ION CHANNELS: Diagrams
|
Calcium Channels Potassium Channels Sodium Channels |
SODIUM CHANNELS
|
|
|
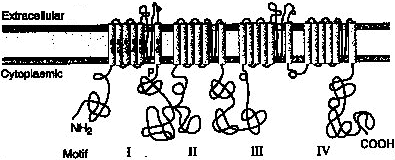
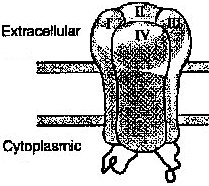
Voltage gated Na+ channel: α-subunit 4 repeated domains. Each domain has 6 membrane spanning subunits. Subunit 4 acts as a voltage sensor. |
|
|
|
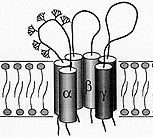
Non-Voltage gated Na+ channel Each subunit has 2 membrane spanning subunits. The channel is a heterotrimer. |
POTASSIUM CHANNELS
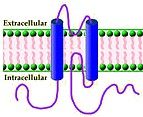
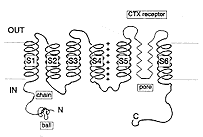 CTX: Charybdotoxin Ball & chain: Inactivation domain From: Goldstein |
|
|
Voltage-gated Shaker K+ channel |
Inwardly rectifying K+ channel |
CALCIUM CHANNELS
| Voltage gated Ca++ channel |
|---|
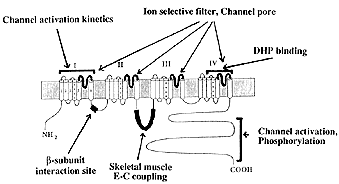 From Queens University |
|
| Excitation-Contraction Coupling: Muscle |
|---|
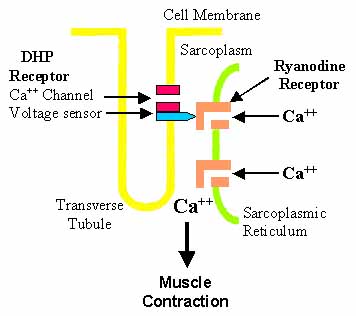
|
Return to Calcium channels
Return to Sodium channels
Return to Potassium channels
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
4/14/2021