- Genetics
- > 60 mutations
- Mutation locations
- Common sites: Exons 10, 12 & 14 (35% to 50%)
- None in exons 2 & 13
- Mutations commonly unique to individual or very few families
- Mutation types: Missense 41%; Truncating 59%
- Porphobilinogen deaminase deficient mice
- Porphyric syndrome + Neuropathy
- Incomplete penetrance
- More frequently manifest in females (65%) than males (35%)
- Allelic disorder: Leukoencephalopathy, Childhood-onset, Recessive
3
- HMBS protein
- Heme biosynthetic pathway
- Catalyzes condensation of 4 molecules of PBG to form hydroxymethylbilane
- Clinical features
- Acute attacks
- Onset: Post puberty to 5th decade
- Abdominal pain
- Usually 1st sign of attacks
- Precedes neuropathy
- Neuropathy
2
- Frequency: 10% to 60% of patients
- Weakness
- May be severe, cause respiratory failure
- Proximal > Distal
- Symmetric or Asymmetric
- Arms > Legs
- Sensory
- Loss: Usually mild, distal, symmetric
- Pain syndrome: Diffuse, Proximal & Distal; Abdominal
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced
- Autonomic: Sympathetic & Parasympathetic involvement
- Course
- Precedes motor neuropathy
- Progressive
- Parasympathetic > Sympathetic
- Circulatory
- Tachycardia
- Blood pressure: High
- Vasospasm
- Urinary retention
- GI
- Constipation or Diarrhea
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Temperature dysregulation
- Cranial nerve: Facial; Dysphagia
- CNS
- Mental status changes: Psychosis; depression; Dementia
- Seizures
- Course
- Duration: Days to Weeks
- Usually complete recovery
- Recurrence not uncommon
- Other: No photosensitivity
- Treatment
- Glucose, IV
- Givosiran
- Liver transplant
- Hematin: Suppresses symptoms of acute attack by 3 or 4 days
- Chlorpromazine: Abdominal pain & Psychotic disorders
- Meperidine: Pain
- Phenytoin: Probably least toxic anticonvulsant
- Unsafe drugs: Numerous
- Laboratory features
- Reduced porphobilinogen deaminase in erythrocytes
- EXCEPTION: Some mutations affect only non-erythroid tissues
- Urine: High PBG & ALA
- Normal fecal coproporphyrin & protoporphyrin between attacks
- Neuropathy
- CSF
- Often normal
- Occasional: Mild increase in protein or cells
- Nerve conduction studies
- CMAPs: Small
- No evidence of demyelination
- Sensory: Normal or small SNAPs
- EMG: Denervation; Some myopathic potentials
- Pathology
- Neuropathy: Predominantly axonal
- CNS: Patchy demyelination
- Tests
- Aminolevulinic acid: 24 hour urine
- Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase
 : Erythrocyte : Erythrocyte
- Porphobilinogen deaminase
 : Erythrocyte : Erythrocyte
- Urinary porphobilinogen: High in 88% between attacks
- HMBS variant: Leukoencephalopathy, Childhood onset (Spastic-Ataxia)
3
- Epidemiology: 6 patients with survival to adulthood
- Genetics
- Mutations: Missense; Ala84Asp, Arg167Gln, Arg225Gln
- Inheritance: Recessive
- Clinical
- Onset ages: 4 to 22 years
- Spastic paraparesis: Legs > Arms
- Polyneuropathy: Sensory loss, Distal
- Ataxia
- Cognitive impairment: None or Mild
- Cataracts: Some patients
- Porphyric attacks: 1 patient
- Course: Slow progression
- Treatment: ? Regular carbohydrate-containing meals
- Laboratory
- NCV: SNAPs & CMAPs small amplitude
- Brain MRI
- Signal: Periventricular; White matter, deep & Thalami
- Cerebral & Cerebellar atrophy
- Urine: PBG & Porphyrin High
- History:
King George III of England probably had porphyria
|
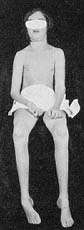
From: F Ford
Distal Atrophy
& Weakness:
Child
|
|