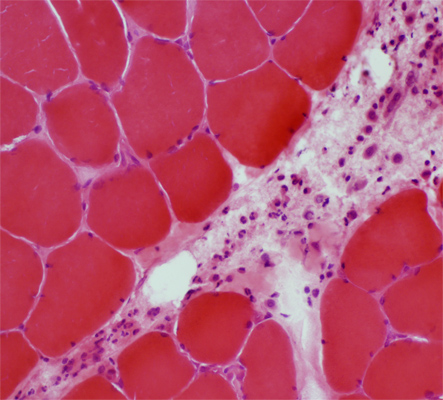
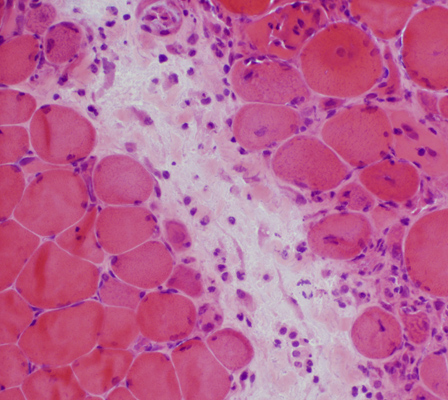 H&E stain |
Size: Large
Nuclei: Large
Cytoplasm: Visible around nucleus
Distribution: Scattered in regions of perimysium
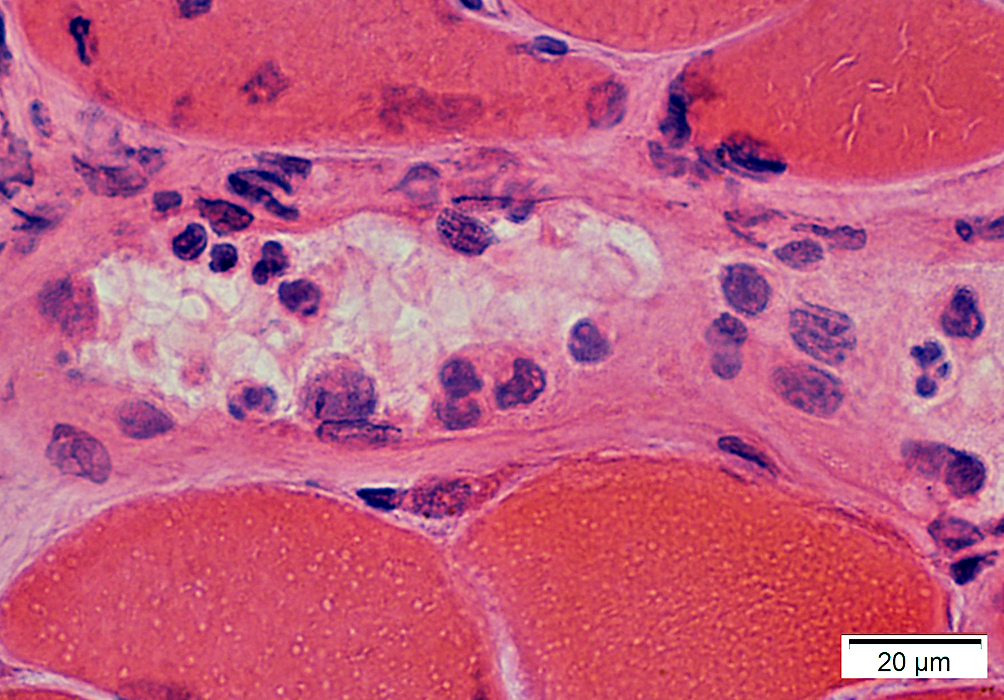 H&E stain |
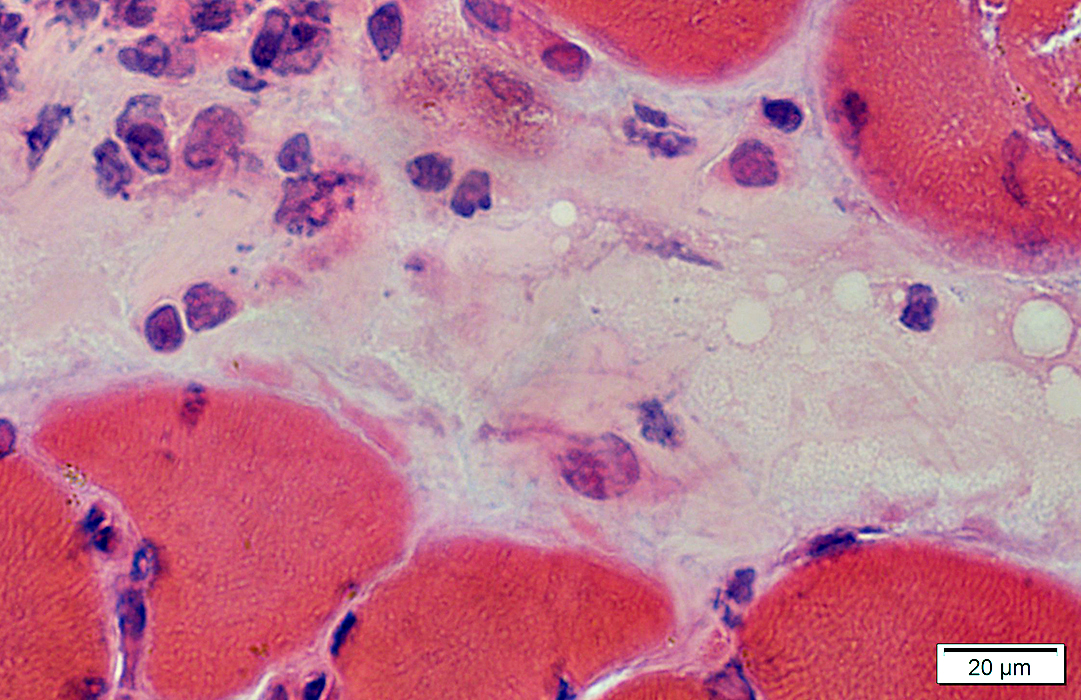 H&E stain |
Cells in perimysium: Histiocytic
Stain for Acid phosphatase, Esterase & CD68
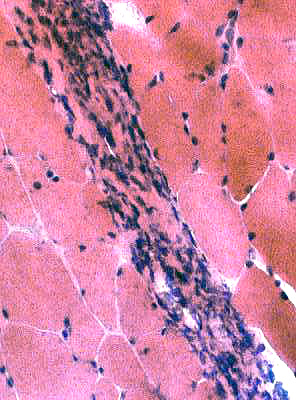 H&E stain |
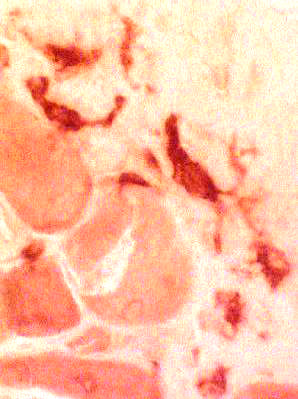 Esterase Esterase positive macrophages |
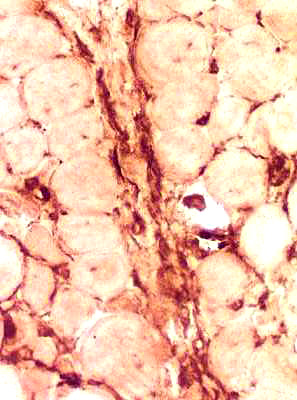 CD68 stain CD-68 positive cells in perimysium and endomysium |
