Dermatomyositis with Vascular Pathology (DM-VP) 2
|
 Br J Child Dis 1912;9:247 |
||||||
Dermatomyositis with Vascular Pathology (DM-VP): Pathogenesis & Pathology
General Principles- 1° Causative Pathology
- Damage to: Intermediate-sized Perimysial vessels
- Effects of vessel damage: 2° Derivative pathology
- Reduced blood flow in muscle & skin
- Chronic partial hypoxia in border-zone regions of muscle
- Muscle Pathology: Involves 3 tissues in hypoxic regions
- Muscle fibers: Perifascicular atrophy; Aggregates; Mitochondrial pathology
- Capillaries: Damaged most within regions of perifascicular atrophy
- Perimysial connective tissue: Damage
- DM Variant: Region Ischemic Immune Myopathy (RIIM)
- Perimysial Vessels, Intermediate-sized
- Walls: Fibrils reduced in arteries & veins
- More severe damage: Vessel remnants in perimysium
- Inflammation: Lymphocyte foci
- Often contain B-cells
- Contain some vessels: Vessels often have
- Endothelial cells: Large
- Wall: No fibrils
- Capillaries: Regionally varied pathology
- Hypoxic perifascicular border-zone region
- Intermediate zone
- Size: Enlarged
- Alkaline phosphatase stain
- Ultrastructure: Endothelial cells contain tubulo-reticular structures
- Zone near damaged intermediate-sized vessels & inflammation
- Capillary morphology normal
- Atrophic Muscle Fibers: Patterns & Features
- Location
- Border zone perifascicular regions of vascular supply
- Edge of fascicles: Near
- "Avascular" perimysium
- Edge of muscle (Epimysium)
- Fiber Morphology/Histology
- Sizes: Small
- Perifascicular muscle fiber atrophy without necrosis
- Shapes: Oval
- Internal architecture
- Aggregates: LC3+
- Vacuoles: In perifascicular small muscle fibers
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum: Coarse, Irregular (NADH)
- Nuclei: Large; Commonly internal
- Fiber types: Many 2C
- Molecular: Especially perifascicular
- MxA expression
- MHC I expression
- Mitochondrial pathology: COX reduced with normal or increased SDH
- Glycogen: PAS increased
- Necrosis: Uncommon
- More common in: DM-like disorders in adults (IMPP)
- Sizes: Small
- Location
- Larger or normal muscle fibers: In regions near perimysial vessels
- Location: Hypoxic zone neighboring perifascicular muscle fiber atrophy
- Damage pattern: C5b-9 stain
Dermatomysitis with Vascular Pathology (DM-VP): Original Pathologic Description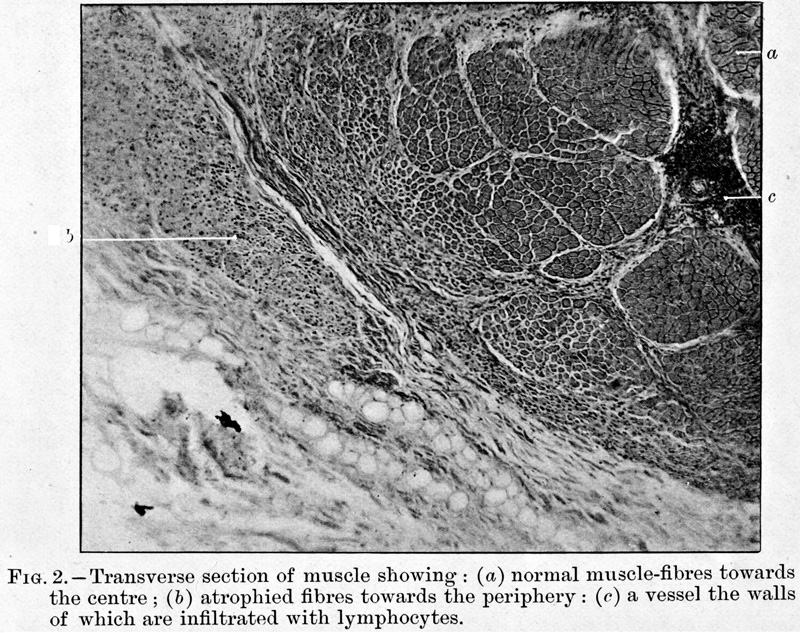 Batten FE Br J Child Dis 1912;9:247 |
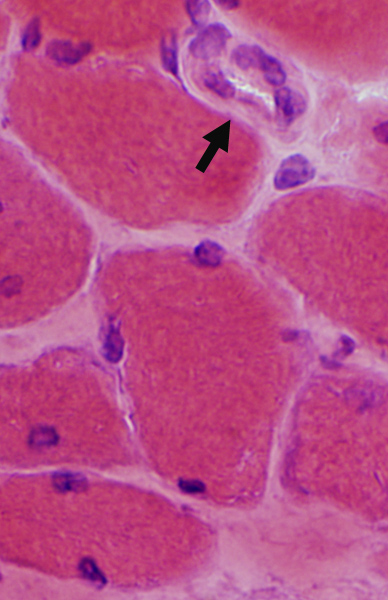
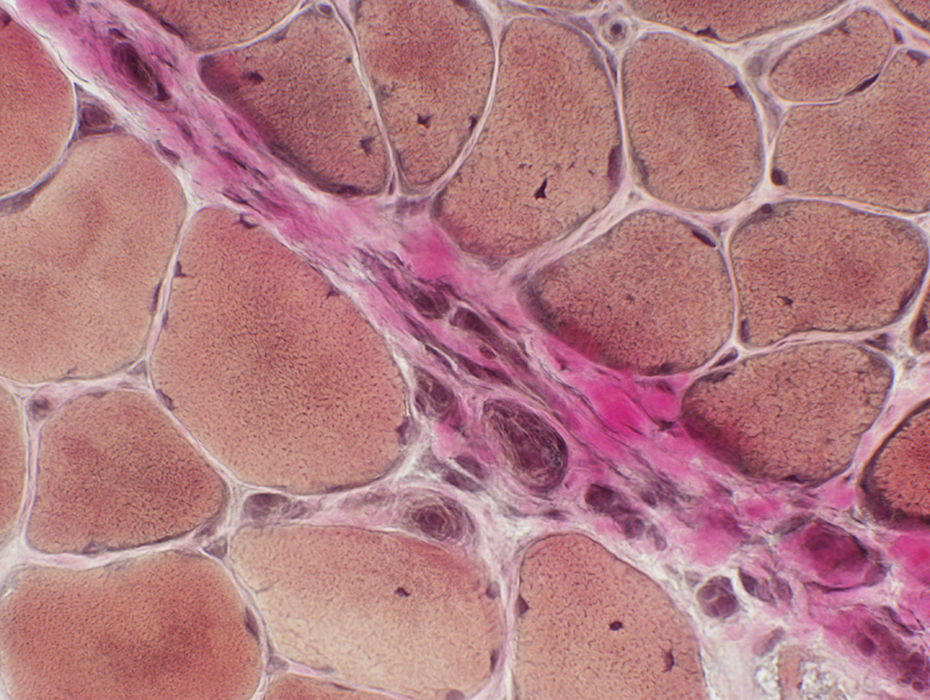
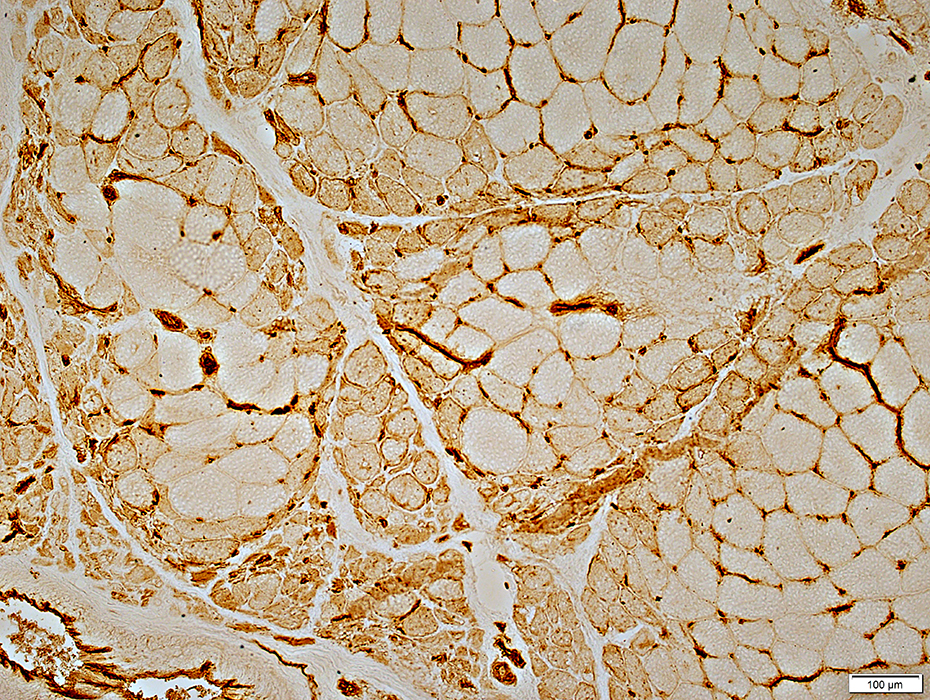
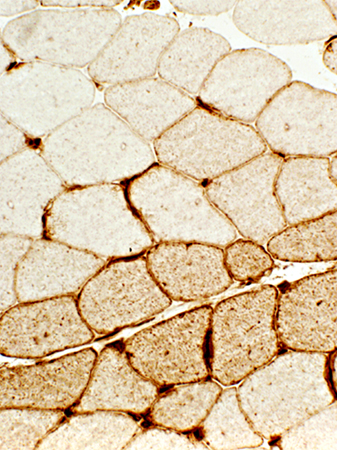
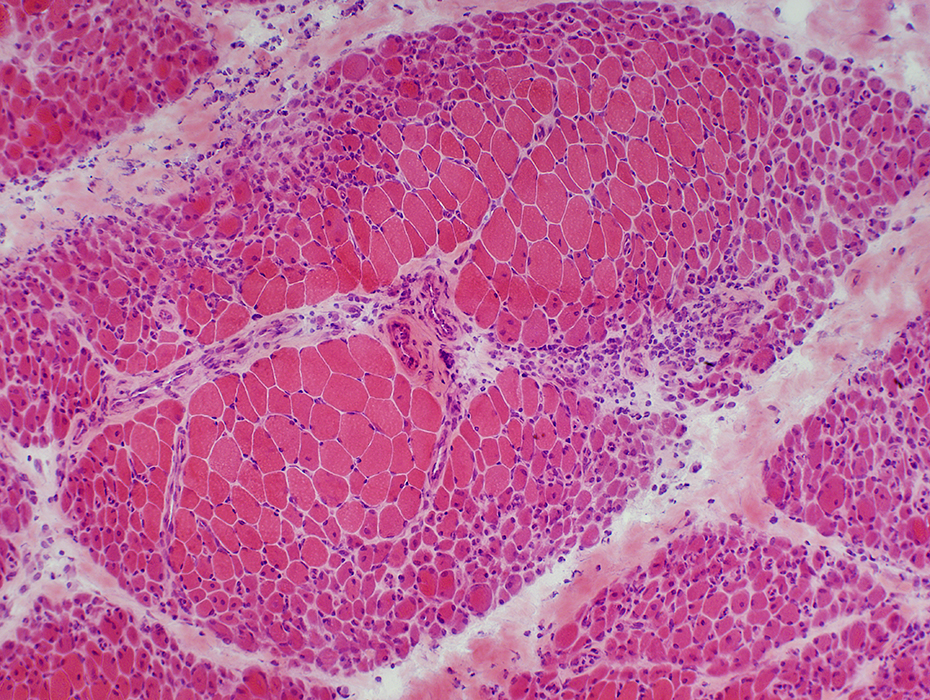
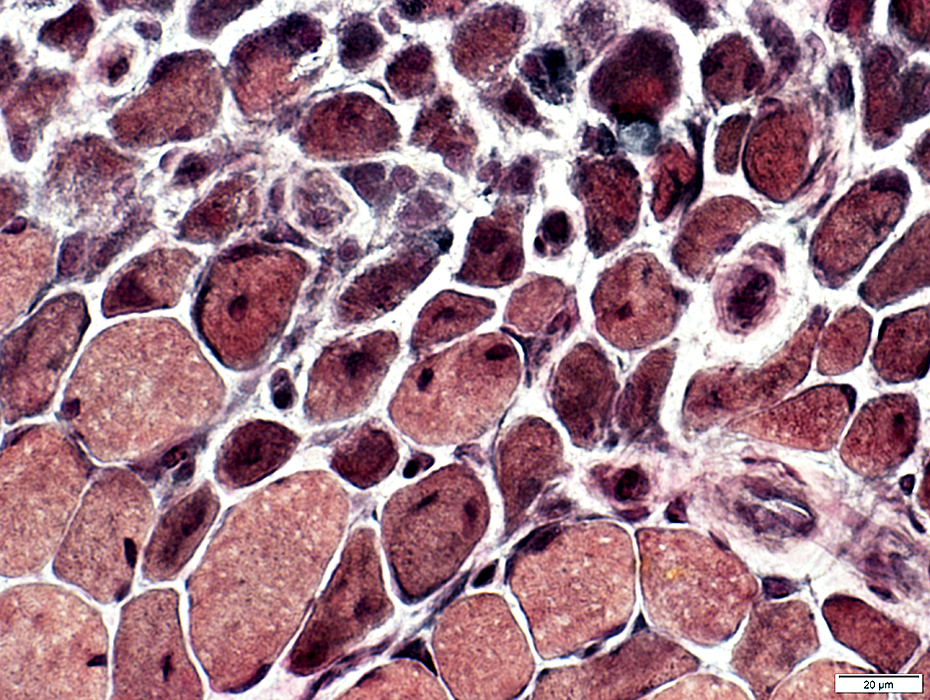
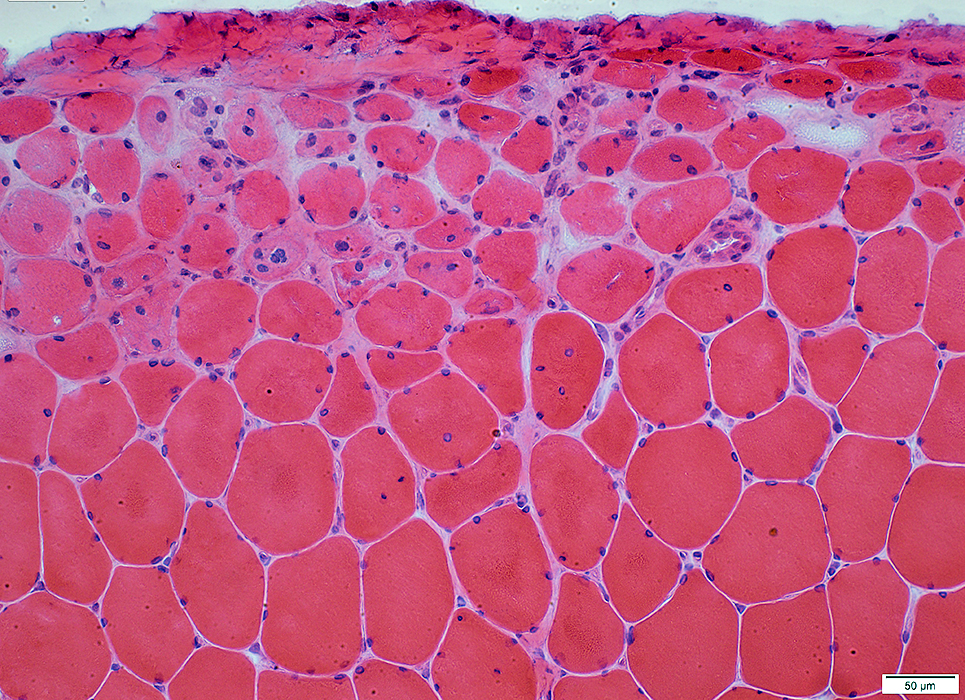
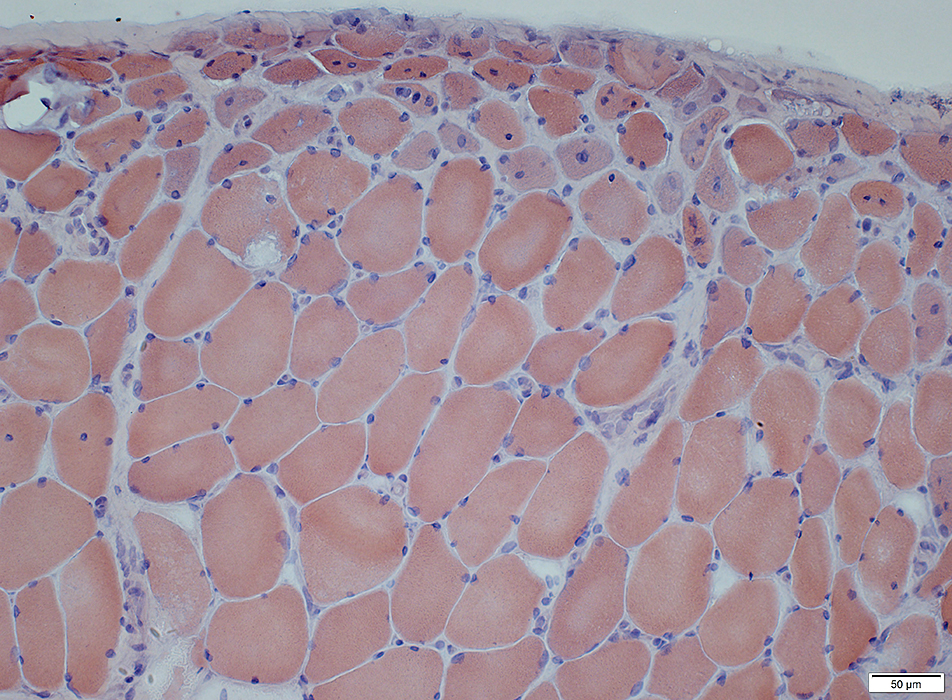
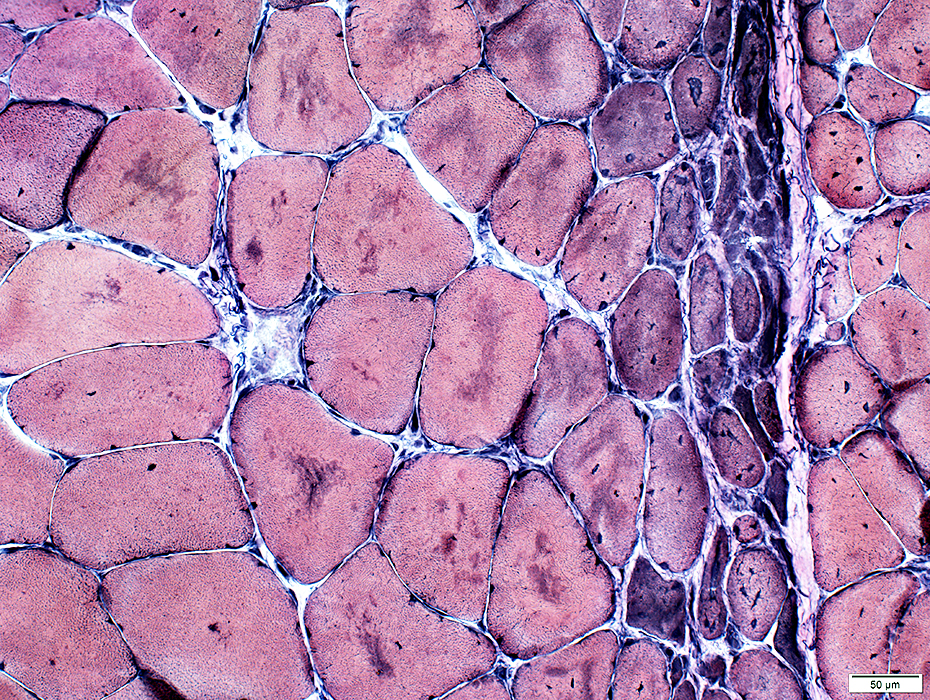
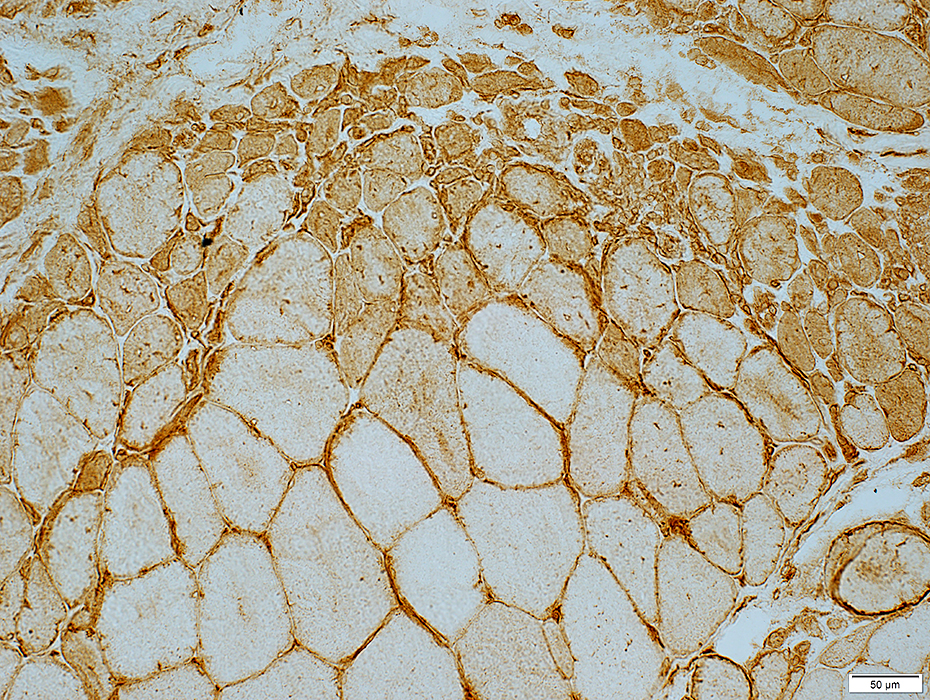
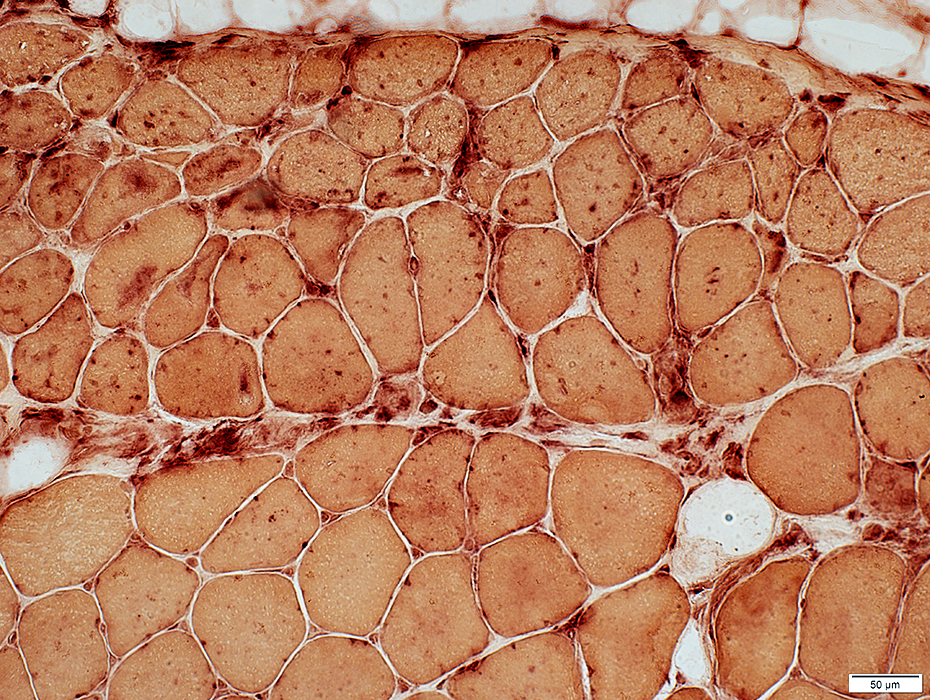
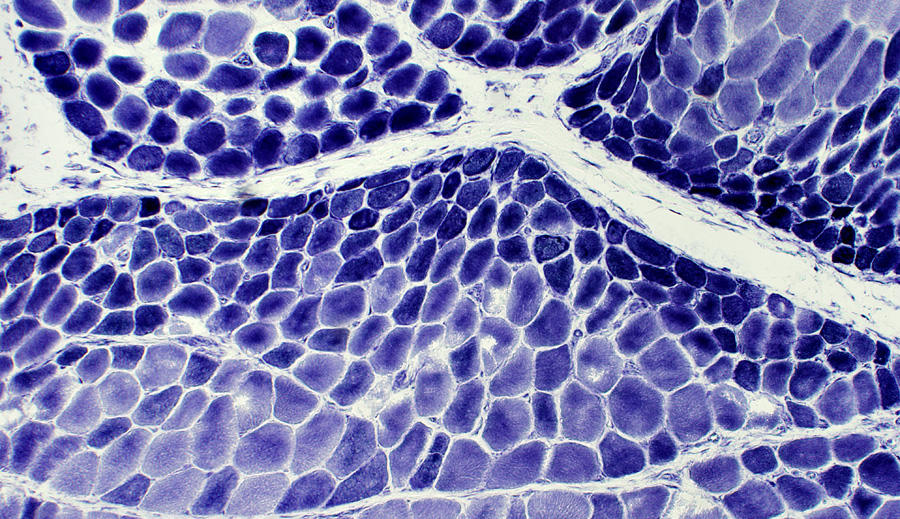
DM-VP: Perifascicular/Border-zone Muscle Fiber Smallness/Atrophy
Atrophic Muscle Fibers: Near Avascular Perimysial Connective tissue (Dark arrow) surrounding fascicleLarger Muscle fibers: Within fascicle near intermediate sized perimysial vessels
Vessel in Vascular Perimysium: White Arrow
Molecular features
LC3 Aggregates
MHC Class I
Mitochondrial
MxA
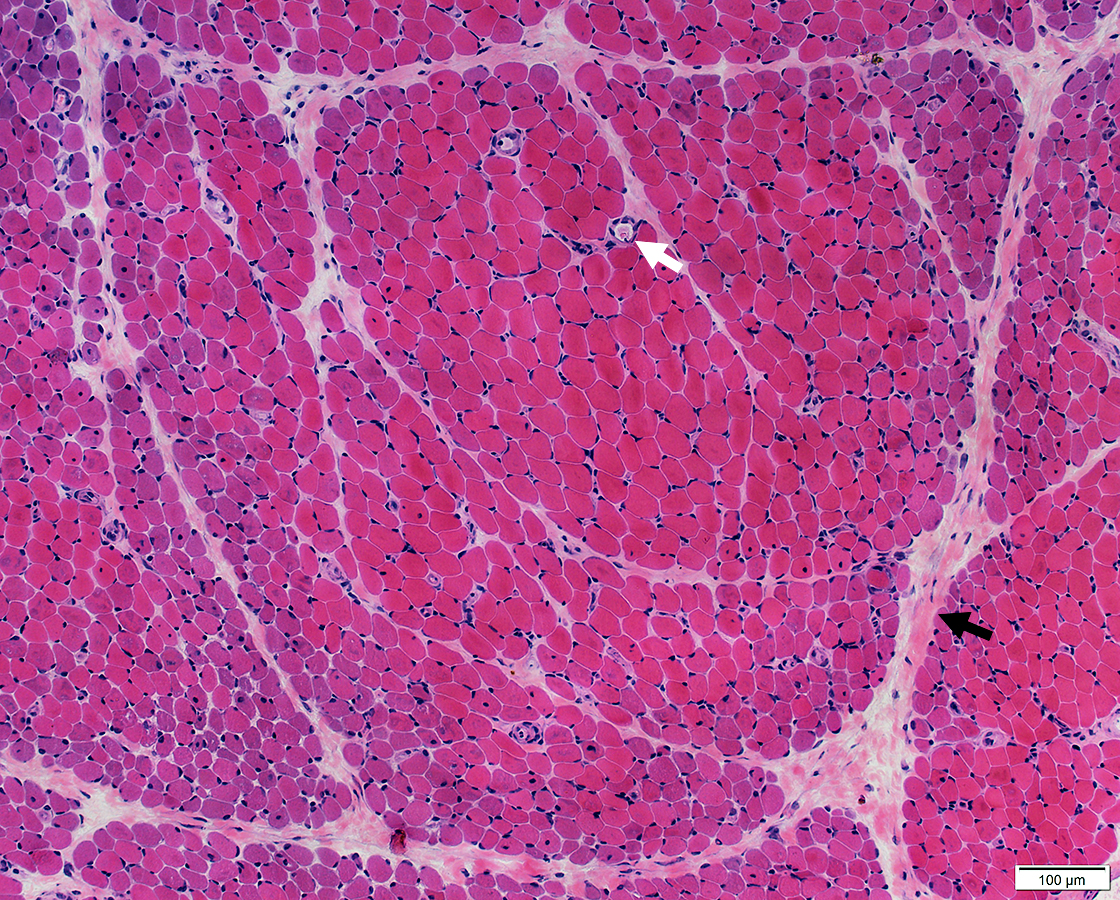 H&E stain |
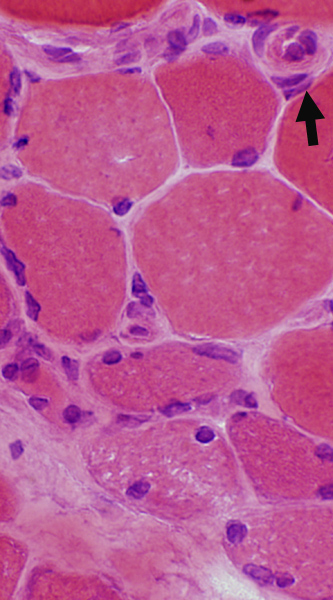
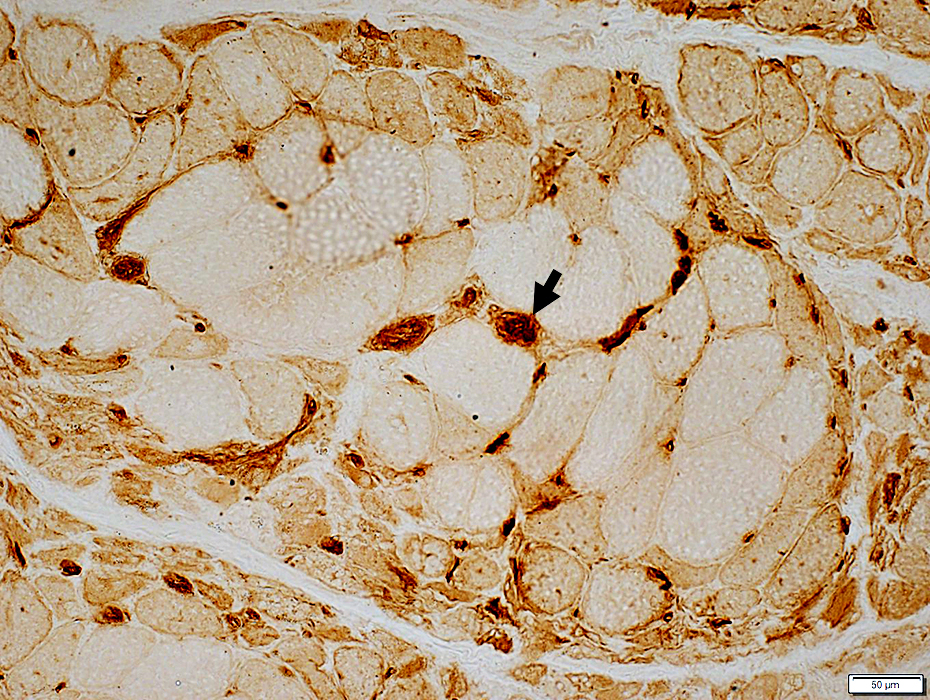
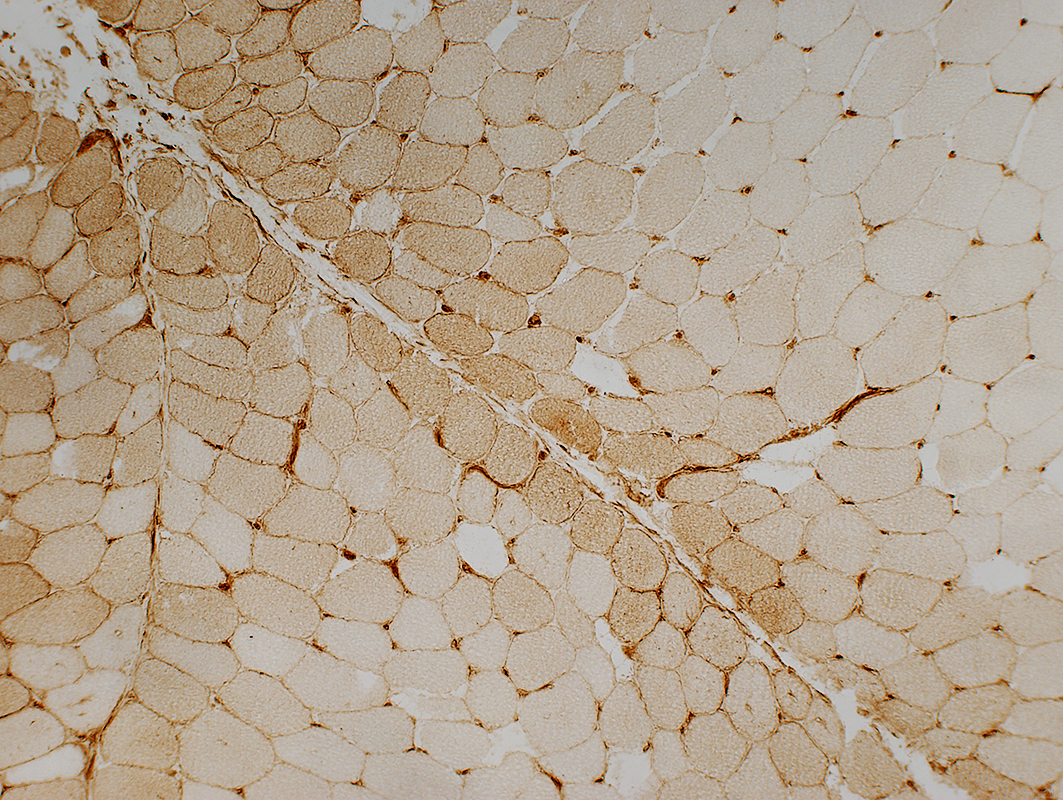
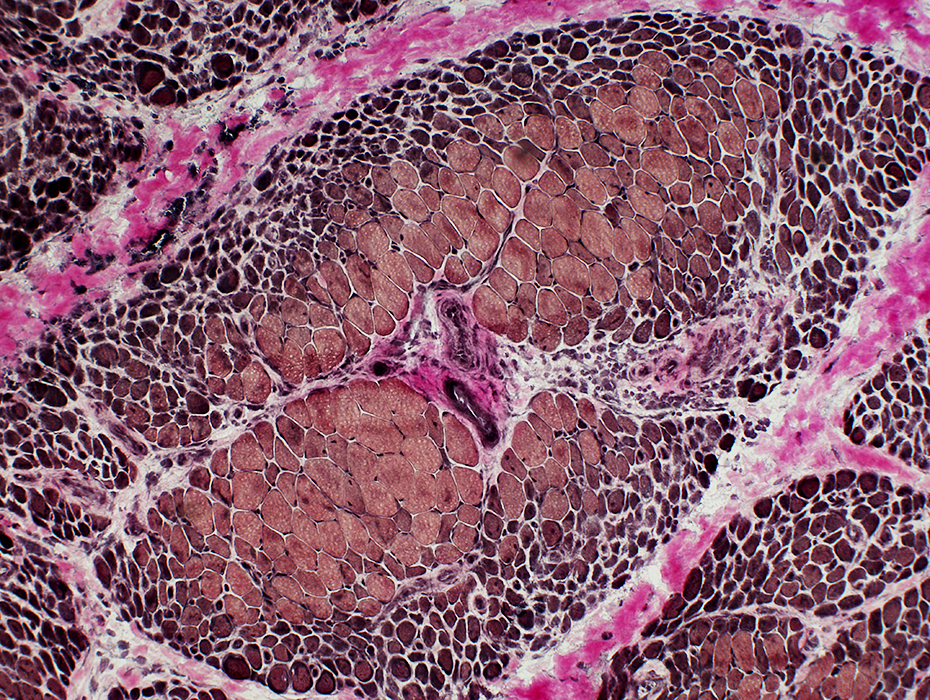
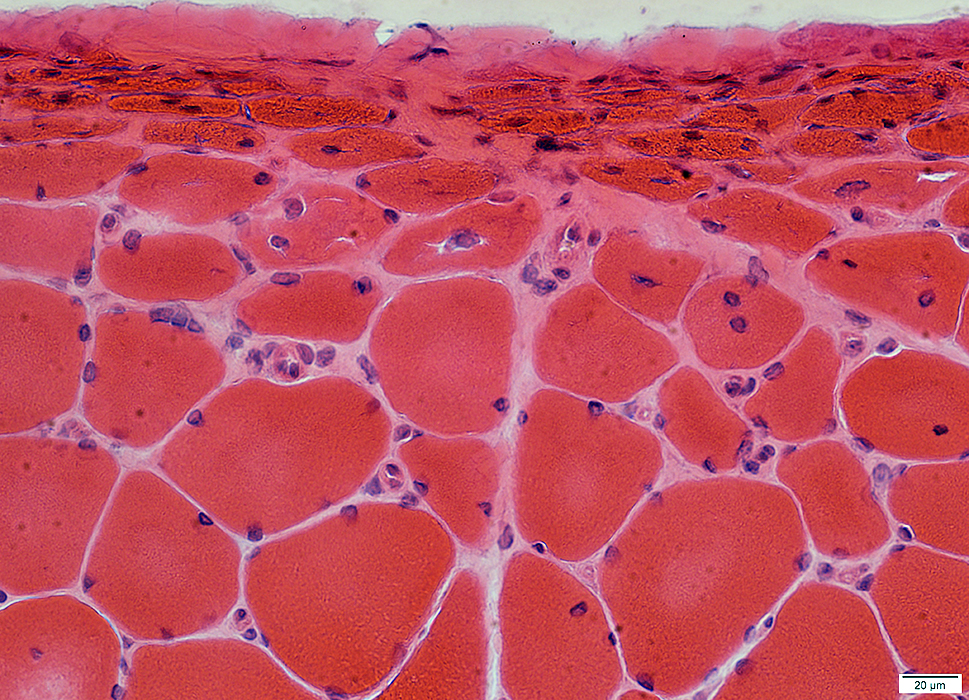
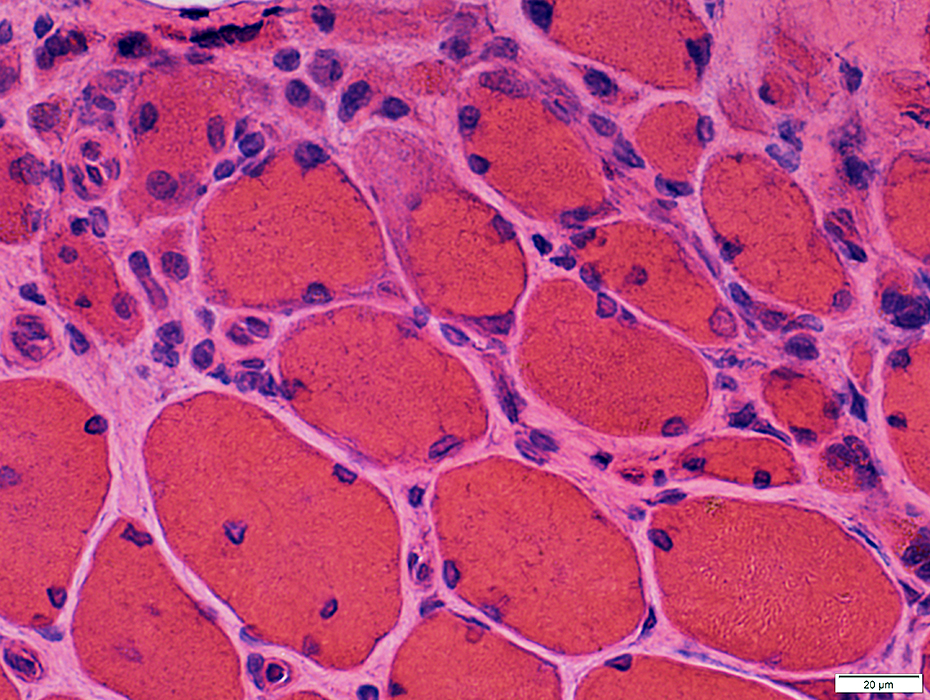
DM-VP: Border-zone Muscle Fiber Pathology
Perifascicular Muscle Fiber Atrophy: Along Avascular PerimysiumAtrophic perifascicular muscle fibers neighbor a long region of avascular perimysium with irregular structure (Center; Dark arrow).
