Polio
- Polio virus
- Enterovirus
- RNA, single stranded
- Subgroup of Picornaviridae
- 3 serotypes
- All can cause paralytic disease
- Type 1: Most common cause of epidemic paralytic polio
- Transmission: Fecal-Oral
- Human susceptibility
- 2° to Polio virus receptor (PVR; CD155; NECL5)


- Spread: Lymphatics to Blood to CNS
- Neurons: Virus replicates & releases RNA into cytoplasm
- Epidemiology
- Outbreaks: Most common in late summer
- Affected patients: Usually > 6 month of age; 6 mo to 3 years
- Most cases: Afghanistan, Nigeria, Pakistan, Egypt, Syria
- Paralytic disease
- 1% to 2% of infections
- More likely with increased age
- Male > Female
- Course: Events after viral exposure
- Asymptomatic with viremia: 90% to 95%
- Minor illness: 1 to 5 days after exposure
- Fever
- Malaise, Myalgia
- Sore throat, GI upset
- Major illness
- Timing: 4 to 20 days post-infection; Usually < 1 week
- Aseptic meningitis
- Fever
- Pain
- Headache
- Stiff neck & Back pain: Muscle stiffness
- Paralytic disease
- Frequency
- 50% of those with major illness
- 0.1% to 1% of infected patients; Mean 0.2%
- Timing: After 2 to 5 days of illness; Up to 3 weeks
- Motor: Weakness +
- Onset: Fulminent, Acute, or Subacute
- Focal or Asymmetric
- Proximal > Distal
- Legs > Arms > Bulbar (20%)
- Tendon reflexes
- Early
- Paralytic phase
- Reduced in affected limbs after 12 to 24 hours
- Muscle atrophy: After 2 to 3 weeks
- Course
- Improvement
- Onset: After few weaks
- Maximal: At 6 to 9 months
- Residual weakness: 60% to 70%
- Dysautonomia, Acute
- Blood pressure instability
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- GI: Atony, Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Sweating: Increased or Decreased
- Other clinical
- Fasciculations: Localized
- Pain: Intense myalgia, hyperesthesia
- Mortality
- Children: 2% to 5%
- Adults: 15% to 30%
- Differential diagnosis
- Lab
- CSF
- Pleocytosis
- Acute: Polys
- > 72 hours: Lymphocytes
- Clear from CSF after 1 week
- Protein: High; Increase over 1st 3 weeks
- Diagnostic
- Serology
- Serum: 4-fold titer rise
- CSF: IgM poliovirus specific
- Culture: Stool positive in 90% by 20 days
- Electrodiagnostic
- Early
- Selective loss of motor axons at 7 to 10 days
- NCV: Normal velocities
- Sensory: Normal
- EMG
- Acute
- Fibrillations & PSW: After 2 to 3 weeks
- Reduced recruitment
- Chronic
- CMAPs: Large amplitude; Long duration
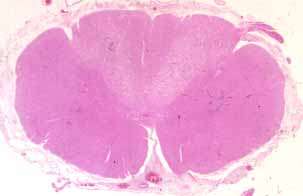
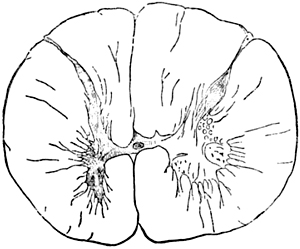
- Spinal cord pathology: Anterior horn
- Inflammation
- Perivascular
- Mononuclear cell
- Anterior horn cells
- Loss
- Abnormal morphology
- Chromatolysis
- Muscle: Chronic
- Fiber type grouping: Large
- Also see
|

Wikipedia
Polio: Leg atrophy Egypt 1403-1365 BC
|
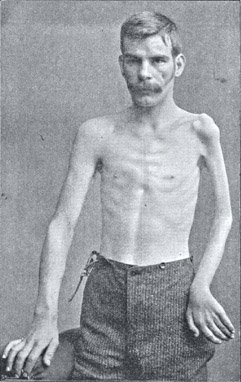
From Bramwell: Atlas of Clinical Medicine
Polio: Arm atrophy
|

|
From Bramwell: Diseases of the Spinal Cord
Polio: Small ventral horn
|

Polio: Abnormal motor neuron cell bodies
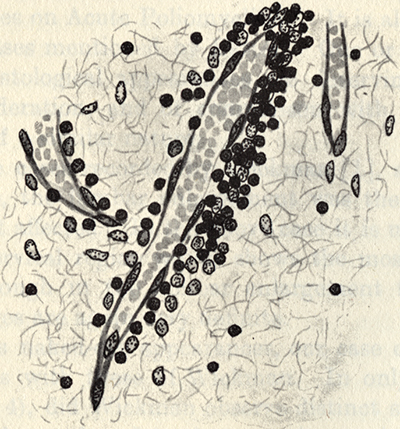
Polio: Spinal cord perivascular inflammation
From Barnes & Miller: Brain 1907;30;101
|
|