|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
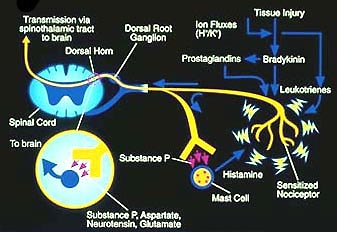
NEUROPATHIES: PAINFUL
PAINFUL NEUROPATHIES: Differential Diagnosis
- Toxic
- Alcohol
- Metals: Thallium; Arsenic
- Medications:
- Mushroom: Clitocybe acromelalga
- Immune
- Acute onset
- Guillain Barré
- Diffuse pain during acute course
- Distal pain with incomplete recovery
- Immobility
- Acute panautonomic
- Guillain Barré
- IgM antibody associated polyneuropathies
- IgG antibody associated polyneuropathies
- M-protein
- Ganglionopathies
- Cryoglobulinemia
- Connective tissue disease
- HIV (DILS)
- Vasculitis
- Acute onset
- Hereditary
- α-galactosidase (Fabry's)
- GM2 gangliosidosis: Late-onset
- Sensory Neuropathy I: Lancinating pains
- Motor-Sensory Neuropathy I & II: Foot deformity
- SCN9A (Nav1.7)
- SCN10A (Nav1.8)
- SCN11A (Nav1.9)
- Amyloidosis
- Polyneuropathy: Pain & Paraesthesias in legs
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: Pain in hands
- Porphyria
- Episodic pain syndromes, Familial (FEPS)
- Restless legs syndromes: Some with PNS involvement
- Hereditary (Acromelalgia)
 : 12q
: 12q - HSN 1
- HMSN 5
- CMT 2
- Huntington disease-like 1

- Also: Renal failure
- Hereditary (Acromelalgia)
- Metabolic
- Diabetic
- Acute: Lumbar or Thoracic radiculopathy; Distal sensory
- Chronic: "Small fiber" neuropathy
- Alcoholic: Acute
- Pellagra (niacin)
- Beriberi (thiamine)
- Strachan syndrome (Cuban neuropathy)
- Post gastroplasty
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Chronic mountain sickness
- Diabetic
- Idiopathic
- Mononeuritis multiplex
- Motor disorders with pain
- Infections
- Localized disorders
- Nerve lesions:
- Trigeminal
- Brachial plexus
- Lumbosacral plexopathy
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Median
- Posterior tibial (Tarsal tunnel syndrome)
- Radiculopathies: Upper & Lower Extremities
- Burning mouth syndrome
- Diabetic Amyotrophy
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (Complex regional pain syndrome)
- Infections: Herpes zoster
- Neoplastic infiltration: Burning pain with dysesthesia in area of sensory loss
- Post surgical localized pain syndromes
- Nerve lesions:
- Acute onset of pain & paresthesias
- Acute porphyria
- Toxic: Thallium; Arsenic; Perhexiline; Vinca alkaloids
- Guillain-Barré
- Acute sensory neuropathies
- Spinal: Myelopathy; Radiculopathy
Sensory polyneuropathy syndromes: Idiopathic
|
Acute onset Small fiber Neuropathy, Chronic Neuronopathy |
- Epidemiology
Axon loss: Especially small axons- Increased frequency > 50 years
- Female > Male: 2 to 1
- Clinical syndrome: Chronic small fiber neuropathy syndrome, Common
- Age: 40 to 84 years
- Onset: Legs
- Sensory loss: Small ± Large fiber
- Pin loss: Distal; Most patients
- Vibration: Commonly (50%) reduced
- Sensory ataxia: Increased falling in some patients
- Pain: Some patients
- Distal > Proximal: May be prominent in proximal regions
- ± Paresthesia
- Burning
- Increased at night
- Motor: Fatigue; Occasional distal weakness in toes (Plantar flexion; Abduction)
- Tendon reflexes: Generally preserved; ± Reduced distally
- Autonomic disorders: Especially cholinergic
4
- Pain
- Vasomotor: Skin; Secretory
- Hypertension
- Impotence
- Hypohidrosis: Distal
- Progression: More proximally in legs; Hands in some
- Clinical syndrome: Acute onset small fiber neuropathy/neuronopathy
- Age: 48 to 65 years
- Sensory loss: Proximal & Distal
- Pain: Burning & Hyperesthesia
- Course: Slow partial recovery
- NCV: Axon loss, Sensory or Normal
- Pathology: Proximal & Distal axon loss in skin
- Clinical syndrome: Non-length dependent Small fiber polyneuropathy (SFPN)
18
- Age
- Range: 19 to 72 years
- Mean 46 years
- Epidemiology vs Length dependent SFPN
- Younger
- Females more common
- Age
- Etiologies
- Clinical
- Strength: Normal
- Sensory
- Loss
- Distribution: Diffuse; Patchy; Arms (50%), Legs (60%), Trunk (20%) & Face (20%)
- Modalities: Pin; Light touch
- Discomfort: Pain, Burning, Tingling, Myalgias
- Loss
- Tendon reflexes: Normal
- Laboratory
- NCV: Normal
- Skin biopsy: Reduced intraepidermal axons, Proximal & Distal
- Diabetes: Less common than Length dependent neuropathies
- NCV
