Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes,
Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info
|
Home, Search, Index, Links, Pathology, Molecules, Syndromes, Muscle, NMJ, Nerve, Spinal, Ataxia, Antibody & Biopsy, Patient Info |
|
Classification Biochemical Clinical Pathology Images Stains Lipids General Also see Carbohydrates |
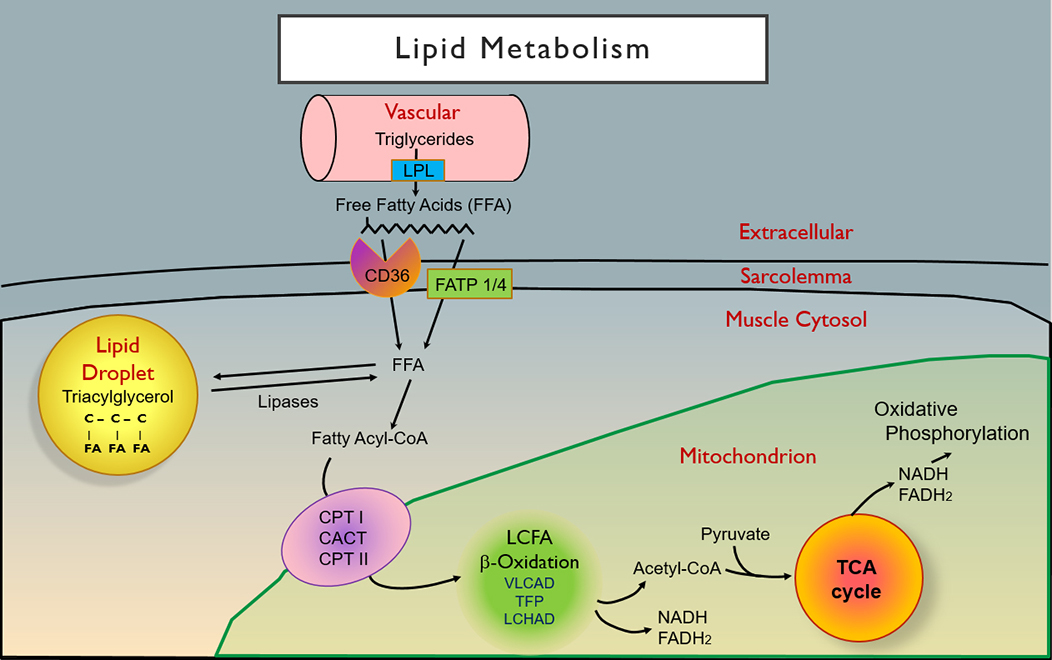 From: R Brian Sommerville |
Lipids: General
|
|
| Disorder | Gene (Common mutation) |
Clinical, Other | Muscle Lipid |
Acylcarnitine Increase & Other |
Carnitine |
| Weakness, Fixed | |||||
| Carnitine deficiency | SLC22A5 (OCTN2) |
Cardiomyopathy | +++ Type 1 |
Normal | Very low |
| SCAD | ACADS (Arg171Trp Gly209Ser) |
Ophthalmoplegia | - | Butyrylcarnitine (C4) Ethylmalonic aciduria |
|
| Multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MADD) |
ETFA | CoQ10 deficiency | + Type 1 |
All lengths ↑ Glutaric aciduria |
Low |
| Multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MADD) |
ETFDH | GI: Vomiting | ++ Type 1 |
All lengths ↑ Glutaric aciduria |
Low |
| LSMFLAD | FLAD1 | Scoliosis | ++ | Increased | ? |
| Neutral lipid storage + Ichthyosis (NLSDI) |
ABHD5 | Hepatomegaly | +++ Type 1 & 2 |
Normal Leukocyte lipid vacuoles |
Normal |
| Neutral lipid storage + Myopathy (NLSDM) |
PNPLA2 | Cardiomyopathy | +++ Type 1 & 2 |
Normal or Low Leukocyte Lipid vacuoles |
Normal |
| Rhabdomyolysis ± Exercise intolerance & Cramps | |||||
| CPT II deficiency | CPT2 (Ser113Leu 413delAG) |
± | Long chain | Normal | |
| VLCAD | ACADVL | Cardiomyopathy | ± | Long chain | Mildly low |
| Short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCHAD) |
HADH | Hepatic Hypoclycemia |
Hydroxybutyrylcarnitine | Normal | |
| Mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) A |
HADHA | Polyneuropathy | ± | Long-chain Dicarboxylic & 3-Hydroxyacylcarnitines |
Low |
| Mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) B |
HADHB | Cardiomyopathy Hepatic |
± | Long-chain Dicarboxylic & 3-Hydroxyacylcarnitines |
Low |
| Medium chain 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (MCKAT) |
Hepatic Hypoglycemia |
3-Hydroxybutyric acid C12-C16 dicarboxylic acids, unsaturated |
|||
| Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) |
ACADM (Lys304Glu) |
Hepatic | ± | Medium chain Acylglycines |
Low |
| Phosphatidic acid phosphatase |
LIPIN1 | ± | Normal | Normal | |