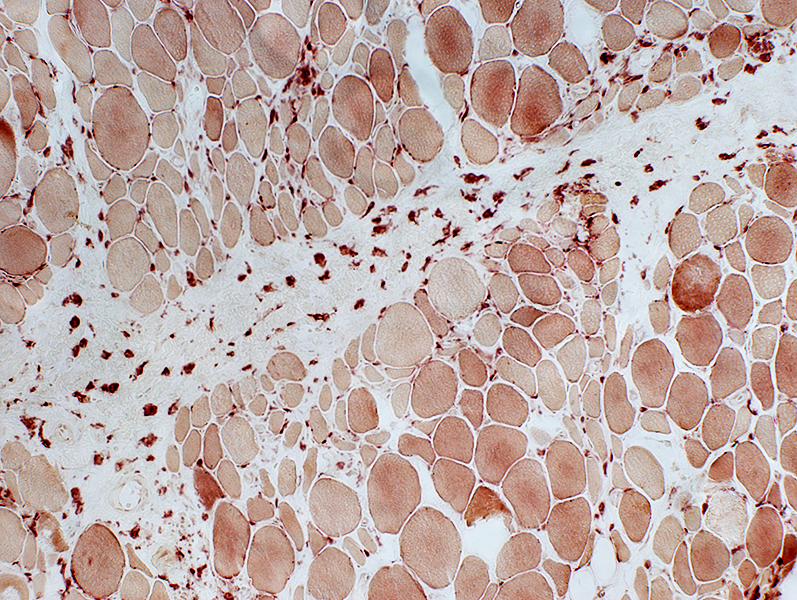 Esterase Perimysium: Esterase positive macrophages | ||
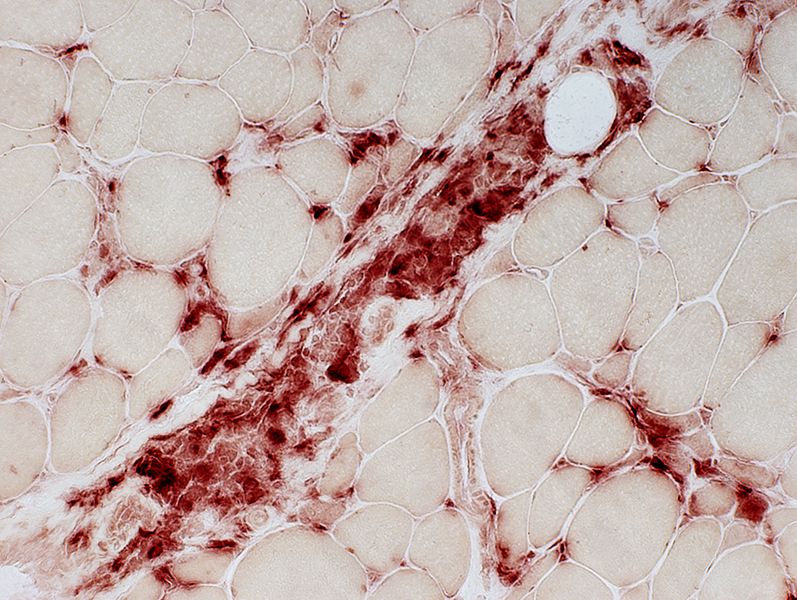
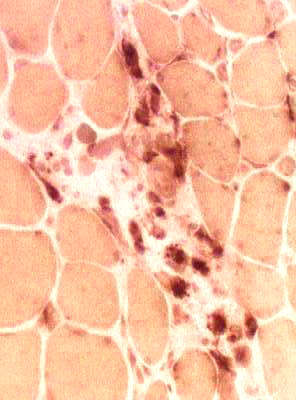 Acid phosphatase |
 Acid phosphatase |
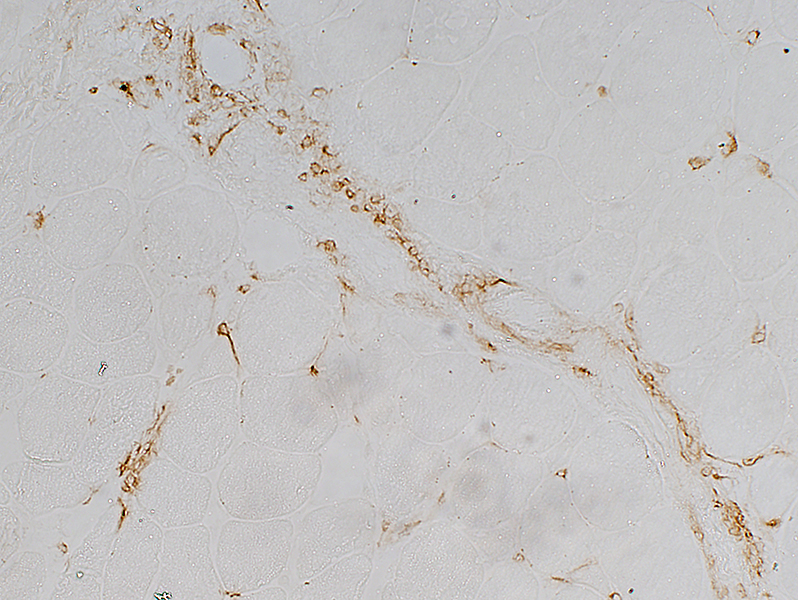
| Acid phosphatase positive cells: Predominantly in Perimysium; Scattered in endomysium | |
 Acid phosphatase |
 CD4 stain |
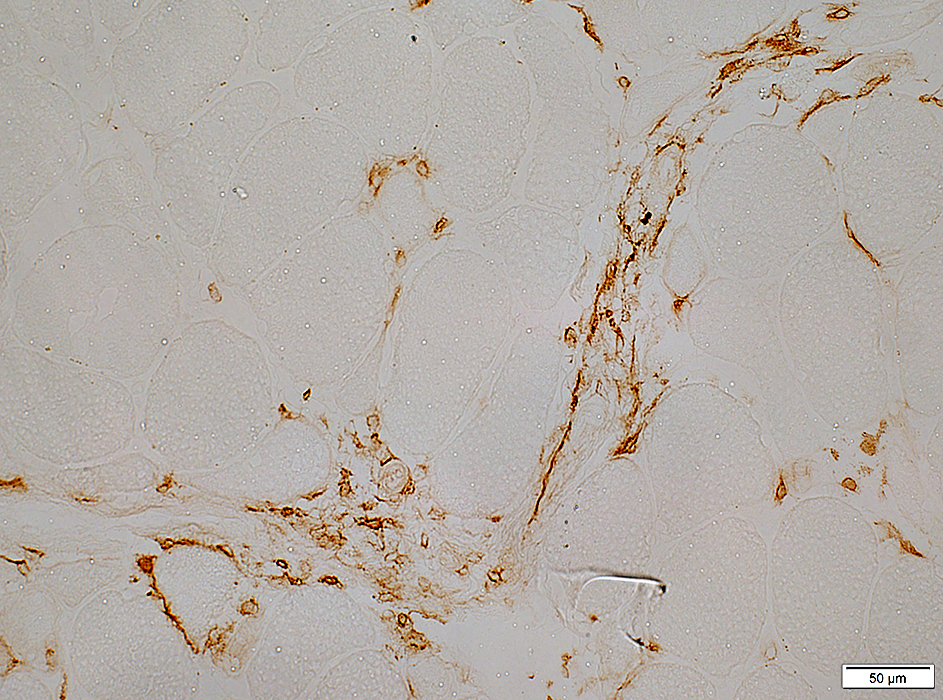 CD4 stain |
Endomysial Histiocytes: Activated
Stain: Acid phosphataseLocation: Often near endomysial capillaries