- Conduction velocity: Unremarkable
- Sensory action potentials: Usually normal or reduced amplitude
- Quantitative sensory testing: Abnormal in ~60%
- EMG
- Proximal muscles: Normal
- Distal: Denervation in some patients
- Triglycerides: Higher than in controls
- ? Increased frequency of abnormal glucose tolerance tests
6
- Not clearly more common than in age matched controls
- Abnomal GTT may be more common with painful polyneuropathy
- ? Related to
- Disuse of muscle
- Metabolic syndrome
- Skin biopsy: Reduced epidermal axon density
- Nerve biopsy
- ± Reduced numbers of small & large axons
- Inflammation: Epineurial vessels in some patients with severe pain & absent SNAPs 10
- ? History of exposure to environmental toxins: More common in neuropathy patients
- Family history of neuropathy & foot deformity: More common in neuropathy patients
Post surgical localized pain syndromes
- Postradical neck dissection:
- Cervical plexus lesion
- Drooped-shoulder syndrome
- Postmastectomy
- Posterior arm, axilla, and anterior chest wall
- Exacerbated by arm movement
- Postthoracotomy
- In distribution of the incision with sensory loss
- Point tenderness at most medial & apical points of scar
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
- Postnephrectomy
- Flank, anterior abdomen, and groin
- Dysesthesias, numbness & heaviness
- Postlimb amputation
- Phantom limb: Usually occurs after pain in the same site before amputation
- Stump pain
- At site of the surgical scar
- Onset: Months to years after surgery
- Burning dysesthesias exacerbated by movement
- At site of the surgical scar
- Nerve tumors: Radiation-induced
- Fibrosarcoma
- Painful, enlarging mass in previously irradiated area
- Especially with neurofibromatosis
α-Galactosidase Deficiency (Fabry disease)
 20
20
●
α-Galactosidase
- Epidemiology: Prevalence
- 1 in 366,000 males in UK
- Birth frequency: 1 in 117,000
- Genetics: Mutations
12
- > 600 different mutations identified
- Missense point mutations: 75%
- Two major types
- Active site: Reduces enzyme activity; Hotspot for mutations
- Folding
- Disrupted hydrophobic core
- Reduces stability of α-Galactosidase
- Locations: All through molecule
- Severe phenotype: Mutations buried deep in molecule
- Milder phenotype: Less disruptive to hydrophobic core
- Two major types
- Deletions/Insertions: 15%
- Splice site mutations: 5%
- Specific mutations
- Most families have private mutation
- Taiwan
- Mutation: IVS4+919G>A
- Frequency: 1:875 male & 1:399 female live births
- Phenotype: Mild
- D313Y: Exonic variant
21
- 60% of wild-type activity in vitro
- Reduced activity at neutral pH: Low plasma α-Gal A activity
- Female carriers: Small fiber neuropathy in 75%; Pain; Sweating disorders
- Incidence
- Higher: Young stroke patients; Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Not frequent: Isolated small fiber neuropathy
- α-galactosidase function
- Normal: Cleaves terminal galactose from ceramide trihexoside
- Fabry's
23
- Ceramide trihexoside (globotriaosylceramide (GL-3; Gb3)) accumulates in
- CNS neurons
- PNS Ganglia
- Systemic: Heart, Kidney
- Smooth muscle
- Skin
- Frequency: Most in classic FD; Rare in late onset
- Correlate with loss of skin innervation
- Enzyme activity
- Residual activity in Fabry's: 1% to 17%
- Disease severity correlates with residual enzyme activity
- Highest residual levels: Asymptomatic; Selective cardiac disease
- Calcium: Increased levels in sensory neurons
- Plasma
- Deacylated globotriaosylceramide (lyso-globotriaosylceramide (lyso-GL-3)) increased
- Ceramide trihexoside (globotriaosylceramide (GL-3; Gb3)) accumulates in
- Clinical features: Males with disease
8
- General
- Childhood: Neuropathic; Pain, Hypohidrosis, GI
- Progression: Systemic features; Renal, Heart, Brain
- Onset age: Late childhood to Early adult; Mean 21 years
- Polyneuropathy
19
- Onset
- Age: Childhood or Adolescence; < 18 years; Mean Dx 21 years
- Burning pain
- Location: Palms & Soles of feet
- Precipitated by: Fever or Hot weather; Physical activity; Stress; Alcohol
- Children: Painful feet during febrile episodes
- Hypohidrosis
- Onset
- Pain (77%)
- Onset: 10 years
- Locations: Hands, Feet, Abdomen +...