Normal sized muscle fibers neighbor vascular perimysium (Sides; White arrow).
Control: Vessels & Perimysium
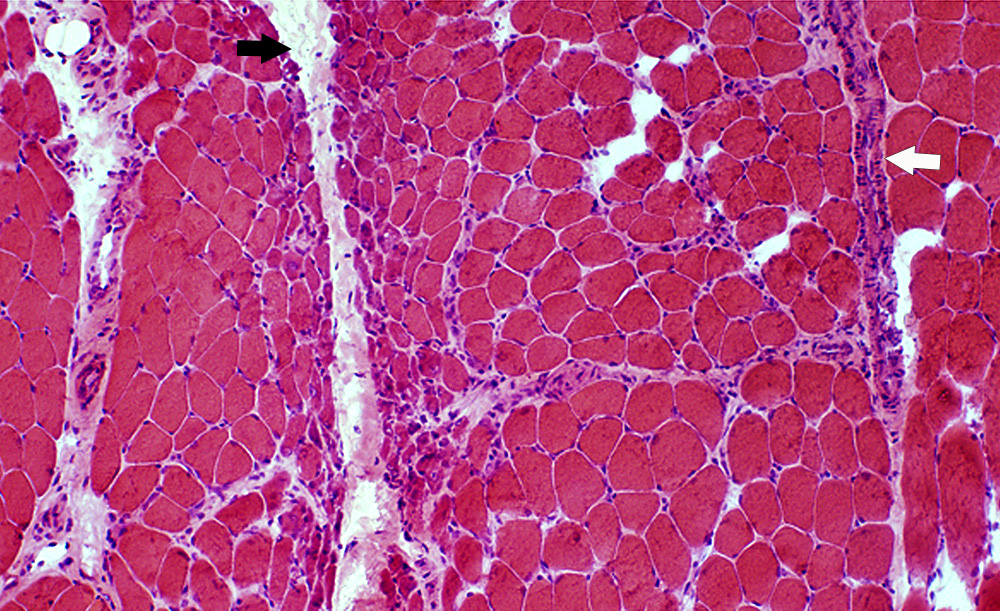 H&E stain |
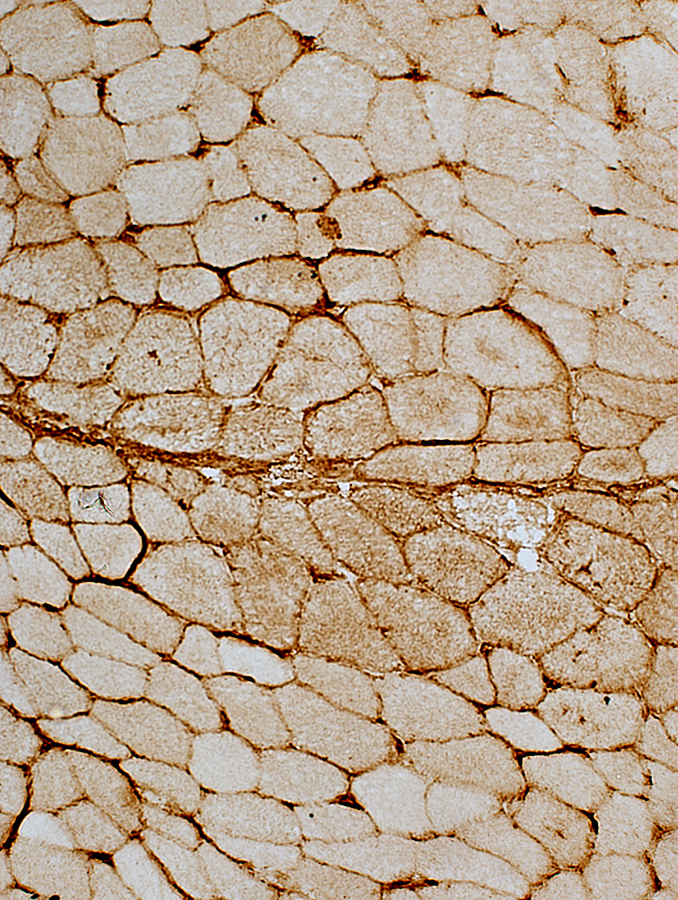
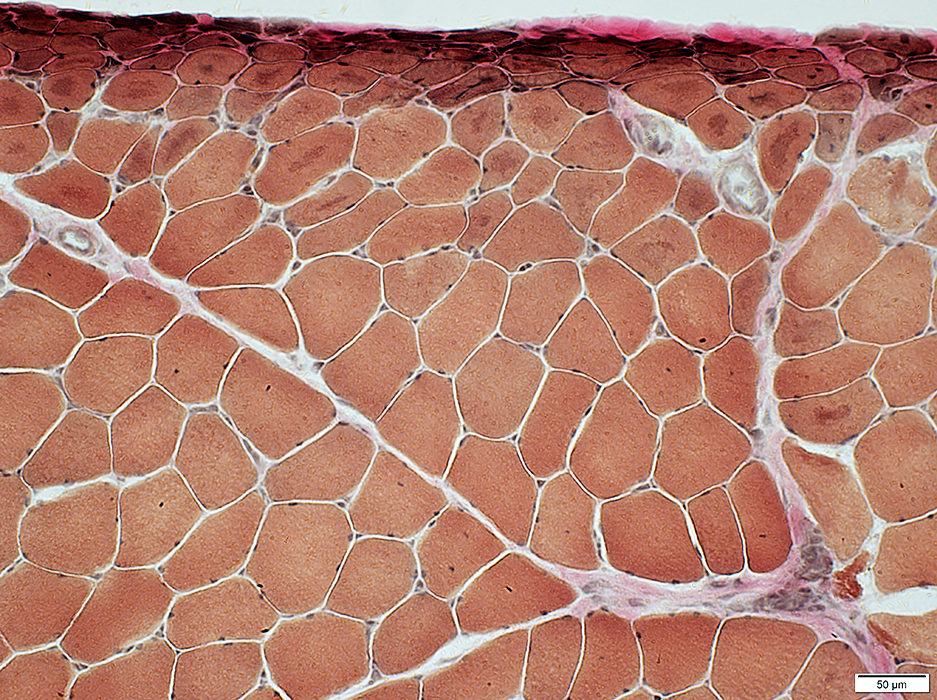
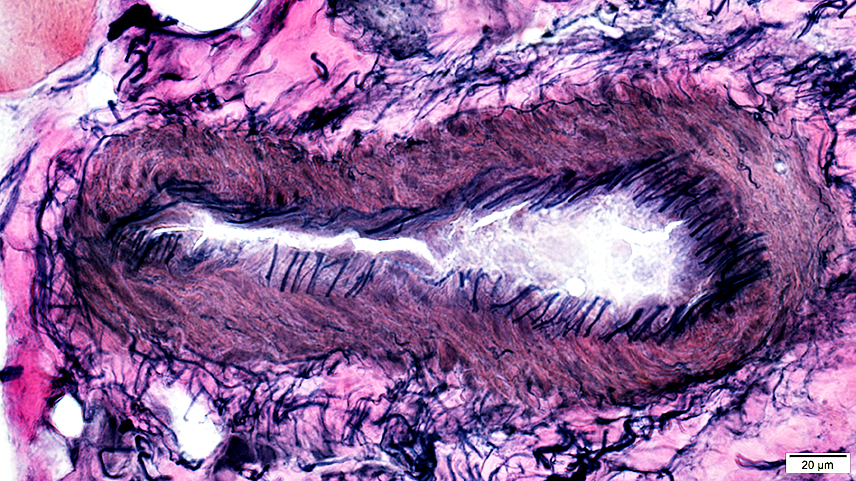
Vessels & Vascular Perimysium: Within fascicle, Within region containing larger muscle fibers (Dark Arrow)
Avascular Perimysium: Neighbors small muscle fibers (Top & Left)
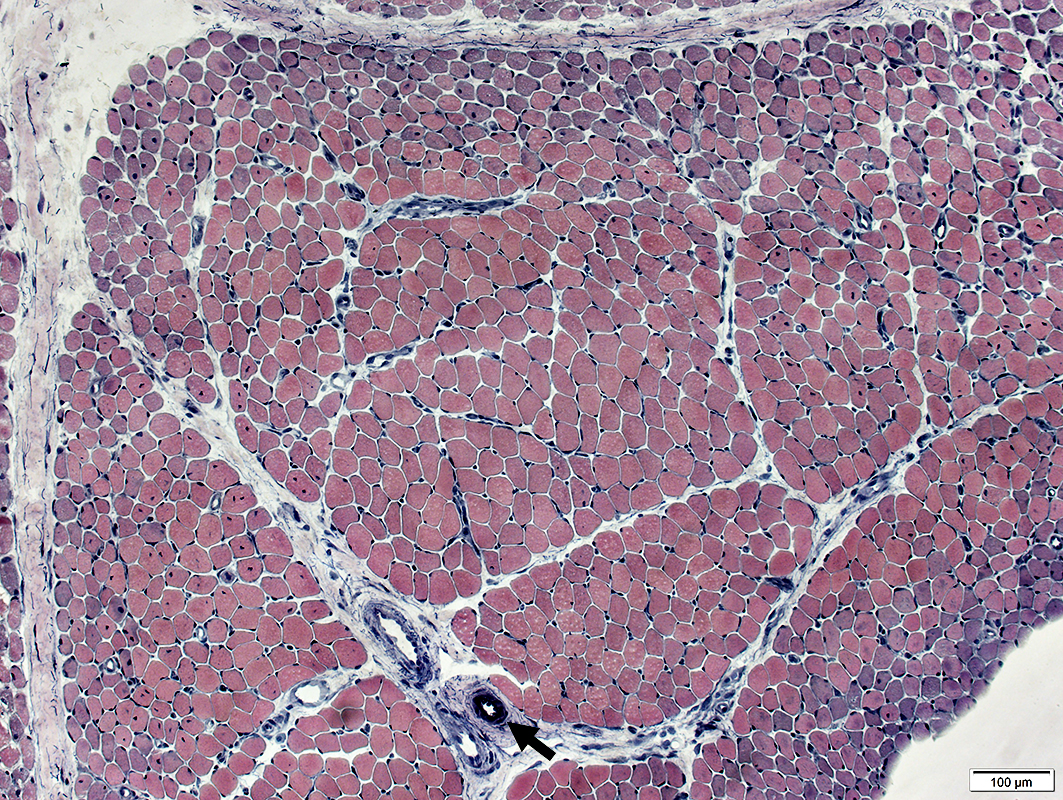 VvG stain |
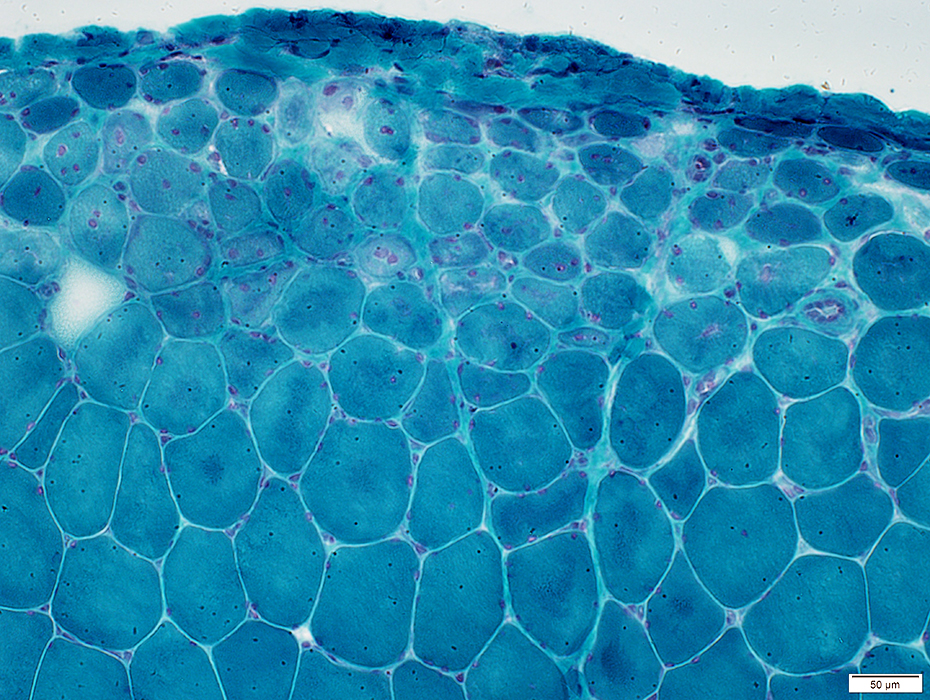
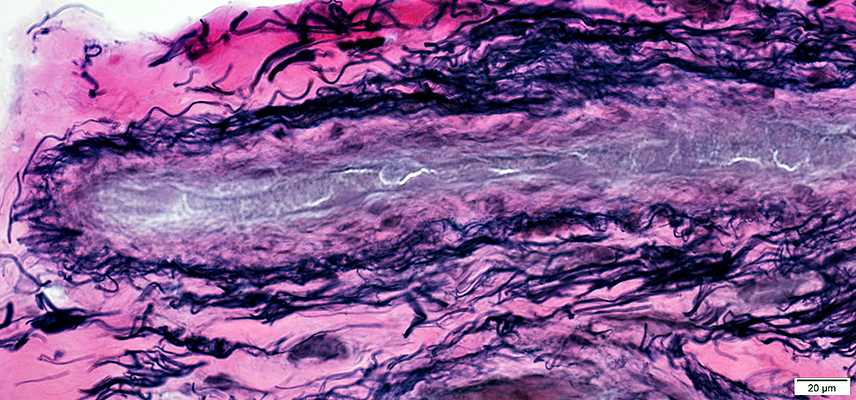
Vessels & Vascular Perimysium: Within fascicle, Within region containing larger muscle fibers (Dark Arrow)
Avascular Perimysium: Neighbors small muscle fibers (Surrounding perimysium)
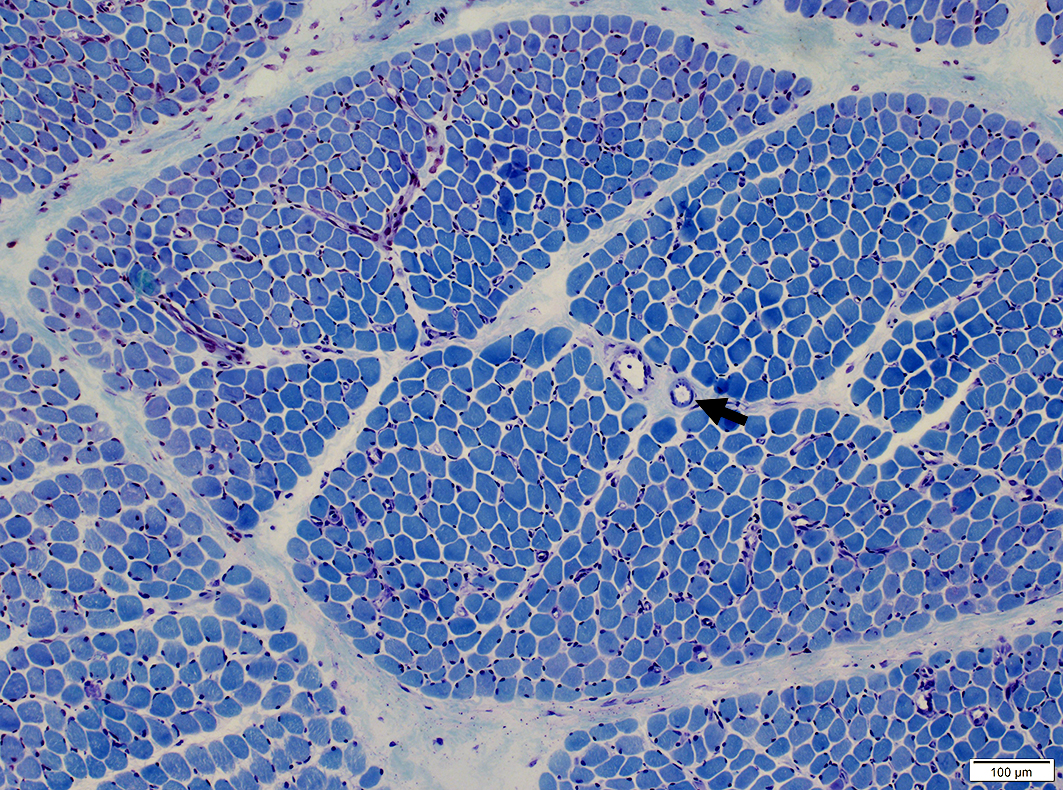 Toluidine Blue stain |
Vessels & Vascular Perimysium: Within fascicle, Within region containing larger muscle fibers (White Arrow)
Endomysial capillaries: Abnormal ATPase staining in areas near muscle fiber atrophy
Avascular Perimysium: Neighbors small muscle fibers (Surrounding perimysium) (Dark Arrow)
Small muscle fibers near edge of fascicle: Often type 2 or 2C
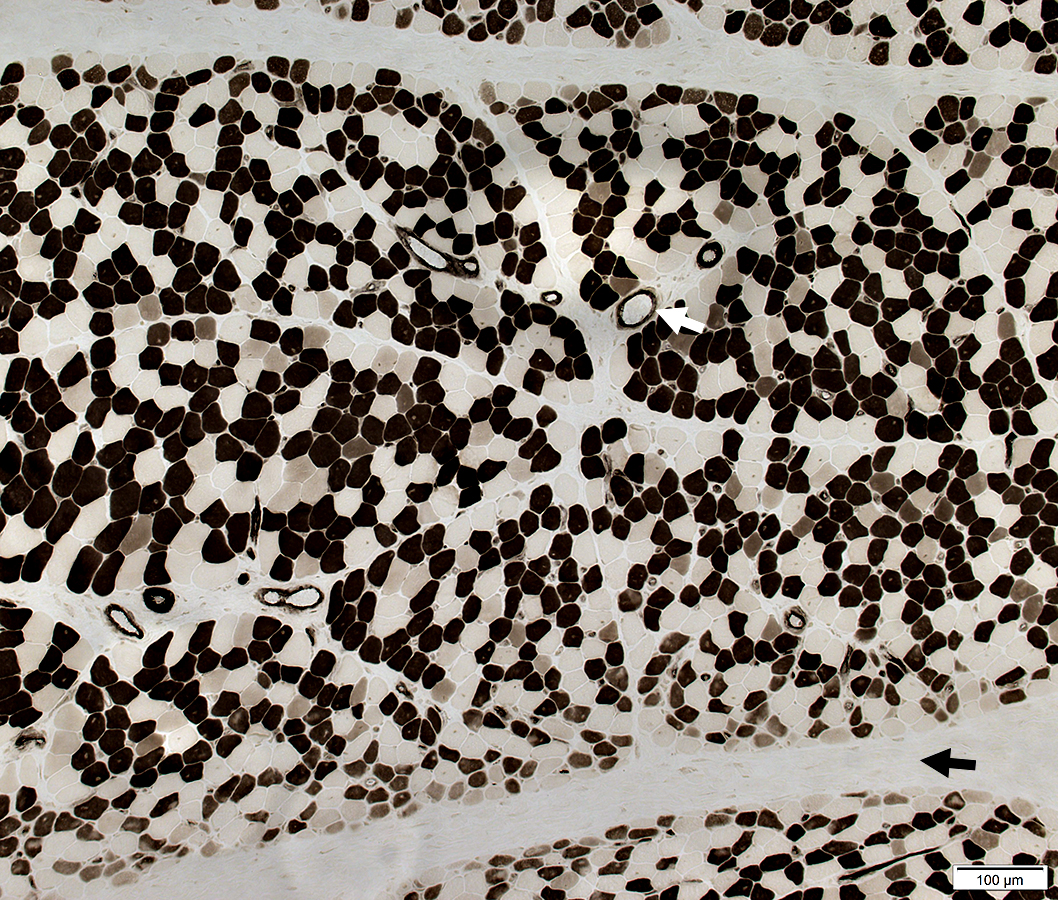 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
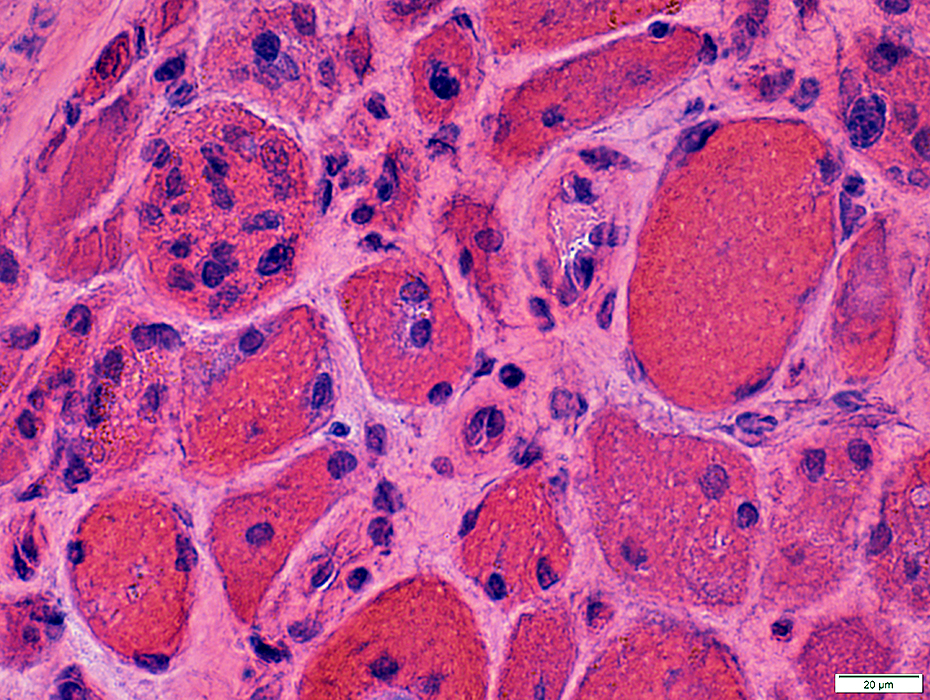
Atrophic perifascicular muscle fibers neighbor long regions of avascular perimysium.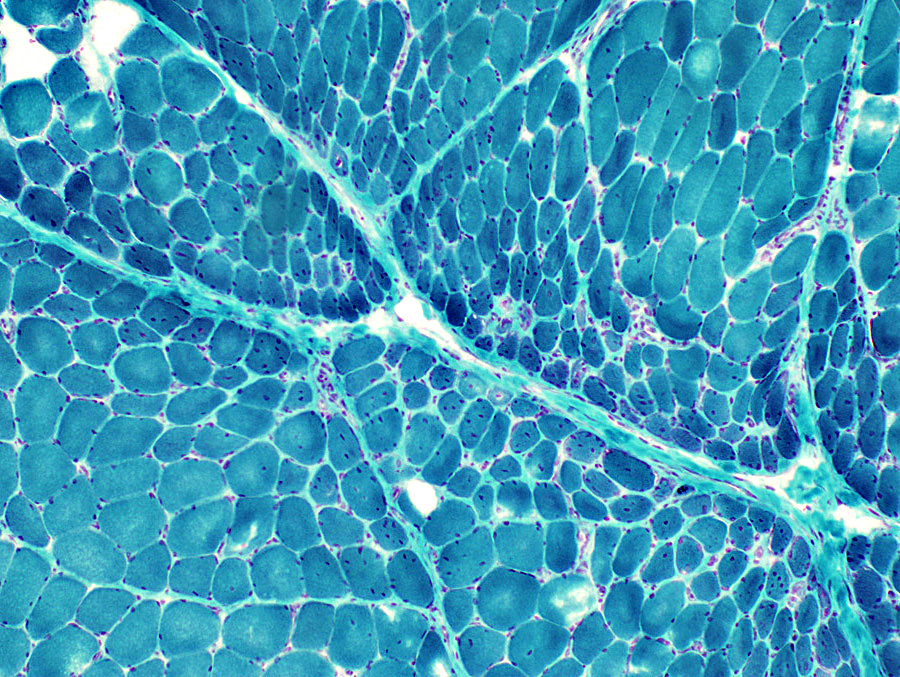 Gomori trichrome stain |
Atrophic perifascicular muscle fibers
Neighbor a long region of avascular perimysium.

H&E stain
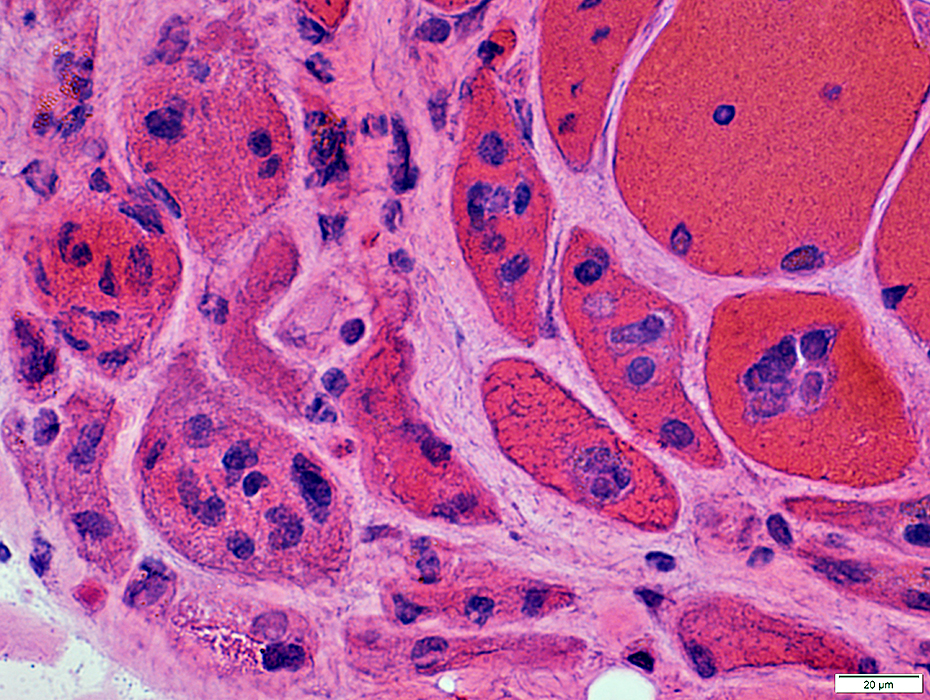
Atrophic perifascicular muscle fibers
Basophilic cytoplasm
Large nuclei
Some fibers have basophilic or eosinophilic aggregates
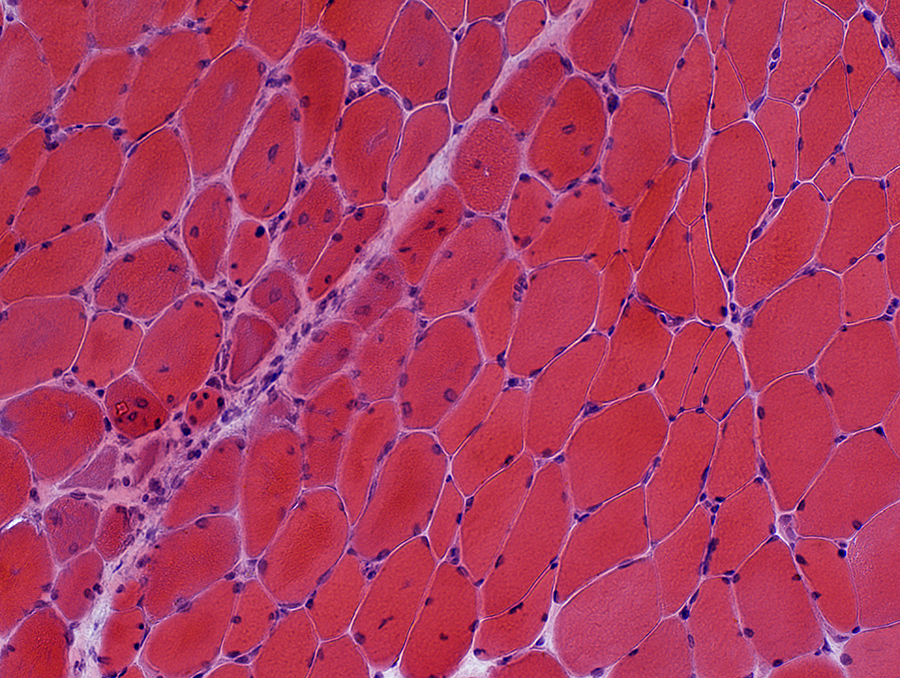 H&E stain |
Perifascicular muscle fiber pathology
Size: Small
Cytoplasmic aggregates (Dark stained)
Internal nuclei
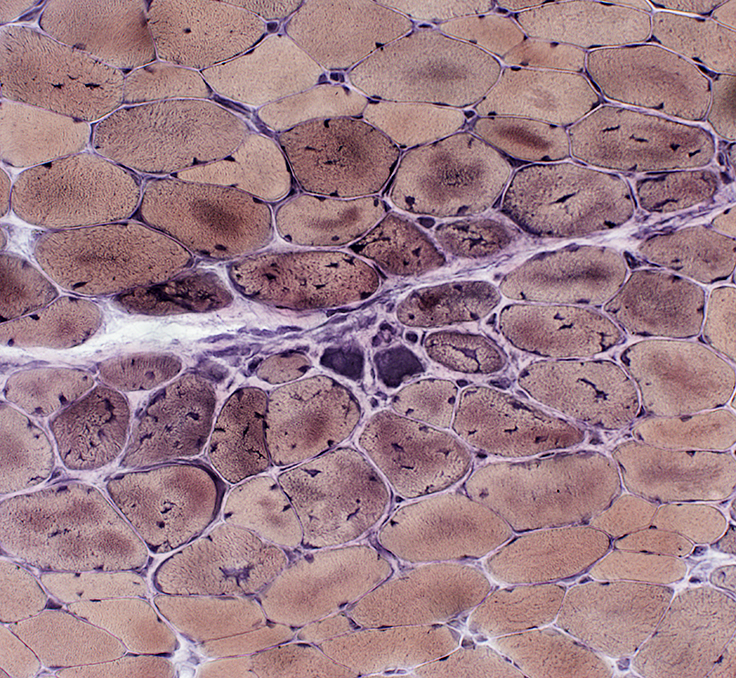 VvG stain |
Perifascicular pathology: Other stains
NADH
 NADH stain Muscle fibers near avascular perimysium: Small & Stain darkly Muscle fibers near vascular perimysium (Below, Arrow): More normal 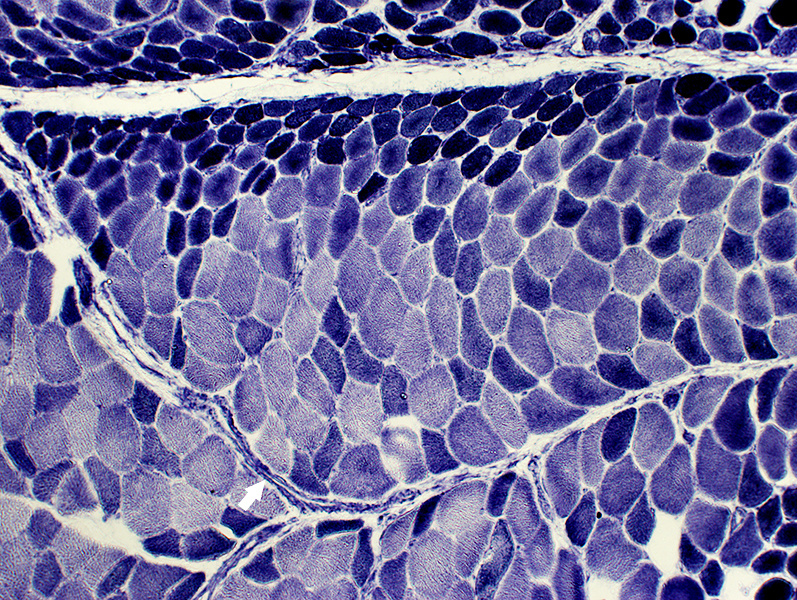 NADH stain |
MHC Class I
Upregulated at edges of fascicles near avascular perimysium.