Commonly occur with: MHC-I upregulation by neighboring muscle fibers
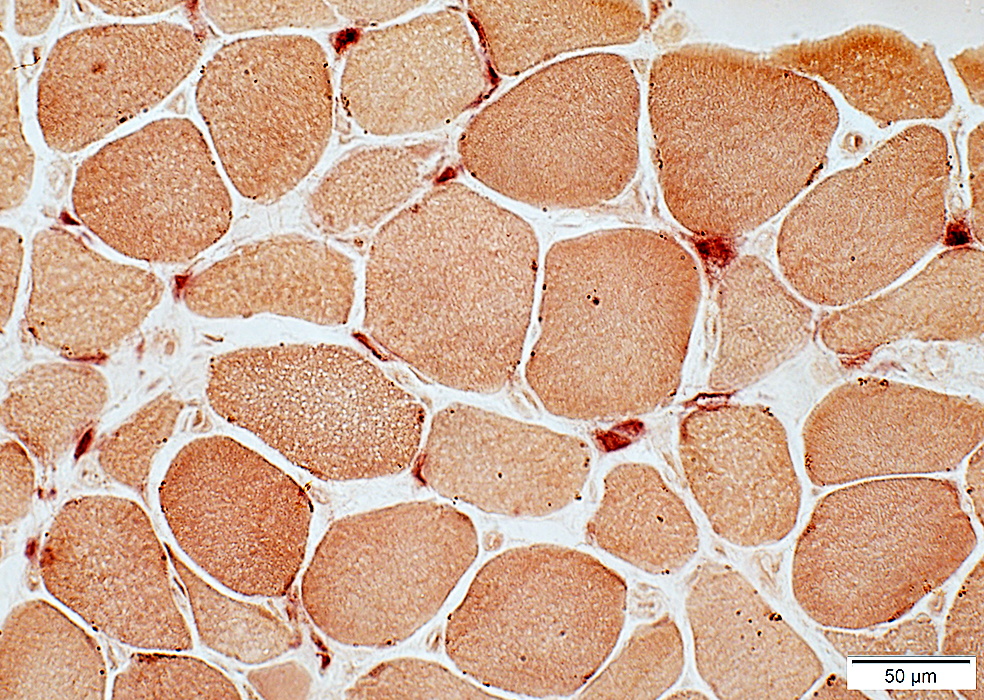 Acid phosphatase stain |
Scattered in endomysium
Often with neighboring: Capillary (Arrow) or Small endomysial vessel
Pattern is common to many active myopathies: Not specific for Jo-1
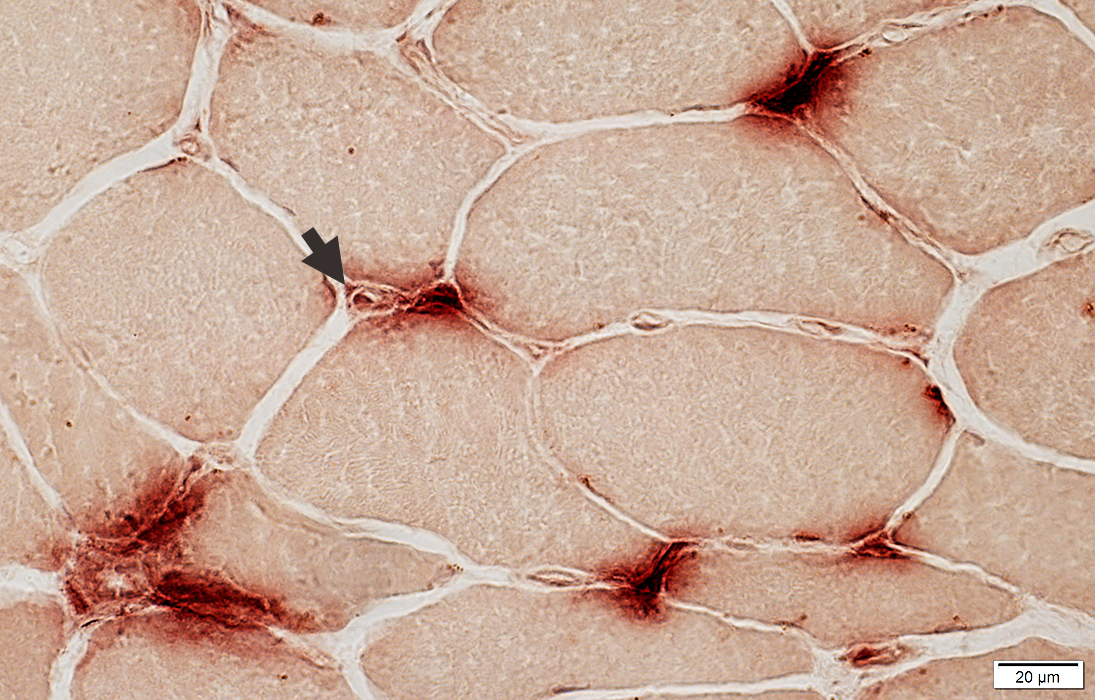 Acid phosphatase stain |
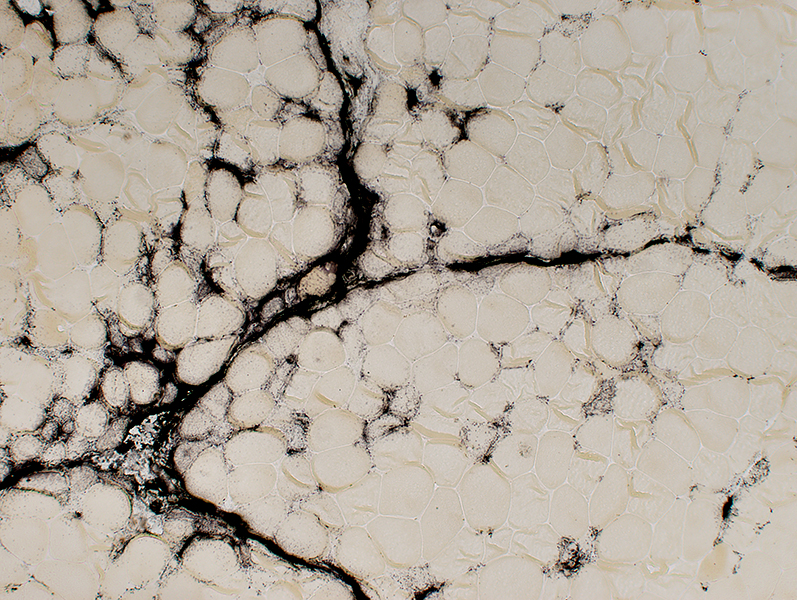 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Perimysium
Extends into endomysium
Muscle fiber cytoplasm (Smaller, immature fibers)