- Episodic severe
- Attack duration: Minutes to Weeks
- Triggered by: Heat; Ethanol
- Chronic & Continuous (89%)
- Tingling, Shooting & Burning
- Life-long (90%)
- Increases over time
- Fatigue (60%)
- Course: Worst in 3rd or 4th decades
- Treatment
- Neurontin
- Poor response to: Carbamazepine or Opiates
- Sensory loss
- Increased threshhold
- Cold
- Warm
- Heat pain
- Large fiber modalities: Spared
- Length dependent
- Unless renal failure present
- Course: More with increased age
- Increased threshhold
- Autonomic
- Hypohidrosis
- Impotence
- Course: Progressive with age
- Electrodiagnostic testing 11
- NCV: Often normal; Some (25%) with carpal tunnel syndrome
- Sympathetic skin responses: Preserved
- QST: Abnormal thermal detection; Cold worse than warm
- MRI
- Dorsal root ganglion T2 signal: More common with Fabry PN with pain 24
- Pathology: Axon loss
- Nerve
- Small axon loss: Early in disease
- Pansensory axon loss: With renal failure
- Ganglion cells & Endothelium
- Osmophilic (or Sudan black+) lipid inclusions
- Skin biopsy: Loss of intraepidermal nerve fibers
- Lipid inclusions
- Inclusion staining
- Sensory perikarya & Endothelial cells: Sudan black
- Ultrastructure: Osmophilic
- Maltese cross birefringence
- Tissue locations
- Vessels (Small): Endothelial cells & Media
- Kidney: Renal tubules & Glomeruli
- Cardiac: Muscle & conducting fibers
- Perineurial cell
- Spinal autonomic neurons
- CNS: Cortical & brainstem structures
- Subcellular location: Initially in lysosomes
- Inclusion staining
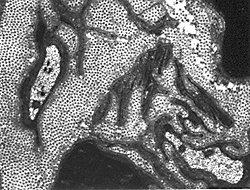
Fabry disease: Peripheral nerve
Loss of unmyelinated axons
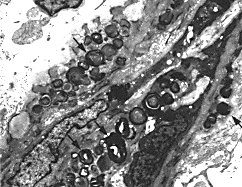
Osmophilic Inclusions
- Electrodiagnostic testing 11
- General
- CNS
- Strokes (24%)
- Onset: Mean ~40 years; Range 28 to 54
- Frequency
- General: 5.5ľ12.2-fold increased
- Males 12x control population; Female 4x control
- High serum myeloperoxidase level
17
- Increased risk for developing cerebrovascular disease
- No change after enzyme replacement therapy
- May occur after enzyme replacement therapy
- Vascular pathology
- Early: Microvasculature dysfunction; Lipid in endothelial cells
- Progression in medium-to-large vessels
- Arterial remodeling
- Intima-Media thickening
- Ectatic vessels
- Especially posterior circulation
- CNS pathology
- Common: Ischemia; TIA
- Other: Hemorrhage, intracerebral or subarachnoid; Vein thrombosis
- MRI
- T2 white matter hyperintensities
- Single, multiple, or confluent
- 100% by age 54
- Pulvinar sign (20%)
- Bilateral T1 hyperintensity in thalamic posterior area
- ? Related to calcification
- Not specific
- T2 white matter hyperintensities
- Personality: Passive; Depression
- Dementia (18%): Associated with CVAs
- Hearing
16
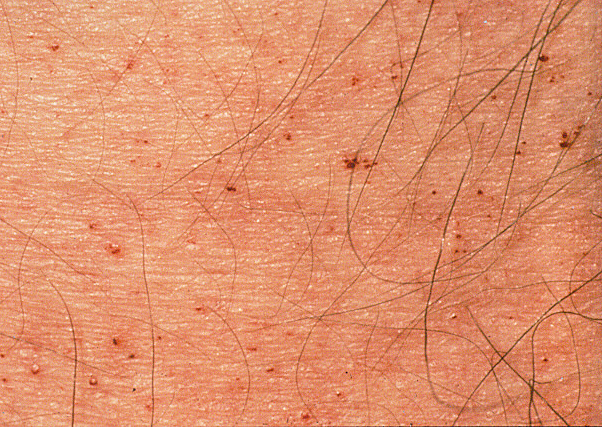
Angiokeratoma
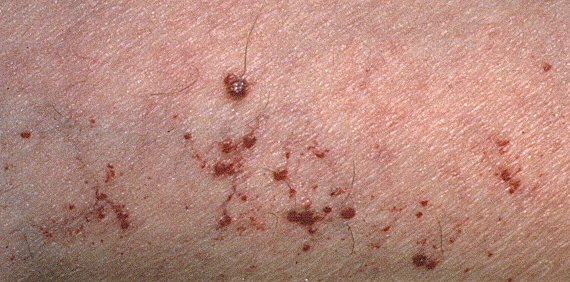
- Loss (78%)
- Sensorineural
- All frequencies
- Mild to Severe: Worse with
- Neuropathy