Less, or no, staining, near perimysium containing larger vessels (Arrows)
 MHC Class I stain |
|
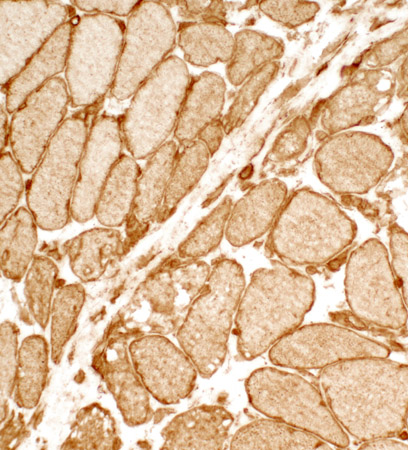
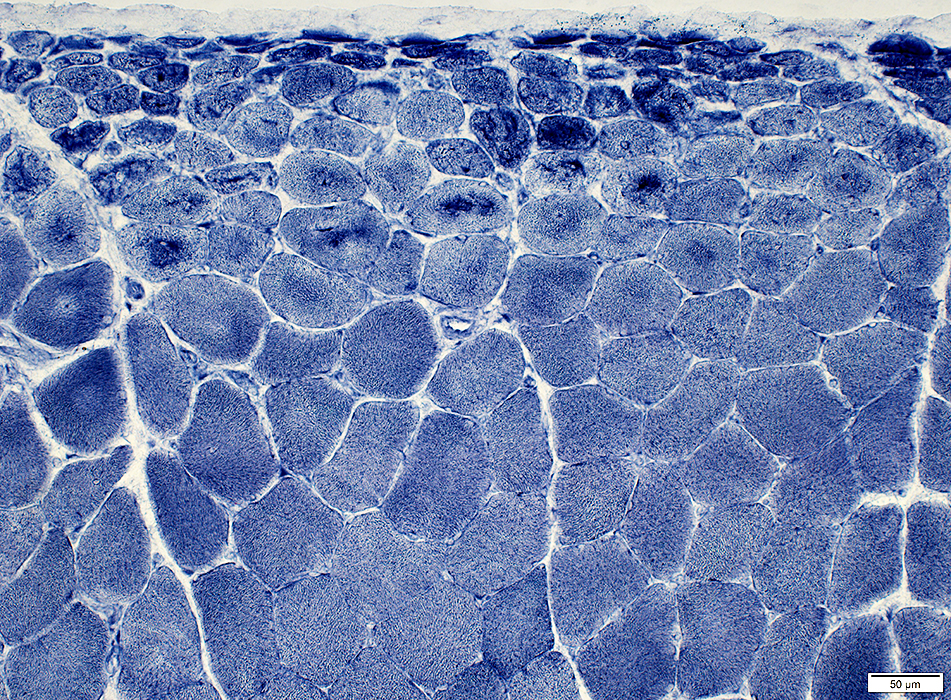
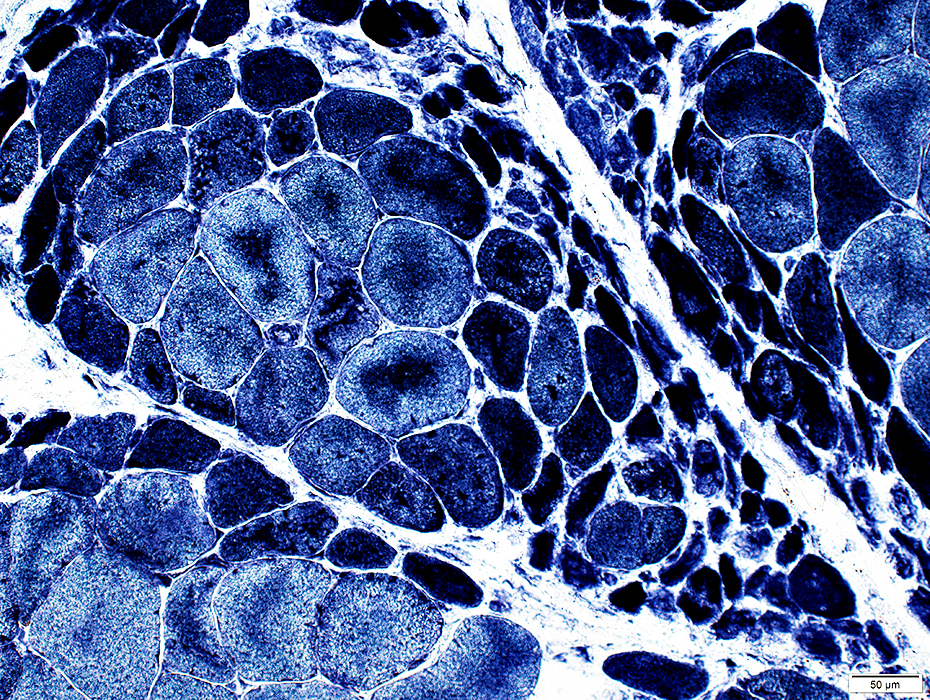
Muscle Fibers: Perifascicular atrophy ATPase pH 9.4 stain: May be reduced in small perifascicular muscle fibers 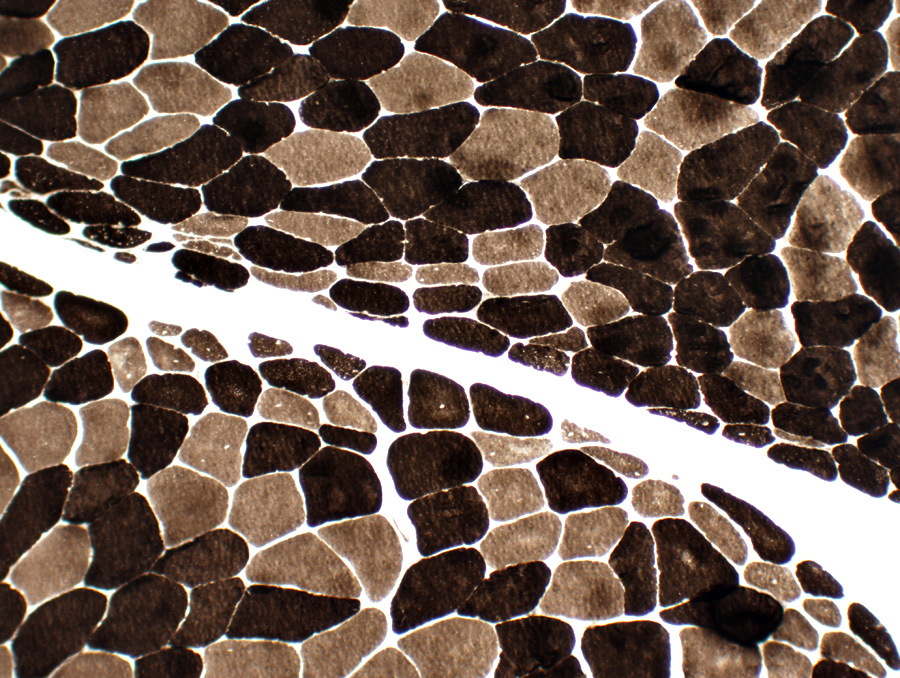 ATPase pH 9.4 stain Perifascicular atrophy is often especially obvious on ATPase stains. Small fibers: Both types I & II. |
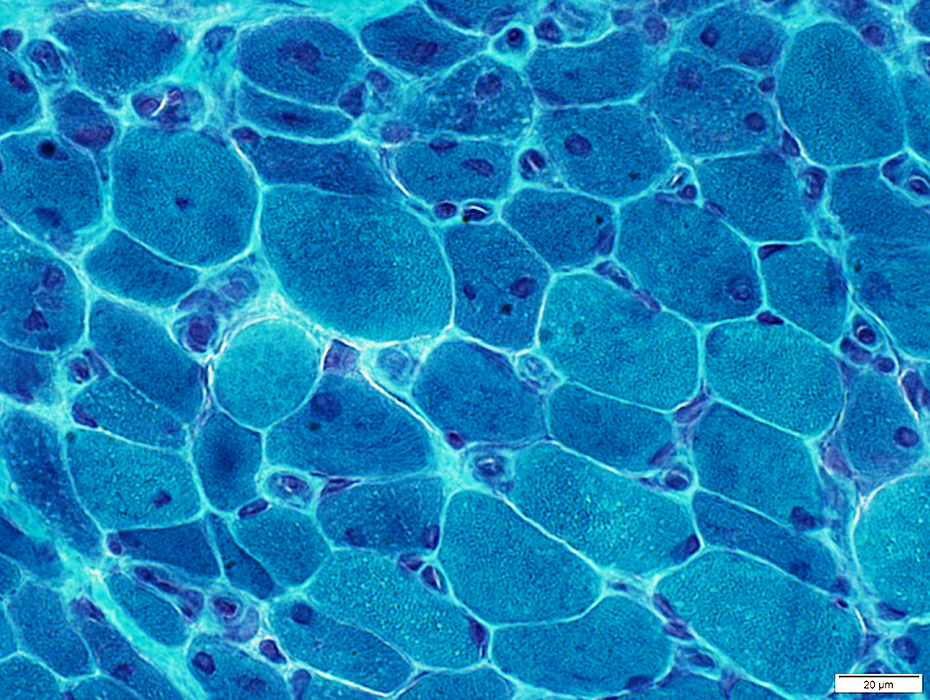
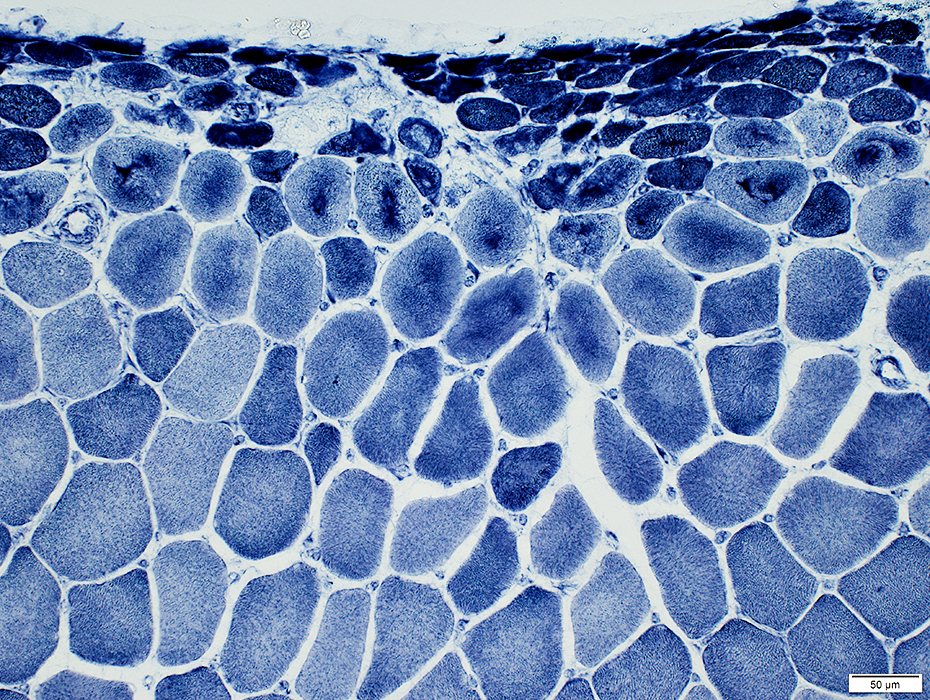
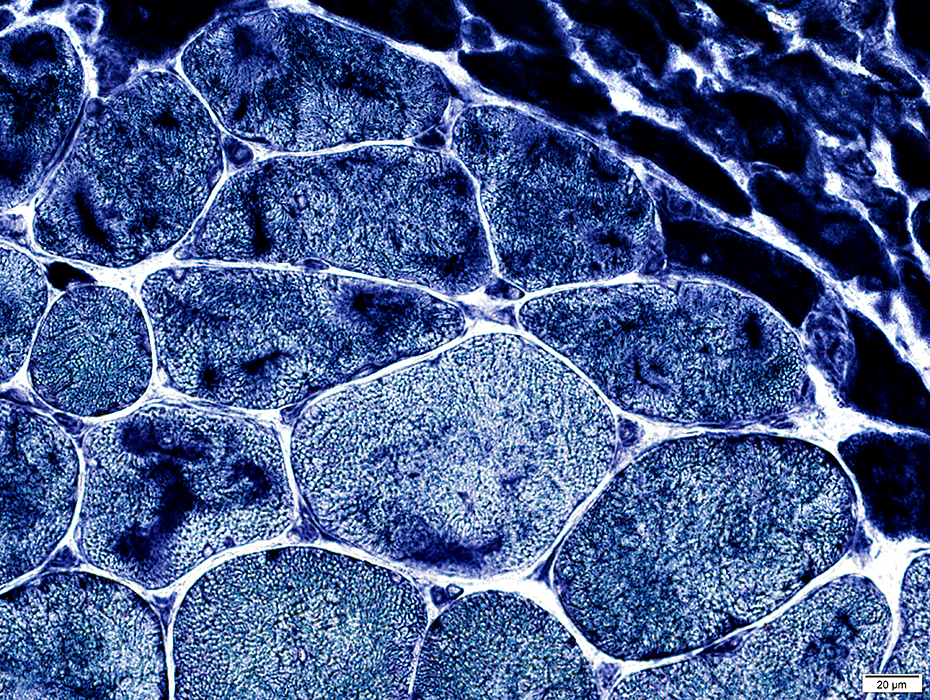
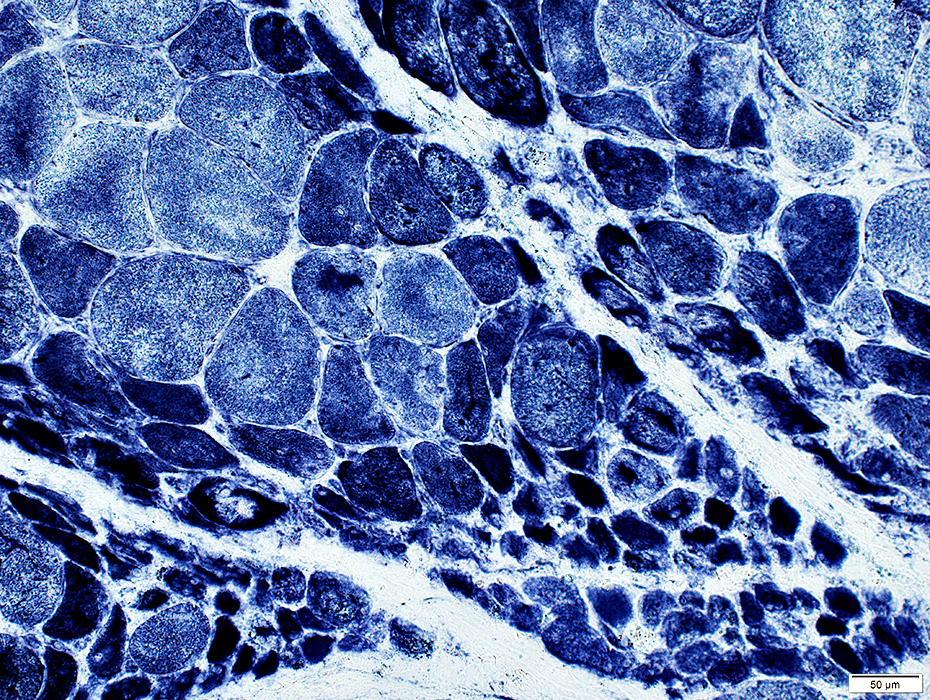
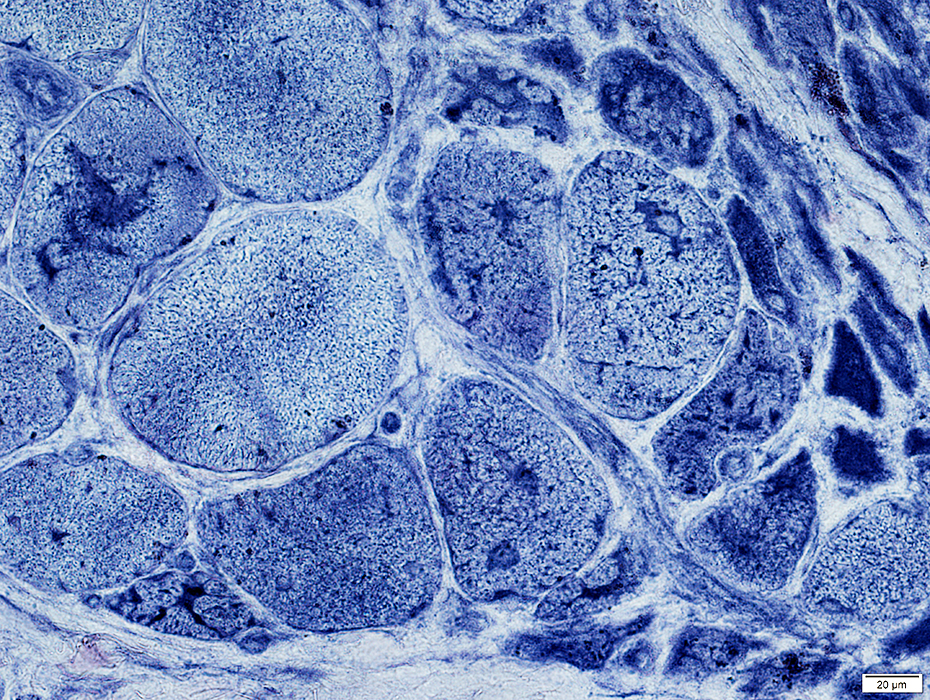
Perifascicular atrophy: Toluidine blue-stained plastic sections
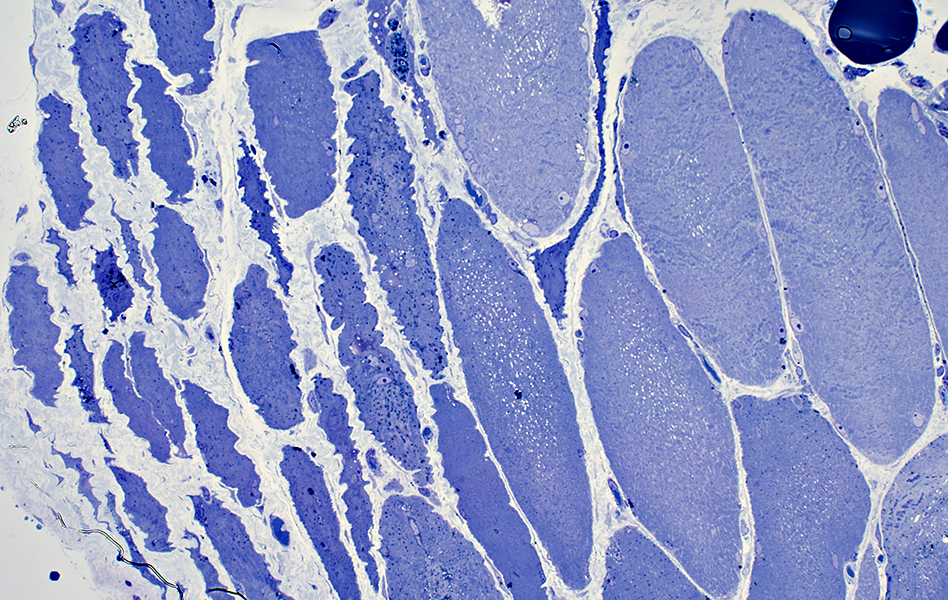
|
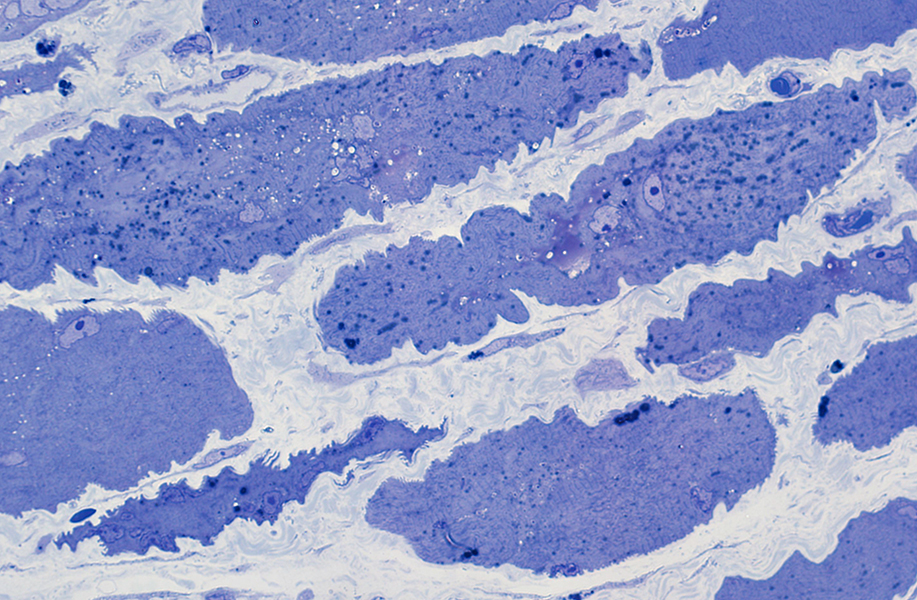
|
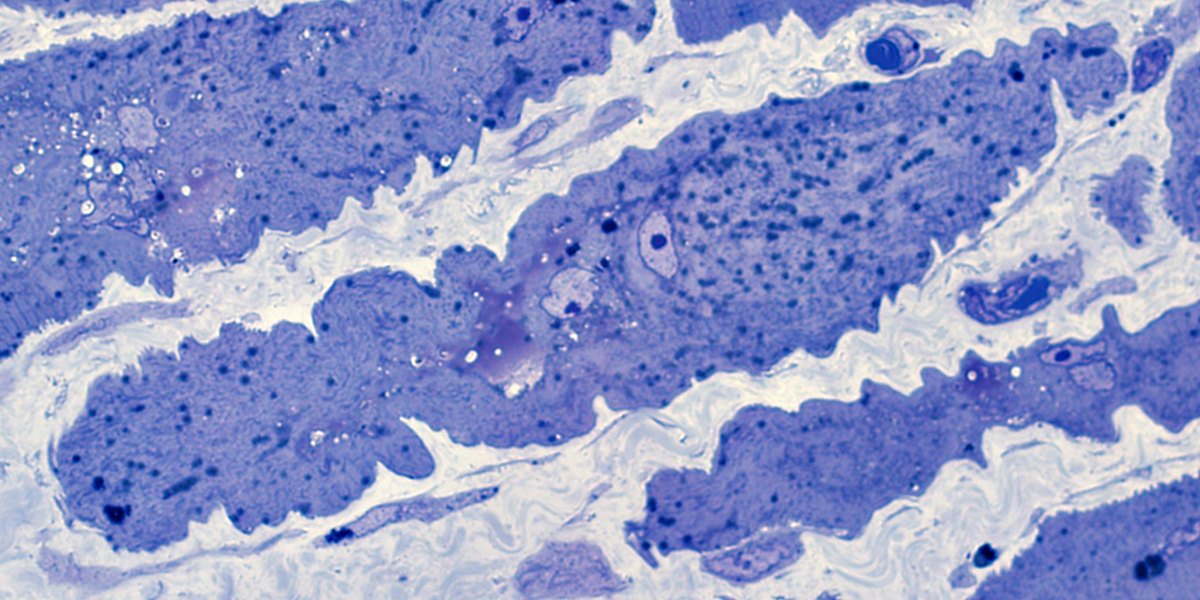
|
Size: Atrophic
Sarcolemmal membrane: Irregular
Contain lipid droplets
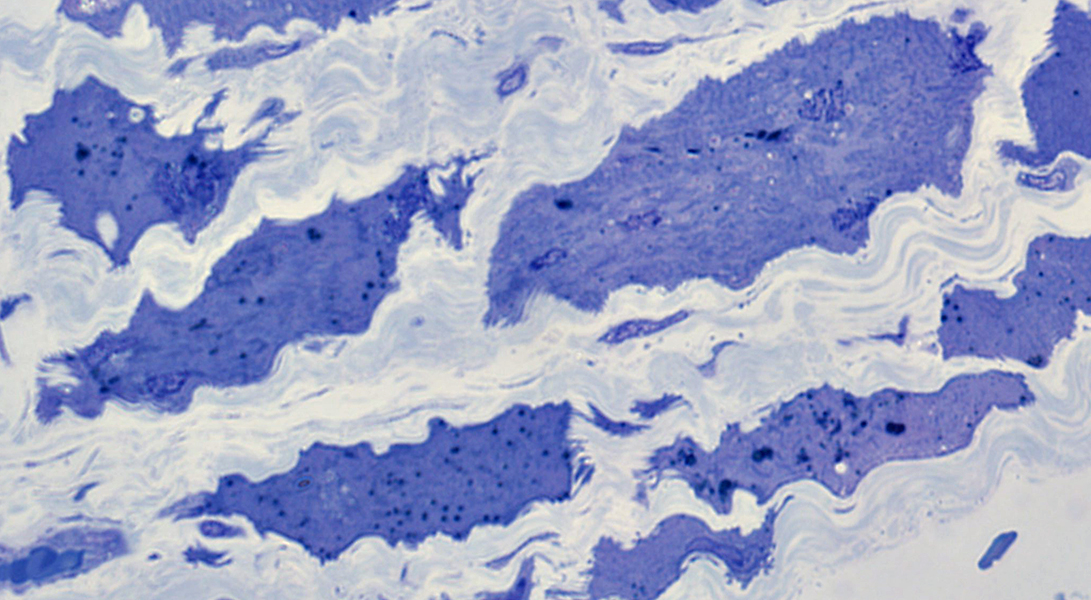
|
|
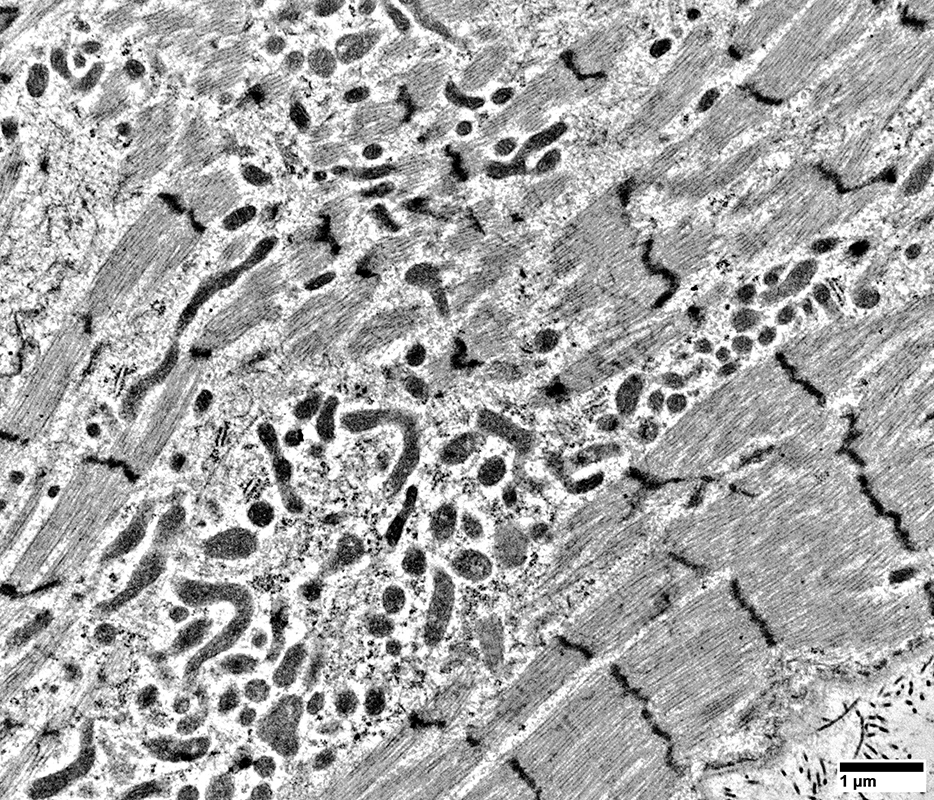
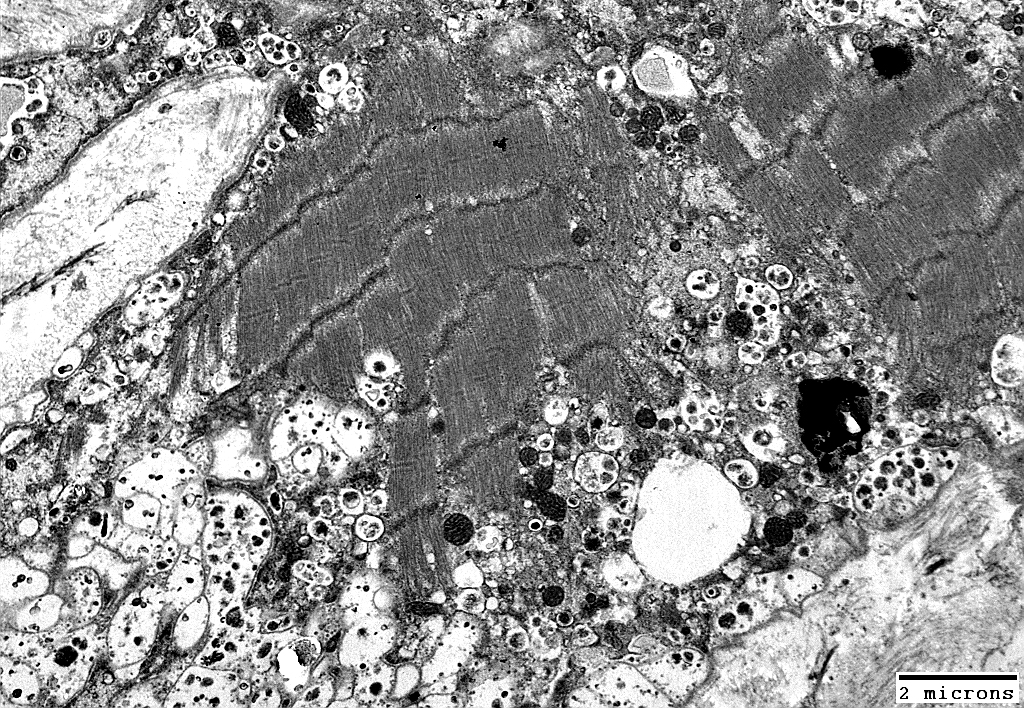
DM-VP Muscle Fibers: Sarcoplasm Ultrastructural Morphology
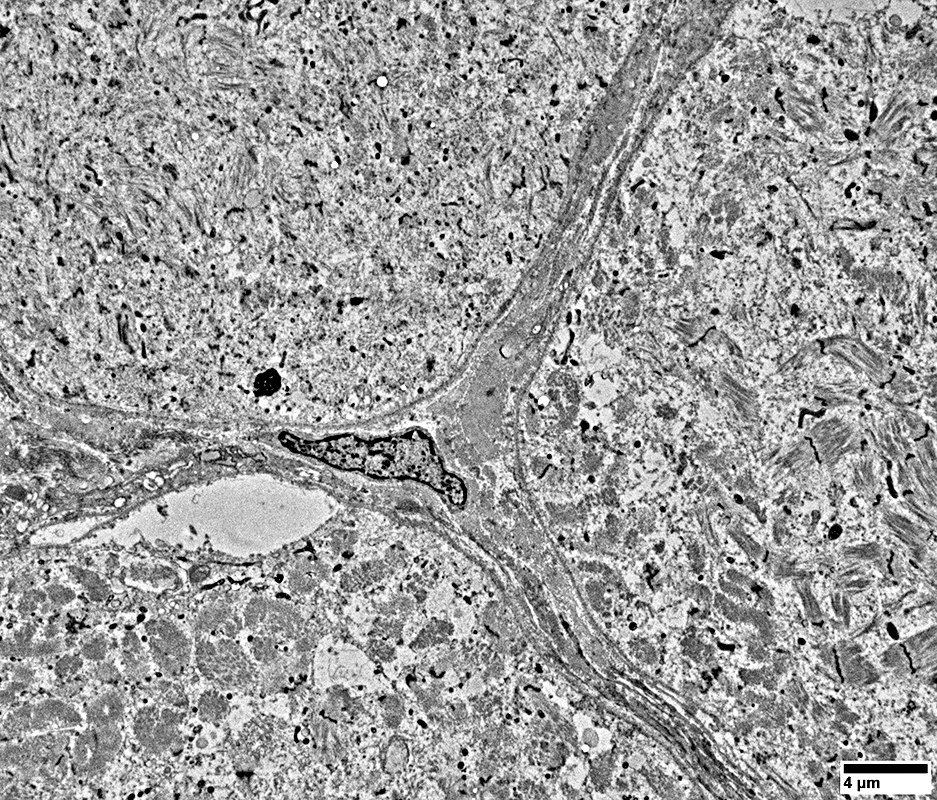 From: R Schmidt |
Fibers at top left & right have marked sarcomere disorganization
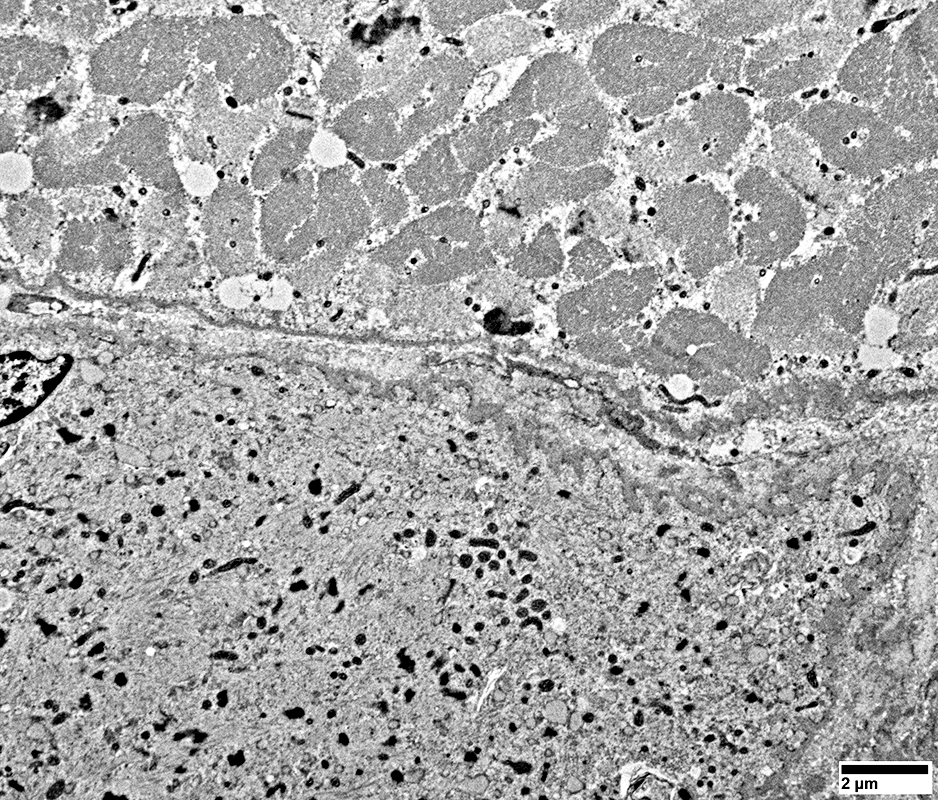 From: R Schmidt |
Muscle Fiber at bottom of images has
Sarcomeres: Marked disorganization
Mitochondria: Proliferation; Coarse cristae; Often small size
Basal lamina: Thick undulating (Compare to normal muscle fiber above)
Cytoplasmnic vacuoles: Possibly derived from Endoplasmic Reticulum
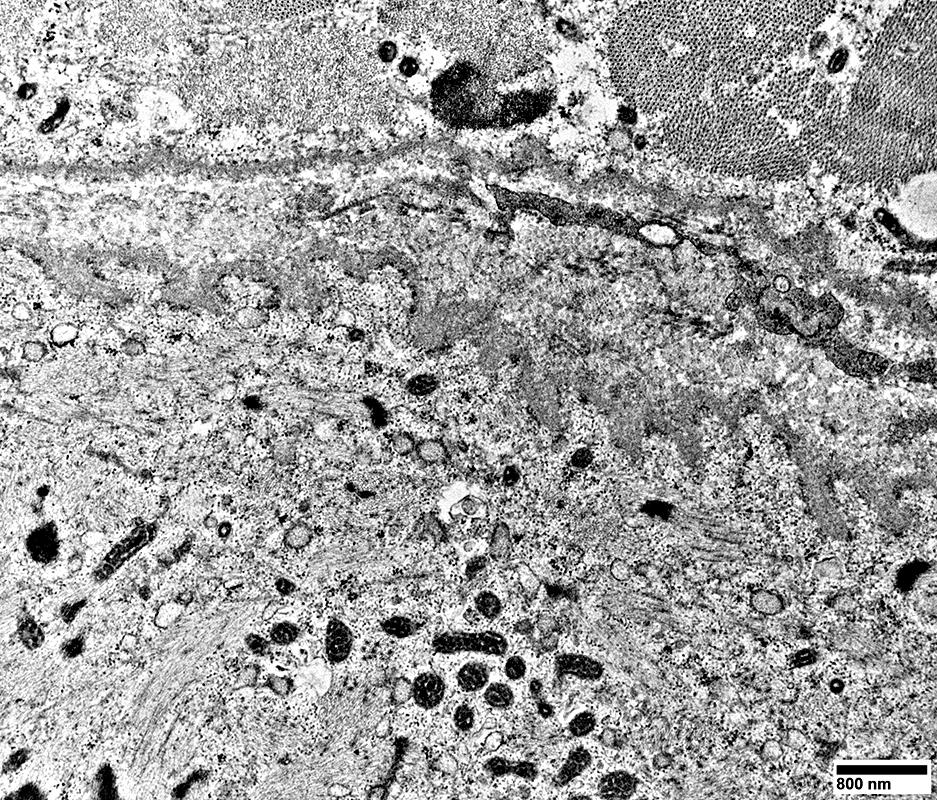 From: R Schmidt |
Mitochondrial Pathology
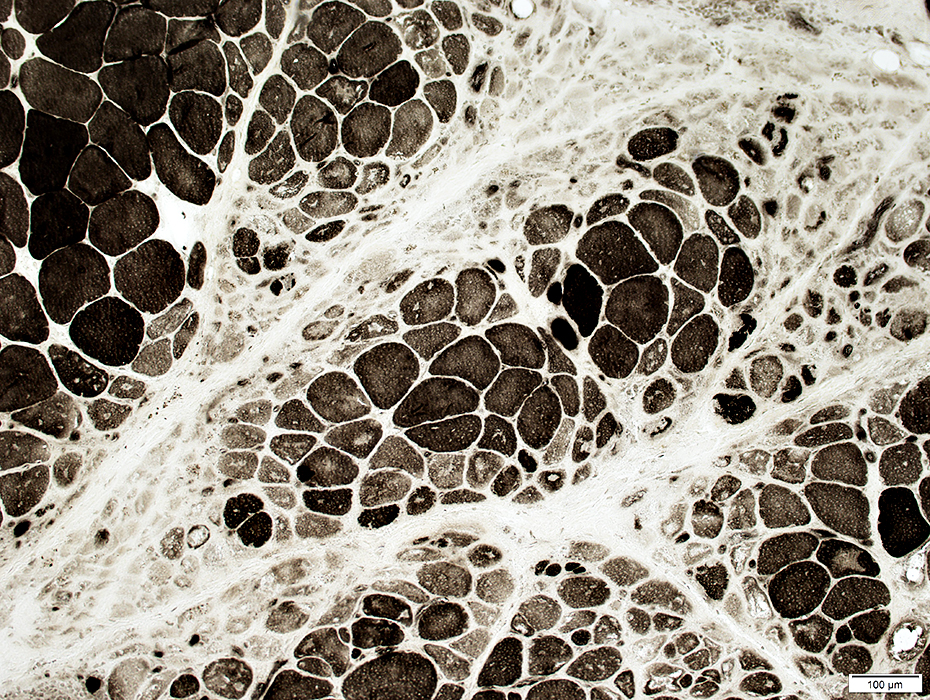
The extent of the perifascicular muscle fiber pathology in active DM-VP may be more prominent on Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stainCOX is reduced in perifascicular muscle fibers
SDH is normal or increased in the same fibers
Reduced perifascicular cytochrome oxidase staining is not present in IMPP syndromes
IMPP have a different pattern of perifascicular muscle fiber pathology with fiber necrosis
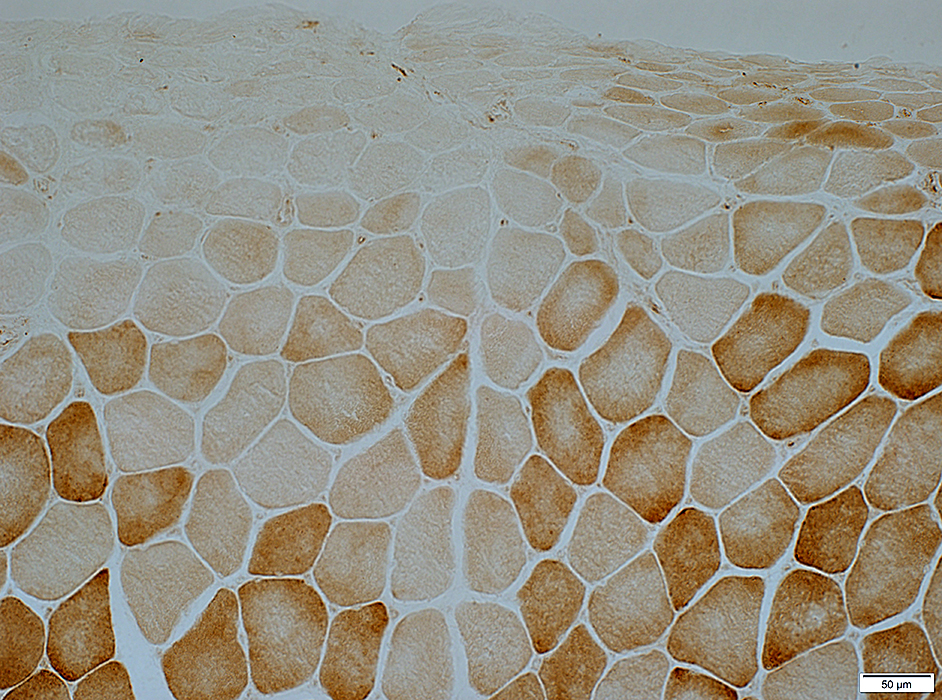