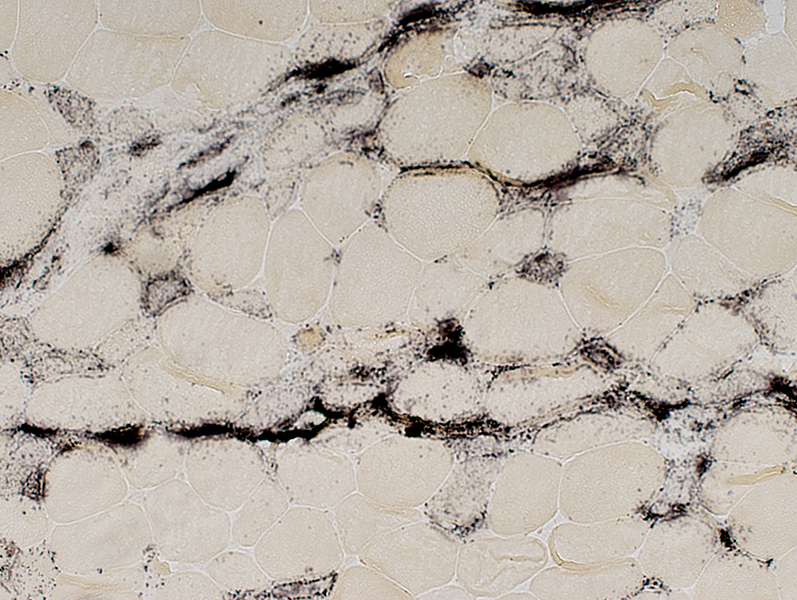 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Jo-1 myopathy: Muscle fiber pathology
Type: Necrosis & Regeneration
Distribution: Perifascicular; Near damaged perimysium (Arrows)
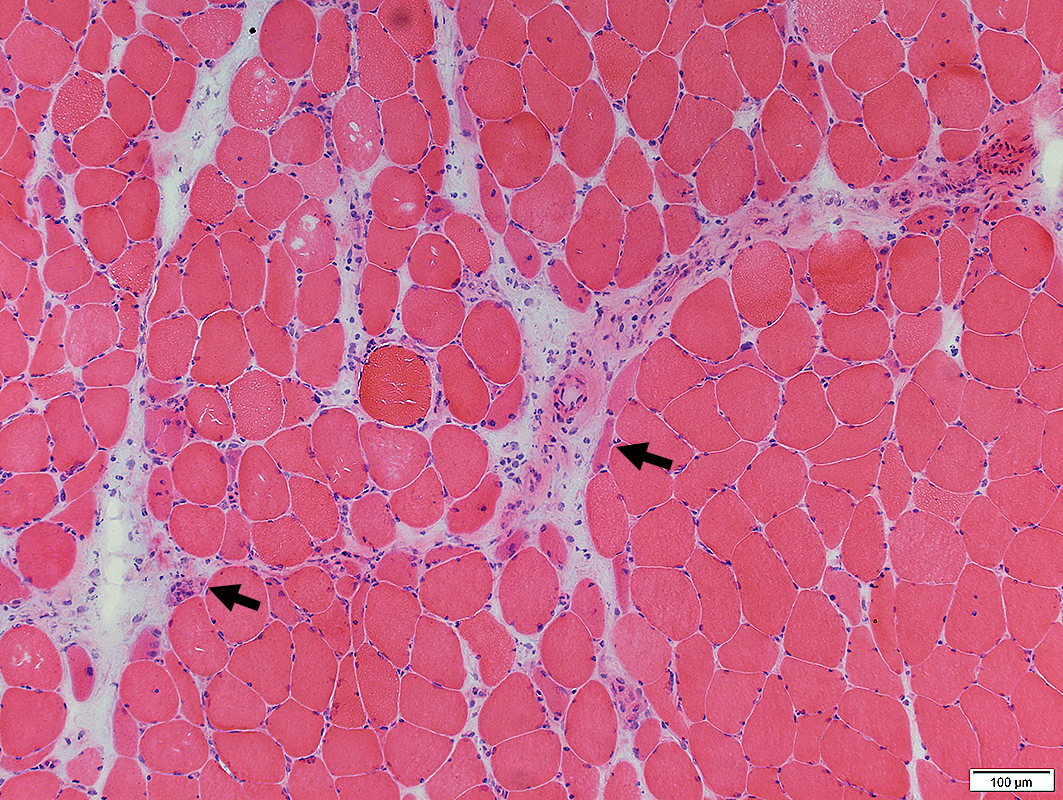 H&E stain |
Myopathic
Necrotic & Immature Muscle Fibers
Predominantly at edge of fascicles, near damaged perimysium (Arrows)
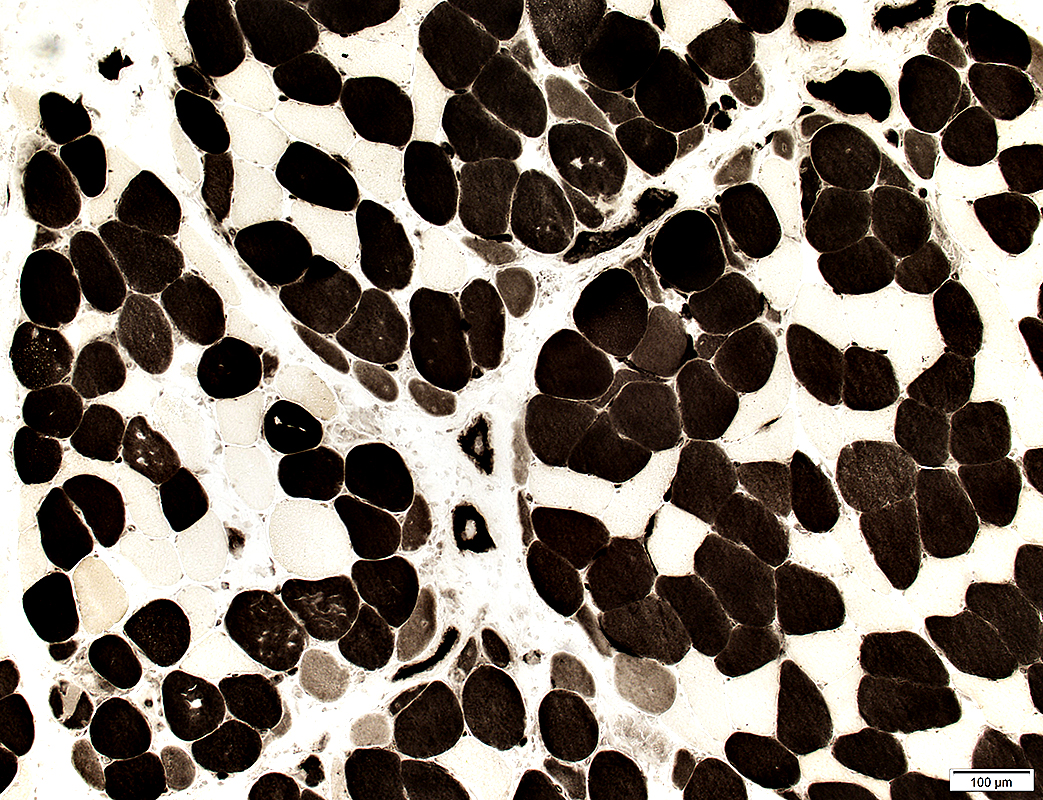 H&E stain |
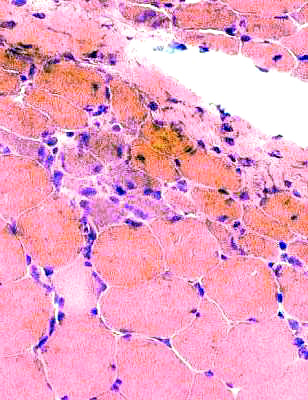 H&E stain Perifascicular myopathy Regeneration & Necrosis of perifascicular muscle fibers |
