MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE PATHOLOGY
MITOCHONDRIAL PROLIFERATION
Ragged Red Muscle Fibers (Gomori trichrome stain)SDH stain: More sensitive for detecting mitochondrial proliferation
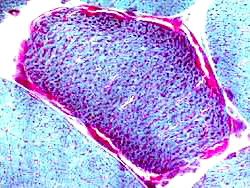  |
 Gomori trichrome stain |
(Red rim & Irregular sarcoplasm)
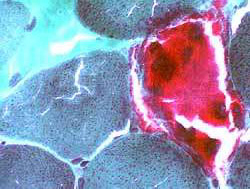 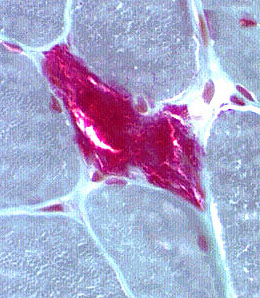 |
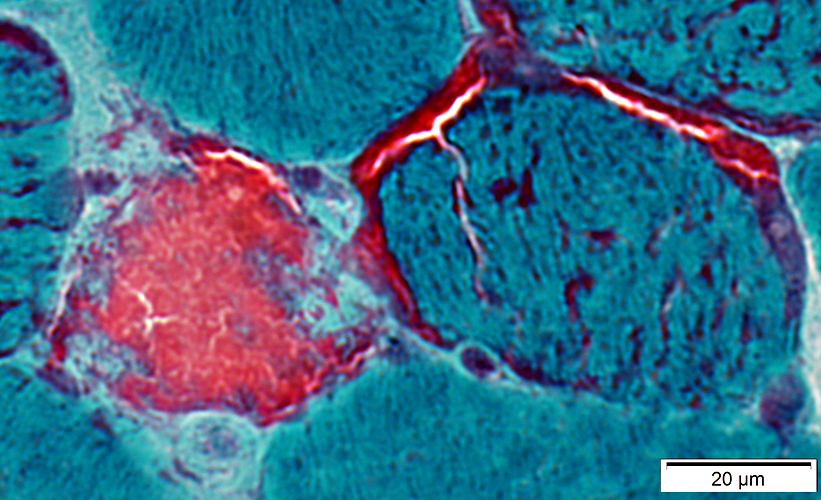 Gomori trichrome stain |
Mitochondrial Proliferation
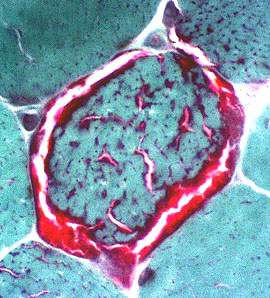
Muscle fibers with mitochondrial proliferation: Increased SDH staining
Adult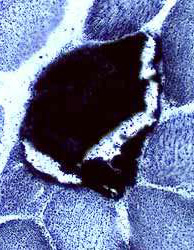 Succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) stain |
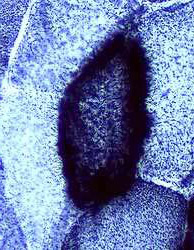
|
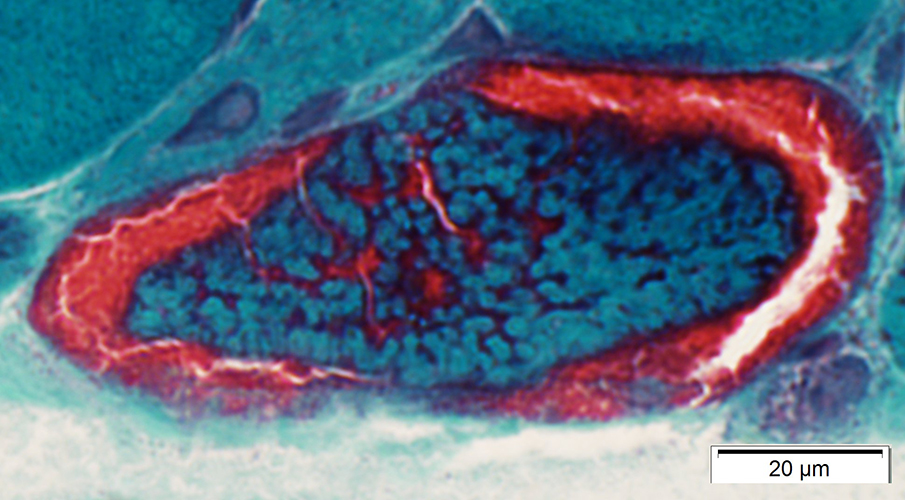
Child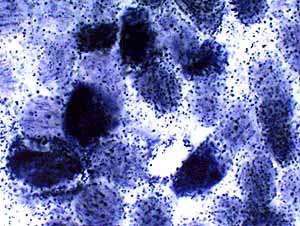 Succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) stain Mitochondrial disorder |
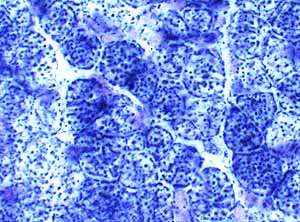 Succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) stain Normal |
SDH is the most sensitive stain for detecting mitochondrial proliferation.
