Schwannoma
- Epidemiology
- Most common peripheral nerve tumors in adults
- Incidence
- 8% of intracranial tumors
- 29% of primary spinal tumors
- Sex
- Overall: Male = Female
- Intracranial lesions: Female predominance (2:1)
- Genetics
- Family history

- Usually sporadic
- Multiple (Schwannomatosis 1 (SWNTS1)) in NF2
- Family tumor syndromes
- Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)
- Schwannomatosis
- Carney complex
- General
- NF2 mutations or 22q deletion: 77%
- Loss of function of tumor suppressor gene Merlin (Schwannomin)
- SMARCB1

- Heterozygous: Susceptibility
- Germline or Somatic mutations
- Tumors: May show loss of wild type allele
- Also associated with: Meningiomas
- Clinical: Multiple or single tumors
- Other related genes
- LZTR1
 ,
ARID1A ,
ARID1A
 ,
ARID1B ,
ARID1B
 ,
CABIN1 ,
CABIN1
 ,
DDR1 ,
DDR1
 , ,
COQ6
 ,
TAB3 ,
TAB3
 ,
ALPK2 ,
ALPK2
 ,
CAST ,
CAST
 ,
TSC1 ,
TSC1
 ,
TSC2 ,
TSC2

- Associated disorders
- Clinical
- Onset age: Peak 30 to 50 years; All ages affected
- Location
- Solitary (90%)
- Arise eccentrically from within nerve
- Often at origins of spinal or cranial nerves
- Fascicles stretched over surface of tumor
- Schwannomas: No axons within tumor
- Neurofibromas: Axons pass through neoplasm
- Cranial nerves
- VIII: Vestibular division
- Vagus (Recurrent laryngeal)
- Peripheral nerves
- Roots
- Most at dorsal
- Cauda equina: Intradural
- Flexor surfaces of limbs: Near joints
- Main nerve trunks: Peroneal; Ulnar; Sural
- Brachial > Lumbar plexus
- Sensory > Motor nerves
- Digital or Cutaneous nerve: Dull pain or Tenderness
- Symptoms
- Most: Asymptomatic & incidentally diagnosed
- Painful swelling
- Shooting pain & paresthesias induced by nerve palpation
- Spontaneous pain: Unusual; Some radicular pain
- Sensory loss & Weakness
- Unusual: Unless tumor located in confined space (Carpal tunnel)
- Specific tumor locations
- Spinal
- Weakness
- Bladder dysfunction
- Cranial nerve regions
- Hearing loss
- Facial weakness
- Deep tumors (e.g. mediastinal)
- May grow large before symptoms & detection
- Course
- Slow growing
- Usually benign
- Malignant transformation
- Not in typical tumors
- Small risk in atypical tumors
- Symptomatic regrowth: Rare
- Treatment
- Resection: Preserve nerve function & continuity
- May be monitored if asymptomatic
- MRI
- T2: Hyperintense
- T1: Isointense; Intermediate or no signal
- Gadolinium enhancement: Most sensitive; Homogeneous
- Eccentric position to nerve
- Cystic degeneration: Common
- Ultrasound: Cystic lesions with sharp borders
- Pathology
- Tumor anatomy
- Surround
- Well-circumscribed
- Encapsulated: Usual
- Surface: Smooth
- Shape: Elliptical or spherical
- Extra-fasicular growth
- Nerves of origin apparent
- Fascicles displaced around tumor capsule
- Location: Beyond oligodendoglial-Schwann cell junction
- Flexor surfaces
- May involve any nerve
- Tissue components
- Bimodal
- Antoni, Type A: Cellular, closely packed; Verocay bodies; Whorls
- Antoni, Type B: Loose, myxoid
- Degenerative changes
- Cysts; Calcification; Hemorrhage; Hyalinization
- Especially in large, deep tumors
- Vessels
- Intermediate-sized: Sclerotic, Thick walls
- Axons: No intratumoral
- Cells
- Tapered ends
- Nuclei spindled
- Palisading: Verocay bodies
- Mitotic figures: Few
- Cell components
- Malignant transformation: Rare
- Immunoreactivity
- S-100 protein (100%) > Leu-7
- CD56 (NCAM)
- SOX10
- Calbindin 2 (Calretinin; CALB2)
 : Strong : Strong
- Collagen IV
- Collagen VI
- Variable: CD34
- No: Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA); Desmin; Neurofilament; Factor XIIIa
- Genetics
- NF2 gene (merlin protein): Sporadic schwannomas (60%)
- Chromosome 22q loss
- SMARCB1
 : Schwannomatosis 1 : Schwannomatosis 1

- Schwannoma: Atypical types
- Ancient
- Pathology: Cysts; Stromal edema; Xanthomatous changes; Degenerative changes; Fibrosis
- Course: Benign
- Psammomatous melanotic
- Pathology: Melanin; Lamellated calcospherules
- May occur sporadically or with Carney syndrome
- Location: Nerve roots
- Benign
- Associated with cardiac myxomas
- Cellular
- Histology: Predominantly Antoni, Type A; May mimic malignant lesion
- Location: Paravertebral region of retroperitoneum, pelvis, mediastinum
- Hyperchromasia; Frequent mitoses
- Benign Epithelioid
- Clinical
- Location: Extremities & Trunk (85%); Visceral (15%)
- Metastasis: Rare
- Histology
- Epithelioid cells in cords or nests
- Occasional features of degeneration (Nuclear atypia)
- Somatic tumors
- Dermis/subcutis
- Encapsulated (Epithelial membrane antigen+ perineurial capsule)
- Visceral tumors: Unencapsulated
- Loss of SMARCB1/INI1 expression: 42%
- Molecular: S-100 & SOX10 positive in 100%
- Neuroblastoma-like
- Histology: Giant rosettes; May simulate neuroblastoma
- Plexiform
- Conglomerate of multiple schwannomas: Occur in large nerves or plexus
- May occur sporadically, with NF2 or with Schwannomatosis
- Benign
- Location: Subcutaneous tissue
- Young adults
|
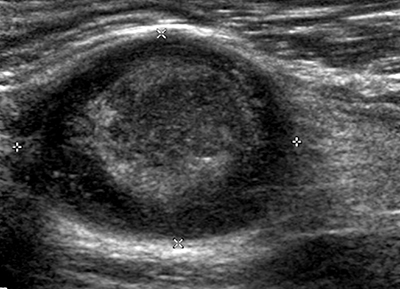
From: C Zaidman; C Garcia
Schwannoma: Ultrasound image
|

From: C Zaidman; C Garcia
Schwannoma: MRI T1 image
|
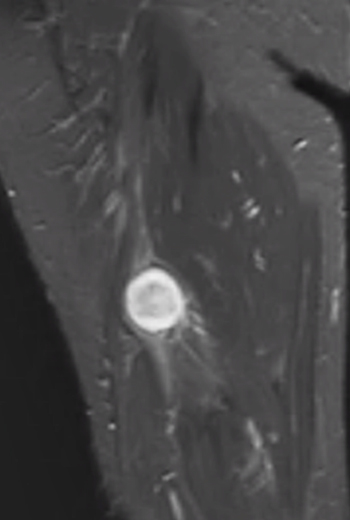
From: C Zaidman; C Garcia
Schwannoma: MRI T2 image
|
|