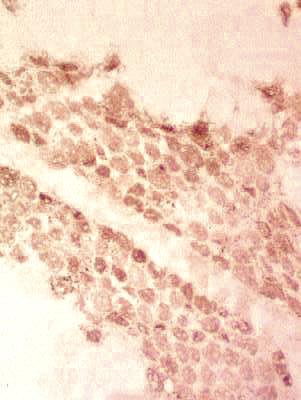 NCAM stain N-CAM positive atrophic muscle fibers |
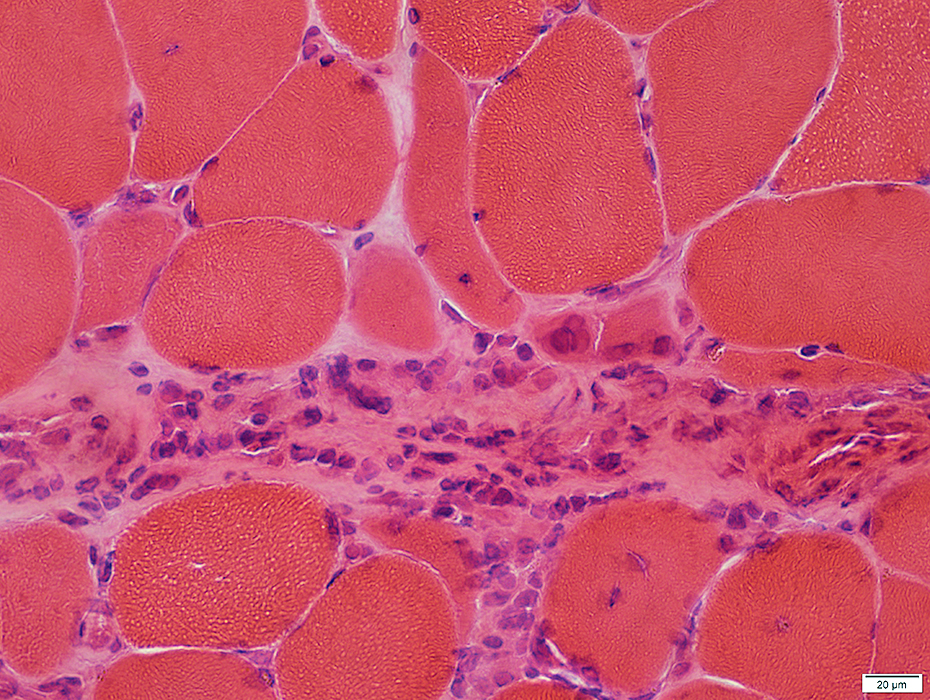 H&E stain |
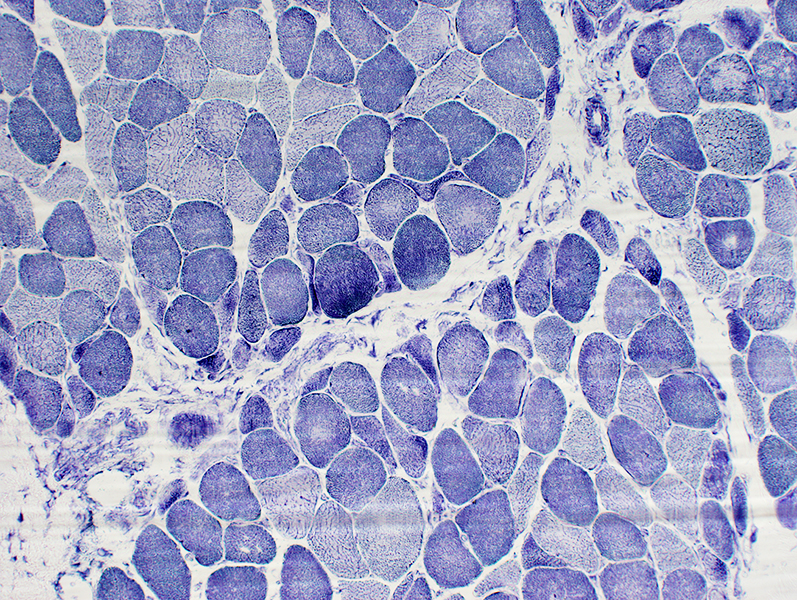 NADH stain |
Perifascicular atrophy: Small Muscle fibers are more frequent at the edge of fascicles NADH stain |
Perifascicular Myopathy
Immature (Smaller, Intermediate-stained) muscle fibers: More common at edge of fascicles
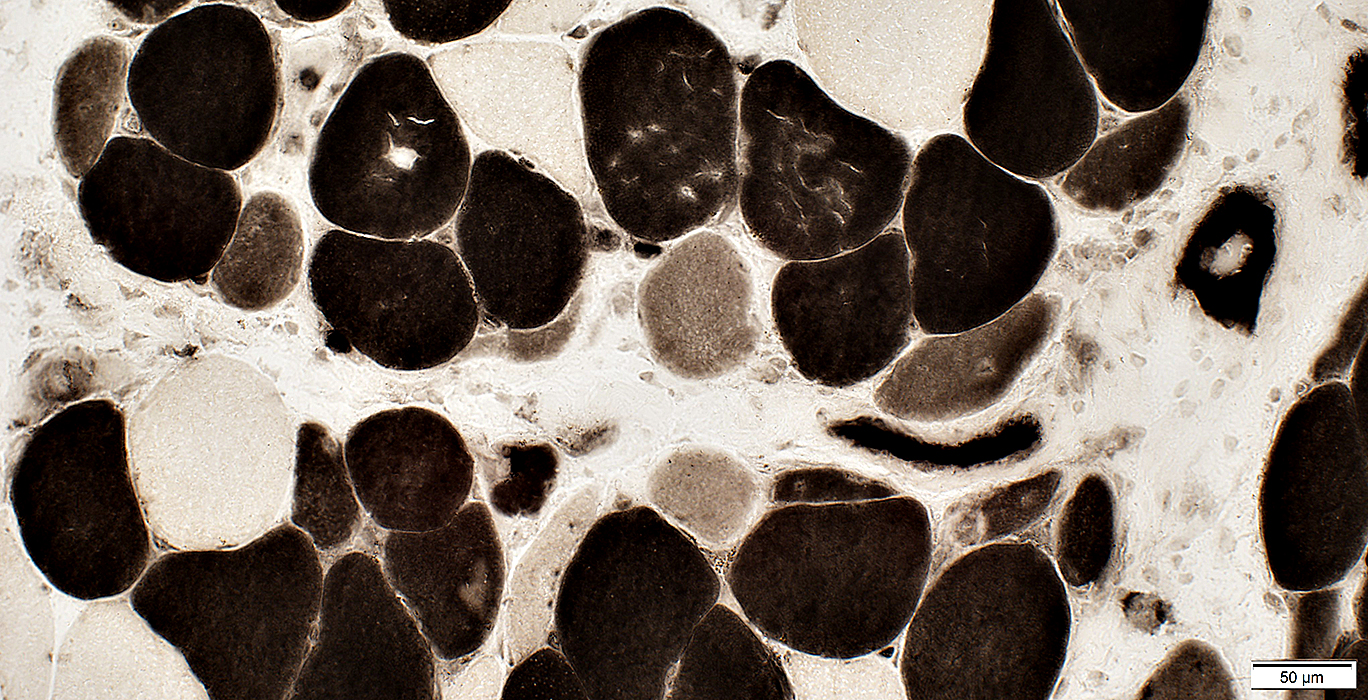 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
Myopathy with Jo-1 antibodies
MHC-I stainDiffusely on muscle fiber surface membranes
