- Epidemiology: Especially common in Japan
- Genetics: Mutations
- Japanese: Frameshift 260-BP deletion
- Other: Missense & Nonsense
- VPS13A Protein
- Clinical
- Onset: 3rd to 5th decade; Mean 32 years; Range 8 to 62 years
- CNS
- Movement disorders
- Oro-facial-lingual dyskinesia
- Chorea
- Limbs, especially legs
- Frequent but not all patients
- Parkinsonism
- Cortical: Dementia; Personality disorders; Seizures (50%)
- Pathology
- Neuronal loss & Gliosis
- Locations: Caudate, Putamen, Pallidum & Substantia nigra
- PNS
- Motor
- Distal wasting
- Anterior horn cell loss
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced or Absent
- Laboratory
- EMG: Distal denervation
- NCV
- Sensory: Small SNAPs
- Motor potentials: Normal
- Nerve pathology
- Distal axonopathy
- Loss of large myelinated axons
- Muscle
5
- Imaging: Distal symmetric wasting
- Serum CK: May be elevated
- Autophagy: Impaired; LC3II increased; Acid phosphatase+ granules
- Brain MRI
- Head of caudate nuclei & putamen: Atrophy
- Hyperintense in T2
- Isointense in T1
- SWI positive iron deposition: Some patients
- Adults
- White matter: T2 signal; Cerebral peduncles & Corpus callosum
- Other: Basal ganglia, Thalamus, Pons
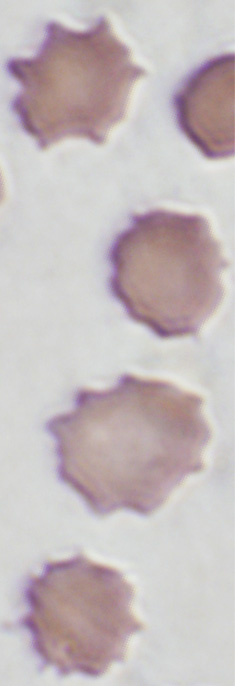
- Blood: Acanthocytosis
- Differential diagnosis:
- Carriers: Mild acanthocytosis
|
From: Leo Wang
|
|