- Reduced renal function
- White matter lesions: Cerebrovascular disease
- Subclinical involvement: Early
- Residual enzyme activity > 1.5%: Protective against hearing loss
- Tinnitus (40%)
- Course: Progressive
- Loss (78%)
- Vertigo
- Strokes (24%)
- Skin
- Angiokeratoma (90%)
- Dilatated capillaries of dermal papillae overlying keratotic epidermis
- Description
- Papules: Raised
- Red-Purple
- Venous or Capillary lesions: Bleeding tendency
- Locations: Navel & Lower abdomen; Scrotum & Buttocks; Thighs
- Onset: Mean 17 years; Umbilical rash may ocur at birth
- Rash: Red-purple; Abdomen & Sacral regions
- Facial telangectasia
- Angiokeratoma (90%)
- Renal
- Proteinuria
- Glomerular filtration rate: Progressive decline
- Failure (30%): Onset 36 years
- Cardiovascular
- Cardiomyopathy
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Conduction disorders
- Heart may be selectively involved
- Vascular disease
- Stroke
- Ectatic vessels with clot
- Embolic
- Treatment: Aspirin; Coumadin
- Hypertension
- Treatment: ACE inhibitors
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke
- Cardiomyopathy
- GI (69%)
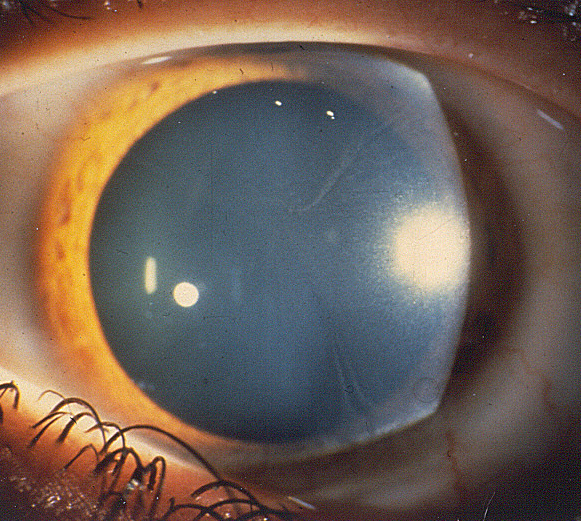
Cornea verticillata
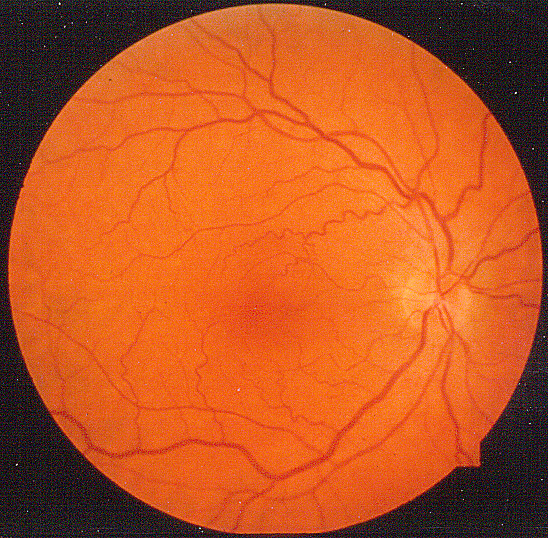
Retinal vessels: TortuousFrom L Scott- Abdominal pain: Episodic; After meals
- Fat intolerance
- Episodic diarrhea
- Nausea & vomiting
- Most patients are thin
- Treatment: Lipisorb
- Face dysmorphisms (60%)
- Upper face: Periorbital fullness, Eyebrows bushy, Forehead recessed
- Ears: Lobules prominent, Posteriorly rotated
- Nose: Angle pronounced, Large nose/bulbous tip, Prominent supraorbital ridge & bridge
- Lips: Full
- Eye
- Corneal opacity: Cornea verticillata
- Conjunctival & Retinal vessels: Tortuous
- Systemic, Other
- Episodic fever: < 20 years
- Edema (50%)
- Hypothyroid
- Prognosis
- Survival
- Median: 50 years; 20 year reduction
- Decline starts at 30 to 35 years
- Causes of death: Most common Renal failure or Cerebrovascular
- Social: Reduced attendance at school, sports, social activity
- Psychosexual difficulties: Genital angiokeratoma; Genital pain; Impotence
- Survival
- Diagnosis
- Measure α-galactosidase enzyme levels
- Best in cultured fibroblasts
- Skin biopsy: Sudan+ inclusions
- Measure α-galactosidase enzyme levels
- Treatment: Enzyme replacement
- Agalsidase alfa: 0.2 mg/kg q 2 weeks
- Agalsidase beta: 1.0 mg/kg q 2 weeks
- Benefit: Slowed decline of renal disease; Some reduced pain
- Penetrance
- 30% to 50% asymptomatic
- Related partly to: X chromosome inactivation
- Neuropathy
- Small fiber modalities: Partially reduced
- Peripheral pain (10% to 70%)
- Especially with fever or hot weather
- Less pain in some older patients (> 50 years)
- Fatigue
- Skin: Angiokeratomas, mild (10% to 35%)
- GU
- Renal dysfunction
- Bladder dysfunction
- GI symptoms
- Long tract signs
- Eye (70%): Cornea verticillata; Cataract, posterior lenticular