Cytochrome Oxidase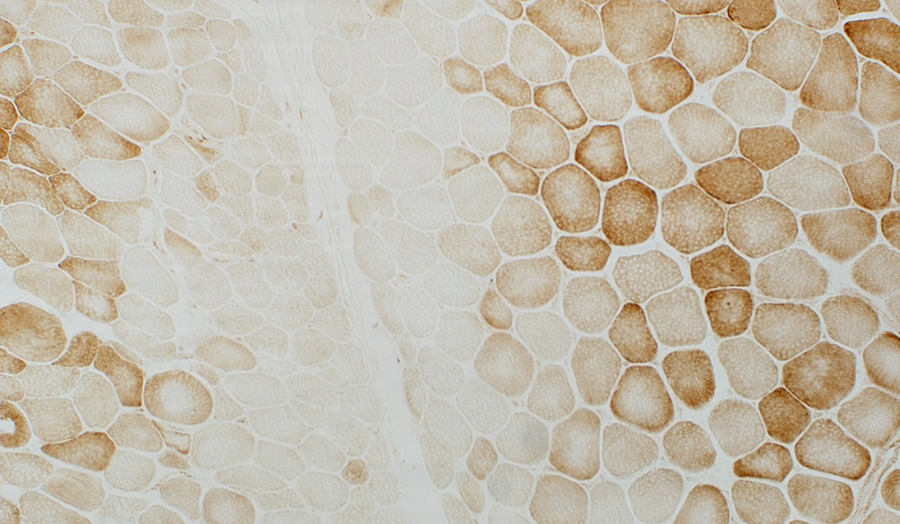 COX stain Muscle fibers near avascular perimysium are small & have pale COX staining Succinate Dehydrogenase 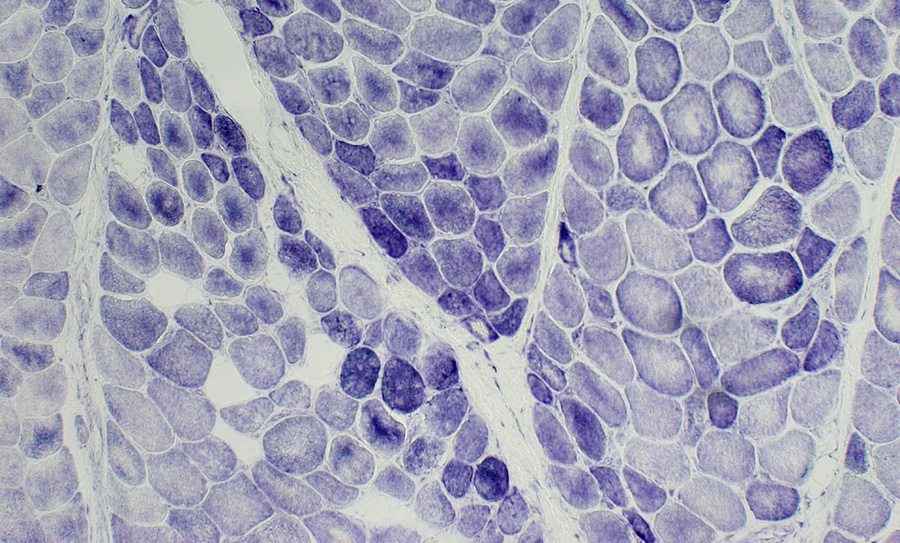 SDH stain Muscle fibers near the avascular perimysium are small & have normal or dark SDH staining |
Perifascicular muscle fibers near avascular perimysium: Small; Pale COX staining, Blue (SDH) color
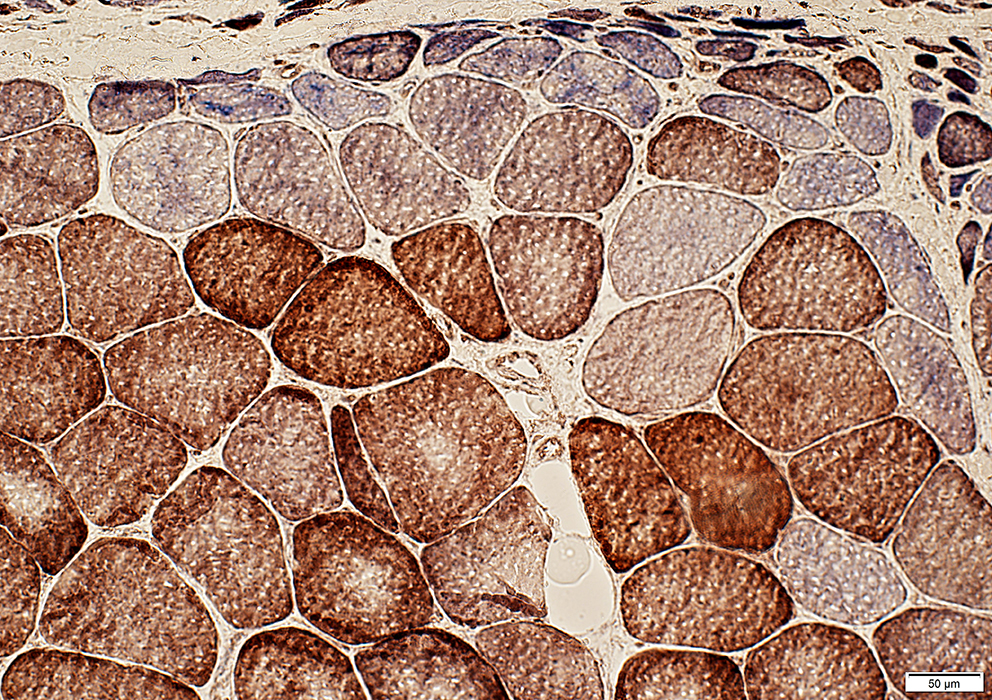 COX + SDH stain |
Mildy reduced COX stain in perifascicular muscle fibers with normal size. (Arrow; Right)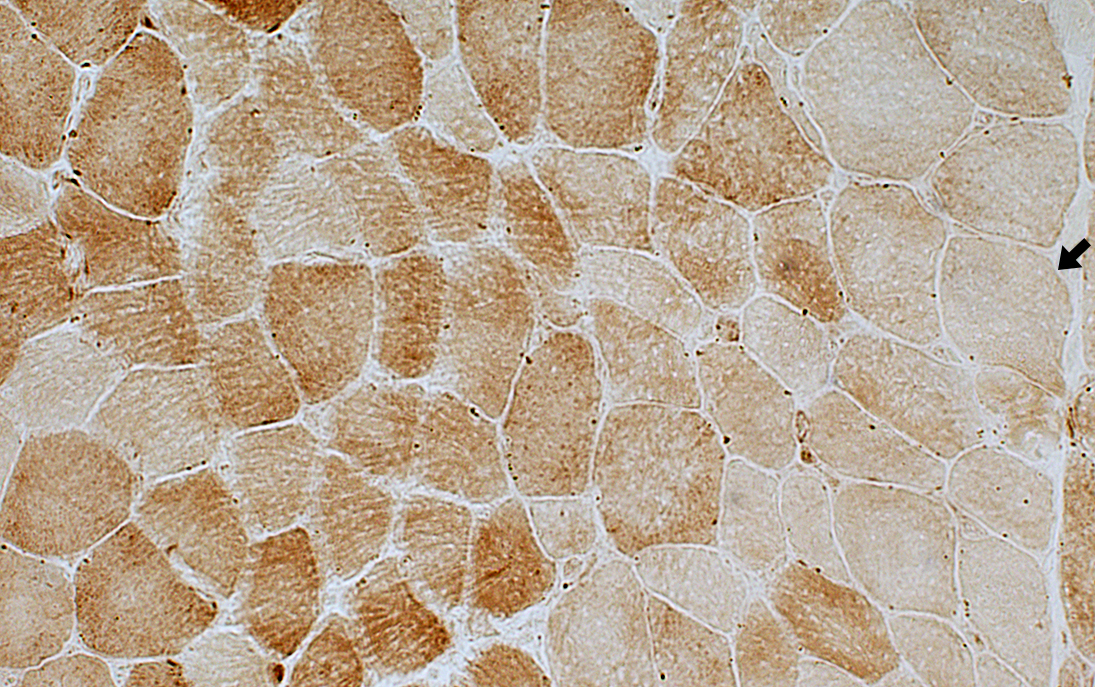 COX stain |
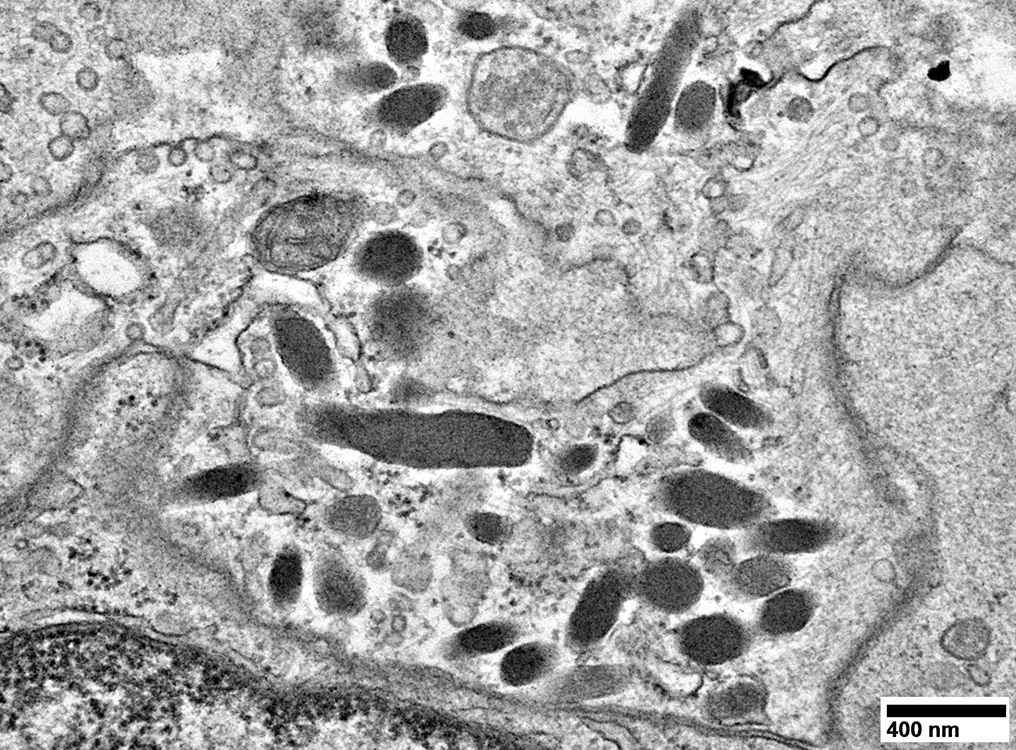
DM-VP Ultrastructure: Abnormal Mitochondria
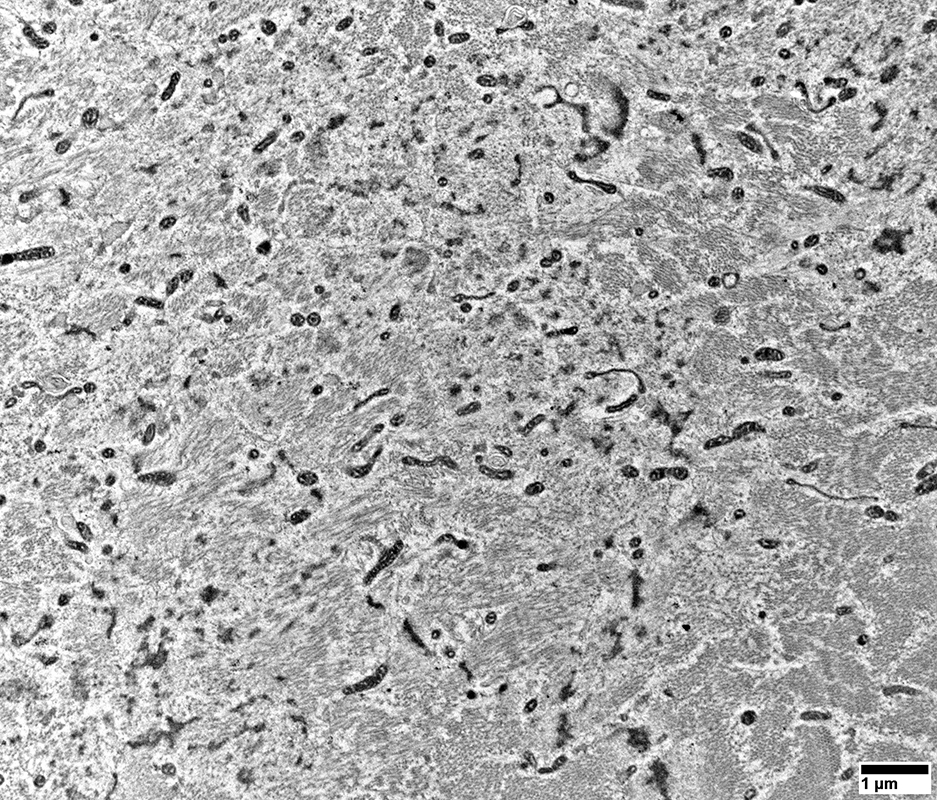 From: R Schmidt |
Abnormal Mitochondria
Sizes: Generally small
Cristae: Dense
Shapes: Some elongated
No filamentous inclusions
Muscle fiber morphology
Sarcomere structure is missing or abnormal
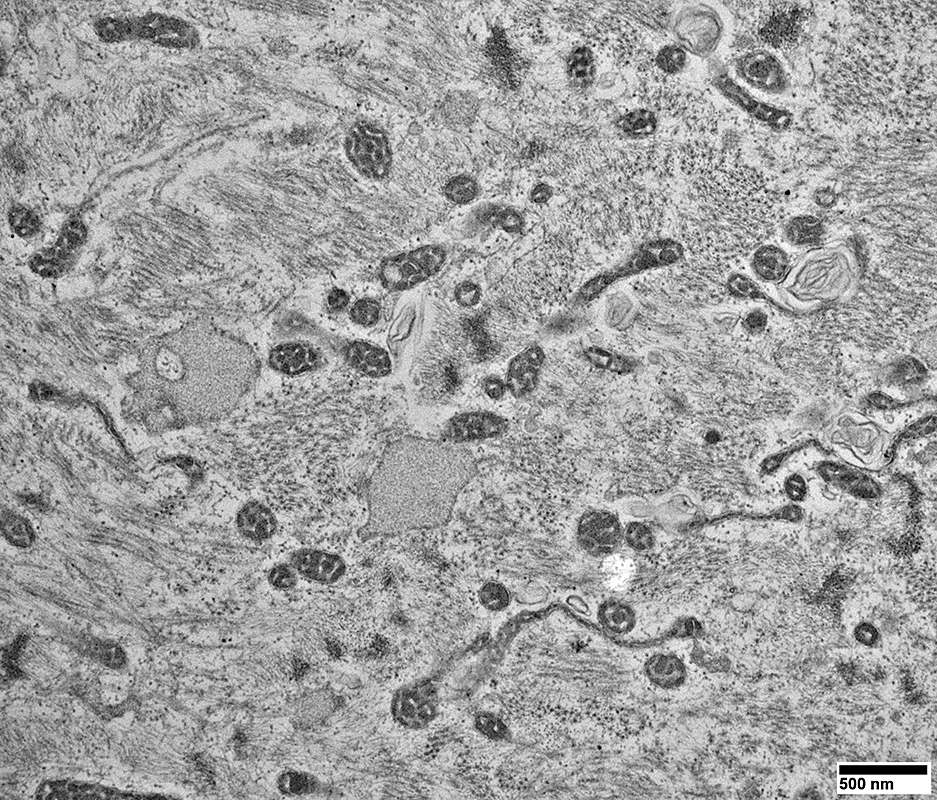 From: R Schmidt |
Many are Small & Round (Arrow, Below)
Sarcoplamic Aggregates (Below)
Small, Irregularly shaped, Amorpohous
 From: R Schmidt |
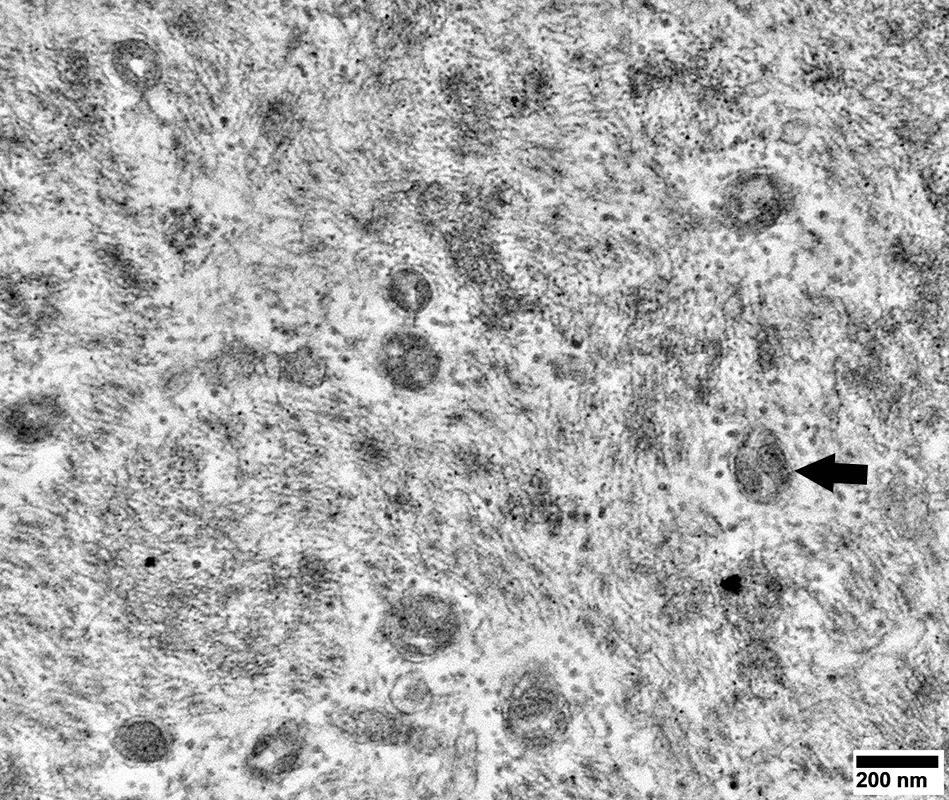
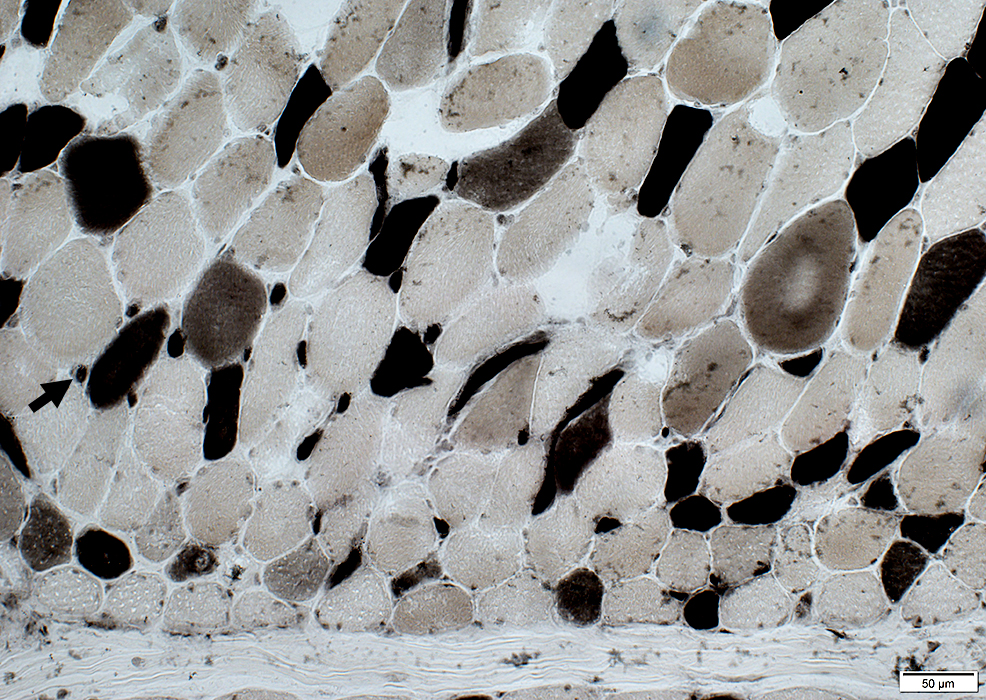
DM-VP: Endomysial capillaries
ATPase pH 4.3
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
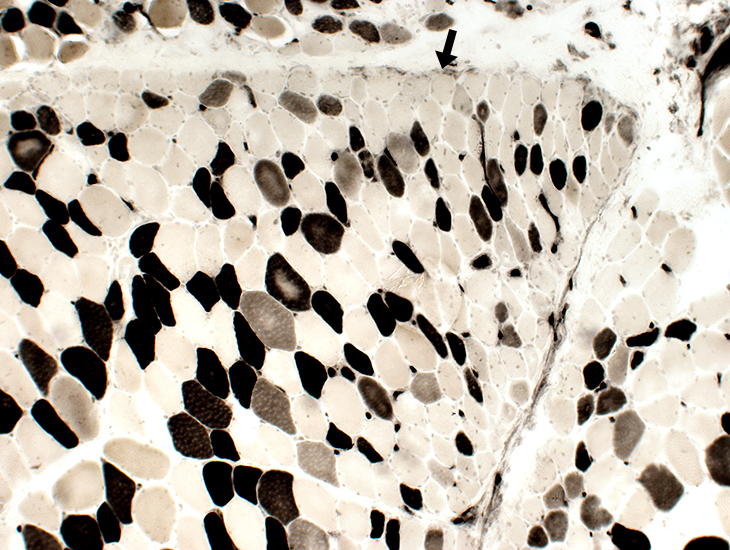 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
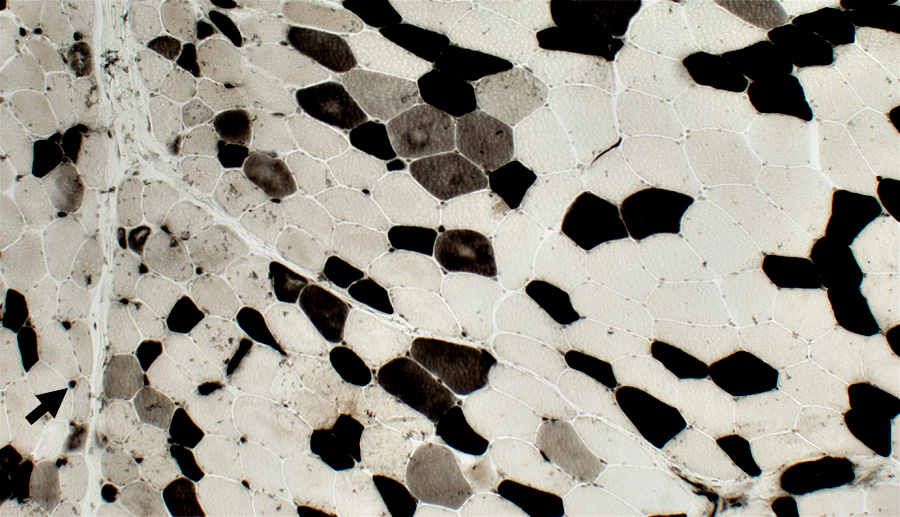
Type IIC muscle fibers (intermediate staining): Present in regions of atrophy & larger muscle fibers.
Type 1 muscle fibers: Few, or none, in regions of most severe atrophy at edge of fascicles (Above; Dark arrow).
Small muscle fibers: Located near avascular perimysium.
Fibers near intermediate-sized perimysial vessel (Below; White arrow): Larger size.
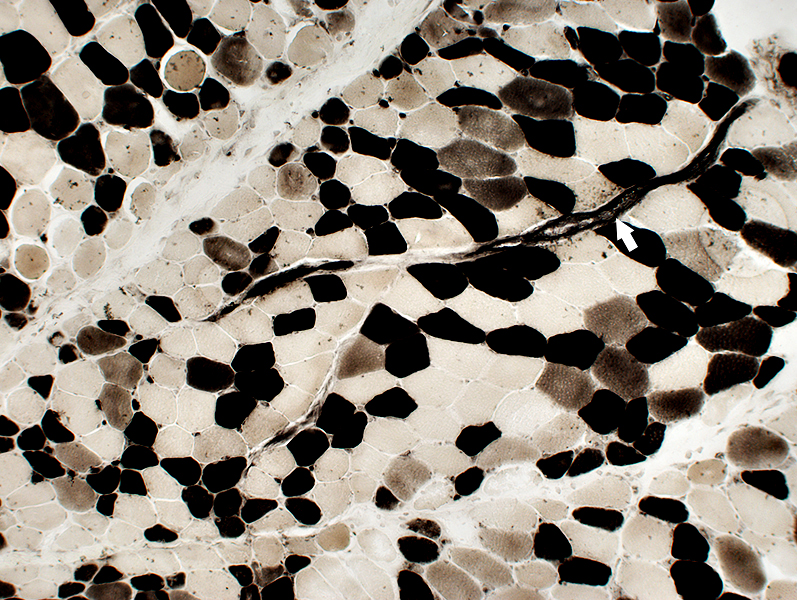 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
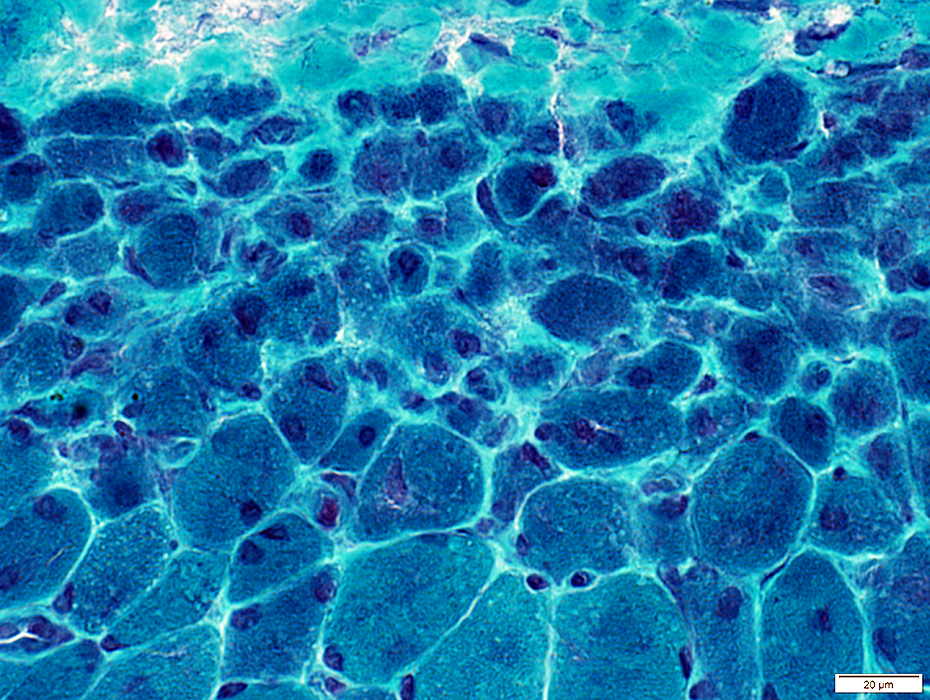
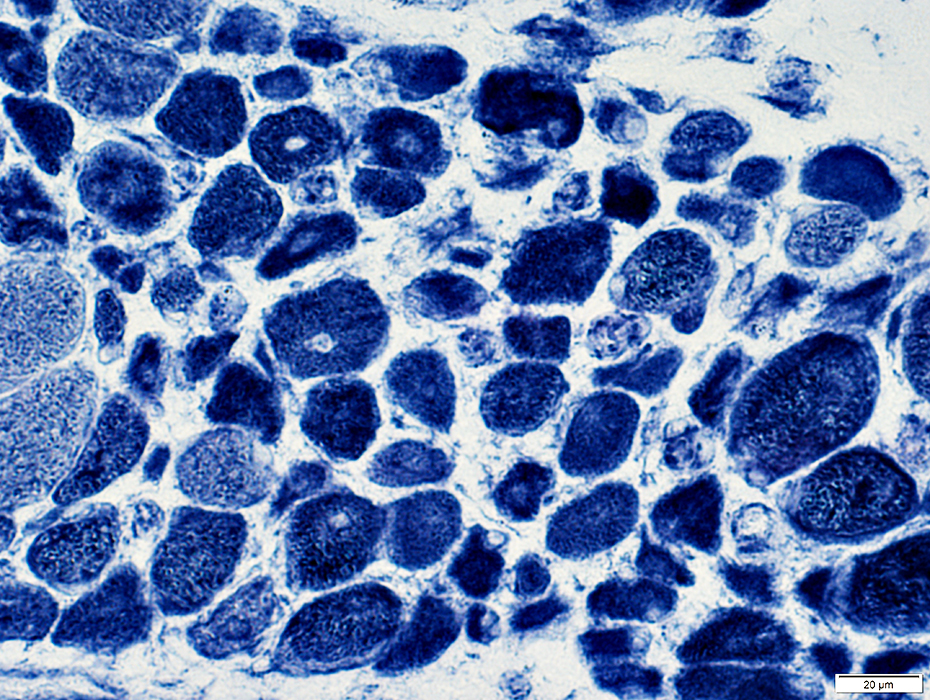
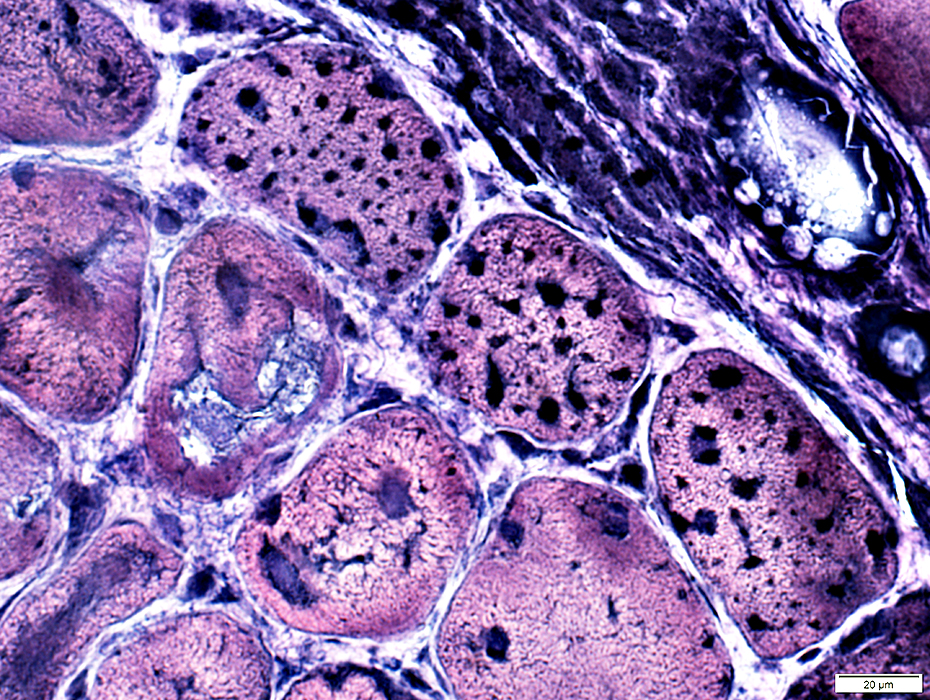
PAS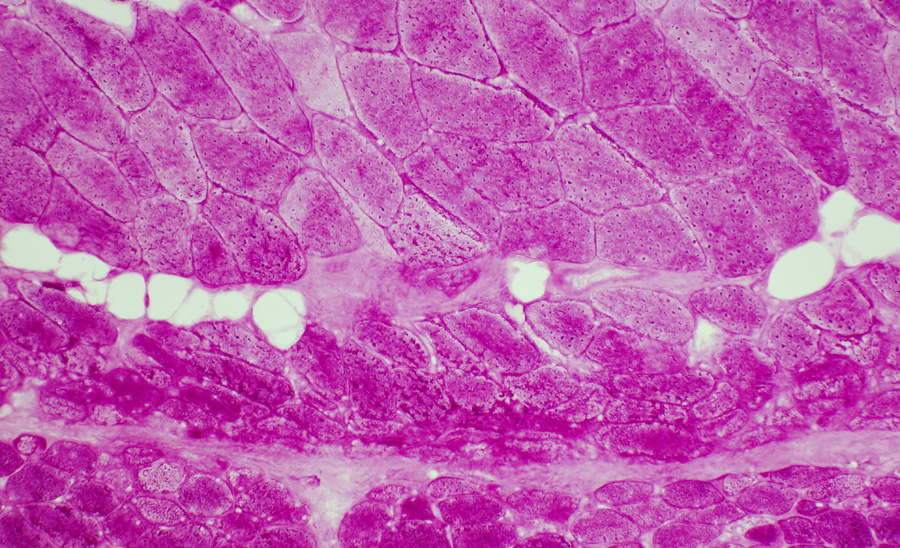 PAS stain DM-VP: Increased glycogen staining in small perifascicular muscle fibers 1 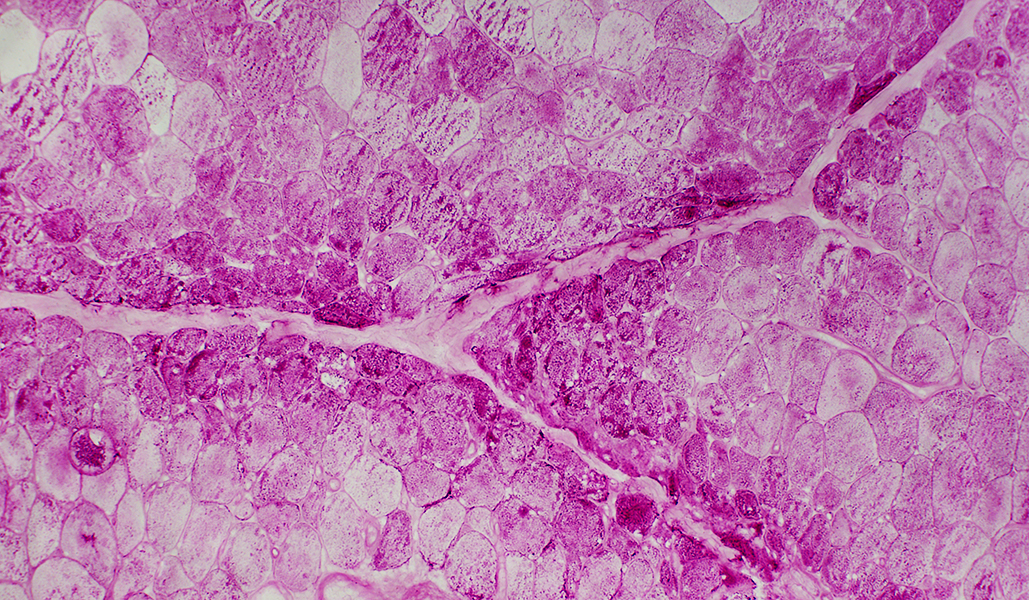
|
Perifascicular muscle fiber atrophy: Fiber pathology
Muscle fibers in regions of perifascicular pathology: Several additional abnormalitiesVacuolar or reticulated cytoplasm (Below).
