- General
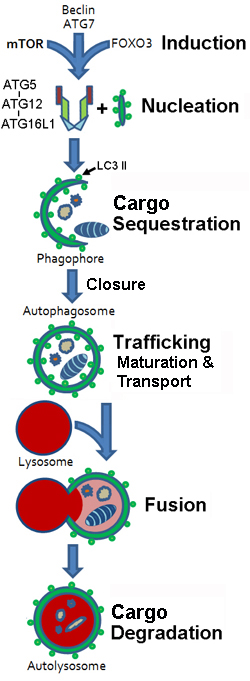
- Stages
- Membrane sequestration of cytoplasm & organelles
- Organelle: Double-membrane Autophagosome
- Autophagosome formation & maturation
- Fusion of membrane bound vesicles with lytic component (Lysosomes)
- Cargo Degradation
- End products: Release of degradation products or Cell death
- Action: Bulk lysosomal degradation
- Targets
- Larger cytoplasmic proteins: Folded or unfolded
- Organelles: Mitochondria; Fractured endoplasmic reticulum; Peroxisomes
- Mechanisms: Formation of double-membrane, non-Lysosomal vesicle (Autophagosome)
- Several phases: All ATP dependent
- Initiation
- Phagophore (Crescent-shaped isolation membrane) generation
- Membrane is formed de novo, not by budding
- Sequestering membrane
- Double layer
- Separate from Lysosome
- Contains
- Proteins
- LC3-II: Membrane bound
- Other ATG8 ortholog: GABARAP proteins
- Protein modification: Phosphatidylethanolamine-conjugated
- Location: Bound to inner & outer membranes
- Phagophore transport
- From: Perinuclear area
- To: Cell periphery
- Cargo is sequestered
- Autophagosomes formed
- Kinesin- & FYCO1-mediated centrifugal transport
- Phagophore Sequestration
- Sequestered Contents: Cytoplasm & Organelles
- Mechanism: Binding to
- LC3-II, or
- Autophagy receptors
- p62
- NDP52/CALCOCO2
 : Participates in : Participates in
- Mitophagy
- Xenophagy (Removal of pathogenic organisms)
- Expansion & Closing of Phagophore
- Gives rise to Autophagosome
- Autophagosome
- Double-walled vesicle
- Maturation
- External proteins
- LC3: Released & Reused
- Binding of proteins mediating Autophagosome–Lysosome fusion
- Transport
- Binding to dynein–dynactin molecular motor
- Transports autophagosome centripetally: Toward
- Center of cell
- Lysosomes at minus end of microtubules
- Amphisome-formation
- May fuse with Late endosome: Prior to fusion with lysosome
- Actions
- Induction
- Upregulation of HDAC6

- Rapamycin
- Starvation (Low amino acids)
- Autophagy: Proteins required
- General
- Function: Most at step of vesicle formation
- Localization: At phagophore assembly site/preautophagosomal structure
- Autophagy-related proteins
- Ubiquitin-like
- General
- ATG12

- Conjugated to ATG5 during active autophagy
- Microtubule-associated protein 1, light chain 3, alpha (MAP1LC3A)

- Conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine
- Cleaved by ATG4
- Associated with completed autophagosome
- Function: Unknown
- ATG7

- Ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1-like protein
- Essential for ATG12 conjugation system
- Associated with membrane fusion in autophagy
- Disease: SCAR31
- ATG5

- Essential for autophagy
- Conjugated to ATG12
- Binds Atg16: Part of tetrameric complex of unknown function
- Conditional knock-out in brain
- Develops: Aggregates & Ubiquitinated inclusions
- Disease: SCAR25
- ATG3

- E2-like protein-conjugating enzyme
- Covalently attaches ATG/LC3 to phosphatidylethanolamine
- ATG4

- Cysteine protease
- Cleaves C-terminus of Atg8/LC3
- Exposes glycine residue for subsequent conjugation
- Beclin 1 (BECN1; ATG6)

- Component of complex
- Other component
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Class 3 (PIK3C3; Vps34)

- Produces PtdIns(3)-phosphate
- Stimulatory for autophagy
- Haploinsufficient & Mutated in some cancer lines
- Especially breast tumours
- Transmembrane proteins
- ATG9

- Involved in: Autophagosome formation
- ? Marks site(s) of donor membrane used for phagophore expansion
- Initial nucleating membrane: Develops into autophagosome
- May be involved in: Membrane delivery to forming autophagosome
- ATG27
- Complex with ATG23
- ATG10

- Function: Ubiquitin-conjugating-like enzyme
- Covalently attaches ATG12 to ATG5
- ATG16L1

- Binds ATG5
- Homo-oligomerizes to form a tetrameric complex
- Mutations: Missense; Related to Crohn's disease
 susceptibility
susceptibility
- ATG32
 : May play role in mitophagy : May play role in mitophagy
- Recruits autophagic machinery to mitochondria
- Regulates selective degradation of mitochondria
- ULK1 (ATG1 homologue)

- Serine/threonine protein kinase
- May be involved in regulation & vesicle formation
- Involved in axon growth
- LAMP2: Danon disease
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Class I
- Controls activation of
- Kinases: Akt1
 & Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) & Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)

- Composed of
- Catalytic p110 subunits
- p85 adaptor
- Main product: PtdIns(3,4,5)P3
- Inhibitory for autophagy
- Autophagy: End pathway results
- Autophagosome vesicles: Fuse with Lysosomes
- Requirement: Microtubular system
- Structure Formed: Autophagolysosome
- Degradation
- Contents exposed to acid hydrolases
- Contents Degraded
- Sequesterd Cargo molecules
- Inner membrane with LC3-II
- Autophagy receptors
- Pathways after degradation
- Macromolecules released back into the cytosol
- Through permeases
- For reuse in metabolic processes (during starvation)
- Cargo inactivated or killed
- When macroautophagy acts in immune response to eliminate microbial pathogens
- Removal of cytoplasm may result in cell death
- Major catabolic pathway for
- Energy generation
- Breakdown of macromolecules & damaged organelles into their essential constituents
- Most prominent: During periods of stress or nutrient deprivation
|
|
From: Chris Weihl
|
ULK complex
- ULK1
- ATG13
- ATG101
- FIP200
- Association: Class III PI3K complex
VPS34, VPS15, Beclin1, RUBCN
ATG14, WIPI2, DFCP1
Membrane expansion
- ATG9: Phospholipid delivery
Conjugation System
Fusion Machinery
Autolysosome-related Molecules
- SNX4/5/17 complex
- TEFB/TEF13
- INPP5K
Alternate Pathway
|
|