- Hearing loss: Mild
- Survival
- Mean 70 years: Reduced 10 to 15 years
- Death: Due to
- Cerebrovascular disease: Most common
- Renal failure
- Cardiomyopathy
- Proteinuria
- CSF: Normal
- MRI (T2)
- Small lesions in grey or white matter
- 37% symptomatic
- Age: > 26
- Lyso-Gb3 (globotriaosylsphingosine): 50x high in blood
Burning Mouth Syndrome 7
- Epidemiology
- Females (88%) > Males
- Age: Middle aged & Elderly; Median 60 years; Range 30 to 82 years
- Clinical
- Onset: Spontaneous or with precipitating factor
- Pain: Burning & Painful sensations in mouth
- Location: Tongue (100%); Hard palate (Anterior) & Inner lip
- Bilateral (85%)
- Not in distribution of single peripheral nerve
- Temporal
- Reduced in morning
- Increases through day
- Not aggravated by eating or drinking
- No effect on sleep
- Taste: Lost or Altered (Bitter, Metallic)
- Dry mouth (Xerostomia): May be transient
- No mucosal lesions
- Causes & Associations: No strong relations
- Anemias: Pernicious; Megaloblastic; Iron-deficiency
- Endocrine: Diabetes mellitus; Thyroid
- Menopause
- Medications: Diuretics; Antidepressants; Clonazepam
- Smoking
- Laboratory: Some abnormality in electrophysiology in 89%
- Blink reflex
- Brainstem pathology, or Peripheral trigeminal neuropathy: 20%
- Increased excitability: 20%
- Quantitative sensory threshhold
- Small fiber abnormality: Abnormal sensory threshhold; 76%
- Thermal hypoesthesia (15%)
- Pathology: Small fiber neuropathy
- Increased TRPV1 & NGF positive axons
- Reduced intra-epidermal axons
- Blink reflex
Erythromelalgia (Erythermalgia) 5
|
|
Burning Feet Syndrome
 1
1
●
SCN9A
- See: Erythermalgia
- Clinical
- Onset: 12 to 40 years; Mean 27 years
- Pain
- Distribution
- Symmetric
- Soles & toes of feet: Progresses to ankles & lower legs
- Burning & Dull ache
- Increased with warm; Reduced with cold
- Distribution
- Normal touch, pain, temperature,and vibration & position sense
- Normal strength; No wasting
- Laboratory
- Electrophysiology: Normal, or mildly abnormal, nerve conduction studies
- Nerve biopsy
- Unmyelinated axons: Markedly reduced
- Myelinated axons: Mildly reduced
- Regeneration
Small Fiber Neuropathy 5
● SCN9A- Epidemiology
- Some patients with definite small fiber neuropathy
- Positive family history: Usual
- Genetics
- Mutations: Heterozygous; Gain-of-function
- Most true mutations: Patients with a positive family history
- "Mutations" in spontaneous cases: Often polymorphisms; Frequent occurrence in genetic databases
- Allelic disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: Adult; 14 to 68 years
- Sensations reduced: Pain; Temperature
- Pain
- Distal > Proximal
- Legs > Arms
- Other: Some patients
- Myalgias
- Jaw
- Diffuse
- Exacerbation by warmth: 35%
- Autonomic symptoms
- Orthostatic dizziness
- Palpitations
- Dry eyes & mouth
- Other (Few patients): Blurred vision, Constipation/Diarrhea, Hyperhydrosis
- Strength: Normal
- Tendon reflexes: Normal