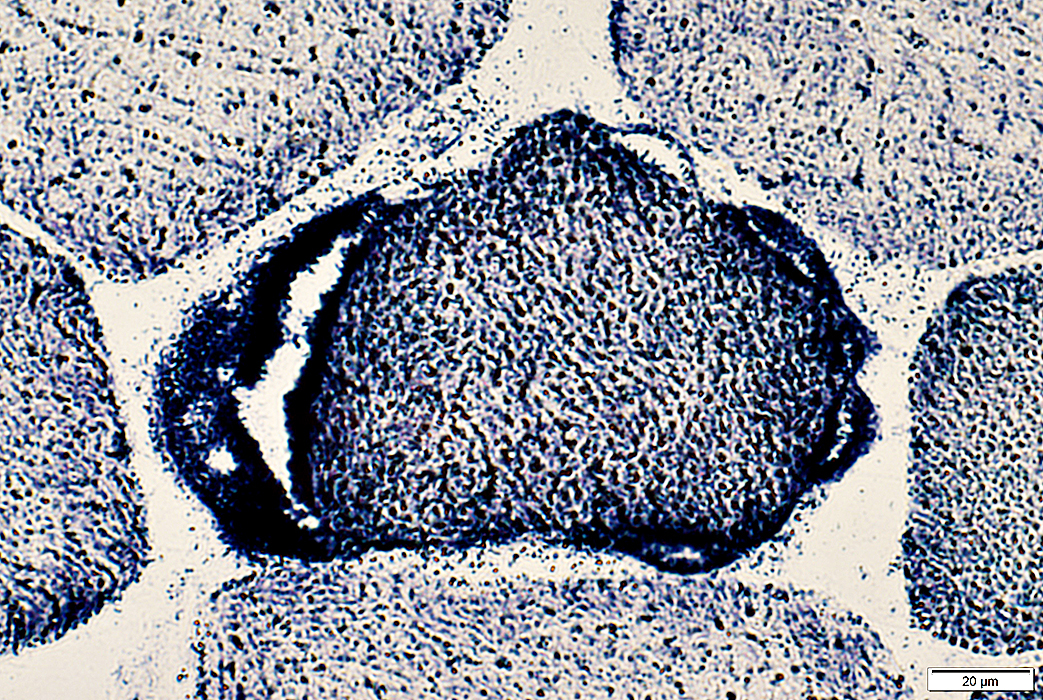 Succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) stain |
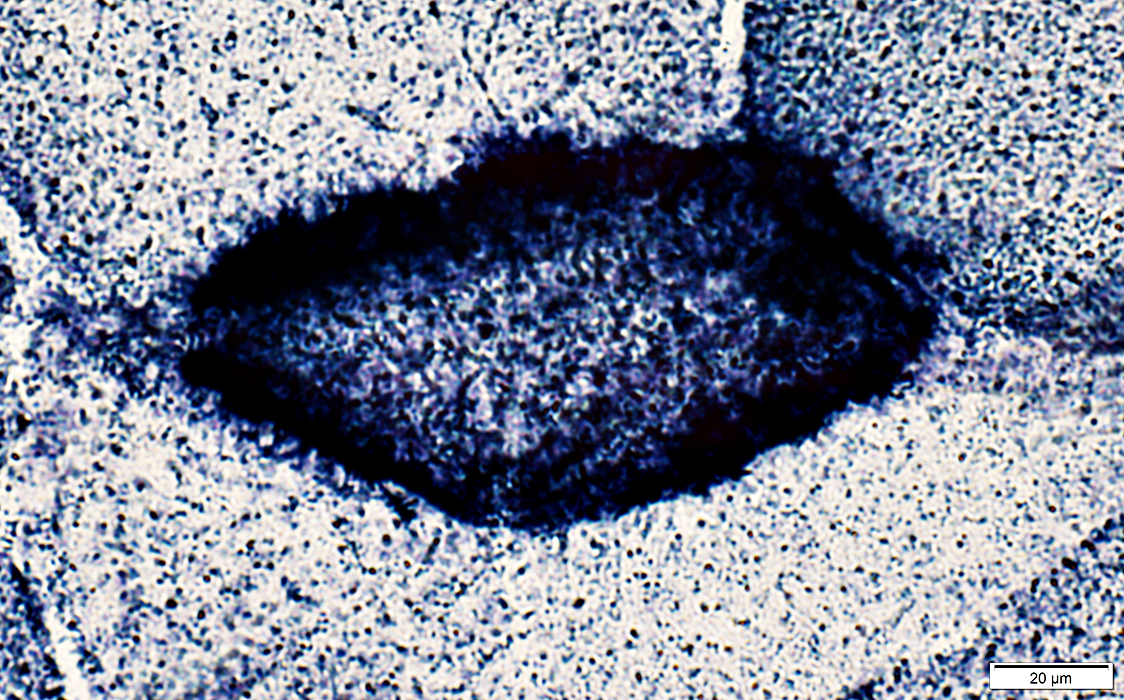 Succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) stain |
Other stains
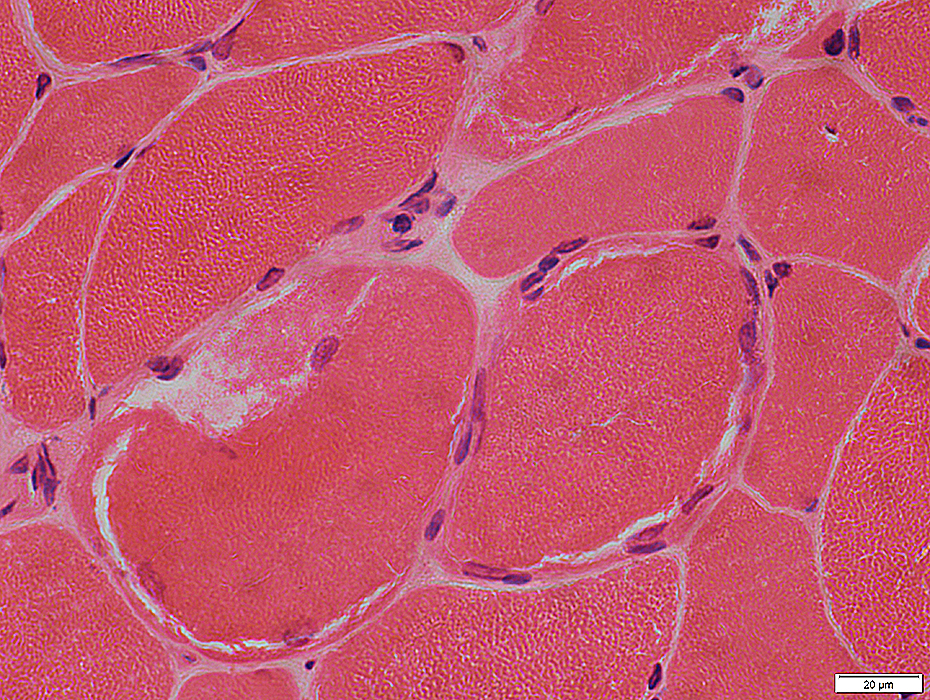 H & E stain |
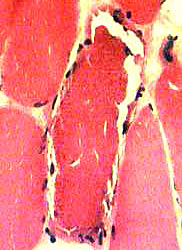 H & E stain |
Clear, or stained, external rim on H & E stain (Above)
Increased lipid: Many small lipid droplets (Below)
