- Epidemiology: > 30 patients
- Genetics
- ACOX1 protein
- Fatty acid β-oxidation of VLCFA
- First & Rate-limiting enzyme
- Major producer of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
- Tissue Expression: Glia
- Clinical
- Onset ages: < 3 years
- Hypotonia
- Seizures
- Behavior: Loss of learning & speaking skills
- Vision loss: Optic atrophy
- Hearing loss
- Muscle tone: Increased
- Course
- Progressive
- Often death in childhood
- Laboratory
- Very long chain Fatty acids: Increased
- Brain MRI: Leukodystrophy; Brain atrophy
- Pathology: Demyelination
- Pontomedullary corticospinal tracts
- Cerebellar white matter
- ACOX1 variant: Mitchell Syndrome
 1
1
- Epidemiology: 12 patients
- Genetics
- Inheritance: de novo; Dominant effect
- Mutation
- Missense: N237S (Most or all patients)
- Heterozygous
- ACOX1 protein
- Mutant protein
- Gain-of function
- Increased ROS in glia
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 0.5 to 14 years
- Hearing loss: Early in disease
- Polyneuropathy
- Sensory loss
- Large fiber modalities
- Ataxia
- Motor
- Autonomic
- NCV: Axon loss
- Spinal cord
- Paraparesis
- Leg weakness
- Sensory loss
- Bladder & Bowel Δ
- Course: Progressive
- Cognition
- Reduced in later disease
- Progressive loss
- Ataxia
- Skin: Keratosis pilaris
- Eye: Dry; Photosensitive
- Course
- Episodic Demyelination
- Progressive
- Possible treatments
- Riboflavin
- N-Acetylcysteine amide (NACA)
- ? Immuno-modulation
- Laboratory
- NCV: Axon loss
- CMAP & SNAP amplitudes: Reduced
- Course: Progressive
- MRI
- Spinal cord pathology
- White matter
- Demyelination: U-fiber sparing
- Nerve pathology
- Axon loss: Chronic & Active
- CNS pathology
- White matter & Spinal cord tracts
- Oligodendrocyte pathology
- VLCFA: Normal
|
|
Mitchell Syndrome
Spinal Cord Atrophy & Posterior Cord lesions (T2 signal)
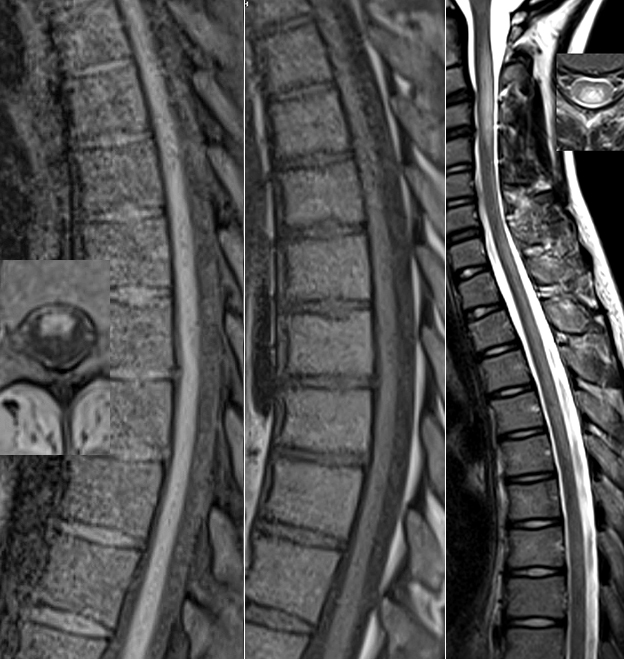
|
|