- Vibratory sense: Normal
- symptom duration: 1 to 37 years
- Laboratory
- Nerve conduction studies: Normal
- Quantitative sensory testing (QST): Abnormal
- Intraepidermal nerveüfiber density (IENFD): Reduced
Episodic pain syndrome, Familial 1 (FEPS1)

●
Transient receptor potential cation channel, Subfamily A, MEMBER 1 (TRPA1)
- Epidemiology: Colombian family, 21 members
- Genetics
- Mutation: Asn855Ser
- TRPA1 Protein
- Cation channel
- Expressed in primary afferent nociceptors
- Mutation: 5-fold increase in inward current when stimulated by agonist cinnamaldehyde
- Clinical
- Onset age: Infancy
- Triggers
- Types: Fasting, Fatigue, Cold, Illness, Physical exertion
- Combination of factors more likely to precipitate episodes
- Episodes
- Upper body pain: Severe
- Breathing difficulties
- Tachycardia
- Sweating
- Pallor generalized pallor
- Peribuccal cyanosis
- Abdominal wall stiffness
- Duration: 1.5 hours
- Prodrome: Episode may be aborted
- Post episode: Exhaustion & Deep sleep
- Between episodes
- No altered pain sensitivity
- Neurologic exam: Normal
- Laboratory
- Skin biopsies: Normal
- Quantitative sensory testing: Normal
- Mustard oil (Activates TRPA1 receptors): Higher flare responses & secondary hyperalgesia
- Differential diagnosis: Episodic pain syndromes
Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (Complex regional pain syndrome)

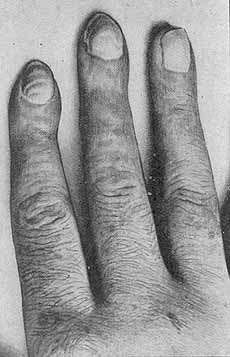 Tinel 1918 Causalgia after
median nerve lesion |
- General
14
- Features
- Discomfort: Spontaneous pain or hyperalgesia/hyperesthesia
- Distribution: Not limited to single nerve territory
- Disproportionate to inciting event
- Other associated features on affected limb, especially distal
- Edema
- Skin blood flow (temperature) or sudomotor abnormalities
- Motor symptoms
- Trophic changes
- Other diagnoses are excluded
- Discomfort: Spontaneous pain or hyperalgesia/hyperesthesia
- Types
- I: No definable nerve lesion
- II: Nerve lesion present
- Features
- Epidemiology
- Patient features
- Female:Male 2:1
- Age: Mean 50 years; Range 15 to 80 years
- Associated features
- Serious life event (40%)
- History of chronic pain (40%): Back; Headache; Multiple
- ? Genetic susceptibility
- ? Precipitating events
- Limb fractures
- General surgery
- Soft tissue injury
- Carpal tunnel surgery
- Radiculopathy
- ? Drugs
-
Phenobarbital; Phenytoin; Isoniazid;
Cyclosporin; Tacrolimus; Rapamycin
- ? Medical conditions
-
Diabetes mellitus; HyperThyroid;
HyperParathyroid; Type IV hyperlipidemia
- Patient features
- Onset: Weeks after precipitating event
- Location
- Distal extremity
- Hands > Feet; Knees
- Asymmetric or Unilateral most commonly
- Pain
- Character: Burning; Pricking
- Continuous
- Deep 2x more common than superficial
- Hyperalgesia (100%)
- Stimulus
- Mechanical impact (Pin) stimuli
- May be associated with central sensitization
- Thermal hyperalgesia: Less common
- Position dependent amplification