Cytoplasm of perifascicular muscle fibers
Perimysium: Damaged connective tissue & Scattered cells
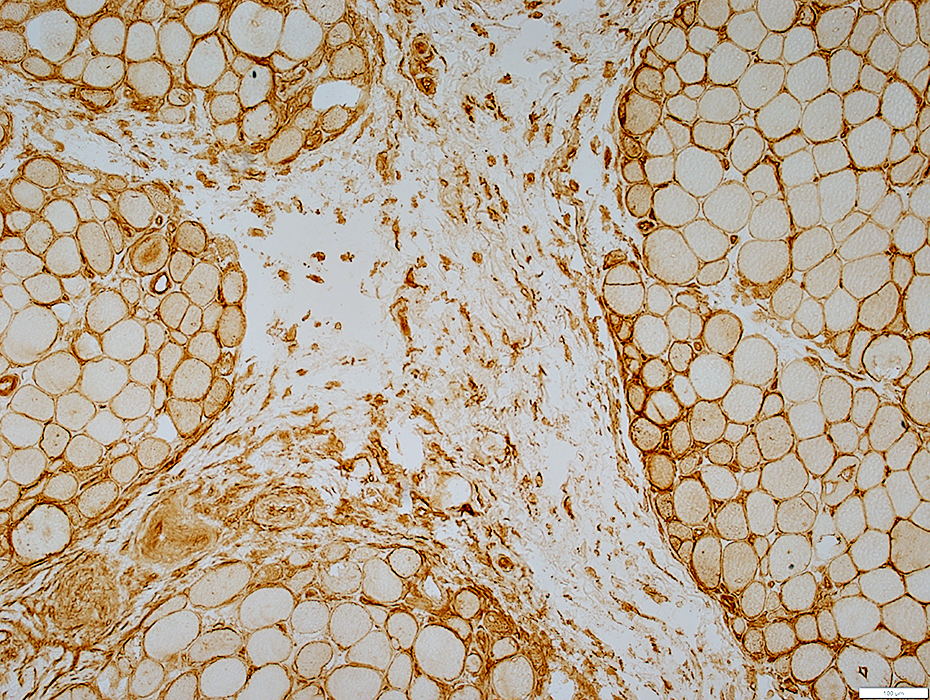 MHC-I stain |
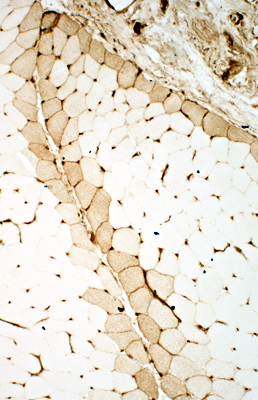 MHC-I stain MHC Class 1 staining Positive muscle fibers are Perifascicular (Above), or Diffuse (Right) Have Similar patterns in DM + Vascular Pathology Perimysial cells also stain (Below) |
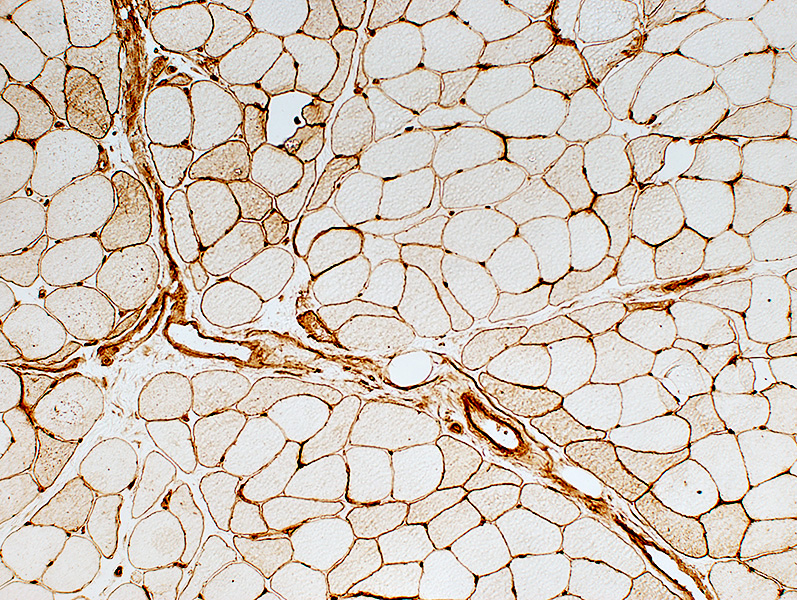 MHC-I stain |
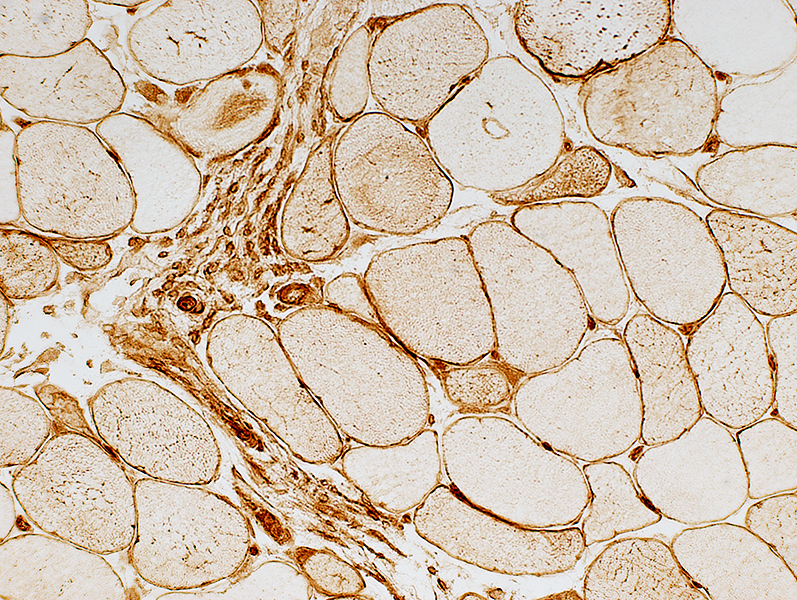 MHC-I stain | |
Jo-1 Immune Myopathy: Muscle Fiber Necrosis & Regeneration
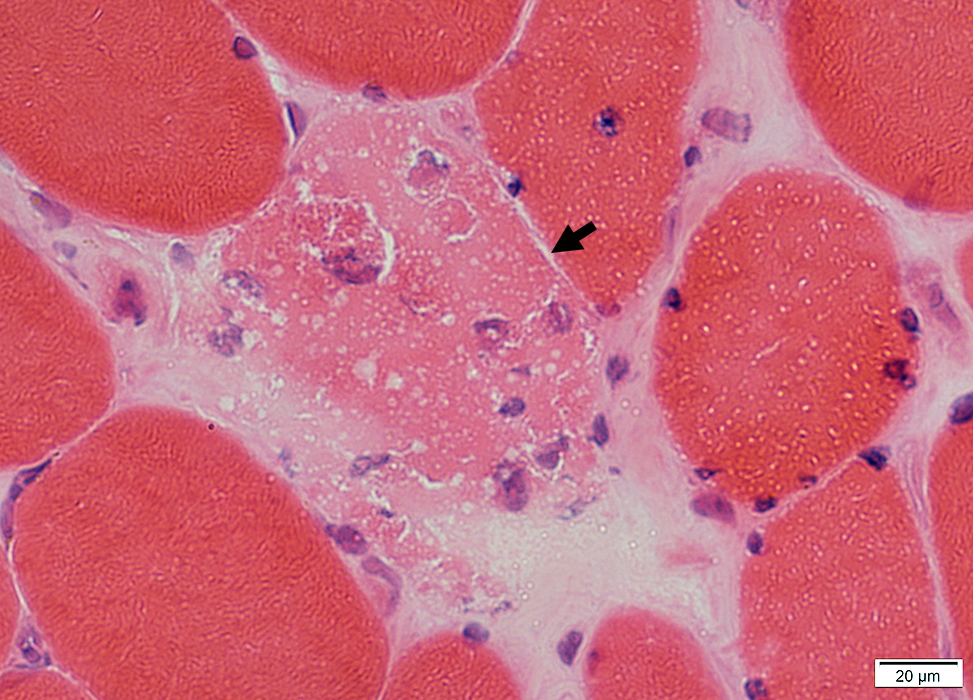 H&E stain |
