Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SCA) 1: Ataxin-1; CAG repeat; 6p22 2: Ataxin-2; CAG repeat; 12q24 3: Ataxin-3; CAG repeat; 14q32 4: ZFHX3; GGC repeat; 16q22 5: β-III Spectrin; 11q13 6: CACNA1A; CAG repeat; 19p13 7: Ataxin-7; CAG repeat; 3p21 8: ATXN8OS; CTG repeat; 13q21 9: ? 10: ATXN10; ATTCT repeat; 22q13 11: TTBK2; 15q14 12: PPP2R2B; CAG repeat; 5q31 13: KCNC3; 19q13.33 14: PRKCG; 19q13.42 15, 16, 29: ITPR1; 3p26 17: TBP; CAG repeat; 6q27 18: 7q31 19: KCND3; 1p13 20: 11q12, Duplication 21: TMEM240; 1p36 22: KCND3; 1p13 23: PDYN; 20p13 25: PNPT1; 2p16 26: EEF2; 19p13 27: FGF14; 13q33 28: AFG3L2; 18p11 30: 4q34 31: TGGAA repeat; 16q22 32: 7q32 34: ELOVL4; 6q14 35: TGM6; 20p13 36: NOP56; 20p13 37: DAB1; 1p32 38: ELOVL5; 6p12 39: 11q21 40: CCDC88C; 14q32 41: TRPC3; 4q27 42: CACNA1G; 17q21 43: MME; 3q25 44: GRM1; 6q24 45: FAT2; 5q32 46: PLD3; 19q13 47: PUM1; 1p35 48: STUB1; 16p13 49: SAM9DL; 7q21 50: NPTX1; 17q25 51: THAP11: 16q22 RAB3A: 19p13 SLC1A3; 5p13 SCA: Differential features |
Dominant ataxia syndromes, Other Ataxia + Epilepsy: KCNA2; 1p13 CANPMR: CAMTA1; 1p36 CAPOS: ATP1A3; 19q13 Cerebral Palsy CIAT: SCN8A Congenital ataxia Cough, Spasmodic Deafness & Narcolepsy: DNMT1; 19p13 DRPLA: ATN1; CAG repeat; 12p13 DYT28: KMT2B; 19q13 Familial dementia: ITM2B; 13q14 Gillespie: PAX6; 11p13 HADDS: EBF3; 10q26 HADDTS: CTBP1; 4p16 Hemiplegia, alternating: 1; 2 Holmes ataxia Huntington 2: JPH3; CAG/CTG repeat; 16q23 Leukodystrophy Adult-onset: Lamin B1; 5q23 H-ABC (HLD6): TUBB4A; 19p13 Multiple hamartoma syndrome: PTEN; 10q23 Myasthenia + CNS: SNAP25b; 20p12 Myelocerebellar: SAMD9L; 7q21 Myoclonic epilepsy KCNA2; 1p13 MEAK: KCNC1; 11p15 Myoclonus Cortical: NOL3; 16q22 Branchial & Spasticity: GFAP; 17q21 Episodic ataxia + Epilepsy: SCN2A; 2q24 Neurodevelopmental Ataxia+: CAPRIN1; 11p13 NEDLAS: GRIK2; 6q16 Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease Nystagmus Parenchymal degeneration Peripheral Neuropathy CMT 1F: NFL Rigidity Saccades slow + Orthostatism SANDO: POLG1; 15q25 Sensory ataxia: 16q22 Sensory-Motor: IFRD1; 7q22 Thermoanalgesia & Fungiform papillae loss Prion disease: Prion protein; 20p12 Seizures GLUT1DS2: SLC2A1; 1p35 MRD55: NUS1; 6q22 SMEI (Dravet; EIEE6): SCN1A; 2q24 SPAR Spastic ataxia syndromes Tremor, Essential: 3q13 TUBA4A Vanishing white matter Vermal aplasia Von Hippel-Lindau: VHL protein; 3p26 |