 Sudan stain |
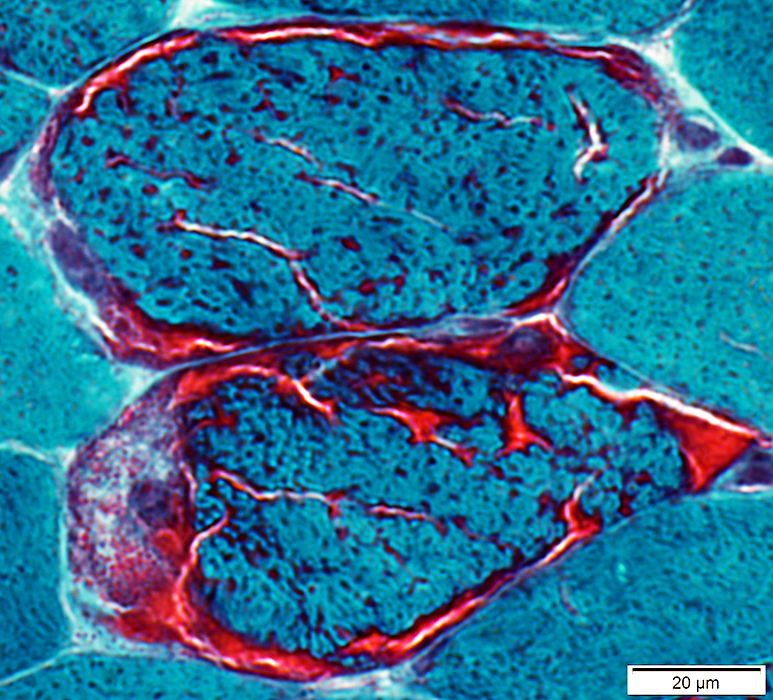 Gomori trichrome stain |
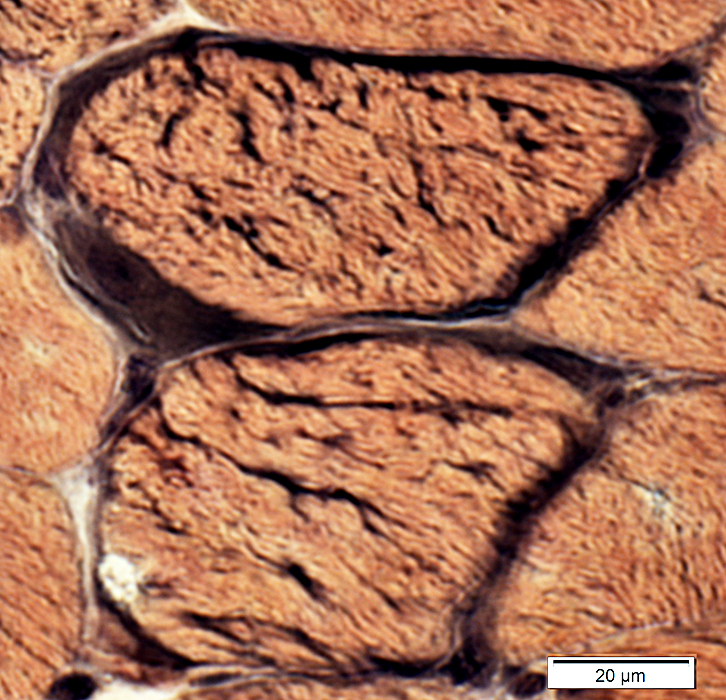 VvG stain |
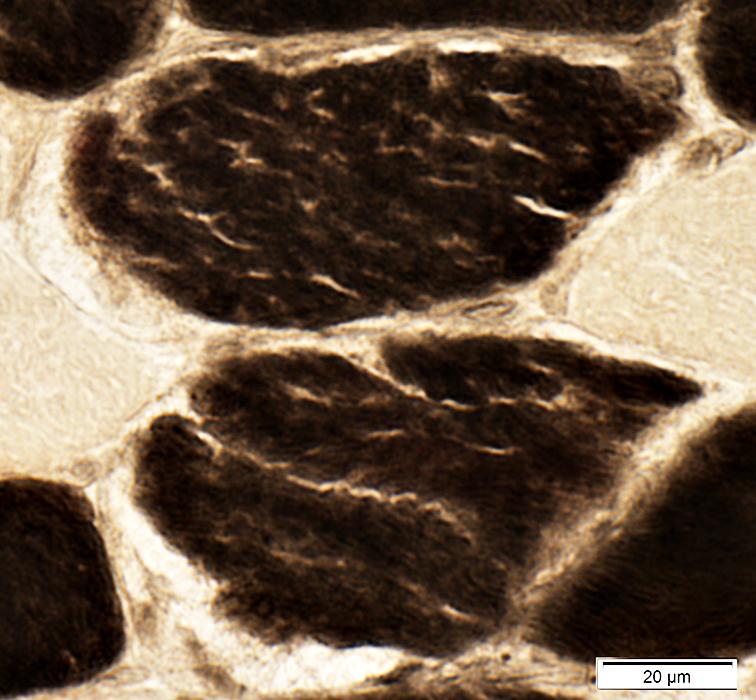 ATPase pH 4.3 stain |
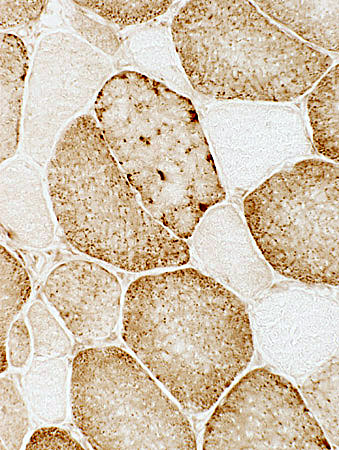
CYTOCHROME OXIDASE (COX)
AdultScattered COX- muscle fibers
 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
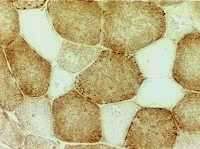 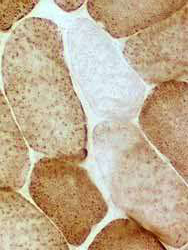 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