Cytochrome oxidase: Reduced stain in region of small fibers
MHC-I upregulation: Perifascicular fibers or Diffuse
Aggregates: LC3
MxA expression
Muscle fiber nuclei: Large
Muscle fiber necrosis: Rare
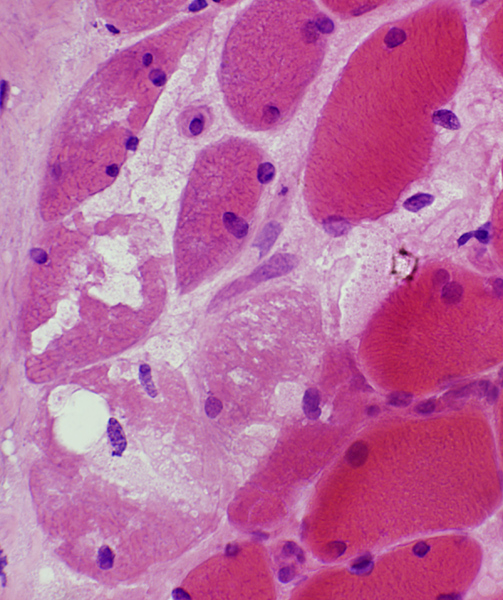
 H&E stain |
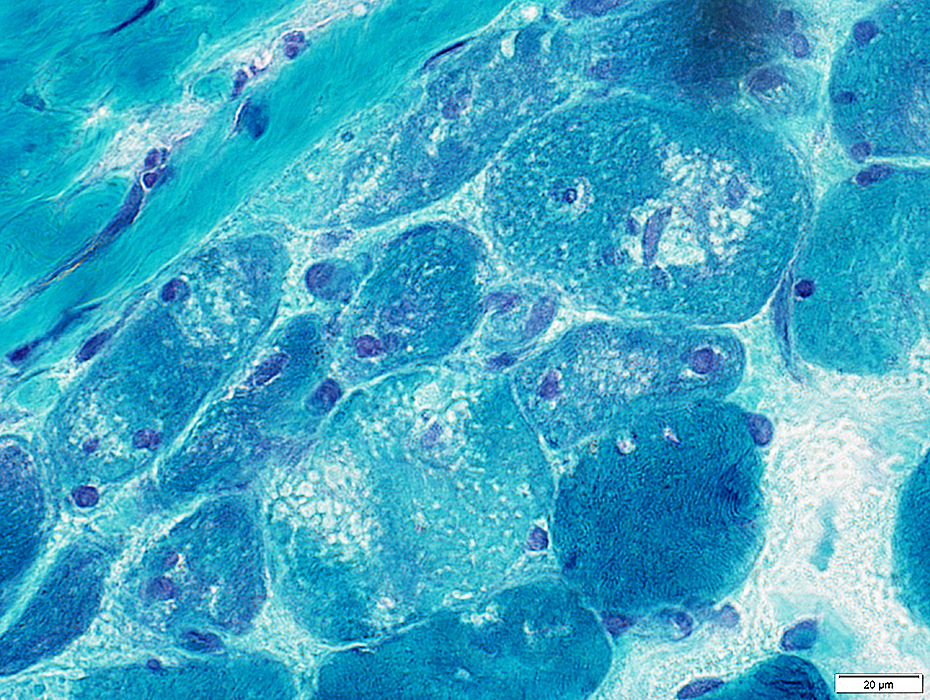 GT stain |
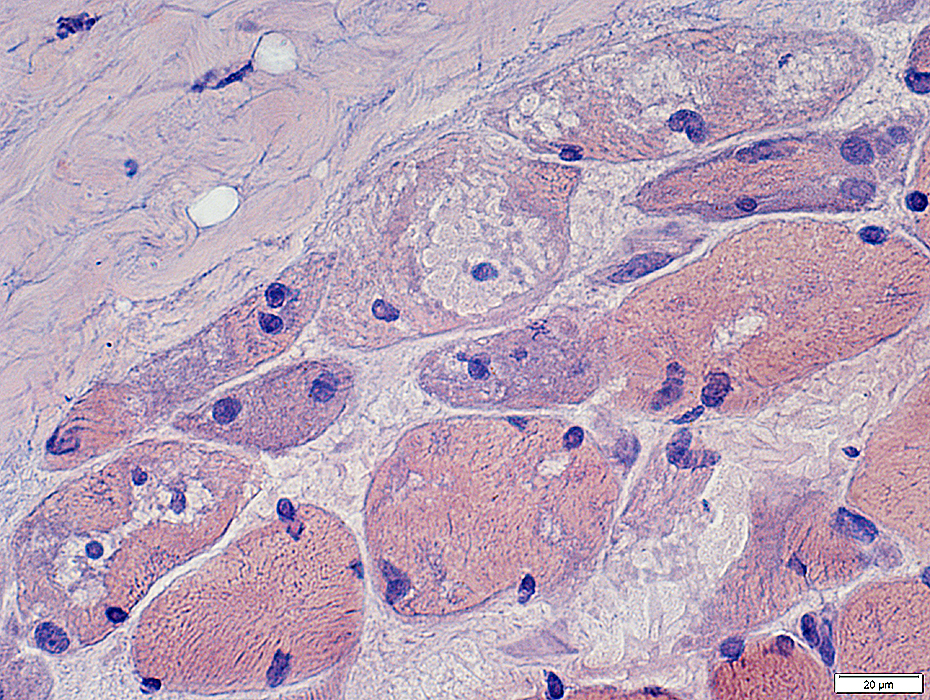 Congo red stain |
DM-VP: Muscle fiber cytoplasm may contain
Multiple small vacuoles
Membranous whorls
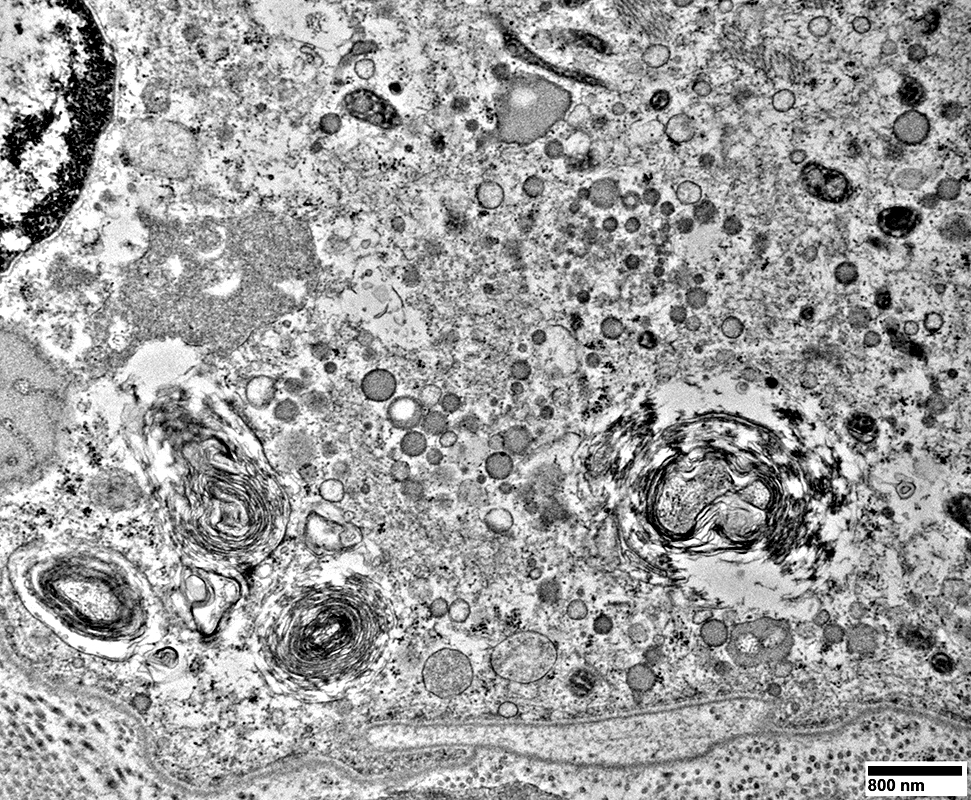 From: R Schmidt |
|
Muscle fibers may also have Coarse internal architecture with basophilia (Left, Arrow), or Internal nuclei (Right). The abnormal internal architecture may be better visualized on Gomori trichrome 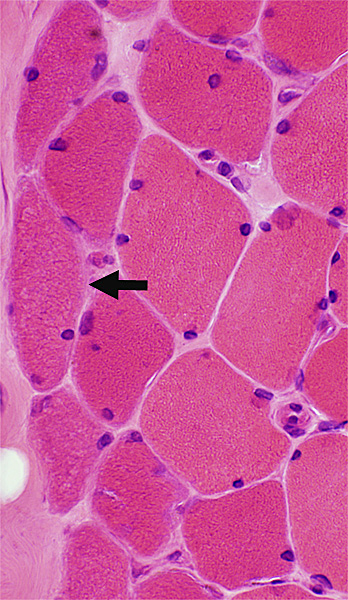
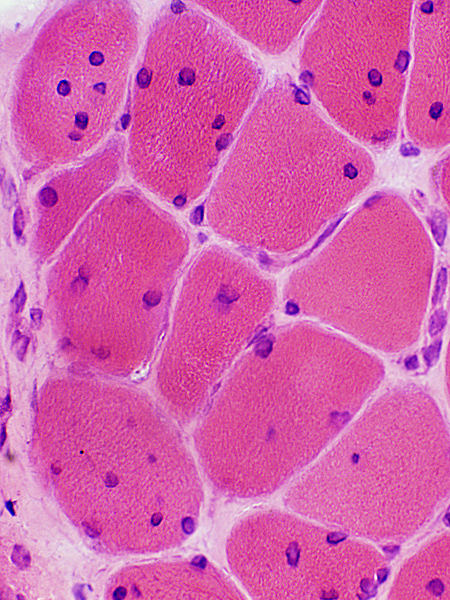 H&E stain |
Abnormal internal architecture in dermatomyositis muscle fibers is more apparent on Gomori trichrome stains.
The abnormalities may be present in both small and large muscle fibers.
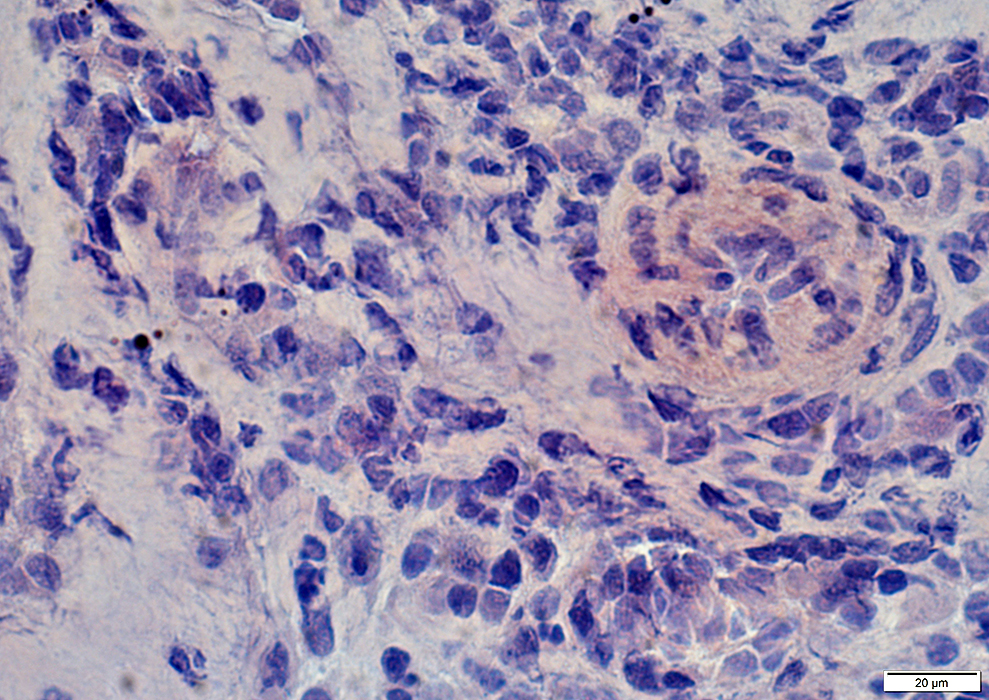
Cytoplasmic bodies may occur
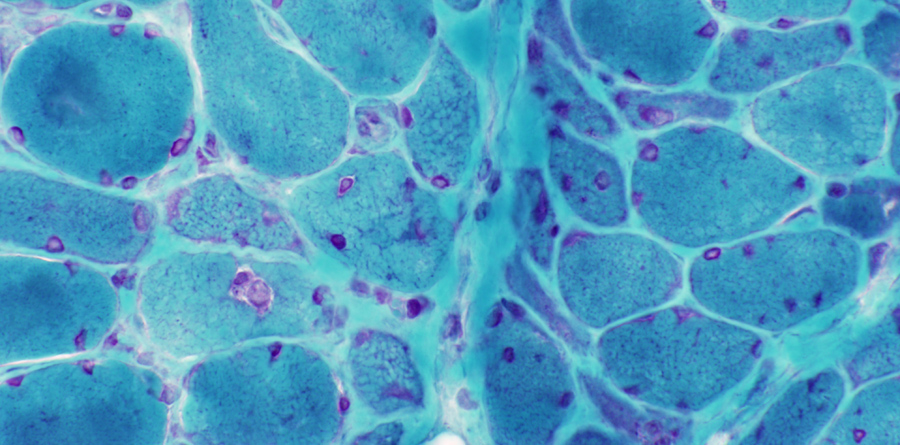 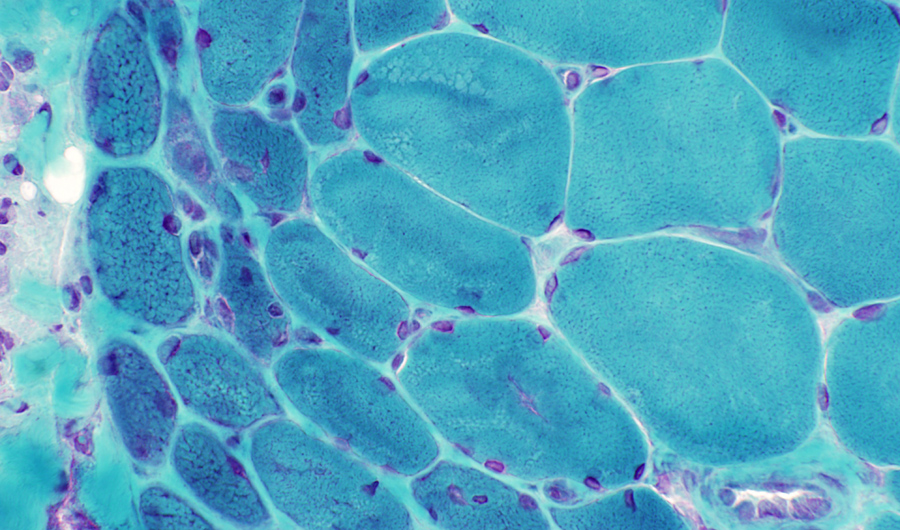 |
Cytoplasmic bodies
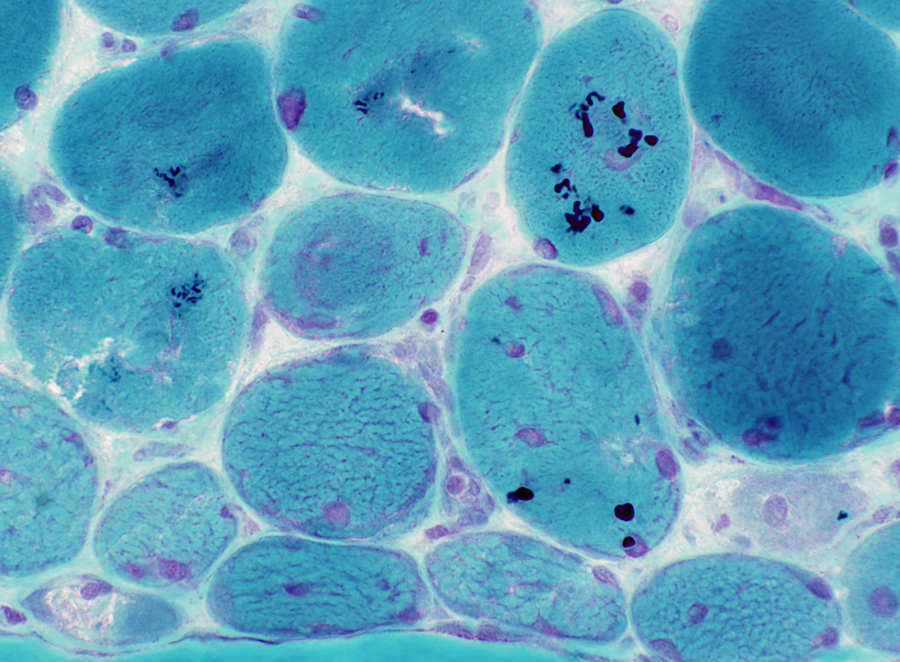 GT stain |
|
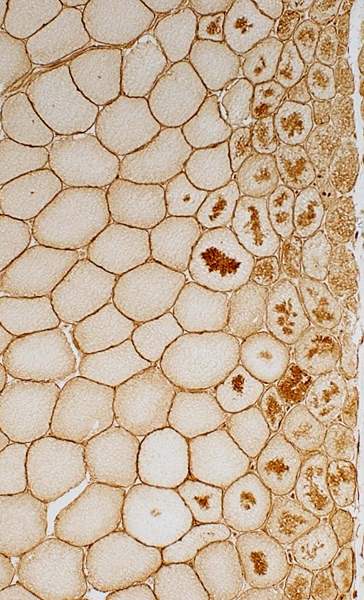
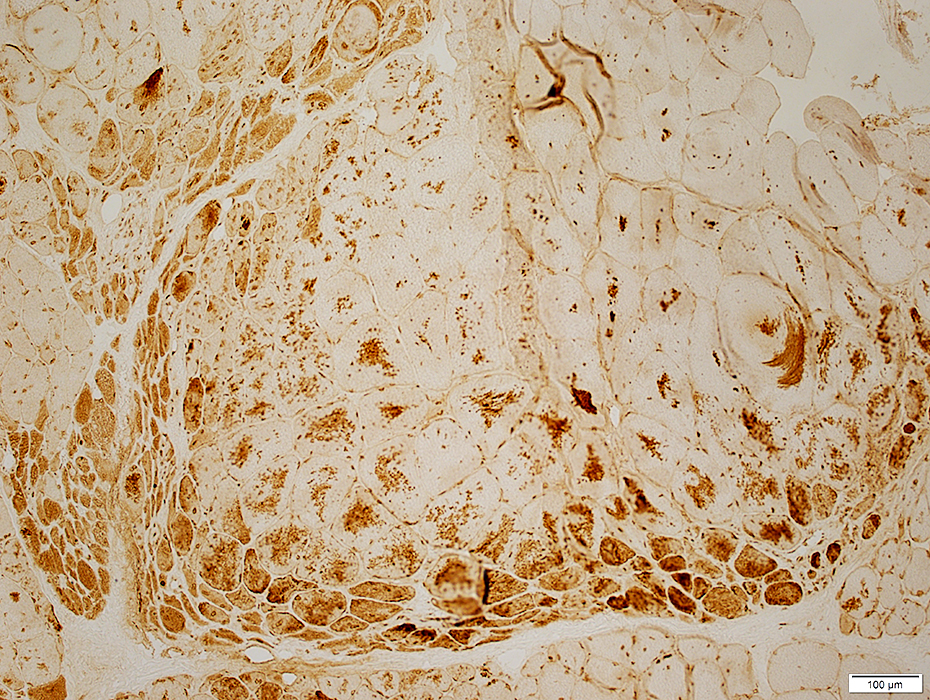
Autophagic Aggregates: LC-3 & Caveolin-3 Aggregates and increased cytoplasmic staining are common in perifascicular muscle fibers with abnormal internal architecture in DM-VP. 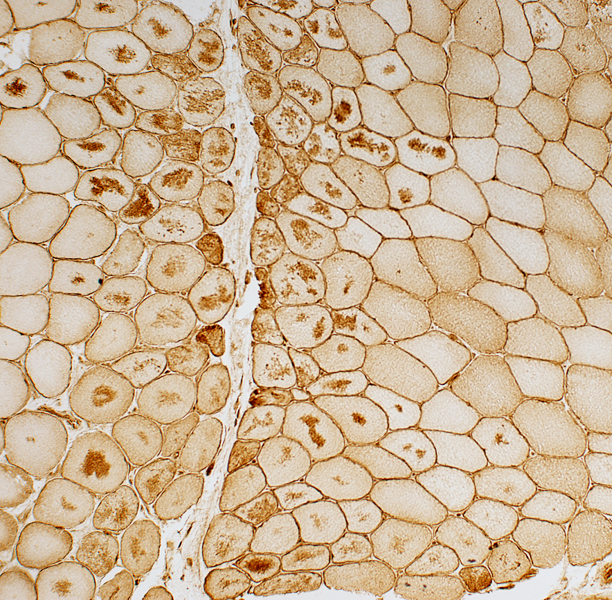
 Caveolin-3 stain |
 LC3 stain |
|
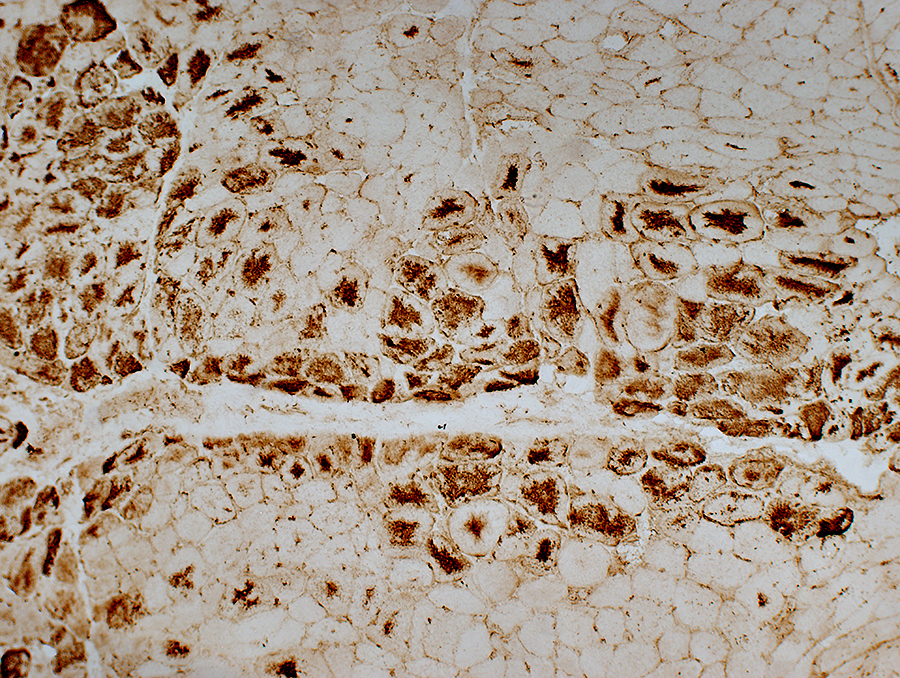
LC-3 aggregates: Irregular shaped in muscle fiber cytoplasm
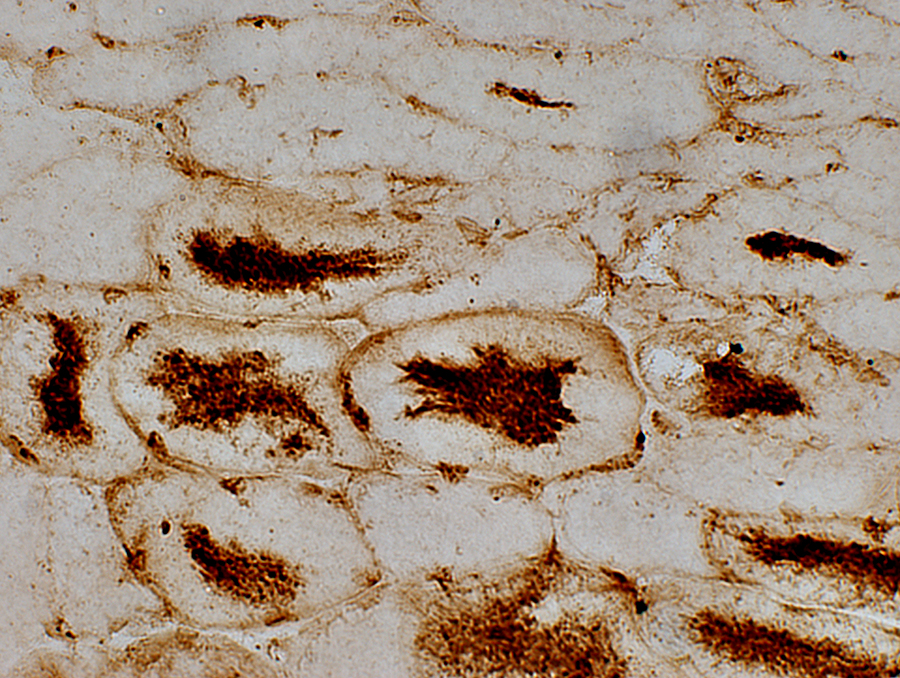 |
 AMPDA stain Aggregates in the center of muscle fibers |
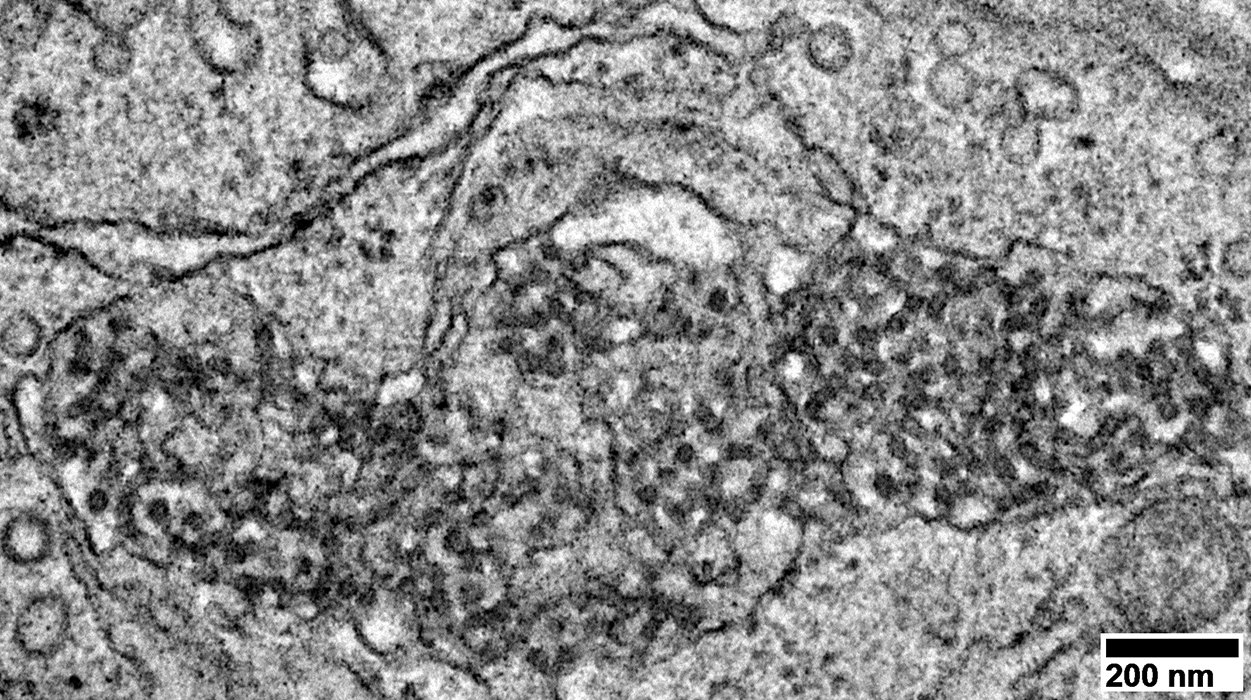
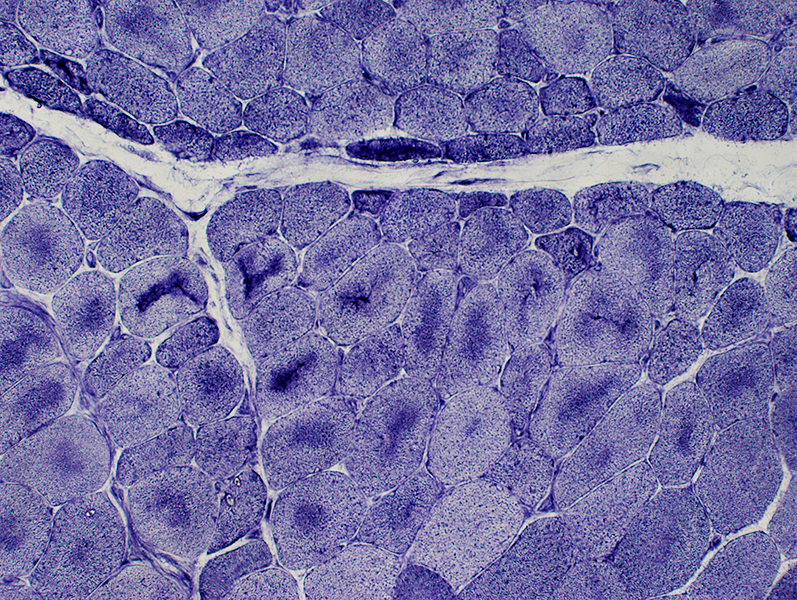
DM-VP: Aggregate Ultrastructure
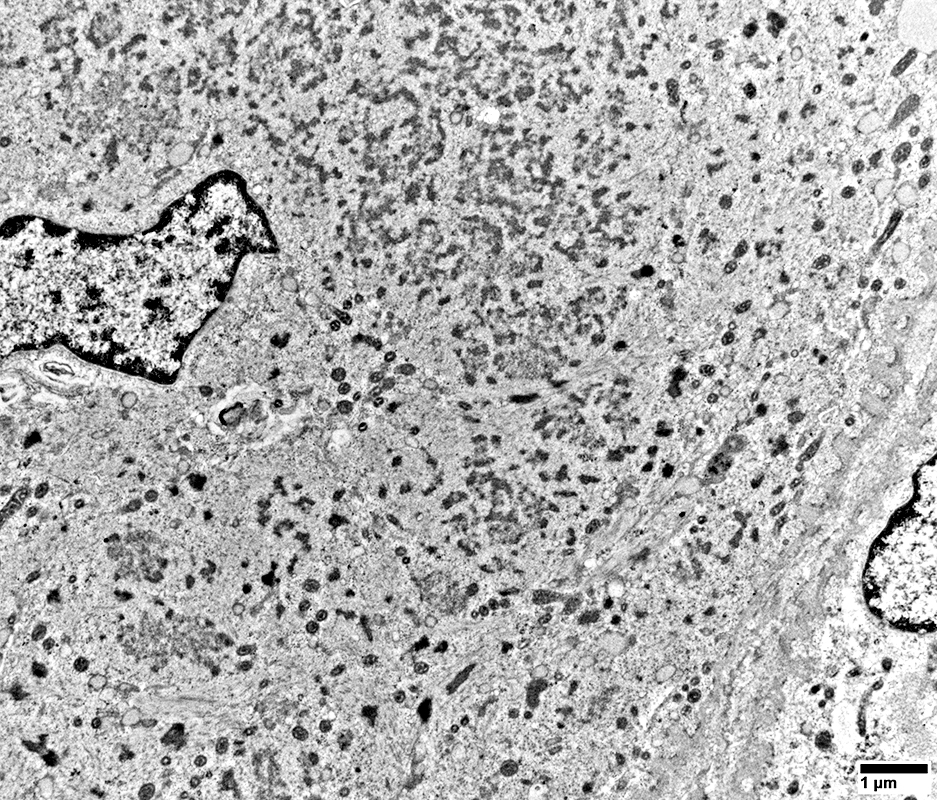 From: R Schmidt |
Aggregates: Small; Multiple; Scattered
Mitochondria: Mostly small
Few sarcomeres
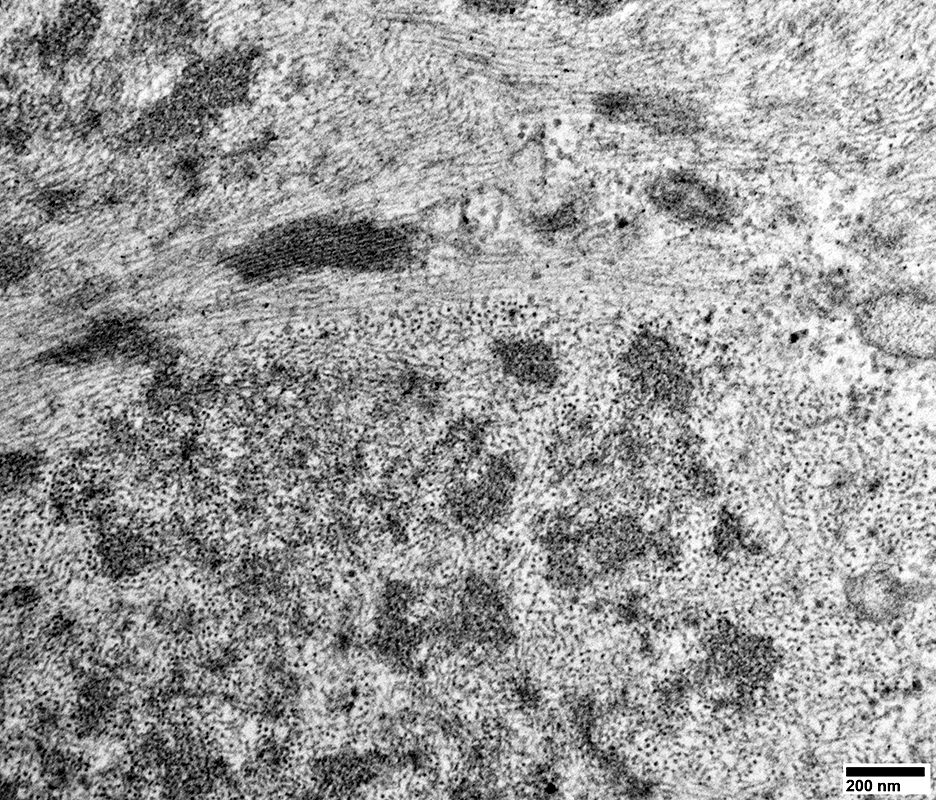 From: R Schmidt |
Shape: Irregular
internal architecture: Punctate
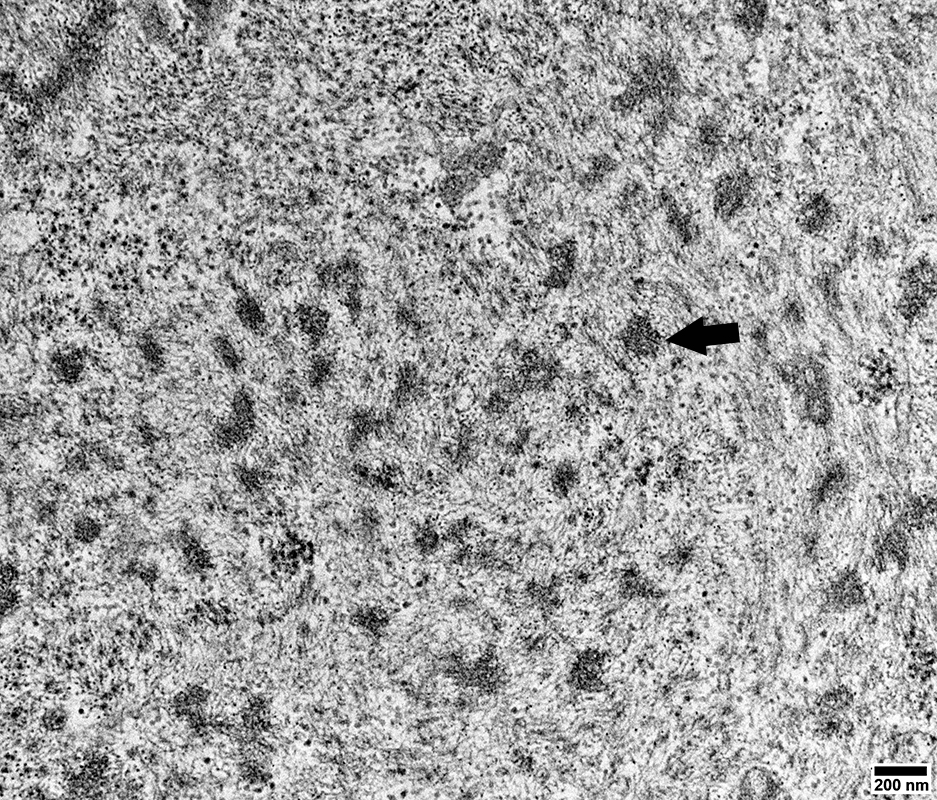 From: R Schmidt |
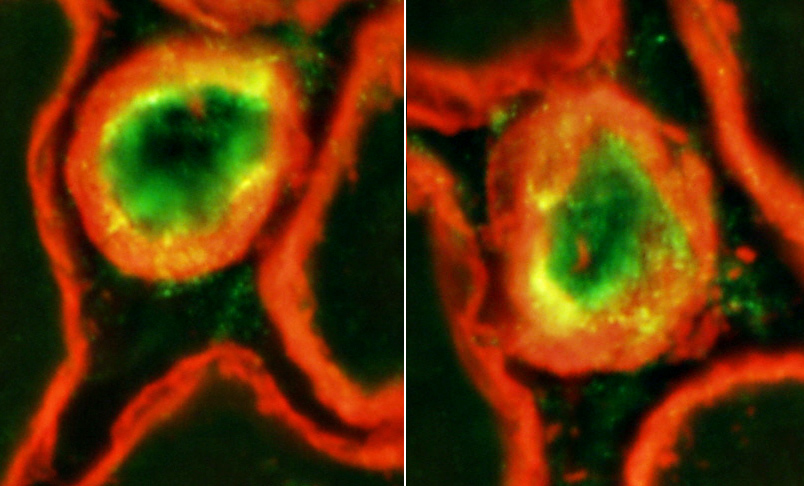
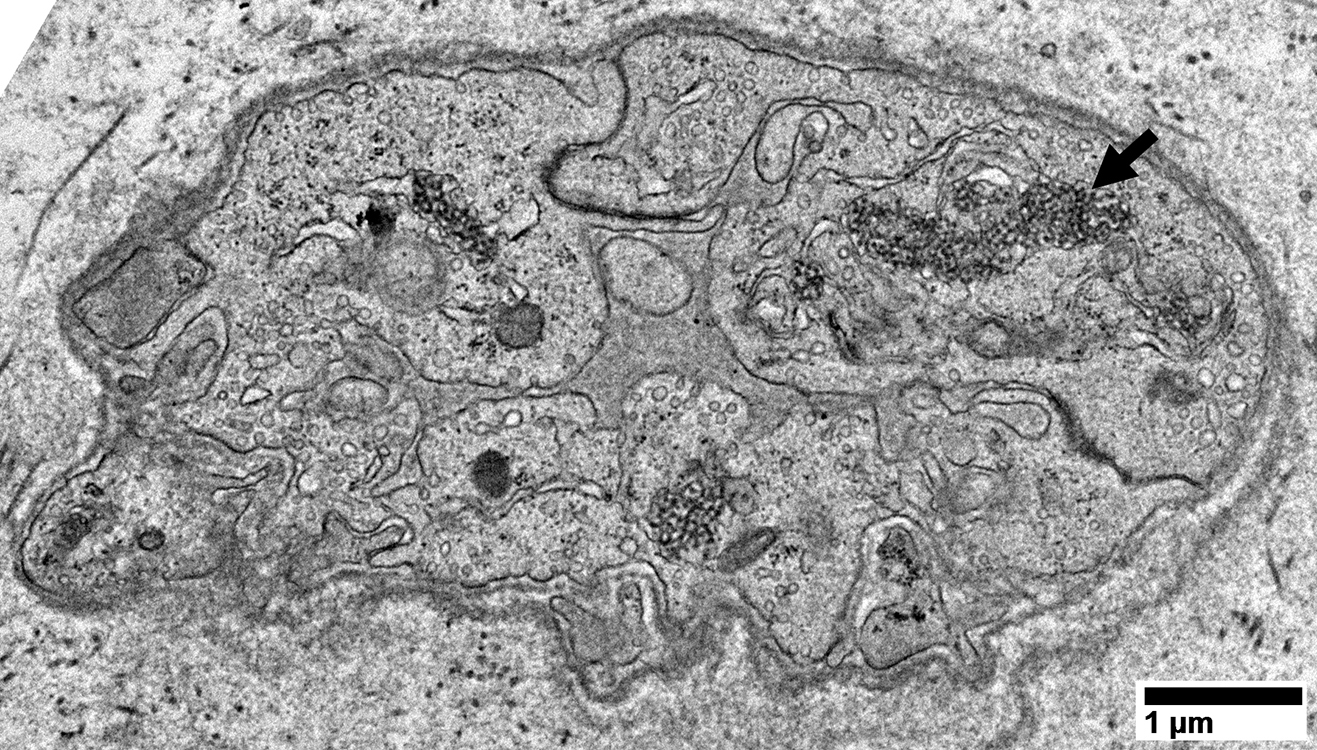
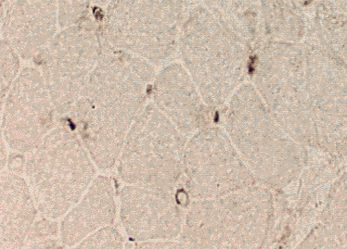
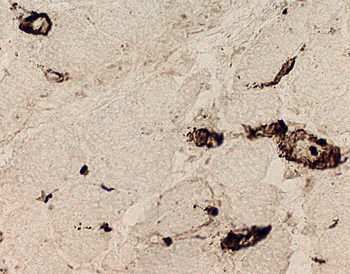
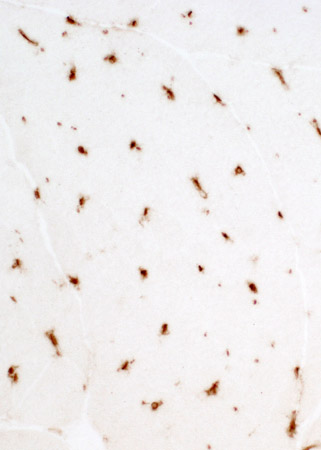
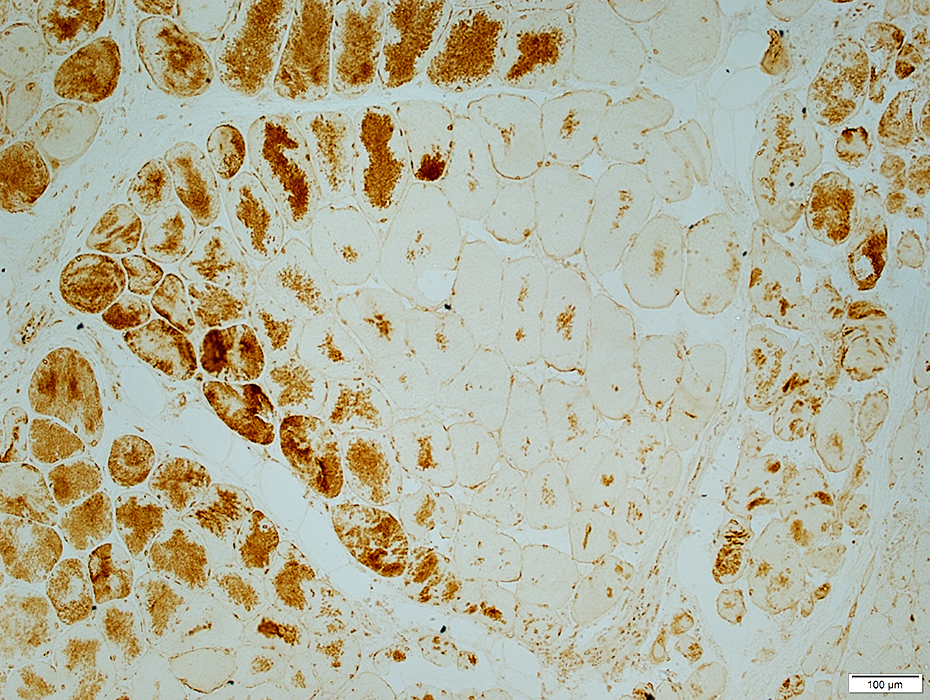
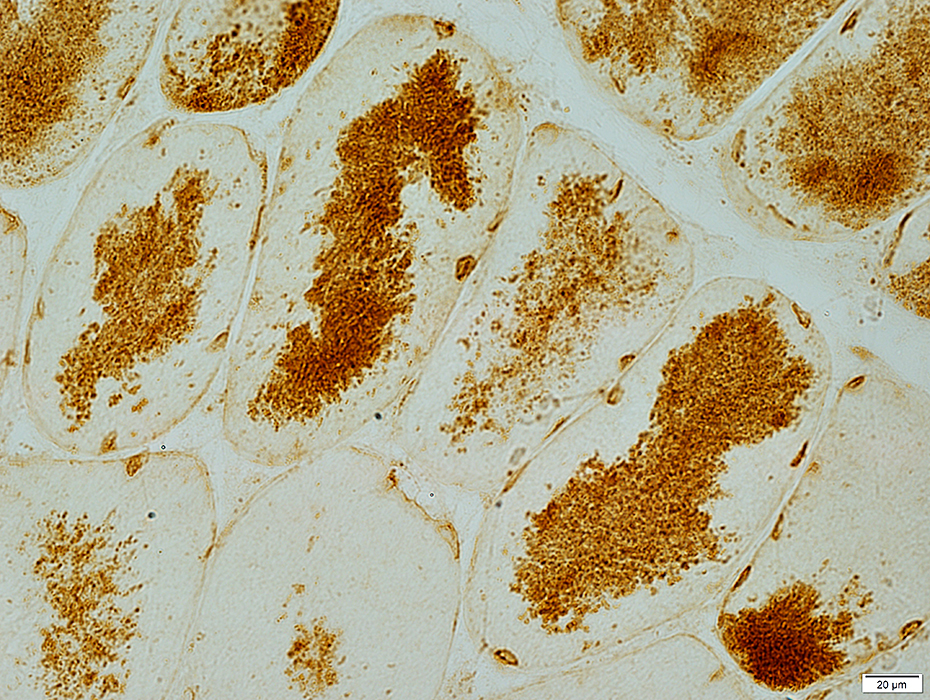
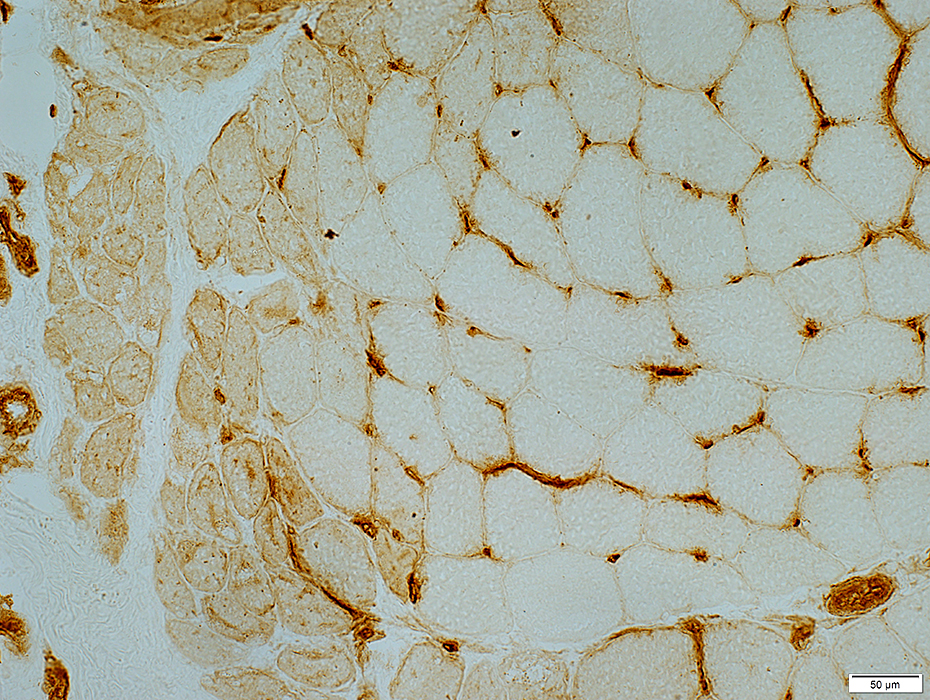
Dermatomyositis (DM-VP): MxA staining
|