Muscle fiber pathology: More prominent near edges of fascicles
Necrotic Muscle Fibers (Dark arrow)
Pale cytoplasm
Invaded by histiocytic cells
Regenerating Muscle Fiber (White arrow)
Nuclei: Large
Cytoplasm: Basophilic
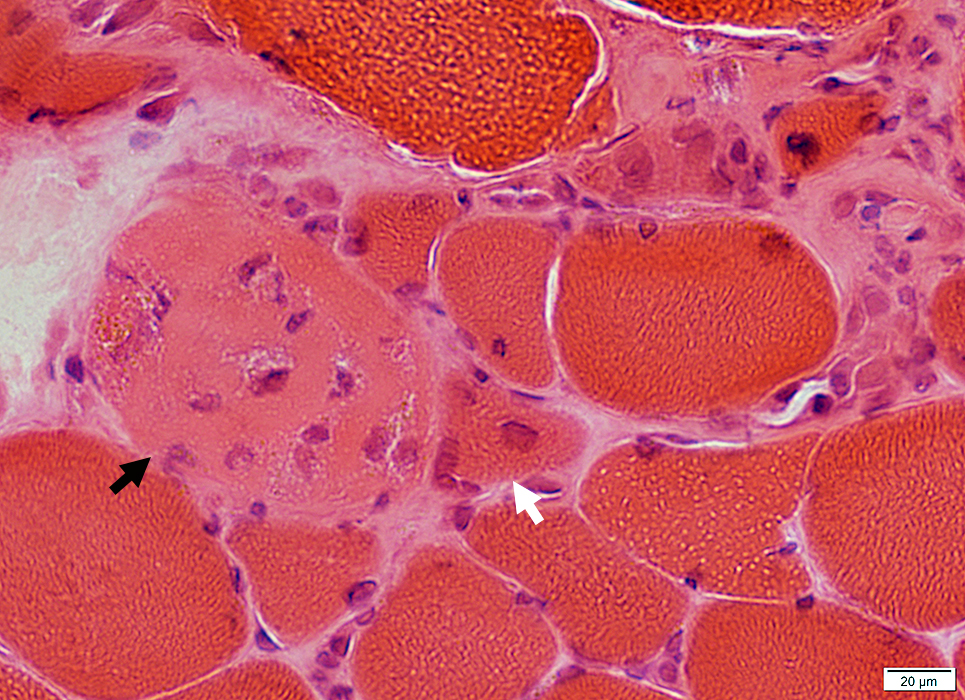 H&E stain |
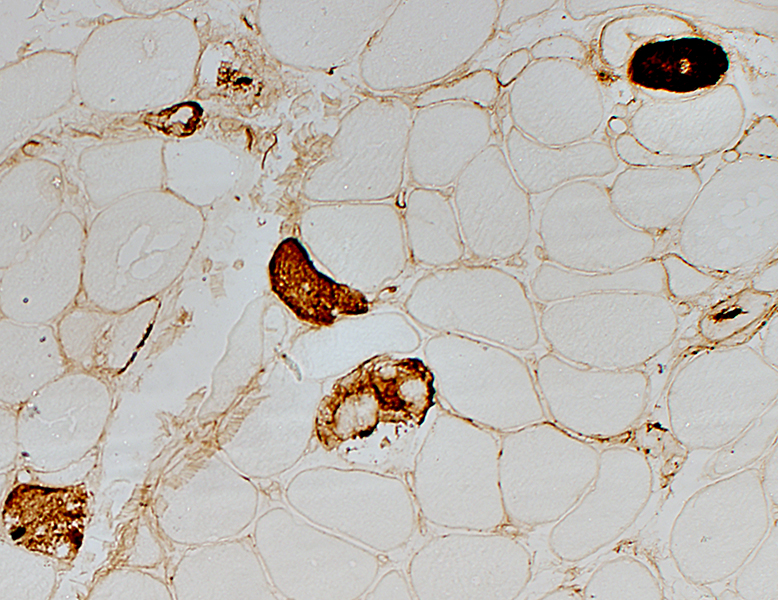 C5b-9 stain |
Necrotic muscle fibers with cytoplasm staining for C5b-9
More common in near edge of fascicles
Scattered in these areas
C5b-9 is also present on the surface of muscle fibers
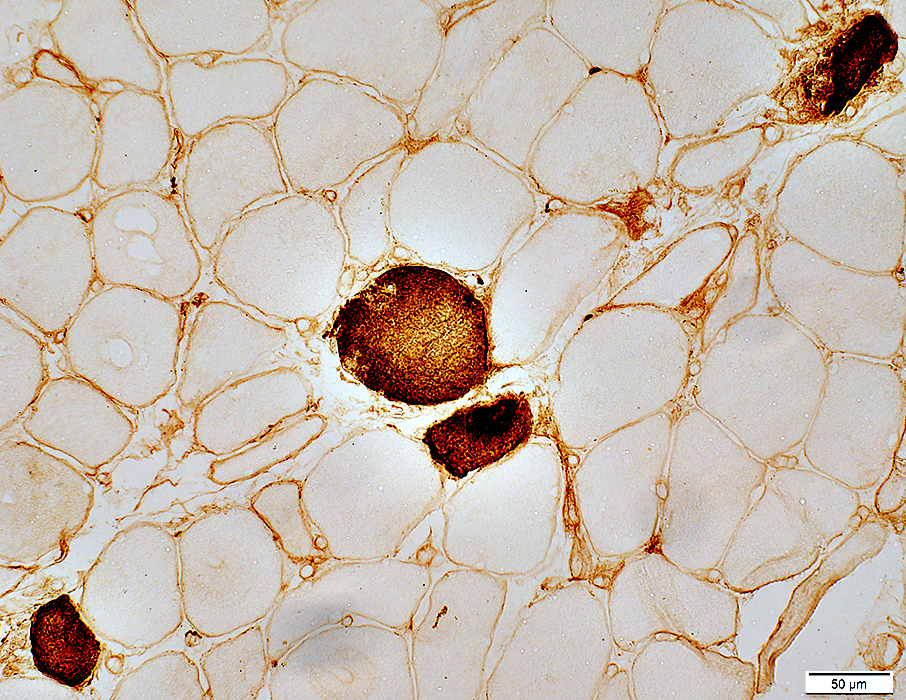 C5b-9 stain |