- Stimulus
- Allodynia: More in chronic syndromes
- Exacerbated by
- Movement: Especially lowering limb
- Cutaneous stimulation
- Stress
- Temperature change
- Cold pain
- More common with nerve lesions
- Sympathetically-maintained
- Sensory loss
- Distribution: Glove or Stocking
- Modalities: Pain; Touch
- Autonomic
- Skin temperature
- Increased (80%) or Decreased (20%)
- Temperature difference between extremities: > 1°C
- Hyperhidrosis (50%)
- Edema (81%): Distal limb; More common early
- Skin color change
- Reddish: Early in course
- Cyanotic: Chronic syndromes
- Norepinephrine in RSD extremity: Reduced
- Skin temperature
- Motor disorders
- Sense of weakness with complex motor tasks (79%): "Give-way"
- Difficulty initiating movements
- Limited range of motion: Wrist; Ankle
- Involuntary movements
- More common with nerve lesions
- Tremor (48%)
- Irregular myoclonic jerks, dystonia or muscle spasm (30%)
- Tendon reflexes: Increased, On affected side 46%
- Trophic changes (50%)
- "Plus"
- Early: Days after injury
- Increased hair- & nail growth
- "Minus"
- Late
- Reduced hair- and nail growth
- Atrophy of skin & muscles
- Contractures
- "Plus"
- Late features
- Skin: Atrophic; Red
- Bone: Sudek's atrophy
- Extremity: Cold; Pallor; Cyanosis; Hair loss
- Pain: Hyperalgesia in anesthetic skin
- HLA-DQ1
 association: 69% vs 42% in controls
association: 69% vs 42% in controls
- Quantitative sensory testing: Patients with sympathetic maintained pain
- Warm thresholds: Increased
- Hyperalgesia to painful cold stimuli
- X-ray: Osteoporosis
- Patchy
- Time: After 4 to 8 weeks
- Frequency 40%
- Bone scintigraphy: Increased metabolism
- MRI: "Edema" in deep tissues
- Serum CGRP: Increased in acute syndromes
- Sympathethetic nervous system disorders: ? Central
- Vasoconstrictor activity altered: Decreased early; Increased late
- Sudomotor abnormalities
- Nerve
- C-fibers: Loss (50% of patients)
- Myelinated axons: Normal
- Muscle
- Capillaries: Increased basement membrane thickness; Necrosis
- Type 1 muscle fibers: reduced
- Corticosteroids: Early in disease course
- Glutethimide & sympathetic blocks: Early in 1st few months
- Pain management: Analgesics often provide little benefit
- Antidepressants: Amitriptyline; Venlafaxine; Fluoxitine
- Local anesthetic type antiarrythmics: Flecainide
- Opiates: Morphine
- Other drugs
- Ca++ blocking agents: Nifedipine
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone; Solumedrol
- Calcitonin
- Biphosphonates
- Gabapentin
- Baclofen
- Intrathecal
- Mainly beneficial for predominantly arm syndromes
- Topical DMSO: Early in disease course
- Physical therapy: Reduce contractures
- Limb amputation rarely reduces pain
- ? Upregulated sensitivity of α-adrenooceptors for catecholamines
- ? Regional inflammatory response 2° O2 derived free radicals or neuropeptides
- Erythralgia (ABC Syndrome):
- Spontaneous pain
- Hyperalgesia: Thermal & Mechanical