- Type I fibers stain more darkly than type II.
- Several fibers have no staining for cytochrome oxidase (COX).
- On SDH, COX- muscle fibers may be normal or have increased staining
- In normal biopsies virtually all fibers have staining for COX.
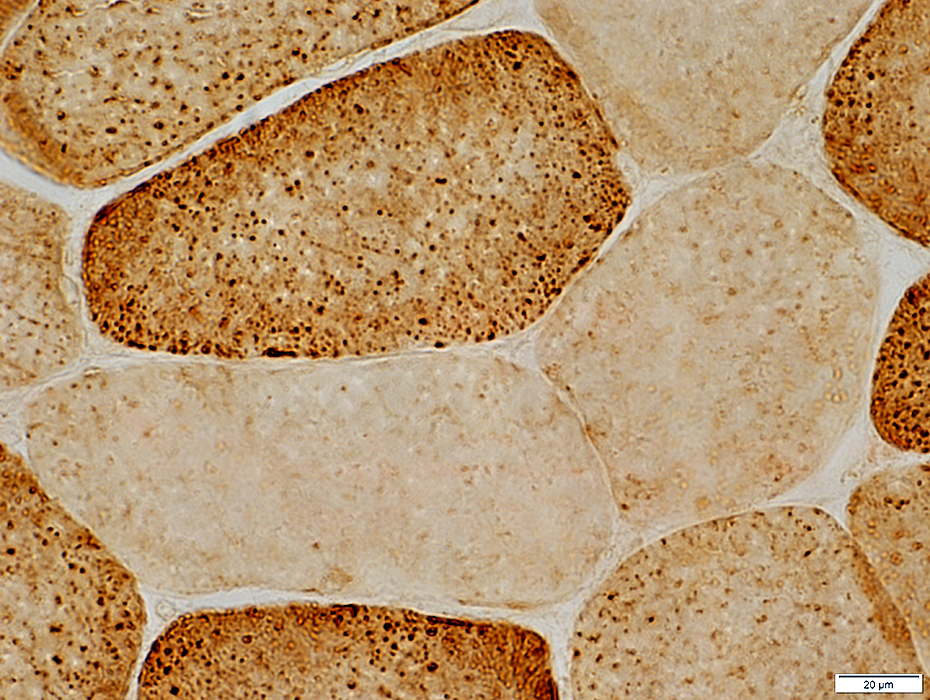 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
COX staining is markedly reduced
Punctate mitochondria are reduced or not visible