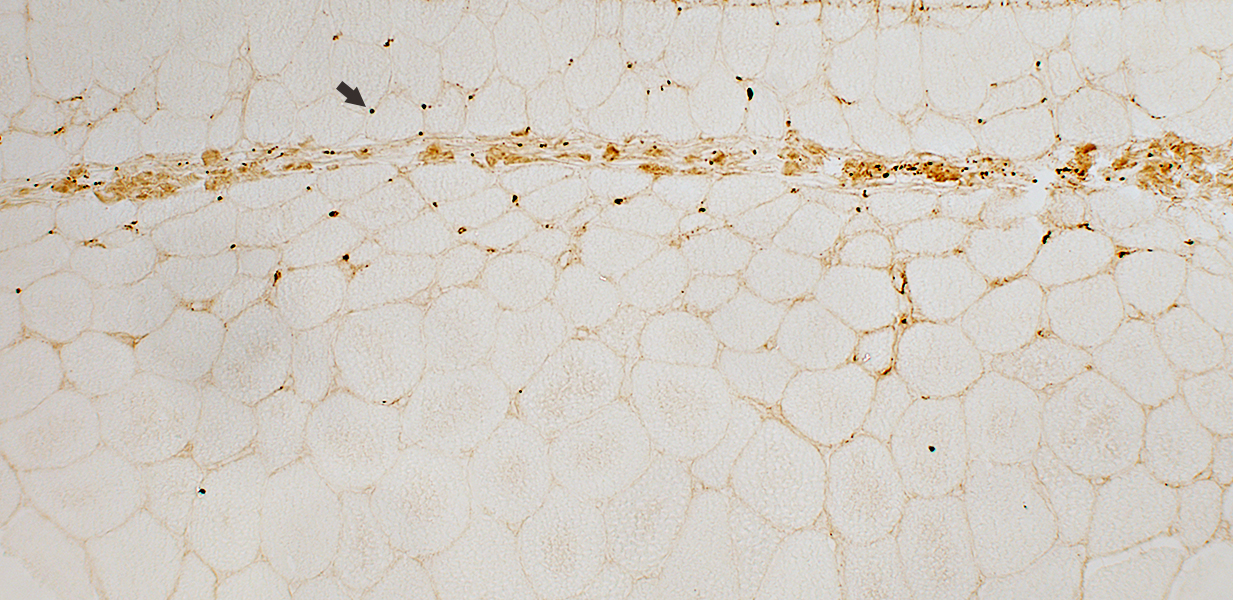
DM-VP MxA strongly stains Perifascicular muscle fibers Endomysial capillaries  MxA stain |
|
Control Muscle No MxA staining of: Muscle fibers or Endomysial capillaries  MxA stain |
Dermatomyositis (DM-VP): Muscl;e Fiber Ultrastructure
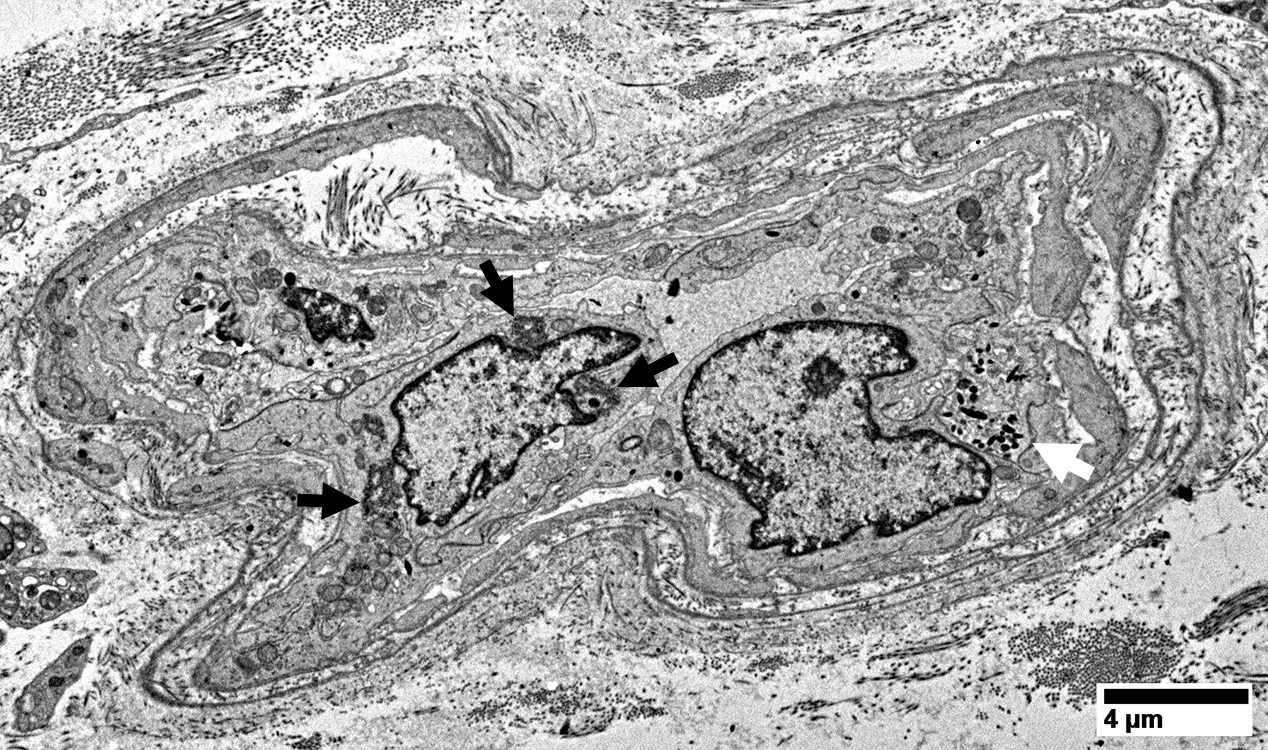
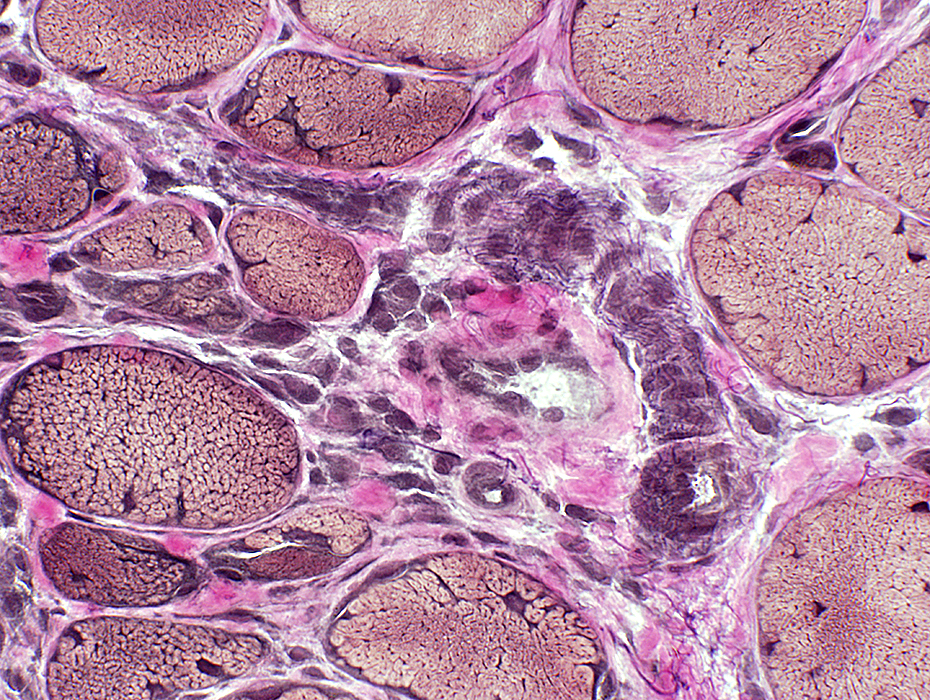
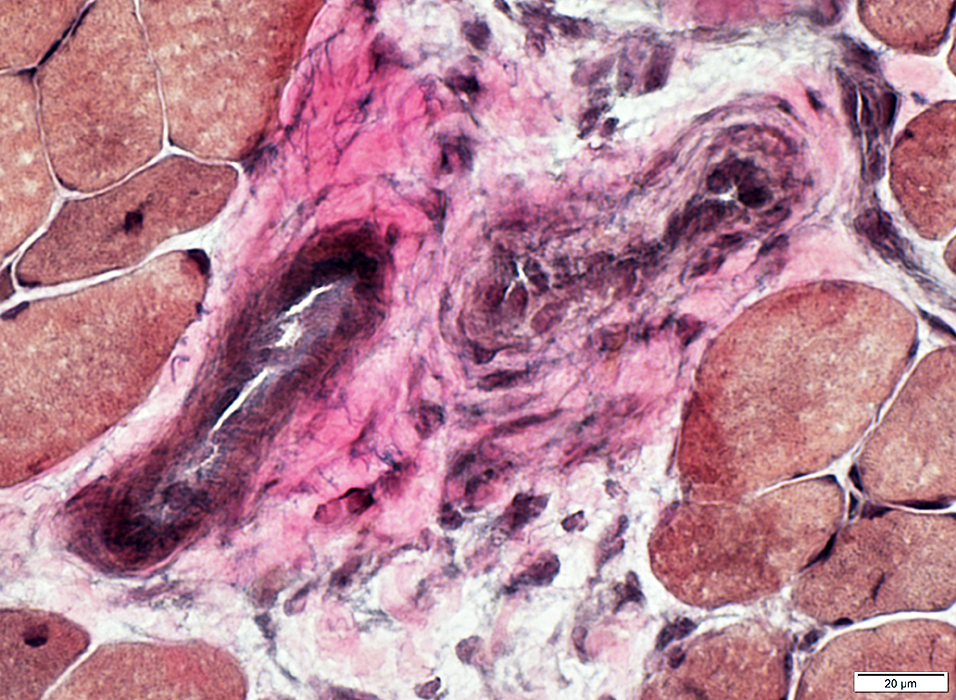
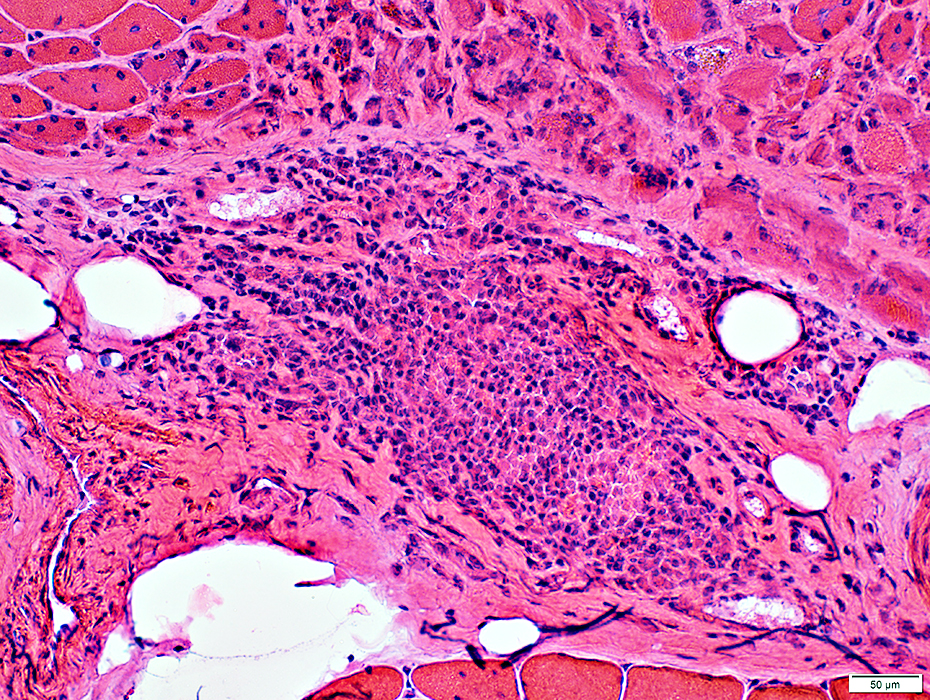
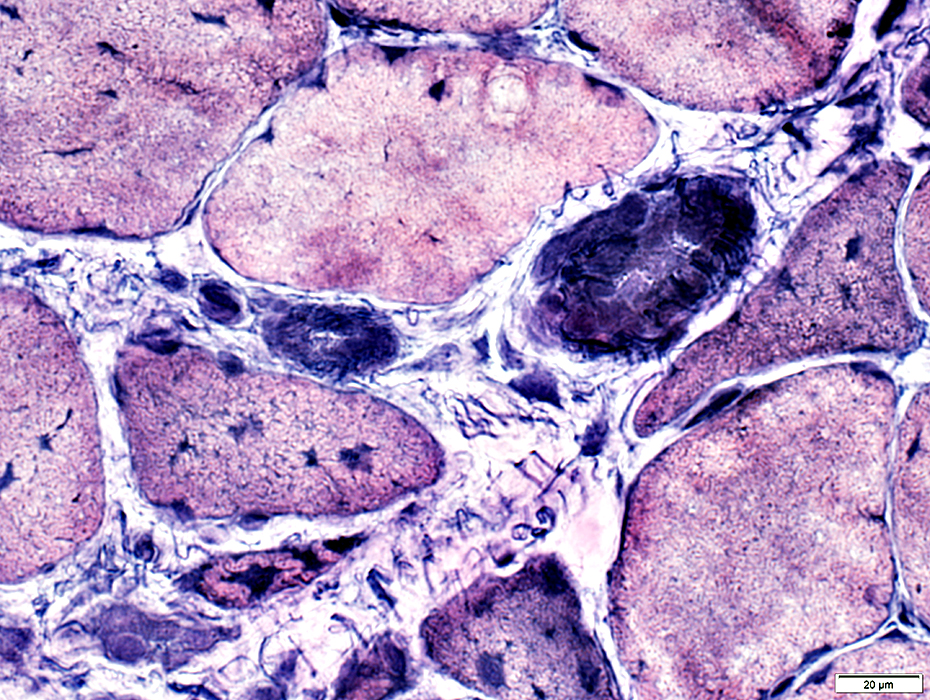
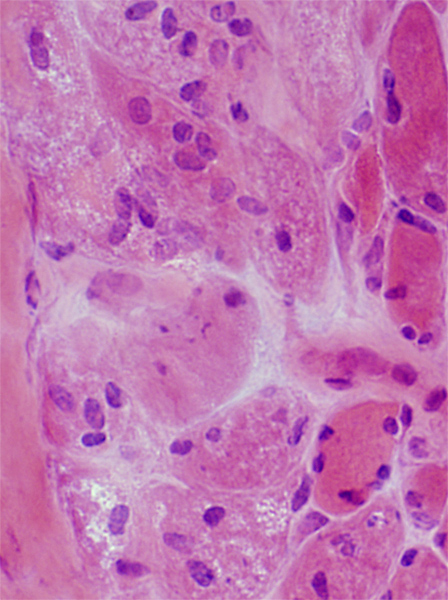
Dermatomyositis (DM-VP): Inflammation
Region of muscle withPerifascicular muscle fiber atrophy near avascular perimysium (Top)
Lymphocyte focus in vascular perimysium, near vessels
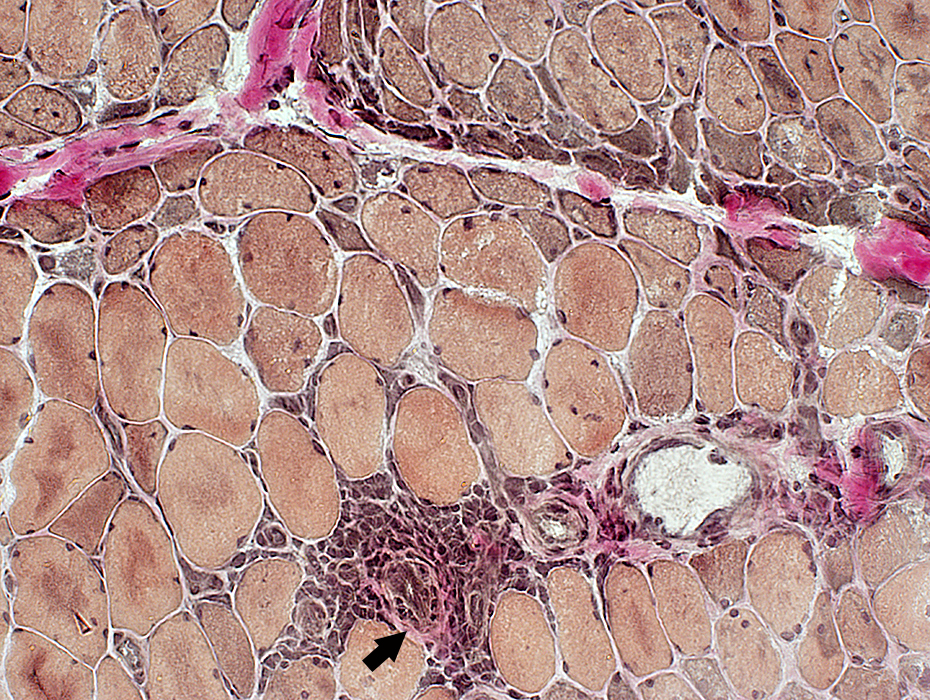 VvG stain |
Location
Vascular perimysium
Neighbors: Several larger perimysial vessels
Separate from atrophic perifascicular muscle fibers
Contains
Lymphocytes
Vessels: Intermediate-sized (Arrow) & small with large endothelial cells & featureless wall
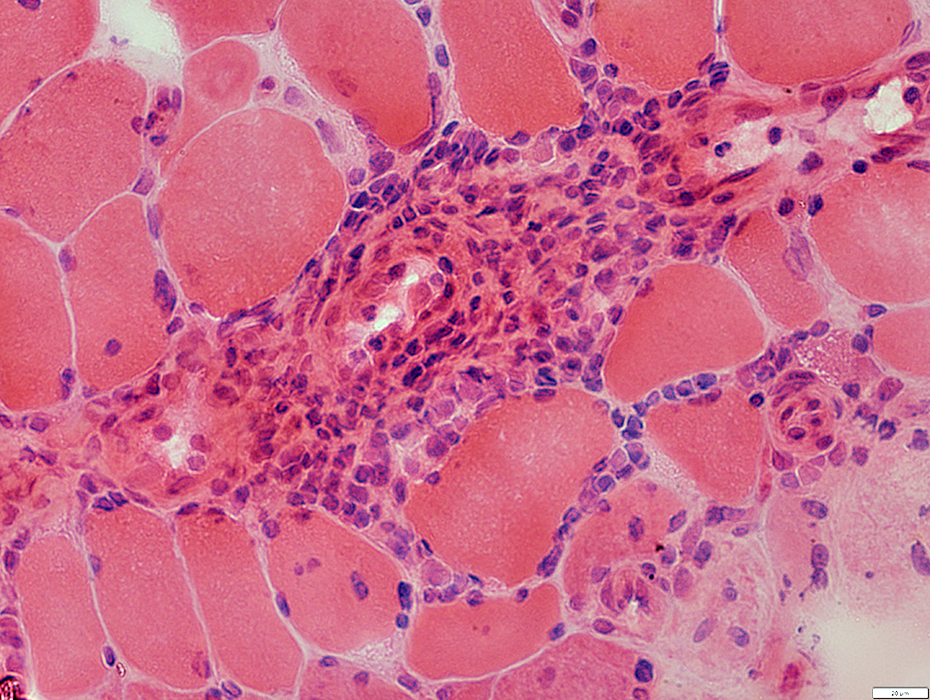 H&E stain |
Cell types: Lymphocytes + Scattered histiocytes
Location: Vascular Perimysium
Also Contains: Intermediate-sized vessels
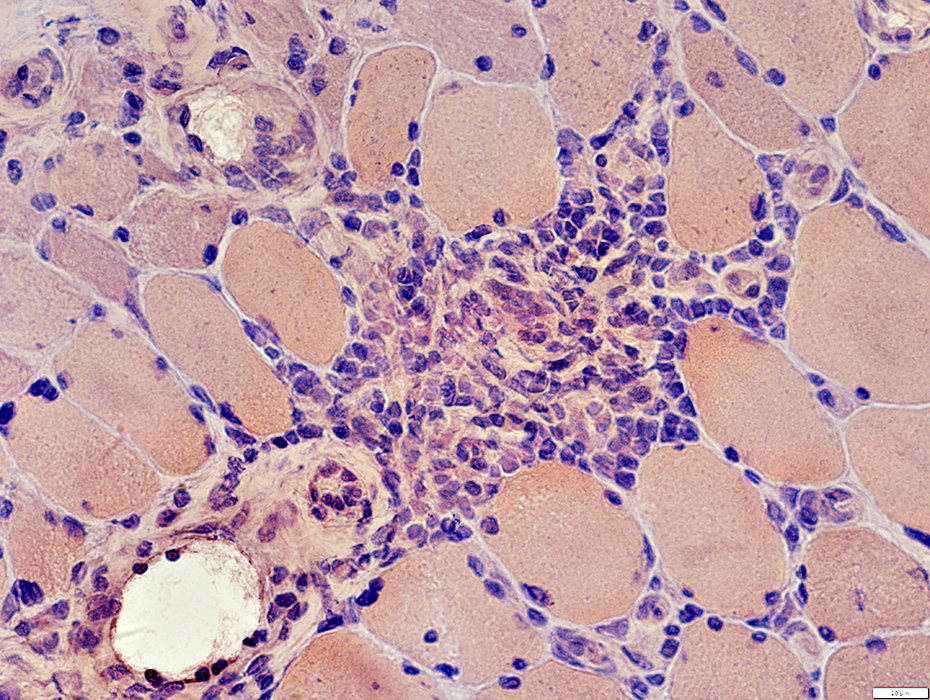 Congo Red stain |
Lymphocyte foci contain: Intermediate sized vessels
 VvG stain |
Cell foci: Contain scattered histiocytes (Acid phosphatase +)
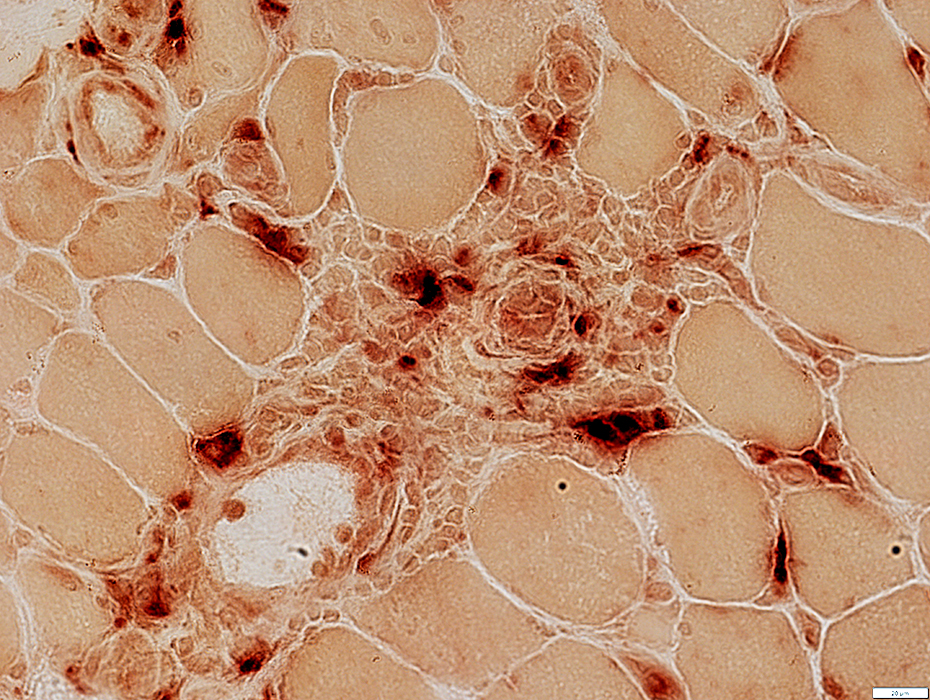 Acid phosphatase stain |
Vessels within cell foci (Arrow)
Endothelial cells may stain for esterase
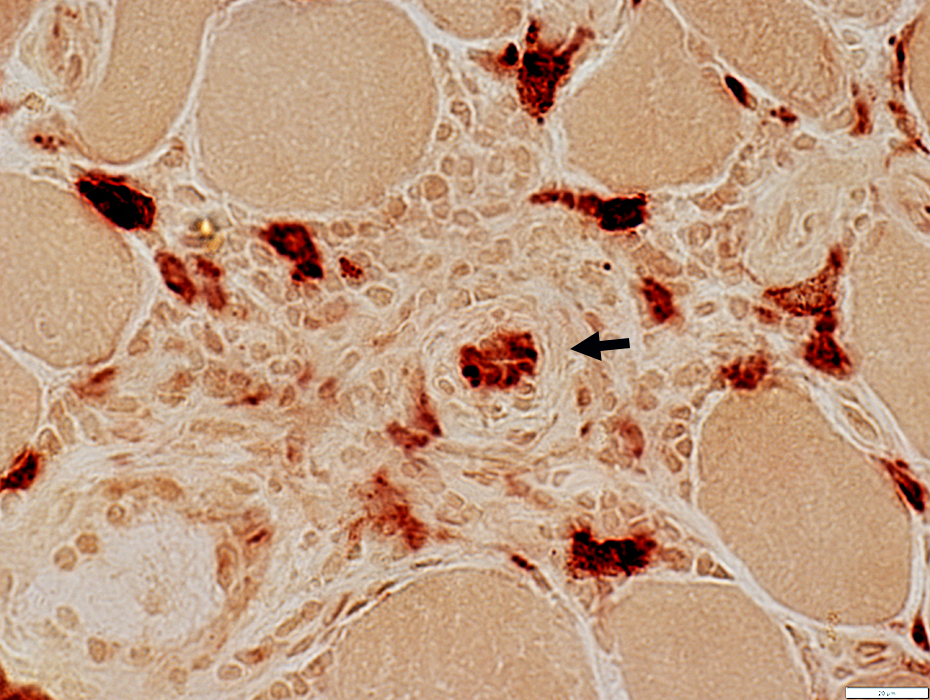 Esterase stain |
|
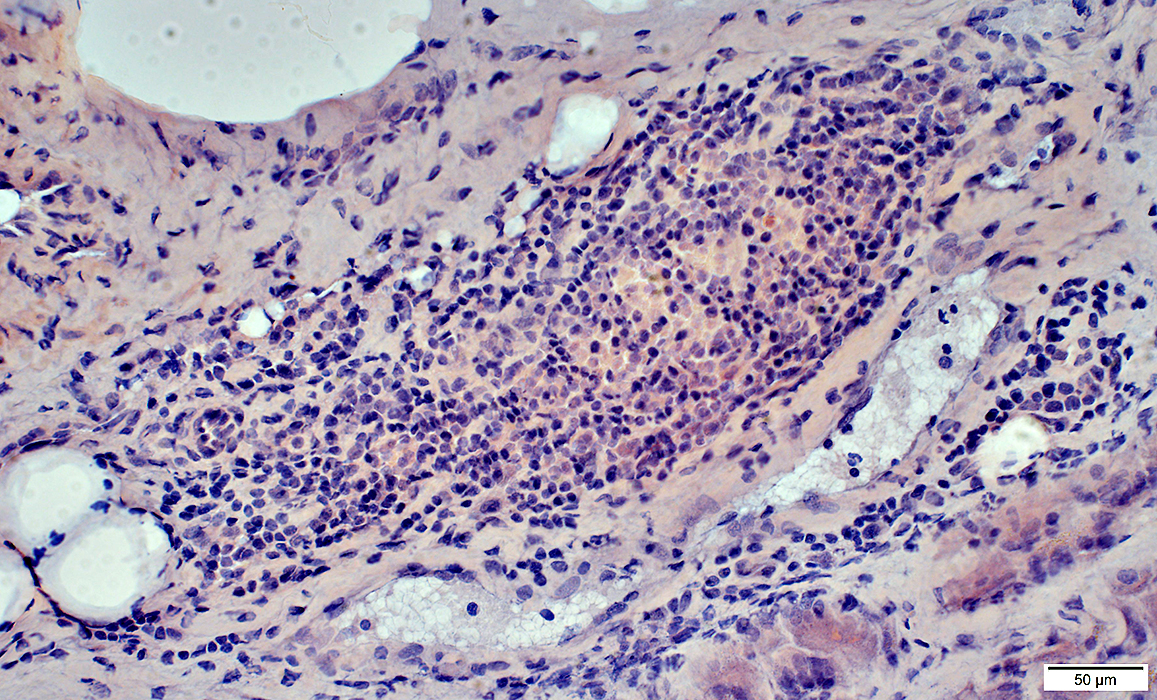
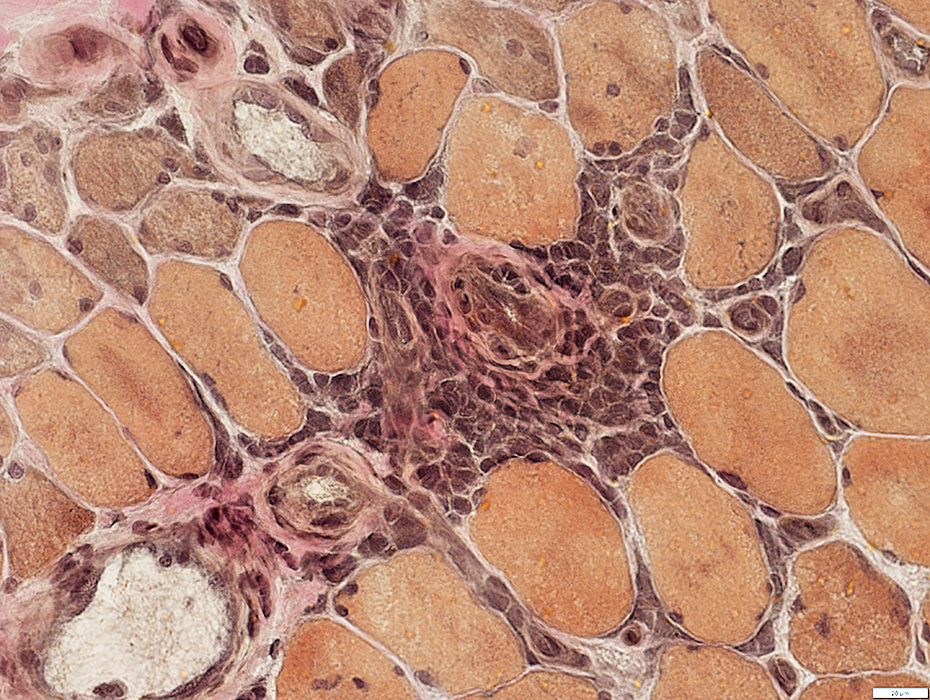
Mononuclear cell inflammation: Foci Cell types: Lymphocytes + Scattered histiocytes Location Perimysium Distant from muscle fiber atrophy Contain: Intermediate-sized vessels 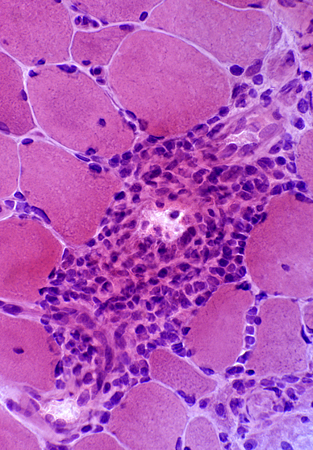
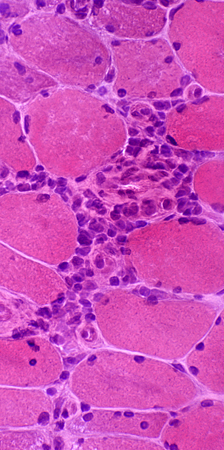 H&E stain |
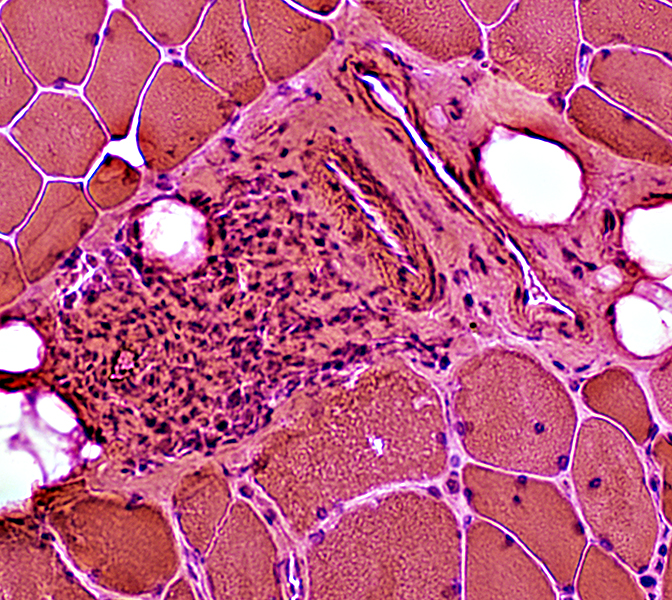 H&E stain |
|
Mononuclear cell inflammation: Stains for CD4 and, in some regions, CD20 (B-cells) Commonly perivascular. | ||
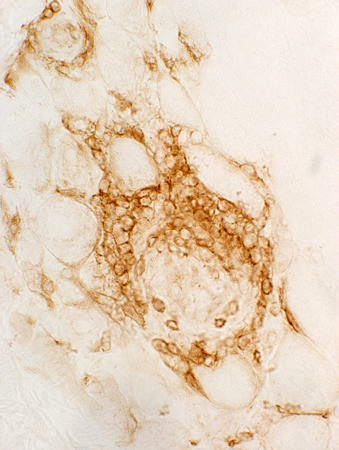 CD4 stain |
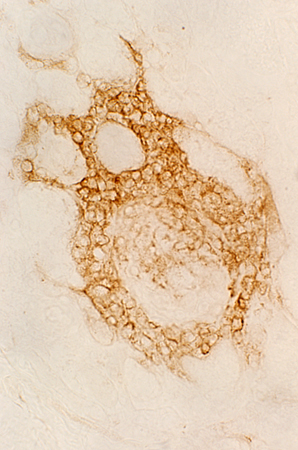 CD20 stain |
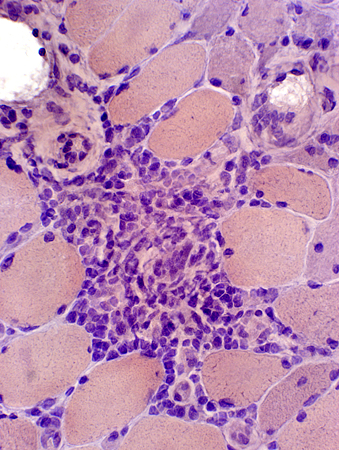 Congo red stain |
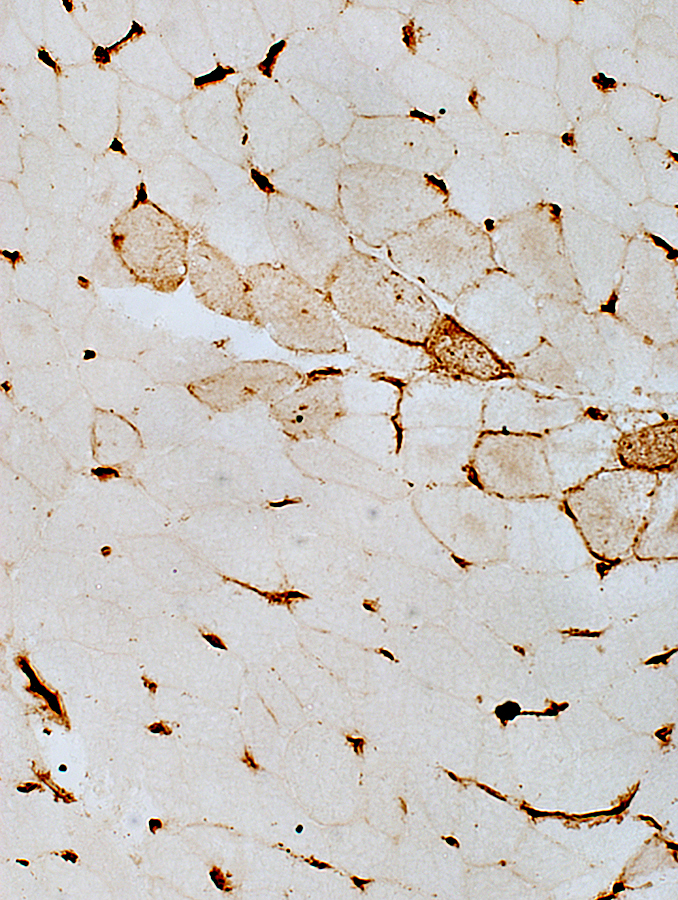
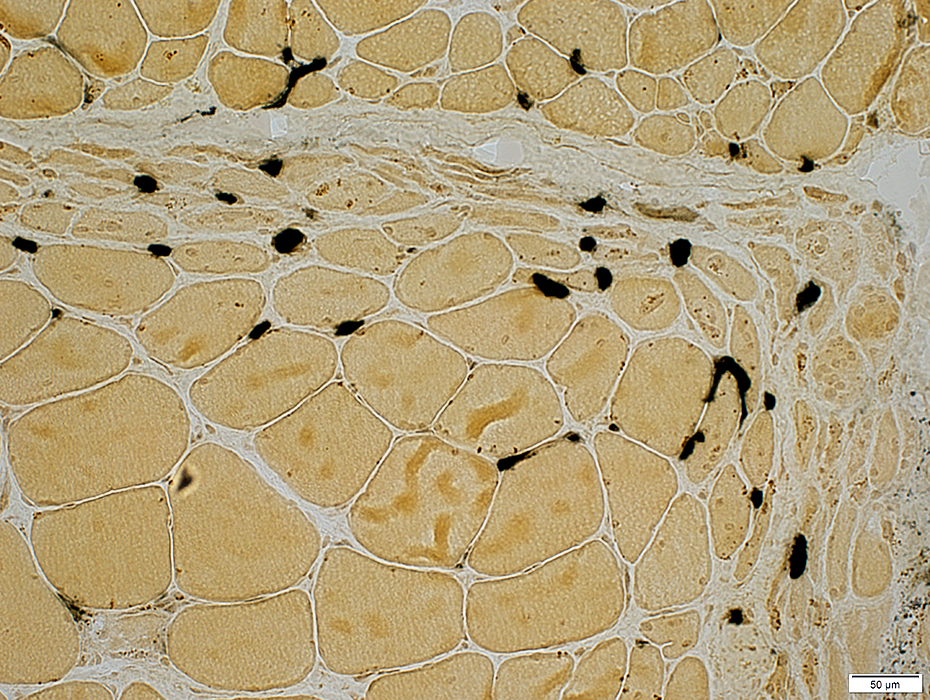
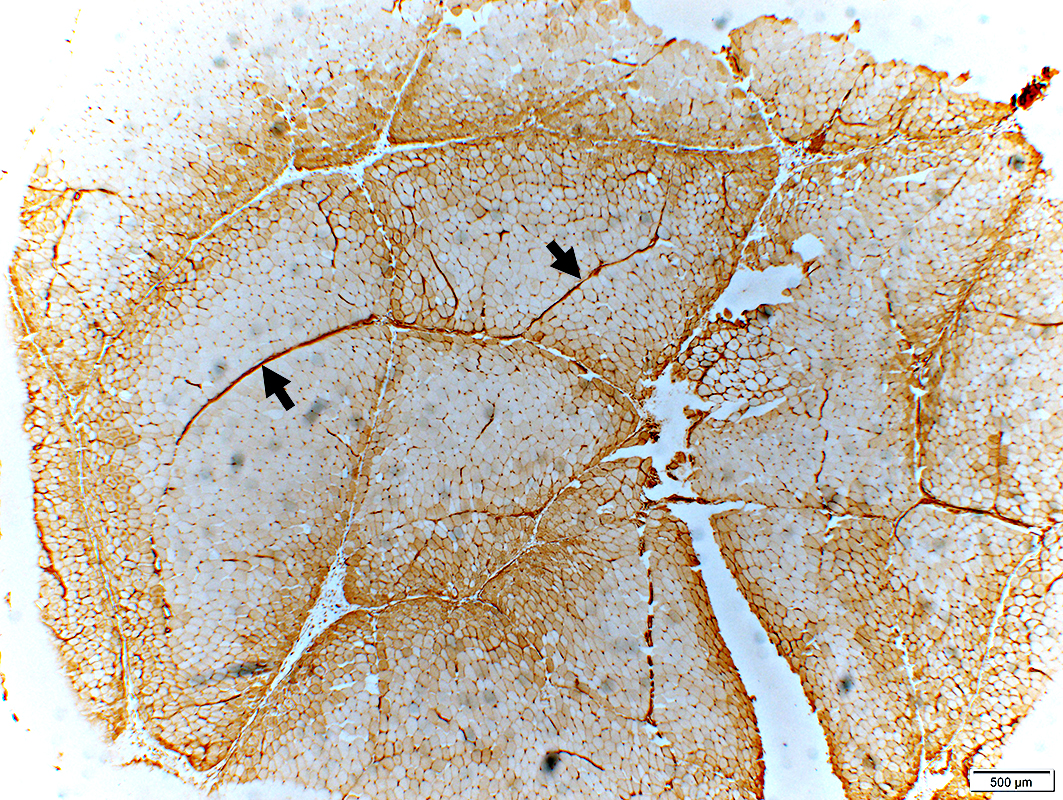
DM-VP: Capillary pathology
Capillaries: Ulex staining of Endothelium
Lost in regions of perifascicular muscle fiber pathology
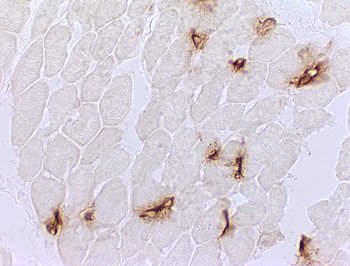