- Pathophysiology: Related to sensitized C nociceptors
- Ectopic activity
- Antidromic secretion of vasoactive substances
- Related general syndrome: Erythromelalgia
- CCC Syndrome: Defective Aδ cold specific input
- Cold hypoesthesia
- Cold hyperalgesia
- C-nociceptor pain with paradoxical burning character
- Cold skin
- Related to partial sympathetic denervation supersensitivity & vasospasm

|
Chronic Mountain Sickness 3
- Epidemiology
- Andean natives living at high altitude
- Sex & Age predominance: Males; Ages 20 to 50 years
- Occupation: Miners in Cerro de Pasco, Peru
- Clinical
- General: Malaise; Depression
- Headaches (Migraine-like) (100%)
- Dizziness (50%)
- Fatiguability; Somnolence; Coma (occasional)
- Paresthesias: Burning feet-Burning hands syndrome
- Burning pain: Distal; Hands & Feet
- Distal sensory loss: Mild; 30%; Lower extremities
- Tendon reflexes: Reduced (30%)
- Hyperaesthesia (30%)
- Relation to altitude
- Resolves after 1 to 14 days at sea level
- Recurs with return to high altitude in hands, then legs
- Strength: Normal
- Ataxia: 20%
- Circulatory
- Cyanosis
- Suffused conjunctiva, cheeks & earlobes
- Peripheral edema
- Clubbing of fingers & toes
- Splinter hemorrhages
- Heart failure: Congestive; Especially right sided
- Laboratory
- Polycythemia (Hct > 64)
- Red cell mass increased: Hemoglobin > 21.3 mg/dl
- O2 saturation reduced: 70% or less
- Respiratory function
- No hyperventilation: Failure of respiratory centers to respond to CO2 stimunation
- Ventilatory response to hypoxia: Reduced
- Disordered respiration during sleep: Episodic hypopnea & Apnea
- Neuropathy: Pathology
- Vessels: Reduced basal lamina thickness
- Demyelination: Thin myelin sheaths
- Axons: Myelinated & unmyelinated axon number most often normal
Return to Polyneuropathy Index
Return to Neuromuscular Home Page
References
1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:78-81
2. Acta Neurol Scand 2000;101:262-269
3. JNNP 2000;69:447-452
4. Neurology 2001;56:861-868
5. J Child Neurology 2001;16:199-202; Am J Hum Genet 2001;68:1277-1282; Ann Neurol 2006 Jan 3, Ann Neurol 2011; Online May
6. Muscle Nerve 2001;24:1109-1112, 1225-1228, 1229-1231; Brain 2004; Online June
7. Ann Pharmacother 2001;35:874-876, Pain 2002;99:41ľ47, Oral Dis 2016 Feb 4
8. J Med Genet 2001;38:750-760
9. J Med Genet 2001;38:769-775
10. Muscle Nerve 2002;July Online
11. Muscle Nerve 2002;September Online
12. Molec Genet Metab 2002;September Online
13. J Med Genet 2004;41:171ľ174
14. J Neurol 2005;252:131ľ138
15. Arch Dermatol 2006;142:283-286
16. Brain 2007;130:143ľ150
17. Neurology 2006;67:2045ľ2047
18. Muscle Nerve 2012;45:86ľ91
19. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 2012;106:135ľ141, Biomed J 2021 May 3
20. Handb Clin Neurol 2015;132:231-248
21. Muscle Nerve 2021 Feb 5
22. Brain 2022;145:3637-3653
23. Brain Commun 2024 Apr 3
24. Brain Commun 2024;6(3):fcae155
8/22/2025