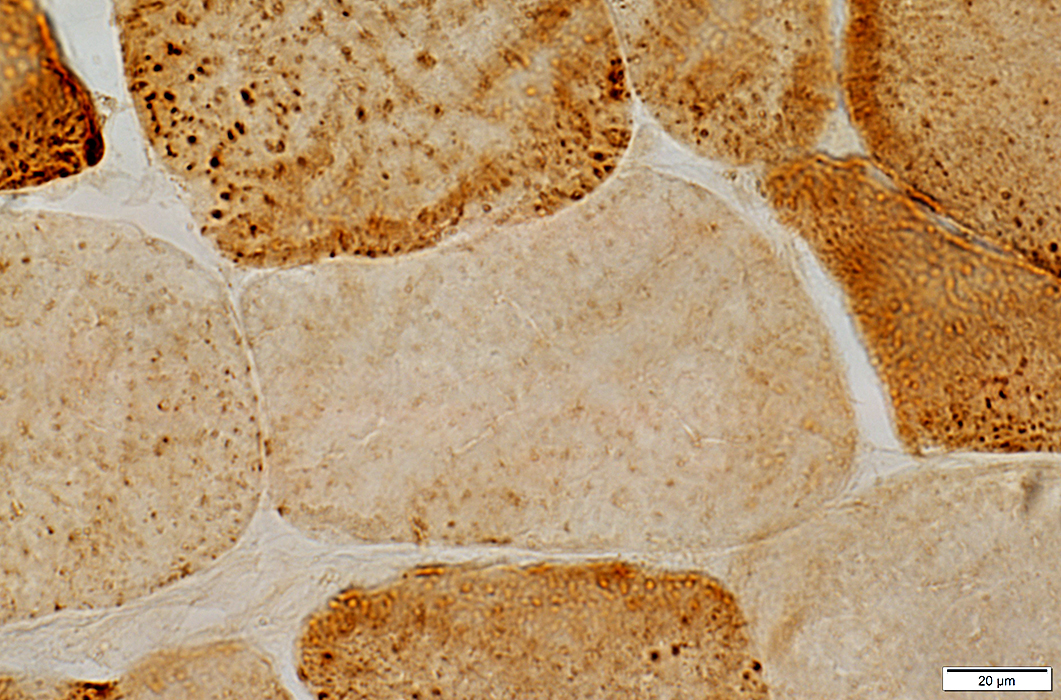 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
Reduced COX staining is often segmental: Other areas along the length of the muscle fiber may be normal
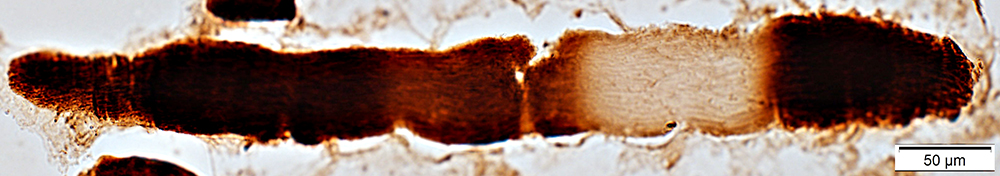 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
Adult: COX + SDH stain
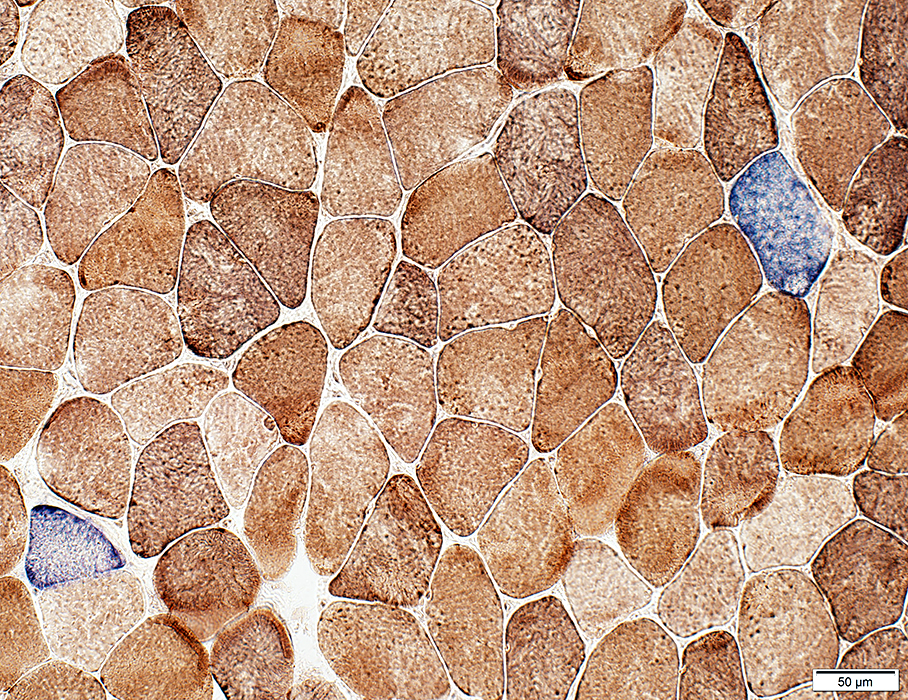 COX + SDH stain |
Stain varying shades of blue