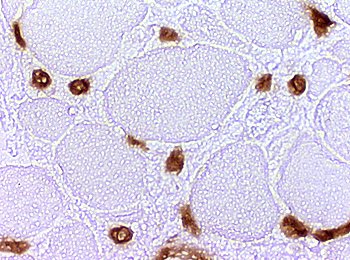 Stain: Ulex europaeus agglutinin I Dermatomyositis: Capillaries Capillary pathology is patchy and most prominent in perifascicular regions. Capillary staining with Ulex lectin is often absent in regions with small perifascicular muscle fibers (Above left). Capillaries in regions near perifascicular atrophy are often enlarged (Above right). |
 Stain: Ulex europaeus agglutinin I |
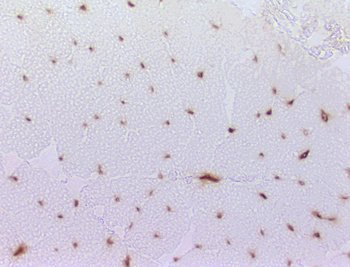
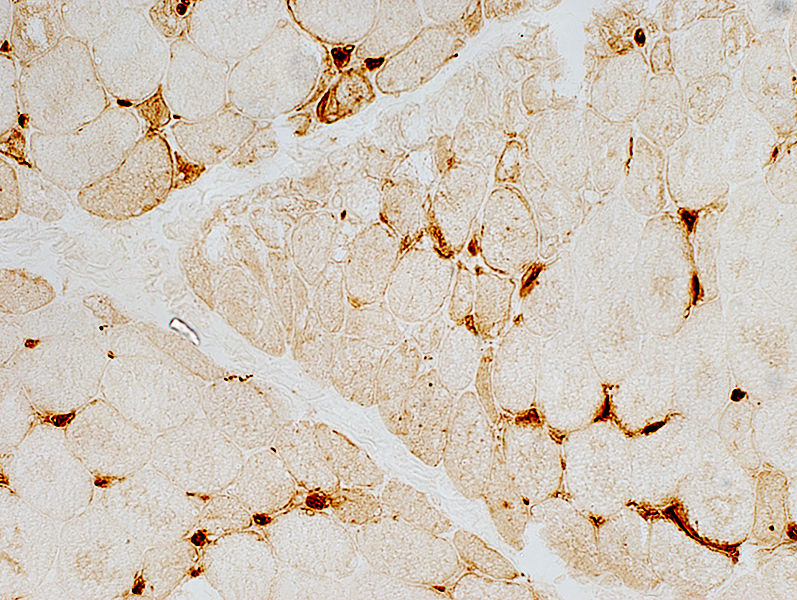
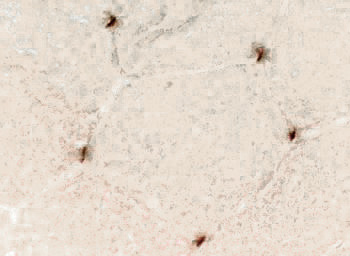 Stain: Ulex europaeus agglutinin I Control: Capillaries are abundant & small CAPILLARY PATHOLOGY: Regional 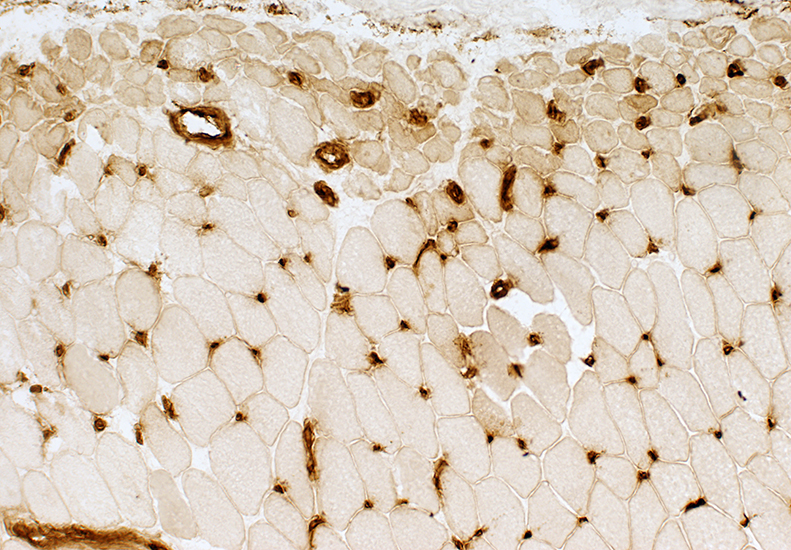 Stain: Ulex europaeus agglutinin I (UEAI) Muscle fiber atrophy (Top) Few stained capillaries Many muscle fibers with no adjacent capillary. Region neighboring muscle fiber atrophy (Purlieu; Middle & Below) Enlarged capillaries Increased staining for alkaline phosphatase; Also see Region distant from muscle fiber atrophy: Capillaries have nearly normal size and number Endomysial capillaries in region neighboring muscle fiber atrophy (Purlieu): Abnormal staining for alkaline phosphatase: Also see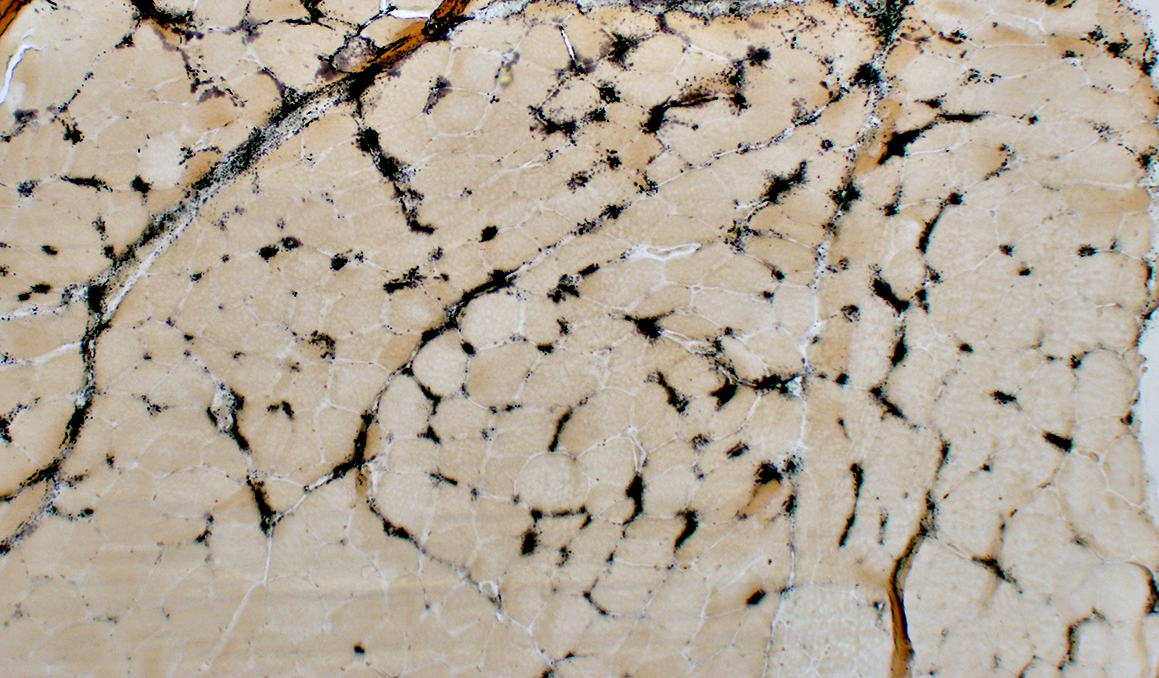  Alkaline phosphatase stain |
Alkaline Phosphatase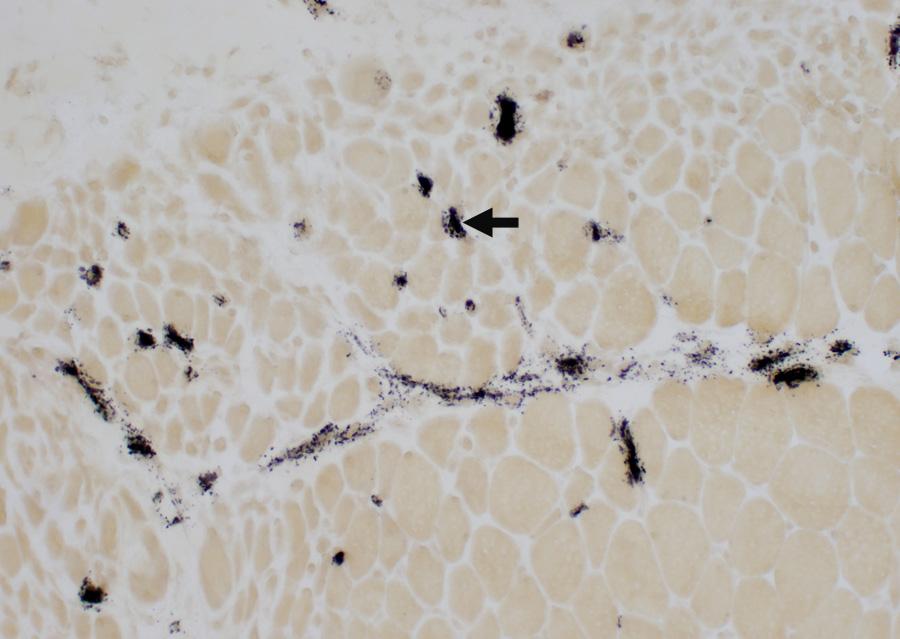 Enlarged capillaries (Arrows): In regions neighboring the smallest muscle fibers: Also see Fewer capillaries stain among larger fibers or amid the smallest fibers at the edge of fascicles. 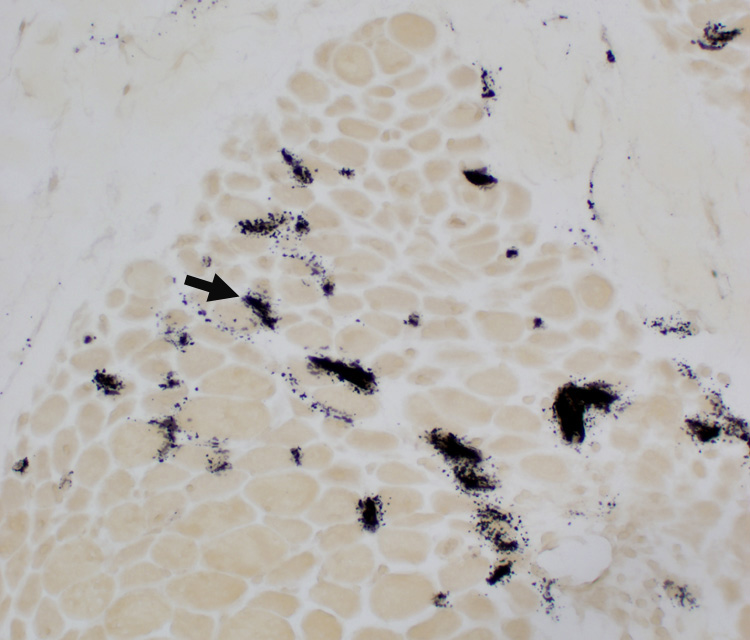 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
|
Endomysial Capillaries Alkaline phosphatase Staining: Especially in perifascicular regions | ||
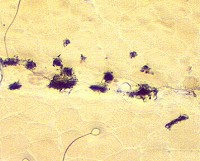 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
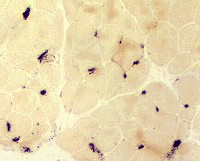 Alkaline phosphatase stain |
|
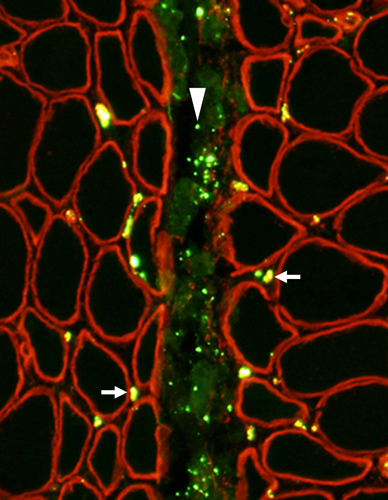
Capillaries: PECAM-1 & Collagen IV stains
|
Normal capillaries Dermatomyositis Enlarged capillaries Capillary remnants |
|
NORMAL ENDOMYSIAL CAPILLARIES Ultrastructure Endothelium + Collagen IV Collagen IV: Stains Capillary walls (Red & Yellow) & Basal lamina around muscle fibers (Red). PECAM1: Stains Capillary endothelium in lumens (Green) and overlaps Collagen IV (Yellow) in walls. 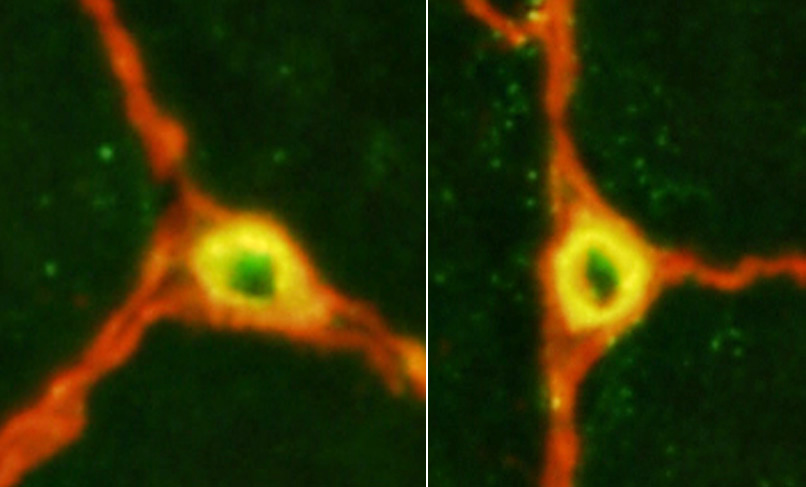
|
Capillary amidst Normal muscle fibers: Normal size & morphology.
Capillary compositon
Endothelial cells (E): Next to lumen
Basal lamina: Thick; Surrounds endothelial cellls
Pericyte (processes) (P).