Episodic ataxias (EA): Usually Dominant EA1 + Myokymia: KCNA 1; 12p13 EA2, Paroxysmal: α1A Ca++ channel; 19p13 EA3 + Vertigo & Tinnitus: 1q42 EA4 (PATX) EA5: CACNB4β4; 2q22 EA6 + Migraine & CNS: SLC1A3; 5p13 EA7: 19q13 EA8: ? UBR4; 1p36 EA9: FGF14; 13q33 EA: SCN8A; 12q13 CAPOS: ATP1A3; 19q13 Other + Choreoathetosis & Spasticity: SLC2A1; 1p34 + Epilepsy & Myoclonus: SCN2A; 2q24 + Optic atrophy & Hearing loss: ATP1A3; 19q13 INNFD: NALCN; 13q23 + Seizures & Dyskinesias: PRRT2; 16p11 + Movements & Spasticity: SLC2A1; 1p34 Recessive LBSL: DARS2; 1125 Joubert 5: CEP290; 12q21 PDHA1: Xp22 Differential diagnosis Ataxia Syndromes: Other Recessive X-linked Congenital DNA repair defects DNA repeat disorders Metabolic disorders Mitochondrial Multisystem disorders Spastic Acquired  Cajal |
|
Age Polyneuropathy Syndromes Other |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||
| SCA1 | Ataxia Reflexes increased |
Spasticity | |||||||
| SCA2 | Tremor: Postural | Ataxia Reflexes reduced |
Ataxia; Chorea; Dementia |
||||||
| SCA3 | Neuropathy (Axonal) |
Ataxia; Nystagmus | |||||||
| SCA6 | Ataxia: Episodic | Ataxia | |||||||
| SCA7 | Ataxia | Ataxia Macular degeneration |
Visual loss before ataxia |
||||||
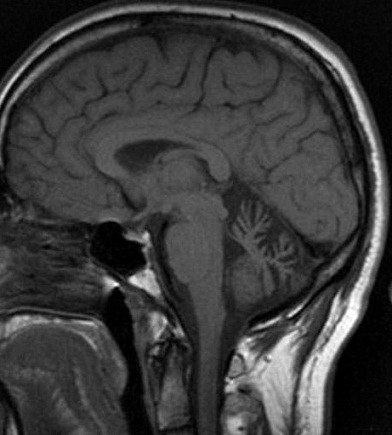
SCA 6: Cerebellar atrophy on MRI
|
|
|
|
SCA 15
● Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 1 (ITPR1)
|
|
|
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Familial Fatal Insomnia Gerstmann-Straüssler-Schienker Neuropathy: Autonomic & Sensory Other variants Prion-like domains |
| Episodic ataxias: Differential diagnosis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Onset age (yrs) |
Attack duration |
Symptoms | Interictal features | Triggers |
| EA1: KCNA1 | < 20 | Minutes | Muscle spasms | Seizures, Myokymia | Exertion; Posture Δ, Stress; Startle |
| EA2: CACNA1A | < 20 | Hours | Vertigo, Weakness | Ataxia, Nystagmus | Exertion; Stress; Alcohol |
| EA3: 1q42 | < 20 | Minutes | Vertigo, Tinnitus, Headache | None | Kinesigenic |
| EA4: ? | 20-50 | Hours | Vertigo, Diplopia | Nystagmus, Smooth pursuit Δ | |
| EA5: CACNB4 | 20-60 | Hours | Vertigo | Nystagmus, Ataxia | |
| EA6: EAAT1 | < 10 | Hours | Cognitive impairment | Seizures, Ataxia | Fever |
| EA7: 19q13 | < 20 | Hours | Vertigo, Weakness | None | Exertion; Excitement |
| EA8: UBR4 | < 2 | Mins to Hrs | Ataxia, Weakness | Tremor | Tiredness; Stress |
| EA9: FGF14 | 2 to 8 | Mins to Days | Ataxia | Tremor, Nystagmus | Fever; Stress |
| EA: SCN8A | 10 | 2 to 3 Days | Ataxia; Diplopia | None | Fever |
| CSE: GLUT1 | 2 to 15 | 20 minutes | Chorea; Ataxia; Headache | Spasticity | Alcohol, Fatigue, Stress, Exercise |
| EA: SCN2A | < 1 yr | Mins to Hrs | Ataxia; Dysarthria | Seizures | |
| EA: CEP290 | 46 yrs | Mins to Hrs | Ataxia; Dysarthria; Diplopia | Seizures | |
| SCA19: KCND3 | Ataxia | Seizures; Cognitive; PN | |||