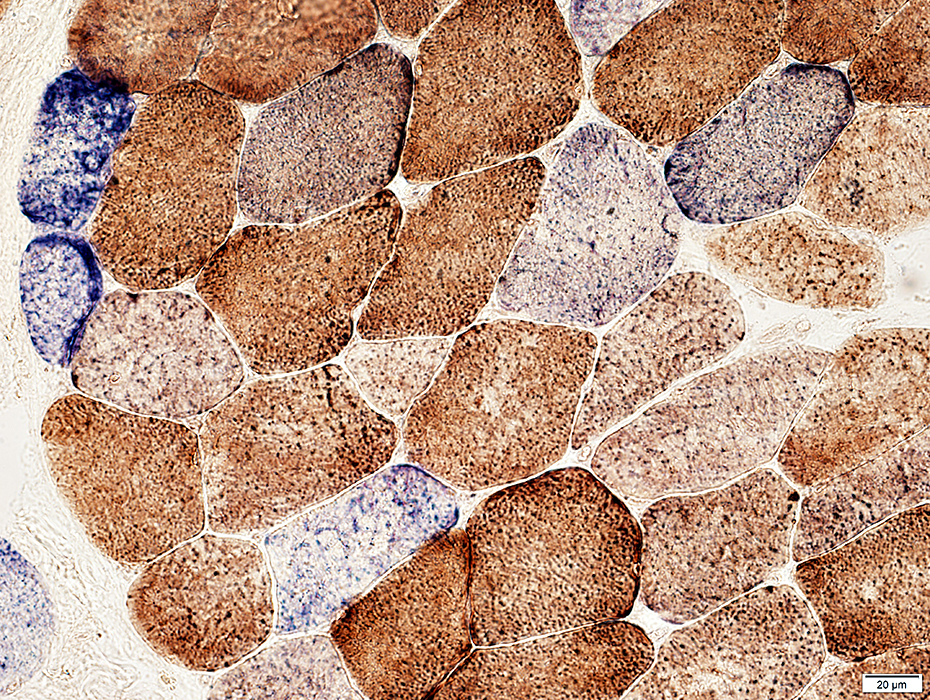 COX + SDH stain |
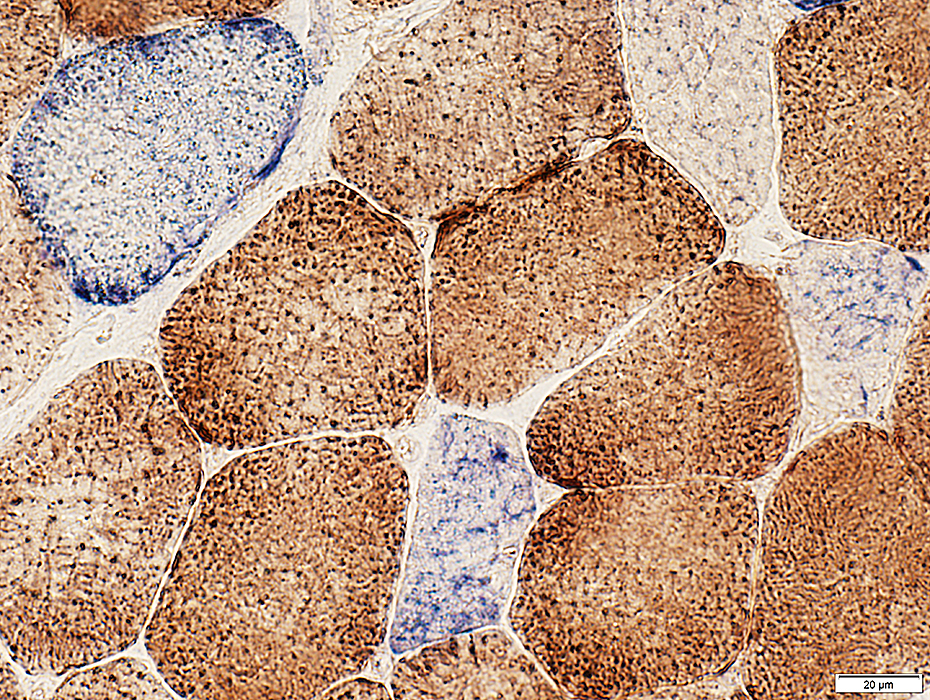 COX + SDH stain |
Child
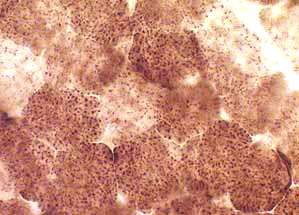
COX deficiency in all muscle fibers
 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain Mitochondrial disorder |
 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain Normal |
|
|
Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (PEO)
PEO: Single large mitochondrial DNA deletion