Red blood cell: In capillary lumen
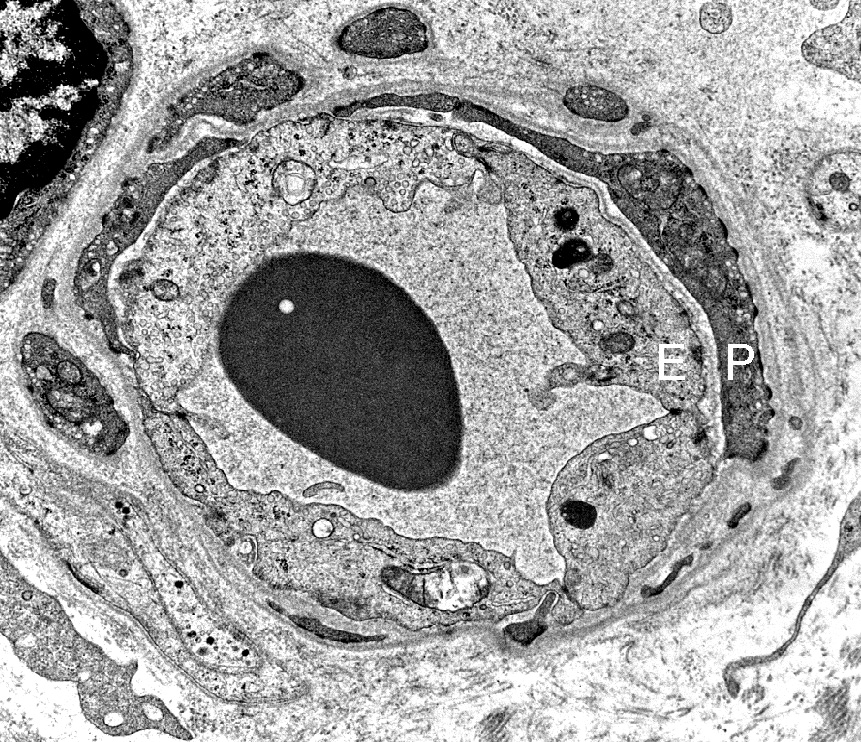 |
|
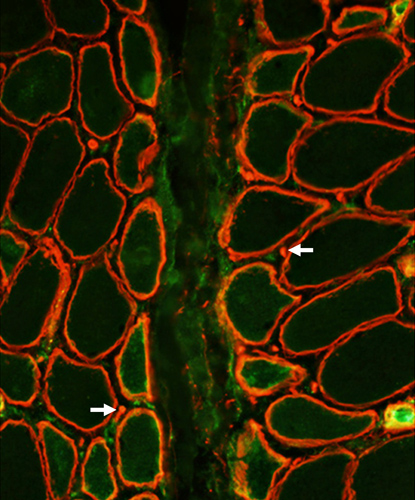
Dermatomyositis (DM-VP): SMALL ENDOMYSIAL CAPILLARY REMNANTS in areas of Perifascicular Atrophy Ultrastructure Endothelium + Collagen IV Collagen IV (Red) stains small capillary wall remnants (Arrow) without lumens. PECAM1 stains little, or no, capillary endothelium. 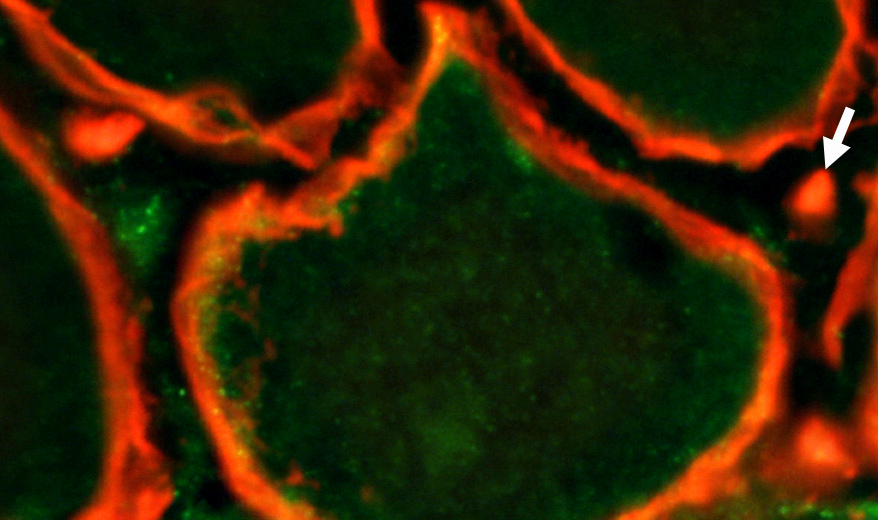 Pericytes & Cells + Collagen IV Collagen IV (Red & Yellow) stains round capillary remnants and basal lamina around muscle fibers. PDGFRβ stains capillary pericytes (Yellow) overlapping Collagen IV & elongated endomysial cells (Green). 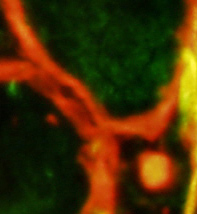
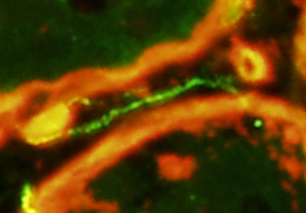
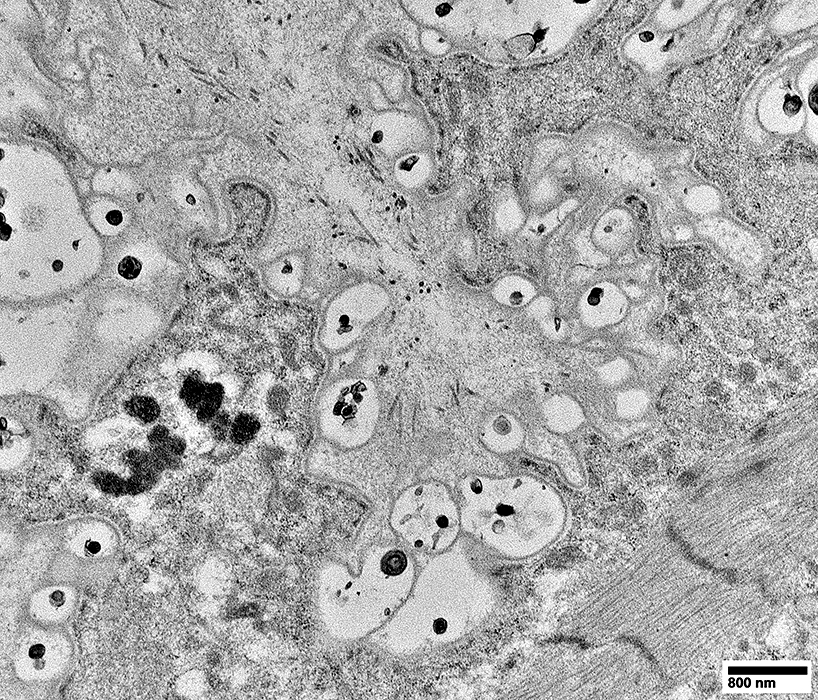
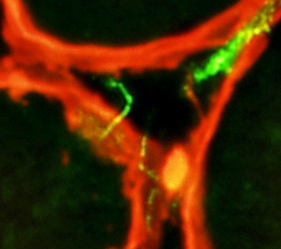 Dermatomyositis (DM-VP): Capillary Ultrastructure
Capillary in area of Perifascicular atrophy: Small endomysial capillary residua (Arrow) Basal lamina (Arrow) Thicker than muscle fiber basal lamina See: Thin basal lamina of nearby muscle fibers (Arrowhead) Lumen: No endothelium within basal lamina Neighboring Pericyte (Right): Provides evidence of the pathologic vessel's microvascular origin)
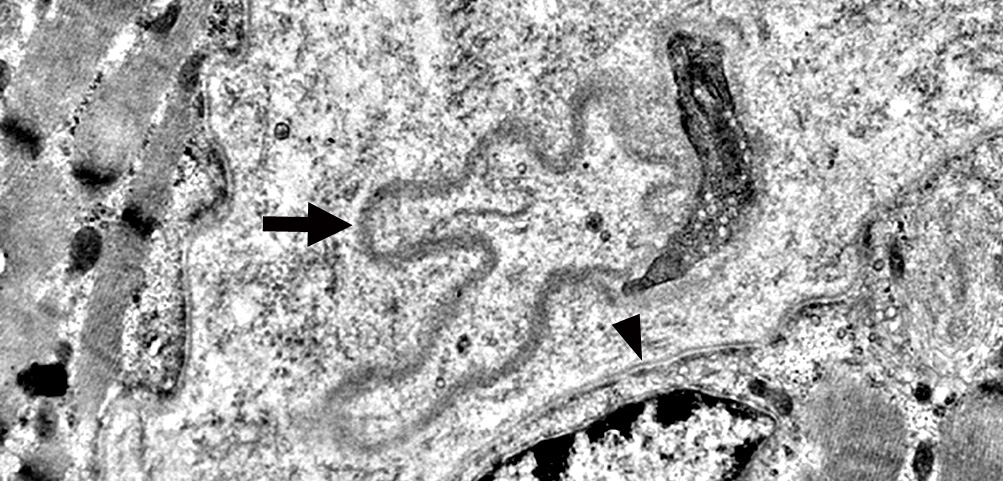
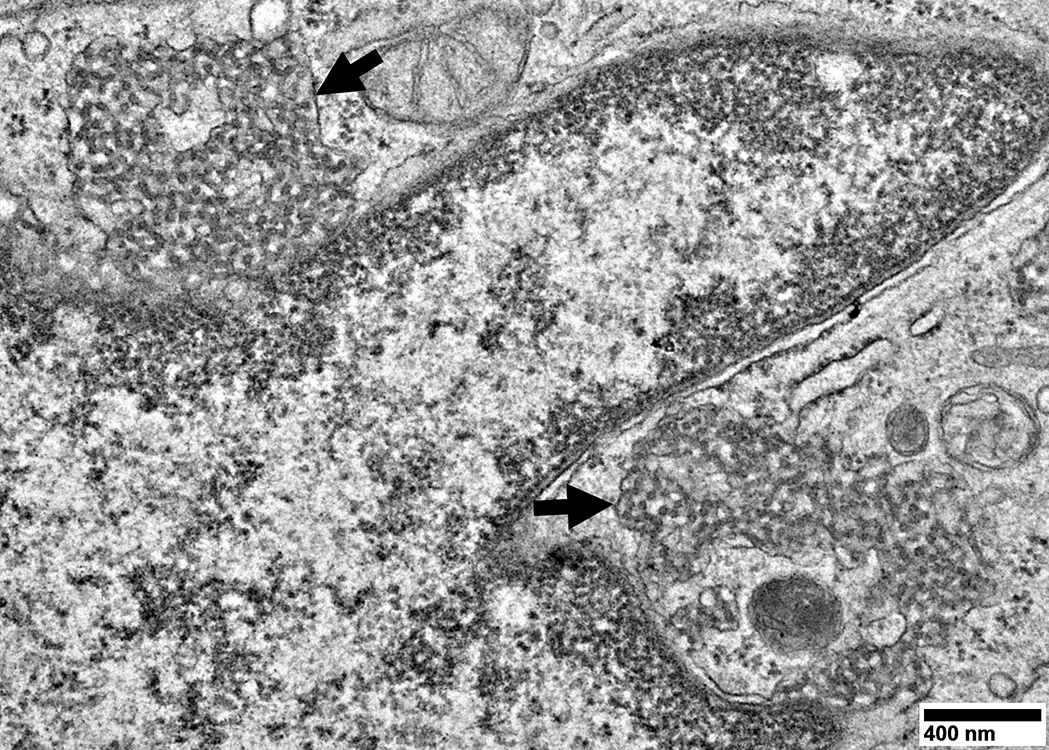
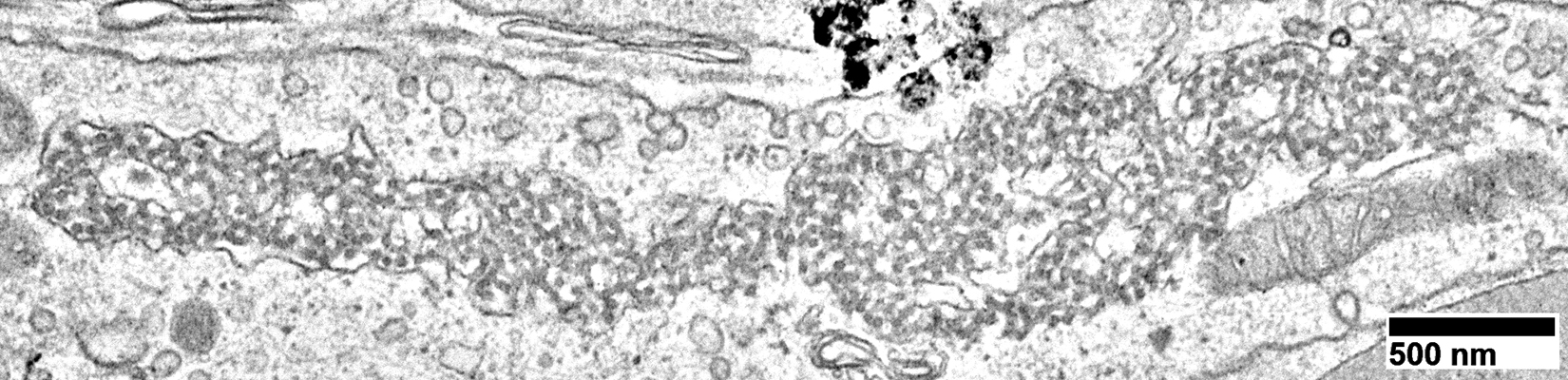
Capillaries in Intermediate zones Size: Enlarged Endothelial cells Size: Enlarged & Abundant cytoplasm Tubular reticular profiles (Dark arrows): Present in cytoplasm Abnormal mitochondria (White arrow): Present in some cells Capillary components
Location: Cytoplasm of capillary endothelial cells Continuous with: Endoplasmic reticulum Surounded by: Thin membrane (Arrows) Neighbor: Endothelial cell nucleus Associated IIM 3 MDA5 antibodies: 100% IMPP (Jo-1 antibodies): 40% DM-VP: 50%
Endothelial cells have Abundant cytoplasm Tubular reticular structures (Arrow)
Tubular Reticular Structures
Endothelial cell cytoplasm: Contains Mitochondria & Weibel Palade bodies
Structure: Elongated, cigar-like shape (0.2 μm in width; Up to 4 μm in length) Location: Endothelial cells Function: Secretory organelles; May be exocytosed Contents: Proteins that contribute to inflammation, angiogenesis & tissue repair von Willebrand factor (VWF) Other tPA, P-selectin, Interleukin-8 (IL-8), Eotaxin-3, Angiopoietin-2 Osteoprotegerin, Endothelin-1, Endothelin-converting enzyme, Calcitonin gene-related peptide Childhood dermatomyositis (DM-VP): Complement (C5b-9) deposition on Endomysial capillaries
C5b-9 stains: Endomysial capillaries (Arrow) & Regions of perimysium
C5b-9 complement compared to PECAM1 staining of Punctate Capillary Remnants
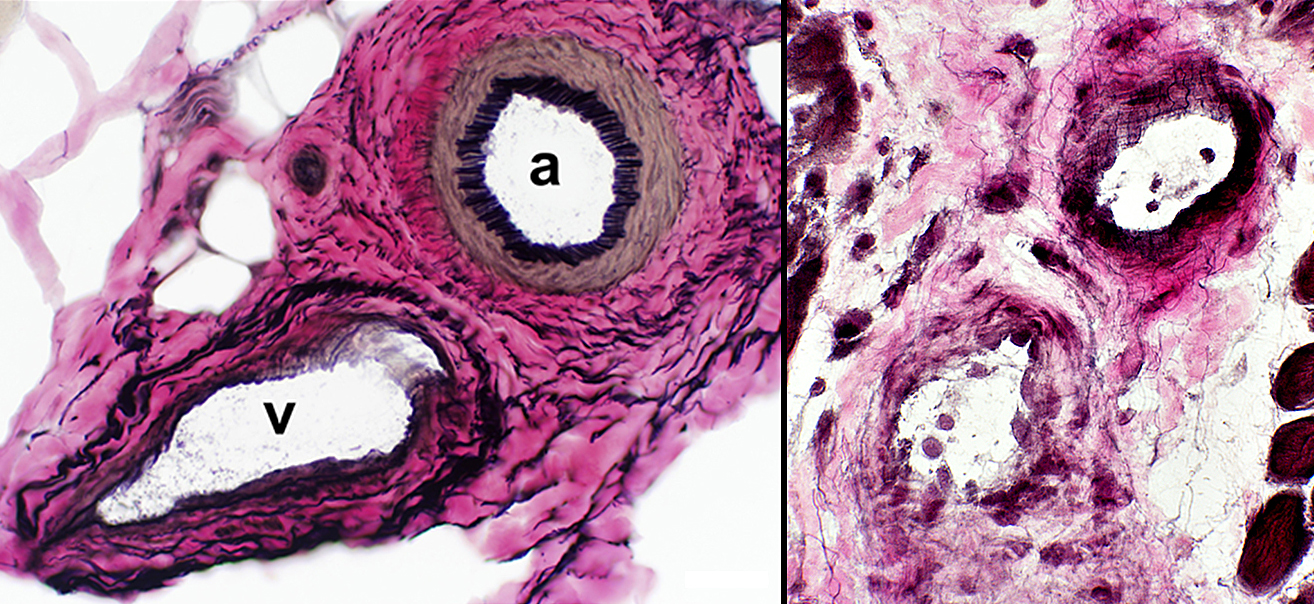
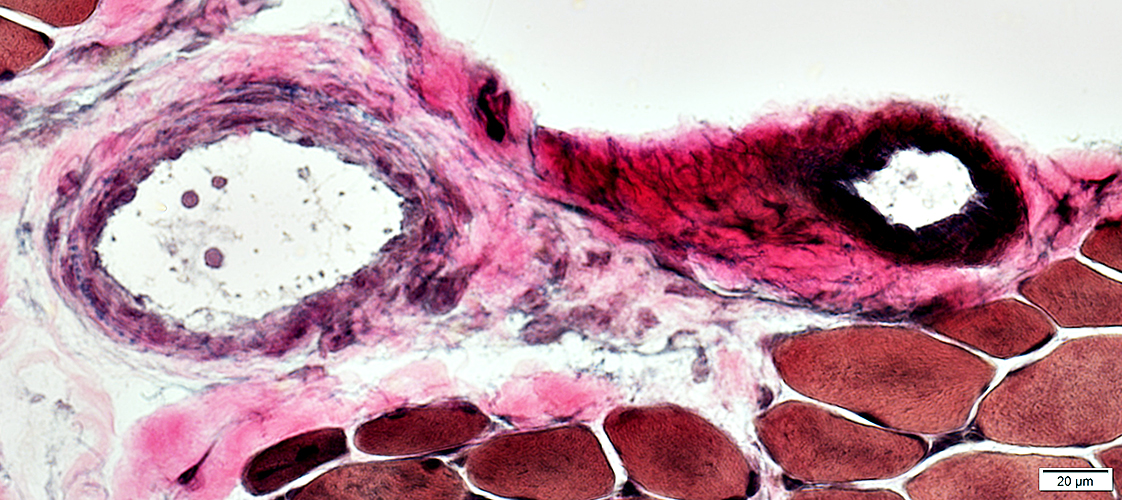
Childhood dermatomyositis (DM-VP): Perimysial Vascular Pathology
Perimysial Arteries (a) & Veins (v)
DM-VP (Above Right & Below) Loss or thinning of fibrils in walls of arteries & veins Endothelial cells: Enlarged, May contain tubulo-reticular profiles
Fibrils in wall reduced
Endothelial cells large Wall: No fibrils Perimysial vascular fragments: No lumen
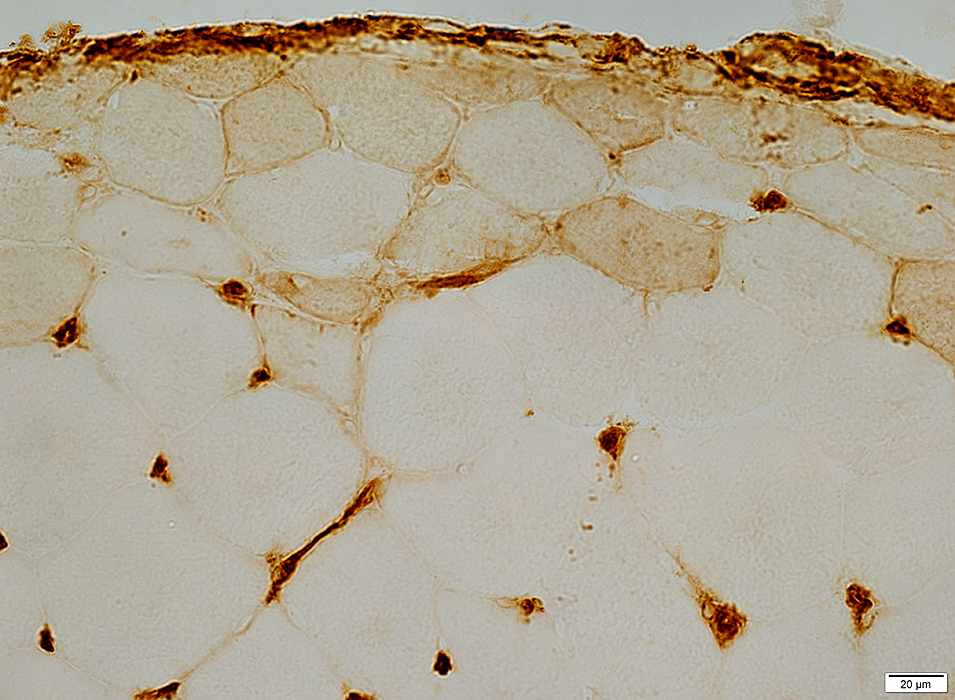
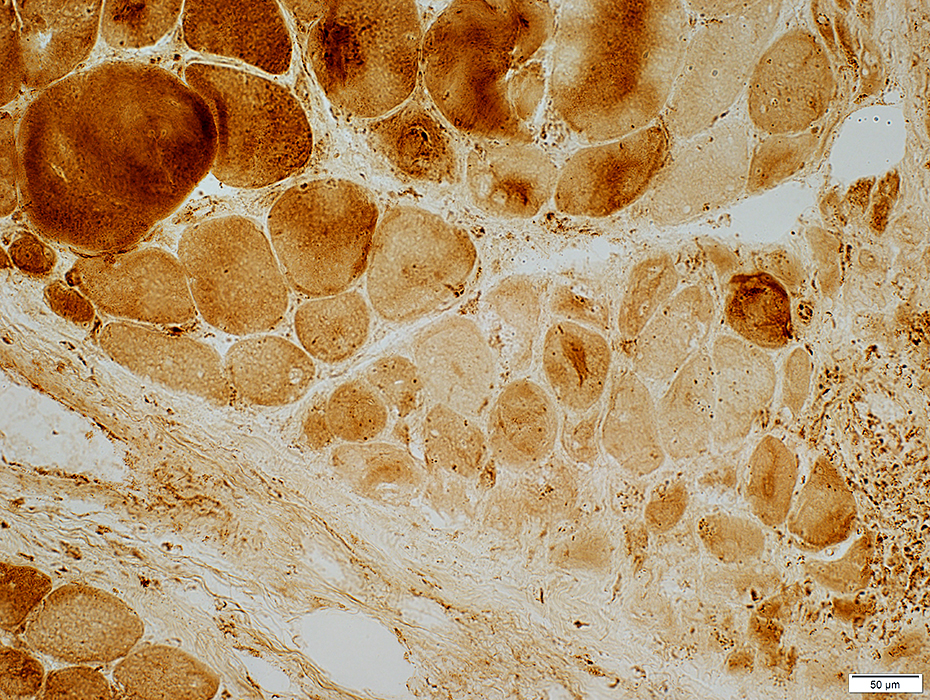
DM-VP (Childhood dermatomyositis): MHC Class I upregulation
DM-VP, Moderately severe: MHC-I up-regulation by muscle fibers, more in small fibers at edge of fascicle
Perifascicular muscle fibers near avascular perimysium express MHC-I Central muscle fibers near vessel (Arrow; Below) express less, or no, MHC-I
DM-VP, Mild: Patterns of MHC-I staining MHC-I up-regulation more in muscle fibers at edge of fascicle, or diffusely Affected muscle fibers may be normal size, or small.
Dermatomyositis with Vascular Pathology (DM-VP): Severe
Periphery of Fascicle: Atrophic muscle fibers near avascular perimysium
Small Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers: Intermediate-sized Endomysial capillaries: Large
Near perimysium Nuclei: Often internal Surface: Irregular Cytoplasm: Dark NADH stain
Abnormal structure: Loss of fibrils in arteries & veins Also see: DM-VP Vessels
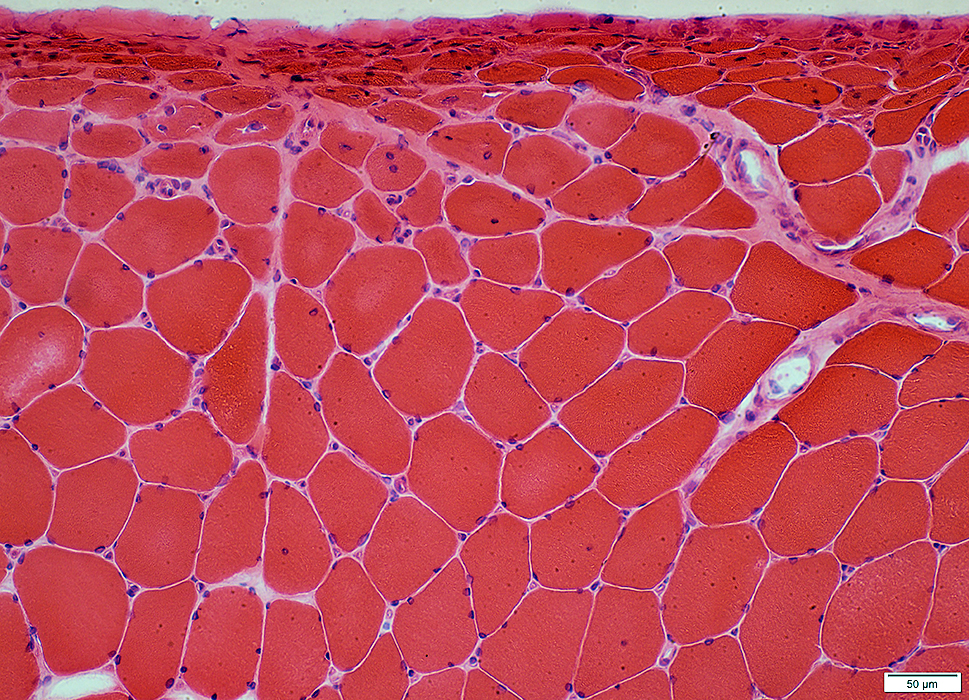
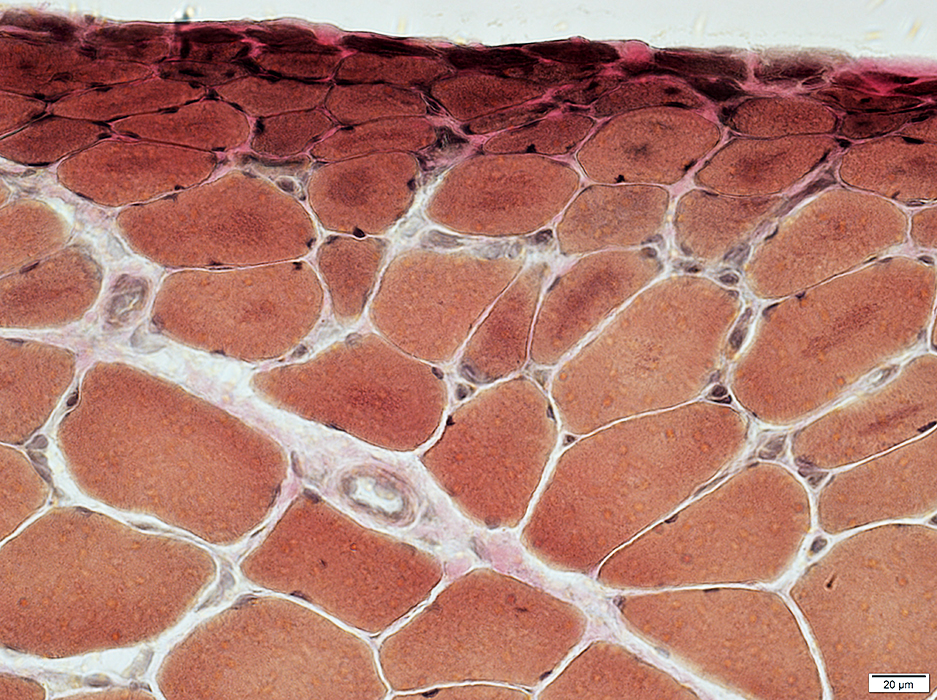
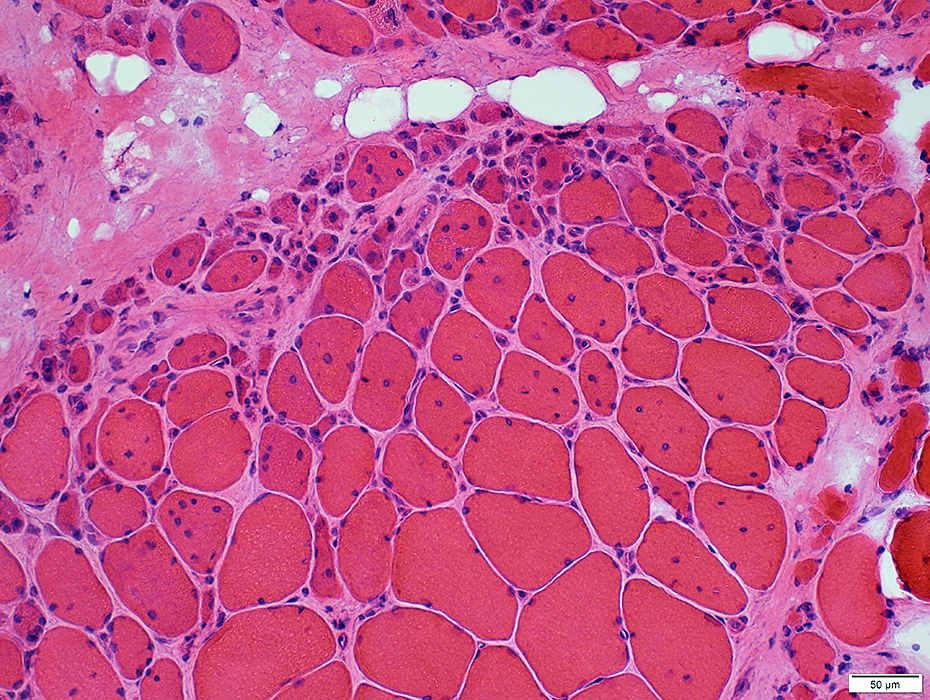
DM-VP (Childhood): Muscle fiber Atrophy at Muscle Surface (Epimysium)Severe atrophy of muscle fibers at edge of muscle
Nuclei: Enlarged: Internal Muscle fibers: Intermediate size Endomysial capillaries: Large
Internal Architecture Smallest muscle fibers: Very dark stained Intermediate-sized muscle fibers: Irregular staining & aggregates Endomysial capillaries: Positive staining
Muscle fibers in, & near, region of atrophy have reduced COX Muscle fibers in, & near, region of atrophy have inreased SDH, diffusely, or as aggregates
Muscle fibers in purlieu zone contain aggregated, cytoplasmic material
Endomysial Capillaries: Reduced staining in regions with small muscle fibers Some small mnuscle fibers have no adjacent capillary
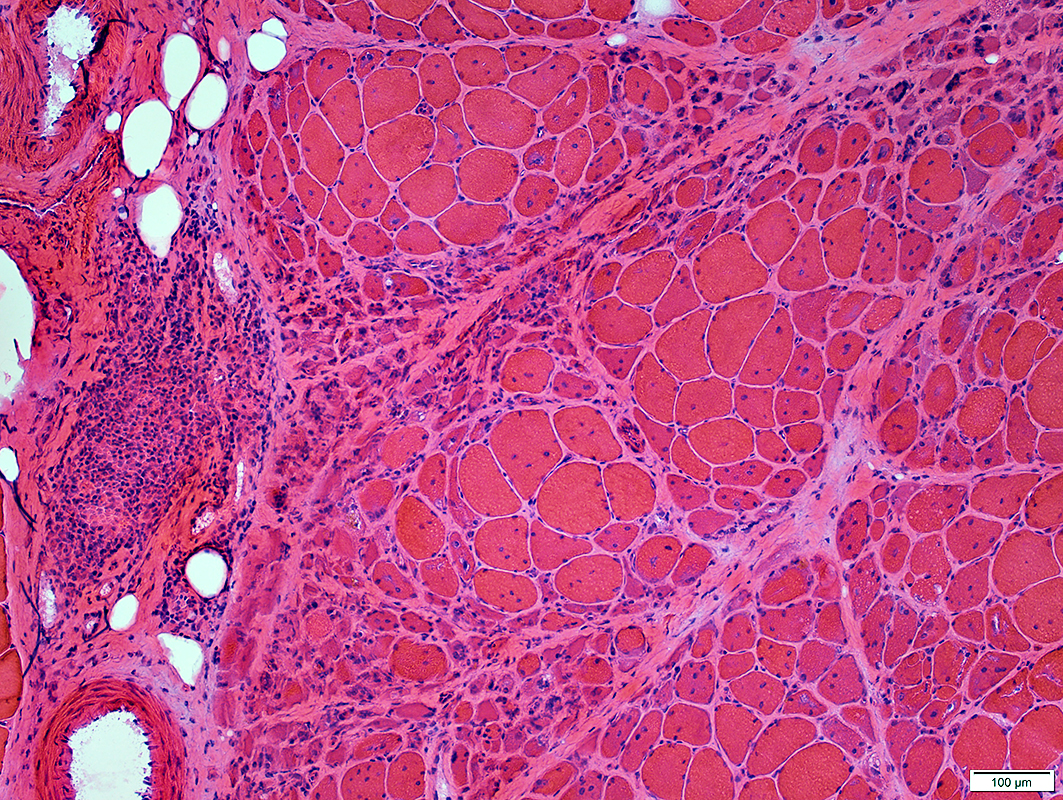
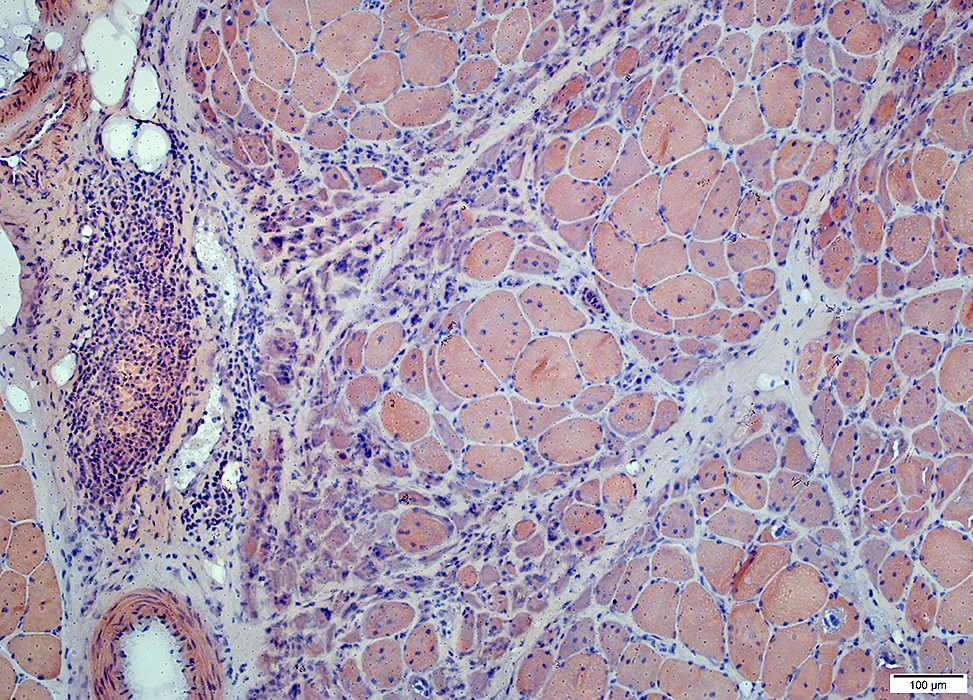
DM-VP (Adult)
Lymphocyte focus: In perimysium
Location: Perimysium Contents: Lymphocytes & Small vessels
Vessels within Lymphocyte foci
Small at edge of fascicles Nuclei: Large; Often internal Internal architecture: Abnormal; Aggregates
Small Nuclei: Large; Often several internal
Small Nuclei: Large; Often several internal Internal architecture: Aggregates & Vacuoles
Small Muscle fibers: Dark stained Larger Muscle Fibers: Sarcoplasmic reticulum aggregates
Myosin ATPase Small muscle fibers at edge of fascicles: Reduced staining
DM-VP: MHC Class I
DM-VP: Mitochondrial Pathology
Cytochrome oxidase (COX): Reduced (Above) Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH): Increased (Below)
DM-VP: Aggregates in Muscle Fibers
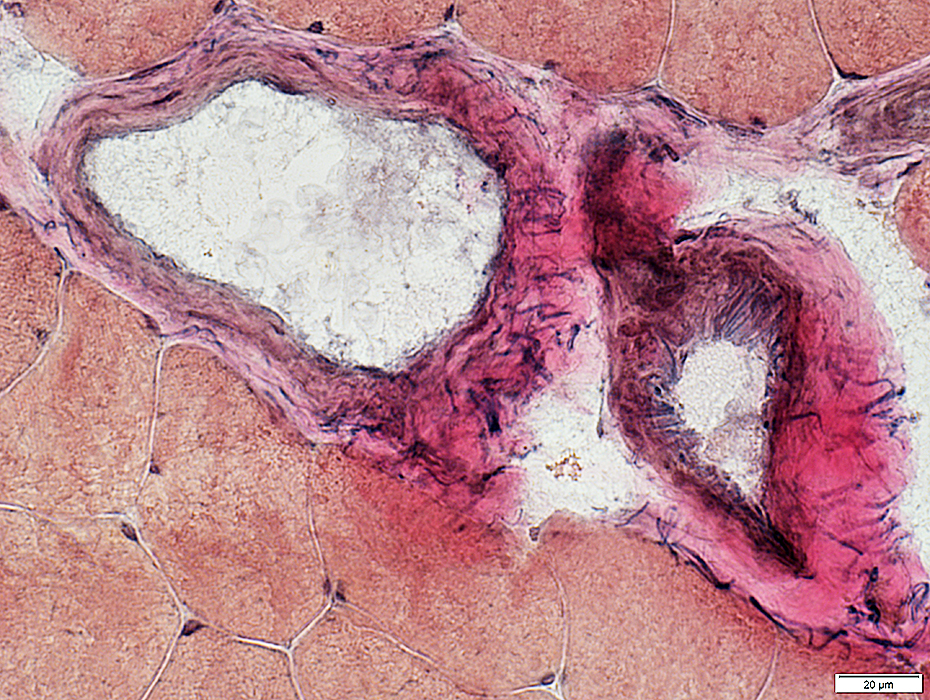
Large Artery Abnormal structure: Patchy loss of internal fibrils
Large Vein Abnormal; Endothelial layer is widened
Perimysial Smaller Vessel Thick wall
DM-VP: Capillaries
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page Return to Dermatomyositis, Adult pattern Return to Inflammation Return to Inflammatory myopathies Return to Dermatomyositis References 1. Neuromuscul Disord 2006;16:391-393 2. Muscle Nerve 2010; Online April 3. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2025 Dec 9 12/15/2025 |