|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
Sensory Disorders: Large Fiber & Ataxic
|
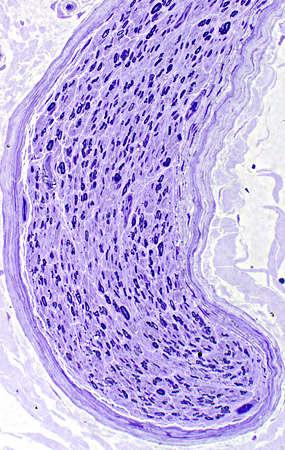 Peripheral Nerve
Loss of large myelinated axons |
Posterior column ataxia (Biemond)

●
Autosomal Dominant or Single generation
- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Clinical features
- Onset age: 19 to 30 years
- Sensory loss
- Large fiber modalities: Position & Vibration
- Sensory ataxia: Limbs & Gait; Worse in dark
- Pain & Temperature sensations: Preserved
- Course: Progressive
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Plantar responses: Flexor
- Scoliosis
- Pathology: Loss of large axons in dorsal root & posterior columns
- Also see
- PCARP: FLVCR1
Sensory neuropathy with Scoliosis (Robinson)

●
Autosomal Dominant- Epidemiology: 2 families
- Clinical features
- Onset age: 1st to 6th decades
- Sensory neuropathy
- Sensory ataxia: Gait; Romberg positive
- No ulcerating acropathy or pain
- Tendon reflexes: Absent
- Autonomic: Normal
- Cranial nerves
- Oculomotor dysfunction: 1 patient
- Hearing loss: Occasional
- Extensor plantar response: 1 patient
- Scoliosis
- Electrophysiology
- SNAPS: Absent
- Motor potentials: Normal
- Pathology: Loss of myelinated axons
- Also see: Sensory neuropathy + Scoliosis, Recessive: PIEZO2
SCA46: Ataxia, Sensory Neuropathy + Cerebellar
●
Phospholipase D family, member 3 (PLD3)
|
|
Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy 2/SCA4
 3
3
●
ZFHX3
- Epidemiology: Swedish-Scandanavian, German & Chilean families
- Genetics
- Mutations
- GGC repeat: Expanded; Loss of interruptions
- Exonic: Poly-Glycine
- GGC Repeat numbers
- Disease: 42 to 74
- Control: 14 to 26; Median 21
- Anticipation: Common in families; Correlates with repeat length
- Onset age: Younger with longer repeat length
- Allelic disorders
- Atrial fibrillation 8, susceptibility to, Dominant (ATFB8)

- Epilepsy, idiopathic generalized 20, Recessive (EIG20)

- Prostate cancer, somatic

- Spinocerebellar ataxia 4
- Atrial fibrillation 8, susceptibility to, Dominant (ATFB8)
- Mutations
- ZFHX3 protein
- CNS & PNS
- Neuronal developmant & differentiation
- Clinical
- Onset age
- 12 to 65 years; Mean = 39
- Anticipation: 5 to 7 years earlier per generation
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss
- All modalities
- Distal
- Facial
- Ataxia: Gait disorder
- Weakness: Distal 20%
- Dysarthria
- Reflexes
- Tendon reflexes absent: Ankles 100%; Knees 85%
- Plantar responses: Extensor in 10% to 20%
- Course: Progressive over decades; Wheelchair common
- Autonomic
- Orthostatic dysfunction
- GI: Constipation or Diarrhea
- Urinary retention
- In most severely affected patients
- Sensory loss
- Cerebellar
- Saccades: Slow
- Gait ataxia
- Systemic
- Weight loss
- Cough
- Onset age
- Laboratory
- Electrodiagnostic: Axon loss (Sensory > Motor)
- Sural SNAP: Absent in > 90%
- CMAP: Reduced in 38%
- Brain MRI: Cerebellar atrophy
- Pathology
- Spinal cord: Loss of axons in posterior columns
- Sensory
- Dorsal root ganglion cells: Reduced
- Axons in peripheral nerve: Reduced
- CNS: Brainstem & Cerebellar pathology
- Inclusions
- p62 & α-Synuclein
- In neuronal & enteric nuclei & cytoplasm
- Electrodiagnostic: Axon loss (Sensory > Motor)
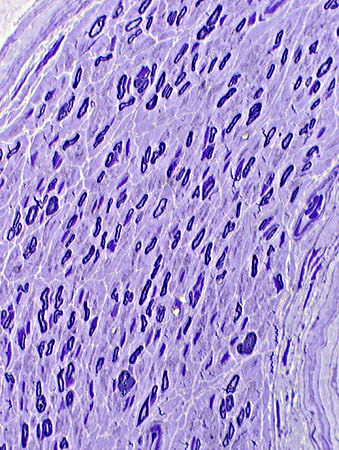
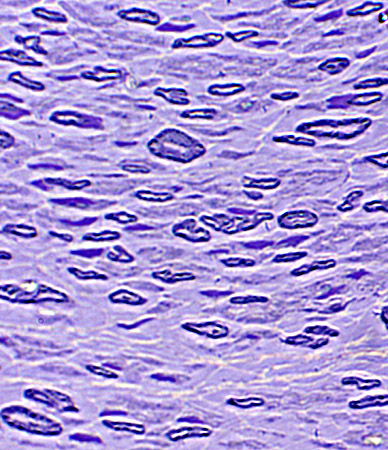 Toluidine blue stain Loss of large myelinated axons with relative preservation of small myelinated axons
|
Return to Polyneuropathy Index
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
References
1. Brain 1995;118:1557-1563
2. Nat Rev Neurol 2022 Mar 24
3. Am J Hum Genet 2023 Nov 28, J Neurol 2024 Aug 2
12/20/2024