Biopsy from muscle with normal strength
 H & E stain |
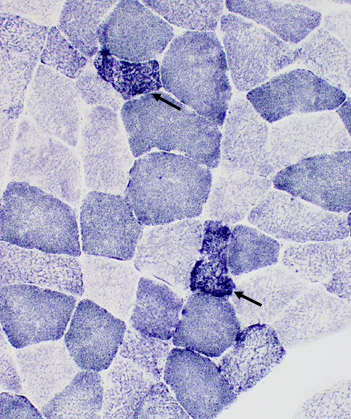 SDH stain |
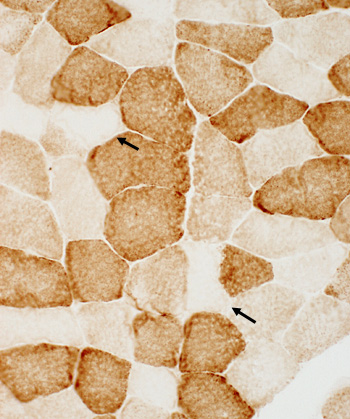 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
| Scattered intermediate sized polygonal muscle fibers |
Muscle fibers with excessive SDH staining (left) have reduced or absent COX (right) staining (arrows) |
|
PEO: Autosomal Dominant
Biopsy from weak muscle
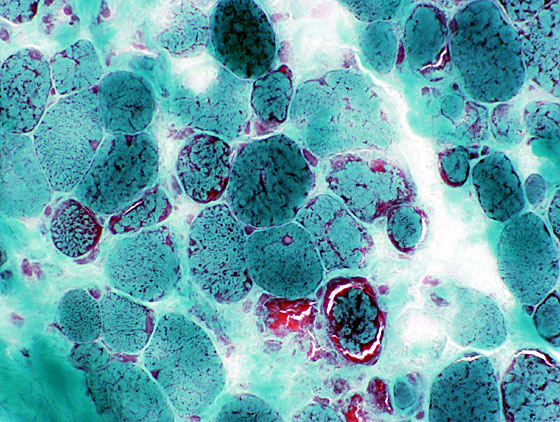 Gomori Trichrome stain |
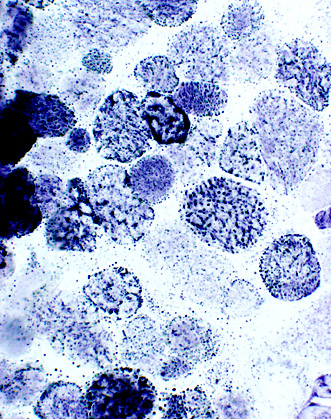 SDH stain |
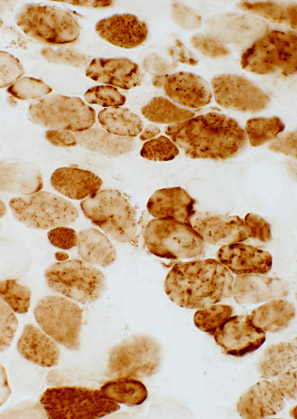 Cytochrome oxidase (COX) stain |
|
Varied muscle fiber size: Small fibers are rounded Increased endomysial connective tissue |
Muscle fibers with excessive SDH staining (left): COX is present in all fibers (right) | |
Return to Mitochondrial Ultrastructure
Return to Mitochondrial syndromes
Return to Muscle biopsies
6/13/2025