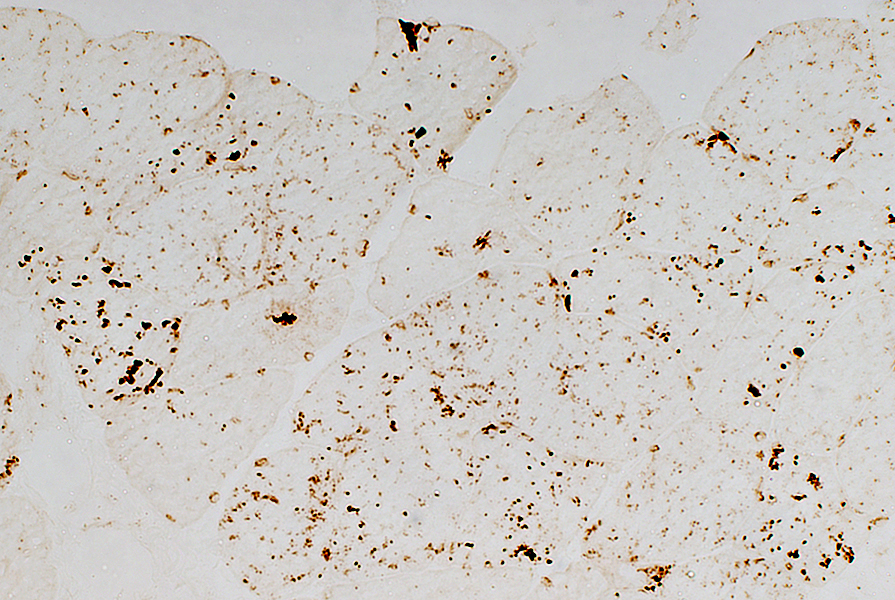 LC3 stain |
Scattered, small LC3 aggregates in muscle fiber cytoplasm (Above)
Abnormal vacuoles in muscle fiber cytoplasm (Below)
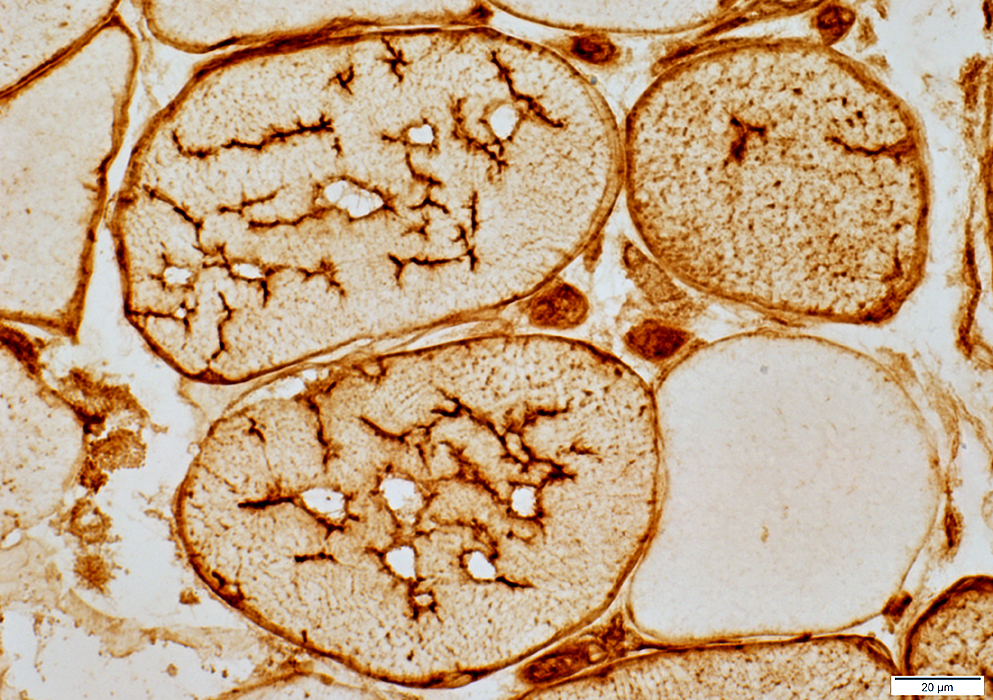 MHC-1 stain |
Return to Inflammatory myopathies
Return to Jo-1 myositis
References
1. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23:595-604, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e434
2. JAMA Dermatol 2019 Jul 10
3. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e21733, Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2022 Aug 12
10/27/2025